
www.springer.com The European Mathematical Society
- StatProb Collection
- Recent changes
- Current events
- Random page
- Project talk
- Request account
- What links here
- Related changes
- Special pages
- Printable version
- Permanent link
- Page information
- View source

Assignment problem
The problem of optimally assigning $ m $ individuals to $ m $ jobs. It can be formulated as a linear programming problem that is a special case of the transport problem :
maximize $ \sum _ {i,j } c _ {ij } x _ {ij } $
$$ \sum _ { j } x _ {ij } = a _ {i} , i = 1 \dots m $$
(origins or supply),
$$ \sum _ { i } x _ {ij } = b _ {j} , j = 1 \dots n $$
(destinations or demand), where $ x _ {ij } \geq 0 $ and $ \sum a _ {i} = \sum b _ {j} $, which is called the balance condition. The assignment problem arises when $ m = n $ and all $ a _ {i} $ and $ b _ {j} $ are $ 1 $.
If all $ a _ {i} $ and $ b _ {j} $ in the transposed problem are integers, then there is an optimal solution for which all $ x _ {ij } $ are integers (Dantzig's theorem on integral solutions of the transport problem).
In the assignment problem, for such a solution $ x _ {ij } $ is either zero or one; $ x _ {ij } = 1 $ means that person $ i $ is assigned to job $ j $; the weight $ c _ {ij } $ is the utility of person $ i $ assigned to job $ j $.
The special structure of the transport problem and the assignment problem makes it possible to use algorithms that are more efficient than the simplex method . Some of these use the Hungarian method (see, e.g., [a5] , [a1] , Chapt. 7), which is based on the König–Egervary theorem (see König theorem ), the method of potentials (see [a1] , [a2] ), the out-of-kilter algorithm (see, e.g., [a3] ) or the transportation simplex method.
In turn, the transportation problem is a special case of the network optimization problem.
A totally different assignment problem is the pole assignment problem in control theory.
- This page was last edited on 5 April 2020, at 18:48.
- Privacy policy
- About Encyclopedia of Mathematics
- Disclaimers
- Impressum-Legal
The assignment problem revisited
- Original Paper
- Published: 16 August 2021
- Volume 16 , pages 1531–1548, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
- Carlos A. Alfaro ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9783-8587 1 ,
- Sergio L. Perez 2 ,
- Carlos E. Valencia 3 &
- Marcos C. Vargas 1
937 Accesses
4 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
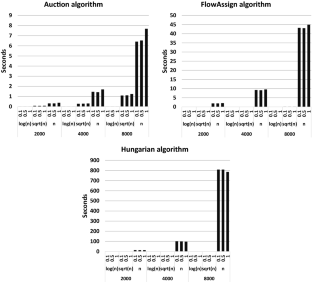
First, we give a detailed review of two algorithms that solve the minimization case of the assignment problem, the Bertsekas auction algorithm and the Goldberg & Kennedy algorithm. It was previously alluded that both algorithms are equivalent. We give a detailed proof that these algorithms are equivalent. Also, we perform experimental results comparing the performance of three algorithms for the assignment problem: the \(\epsilon \) - scaling auction algorithm , the Hungarian algorithm and the FlowAssign algorithm . The experiment shows that the auction algorithm still performs and scales better in practice than the other algorithms which are harder to implement and have better theoretical time complexity.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

An exhaustive review of the metaheuristic algorithms for search and optimization: taxonomy, applications, and open challenges
Kanchan Rajwar, Kusum Deep & Swagatam Das
Solving Maxmin Optimization Problems via Population Games
Anne G. Balter, Johannes M. Schumacher & Nikolaus Schweizer

