- 0 Shopping Cart


Kerala flood case study
Kerala flood case study.
Kerala is a state on the southwestern Malabar Coast of India. The state has the 13th largest population in India. Kerala, which lies in the tropical region, is mainly subject to the humid tropical wet climate experienced by most of Earth’s rainforests.
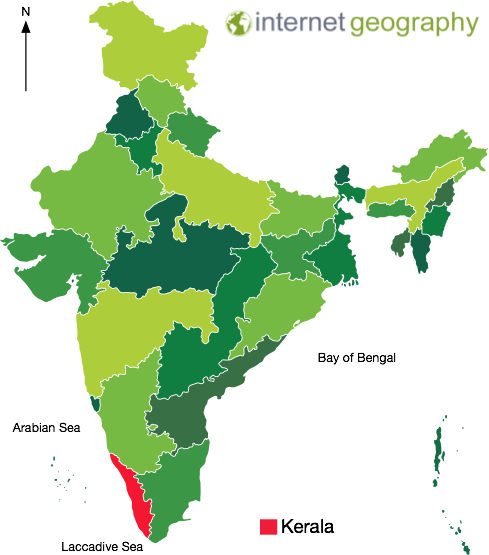
A map to show the location of Kerala
Eastern Kerala consists of land infringed upon by the Western Ghats (western mountain range); the region includes high mountains, gorges, and deep-cut valleys. The wildest lands are covered with dense forests, while other areas lie under tea and coffee plantations or other forms of cultivation.
The Indian state of Kerala receives some of India’s highest rainfall during the monsoon season. However, in 2018 the state experienced its highest level of monsoon rainfall in decades. According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), there was 2346.3 mm of precipitation, instead of the average 1649.55 mm.
Kerala received over two and a half times more rainfall than August’s average. Between August 1 and 19, the state received 758.6 mm of precipitation, compared to the average of 287.6 mm, or 164% more. This was 42% more than during the entire monsoon season.
The unprecedented rainfall was caused by a spell of low pressure over the region. As a result, there was a perfect confluence of the south-west monsoon wind system and the two low-pressure systems formed over the Bay of Bengal and Odisha. The low-pressure regions pull in the moist south-west monsoon winds, increasing their speed, as they then hit the Western Ghats, travel skywards, and form rain-bearing clouds.
Further downpours on already saturated land led to more surface run-off causing landslides and widespread flooding.
Kerala has 41 rivers flowing into the Arabian Sea, and 80 of its dams were opened after being overwhelmed. As a result, water treatment plants were submerged, and motors were damaged.
In some areas, floodwater was between 3-4.5m deep. Floods in the southern Indian state of Kerala have killed more than 410 people since June 2018 in what local officials said was the worst flooding in 100 years. Many of those who died had been crushed under debris caused by landslides. More than 1 million people were left homeless in the 3,200 emergency relief camps set up in the area.
Parts of Kerala’s commercial capital, Cochin, were underwater, snarling up roads and leaving railways across the state impassable. In addition, the state’s airport, which domestic and overseas tourists use, was closed, causing significant disruption.
Local plantations were inundated by water, endangering the local rubber, tea, coffee and spice industries.
Schools in all 14 districts of Kerala were closed, and some districts have banned tourists because of safety concerns.
Maintaining sanitation and preventing disease in relief camps housing more than 800,000 people was a significant challenge. Authorities also had to restore regular clean drinking water and electricity supplies to the state’s 33 million residents.
Officials have estimated more than 83,000km of roads will need to be repaired and that the total recovery cost will be between £2.2bn and $2.7bn.
Indians from different parts of the country used social media to help people stranded in the flood-hit southern state of Kerala. Hundreds took to social media platforms to coordinate search, rescue and food distribution efforts and reach out to people who needed help. Social media was also used to support fundraising for those affected by the flooding. Several Bollywood stars supported this.
Some Indians have opened up their homes for people from Kerala who were stranded in other cities because of the floods.
Thousands of troops were deployed to rescue those caught up in the flooding. Army, navy and air force personnel were deployed to help those stranded in remote and hilly areas. Dozens of helicopters dropped tonnes of food, medicine and water over areas cut off by damaged roads and bridges. Helicopters were also involved in airlifting people marooned by the flooding to safety.
More than 300 boats were involved in rescue attempts. The state government said each boat would get 3,000 rupees (£34) for each day of their work and that authorities would pay for any damage to the vessels.
As the monsoon rains began to ease, efforts increased to get relief supplies to isolated areas along with clean up operations where water levels were falling.
Millions of dollars in donations have poured into Kerala from the rest of India and abroad in recent days. Other state governments have promised more than $50m, while ministers and company chiefs have publicly vowed to give a month’s salary.
Even supreme court judges have donated $360 each, while the British-based Sikh group Khalsa Aid International has set up its own relief camp in Kochi, Kerala’s main city, to provide meals for 3,000 people a day.
International Response
In the wake of the disaster, the UAE, Qatar and the Maldives came forward with offers of financial aid amounting to nearly £82m. The United Arab Emirates promised $100m (£77m) of this aid. This is because of the close relationship between Kerala and the UAE. There are a large number of migrants from Kerala working in the UAE. The amount was more than the $97m promised by India’s central government. However, as it has done since 2004, India declined to accept aid donations. The main reason for this is to protect its image as a newly industrialised country; it does not need to rely on other countries for financial help.
Google provided a donation platform to allow donors to make donations securely. Google partners with the Center for Disaster Philanthropy (CDP), an intermediary organisation that specialises in distributing your donations to local nonprofits that work in the affected region to ensure funds reach those who need them the most.
Google Kerala Donate
Tales of humanity and hope
Check your understanding.

Premium Resources
Please support internet geography.
If you've found the resources on this page useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.
River flooding and management
Topic home, wainfleet floods case study, share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Top posts and pages.
Latest Blog Entries
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly
Study Material
.webp)
Class 9 SST Project Work On Disaster Management
Home > Class 9 Subject-wise Material
Disaster Management Project
As part of the CBSE 2024–25 syllabus, students are required to prepare and submit Class 9 Social Science projects on disaster management. Educart has created a special page filled with inspiring ideas for various parts of this project.
Here, you will find creative cover page designs, well-designed acknowledgment pages, and even complete project files (in video form) showcasing the top projects on disaster management from previous years.

| Serial No. | Content |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 |
Project Structure
The index, also called the Table of Contents, usually comes after acknowledgment. It contains the main heading of the topics arranged in a sequence. Here is an example for reference purpose.
Start your class 9 SST project on disaster management by providing a brief introduction and overview of disaster management. Define disaster followed by the definition of disaster management. Use the following reference to understand the meaning of disaster management, and write the intro part of the project.

https://www.undrr.org/terminology/disaster-management
https://nidm.gov.in/PDF/Disaster_about.pdf
https://publichealth.tulane.edu/blog/what-is-disaster-management/
https://www.iwapublishing.com/news/disaster-management
Explain why disaster management is important given India’s diversified climatic conditions. Explain natural catastrophes such as earthquakes, cyclones, floods, droughts, etc.

https://publichealth.tulane.edu/blog/disaster-management-cycle/
Write two different types of natural and man-made disasters, along with examples.
3.1 Natural Disasters
Start with the definition—Natural hazards are environmental events that can affect societies and the human environment. They are different from man-made hazards. For example, a flood caused by changes in river flows is a natural hazard, while a flood caused by a dam failure is a man-made hazard.
Now, describe various natural disasters and their impacts. Quote a few, e.g., of natural disasters like:
- Earthquakes
- Hurricanes/Cyclones
- Volcanic Eruptions
- Avalanche, etc.

https://hazards.fema.gov/nri/natural-hazards
3.2 Man-Made Disasters
Next, write about man-made disasters, how they are caused, etc., along with quoting a few examples, like:
- Industrial Accidents
- Nuclear Disasters
- Environmental degradation

https://sdma-arunachal.in/manmade-disasters/
Mention the vulnerability profile of India, discussing the States and Union Territories that are disaster-prone. Describe all the factors, both natural and man-induced, responsible for the vulnerability of these states.
.webp)
https://iasscore.in/data-story/vulnerability-profile-of-india
https://www.drishtiias.com/to-the-points/paper3/disaster-management-i
Write about the two worst disaster cases in India that impacted the lives of millions of people. Mention the following two:
5.1 Natural Disaster: 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami

5.2 Man-Made Disaster: Bhopal Gas Tragedy

https://recovery.preventionweb.net/collections/recovery-collection-2004-indian-ocean-earthquake-and-tsunami
Define what disaster risk reduction is, write about all phases and also describe the disaster management cycle.
6.1 Phases of Disaster Management
Under this topic, describe the key phases of disaster management i.e., the pre-disaster phase, the disaster phase, and the post-disaster phase, and mention all the key components of this phase.
- Preparedness
- Rehabilitation

https://home.akitabox.com/blog/4-phases-of-disaster-management/
6.2 Disaster Management Cycle

Mention various national and international bodies and their role in disaster management.
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)

Mention the Disaster Management Act of 2005. Highlight the key points and explain how the act is beneficial in disaster management.
As technology develops, so does its application, and it has not left any field unaffected. So, describe how technology helps predict, prepare for, and respond to disasters. Provide examples of technologies used in disaster management, such as early warning systems, GIS mapping, and communication tools.

https://www.drishtiias.com/blog/tech-driven-disaster-management-changing-the-game
Other Measures to Prevent Disasters
Write some of the measures that should be taken to mitigate disasters, for eg:
- Disaster resilient infrastructure
- Climate Change Adaptation
- Environmentally Sustainable Development
- Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Mapping
- Urban Planning and Development
https://www.nextias.com/blog/disaster-management/
Once you have written down all the important points in your disaster management project for class 9, you should summarize the key points discussed in your project and highlight the importance of effective disaster management for community resilience and safety.
The last page of your project should be a bibliography. Here, you have to provide a list of sources you used for your research, whether books, websites, articles, or any other relevant materials.
Below is the list of references used to provide you with all the important information on the disaster management project for class 9. This might be useful for you, so please do check this out.
https://www.iwapublishing.com/news/disaster-management
https://iasscore.in/data-story/vulnerability-profile-of-india https://ebooks.inflibnet.ac.in/geop15/chapter/issues-and-challenges-in-disaster-management/
- Explain the main difference between natural and man-made disasters with examples?
- How many phases are there in Disaster Management cycle?
- What measures can be taken to improve disaster preparedness in communities?
- Describe the role of government agencies in disaster mitigation.
- What are some challenges faced during the response phase of disaster management?
Examples: Cover Images
Here are a few cover page ideas for the disaster management project for class 9.

