Subscribe or renew today
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

Science News

The smallest known molecular knot is made of just 54 atoms
Chemists are still trying to figure out why this combination of gold, phosphorus, oxygen and carbon atoms resulted in a molecular knot in the first place.
Here’s how tardigrades go into suspended animation
Capturing methane from the air would slow global warming. can it be done.

How air pollution may make it harder for pollinators to find flowers
Certain air pollutants that build up at night can break down the same fragrance molecules that attract pollinators like hawk moths to primroses.
Waterlogged soils can give hurricanes new life after they arrive on land
Ancient trees’ gnarled, twisted shapes provide irreplaceable habitats.

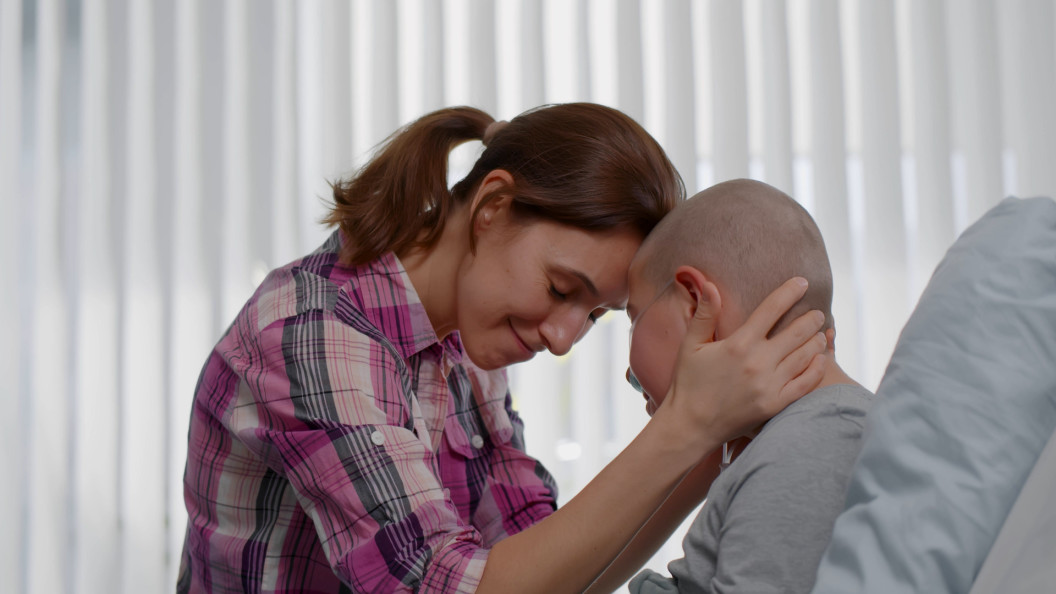
Brain fog is a debilitating symptom commonly reported by people with long COVID. Now, scientists have linked the symptom to leaky boundaries in the brain.
Long COVID brain fog may be due to damaged blood vessels in the brain
MRI scans of long COVID patients with brain fog suggest that the blood brain barrier may be leaky.
Don’t use unsterilized tap water to rinse your sinuses. It may carry brain-eating amoebas
The u.s. now has a drug for severe frostbite. how does it work.

Daddy longlegs look like they have two eyes. That doesn’t count the hidden ones
Despite its two-eyed appearance, Phalangium opilio has six peepers. The four optical remnants shed light on the arachnids’ evolutionary history.
Male dragonflies’ wax coats might protect them against a warming climate
Male mammals aren’t always bigger than females.

How two outsiders tackled the mystery of arithmetic progressions
Computer scientists made progress on a decades-old puzzle in a subfield of mathematics known as combinatorics.
A predicted quasicrystal is based on the ‘einstein’ tile known as the hat
Here’s how much fruit you can take from a display before it collapses.

Forests might serve as enormous neutrino detectors
Trees could act as antennas that pick up radio waves of ultra-high energy neutrinos interactions, one physicist proposes.
‘Countdown’ takes stock of the U.S. nuclear weapons stockpile
Physicist sekazi mtingwa considers himself an apostle of science, science & society.

‘Space: The Longest Goodbye’ explores astronauts’ mental health
The documentary follows NASA astronauts and the psychologists helping them prepare for future long-distance space trips to the moon and Mars.
Why large language models aren’t headed toward humanlike understanding

Titan’s dark dunes could be made from comets
Saturn’s largest moon could have gotten its sands from an ancient reshuffling of the solar system. If true, that would solve a long-standing mystery.
Did the James Webb telescope ‘break the universe’? Maybe not

Unlike people, today's generative AI isn’t good at learning concepts that it can apply to new situations.
Could a rice-meat hybrid be what’s for dinner?
How do babies learn words an ai experiment may hold clues.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber? Become one now .
Top Science News
Latest top headlines.
- Educational Psychology
- Intelligence
- Healthy Aging
- Alzheimer's
- Cows, Sheep, Pigs
- Cell Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Materials Science
- Civil Engineering
- Nanotechnology
- 3-D Printing
- Photography
- Mathematics
- Computer Modeling
- Energy Technology
- Nature of Water
- Electricity
- Global Warming
- Air Quality
- Dolphins and Whales
- Evolutionary Biology
- New Species
- Earthquakes
- Natural Disasters
- Oceanography
- Best Way to Memorize Stuff? It Depends...
- Healthier Diet: Reduced Dementia Risk
- Milk to the Rescue for Diabetics?
- Fertility: Skin Cell Turned Into an Egg
Top Physical/Tech
- A New World of 2D Material Is Opening Up
- High-Speed Microscale 3D Printing
- 3D Capture and Editing of Real-Life Objects
- Generator Inspired by Drinking Bird Toy
Top Environment
- Climate Change Feedback Loop: Drought
- Why Some Female Whales Live So Long: Menopause
- What Made the 'Swift Quake' at LA Concert?
- Accelerated Melting Under Greenland's Glaciers
Health News
Latest health headlines.
- Medical Devices
- Medical Technology
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Engineering
- Lung Cancer
- Immune System
- Medical Topics
- Microbes and More
- Infectious Diseases
- K-12 Education
- Neuroscience
- Brain Injury
- Foot Health
- Social Psychology
- Child Psychology
- Medical Education and Training
- Microbiology
- Pregnancy and Childbirth
- Public Health
- Sleep Disorder Research
- Sleep Disorders
- Insomnia Research
Health & Medicine
- Speaking Without Vocal Cords: New Device
- Making Automated Dosing Systems Universal
- How Gut Bacteria Shape Newborn Immune System
- Steroid Drugs May Combat E. Coli and MRSA
Mind & Brain
- What Makes Kids Feel Engaged at School?
- Brain: From Motivation to Action
- 'Curved' Walking and Cognitive Decline
- Lonely Pre-Teens and Employment Later
Living Well
- Explicit Socioemotional Learning in PE Class
- Hacking Genome of Fungi for Smart Foods
- US Maternal Death Rate Is Stable
- Hope for Treating Sleep Disorders: No Pills
Physical/Tech News
Latest physical/tech headlines.
- Electronics
- Nuclear Energy
- Dark Matter
- Astrophysics
- Biotechnology
- Biotechnology and Bioengineering
- Extreme Survival
- Space Telescopes
- Black Holes
- Headache Research
- Space Station
- Information Technology
- Computer Science
- Computers and Internet
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Neural Interfaces
- Distributed Computing
Matter & Energy
- Breakthrough in Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
- Mass-Producing Polymer Solid Electrolytes
- Commercial Fusion Energy
- Roadmap to Better Combustion Engines
Space & Time
- Maybe Our Universe Has No Dark Matter
- Two New 'Extremophile' Microbes Discovered
- Ultrablack Coating to Improve Telescopes
- Do Astronauts Experience 'Space Headaches'?
Computers & Math
- Analog Computing Efficient With Complex Math
- Straightening Teeth? AI Can Help
- Making It Stick, With Electricity, Not Glue
- How Do Neural Networks Learn?
Environment News
Latest environment headlines.
- Animal Learning and Intelligence
- Earth Science
- Marine Biology
- Snow and Avalanches
- Drought Research
- Severe Weather
- Coral Reefs
- Origin of Life
- Paleontology
- Wild Animals
Plants & Animals
- 'Noisy' Roundworm Brains: Individuality
- Seabird Colony Bursts With Sound at Night
- Shark-Bitten Orcas in Pacific: New Population?
- Leatherback Turtle Activity Along U.S. Coastline
Earth & Climate
- How Much Water Is Stored in Snow?
- Weather Prediction
- Coral Bay Faces Mass Loss of Coral and Fish
- Giant Sequoias Growing Well in the UK
Fossils & Ruins
- Sulfur and the Origin of Life
- Carnivorous Dinosaur Biodiversity
- Gene Flow in Giraffes
- Rock Weathering and Climate
Society/Education News
Latest society/education headlines.
- Artificial Intelligence
- Robotics Research
- Forensic Research
- Rainforests
- STEM Education
- Environmental Issues
- Air Pollution
- Mental Health
- Mental Health Research
- Teen Health
- Video Games
- Sports Science
- Gender Difference
- Racial Issues
- Consumer Behavior
Science & Society
- Advanced Army Robots: People's Perceptions
- New Forensics Test Helps Identify Touch DNA
- Revealing Illegal Timber Exports
- Information Overload: Societal Danger
Education & Learning
- Open Windows and Air Filters Make a Difference
- Happiness Can Be Learnt
- 'Study Drugs': Mental Health Decline
- Free Access to 3D Images of Animals
Business & Industry
- Tensions Between Individual and Team Wellbeing
- AI Can Track Hockey Data
- How Early Retirement Impacts Mental Health
- Negative Attitude Predicts Procrastination
- Chimp: Persistence of Mother-Child Play
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat, about this site.
ScienceDaily features breaking news about the latest discoveries in science, health, the environment, technology, and more -- from leading universities, scientific journals, and research organizations.
Visitors can browse more than 500 individual topics, grouped into 12 main sections (listed under the top navigational menu), covering: the medical sciences and health; physical sciences and technology; biological sciences and the environment; and social sciences, business and education. Headlines and summaries of relevant news stories are provided on each topic page.
Stories are posted daily, selected from press materials provided by hundreds of sources from around the world. Links to sources and relevant journal citations (where available) are included at the end of each post.
For more information about ScienceDaily, please consult the links listed at the bottom of each page.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Research News
- Subscribe to NPR's Up First Email

This close-up of the Verona astrolabe shows Arabic and Hebrew markings. Federica Gigante hide caption
This medieval astrolabe has both Arabic and Hebrew markings. Here's what it means
March 16, 2024 • This discovery sheds new light on the rich history of scholarship and intellectual exchange between Muslims, Jews and Christians during a time of Muslim rule in medieval Spain.

Flares burn off methane and other hydrocarbons at an oil and gas facility in Lenorah, Texas in 2021. New research shows drillers emit about three times as much climate-warming methane as official estimates. David Goldman/AP hide caption
Oil and gas companies emit more climate-warming methane than EPA reports
March 13, 2024 • Oil and gas drillers are releasing more climate-warming methane than the government estimates, a new study shows.

This type of staghorn coral ( Acropora pulchra ) appeared to benefit from the presence of sea cucumbers ( Holothuria atra ), a new study finds. Terry Moore/Stocktrek Images / Science Source hide caption
This often-overlooked sea creature may be quietly protecting the planet's coral reefs
March 13, 2024 • The pickle-shaped bottom feeders may reduce the amount of microbes on the seafloor that could potentially sicken coral, scientists suggest

Millions of people are affected by long COVID, a disease that encompasses a range of symptoms — everything from brain fog to chronic fatigue — and that manifests differently across patients. The Washington Post/The Washington Post via Getty Images hide caption
What we know about long COVID — from brain fog to physical fatigue
March 13, 2024 • "Long COVID has affected every part of my life," said Virginia resident Rachel Beale said at a recent Senate hearing. "I wake up every day feeling tired, nauseous and dizzy. I immediately start planning when I can lay down again." Beale is far from alone. Many of her experiences have been echoed by others dealing with long COVID. It's a constellation of debilitating symptoms that range from brain fog and intense physical fatigue to depression and anxiety. But there's new, promising research that sheds light onto some symptoms. NPR health correspondent Will Stone talks with Short Wave host Regina G. Barber about the state of long COVID research — what we know, what we don't and when we can expect treatments or even cures for it. Have more COVID questions you want us to cover? Email us at [email protected] — we'd love to hear from you.

Maria E. Garay-Serratos holds a framed photograph of her mother, who died after suffering decades of domestic violence. Scientists are trying to understand how domestic violence damages the brain. Julio Serratos/Maria E. Garay-Serratos hide caption
Shots - Health News
Domestic violence may leave telltale damage in the brain. scientists want to find it.
March 8, 2024 • Traumatic brain injuries from intimate partner violence are common, and potentially more severe than those seen in sports.