The Frank-Wolfe Algorithm: A Short Introduction
Sebastian Pokutta
Bertsekas, D.P.: The auction algorithm: a distributed relaxation method for the assignment problem. Annal Op. Res. 14 , 105–123 (1988)
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Bertsekas, D.P., Castañon, D.A.: Parallel synchronous and asynchronous implementations of the auction algorithm. Parallel Comput. 17 , 707–732 (1991)
Article Google Scholar
Bertsekas, D.P.: Linear network optimization: algorithms and codes. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (1991)
MATH Google Scholar
Bertsekas, D.P.: The auction algorithm for shortest paths. SIAM J. Optim. 1 , 425–477 (1991)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Auction algorithms for network flow problems: a tutorial introduction. Comput. Optim. Appl. 1 , 7–66 (1992)
Bertsekas, D.P., Castañon, D.A., Tsaknakis, H.: Reverse auction and the solution of inequality constrained assignment problems. SIAM J. Optim. 3 , 268–299 (1993)
Bertsekas, D.P., Eckstein, J.: Dual coordinate step methods for linear network flow problems. Math. Progr., Ser. B 42 , 203–243 (1988)
Bertsimas, D., Tsitsiklis, J.N.: Introduction to linear optimization. Athena Scientific, Belmont, MA (1997)
Google Scholar
Burkard, R., Dell’Amico, M., Martello, S.: Assignment Problems. Revised reprint. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA (2011)
Gabow, H.N., Tarjan, R.E.: Faster scaling algorithms for network problems. SIAM J. Comput. 18 (5), 1013–1036 (1989)
Goldberg, A.V., Tarjan, R.E.: A new approach to the maximum flow problem. J. Assoc. Comput. Mach. 35 , 921–940 (1988)
Goldberg, A.V., Tarjan, R.E.: Finding minimum-cost circulations by successive approximation. Math. Op. Res. 15 , 430–466 (1990)
Goldberg, A.V., Kennedy, R.: An efficient cost scaling algorithm for the assignment problem. Math. Programm. 71 , 153–177 (1995)
MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Goldberg, A.V., Kennedy, R.: Global price updates help. SIAM J. Discr. Math. 10 (4), 551–572 (1997)
Kuhn, H.W.: The Hungarian method for the assignment problem. Naval Res. Logist. Quart. 2 , 83–97 (1955)
Kuhn, H.W.: Variants of the Hungarian method for the assignment problem. Naval Res. Logist. Quart. 2 , 253–258 (1956)
Lawler, E.L.: Combinatorial optimization: networks and matroids, Holt. Rinehart & Winston, New York (1976)
Orlin, J.B., Ahuja, R.K.: New scaling algorithms for the assignment ad minimum mean cycle problems. Math. Programm. 54 , 41–56 (1992)
Ramshaw, L., Tarjan, R.E., Weight-Scaling Algorithm, A., for Min-Cost Imperfect Matchings in Bipartite Graphs, : IEEE 53rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. New Brunswick, NJ 2012 , 581–590 (2012)
Zaki, H.: A comparison of two algorithms for the assignment problem. Comput. Optim. Appl. 4 , 23–45 (1995)
Download references

Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by SNI and CONACyT.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Banco de México, Mexico City, Mexico
Carlos A. Alfaro & Marcos C. Vargas
Mountain View, CA, 94043, USA
Sergio L. Perez
Departamento de Matemáticas, CINVESTAV del IPN, Apartado postal 14-740, 07000, Mexico City, Mexico
Carlos E. Valencia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Carlos A. Alfaro .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
There is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The authors were partially supported by SNI and CONACyT.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Alfaro, C.A., Perez, S.L., Valencia, C.E. et al. The assignment problem revisited. Optim Lett 16 , 1531–1548 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-021-01791-4
Download citation
Received : 26 March 2020
Accepted : 03 August 2021
Published : 16 August 2021
Issue Date : June 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-021-01791-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Assignment problem
- Bertsekas auction algorithm
- Combinatorial optimization and matching
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The assignment problem is a special case of the transportation problem, which is a special case of the minimum cost flow problem, which in turn is a special case of a linear program. While it is possible to solve any of these problems using the simplex algorithm , each specialization has a smaller solution space and thus more efficient ...
Assignment problem. The problem of optimally assigning $ m $ individuals to $ m $ jobs. It can be formulated as a linear programming problem that is a special case of the transport problem : maximize $ \sum _ {i,j } c _ {ij } x _ {ij } $. subject to. $$ \sum _ { j } x _ {ij } = a _ {i} , i = 1 \dots m $$. (origins or supply),
The assignment problem is a special case of the transportation problem where the supply from every source and the demand at every sink are equal to 1. Such a situation arises naturally in the setting of assigning workers to jobs, or of assigning workers to a time schedule.
Matrix model of the assignment problem. The network model is in Fig. 13. It is very similar to the transportation model except the external flows are all +1 or -1. The only relevant parameter for the assignment model is arc cost (not shown in the figure for clarity) ; all other parameters should be set to default values.
Assignment problems (covered under this chapter) The assignment problem is a special case of transportation problem in which the objective is to assign a number of origins to the equal number of destinations at the minimum cost(or maximum profit). Assignment problem is one of the special cases of the transportation problem.
This video explains a simple example of Unbalanced Matrix,which is one of the special/exceptional cases in Assignment Problems. Please watch this video till ...
As assignment is a special case of transportation problem, it can also be solved using transportation model discussed in module 3. The solution obtained by applying this method would be degenerate. This is because the optimality test in the transportation method requires that there must be m+n-1= (2n-1) basic variables.
Connection Between Transportation and Assignment Problem An assignment problem is a special case of transportation problem in which m = n, all a i and b j are unity and each is limited to either 0 or 1. Hungarian Method for Solving an Assignment Problem 1. Prepare a square n n matrix. If not, make it square by adding suitable number of dummy ...
The assignment problems are a well-studied topic in combinatorial optimization. These problems find numerous applications in production planning, telecommunication VLSI design, economic etc. The assignment problem is a special case of the transportation problem where the supply from every source and the demand at every sink are equal to 1.
First, we give a detailed review of two algorithms that solve the minimization case of the assignment problem, the Bertsekas auction algorithm and the Goldberg & Kennedy algorithm. It was previously alluded that both algorithms are equivalent. We give a detailed proof that these algorithms are equivalent. Also, we perform experimental results comparing the performance of three algorithms for ...