Examples: Acknowledgement / Index page
Have a look at few creative examples for your project acknowledgement and Index Page.

Videos: Topper Project Files
Here are some video links to inspire your disaster management project.
Project Idea- Video 1
Project Idea- Video 2
Project Idea- Video 3
Project Idea- Video 4
Pdfs: full projects.
Download full project PDF of disaster management file for CBSE class 9

Sample Project 1
Sample Project 2
Sample project 3, sample project 4, sample project 5, sample project 6, other projects.
<red> → <red> SST Social Issues Project for Class 10
<red> → <red> SST Sustainable Development Project for Class 10
<red> → <red> SST Consumer Awareness Project for Class 10
- Mathematics (Standard)
- Mathematics (Basic)
- Social Science
- Computer Application
- Information Technology
- English Core
- Mathematics
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political Science
- Science (Hindi )
- Maths (Hindi)
- Social Science (Hindi )
- Applied Maths
- Physical Education
- English Language
- History & Civics
- 10 Year Solved Papers
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 English
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Math Standard
- Computer Applications
- Class 12 PCB Combo
- Class 12 PCM Combo
- Entrance Exam
- K-8 Raspberry Solutions
- K-8 Kiwi Solutions

Disaster Management Project for Class 9 – Complete Guide

Written By Avinash Sharan
Class 9 | projects 9, 13 comment(s), 10th may 2020, disaster management project.
It is mandatory to do a Disaster Management project for class 9 students every year.
According to CBSE, students studying in class IX have to submit a handwritten project on Disaster Management.
Topics will be provided by the school. The topic may be Natural Disasters or Man-Made disasters.
The purpose of giving this Disaster Management project to class 9 students is to make them prepared for any disaster.
Further, they can also spread awareness to the mass about the precautions to be taken at the time of National/Local Disasters.
Are you looking for a project on Tsunamis? Simply click the link https://shapingminds.in/project-on-tsunami/
To get the latest project on Sustainable Developmen t, click on the link.
“Project On Heat Stroke”- Understanding the Risks and Prevention
Things to be kept in mind while doing the project
Follow cbse guidelines strictly..
- Firstly, USE A-4 size file paper (one side ruled)
- Secondly, Use blue or black ink to write your project.
- Thirdly, design the cover page in such a way that it reflects your topic.
- Fourthly, write the Topic of the project, Name, Class, and Sec, and Roll no. on the cover page in bold letters.
- Use the bottom space for your Name, Class, and sec, Roll no.
- However, the project work should not be less than 15 pages (including the cover page)
- Be ready for Viva or written assignments based on your project.
- Utilize summer vacation / Lockdown time to complete your project.
- Lastly, do not use plastic covers.
Disaster Management Project Page-Wise With Subheadings
SEQUENCE OF PAGES: DISASTER MANAGEMENT PROJECT
will be your cover page with topics like
TOPIC: COVID-19 PANDEMIC IN INDIA and then show your creativity in designing the page.
Page No. 2:
Acknowledgment: (what should be written) see an example below.
Acknowledgment
From the core of my heart, I am very thankful to everyone who all supported me, for I have completed my project effectively and moreover on time. I am overwhelmed in all humility and grateful to acknowledge my depth to all those who helped me to put these ideas well. equally grateful to my ( NAME OF SUBJECT TEACHER ) for giving me moral support and guidance in doing this project. It would be an injustice if I do not thank my parents who helped me a lot in collecting data, pictures, and continuous help and support. With their able guidance, encouragement, and support, I could complete my project on time.
Thanking you,
( Name of the student)
You may be interested in:
11 Points To Include In Your Industrial Disaster Management Project
11 Points You Must Include In Your Disaster Management Project On Climate Change
This page will be of Index as given in every textbook where the name of the chapters in the sequence is given along with page numbers. For example…….
INDEX
i) Introduction: pg 4.
ii) How the disaster takes place…………pg 5
iii) Preparedness before disaster………….pg 6
iv) Preparedness during disaster………..pg 7 & 8
v) Preparedness after disaster…………….pg 9 & 10.
Page No.4 & 5:
a short description of COVID-19 and a brief history of how it spread. Take the help of Newspapers or the Internet. (minimum 2 pages i.e. pg 4 & 5):
Read about the seven most frequently asked questions on International Date Line
Introduction – A brief History of COVID 19
Coronavirus actually belongs to the Coronaviridae family. It represents crown-like spikes on the outer surface of the virus, therefore, it was named as coronavirus. This virus is minute in size and causes the acute respiratory syndrome. These viruses were thought to infect only animals until the world witnessed a severe outbreak caused by SARS in Guangdong, China.
At the end of 2019, Wuhan- a fast-emerging business hub of China experienced an outbreak of coronavirus, killing more than 1800 and infected our 70 thousand individuals in just a span of 50 days. Health officials are still tracing the exact source of this new coronavirus, early findings (hypothesis) thought it may be linked to s seafood market in Wuhan. However, the first reported case came on 1st December, which had no link to the seafood market. Therefore, investigations are going on to find the exact reason for the originating and spread of COVID-19.
In 2003, an outbreak of SARS stands for the severe acute respiratory syndrome. An outbreak of SARS started in China and spread to other countries before ending in 2004. Coronavirus also known as COVID-19 seems to spread faster than the 2003 SARS and also may cause severe illness.
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses named the virus as SARS- CoV 19 and the disease COVID-19.
The Disaster Management Project 2024 On Nuclear War
IF YOU ARE IN CLASS IX, THE FOLLOWING LINKS MAY BE HELPFUL TO YOU
Clear And Unbiased Facts About Project On Global Warming
Project On Tsunami: 13 Pages You Must Include In Your Disaster Management Project
Page No. 6 & 7
Mention the causes and symptoms:
Coronavirus typically affects the respiratory tracts of birds and mammals including humans. Doctors associate them with the common cold, Bronchitis, Pneumonia, and severe acute respiratory syndrome.
The main way the disease spreads is through respiratory droplets expelled by someone who is coughing. The risk of catching COVID-19 from someone with no symptoms at all is very low.
However, many people with COVID-19 experience only mild symptoms. This is particularly true at the early stages of the disease. It is therefore possible to catch COVID-19 from someone who has, for example, just a mild cough and does not feel ill.
Empowering Women: Legal and Political challenges for women in West Asian countries
Common Symptoms
Researchers in China found that the most common symptoms among people who had COVID-19 include:
Loss of appetite
Shortness of breath and Mucus.
However, these symptoms usually begin 2 to 14 days after you come into contact with the virus.
There may be other symptoms as well such as sore throat, headache vomiting etc.
If you have any of these symptoms then
i) isolate yourself.
ii) stay away from others as much as possible.
iii) stay in a closed room and use a separate soap, towel, clothes, handkerchief and if possible toilet and bathroom.
If you are below 10 years of age or above 50 years of age with diabetes, blood pressure, weakness etc., then you are at a high risk of complications.
Therefore, immediately call your doctor and seek immediate medical help.
Page No. 8:
The extent of damage : On this page, you have to mention the extent of damage done in different countries. Take the help of newspapers or the internet for the latest information. You can also show the spread of this virus in different countries on the world map with different colors.
Uncovering the Effects of Natural Disasters on Communities – A Disaster Management Project
Steps taken by the government to combat this disaster: You may explain:
i) Lockdown
ii) Precautions to be taken during the lockdown period like social distancing, sanitizing hands, etc.
Very Important for TERM II (Case study-based questions)
TERM II CLASS IX – GEOGRAPHY WORKSHEET ON CLIMATE – SOLVED
Case Study Based Questions From Natural Vegetation And Wildlife – Term II (SOLVED)
Page No 10 & 11
Contribution of people who are involved in combating this disaster. In this page you can mention about the role of Doctors, Nurses, Police, people involved in maintaining cleanliness etc. in details along with images, drawings, pictures, newspaper cuttings etc on the left side of your page.
Page No. 12
Lessons Learnt:
what lessons have you learnt from this disaster.
Page No 13 INCLUDE DO’S AND DONT’S IN YOUR DISASTER MANAGEMENT PROJECT
HEADING: Do’s and dont’s for next time to avoid such disasters.
Mention about a few things which can be done everyday to protect yourself from this disaster in points.
Similarly Mention about a few things which you should not do to protect yourself from this disaster in points.
Page No. 14:
Bibliography: A bibliography usually contains about the websites you visited, the newspapers name from where you have collected the data or pictures, etc. Whichever book, magazine, shops or websites you have visited, you must mention about that.
Page No. 15:
Keep the last page of your project for teacher’s remarks and grade/marks.
6. Lastly, go for spiral bound cover and submit your project.
Just invest 1 day and 13 pages to complete your project on Tsunami as per CBSE norms.
THERE IS NO RULE FOR NUMBER OF PAGES BUT IT SHOULD NOT BE LESS THAN 15. YOU MAY ADD FEW MORE PAGES ALSO IF YOU WANT.
Follow Guidelines of CBSE strictly on Disaster Management Project.
Was this article helpful to you? Please like , share and subscribe .
Do You Want To Do A Project On Man Made Disaster, Then Click On The Given Link.
Get the latest project on Sustainable Developmen t, click on the link.
“Project On Heat Stroke”- Understanding the Risks and Prevention
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

“From Polls to Parliament: The Mechanics of Lok Sabha Elections in India”
Jun 20, 2024
How Are Lok Sabha Elections Conducted in India? As a student, you must be curious to know How Lok Sabha Elections are...

“From Waste to Wonder: The Power of Recycling in Carbon Footprint Reduction”
Jun 9, 2024
Carbon Footprint Reduction: A School Project On a Greener Planet Are you looking to make a positive impact on the...

