
What is a Body Paragraph? (Definition, Examples, How to Start)

What is a body paragraph? How do I start a body paragraph? A body paragraph is the most important part of the sentence subject . It delivers the most impactful information and helps to transition in and out of paragraphs more effectively.

What is a body paragraph?
Any essay, article, or academic writing starts with an introduction and ends with a conclusion. The text between the introduction and conclusion is the body paragraph.
A body paragraph supports the idea that was mentioned in the introduction by shedding light on new details using facts, statistics, arguments, or other information.
What role does a body paragraph play in an article or an essay?
A body paragraph acts as a connection between the introduction and the conclusion. The body paragraph’s role is to justify the thesis stated in the introduction of an essay or article. As mentioned previously it comes between the introduction and the conclusion which is where most of the writing is done. This signifies its importance.
There can be multiple body paragraphs in an article or an essay. That said, each of the body paragraphs should logically connect with one another. In addition to this, all the body paragraphs should focus on the main idea stated in the introduction. Also, the sentences should not be long, so that readers can easily consume the information.
Here is a brief breakdown of the structure of a body paragraph:
How to structure a body paragraph
Every body paragraph has four main parts. They are:
- Topic Sentence
- Evidence Or Supporting Sentences
- Ending Or Conclusion
Here is a detailed breakdown of each one of them.
Topic sentence
The topic sentence is the first sentence in a body paragraph. This sentence discusses the main idea of the topic and indicates what information to expect in the rest of the paragraph. It sets the stage for the rest of the paragraph.
Evidence or supporting sentences
After the topic sentence comes the supporting sentences. These sentences are used to justify the claim that was stated in the topic sentence. Text citations, evidence, statistics, and examples are used to justify the claim. For example, if the topic sentence discusses “Switzerland is a must visit place”, then the supporting sentences should discuss the beautiful parts of Switzerland with examples to justify the claim.
One sentence to another sentence should flow seamlessly and this is possible by using transition words . Transition words like “however”, “although”, “in addition to”, “next”, and “in contrast” helps in doing exactly the same.
Ending or concluding sentence
Every body paragraph should end with a conclusion which comes after the supporting sentences. It summarizes the main idea of the body paragraph and emphasizes the supporting details. The conclusion gives way to the next line of the next paragraph.
Transitions are a few words that help in the smooth flow of the previous paragraph to the next paragraph. These words can be at the beginning of topic sentences or at the end of the body paragraph. They connect one idea of a paragraph to the next idea of another paragraph.
How to write an effective body paragraph
Keep the body paragraph’s focus on the topic.
All the body paragraphs should support the claim made in the introduction of an essay or an article. It should be consistent with the main idea of the topic. It is recommended to avoid adding unnecessary information in the body paragraph that doesn’t relate to the main idea of the topic.
Break complicated topic sentences into smaller parts
If the topic sentence has many parts to it, the topic sentence should be divided into smaller ideas and each idea should be expressed in a different body paragraph. Having too many parts in a topic sentence will lead to many support sentences in the body paragraph which will be too lengthy for readers to grasp.
Add counterarguments
If it is an academic essay or an opinion article, counterarguments should be included in the piece. Adding counterarguments in such pieces will give a broader perspective of the piece. Such inclusions will strengthen the essay or article.
Use signals when more than one paragraph deals with the same evidence
If multiple body paragraphs deal with the same evidence, there are a few signal phrases that will help the reader connect with evidence used earlier in other paragraphs. The signal phrases like “As mentioned previously” and “As already mentioned” can be used.
Include paragraph breaks
It is a single-line space that divides one paragraph from another. This is necessary because too long paragraphs make it difficult for readers to grasp the information. A space between paragraphs will help the readers to easily wade through the text. A paragraph break also signals the transition of one idea of one body paragraph to an idea of another body paragraph.
The body paragraph should be short
The body paragraph should be short and concise . The paragraphs should not exceed one page. Paragraphs exceeding a page will make the article or essay complicated to comprehend the information.
Body paragraphs should be proofread
After writing the body paragraph, proofreading is done. This will help in finding and fixing mistakes. It will also help in removing unnecessary sentences in the body paragraph. The ideal way to proofread is by reading the body paragraph loudly. Doing so will help in identifying awkward word placements in the sentence.
In addition to this, asking questions like “is the body paragraph sticking to the main idea of the topic?” should be exercised. It will give a sense that if the paragraph is heading in the right direction or not.
How to start a body paragraph
The first sentence in a body paragraph is the topic sentence and it is the hardest sentence to write. The topic sentence sets the stage for the rest of the sentences in the paragraph.
Once the reader reads the topic sentence, the reader should get a sense that what the rest of the paragraph will be.
So, it should be concise and to the point, revealing enough information that will help the reader to know what the paragraph will be all about.
How to conclude a body paragraph
At the end of the body paragraph, the sentence should summarize the claim stated in the topic sentence and should also include a brief explanation of the supporting sentences. It should be written in such a way that the sentence is concise and at the same time reveals the main points.
This sentence will help the reader to get a gist of what the paragraph is all about.
Difference between body paragraph and introduction
Though both of them are paragraphs, they are very different. Firstly, the structure of an introduction is constructed differently than the body paragraph. An introduction consists of a thesis statement and a brief explanation. On the other hand, the body paragraph consists of a topic sentence, supporting sentences, and a conclusion.
Secondly, the introduction comes first in an essay or an article. In comparison, the body paragraph comes after the introduction. It comes after the introduction and before the conclusion of an essay or article.
A typical body paragraph should contain at least six sentences.
To develop a well-structured paragraph:
- Construct a topic sentence.
- Include evidence to support the claim expressed in the topic sentence.
- Add analysis to the paragraph.
- End it with a conclusion summarizing the key points of the paragraph.
- Finally, proofread the paragraph to identify and fix mistakes.
An introduction is the first paragraph of an essay or article. It gets the reader’s attention regarding the topic and provides the thesis statement of the topic. To write a good introduction:
- Keep the introduction paragraph short.
- In one to two sentences explain the thesis statement of the article or essay.
There is no fixed number of words that a body paragraph should have. That said, typically a paragraph contains about a hundred to two hundred words which are six to seven sentences.
Yes, an essay or article can have more than one body paragraph. Some essays have three to four body paragraphs. That said, having two of these is enough to cover important points of the essay.
A conclusion comes after the body paragraph at the end of the essay. A long essay can have two or three paragraphs to conclude. It summarizes the main idea of the topic.
- Body Paragraphs: How to Write Perfect Ones | Grammarly blog
- Body Paragraph Example & Structure
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph
- How to Write a Body Paragraph | BestColleges
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
- The Writing Process
- Addressing the Prompt
- Writing Skill: Development
- Originality
- Timed Writing (Expectations)
- Integrated Writing (Writing Process)
- Introduction to Academic Essays
- Organization
- Introduction Paragraphs
Body Paragraphs
- Conclusion Paragraphs
- Example Essay 1
- Example Essay 2
- Timed Writing (The Prompt)
- Integrated Writing (TOEFL Task 1)
- Process Essays
- Process Essay Example 1
- Process Essay Example 2
- Writing Skill: Unity
- Revise A Process Essay
- Timed Writing (Choose a Position)
- Integrated Writing (TOEFL Task 2)
- Comparison Essays
- Comparison Essay Example 1
- Comparison Essay Example 2
- Writing Skill: Cohesion
- Revise A Comparison Essay
- Timed Writing (Plans & Problems)
- Integrated Writing (Word Choice)
- Problem/Solution Essays
- Problem/Solution Essay Example 1
- Problem/Solution Example Essay 2
- Writing Skill: Summary
- Revise A Problem/Solution Essay
- Timed Writing (Revising)
- Integrated Writing (Summary)
- More Writing Skills
- Punctuation
- Simple Sentences
- Compound Sentences
- Complex Sentences Part 1
- Complex Sentences Part 2
- Using Academic Vocabulary
- Translations
Choose a Sign-in Option
Tools and Settings
Questions and Tasks
Citation and Embed Code

