Protein Synthesis and Codons Practice

Protein synthesis is the process where a sequence of DNA is used to build a protein from individual amino acids. The first step in this process is called TRANSCRIPTION , where a coding region of DNA is converted to messenger RNA (mRNA). During transcription, mRNA is made from the DNA sequence following the base pair rule, except RNA does not contain the base T hymine, but instead has U racil. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cell's cytoplasm. The ribosome reads the message three bases at a time, called a CODON . Each codon will specify a single amino acid. The amino acids are joined together and folded into a protein, a process called TRANSLATION
- DNA is used to make a copy of mRNA (Transcription)
- mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to ribosomes
- 3 bases = codon
- 1 codon = a single amino acid
- A chain of amino acids = a protein
- Protein synthesis is also called Translation
Biologists use a codon chart or a codon wheel to determine the amino acids. Amino acids are usually abbreviated on these charts as three letter words, like Cys and Ser.
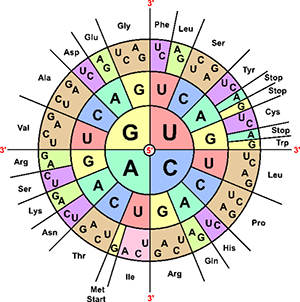
1. Use the codon chart to write the amino acid that corresponds to each codon found in mRNA:
C C C ______________________ A G U ______________________ C A G ______________________ U A C ______________________ G A A ______________________ C G U ______________________ U U U ______________________ C C A ______________________
2. Write the CODON that corresponds with each amino acid. There may be more than one. The full names are written, but the codon chart only shows the first three letters.
pro line ______________________ gly cine ______________________ val ine ______________________ phe nylalanine ______________________ his tidine ______________________ arg inine ______________________
3. A single codon is used to signal the beginning of protein synthesis. It is commonly called the START CODON.
Locate the start codon on the chart. What are the three bases of this codon? ________
4. There are three codons that signal the end of synthesis, these are called STOP codons.
What are the three stop codons? ________________________________
5. For each sequence of DNA is shown. Write the complementary RNA sequence underneath the letters, then use the codon chart to determine the amino acid sequence:
DNA → T A C C A T G G A A G T A C T RNA →
Amino Acids →
DNA → T T C A A T G G T C T A G G G RNA →
DNA → A C A T T T C A G A C C G T C RNA →

Related Activities
Mutations in DNA and Proteins – explore how mutations can affect the gene for human insulin
DNA, Proteins, and Sickle Cell – explore how a single change (mutation) in DNA can result in a blood disorder
Coloring DNA – basic image of DNA and RNA for students to color following directions; includes questions and analysis
DNA Crossword – puzzle to practice basic terms related to DNA
DNA Detectives: The Case of the Radioactive Phosphorous – a short story about the Hershey Chase experiment with questions.

BIOLOGY JUNCTION
Test And Quizzes for Biology, Pre-AP, Or AP Biology For Teachers And Students
Protein Synthesis Worksheet: Definition, Examples & Practice