Hirakud Dam: Exploring India’s Longest Earthen Dam and It’s Significance
May 22, 2024
Hirakud Dam: Key Facts, Benefits, Tourism Tips, Nearby Attractions The Hirakud Dam is a monumental structure that...
13 Comments
Thank you ji
Thanku it really helps me
Bro you helped me alot
Thank you once again. Avinash Sharan.
I want disaster management on earthquake
very good this helped me in making my project
Welcome Purushottam.
It is very much helpful . Thank You so much Sir.
Thank you Bhoomi.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Submit Comment

Class 9 Geography Case Study Questions of Chapter 3 Drainage
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions in Class 9 Social Science Chapter 3 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Social Science Chapter 10 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 9 Geography Case Study Questions Chapter 3 Drainage
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 9 Social Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Drainage Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Social Science Chapter 3 Drainage
Case Study 1: The drainage system of India is mainly controlled by the broad relief features of the subcontinent. Accordingly, the Indian rivers are divided into two major groups: the Himalayan rivers; and the Peninsular Rivers. Apart from originating from the two major physiographic regions of India, the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers are different from each other in many ways. Most of the Himalayan rivers are perennial. It means that they have water throughout the year. These rivers receive water from rain as well as from melted snow from the loft mountains. The two major Himalayan rivers, the Indus and the Brahmaputra originate from the North of the mountain ranges. They have cut through the mountains making gorges. The Himalayan rivers have long courses from their source to the sea. They perform an intensive erosional activity in their upper courses from their source to the sea. They perform an intensive erosional activity in their upper courses and carry huge loads of silt and sand. In the middle and lower courses, these rivers form meanders, oxbow lakes, and many other depositional features in their flood plains. They also have well-developed deltas.
Which of the following is not the Himalayan river? (a) Godavari (b) Indus (c) Ganga (d) Brahmaputra
Answer: (a) Godavari
Which of the following is not the feature of the Himalayan rivers? (a) Some Himalayan rivers originate from the North of the mountain range. (b) The Himalayan rivers have shorter and shallower courses. (c) Brahmaputra is the example of Himalayan rivers. (d) None of the above
Answer: (b) The Himalayan rivers have shorter and shallower courses.
Why do some Himalayan rivers perform the intensive erosional activity? Identify the best suitable options. (a) Because they originates from high altitude. (b) These are small rivers. (c) These rivers are flows from West to East. (d) These river are non-perennial.
Answer: (a) Because they originates from high altitude.
Himalayan rivers has well developed deltas. Which among the following is the prominent cause? (a) Himalayan rivers have long courses from their source to sea. (b) They flows from mountain and carry huge loads of silt and sand. (c) They flow with high density of water. (d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Which of the following is not the characteristics of Himalayan rivers? (a) This rivers formed deltas at their mouth. (b) The Himalayan rivers are short in length. (c) These rivers are seasonal. (d) All of the above
Answer: (a) This rivers formed deltas at their mouth.
Two statements are given in the question below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the appropriate option. Assertion (A) Peninsular river are perennial river. Reason (R) Perennial rivers receives water from rain as well as from melted snow from the lofty mountains. Codes (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A (c) A is true, but R is false (d) A is false, but R is true
Answer: (d) A is false, but R is true
Case Study 2: The drainage system plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape and determining the flow of water in an area. In India, the drainage patterns are diverse and influenced by various factors such as topography, climate, and geological formations. The major drainage basins in India are the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra. The Himalayan rivers have a snow-fed perennial source, resulting in the formation of large river systems. The Peninsular rivers, on the other hand, have a rain-fed source and exhibit seasonal variations in their water flow. The rivers in India not only provide water for irrigation, drinking, and industrial purposes but also serve as important transportation routes. However, the improper management of drainage systems can lead to issues such as floods, soil erosion, and water pollution.
What factors influence the drainage patterns in India? a) Political boundaries and population density b) Topography, climate, and geological formations c) Religious diversity and cultural practices d) Economic development and industrialization
Answer: b) Topography, climate, and geological formations
Which are the major drainage basins in India? a) Yamuna, Godavari, and Krishna b) Narmada, Mahanadi, and Tapti c) Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra d) Cauvery, Tungabhadra, and Pennar
Answer: c) Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra
What is the source of Himalayan rivers in India? a) Underground springs b) Lakes and reservoirs c) Rainfall and monsoons d) Snow-fed perennial glaciers
Answer: d) Snow-fed perennial glaciers
How do Peninsular rivers in India differ from Himalayan rivers? a) Peninsular rivers have a snow-fed source. b) Peninsular rivers are rain-fed and exhibit seasonal variations. c) Peninsular rivers flow through the Himalayan region. d) Peninsular rivers have a larger water volume.
Answer: b) Peninsular rivers are rain-fed and exhibit seasonal variations.
Besides water supply, what other functions do rivers serve in India? a) Formation of deltas and estuaries b) Generation of electricity through hydropower projects c) Creation of tourist attractions and scenic spots d) Development of recreational activities like boating and fishing
Answer: b) Generation of electricity through hydropower projects
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Social Science Chapter 3 Drainage with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Social Science Drainage Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Cbse class 9 science term 1 mcq questions with answers pdf download, mcq questions of class 9 maths chapter 6 lines and angles with answers, mcq questions of class 9 maths chapter 9 areas of parallelogram and triangles with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
K erala Flood 2021 — An environmental case study
Amirul Haqe
Being a coastal state of India and much of the land being part of the fragile Western Ghats, Kerala is very sensitive to climate change and unsustainable developments. Climate change affects the entire globe, but places like Kerala will be the first and the worst affected.
Kerala cannot copy the developments of Western countries. America and other countries have got a large proportion of plain land. Even Tamil Nadu, the neighboring state of Kerala, has enough level lands for their developments. But Kerala is just a strip of coastal area with 35 million people living in the folds of Western Ghats.
Yes, infrastructure developments have become a necessity in this modern world, but it has to be sustainable. In some regions, the consequence of unsustainable activities will be seen only after a long time, while for some regions the impacts are immediate. Therefore, places like Kerala have to consider sustainability more than others.
W hat led to the Flood?
After a few weeks of continuous rain in Kerala, monsoon rains were almost about to end. Most of the water bodies and reservoirs were saturated and the soil’s water-holding capacity was reached. The days were calm, but then spontaneously, a low-pressure system was observed in the east-central Arabian Sea on October 14. Because of this system, Kerala experienced very heavy to extremely heavy rain, with a record of 347 mm of rain in just 24 hours in Kottayam’s Mundakkayam.
No dam was opened, still, there was a sudden rush of water downhill. Experts say that a mini cloudburst, 20 mm of rain in just 3 hours, happened over the border of Kottayam and Idukki districts, causing major landslides in Kottayam’s Koottickal and Idukki’s Kokkayar. It is reported that these clouds are formed due to the rise in temperature levels in the Arabian sea. At present, the temperature level in the sea is recorded at 29 degrees celsius. Usually, it is recorded from 26 to 27 degrees celsius, said MG Manoj, a scientist at Advanced Centre for Atmospheric Radar Research (ACARR), CUSAT.
Cloudbursts are extreme amounts of precipitation, of about 10mm rain in an hour, resulting due to the cumulonimbus clouds. Kerala has no record of cloudbursts, but mini cloudbursts are being observed since 2019. Floods in 2018 were due to prolonged rain and the opening of dams, and the flood was gradual. But after 2019, mini cloudbursts have been increasing and causing flash floods and landslides. This phenomenon was also responsible for the 2019 landslides at Kavalappara and Puthumala.
Due to this low-pressure system, heavy rains lashed throughout Kerala, and these rains are predictable by a range of 2–3 days. But within this rain pattern, some regions experience extreme rains in the form of cloudbursts, which is almost unpredictable. This gives no time for preparation.
Very heavy rainfall indicates 200 mm of rain in a day, that could be 200 mm in 24 hours, or sometimes 200 mm in just 1–2 hours. So, even ideally, the rate of draining of floodwater cannot match with the rate of rainfall, thus causing flash floods. And practically, all natural drainage systems are deteriorated by poor land management and construction activities, thus increasing the destruction.
Kerala weather was uniform and predictable will 2018, the year in which nearly 500 people were killed in Kerala when it was ravaged by the worst floods to hit the state in almost a century. Also, Kerala was relatively safe from devastating cyclones. In 100 years from 1908 to 2008, the State was hit by just 18 coastal cyclones of low intensity.
The weather pattern over the Arabian sea and the Bay of Bengal have become very bizarre in recent years, with an increasing number of devastating cyclones. There has been a 52% rise in the frequency of cyclones in the Arabian Sea over two decades. 2019 saw the most intense cyclonic activity in more than 100 years in the Arabian sea. Five cyclones originated in the area. This year,
Warming Arabian Sea turning hotbed for intense cyclones: Study (indianexpress.com)
All these cyclonic activities and cloudbursts are linked to global warming and climate change.
2. Land use
These disasters were caused due to higher economic activities like rock quarrying, construction of new buildings and roads and destruction of natural forest in the highly economic zones, says Madhav Gadgil
It was way back in August 2011 that the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel chaired by Madhav Gadgil had submitted its report. Even after 10 years and the appointment of another committee led by K Kasturirangan, the highly ecologically sensitive region in Kerala continued to be an epi-center of construction activities. No action was taken on these reports after widespread protests.
Gadgil said, “Due to the vested interests of a small group of people, measures that could have helped an entire area were blocked. We had asked to stop economic activities only in a small area of the state, which came under the highly sensitive zones. Not paying attention to that has resulted in the landslides and massive floods in recent years. Some of the encroachments and constructions are relatively recent too. This is an invited disaster. These constructions are not only leading to landslides but also affecting the overall ecosystem and natural resources in Kerala, including rivers.”
Kerala’s dream projects like Vizhinjam Port and K-Rail, are being criticized for their environmental impact. It is destructive to the construction region and also requires other regions to be mined for the construction materials, thus having a double impact.
Exponential damage
On one hand, floods are increasing due to climate change, and on the other side, lands are being deteriorated making it difficult to hold even a normal flood. Thus causing exponential damage.
As one of the reasons for the recent flash floods is global climate change, which humankind has already accelerated, Kerala alone cannot do anything in that regard. Recent IPCC report is a ‘Code Red for humanity’. This has to be solved by global cooperation.
All development activities ranging from state-owned grand projects to the building of a small house, have to be eco-friendly. A ground-level awareness is important to convince local people about considering the long-term impacts that their regular activities can make. All activities that block or hinder the natural drainage system, like building houses, roads, etc, have to be under the supervision of local authorities.
Natural drainage systems have to be well maintained, and artificial drainage systems in required areas as well.
I am not a weather or environmental expert. This is from my years of observation and research. Do correct me if there are any factual errors, in the comments.

