Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods

What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved April 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: Apr 12, 2024 11:40 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
Human-generated content, empowered by AI.
FREE eBook: Establish Authorship & Build Authority Online
When and How to Use a Case Study for Research
May 17, 2021 (Updated: May 4, 2023)

Quick Navigation
What Is Case Study Research?
Types of case studies, when should you use a case study, case study benefits, case study limitations, how to write a case study.
Imagine your company receives a string of negative reviews online. You notice a few common themes among the complaints, but you still aren’t quite sure what went wrong. Or suppose an old blog post suddenly went viral, and you’d like to know why and how to do it again. In both of these situations, a case study could be the best way to find answers.
A case study is a process whereby researchers examine a specific subject in a thorough, detailed way. The subject of a case study could be an individual, a group, a community, a business, an organization, an event, or a phenomenon. Regardless of the type of subject, case studies are in-depth investigations designed to identify patterns and cause-and-effect relationships. Case studies are often used by researchers in the field of psychology , medicine, business, social work, anthropology, education, or political science.
Because they are singular in their focus and often rely on qualitative data, case studies tend to be highly subjective. The results of a single case study cannot always be generalized and applied to the larger population. However, case studies can be valuable tools for developing a thesis or illustrating a principle. They can help researchers understand, describe, compare, and evaluate different aspects of an issue or question.

Image via Flickr by plings
Case studies can be classified according to their purpose or their subject. For instance, a case study can focus on any of the following:
- A person: Some case studies focus on one particular person. Often, the subject will be an individual with some rare characteristic or experience.
- A group: Group case studies could look at a family, a group of coworkers, or a friend group. It could be people thrown together by circumstance or who share some bond or relationship. A group case study could even focus on an entire community of people.
- An organization: An organizational case study could focus on a business, a nonprofit, an institution, or any other formal entity. The study could look at the people in the organization, the processes they use, or an incident at the organization.
- A location: An event case study focuses on a specific area. It could be used to study environmental and population changes or to examine how people use the location.
- An event: Event case studies can be used to cover anything from a natural disaster to a political scandal. Often, these case studies are conducted retrospectively, as an investigation into a past event.
In addition to different types of subjects, case studies often have different designs or purposes. Here are a few of the most common types of case studies:
- Explanatory: An explanatory case study tries to explain the why or how behind something. This type of case study works well when studying an event or phenomenon, like an airplane crash or unexpected power outage.
- Descriptive: A descriptive, or illustrative, case study is designed to shed light on an unfamiliar subject. Case studies like this provide in-depth, real-world examples of whatever the researcher wants to help the audience understand. For instance, a descriptive case study could focus on the experience of a mother with postpartum depression or on a young adult who has aged out of the foster care system.
- Exploratory: An exploratory case study, or pilot case study, often serves as the first step in a larger research project. Researchers may use a case study to help them narrow their focus, draft a specific research question, and guide the parameters of a formal, large-scale study.
- Intrinsic: An intrinsic case study has no goal beyond a deeper understanding of its subject. In this type of study, researchers are not trying to make generalized conclusions, challenge existing assumptions, or make any compare-and-contrast connections. The most interesting thing about the study is the subject itself.
- Critical Instance: A critical instance case study is similar to an explanatory or intrinsic study. Like an intrinsic study, it may have no predetermined purpose beyond investigating the subject. Like an explanatory study, it may be used to explain a cause-and-effect relationship. A critical instance case study may also be used to call into question a commonly held assumption or popular theory.
- Instrumental: An instrumental case study is the opposite of an intrinsic study because it serves a purpose beyond understanding the immediate subject. In this type of study, researchers explore a larger question through an individual case or cases. For instance, researchers could use a handful of case studies to investigate the relationship between social media use and happiness.
- Cumulative: A cumulative, or collective, case study uses information from several past studies as the basis for a new study. Because it takes into account multiple case studies, a cumulative study allows for greater generalization than a single case study. It can also be a more time- and cost-effective option since it makes use of existing research.
Case studies are often used in the exploratory phase of research to gather qualitative data. They can also be used to create, support, or refute a hypothesis and guide future research. For instance, a marketing professional might conduct a case study to discover why a viral ad campaign was so successful . They can then take any lessons they glean from the case study and apply them to future marketing efforts. A psychologist could use a case study to form a theory about the best way to treat a specific disorder. That theory could then be tested later through a large-scale controlled study.
Case studies are a good way to explore a real-world topic in-depth, illustrate a point, discuss the implications or meaning of an event, or compare the experiences of different individuals. A trainer may use a case study to bring to life what would otherwise be an abstract series of recommended action steps or to spark a conversation about how to respond in a specific scenario. Similarly, professors can use case studies to highlight key concepts from a lecture and pose questions to test students’ understanding of the material.
In some situations, case studies are the only way to compile quantitative data in an ethical manner. For instance, many of the recommendations that doctors make regarding what is or is not safe during pregnancy are based on case studies. It wouldn’t be ethical to conduct a controlled study that exposes pregnant women to potentially harmful substances, so doctors rely on the anecdotal evidence provided by case studies to find correlations and draw their conclusions.
Case studies can also be used to gather data that would be otherwise impossible or impractical to obtain. Students often use case studies for their thesis or dissertation when they lack the time or resources to conduct large-scale research. Zoologists might use existing case studies to determine the success rate of reintroducing rehabilitated animals into the wild. A historian could use case studies to explore the strategies used by dictators to gain and maintain power.

Image via Flickr by calebmmartin
Case studies can be used on their own or as a complement to other research methods, depending on the situation. The examples above are just a few instances where case studies can be useful. Case studies also work well for the following:
Providing Insight Through Qualitative Data
Case studies generally provide more qualitative data as opposed to quantitative data , and that makes them an invaluable tool for gathering insight into complex topics. Psychologists, for instance, use case studies to better understand human behavior. Crafting theories on the motives behind human actions would be difficult with quantitative data alone. The information gleaned through case studies may be subjective, but so is much of what makes us human. As individuals, we each have a unique blend of emotions, attitudes, opinions, motivations, and behaviors. Objective quantitative data is rarely the best way to identify and explain these nuances.
By their very nature, case studies allow more more intensive, in-depth study than other research methods. Rather than aiming for a large sample size, case studies follow a single subject. Often case studies are conducted over a longer period of time, and the narrow focus allows researchers to gather more detail than would be possible in a study of thousands of people. The information gleaned may not be representative of the broader population, but it does provide richer insight into the subject than other research methods.
Identifying Avenues for Future Research
Case studies are often used as the first step in a larger research project. The results of a case study cannot necessarily be generalized, but they can help researchers narrow their focus. For instance, researchers in the medical field might conduct a case study on a patient who survived an injury that typically proves fatal.
Over the course of the study, researchers may identify two or three ways in which this patient’s situation differed from others they have seen. Perhaps they identify something unique in the patient’s DNA or lifestyle choices or in the steps doctors took to treat the injury. Letting that information guide them, researchers could use other methods to deepen their understanding of those factors and perhaps develop new treatments or preventative recommendations.
Case studies can also be used in the fields of social work, politics, and anthropology to draw attention to a widespread problem and spur more research. A detailed narrative about one person’s experience will inspire more compassion than an academic paper filled with quantitative data. Stories often have a greater impact than statistics.
Challenging, Testing, or Developing Theories
Case studies can be particularly useful in the process of forming and testing theories. A case study may lead researchers to form a new theory or call into a question an existing one. They are an invaluable tool for identifying exceptions to a rule or disproving conventional wisdom.
For instance, a medical professional may write a case study about a patient who exhibited atypical symptoms to assert that the list of symptoms for a condition should be expanded. A psychologist could use a case study to determine whether the new treatment they devised for depression is effective, or to demonstrate that existing treatment methods are flawed. As the result of a case study, a marketing professional could suggest that consumers values have changed and that marketing best practices should be updated accordingly.
Enabling the Study of Unique Subjects
Some subjects would be impossible, impractical, or unethical to study through other research methods. This is true in the case of extremely rare phenomenon, many aspects of human behavior, and even some medical conditions.
Suppose a medical professional would like to gather more information about multiple-birth pregnancies with four or more fetuses. More information would be helpful because we have less information about them, but the reason we have less information is because they are so rare. Conducting case studies of a few women who are currently pregnant with multiples or have given birth to multiples in the past may be the only practical way to research them.
Case studies can also be used to gain insight into historical events and natural phenomenon — things we are not able to repeat at will. Case studies have also been used to study subjects such as a feral child , child prodigies, rare psychological conditions, crisis response, and more.
Helping People Better Understand Nuanced Concepts
Educators incorporate case studies into their lectures for a reason. Walking students through a detailed case study can make the abstract seem more real and draw out the nuances of a concept. Case studies can facilitate engaging discussions, spark thoughtful questions, and give students a chance to apply what they have learned to real-world situations.
Outside the classroom, case studies can be used to illustrate complex ideas. For instance, a well-constructed case study can highlight the unintended consequences of a new piece of legislation or demonstrate that depression does not always manifest in an obvious way. Case studies can help readers and listeners understand and care about an issue that does not directly affect them.
Despite their benefits, case studies do come with a few limitations. Compared to other research methods, case studies are often at a disadvantage in terms of the following:
Replicability
In most cases, scientists strive to create experiments that can be repeated by others. That way, other scientists can perform their own research and compare their results to those of the initial study. Assuming these other scientists achieve similar results, the replicability of the experiment lends credibility to the findings and theories of the original researchers.
One limitation of case studies is that they are often difficult, if not impossible, to replicate. Although this fact does not diminish the value of case studies, it does demonstrate that case studies are not a good fit for every research problem — at least, not on their own. Additional research would have to be performed to corroborate the results and prove or disprove any generalized theories generated by a case study.
Generalization
Generalization is another area in which case studies cannot match other research methods. A case study can help us challenge existing theories and form new ones, but its results cannot necessarily be generalized. The data we gather from a case study is only valid for that specific subject, and we cannot assume that our conclusions apply to the broader population.
Researchers or readers can attempt to apply the principles from a particular case to similar situations or incorporate the results into a more comprehensive theory. However, a case study by itself can only prove the existence of certain possibilities and exceptions, not a general rule.
Reliability
The reliability of case studies may be called into question for two reasons. The first objection centers on the fallibility of human memory and the question of whether subjects are being honest. Many case studies rely on subjects to self-report biographical details, their state of mind, their thoughts and feelings, or their behaviors.
The second issue is the Hawthorne effect, which refers to the tendency of individuals to modify their behavior when they know they are being observed. This effect makes it nearly impossible for researchers to ensure that the observations and conclusions of their case study are reliable.
Researcher Bias
Researcher bias is another potential issue with case studies. The results of a case study are by nature subjective and qualitative rather than objective and qualitative, and any findings rely heavily on the observations and narrative provided by the researcher. Even the best researchers are still human, and no matter how hard they try to remain objective, they will not be able to keep their findings completely free of bias.
Researchers may have biases they are not even aware of. A researcher may over-identify with the subject and lose the benefit of a dispassionate outside perspective. If the researcher already has an opinion on the subject, they may subconsciously overlook or discount facts that contradict their pre-existing assumptions. Researcher bias can affect what the researcher observes and records, as well as how they interpret and apply their observations.