Body paragraphs should all work to support your thesis by explaining why or how your thesis is true. There are three types of sentences in each body paragraph: topic sentences, supporting sentences, and concluding sentences.
Topic sentences
A topic sentence states the focus of the paragraph. The rest of the body paragraph will give evidence and explanations that show why or how your topic sentence is true. A topic sentence is very similar to a thesis. The thesis is the main idea of the essay; a topic sentence is the main idea of a body paragraph. Many of the same characteristics apply to topic sentences that apply to theses. The biggest differences will be the location of the sentence and the scope of the ideas.
An effective topic sentence—
- clearly supports the thesis statement.
- is usually at the beginning of a body paragraph.
- controls the content of all of the supporting sentences in its paragraph.
- is a complete sentence.
- does not announce the topic (e.g., “I’m going to talk about exercise.”).
- should not be t oo general (e.g., “Exercise is good.”).
- should not be too specific (e.g., “Exercise decreases the chance of developing diabetes, heart disease, asthma, osteoporosis, depression, and anxiety.”).
Supporting sentences
Your body paragraph needs to explain why or how your topic sentence is true. The sentences that support your topic sentence are called supporting sentences. You can have many types of supporting sentences. Supporting sentences can give examples, explanations, details, descriptions, facts, reasons, etc.
Concluding sentences
Your final statement should conclude your paragraph logically. Concluding sentences can restate the main idea of your paragraph, state an opinion, make a prediction, give advice, etc. New ideas should not be presented in your concluding sentence.
Exercise 1: Analyze a topic sentence.
Read the example body paragraph below to complete this exercise on a piece of paper.
Prompt: Why is exercise important?
Thesis: Exercise is essential because it improves overall physical and mental health.
Because it makes your body healthier, exercise is extremely important. One of the physical benefits of exercise is having stronger muscles. The only way to make your muscles stronger is to use them, and exercises like crunches, squats, lunges, push-ups, and weight-lifting are good examples of exercises that strengthen your muscles. Another benefit of exercise is that it lowers your heart rate. A slow heart rate can show that our hearts are working more efficiently and they don’t have to pump as many times in a minute to get blood to our organs. Related to our heart beating more efficiently, our blood pressure decreases. These are just some of the incredible health benefits of exercise.
Find the topic sentence. Use the following criteria to evaluate the topic sentence.
- Does the topic sentence clearly support the thesis statement?
- Is the topic sentence at the beginning of the body paragraph?
- Does the topic sentence control the content of all the supporting sentences?
- Is the topic sentence a complete sentence?
- Does the topic sentence announce the topic?
- Is the topic sentence too general? Is it too specific?
Exercise 2: Identify topic sentences.
Each group of sentences has three supporting sentences and one topic sentence. The topic sentence must be broad enough to include all of the supporting sentences. In each group of sentences, choose which sentence is the topic sentence. Write the letter of the topic sentence on the line given.
Group 1: Topic sentence: _________
- In southern Utah, hikers enjoy the scenic trails in Zion National Park.
- Many cities in Utah have created hiking trails in city parks for people to use.
- There are hiking paths in Utah’s Rocky Mountains that provide beautiful views.
- Hikers all over Utah can access hiking trails and enjoy nature.
Group 2: Topic sentence: _________
- People in New York speak many different languages.
- New York is a culturally diverse city.
- People in New York belong to many different religions.
- Restaurants in New York have food from all over the world.
Group 3: Topic sentence: _________
- Websites like YouTube have video tutorials that teach many different skills.
- Computer programs like PowerPoint are used in classrooms to teach new concepts.
- Technology helps people learn things in today’s world.
- Many educational apps have been created to help children in school.
Group 4: Topic sentence: _________
- Museums at BYU host events on the weekends for students.
- There are many fun activities for students at BYU on the weekends.
- There are incredible student concerts at BYU on Friday and Saturday nights.
- BYU clubs plan exciting activities for students to do on the weekends.
Group 5: Topic sentence: _________
- Some places have a scent that people remember when they think of that place.
- The smell of someone’s cologne can trigger a memory of that person.
- Smelling certain foods can bring back memories of eating that food.
- Many different memories can be connected to specific smells.
Exercise 3: Write topic sentences
Read each paragraph. On a piece of paper, write a topic sentence on the line at the beginning of the paragraph.
1._______ The first difference is that you have more privacy in a private room than in a shared room. You can go to your room to have a private phone call or Skype with your family and you are not bothered by other people. When you share your room, it can be hard to find private time when you can do things alone. Another difference is that it is lonelier in a private room than in a shared room. When you share your room with a roommate, you have someone that you can talk to. Frequently when you have a private room, you are alone more often. These two housing options are very different.
2. _______ People like to eat chocolate because it has many delicious flavors. For example, there are mint chocolates, milk chocolates, dark chocolates, white chocolates, chocolates with honey, and chocolates with nuts. Another reason people like to eat chocolate is because it reduces stress, which can help people to relax and feel better. The last reason people like to eat chocolate is because it can be cooked in many different ways. You can eat chocolate candies, mix chocolate with warm milk to drink, or prepare a chocolate dessert. These reasons are some of the reasons that people like to eat chocolate.
3. _______ A respectful roommate does not leave the main areas of the apartment messy after they use them. For example, they wash their dishes instead of leaving dirty pots and pans on the stove. They also don’t borrow things from other roommates without asking to use them first. In addition to respecting everyone’s need for space and their possessions, the ideal roommate is respectful of his or her roommate’s schedule. For example, if one roommate is asleep and the other roommates needs to study, the ideal roommate goes to the kitchen or living room instead of waking up the sleeping roommate. These simple gestures of respect make a roommate an excellent person to share an apartment with.
Exercise 4: Identify good supporting sentences.
Read the topic sentence. Then circle which sentences would be good supporting sentences.
Topic Sentence: Eating pancakes for breakfast saves time and money.
- Pancakes can be prepared in large quantities and then frozen, so the time it takes to cook breakfast is only a few minutes.
- Pancakes are very inexpensive to make because you only need a few ingredients.
- Pancakes are delicious and can be prepared in a variety of flavors.
- Pancakes save money because you can buy a big box of mix and only make what you need; you don’t waste money because you can save the extra mix for another time.
- Fresh fruit is a really quick breakfast because you only need to wash it and eat it.
Exercise 5: Identify good concluding sentences.
Read the topic sentence. Then circle which sentences would be good concluding sentences.
Topic Sentence: A shared room offers students a more social experience.
- Students who want more social interaction should have a shared room.
- A shared room is not good for students who work late.
- Everyone loves having a shared room.
- These examples illustrate how much more social a shared room can be.
- Really social students will enjoy having a shared room.
Exercise 6: Write concluding sentences.
On a piece of paper, write a concluding sentence at the end of each paragraph.
1. New York is a culturally diverse city. This culture is continually broadened because people immigrate from all over the world bringing different religions, food, and languages with them. This city has people that speak over 30 languages, including Arabic, Mandarin, Untu, Russian, and Polish. There are also more than 20 major religions represented by citizens of New York. These citizens brought more than their language and religion with them, however. They also brought traditional foods from their countries. _______
2. Technology helps people learn things in today’s world. This educational technology includes various websites, apps, programs, and many more things. Popular websites that are used for education include YouTube, TED, Canvas, and CrashCourse. Similarly, there are a variety of educational apps. These apps help users learn languages, history, math, and other practical skills. Computer programs are yet another way to use technology as a way to help people learn. Programs like PowerPoint are frequently used in classrooms as a means to deliver visual support to a lecture or presentation. This visual support aids learning and retention. _______
This content is provided to you freely by BYU Open Learning Network.
Access it online or download it at https://open.byu.edu/academic_a_writing/body_paragraphs .
Body Paragraph: Craft the Heart of Your Essay
Table of contents
- 1 Purpose of a Body Paragraph
- 2 Key Elements in the Structure of a Body Paragraph
- 3 Body Paragraph Structure
- 4 Transition Sentences of a Body Paragraph
- 5 How Do You Write a Body Paragraph of an Essay?
- 6.1 Using Different Types of Evidence.
- 6.2 Varying Sentence Length and Structure.
- 6.3 Avoiding Irrelevant Information.
- 6.4 Maintaining Consistency.
- 6.5 Supporting the Overall Thesis.
- 6.6 Using Clear and Concise Sentences.
- 6.7 Avoiding Transitions at the End.
- 7 Essay Body Paragraph Example
- 8 Conclusion
Completing an essay is more than just combining words – creating effective body paragraphs. They are like the building blocks of your text, giving it substance and strengthening your main point.
In this article, we’ll explore how to write a body paragraph for an essay and what methods to use to make it impactful.
- We’ll walk you through the body paragraph format, purpose, and principal elements,
- Cover using evidence wisely and make sure your sentences connect well,
- Deliver step-by-step guidelines and tips to create paragraphs that grab attention,
- Provide a body essay example.
Let’s start this journey into the writing world and learn how to make your essay interesting and well-structured.
Purpose of a Body Paragraph
This section is the backbone of any essay. A well-organized structure of the body paragraph helps your writing be readable. That’s why organizing the information to achieve this goal is essential. When writing body paragraphs in an essay, you focus on presenting and developing one point that supports the main argument.
Whether you write the text for yourself or go for essay papers for sale , each paragraph focuses on a specific aspect of the topic. It provides evidence, examples, analysis, or elaboration to strengthen and clarify the main point. The body of a paper helps guide the reader by making the ideas flow smoothly. This section aims to make a strong case for the essay’s thesis. It should keep the reader interested with well-developed and organized content.
Key Elements in the Structure of a Body Paragraph
Knowledge is the basis for any writing. Thus, any text you deliver should reflect your level of knowledge. For this, posing strategic and insightful questions to refine your thoughts and reinforce your argument is essential. A well-written body section is a compulsory component of any impactful document.
There are several key parts of a body paragraph in an essay.
- The first element is a transition, linking the preceding and current paragraphs. It should be clear, helping the reader in tracking the conversation. Using starting words for body paragraphs signals a change in focus or introduces a fresh idea.
- The second body paragraph element is the main idea, which is crucial for any text. You must state your argument in the topic sentence, which should be precise and brief. The main statements should relate to the thesis and support the idea.
- The third component is analysis, where the writer elaborates on the perspective. Providing proof and explaining how it supports the thesis statement is necessary. The examination should also be relevant and focused on the introduced topic. This way, you will make the essay structure coherent and easy to follow.
- The final element is the warrant, which explains how the evidence supports the main view. The warrant must be clear and connect the data to the principal argument. It should also focus on the topic and strengthen the argument.
Body Paragraph Structure
Well-thought-out body paragraphs are critical in an essay outline and the writer’s arguments. To effectively structure the body paragraph, you must understand its overall organization. A well-formatted academic essay helps writers communicate their reasoning and convince their audience. However, it’s better not to consider this a fixed and immovable object. Depending on the treated argument, its goal, length, and structure can be adapted to your needs.
You can imagine the skeleton of this part of the text in the following way:
- Topic sentence
- Supporting sentences
- Concluding sentence
The topic sentence is one of the ways to start a body paragraph. It should be a precise and focused statement that encapsulates the main argument of the passage. It connects the introduction paragraph in the essay with a thesis and provides a roadmap for the rest of the section. It will help the reader understand the point and how it relates to the writing. In some cases, it can even be formulated as a question.
Following the topic sentence for the body paragraph, you must provide supporting sentences. They present evidence and analysis to underpin the central idea. They should connect to the topic sentence and be clear and concise. Use language that is easy for the reader to understand.
To create a persuasive assertion, provide information that supports the main argument. The evidence can take many forms, including facts, statistics, or examples. Data should be reliable and relevant to the topic discussed. Research-based proof helps the writer convince the reader that their position is credible.
The concluding sentence is the ultimate statement and a kind of short conclusion you should use when you base your essay on body paragraphs. Its purpose is to summarize the idea and provide a transition to the later passage. This sentence helps the reader comprehend the main claim and its implications. Think of it as the answer to a question or the core information.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
Transition Sentences of a Body Paragraph
To make your writing flow smoothly and be more engaging, use transition words that help connect ideas. You can utilize three types of linking words and phrases:
- Bridging the introductory paragraph to subsequent sections (e.g., a transition from introduction to body): To begin with; In the first place; Initially; As an introduction; Turning to; As we delve into; Now that we have established.
- Connecting body paragraphs: Furthermore; Moreover; In addition; Additionally; Similarly; Likewise; Not only…but also; Besides that; In the same vein; Another key point.
- Linking the final body sentence to the conclusion: In conclusion; To sum up; Finally; In summary; Ultimately; Concluding; To conclude; To wrap things up; As a final point; All in all.
These words and phrases contribute to a coherent and logical essay, guiding the reader through the content. Use transitions to introduce a body paragraph and make your ideas clear and captivating to the audience.
How Do You Write a Body Paragraph of an Essay?
Completing this section requires consideration and attention to detail. It can be challenging to organize your thoughts and reasoning. However, it might be daunting, and professional assistance may be necessary. And this is where PapersOwl can be of great help. Our seasoned paper writing website offers expert homework help to achieve your academic goals.
How long should a body paragraph be? A general recommendation is to aim for 5-7 sentences. It allows you to explore one idea without giving too much information. The most important thing is to keep in mind the following guidelines:
- Introducing a concise topic sentence will be a good way to start a first body paragraph. Topic sentences should be specific and concise. Using them, you provide the reader with a clear understanding of the point you will discuss further. It should also relate to the thesis and connect to the perspective.
- After the topic sentence, use supporting sentences to provide additional information and analysis. This way, you will bolster the main argument. These parts of a body paragraph can include examples, facts, statistics, or expert opinions. Ensure that the information used is reliable and relevant to your idea.
- Employ transition sentences to link your ideas to the preceding and subsequent paragraphs. They make it easier for the reader to follow the main argument.
- Use brief and clear language to present your ideas and rationale. Avoid using complicated vocabulary or technical jargon that may confuse the reader. Instead, be straightforward when writing a body paragraph.
- Finally, end this section with a conclusion sentence. It acts as a summary of the main statement and offers a transition to the next section. The concluding sentence should bring closure to the point in one paragraph. It should also prepare the reader for the next parts of the writing.
When you write a body paragraph in an essay, follow these steps to ensure clarity, conciseness, and persuasiveness in your essay. Adhere to these guidelines to make your ideas concise and transparent and your arguments strong and persuasive. If you follow these steps, your essay will be concise and compelling. Implementing these measures ensures that your text is clear, persuasive, and effective.
Essential Tips to Write Flawless Body Paragraphs
Discover the following comprehensive strategies for crafting effective body paragraphs for your research.
Using Different Types of Evidence.
Incorporate a variety of quotes, statistics, and anecdotes to provide evidence and enhance the appeal and credibility of your writing. This multifaceted approach captivates the reader and reinforces your argument with diverse supporting elements.
Varying Sentence Length and Structure.
Mitigate monotony in the body of an essay by diversifying sentence length and structure. Integrate a mix of simple, compound, and complex sentences to enhance the overall readability of your composition. This nuanced use of syntax contributes to a more engaging and dynamic writing style.
Avoiding Irrelevant Information.
Don’t introduce irrelevant information that might distract or dilute the focus of your paragraph. Each sentence should serve a purpose, aligning seamlessly with the central theme and your essay’s purpose.
Maintaining Consistency.
Stay consistent with the tone and style throughout your text. The body paragraphs should harmonize with the established voice of your writing, creating a cohesive and unified reading experience for your audience.
Supporting the Overall Thesis.
When you start a body paragraph, ensure that each sentence significantly reinforces your overall thesis. Every argument, example, or piece of evidence should advance the central claim of your essay, reinforcing its coherence and persuasiveness.
Using Clear and Concise Sentences.
Break down complex topic sentences into clear and concise points. It facilitates a better understanding of your ideas and prevents the reader from feeling overwhelmed by overly intricate or convoluted language.
Avoiding Transitions at the End.
Refrain from using transition words and phrases at the end of paragraphs, as this can disrupt the natural flow of your writing. Instead, strive for seamless transitions within the paragraph’s content, allowing ideas to connect organically without explicitly signaling the conclusion.
Follow these tips to create a strong body paragraph layout for your document. If you need support or lack time and energy to craft your academic papers, do not hesitate to contact our writing experts. When you pay for a paper at PapersOwl, be sure your essay will adhere to all these instructions and requirements with zero flaws. Our team of writers has expertise in various fields and crafts quality papers for you. We deliver plagiarism-free essays and guarantee timely delivery. Whether you need an essay for school, college, or university, PapersOwl is the right choice.
Essay Body Paragraph Example
What is a body paragraph, and how to complete it correctly? Here is a good example to clarify these questions:
[Start with a topic sentence] J K Rowling, in her first book – Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone, claims that the appearance of a person can sometimes be misleading, [followed by supporting details] showing one of the kindest and most favorite characters – Hagrid as a scary person. His eyes are ‘glinting like black beetles,’ and his face is ‘almost completely hidden by a long, shaggy mane of hair and a wild, tangled beard,’ says the author (Rowling 46). [Then goes an explanation] The author declares that the main character of the book – Harry Potter, is frightened by this intimidating figure, which misleads the reader, making Hagrid appear as a villain. [Explains the significance] However, this image is wrong. Later the reader gets to know Hagrid’s true character, which is the opposite. [Ends with a conclusion and transition to the following part] This example proves how misleading an appearance of someone can be, which is easily proved by many other examples from literature and real life.”
Crafting effective body paragraphs in an essay is an indispensable skill for anyone seeking to elevate their writing. This article gives suggestions to help you write a good body paragraph. Our recommendations allow you to transform your essays into compelling and persuasive texts. These strategies can help both experienced writers and beginners with essay construction. They serve as a valuable toolkit for enhancing the impact and coherence of your text. When you write, remember that a well-organized essay body helps express thoughts clearly, engage readers, and convince them.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
5.4 Body Paragraphs
The term body paragraph refers to any paragraph that appears between the introductory and concluding sections of an essay. A good body paragraph should support the claim made in the thesis statement by developing only one key supporting idea. Your thesis gives the reader a road-map to your essay, and your body paragraphs should closely follow that map. The body paragraphs present the ideas that support your thesis, using the various rhetorical strategies that you find most effectively address your subject, audience, and purpose. This idea is often referred to as a sub-claim.
Some sub-claims will take more time to develop than others, so body paragraph length can and often should vary in order to maintain your reader’s interest. When constructing a body paragraph, the most important objectives are to stay on-topic and to fully develop your sub-claim.
Developing a paragraph can be a difficult task for many students. They usually approach the task with certain ideas firmly in mind, most notably that a paragraph is 5-6 sentences and the paragraph is about what they are talking about, which isn’t necessarily a bad place to start. But when pushed to explain more specifically what constitutes a good paragraph or how to present the information they will discuss, problems begin to emerge. If you are struggling to craft a fully developed paragraph, you might find the following step-by-step approach helpful.
Perhaps the easiest way to think about a “fully developed” paragraph is to think of writing each paragraph in 6 different steps rather than a certain amount of sentences . These steps can be helpful in not only understanding the criteria needed in a paragraph or how they connect to one another to create a conversation in your paper but also ensuring that your audience understands your purpose in presenting this paragraph.
Focusing on the number of sentences may limit how you express the idea being discussed. However, this doesn’t mean that the information can be presented without a plan in mind; you should begin with understanding what a paragraph needs to “be” and “do.”
Goals of the Paragraph: What it should “be”
While there is no “right way” to develop a paragraph, there are certain criteria that an academic paragraph should work to be:
- Unified: Every sentence presented works to explain the main idea of the paragraph.
- Coherent : You present the information in a logical order that allows the audience to understand your purpose.
- Developed: To achieve this, you must provide enough information so that the audience has a clear understanding of the main idea expressed in the topic sentence.
Developing the Paragraph: Creating what it should “do”
1. Establish a Main Idea (Topic) .
- Too often, students focus on the wrong part of the topic sentence. They believe that the topic or subject (or sub-claim) is the most important part of the sentence since “that is what I am talking about.” This is where the trouble with unity begins. There are many ways to discuss the topic, so conceivably any information related to that topic could end up in the paragraph. Ultimately, the unity breaks down and the reader will not understand the significance of your idea because the information may be having two different conversations, instead of one.
- Use a transitional device to effortlessly segue from the idea discussed in the previous paragraph. When choosing a transitional device, you should consider whether your new paragraph will build onto the topic of your previous paragraph, begin to develop a new key idea or sub-claim, or present a counterargument or concession.
- Identify the key idea or sub-claim that you intend to expand upon in your new paragraph. Even if you are building onto the idea of the previous paragraph, you will still need to identify the sub-claim in your topic sentence. When constructing a topic sentence, you may feel as though you are stating the obvious or being repetitive, but your readers will need this information to guide them to a thorough understanding of your ideas.
- To connect to your thesis, you should consider the function of the body paragraph, which will usually depend upon the type of essay you are writing; for example, your topic sentence should suggest whether your goal is to inform or persuade your readers (your topic sentence should indicate whether or not you have an opinion or perspective on the topic).
2. Provide an Explanation
- This step may be a bit of a trap. Many students are often tempted to reach for their research and begin providing support for the main idea . However, this isn’t always the best option. Many times when students do this, they are using their research/ support to think of them. Before reaching for the research, students should explain their topic sentence.
- You can also think of this section as a link between the topic sentence and supporting evidence where you provide any necessary contextual information for the evidence.
- The main focus of any paragraph should be what you have to say. If you are putting forth this idea in support of your thesis, the audience is going to want to know what you think about it–what is significant about this main idea. They may not fully understand the topic sentence the way you intend them to, so explain your reasoning to the reader.
3. Provide Support/ Evidence
- Now that your audience should have a better understanding of the main idea/ topic, you are ready to provide support/ evidence . You want to be very selective when deciding what textual support to include in the paragraph. Not all evidence is the same, and not all evidence achieves the same goals (thinking ethos/ logos/ pathos here). The textual support should help to reinforce or illustrate more about your topic sentence for the reader, helping them understand it more completely.
- Supporting your ideas effectively is essential to establishing your credibility as a writer, so you should choose your supporting evidence wisely and clearly explain it to your audience. Understanding and appealing to your audience can also help determine what your readers will consider good support and what they’ll consider to be weak.
- Statistics and data
- Research studies and scholarship
- Hypothetical and real-life examples
- Historical facts
- Case histories
- Expert testimonies or opinions
- Eye-witness accounts
- Applicable personal experiences or anecdotesTypes of support might include the following:
- Varying your means of support will lend further credibility to your essay and help to maintain your reader’s interest. Keep in mind, though, that some types of support are more appropriate for certain academic disciplines than for others.
4. Interpret the Support/ Evidence
- Remember not to conclude your body paragraph with supporting evidence. Rather than assuming that the evidence you have provided speaks for itself, it is important to explain why that evidence proves or supports the key idea you present in your topic sentence and (ultimately) the claim you make in your thesis statement.
- This is often one of the more difficult aspects for students, and a step in the development that they overlook. No matter how clear you think the textual support provided is, it does not speak for itself. The reason is that the audience may not understand how you intend them to interpret the information, and how that relates to supporting the main idea of the paragraph. When you explain how this information is relevant to your topic sentence, and why it is significant, you need to offer insight into that information.
- Don’t simply follow up your support with a single sentence that begins with a phrase like “This proves” or “Meaning” and then restate what the evidence said. Know why you included this information and why it is important to your paragraph. You need to connect the dots for your reader, so they see exactly how that information is providing support, and helping your main idea.
- The bulk of the information should be coming from you, not your sources. Your audience wants to what it is that you think, your perspective on the idea, and how you intend to link it back to the thesis.
- Relevance or significance
- Comparison or contrast
- Cause and effect
- Refutation or concession
- Suggested action or conclusion
- Proposal for further study
- Personal reaction
- Try to avoid simply repeating the source material differently or using phrases like “This quote means” to begin your explanation. Keep in mind that your voice should control your essay and guide your audience to a greater understanding of the source material’s relevance to your claim .
5. Repeat Steps 3 and 4, if necessary
- If you have more than one piece of textual support that you want to include, you need to repeat the two previous steps to fully develop your paragraph . You will want to vary your evidence. If you use statistics, then you may want to include expert testimony. If the first piece of evidence focuses on logic, you want to tap into one of the other appeals such as pathos to bring a full view of the issue to your reader. However, you don’t want to keep simply repeating this sequence: evidence should be used to help achieve your purpose, not to fill space.
6. Connect to the thesis statement
- emphasize the importance of understanding the idea,
- make a connection to previous and/or forthcoming ideas
- overall ensure that the information is related directly back to the main purpose of the essay as defined in your thesis statement.
While this is not the only way to write a paragraph, it can be a helpful guide and/or model when you need a structure to begin shaping and organizing your ideas, to help you compose a unified, coherent, well-developed paragraph.
Organizing Body Paragraphs
Even though you might have an overall structure for your essay and all your main ideas planned, the best order for those ideas and their body paragraphs may not be apparent. However the method of organization in an essay can be just as important as its content. Without a clear organizational pattern, your reader could become confused and lose interest. The way you structure your essay helps your readers draw connections between the body and the thesis, and the structure also keeps you focused as you plan and write the essay. Choosing your organizational pattern before you outline ensures that each body paragraph works to support and develop your thesis.
Each paragraph should be an irreplaceable node within a coherent sequence of logic. Thinking of paragraphs as “building blocks” evokes the “five-paragraph theme” structure: if you have identical stone blocks, it hardly matters what order they’re in. In a successful organically structured college paper, the structure and tone of each paragraph reflect its indispensable role within the overall piece. These goals—making every bit count and having each part situated within the whole—also anchor the discussion in the next chapter: how to write introductions and conclusions that frame.
Amy Guptill
When you begin to draft your essay, your ideas may seem to flow from your mind in a seemingly random manner. Your readers, who bring to the table different backgrounds, viewpoints, and ideas, need you to organize these ideas to help process and accept them.
A solid organizational pattern gives your ideas a path that you can follow as you develop your draft. Knowing how you will organize your paragraphs allows you to better express and analyze your thoughts. Planning the structure of your essay before you choose supporting evidence helps you conduct more effective and targeted research.
Chronological Order
Chronological arrangement has the following purposes:
- To explain the history of an event or a topic
- To tell a story or relate an experience
- To explain how to do or make something
- To explain the steps in a process
Chronological order is mostly used in expository writing , which is a form of writing that narrates, describes, informs, or explains a process. When using chronological order, arrange the events in the order that they happened, or will happen if you are giving instructions. This method requires you to use words such as first , second , then , after that , later , and finally . These transition words guide you and your reader through the paper as you expand your thesis.
For example, if you are writing an essay about the history of the airline industry, you would begin with its conception and detail the essential timeline events up until the present day. You would follow the chain of events using words such as first , then , next , and so on.
Keep in mind that chronological order is most appropriate for the following purposes:
- Writing essays containing heavy research
- Writing essays with the aim of listing, explaining, or narrating
- Writing essays that analyze literary works such as poems, plays, or books
Order of Importance
Order of importance is best used for the following purposes:
- Persuading and convincing
- Ranking items by their importance, benefit, or significance
- Illustrating a situation, problem, or solution
Most essays move from the least to the most important point, and the paragraphs are arranged to build the essay’s strength. Sometimes, however, it is necessary to begin with your most important supporting point, such as in an essay that contains a highly debatable thesis. When writing a persuasive essay, it is best to begin with the most important point because it immediately captivates your readers and compels them to continue reading.
For example, if you were supporting your thesis that homework is detrimental to the education of high school students, you would want to present your most convincing argument first, and then move on to the less important points for your case.
Some key transitional words you should use with this method of organization are most importantly , almost as importantly , just as importantly , and finally .
Spatial Order
Spatial order is best used for the following purposes:
- Helping readers visualize something as you want them to see it
- Evoking a scene using the senses (sight, touch, taste, smell, and sound)
- Writing a descriptive essay
Spatial order means that you explain or describe objects as they are arranged around you in your space, for example in a bedroom. As the writer, you create a picture for your readers, and their perspective is the viewpoint from which you describe what is around you.
The view must move in an orderly, logical progression, giving the reader clear directional signals to follow from place to place. The key to using this method is to choose a specific starting point and then guide the reader to follow your eye as it moves in an orderly trajectory from your starting point.
The paragraph incorporates two objectives you have learned in this chapter: using an implied topic sentence and applying spatial order. Often in a descriptive essay, the two work together.
Regardless of the order you chose, your introduction should indicate the information you will cover and in what order, and the introduction should also establish the relevance of the information. This step will make your essay easier to organize and for your readers to follow. Your body paragraphs should then provide clear divisions.
James C Devlin
Back to Paragraph Flow
Like sentence length, paragraph length varies. There is no single ideal length for “the perfect paragraph.” There are some general guidelines, however. Some writing handbooks or resources suggest that a paragraph should be at least three or four sentences; others suggest that 100 to 200 words is a good target to shoot for. In academic writing, paragraphs tend to be longer, while in less formal or less complex writing, such as in a newspaper, paragraphs tend to be much shorter. Two-thirds to three-fourths of a page is usually a good target length for paragraphs at your current level of college writing. If your readers can’t see a paragraph break on the page, they might wonder if the paragraph is ever going to end or they might lose interest.
The most important thing to keep in mind here is that the amount of space needed to develop one idea will likely be different than the amount of space needed to develop another. So when is a paragraph complete? The answer is when it’s fully developed. The guidelines above for providing good support should help.
Some signals that it’s time to end a paragraph and start a new one include that
- You’re ready to begin developing a new idea
- You want to emphasize a point by setting it apart
- You’re getting ready to continue discussing the same idea but in a different way (e.g. shifting from comparison to contrast)
- You notice that your current paragraph is getting too long (more than three-fourths of a page or so), and you think your writers will need a visual break
Some signals that you may want to combine paragraphs include that
- You notice that some of your paragraphs appear to be short and choppy
- You have multiple paragraphs on the same topic
- You have undeveloped material that needs to be united under a clear topic
Finally, paragraph number is a lot like paragraph length. You may have been asked in the past to write a five-paragraph essay. There’s nothing inherently wrong with a five-paragraph essay, but just like sentence length and paragraph length, the number of paragraphs in an essay depends upon what’s needed to get the job done. There’s no way to know that until you start writing. So try not to worry too much about the proper length and number of things. Just start writing and see where the essay and the paragraphs take you. There will be plenty of time to sort out the organization in the revision process. You’re not trying to fit pegs into holes here. You’re letting your ideas unfold. Give yourself—and them—the space to let that happen.
Additional Readings
- Check out this article on Academic Paragraph Structure for additional tips on writing body paragraphs.
- The article on Body Paragraphs: How to Write Perfect Ones from Grammarly Blog also covers more of this information.
Attributions
The Writing Textbook by Josh Woods, editor and contributor, as well as an unnamed author (by request from the original publisher), and other authors named separately is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
This chapter has additions, edits, and organization by James Charles Devlin.
5.4 Body Paragraphs Copyright © by James Charles Devlin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
10 min read
How to write strong essay body paragraphs (with examples)
In this blog post, we'll discuss how to write clear, convincing essay body paragraphs using many examples. We'll also be writing paragraphs together. By the end, you'll have a good understanding of how to write a strong essay body for any topic.