Elephantnose Fish, Gnathonemus petersii, Congo ullstein bild hide caption
The "shocking" tactic electric fish use to collectively sense the world
March 8, 2024 • Neuroscientist Nathan Sawtell has spent a lot of time studying the electric elephantnose fish. These fish send and decipher weak electric signals, which Sawtell hopes will eventually help neuroscientists better understand how the brain filters sensory information about the outside world. As Sawtell has studied these electric critters, he's had a lingering question: why do they always seem to organize themselves in a particular orientation. At first, he couldn't figure out why, but a new study released this week in Nature may have an answer: the fish are creating an electrical network larger than any field a single fish can muster alone, and providing collective knowledge about potential dangers in the surrounding water.
The "shocking" tactic electric fish use to collectively sense the world

A digital illustration of a circle of hands extending from the edge of the image, each holding a sheet of paper. The papers overlap in the center and, like a puzzle, come together to reveal a drawing of a handgun. Oona Tempest/KFF Health News hide caption
Meet the public health researchers trying to rein in America's gun violence crisis
Kff health news.
March 6, 2024 • After the 1996 Dickey Amendment halted federal spending on gun violence research, a small group of academics pressed on, with little money or support. Now a new generation is taking up the charge.

This artist's concept shows the Voyager 1 spacecraft entering the space between stars. Interstellar space is dominated by plasma, ionized gas (illustrated here as brownish haze). NASA/JPL-Caltech hide caption
The Voyager 1 spacecraft has a big glitch. Now, NASA must figure out how to fix it
March 6, 2024 • The Voyager 1 space probe is the farthest human-made object in space. It launched in 1977 with a golden record on board that carried assorted sounds of our home planet: greetings in many different languages, dogs barking, and the sound of two people kissing, to name but a few examples. The idea with this record was that someday, Voyager 1 might be our emissary to alien life – an audible time capsule of Earth's beings. Since its launch, it also managed to complete missions to Jupiter and Saturn. In 2012, it crossed into interstellar space.

A case of bronchitis in 2014 left Sanna Stella, a therapist who lives in the Chicago area, with debilitating fatigue. Stacey Wescott/Tribune News Service via Getty Images hide caption
Clues to a better understanding of chronic fatigue syndrome emerge from a major study
February 23, 2024 • After seven years of research, the findings shed light on the long-neglected illness. Scientists say the results could lead to future trials for potential treatments.

A 3D model of a short section of the stone wall. The scale at the bottom of the image measures 50 cm. Photos by Philipp Hoy, University of Rostock; model created using Agisoft Metashape by J. Auer, LAKD M-V hide caption
Scientists scanning the seafloor discover a long-lost Stone Age 'megastructure'
February 22, 2024 • The more than half mile long wall, called the Blinkerwall, was likely used by Stone Age hunter-gatherers to herd reindeer toward a shooting blind.

The sun emits a mid-level solar flare releasing a burst of solar material. NASA hide caption
In light of the solar maximum, a look at the biggest solar storm in recorded history
February 21, 2024 • We are at the height of the Sun's activity in its eleven year cycle, known to astronomers as the solar maximum. This means that over the next several months there's going to be a lot of solar activity. It's got us thinking back to 1859. That's when astronomer Richard Carrington was studying the Sun when he witnessed the most intense geomagnetic storm recorded in history. The storm, triggered by a giant solar flare, sent brilliant auroral displays across the globe causing electrical sparking and fires in telegraph stations. This encore episode, Regina talks to solar physicist Dr. Samaiyah Farid about what's now known as the Carrington event and about what may happen the next time a massive solar storm hits Earth.

One woolly mammoth's journey at the end of the Ice Age
February 19, 2024 • Lately, paleoecologist Audrey Rowe has been a bit preoccupied with a girl named Elma. That's because Elma is ... a woolly mammoth. And 14,000 years ago, when Elma was alive, her habitat in interior Alaska was rapidly changing. The Ice Age was coming to a close and human hunters were starting early settlements. Which leads to an intriguing question: Who, or what , killed her? In the search for answers, Audrey traces Elma's life and journey through — get this — a single tusk. Today, she shares her insights on what the mammoth extinction from thousands of years ago can teach us about megafauna extinctions today with guest host Nate Rott .

Tai chi has many health benefits. It improves flexibility, reduces stress and can help lower blood pressure. Ruth Jenkinson/Getty Images/Science Photo Library hide caption
Tai chi reduces blood pressure better than aerobic exercise, study finds
February 14, 2024 • The slow-moving Chinese martial art tai chi is known to increase flexibility and balance. Now, research suggests it's more effective at reducing blood pressure than more vigorous forms of exercise.

Manny and Cayenne wrestle and kiss. LA Johnson/NPR hide caption
Manny loves Cayenne. Plus, 5 facts about queer animals for Valentine's Day
February 14, 2024 • In a Valentine's Day exclusive report, NPR has learned there is currently a gay anteater couple at Smithsonian's National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute in Washington D.C.But this couple is just the tip of the proverbial iceberg when it comes to queerness in the animal world – it's been documented in hundreds of species. We spoke with wildlife ecologist Christine Wilkinson of the "Queer is Natural" TikTok series to uncover the wildest, queerest animals of the bunch.

Ninety-seven percent of migratory fish species are facing extinction. Whale sharks, the world's largest living fish, are among the endangered. Ullstein Bild/Ullstein Bild hide caption
Across the world, migrating animal populations are dwindling. Here's why
February 12, 2024 • In a landmark U.N. study, researchers found nearly half of the world's threatened migratory species have declining populations. More than a fifth of the assessed animals face extinction.

Clownfish might be counting their potential enemies' stripes
February 9, 2024 • At least, that's what a group of researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University thinks. The team recently published a study in the journal Experimental Biology suggesting that Amphiphrion ocellaris , or clown anemonefish, may be counting. Specifically, the authors think the fish may be looking at the number of vertical white stripes on each other as well as other anemonefish as a way to identify their own species. Not only that — the researchers think that the fish are noticing the minutiae of other anemonefish's looks because of some fishy marine geopolitics.

A sea otter in the estuarine water of Elkhorn Slough, Monterey Bay, Calif. Emma Levy hide caption
California sea otters nearly went extinct. Now they're rescuing their coastal habitat
February 8, 2024 • California sea otter populations have rebounded in recent decades. New research finds that by feasting on shore crabs, these otters are helping to protect their coastal marsh habitat against erosion.

Why wolves are thriving in this radioactive zone
February 5, 2024 • In 1986 the Chernobyl nuclear power plant exploded, releasing radioactive material into northern Ukraine and Belarus. It was the most serious nuclear accident in history. Over one hundred thousand people were evacuated from the surrounding area. But local gray wolves never left — and their population has grown over the years. It's seven times denser than populations in protected lands elsewhere in Belarus. This fact has led scientists to wonder whether the wolves are genetically either resistant or resilient to cancer — or if the wolves are simply thriving because humans aren't interfering with them.

Spiderwebs can act as air filters that catch environmental DNA from terrestrial vertebrates, scientists say. Rob Stothard/Getty Images hide caption
Need to track animals around the world? Tap into the 'spider-verse,' scientists say
February 1, 2024 • Spiderwebs can capture environmental DNA, or eDNA, from vertebrate animals in their area, potentially making them a useful tool in animal monitoring, tracking and conservation.

Scientists have found that artificial light can interfere with many insects' ability to position themselves relative to the sky. Scott Linstead / Science Source hide caption
'Like moths to a flame'? Here's what's going on with insects and porch lights
January 30, 2024 • Those insects you see flying in crazed circles are trying to keep their backs towards the light because they think that direction is up, new research suggests.

Goats and Soda
Coronavirus faq: how long does my post-covid protection last when is it booster time.
January 28, 2024 • How long does immunity last after an infection? Are rapid tests always accurate? How often is a booster in order? In this installment of our FAQ series, we look into questions about "COVID time."

Hotter than normal temperatures are exacerbating the megadrought that's depleted Western water reserves, like Elephant Butte Reservoir in southern New Mexico, new research finds. Mario Tama/Getty Images hide caption
'Hot droughts' are becoming more common in the arid West, new study finds
January 26, 2024 • Scientists looked at trees to better understand the interplay between temperatures and droughts in the Western U.S. Human-caused climate change is exacerbating both.
1000+ FREE Research Topics & Ideas
If you’re at the start of your research journey and are trying to figure out which research topic you want to focus on, you’ve come to the right place. Select your area of interest below to view a comprehensive collection of potential research ideas.

Research Topic FAQs
What (exactly) is a research topic.
A research topic is the subject of a research project or study – for example, a dissertation or thesis. A research topic typically takes the form of a problem to be solved, or a question to be answered.
A good research topic should be specific enough to allow for focused research and analysis. For example, if you are interested in studying the effects of climate change on agriculture, your research topic could focus on how rising temperatures have impacted crop yields in certain regions over time.
To learn more about the basics of developing a research topic, consider our free research topic ideation webinar.
What constitutes a good research topic?
A strong research topic comprises three important qualities : originality, value and feasibility.
- Originality – a good topic explores an original area or takes a novel angle on an existing area of study.
- Value – a strong research topic provides value and makes a contribution, either academically or practically.
- Feasibility – a good research topic needs to be practical and manageable, given the resource constraints you face.
To learn more about what makes for a high-quality research topic, check out this post .
What's the difference between a research topic and research problem?
A research topic and a research problem are two distinct concepts that are often confused. A research topic is a broader label that indicates the focus of the study , while a research problem is an issue or gap in knowledge within the broader field that needs to be addressed.
To illustrate this distinction, consider a student who has chosen “teenage pregnancy in the United Kingdom” as their research topic. This research topic could encompass any number of issues related to teenage pregnancy such as causes, prevention strategies, health outcomes for mothers and babies, etc.
Within this broad category (the research topic) lies potential areas of inquiry that can be explored further – these become the research problems . For example:
- What factors contribute to higher rates of teenage pregnancy in certain communities?
- How do different types of parenting styles affect teen pregnancy rates?
- What interventions have been successful in reducing teenage pregnancies?
Simply put, a key difference between a research topic and a research problem is scope ; the research topic provides an umbrella under which multiple questions can be asked, while the research problem focuses on one specific question or set of questions within that larger context.
How can I find potential research topics for my project?
There are many steps involved in the process of finding and choosing a high-quality research topic for a dissertation or thesis. We cover these steps in detail in this video (also accessible below).
How can I find quality sources for my research topic?
Finding quality sources is an essential step in the topic ideation process. To do this, you should start by researching scholarly journals, books, and other academic publications related to your topic. These sources can provide reliable information on a wide range of topics. Additionally, they may contain data or statistics that can help support your argument or conclusions.
Identifying Relevant Sources
When searching for relevant sources, it’s important to look beyond just published material; try using online databases such as Google Scholar or JSTOR to find articles from reputable journals that have been peer-reviewed by experts in the field.
You can also use search engines like Google or Bing to locate websites with useful information about your topic. However, be sure to evaluate any website before citing it as a source—look for evidence of authorship (such as an “About Us” page) and make sure the content is up-to-date and accurate before relying on it.
Evaluating Sources
Once you’ve identified potential sources for your research project, take some time to evaluate them thoroughly before deciding which ones will best serve your purpose. Consider factors such as author credibility (are they an expert in their field?), publication date (is the source current?), objectivity (does the author present both sides of an issue?) and relevance (how closely does this source relate to my specific topic?).
By researching the current literature on your topic, you can identify potential sources that will help to provide quality information. Once you’ve identified these sources, it’s time to look for a gap in the research and determine what new knowledge could be gained from further study.
How can I find a good research gap?
Finding a strong gap in the literature is an essential step when looking for potential research topics. We explain what research gaps are and how to find them in this post.
How should I evaluate potential research topics/ideas?
When evaluating potential research topics, it is important to consider the factors that make for a strong topic (we discussed these earlier). Specifically:
- Originality
- Feasibility
So, when you have a list of potential topics or ideas, assess each of them in terms of these three criteria. A good topic should take a unique angle, provide value (either to academia or practitioners), and be practical enough for you to pull off, given your limited resources.
Finally, you should also assess whether this project could lead to potential career opportunities such as internships or job offers down the line. Make sure that you are researching something that is relevant enough so that it can benefit your professional development in some way. Additionally, consider how each research topic aligns with your career goals and interests; researching something that you are passionate about can help keep motivation high throughout the process.
How can I assess the feasibility of a research topic?
When evaluating the feasibility and practicality of a research topic, it is important to consider several factors.
First, you should assess whether or not the research topic is within your area of competence. Of course, when you start out, you are not expected to be the world’s leading expert, but do should at least have some foundational knowledge.
Time commitment
When considering a research topic, you should think about how much time will be required for completion. Depending on your field of study, some topics may require more time than others due to their complexity or scope.
Additionally, if you plan on collaborating with other researchers or institutions in order to complete your project, additional considerations must be taken into account such as coordinating schedules and ensuring that all parties involved have adequate resources available.
Resources needed
It’s also critically important to consider what type of resources are necessary in order to conduct the research successfully. This includes physical materials such as lab equipment and chemicals but can also include intangible items like access to certain databases or software programs which may be necessary depending on the nature of your work. Additionally, if there are costs associated with obtaining these materials then this must also be factored into your evaluation process.
Potential risks
It’s important to consider the inherent potential risks for each potential research topic. These can include ethical risks (challenges getting ethical approval), data risks (not being able to access the data you’ll need), technical risks relating to the equipment you’ll use and funding risks (not securing the necessary financial back to undertake the research).
If you’re looking for more information about how to find, evaluate and select research topics for your dissertation or thesis, check out our free webinar here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1:1 help with the topic ideation process, consider our private coaching services .