Case studies can be time-consuming and expensive to conduct. Crafting a thorough case study can be a lengthy project due to the intensive, detailed nature of this type of research. Plus, once the information has been gathered, it must be interpreted. Between the observation and analysis, a case study could take months or even years to complete. Researchers will need to be heavily involved in every step of the process, putting in a lot of time, energy, focus, and effort to ensure that the case study is as informative as possible.
Now that you understand the benefits, limitations, and types of case studies, you can follow these steps to write your own:
- Determine your objective. Write out your research problem, question, or goal. If you aren’t sure, ask yourself questions like, “What am I trying to accomplish? What do I need to know? What will success look like?” Be clear and specific. Your answers will help you choose the right type of case study for your needs.
- Review the research. Before delving into your case study, take some time to review the research that is already available. The information you gather during this preliminary research can help guide your efforts.
- Choose a subject. Decide what or who the subject of your case study will be. For instance, if you are conducting a case study to find out how businesses have been affected by new CDC guidelines, you will need to choose a specific restaurant or retailer. In some cases, you may need to draft a release form for the subject to sign so that you will be able to publish your study.
- Gather information. Case studies about a person, organization, or group may rely on questionnaires or interviews to gather information. If you are studying an event, you might use a combination of academic research and witness interviews. In some cases, you will record your own observations as part of the study.
- Write a report. Most case studies culminate in a written report, similar to a research paper. Most case studies include five sections : an introduction, a literature review, an explanation of your methods, a discussion of your findings and the implications, followed by a conclusion.
- Publish your findings. Once you’ve written your case study, consider the most engaging way to present your findings. A well-written research article is a good place to start, but going a step further will maximize the impact of your research. For instance, you could design an infographic to highlight key findings or commission an animated video to turn your case study into a visual narrative.
Whether research is your primary occupation or only an incidental part of your job, you can benefit from a solid understanding of what case studies are, how they work, and when to use them. Use the information and steps above to design and write a case study that will provide the answers you’re looking for.
CopyPress writer
More from the author:
Quick Navigation What Does a Content Manager Do? Who Does a Content Manager Report To? Are Content Managers Paid...
In our digital age, it’s important to know the best ways to reach your target audience and boost your...
The best content marketing conferences offer the chance to learn more about the industry and provide networking opportunities with...
RECENT ARTICLES
Read More About Measurement

27 Nov 2023

31 Oct 2023

23 May 2023
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.24(6); 2019 Sep

Lessons learnt: examining the use of case study methodology for nursing research in the context of palliative care
Paula brogan.
School of Communication and Media, University of Ulster, Northern Ireland, UK
Felicity Hasson
Institute of Nursing Research, University of Ulster, Northern Ireland, UK
An empirical social research approach, facilitating in-depth exploration of complex, contemporary contextualised phenomena, case study research has been used internationally in healthcare studies across clinical settings, to explore systems and processes of care delivery. In the United Kingdom, case study methods have been championed by nurse researchers, particularly in the context of community nursing and palliative care provision, where its applicability is well established. Yet, dogged by conceptual confusion, case study remains largely underutilised as a research approach.
Drawing on examples from nursing and palliative care studies, this paper clarifies case study research, identifies key concepts and considers lessons learned about its potential for nursing research within the unique and complex palliative and end of life context.
A case study approach offers nurse researchers the opportunity for in-depth, contextualised understanding of the systems and processes which influence their role in palliative care delivery across settings. However, philosophical and conceptual understandings are needed and further training in case study methodology is required to enable researchers to articulate and conduct case study.
Introduction
An empirical social research approach, facilitating in-depth exploration of a contemporary phenomenon ( Yin, 2009 ), case study research has been used internationally in healthcare studies ( Anthony and Jack, 2009 ) to explore systems of palliative care ( Lalor et al., 2013 ), diverse contexts for palliative care delivery ( Sussman et al., 2011 ), roles of professional groups such as pharmacy ( O’Connor et al., 2011 ), the impact of services such as complementary therapy ( Maddalena et al., 2010 ) and nursing (Kaasalainen et al., 2013). In the United Kingdom, case study methods have been championed by nurse researchers ( Payne et al., 2006 ), particularly in the context of community nursing and palliative care provision ( Kennedy, 2005 ; Walshe et al., 2004 , 2008 ) and its applicability to palliative and end-of-life care research is established ( Goodman et al., 2012 ). Suited to the study of complex processes ( Walshe, 2011 ), case study methodology is embedded in professional guidance on the development of complex interventions ( Medical Research Council, 2008 ). Yet, case study is dogged by conceptual confusion (Flyvberg, 2006), and, despite sporadic use, remains underutilised as a research approach in healthcare settings ( Froggatt et al., 2003 ).
Illustrated by examples from nursing and palliative care studies, this paper aims to clarify conceptual understanding and identify key lessons for its application within these unique and complex contexts and, more broadly, for nursing research.
Origins and definitions
French sociologist Frederic Le Play (1806–1882) is associated with the origin of the case study approach ( Hamel et al., 1993 ). Using a purposive sample of working class families and fieldwork methods of observation and individual interview, he sought a contextualised and in-depth understanding of their individual experiences. Each family case study uncovered the unique experience of that family, but each additional family studied was another ‘ case of the lived experience’ of working class families in mid-18th century France. Thereby, Le Play used the lens of individual experience ( Yin, 2013 ) to build comparisons across families and enrich overall understanding of that complex society.
This early glimpse of the case study approach showed it to be a straightforward ‘field investigation’ ( Hamel et al., 1993 ); epistemologically pragmatic as it generated knowledge through data drawn from diverse sources, such as family members, and used the best available data collection methods then, to inform a holistic and contextualised understanding of how people operated within a complex social system ( Stake, 1995 ).
However, defining case study has become increasingly challenging since its expansion into North America in the 1800s ( Platt, 1992 ), and its use across a range of disciplines such as politics ( Gerring, 2004 ), social science ( George and Bennett, 2005 ), education ( Merriam, 1998 ) and healthcare ( Yin, 2013 ). Variously characterised as a case report, data collection method and methodology ( Anthony and Jack, 2009 ), the development of case histories as illustrations in health and social care and in education ( Merriam, 1998 ) has contributed to further confusion for researchers and readers of case study research ( Gomm et al., 2000 ). Critiques of case study note that it lacks a single definition, such that a plethora of discipline dependant interpretations ( Simons, 2009 ) and loose use of the term case study ( Tight, 2010 ) have contributed to confusion and undermined case study credibility. However, Simons ( 2009 , p. 63) advises researchers that case study must be seen within the complex nexus of political, methodological and epistemological convictions that constitute the field of enquiry, and variations of these may be glimpsed in Table 1 as definitions from four eminent and frequently cited case study authors illustrate philosophical and discipline-influenced differences in emphasis. Consequently, the case study definition selected, with its underpinning ontology and epistemology has important implications for the coherent outworking of the overall research design. It is therefore notable that many of the palliative care case studies contained in Table 2 fail to identify any such definition and this may have implications for interpretation of the quality of studies.
Definitions of case study by four key authors, showing the variation in meaning and interpretation.
Examples of Case Studies (CS) conducted in palliative care contexts.

Case study as a philosophy for the epistemology of knowledge generation
Although frequently linked to naturalistic inquiry ( Lincoln and Guba, 1986 ), interpretative/constructivist philosophy and qualitative methodology ( Stake, 1995 ), case study is not in fact bound to any single research paradigm ( Creswell, 2013 ). It is philosophically pragmatic, such that the case study design should reflect the ontological positions and epistemological considerations of the researchers and their topic of interest ( Luck et al., 2006 ). In practice, this means that case study research may pragmatically employ both qualitative and quantitative methods independently or together in order to respond to the research objectives ( Cooper et al., 2012 ; Simons, 1987 ; Stake, 2006 ). So whilst Table 2 shows that qualitative case studies are common in palliative care, epistemological variation is evident and reflects the study topic, purpose and context of the research. For example, Maddalena et al. (2010) used in-depth interview and discourse analysis to understand individual patient meaning-making; Brogan et al. (2017) used focus groups and thematic analysis as part of an embedded element of a multiple case study, to contrast the diverse perspectives of multi-disciplinary healthcare practitioners on end-of-life decision-making; Sussman et al. (2011) incorporated survey data into a mixed methods multiple case study which explored health system characteristics and quality of care delivery for cancer patients across four regions of Canada. Consequently, it is useful to ‘conceptualise (case study) as an approach to research rather than a methodology in its own right’ ( Rosenberg and Yates, 2007 , p. 448), so that a non-standardised approach exists and the case study design, its boundaries, numbers of cases and methods are guided by the stated underpinning ontological perspectives of the researcher and their topic of interest. The study then flexibly adopts the best methods to gain an in-depth, holistic and contextualised understanding of the phenomenon of interest – the latter objectives being at the core of any definition of case study research.
Key case study concepts and lessons for practice
When considering the utility of a case study approach, research conducted in complex palliative care contexts offers several insights into how central concepts translate to practice.
Contextualised understanding
Drawing on the definitions in Table 1 , Stake emphasised the particularity and intrinsic value of each individual case ( Stake, 1995 ), to emphasise the usefulness of multiple cases to increase insight ( Stake, 2006 ), analyse patterns ( Gerring, 2004 ; George and Bennett, 2005 ) and develop causal hypotheses ( Yin, 2013 ). Yet, whatever the purpose, all case studies are concerned with the crucial relationship between a phenomenon and the environment in which it has occurred. In practice therefore, case study researchers must be concerned with understanding the background systems, structures and processes that influence and interact with the phenomenon under study. This capacity for contextualised and holistic understanding is underpinned by use of multiple data collection methods, such as observation, interview and document review, used simultaneously or sequentially ( Stake, 2006 ; Scholz and Tietje, 2002 ), to mine multiple sources of data, such as participant experience ( Brogan et al., 2017 ; Kaasalainen et al., 2012 ), documents (Lalor et al., 2003) service evaluations ( Walshe et al., 2008 ), and diaries ( Skilbeck and Seymour, 2002 ). This is exemplified in a study by Walshe et al. (2011) , who investigated referral decisions made by community palliative care nurses in the UK, by capturing interview data on the self-reported perspectives of healthcare professionals, in combination with observed team meetings in which decisions were influenced, and review of the written referral policies, protocols and palliative healthcare strategies specific to those decisions. This comprehensive and complex data enabled comparison of decisional processes and their influencing factors both within and across three Primary Care Trusts, thus providing a contemporaneous understanding of the complex relationship between individual nurse's referral decisions and the impact of the organisational and professional systems that underpinned them. Enhancing rigor, such methodological triangulation importantly contributed to the richness of data analysis and the development of assertions which might be drawn from the findings ( Cooper et al., 2012 ; Stake, 2006 ).
Process-focused
Flexible data collection methods, linked to the research purpose, enables case study researchers to gather both historical and real-time data in a variety of ways. For example, Kennedy’s longitudinal case study ( Kennedy, 2002 ) observed snapshots of the initial and follow-up assessment conducted by 11 district nurses over the subsequent 12 months, enabling an exploration of the outcome and impact of their decision-making, demonstrating the usefulness of case study to understand complex roles and processes which are fluid and elusive ( Yin, 2013 ), or otherwise difficult to capture, particularly in the intimate interpersonal contexts where nursing happens.