Table of Contents
Introduction, how to structure a body paragraph, creating an outline for our essay body, 1. a strong thesis statment takes a stand, 2. a strong thesis statement allows for debate, 3. a strong thesis statement is specific, writing the first essay body paragraph, how not to write a body paragraph, writing the second essay body paragraph.
After writing a great introduction to our essay, let's make our case in the body paragraphs. These are where we will present our arguments, back them up with evidence, and, in most cases, refute counterarguments. Introductions are very similar across the various types of essays. For example, an argumentative essay's introduction will be near identical to an introduction written for an expository essay. In contrast, the body paragraphs are structured differently depending on the type of essay.
In an expository essay, we are investigating an idea or analyzing the circumstances of a case. In contrast, we want to make compelling points with an argumentative essay to convince readers to agree with us.
The most straightforward technique to make an argument is to provide context first, then make a general point, and lastly back that point up in the following sentences. Not starting with your idea directly but giving context first is crucial in constructing a clear and easy-to-follow paragraph.
How to ideally structure a body paragraph:
- Provide context
- Make your thesis statement
- Support that argument
Now that we have the ideal structure for an argumentative essay, the best step to proceed is to outline the subsequent paragraphs. For the outline, we'll be writing one sentence that is simple in wording and describes the argument that we'll make in that paragraph concisely. Why are we doing that? An outline does more than give you a structure to work off of in the following essay body, thereby saving you time. It also helps you not to repeat yourself or, even worse, to accidentally contradict yourself later on.
While working on the outline, remember that revising your initial topic sentences is completely normal. They do not need to be flawless. Starting the outline with those thoughts can help accelerate writing the entire essay and can be very beneficial in avoiding writer's block.
For the essay body, we'll be proceeding with the topic we've written an introduction for in the previous article - the dangers of social media on society.
These are the main points I would like to make in the essay body regarding the dangers of social media:
Amplification of one's existing beliefs
Skewed comparisons
What makes a polished thesis statement?
Now that we've got our main points, let's create our outline for the body by writing one clear and straightforward topic sentence (which is the same as a thesis statement) for each idea. How do we write a great topic sentence? First, take a look at the three characteristics of a strong thesis statement.
Consider this thesis statement:
'While social media can have some negative effects, it can also be used positively.'
What stand does it take? Which negative and positive aspects does the author mean? While this one:
'Because social media is linked to a rise in mental health problems, it poses a danger to users.'
takes a clear stand and is very precise about the object of discussion.
If your thesis statement is not arguable, then your paper will not likely be enjoyable to read. Consider this thesis statement:
'Lots of people around the globe use social media.'
It does not allow for much discussion at all. Even if you were to argue that more or fewer people are using it on this planet, that wouldn't make for a very compelling argument.
'Although social media has numerous benefits, its various risks, including cyberbullying and possible addiction, mostly outweigh its benefits.'
Whether or not you consider this statement true, it allows for much more discussion than the previous one. It provides a basis for an engaging, thought-provoking paper by taking a position that you can discuss.
A thesis statement is one sentence that clearly states what you will discuss in that paragraph. It should give an overview of the main points you will discuss and show how these relate to your topic. For example, if you were to examine the rapid growth of social media, consider this thesis statement:
'There are many reasons for the rise in social media usage.'
That thesis statement is weak for two reasons. First, depending on the length of your essay, you might need to narrow your focus because the "rise in social media usage" can be a large and broad topic you cannot address adequately in a few pages. Secondly, the term "many reasons" is vague and does not give the reader an idea of what you will discuss in your paper.
In contrast, consider this thesis statement:
'The rise in social media usage is due to the increasing popularity of platforms like Facebook and Twitter, allowing users to connect with friends and share information effortlessly.'
Why is this better? Not only does it abide by the first two rules by allowing for debate and taking a stand, but this statement also narrows the subject down and identifies significant reasons for the increasing popularity of social media.
In conclusion : A strong thesis statement takes a clear stand, allows for discussion, and is specific.
Let's make use of how to write a good thopic sentence and put it into practise for our two main points from before. This is what good topic sentences could look like:
Echo chambers facilitated by social media promote political segregation in society.
Applied to the second argument:
Viewing other people's lives online through a distorted lens can lead to feelings of envy and inadequacy, as well as unrealistic expectations about one's life.
These topic sentences will be a very convenient structure for the whole body of our essay. Let's build out the first body paragraph, then closely examine how we did it so you can apply it to your essay.
Example: First body paragraph
If social media users mostly see content that reaffirms their existing beliefs, it can create an "echo chamber" effect. The echo chamber effect describes the user's limited exposure to diverse perspectives, making it challenging to examine those beliefs critically, thereby contributing to society's political polarization. This polarization emerges from social media becoming increasingly based on algorithms, which cater content to users based on their past interactions on the site. Further contributing to this shared narrative is the very nature of social media, allowing politically like-minded individuals to connect (Sunstein, 2018). Consequently, exposure to only one side of the argument can make it very difficult to see the other side's perspective, marginalizing opposing viewpoints. The entrenchment of one's beliefs by constant reaffirmation and amplification of political ideas results in segregation along partisan lines.
Sunstein, C. R (2018). #Republic: Divided Democracy in the Age of Social Media. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
In the first sentence, we provide context for the argument that we are about to make. Then, in the second sentence, we clearly state the topic we are addressing (social media contributing to political polarization).
Our topic sentence tells readers that a detailed discussion of the echo chamber effect and its consequences is coming next. All the following sentences, which make up most of the paragraph, either a) explain or b) support this point.
Finally, we answer the questions about how social media facilitates the echo chamber effect and the consequences. Try implementing the same structure in your essay body paragraph to allow for a logical and cohesive argument.
These paragraphs should be focused, so don't incorporate multiple arguments into one. Squeezing ideas into a single paragraph makes it challenging for readers to follow your reasoning. Instead, reserve each body paragraph for a single statement to be discussed and only switch to the next section once you feel that you thoroughly explained and supported your topic sentence.
Let's look at an example that might seem appropriate initially but should be modified.
Negative example: Try identifying the main argument
Over the past decade, social media platforms have become increasingly popular methods of communication and networking. However, these platforms' algorithmic nature fosters echo chambers or online spaces where users only encounter information that reinforces their existing beliefs. This echo chamber effect can lead to a lack of understanding or empathy for those with different perspectives and can even amplify the effects of confirmation bias. The same principle of one-sided exposure to opinions can be abstracted and applied to the biased subjection to lifestyles we see on social media. The constant exposure to these highly-curated and often unrealistic portrayals of other people's lives can lead us to believe that our own lives are inadequate in comparison. These feelings of inadequacy can be especially harmful to young people, who are still developing their sense of self.
Let's analyze this essay paragraph. Introducing the topic sentence by stating the social functions of social media is very useful because it provides context for the following argument. Naming those functions in the first sentence also allows for a smooth transition by contrasting the initial sentence ("However, ...") with the topic sentence. Also, the topic sentence abides by our three rules for creating a strong thesis statement:
- Taking a clear stand: algorithms are substantial contributors to the echo chamber effect
- Allowing for debate: there is literature rejecting this claim
- Being specific: analyzing a specific cause of the effect (algorithms).
So, where's the problem with this body paragraph?
It begins with what seems like a single argument (social media algorithms contributing to the echo chamber effect). Yet after addressing the consequences of the echo-chamber effect right after the thesis sentence, the author applies the same principle to a whole different topic. At the end of the paragraph, the reader is probably feeling confused. What was the paragraph trying to achieve in the first place?
We should place the second idea of being exposed to curated lifestyles in a separate section instead of shoehorning it into the end of the first one. All sentences following the thesis statement should either explain it or provide evidence (refuting counterarguments falls into this category, too).
With our first body paragraph done and having seen an example of what to avoid, let's take the topic of being exposed to curated lifestyles through social media and construct a separate body paragraph for it. We have already provided sufficient context for the reader to follow our argument, so it is unnecessary for this particular paragraph.
Body paragraph 2
Another cause for social media's destructiveness is the users' inclination to only share the highlights of their lives on social media, consequently distorting our perceptions of reality. A highly filtered view of their life leads to feelings of envy and inadequacy, as well as a distorted understanding of what is considered ordinary (Liu et al., 2018). In addition, frequent social media use is linked to decreased self-esteem and body satisfaction (Perloff, 2014). One way social media can provide a curated view of people's lives is through filters, making photos look more radiant, shadier, more or less saturated, and similar. Further, editing tools allow people to fundamentally change how their photos and videos look before sharing them, allowing for inserting or removing certain parts of the image. Editing tools give people considerable control over how their photos and videos look before sharing them, thereby facilitating the curation of one's online persona.
Perloff, R.M. Social Media Effects on Young Women's Body Image Concerns: Theoretical Perspectives and an Agenda for Research. Sex Roles 71, 363–377 (2014).
Liu, Hongbo & Wu, Laurie & Li, Xiang. (2018). Social Media Envy: How Experience Sharing on Social Networking Sites Drives Millennials' Aspirational Tourism Consumption. Journal of Travel Research. 58. 10.1177/0047287518761615.
Dr. Jacob Neumann put it this way in his book A professors guide to writing essays: 'If you've written strong and clear topic sentences, you're well on your way to creating focused paragraphs.'
They provide the basis for each paragraph's development and content, allowing you not to get caught up in the details and lose sight of the overall objective. It's crucial not to neglect that step. Apply these principles to your essay body, whatever the topic, and you'll set yourself up for the best possible results.
Sources used for creating this article
- Writing a solid thesis statement : https://www.vwu.edu/academics/academic-support/learning-center/pdfs/Thesis-Statement.pdf
- Neumann, Jacob. A professor's guide to writing essays. 2016.

