- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students

Online Guide to Writing and Research
College writing, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
What Is College Writing?
College writing, also called academic writing, teaches critical thinking and writing skills useful both in class and in other areas of life. College courses demand many different kinds of writing using a variety of strategies for different audiences. Sometimes your instructor will assign a topic and define the audience; sometimes you will have to define the topic and audience yourself.

Types of Assignments
You will write many different types of assignments throughout your college career. Each type of assignment has specific requirements for content and format. The process of completing these assignments teaches you about the series of decisions you must make as you forge the link between your information and your audience. Click on the arrows below for some assignment types typically assigned in college.
written arguments
Short answers (such as discussion posts or essay questions on tests), lab reports, documentation of the research process, design documents (brochures, newsletters, powerpoints), business reports or plans, research essays, literature reviews, case studies, educating yourself through research.
Most college writing emphasizes the knowledge you gain in class and through research. This makes such writing different from your previous writing and perhaps more challenging. Instructors may expect your essays to contain more research and to show that you are capable of effectively evaluating those sources. You might be expected to incorporate sophisticated expository techniques, such as argument and persuasion, and to avoid flawed thinking, such as false assumptions and leaps in logic. You will often use the skills you learn in college writing throughout your life.
Key Takeaways
College writing
- teaches critical thinking skills.
- allows you to demonstrate your knowledge.
- takes many forms, depending on the discipline, the audience, the knowledge involved, and the goal of the assignment.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Understanding Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource describes some steps you can take to better understand the requirements of your writing assignments. This resource works for either in-class, teacher-led discussion or for personal use.
How to Decipher the Paper Assignment
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing.
- Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
- Underline or circle the portions that you absolutely must know. This information may include due date, research (source) requirements, page length, and format (MLA, APA, CMS).
- Underline or circle important phrases. You should know your instructor at least a little by now - what phrases do they use in class? Does he repeatedly say a specific word? If these are in the prompt, you know the instructor wants you to use them in the assignment.
- Think about how you will address the prompt. The prompt contains clues on how to write the assignment. Your instructor will often describe the ideas they want discussed either in questions, in bullet points, or in the text of the prompt. Think about each of these sentences and number them so that you can write a paragraph or section of your essay on that portion if necessary.
- Rank ideas in descending order, from most important to least important. Instructors may include more questions or talking points than you can cover in your assignment, so rank them in the order you think is more important. One area of the prompt may be more interesting to you than another.
- Ask your instructor questions if you have any.
After you are finished with these steps, ask yourself the following:
- What is the purpose of this assignment? Is my purpose to provide information without forming an argument, to construct an argument based on research, or analyze a poem and discuss its imagery?
- Who is my audience? Is my instructor my only audience? Who else might read this? Will it be posted online? What are my readers' needs and expectations?
- What resources do I need to begin work? Do I need to conduct literature (hermeneutic or historical) research, or do I need to review important literature on the topic and then conduct empirical research, such as a survey or an observation? How many sources are required?
- Who - beyond my instructor - can I contact to help me if I have questions? Do you have a writing lab or student service center that offers tutorials in writing?
(Notes on prompts made in blue )
Poster or Song Analysis: Poster or Song? Poster!
Goals : To systematically consider the rhetorical choices made in either a poster or a song. She says that all the time.
Things to Consider: ah- talking points
- how the poster addresses its audience and is affected by context I'll do this first - 1.
- general layout, use of color, contours of light and shade, etc.
- use of contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity C.A.R.P. They say that, too. I'll do this third - 3.
- the point of view the viewer is invited to take, poses of figures in the poster, etc. any text that may be present
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing I'll cover this second - 2.
- ethical implications
- how the poster affects us emotionally, or what mood it evokes
- the poster's implicit argument and its effectiveness said that was important in class, so I'll discuss this last - 4.
- how the song addresses its audience
- lyrics: how they rhyme, repeat, what they say
- use of music, tempo, different instruments
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing
- emotional effects
- the implicit argument and its effectiveness
These thinking points are not a step-by-step guideline on how to write your paper; instead, they are various means through which you can approach the subject. I do expect to see at least a few of them addressed, and there are other aspects that may be pertinent to your choice that have not been included in these lists. You will want to find a central idea and base your argument around that. Additionally, you must include a copy of the poster or song that you are working with. Really important!
I will be your audience. This is a formal paper, and you should use academic conventions throughout.
Length: 4 pages Format: Typed, double-spaced, 10-12 point Times New Roman, 1 inch margins I need to remember the format stuff. I messed this up last time =(
Academic Argument Essay
5-7 pages, Times New Roman 12 pt. font, 1 inch margins.
Minimum of five cited sources: 3 must be from academic journals or books
- Design Plan due: Thurs. 10/19
- Rough Draft due: Monday 10/30
- Final Draft due: Thurs. 11/9
Remember this! I missed the deadline last time
The design plan is simply a statement of purpose, as described on pages 40-41 of the book, and an outline. The outline may be formal, as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline.
This project is an expansion of your opinion editorial. While you should avoid repeating any of your exact phrases from Project 2, you may reuse some of the same ideas. Your topic should be similar. You must use research to support your position, and you must also demonstrate a fairly thorough knowledge of any opposing position(s). 2 things to do - my position and the opposite.
Your essay should begin with an introduction that encapsulates your topic and indicates 1 the general trajectory of your argument. You need to have a discernable thesis that appears early in your paper. Your conclusion should restate the thesis in different words, 2 and then draw some additional meaningful analysis out of the developments of your argument. Think of this as a "so what" factor. What are some implications for the future, relating to your topic? What does all this (what you have argued) mean for society, or for the section of it to which your argument pertains? A good conclusion moves outside the topic in the paper and deals with a larger issue.
You should spend at least one paragraph acknowledging and describing the opposing position in a manner that is respectful and honestly representative of the opposition’s 3 views. The counterargument does not need to occur in a certain area, but generally begins or ends your argument. Asserting and attempting to prove each aspect of your argument’s structure should comprise the majority of your paper. Ask yourself what your argument assumes and what must be proven in order to validate your claims. Then go step-by-step, paragraph-by-paragraph, addressing each facet of your position. Most important part!
Finally, pay attention to readability . Just because this is a research paper does not mean that it has to be boring. Use examples and allow your opinion to show through word choice and tone. Proofread before you turn in the paper. Your audience is generally the academic community and specifically me, as a representative of that community. Ok, They want this to be easy to read, to contain examples I find, and they want it to be grammatically correct. I can visit the tutoring center if I get stuck, or I can email the OWL Email Tutors short questions if I have any more problems.
Search form
How to write the best college assignments.
By Lois Weldon
When it comes to writing assignments, it is difficult to find a conceptualized guide with clear and simple tips that are easy to follow. That’s exactly what this guide will provide: few simple tips on how to write great assignments, right when you need them. Some of these points will probably be familiar to you, but there is no harm in being reminded of the most important things before you start writing the assignments, which are usually determining on your credits.
The most important aspects: Outline and Introduction
Preparation is the key to success, especially when it comes to academic assignments. It is recommended to always write an outline before you start writing the actual assignment. The outline should include the main points of discussion, which will keep you focused throughout the work and will make your key points clearly defined. Outlining the assignment will save you a lot of time because it will organize your thoughts and make your literature searches much easier. The outline will also help you to create different sections and divide up the word count between them, which will make the assignment more organized.
The introduction is the next important part you should focus on. This is the part that defines the quality of your assignment in the eyes of the reader. The introduction must include a brief background on the main points of discussion, the purpose of developing such work and clear indications on how the assignment is being organized. Keep this part brief, within one or two paragraphs.
This is an example of including the above mentioned points into the introduction of an assignment that elaborates the topic of obesity reaching proportions:
Background : The twenty first century is characterized by many public health challenges, among which obesity takes a major part. The increasing prevalence of obesity is creating an alarming situation in both developed and developing regions of the world.
Structure and aim : This assignment will elaborate and discuss the specific pattern of obesity epidemic development, as well as its epidemiology. Debt, trade and globalization will also be analyzed as factors that led to escalation of the problem. Moreover, the assignment will discuss the governmental interventions that make efforts to address this issue.
Practical tips on assignment writing
Here are some practical tips that will keep your work focused and effective:
– Critical thinking – Academic writing has to be characterized by critical thinking, not only to provide the work with the needed level, but also because it takes part in the final mark.
– Continuity of ideas – When you get to the middle of assignment, things can get confusing. You have to make sure that the ideas are flowing continuously within and between paragraphs, so the reader will be enabled to follow the argument easily. Dividing the work in different paragraphs is very important for this purpose.
– Usage of ‘you’ and ‘I’ – According to the academic writing standards, the assignments should be written in an impersonal language, which means that the usage of ‘you’ and ‘I’ should be avoided. The only acceptable way of building your arguments is by using opinions and evidence from authoritative sources.
– Referencing – this part of the assignment is extremely important and it takes a big part in the final mark. Make sure to use either Vancouver or Harvard referencing systems, and use the same system in the bibliography and while citing work of other sources within the text.
– Usage of examples – A clear understanding on your assignment’s topic should be provided by comparing different sources and identifying their strengths and weaknesses in an objective manner. This is the part where you should show how the knowledge can be applied into practice.
– Numbering and bullets – Instead of using numbering and bullets, the academic writing style prefers the usage of paragraphs.
– Including figures and tables – The figures and tables are an effective way of conveying information to the reader in a clear manner, without disturbing the word count. Each figure and table should have clear headings and you should make sure to mention their sources in the bibliography.
– Word count – the word count of your assignment mustn’t be far above or far below the required word count. The outline will provide you with help in this aspect, so make sure to plan the work in order to keep it within the boundaries.
The importance of an effective conclusion
The conclusion of your assignment is your ultimate chance to provide powerful arguments that will impress the reader. The conclusion in academic writing is usually expressed through three main parts:
– Stating the context and aim of the assignment
– Summarizing the main points briefly
– Providing final comments with consideration of the future (discussing clear examples of things that can be done in order to improve the situation concerning your topic of discussion).
Normal 0 false false false EN-US X-NONE X-NONE /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-priority:99; mso-style-parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt; mso-para-margin:0in; mso-para-margin-bottom:.0001pt; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:11.0pt; font-family:"Calibri","sans-serif"; mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri; mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri; mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;}
Lois Weldon is writer at Uk.bestdissertation.com . Lives happily at London with her husband and lovely daughter. Adores writing tips for students. Passionate about Star Wars and yoga.
7 comments on “How To Write The Best College Assignments”
Extremely useful tip for students wanting to score well on their assignments. I concur with the writer that writing an outline before ACTUALLY starting to write assignments is extremely important. I have observed students who start off quite well but they tend to lose focus in between which causes them to lose marks. So an outline helps them to maintain the theme focused.
Hello Great information…. write assignments
Well elabrated
Thanks for the information. This site has amazing articles. Looking forward to continuing on this site.
This article is certainly going to help student . Well written.
Really good, thanks
Practical tips on assignment writing, the’re fantastic. Thank you!
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1 Chapter 1: An Introduction to College Writing
In all likelihood, college-level writing will be different from other forms of writing students might have done in the past. This is because academic writing (as opposed to personal writing or creative writing) consists of writing that exists for a school-like or college-based setting. While many students have written essays for classes in the past, they might have been given a wide range of latitude in their assignments. Essays that are written for college classes and for professional contexts typically shift the focus away from the student (or employee) and onto the priorities of the readers.