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research Roundup: How the Pandemic Changed Management
- Mark C. Bolino,
- Jacob M. Whitney,
- Sarah E. Henry

Lessons from 69 articles published in top management and applied psychology journals.
Researchers recently reviewed 69 articles focused on the management implications of the Covid-19 pandemic that were published between March 2020 and July 2023 in top journals in management and applied psychology. The review highlights the numerous ways in which employees, teams, leaders, organizations, and societies were impacted and offers lessons for managing through future pandemics or other events of mass disruption.
The recent pandemic disrupted life as we know it, including for employees and organizations around the world. To understand such changes, we recently reviewed 69 articles focused on the management implications of the Covid-19 pandemic. These papers were published between March 2020 and July 2023 in top journals in management and applied psychology.
- Mark C. Bolino is the David L. Boren Professor and the Michael F. Price Chair in International Business at the University of Oklahoma’s Price College of Business. His research focuses on understanding how an organization can inspire its employees to go the extra mile without compromising their personal well-being.
- JW Jacob M. Whitney is a doctoral candidate in management at the University of Oklahoma’s Price College of Business and an incoming assistant professor at Kennesaw State University. His research interests include leadership, teams, and organizational citizenship behavior.
- SH Sarah E. Henry is a doctoral candidate in management at the University of Oklahoma’s Price College of Business and an incoming assistant professor at the University of South Florida. Her research interests include organizational citizenship behaviors, workplace interpersonal dynamics, and international management.
Partner Center

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 great research paper topics.
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.

These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Frontiers | Science News
- Science News
Research Topics
10 most viewed research topics in 2023.

This year, researchers explored a wide range of topics, including:
cancer combinational immunotherapy
COVID-19 research
the physiology of breathing during exercise
and the future of animal experimentation
With over 1.8 million views, the following Research Topics sought answers to your biggest research questions from 2023.
1 | Towards a New 3Rs Era in Experimental Research
36 articles │ 177,000 views
With the persisting need of animal experimentation for fundamental and applied research, the relevance and importance of the 3Rs Principle cannot be ignored. The 3Rs Principle of Replace, Reduce, Refine provides an essential framework for more humane animal experimentation in research.
This multi-disciplinary research review is a pan-European initiative supported by all EU 3R centers exploring the 3Rs Principle advances, challenges, and opportunities. The Research Topic draws upon multiple scientific disciplines, including biomedical, veterinary, biostatistical, biotechnology, and computer science, as well as perspectives from education, social, political, and ethical research in the 3Rs field.
2 | Combinational Immunotherapy of Cancer: Novel Targets, Mechanisms, and Strategies
84 articles │ 176,000 views
Cancer immunotherapy, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, has revolutionized the paradigm in cancer treatment. However, the clinical outcome of immunotherapy varies considerably among patients, and only a minority of patients achieve long-term clinical benefits.
This Research Topic gathers novel insights into the cancer immunity mechanisms, novel therapeutic targets, and effective combinational strategies of cancer immunotherapies. It also addresses the fundamental understanding of mechanisms underlying cancer immunotherapy and the therapeutic potential of novel combinational therapy.
3 | Breathing in Sport and Exercise: Physiology, Pathophysiology and Applications
37 articles │ 180,000 views
The respiratory system has long been considered overbuilt for exercise as it is usually not the limiting factor for maximal oxygen uptake. However, growing evidence suggests that ventilatory variables such as respiratory frequency (ƒR) especially are closely associated with perceived exertion and exercise tolerance in different populations and exercise conditions, with important implications for endurance physiology and performance.
This Research Topic advances our understanding of the physiology and pathophysiology of breathing during exercise to advance the field of respiratory monitoring in applied settings. It also bridges the gap between the physiology/pathophysiology of breathing and respiratory monitoring.
4 | Multidisciplinary COVID-19 research
91 articles │ 148,000 views
The outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has seriously impacted mental and physical health worldwide. New and emerging solutions to global health threats posed by COVID-19 are urgently needed.
This second volume brings together scientists and clinicians in artificial intelligence, mathematics and statistics, neural science, neurorobotics, social sciences, computational biology, medical health care, psychiatry, and psychology to promote COVID-19 research and stimulate collaboration between researchers in these diverse fields.
5 | Sustainable Career Development in the Turbulent, Boundaryless and Internet Age
40 articles │ 115,000 views
Government’s social policies, such as school-to-work transitional regulations, and the extended retirement age, suggest that people today may face a different labor market situation, compared to other generations.
Career sustainability is a key issue, and it is particularly the case for vulnerable groups, such as the underemployed, (re) employment of laidoff workers, and those who strive to balance between work and personal life. Therefore, this research topic investigates the antecedents and outcomes of career sustainability in different social contexts.
6 | The Nobel collection, Volume 2 - Frontiers for Young Minds
10 articles │ 673,000 views
This second Volume of our unique Nobel Collection brings you more articles by Nobel Prize winners written specifically for young minds. These amazing research leaders explain their ground-breaking discoveries and how they achieved them, and also share their thoughts on making a career path in science with advice for becoming a successful researcher and having a happy life.
7 | Psychiatrization of society
17 articles │104,000 views
Worldwide, there have been consistently rising incidences of people classified as mentally ill, paired with increasing mental healthcare service utilization over the last decades. This process can be described as the psychiatrization of society.
Individuals or groups might well benefit from aspects of psychiatrization. Yet psychiatrization can be potentially harmful to individuals and to public healthcare, through overdiagnosis and overtreatment, the psychological burden of being labeled, and, in the Global North, exploding costs to meet the needs of the ‘worried well’.
This article collection seeks to theoretically and empirically assesses the causes, mechanisms, and effects of psychiatrization, as well to understand, prevent, and manage its negative aspects.
8 | Patterns, Functions, and Processes of Alpine Grassland Ecosystems under Global Change
76 articles │ 102,000 views
Alpine grassland ecosystems provide important ecological services and functions, such as biodiversity conservation, carbon storage, and water resource regulation, and critical ecosystem services, such as pastoral production, cultural inheritance, tourism, and recreation. In recent decades, some of these regions have experienced rapid climatic warming and changes in precipitation regimes.
This Research Topic elucidates the patterns, functions, processes, and mechanisms of alpine grassland ecosystems responding to changing environments. The goal is to influence the development of adaptive management practices for alpine grassland ecosystems under future environmental change.
9 | Abiotic Stress-Induced Responses and Tolerance Mechanisms in Plants : Molecular, Cellular, Physiological and Biochemical Levels
59 articles │ 99,000 views
In nature, plants are constantly facing adverse environmental conditions, including abiotic stresses caused by extreme low and high temperature, salinity, drought, flood, heavy metal toxicity and oxidative stress. These stresses, especially drought, salinity, and high temperature, are the major causes of crop loss around the globe.
This Research Topic advances our understanding of the fundamental processes, stress signaling, and adaptation mechanisms that develop in plants in response to various abiotic stresses.
10 | Serving Vulnerable and Marginalized Populations in Social and Educational Contexts
26 articles │ 97,000 views
There is evidence that the global COVID-19 crisis is exacerbating existing inequalities and marginalization of vulnerable groups. These multi-sectoral and intersecting challenges require multi- and interdisciplinary interventions to inform inclusive responses.
This Research Topic addresses the educational and socio-emotional needs of marginalized, vulnerable, at-risk, and exceptional learners during and after crises. It also addresses the psychological, educational, sociological, health, gender, cultural, and economic aspects of vulnerable and marginalized children and adolescents in developed and developing countries.
Post related info
November 30, 2023
Frontiers Science Communications
Post categories, featured news, related subjects, research topics, related content.

Frontiers Research Topics has a new look


Second annual Frontiers Spotlight Award announced for 2018

What is a Frontiers Research Topic, and why should I participate in one?
Latest posts.

Women involved in car crashes may be more likely to go into shock than men

Chronic stress and inflammation linked to societal and environmental impacts in new study
Beer byproduct behind Marmite could help us recycle metal waste

New dinosaur skeleton closes evolutionary gap: Here are five Frontiers articles you won’t want to miss

Olusola Ololade - The lifeline of the future: The role of women scientists in water resource management
- Data, AI, & Machine Learning
- Managing Technology
- Social Responsibility
- Workplace, Teams, & Culture
- AI & Machine Learning
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Big ideas Research Projects
- Artificial Intelligence and Business Strategy
- Responsible AI
- Future of the Workforce
- Future of Leadership
- All Research Projects
- AI in Action
- Most Popular
- The Truth Behind the Nursing Crisis
- Work/23: The Big Shift
- Coaching for the Future-Forward Leader
- Measuring Culture

The spring 2024 issue’s special report looks at how to take advantage of market opportunities in the digital space, and provides advice on building culture and friendships at work; maximizing the benefits of LLMs, corporate venture capital initiatives, and innovation contests; and scaling automation and digital health platform.
- Past Issues
- Upcoming Events
- Video Archive
- Me, Myself, and AI
- Three Big Points

The 10 Most Popular Articles in 2022 (So Far)
Managers are seeking ways to improve employee well-being and build a strong workplace culture.

- Workplace, Teams, & Culture
- Talent Management
- Organizational Behavior

Year three of a global pandemic. A war in Ukraine. Inflation in the U.S. at a 40-year high. Small talk around the watercooler (mainly the virtual one, nowadays) certainly feels heavier than it used to.
Recent Gallup data indicates that in 2022, companies and managers remain challenged by the task of raising employee engagement to pre-pandemic levels. Nearly half of global workers (44%) surveyed reported feeling “a lot” of stress in the previous day. The Great Resignation has demonstrated the power of employees to vote with their feet, and a resurgence of the labor movement in the U.S. has put pressure on even top-tier companies to improve working conditions.
Get Updates on Transformative Leadership
Evidence-based resources that can help you lead your team more effectively, delivered to your inbox monthly.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up
Privacy Policy
Companies that have thrived amid the pandemic and worker reshuffling have focused on worker well-being from the start. Unfortunately, for many employees across the globe, this may be the exception rather than the norm. As Gallup’s Jon Clifton put it, “Improving life at work isn’t rocket science, but the world is closer to colonizing Mars than it is to fixing the world’s broken workplaces.”
To begin to fix these issues, managers must focus on two areas in particular: leadership and culture. In the first months of the year, many MIT SMR readers turned their attention to articles focused on workplace culture, talent management, and employee retention.
With many companies now adopting permanent remote and hybrid work policies, other popular articles include data-driven approaches to managing well-being on virtual teams — from scheduling meeting-free days to creating systems for supporting mental health.
The following are the 10 most popular articles of the year so far. We hope they will continue to help managers who are looking to support employee engagement and build thriving workplaces.
#1 Toxic Culture Is Driving the Great Resignation
Donald sull, charles sull, and ben zweig.
In this article, the authors discuss the top five predictors of employee turnover uncovered by their analysis of attrition data during the Great Resignation and share four actions that managers can take in the short term to improve employee satisfaction.
#2 Top Performers Have a Superpower: Happiness
Paul b. lester, ed diener, and martin seligman.
Research has found that happiness, a sense of well-being, and an optimistic outlook are powerful predictors of how well an employee will perform. Managers who consciously promote employee well-being and take steps to eliminate toxic leadership in their business units will reap the benefits.
#3 The Surprising Impact of Meeting-Free Days
Ben laker, vijay pereira, pawan budhwar, and ashish malik.
Spending too much time in meetings can detract from effective collaboration, derail workers during their most productive hours, and interrupt people’s train of thought. No-meeting policies permit team members to excel without breaking their momentum, but specific plans must be tailored to each unique organizational context to maximize the benefits. The authors suggest several ways to deploy a no-meeting policy or adjust an existing one.
#4 Orchestrating Workforce Ecosystems
Elizabeth j. altman, david kiron, robin jones, and jeff schwartz.
Research conducted by MIT SMR and Deloitte examines the challenges companies and managers face in leading and coordinating workforces that increasingly rely on external contributors.
#5 Why Every Leader Needs to Worry About Toxic Culture
Donald sull, charles sull, william cipolli, and caio brighenti.
According to research, the five most common elements of toxic workplace cultures — being disrespectful, noninclusive, unethical, cutthroat, and abusive — contribute the most to employee attrition and can damage company reputation. Being aware of these elements and understanding how they spread can help employers prevent and address them.
#6 Building the Cognitive Budget for Your Most Effective Mind
Jordan birnbaum.
There’s a limit to how much mental energy is available to us on any given day, so it’s essential that we spend it deliberately and thoughtfully. This article details the process of creating a cognitive budget, using techniques from positive psychology, cognitive behavioral therapy, and behavioral economics.
#7 Stop Telling Employees to Be Resilient
Liz fosslien and mollie west duffy.
When it comes to leadership, there’s a difference between demanding that employees be mentally tough and actually helping them take care of their mental health. The authors suggest five actions leaders can take to create a workplace that supports employees and fosters resilience.
#8 Effective Leaders Decide About Deciding
Nancy duarte.
Categorizing decisions by riskiness and urgency helps clarify when employees should move autonomously and when they should pull leaders into decision-making.
Related Articles
#9 leading change means changing how you lead, b. tom hunsaker and jonathan knowles.
Adapting your leadership approach is necessary for achieving the change your organization requires. The authors discuss three tasks — drawing the map, establishing the mindset, and communicating the message — that are essential to becoming a contextually effective leader.
#10 How Well-Designed Work Makes Us Smarter
Sharon k. parker and gwenith g. fisher.
Work that permits autonomy and demands problem-solving can bolster employees’ cognitive skills and ongoing learning. This article looks at how organizations and managers can use good work design to strengthen their workforce’s ability to adapt to new processes, tools, and roles.
About the Author
Ally MacDonald ( @allymacdonald ) is senior editor at MIT Sloan Management Review .
More Like This
Add a comment cancel reply.
You must sign in to post a comment. First time here? Sign up for a free account : Comment on articles and get access to many more articles.
Comment (1)
Peter bheda.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion
130 New Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Questions on everything from mental health and sports to video games and dating. Which ones inspire you to take a stand?