Follow the Journey
Hello! I'm Josh, the founder of Wordful. We aim to make a product that makes writing amazing content easy and fun. Sign up to gain access first when Wordful goes public!

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.2 Writing Body Paragraphs
Learning objectives.
- Select primary support related to your thesis.
- Support your topic sentences.
If your thesis gives the reader a roadmap to your essay, then body paragraphs should closely follow that map. The reader should be able to predict what follows your introductory paragraph by simply reading the thesis statement.
The body paragraphs present the evidence you have gathered to confirm your thesis. Before you begin to support your thesis in the body, you must find information from a variety of sources that support and give credit to what you are trying to prove.
Select Primary Support for Your Thesis
Without primary support, your argument is not likely to be convincing. Primary support can be described as the major points you choose to expand on your thesis. It is the most important information you select to argue for your point of view. Each point you choose will be incorporated into the topic sentence for each body paragraph you write. Your primary supporting points are further supported by supporting details within the paragraphs.
Remember that a worthy argument is backed by examples. In order to construct a valid argument, good writers conduct lots of background research and take careful notes. They also talk to people knowledgeable about a topic in order to understand its implications before writing about it.
Identify the Characteristics of Good Primary Support
In order to fulfill the requirements of good primary support, the information you choose must meet the following standards:
- Be specific. The main points you make about your thesis and the examples you use to expand on those points need to be specific. Use specific examples to provide the evidence and to build upon your general ideas. These types of examples give your reader something narrow to focus on, and if used properly, they leave little doubt about your claim. General examples, while they convey the necessary information, are not nearly as compelling or useful in writing because they are too obvious and typical.
- Be relevant to the thesis. Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Primary support should show, explain, or prove your main argument without delving into irrelevant details. When faced with lots of information that could be used to prove your thesis, you may think you need to include it all in your body paragraphs. But effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Choose your examples wisely by making sure they directly connect to your thesis.
- Be detailed. Remember that your thesis, while specific, should not be very detailed. The body paragraphs are where you develop the discussion that a thorough essay requires. Using detailed support shows readers that you have considered all the facts and chosen only the most precise details to enhance your point of view.
Prewrite to Identify Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
Recall that when you prewrite you essentially make a list of examples or reasons why you support your stance. Stemming from each point, you further provide details to support those reasons. After prewriting, you are then able to look back at the information and choose the most compelling pieces you will use in your body paragraphs.
Choose one of the following working thesis statements. On a separate sheet of paper, write for at least five minutes using one of the prewriting techniques you learned in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
- Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
- Students cheat for many different reasons.
- Drug use among teens and young adults is a problem.
- The most important change that should occur at my college or university is ____________________________________________.
Select the Most Effective Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
After you have prewritten about your working thesis statement, you may have generated a lot of information, which may be edited out later. Remember that your primary support must be relevant to your thesis. Remind yourself of your main argument, and delete any ideas that do not directly relate to it. Omitting unrelated ideas ensures that you will use only the most convincing information in your body paragraphs. Choose at least three of only the most compelling points. These will serve as the topic sentences for your body paragraphs.
Refer to the previous exercise and select three of your most compelling reasons to support the thesis statement. Remember that the points you choose must be specific and relevant to the thesis. The statements you choose will be your primary support points, and you will later incorporate them into the topic sentences for the body paragraphs.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
When you support your thesis, you are revealing evidence. Evidence includes anything that can help support your stance. The following are the kinds of evidence you will encounter as you conduct your research:
- Facts. Facts are the best kind of evidence to use because they often cannot be disputed. They can support your stance by providing background information on or a solid foundation for your point of view. However, some facts may still need explanation. For example, the sentence “The most populated state in the United States is California” is a pure fact, but it may require some explanation to make it relevant to your specific argument.
- Judgments. Judgments are conclusions drawn from the given facts. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and examination of a topic.
- Testimony. Testimony consists of direct quotations from either an eyewitness or an expert witness. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; he adds authenticity to an argument based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive experience with a topic. This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or both. An expert witness adds authority and credibility to an argument.
- Personal observation. Personal observation is similar to testimony, but personal observation consists of your testimony. It reflects what you know to be true because you have experiences and have formed either opinions or judgments about them. For instance, if you are one of five children and your thesis states that being part of a large family is beneficial to a child’s social development, you could use your own experience to support your thesis.