ACADEMIC WRITING
Overview: Unlike personal writing, academic writing is not about you, the author. Instead, it is about answering a particular assignment, in a particular situation, for a particular reader. For the most part, academic writing exists for a readership that is different from the writer. Because academic writing exists for other people , the expectations and requirements of those other people tend to dictate the form and scope of an academic essay.
Most importantly, academic writing tends to be about what the student can prove, or what the student has learned from outside sources, and not about what the student feels . Sometimes this need for proof will take the form of taking a handful of ‘given’ or axiomatic facts and assembling them logically into a written work that resembles a ‘proof’ from geometry.
- Socrates is a man, and
- All men are mortal, therefore
- Socrates is mortal
Other times, very little will be given, and it will be the responsibility of the student to establish not just the argument but the conditions of the argument.
One of the first things that a college-level writer should consider is what goals an instructor might have had for assigning an essay. Because most college-level essays are not intended to be read by a large population of people, these assignments tend to be given for the sake of the assignment itself. Even if the instructor says “write a letter to the editor of a newspaper for a general audience,” what the instructor probably means is “write a letter to the editor of a newspaper for what I think a general audience should be like .” At the same time, the student writer should consider what might be learned from completing the assignment.
Application: In some ways, academic writing is a kind of ‘training’ or ‘practice.’ It often involves practicing skills taught during class, and it also involves applying the content of the class in a new context. Even if the student does not feel the essay ‘does anything,’ it is uncommon for essays in an academic setting to be ‘busywork.’ When a tennis player practices forehands (even though there is no ‘game’ going on) or a weightlifter lifts in order to condition muscles (as opposed to, say, helping a friend to move into a new apartment), it’s not busywork. The application of the skills and the development of the physical tools are, ultimately, the point. They are practice. Academic writing, like many college assignments, is about the development of mental tools.
In other words, a term paper in a college class is a great way for an instructor to make sure that the student has learned, at least temporarily, enough about the subject to write the term paper. The instructor wants students to show that they have thought about the subject and understood it, so a short paragraph that simply repeats a point the instructor made in class lecture is unlikely to fulfill the instructor’s goals. Be careful to look at any assignment and to understand its context (i.e. the teacher who assigns the paper, the class the paper is assigned in, and the stated goals of that class).
What to Avoid: Try not to make the writing personal. Maybe you will have a teacher who encourages you to introduce more of yourself into an essay, but it is usually safer to begin from a more neutral and more balanced perspective. This does not mean that academic writing has to be boring–it means that it needs to appeal to multiple readers, and not just the tastes of one writer. Academic writing asks for things like evidence and proof, and students who rely too heavily on personal opinion run the risk of writing for themselves, instead of for their readers. Most of the time, the writing assignment is about the process (i.e. the thought that goes into writing) and not the product (i.e. the five-page thing you turn in the next day).
WRITING FOR OTHERS
Probably more than at any other point in history, writing has become a personal activity. Social media encourages us to express our own thoughts, feelings, and beliefs. We write about personal experiences, and we are accountable only in the general sense that others might (or might not) care about what we have written. However, even here an echo chamber is created, where those who like to read our feelings do, and those who do not share these ideas simply go somewhere else and listen to the voices that they do like.
Academic writing is not about the personal. It is not about writers, and the students writing academic essays don’t have the option of saying “if you don’t like it, just don’t read it.” Truthfully, academic writing is only partially about readers. Instead, it is about presenting valid and reliable information to our readers. This means that even if an academic essay might make its readers happy, if it does not represent facts accurately, it is still flawed. We are accountable to give those who receive our messages accurate information in a form that they can understand, and this requires a change in mindset.
Overview: Typically, a piece of writing can be thought of as existing for the sake of the writer (like a personal journal or a grocery list) or for the sake of a reader (like a set of instructions or an exam essay). Knowing who will read the essay lets a writer know what can and cannot be assumed about a subject. For example, a recipe for cookies probably does not need to educate readers on what a cookie is, and probably does not even need to include a review on how to turn on an oven. It might need an explanation of certain terms (like ‘creaming’). It probably will need a list of ingredients. By contrast, an essay on the history of the chocolate chip cookie might need a few sentences establishing the historical context, but it does not need to launch into a complete history of World War II (during which time the cookies became very popular).
Good writers keep in mind at all times who will be reading their work and how those readers will be using the work. In the above example, the person writing the cookie recipe can be pretty sure that the reader will be making cookies, but will probably be a little less certain about what the future baker’s personal tastes are going to be (or where the baker might live). This might result in additional directions about how to substitute chocolate candies for chocolate chips or how to adjust for baking at a higher altitude.
Application: A college-level essay usually has multiple readers, but the ultimate reality is that there is one reader that matters more than others—the person grading the essay. What this means is that a student writer needs to consider what reasons the instructor might have had for assigning the essay. These reasons might not be stated aloud. Maybe the assigned “goal” of the essay is to “teach your readers about the meaning of marriage in Twelfth Night ,” but as far as a student is concerned, the “goal” of the essay is to get a decent grade. Remember, though that as far as the instructor is concerned, the “goal” of the essay is to make sure that each student has at least some practice with analysis. In other words, the way for a student to get that “decent grade” is to show the instructor the skill that is being asked for—in this case, analysis.
In this case, there are three goals, and they work together. The teacher gets the student to practice analysis (goal one) by assigning a paper on Twelfth Night . The student writes about Twelfth Night (goal two) as a way of motivating the teacher to assign a high grade (goal three).
What to Avoid: Do not write the essay for the wrong readers. Writing an essay that a parent, a significant other, or a roommate likes is not the same thing as writing an essay that meets an instructor’s expectations. Most importantly, do not write the essay in a vacuum. Make sure that you do not assume that just because one of your instructors in high school always let you get away with poor use of punctuation because “it’s the ideas that count” does not mean that your new instructor (or, in another setting, your employer) will agree.
CREATING A CONNECTION
Even two people with most things in common (imagine, say, siblings—who share parents, schools, neighbors, culture, etc.) sometimes have breakdowns in communication. People with the best of intentions often struggle to understand one another. When Person A talks to Person B, sometimes differences in how words are defined, how facts are viewed, and how issues are weighed can lead to disagreement. Because academic writing is for others, overcoming the ‘disconnect’ is the responsibility of the writer.
Overview: Being disconnected happens when the person trying to communicate fails to do so because something else (another idea, another person, or even just time or culture) gets in the way. Sometimes, it’s a matter of definition. If I refer to a specific professional athlete as a “great” player, what is my threshold for great? Do I mean the player is better that average? Better than the person playing the same position for my team? One of the best alive? One of the best all-time? All could be ‘great,’ and knowing which one of those definitions I mean could help prevent a disagreement.
Sometimes, being disconnected comes about because the writer makes an assumption about how facts are viewed. Imagine that the writer finds an authoritative statement from a world leader that says “X is very, very bad” as a way of trying to convince the reader to stop doing it. The reader might agree that the politician said exactly that; however, if the reader voted against the politician and really dislikes the stance of that politician’s political party, then the quotation actually serves an opposite purpose.
Finally, writer and reader alike might largely agree on definitions and viewpoint, but they disagree on what is of the greatest importance. Perhaps they might agree that the household budget needs to be cut, and they agree that the best place to start is with the luxuries they have in their budget. However, one person considers the cable bill to be a luxury and the other thinks that it’s time to switch to generic soft drinks, instead of Pepsi or Coke (or, perhaps, it’s time to cut soft drinks completely).
Application: In college-level writing, it’s essential that the student writer establish a connection with potential readers (see Writing for Others ). One of the best ways to do this is to spend some time thinking like the reader. If the student has an argument, he or she should wonder what reasons people might have for disagreeing with that argument. Moreover, all students should spend some time thinking about the assumptions that they make.
Many cases of being disconnected come not from deliberate moves, but rather from what the writer doesn’t think about. Student writers will frequently find it useful to clarify how key terms will be used during an essay. Likewise, they might find it useful to explain what they will not be addressing. For example, an argument about tuition in college is likely to be emotionally taxing enough, so a student might explain that while debates about student loan programs are valid, they will not be the focus of the given essay.
What to Avoid: The most important for student writers to avoid is the assumption. Student writers will frequently make the mistake of assuming that something they believe is either true or at least widely accepted by most people. Almost as important is for the student writer not to fall into the trap of thinking “I explained everything fine, so it’s the reader’s fault if he or she doesn’t understand my point. Not my problem.” Because academic writing exists for the reader, the burden is on the writer. Failing to connect with your audience is your problem.
TYPES OF ASSIGNMENTS
As was mentioned before, very little college writing is initiated by students. Instead, a typical piece of college writing is a response to an instructor’s assignment. The vast majority of these assignments are information-based (the instructor wants the student to report information), with both analysis and argumentation filling secondary rolls. Understanding the ways these goals interact is important for college writers.
Overview: In the past, students might have encountered general categories of writing like informative , persuasive , or narrative. Other times, students might have encountered the five paragraph theme . What’s important to remember about these categories is that they are not exclusive, and that the goals often overlap. Imagine a tiger—is it a striped animal, a furred animal, or a clawed animal? It is difficult to inform readers without persuading them that the information is correct, and it is really difficult to create a narrative that contains no information.
Types and categories are only useful when they help us, and they are spectacularly not useful when we assume that the mental boxes we used to sort things a few years ago are the same categories that apply now.
Application: When writing, student writers need to let the assignment and the content dictate their organizational pattern. Many times, an idea that would fit into a 5-paragraph essay format for a high school class will, in fact, require vastly greater development in college; suddenly, there are more than five paragraphs. Likewise, while the student might prefer it if all assignments fit nicely into modes that have been learned in the past, the most common mode found in a college essay is the challenging paper . Instructors often deliberately construct assignments that combine paper types and that ask for the student to do new things.
The teacher is not being difficult for the sake of being difficult (well, probably not, anyway). However, remember the purpose of college writing—the teacher is trying to use the writing assignment as a way of getting at some other, probably more important—skill or issue. In other words, the point of the assignment is to learn something. An assignment that exists only on one level is likely to let the student fall back into ‘auto pilot’ mode and stop learning.
What to Avoid: Do not assume that papers exist in separate boxes. The truth of the matter is that most college papers are going to consist of multiple “modes” or “formats” at the same time. More importantly, the rules that work for one teacher might not work for another. Because the two top goals should be to learn and to do well on the assignment, a student writer needs to look at what the teacher is asking for. If it fits a pattern that the student has already learned, that’s fine. Otherwise, students need to be able to adapt.
Writing Academic Arguments Copyright © by Joshua P. Sunderbruch. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8.1 What’s Different about College Writing?
Learning objectives.
- Define “academic writing.”
- Identify key differences between writing in college and writing in high school or on the job.
- Identify different types of papers that are commonly assigned.
- Describe what instructors expect from student writing.
Academic writing refers to writing produced in a college environment. Often this is writing that responds to other writing—to the ideas or controversies that you’ll read about. While this definition sounds simple, academic writing may be very different from other types of writing you have done in the past. Often college students begin to understand what academic writing really means only after they receive negative feedback on their work. To become a strong writer in college, you need to achieve a clear sense of two things:
- The academic environment
- The kinds of writing you’ll be doing in that environment
Differences between High School and College Writing
Students who struggle with writing in college often conclude that their high school teachers were too easy or that their college instructors are too hard. In most cases, neither explanation is fully accurate or fair. A student having difficulty with college writing usually just hasn’t yet made the transition from high school writing to college writing. That shouldn’t be surprising, for many beginning college students do not even know that there is a transition to be made.