Analytic frame
Palliative care studies reviewed frequently report the use of thematic analysis. However, whilst this approach is certainly useful to process data generated in qualitative case studies, the approach to analysis must be congruent with the research design and reflect the purpose of the research and methods used. Moreover, beyond decisions about use of thematic analysis or descriptive statistics etc., in case study, important decisions must be made about the analytic frame of the research. Gerring’s definition (2004) set out the analytic frame in which the cases studied might be understood, explaining that each unit of analysis (or case), sheds light on other units (or cases). Thus defined, an individual case offers intrinsically valuable information about a phenomenon ( Stake, 1995 ) and the purposeful selection of cases is central to case study design. This is because, viewed from a certain angle, each case is also a case of something else, such that the findings have broader implications ( Gerring, 2004 ; Simons, 2009 , 1987 ; Yin, 2013 ). In practice, this means that the case and what it is a case of, must be clearly identified and well defined at the outset of a study, since this has implications for the relevance of findings. This can be seen in a study by O’Connor et al., (2011) , who considered the perceived role of community pharmacists in palliative care teams in Australia. Each unique case included multi-disciplinary healthcare team members, such as pharmacists, doctors and nurses working in localities, whose perspectives were sought. Each locality group was a case of community pharmacy provision in palliative care settings in Australia, and findings had implications for the planning of community services overall. So, insight development was possible at an individual, group and organisational level, and inferences were made directly in relation to the parameters of that case study.
The addition of several carefully selected cases, as in multiple case studies, offers the opportunity to analyse data gained within and across cases ( Stake, 2006 ). Case selection may be made in order to explore similarities and contrasting perspectives ( Brogan et al., 2017 ), understand the various impacts of geographical differences ( Sussman et al., 2011 ), and different organisational influences ( Walshe et al., 2008 ). However, whilst repetition of data across cases may reinforce propositions made at the outset of a study, the purpose of increasing the number of cases in case study research is primarily about increasing insight development into the complexity of a phenomenon ( Stake, 2006 ). Since case study is the study of a boundaried phenomenon ( Yin, 2013 ), establishing the analytic frame then underpins the selection criteria for potentially useful cases. Such clarification is essential since it provides the lens through which to focus research ( Gerring, 2004 ; Scholz and Tietje, 2002 ; Stake, 2006 ) and permits key decisions to be made about data which may be included and that which is not applicable.
However, significantly, this information is rarely articulated within published case studies in palliative care. This is an important issue for the quality of case study research, since description of the process of refining case study parameters, establishing clear boundaries of the case, articulating propositions based on existing literature, identifying the sources of data (people, records, policies, etc.) and the ways in which data would be captured, establishes clarity and underpins a rigorous, systematic and comprehensive process ( Gibbert et al., 2008 ), which can usefully contribute to practice and policy development ( George and Bennett, 2005 ).
Shaped by organisational systems, intimate settings and significant life stage contexts, the interconnection between context and participant experience of palliative care is one example of a process of healthcare provision that is often complex, subtle and elusive ( Walshe et al., 2011 ). Case studies conducted in these swiftly changing contexts illustrate several characteristics of case study research, which make it an appropriate methodological option for nurse researchers, providing the opportunity for in-depth, contextualised understanding of the systems and processes which influence their role in palliative care delivery across settings ( Walshe et al., 2004 ) and many others who seek a contextualised, contemporaneous understanding of any complex role or process ( Yin, 2013 ; Simons, 2009 ). This fieldwork-based approach has the potential to achieve depth and breadth of insight through the pragmatic, but carefully planned and articulated, use of multiple methods of data collection in order to answer the research question ( Stake, 2006 ) when analysed systematically within a frame determined at the outset by the definition of the case and its boundaries ( Gerring, 2004 ). Yet, the methodological flexibility that is advantageous in complex contexts, may be misunderstood ( Hammersley, 2012 ), particularly where terminology is unclear ( Lather, 1996 ) or where description of the systematic and rigorous application of the approach is missing from the report ( Morrow, 2005 ). Taken as an example of one area of healthcare research, evidence suggests that palliative care studies that deal meaningfully with underpinning philosophical perspectives for their selected case study approach, or which articulate coherent links between the defined case, its boundaries and the analytical frame are rare. The impact of such omissions may be the perpetuation of confusion and out-dated perceptions about the personality and quality of case study research ( King et al., 1994 ), with implications for its wider adoption by nurses in healthcare research. Further training in case study methodology is required to promote philosophical and conceptual understanding, and to enable researchers to fully articulate, conduct and report case study, to underpin its credibility, relevance and future use ( Hammersley et al., 2000 ; Stake and Turnbull, 1982).
Key points for policy, practice and/or research
- Case study is well suited to nursing research in palliative care contexts, where in-depth understanding of participant experience, complex systems and processes of care within changing contexts is needed.
- Not bound to any single paradigm, nor defined by any methodology, case study’s pragmatism and flexibility makes it useful for studies in palliative care.
- Training is needed in the underpinning philosophical and conceptual basis of case study methodology, in order to articulate, conduct and report credible case study research, and take advantage of the opportunities it offers for the conduct of palliative and end-of-life care research.
Paula Brogan is a Lecturer in counselling and communication in the School of Communication and Media, and was recently appointed as Faculty Partnership Manager, University of Ulster. Dual qualified as a Registered Nurse with specialism in District Nursing and as a Counsellor/couple psychotherapist (Reg MBACPaccred), she has over 30 years’ clinical practice experience in community palliative care nursing and the provision of psychological care to patients and families dealing with palliative and chronic illness. Having worked across statutory, voluntary and private sectors, her PhD focused on multi-disciplinary decision-making at the end of life with patients and families in the community setting. Currently secretary of the Palliative Care Research Forum for Northern Ireland (PCRFNI), Paula’s ongoing research interests include communication and co-constructed decision-making in palliative and chronic illness, and the psychological support of individuals, couples, patient-family groups and multi-disciplinary staff responding to challenges of advanced progressive illness.
Felicity Hasson is a Senior Lecturer in the Institute of Nursing Research at the University of Ulster with 20 years’ experience in research. A social researcher by background, she has extensive experience and knowledge of qualitative, quantitative and mixed method research and has been involved in numerous research studies in palliative and end-of-life care. She completed her MSc in 1996 and her PhD from University of Ulster in 2012. Felicity sits on the Council of Partners for the All Ireland Institute of Hospice and the Palliative Care Palliative Care Research Network (PCRN) and is an executive board member for the UK Palliative Care Research Society. She holds an editorial board position on Futures and Foresight Science. Felicity has an established publication track recorded and successful history of grant applications. Her research interests include nurse and assistant workforce, workforce training, palliative care and chronic illness (malignant and non-malignant with patients, families and multi-disciplinary health care professionals) and public awareness of palliative care and end of life issues.
Sonja McIlfatrick is a Professor in Nursing and Palliative Care and has recently been appointed as the Head of School of Nursing at University of Ulster. She is an experienced clinical academic with experience in nursing and palliative care practice, education and research. She previously worked as the Head of Research for the All Ireland Institute of Hospice and Palliative Care (2011-2014) and led the establishment of the All Ireland Palliative Care Research Network (PCRN) and is the current Chair of the Strategic Scientific Committee for the PCRN (AIIHPC). Sonja is an Executive Board member for the UK, Palliative Care Research Society and is member of the Research Scientific Advisory Committee for Marie Curie, UK. Sonja holds an Editorial Board position on the International Journal of Palliative Nursing and Journal of Research in Nursing. Professor McIlfatrick has published widely in academic and professional journals focused on palliative care research and has a successful history of grant acquisition. Sonja has a keen interest in doctoral education and is the current President of the International Network of Doctoral Education in Nursing (INDEN). Her research interests include, palliative care in chronic illness, decision making at end of life; public awareness of palliative care and psychosocial support for family caregivers affected by advanced disease.
Declaration of conflicting interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethics statement
Ethical permission was not required for this paper.
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
- Anthony S, Jack S. (2009) Qualitative case-study methodology in nursing research: An integrative review . Journal of Advanced Nursing 65 ( 6 ): 1171–1181. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brogan P, Hasson F, McIlfatrick S. (2017) Shared decision-making at the end of life: A focus group study exploring the perceptions and experiences of multi-disciplinary healthcare professionals working in a home setting . Palliative Medicine 32 ( 1 ): 123–132. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper B, Glaesser J, Gomm R, et al. (2012) Challenging the Qualitative-Quantitative Divide: Explorations in Case-focused Causal Analysis , London: Continuum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell JW. (2013) Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among five approaches , 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flyvbjerg B. (2006) Five misunderstandings about case-study research . Qualitative Inquiry 12 ( 2 ): 219–245. [ Google Scholar ]
- Froggatt KA, Field D, Bailey C, et al. (2003) Qualitative research in palliative care 1990–1999: A descriptive review . International Journal of Palliative Nursing 9 ( 3 ): 98–104. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- George AL, Bennett A. (2005) Case Studies and Theory Development in the Social Sciences , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gerring J. (2004) What is case-study and what is it good for? The American Political Science Review 98 ( 2 ): 341–354. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gibbert M, Ruigrok W, Wicki B. (2008) What passes as rigorous case-study? Strategic Management Journal 29 : 1465–1474. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gomm R, Hammersley M, Foster P. (2000) Case Study Method: Key Issues, Key Texts , London: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goodman C, Froggatt KA, Mathie E. (2012) End-of-life Care. Methods Review 12 , London: National Institute for Health Research and School for Social Care Research. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hamel J, Defour S, Fortin D. (1993) Case-study Methods. Qualitative Research Methods Series. 32 , Newbury Park: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley M, Foster P, Gomm R. (2000) Case study and generalisation . In: Gomm R, Hammersley M, Foster P. (eds) Case Study Method: Key Issues, Key Texts , London: SAGE, pp. 98–115. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley M. (2012) Troubling theory in case study research . Higher Education Research and Development 31 ( 3 ): 393–405. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaasalainen S, Ploeg J, McAiney C, et al. (2012) Role of the nurse practitioners in providing palliative care in long-term care homes . International Journal of Palliative Nursing 19 ( 10 ): 477–485. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kennedy C. (2005) District nursing support for patients with cancer requiring palliative care . British Journal of Community Nursing 10 ( 12 ): 566–574. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kennedy C. (2002) The decision-making process in a district nursing assessment . British Journal of Community Nursing 7 ( 10 ): 505–513. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane RO, Verba S. (1994) Designing Social Inquiry: Scientific Inference in Qualitative Research , Princeton: Princeton University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lalor JG, Casey D, Elliott N, et al. (2013) Using case-study within a sequential explanatory design to evaluate the impact of specialist and advanced practice roles on clinical outcomes: The SCAPE study . BMC Medical Research Methodology 13 ( 1 ): 55. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lather P. (1996) Troubling clarity: The politics of accessible language . Harvard Educational Review 66 ( 3 ): 525–554. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln YS, Guba EG. (1986) But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation . In: Williams DD. (eds) Naturalistic Evaluation , San Francisco: Josey-Bass, pp. 73–84. [ Google Scholar ]
- Luck L, Jackson D, Usher K. (2006) Case-study: A bridge across paradigms . Nursing Inquiry 13 ( 2 ): 103–109. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maddalena VJ, Bernard WT, Etowa J, et al. (2010) Cancer care experiences and the use of complementary and alternative medicine at the end-of-life in Nova Scotia’s black communities . J Transcultural Nursing 21 ( 2 ): 114–122. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Medical Research Council (2008) Complex Interventions Guidance, www.mrc.ac.uk/complexinterventionsguidance (accessed 14 March 2014).