By The Learning Network
Note: We have an updated version of this list, with 300 new argumentative writing prompts .
What issues do you care most about? What topics do you find yourself discussing passionately, whether online, at the dinner table, in the classroom or with your friends?
In Unit 5 of our free yearlong writing curriculum and related Student Editorial Contest , we invite students to research and write about the issues that matter to them, whether that’s Shakespeare , health care , standardized testing or being messy .
But with so many possibilities, where does one even begin? Try our student writing prompts.
In 2017, we compiled a list of 401 argumentative writing prompts , all drawn from our daily Student Opinion column . Now, we’re rounding up 130 more we’ve published since then ( available here as a PDF ). Each prompt links to a free Times article as well as additional subquestions that can help you think more deeply about it.
You might use this list to inspire your own writing and to find links to reliable resources about the issues that intrigue you. But even if you’re not participating in our contest, you can use these prompts to practice the kind of low-stakes writing that can help you hone your argumentation skills.
So scroll through the list below with questions on everything from sports and mental health to dating and video games and see which ones inspire you to take a stand.
Please note: Many of these prompts are still open to comment by students 13 and up.
Technology & Social Media
1. Do Memes Make the Internet a Better Place? 2. Does Online Public Shaming Prevent Us From Being Able to Grow and Change? 3. How Young Is Too Young to Use Social Media? 4. Should the Adults in Your Life Be Worried by How Much You Use Your Phone? 5. Is Your Phone Love Hurting Your Relationships? 6. Should Kids Be Social Media Influencers? 7. Does Grammar Still Matter in the Age of Twitter? 8. Should Texting While Driving Be Treated Like Drunken Driving? 9. How Do You Think Technology Affects Dating?
10. Are Straight A’s Always a Good Thing? 11. Should Schools Teach You How to Be Happy? 12. How Do You Think American Education Could Be Improved? 13. Should Schools Test Their Students for Nicotine and Drug Use? 14. Can Social Media Be a Tool for Learning and Growth in Schools? 15. Should Facial Recognition Technology Be Used in Schools? 16. Should Your School Day Start Later? 17. How Should Senior Year in High School Be Spent? 18. Should Teachers Be Armed With Guns? 19. Is School a Place for Self-Expression? 20. Should Students Be Punished for Not Having Lunch Money? 21. Is Live-Streaming Classrooms a Good Idea? 22. Should Gifted and Talented Education Be Eliminated? 23. What Are the Most Important Things Students Should Learn in School? 24. Should Schools Be Allowed to Censor Student Newspapers? 25. Do You Feel Your School and Teachers Welcome Both Conservative and Liberal Points of View? 26. Should Teachers and Professors Ban Student Use of Laptops in Class? 27. Should Schools Teach About Climate Change? 28. Should All Schools Offer Music Programs? 29. Does Your School Need More Money? 30. Should All Schools Teach Cursive? 31. What Role Should Textbooks Play in Education? 32. Do Kids Need Recess?
College & Career
33. What Is Your Reaction to the College Admissions Cheating Scandal? 34. Is the College Admissions Process Fair? 35. Should Everyone Go to College? 36. Should College Be Free? 37. Are Lavish Amenities on College Campuses Useful or Frivolous? 38. Should ‘Despised Dissenters’ Be Allowed to Speak on College Campuses? 39. How Should the Problem of Sexual Assault on Campuses Be Addressed? 40. Should Fraternities Be Abolished? 41. Is Student Debt Worth It?
Mental & Physical Health
42. Should Students Get Mental Health Days Off From School? 43. Is Struggle Essential to Happiness? 44. Does Every Country Need a ‘Loneliness Minister’? 45. Should Schools Teach Mindfulness? 46. Should All Children Be Vaccinated? 47. What Do You Think About Vegetarianism? 48. Do We Worry Too Much About Germs? 49. What Advice Should Parents and Counselors Give Teenagers About Sexting? 50. Do You Think Porn Influences the Way Teenagers Think About Sex?
Race & Gender
51. How Should Parents Teach Their Children About Race and Racism? 52. Is America ‘Backsliding’ on Race? 53. Should All Americans Receive Anti-Bias Education? 54. Should All Companies Require Anti-Bias Training for Employees? 55. Should Columbus Day Be Replaced With Indigenous Peoples Day? 56. Is Fear of ‘The Other’ Poisoning Public Life? 57. Should the Boy Scouts Be Coed? 58. What Is Hard About Being a Boy?
59. Can You Separate Art From the Artist? 60. Are There Subjects That Should Be Off-Limits to Artists, or to Certain Artists in Particular? 61. Should Art Come With Trigger Warnings? 62. Should Graffiti Be Protected? 63. Is the Digital Era Improving or Ruining the Experience of Art? 64. Are Museums Still Important in the Digital Age? 65. In the Age of Digital Streaming, Are Movie Theaters Still Relevant? 66. Is Hollywood Becoming More Diverse? 67. What Stereotypical Characters Make You Cringe? 68. Do We Need More Female Superheroes? 69. Do Video Games Deserve the Bad Rap They Often Get? 70. Should Musicians Be Allowed to Copy or Borrow From Other Artists? 71. Is Listening to a Book Just as Good as Reading It? 72. Is There Any Benefit to Reading Books You Hate?
73. Should Girls and Boys Sports Teams Compete in the Same League? 74. Should College Athletes Be Paid? 75. Are Youth Sports Too Competitive? 76. Is It Selfish to Pursue Risky Sports Like Extreme Mountain Climbing? 77. How Should We Punish Sports Cheaters? 78. Should Technology in Sports Be Limited? 79. Should Blowouts Be Allowed in Youth Sports? 80. Is It Offensive for Sports Teams and Their Fans to Use Native American Names, Imagery and Gestures?
81. Is It Wrong to Focus on Animal Welfare When Humans Are Suffering? 82. Should Extinct Animals Be Resurrected? If So, Which Ones? 83. Are Emotional-Support Animals a Scam? 84. Is Animal Testing Ever Justified? 85. Should We Be Concerned With Where We Get Our Pets? 86. Is This Exhibit Animal Cruelty or Art?
Parenting & Childhood
87. Who Should Decide Whether a Teenager Can Get a Tattoo or Piercing? 88. Is It Harder to Grow Up in the 21st Century Than It Was in the Past? 89. Should Parents Track Their Teenager’s Location? 90. Is Childhood Today Over-Supervised? 91. How Should Parents Talk to Their Children About Drugs? 92. What Should We Call Your Generation? 93. Do Other People Care Too Much About Your Post-High School Plans? 94. Do Parents Ever Cross a Line by Helping Too Much With Schoolwork? 95. What’s the Best Way to Discipline Children? 96. What Are Your Thoughts on ‘Snowplow Parents’? 97. Should Stay-at-Home Parents Be Paid? 98. When Do You Become an Adult?
Ethics & Morality
99. Why Do Bystanders Sometimes Fail to Help When They See Someone in Danger? 100. Is It Ethical to Create Genetically Edited Humans? 101. Should Reporters Ever Help the People They Are Covering? 102. Is It O.K. to Use Family Connections to Get a Job? 103. Is $1 Billion Too Much Money for Any One Person to Have? 104. Are We Being Bad Citizens If We Don’t Keep Up With the News? 105. Should Prisons Offer Incarcerated People Education Opportunities? 106. Should Law Enforcement Be Able to Use DNA Data From Genealogy Websites for Criminal Investigations? 107. Should We Treat Robots Like People?
Government & Politics
108. Does the United States Owe Reparations to the Descendants of Enslaved People? 109. Do You Think It Is Important for Teenagers to Participate in Political Activism? 110. Should the Voting Age Be Lowered to 16? 111. What Should Lawmakers Do About Guns and Gun Violence? 112. Should Confederate Statues Be Removed or Remain in Place? 113. Does the U.S. Constitution Need an Equal Rights Amendment? 114. Should National Monuments Be Protected by the Government? 115. Should Free Speech Protections Include Self Expression That Discriminates? 116. How Important Is Freedom of the Press? 117. Should Ex-Felons Have the Right to Vote? 118. Should Marijuana Be Legal? 119. Should the United States Abolish Daylight Saving Time? 120. Should We Abolish the Death Penalty? 121. Should the U.S. Ban Military-Style Semiautomatic Weapons? 122. Should the U.S. Get Rid of the Electoral College? 123. What Do You Think of President Trump’s Use of Twitter? 124. Should Celebrities Weigh In on Politics? 125. Why Is It Important for People With Different Political Beliefs to Talk to Each Other?
Other Questions
126. Should the Week Be Four Days Instead of Five? 127. Should Public Transit Be Free? 128. How Important Is Knowing a Foreign Language? 129. Is There a ‘Right Way’ to Be a Tourist? 130. Should Your Significant Other Be Your Best Friend?
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals

Latest research and news by subject
Learn about the latest research, reviews and news from across all of the Nature journals by subject
Biological sciences
- Biochemistry
- Biological techniques
- Biotechnology
- Cell biology
- Chemical biology
- Computational biology and bioinformatics
- Developmental biology
- Drug discovery
- Microbiology
- Molecular biology
- Neuroscience
- Plant sciences
- Structural biology
- Systems biology
Business and commerce
- Business and management
- Information systems and information technology
- Operational research
Earth and environmental sciences
- Biogeochemistry
- Climate sciences
- Environmental sciences
- Environmental social sciences
- Natural hazards
- Ocean sciences
- Planetary science
- Solid Earth sciences
- Space physics
Health sciences
- Endocrinology
- Gastroenterology
- Health care
- Health occupations
- Medical research
- Molecular medicine
- Pathogenesis
- Rheumatology
- Risk factors
- Signs and symptoms
- Complex networks
- Cultural and media studies
- Health humanities
- Language and linguistics
- Medical humanities
- Theatre and performance studies
Physical sciences
- Astronomy and planetary science
- Energy science and technology
- Engineering
- Materials science
- Mathematics and computing
- Nanoscience and technology
- Optics and photonics
Scientific community and society
- Agriculture
- Business and industry
- Developing world
- Energy and society
- Scientific community
- Social sciences
- Water resources
Social science
- Anthropology
- Criminology
- Development studies
- Environmental studies
- Politics and international relations
- Science, technology and society
- Social policy
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
share this!
March 15, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
New research suggests that our universe has no dark matter
by Bernard Rizk, University of Ottawa
The current theoretical model for the composition of the universe is that it's made of normal matter, dark energy and dark matter. A new University of Ottawa study challenges this.
A study, published today in The Astrophysical Journal , challenges the current model of the universe by showing that, in fact, it has no room for dark matter.
In cosmology , the term "dark matter" describes all that appears not to interact with light or the electromagnetic field , or that can only be explained through gravitational force . We can't see it, nor do we know what it's made of, but it helps us understand how galaxies, planets and stars behave.
Rajendra Gupta, a physics professor at the Faculty of Science, used a combination of the covarying coupling constants (CCC) and "tired light" (TL) theories (the CCC+TL model) to reach this conclusion.
This model combines two ideas—about how the forces of nature decrease over cosmic time and about light losing energy when it travels a long distance. It's been tested and has been shown to match up with several observations, such as about how galaxies are spread out and how light from the early universe has evolved.
This discovery challenges the prevailing understanding of the universe, which suggests that roughly 27% of it is composed of dark matter and less than 5% of ordinary matter , remaining being the dark energy.
Challenging the need for dark matter in the universe
"The study's findings confirm that our previous work ("JWST early universe observations and ΛCDM cosmology") about the age of the universe being 26.7 billion years has allowed us to discover that the universe does not require dark matter to exist," explains Gupta.
"In standard cosmology, the accelerated expansion of the universe is said to be caused by dark energy but is in fact due to the weakening forces of nature as it expands, not due to dark energy ."
"Redshifts" refer to when light is shifted toward the red part of the spectrum. The researcher analyzed data from recent papers on the distribution of galaxies at low redshifts and the angular size of the sound horizon in the literature at high redshift.
"There are several papers that question the existence of dark matter, but mine is the first one, to my knowledge, that eliminates its cosmological existence while being consistent with key cosmological observations that we have had time to confirm," says Gupta.
By challenging the need for dark matter in the universe and providing evidence for a new cosmological model, this study opens up new avenues for exploring the fundamental properties of the universe.
Journal information: Astrophysical Journal
Provided by University of Ottawa
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Greenland Ice Sheet motion minimally impacted by late-season melting, study finds
9 hours ago
Ebola: Scientists reveal a new way it replicates
10 hours ago

Investigating the many flavors of edible ants
12 hours ago

Dune: What the climate of Arrakis can tell us about the hunt for habitable exoplanets
Mar 16, 2024

Saturday Citations: The volcanoes of Mars; Starship launched; 'Try our new menu item,' say Australian researchers

Researchers take deep dive into how much water is stored in snow

Ultra-flat optics for broadband thermal imaging
Mar 15, 2024

Shark-bitten orcas in the Northeastern Pacific could be a new population of killer whale