Written by Amirul Haqe
Text to speech

Disaster Management Project for Class 9 and 10 PDF Download
Developing a disaster management project for Class 9 and 10 students not only enhances their knowledge and understanding but also equips them with essential life skills. The field of disaster management is of utmost importance in India, a country prone to various natural and man-made disasters.
Disaster management plays a vital role in minimizing the impact of disasters and ensuring the safety and well-being of communities. In this blog post, we will delve into the various aspects of disaster management, including its definition, types of disasters, the disaster management cycle, relevant acts, agencies in India, and tips for developing a disaster management project for Class 9 and 10 students.
This project provides an opportunity for students to explore different aspects of disaster management, develop critical thinking abilities, and contribute to building a safer and more resilient society. Here is a comprehensive outline for a disaster management project suitable for Class 9 and 10 students in India.
Disaster Management Project PDF Download
Table of Content:
- Define disaster management and its significance.
- Discuss the need for disaster management in India.
- Highlight the objectives and benefits of studying disaster management.
- Categorize disasters into natural and man-made disasters.
- Provide examples of common natural disasters in India (e.g., floods, earthquakes, cyclones, droughts).
- Discuss man-made disasters prevalent in India (e.g., industrial accidents, chemical spills, fires).
- Explain the four phases of the disaster management cycle (mitigation, preparedness, response, recovery).
- Describe the activities involved in each phase.
- Provide examples of initiatives or programs undertaken in India for each phase.
- Discuss the Disaster Management Act, 2005, and its key provisions.
- Explore the roles and responsibilities of national, state, and district-level disaster management authorities in India.
- Highlight the importance of coordination and collaboration among different agencies.
- Select two or more major disasters that have occurred in India (e.g., Uttarakhand floods, Cyclone Fani).
- Analyze the causes, impacts, and response strategies employed during these disasters.
- Discuss the lessons learned and recommendations for future disaster management.
- Explore various preparedness measures for different types of disasters (e.g., early warning systems, evacuation plans).
- Discuss mitigation strategies to reduce the impact of disasters (e.g., building resilient infrastructure, afforestation).
- Provide examples of successful preparedness and mitigation initiatives in India.
- Emphasize the importance of individual responsibility in disaster management.
- Discuss ways in which individuals can contribute to disaster preparedness and response.
- Encourage students to create awareness campaigns or develop community-level initiatives for disaster preparedness.
- Prepare a visual presentation summarizing the project.
- Include relevant images, charts, and graphs to enhance understanding.
- Deliver a concise and engaging presentation to the class.
In India, the need for effective disaster management is paramount due to the country’s geographical location and diverse climatic conditions. India is prone to a wide range of natural disasters, including floods, cyclones, earthquakes, droughts, landslides, and forest fires. Additionally, man-made disasters such as industrial accidents, chemical spills, and terrorist attacks pose significant risks. These disasters can cause loss of life, widespread damage to infrastructure, economic disruptions, and displacement of populations.
What is Disaster Management?
Disaster management is a process of preparing for, responding to, and recovering from an emergency or disaster. It involves various activities such as risk assessment, planning, communication, and coordination of resources to reduce the impact of disasters. The primary goal of disaster management is to save lives, protect property, and ensure the continuity of essential services.
Types of Disasters
Disasters can be classified into two broad categories, namely natural disasters and man-made disasters. Natural disasters are caused by natural phenomena such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, tsunamis, and landslides. Man-made disasters, on the other hand, are caused by human activities such as fires, explosions, industrial accidents, and terrorist attacks.
Natural disasters are more common and can have a severe impact on human life and property. For example, earthquakes can cause buildings to collapse, floods can destroy homes and businesses, hurricanes can cause widespread power outages and damage infrastructure, and landslides can disrupt transportation and communication.
Man-made disasters are less common but can also have a severe impact on human life and property. For example, industrial accidents can result in chemical spills, fires can destroy buildings and homes, explosions can cause widespread damage, and terrorist attacks can cause widespread panic and loss of life.