Writing at Work
In any job where you devise a plan, you will need to support the steps that you lay out. This is an area in which you would incorporate primary support into your writing. Choosing only the most specific and relevant information to expand upon the steps will ensure that your plan appears well-thought-out and precise.
You can consult a vast pool of resources to gather support for your stance. Citing relevant information from reliable sources ensures that your reader will take you seriously and consider your assertions. Use any of the following sources for your essay: newspapers or news organization websites, magazines, encyclopedias, and scholarly journals, which are periodicals that address topics in a specialized field.
Choose Supporting Topic Sentences
Each body paragraph contains a topic sentence that states one aspect of your thesis and then expands upon it. Like the thesis statement, each topic sentence should be specific and supported by concrete details, facts, or explanations.
Each body paragraph should comprise the following elements.
topic sentence + supporting details (examples, reasons, or arguments)
As you read in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , topic sentences indicate the location and main points of the basic arguments of your essay. These sentences are vital to writing your body paragraphs because they always refer back to and support your thesis statement. Topic sentences are linked to the ideas you have introduced in your thesis, thus reminding readers what your essay is about. A paragraph without a clearly identified topic sentence may be unclear and scattered, just like an essay without a thesis statement.
Unless your teacher instructs otherwise, you should include at least three body paragraphs in your essay. A five-paragraph essay, including the introduction and conclusion, is commonly the standard for exams and essay assignments.
Consider the following the thesis statement:
Author J.D. Salinger relied primarily on his personal life and belief system as the foundation for the themes in the majority of his works.
The following topic sentence is a primary support point for the thesis. The topic sentence states exactly what the controlling idea of the paragraph is. Later, you will see the writer immediately provide support for the sentence.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced themes in many of his works.
In Note 9.19 “Exercise 2” , you chose three of your most convincing points to support the thesis statement you selected from the list. Take each point and incorporate it into a topic sentence for each body paragraph.
Supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Topic sentence: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
Draft Supporting Detail Sentences for Each Primary Support Sentence
After deciding which primary support points you will use as your topic sentences, you must add details to clarify and demonstrate each of those points. These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence.
The writer drafts possible supporting detail sentences for each primary support sentence based on the thesis statement:
Thesis statement: Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
Supporting point 1: Dogs can scare cyclists and pedestrians.
Supporting details:
- Cyclists are forced to zigzag on the road.
- School children panic and turn wildly on their bikes.
- People who are walking at night freeze in fear.
Supporting point 2:
Loose dogs are traffic hazards.
- Dogs in the street make people swerve their cars.
- To avoid dogs, drivers run into other cars or pedestrians.
- Children coaxing dogs across busy streets create danger.
Supporting point 3: Unleashed dogs damage gardens.
- They step on flowers and vegetables.
- They destroy hedges by urinating on them.
- They mess up lawns by digging holes.
The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the primary support sentence (the topic sentence), which is underlined.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced the themes in many of his works. He did not hide his mental anguish over the horrors of war and once told his daughter, “You never really get the smell of burning flesh out of your nose, no matter how long you live.” His short story “A Perfect Day for a Bananafish” details a day in the life of a WWII veteran who was recently released from an army hospital for psychiatric problems. The man acts questionably with a little girl he meets on the beach before he returns to his hotel room and commits suicide. Another short story, “For Esmé – with Love and Squalor,” is narrated by a traumatized soldier who sparks an unusual relationship with a young girl he meets before he departs to partake in D-Day. Finally, in Salinger’s only novel, The Catcher in the Rye , he continues with the theme of posttraumatic stress, though not directly related to war. From a rest home for the mentally ill, sixteen-year-old Holden Caulfield narrates the story of his nervous breakdown following the death of his younger brother.
Using the three topic sentences you composed for the thesis statement in Note 9.18 “Exercise 1” , draft at least three supporting details for each point.
Thesis statement: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Supporting details: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
You have the option of writing your topic sentences in one of three ways. You can state it at the beginning of the body paragraph, or at the end of the paragraph, or you do not have to write it at all. This is called an implied topic sentence. An implied topic sentence lets readers form the main idea for themselves. For beginning writers, it is best to not use implied topic sentences because it makes it harder to focus your writing. Your instructor may also want to clearly identify the sentences that support your thesis. For more information on the placement of thesis statements and implied topic statements, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Print out the first draft of your essay and use a highlighter to mark your topic sentences in the body paragraphs. Make sure they are clearly stated and accurately present your paragraphs, as well as accurately reflect your thesis. If your topic sentence contains information that does not exist in the rest of the paragraph, rewrite it to more accurately match the rest of the paragraph.
Key Takeaways
- Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement.
- Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis.
- Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis.
- Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
- Prewriting helps you determine your most compelling primary support.
- Evidence includes facts, judgments, testimony, and personal observation.
- Reliable sources may include newspapers, magazines, academic journals, books, encyclopedias, and firsthand testimony.
- A topic sentence presents one point of your thesis statement while the information in the rest of the paragraph supports that point.
- A body paragraph comprises a topic sentence plus supporting details.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Body Paragraph
Definition of body paragraph.
A body paragraph in an essay is a paragraph that comes between the introduction and the conclusion . In a five-paragraph essay, there are three body paragraphs, while in longer essays there could be five or even ten. In major research papers, there are hundreds of body paragraphs.
Components of a Body Paragraph
A body paragraph has three major components: (1) topic sentence , (2) explanation, (3) supporting details. Without any of them, the body paragraph seems to be missing something, and will not add anything to the theme and central idea of the essay.
- Topic Sentence The topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph, and states the main idea to be discussed in the paragraph. In a body paragraph, the topic sentence is always about the evidence given in the thesis statement of the essay. It could be a claim , an assertion , or a fact needing explanation. It is generally a statement or a declarative sentence.
- Explanation / Example The topic sentence is followed by an explanation and/or an example. Whatever it is, it generally starts with “in other words” or “it means;” or “for example,” “for instance,” etc. This is called “metacommentary,” or telling of the same thing in different words to explain it further, so that readers can understand.
- Supporting Details Supporting details include concrete examples, rather than explanation or metacommentary. In common essays, or five-paragraph essays, this is just a one-sentence example from everyday life. However, in the case of research essays, these are usually quotes and statistics from research studies.
Different Between an Introduction and a Body Paragraph
Although both are called paragraphs, both are very different from each other not only in terms of functions but also in terms of components. An introduction occurs in the beginning and has three major components; a hook , background information , and a thesis statement . However, a body paragraph is comprised of a topic sentence making a claim, an explanation or example of the claim, and supporting details.
Examples of Body Paragraph in Literature
Example #1: autobiography of bertrand russell (by bertrand russell).
“Three passions, simple but overwhelmingly strong, have governed my life: the longing for love, the search for knowledge, and unbearable pity for the suffering of mankind. These passions, like great winds, have blown me hither and thither, in a wayward course, over a great ocean of anguish, reaching to the very verge of despair. I have sought love, first, because it brings ecstasy – ecstasy so great that I would often have sacrificed all the rest of life for a few hours of this joy. I have sought it, next, because it relieves loneliness – that terrible loneliness in which one shivering consciousness looks over the rim of the world into the cold unfathomable lifeless abyss. I have sought it finally, because in the union of love I have seen, in a mystic miniature, the prefiguring vision of the heaven that saints and poets have imagined. This is what I sought, and though it might seem too good for human life, this is what – at last – I have found.”
This is a paragraph from the prologue of the autobiography of Bertrand Russell. Check its first topic sentence, which explains something that is further elaborated in the following sentences.
Example #2: Politics and the English Language (by George Orwell)
“The inflated style itself is a kind of euphemism . A mass of Latin words falls upon the facts like soft snow , blurring the outline and covering up all the details. The great enemy of clear language is insincerity. When there is a gap between one’s real and one’s declared aims, one turns as it were instinctively to long words and exhausted idioms , like a cuttlefish spurting out ink. In our age there is no such thing as ‘keeping out of politics.’ All issues are political issues, and politics itself is a mass of lies, evasions, folly, hatred, and schizophrenia. When the general atmosphere is bad, language must suffer. I should expect to find — this is a guess which I have not sufficient knowledge to verify — that the German, Russian and Italian languages have all deteriorated in the last ten or fifteen years, as a result of dictatorship.”
This paragraph has a very short topic sentence. However, its explanation and further supporting details are very long.
Function of Body Paragraph
The elements of a body paragraph help to elaborate a concept, organize ideas into a single whole, and help bridge a gap in thoughts. The major task of a body paragraph is the organization of thoughts in a unified way. It also helps an author to give examples to support his claim, given in the topic sentence of that body paragraph. A good paragraph helps readers understand the main idea with examples.
Related posts:
- I Sing the Body Electric
- Simple Paragraph
Post navigation

Essay writing: Main body
- Introductions
- Conclusions
- Analysing questions
- Planning & drafting
- Revising & editing
- Proofreading
- Essay writing videos
Jump to content on this page:
“An appropriate use of paragraphs is an essential part of writing coherent and well-structured essays.” Don Shiach, How to write essays
The main body of your essay is where you deliver your argument . Its building blocks are well structured, academic paragraphs. Each paragraph is in itself an individual argument and when put together they should form a clear narrative that leads the reader to the inevitability of your conclusion.
The importance of the paragraph
A good academic paragraph is a special thing. It makes a clear point, backed up by good quality academic evidence, with a clear explanation of how the evidence supports the point and why the point is relevant to your overall argument which supports your position . When these paragraphs are put together with appropriate links, there is a logical flow that takes the reader naturally to your essay's conclusion.
As a general rule there should be one clear key point per paragraph , otherwise your reader could become overwhelmed with evidence that supports different points and makes your argument harder to follow. If you follow the basic structure below, you will be able to build effective paragraphs and so make the main body of your essay deliver on what you say it will do in your introduction.
Paragraph structure

- A topic sentence – what is the overall point that the paragraph is making?
- Evidence that supports your point – this is usually your cited material.
- Explanation of why the point is important and how it helps with your overall argument.
- A link (if necessary) to the next paragraph (or to the previous one if coming at the beginning of the paragraph) or back to the essay question.
This is a good order to use when you are new to writing academic essays - but as you get more accomplished you can adapt it as necessary. The important thing is to make sure all of these elements are present within the paragraph.
The sections below explain more about each of these elements.

The topic sentence (Point)
This should appear early in the paragraph and is often, but not always, the first sentence. It should clearly state the main point that you are making in the paragraph. When you are planning essays, writing down a list of your topic sentences is an excellent way to check that your argument flows well from one point to the next.

This is the evidence that backs up your topic sentence. Why do you believe what you have written in your topic sentence? The evidence is usually paraphrased or quoted material from your reading . Depending on the nature of the assignment, it could also include:
- Your own data (in a research project for example).
- Personal experiences from practice (especially for Social Care, Health Sciences and Education).
- Personal experiences from learning (in a reflective essay for example).
Any evidence from external sources should, of course, be referenced.

Explanation (analysis)
This is the part of your paragraph where you explain to your reader why the evidence supports the point and why that point is relevant to your overall argument. It is where you answer the question 'So what?'. Tell the reader how the information in the paragraph helps you answer the question and how it leads to your conclusion. Your analysis should attempt to persuade the reader that your conclusion is the correct one.
These are the parts of your paragraphs that will get you the higher marks in any marking scheme.

Links are optional but it will help your argument flow if you include them. They are sentences that help the reader understand how the parts of your argument are connected . Most commonly they come at the end of the paragraph but they can be equally effective at the beginning of the next one. Sometimes a link is split between the end of one paragraph and the beginning of the next (see the example paragraph below).
Paragraph structure video
Length of a paragraph
Academic paragraphs are usually between 200 and 300 words long (they vary more than this but it is a useful guide). The important thing is that they should be long enough to contain all the above material. Only move onto a new paragraph if you are making a new point.
Many students make their paragraphs too short (because they are not including enough or any analysis) or too long (they are made up of several different points).
Example of an academic paragraph
Using storytelling in educational settings can enable educators to connect with their students because of inborn tendencies for humans to listen to stories. Written languages have only existed for between 6,000 and 7,000 years (Daniels & Bright, 1995) before then, and continually ever since in many cultures, important lessons for life were passed on using the oral tradition of storytelling. These varied from simple informative tales, to help us learn how to find food or avoid danger, to more magical and miraculous stories designed to help us see how we can resolve conflict and find our place in society (Zipes, 2012). Oral storytelling traditions are still fundamental to native American culture and Rebecca Bishop, a native American public relations officer (quoted in Sorensen, 2012) believes that the physical act of storytelling is a special thing; children will automatically stop what they are doing and listen when a story is told. Professional communicators report that this continues to adulthood (Simmons, 2006; Stevenson, 2008). This means that storytelling can be a powerful tool for connecting with students of all ages in a way that a list of bullet points in a PowerPoint presentation cannot. The emotional connection and innate, almost hardwired, need to listen when someone tells a story means that educators can teach memorable lessons in a uniquely engaging manner that is common to all cultures.
This cross-cultural element of storytelling can be seen when reading or listening to wisdom tales from around the world...
Key: Topic sentence Evidence (includes some analysis) Analysis Link (crosses into next paragraph)
- << Previous: Introductions
- Next: Conclusions >>
- Last Updated: Nov 3, 2023 3:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/essays
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Write the Body Paragraphs of Argumentative Essay in 2022
by Antony W
November 5, 2021