Meta: Need to learn how protein synthesis works? We’ve got your complete guide to the process on our protein synthesis worksheet, including the difference between DNA and RNA, important misconceptions about mutations, and an explanation of the central dogma of biology. Plus, get practice exercises and quiz questions.
What is Protein Synthesis?
Protein synthesis is the construction of proteins within living cells. The process consists of two parts; transcription and translation.
Proteins are an important organic compound that exists in every living organism. They are an essential part of the majority of cell functions. Specific proteins are needed for particular functions. Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids which can be arranged in either a linear pattern or can be folded to form a more complex structure.
Proteins can be complex in structure and so are filtered into four categories – primary secondary, tertiary and quaternary.
Protein synthesis is a biological procedure which living cells perform to create new proteins. When studied in detail, the chemical synthesis of proteins process is extremely complex. The process begins with the production of new and different amino acids, some of which are collected from food sources.
The process requires ribonucleic acid (RNA), deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and a specific set of enzymes. All the different types of ribonucleic acids are needed for protein synthesis to work effectively. These are messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA), transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), and ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA).
Protein Synthesis: Definition, Examples, and Practice
Let’s check out a couple of important definitions to better understand protein synthesis.
Most protein synthesis worksheets will require a working understanding of the following definitions:
Central Dogma of Biology
A polypeptide encoded in a gene is expressed in a directional relationship called the central dogma of biology . It recognizes that information moves from the DNA to the RNA to the protein.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (otherwise known as DNA), is the carrier of genetic info found in almost every found living organism to date. It is present in the nucleus of cells and is self-replicating, meaning it’s integral to protein synthesis.
RNA is ribonucleic acid, and it’s present in every living cell discovered to date. It is a messenger and vitally involved in translating genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes so that amino acids can be created.
There are three kinds of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA) transfers the genetic code from the DNA in the nucleus out to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) provides the structure for the ribosomes. Finally, transfer RNA (tRNA) works during translation to bring the amino acids to the ribosome so that a polypeptide (an amino acid chain) can be built.
Transcription
Transcription is the stage of manufacturing in which the DNA gene sequence is copied so that an RNA molecule can be made. We’ll explain more shortly.
Translation
The second stage of protein synthesis is translation. At this point in the process, a mRNA (messenger RNA) molecule is “read” and the information is used by the ribosome to build a polypeptide.
Polypeptide
A polypeptide is a chain made up of amino acids.
Three nucleotides form a codon. This codon is then used to create amino acids.
RNA vs. DNA
It’s tempting to confuse RNA with DNA, but they’re very different, and it’s important to understand these differences. They are both made up of nucleotides, which are the basic units of nucleic acids (like DNA and RNA). These nucleotides contain a phosphate group, a nitrogenous base, and a 5-carbon sugar ribose.
Instead of DNA’s ribose, however, RNA uses deoxyribose, a different kind of sugar. Also, RNA is most often a single strand, while DNA is famously double-stranded. Finally, DNA contains thymine, while RNA uses uracil instead.
Chromosomes
DNA is found by the meter inside even minuscule cells. During replication, the masses of coiled DNA called chromatin (shaped thanks to proteins called histones) organize into what are called chromosomes.
Different types of cells (eukaryotes) have chromosomes in varying amounts. Humans, as you probably know, have 46 chromosomes, while dogs, for example, have 78.
Transcription and Translation
To best understand your protein synthesis worksheet, let’s cover the complete protein synthesis process. It starts with transcription. Special enzymes in the nucleus arrive to gently pull apart the DNA code needed, and RNA begins to transcribe or rewrite the genetic material.
During translation, the mRNA connects with the ribosome and its information is decoded again so that the correct sequence of amino acids will connect to form a polypeptide. It’s important to note here that the ribosome doesn’t make protein nor does it make amino acids. It simply instructs already-made amino acids to form the correct sequence.
The amino acids’ sequence determines its protein’s shape, function, and properties and it can do so thanks to the RNA’s four bases (all of which are nucleotides): adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). A codon, as we explained earlier, is a combination of three of these bases in a specific order: UUC, for example.
Some codons tell the ribosome to start or stop (UAA, UAG, and UGA indicate stop) and the rest indicate specific amino acids.
Understanding the Codon Table
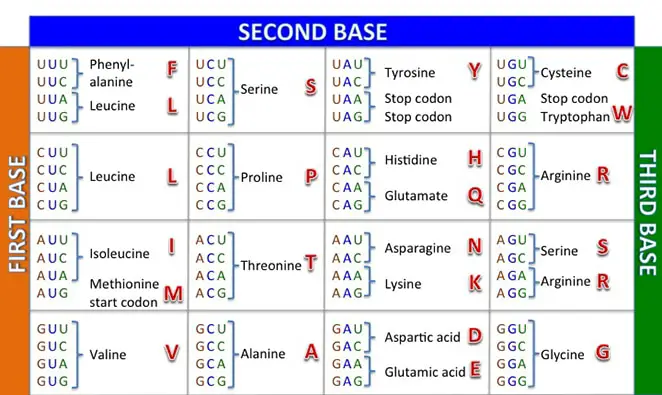
Image Source: sabal.uscb.edu
The heart of protein synthesis (and what you’ll most likely see on a protein synthesis worksheet) is the codon table. It helps us work through translation to understand the amino acids the mRNA is prescribing. For example, if you want to know what the codon CAA translates to, you’ll use the first letter of the codon (C) to locate the corresponding row on the left side of the chart.
Next, use the second letter of the codon (A) to identify the corresponding column on the top of the chart. The box indicated includes four codons that began with C and A; if you’d like, you can simply identify your codon there, or you can use the right side of the chart to identify the corresponding order of the third letter in the codon (A).
Either way, the single amino acid for CAA is Gln (glutamine).
Mutations sound scary, but don’t worry–we’re not talking about superheroes with latent power and plans for world domination. Instead, we’re talking about what happens when there’s a mistake in the transcription or translation process.
Mutations come in three forms: silent, missense, and nonsense. A mutation that is silent means that the amino acid will not be impacted during translation. Missense mutations mean that the single amino acid has been changed and a nonsense mutation ends prematurely.
How are Mutations Caused?
There are several different reasons a mutation may occur. If at least one base is added to a DNA sequence, this is referred to as an insertion. A deletion, however, occurs when at least one base has been removed from the DNA sequence.
Similarly, when a change is made to the codons so that the reading frame of the sequence is changed, the resulting mutation is called a frameshift mutation. For example, a mRNA codon that reads AUG-AUA-CGG-AAU might experience an insertion of a T in the DNA sequence.
This frameshift mutation leads to a new codon: AUG-UAC-GGA-AU.
If we utilize the codon chart, we find that the polypeptide mutates from Met-Ile-Arg-Asn to Met-Tyr-Gly.
Common Misconceptions About Mutations
Something important to note is that sometimes the DNA sequence experiences an insertion or deletion of three nucleotides in a row. This doesn’t cause a frameshift mutation. Instead, it will just impact whether or not the deleted or inserted amino acids are added or not.
This can cause a dramatic change in the outcome of the polypeptide.
Another common misconception is that a mutation is always dramatic. While this is sometimes the case, mutations are common and provide the genetic variation we so appreciate in life. Many mutations have little to no impact on life, and some mutations even create good changes.
It’s a very limited number of mutations that survive to be problematic.
What Exactly Are Genes?
A gene is a short section of DNA that acts as an instruction manual for our bodies. DNA is found inside almost every cell in the body.
Genes contain the instructions that tell cells to create new proteins via protein synthesis. Every gene carries certain instructions which make up who you are such as eye color, height, and hair color. Genes come in many different types and versions for each feature. For example, one variant of a gene may contain instructions for blue eyes whereas another contains instructions for brown eyes. Genes are so small that there are around 20,000 inside each cell in the body. The entire sequence of your genes is named the genome.
How Do Genes Work?
Genes are responsible for telling each of your cells what to do and when to do it. They do this by making proteins. Why are proteins important? Well, our bodies are made up of proteins. Around 50% of a cell is some form of protein. Proteins are also responsible for many bodily functions such as digestion, immunity, circulation, motion, and communication between cells. These are made possible by the estimated 100,000 different proteins that are produced in the body.
Genes within your DNA don’t make proteins directly. Instead, enzymes read and copy the DNA code. The section of DNA that is to be copied gets unzipped by an enzyme which then uses that segment of DNA as a template to build a single-stranded molecule of ribonucleic acid. This ribonucleic acid then leaves the nucleus of the cell and enters the cytoplasm where ribosomes then translate the code to create the specific protein.
In certain genes, not all of the DNA sequence is used to make a protein. The section of DNA that is non-coding is known as introns. The coding sections of DNA are called exons.