In high school, most students think of writing as the subject of English classes. Few teachers in other courses give much feedback on student writing; many do not even assign writing. This says more about high school than about the quality of teachers or about writing itself. High school teachers typically teach five courses a day and often more than 150 students. Those students often have a very wide range of backgrounds and skill levels.
Thus many high school English instructors focus on specific, limited goals. For example, they may teach the “five paragraph essay” as the right way to organize a paper because they want to give every student some idea of an essay’s basic structure. They may give assignments on stories and poems because their own college background involved literature and literary analysis. In classes other than English, many high school teachers must focus on an established body of information and may judge students using tests that measure only how much of this information they acquire. Often writing itself is not directly addressed in such classes.
This does not mean that students don’t learn a great deal in high school, but it’s easy to see why some students think that writing is important only in English classes. Many students also believe an academic essay must be five paragraphs long or that “school writing” is usually literary analysis.
Think about how college differs from high school. In many colleges, the instructors teach fewer classes and have fewer students. In addition, while college students have highly diverse backgrounds, the skills of college students are less variable than in an average high school class. In addition, college instructors are specialists in the fields they teach, as you recall from Chapter 7 “Interacting with Instructors and Classes” . College instructors may design their courses in unique ways, and they may teach about specialized subjects. For all of these reasons, college instructors are much more likely than high school teachers to
- assign writing,
- respond in detail to student writing,
- ask questions that cannot be dealt with easily in a fixed form like a five-paragraph essay.
Your transition to college writing could be even more dramatic. The kind of writing you have done in the past may not translate at all into the kind of writing required in college. For example, you may at first struggle with having to write about very different kinds of topics, using different approaches. You may have learned only one kind of writing genre (a kind of approach or organization) and now find you need to master other types of writing as well.
What Kinds of Papers Are Commonly Assigned in College Classes?
Think about the topic “gender roles”—referring to expectations about differences in how men and women act. You might study gender roles in an anthropology class, a film class, or a psychology class. The topic itself may overlap from one class to another, but you would not write about this subject in the same way in these different classes. For example, in an anthropology class, you might be asked to describe how men and women of a particular culture divide important duties. In a film class, you may be asked to analyze how a scene portrays gender roles enacted by the film’s characters. In a psychology course, you might be asked to summarize the results of an experiment involving gender roles or compare and contrast the findings of two related research projects.
It would be simplistic to say that there are three, or four, or ten, or any number of types of academic writing that have unique characteristics, shapes, and styles. Every assignment in every course is unique in some ways, so don’t think of writing as a fixed form you need to learn. On the other hand, there are certain writing approaches that do involve different kinds of writing. An approach is the way you go about meeting the writing goals for the assignment. The approach is usually signaled by the words instructors use in their assignments.
When you first get a writing assignment, pay attention first to keywords for how to approach the writing. These will also suggest how you may structure and develop your paper. Look for terms like these in the assignment:
- Summarize. To restate in your own words the main point or points of another’s work.
- Define. To describe, explore, or characterize a keyword, idea, or phenomenon.
- Classify. To group individual items by their shared characteristics, separate from other groups of items.
- Compare/contrast. To explore significant likenesses and differences between two or more subjects.
- Analyze. To break something, a phenomenon, or an idea into its parts and explain how those parts fit or work together.
- Argue. To state a claim and support it with reasons and evidence.
- Synthesize. To pull together varied pieces or ideas from two or more sources.
Note how this list is similar to the words used in examination questions that involve writing. (See Table 6.1 “Words to Watch for in Essay Questions” in Chapter 6 “Preparing for and Taking Tests” , Section 6.4 “The Secrets of the Q and A’s” .) This overlap is not a coincidence—essay exams are an abbreviated form of academic writing such as a class paper.
Sometimes the keywords listed don’t actually appear in the written assignment, but they are usually implied by the questions given in the assignment. “What,” “why,” and “how” are common question words that require a certain kind of response. Look back at the keywords listed and think about which approaches relate to “what,” “why,” and “how” questions.
- “What” questions usually prompt the writing of summaries, definitions, classifications, and sometimes compare-and-contrast essays. For example, “ What does Jones see as the main elements of Huey Long’s populist appeal?” or “ What happened when you heated the chemical solution?”
- “Why” and “how” questions typically prompt analysis, argument, and synthesis essays. For example, “ Why did Huey Long’s brand of populism gain force so quickly?” or “ Why did the solution respond the way it did to heat?”
Successful academic writing starts with recognizing what the instructor is requesting, or what you are required to do. So pay close attention to the assignment. Sometimes the essential information about an assignment is conveyed through class discussions, however, so be sure to listen for the keywords that will help you understand what the instructor expects. If you feel the assignment does not give you a sense of direction, seek clarification. Ask questions that will lead to helpful answers. For example, here’s a short and very vague assignment:
Discuss the perspectives on religion of Rousseau, Bentham, and Marx. Papers should be four to five pages in length.
Faced with an assignment like this, you could ask about the scope (or focus) of the assignment:
- Which of the assigned readings should I concentrate on?
- Should I read other works by these authors that haven’t been assigned in class?
- Should I do research to see what scholars think about the way these philosophers view religion?
- Do you want me to pay equal attention to each of the three philosophers?
You can also ask about the approach the instructor would like you to take. You can use the keywords the instructor may not have used in the assignment:
- Should I just summarize the positions of these three thinkers, or should I compare and contrast their views?
- Do you want me to argue a specific point about the way these philosophers approach religion?
- Would it be OK if I classified the ways these philosophers think about religion?
Never just complain about a vague assignment. It is fine to ask questions like these. Such questions will likely engage your instructor in a productive discussion with you.
Key Takeaways
- Writing is crucial to college success because it is the single most important means of evaluation.
- Writing in college is not limited to the kinds of assignments commonly required in high school English classes.
- Writers in college must pay close attention to the terms of an assignment.
- If an assignment is not clear, seek clarification from the instructor.
Checkpoint Exercises
What kind(s) of writing have you practiced most in your recent past?
____________________________________________________________________
Name two things that make academic writing in college different from writing in high school.
Explain how the word “what” asks for a different kind of paper than the word “why.”
College Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Academic writing
What Is Academic Writing? | Dos and Don’ts for Students
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You’ll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you’ll be expected to write your essays , research papers , and dissertation in academic style.
Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but it has specific conventions in terms of content, structure and style.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Types of academic writing, academic writing is…, academic writing is not…, useful tools for academic writing, academic writing checklist.
Academics mostly write texts intended for publication, such as journal articles, reports, books, and chapters in edited collections. For students, the most common types of academic writing assignments are listed below.
Different fields of study have different priorities in terms of the writing they produce. For example, in scientific writing it’s crucial to clearly and accurately report methods and results; in the humanities, the focus is on constructing convincing arguments through the use of textual evidence. However, most academic writing shares certain key principles intended to help convey information as effectively as possible.
Whether your goal is to pass your degree, apply to graduate school , or build an academic career, effective writing is an essential skill.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Formal and unbiased
Academic writing aims to convey information in an impartial way. The goal is to base arguments on the evidence under consideration, not the author’s preconceptions. All claims should be supported with relevant evidence, not just asserted.
To avoid bias, it’s important to represent the work of other researchers and the results of your own research fairly and accurately. This means clearly outlining your methodology and being honest about the limitations of your research.
The formal style used in academic writing ensures that research is presented consistently across different texts, so that studies can be objectively assessed and compared with other research.
Because of this, it’s important to strike the right tone with your language choices. Avoid informal language , including slang, contractions , clichés, and conversational phrases:
- Also , a lot of the findings are a little unreliable.
- Moreover , many of the findings are somewhat unreliable.
Clear and precise
It’s important to use clear and precise language to ensure that your reader knows exactly what you mean. This means being as specific as possible and avoiding vague language :
- People have been interested in this thing for a long time .
- Researchers have been interested in this phenomenon for at least 10 years .
Avoid hedging your claims with words like “perhaps,” as this can give the impression that you lack confidence in your arguments. Reflect on your word choice to ensure it accurately and directly conveys your meaning:
- This could perhaps suggest that…
- This suggests that…
Specialist language or jargon is common and often necessary in academic writing, which generally targets an audience of other academics in related fields.
However, jargon should be used to make your writing more concise and accurate, not to make it more complicated. A specialist term should be used when:
- It conveys information more precisely than a comparable non-specialist term.
- Your reader is likely to be familiar with the term.
- The term is commonly used by other researchers in your field.
The best way to familiarize yourself with the kind of jargon used in your field is to read papers by other researchers and pay attention to their language.
Focused and well structured
An academic text is not just a collection of ideas about a topic—it needs to have a clear purpose. Start with a relevant research question or thesis statement , and use it to develop a focused argument. Only include information that is relevant to your overall purpose.
A coherent structure is crucial to organize your ideas. Pay attention to structure at three levels: the structure of the whole text, paragraph structure, and sentence structure.
Well sourced
Academic writing uses sources to support its claims. Sources are other texts (or media objects like photographs or films) that the author analyzes or uses as evidence. Many of your sources will be written by other academics; academic writing is collaborative and builds on previous research.
It’s important to consider which sources are credible and appropriate to use in academic writing. For example, citing Wikipedia is typically discouraged. Don’t rely on websites for information; instead, use academic databases and your university library to find credible sources.
You must always cite your sources in academic writing. This means acknowledging whenever you quote or paraphrase someone else’s work by including a citation in the text and a reference list at the end.
There are many different citation styles with different rules. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago . Make sure to consistently follow whatever style your institution requires. If you don’t cite correctly, you may get in trouble for plagiarism . A good plagiarism checker can help you catch any issues before it’s too late.
You can easily create accurate citations in APA or MLA style using our Citation Generators.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
Correct and consistent
As well as following the rules of grammar, punctuation, and citation, it’s important to consistently apply stylistic conventions regarding:
- How to write numbers
- Introducing abbreviations
- Using verb tenses in different sections
- Capitalization of terms and headings
- Spelling and punctuation differences between UK and US English
In some cases there are several acceptable approaches that you can choose between—the most important thing is to apply the same rules consistently and to carefully proofread your text before you submit. If you don’t feel confident in your own proofreading abilities, you can get help from Scribbr’s professional proofreading services or Grammar Checker .
Academic writing generally tries to avoid being too personal. Information about the author may come in at some points—for example in the acknowledgements or in a personal reflection—but for the most part the text should focus on the research itself.
Always avoid addressing the reader directly with the second-person pronoun “you.” Use the impersonal pronoun “one” or an alternate phrasing instead for generalizations:
- As a teacher, you must treat your students fairly.
- As a teacher, one must treat one’s students fairly.
- Teachers must treat their students fairly.
The use of the first-person pronoun “I” used to be similarly discouraged in academic writing, but it is increasingly accepted in many fields. If you’re unsure whether to use the first person, pay attention to conventions in your field or ask your instructor.
When you refer to yourself, it should be for good reason. You can position yourself and describe what you did during the research, but avoid arbitrarily inserting your personal thoughts and feelings:
- In my opinion…
- I think that…
- I like/dislike…
- I conducted interviews with…
- I argue that…
- I hope to achieve…
Long-winded
Many students think their writing isn’t academic unless it’s over-complicated and long-winded. This isn’t a good approach—instead, aim to be as concise and direct as possible.