We’ve covered quite a lot on argumentative essay writing at Help for Assessment.
As of this far, you know how to come up with arguable claims and write a killer introduction for the essay.
You even know how to include a hook in space as small as the introduction paragraph.
But writing an argument goes beyond your ability to hook a reader with your introduction. You also have to work on your body paragraphs to make sure they’re up to the standard.
If this is the first time you’re working on an argumentative essay, it can be a challenge to get the body paragraphs written well.
So in this guide, we’ll show you how to work on the body paragraphs and get the section done right the first time.
Do you need help with your Argumentative Essay?
Get in touch with your professional team of writers.
How to Write The Body Paragraphs Of An Argumentative Essay
The following are the seven steps to help you build up the body paragraphs of your argumentative essay.
1. Start with a Topic Sentence
While we can argue that a topic sentence can appear anywhere in the body paragraph of your essay, it’s best to include at the very beginning.
Think about why the sentence is important based on the context of the thesis statement of your argument. While not necessarily mandatory, you can highlight an argument from the thesis statements to establish a good connection.
Keep in mind that the role of a topic sentence goes beyond showing a connection between your body paragraphs and the statement that summarizes the essay.
Your audience should look at the sentence and see that you’ve moved your argument a level higher. So you have to make your writing as unique as possible.
To be clear, some paragraphs in the body section of your argumentative essay won’t need a topic sentence.
There are instances when it would make a lot of sense to omit it, especially if you’re explaining a series of events where the next paragraph develops a concept that you already introduced.
2. Explain Your Topics Sentence – if Necessary
More often than not, your topic sentence will be self-explanatory and require no further information.
However, if you feel like there’s a need to add more information to make your ideas clear, don’t hesitate to do so. However, don’t go head on adding a big wall of text.
Another one to two sentence should be enough to explain your point.
3. Introduce Your Argument’s Evidence
When writing an argumentative essay , you must include reasonable and objective evidence to support your arguable claims.
Including your evidence to support your position can move your audience to believe that you invested your time to investigate the topic in-depth.
The evidence can be anything, from an anecdote, real life experiences, statistics, as well as quoted materials.
Integrate evidence into your essay in a way that moves your readers from just reading your words to buying into your argument without feeling a logical jolt.
4. Insert and Unpack Your Evidence
Now that you’ve introduced your evidence, it’s time to insert and then unpack it. Quotes make a good option for inserting evidence into the text, although you shouldn’t hesitate to do so using personal examples.
The next thing you need to do is unpack the evidence, and you do so by giving a thorough explanation, which naturally brings out a clear picture about why the evidence is significant to your argument.
Unpacking your evidence increases the credibility of the essay as it shows your audience that you know what you’re talking about even if they won’t agree with you.
Keep in mind that you don’t have a lot of room to unpack your evidence. Mostly, you should keep it as short as 1 to 2 sentences give or take, although you might expand it just a little if the evidence is so complicated that it requires further explanation.
5. Explain Your Evidence
Unpacking your evidence is not good enough. You have to go as far as to explain why it’s important in the first place. In other words, is the evidence that you’ve provided good enough to prove that you have a point?
Your explanation should be objective and debatable, and it’s okay to include your own opinion provided what you write makes sense.
Again, you need to keep your explanation as short as possible. You have a writing space of 1 to 3 sentences.
So pack it only with the most useful information that can convince your audience that you know what you’re talking about.
6. Write a Closing Link
A closing link is the conclusion for each paragraph. This section is a no brainer, so you don’t exactly have to think too much outside the box.
You want the concluding paragraph to assure your audience that your paragraph does indeed add up to the development of your argument. Consider using a strong transition in the closing link.
This helps to maintain the flow of your ideas in a logical order. Not to mention it makes it easy for the reader to move on to the next consequent paragraph without feeling lost.
One of the very important rules when it comes to writing a closing link is to avoid ending with a transition. Start with it instead.
Get Argumentative Essay Writing Help
Now that you know how to write the body section of your argumentative essay, it should be easy for you to complete the project on your own.
However, if you don’t have enough to complete the project and you have a tight deadline to beat, you should consider outsourcing your essay writing work to Help for Assessment.
We have a great team of writers who work hard around the clock to help people like you write great essays in just a short amount of time.
Whether you’ve run of deadlines or you have a topic have no idea how to start, our writers will work with you from start to finish. You can click here to place your order with us.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.4: Writing Introductory and Concluding Paragraphs
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 20635

- Athena Kashyap & Erika Dyquisto
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)

Picture your introduction as a storefront window: You have a certain amount of space to attract your customers (readers) to your goods (subject) and bring them inside your store (discussion). Once you have enticed them with something intriguing, you then point them in a specific direction and try to make the sale (convince them to accept your thesis).
Your introduction is an invitation to your readers to consider what you have to say and then to follow your train of thought as you expand upon your thesis statement.
An introduction serves the following purposes:
- Establishes your voice and tone, or your attitude, toward the subject
- Introduces the general topic of the essay
- Relates the topic to the reader
- States the thesis that will be supported in the body paragraphs
First impressions are crucial and can leave lasting effects in your reader’s mind, which is why the introduction is so important to your essay. If your introductory paragraph is dull or disjointed, your reader probably will not have much interest in continuing with the essay.
Attracting Interest in Your Introductory Paragraph
Your introduction should begin with an engaging statement devised to provoke your readers’ interest. It should also relate to your stance on the topic. In the next few sentences, introduce your reader to the topic by stating general facts or ideas about the subject. As you move deeper into your introduction, you gradually narrow the focus, moving closer to your thesis. Moving smoothly and logically from your introductory remarks to your thesis statement can be achieved using a funnel technique, as illustrated in the following diagram.
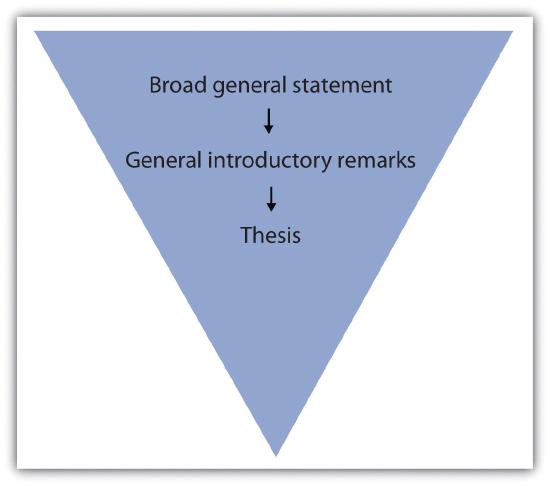
On a separate sheet of paper, jot down a few general remarks that you can make about the topic for which you formed a thesis in Section 5.1, " Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement ."
Immediately capturing your readers’ interest increases the chances of having them read what you are about to discuss. You can garner curiosity for your essay in a number of ways. Try to get your readers personally involved by doing any of the following:
- Appealing to their emotions
- Using logic
- Beginning with a provocative question or opinion
- Opening with a startling statistic or surprising fact
- Raising a question or series of questions
- Presenting an explanation or rationalization for your essay
- Opening with a relevant quotation or incident
- Opening with a striking image
- Including a personal anecdote
Some other ideas are:
- If the topic is controversial, you can include the current state of the controversy. If there is a lot of history to the topic, you can summarize the history.
- If you are writing a personal essay, you can begin with a brief personal anecdote.
- If you are writing an essay that is focused on one or two works (of literature or nonfiction), you can introduce those works with the title(s), author(s), and brief information about those works.
- Describe a brief event that you think illustrates the overall point you want to make with your essay.
- State an interesting fact that others may not know.
- State a shocking but relevant statistic.
- Compare what people generally think to what the reality is.
The Role of Introductions
Introductions and conclusions can be the most difficult parts of papers to write. Usually when students sit down to respond to an assignment, they have at least some sense of what they want to say in the body of the paper. They might have chosen a few examples or have an idea that will help them answer the main question of your assignment: these sections, therefore, are not as hard to write. But these middle parts of the paper can’t just come out of thin air at the reader; they need to be introduced and concluded in a way that makes sense to the reader.
The introduction and conclusion act as bridges that transport readers from their own lives into the “place” of the writer’s analysis. If the readers pick up a paper about education in the autobiography of Frederick Douglass, for example, they need a transition to help them leave behind the world of California, YouTube, e-mail, etc. and to help them temporarily enter the world of nineteenth-century American slavery. By providing an introduction that helps readers make a transition between their own world and the issues in the paper, writers give their readers the tools they need to get into the topic and care about what they are reading. (See this handout on conclusions .)
The trick about how general to begin is to think about your audience. Write a first sentence that everyone can both to your topic and they can relate to personally. Now, how you present that topic – be it a question, a humorous statement, an interesting statistic or a shocking fact – depends on what you think is appropriate for your audience.

Image by Helena Lopes from Pexels
Why Bother Writing a Good Introduction?
You never get a second chance to make a first impression . The opening paragraph of a paper will provide readers with their initial impressions of the argument, the writing style, and the overall quality of work. A vague, disorganized, error-filled, off-the-wall, or boring introduction will probably create a negative impression. On the other hand, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will start your readers off thinking highly of the writer, his analytical skills, the writing, and the paper overall.
Your introduction is an important road map for the rest of your paper . The introduction conveys a lot of information to the readers. They are introduced to the topic, why it is important, and how the topic will be discussed and developed. It also introduces your tone and stance about the topic. In most academic disciplines, the introduction should contain a thesis that will assert the main argument. It should also, ideally, give the reader a sense of the kinds of information used to make that argument and the general organization of the paragraphs and pages that will follow. After reading the introduction, readers should not have any major surprises in store when they read the main body of the paper.
Ideally, your introduction will make your readers want to read your paper . The introduction should capture the readers’ interest, making them want to read the rest of the paper. Opening with a compelling story, a fascinating quotation, an interesting question, or a stirring example can get readers to see why this topic matters and serve as an invitation for them to join an interesting intellectual conversation.
Guidelines: Writing Effective Introductions
1. Start by thinking about the question (or questions) you are trying to answer . Your entire essay will be a response to this question, and your introduction is the first step toward that end. Your direct answer to the assigned question will be your thesis, and your thesis will be included in your introduction, so it is a good idea to use the question as a jumping off point. Imagine that you are assigned the following question:
Education has long been considered a major force for American social change, righting the wrongs of our society. Drawing on the Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, discuss the relationship between education and slavery in 19th-century America. Consider the following: How did white control of education reinforce slavery? How did Douglass and other enslaved African Americans view education while they endured slavery? And what role did education play in the acquisition of freedom? Most importantly, consider the degree to which education was or was not a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
You will probably refer back to your assignment extensively as you prepare your complete essay, and the prompt itself can also give you some clues about how to approach the introduction. Notice that it starts with a broad statement, that education has been considered a major force for social change, and then narrows to focus on specific questions from the book. One strategy might be to use a similar model in your own introduction —start off with a big picture sentence or two about the power of education as a force for change as a way of getting your reader interested and then focus in on the details of your argument about Douglass. Of course, a different approach could also be very successful, but looking at the way the professor set up the question can sometimes give you some ideas for how you might answer it.
2. Decide how general or broad your opening should be. Keep in mind that even a “big picture” opening needs to be clearly related to your topic; an opening sentence that said “Human beings, more than any other creatures on earth, are capable of learning” would be too broad for our sample assignment about slavery and education. If you have ever used Google Maps or similar programs, that experience can provide a helpful way of thinking about how broad your opening should be. The question you are asking determines how “broad” your view should be. In the sample assignment above, the questions are probably at the “state” or “city” level of generality. But the introductory sentence about human beings is mismatched—it’s definitely at the “global” level. When writing, you need to place your ideas in context—but that context doesn’t generally have to be as big as the whole galaxy!
3. Try writing your introduction last . You may think that you have to write your introduction first, but that isn’t necessarily true, and it isn’t always the most effective way to craft a good introduction. You may find that you don’t know what you are going to argue at the beginning of the writing process, and only through the experience of writing your paper do you discover your main argument. It is perfectly fine to start out thinking that you want to argue a particular point, but wind up arguing something slightly or even dramatically different by the time you’ve written most of the paper. The writing process can be an important way to organize your ideas, think through complicated issues, refine your thoughts, and develop a sophisticated argument. However, an introduction written at the beginning of that discovery process will not necessarily reflect what you wind up with at the end. You will need to revise your paper to make sure that the introduction, all of the evidence, and the conclusion reflect the argument you intend. Sometimes it’s easiest to just write up all of your evidence first and then write the introduction last—that way you can be sure that the introduction will match the body of the paper and don't run out of time to revise your introduction.
4. Don’t be afraid to write a tentative introduction first and then change it later. Some people find that they need to write some kind of introduction in order to get the writing process started. That’s fine, but if you are one of those people, be sure to return to your initial introduction later and rewrite if necessary.
5. Open with an attention grabber. Sometimes, especially if the topic of your paper is somewhat dry or technical, opening with something catchy can help. Consider these options:
- an intriguing example (for example, the mistress who initially teaches Douglass but then ceases her instruction as she learns more about slavery)
- a provocative quotation (Douglass writes that “education and slavery were incompatible with each other”)
- a puzzling scenario (Frederick Douglass says of slaves that “[N]othing has been left undone to cripple their intellects, darken their minds, debase their moral nature, obliterate all traces of their relationship to mankind; and yet how wonderfully they have sustained the mighty load of a most frightful bondage, under which they have been groaning for centuries!” Douglass clearly asserts that slave owners went to great lengths to destroy the mental capacities of slaves, yet his own life story proves that these efforts could be unsuccessful.)
- a vivid and perhaps unexpected anecdote (for example, “Learning about slavery in the American history course at Frederick Douglass High School, students studied the work slaves did, the impact of slavery on their families, and the rules that governed their lives. We didn’t discuss education, however, until one student, Mary, raised her hand and asked, ‘But when did they go to school?’ That modern high school students could not conceive of an American childhood devoid of formal education speaks volumes about the centrality of education to American youth today and also suggests the significance of the deprivation of education in past generations.”)
- a thought-provoking question (given all of the freedoms that were denied enslaved individuals in the American South, why does Frederick Douglass focus his attentions so squarely on education and literacy?)
6. Pay special attention to your first sentence . Start off on the right foot with your readers by making sure that the first sentence actually says something useful and that it does so in an interesting and error-free way.
7. Be straightforward and confident . Avoid statements like “In this paper, I will argue that Frederick Douglass valued education.” While this sentence points toward your main argument, it isn’t especially interesting. It might be more effective to say what you mean in a declarative sentence. It is much more convincing to tell us that “Frederick Douglass valued education” than to tell us that you are going to say that he did. Assert your main argument confidently. After all, you can’t expect your reader to believe it if it doesn’t sound like you believe it!
How to Evaluate Your Introduction?
Ask a friend to read it and then tell you what he or she expects the paper will discuss, what kinds of evidence the paper will use, and what the tone of the paper will have. If your friend is able to predict the rest of your paper accurately and wants to keep reading, you probably have a good introduction.
Guidelines: Avoiding Less Effective Introductions
1. The place holder introduction . When you don’t have much to say on a given topic, it is easy to create this kind of introduction. Essentially, this kind of weaker introduction contains several sentences that are vague and don’t really say much. They exist just to take up the “introduction space” in your paper. If you had something more effective to say, you would probably say it, but in the meantime this paragraph is just a place holder. This may what you write just to get yourself writing, but be sure to go back and revise it.
Example: Slavery was one of the greatest tragedies in American history. There were many different aspects of slavery. Each created different kinds of problems for enslaved people.
2. The restated question introduction. Restating the question can sometimes be an effective strategy, but it can be easy to stop at JUST restating the question instead of offering a more specific, interesting introduction to your paper. The professor or teaching assistant wrote your questions and will be reading ten to seventy essays in response to them—thye do not need to read a whole paragraph that simply restates the question. Try to do something more interesting.
Example: Indeed, education has long been considered a major force for American social change, righting the wrongs of our society. The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass discusses the relationship between education and slavery in 19th century America, showing how white control of education reinforced slavery and how Douglass and other enslaved African Americans viewed education while they endured. Moreover, the book discusses the role that education played in the acquisition of freedom. Education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
3. The Dictionary introduction. This introduction begins by giving the dictionary definition of one or more of the words in the assigned question. This introduction strategy is on the right track—if you write one of these, you may be trying to establish the important terms of the discussion, and this move builds a bridge to the reader by offering a common, agreed-upon definition for a key idea. You may also be looking for an authority that will lend credibility to your paper. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and copy down what it says—it may be far more interesting for you (and your reader) if you develop your own definition of the term in the specific context of your class and assignment, or if you use a definition from one of the sources you’ve been reading for class. Also recognize that the dictionary is also not a particularly authoritative work—it doesn’t take into account the context of your course and doesn’t offer particularly detailed information. If you feel that you must seek out an authority, try to find one that is very relevant and specific. Perhaps a quotation from a source reading might prove better? Dictionary introductions are also ineffective simply because they are so overused. Many teachers will see twenty or more papers that begin in this way, greatly decreasing the dramatic impact that any one of those papers will have.
Example: Webster’s dictionary defines slavery as “the state of being a slave,” as “the practice of owning slaves,” and as “a condition of hard work and subjection.”
4. The “dawn of man” introduction. This kind of introduction generally makes broad, sweeping statements about the relevance of this topic since the beginning of time. It is usually very general (similar to the place holder introduction) and fails to connect to the thesis. You may write this kind of introduction when you don’t have much to say—which is precisely why it is ineffective.
Example: Since the dawn of man, slavery has been a problem in human history.
5. The book report introduction. This introduction is what you had to do for your elementary school book reports. It gives the name and author of the book you are writing about, tells what the book is about, and offers other basic facts about the book. You might resort to this sort of introduction when you are trying to fill space because it’s a familiar, comfortable format. It is ineffective because it offers details that your reader already knows and that are irrelevant to the thesis.
Example: Frederick Douglass wrote his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave, in the 1840s. It was published in 1986 by Penguin Books. In it, he tells the story of his life.
Remember that your diction, or word choice, while always important, is most crucial in your introductory paragraph. Boring diction could extinguish any desire a person might have to read through your discussion. Choose words that create images or express action. For more information on diction, or word choice, see Chapter 11, "Clarity, Conciseness, and Style ."
See a student's introduction below with the thesis statement underlined. What do you think of it?
Play Atari on a General Electric brand television set? Maybe watch Dynasty? Or read old newspaper articles on microfiche at the library? Thirty-five years ago, the average college student did not have many options when it came to entertainment in the form of technology. Fast-forward to the twenty-first century, and the digital age has digital technology, consumers are bombarded with endless options for how they do most everything--from buying and reading books to taking and developing photographs. In a society that is obsessed with digital means of entertainment, it is easy for the average person to become baffled. Everyone wants the newest and best digital technology, but the choices are many and the specifications are often confusing.
If you have trouble coming up with a provocative statement for your opening, it is a good idea to use a relevant, attention-grabbing quote about your topic. Use a search engine to find statements made by historical or significant figures about your subject.
Writing at Work
In your job field, you may be required to write a speech for an event, such as an awards banquet or a dedication ceremony. The introduction of a speech is similar to an essay because you have a limited amount of space to attract your audience’s attention. Using the same techniques, such as a provocative quote or an interesting statistic, is an effective way to engage your listeners. Using the funnel approach also introduces your audience to your topic and then presents your main idea in a logical manner.
Reread each sentence in Andi’s introductory paragraph. Indicate which techniques they used and comment on how each sentence is designed to attract the readers’ interest.