Importance of Disaster Management
Disaster management is essential for several reasons. Firstly, disasters can strike anytime, anywhere, and without warning. Therefore, it is crucial to be prepared for disasters to reduce the impact of disasters and save lives. Secondly, disasters can have severe consequences on human life and property, which can lead to economic losses and social disruption. Effective disaster management measures can help to reduce the impact of disasters and ensure the continuity of essential services. Thirdly, disasters can cause psychological trauma to people affected by disasters, and effective disaster management measures can help to provide psychological support and counseling to those affected.
Disaster Management Cycle
The disaster management cycle consists of four phases: mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery. Each phase plays a crucial role in minimizing the impact of disasters, enhancing preparedness, and facilitating effective response and recovery efforts. In India, various initiatives and programs have been undertaken at each phase to mitigate risks, build preparedness, respond swiftly, and facilitate long-term recovery and reconstruction.
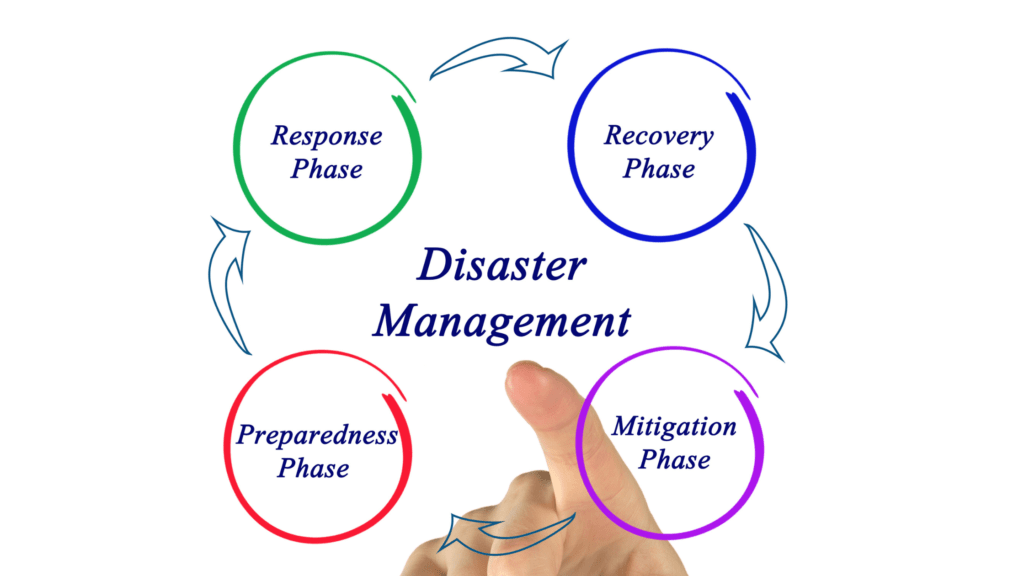
- The mitigation phase involves activities that aim to reduce the risk of disasters, such as identifying hazards and assessing risks.
- The preparedness phase involves activities that aim to prepare individuals, communities, and organizations to respond to disasters, such as developing emergency plans, conducting drills, and training first responders.
- The response phase involves activities that aim to provide immediate assistance to people affected by disasters, such as search and rescue, evacuation, and providing basic needs such as food, water, and shelter.
- The recovery phase involves activities that aim to restore normalcy after a disaster, such as rebuilding infrastructure, providing psychological support, and restoring essential services.
Case Studies of Major Disasters in India
India has witnessed several major disasters in the past, and effective disaster management measures have helped to reduce the impact of disasters and save lives. For example, during the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami, effective disaster management measures such as warning systems, evacuation, and search and rescue operations helped to reduce the number of casualties. Similarly, during the 2013 Uttarakhand floods, effective disaster management measures such as rescue and relief operations helped to save many lives.
However, there have also been instances where ineffective disaster management measures have resulted in severe consequences. For example, during the 1984 Bhopal gas tragedy, ineffective disaster management measures resulted in widespread loss of life and property.
The case studies of major disasters in India highlight the importance of effective disaster management measures and the need for continuous improvement in disaster management strategies.
Preparedness for disasters
preparedness measures and mitigation strategies are crucial for effective disaster management. Early warning systems, evacuation plans, resilient infrastructure, afforestation, and community-based initiatives play significant roles in reducing the risks and impacts of disasters. India has implemented successful initiatives that highlight the importance of preparedness and mitigation, contributing to the overall resilience of communities in the face of various hazards.
Preparedness for disasters is essential to reduce the impact of disasters and save lives. Students can prepare for disasters by following some simple steps, such as creating an emergency kit, developing an emergency plan, and staying informed about potential hazards.
Preparedness Measures for Different Types of Disasters:
- Early Warning Systems: Example: The Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System (IOTWS), implemented by the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), provides real-time tsunami warnings and alerts to coastal communities.
- Evacuation Plans: Example: The Odisha State Disaster Management Authority has implemented a successful evacuation plan during cyclones, including Cyclone Phailin in 2013, which resulted in minimal loss of life due to timely evacuation. Mitigation Strategies to Reduce the Impact of Disasters:
- Building Resilient Infrastructure Example: The Gujarat State Disaster Management Authority implemented strict building codes and regulations after the devastating earthquake in 2001. This has led to the construction of earthquake-resistant buildings and infrastructure, reducing the vulnerability to seismic events.
- Afforestation and Ecosystem Restoration: Example: The Miyawaki Forest technique, implemented in various cities across India, involves dense plantation of native tree species, enhancing biodiversity, restoring ecosystems, and providing natural protection against disasters. Successful Preparedness and Mitigation Initiatives in India:
- Kerala’s Community-Based Disaster Management Initiatives: – Kerala has implemented community-based disaster management initiatives, including the ‘Arangu’ program, which involves training local volunteers to respond during disasters. – The ‘Rebuild Kerala Initiative’ focuses on building resilient infrastructure, restoring livelihoods, and providing financial assistance to affected communities.
- Gujarat’s School Safety Program – The School Safety Program in Gujarat aims to enhance the safety and preparedness of schools during disasters. – It includes developing school disaster management plans, conducting safety audits, training teachers and students in disaster response, and establishing early warning systems.
Role of individuals in Disaster Management
Individuals play a crucial role in disaster management, and their actions can have a significant impact on the outcome of disasters. Individuals can contribute to disaster management by following some simple steps, such as staying informed about potential hazards, creating an emergency kit, developing an emergency plan, and volunteering during emergencies.
Staying informed about potential hazards involves monitoring weather updates, staying informed about potential hazards, and following the instructions of authorities during emergencies. Creating an emergency kit involves assembling essential items such as food, water, first aid kit, flashlight, and other essential items that may be required during an emergency. Developing an emergency plan involves identifying potential hazards, developing a communication plan, identifying safe zones, and practicing emergency drills. Volunteering during emergencies involves providing support to those affected by disasters, such as providing basic needs, psychological support, and assisting in search and rescue operations.
Strategic Management: Key Concepts and Proven Strategies
Disaster Management Project Presentation:
Tips for developing the disaster management project:.
- Conduct thorough research using reliable sources such as government publications, scientific journals, and reputable websites.
- Organize the project into clear sections with headings and subheadings.
- Use a variety of media, including text, images, and infographics, to present information effectively.
- Incorporate real-life examples, case studies, and statistics to support your points.
- Cite all sources properly using a standard citation format (e.g., APA or MLA).
- Practice your presentation beforehand to ensure clarity and confidence.
SST Class 9 Disaster Management Project
Disaster management Project For Class 9
Disaster Project Management Conclusion:
The disaster management project for Class 9 and 10 students in India provides an excellent opportunity to deepen their understanding of disaster management concepts and their practical application. By exploring various aspects of disaster management, students can develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and leadership skills necessary to contribute effectively in times of crisis. Through this project, students not only gain knowledge but also become proactive agents of change in building resilient communities and promoting disaster preparedness in India.
Related Post
Marketing management project on chocolate class 12 download pdf, guide to mba mcqs – all subjects – download pdf, explore the hotel management colleges in kerala, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Best Topics for Presentation for Students
The best of marketing management by philip kotler, importance of marketing management.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Drainage
- Last modified on: 11 months ago
- Reading Time: 5 Minutes
Case Study Questions
Question 1:
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follows:
The headwaters of the Ganga, called the ‘Bhagirathi’ is fed by the Gangotri Glacier and joined by the Alaknanda at Devaprayag in Uttarakhand. At Haridwar the Ganga emerges from the mountains on to the plains. The Ganga is joined by many tributaries from the Himalayas, a few of them being major rivers such as the Yamuna, the Ghaghara, the Gandak and the Kosi. The river Yamuna rises from
the Yamunotri Glacier in the Himalayas. It flows parallel to the Ganga and as a right bank tributary, meets the Ganga at Allahabad. The Ghaghara, the Gandak and the Kosi rise in the Nepal Himalaya. They are the rivers, which flood parts of the northern plains every year, causing widespread damage to life and property but enriching the soil for the extensive agricultural lands. The main tributaries, which come from the peninsular uplands, are the Chambal, the Betwa and the Son. These rise from semi-arid areas, have shorter courses and do not carry much water in them. Enlarged with the waters from its right and left bank tributaries, the Ganga flows eastwards till Farakka in West Bengal. This is the northernmost point of the Ganga delta. The river bifurcates here; the Bhagirathi-Hooghly (a distributary) flows southwards through the deltaic plains to the Bay of Bengal. The mainstream, flows southwards into Bangladesh and is joined by the Brahmaputra. Further downstream, it is known as the Meghna. This mighty river, with waters from the Ganga, and the Brahmaputra, flows into the Bay of Bengal. The delta formed by these rivers is known as the Sunder ban delta.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(i) What glacier Ganga is fed by? (A) Himalayan (B) Ladakh (C) Gangotri (D) None of the above
(ii) Which is one of the tributaries, mentioned in the paragraph, joins Ganga? (A) Ghaghara (B) Narmada (C) Tapi (D) All the above
(iii) Where does Yamuna rise from? (A) Gangotri (B) Himalaya (C) Chenab (D) Yamunotri
(iv) What is the northernmost point of the Ganga delta? (A) Bangladesh (B) Tamil Nadu (C) Farakka (D) None of the above
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Disaster Management Project Class 9
- 1 What is disaster management?
- 2 Why do we learn disaster management?
- 3 What are the most common disaster management scenarios?
- 4 What are the steps of disaster management?
- 5 What are the different types of disasters?
- 6 What are the different levels of disaster management?
- 7 What are some of the benefits of disaster management?
- 8 What are the risks of disaster management?
- 9 What are some steps you can take to be prepared?
- 10 What are some skills you should learn to prepare for a disaster?
- 11 What are some of the disasters that have recently happened?
Throughout history, the world has seen numerous disasters. From climate change to war to natural disasters, these forces have been wreaking havoc on the world. A disaster is something that interrupts everyday life, and takes place without warning. Operating with a disaster management plan in place is the best way to prepare for disaster emergencies. In this blog, we will look into how you can create a disaster management Project for Class 9 plan that is successful.
What is disaster management?
Disaster management is the process of managing the effects of a disaster or unexpected event in order to minimize its impact. It is often the response to natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, or volcanic eruptions, but it also includes man-made disasters such as terrorist attacks, industrial accidents or nuclear accidents.
Why do we learn disaster management?
There are many reasons that people learn disaster management. Some people learn disaster management because they plan on a career in the field, and others do so because they want to know how to react in the event that a disaster does strike. Some people know that they need to learn disaster management to be prepared for a disaster, and want to be an asset to their family in the event that their plans change.
When a disaster strikes, you will need to know how to help these people. For example , you will need to be able to communicate with them, provide them with food, water and shelter and keep them safe. You will also need to know how to prepare for a natural disaster and save yourself and your family in case of an emergency.
What are the most common disaster management scenarios?
Disasters come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Generally, they are defined as being either a natural or man-made event that results in the loss of human life.
There are many classifications of disaster, but the most common disaster management scenarios tend to be natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, tornadoes, hurricanes, and tsunamis.
Man-made disasters are usually classified as accidents, such as nuclear accidents, chemical accidents, and terrorist attacks.
What are the steps of disaster management?
There are a number of steps that are followed during a disaster management process. The first step is to make sure that you have a disaster management plan in place before you need it.
- The first step should be to identify the areas where you are vulnerable to a disaster and develop strategies to protect yourself.
- The second step is to train your staff so that they are ready for a disaster.
- The third step is to ensure that you have an emergency plan in place.
- The fourth step is to make sure that you have a clear communication system in place.
- The fifth step is to have an action plan in place. Finally, the sixth step is to make sure that you have a backup plan in place.
What are the different types of disasters?
There are different types of disasters that can impact your life. They are natural disasters, such as floods, earthquakes, landslides, tornadoes, and lightning.
There are also man-made disasters, such as fires, riots, and hurricanes.
There are also disasters that are both natural and man-made, such as wildfires and volcanic eruptions. A disaster can occur anywhere on Earth, and it can happen at any time.
What are the different levels of disaster management?
Disaster management is the practice of trying to prevent or reduce damage, injury, or death resulting from natural or man-made disasters. There are different levels of levels of disaster management. The 4 levels of disaster management are mitigation , preparedness , response , and recovery .
Mitigation is the process of reducing the impact of a disaster by taking preventative measures.
Preparedness is the process of being proactive, taking steps to reduce the impact of a disaster by taking preventative measures.
Response is the process of taking immediate measures to reduce the impact of a disaster.
Recovery is the process of repairing and rebuilding after a disaster.
What are some of the benefits of disaster management?
There are many benefits of disaster management. A disaster management plan can help to ensure that the community is ready for a disaster. It also helps to ensure that your community is safe and secure. It also helps to provide an overall sense of security to your community. The main benefits of disaster management are that it helps to prepare for a disaster and it helps to reduce the damages that a disaster might cause.
What are the risks of disaster management?
When it comes to disaster management, there are a number of risks that come with the job. Some of these risks are physical, while others are more emotional. Some risk factors for disaster management include psychological trauma, high stress, and the risk of high-level disasters.
In many cases, disaster management can be a high-risk profession. Despite the risks, disaster management is a profession that is on the rise. In many ways, disaster management is similar to crime scene investigation. There is always a risk when it comes to working in this industry, but the rewards are well worth the risk.
What are some steps you can take to be prepared?
Preparation can take many forms, from the simple and often forgettable, such as installing smoke alarms in your home, to the more advanced and expensive, such as constructing a flood-safe building or buying an emergency generator. In general, disaster management is the planning and preparation for dealing with the consequences of natural or man-made disasters. Preparation can take many forms, from the simple and often forgettable, such as installing smoke alarms in your home, to the more advanced and expensive, such as constructing a flood-safe building or buying an emergency generator.
What are some skills you should learn to prepare for a disaster?
ealing with an emergency can be stressful. But it doesn’t have to be like that. You can learn these skills now and prepare for the worst that could happen. A lot of people find that they are more capable and confident when they know how to deal with a disaster. Here are some skills you should learn to prepare for a disaster: • Shelter Building: Know how to make your own shelter. Make sure that you know how to use a tarp, tent and a sleeping bag.
• Fire-Building : Know how to control on fire. You should also know how to use fire extinguisher and all other equipment.
• Medicinal Herbs: Know how to make your own herbal remedies. You should know how to identify plants and use them as a source of medicine.
• Wilderness Survival: Know how to build shelter, build a fire, and make a good meal.
• Emergency Preparedness: You should have a basic knowledge of emergency situations to face them.
What are some of the disasters that have recently happened?
In India, one of the most common natural disasters is floods. In the past few years, there have been many floods in India, the most recent being the floods in the state of Tamil Nadu. There are many other natural disasters that have happened in India, including cyclones, earthquakes, tsunamis, and severe storms. The following are some of the disasters that have recently happened in India:
- Assam Earthquake on April 28, 2021.
- Cyclone Gulab: Cyclone Gulab was a storm that impacted eastern India on September 24, 2021, in the Bay of Bengal.
- Maharashtra Floods.
- Tamil Nadu Floods.
Related Posts:
![Packing Class 9 Questions and Answers [Class 9 English Beehive Chapter 7 ] Packing Class 9 Questions and Answers [Class 9 English Beehive Chapter 7 ]](https://edukar.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Packing-Class-9-Questions-and-Answers-1024x640.webp)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Home keyboard_arrow_right
Flood project case study rk
This document provides an overview of floods including causes, effects, types, and management. It begins with an introduction to floods and then discusses the main causes of floods such as intense rainfall, topography, obstruction of river flows, and sedimentation. The effects of floods are categorized as primary, secondary, and tertiary. The types of floods covered are coastal floods, river floods, and flash floods. Flood management techniques include both hard engineering methods like embankments and dams as well as soft engineering methods like flood plain zoning and forecasting. A case study on the 2013 Uttarakhand floods in India details the impacts and damage caused by heavy rainfall and landslides in the region. In conclusion, some benefits of floods are Read less