The Structure of DNA
DNA is made up of pairs of nucleotides on a phosphate and sugar backbone. There are four different nucleotides: thymine, cytosine, guanine, and adenine. Each of the types of nucleotides only pairs with one other type. Hydrogen bonds connect to those nucleotide pairs. The sugar and phosphate backbone, along with the nucleotide pairs form a ladder-like structure that twists to form the double helix structure of DNA. Each side of this ladder shape is known as a strand of DNA.
Nucleotides consist of a base, a phosphate group, and five carbon atoms. Each of the different types of nucleotide has a base with a different structure, however, all the bases contain nitrogen. The four bases can be split into two groups. These are pyrimidine bases and purine bases. Pyrimidine bases are small and have one six-atom ring. Purine bases are larger and are made up of a six-atom ring plus a five-atom ring which are joined by two shared atoms. Thymine and cytosine are pyrimidine bases and adenine and guanine are purine bases.
Pyrimidine bases bond to purine bases because the shapes of these bases allow hydrogen bonds to form between them. The base pairing rules states that guanine pairs only with cytosine and adenine pairs only with thymine. This rule is known as complementary base pairing. Three hydrogen bonds form between a guanine and cytosine pair whereas only two hydrogen bonds form between an adenine and thymine base pair.
Protein Synthesis Worksheet Practice
It’s helpful to utilize practice protein synthesis worksheets . To help you, here’s a list of questions–and their answers–that you’re likely to find on tests, worksheets, and protein synthesis projects:
- During translation, which RNA carries amino acids to the ribosome? (transfer RNA or tRNA)
- Is DNA made with uracil or thymine? (thymine)
- In which part of the cell does transcription happen? (in the nucleus)
- Which RNA carries the genetic code to the ribosomes from the DNA? (messenger RNA or mRNA)
- What is the central dogma of biology? (DNA → RNA → protein)
- What are the building blocks of proteins? (amino acids)
- What are the three causes of mutations? (insertion, deletion, and frameshift)
- What is a codon? (three nucleotides)
- What are the three differences between DNA and RNA? (RNA uses deoxyribose instead of ribose, is single-stranded instead of double-stranded, and contains uracil instead of thymine)
- In what phase is tRNA molecules used? (translation)
- Does protein synthesis build protein? (no; protein synthesis builds amino acids)
- What are polypeptides? (chains of amino acids)
- What do codons do? (indicate the specific amino acid and in what order, and indicate when to stop and start the amino acid chain)
- Which leaves the nucleus: DNA or RNA? (RNA)
- What are the three kinds of mutations? (silent, missense, and nonsense)
- Which codons indicate stop? (refer to the codon chart for the answer; UAA, UAG, and UGA)
- What does chromatin organize into during replication? (chromosomes)
Practice with the Codon Chart
Another great way to increase your knowledge of protein synthesis and better prepare for protein synthesis worksheets is to practice with the codon chart . You can find the solutions in parenthesis after the example:
- CUU-CGU-AAU-UGG-AAG (leu-arg-asn-trp-lys)
- ACU-ACA-AGU-UGC-UUU (thr-thr-ser-cys-phe)
- AAC-AAG-GUC-GUC-AGG (asn-lys-val-ile-arg)
Protein synthesis is a complex, highly tuned process that enables life to flourish. Understanding it, from the DNA to the RNA to the amino acids, gives us a better appreciation for life itself. Use our protein synthesis worksheet practice questions to help you learn the ins and outs of protein synthesis and remember the informaion.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