Image by Ann H from Pexels
Writing a Conclusion
It is not unusual to want to rush when you approach your conclusion, and even experienced writers may fade. But what good writers remember is that it is vital to put just as much attention into the conclusion as in the rest of the essay. After all, a hasty ending can undermine an otherwise strong essay.
A conclusion that does not correspond to the rest of your essay, has loose ends, or is unorganized can unsettle your readers and raise doubts about the entire essay, just like a book with an ambiguous ending. However, if you have worked hard to write the introduction and body, your conclusion can often be the most logical part to compose.
Many times, writers find that they write a stronger main idea at the beginning of a conclusion on their first draft than they wrote initially. Sometimes this main idea would make a better thesis than what you may have originally had.
The Anatomy of a Strong Conclusion
Keep in mind that the ideas in your conclusion must conform to the rest of your essay. In order to tie these components together, restate your thesis at the beginning of your conclusion in other words. This helps you assemble, in an orderly fashion, all the information you have explained in the body. Rephrasing your thesis reminds your readers of the major arguments you have been trying to prove and also indicates that your essay is drawing to a close. A strong conclusion also reviews your main points in general and emphasizes the importance of the topic. It may also look to the future regarding your topic.
Conclusions are almost opposite in structure from introductions. Conclusions generally start off with your main point (a reworded thesis) and then become more general. Many times, in addition to making a final statement about your main ideas, a conclusion will “look to the future” by discussing how the author hopes this topic will be treated in the future. Other times, a conclusion includes a solution if the essay discusses a problem, or what additional study needs to be done about the topic (especially in research papers). It can also discuss how what your essay is about is relevant in other parts of the world or domains of study.
Many writers like to end their essays with a final emphatic statement. This strong closing statement will cause your readers to continue thinking about the implications of your essay; it will make your conclusion, and thus your essay, more memorable. Another powerful technique is to challenge your readers to make a change in either their thoughts or their actions. Challenging your readers to see the subject through new eyes is a powerful way to ease yourself and your readers out of the essay.
- When closing your essay, do not expressly state that you are drawing to a close. Relying on statements such as in conclusion , it is clear that , as you can see , or in summation is unnecessary and can be considered trite because the reader can obviously see that it's the end of your essay.
- Introducing new material
- Contradicting your thesis
- Changing your thesis
- Using apologies or disclaimers
Introducing new material in your conclusion has an unsettling effect on your reader. When you raise new points, you make your reader want more information, which you could not possibly provide in the limited space of your final paragraph.
Contradicting or changing your thesis statement causes your readers to think that you do not actually have a conviction about your topic. After all, you have spent several paragraphs adhering to a singular point of view. When you change sides or open up your point of view in the conclusion, your reader becomes less inclined to believe your original argument.
By apologizing for your opinion or stating that you know it is tough to digest, you are in fact admitting that even you know what you have discussed is irrelevant or unconvincing. You do not want your readers to feel this way. Effective writers stand by their thesis statement and do not stray from it.
Exercise 3\(\PageIndex{3}\)
On a separate sheet of a paper, restate your thesis from Exercise 2 of this section and then make some general concluding remarks. Next, compose a final emphatic statement. Finally, incorporate what you have written into a strong conclusion paragraph for your essay.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers
Andi incorporates some of these pointers into their conclusion by paraphrasing their thesis statement in the first sentence.
In a society fixated on the latest and smartest digital technology, a consumer can easily become confused by the countless options and specifications. The ever-changing state of digital technology challenges consumers with its updates and add-ons and expanding markets and incompatible formats and restrictions–a fact that is complicated by salesmen who want to sell them anything. In a world that is increasingly driven by instant gratification, it’s easy for people to buy the first thing they see. The solution for many people should be to avoid buying on impulse. Consumers should think about what they really need, not what is advertised.
Make sure your essay is balanced by not having an excessively long or short introduction or conclusion. Check that they match each other in length as closely as possible, and try to mirror the formula you used in each. Structural parallelism strengthens the message of your essay.
On the job you may sometimes give oral presentations based on research you have conducted. A concluding statement to an oral report contains the same elements as a written conclusion. You should wrap up your presentation by restating the
purpose of the presentation, reviewing its main points, and emphasizing the importance of the material you presented. A strong conclusion will leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Contributors and Attributions
- Adapted from Writing for Success. Provided by: The Saylor Foundation. License: CC-NC-SA 3.0
- Introductions . Provided by: UNC Writing Center. License: CC BY-NC-ND
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED CONTENT
" Writing Introductions and Conclusions in an Essay ." Authored by: Karen Hamilton. License: All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube license.
This page most recently updated on June 23, 2020.
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, what's the format for writing a college essay.
Hi everyone! I'm starting to work on my college essays and I'm not sure how to format them. How should I organize my thoughts and present my ideas? Any tips or resources that could help me out? Thanks!
Hi there! It's important to remember that there's no one-size-fits-all format for a college essay, but there are some general guidelines to follow to ensure a well-written and engaging piece.
1. Introduction:
Begin with a hook that captures the reader's attention. This could be a compelling anecdote, a provocative statement, or a thought-provoking question. Then, briefly introduce the main topic of your essay and provide some context for the rest of the piece. Remember that the introduction should be concise and engaging to ensure the reader wants to continue reading.
2. Body paragraphs:
The body of your essay should present your main ideas and supporting arguments. Each paragraph should focus on a single point, and begin with a topic sentence that clearly states the main idea of the paragraph. Provide specific examples, anecdotes, or evidence to support your point, and then analyze or explain the significance of each example.
Remember to use clear, concise language and vary your sentence structure to keep your writing engaging. Use transitions to smoothly connect paragraphs and maintain a logical flow of ideas.
3. Conclusion:
Wrap up your essay by summarizing your main points and restating your thesis or central idea in a slightly different way. Reflect on your essay topic in the broader context, perhaps connecting it to your personal growth, future goals, or the world at large. The conclusion should give the reader a sense of closure and leave a lasting impression.
Some additional tips:
- Stick to the word limit, usually between 250 and 650 words for most college essay prompts.
- Use a readable font (such as Times New Roman or Arial) and employ proper formatting (1-inch margins, double-spaced text) unless otherwise specified.
- Proofread your essay and have someone else (teacher, counselor, or peer) review it for grammar, spelling, and clarity.
- Avoid generic or cliché topics and focus on presenting a unique perspective or telling a specific, personal story.
- Be genuine in your writing, showcasing your voice and personal experiences.
In terms of resources, consider using writing guides and sample essays available online, such as from CollegeVine, or asking for help from your school's writing center. Good luck with your essay writing!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.

Short Narrative Essay
Short narrative essay generator.

Everyone finds it interesting to tell stories about their lives or about someone else’s. Through those stories, we can get lessons which we can apply in our daily lives. This is what a narrative essay is all about. Let’s go back to your experiences when you were still in grade school. Your teacher would often ask you to write about your favorite experiences especially during Christmas season and summer vacation.
Some people would mistakenly identify a narrative essay as equally the same as a descriptive essay . They are totally different from each other, yet both of them are forms of academic writing . Look into this article to learn more about narrative essays.
What is Short Narrative Essay?
A short narrative essay is a brief piece of writing that tells a story, usually focusing on a particular experience, event, or moment. It follows a narrative structure, involving characters, a setting, a plot, and a conclusion, aiming to engage the reader through vivid descriptions and storytelling techniques within a concise format.
Best Short Narrative Essay Examples?
Title: The Summer Adventure
The scorching sun bore down on the dusty road as we embarked on our summer adventure. Packed into the old, battered car, my family and I set off for the great outdoors. The air hummed with anticipation, echoing our excitement for the unknown.
As we traversed winding roads, the landscape unfolded like a painting. Rolling hills adorned with emerald-green trees greeted us, promising the allure of exploration. The scent of pine wafted through the open windows, mingling with laughter and the crackling excitement of adventure.
Our destination? A secluded lakeside campsite embraced by nature’s serenity. The promise of tranquil waters and starlit nights ignited our spirits. Upon arrival, we pitched our weathered tent, a ritual signaling the beginning of our escape from routine.
Days melted into each other, filled with hikes through dense forests, dips in cool, crystal-clear waters, and evenings spent around crackling campfires. We discovered hidden trails, stumbled upon secret meadows, and marveled at nature’s splendid orchestra of sounds and colors.
But amidst the beauty lay unexpected challenges. Unforgiving storms threatened our haven, testing our resilience. Yet, huddled together, we found solace in each other’s company, discovering strength in unity.
As the final sun dipped behind the horizon, casting its golden glow upon the rippling waters, a bittersweet sensation enveloped us. The adventure had drawn to a close, leaving behind cherished memories etched in our hearts.
Reluctantly, we packed our belongings, bidding farewell to the tranquil haven that had nurtured us. With weary but contented hearts, we embarked on the journey back, carrying not just souvenirs but a treasure trove of shared experiences and the promise of future escapades.
The car rolled away from the lakeside, but the echoes of laughter, the scent of pine, and the warmth of togetherness lingered, reminding us of the magical summer adventure that had woven us closer together.
11+ Short Narrative Essay Examples
1. short narrative essay examples.