- Merriam SB. (1998) Qualitative research and case-study applications in education , San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morrow SL. (2005) Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counselling psychology . Journal of Counseling Psychology 52 ( 2 ): 256–260. [ Google Scholar ]
- O’Connor M, Fisher C, French L, et al. (2011) Exploring the community pharmacist’s role in palliative care: Focusing on the person not just the prescription . Patient Education and Counseling 83 : 458–464. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Payne S, Field D, Rolls L, et al. (2006) Case-study research methods in end-of-life care: Reflections on three studies . Journal of Advanced Nursing 58 ( 3 ): 236–245. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Platt J. (1992) Case study in American methodological thought . Current Sociology 40 ( 1 ): 17–48. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenberg JP, Yates PM. (2007) Schematic representation of case-study research designs . Journal of Advanced Nursing 60 ( 4 ): 447–452. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scholz RW, Tietje O. (2002) Embedded Case Study Methods: Integrating Quantitative and Qualitative Knowledge , Los Angeles: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Simons H. (1987) The paradox of case-study . Cambridge Journal of Education 26 ( 2 ): 225–240. [ Google Scholar ]
- Simons H. (2009) Case-study Research in Practice , Thousand Oaks: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Skilbeck J, Seymour J. (2002) Meeting complex needs: And analysis of Macmillan nurses’ work with patients . International Journal of Palliative Nursing 8 ( 12 ): 574–582. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. (1995) The Art of Case-study Research , Thousand Oaks: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE, Trumbull DJ. (1987) Naturalistic generalizations . Review Journal of Philosophy and Social Science 7 : 1–12. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. (2006) Multiple case-study analysis , New York: The Guilford Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sussman J, Barbera L, Bainbridge D, et al. (2011) Health system characteristics and quality of care delivery: A comparative case-study examination of palliative care for cancer patients in four regions in Ontario, Canada . Palliative Medecine 26 ( 4 ): 322–335. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tight M. (2010) The curious case of case study: A viewpoint . International Journal of Social Research Methodology 13 ( 4 ): 329–339. [ Google Scholar ]
- Walshe C. (2011) The evaluation of complex interventions in palliative care: An exploration of the potential of case-study . Palliative Medicine 25 ( 8 ): 774–781. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Walshe C, Chew-Graham C, Todd C, et al. (2008) What influences referrals within community palliative care services? A qualitative case-study . Social Science and Medicine 6 : 137–146. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Walshe CE, Caress AL, Chew-Graham C, et al. (2004) Case studies: A research strategy appropriate for palliative care?’ . Palliative Medicine 18 : 677–684. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin RK. (2013) Case-study Research: Design and Methods (Applied Social Research Methods) , Newbury Park: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin RK. (2009) Case-study Research: Design and Methods , 4th ed. Newbury Park: SAGE. [ Google Scholar ]
- Open access
- Published: 27 June 2011
The case study approach
- Sarah Crowe 1 ,
- Kathrin Cresswell 2 ,
- Ann Robertson 2 ,
- Guro Huby 3 ,
- Anthony Avery 1 &
- Aziz Sheikh 2
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 11 , Article number: 100 ( 2011 ) Cite this article
766k Accesses
1031 Citations
37 Altmetric
Metrics details
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business, law and policy, but somewhat less so in health services research. Based on our experiences of conducting several health-related case studies, we reflect on the different types of case study design, the specific research questions this approach can help answer, the data sources that tend to be used, and the particular advantages and disadvantages of employing this methodological approach. The paper concludes with key pointers to aid those designing and appraising proposals for conducting case study research, and a checklist to help readers assess the quality of case study reports.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. Our aim in writing this piece is to provide insights into when to consider employing this approach and an overview of key methodological considerations in relation to the design, planning, analysis, interpretation and reporting of case studies.
The illustrative 'grand round', 'case report' and 'case series' have a long tradition in clinical practice and research. Presenting detailed critiques, typically of one or more patients, aims to provide insights into aspects of the clinical case and, in doing so, illustrate broader lessons that may be learnt. In research, the conceptually-related case study approach can be used, for example, to describe in detail a patient's episode of care, explore professional attitudes to and experiences of a new policy initiative or service development or more generally to 'investigate contemporary phenomena within its real-life context' [ 1 ]. Based on our experiences of conducting a range of case studies, we reflect on when to consider using this approach, discuss the key steps involved and illustrate, with examples, some of the practical challenges of attaining an in-depth understanding of a 'case' as an integrated whole. In keeping with previously published work, we acknowledge the importance of theory to underpin the design, selection, conduct and interpretation of case studies[ 2 ]. In so doing, we make passing reference to the different epistemological approaches used in case study research by key theoreticians and methodologists in this field of enquiry.
This paper is structured around the following main questions: What is a case study? What are case studies used for? How are case studies conducted? What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided? We draw in particular on four of our own recently published examples of case studies (see Tables 1 , 2 , 3 and 4 ) and those of others to illustrate our discussion[ 3 – 7 ].
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table 5 ), the central tenet being the need to explore an event or phenomenon in depth and in its natural context. It is for this reason sometimes referred to as a "naturalistic" design; this is in contrast to an "experimental" design (such as a randomised controlled trial) in which the investigator seeks to exert control over and manipulate the variable(s) of interest.
Stake's work has been particularly influential in defining the case study approach to scientific enquiry. He has helpfully characterised three main types of case study: intrinsic , instrumental and collective [ 8 ]. An intrinsic case study is typically undertaken to learn about a unique phenomenon. The researcher should define the uniqueness of the phenomenon, which distinguishes it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study uses a particular case (some of which may be better than others) to gain a broader appreciation of an issue or phenomenon. The collective case study involves studying multiple cases simultaneously or sequentially in an attempt to generate a still broader appreciation of a particular issue.
These are however not necessarily mutually exclusive categories. In the first of our examples (Table 1 ), we undertook an intrinsic case study to investigate the issue of recruitment of minority ethnic people into the specific context of asthma research studies, but it developed into a instrumental case study through seeking to understand the issue of recruitment of these marginalised populations more generally, generating a number of the findings that are potentially transferable to other disease contexts[ 3 ]. In contrast, the other three examples (see Tables 2 , 3 and 4 ) employed collective case study designs to study the introduction of workforce reconfiguration in primary care, the implementation of electronic health records into hospitals, and to understand the ways in which healthcare students learn about patient safety considerations[ 4 – 6 ]. Although our study focusing on the introduction of General Practitioners with Specialist Interests (Table 2 ) was explicitly collective in design (four contrasting primary care organisations were studied), is was also instrumental in that this particular professional group was studied as an exemplar of the more general phenomenon of workforce redesign[ 4 ].
What are case studies used for?
According to Yin, case studies can be used to explain, describe or explore events or phenomena in the everyday contexts in which they occur[ 1 ]. These can, for example, help to understand and explain causal links and pathways resulting from a new policy initiative or service development (see Tables 2 and 3 , for example)[ 1 ]. In contrast to experimental designs, which seek to test a specific hypothesis through deliberately manipulating the environment (like, for example, in a randomised controlled trial giving a new drug to randomly selected individuals and then comparing outcomes with controls),[ 9 ] the case study approach lends itself well to capturing information on more explanatory ' how ', 'what' and ' why ' questions, such as ' how is the intervention being implemented and received on the ground?'. The case study approach can offer additional insights into what gaps exist in its delivery or why one implementation strategy might be chosen over another. This in turn can help develop or refine theory, as shown in our study of the teaching of patient safety in undergraduate curricula (Table 4 )[ 6 , 10 ]. Key questions to consider when selecting the most appropriate study design are whether it is desirable or indeed possible to undertake a formal experimental investigation in which individuals and/or organisations are allocated to an intervention or control arm? Or whether the wish is to obtain a more naturalistic understanding of an issue? The former is ideally studied using a controlled experimental design, whereas the latter is more appropriately studied using a case study design.
Case studies may be approached in different ways depending on the epistemological standpoint of the researcher, that is, whether they take a critical (questioning one's own and others' assumptions), interpretivist (trying to understand individual and shared social meanings) or positivist approach (orientating towards the criteria of natural sciences, such as focusing on generalisability considerations) (Table 6 ). Whilst such a schema can be conceptually helpful, it may be appropriate to draw on more than one approach in any case study, particularly in the context of conducting health services research. Doolin has, for example, noted that in the context of undertaking interpretative case studies, researchers can usefully draw on a critical, reflective perspective which seeks to take into account the wider social and political environment that has shaped the case[ 11 ].
How are case studies conducted?
Here, we focus on the main stages of research activity when planning and undertaking a case study; the crucial stages are: defining the case; selecting the case(s); collecting and analysing the data; interpreting data; and reporting the findings.
Defining the case
Carefully formulated research question(s), informed by the existing literature and a prior appreciation of the theoretical issues and setting(s), are all important in appropriately and succinctly defining the case[ 8 , 12 ]. Crucially, each case should have a pre-defined boundary which clarifies the nature and time period covered by the case study (i.e. its scope, beginning and end), the relevant social group, organisation or geographical area of interest to the investigator, the types of evidence to be collected, and the priorities for data collection and analysis (see Table 7 )[ 1 ]. A theory driven approach to defining the case may help generate knowledge that is potentially transferable to a range of clinical contexts and behaviours; using theory is also likely to result in a more informed appreciation of, for example, how and why interventions have succeeded or failed[ 13 ].
For example, in our evaluation of the introduction of electronic health records in English hospitals (Table 3 ), we defined our cases as the NHS Trusts that were receiving the new technology[ 5 ]. Our focus was on how the technology was being implemented. However, if the primary research interest had been on the social and organisational dimensions of implementation, we might have defined our case differently as a grouping of healthcare professionals (e.g. doctors and/or nurses). The precise beginning and end of the case may however prove difficult to define. Pursuing this same example, when does the process of implementation and adoption of an electronic health record system really begin or end? Such judgements will inevitably be influenced by a range of factors, including the research question, theory of interest, the scope and richness of the gathered data and the resources available to the research team.
Selecting the case(s)
The decision on how to select the case(s) to study is a very important one that merits some reflection. In an intrinsic case study, the case is selected on its own merits[ 8 ]. The case is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because of its uniqueness, which is of genuine interest to the researchers. This was, for example, the case in our study of the recruitment of minority ethnic participants into asthma research (Table 1 ) as our earlier work had demonstrated the marginalisation of minority ethnic people with asthma, despite evidence of disproportionate asthma morbidity[ 14 , 15 ]. In another example of an intrinsic case study, Hellstrom et al.[ 16 ] studied an elderly married couple living with dementia to explore how dementia had impacted on their understanding of home, their everyday life and their relationships.
For an instrumental case study, selecting a "typical" case can work well[ 8 ]. In contrast to the intrinsic case study, the particular case which is chosen is of less importance than selecting a case that allows the researcher to investigate an issue or phenomenon. For example, in order to gain an understanding of doctors' responses to health policy initiatives, Som undertook an instrumental case study interviewing clinicians who had a range of responsibilities for clinical governance in one NHS acute hospital trust[ 17 ]. Sampling a "deviant" or "atypical" case may however prove even more informative, potentially enabling the researcher to identify causal processes, generate hypotheses and develop theory.
In collective or multiple case studies, a number of cases are carefully selected. This offers the advantage of allowing comparisons to be made across several cases and/or replication. Choosing a "typical" case may enable the findings to be generalised to theory (i.e. analytical generalisation) or to test theory by replicating the findings in a second or even a third case (i.e. replication logic)[ 1 ]. Yin suggests two or three literal replications (i.e. predicting similar results) if the theory is straightforward and five or more if the theory is more subtle. However, critics might argue that selecting 'cases' in this way is insufficiently reflexive and ill-suited to the complexities of contemporary healthcare organisations.