Recommended
More related content, what's hot, what's hot ( 20 ), viewers also liked, viewers also liked ( 20 ), similar to flood project case study rk, similar to flood project case study rk ( 20 ), recently uploaded, recently uploaded ( 20 ).
- 2. CREATED BY : • ANKIT KALARIYA • 12SOECV11087 • SEMESTER 7th CIVIL (B) UNDER GUIDANCE OF: • SANDIP MISHARA • ASST PROF R K UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING SEMINAR ON FLOOD
- 3. • Introduction • Causes of flood • Effects of flood • Type of flood • Flood management • Case study • Conclusion Contents
- 4. Introduction • Flood is overflow of excess water that submerges land and inflow of tide onto land • The flood is the result of runoff from rainfall and /or melting snow in quantities too great to be confined in the low water channels of streams • A flood is usually caused by rain, heavy thunderstorms, and thawing of snow Source : google image
- 5. • Intensity of rainfall • Topography of the catchment • Obstruction in river flow • Sedimentation of rivers • earthquake • Contraction of river • Bank erosion • failure of Dam • Failure of river embankment Causes of flood Natural Man-made Source : text book
- 6. • Whenever there is heavy precipitation over the catchment in terms of intensity, duration and spread, the river will carry high flow and thus results into flood. • The intensity of rainfall in the catchment area is the main cause of flood. Causes of flood Intensity of rainfall
- 7. • Larger the size of the catchment more will be the flood. • The catchment area with steep slope increases the run off and also the sediment inflow due to high velocity of flow. Causes of flood Topography of the catchment
- 8. • Whenever there is heavy landslide in the river it may cause flood on the u/s side due to arrest of flow and consequently rise in the water level. Causes of flood Obstruction in river flow
- 9. • If the tributaries of the river carry heavy sediment load the river bed goes on silting up gradually every year. • It will affect the carrying capacity of the river. Causes of flood Sedimentation of rivers
- 10. • Inadequate waterway at rail and road crossing will affect river flow. • While constructing road or railway bridges across a river, the approach works are done on both bank which reduce c/s of the river. Causes of flood Contraction of river
- 11. Effects of flood SECONDARYPRIMARY TERTIARY Due to direct contact of flood water Due to result of primary effect Due to combined effect of primary & secondary effect Physical damage Disruption of essential services Long term effect
- 12. Effects of flood Primary effect Secondary effect Tertiary effect Source : wikipidea
- 13. • Human Loss • Property Loss • Affects the Major Roads • Disruption of Air / Train / Bus services • Communication Breakdown • Electricity Supply Cut off • Economic and Social Disruption • Increase in Air / Water Pollution Effects of flood
- 14. 1 Coastal Flood 2 River Flood 3 Flash Flood Type of flood Source : wikipidea
- 15. - Low-lying coastal land are more prone to coastal floods - Caused by Intense Storms such as tropical storms and tropical cyclones - Tropical cyclones are also known as hurricanes - Strong winds during these storms generate large waves known as storm surge - Storm surges can bring about higher water level and cause coastal floods Type of flood 1 Coastal Flood
- 16. • Sudden increase in river’s flow (water) • Water overflows the banks • Leads to deposit of sediments on floodplains • Caused by snowmelt, heavy rainfall, dam failure, etc. Type of flood 2 River Flood
- 17. • Sudden floods, lasts for a short duration. • Caused by sudden and heavy rainfall. • Can also be caused by Coastal and River floods. Type of flood 3 Flash Flood
- 18. Flood management Aims of flood management Protection of people & property Reduction of flood risk Monitoring, research, forecasting & warning Cannot be absolutely controlled only managed
- 19. Flood management • Hard engineering • (Structural) • Soft engineering • (Non-structural) • Embankments • Dams & reservoirs • Channel improvement • Drainage improvement • Diversion of flood rivers • Flood plain zoning • Flood preparedness • Flood forecasting • Afforestation • Public relief
- 20. Flood management • Embankments • Dams & reservoirs Source : book
- 21. Flood management Drainage improvement Diversion of flood river Source : book
- 22. Flood management Flood plain Zoning Source : book
- 23. Flood management Forecasting consists of 4 steps: 1. Data collection 2. Data transmission 3. Data analysis and forecast formulation 4. Dissemination Flood Forecasting
- 24. Case study Flood in uttarakhand • From 14 to 17 June 2013, Indian state of Uttarakhand and near by received heavy rainfall. • The rainfall was above benchmark which is above 375 percent. • A multi-day cloudburst ,centered on the state Uttarakhand caused devastating floods and landslides. • Due to Continuous Rain the Chorabari Glacier melted and this triggered the flooding of the Mandakini river which led to heavy floods near Gobindghat, Kedar Dome, Rudraprayag district, Uttarakhand.
- 25. Case study Flood in uttarakhand
- 26. Case study Flood in uttarakhand
- 27. Case study Loss and Damage • Around a million people affected • 6000 reported dead or missing • 4200 villages affected • 10,000 cattle livestock lost • 3500 houses totally or partially damaged • 80% of the people in the productive age (shop owners, laborers working in petty shops, mule owners, laborers, palanquin bearers)
- 28. Case study LANDSLIDE HAZARD ZONATION MAPPING • Landslides cause widespread damage in the Himalayas. Landslide Hazard Zonation is important to take quick and safe mitigation measures and make strategic planning for the future. • GIS based mapping to understand the causes and likelihood of a particular hazard. The need for such landslide hazard information may vary according to the future land use. • Landslide hazard zonation mapping at regional level of a large area provides a broad trend of landslide potential zones. These maps are useful for development plans, town planning , master plan for cities , construction of highways etc., land use planning in the sense of avoiding high risk zones & decision making during disaster response.
- 29. Although flood is the most deadliest disaster still, but it has some benefits like: • Recharges ground water • Fresh water flood help in maintaining food plain ecosystem • Boost in food production for birds • Facilitation of weather fish to new habitat Conclusion
Case Studies
In the first phase of the AFPM, a number of case studies on flood management were collected from various regions, based on the experiences of organizations active in flood management. These case studies were essential in formulating the Integrated Flood Management concepts, as they helped to:
- Identify the extent to which integrated flood management has been carried out;
- Understand shortcoming in flood management practices worldwide;
- Extract lessons learned and good practices in flood management;
- Catalogue the policy changes required to support IFM; and
- Identify the institutional changes required to achieve IFM.
The case studies are presented here for “historical purposes”: having been compiled almost 20 years ago, they are reflecting national situations that might since have developed. As such, the case studies might be used as baseline or reference material for studies that aim to check the improvements in flood management since the beginning of the century.
The Overview Situation Paper on flood management practices extracts the essence of each case study, emphasizes findings and recommendations with relevance to the aspects of Integrated Flood Management and the potential for practices to be replicated in other locations. Download the Overview Situation Paper here .
| – River Logone Flood Plain | |||
| – Niger River Inland Delta | |||
| Managed Flood Releases and Livelihoods – Lower Delta Senegal River | |||
| Flood Management Practices – Selected Flood-Prone Areas Zambezi Basin | |||
| in: Climate risk management in Africa:Learning from practice | |||
| : > Flood Management in Damodar River Basin > Flood and Drought Management through water resources development – in: WMO | |||
| – Tokai Heavy Rain | |||
| > River Chenab from Marala to Khanki > Lai Nullah Basin Flood Problem Islamabad, Rawalpindi Cities | | | |
| – Metropolitan Curitiba Area | |||
| – Red River Basin, Manitoba | |||
| – Rio Grilalva | |||
| > Mississippi River > No Adverse Impact: A New Direction in Floodplain Management Strategy | | | |
| – Rewa River Basin | |||
| – Rhine and Elbe Rivers | |||
| Piemonte Region meteo-hydrological alert and real-time flood forecasting system | |||
| Recent Flood Disasters In Northwestern Black Sea Region | |||
| – Parrett Catchment Project | |||
| – Tisza River Basin |
myCBSEguide
- Social Science
- Class 9 Social Science...
Class 9 Social Science Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you’re seeking Class 9 Social Science Case Study Questions, you’ve come to the correct spot. Students can use Class 9 Social Science Case Study Questions to help them answer a variety of questions about the Class 9 Social Science case study.
The CBSE Board has included case study questions in Class 9 Social Science examination pattern. As a result, it becomes an indispensable study tool.
The need for a student-friendly app to explain and facilitate the understanding of the social sciences subject has been felt for a long. Especially for students who do not have a strong foundation in Class 9 Social Science. With myCBSEguide , class 9 social science students now have a place where they can find resources that are student-friendly, interesting and easy to understand.
Class 9 Social Science Case Study questions are intended to assess student’s abilities to apply their learning to practical scenarios. You’ll need to employ your critical thinking and problem-solving skills to come up with the best solution. Class 9 Social Science case study questions are designed to test your knowledge and help you improve your skills.
Class 9 Social Science Case Study Questions Samples
myCBSEguide has identified the essential themes connected to CBSE case study questions for Class 9 Social Science that every student should be aware of following a comprehensive examination of CBSE Sample Papers and Marking Scheme. Students in Class 9 Social Science will benefit from this information in understanding the changes in the Class 9 Social Science. For a better understanding and analysis, students should refer to the example of Class 9 Social Science case study questions attached below:
Class 9 Social Science Case Study Question 1
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: On the morning of 14 July 1789, the city of Paris was in a state of alarm. The king had commanded troops to move into the city. Rumours spread that he would soon order the army to open fire upon the citizens. Some 7,000 men and women gathered in front of the town hall and decided to form a peoples’ militia. They broke into a number of government buildings in search of arms. Finally, a group of several hundred people marched towards the eastern part of the city and stormed the fortress-prison, the Bastille, where they hoped to find hoarded ammunition. In the armed fight that followed, the commander of the Bastille was killed and the prisoners released – though there were only seven of them. Yet the Bastille was hated by all because it stood for the despotic power of the king. The fortress was demolished and its stone fragments were sold in the markets to all those who wished to keep a souvenir of its destruction. The days that followed saw more rioting both in Paris and the countryside. Most people were protesting against the high price of bread. Much later, when historians looked back upon this time, they saw it as the beginning of a chain of events that ultimately led to the execution of the king in France, though most people at the time did not anticipate this outcome. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
On 14th July, 1789 the people of the ________ estate attacked the Bastille prison and freed all the prisoners signalling the start of the _________.
- first, civil war
- fourth, Russian war
- second, movement
- third, revolution
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- The Bastille was the fortress-prison.
- The Bastille stood for the democratic power of the king.
- On the morning of 14 July 1789, the people of Paris stormed Bastille
- All are correct
In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and chose the correct option: Assertion (A): The people of France storm the Bastille. Reason (R): They were hopeful to find King Louis XIV and commander of the Bastille there.
- Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- A is correct but R is wrong.
- Both A and R are wrong.
What was the immediate cause of rioting in Paris?
- Atrocities by the commander
- The high price of bread
- The killing of women and children
- All of these
Answer Key:
- (d) third, revolution
- (b) The Bastille stood for the democratic power of the king. [Explanation: The Bastille stood for the despotic power of the king.]
- (c) A is correct but R is wrong. [Explanation: The people of France stormed the fortress-prison, the Bastille because they were hopeful to find hoarded ammunition there.]
- (b) high price of bread
Class 9Social Science Case Study Question 2
Read the extracts and answer the question that follows:
The Himalayas, geologically young and structurally fold mountains stretch over the Himalayas northern borders of India. These mountain ranges run in a west-east direction from the Indus to the Brahmaputra. The Himalayas represent the loftiest and one of the most rugged mountain barriers of the world. They form an arc, which covers a distance of about 2,400 Km. Their width varies from 400 Km in Kashmir to 150 Km in Arunachal Pradesh. The altitudinal variations are greater in the eastern half than those in the western half. The Himalaya consists of three parallel ranges in its longitudinal extent. A number of valleys lie between these ranges. The northern most range is known as the Great or Inner Himalayas. It is the most continuous range consisting of the loftiest peaks with an average height of 6,000 metres. It contains all the prominent Himalayan peaks.
The folds of Great Himalayas are asymmetrical in nature. The core of this part of Himalayas is composed of granite. It is perennially snow bound, and a number of glaciers descend from this range.
- The Great or Inner Himalayas is also known as?
- Give two features of the folds of Great Himalayas.
- Give two features of the Inner Himalayas.
- The Great or Inner Himalayas is also known as the ‘Himadri’.
- (Any two relevant points)
- The folds of Great Himalayas are asymmetrical in nature.
- The core of this part of Himalayas is composed of granite.
- It is perennially snow bound, and a number of glaciers descend from this range.
- Features of the Inner Himalayas:
- It is the most continuous range consisting of the loftiest peaks with an average height of 6,000 metres.
- It contains all the prominent Himalayan peaks.
Class 9 Social Science Case Study Question 3
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: In Pakistan, General Pervez Musharraf led a military coup in October 1999. He overthrew a democratically elected government and declared himself the ‘Chief Executive’ of the country. Later he changed his designation to President and in 2002 held a referendum in the country that granted him a five-year extension. Pakistani media, human rights organisations and democracy activists said that the referendum was based on malpractices and fraud. In August 2002 he issued a ‘Legal Framework Order’ that amended the Constitution of Pakistan. According to this Order, the President can dismiss the national and provincial assemblies. The work of the civilian cabinet is supervised by a National Security Council which is dominated by military officers. After passing this law, elections were held to the national and provincial assemblies. So Pakistan has had elections, elected representatives have some powers. But the final power rested with military officers and General Musharraf himself. Clearly, there are many reasons why Pakistan under General Musharraf should not be called a democracy. People may have elected their representatives to the national and provincial assemblies but those elected representatives were not really the rulers. They cannot take the final decisions. The power to take final decision rested with army officials and with General Musharraf, and none of them were elected by the people. This happens in many dictatorships and monarchies. They formally have an elected parliament and government but the real power is with those who are not elected. In a few countries, the real power was with some external powers and not with locally elected representatives. This cannot be called people’s rule. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
What is the meaning of Referendum?
- Direct vote in which the entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal
- A form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people
- A system where the majority or elected representatives are allowed to take decisions on behalf of all the people
In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and chose the correct option: Assertion (A): Pakistan not considered a democratic country even after having elections Reason (R): Despite elections to the national and provincial assemblies, the final powers rested with General Musharraf and military officers.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- A is wrong but R is correct.
After the passage of the ________, elections were held to the national and state assemblies.
- Military rule
- Legal Framework Order
- Both (b) and (c)
Does the given source explain the significance of which feature of democracy?
- Democracy must be based on a free and fair election
- In a democracy, the final decision-making power must rest with those elected by the people
- In a democracy, each adult citizen must have one vote
- Democratic government rules within limits set by constitutional law and citizens’ rights
- (a) Direct vote in which the entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal
- (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- (c) Legal Framework Order
- (b) In a democracy, the final decision-making power must rest with those elected by the people
Steps to Master Class 9 Social Science Case Study Questions
Class 9 Social Science case study questions can be daunting, but there are some strategies you can use to ace them. There is no one-size-fits-all answer to Class 9 social science case study questions. The best way to solve a social science case study will vary depending on the specific case in question. However, there are some general tips that can be followed in order to improve your chances of success while answering class 9 social science case study questions.
- First, make sure to read the question carefully and understand what is being asked. It is often helpful to re-read the question after gathering all of your information.
- Next, organize your thoughts and create an outline of your answer. This will help you to stay on track and include all relevant information.
- Finally, write your answer in a clear and concise manner.
Class 9 Social Science Content Structure
Class 9 social science content is divided into four parts: History, Geography, Economics and Political Science. Each part is further divided into smaller themes/chapters.
Each of these topics given in Class 9 Social Science is important in its own right, and together they provide a comprehensive overview that affect our world today. The content is structured in such a way as to provide Class 9 Social Science students with a broad understanding of each issue, while also allowing them to focus on specific areas that are of particular interest to Class 9 Social Science students.
Class 9 Social Science COURSE CONTENT
| (All the three themes are compulsory) |
| I. The French Revolution |
| II. Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution |
| III. Nazism and the Rise of Hitler |
| IV. Forest Society and Colonialism |
| V. Pastoralists in the Modern World |
| 1. India |
| 2. Physical Features of India |
| 3. Drainage |
| 4. Climate |
| 5. Natural Vegetation and Wild Life |
| 6. Population |
| 1. What is Democracy? Why Democracy? |
| 2. Constitutional Design |
| 3. Electoral Politics |
| 4. Working of Institutions |
| 5. Democratic Rights |
| 1. The Story of Village Palampur |
| 2. People as Resource |
| 3. Poverty as a Challenge |
| 4. Food Security in India |
myCBSEguide: Step towards success
There are many reasons to download myCBSEguide.
- First and foremost, it is a great way to access high-quality study material for CBSE students.
- Secondly, it is a great way to keep track of your studies and progress.
- Thirdly, myCBSEguide provides access to a wide range of resources that can help you in your studies. Finally, myCBSEguide is a great way to connect with other CBSE students and get help and support from them.
So, how long are you going to wait? Make exam time a breeze by downloading the myCBSEguide app today!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
19 thoughts on “Class 9 Social Science Case Study Questions”
Not helpful I’m disappointed ???
Was helpful
It’s good
Thanks !it helps me in revising case based study ?
nice helps alot??
Bekar hai bhiya me to tuut gaya
Bkl chiz hai
I am very lucky that l have a google ?? thanx !!?
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Case Study of Kerala Floods