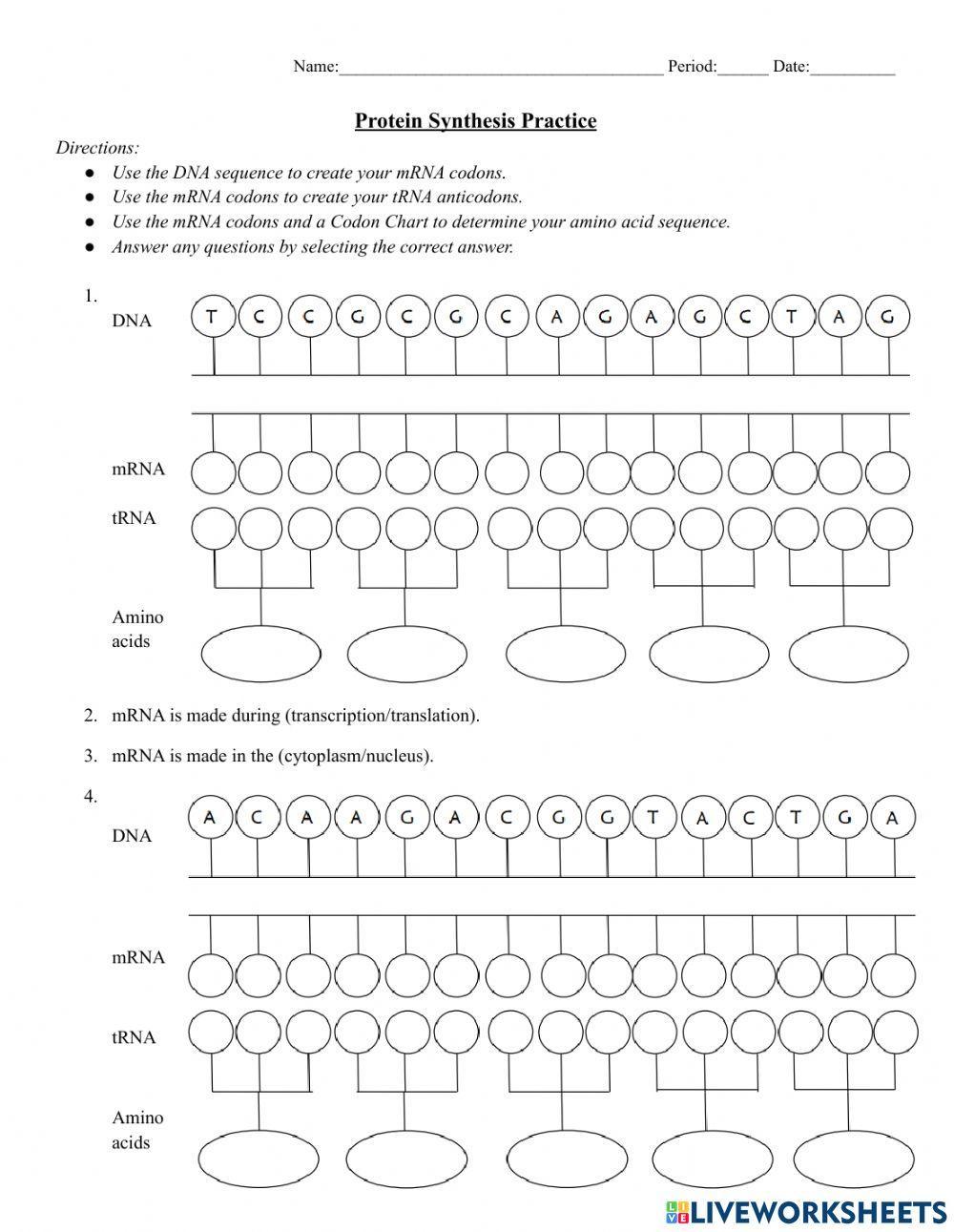
Protein Synthesis Worksheet *Answer Key Included*