If a term can be cut or replaced with a more straightforward one without affecting your meaning, it should be. Avoid redundant phrasings in your text, and try replacing phrasal verbs with their one-word equivalents where possible:
- Interest in this phenomenon carried on in the year 2018 .
- Interest in this phenomenon continued in 2018 .
Repetition is a part of academic writing—for example, summarizing earlier information in the conclusion—but it’s important to avoid unnecessary repetition. Make sure that none of your sentences are repeating a point you’ve already made in different words.
Emotive and grandiose
An academic text is not the same thing as a literary, journalistic, or marketing text. Though you’re still trying to be persuasive, a lot of techniques from these styles are not appropriate in an academic context. Specifically, you should avoid appeals to emotion and inflated claims.
Though you may be writing about a topic that’s sensitive or important to you, the point of academic writing is to clearly communicate ideas, information, and arguments, not to inspire an emotional response. Avoid using emotive or subjective language :
- This horrible tragedy was obviously one of the worst catastrophes in construction history.
- The injury and mortality rates of this accident were among the highest in construction history.
Students are sometimes tempted to make the case for their topic with exaggerated , unsupported claims and flowery language. Stick to specific, grounded arguments that you can support with evidence, and don’t overstate your point:
- Charles Dickens is the greatest writer of the Victorian period, and his influence on all subsequent literature is enormous.
- Charles Dickens is one of the best-known writers of the Victorian period and has had a significant influence on the development of the English novel.
There are a a lot of writing tools that will make your writing process faster and easier. We’ll highlight three of them below.
Paraphrasing tool
AI writing tools like ChatGPT and a paraphrasing tool can help you rewrite text so that your ideas are clearer, you don’t repeat yourself, and your writing has a consistent tone.
They can also help you write more clearly about sources without having to quote them directly. Be warned, though: it’s still crucial to give credit to all sources in the right way to prevent plagiarism .
Grammar checker
Writing tools that scan your text for punctuation, spelling, and grammar mistakes. When it detects a mistake the grammar checke r will give instant feedback and suggest corrections. Helping you write clearly and avoid common mistakes .
You can use a summarizer if you want to condense text into its most important and useful ideas. With a summarizer tool, you can make it easier to understand complicated sources. You can also use the tool to make your research question clearer and summarize your main argument.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Use the checklist below to assess whether you have followed the rules of effective academic writing.
- Checklist: Academic writing
I avoid informal terms and contractions .
I avoid second-person pronouns (“you”).
I avoid emotive or exaggerated language.
I avoid redundant words and phrases.
I avoid unnecessary jargon and define terms where needed.
I present information as precisely and accurately as possible.
I use appropriate transitions to show the connections between my ideas.
My text is logically organized using paragraphs .
Each paragraph is focused on a single idea, expressed in a clear topic sentence .
Every part of the text relates to my central thesis or research question .
I support my claims with evidence.
I use the appropriate verb tenses in each section.
I consistently use either UK or US English .
I format numbers consistently.
I cite my sources using a consistent citation style .
Your text follows the most important rules of academic style. Make sure it's perfect with the help of a Scribbr editor!
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Taboo words in academic writing
- How to write more concisely
- Transition Words & Phrases | List & Examples
More interesting articles
- A step-by-step guide to the writing process
- Active vs. Passive Constructions | When to Use the Passive Voice
- Avoid informal writing
- Avoid rhetorical questions
- Be conscious of your adverb placement
- Capitalization in titles and headings
- Exclamation points (!)
- Forging good titles in academic writing
- Free, Downloadable Educational Templates for Students
- Free, Downloadable Lecture Slides for Educators and Students
- How to avoid repetition and redundancy
- How to write a lab report
- How to write effective headings
- Language mistakes in quotes
- List of 47 Phrasal Verbs and Their One-Word Substitutions
- Myth: It’s incorrect to start a sentence with “because”
- Myth: It’s an error to split infinitives
- Myth: It’s incorrect to start a sentence with a coordinating conjunction (and, but, or, for, nor, yet, so)
- Myth: Paragraph transitions should be placed at the ends of paragraphs
- Tense tendencies in academic texts
- Using abbreviations and acronyms
- What Is Anthropomorphism? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Sentence Case? | Explanation & Examples
- What Is Title Case? | Explanation & Worksheet
- Writing myths: The reasons we get bad advice
- Writing numbers: words and numerals
What is your plagiarism score?
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1-College Writing
Common Types of Writing Assignments
While much of the writing you did in high school may have been for an English or literature class, in college, writing is a common form of expression and scholarship in many fields and thus in many courses.
You may have to write essays, reflections, discussion board posts, or research papers in your history, biology, psychology, art history, or computer science classes.
Writing assignments in college vary in length, purpose, and the relationship between the writer (you) and the topic. Sometimes you may be asked to gather information and write a report on your findings . Sometimes you may be asked to compare opinions expressed by experts. You might be asked to answer a question or state your position and defend it with evidence . Some assignments require a mixture of several of these tasks.
When a writing assignment is mentioned in the syllabus of a course, make sure you understand the assignment long before you begin to do it. The university’s Writing Center recommends that you note the vocabulary used in assignment descriptions and make sure you understand what actions certain words suggest or require. You should also talk to peers in your class to compare understandings and expectations.
The university’s Writing Center consultants will help you with questions about an assignment and how to ask your instructor for more information if necessary. They will help you strengthen your writing, give you feedback on your ideas, and offer suggestions for organizing your content. They can tell you if you are appropriately using sources.
The Writing Center is not only for students who have questions or are puzzled about assignments. It offers support to experienced writers, too. Faculty and graduate students routinely schedule sessions with Writing Center consultants.
Strong, experienced writers enjoy conversation about their writing decisions and find it helpful to have an outside reader for their work.
Conferences with a writing consultant can be face-to-face or online.
If you are uneasy about talking with your instructor, make an appointment at the Writing Center: https://cstw.osu.edu/writing-center
Common characteristics of writing in college:
- Based on evidence
- Is written for a very or moderately knowledgeable audience rather than general public
- Style is formal, objective, often technical
- Uses conventional formatting
- Documents evidence using a professional citation style
(From: Lunsford & Ruszkiewicz, p. 367)
An Introduction to Choosing & Using Sources Copyright © 2015 by Teaching & Learning, Ohio State University Libraries is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


1.3: In College, Everything’s an Argument- A Guide for Decoding College Writing Assignments
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 57093
Let’s restate this complex “literacy task” you’ll be asked repeatedly to do in your writing assignments. Typically, you’ll be required to write an “essay” based upon your analysis of some reading(s). In this essay you’ll need to present an argument where you make a claim (i.e. present a “thesis”) and support that claim with good reasons that have adequate and appropriate evidence to back them up. The dynamic of this argumentative task often confuses first year writers, so let’s examine it more closely.
Academic Writing Is an Argument
To start, let’s focus on argument. What does it mean to present an “argument” in college writing? Rather than a shouting match between two disagreeing sides, argument instead means a carefully arranged and supported presentation of a viewpoint. Its purpose is not so much to win the argument as to earn your audience’s consideration (and even approval) of your perspective. It resembles a conversation between two people who may not hold the same opinions, but they both desire a better understanding of the subject matter under discussion. My favorite analogy, however, to describe the nature of this argumentative stance in college writing is the courtroom. In this scenario, you are like a lawyer making a case at trial that the defendant is not guilty, and your readers are like the jury who will decide if the defendant is guilty or not guilty. This jury (your readers) won’t just take your word that he’s innocent; instead, you must convince them by presenting evidence that proves he is not guilty. Stating your opinion is not enough—you have to back it up too. I like this courtroom analogy for capturing two importance things about academic argument: 1) the value of an organized presentation of your “case,” and 2) the crucial element of strong evidence.
Academic Writing Is an Analysis
We now turn our attention to the actual writing assignment and that confusing word “analyze.” Your first job when you get a writing assignment is to figure out what the professor expects. This assignment may be explicit in its expectations, but often built into the wording of the most defined writing assignments are implicit expectations that you might not recognize. First, we can say that unless your professor specifically asks you to summarize, you won’t write a summary. Let me say that again: don’t write a summary unless directly asked to. But what, then, does the professor want? We have already picked out a few of these expectations: You can count on the instructor expecting you to read closely, research adequately, and write an argument where you will demonstrate your ability to apply and use important concepts you have been studying. But the writing task also implies that your essay will be the result of an analysis. At times, the writing assignment may even explicitly say to write an analysis, but often this element of the task remains unstated.
So what does it mean to analyze? One way to think of an analysis is that it asks you to seek How and Why questions much more than What questions. An analysis involves doing three things:
1. Engage in an open inquiry where the answer is not known at first (and where you leave yourself open to multiple suggestions)
2. Identify meaningful parts of the subject
3. Examine these separate parts and determine how they relate to each other
An analysis breaks a subject apart to study it closely, and from this inspection, ideas for writing emerge. When writing assignments call on you to analyze, they require you to identify the parts of the subject (parts of an ad, parts of a short story, parts of Hamlet’s character), and then show how these parts fit or don’t fit together to create some larger effect or meaning. Your interpretation of how these parts fit together constitutes your claim or thesis, and the task of your essay is then to present an argument defending your interpretation as a valid or plausible one to make. My biggest bit of advice about analysis is not to do it all in your head. Analysis works best when you put all the cards on the table, so to speak. Identify and isolate the parts of your analysis, and record important features and characteristics of each one. As patterns emerge, you sort and connect these parts in meaningful ways. For me, I have always had to do this recording and thinking on scratch pieces of paper. Just as critical reading forms a crucial element of the literacy task of a college writing assignment, so too does this analysis process. It’s built in.
Three Common Types of College Writing Assignments
We have been decoding the expectations of the academic writing task so far, and I want to turn now to examine the types of assignments you might receive. From my experience, you are likely to get three kinds of writing assignments based upon the instructor’s degree of direction for the assignment. We’ll take a brief look at each kind of academic writing task.
The Closed Writing Assignment
• Is Creon a character to admire or condemn?
• Does your advertisement employ techniques of propaganda, and if so what kind?
• Was the South justified in seceding from the Union?
• In your opinion, do you believe Hamlet was truly mad?
These kinds of writing assignments present you with two counter claims and ask you to determine from your own analysis the more valid claim. They resemble yes-no questions. These topics define the claim for you, so the major task of the writing assignment then is working out the support for the claim. They resemble a math problem in which the teacher has given you the answer and now wants you to “show your work” in arriving at that answer.
Be careful with these writing assignments, however, because often these topics don’t have a simple yes/no, either/or answer (despite the nature of the essay question). A close analysis of the subject matter often reveals nuances and ambiguities within the question that your eventual claim should reflect. Perhaps a claim such as, “In my opinion, Hamlet was mad” might work, but I urge you to avoid such a simplistic thesis. This thesis would be better: “I believe Hamlet’s unhinged mind borders on insanity but doesn’t quite reach it.”
The Semi-Open Writing Assignment
• Discuss the role of law in Antigone.
• Explain the relationship between character and fate in Hamlet.
• Compare and contrast the use of setting in two short stories.
• Show how the Fugitive Slave Act influenced the Abolitionist Movement.
Although these topics chart out a subject matter for you to write upon, they don’t offer up claims you can easily use in your paper. It would be a misstep to offer up claims such as, “Law plays a role in Antigone” or “In Hamlet we can see a relationship between character and fate.” Such statements express the obvious and what the topic takes for granted. The question, for example, is not whether law plays a role in Antigone, but rather what sort of role law plays. What is the nature of this role? What influences does it have on the characters or actions or theme? This kind of writing assignment resembles a kind of archeological dig. The teacher cordons off an area, hands you a shovel, and says dig here and see what you find.