Einasto Supercluster: The new heavyweight contender in the universe

Protein fragments ID two new 'extremophile' microbes—and may help find alien life
Relevant physicsforums posts, u.s. solar eclipses - oct. 14, 2023 (annular) & apr. 08, 2024 (total).
6 hours ago
Eye protection while watching a total solar eclipse
18 hours ago
Neutron Star vs Black hole
How do i determine the surface magnitude of a galaxy from a sed.
Mar 14, 2024
Our Beautiful Universe - Photos and Videos
Photographing a solar eclipse with a smartphone (safely).
Mar 13, 2024
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

Dynamical dark energy might explain strange 21-cm signal
Jul 13, 2023

Examining the accelerating universe
Oct 22, 2021

New research puts age of universe at 26.7 billion years, nearly twice as old as previously believed

The universe is expanding faster than theory predicts—physicists are trying to explain the mismatch
Nov 15, 2023
Dark matter can make dark atoms, say theoretical astrophysicists
May 12, 2023

New study sows doubt about the composition of 70 percent of our universe
Mar 31, 2021
Recommended for you
GALILEO: Scientists propose a new method to search for light dark matter

The 'baritone' of red giants refines cosmic distance measurements

Study reveals ancient ice may still exist in distant space objects
Citizen astronomers and AI discover 30,000 ring galaxies

Astronomers perform a comprehensive study of the young open cluster NGC 2345
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024
It’s time for a generative AI (gen AI) reset. The initial enthusiasm and flurry of activity in 2023 is giving way to second thoughts and recalibrations as companies realize that capturing gen AI’s enormous potential value is harder than expected .
With 2024 shaping up to be the year for gen AI to prove its value, companies should keep in mind the hard lessons learned with digital and AI transformations: competitive advantage comes from building organizational and technological capabilities to broadly innovate, deploy, and improve solutions at scale—in effect, rewiring the business for distributed digital and AI innovation.
About QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey
QuantumBlack, McKinsey’s AI arm, helps companies transform using the power of technology, technical expertise, and industry experts. With thousands of practitioners at QuantumBlack (data engineers, data scientists, product managers, designers, and software engineers) and McKinsey (industry and domain experts), we are working to solve the world’s most important AI challenges. QuantumBlack Labs is our center of technology development and client innovation, which has been driving cutting-edge advancements and developments in AI through locations across the globe.
Companies looking to score early wins with gen AI should move quickly. But those hoping that gen AI offers a shortcut past the tough—and necessary—organizational surgery are likely to meet with disappointing results. Launching pilots is (relatively) easy; getting pilots to scale and create meaningful value is hard because they require a broad set of changes to the way work actually gets done.
Let’s briefly look at what this has meant for one Pacific region telecommunications company. The company hired a chief data and AI officer with a mandate to “enable the organization to create value with data and AI.” The chief data and AI officer worked with the business to develop the strategic vision and implement the road map for the use cases. After a scan of domains (that is, customer journeys or functions) and use case opportunities across the enterprise, leadership prioritized the home-servicing/maintenance domain to pilot and then scale as part of a larger sequencing of initiatives. They targeted, in particular, the development of a gen AI tool to help dispatchers and service operators better predict the types of calls and parts needed when servicing homes.
Leadership put in place cross-functional product teams with shared objectives and incentives to build the gen AI tool. As part of an effort to upskill the entire enterprise to better work with data and gen AI tools, they also set up a data and AI academy, which the dispatchers and service operators enrolled in as part of their training. To provide the technology and data underpinnings for gen AI, the chief data and AI officer also selected a large language model (LLM) and cloud provider that could meet the needs of the domain as well as serve other parts of the enterprise. The chief data and AI officer also oversaw the implementation of a data architecture so that the clean and reliable data (including service histories and inventory databases) needed to build the gen AI tool could be delivered quickly and responsibly.
Our book Rewired: The McKinsey Guide to Outcompeting in the Age of Digital and AI (Wiley, June 2023) provides a detailed manual on the six capabilities needed to deliver the kind of broad change that harnesses digital and AI technology. In this article, we will explore how to extend each of those capabilities to implement a successful gen AI program at scale. While recognizing that these are still early days and that there is much more to learn, our experience has shown that breaking open the gen AI opportunity requires companies to rewire how they work in the following ways.
Figure out where gen AI copilots can give you a real competitive advantage
The broad excitement around gen AI and its relative ease of use has led to a burst of experimentation across organizations. Most of these initiatives, however, won’t generate a competitive advantage. One bank, for example, bought tens of thousands of GitHub Copilot licenses, but since it didn’t have a clear sense of how to work with the technology, progress was slow. Another unfocused effort we often see is when companies move to incorporate gen AI into their customer service capabilities. Customer service is a commodity capability, not part of the core business, for most companies. While gen AI might help with productivity in such cases, it won’t create a competitive advantage.
To create competitive advantage, companies should first understand the difference between being a “taker” (a user of available tools, often via APIs and subscription services), a “shaper” (an integrator of available models with proprietary data), and a “maker” (a builder of LLMs). For now, the maker approach is too expensive for most companies, so the sweet spot for businesses is implementing a taker model for productivity improvements while building shaper applications for competitive advantage.
Much of gen AI’s near-term value is closely tied to its ability to help people do their current jobs better. In this way, gen AI tools act as copilots that work side by side with an employee, creating an initial block of code that a developer can adapt, for example, or drafting a requisition order for a new part that a maintenance worker in the field can review and submit (see sidebar “Copilot examples across three generative AI archetypes”). This means companies should be focusing on where copilot technology can have the biggest impact on their priority programs.
Copilot examples across three generative AI archetypes
- “Taker” copilots help real estate customers sift through property options and find the most promising one, write code for a developer, and summarize investor transcripts.
- “Shaper” copilots provide recommendations to sales reps for upselling customers by connecting generative AI tools to customer relationship management systems, financial systems, and customer behavior histories; create virtual assistants to personalize treatments for patients; and recommend solutions for maintenance workers based on historical data.
- “Maker” copilots are foundation models that lab scientists at pharmaceutical companies can use to find and test new and better drugs more quickly.
Some industrial companies, for example, have identified maintenance as a critical domain for their business. Reviewing maintenance reports and spending time with workers on the front lines can help determine where a gen AI copilot could make a big difference, such as in identifying issues with equipment failures quickly and early on. A gen AI copilot can also help identify root causes of truck breakdowns and recommend resolutions much more quickly than usual, as well as act as an ongoing source for best practices or standard operating procedures.
The challenge with copilots is figuring out how to generate revenue from increased productivity. In the case of customer service centers, for example, companies can stop recruiting new agents and use attrition to potentially achieve real financial gains. Defining the plans for how to generate revenue from the increased productivity up front, therefore, is crucial to capturing the value.
Upskill the talent you have but be clear about the gen-AI-specific skills you need
By now, most companies have a decent understanding of the technical gen AI skills they need, such as model fine-tuning, vector database administration, prompt engineering, and context engineering. In many cases, these are skills that you can train your existing workforce to develop. Those with existing AI and machine learning (ML) capabilities have a strong head start. Data engineers, for example, can learn multimodal processing and vector database management, MLOps (ML operations) engineers can extend their skills to LLMOps (LLM operations), and data scientists can develop prompt engineering, bias detection, and fine-tuning skills.
A sample of new generative AI skills needed
The following are examples of new skills needed for the successful deployment of generative AI tools:
- data scientist:
- prompt engineering
- in-context learning
- bias detection
- pattern identification
- reinforcement learning from human feedback
- hyperparameter/large language model fine-tuning; transfer learning
- data engineer:
- data wrangling and data warehousing
- data pipeline construction
- multimodal processing
- vector database management
The learning process can take two to three months to get to a decent level of competence because of the complexities in learning what various LLMs can and can’t do and how best to use them. The coders need to gain experience building software, testing, and validating answers, for example. It took one financial-services company three months to train its best data scientists to a high level of competence. While courses and documentation are available—many LLM providers have boot camps for developers—we have found that the most effective way to build capabilities at scale is through apprenticeship, training people to then train others, and building communities of practitioners. Rotating experts through teams to train others, scheduling regular sessions for people to share learnings, and hosting biweekly documentation review sessions are practices that have proven successful in building communities of practitioners (see sidebar “A sample of new generative AI skills needed”).
It’s important to bear in mind that successful gen AI skills are about more than coding proficiency. Our experience in developing our own gen AI platform, Lilli , showed us that the best gen AI technical talent has design skills to uncover where to focus solutions, contextual understanding to ensure the most relevant and high-quality answers are generated, collaboration skills to work well with knowledge experts (to test and validate answers and develop an appropriate curation approach), strong forensic skills to figure out causes of breakdowns (is the issue the data, the interpretation of the user’s intent, the quality of metadata on embeddings, or something else?), and anticipation skills to conceive of and plan for possible outcomes and to put the right kind of tracking into their code. A pure coder who doesn’t intrinsically have these skills may not be as useful a team member.
While current upskilling is largely based on a “learn on the job” approach, we see a rapid market emerging for people who have learned these skills over the past year. That skill growth is moving quickly. GitHub reported that developers were working on gen AI projects “in big numbers,” and that 65,000 public gen AI projects were created on its platform in 2023—a jump of almost 250 percent over the previous year. If your company is just starting its gen AI journey, you could consider hiring two or three senior engineers who have built a gen AI shaper product for their companies. This could greatly accelerate your efforts.
Form a centralized team to establish standards that enable responsible scaling
To ensure that all parts of the business can scale gen AI capabilities, centralizing competencies is a natural first move. The critical focus for this central team will be to develop and put in place protocols and standards to support scale, ensuring that teams can access models while also minimizing risk and containing costs. The team’s work could include, for example, procuring models and prescribing ways to access them, developing standards for data readiness, setting up approved prompt libraries, and allocating resources.
While developing Lilli, our team had its mind on scale when it created an open plug-in architecture and setting standards for how APIs should function and be built. They developed standardized tooling and infrastructure where teams could securely experiment and access a GPT LLM , a gateway with preapproved APIs that teams could access, and a self-serve developer portal. Our goal is that this approach, over time, can help shift “Lilli as a product” (that a handful of teams use to build specific solutions) to “Lilli as a platform” (that teams across the enterprise can access to build other products).
For teams developing gen AI solutions, squad composition will be similar to AI teams but with data engineers and data scientists with gen AI experience and more contributors from risk management, compliance, and legal functions. The general idea of staffing squads with resources that are federated from the different expertise areas will not change, but the skill composition of a gen-AI-intensive squad will.
Set up the technology architecture to scale
Building a gen AI model is often relatively straightforward, but making it fully operational at scale is a different matter entirely. We’ve seen engineers build a basic chatbot in a week, but releasing a stable, accurate, and compliant version that scales can take four months. That’s why, our experience shows, the actual model costs may be less than 10 to 15 percent of the total costs of the solution.
Building for scale doesn’t mean building a new technology architecture. But it does mean focusing on a few core decisions that simplify and speed up processes without breaking the bank. Three such decisions stand out:
- Focus on reusing your technology. Reusing code can increase the development speed of gen AI use cases by 30 to 50 percent. One good approach is simply creating a source for approved tools, code, and components. A financial-services company, for example, created a library of production-grade tools, which had been approved by both the security and legal teams, and made them available in a library for teams to use. More important is taking the time to identify and build those capabilities that are common across the most priority use cases. The same financial-services company, for example, identified three components that could be reused for more than 100 identified use cases. By building those first, they were able to generate a significant portion of the code base for all the identified use cases—essentially giving every application a big head start.
- Focus the architecture on enabling efficient connections between gen AI models and internal systems. For gen AI models to work effectively in the shaper archetype, they need access to a business’s data and applications. Advances in integration and orchestration frameworks have significantly reduced the effort required to make those connections. But laying out what those integrations are and how to enable them is critical to ensure these models work efficiently and to avoid the complexity that creates technical debt (the “tax” a company pays in terms of time and resources needed to redress existing technology issues). Chief information officers and chief technology officers can define reference architectures and integration standards for their organizations. Key elements should include a model hub, which contains trained and approved models that can be provisioned on demand; standard APIs that act as bridges connecting gen AI models to applications or data; and context management and caching, which speed up processing by providing models with relevant information from enterprise data sources.
- Build up your testing and quality assurance capabilities. Our own experience building Lilli taught us to prioritize testing over development. Our team invested in not only developing testing protocols for each stage of development but also aligning the entire team so that, for example, it was clear who specifically needed to sign off on each stage of the process. This slowed down initial development but sped up the overall delivery pace and quality by cutting back on errors and the time needed to fix mistakes.
Ensure data quality and focus on unstructured data to fuel your models
The ability of a business to generate and scale value from gen AI models will depend on how well it takes advantage of its own data. As with technology, targeted upgrades to existing data architecture are needed to maximize the future strategic benefits of gen AI:
- Be targeted in ramping up your data quality and data augmentation efforts. While data quality has always been an important issue, the scale and scope of data that gen AI models can use—especially unstructured data—has made this issue much more consequential. For this reason, it’s critical to get the data foundations right, from clarifying decision rights to defining clear data processes to establishing taxonomies so models can access the data they need. The companies that do this well tie their data quality and augmentation efforts to the specific AI/gen AI application and use case—you don’t need this data foundation to extend to every corner of the enterprise. This could mean, for example, developing a new data repository for all equipment specifications and reported issues to better support maintenance copilot applications.
- Understand what value is locked into your unstructured data. Most organizations have traditionally focused their data efforts on structured data (values that can be organized in tables, such as prices and features). But the real value from LLMs comes from their ability to work with unstructured data (for example, PowerPoint slides, videos, and text). Companies can map out which unstructured data sources are most valuable and establish metadata tagging standards so models can process the data and teams can find what they need (tagging is particularly important to help companies remove data from models as well, if necessary). Be creative in thinking about data opportunities. Some companies, for example, are interviewing senior employees as they retire and feeding that captured institutional knowledge into an LLM to help improve their copilot performance.
- Optimize to lower costs at scale. There is often as much as a tenfold difference between what companies pay for data and what they could be paying if they optimized their data infrastructure and underlying costs. This issue often stems from companies scaling their proofs of concept without optimizing their data approach. Two costs generally stand out. One is storage costs arising from companies uploading terabytes of data into the cloud and wanting that data available 24/7. In practice, companies rarely need more than 10 percent of their data to have that level of availability, and accessing the rest over a 24- or 48-hour period is a much cheaper option. The other costs relate to computation with models that require on-call access to thousands of processors to run. This is especially the case when companies are building their own models (the maker archetype) but also when they are using pretrained models and running them with their own data and use cases (the shaper archetype). Companies could take a close look at how they can optimize computation costs on cloud platforms—for instance, putting some models in a queue to run when processors aren’t being used (such as when Americans go to bed and consumption of computing services like Netflix decreases) is a much cheaper option.
Build trust and reusability to drive adoption and scale
Because many people have concerns about gen AI, the bar on explaining how these tools work is much higher than for most solutions. People who use the tools want to know how they work, not just what they do. So it’s important to invest extra time and money to build trust by ensuring model accuracy and making it easy to check answers.
One insurance company, for example, created a gen AI tool to help manage claims. As part of the tool, it listed all the guardrails that had been put in place, and for each answer provided a link to the sentence or page of the relevant policy documents. The company also used an LLM to generate many variations of the same question to ensure answer consistency. These steps, among others, were critical to helping end users build trust in the tool.
Part of the training for maintenance teams using a gen AI tool should be to help them understand the limitations of models and how best to get the right answers. That includes teaching workers strategies to get to the best answer as fast as possible by starting with broad questions then narrowing them down. This provides the model with more context, and it also helps remove any bias of the people who might think they know the answer already. Having model interfaces that look and feel the same as existing tools also helps users feel less pressured to learn something new each time a new application is introduced.
Getting to scale means that businesses will need to stop building one-off solutions that are hard to use for other similar use cases. One global energy and materials company, for example, has established ease of reuse as a key requirement for all gen AI models, and has found in early iterations that 50 to 60 percent of its components can be reused. This means setting standards for developing gen AI assets (for example, prompts and context) that can be easily reused for other cases.
While many of the risk issues relating to gen AI are evolutions of discussions that were already brewing—for instance, data privacy, security, bias risk, job displacement, and intellectual property protection—gen AI has greatly expanded that risk landscape. Just 21 percent of companies reporting AI adoption say they have established policies governing employees’ use of gen AI technologies.
Similarly, a set of tests for AI/gen AI solutions should be established to demonstrate that data privacy, debiasing, and intellectual property protection are respected. Some organizations, in fact, are proposing to release models accompanied with documentation that details their performance characteristics. Documenting your decisions and rationales can be particularly helpful in conversations with regulators.
In some ways, this article is premature—so much is changing that we’ll likely have a profoundly different understanding of gen AI and its capabilities in a year’s time. But the core truths of finding value and driving change will still apply. How well companies have learned those lessons may largely determine how successful they’ll be in capturing that value.