The selected case study site(s) should allow the research team access to the group of individuals, the organisation, the processes or whatever else constitutes the chosen unit of analysis for the study. Access is therefore a central consideration; the researcher needs to come to know the case study site(s) well and to work cooperatively with them. Selected cases need to be not only interesting but also hospitable to the inquiry [ 8 ] if they are to be informative and answer the research question(s). Case study sites may also be pre-selected for the researcher, with decisions being influenced by key stakeholders. For example, our selection of case study sites in the evaluation of the implementation and adoption of electronic health record systems (see Table 3 ) was heavily influenced by NHS Connecting for Health, the government agency that was responsible for overseeing the National Programme for Information Technology (NPfIT)[ 5 ]. This prominent stakeholder had already selected the NHS sites (through a competitive bidding process) to be early adopters of the electronic health record systems and had negotiated contracts that detailed the deployment timelines.
It is also important to consider in advance the likely burden and risks associated with participation for those who (or the site(s) which) comprise the case study. Of particular importance is the obligation for the researcher to think through the ethical implications of the study (e.g. the risk of inadvertently breaching anonymity or confidentiality) and to ensure that potential participants/participating sites are provided with sufficient information to make an informed choice about joining the study. The outcome of providing this information might be that the emotive burden associated with participation, or the organisational disruption associated with supporting the fieldwork, is considered so high that the individuals or sites decide against participation.
In our example of evaluating implementations of electronic health record systems, given the restricted number of early adopter sites available to us, we sought purposively to select a diverse range of implementation cases among those that were available[ 5 ]. We chose a mixture of teaching, non-teaching and Foundation Trust hospitals, and examples of each of the three electronic health record systems procured centrally by the NPfIT. At one recruited site, it quickly became apparent that access was problematic because of competing demands on that organisation. Recognising the importance of full access and co-operative working for generating rich data, the research team decided not to pursue work at that site and instead to focus on other recruited sites.
Collecting the data
In order to develop a thorough understanding of the case, the case study approach usually involves the collection of multiple sources of evidence, using a range of quantitative (e.g. questionnaires, audits and analysis of routinely collected healthcare data) and more commonly qualitative techniques (e.g. interviews, focus groups and observations). The use of multiple sources of data (data triangulation) has been advocated as a way of increasing the internal validity of a study (i.e. the extent to which the method is appropriate to answer the research question)[ 8 , 18 – 21 ]. An underlying assumption is that data collected in different ways should lead to similar conclusions, and approaching the same issue from different angles can help develop a holistic picture of the phenomenon (Table 2 )[ 4 ].
Brazier and colleagues used a mixed-methods case study approach to investigate the impact of a cancer care programme[ 22 ]. Here, quantitative measures were collected with questionnaires before, and five months after, the start of the intervention which did not yield any statistically significant results. Qualitative interviews with patients however helped provide an insight into potentially beneficial process-related aspects of the programme, such as greater, perceived patient involvement in care. The authors reported how this case study approach provided a number of contextual factors likely to influence the effectiveness of the intervention and which were not likely to have been obtained from quantitative methods alone.
In collective or multiple case studies, data collection needs to be flexible enough to allow a detailed description of each individual case to be developed (e.g. the nature of different cancer care programmes), before considering the emerging similarities and differences in cross-case comparisons (e.g. to explore why one programme is more effective than another). It is important that data sources from different cases are, where possible, broadly comparable for this purpose even though they may vary in nature and depth.
Analysing, interpreting and reporting case studies
Making sense and offering a coherent interpretation of the typically disparate sources of data (whether qualitative alone or together with quantitative) is far from straightforward. Repeated reviewing and sorting of the voluminous and detail-rich data are integral to the process of analysis. In collective case studies, it is helpful to analyse data relating to the individual component cases first, before making comparisons across cases. Attention needs to be paid to variations within each case and, where relevant, the relationship between different causes, effects and outcomes[ 23 ]. Data will need to be organised and coded to allow the key issues, both derived from the literature and emerging from the dataset, to be easily retrieved at a later stage. An initial coding frame can help capture these issues and can be applied systematically to the whole dataset with the aid of a qualitative data analysis software package.
The Framework approach is a practical approach, comprising of five stages (familiarisation; identifying a thematic framework; indexing; charting; mapping and interpretation) , to managing and analysing large datasets particularly if time is limited, as was the case in our study of recruitment of South Asians into asthma research (Table 1 )[ 3 , 24 ]. Theoretical frameworks may also play an important role in integrating different sources of data and examining emerging themes. For example, we drew on a socio-technical framework to help explain the connections between different elements - technology; people; and the organisational settings within which they worked - in our study of the introduction of electronic health record systems (Table 3 )[ 5 ]. Our study of patient safety in undergraduate curricula drew on an evaluation-based approach to design and analysis, which emphasised the importance of the academic, organisational and practice contexts through which students learn (Table 4 )[ 6 ].
Case study findings can have implications both for theory development and theory testing. They may establish, strengthen or weaken historical explanations of a case and, in certain circumstances, allow theoretical (as opposed to statistical) generalisation beyond the particular cases studied[ 12 ]. These theoretical lenses should not, however, constitute a strait-jacket and the cases should not be "forced to fit" the particular theoretical framework that is being employed.
When reporting findings, it is important to provide the reader with enough contextual information to understand the processes that were followed and how the conclusions were reached. In a collective case study, researchers may choose to present the findings from individual cases separately before amalgamating across cases. Care must be taken to ensure the anonymity of both case sites and individual participants (if agreed in advance) by allocating appropriate codes or withholding descriptors. In the example given in Table 3 , we decided against providing detailed information on the NHS sites and individual participants in order to avoid the risk of inadvertent disclosure of identities[ 5 , 25 ].
What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided?
The case study approach is, as with all research, not without its limitations. When investigating the formal and informal ways undergraduate students learn about patient safety (Table 4 ), for example, we rapidly accumulated a large quantity of data. The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted on the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources. This highlights a more general point of the importance of avoiding the temptation to collect as much data as possible; adequate time also needs to be set aside for data analysis and interpretation of what are often highly complex datasets.
Case study research has sometimes been criticised for lacking scientific rigour and providing little basis for generalisation (i.e. producing findings that may be transferable to other settings)[ 1 ]. There are several ways to address these concerns, including: the use of theoretical sampling (i.e. drawing on a particular conceptual framework); respondent validation (i.e. participants checking emerging findings and the researcher's interpretation, and providing an opinion as to whether they feel these are accurate); and transparency throughout the research process (see Table 8 )[ 8 , 18 – 21 , 23 , 26 ]. Transparency can be achieved by describing in detail the steps involved in case selection, data collection, the reasons for the particular methods chosen, and the researcher's background and level of involvement (i.e. being explicit about how the researcher has influenced data collection and interpretation). Seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, help readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report. Stake provides a critique checklist for a case study report (Table 9 )[ 8 ].
Conclusions
The case study approach allows, amongst other things, critical events, interventions, policy developments and programme-based service reforms to be studied in detail in a real-life context. It should therefore be considered when an experimental design is either inappropriate to answer the research questions posed or impossible to undertake. Considering the frequency with which implementations of innovations are now taking place in healthcare settings and how well the case study approach lends itself to in-depth, complex health service research, we believe this approach should be more widely considered by researchers. Though inherently challenging, the research case study can, if carefully conceptualised and thoughtfully undertaken and reported, yield powerful insights into many important aspects of health and healthcare delivery.
Yin RK: Case study research, design and method. 2009, London: Sage Publications Ltd., 4
Google Scholar
Keen J, Packwood T: Qualitative research; case study evaluation. BMJ. 1995, 311: 444-446.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge M, Car J, et al: Facilitating the Recruitment of Minority Ethnic People into Research: Qualitative Case Study of South Asians and Asthma. PLoS Med. 2009, 6 (10): 1-11.
Article Google Scholar
Pinnock H, Huby G, Powell A, Kielmann T, Price D, Williams S, et al: The process of planning, development and implementation of a General Practitioner with a Special Interest service in Primary Care Organisations in England and Wales: a comparative prospective case study. Report for the National Co-ordinating Centre for NHS Service Delivery and Organisation R&D (NCCSDO). 2008, [ http://www.sdo.nihr.ac.uk/files/project/99-final-report.pdf ]
Robertson A, Cresswell K, Takian A, Petrakaki D, Crowe S, Cornford T, et al: Prospective evaluation of the implementation and adoption of NHS Connecting for Health's national electronic health record in secondary care in England: interim findings. BMJ. 2010, 41: c4564-
Pearson P, Steven A, Howe A, Sheikh A, Ashcroft D, Smith P, the Patient Safety Education Study Group: Learning about patient safety: organisational context and culture in the education of healthcare professionals. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010, 15: 4-10. 10.1258/jhsrp.2009.009052.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
van Harten WH, Casparie TF, Fisscher OA: The evaluation of the introduction of a quality management system: a process-oriented case study in a large rehabilitation hospital. Health Policy. 2002, 60 (1): 17-37. 10.1016/S0168-8510(01)00187-7.
Stake RE: The art of case study research. 1995, London: Sage Publications Ltd.
Sheikh A, Smeeth L, Ashcroft R: Randomised controlled trials in primary care: scope and application. Br J Gen Pract. 2002, 52 (482): 746-51.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
King G, Keohane R, Verba S: Designing Social Inquiry. 1996, Princeton: Princeton University Press
Doolin B: Information technology as disciplinary technology: being critical in interpretative research on information systems. Journal of Information Technology. 1998, 13: 301-311. 10.1057/jit.1998.8.
George AL, Bennett A: Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. 2005, Cambridge, MA: MIT Press
Eccles M, the Improved Clinical Effectiveness through Behavioural Research Group (ICEBeRG): Designing theoretically-informed implementation interventions. Implementation Science. 2006, 1: 1-8. 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Netuveli G, Hurwitz B, Levy M, Fletcher M, Barnes G, Durham SR, Sheikh A: Ethnic variations in UK asthma frequency, morbidity, and health-service use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005, 365 (9456): 312-7.
Sheikh A, Panesar SS, Lasserson T, Netuveli G: Recruitment of ethnic minorities to asthma studies. Thorax. 2004, 59 (7): 634-
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hellström I, Nolan M, Lundh U: 'We do things together': A case study of 'couplehood' in dementia. Dementia. 2005, 4: 7-22. 10.1177/1471301205049188.
Som CV: Nothing seems to have changed, nothing seems to be changing and perhaps nothing will change in the NHS: doctors' response to clinical governance. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2005, 18: 463-477. 10.1108/09513550510608903.
Lincoln Y, Guba E: Naturalistic inquiry. 1985, Newbury Park: Sage Publications
Barbour RS: Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?. BMJ. 2001, 322: 1115-1117. 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115.
Mays N, Pope C: Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ. 2000, 320: 50-52. 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50.
Mason J: Qualitative researching. 2002, London: Sage
Brazier A, Cooke K, Moravan V: Using Mixed Methods for Evaluating an Integrative Approach to Cancer Care: A Case Study. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008, 7: 5-17. 10.1177/1534735407313395.
Miles MB, Huberman M: Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. 1994, CA: Sage Publications Inc., 2
Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N: Analysing qualitative data. Qualitative research in health care. BMJ. 2000, 320: 114-116. 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114.