- Find Kerala Floods
- Kerala Floods
- Kerala Floods 2018
- Kerala Floods News
What is to Study?
1. Introduction
2. Geography of the Region.
3. Causes of Floods
4. How to avoid such disasters in near future?
5. Strategy and Challenges for Rehabilitation
Introduction
The ongoing south-west monsoon has wreaked havoc in Kerala . Heavy flooding has caused the deaths of at least 360 people in Kerala since June, the worst natural disaster to strike the southern Indian state in decades. More than 1 million people have been displaced and are recovering in relief camps after 80 dams were overrun by torrential rains. In this lecture, we will study the mains causes of such floods along with current challenges in rehabilitation.
Geography of Kerala
Kerala is situated between the Arabian Sea to the west and the Western Ghats to the east. The topography consists of a hot and wet coastal plain gradually rising in elevation to the high hills and mountains of the Western Ghats. Kerala’s climate is mainly wet and maritime tropical, heavily influenced by the seasonal heavy rains brought up by the monsoon. There are 44 rivers in Kerala, all but three originating in the Western Ghats . 41 of them flow westward and 3 eastward. The rivers of Kerala are small, in terms of length, breadth and water discharge. The rivers flow faster, owing to the hilly terrain and as the short distance between the Western Ghats and the sea. All the rivers are entirely monsoon-fed and many of them shrink into rivulets or dry up completely during summer