The authors wish to thank Michael Chui, Juan Couto, Ben Ellencweig, Josh Gartner, Bryce Hall, Holger Harreis, Phil Hudelson, Suzana Iacob, Sid Kamath, Neerav Kingsland, Kitti Lakner, Robert Levin, Matej Macak, Lapo Mori, Alex Peluffo, Aldo Rosales, Erik Roth, Abdul Wahab Shaikh, and Stephen Xu for their contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Barr Seitz, an editorial director in the New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier

Rewired to outcompete

Meet Lilli, our generative AI tool that’s a researcher, a time saver, and an inspiration
Read our research on: TikTok | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
How teens and parents approach screen time, most teens at least sometimes feel happy and peaceful when they don’t have their phone, but 44% say this makes them anxious. half of parents say they have looked through their teen’s phone.
Pew Research Center conducted this study to better understand teens’ and parents’ experiences with screen time.
The Center conducted an online survey of 1,453 U.S. teens and parents from Sept. 26 to Oct. 23, 2023, through Ipsos. Ipsos invited one parent from each of a representative set of households with parents of teens in the desired age range from its KnowledgePanel . The KnowledgePanel is a probability-based web panel recruited primarily through national, random sampling of residential addresses. Parents were asked to think about one teen in their household (if there were multiple teens ages 13 to 17 in the household, one was randomly chosen). At the conclusion of the parent’s section, the parent was asked to have this chosen teen come to the computer and complete the survey in private.
The survey is weighted to be representative of two different populations: 1) parents with teens ages 13 to 17 and 2) teens ages 13 to 17 who live with parents. For each of these populations, they survey is weighted to be representative by age, gender, race and ethnicity, household income and other categories.
This research was reviewed and approved by an external institutional review board (IRB), Advarra, an independent committee of experts specializing in helping to protect the rights of research participants.
Here are the questions among parents and among teens used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology .
Today’s teenagers are more digitally connected than ever. Most have access to smartphones and use social media , and nearly half say they are online almost constantly. But how are young people navigating this “always on” environment?
To better understand their experiences, we surveyed both teens and parents on a range of screen time-related topics. Our questions explored the emotions teens tie to their devices, the impact of smartphones on youth, and the challenges parents face when raising children in the digital age.
Key findings from the survey:
- Phone-less: 72% of U.S. teens say they often or sometimes feel peaceful when they don’t have their smartphone; 44% say it makes them feel anxious.
- Good for hobbies, less so for socialization: 69% of teens say smartphones make it easier for youth to pursue hobbies and interests; fewer (30%) say it helps people their age learn good social skills.
- Parental snooping: Half of parents say they have looked through their teen’s phone.
- Smartphone standoffs: About four-in-ten parents and teens report regularly arguing with one another about time spent on their phone.
- Distracted parenting: Nearly half of teens (46%) say their parent is at least sometimes distracted by their phone when they’re trying to talk to them.
This Pew Research Center survey of 1,453 U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 and their parents was conducted Sept. 26-Oct. 23, 2023. 1
Jump to read about views among teens on: Screen time | Feelings when disconnected from phones | Thoughts on smartphones’ impact
Jump to read about views among parents on: Parenting in the smartphone age | Their own screen time struggles
Teens’ views on screen time and efforts to cut back
Fully 95% of teens have access to a smartphone, and about six-in-ten say they use TikTok, Snapchat or Instagram . But do teens think they spend too much time in front of screens?
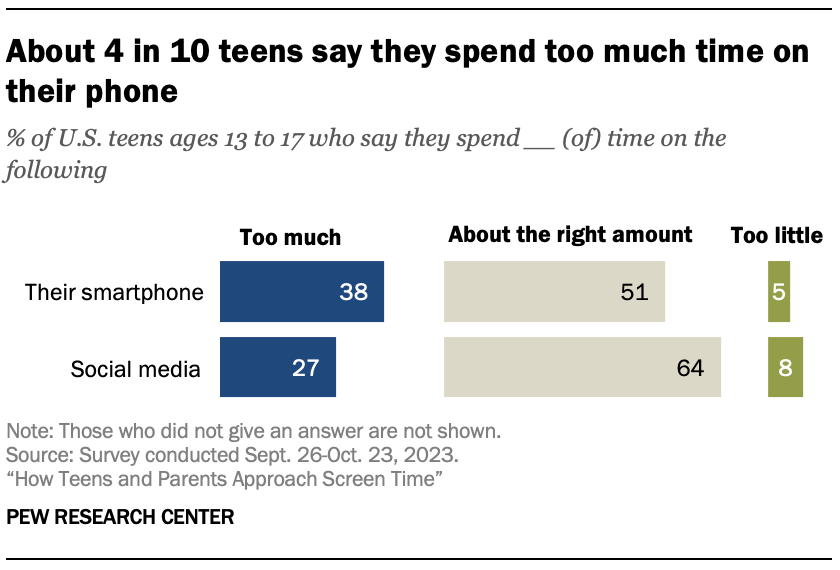
More teens say they spend too much time on their phone or social media than say they don’t spend enough time on them. We found that 38% of teens say they spend too much time on their smartphone. About a quarter say the same regarding their social media use. 2
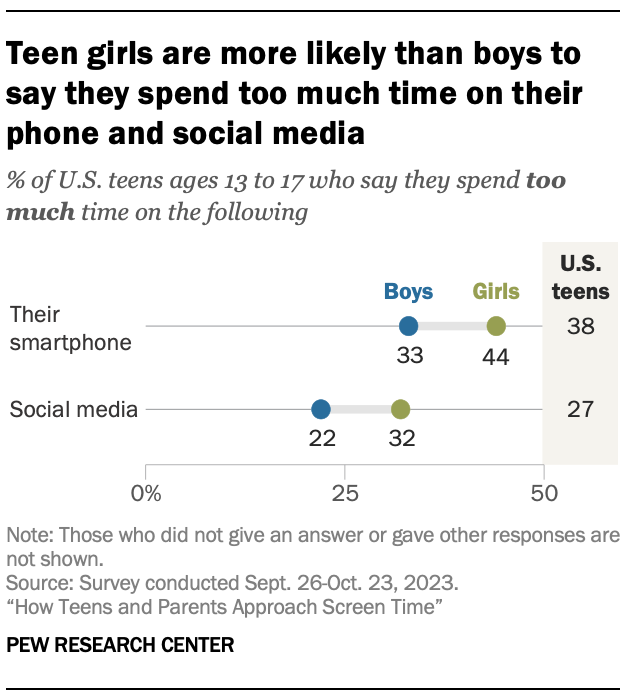
But the largest shares say the amount of time they spend on their phone (51%) or on social media (64%) is about right. Relatively few teens say they don’t spend enough time with these technologies.
Views on this differ by gender. Teen girls are more likely than boys to say they spend too much time on their smartphone (44% vs. 33%) or social media (32% vs. 22%).
Teens’ efforts to curb their screen time
A minority of teens have taken steps to reduce their screen time. Roughly four-in-ten teens (39%) say they have cut back on their time on social media. A similar share says the same about their phone (36%).
Still, most teens have not limited their smartphone (63%) or social media (60%) use.
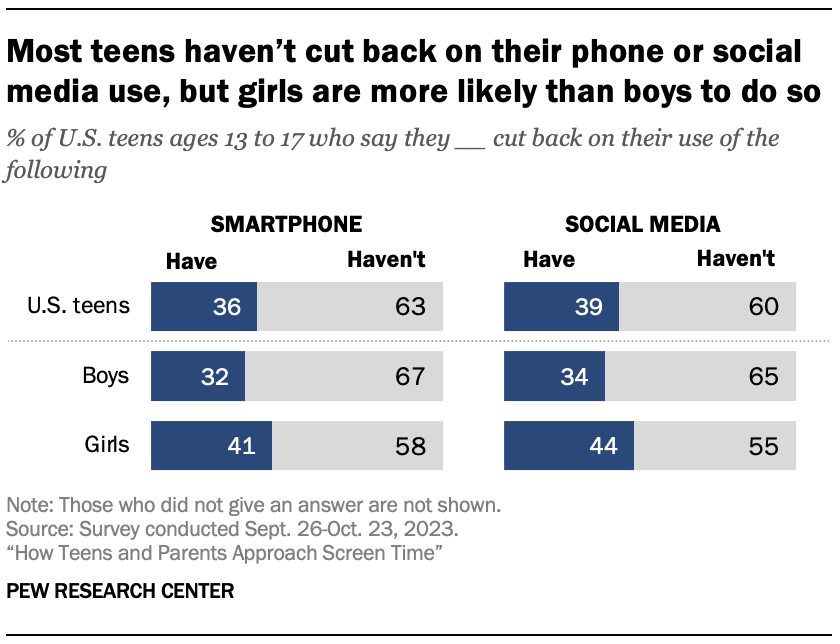
How teens’ behaviors vary by gender
About four-in-ten or more girls say they have cut back on their smartphone or social media use. For boys, those figures drop to roughly one-third.
How teens’ behaviors vary based on their screen time
Teens who report spending too much time on social media and smartphones are especially likely to report cutting back on each. For instance, roughly six-in-ten teens who say they are on social media too much say they have cut back (57%). This is far higher than the 32% among those who say they are on social media too little or the right amount.
How teens feel when they don’t have their phone
Teens encounter a range of emotions when they don’t have their phones, but we asked them about five specific ones. Roughly three-quarters of teens say it often or sometimes makes them feel happy (74%) or peaceful (72%) when they don’t have their smartphone.
Smaller but notable shares of teens equate not having their phone with more negative emotions. Teens say not having their phone at least sometimes makes them feel anxious (44%), upset (40%) and lonely (39%).
It is worth noting that only a minority of teens – ranging from 7% to 32% – say they often feel these emotions when they’re phone-less.
Teens’ feelings on this differ by some demographic factors:
- Age and gender: Older girls ages 15 to 17 (55%) are more likely than younger girls (41%) and teen boys who are younger (41%) and older (40%) to say they feel anxious at least sometimes when they don’t have their smartphone.
- Gender: 45% of teen girls say not having their phone makes them feel lonely regularly, compared with 34% of teen boys.
Do teens think smartphones are negatively impacting young people?
As smartphones have become a universal part of teen life, many have asked what impact, if any, phones are having on today’s youth.
Teens shared their perspectives on smartphones’ impact on people their age and whether these devices have made certain aspects of growing up more or less challenging.
Most teens think the benefits of smartphones outweigh the harms for people their age. Seven-in-ten teens say smartphones provide more benefits than harms for people their age, while a smaller share (30%) take the opposing view, saying there are more harms than benefits.
Teens’ views, by gender and age
Younger girls ages 13 and 14 (39%) are more likely than older teen girls (29%) and teen boys who are younger (29%) and older (25%) to say that the harms of people their age using smartphones outweigh the benefits.
The survey also shows that teens see these devices’ impacts on specific aspects of life differently.
More teens believe smartphones make it easier, rather than harder, to be creative, pursue hobbies and do well in school. Majorities of teens say smartphones make it a little or a lot easier for people their age to pursue hobbies and interests (69%) and be creative (65%). Close to half (45%) say these devices have made it easier for youth to do well in school.
Views are more mixed when it comes to developing healthy friendships. Roughly four-in-ten teens say smartphones make it easier for teens to develop healthy friendships, while 31% each say they make it harder or neither easier nor harder.
But they think smartphones have a more negative than positive impact on teens’ social skills. A larger percentage of teens say smartphones make learning good social skills harder (42%) rather than easier (30%). About three-in-ten say it neither helps nor hurts.
How parents navigate raising teens in the smartphone age
With the rise of smartphones, today’s parents must tackle many questions that previous generations did not. How closely should you monitor their phone use? How much screen time is too much? And how often do phones lead to disagreements?