Cresswell KM, Worth A, Sheikh A: Actor-Network Theory and its role in understanding the implementation of information technology developments in healthcare. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010, 10 (1): 67-10.1186/1472-6947-10-67.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malterud K: Qualitative research: standards, challenges, and guidelines. Lancet. 2001, 358: 483-488. 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05627-6.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Yin R: Case study research: design and methods. 1994, Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing, 2
Yin R: Enhancing the quality of case studies in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999, 34: 1209-1224.
Green J, Thorogood N: Qualitative methods for health research. 2009, Los Angeles: Sage, 2
Howcroft D, Trauth E: Handbook of Critical Information Systems Research, Theory and Application. 2005, Cheltenham, UK: Northampton, MA, USA: Edward Elgar
Book Google Scholar
Blakie N: Approaches to Social Enquiry. 1993, Cambridge: Polity Press
Doolin B: Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information system. Info Systems J. 2004, 14: 343-362. 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2004.00176.x.
Bloomfield BP, Best A: Management consultants: systems development, power and the translation of problems. Sociological Review. 1992, 40: 533-560.
Shanks G, Parr A: Positivist, single case study research in information systems: A critical analysis. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems. 2003, Naples
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/11/100/prepub
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants and colleagues who contributed to the individual case studies that we have drawn on. This work received no direct funding, but it has been informed by projects funded by Asthma UK, the NHS Service Delivery Organisation, NHS Connecting for Health Evaluation Programme, and Patient Safety Research Portfolio. We would also like to thank the expert reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback. Our thanks are also due to Dr. Allison Worth who commented on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Primary Care, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
Sarah Crowe & Anthony Avery
Centre for Population Health Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Kathrin Cresswell, Ann Robertson & Aziz Sheikh
School of Health in Social Science, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sarah Crowe .
Additional information
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AS conceived this article. SC, KC and AR wrote this paper with GH, AA and AS all commenting on various drafts. SC and AS are guarantors.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A. et al. The case study approach. BMC Med Res Methodol 11 , 100 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Download citation
Received : 29 November 2010
Accepted : 27 June 2011
Published : 27 June 2011
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Case Study Approach
- Electronic Health Record System
- Case Study Design
- Case Study Site
- Case Study Report
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Discounts and promotions
- Delivery and payment
Cart is empty!
Case study definition

Case study, a term which some of you may know from the "Case Study of Vanitas" anime and manga, is a thorough examination of a particular subject, such as a person, group, location, occasion, establishment, phenomena, etc. They are most frequently utilized in research of business, medicine, education and social behaviour. There are a different types of case studies that researchers might use:
• Collective case studies
• Descriptive case studies
• Explanatory case studies
• Exploratory case studies
• Instrumental case studies
• Intrinsic case studies
Case studies are usually much more sophisticated and professional than regular essays and courseworks, as they require a lot of verified data, are research-oriented and not necessarily designed to be read by the general public.
How to write a case study?
It very much depends on the topic of your case study, as a medical case study and a coffee business case study have completely different sources, outlines, target demographics, etc. But just for this example, let's outline a coffee roaster case study. Firstly, it's likely going to be a problem-solving case study, like most in the business and economics field are. Here are some tips for these types of case studies:
• Your case scenario should be precisely defined in terms of your unique assessment criteria.
• Determine the primary issues by analyzing the scenario. Think about how they connect to the main ideas and theories in your piece.
• Find and investigate any theories or methods that might be relevant to your case.
• Keep your audience in mind. Exactly who are your stakeholder(s)? If writing a case study on coffee roasters, it's probably gonna be suppliers, landlords, investors, customers, etc.
• Indicate the best solution(s) and how they should be implemented. Make sure your suggestions are grounded in pertinent theories and useful resources, as well as being realistic, practical, and attainable.
• Carefully proofread your case study. Keep in mind these four principles when editing: clarity, honesty, reality and relevance.
Are there any online services that could write a case study for me?
Luckily, there are!
We completely understand and have been ourselves in a position, where we couldn't wrap our head around how to write an effective and useful case study, but don't fear - our service is here.
We are a group that specializes in writing all kinds of case studies and other projects for academic customers and business clients who require assistance with its creation. We require our writers to have a degree in your topic and carefully interview them before they can join our team, as we try to ensure quality above all. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
• Select the topic and the deadline of your case study.
• Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the writing process you struggle with.
• Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
• Select your payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed writers, online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
- Open access
- Published: 09 April 2024
Creating culturally-informed protocols for a stunting intervention using a situated values-based approach ( WeValue InSitu ): a double case study in Indonesia and Senegal
- Annabel J. Chapman 1 ,
- Chike C. Ebido 2 , 3 ,
- Rahel Neh Tening 2 ,
- Yanyan Huang 2 ,
- Ndèye Marème Sougou 4 ,
- Risatianti Kolopaking 5 , 6 ,
- Amadou H. Diallo 7 ,
- Rita Anggorowati 6 , 8 ,
- Fatou B. Dial 9 ,
- Jessica Massonnié 10 , 11 ,
- Mahsa Firoozmand 1 ,
- Cheikh El Hadji Abdoulaye Niang 9 &
- Marie K. Harder 1 , 2
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 987 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
127 Accesses
Metrics details
International development work involves external partners bringing expertise, resources, and management for local interventions in LMICs, but there is often a gap in understandings of relevant local shared values. There is a widespread need to better design interventions which accommodate relevant elements of local culture, as emphasised by recent discussions in global health research regarding neo-colonialism. One recent innovation is the concept of producing ‘cultural protocols’ to precede and guide community engagement or intervention design, but without suggestions for generating them. This study explores and demonstrates the potential of an approach taken from another field, named WeValue InSitu , to generate local culturally-informed protocols. WeValue InSitu engages stakeholder groups in meaning-making processes which ‘crystallize’ their envelope of local shared values, making them communicable to outsiders.
Our research context is understanding and reducing child stunting, including developing interventions, carried out at the Senegal and Indonesia sites of the UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub. Each national research team involves eight health disciplines from micro-nutrition to epigenetics, and extensive collection of samples and questionnaires. Local culturally-informed protocols would be generally valuable to pre-inform engagement and intervention designs. Here we explore generating them by immediately following the group WeValue InSitu crystallization process with specialised focus group discussions exploring: what local life practices potentially have significant influence on the environments affecting child stunting, and which cultural elements do they highlight as relevant. The discussions will be framed by the shared values, and reveal linkages to them. In this study, stakeholder groups like fathers, mothers, teachers, market traders, administrators, farmers and health workers were recruited, totalling 83 participants across 20 groups. Themes found relevant for a culturally-informed protocol for locally-acceptable food interventions included: specific gender roles; social hierarchies; health service access challenges; traditional beliefs around malnutrition; and attitudes to accepting outside help. The concept of a grounded culturally-informed protocol, and the use of WeValue InSitu to generate it, has thus been demonstrated here. Future work to scope out the advantages and limitations compared to deductive culture studies, and to using other formative research methods would now be useful.
Peer Review reports
Although progress has been made towards the SDG of ‘Zero Hunger by 2025’, the global rates of malnutrition and stunting are still high [ 1 ]. Over the past 20 years, researchers have implemented interventions to reduce undernutrition, specifically focussing on the first 1000 days of life, from conception to 24 months [ 2 ]. However, due to both differing determinants between countries [ 3 , 4 ] as well as varying contextual factors, it is clear that no single fixed approach or combination of approaches can be relied on when implementing stunting interventions [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. Furthermore, when external researchers design interventions for local areas in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) they can often overlook relevant local cultural factors that consequently act as barriers to intervention uptake and reduce their effectiveness, such as geographical factors and the levels of migration in certain populations [ 8 , 9 ], or social norms or perceptions relating to accepting outside help, and power dynamics related to gender [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. The inclusion of cultural level factors in behaviour change interventions has been proposed as a requirement for effective interventions [ 13 ]. However, despite the breadth of literature highlighting the negative impacts from failing to do this, the lack of integration or even regard of local culture remains a persistent problem in Global Health Research [ 14 ], possibly hindering progress towards the SDGs. Thus, there is a need for approaches to integrate local cultural elements into intervention design.
This lack of understanding of relevant local culture, social norms and shared values also has ethical implications. The field of Global Health Ethics was predominantly developed in the Global North, in High Income Countries (HICs), embedding values common in those countries such as the prominence of individual autonomy [ 15 , 16 ]. Researchers from HICs carrying out research in LMICs may wrongly assume that values held in the Global North are universal [ 14 ] and disregard some local values, such as those related to family and collective decision making, which are core to many communities in LMICs. It is therefore important for outside researchers to have an understanding of relevant local values, culture and social norms before conducting research in LMICs so as not to impose values that do not align with local culture and inadvertently cause harm or offence [ 16 , 17 ]. The importance of this is compounded by the colonial history that is often present in relationships between research communities in HICs and LMICs, and the fact that the majority of the funding and leading institutions are still located in the Global North [ 18 , 19 ]. Thus, conscious steps must be taken to avoid neo-colonialism in Global Health Research [ 20 ]. From a health-equity perspective, it is essential to ensure that those in vulnerable communities are not hindered from involvement in interventions to improve nutrition. Encouraging uptake by such communities could be provided if salient local shared values, norms and culture were taken into account [ 21 ].
In a recent paper, Memon et al., (2021) highlight the usefulness of first creating a cultural protocol that can precede and guide subsequent stages of community engagement or intervention design to ensure that salient local values are known to external researchers coming into the community [ 16 ]. We adopt the use of the concept of a cultural protocol, referring to locally-generated guidance about key values, norms, behaviours and customs relevant to working with the local community. However, we prefer the term, ‘culturally-informed protocol’ since this relates to only cultural elements deemed salient by the researchers, and locally, rather than any comprehensive notion of culture, nor extending beyond the research context.
Memon et al. (2021), point out links between the creation of such a protocol and existing codes of practice that have already been created for some cultures such as the Te Ara Tika, a Guideline for Māori Research Ethics [ 22 ]. Currently, research and interventions in Global Health can be informed by a stage of formative research involving one-to-one interviews, focus groups or direct observations, which can sometimes be ethnographic in nature such as within Focussed Ethnographic Studies or Rapid Assessment Procedures [ 23 , 24 , 25 ]. Although these methods can be effective to inform intervention designs, they have disadvantages like: can take long periods to complete [ 26 ], can be resource intensive [ 26 ] and can lack cultural acceptability [ 27 ]. These limitations may account for the frequent neglect of their use generally, highlighted by Aubel and Chibanda (2022) [ 14 ]. Additionally, none of these methods work towards making explicit local values, or towards the creation of a culturally-informed protocol. In brief, the literature suggests a need to develop alternative methods of Formative Research for understanding locally relevant cultural elements, that are less time-consuming and can generate data that is more easily translatable to intervention design. In addition, these approaches must be applicable in different cultures. Additionally, the protocols produced must be actionable and practical not only for guiding interactions between research teams but also for guiding the initial stages of intervention design.