Be sure to avoid summary and mere explanation in this kind of assignment. Despite using key words in the assignment such as “explain,” “illustrate,” analyze,” “discuss,” or “show how,” these topics still ask you to make an argument. Implicit in the topic is the expectation that you will analyze the reading and arrive at some insights into patterns and relationships about the subject. Your eventual paper, then, needs to present what you found from this analysis—the treasure you found from your digging. Determining your own claim represents the biggest challenge for this type of writing assignment.
The Open Writing Assignment
• Analyze the role of a character in Dante’s The Inferno.
• What does it mean to be an “American” in the 21st Century?
• Analyze the influence of slavery upon one cause of the Civil War.
• Compare and contrast two themes within Pride and Prejudice.
These kinds of writing assignments require you to decide both your writing topic and you claim (or thesis). Which character in the Inferno will I pick to analyze? What two themes in Pride and Prejudice will I choose to write about? Many students struggle with these types of assignments because they have to understand their subject matter well before they can intelligently choose a topic. For instance, you need a good familiarity with the characters in The Inferno before you can pick one. You have to have a solid understanding defining elements of American identity as well as 21st century culture before you can begin to connect them. This kind of writing assignment resembles riding a bike without the training wheels on. It says, “You decide what to write about.” The biggest decision, then, becomes selecting your topic and limiting it to a manageable size.
Picking and Limiting a Writing Topic
Let’s talk about both of these challenges: picking a topic and limiting it. Remember how I said these kinds of essay topics expect you to choose what to write about from a solid understanding of your subject? As you read and review your subject matter, look for things that interest you. Look for gaps, puzzling items, things that confuse you, or connections you see. Something in this pile of rocks should stand out as a jewel: as being “do-able” and interesting. (You’ll write best when you write from both your head and your heart.) Whatever topic you choose, state it as a clear and interesting question. You may or may not state this essay question explicitly in the introduction of your paper (I actually recommend that you do), but it will provide direction for your paper and a focus for your claim since that claim will be your answer to this essay question. For example, if with the Dante topic you decided to write on Virgil, your essay question might be: “What is the role of Virgil toward the character of Dante in The Inferno?” The thesis statement, then, might be this: “Virgil’s predominant role as Dante’s guide through hell is as the voice of reason.” Crafting a solid essay question is well worth your time because it charts the territory of your essay and helps you declare a focused thesis statement.
Many students struggle with defining the right size for their writing project. They chart out an essay question that it would take a book to deal with adequately. You’ll know you have that kind of topic if you have already written over the required page length but only touched one quarter of the topics you planned to discuss. In this case, carve out one of those topics and make your whole paper about it. For instance, with our Dante example, perhaps you planned to discuss four places where Virgil’s role as the voice of reason is evident. Instead of discussing all four, focus your essay on just one place. So your revised thesis statement might be: “Close inspection of Cantos I and II reveal that Virgil serves predominantly as the voice of reason for Dante on his journey through hell.” A writing teacher I had in college said it this way: A well tended garden is better than a large one full of weeds. That means to limit your topic to a size you can handle and support well.
Three Characteristics of Academic Writing
I want to wrap up this section by sharing in broad terms what the expectations are behind an academic writing assignment. Chris Thaiss and Terry Zawacki conducted research at George Mason University where they asked professors from their university what they thought academic writing was and its standards. They came up with three characteristics:
1. Clear evidence in writing that the writer(s) have been persistent, open-minded, and disciplined in study. (5)
2. The dominance of reason over emotions or sensual perception. (5)
3. An imagined reader who is coolly rational, reading for information, and intending to formulate a reasoned response. (7)
Your professor wants to see these three things in your writing when they give you a writing assignment. They want to see in your writing the results of your efforts at the various literacy tasks we have been discussing: critical reading, research, and analysis. Beyond merely stating opinions, they also want to see an argument toward an intelligent audience where you provide good reasons to support your interpretations.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.1: What’s Different about College Writing?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 20779

Learning Objectives
- Define “academic writing.”
- Identify key differences between writing in college and writing in high school or on the job.
- Identify different types of papers that are commonly assigned.
- Describe what instructors expect from student writing.
Academic writing refers to writing produced in a college environment. Often this is writing that responds to other writing—to the ideas or controversies that you’ll read about. While this definition sounds simple, academic writing may be very different from other types of writing you have done in the past. Often college students begin to understand what academic writing really means only after they receive negative feedback on their work. To become a strong writer in college, you need to achieve a clear sense of two things:
- The academic environment
- The kinds of writing you’ll be doing in that environment
Differences between High School and College Writing
Students who struggle with writing in college often conclude that their high school teachers were too easy or that their college instructors are too hard. In most cases, neither explanation is fully accurate or fair. A student having difficulty with college writing usually just hasn’t yet made the transition from high school writing to college writing. That shouldn’t be surprising, for many beginning college students do not even know that there is a transition to be made.
In high school, most students think of writing as the subject of English classes. Few teachers in other courses give much feedback on student writing; many do not even assign writing. This says more about high school than about the quality of teachers or about writing itself. High school teachers typically teach five courses a day and often more than 150 students. Those students often have a very wide range of backgrounds and skill levels.
Thus many high school English instructors focus on specific, limited goals. For example, they may teach the “five paragraph essay” as the right way to organize a paper because they want to give every student some idea of an essay’s basic structure. They may give assignments on stories and poems because their own college background involved literature and literary analysis. In classes other than English, many high school teachers must focus on an established body of information and may judge students using tests that measure only how much of this information they acquire. Often writing itself is not directly addressed in such classes.
This does not mean that students don’t learn a great deal in high school, but it’s easy to see why some students think that writing is important only in English classes. Many students also believe an academic essay must be five paragraphs long or that “school writing” is usually literary analysis.
Think about how college differs from high school. In many colleges, the instructors teach fewer classes and have fewer students. In addition, while college students have highly diverse backgrounds, the skills of college students are less variable than in an average high school class. In addition, college instructors are specialists in the fields they teach, as you recall from Chapter 7 “Interacting with Instructors and Classes”. College instructors may design their courses in unique ways, and they may teach about specialized subjects. For all of these reasons, college instructors are much more likely than high school teachers to
- assign writing,
- respond in detail to student writing,
- ask questions that cannot be dealt with easily in a fixed form like a five-paragraph essay.
Your transition to college writing could be even more dramatic. The kind of writing you have done in the past may not translate at all into the kind of writing required in college. For example, you may at first struggle with having to write about very different kinds of topics, using different approaches. You may have learned only one kind of writing genre (a kind of approach or organization) and now find you need to master other types of writing as well.
What Kinds of Papers Are Commonly Assigned in College Classes?
Think about the topic “gender roles”—referring to expectations about differences in how men and women act. You might study gender roles in an anthropology class, a film class, or a psychology class. The topic itself may overlap from one class to another, but you would not write about this subject in the same way in these different classes. For example, in an anthropology class, you might be asked to describe how men and women of a particular culture divide important duties. In a film class, you may be asked to analyze how a scene portrays gender roles enacted by the film’s characters. In a psychology course, you might be asked to summarize the results of an experiment involving gender roles or compare and contrast the findings of two related research projects.
It would be simplistic to say that there are three, or four, or ten, or any number of types of academic writing that have unique characteristics, shapes, and styles. Every assignment in every course is unique in some ways, so don’t think of writing as a fixed form you need to learn. On the other hand, there are certain writing approaches that do involve different kinds of writing. An approach is the way you go about meeting the writing goals for the assignment. The approach is usually signaled by the words instructors use in their assignments.
When you first get a writing assignment, pay attention first to keywords for how to approach the writing. These will also suggest how you may structure and develop your paper. Look for terms like these in the assignment:
- Summarize. To restate in your own words the main point or points of another’s work.
- Define. To describe, explore, or characterize a keyword, idea, or phenomenon.
- Classify. To group individual items by their shared characteristics, separate from other groups of items.
- Compare/contrast. To explore significant likenesses and differences between two or more subjects.
- Analyze. To break something, a phenomenon, or an idea into its parts and explain how those parts fit or work together.
- Argue. To state a claim and support it with reasons and evidence.
- Synthesize. To pull together varied pieces or ideas from two or more sources.
Note how this list is similar to the words used in examination questions that involve writing. (See Table 6.1 “Words to Watch for in Essay Questions” in Chapter 6 “Preparing for and Taking Tests”, Section 6.4 “The Secrets of the Q and A’s”.) This overlap is not a coincidence—essay exams are an abbreviated form of academic writing such as a class paper.
Sometimes the keywords listed don’t actually appear in the written assignment, but they are usually implied by the questions given in the assignment. “What,” “why,” and “how” are common question words that require a certain kind of response. Look back at the keywords listed and think about which approaches relate to “what,” “why,” and “how” questions.
- “What” questions usually prompt the writing of summaries, definitions, classifications, and sometimes compare-and-contrast essays. For example, “ What does Jones see as the main elements of Huey Long’s populist appeal?” or “ What happened when you heated the chemical solution?”
- “Why” and “how” questions typically prompt analysis, argument, and synthesis essays. For example, “ Why did Huey Long’s brand of populism gain force so quickly?” or “ Why did the solution respond the way it did to heat?”
Successful academic writing starts with recognizing what the instructor is requesting, or what you are required to do. So pay close attention to the assignment. Sometimes the essential information about an assignment is conveyed through class discussions, however, so be sure to listen for the keywords that will help you understand what the instructor expects. If you feel the assignment does not give you a sense of direction, seek clarification. Ask questions that will lead to helpful answers. For example, here’s a short and very vague assignment:
Discuss the perspectives on religion of Rousseau, Bentham, and Marx. Papers should be four to five pages in length.
Faced with an assignment like this, you could ask about the scope (or focus) of the assignment:
- Which of the assigned readings should I concentrate on?
- Should I read other works by these authors that haven’t been assigned in class?
- Should I do research to see what scholars think about the way these philosophers view religion?
- Do you want me to pay equal attention to each of the three philosophers?
You can also ask about the approach the instructor would like you to take. You can use the keywords the instructor may not have used in the assignment:
- Should I just summarize the positions of these three thinkers, or should I compare and contrast their views?
- Do you want me to argue a specific point about the way these philosophers approach religion?
- Would it be OK if I classified the ways these philosophers think about religion?
Never just complain about a vague assignment. It is fine to ask questions like these. Such questions will likely engage your instructor in a productive discussion with you.
Key Takeaways
- Writing is crucial to college success because it is the single most important means of evaluation.
- Writing in college is not limited to the kinds of assignments commonly required in high school English classes.
- Writers in college must pay close attention to the terms of an assignment.
- If an assignment is not clear, seek clarification from the instructor.
Checkpoint Exercises
What kind(s) of writing have you practiced most in your recent past?
____________________________________________________________________
Name two things that make academic writing in college different from writing in high school.
Explain how the word “what” asks for a different kind of paper than the word “why.”
Module 4: Writing in College
Writing assignments, learning objectives.
- Describe common types and expectations of writing tasks given in a college class

Figure 1 . All college classes require some form of writing. Investing some time in refining your writing skills so that you are a more confident, skilled, and efficient writer will pay dividends in the long run.