We developed a set of parallel questions to understand the perspectives of both parents and teens. Here’s what we found:
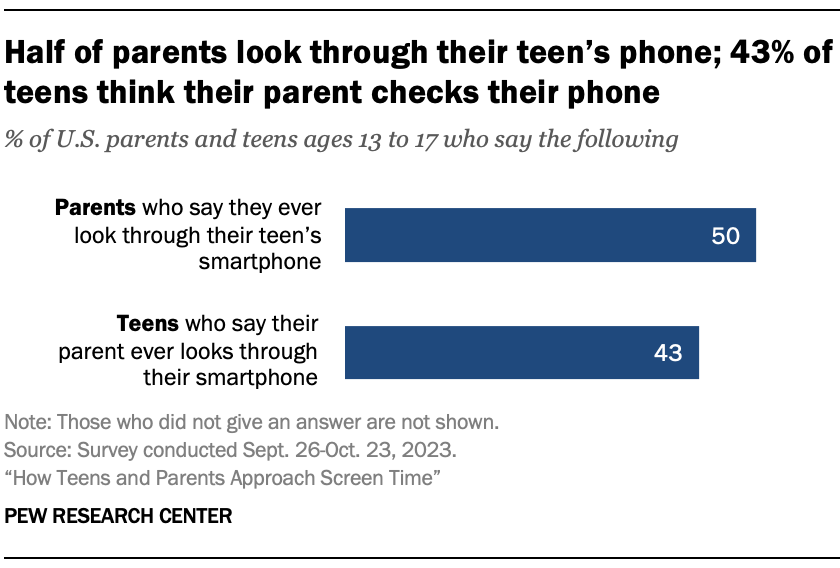
It’s common for parents to look through their teen’s phone – and many of their teens know it. Half of parents of teens say they look through their teen’s phone. When we asked teens if they thought their parents ever look through their phones, 43% believed this had happened.
Whether parents report looking through their child’s smartphone depends on their kid’s age. While 64% of parents of 13- to 14-year-olds say they look through their teen’s smartphone, this share drops to 41% among parents of 15- to 17-year-olds.
Teens’ accounts of this also vary depending on their age: 56% of 13- to 14-year-olds say their parent checks their smartphone, compared with 35% of teens ages 15 to 17.
How often do parents and teens argue about phone time?
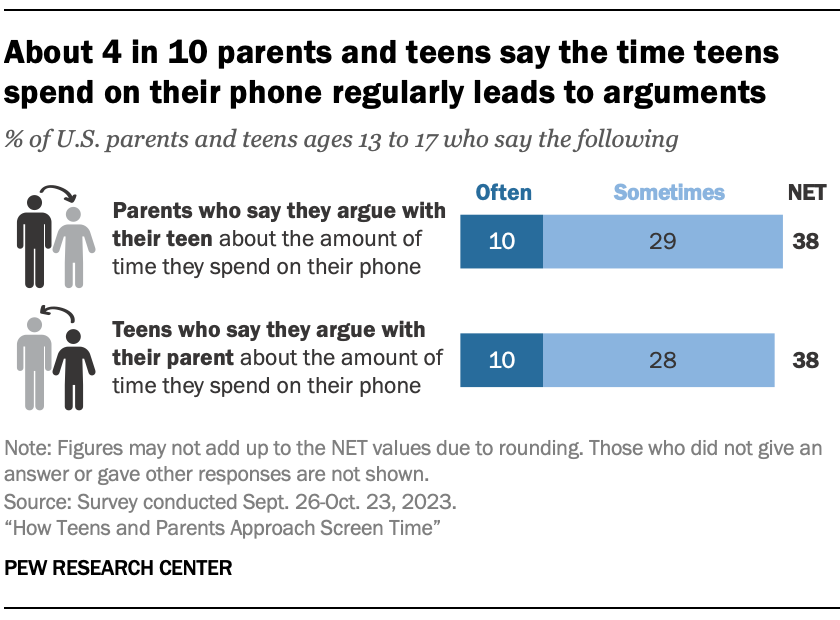
Parents and teens are equally likely to say they argue about phone use. Roughly four-in-ten parents and teens (38% each) say they at least sometimes argue with each other about how much time their teen spends on the phone. This includes 10% in each group who say this happens often .
Still, others say they never have these types of disagreements. One-quarter of parents say they never argue with their teen about this, while 31% of teens say the same.
Teens’ and parents’ views, by race and ethnicity
Hispanic Americans stand out for reporting having these disagreements often. While 16% of Hispanic teens say they often argue with their parent about how much time they’re spending on their phone, that share drops to 9% for White teens and 6% for Black teens. 3
A similar pattern is present among parents. Hispanic parents (19%) are more likely than White (6%) or Black (7%) parents to say they often argue with their teen about this.
Teens’ views, by frequency of internet use
The amount of time teens report being online is also a factor. About half (47%) of teens who report being online almost constantly say they at least sometimes argue with their parent about the amount of time they spend on their phone, compared with those who are online less often (30%).
How much do parents prioritize tracking their teen’s phone use?
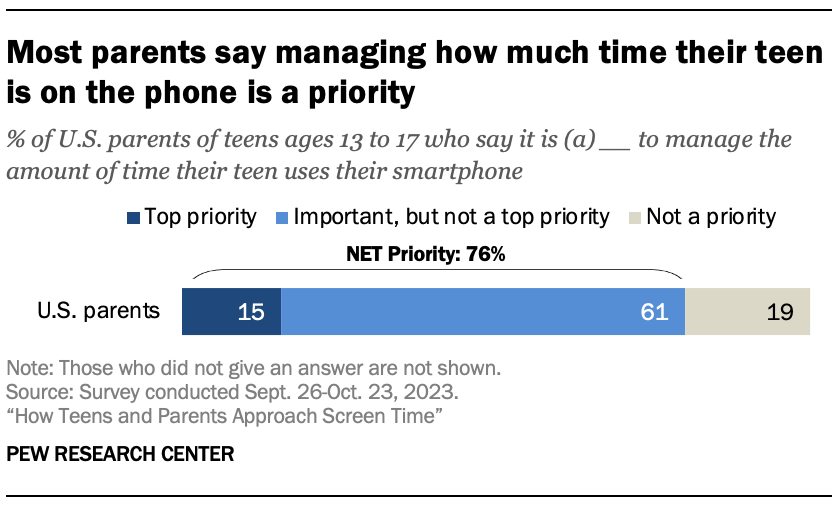
Most parents prioritize managing the amount of time their teen spends on the phone. Roughly three-quarters of parents (76%) say managing how much time their teen spends on the phone is an important or a top priority. Still, 19% of parents don’t consider this a priority.
Parents’ views, by race and ethnicity
Majorities of parents across racial and ethnic groups think of this as a priority. But some groups stand out for how much they prioritize this. For example, Hispanic (25%) or Black (24%) parents are more likely to say managing how much time their teen is on the phone is a top priority. That share drops to 10% among White parents.
Parents’ views, by household income
We also see differences between the lowest and highest income households: 22% of parents whose annual household income is less than $30,000 consider managing the amount of time their teen is on the phone a top priority, compared with 14% of those whose household income is $75,000 or more a year. Those whose household income is $30,000 to $74,999 a year do not meaningfully differ from either group.
Do parents set time limits on their teen’s phone use?
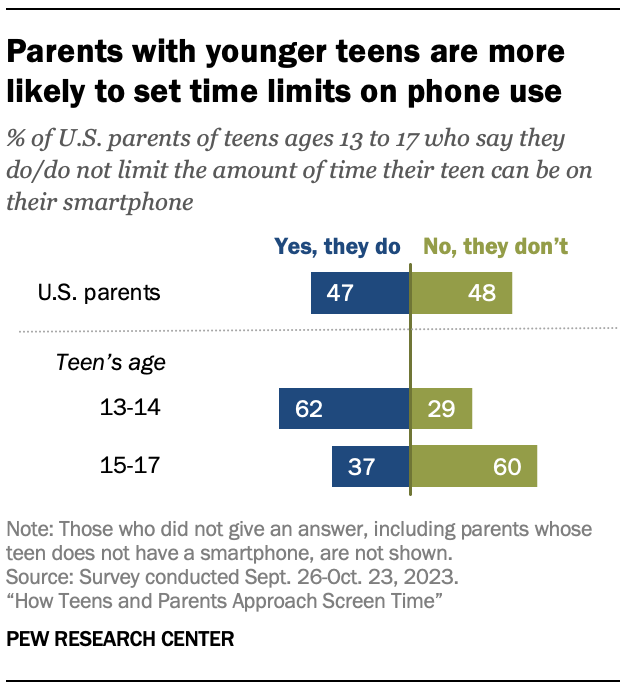
There’s a nearly even split between parents who restrict their teen’s time on their phone and those who don’t. About half of parents (47%) say they limit the amount of time their teen can be on their phone, while a similar share (48%) don’t do this.
Parents’ views, by teen’s age
Parents of younger teens are far more likely to regulate their child’s screen time. While 62% of parents of 13- to 14-year-olds say they limit how much time their teen can be on their phone, that share drops to 37% among those with a 15- to 17-year-old.
How difficult is it for parents to keep up with their teen’s phone use?
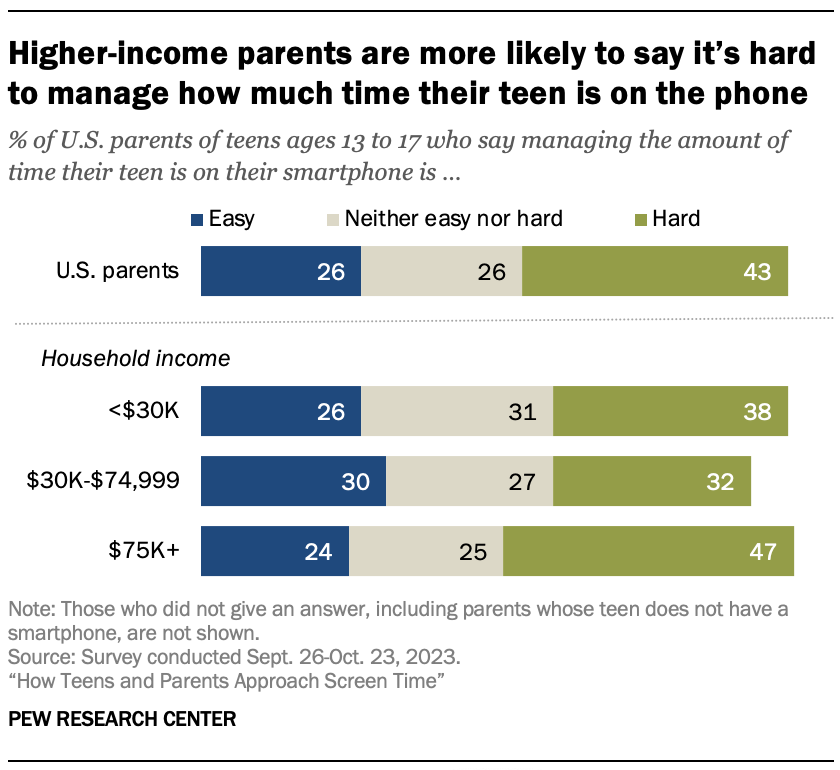
Managing screen time can feel like an uphill battle for some parents. About four-in-ten say it’s hard to manage how much time their teen spends on their phone. A smaller share (26%) says this is easy to do.
Another 26% of parents fall in the middle – saying it’s neither easy nor hard.
Higher-income parents are more likely to find it difficult to manage their teen’s phone time. Roughly half (47%) of parents living in households earning $75,000 or more a year say managing the amount of time their teen is on their phone is hard. These shares are smaller among parents whose annual household income falls below $30,000 (38%) or is between $30,000 and $74,999 (32%).
Parents’ own struggles with device distractions, screen time
Teens aren’t the only ones who can be glued to their phones. Parents, too, can find themselves in an endless cycle of checking emails , text messages and social media.
With that in mind, we asked parents to think about their own screen time – both the time they spend on their phone, and if it ever gets in the way of connecting with their teen.
Do parents think they spend too much time on their phone?
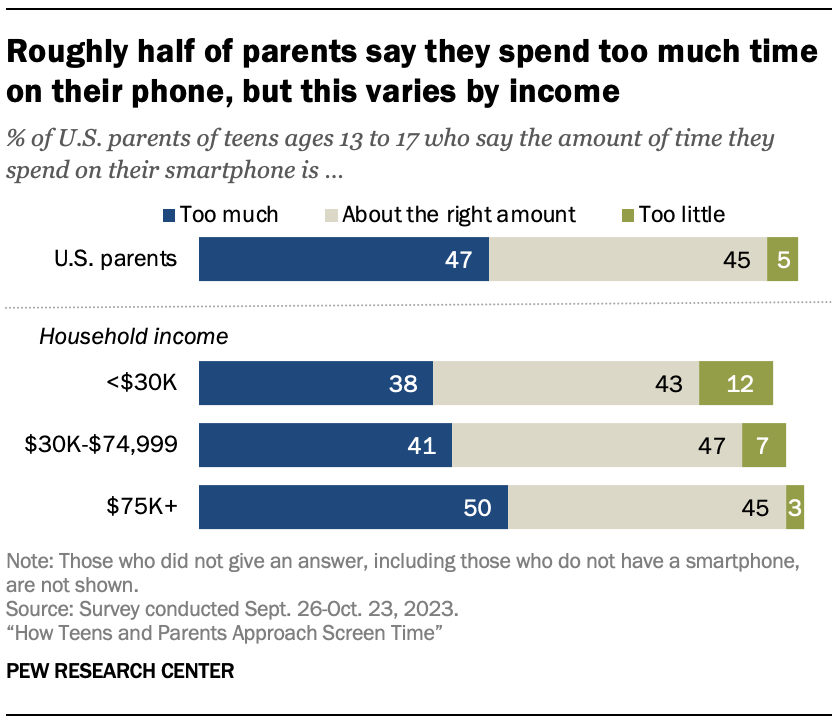
Like teens, parents are far more likely to say they spend too much rather than not enough time on their phone. About half of parents (47%) say they spend too much time on their smartphone. Just 5% think they spend too little time on it. And 45% believe they spend the right amount of time on their phone.
Parents’ views differ by:
- Household Income: 50% of parents with annual household incomes of $75,000 or more say they spend too much time on their phone. This share drops to 41% among those living in households earning $30,000 to $74,999 a year and 38% among those earning under $30,000.
- Race and ethnicity: 57% of White parents believe they spend too much time on their phone, compared with 38% of Black parents and 34% of Hispanic parents.
How often are parents distracted by their phone when talking with their teen?
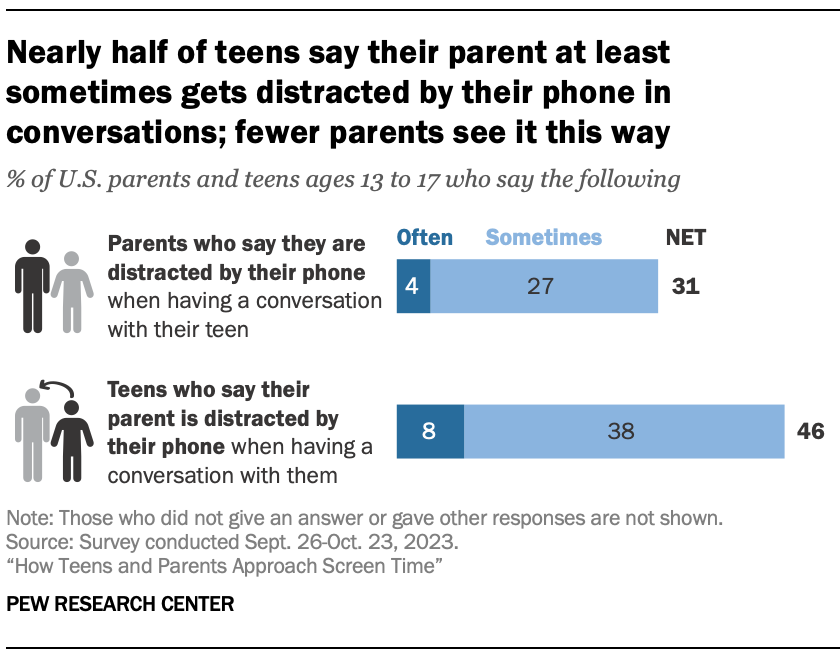
When it comes to distracted parenting, parents paint a rosier picture than teens. Nearly half of teens (46%) say their parent is at least sometimes distracted by their phone when they’re trying to talk to them, including 8% who say this happens often.
But when parents were asked to assess their own behavior, fewer – 31% – say this happens regularly.
- Throughout this report, “teens” refers to those ages 13 to 17 and “parents” refers to those with a child ages 13 to 17. ↩
- A 2018 Center survey also asked U.S teens some of the same questions about experiences and views related to smartphone and social media. Direct comparisons cannot be made across the two surveys due to mode, sampling and recruitment differences. Please read the Methodology section to learn more about how the current survey was conducted. ↩
- There were not enough Asian respondents in the sample to be broken out into a separate analysis. As always, their responses are incorporated into the general population figures throughout the report. ↩
Sign up for our Internet, Science and Tech newsletter
New findings, delivered monthly
Report Materials
Table of contents, teens and internet, device access fact sheet, teens and social media fact sheet, a declining share of adults, and few teens, support a u.s. tiktok ban, teens, social media and technology 2023, about 1 in 5 u.s. teens who’ve heard of chatgpt have used it for schoolwork, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Official websites use .gov
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
Department of Defense Announces Fiscal Year 2024 University Research Funding Awards
The Department of Defense today announced $221 million in awards for basic defense-related research projects as part of the Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative (MURI) program. At an average award amount of $7.5 million over five years, these competitive grants will support 30 teams located at 73 U.S. academic institutions, subject to satisfactory research progress and the availability of funds.
"The science and engineering challenges we face today are highly complex and cross disciplinary," said Dr. Bindu Nair, director of the Basic Research Office in the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering. "The MURI program acknowledges these complexities by supporting teams whose members have diverse sets of expertise as well as creative scientific approaches to tackling problems.
"This cross-fertilization of ideas can accelerate research progress to enable more rapid scientific breakthroughs and hasten the transition of basic research funding to practical applications. The program is a cornerstone of DoD's basic research portfolio and a strong contributor to its legacy of scientific impact."