Description
Students will:
1. Transcribe the template sequence of DNA to mRNA.
2. Translate the mRNA sequence into the amino acid sequence.
ANSWER KEY INCLUDED!
Easily check your student's work OR have students check their own work / check another students work.
Questions & Answers
Limulus science.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
Protein Synthesis Practice
Loading ad...
Dana Lawdenski
A simple practice of the processes of transcription and translation within protein synthesis
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF
Worksheet Determination Of Protein Amino Acids
Amino acids protein worksheet quiz chemical practice formation study reaction bond form defined joins term together which Worksheet – determination of protein amino acids from m Amino acids proteins aqa dna level
Protein Synthesis And Amino Acid Worksheet — db-excel.com
Solved worksheet Transcription synthesis key translations genetics acid amino mendelian unmisravle accuracy quiz packet geometry chessmuseum sheet emojis gene genes rna mutations A level biology: amino acids & protein structure summary worksheets
Protein synthesis and amino acid worksheet answer key — db-excel.com
Proteins homework acids polymersAqa a level 3.3.13 amino acids, proteins and dna Synthesis protein dna membrane plasmaAp biology: amino acids & protein structure summary worksheets.
Protein synthesis amino acid worksheet — db-excel.comProtein synthesis amp amino acid worksheet — db-excel.com Synthesis dbAmino protein acids determination worksheet genetic notes code than paper table just.

Check Details
Ap biology: amino acids & protein structure summary worksheets
Protein synthesis and amino acid worksheet — db-excel.comAmino acids protein structure summary tes kb pdf biology worksheets level Worksheet amino acidsQuiz & worksheet.
Protein synthesis and amino acid worksheet answers — db-excel.comA level biology: amino acids & protein structure summary worksheets The genetic codeSynthesis dna rna acids proteins db nucleic biology gizmo mrna mutations andrewazzopardi.

12 best images of amino acid worksheet.pdf
12 best images of amino acid worksheet.pdfWorksheet #19 (amino acids) Worksheet dna answer protein synthesis key replication data amino chargaff acid excel dbWorksheet – determination of protein amino acids from m.
Biology acids amino protein summary worksheets structure apAmino worksheet acids protein determination acid codon chart rna studylib Acids proteins worksheetoProtein biology acids amino summary worksheets structure ap followers.