What to Do With Writing Assignments
Writing assignments can be as varied as the instructors who assign them. Some assignments are explicit about what exactly you’ll need to do, in what order, and how it will be graded. Others are more open-ended, leaving you to determine the best path toward completing the project. Most fall somewhere in the middle, containing details about some aspects but leaving other assumptions unstated. It’s important to remember that your first resource for getting clarification about an assignment is your instructor—they will be very willing to talk out ideas with you, to be sure you’re prepared at each step to do well with the writing.
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments.
Link to Learning
Empire State College offers an Assignment Calculator to help you plan ahead for your writing assignment. Just plug in the date you plan to get started and the date it is due, and the calculator will help break it down into manageable chunks.
Summary Assignments
Being asked to summarize a source is a common task in many types of writing. It can also seem like a straightforward task: simply restate, in shorter form, what the source says. A lot of advanced skills are hidden in this seemingly simple assignment, however.
An effective summary does the following:
- reflects your accurate understanding of a source’s thesis or purpose
- differentiates between major and minor ideas in a source
- demonstrates your ability to identify key phrases to quote
- shows your ability to effectively paraphrase most of the source’s ideas
- captures the tone, style, and distinguishing features of a source
- does not reflect your personal opinion about the source
That last point is often the most challenging: we are opinionated creatures, by nature, and it can be very difficult to keep our opinions from creeping into a summary. A summary is meant to be completely neutral.
In college-level writing, assignments that are only summary are rare. That said, many types of writing tasks contain at least some element of summary, from a biology report that explains what happened during a chemical process, to an analysis essay that requires you to explain what several prominent positions about gun control are, as a component of comparing them against one another.
Writing Effective Summaries
Start with a clear identification of the work.
This automatically lets your readers know your intentions and that you’re covering the work of another author.
- In the featured article “Five Kinds of Learning,” the author, Holland Oates, justifies his opinion on the hot topic of learning styles — and adds a few himself.
Summarize the Piece as a Whole
Omit nothing important and strive for overall coherence through appropriate transitions. Write using “summarizing language.” Your reader needs to be reminded that this is not your own work. Use phrases like the article claims, the author suggests, etc.
- Present the material in a neutral fashion. Your opinions, ideas, and interpretations should be left in your brain — don’t put them into your summary. Be conscious of choosing your words. Only include what was in the original work.
- Be concise. This is a summary — it should be much shorter than the original piece. If you’re working on an article, give yourself a target length of 1/4 the original article.
Conclude with a Final Statement
This is not a statement of your own point of view, however; it should reflect the significance of the book or article from the author’s standpoint.
- Without rewriting the article, summarize what the author wanted to get across. Be careful not to evaluate in the conclusion or insert any of your own assumptions or opinions.
Understanding the Assignment and Getting Started

Figure 2 . Many writing assignments will have a specific prompt that sends you first to your textbook, and then to outside resources to gather information.
Often, the handout or other written text explaining the assignment—what professors call the assignment prompt —will explain the purpose of the assignment and the required parameters (length, number and type of sources, referencing style, etc.).
Also, don’t forget to check the rubric, if there is one, to understand how your writing will be assessed. After analyzing the prompt and the rubric, you should have a better sense of what kind of writing you are expected to produce.
Sometimes, though—especially when you are new to a field—you will encounter the baffling situation in which you comprehend every single sentence in the prompt but still have absolutely no idea how to approach the assignment! In a situation like that, consider the following tips:
- Focus on the verbs . Look for verbs like compare, explain, justify, reflect , or the all-purpose analyze . You’re not just producing a paper as an artifact; you’re conveying, in written communication, some intellectual work you have done. So the question is, what kind of thinking are you supposed to do to deepen your learning?
- Put the assignment in context . Many professors think in terms of assignment sequences. For example, a social science professor may ask you to write about a controversial issue three times: first, arguing for one side of the debate; second, arguing for another; and finally, from a more comprehensive and nuanced perspective, incorporating text produced in the first two assignments. A sequence like that is designed to help you think through a complex issue. If the assignment isn’t part of a sequence, think about where it falls in the span of the course (early, midterm, or toward the end), and how it relates to readings and other assignments. For example, if you see that a paper comes at the end of a three-week unit on the role of the Internet in organizational behavior, then your professor likely wants you to synthesize that material.
- Try a free-write . A free-write is when you just write, without stopping, for a set period of time. That doesn’t sound very “free”; it actually sounds kind of coerced, right? The “free” part is what you write—it can be whatever comes to mind. Professional writers use free-writing to get started on a challenging (or distasteful) writing task or to overcome writer’s block or a powerful urge to procrastinate. The idea is that if you just make yourself write, you can’t help but produce some kind of useful nugget. Thus, even if the first eight sentences of your free write are all variations on “I don’t understand this” or “I’d really rather be doing something else,” eventually you’ll write something like “I guess the main point of this is…,” and—booyah!—you’re off and running.
- Ask for clarification . Even the most carefully crafted assignments may need some verbal clarification, especially if you’re new to a course or field. Professors generally love questions, so don’t be afraid to ask. Try to convey to your instructor that you want to learn and you’re ready to work, and not just looking for advice on how to get an A.
Defined-Topic Assignments
Many writing tasks will ask you to address a particular topic or a narrow set of topic options. Defined-topic writing assignments are used primarily to identify your familiarity with the subject matter. (Discuss the use of dialect in Their Eyes Were Watching God , for example.)
Remember, even when you’re asked to “show how” or “illustrate,” you’re still being asked to make an argument. You must shape and focus your discussion or analysis so that it supports a claim that you discovered and formulated and that all of your discussion and explanation develops and supports.
Undefined-Topic Assignments
Another writing assignment you’ll potentially encounter is one in which the topic may be only broadly identified (“water conservation” in an ecology course, for instance, or “the Dust Bowl” in a U.S. History course), or even completely open (“compose an argumentative research essay on a subject of your choice”).

Figure 3 . For open-ended assignments, it’s best to pick something that interests you personally.
Where defined-topic essays demonstrate your knowledge of the content , undefined-topic assignments are used to demonstrate your skills— your ability to perform academic research, to synthesize ideas, and to apply the various stages of the writing process.
The first hurdle with this type of task is to find a focus that interests you. Don’t just pick something you feel will be “easy to write about” or that you think you already know a lot about —those almost always turn out to be false assumptions. Instead, you’ll get the most value out of, and find it easier to work on, a topic that intrigues you personally or a topic about which you have a genuine curiosity.
The same getting-started ideas described for defined-topic assignments will help with these kinds of projects, too. You can also try talking with your instructor or a writing tutor (at your college’s writing center) to help brainstorm ideas and make sure you’re on track.
Getting Started in the Writing Process
Writing is not a linear process, so writing your essay, researching, rewriting, and adjusting are all part of the process. Below are some tips to keep in mind as you approach and manage your assignment.
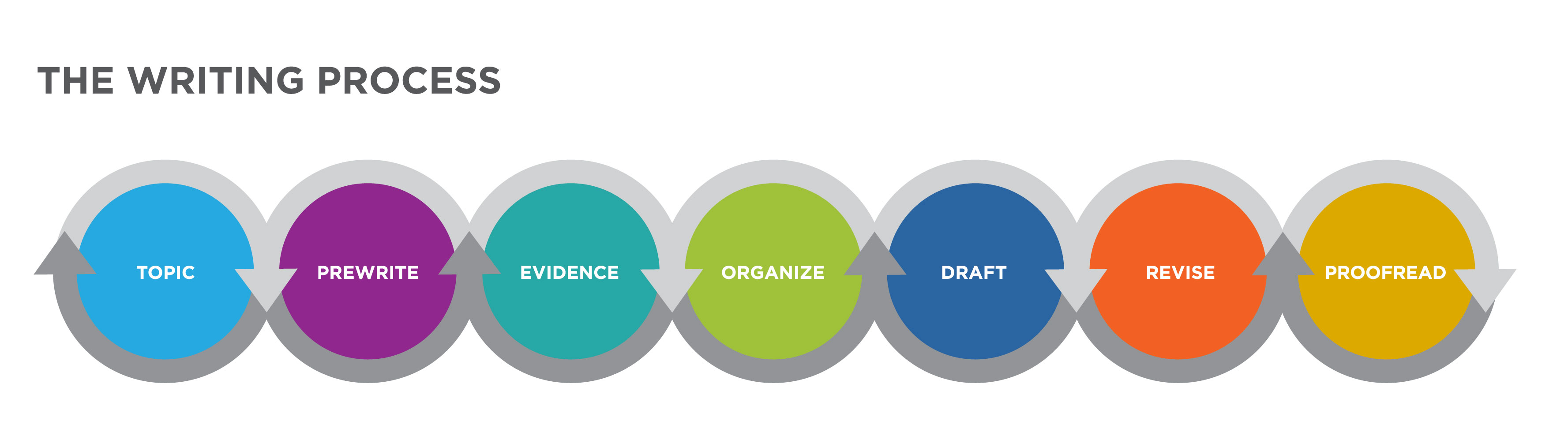
Figure 4 . Writing is a recursive process that begins with examining the topic and prewriting.
Write down topic ideas. If you have been assigned a particular topic or focus, it still might be possible to narrow it down or personalize it to your own interests.
If you have been given an open-ended essay assignment, the topic should be something that allows you to enjoy working with the writing process. Select a topic that you’ll want to think about, read about, and write about for several weeks, without getting bored.

Figure 5 . Just getting started is sometimes the most difficult part of writing. Freewriting and planning to write multiple drafts can help you dive in.
If you’re writing about a subject you’re not an expert on and want to make sure you are presenting the topic or information realistically, look up the information or seek out an expert to ask questions.
- Note: Be cautious about information you retrieve online, especially if you are writing a research paper or an article that relies on factual information. A quick Google search may turn up unreliable, misleading sources. Be sure you consider the credibility of the sources you consult (we’ll talk more about that later in the course). And keep in mind that published books and works found in scholarly journals have to undergo a thorough vetting process before they reach publication and are therefore safer to use as sources.
- Check out a library. Yes, believe it or not, there is still information to be found in a library that hasn’t made its way to the Web. For an even greater breadth of resources, try a college or university library. Even better, research librarians can often be consulted in person, by phone, or even by email. And they love helping students. Don’t be afraid to reach out with questions!
Write a Rough Draft
It doesn’t matter how many spelling errors or weak adjectives you have in it. Your draft can be very rough! Jot down those random uncategorized thoughts. Write down anything you think of that you want included in your writing and worry about organizing and polishing everything later.
If You’re Having Trouble, Try F reewriting
Set a timer and write continuously until that time is up. Don’t worry about what you write, just keeping moving your pencil on the page or typing something (anything!) into the computer.
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Outcome: Writing in College. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence. Authored by : Amy Guptill. Provided by : SUNY Open Textbooks. Located at : http://textbooks.opensuny.org/writing-in-college-from-competence-to-excellence/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of man writing. Authored by : Matt Zhang. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/pAg6t9 . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Writing Strategies. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/lumencollegesuccess/chapter/writing-strategies/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of woman reading. Authored by : Aaron Osborne. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/dPLmVV . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of sketches of magnifying glass. Authored by : Matt Cornock. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/eBSLmg . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- How to Write a Summary. Authored by : WikiHow. Located at : http://www.wikihow.com/Write-a-Summary . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- How to Write. Provided by : WikiHow. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of typing. Authored by : Kiran Foster. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/9M2WW4 . License : CC BY: Attribution

NCI LIBRARY
Academic writing skills guide: understanding assignments.