The work presented here aims to address several of these needs. It includes an exploration of the usefulness of the WeValue InSitu ( WVIS ) approach because that has previously been shown, in environmental management domains, to offer a way to gather in-depth values-based perspectives from a target population [ 28 , 29 ] It was first created through action research, and co-designed to enable civil society organisations to better understand and measure the values-based aspects of their work [ 30 ]. The core WeValue InSitu process (detailed in Table 1 ) involves the crystallization of shared values, with a facilitator guiding a group of participants with shared experiences, through cycles of tacit meaning-making (using a stage of photo-elicitation and triggering) [ 31 ], until they can articulate more explicitly their shared values, in concise and precise statements. These statements are then linked together in a framework by the participants. In an example case in Nigeria, the results of the WVIS approach hinted at the creation of a culturally-informed protocol through an analysis of the shared values frameworks to find cultural themes for the creation of an indicator tool that was used to evaluate several development scenarios based on their social acceptability [ 29 ].
Furthermore, it has been found that if a group of WVIS participants take part in a specialised focus group discussion (FGD), named Perspectives EXploration (PEX:FGD) immediately afterward the main workshop, then they easily and articulately express their perspectives on the topics raised for discussion - and with allusions to the shared values they had crystallised just prior. In an example from Shanghai, the PEX:FGDs focussed on eliciting perspectives on climate change, which were shown to be closely linked with the cultural themes existing within the shared values frameworks produced immediately prior [ 32 ]. In that case, the PEX:FGDs allowed the cultural themes generated during the main WVIS workshop to be linked more closely to the research question. Those results suggested that the WVIS plus PEX:FGD approach could be used to create a specialised culturally-informed protocol for improved intervention design.
In the study presented here, the WVIS approach was explored for the purpose of creating culturally-informed protocols to inform the planning of interventions within two localities of the UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub [ 33 ]. The work was carried out in two parts. Firstly, the WVIS main workshop was used to elicit cultural themes within the target communities, indicating key elements to consider to ensure ethical engagement. Secondly, the PEX focus group discussions focussed on life practices related to stunting which we explored for the purpose of tailoring the culturally-informed protocols to the specific purpose of improving the design of an example intervention. The Action Against Stunting Hub works across three sites where stunting is highly prevalent but via different determinants: East Lombok in Indonesia (estimated 36% of under-fives stunted), Kaffrine in Senegal (estimated 16% of under-fives stunted) and Hyderabad in India (estimated 48% of under-fives stunted) [ 34 ]. We propose that, the information about local shared values in a given site could be used to inform the design of several interventions, but for our specific exploration the focus here is a proposed ‘egg intervention’, in which pregnant women would be provided with an egg three times per week as supplement to their diet. This study proposes that identifying shared values within a community, alongside information about local life practices, provides critical cultural information on the potential acceptability and uptake of this intervention which can be used to generate culturally-informed protocols consisting of recommendations for improved intervention design.
In this paper we aim to explore the use of the WVIS approach to create culturally-informed protocols to guide engagement and inform the design of localised egg interventions to alleviate stunting in East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal. We do this by analysing data about local shared values that are crystallized using the WeValue InSitu ( WVIS ) process to provide clear articulation of local values, followed by an analysis of life practices discussed during PEX:FGD to tailor the culturally-informed protocols for the specific intervention design.
Study setting
This research was exploratory rather than explanatory in nature. The emphasis was on demonstrating the usefulness of the WeValue InSitu ( WVIS ) approach to develop culturally-informed protocols of practical use in intervention design, in different cultural sites. This study was set within a broader shared-values workstream within the UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub project [ 33 ]. The Hub project, which was co-designed and co-researched by researchers from UK, Indonesia, Senegal and India, involves cohorts of 500 women and their babies in each site through pregnancy to 24 months old, using cross-disciplinary studies across gut health, nutrition, food systems, micro-nutrition, home environment, WASH, epigenetics and child development to develop a typology of stunting. Alongside these health studies are studies of the shared values of the communities, obtained via the WVIS approach described here, to understand the cultural contexts of that diverse health data. In this study the data from East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal were used: India’s data were not yet ready, and these two countries were deemed sufficient for this exploratory investigation.
The WVIS approach
The WVIS approach is a grounded scaffolding process which facilitates groups of people to make explicit their shared values in their own vocabulary and within their own frames (details in Fig. 1 and activities in Table 1 ). The first stage of the WVIS is Contextualisation, whereby the group identifies themselves and set the context of their shared experiences, for example, as ‘mothers in East Lombok, Indonesia’. Subsequently, there is a stage of Photo Elicitation, in which the group are first asked to consider what is important, meaningful or worthwhile to them about their context (e.g., ‘being mothers in East Lombok, Indonesia’) and then asked to choose photos from a localised set that they can use as props to help describe their answer to the group [ 29 ]. After this, a localised Trigger List is used. This Trigger List consists of 109 values statements that act as prompts for the group. Examples of these values statements are included below but all the statements begin with “it is important to me/us that…”. The group are asked to choose which statements within the trigger list resonate with them, and those are taken forward for group intersubjective discussion. After a topic of their shared values has been explored, the group begin to articulate and write down their own unique statements of them. These also all begin with “It is important to me/us that…”. After discussing all pressing topics, the group links the written statements on the table into a unique Framework, and one member provides a narrative to communicate it to ‘outsiders’. The WVIS provides a lens of each group’s local shared values, and it is through this lens that they view the topics in the focus group discussions which immediately follow, termed Perspectives EXplorations (PEX:FGDs).
Schematic of the macro-level activities carried out during the WeValue InSitu ( WVIS ) main workshop session
This results in very grounded perspectives being offered, of a different nature to those obtained in questionnaires or using external frameworks [ 31 ]. The specific PEX:FGD topics are chosen as pertinent to stunting contextual issues, including eating habits, food systems and environments, early educational environments, and perceptions of stunting. The local researchers ensured that all topics were handled sensitively, with none that could cause distress to the participants. The data for this study were collected over 2 weeks within December 2019–January 2020 in workshops in East Lombok, Indonesia, and 2 weeks within December 2020 in Kaffrine, Senegal.
The PEX:FGDs were kept open-ended so that participants could dictate the direction of the discussion, which allowed for topics that may not have been pre-considered by the facilitators to arise. Sessions were facilitated by local indigenous researchers, guided in process by researchers more experienced in the approach, and were carried out in the local languages, Bahasa in East Lombok, Indonesia and French or Wolof in Kaffrine, Senegal.
Development of localised WVIS materials
Important to the WVIS approach is the development of localised materials (Table 1 ). The main trigger list has been found applicable in globalised places where English is the first language, but otherwise the trigger lists are locally generated in the local language, incorporating local vocabulary and ways of thinking. To generate these, 5–8 specific interviews are taken with local community members, by indigenous university researchers, eliciting local phrases and ways of thinking. This is a necessary step because shared tacit values cannot be easily accessed without using local language. Examples of localised Trigger Statements produced this way are given below: (they all start with: “It is important to me/us that…”):
…there is solidarity and mutual aid between the people
…I can still be in communication with my children, even if far away
…husbands are responsible for the care of their wives and family
…the town council fulfils its responsibility to meet our needs
…people are not afraid of hard, and even manual work
Study participants
The group participants targeted for recruitment, were selected by local country Hub co-researchers to meet two sets of requirements. For suitability for the WVIS approach they should be between 3 and 12 in number; belong to naturally existing groups that have some history of shared experiences; are over 18 years old; do not include members holding significantly more power than others; and speak the same native language. For suitability in the PEX:FGD to offer life practices with relevance to the research topic of stunting, the groups were chosen to represent stakeholders with connections to the food or learning environment of children (which the Action Against Stunting Hub refer to as the Whole Child approach) [ 33 ]. The university researchers specialising in shared values from the UK, and Senegal and Indonesia respectively, discussed together which stakeholder groups might be appropriate to recruit. The local researchers made the final decisions. Each group was taken through both a WVIS workshop and the immediately-subsequent PEX:FGD.
Data collection and analysis
Standard data output from the WeValue session includes i) the jointly-negotiated bespoke Statements of shared values, linked together in their unique Framework, and ii) an oral recording of a descriptive Narrative of it, given by the group. These were digitized to produce a single presentation for each group as in Fig. 2 . It represents the synthesised culmination of the crystallisation process: a portrait of what was ‘important’ to each stakeholder group. Separately, statements from the group about the authenticity/ownership of the statements are collected.

An illustrative example of one digitized Shared Values Framework and accompanying Narrative from a teacher’s group in East Lombok, Indonesia. The “…” refers to each statement being preceded by “It is important to us that…”
When these Frameworks of ‘Statements of Shared Values’ are viewed across all the groups from one locality (Locality Shared Values Statements), they provide portraits of ‘what is important’ to people living there, often in intimate detail and language. They can be used to communicate to ‘outsiders’ what the general cultural shared values are. In this work the researchers thematically coded them using Charmaz constructionist grounded theory coding [ 35 ] to find broad Major Cultural Themes within each separate locality.
The second area of data collection was in the post- WVIS event: the PEX:FGD for each group. A translator/interpreter provided a running commentary during these discussions, which was audio recorded and then transcribed. The specific topics raised for each group to discuss varied depending on their local expertise. This required completely separate workstreams of coding of the dataset with respect to each topic. This was carried out independently by two researchers: one from UK (using NVivo software (Release 1.3.1)) and one from the local country, who resolved any small differences. All the transcripts were then collated and inductively, interpretively analysed to draw out insights that should be relayed back to the Action Against Stunting Hub teams as contextual material.
The extracts of discussion which were identified as relevant within a particular Hub theme (e.g. hygiene) were then meta-ethnographically synthesised [ 36 ] into ‘Hub Theme Statements’ on each topic, which became the core data for later communication and interrogation by other researchers within the Action Against Stunting Hub. These statements are interpretations of participants’ intended meanings, and links from each of them to data quotes were maintained, enabling future interpretations to refer to them for consistency checks between received and intended meaning.
In this investigation, those Hub Theme Statements (derived from PEX:FGD transcripts) were then deductively coded with respect to any topics with potential implications of the egg intervention. Literature regarding barriers and facilitators to nutrition interventions indicated the following topics could be relevant: attitudes to accepting help; community interactions; cooking and eating habits; traditional beliefs about malnutrition; sharing; social hierarchies [ 12 , 37 , 38 ] to which we added anything related to pregnancy or eggs. This analysis produced our Egg Intervention Themes from the data.
The Major Cultural Themes and Egg Intervention Themes were then used to create a set of culture-based recommendations and intervention specific recommendations respectively for each locality. These recommendations were then combined to form specialized culturally-informed protocols for the egg intervention in each locality: East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal. The process is displayed schematically in Fig. 3 .
Schematic representation of the method of production of the culturally-informed protocol for each locality
The preparation of the localised WVIS materials at each site took 6 hours of interview field work, and 40 person hours for analysis. The 10 workshops and data summaries were concluded within 10 workdays by two people (80 person hours). The analysis of the PEX:FGD data took a further 80 person hours. Thus, the total research time was approximately 200 person hours.
The stakeholder group types are summarised in Table 2 . The data is presented in three parts. Firstly, the Major Cultural Themes found in East Lombok, Indonesia and in Kaffrine, Senegal are described – the ones most heavily emphasised by participants. Then, the Egg Intervention Themes and finally, the combined set of Recommendations to comprise a culturally-informed protocol for intervention design for each location. Quotations are labelled INDO or SEN for East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal, respectively.
Major cultural themes from frameworks and narratives
These were derived from the Locality Shared Values Statements produced in the WVIS .
East Lombok, Indonesia
Religious values.