Since its inception in 1985, the Department's MURI program has allowed teams of investigators from multiple disciplines to generate collective insights, facilitating the growth of cutting-edge technologies to address the Department's unique challenges.
The highly competitive program, which complements the Department's single-investigator basic research grants, has made immense contributions to current and future military capabilities and produced numerous commercial sector applications.
Notable MURI achievements include breakthroughs in cold-atom quantum methods with potential applications in quantum sensing and communication, as well as advances in pulsed magnetic field propagation and Doppler radar detection leading to new detection physics for landmines.
The Fiscal Year 2024 competition identified six topics that received an additional $1.5 million each over the five-year award term specifically to support the participation of historically Black colleges and universities and minority-serving institutions (HBCU/MIs). Seven proposals selected across the six topics will receive support for HBCU/MI participation on the MURI projects.
The Army Research Office, Air Force Office of Scientific Research, and Office of Naval Research solicited Fiscal Year 2024 proposals in 25 topic areas of strategic importance to the Department. After a merit-based review of 276 white papers, a panel of experts narrowed the pool to a subset of 102 full proposals, from which the 30 final awards were selected. The list of winning teams can be downloaded here .
About USD(R&E)
The Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering (USD(R&E)) is the Chief Technology Officer of the Department of Defense. The USD(R&E) champions research, science, technology, engineering, and innovation to maintain the U.S. military's technological advantage. Learn more at www.cto.mil, follow us on Twitter @DoDCTO, or visit us on LinkedIn at https://www.linkedin.com/company/ousdre .
Subscribe to Defense.gov Products
Choose which Defense.gov products you want delivered to your inbox.
Defense.gov
Helpful links.
- Live Events
- Today in DOD
- For the Media
- DOD Resources
- DOD Social Media Policy
- Help Center
- DOD / Military Websites
- Agency Financial Report
- Value of Service
- Taking Care of Our People
- FY 2024 Defense Budget
- National Defense Strategy
The Department of Defense provides the military forces needed to deter war and ensure our nation's security.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
All Topics. Chemistry. ... membership organization dedicated to public engagement in scientific research and education (EIN 53-0196483). Science News Explores; Science News Learning ...
Drought triggers and sustains overnight fires in North America. By examining the hourly diurnal cycle of 23,557 fires in North America during 2017-2020, 1,095 overnight burning events were ...
Article Open Access 15 Mar 2024 Effect of sodium hypochlorite, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and dual-rinse irrigation on dentin adhesion using an etch-and-rinse or self-etch approach Matej Par
Amachine learning algorithm can identify which patients would derive more benefit from cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) versus counseling for depression, suggests research in this Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology (Vol. 88, No. 1) article. Researchers retrospectively explored data from 1,085 patients in the United Kingdom treated ...
Find the answers to your biggest research questions from 2021. With collective views of over 3.7 million, researchers explored topics spanning from nutritional
Breaking science news and articles on global warming, extrasolar planets, stem cells, bird flu, autism, nanotechnology, dinosaurs, evolution -- the latest discoveries ...
The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) is a weekly general medical journal that publishes new medical research and review articles, and editorial opinion on a wide variety of topics of ...
Journal Top 100 - 2022. This collection highlights our most downloaded* research papers published in 2022. Featuring authors from around the world, these papers highlight valuable research from an ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on RESEARCH TOPICS. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on ...
March 6, 2024 • The Voyager 1 space probe is the farthest human-made object in space. It launched in 1977 with a golden record on board that carried assorted sounds of our home planet: greetings ...
1000+ FREE Research Topics & Ideas. If you're at the start of your research journey and are trying to figure out which research topic you want to focus on, you've come to the right place. Select your area of interest below to view a comprehensive collection of potential research ideas. AI & Machine Learning. Blockchain & Cryptocurrency.
December 29, 2021. fotosipsak/Getty Images. Post. Summary. What will it take to make work better? Over the past year, HBR has published a wide array of research-backed articles that explore topics ...
Research Topics . All Publications Methods Short Reads Tools & Resources Experts About. ... About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other ...
Frontiers' Research Topics are collaborative hubs built around an emerging theme. Defined, managed, and led by renowned researchers, they bring together leading experts around a shared area of interest - stimulating collaboration and accelerating science. Managed and disseminated on Frontiers' custom open science platform, topics are free to ...
News about Research, including commentary and archival articles published in The New York Times.
Researchers recently reviewed 69 articles focused on the management implications of the Covid-19 pandemic that were published between March 2020 and July 2023 in top journals in management and ...
113 Great Research Paper Topics. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily ...
Find breaking science news and analysis from the world's leading research journal.
cancer combinational immunotherapy. COVID-19 research. the physiology of breathing during exercise. and the future of animal experimentation. With over 1.8 million views, the following Research Topics sought answers to your biggest research questions from 2023.
Research articles represent the ultimate, final product of a scientific study. You should assume that your published work will be indefinitely available for anyone to access. •. Research articles always consist of a title, abstract, introduction, materials and methods, results, discussion, and references sections, and many include a ...
Inflation in the U.S. at a 40-year high. Small talk around the watercooler (mainly the virtual one, nowadays) certainly feels heavier than it used to. Recent Gallup data indicates that in 2022, companies and managers remain challenged by the task of raising employee engagement to pre-pandemic levels. Nearly half of global workers (44%) surveyed ...
Try our student writing prompts. In 2017, we compiled a list of 401 argumentative writing prompts, all drawn from our daily Student Opinion column. Now, we're rounding up 130 more we've ...
Evidence-based practice in nursing involves providing holistic, quality care based on the most up-to-date research and knowledge rather than traditional methods, advice from colleagues, or personal beliefs. Nurses can expand their knowledge and improve their clinical practice experience by collecting, processing, and implementing research findings.
Latest research and news by subject. Learn about the latest research, reviews and news from across all of the Nature journals by subject. Find a subject. Search. Biological sciences ...
New research puts age of universe at 26.7 billion years, nearly twice as old as previously believed Jul 13, 2023 The universe is expanding faster than theory predicts—physicists are trying to ...
It's time for a generative AI (gen AI) reset. The initial enthusiasm and flurry of activity in 2023 is giving way to second thoughts and recalibrations as companies realize that capturing gen AI's enormous potential value is harder than expected.. With 2024 shaping up to be the year for gen AI to prove its value, companies should keep in mind the hard lessons learned with digital and AI ...
This Pew Research Center survey of 1,453 U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 and their parents was conducted Sept. 26-Oct. 23, 2023. 1 Jump to read about views among teens on: Screen time | Feelings when disconnected from phones | Thoughts on smartphones' impact. Jump to read about views among parents on: Parenting in the smartphone age | Their own screen time struggles
The Army Research Office, Air Force Office of Scientific Research, and Office of Naval Research solicited Fiscal Year 2024 proposals in 25 topic areas of strategic importance to the Department.