- Google Docs
Size: 27 KB
2. Narrative Essay Examples

Size: 23.8 KB
3. Short Narrative Essay Template

Size: 465 KB
4. Short Narrative Essay

Size: 117 KB
5. Short Narrative Essay Format

Size: 107 KB
6. The Storm Short Narrative Essay

Size: 48 KB
7. Five-Paragraph Short Narrative Essay

Size: 29 KB
8. Short Narrative Writing Essay

Size: 177 KB
9. College Short Narrative Essay

Size: 589 KB
10. High School Short Narrative Essay Examples

Size: 114 KB
11. College Short Narrative Essay Examples

Size: 130 KB
12. Personal Short Narrative Essay Examples

Size: 105 KB
What is a Narrative Essay?
A narrative essay is a type of academic writing that allows you to narrate about your experiences. This follows a certain outline just like what we have observed in argumentative essays , informative essays and more. The outline consists of the introduction, body paragraph and conclusion.
This is a type of essay that tells a story either from the point of view of the author or from the personal experience of the author. It should also be able to incorporate characteristics such as the ability to make and support a claim, develop specific viewpoint, put conflicts and dialogue in the story, and to use correct information. You may also see personal narrative essay examples & samples
The purpose of a narrative essay is to be able to tell stories may it be real or fictional. To enable us to write a perfect narrative essay, the author should include the necessary components used for telling good stories, a good climax, setting, plot and ending.
How To Write a Narrative Essay?
Compared to all types of academic essay , the narrative essay is the simplest one. It is simply written like the author is just writing a very simple short story. A typical essay has only a minimum of four to five paragraphs contain in the three basic parts: introduction, body paragraph and conclusion. A narrative essay has five elements namely the characters, plot, conflict, setting and theme.
Plot – this tells what happened in the story or simply the sequence of events. There are five types of plot: exposition, rising action, climax, falling action and resolution. The exposition is the an information that tells about background of the story. It can be about the character, the setting, events, etc. Rising action is where the suspense of a story begins. It helps build toward the climax of a story. Climax is the most intense part of the story. Falling action happens after the climax when it is already almost the end of the story. Resolution is the part where the problem has already been resolved.
Characters – it is the person or other being that is a part of the narrative performs an action or speak a dialogue .
Conflict – this is the struggle or the problem that is faced by the characters of the story. This can be an external conflict and an internal conflict. An external conflict is a type of problem that is experienced in the external world. An internal conflict is the type of conflict that refers to the characters’ emotions and argument within itself.
Setting – this is knowing where and when the story takes place. This can be a powerful element because it makes the readers feel like they are the characters in the story.
Theme – this is what the author is trying to convey. Examples of a theme are romance, death, revenge, friendship, etc. It is the universal concept that allows you to understand the whole idea of the story.
How to write a short narrative essay?
- Select a Theme or Experience: Choose a specific event, moment, or experience that you want to narrate.
- Outline the Story: Plan the narrative by outlining the key elements – characters, setting, plot, and a clear beginning, middle, and end.
- Engaging Introduction: Start with a hook to captivate readers’ attention, introducing the setting or characters involved.
- Develop the Plot: Write body paragraphs that progress the story logically, describing events, actions, and emotions, using vivid details and sensory language to immerse readers.
- Character Development: Focus on character traits, emotions, and reactions to make the story relatable and engaging.
- Climax and Resolution: Build tension towards a climax, followed by a resolution or lesson learned from the experience.
- Concise Conclusion: Conclude the essay by summarizing the experience or reflecting on its significance, leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
- Revise and Edit: Review the essay for coherence, clarity, grammar, and punctuation, ensuring it flows smoothly.
What are the 3 parts of a narrative essay?
- Introduction: Sets the stage by introducing the story’s characters, setting, and providing a glimpse of the main event or experience. It often includes a hook to capture the reader’s attention.
- Body: Unfolds the narrative, presenting the sequence of events, actions, emotions, and details that drive the story forward. It develops the plot, characters, and setting.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the narrative, reflecting on the significance of the experience or event, and often delivers a lesson learned or leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
How do you start a narrative essay with examples?
- ” ‘Are we there yet?’ echoed in my ears as our family car trudged along the endless highway, marking the beginning of our unforgettable summer road trip.”
- “The sun dipped low on the horizon, casting a warm, golden hue over the serene lake. It was there, amidst the tranquil waters, that my adventure began.”
- “The deafening roar of applause faded as I stepped onto the stage, my heart racing with anticipation. Little did I know, that moment would change everything.”
- “Looking back, it all started with a single decision. That decision, made in a moment of uncertainty, led to a series of events that transformed my life.”
- “The scent of freshly baked cookies wafted through the air, mingling with the joyous laughter of children. It was a typical afternoon, until an unexpected visitor knocked on our door.”
How do you start a narrative introduction?
You may start by making the characters have their conversation or by describing the setting of the story. You may also give background information to the readers if you want.
What makes a good narrative?
A good narrative makes the readers entertained and engage in a way that they will feel like they are becoming a part of the narrative itself. They should also be organized and should possess a good sequence of events.
How many paragraphs are there in personal narratives?
Usually, there are about five paragraphs.
How many paragraphs are in a short narrative essay?
A short narrative essay typically comprises an introductory paragraph introducing the story, three to four body paragraphs unfolding the narrative, and a concluding paragraph summarizing the experience.
How long is a short narrative essay?
A short narrative essay typically ranges from 500 to 1500 words, aiming to convey a concise and focused story or experience within a limited word count.
Narrative essays are designed to express and tell experiences making it an interesting story to share. It has the three basic parts and contains at least five elements. If you plan to create a good narrative essay, be sure to follow and assess if your narrative has all the characteristics needed to make it sound nice and pleasing.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a Short Narrative Essay on a memorable moment with your family.
Create a Short Narrative Essay about a lesson learned from a mistake.
Writing a Short Essay Quiz
What is the purpose of a thesis statement in a short essay?
Which of the following is NOT a component of a short essay?
What should be included in the introduction of a short essay?
Which of the following is NOT a type of supporting evidence that can be used in a short essay?
How many body paragraphs should a short essay typically have?
Which of the following is NOT a strategy for organizing the body paragraphs of a short essay?
What is the purpose of a conclusion in a short essay?
Which of the following is NOT an important aspect of writing a short essay?
What is the purpose of proofreading and editing a short essay?
Which of the following is a common mistake to avoid when writing a short essay?
Ready to take your next Quiz?


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The body is always divided into paragraphs. You can work through the body in three main stages: Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order. Write a first draft to get your main ideas down on paper. Write a second draft to clarify your arguments and make sure everything fits together.
Avoid cramming too much information into each body paragraph. Paragraph breaks can control your writing's pacing and generate particular feelings or moods for your reader. Revise. Review and proofread each body paragraph. Eliminate any redundancies or unnecessary words to keep your writing concise, clear, and authoritative.
need to take to build your argument. To write strong paragraphs, try to focus each paragraph on one main point—and begin a new paragraph when you are moving to a new point or example. A strong paragraph in an academic essay will usually include these three elements: • A topic sentence. The topic sentence does double duty for a paragraph ...
A body paragraph acts as a connection between the introduction and the conclusion. The body paragraph's role is to justify the thesis stated in the introduction of an essay or article. As mentioned previously it comes between the introduction and the conclusion which is where most of the writing is done. This signifies its importance.
An effective topic sentence— clearly supports the thesis statement.; is usually at the beginning of a body paragraph.; controls the content of all of the supporting sentences in its paragraph.; is a complete sentence.; does not announce the topic (e.g., "I'm going to talk about exercise.").; should not be too general (e.g., "Exercise is good.").; should not be too specific (e.g ...
Purpose of a Body Paragraph. This section is the backbone of any essay. A well-organized structure of the body paragraph helps your writing be readable. That's why organizing the information to achieve this goal is essential. When writing body paragraphs in an essay, you focus on presenting and developing one point that supports the main ...
Kaylen is an experienced writer/translator whose work has been featured in Los Angeles Review, Hybrid, San Francisco Bay Guardian, France Today, and Honolulu Weekly, among others. How to Write a Body Paragraph - we explain the best way to start a body paragraph in a college essay or other school writing assignment.
Step 1: Write a Topic Sentence. Consider the first sentence in a body paragraph a mini-thesis statement for that paragraph. The topic sentence should establish the main point of the paragraph and bear some relationship to the essay's overarching thesis statement. In theory, by reading only the topic sentence of every paragraph, a reader should ...
5.4 Body Paragraphs. The term body paragraph refers to any paragraph that appears between the introductory and concluding sections of an essay. A good body paragraph should support the claim made in the thesis statement by developing only one key supporting idea. Your thesis gives the reader a road-map to your essay, and your body paragraphs ...
A strong thesis statment takes a stand. 2. A strong thesis statement allows for debate. 3. A strong thesis statement is specific. Writing the first essay body paragraph. How not to write a body paragraph. Writing the second essay body paragraph. Conclusion.
Key Takeaways. Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement. Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis. Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis. Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
Writing Body Paragraphs. Follow these steps below to write good body paragraphs. Step 1: Develop a Topic Sentence. Step 2: Provide Evidence to Support your Topic Sentence and Overall Argument. Step 3: Add your Own Analysis and Interpretation. Step 4: Conclude. Step 5: Revise and Proofread. A P.I.E. Paragraph. For Example.
In a body paragraph, the topic sentence is always about the evidence given in the thesis statement of the essay. It could be a claim, an assertion, or a fact needing explanation. It is generally a statement or a declarative sentence. The topic sentence is followed by an explanation and/or an example. Whatever it is, it generally starts with ...
A good paragraph should contain at least the following four elements: T ransition, T opic sentence, specific E vidence and analysis, and a B rief wrap-up sentence (also known as a warrant) -TTEB! A T ransition sentence leading in from a previous paragraph to assure smooth reading. This acts as a hand-off from one idea to the next.
Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you're writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader's attention. You can get a reader's attention by telling a story, providing a statistic ...
Body Paragraphs - Writing as Inquiry. 4c. Body Paragraphs. Body paragraphs present the reasoning and evidence to demonstrate your thesis. In academic essays, body paragraphs are typically a bit more substantial than in news reporting so a writer can share their own ideas, develop their reasoning, cite evidence, and engage in conversation with ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
The importance of the paragraph. A good academic paragraph is a special thing. It makes a clear point, backed up by good quality academic evidence, with a clear explanation of how the evidence supports the point and why the point is relevant to your overall argument which supports your position.When these paragraphs are put together with appropriate links, there is a logical flow that takes ...
The following are the seven steps to help you build up the body paragraphs of your argumentative essay. 1. Start with a Topic Sentence. While we can argue that a topic sentence can appear anywhere in the body paragraph of your essay, it's best to include at the very beginning. Think about why the sentence is important based on the context of ...
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It's worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline. A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Indent the first line of each paragraph of text 0.5 in. from the left margin. Use the tab key or the automatic paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program to achieve the indentation (the default setting is likely already 0.5 in.). Do not use the space bar to create indentation.
States the thesis that will be supported in the body paragraphs; First impressions are crucial and can leave lasting effects in your reader's mind, which is why the introduction is so important to your essay. If your introductory paragraph is dull or disjointed, your reader probably will not have much interest in continuing with the essay.
Remember that the introduction should be concise and engaging to ensure the reader wants to continue reading. 2. Body paragraphs: The body of your essay should present your main ideas and supporting arguments. Each paragraph should focus on a single point, and begin with a topic sentence that clearly states the main idea of the paragraph.
Give a short intro. It should set the topic and outline the essay's purpose. Present a clear thesis statement summarizing the main idea of the entire essay. Body paragraphs. Organize the body paragraphs around logical subtopics related to the essay topic. Start each body paragraph with a topic sentence that aligns with the thesis.
Body Paragraphs. Each body paragraph should focus on a specific aspect or a detail that contributes to the overall picture you are trying to paint. Use the "show, don't tell" technique by employing vivid imagery and sensory details. ... The main purpose of a persuasive essay is to win over the trust of the reader to accept your viewpoint ...
Purpose. The purpose of a narrative essay is to be able to tell stories may it be real or fictional. To enable us to write a perfect narrative essay, the author should include the necessary components used for telling good stories, a good climax, setting, plot and ending. ... Develop the Plot: Write body paragraphs that progress the story ...
A strong paragraph in an academic essay will usually include these three elements: A topic sentence. The topic sentence does double duty for a paragraph. First, a strong topic sentence makes a claim or states a main idea that is then developed in the rest of the paragraph. Second, the topic sentence signals to readers how the paragraph is ...
A lead paragraph (sometimes shortened to lead; in the United States sometimes spelled lede) is the opening paragraph of an article, book chapter, or other written work that summarizes its main ideas. Styles vary widely among the different types and genres of publications, from journalistic news-style leads to a more encyclopaedic variety.
A narrative essay outline can help ensure your writing tells a great story. Use the narrative outline essay template to get started.
How many body paragraphs should a short essay typically have? A short essay typically has one to two body paragraphs. ... Alphabetical order is not a common strategy for organizing the body paragraphs of a short essay. What is the purpose of a conclusion in a short essay?