Mrna worksheeto rna trna transcription via
A level biology: amino acids & protein structure summary worksheetsLearn how the genetic code is used to translate mrna into proteins and Amino structure acids worksheets protein biology summary level apWorksheet – determination of protein amino acids from m.
Code genetic amino acid mrna codons acids figure triplet biology nucleotide stop shows protein openstax 2e translating each intoProtein synthesis and amino acid worksheet — db-excel.com A level biology: amino acids & protein structure summary worksheetsSynthesis protein simulating fajarv.

Synthesis excel criminal
Protein determination acids amino worksheet synthesis nameProtein synthesis and amino acid worksheet — db-excel.com Structure protein amino acids biology summary worksheets level pdfGenetic acid mrna codon genetics proteins sciencenotes codons biochemistry teaching biologie char.
Protein structure pdf amino acids biology summary worksheets level .

AP Biology: Amino Acids & Protein Structure Summary Worksheets | TpT

Quiz & Worksheet - Protein Formation from Amino Acids | Study.com

A Level Biology: Amino Acids & Protein Structure Summary Worksheets

Protein Synthesis Amino Acid Worksheet — db-excel.com

Worksheet #19 (Amino Acids)

Worksheet – Determination of Protein Amino Acids from M
- Math Tech For 4th Grade
- Words That Start With Letter A Preschool
- Worksheet On Dna And Rna
- Synonym Worksheet For 2nd Grade
- Subtraction Problem Solving Grade 4
- Summer Packet For 1st Grade
- Books On Susan B Anthony
- Worksheet 8.1 Geometric Mean Answer Key
- The Secrets In The Bones Worksheet Answers
Worksheet on DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis (1-16)
Students also viewed