- Key Features of Academic Writing
- The Writing Process
- Understanding Assignments
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Planning Your Assignments
- Thesis Statements
- Writing Drafts
- Structuring Your Assignment
- How to Deal With Writer's Block
- Using Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Introductions
- Revising & Editing
- Proofreading
- Grammar & Punctuation
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting, Transitions & Linking Words/Phrases
- Using Lecturers' Feedback
Below is a list of interpretations for some of the more common directive/instructional words. These interpretations are intended as a guide only but should help you gain a better understanding of what is required when they are used.

Communications from the Library: Please note all communications from the library, concerning renewal of books, overdue books and reservations will be sent to your NCI student email account.
- << Previous: The Writing Process
- Next: Brainstorming Techniques >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 10:00 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ncirl.ie/academic_writing_skills
- Sign Up for Mailing List
- Search Search
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Resources for Teachers: Creating Writing Assignments
This page contains four specific areas:
Creating Effective Assignments
Checking the assignment, sequencing writing assignments, selecting an effective writing assignment format.
Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an “assignment sheet” tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment. Assignment sheets should detail:
- the kind of writing expected
- the scope of acceptable subject matter
- the length requirements
- formatting requirements
- documentation format
- the amount and type of research expected (if any)
- the writer’s role
- deadlines for the first draft and its revision
Providing questions or needed data in the assignment helps students get started. For instance, some questions can suggest a mode of organization to the students. Other questions might suggest a procedure to follow. The questions posed should require that students assert a thesis.
The following areas should help you create effective writing assignments.
Examining your goals for the assignment
- How exactly does this assignment fit with the objectives of your course?
- Should this assignment relate only to the class and the texts for the class, or should it also relate to the world beyond the classroom?
- What do you want the students to learn or experience from this writing assignment?
- Should this assignment be an individual or a collaborative effort?
- What do you want students to show you in this assignment? To demonstrate mastery of concepts or texts? To demonstrate logical and critical thinking? To develop an original idea? To learn and demonstrate the procedures, practices, and tools of your field of study?
Defining the writing task
- Is the assignment sequenced so that students: (1) write a draft, (2) receive feedback (from you, fellow students, or staff members at the Writing and Communication Center), and (3) then revise it? Such a procedure has been proven to accomplish at least two goals: it improves the student’s writing and it discourages plagiarism.
- Does the assignment include so many sub-questions that students will be confused about the major issue they should examine? Can you give more guidance about what the paper’s main focus should be? Can you reduce the number of sub-questions?
- What is the purpose of the assignment (e.g., review knowledge already learned, find additional information, synthesize research, examine a new hypothesis)? Making the purpose(s) of the assignment explicit helps students write the kind of paper you want.
- What is the required form (e.g., expository essay, lab report, memo, business report)?
- What mode is required for the assignment (e.g., description, narration, analysis, persuasion, a combination of two or more of these)?
Defining the audience for the paper
- Can you define a hypothetical audience to help students determine which concepts to define and explain? When students write only to the instructor, they may assume that little, if anything, requires explanation. Defining the whole class as the intended audience will clarify this issue for students.
- What is the probable attitude of the intended readers toward the topic itself? Toward the student writer’s thesis? Toward the student writer?
- What is the probable educational and economic background of the intended readers?
Defining the writer’s role
- Can you make explicit what persona you wish the students to assume? For example, a very effective role for student writers is that of a “professional in training” who uses the assumptions, the perspective, and the conceptual tools of the discipline.
Defining your evaluative criteria
1. If possible, explain the relative weight in grading assigned to the quality of writing and the assignment’s content:
- depth of coverage
- organization
- critical thinking
- original thinking
- use of research
- logical demonstration
- appropriate mode of structure and analysis (e.g., comparison, argument)
- correct use of sources
- grammar and mechanics
- professional tone
- correct use of course-specific concepts and terms.
Here’s a checklist for writing assignments:
- Have you used explicit command words in your instructions (e.g., “compare and contrast” and “explain” are more explicit than “explore” or “consider”)? The more explicit the command words, the better chance the students will write the type of paper you wish.
- Does the assignment suggest a topic, thesis, and format? Should it?
- Have you told students the kind of audience they are addressing — the level of knowledge they can assume the readers have and your particular preferences (e.g., “avoid slang, use the first-person sparingly”)?
- If the assignment has several stages of completion, have you made the various deadlines clear? Is your policy on due dates clear?
- Have you presented the assignment in a manageable form? For instance, a 5-page assignment sheet for a 1-page paper may overwhelm students. Similarly, a 1-sentence assignment for a 25-page paper may offer insufficient guidance.
There are several benefits of sequencing writing assignments:
- Sequencing provides a sense of coherence for the course.
- This approach helps students see progress and purpose in their work rather than seeing the writing assignments as separate exercises.
- It encourages complexity through sustained attention, revision, and consideration of multiple perspectives.
- If you have only one large paper due near the end of the course, you might create a sequence of smaller assignments leading up to and providing a foundation for that larger paper (e.g., proposal of the topic, an annotated bibliography, a progress report, a summary of the paper’s key argument, a first draft of the paper itself). This approach allows you to give students guidance and also discourages plagiarism.
- It mirrors the approach to written work in many professions.
The concept of sequencing writing assignments also allows for a wide range of options in creating the assignment. It is often beneficial to have students submit the components suggested below to your course’s STELLAR web site.
Use the writing process itself. In its simplest form, “sequencing an assignment” can mean establishing some sort of “official” check of the prewriting and drafting steps in the writing process. This step guarantees that students will not write the whole paper in one sitting and also gives students more time to let their ideas develop. This check might be something as informal as having students work on their prewriting or draft for a few minutes at the end of class. Or it might be something more formal such as collecting the prewriting and giving a few suggestions and comments.
Have students submit drafts. You might ask students to submit a first draft in order to receive your quick responses to its content, or have them submit written questions about the content and scope of their projects after they have completed their first draft.
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other’s drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic.
Require consultations. Have students consult with someone in the Writing and Communication Center about their prewriting and/or drafts. The Center has yellow forms that we can give to students to inform you that such a visit was made.
Explore a subject in increasingly complex ways. A series of reading and writing assignments may be linked by the same subject matter or topic. Students encounter new perspectives and competing ideas with each new reading, and thus must evaluate and balance various views and adopt a position that considers the various points of view.
Change modes of discourse. In this approach, students’ assignments move from less complex to more complex modes of discourse (e.g., from expressive to analytic to argumentative; or from lab report to position paper to research article).
Change audiences. In this approach, students create drafts for different audiences, moving from personal to public (e.g., from self-reflection to an audience of peers to an audience of specialists). Each change would require different tasks and more extensive knowledge.
Change perspective through time. In this approach, students might write a statement of their understanding of a subject or issue at the beginning of a course and then return at the end of the semester to write an analysis of that original stance in the light of the experiences and knowledge gained in the course.
Use a natural sequence. A different approach to sequencing is to create a series of assignments culminating in a final writing project. In scientific and technical writing, for example, students could write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic. The next assignment might be a progress report (or a series of progress reports), and the final assignment could be the report or document itself. For humanities and social science courses, students might write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic, then hand in an annotated bibliography, and then a draft, and then the final version of the paper.
Have students submit sections. A variation of the previous approach is to have students submit various sections of their final document throughout the semester (e.g., their bibliography, review of the literature, methods section).
In addition to the standard essay and report formats, several other formats exist that might give students a different slant on the course material or allow them to use slightly different writing skills. Here are some suggestions:
Journals. Journals have become a popular format in recent years for courses that require some writing. In-class journal entries can spark discussions and reveal gaps in students’ understanding of the material. Having students write an in-class entry summarizing the material covered that day can aid the learning process and also reveal concepts that require more elaboration. Out-of-class entries involve short summaries or analyses of texts, or are a testing ground for ideas for student papers and reports. Although journals may seem to add a huge burden for instructors to correct, in fact many instructors either spot-check journals (looking at a few particular key entries) or grade them based on the number of entries completed. Journals are usually not graded for their prose style. STELLAR forums work well for out-of-class entries.
Letters. Students can define and defend a position on an issue in a letter written to someone in authority. They can also explain a concept or a process to someone in need of that particular information. They can write a letter to a friend explaining their concerns about an upcoming paper assignment or explaining their ideas for an upcoming paper assignment. If you wish to add a creative element to the writing assignment, you might have students adopt the persona of an important person discussed in your course (e.g., an historical figure) and write a letter explaining his/her actions, process, or theory to an interested person (e.g., “pretend that you are John Wilkes Booth and write a letter to the Congress justifying your assassination of Abraham Lincoln,” or “pretend you are Henry VIII writing to Thomas More explaining your break from the Catholic Church”).
Editorials . Students can define and defend a position on a controversial issue in the format of an editorial for the campus or local newspaper or for a national journal.
Cases . Students might create a case study particular to the course’s subject matter.
Position Papers . Students can define and defend a position, perhaps as a preliminary step in the creation of a formal research paper or essay.
Imitation of a Text . Students can create a new document “in the style of” a particular writer (e.g., “Create a government document the way Woody Allen might write it” or “Write your own ‘Modest Proposal’ about a modern issue”).
Instruction Manuals . Students write a step-by-step explanation of a process.
Dialogues . Students create a dialogue between two major figures studied in which they not only reveal those people’s theories or thoughts but also explore areas of possible disagreement (e.g., “Write a dialogue between Claude Monet and Jackson Pollock about the nature and uses of art”).
Collaborative projects . Students work together to create such works as reports, questions, and critiques.
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
Gen ed writes, writing across the disciplines at harvard college.
- Types of Assignments
Gen Ed courses transcend disciplinary boundaries in a variety of ways, so the types of writing assignments that they include also often venture outside the traditional discipline-specific essays. You may encounter a wide variety of assignment types in Gen Ed, but most can be categorized into four general types:
- Traditional academic assignments include the short essays or research papers most commonly associated with college-level assignments. Generally speaking, these kinds of assignments are "expository" in nature, i.e., they ask you to engage with ideas through evidence-base argument, written in formal prose. The majority of essays in Expos courses fall into this category of writing assignment types.
- Less traditional academic assignments include elements of engagement in academia not normally encountered by undergraduates.
- Traditional non-academic assignments include types of written communication that students are likely to encounter in real world situations.
- Less traditional non-academic assignments are those that push the boundaries of typical ‘writing’ assignments and are likely to include some kind of creative or artistic component.
Examples and Resources
Traditional academic.
For most of us, these are the most familiar types of college-level writing assignments. While they are perhaps less common in Gen Ed than in departmental courses, there are still numerous examples we could examine.
Two illustrations of common types include:
Example 1: Short Essay Professor Michael Sandel asks the students in his Gen Ed course on Tech Ethics to write several short essays over the course of the semester in which they make an argument in response to the course readings. Because many students will never have written a philosophy-style paper, Professor Sandel offers students a number of resources—from a guide on writing in philosophy, to sample graded essays, to a list of logical fallacies—to keep in mind.
Example 2: Research Paper In Who Lives, Who Dies, Who Cares?, a Gen Ed course co-taught by multiple global health faculty members, students write a 12–15 page research paper on a biosocial analysis of a global health topic of their choosing for the final assignment. The assignment is broken up into two parts: (1) a proposal with annotated bibliography and (2) the final paper itself. The prompt clearly outlines the key qualities and features of a successful paper, which is especially useful for students who have not yet written a research paper in the sciences.
Less Traditional Academic
In Gen Ed, sometimes assignments ask students to engage in academic work that, while familiar to faculty, is beyond the scope of the typical undergraduate experience.