Causes of the Crisis
Kerala received heavy monsoon rainfall on the mid-evening of August 8 resulting in dams filling to capacity; in the first 24 hours of rainfall, the state received 310 mm (12 in) of rain. In fact, the state received 42% more rains in the southwest monsoon than it normally receives and all of it in a short time-span – causing widespread devastation and loss of lives.
Almost all dams have been opened since the water level has risen close to overflow level due to heavy rainfall, flooding local low-lying areas The situation took a turn for the worse around August 15, when shutters of the state’s 34 (out of 42) dams had to be opened following incessant rains in catchment areas. While flooding was initially restricted to the banks of the Periyar river – following the opening of the spillways of the Idukki Dam – it soon engulfed the whole of central Kerala as the rain kept pounding. The opening of two shutters of the Cheruthoni Dam initially meant to be a trial run, could not be paused even for a moment following incessant rain. Soon, all five shutters of the dam had to be opened one after the other. But as this discharge through shutters couldn’t match the inflow, the water level kept rising till it almost touched the danger mark. This water discharge from the reservoirs soon led to flooding of other areas .
The Kerala High Court Appointed Jacob P Alex as the amicus curiae to assist the court in flood-related cases . Mr Alex has informed the court on 2nd April 2019 that the Sudden release of water simultaneously from different reservoirs during the heavy rain in August 2018 had aggravated the damage during the floods.
He also said that dams in the State did not have an effective flood control zone and flood cushions.
Various alerts (blue/orange/red) were issued not in accordance with the EAP (Emergency Action Plan) guidelines. No proper follow-up action and effective precautionary steps, especially for evacuating people and accommodating them in safe locations, were taken after the issue of red alert.
So we can blame Heavy precipitation, Poor Dam management and Weak early Warning and Response system for the damges caused by the worst flood of the Century in Kerala
Question for IAS Mains GS Paper-III:-
Extreme Rainfall Caused Kerala Floods but Man Made Things made it worse. The deluge in Kerala has been a combined result of a set of interacting atmospheric, oceanic and human factors. HOW?
Reports of following committees explain it better
Madhav Gadgil committee on Western Ghats conservation
- Madhav Gadgil committee had strongly recommended a ban on certain new industrial and mining activities in the area and called for strict regulation of many other “developmental” works in consultation with local communities and gram panchayats. The State of Kerala has materially compromised its ability to deal with Natural Disasters since Last several years of developments. This negligence of state Government greatly increased the magnitude of the sufferings from the floods. The scale of the disaster would have been smaller if the state government and local authorities had followed environmental laws.
- Madhav Gadgil concluded that the entire Western Ghats, spread over six states, including Kerala, should be declared ecologically sensitive. We need to divide the ecological sensitive regions of the Western Ghats into three parts
Kasturirangan Report
- The report met with resistance from the governments of all six stakeholder states. Thereafter, the Environment Ministry appointed another panel, headed by space scientist K Kasturirangan, to “examine” the Gadgil committee report in a “holistic and multidisciplinary” fashion, while considering the objections raised by the state governments and responses received from others. The Kasturirangan committee , which submitted its report in 2013. He severely watered down the recommendations of the Gadgil panel, effectively suggesting that only a third of the Western Ghats be identified as being ecologically sensitive.
How to mitigate the risk of such kind floods in future?
It is impossible to anticipate natural disasters such as Cyclones , Flash floods . However, disaster preparedness plans and protocols in the civil administration and public health systems could be very helpful in rescue and relief and in reducing casualties and adverse impact on the human life and socio economic conditions.
- An reliable Early Warning System needs to be developed
- 1. Initial response ( Early warnings by IMD and Deployment of Rescue Force ( Indian Army , NDRF or else) ” Response time is a critical attribute in effective disaster management . There should be no delay in disaster response
- 2. Plan for Search operations and Evacuations (Local Guides and Maps)
- 3. We must keep all Hospitals on alert
- 4.Dedicated Communication system :- The local communication networks and transport services will severely affected. A robust communication channel is required for managing and coordinating the rescue and relief operations.
- 1. Infrastructure of Local hospitals may be destroyed in the disaster so there is strong need to keep hospitals of surrounding cities on alert along with local hospitals .
- 2. A dedicated plan is required to make the roads operational soon after the disaster to ease the evacuations
- 3. There should be a proper plan of logistical support for First AID and to evacuate the injured people to other cities for Treatment
- (iii) Conservation of Natural Drainage system of the state along with other ecologically sensitive regions
- (iv) Efficient Urban Planning
- De-silting of rivers in order to increase the carrying capacity of the water
- Better coordination between states in the case of shared rivers or Dams
- Mullanperiyar Dam is being bone of contention between Kerala and Tamilnadu. Similar examples are there for Mahanadi River in Odisha and Chhatisgarh.
- De-silting of dams in order to increase water storage capacity
- Proper flood cushion or flood control zones are required along the Dam. The flood cushion or flood control zone is a temporary storage space for absorbing high flow for alleviating downstream flood damage.
- Increased public awareness is necessary to ensure an organized and calm approach to disaster management. Periodic mock drills and exercise in disaster management protocols in the general population can be very useful
5. What should be Rehabilitation strategy for such kind disasters?
1. Shelter and relief :- Proper shelter have to be provided to the people who are evacuated from Flood affected regions.
2. Supply of essential items :- Medicines blankets, tents, gumboots, and clothes
If There is a shortage of medical staff including doctors. So the government should use Telemedicine services in order to make medical service accessible
3. Restoration of infrastructure Roads, Electricity, Communication :- Basic Infrastrucre in the state should be restrored as soon as possible because rescue and rehabilitation process cant be executed without Roads, Electricity and Communication access.
4. Water, sanitation, and hygiene :- Administration must insure the supply of Clean Drinking water and hygine conditions in the region and Evacuation camps because there are high chances of spread of contagious waterborne disease . Such outbreak will create more problems for already strained Health and rescure infrastructure of the state
There is a high risk of water-borne diseases following the disaster. Many human bodies may wash away and contaminate water bodies. There will be increased fly and mosquito menace. There will an urgent need to prevent disease transmission due to contaminated drinking water sources, flies and Mosquitoes. The population would have a higher risk of mental health problems like post-traumatic stress disorder, deprivation, and depression. Therefore, relief and rehabilitation would include increased awareness of the symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder and its alleviation through education on developing coping mechanisms.
5. Food and nutrition 6. Avoid social unrest among public
Building confidence of the public to avoid the panic situation is also critical. Community involvement and awareness generation, particularly that of the vulnerable segments of population and women, needs to be emphasized as necessary for sustainable disaster risk reduction.
The Government should also provide some monetary compensation for the people who have lost their house. Some Employment generation policies also need to be implemented in order to provide jobs to the landless laborers who lost their Job due to the impact of the floods.
Next Generation Public Protection and Disaster Relief
We provide quality UPSC Coaching in Chandigarh . For all your queries regarding the class structure, material and mentorship for our programmes concerned with PCS Coaching in Chandigarh , HCS Coaching in Chandigarh and similar civil services coaching in Chandigarh region and beyond, you can contact us directly at o2iasacademy to avail professional quality IAS Coaching in Chandigarh . O2iasacademy wishes you all the best for your preparation.
For Further infromation kindly visit the website of Kerala State Disaster Management Authority
Related posts

Top 12 Tips for Punjab PCS 2024 Exam Preparation
How to get a good rank in the pcs exam (like manjinder singh ).

Difference between UPSC, PCS, HPAS, HCS Exam | O2 IAS Academy
Difference between UPSC, PCS, HPAS, HCS Exam
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Daily Show Fan Page

Explore the latest interviews, correspondent coverage, best-of moments and more from The Daily Show.
Extended Interviews

The Daily Show Tickets
Attend a Live Taping
Find out how you can see The Daily Show live and in-person as a member of the studio audience.
Best of Jon Stewart

The Weekly Show with Jon Stewart
New Episodes Thursdays
Jon Stewart and special guests tackle complex issues.
Powerful Politicos

The Daily Show Shop
Great Things Are in Store
Become the proud owner of exclusive gear, including clothing, drinkware and must-have accessories.
About The Daily Show

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Effects. In some areas, floodwater was between 3-4.5m deep. Floods in the southern Indian state of Kerala have killed more than 410 people since June 2018 in what local officials said was the worst flooding in 100 years. Many of those who died had been crushed under debris caused by landslides.
Disaster Management Project. As part of the CBSE 2024-25 syllabus, students are required to prepare and submit Class 9 Social Science projects on disaster management. Educart has created a special page filled with inspiring ideas for various parts of this project. Here, you will find creative cover page designs, well-designed acknowledgment ...
Sst Class9 Disaster Management Project - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document is a student project on disaster management. It begins with an introduction that defines what a disaster is and lists several types of disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, cyclones, epidemics, floods, droughts, landslides, and industrial hazards.
Students in class IX are required to submit a handwritten project on disaster management as required by the CBSE. The subjects will come from the school. The topic could be either natural disasters or man-made disasters. The purpose of assigning this disaster management homework to class 9 students is to get them ready for any disaster.
Types of Disaster for Class 9 Students. Types of Disasters are categorised into the following types-. Floods, hail storms, cloudbursts, cyclones, heat waves, cold waves, droughts, and hurricanes are all examples of water-related disasters. Landslides, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tornadoes are examples of geological disasters.
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Social Science Chapter 3 Drainage. Case Study 1: The drainage system of India is mainly controlled by the broad relief features of the subcontinent. Accordingly, the Indian rivers are divided into two major groups: the Himalayan rivers; and the Peninsular Rivers.
Oct 19, 2021. Manimalayar witnesses biggest flood in 64 years. Being a coastal state of India and much of the land being part of the fragile Western Ghats, Kerala is very sensitive to climate ...
Incorporate real-life examples, case studies, and statistics to support your points. Cite all sources properly using a standard citation format (e.g., APA or MLA). Practice your presentation beforehand to ensure clarity and confidence. SST Class 9 Disaster Management Project. Disaster management Project For Class 9
project-flood & disaster management - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. 1. The document discusses floods and droughts in India, including their causes, impacts, and mitigation measures. It provides details on regions prone to floods and droughts. 2. Major causes of floods include heavy rainfall, siltation of river beds ...
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Drainage. Case Study Questions. ... They are the rivers, which flood parts of the northern plains every year, causing widespread damage to life and property but enriching the soil for the extensive agricultural lands. The main tributaries, which come from the peninsular uplands ...
There are different types of disasters that can impact your life. They are natural disasters, such as floods, earthquakes, landslides, tornadoes, and lightning. There are also man-made disasters, such as fires, riots, and hurricanes. There are also disasters that are both natural and man-made, such as wildfires and volcanic eruptions.
Disaster management Project For Class 9. This document is a project report submitted by Akash Rana for his M.Com degree. It includes an introduction to disaster management, types of disasters, and the phases of disaster management. It also provides a case study on the Uttarakhand disaster and conclusions. The document contains certificates ...
Flood management played an important role in Kerala 2018 floods. The Disaster Management strategies include Mitigation, Preparedness, Rescue and Recovery. Through this study, we would like to suggest that the Sponge Cities and Flood Resistant Buildings are the most appropriate Risk reducing Strategies, which can reduce Flood hazard risk
Class 9 project on Disaster Management.#Class9 #SocialScienceProject #Disaster Management #ProjectTrends_____Pdf file of th...
Detailed explanation with examples on all-about-floods helps you to understand easily , designed as per NCERT. QnA , Notes & Videos
Beginning on August 15th 2018, severe floods were affected in Kerala due to unusually high rain fall during the monsoon season. It was the worst flooding in Kerala nearly a century. Almost 370 people died and 33000 peoples are rescued. According to Kerala Govt. one sixth of the total population of Kerala had been directly affected by flood.
Drought is a complex phenomenon as it involves elements of meteorology like precipitation, evaporation, evapo-transpiration, ground water, soil moisture, storage and surface run-off, agricultural practices, particularly the types of crops grown, socio-economic practices and ecological conditions. Types of Droughts.
Flood project case study rk. Feb 5, 2016 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 13 likes • 17,455 views. AI-enhanced description. A. ankitkalariya. This document provides an overview of floods including causes, effects, types, and management. It begins with an introduction to floods and then discusses the main causes of floods such as intense ...
These case studies were essential in formulating the Integrated Flood Management concepts, as they helped to: Identify the institutional changes required to achieve IFM. The case studies are presented here for "historical purposes": having been compiled almost 20 years ago, they are reflecting national situations that might since have ...
Class 9 Social Science Case Study Question 1. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: On the morning of 14 July 1789, the city of Paris was in a state of alarm. The king had commanded troops to move into the city. Rumours spread that he would soon order the army to open fire upon the citizens.
For Further infromation kindly visit the website of Kerala State Disaster Management Authority. In August 2018, the state of Kerala (India) witnessed large-scale flooding, which affected millions of people and caused 400 or more deaths. This case study Explains Causes and Rehabilitations Strategies for such Disasters.
nce of Science Key contact: S H M FakhruddinDialogue ProcessSummary of dialogue process: The Decision Support System (DSS) is designed to interpret, translate, and communicate science-based risk information into location-specific flood forecast products tailored to support the needs of particular users, including.
The case studies were chosen to complement and be consistent with the information in the preceding chapters, and to demonstrate aspects of the key messages in the Summary for Policymakers and the Hyogo Framework for Action Priorities. The case studies were grouped to examine types of extreme events, vulnerable regions, and methodological ...
The source for The Daily Show fans, with episodes hosted by Jon Stewart, Ronny Chieng, Jordan Klepper, Dulcé Sloan and more, plus interviews, highlights and The Weekly Show podcast.