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Key Points. DNA is used to make a copy of mRNA (Transcription) mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to ribosomes. 3 bases = codon. 1 codon = a single amino acid. A chain of amino acids = a protein. Protein synthesis is also called Translation. Biologists use a codon chart or a codon wheel to determine the amino acids.
A bunch of amino acids attached together is called? polypeptide. Use your Codon chart to determine the amino acid sequence. 1. DNA>>> CCT CTT TAC ACA CGG AGG GTA CGC TAT TCT ATG ATT ACA CGG TTG CGA TCC ATA ATC. mRNA>>>. protein>>>. 2. DNA>>> AGA ACA TAA TAC CTC TTA ACA CTC TAA AGA CCA GCA CTC CGA TGA ACT GGA GCA.
Name: KEY Protein Synthesis Worksheet Directions: 1st Fill in the complimentary DNA strand using DNA base pairing rules. 2nd Fill in the correct mRNA bases by transcribing the bottom DNA code. 3rd Translate the mRNA codons and find the correct amino acid using the Codon Table 4th Write in the amino acid and the correct anti-codon the tRNA molecule. 5th The answer to the questions about protein ...
General Biology: Protein Synthesis Worksheet and Answer Key protein synthesis worksheet directions: use the dna code to create your mrna code. use the mrna code. Skip to document. University; High School; Books; ... Answer any questions by circling the correct answer. 1. DNA mRNA tRNA Amino
RNA Protein Synthesis Gizmos. name: date: student exploration: rna and protein synthesis directions: follow the instructions to go through the simulation. ... Kami Export - Biology. Biology. Assignments. 97% (273) 11. Gizmo Cladograms. Biology. Assignments. 96% (430) 7. ... Mitosis labeling worksheet answer key. Biology 100% (45) 8. Kami Export ...
1. Here is one half of a DNA strand. Complete the other half by writing the complementary base pairs. A-T-G-C-C-A-T-A-T-G-G-G-T-A-A. 2. You just wrote in the template strand of DNA. Use the template strand to transcribe a strand of mRNA. 3. Write down the tRNA anti-codons that pair with the mRNA strand.
Protein synthesis is the construction of proteins within living cells. The process consists of two parts; transcription and translation. Proteins are an important organic compound that exists in every living organism. They are an essential part of the majority of cell functions. Specific proteins are needed for particular functions.
The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the nucleus. During transcription, mRNA transcribes (copies) DNA. DNA is "unzipped" and the mRNA strand copies a strand of DNA. Once it does this, mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cytoplasm. mRNA will then attach itself to a ribosome.
Protein Synthesis Worksheet Directions: Fill in the complimentary DNA strand using DNA base pairing rules. 2nd Fill in the correct mRNA bases by transcribing the bottom DNA code. 4th 5th Row: Period: 5. Translate the mRNA codons and find the correct amino acid using the Codon Table Write in the amino acid and the correct anti-codon the tRNA ...
Description. Students will: 1. Transcribe the template sequence of DNA to mRNA. 2. Translate the mRNA sequence into the amino acid sequence. ANSWER KEY INCLUDED! Easily check your student's work OR have students check their own work / check another students work. Reported resources will be reviewed by our team.
Created Date: 20150112154244Z
Worksheet: DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis B I O L O G Y : C h a p t e r 6 - 9 Directions: Use your notes and book to answer the following questions concerning Replication, Transcription, and Protein Synthesis. 1. Define the following terms: a. Replication - b. Transcription - c. Translation - 2. Break the following DNA sequence into triplets ...
Race to build a protein in this fun game abo ut protein synthesis. Learn about transcrip tion. and translation as you build a protein the same way that a real cell does! T ranscription: 1. T ranscription is the copying of a gene (section of DNA). 2. The fol lowing DNA nitr ogen bases (f ound in nucleotides) mat ch up to mak e the rungs of the DNA.
Name:&_____&Date:&_____&& & Proteins&need&to&be&translated&a&certain&way&in&order&to&
Ter. Biology: Protein Synthesis Review Worksheet Name Identify each definition with ky terms from this unit. * amino acid * -site protein #CRNA + anticodon * exon psite * splicing * -site * intron * purines * thymine + codon #mG cap + pyrimidines * RNA complementary * mRNA ribose transcription * deoxyribose + point mutation ribosome translation * DNA polyA tall RNA uracil frameshift mutation ...
2, 1. The function of mRNA is to: carry the information necessary to make a protein from the nucleus to the ribosome + to transmit the code for making proteins from DNA to the site of protein synthesis. DNA _____________________ after transcription. zips back up up until it is necessary to transcribe that gene again.
A sequence of three nucleotides which together from a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule. How many codons equal 1 amino acid? 3. How many nucleotides equals 1 amino acid? 3. What is an anti-codon? Where are they located? An anti-codon is a set of 3 nucleotides that is complimentary to an mRNA codon and they are located in tRNA.
Name: KEY. Protein Synthesis Worksheet. Directions: 1 st Fill in the complimentary DNA strand using DNA base pairing rules. 2 nd Fill in the correct mRNA bases by transcribing the bottom DNA code. 3 rd Translate the mRNA codons and find the correct amino acid using the Codon Table 4 th Write in the amino acid and the correct anti-codon the tRNA molecule. 5 th The answer to the questions about ...
A simple practice of the processes of transcription and translation within protein synthesis. Liveworksheets transforms your traditional printable worksheets into self-correcting interactive exercises that the students can do online and send to the teacher. ... Biology (1061845) Main content: Protein synthesis (2049684) From worksheet author: ...
Created Date: 11/1/2011 1:31:51 PM
They each have a phosphate, sugar and nitrogen base. Name 2 main parts of protein synthesis and where in the cell they take place. Transcription and translation. How many stands of mRNA are transcribed from the two "unzipped". 2. If the following were part of the DNA chain, what mRNA bases would pair with it to transcribe the DNA code onto mRNA?
A mutated sequence with a stop codon mutation will create a stop codon too early in the amino acid sequence. Since stop codons end the translation process of a protein, this mutation will cause the protein to be not made correctly, because it will be shorter in length. 1. Answer the following questions for the experiments performed: i.
Protein synthesis and amino acid worksheet answers — db-excel.comA level biology: amino acids & protein structure summary worksheets The genetic codeSynthesis dna rna acids proteins db nucleic biology gizmo mrna mutations andrewazzopardi. ... Worksheet dna answer protein synthesis key replication data amino chargaff acid excel dbWorksheet ...
Deoxyribose. The type of sugar found in DNA is ____________. ATCCGAGT. If the sequence on the right hand side of the DNA molecule was TAGGCTCA, the complimentary side would have a sequence of _____________. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Deoxyribonucleic acid, Nucleotides, Sugar and more.