Here are a couple of examples from Gen Ed courses:
Example 1: Design a conference For the final project in her Gen Ed course, Global Feminisms, Professor Durba Mitra asks her students to imagine a dream conference in the style of the feminist conferences they studied in class. Students are asked to imagine conference panels and events, potential speakers or exhibitions, and advertising materials. While conferences are a normal occurrence for graduate students and professors, undergraduates are much less likely to be familiar with this part of academic life, and this kind of assignment might require more specific background and instructions as part of the prompt.
Example 2: Curate a museum exhibit In his Gen Ed class, Pyramid Schemes, Professor Peter Der Manuelian's final project offers students the option of designing a virtual museum exhibit . While exhibit curation can be a part of the academic life of an anthropologist or archaeologist, it's not often found in introductory undergraduate courses. In addition to selecting objects and creating a virtual exhibit layout, students also wrote an annotated bibliography as well as an exhibit introduction for potential visitors.
Traditional Non-academic
One of the goals of Gen Ed is to encourage students to engage with the world around them. Sometimes writing assignments in Gen Ed directly mirror types of writing that students are likely to encounter in real-world, non-academic settings after they graduate.
The following are several examples of such assignments:
Example 1: Policy memo In Power and Identity in the Middle East, Professor Melani Cammett assigns students a group policy memo evaluating "a major initiative aimed at promoting democracy in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA)." The assignment prompt is actually structured as a memo, providing context for students who likely lack experience with the format. It also outlines the key characteristics of a good memo, and it provides extensive advice on the process—especially important when students are working in groups.
Example 2: Letter In Loss, Professor Kathleen Coleman asks students to write a letter of condolence . The letter has an unusual audience: a mother elephant who lost her calf. Since students may not have encountered this type of writing before, Professor Coleman also provides students with advice on process, pointing to some course readings that might be a good place to start. She also suggests a list of outside resources to help students get into the mindframe of addressing an elephant.
Example 3: Podcast Podcasts are becoming increasingly popular in Gen Ed classes, as they are in the real world. Though they're ultimately audio file outputs, they usually require writing and preparing a script ahead of time. For example, in Music from Earth, Professor Alex Rehding asks students to create a podcast in which they make an argument about a song studied in class. He usefully breaks up the assignments into two parts: (1) researching the song and preparing a script and (2) recording and making sonic choices about the presentation, offering students the opportunity to get feedback on the first part before moving onto the second.
Less Traditional Non-academic
These are the types of assignments that perhaps are less obviously "writing" assignments. They usually involve an artistic or otherwise creative component, but they also often include some kind of written introduction or artist statement related to the work.
The following are several examples from recently offered Gen Ed courses:
Example 1: Movie Professor Peter Der Manuelian offers students in his class, Pyramid Schemes, several options for the final project, one of which entails creating a 5–8 minute iMovie making an argument about one of the themes of the course. Because relatively few students have prior experience making films, the teaching staff provide students with a written guide to making an iMovie as well as ample opportunities for tech support. In addition to preparing a script as part of the production, students also submit both an annotated bibliography and an artist’s statement.
Example 2: Calligram In his course, Understanding Islam and Contemporary Muslim Societies, Professor Ali Asani asks students to browse through a provided list of resources about calligrams, which are an important traditional Islamic art form. Then they are required to "choose a concept or symbol associated with God in the Islamic tradition and attempt to represent it through a calligraphic design using the word Allah," in any medium they wish. Students also write a short explanation to accompany the design itself.
Example 3: Soundscape In Music from Earth, Professor Alex Rehding has students create a soundscape . The soundscape is an audio file which involves layering sounds from different sources to create a single piece responding to an assigned question (e.g. "What sounds are characteristic of your current geographical region?"). Early on, as part of the development of the soundscape, students submit an artist's statement that explains the plan for the soundscape, the significance of the sounds, and the intention of the work.
- DIY Guides for Analytical Writing Assignments
- Unpacking the Elements of Writing Prompts
- Receiving Feedback
Assignment Decoder

Chapter 1: The Introduction
1.1 College Writing
Melanie Gagich
What is a College Writing Course?
Students often enter college writing courses believing they will be taking an “English” course that revolves around reading literature, writing creatively, and/or focusing on grammar. In fact, that is rarely the case.
At Cleveland State University, each student is required to take either ENG 100: Intensive College Writing or ENG 101: College Writing I and also ENG 102: College Writing II. Although each course is tagged as “ENG”, the official titles of each course include the words “College Writing.” Their official titles show that they are situated within the academic discipline, or the field of, Composition and Rhetoric. As members of that field, college writing instructors create, critique, and/or draw from pedagogical (teaching) theories and practices. Instructors might gather information from or publish in various discipline specific academic journals or conferences such as the College Composition and Communication Conference.
In practice, college writing courses teach students about writing and composing processes, how to think critically, use rhetorical knowledge to evaluate sources, integrate legitimate research in formal writing assignments, and write formal expository texts .
Cleveland State University’s First-Year Writing Sequence
ENG 100/101 helps you learn basic academic writing techniques while also examining rhetorical situations and rhetorical appeals. These skills connect to the “real world” in multiple ways. For instance, think of the last political ad you saw or an article you read online–how do you know if it was legit? Do you know who paid for the ad/article or who will profit from it? If you do know, what does that mean? Do you ask yourself, “whose agenda is this?” when you interact with popular media like reality tv shows, news programs, commentary programs, blogs, articles, etc.? In ENG 100/101, you will address some of these questions in various contexts to help you learn how to think critically about the world around you.
ENG 102 teaches you how to do research—find information—and how to use it, which is necessary for any major. We read, research and write to learn, and additionally by doing so, we gain the ability to read and follow both directions and instructions—a skillset desired by all employers. Then, unspoken and perhaps not emphasized is the confidence you gain in a first-year writing class when you discover your voice which after taking a year of composition results in a more mature outlook. This newfound connection to the human world and the natural world is what the critical thinker experiences. Overall, ENG 100/101 and ENG 102 are complimentary to but also different from most “English” courses you might have experienced in the past.
Why Should I Care About College Writing Courses?
Many students who enter college writing courses may at first feel apprehensive or may not see how these courses connect to their intended majors. In reality, college writing courses teach students to use writing to communicate and use critical thinking skills to become savvier consumers of information. Additionally, according to data gathered by Cleveland State’s Undergraduate Studies and Academic Programs using the third-party software platform, Civitas Illume, a student’s successful completion (earning a C or higher) in both ENG 100/101 and ENG 102 have been linked to increased persistence and graduation rates.
The data show that students who earn a B or higher in their college writing courses have an above average likelihood of graduation. Even though some students might find the idea of earning a B or higher daunting, it is important to remember that you are generally evaluated based on completing process-driven and reflective writing assignments, attending class regularly, and participating. Even more exciting is that the data also suggest that a student who simply raises their grade by one letter, for instance increasing your grade from a C to a B or a D to a C, also has a stronger likelihood of graduating. What this means is whether or not you conceptualize yourself as a B or A student in writing, any student who participates in revision opportunities, attends class, participates in class discussions, and communicates clearly with their instructor can increase their course grade, which positively affects the likelihood that he or she will graduate.
This all goes to support the notion that while writing class does not need to be scary it should be taken seriously and it does matter.
Text can refer to the written word: “Proofread your text before submitting the paper.”
A text refers to any form of communication, primarily written or oral, that forms a coherent unit, often as an object of study. A book can be a text, and a speech can be a text, but television commercials, magazine ads, website, and emails can also be texts: “Dieting advertisements formed one of the texts we studied in my Sociology class.”
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Feedback/Errata
Comments are closed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
College writing. teaches critical thinking skills. allows you to demonstrate your knowledge. takes many forms, depending on the discipline, the audience, the knowledge involved, and the goal of the assignment. Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783.
Common Writing Assignments. These OWL resources will help you understand and complete specific types of writing assignments, such as annotated bibliographies, book reports, and research papers. This section also includes resources on writing academic proposals for conference presentations, journal articles, and books.
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing. Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
College writing assignments serve a different purpose than the typical writing assignments you completed in high school. In high school, teachers generally focus on teaching you to write in a variety of modes and formats, including personal writing, expository writing, research papers, creative writing, and writing short answers and essays for ...
Here are some practical tips that will keep your work focused and effective: - Critical thinking - Academic writing has to be characterized by critical thinking, not only to provide the work with the needed level, but also because it takes part in the final mark. - Continuity of ideas - When you get to the middle of assignment, things ...
The five-paragraph model is a good way to learn how to write an academic essay. It's a simplified version of academic writing that requires you to state an idea and support it with evidence. Setting a limit of five paragraphs narrows your options and forces you to master the basics of organization. Furthermore—and for many high school ...
Academic writing, like many college assignments, is about the development of mental tools. In other words, a term paper in a college class is a great way for an instructor to make sure that the student has learned, at least temporarily, enough about the subject to write the term paper. The instructor wants students to show that they have ...
The Writing Center Understanding Assignments What this handout is about The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will ...
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments. Link to Learning. This Assignment Calculator can ...
Writing a rough draft. In this step, the writer uses the work completed in prewriting to develop a first draft. The draft covers the ideas the writer brainstormed and follows the organizational plan that was laid out in the first step. Revising. In this step, the writer revisits the draft to review and, if necessary, reshape its content.
Key Takeaways. Writing is crucial to college success because it is the single most important means of evaluation. Writing in college is not limited to the kinds of assignments commonly required in high school English classes. Writers in college must pay close attention to the terms of an assignment.
Designing Effective Writing Assignments. One of the best ways for students to determine what they know, think, and believe about a given subject is to write about it. To support students in their writing, it is important to provide them with a meaningful writing task, one that has an authentic purpose, clear guidelines, and engages students in ...
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...
Writing assignments in college vary in length, purpose, and the relationship between the writer (you) and the topic. Sometimes you may be asked to gather information and write a report on your findings. ... When a writing assignment is mentioned in the syllabus of a course, make sure you understand the assignment long before you begin to do it. ...
Three Common Types of College Writing Assignments. We have been decoding the expectations of the academic writing task so far, and I want to turn now to examine the types of assignments you might receive. From my experience, you are likely to get three kinds of writing assignments based upon the instructor's degree of direction for the ...
Writing as a College Student. As a college student, you have been writing for years, so you probably think that you have a clear understanding about academic writing. ... You might not think of a typical writing assignment as a group project, but you begin collaborating on a writing assignment the moment you discuss your topic with someone else ...
Key Takeaways. Writing is crucial to college success because it is the single most important means of evaluation. Writing in college is not limited to the kinds of assignments commonly required in high school English classes. Writers in college must pay close attention to the terms of an assignment.
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments.
Understanding the question is the first and most important step when starting your assignments and helps to ensure that your research and writing is more focused and relevant. This means understanding both the individual words, and also the general scope of the question. A common mistake students make with their assignments is to misinterpret ...
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other's drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic. Require consultations.
Traditional Academic. For most of us, these are the most familiar types of college-level writing assignments. While they are perhaps less common in Gen Ed than in departmental courses, there are still numerous examples we could examine. Two illustrations of common types include: Example 1: Short Essay Professor Michael Sandel asks the students ...
Cleveland State University's First-Year Writing Sequence. ENG 100/101 helps you learn basic academic writing techniques while also examining rhetorical situations and rhetorical appeals. These skills connect to the "real world" in multiple ways. For instance, think of the last political ad you saw or an article you read online-how do ...