Islamic values were crucially important for participants from East Lombok, Indonesia and to their way of life. Through living by the Quran, participating in Islamic community practices, and teaching Islamic values to their children, participants felt they develop their spirituality and guarantee a better afterlife for themselves and their children. Participants stated the Quran tells them to breastfeed their children for 2 years, so they do. Despite no explicit religious official curriculum in Kindergarten, the teachers stated that it was important to incorporate religious teaching.
“East Lombok people always uphold the religious values of all aspects of social life.”
“It is important for me to still teach religious values even though they are not clearly stated in the curriculum.” – Workshop 1 INDO (teachers).
“In Quran for instance, we are told to breastfeed our kids for 2 years. We can even learn about that ” – Workshop 3 INDO (mothers).
Related to this was the importance of teaching manners to children and preventing them from saying harsh words. Teachers stated that it was important to create a happy environment for the children and to ensure that they are polite and well-behaved. Similarly, mothers emphasised the need to teach their children good religious values to ensure they will be polite and helpful to their elders.
“Children don’t speak harsh words.”
“My children can help me like what I did to my parents”.
– Workshop 8 INDO (mothers).
Togetherness within families and the community
The Locality Shared Values Frameworks stressed the importance of togetherness, both within family and community. Comments mentioned it being important that people rely heavily on their family and come together in times of need to support each other and provide motivation. This was also important more broadly, in that people in society should support each other, and that children grow up to contribute to society. This was also reflected in comments around roles within the family. Despite women being primary care givers, and men working to finance the family, participants stated that they follow a process of consultation to make decisions, and when facing hardships.
“that we have the sense of kinship throughout our society”.
“We have togetherness as mothers”.
“For the family side, whatever happens we need to be able to be united as a whole family. We need to have the [sense of] forgiveness for the sake of the children” – Workshop 2 INDO (mothers).
Attitudes about extra-marital pregnancy
In East Lombok, Indonesia, it was essential to both mothers and fathers that pregnancy happened within a marriage, this was to ensure that the honour of the family was upheld and that the lineage of the child was clear. The potential danger to health that early pregnancies can cause was also acknowledged.
“If they don’t listen to parents’ advice, there will be the possibility of pre-marital pregnancy happening, which will affect the family [so much].
The affect is going to be ruining the good name, honour and family dignity. When the children [are] born outside [of] marriage, she or he will have many difficulties like getting a birth certificate [and] having a hard time when registering to school or family” - Workshop 4 INDO (mothers).
“ To make sure that our children avoid getting married at a very young age and moreover [avoid] having free sex so that they will not get pregnant before the marriage” - Workshop 9 INDO (fathers).
Kaffrine, Senegal
The Major Cultural Themes which emerged from the Kaffrine data are described below. As these are grounded themes, they are different than those seen in East Lombok, Indonesia.
Access to healthcare
A recurring theme amongst the groups in Kaffrine were aspirations of affordable and easy-to-access healthcare. Community health workers stated the importance of encouraging women to give birth in hospitals and spoke of the importance of preventing early pregnancy which result from early marriages. Giving birth in hospitals was also a concern for Public Office Administrators who highlighted that this leads to subsequent issues with registering children for school. Mothers and fathers stated the importance of being able to afford health insurance and access healthcare so that they could take care of themselves.
“That the women give birth in the hospital” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWS).
“To have affordable health insurance ” – Workshop 10 SEN (mothers).
“To have access to health care ” – Workshop 3 SEN (fathers).
“It is important that women give birth in the hospital in order to be able to have a certificate that allows us to establish the civil status” – Workshop 9 SEN (administrators).
Additionally, Community health workers spoke of their aspiration to have enough supplements to provide to their community so as to avoid frustration at the lack of supply, and mothers spoke of their desire to be provided with supplements.
“To have dietary supplements in large quantities to give them to all those who need them, so as not to create frustration” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWS).
Another aspect of access to healthcare, was mistrust between fathers and community health workers. Community health workers explained that sometimes men can blame them when things go wrong in a pregnancy or consider their ideas to be too progressive. Thus, to these community health workers the quality of endurance was very important.
“Endurance (Sometimes men can accuse us of influencing their wives when they have difficulties in conceiving)” – Workshop 5 SEN (CHWs).
Another recurring theme was the importance of having secure employment and a means to support themselves; that there were also jobs available for young people, and that women had opportunities to make money to help support the family. This included preventing early marriages so girls could stay in school. Having jobs was stated as essential for survival and important to enable being useful to the community and society.
“To have more means of survival (subsistence) to be able to feed our families”.
“To have a regular and permanent job”.
“We assure a good training and education for our children so that they will become useful to us and the community”.
“ Our women should have access to activities that will support us and lessen our burden” – Workshop 3 SEN (fathers).
It was considered very important to have a religious education and respect for religious elders. Moreover, living by, and teaching, religious values such as being hard working, humble and offering mutual aid to others, was significant for people in Kaffrine.
“Have an education in the Islamic Culture (Education that aligns with the culture of Islam)”.
“Respect toward religious leaders” – Workshop 3 SEN (fathers).
“ To organize religious discussions to develop our knowledge about Islam ” - Workshop 10 SEN (mothers).
“ Have belief and be prayerful and give good counselling to people ” - Workshop 4 SEN (grandmothers).
Egg intervention themes from each country from perspectives EXplorations focus group discussion data
Below are results of analyses of comments made during the PEX:FGDs in East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal. The following codes were used deductively: attitudes to accepting outside help, traditional gender roles, food sharing, traditional beliefs, social hierarchies and understanding of stunting and Other. These topics were spoken about during open discussion and were not the subject of direct questions. For example, topics relating to traditional gender roles came up in East Lombok, during conversations around the daily routine. Thus, in order to more accurately reflect the intended meaning of the participants, these were labelled food practices, under the “Other” theme. If any of the themes were not present in the discussion, they are not shown below.
Attitudes to accepting outside help
Few mentions were made that focussed on participants attitudes to accepting outside help, but participants were sure that they would not make changes to their menus based on the advice of outside experts. Additionally, teachers mentioned that they are used to accepting help from local organisations that could to help them to identify under-developed children.
“ We don’t believe that [the outsiders are] going to change our eating habits or our various menus ” – Workshop 3 INDO (Mothers).
Traditional gender roles
In East Lombok, mothers spoke about how their husbands go to work and then provide them with daily money to buy the food for the day. However, this was discussed in relation to why food is bought daily and is thus discussed below in the topics Other – Food practices.
Food sharing
In East Lombok, Indonesia, in times when they have extra food, they share it with neighbours, in the hope that when they face times of hardship, their neighbours will share with them. Within the household, they mentioned sharing food from their plate with infants and encouraging children to share. Some mothers mentioned the importance of weekly meetings with other mothers to share food and sharing food during celebrations.
“ Sometimes we share our food with our family. So, when we cook extra food, we will probably send over the food to our neighbour, to our families. So, sometimes, with the hope that when we don’t have anything to eat, our neighbour will pay for it and will [share with] us.” – Workshop 3 INDO (Mothers).
“Even they serve food for the kids who come along to the house. So, they teach the kids to share with their friends. They provide some food. So, whenever they play [at their] house, they will [eat] the same.” – Workshop 2 INDO (Mothers).
Understanding of stunting
The teachers in East Lombok were aware of child stunting through Children’s Development Cards provided by local healthcare organizations. They stated that they recognise children with nutrition problems as having no patience period, no expression, no energy for activities and less desire to socialise and play with other children. The teachers said that stunted children do not develop the same as other children and are not as independent as children who are the proper height and weight for their development. They also stated that they recognise stunted children by their posture, pale faces and bloated stomachs. They explained how they usually use the same teaching methods for stunting children, but will sometimes allow them to do some activities, like singing, later, once the other children are leaving.
“ They have no patience period, don’t have any energy to do any of the activities. No expression, only sitting down and not mingling around with the kids. They are different way to learn. They are much slower than the other kids .” – Workshop 1 INDO (teachers).
“ When they are passive in singing, they will do it later when everyone else is leaving, they just do it [by] themselves ” – Workshop 1 INDO (teachers).
Specific views on eggs
In East Lombok, Indonesia, there were no superstitions or traditional beliefs around the consumption of eggs. When asked specifically on their views of eggs, and if they would like to be provided with eggs, women in East Lombok said that they would be happy to accept eggs. They also mentioned that eggs were a food they commonly eat, feed to children and use for convenience. Eggs were considered healthy and were common in their house.
“ We choose eggs instead. If we don’t have time, we just probably do some omelettes or sunny side up. So, it happens, actually when we get up late, we don’t have much time to be able to escort our kids to the school, then we fry the eggs or cook the instant noodles. And it happens to all mothers. So, if my kids are being cranky, that’s what happens, I’m not going to cook proper meals so, probably just eggs and instant noodles.” – Workshop 3 INDO (Mothers).
Other important topics – food practices
Some detailed themes about food practices were heard in East Lombok, Indonesia. The women were responsible for buying and preparing the food, which they purchased daily mainly due to the cost (their husbands were paid daily and so provided them with a daily allowance) and lack of storage facilities. They also bought from mobile vendors who came to the street, because they could buy very small amounts and get occasional credit. The mother decided the menu for the family and cooked once per day in the morning: the family then took from this dish throughout the day. Mothers always washed their fruits and vegetables and tried to include protein in their meals when funds allowed: either meat, eggs, tofu or tempeh.
“ One meal a day. They [the mothers] cook one time and they [the children] can eat it all day long. Yes, they can take it all day long. They find that they like [to take the food], because they tend to feel hungry.” – Workshop 6 INDO (Mothers).
“ They shop every day because they don’t have any storage in their house and the other factor is because the husband has a daily wage. They don’t have monthly wage. In the morning, the husband gives the ladies the money and the ladies go to the shop for the food. ” – Workshop 4 INDO (Mothers).
In Kaffrine, the following themes emerged relating to an egg intervention: they were different in content and emphasis to Lombok and contained uniquely local cultural emphases.
Mothers were welcoming of eggs as a supplement to improve their health during pregnancy and acknowledged the importance of good nutrition during pregnancy. However, they also mentioned that their husbands can sometimes be resistant to accepting outside help and provided an example of a vaccination programme in which fathers were hesitant to participate. However, participants stated that the Government should be the source of assistance to them (but currently was not perceived to be so).
“But if these eggs are brought by external bodies, we will hesitate to take it. For example, concerning vaccination some fathers hesitate to vaccinate their children even if they are locals who are doing it. So, educating the fathers to accept this is really a challenge” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
Some traditional gender roles were found to be strong. The participants emphasised that men are considered the head of the household, as expected in Islam, with the mother as primary caregiver for children. This is reflected in the comments from participants regarding the importance of Islam and living their religious values. The men thus made the family decisions and would need to be informed and agree to any family participation in any intervention – regardless of the education level of the mother. The paternal grandmother also played a very important role in the family and may also make decisions for the family in the place of the father. Community Health Workers emphasised that educating paternal grandmothers was essential to improve access to healthcare for women.
“There are people who are not flexible with their wives and need to be informed. Sometimes the mother-in-law can decide the place of the husband. But still, the husband’s [permission] is still necessary.” – Workshop 1 SEN (CHWs).
“[We recommend] communication with mothers-in-law and the community. Raise awareness through information, emphasizing the well-being of women and children.” – Workshop 1 SEN (CHWs).
“The [grand]mothers take care of the children so that the daughters in-law will take care of them in return So it’s very bad for a daughter in law not to take care of her mother in-law. Society does not like people who distance themselves from children.” – Workshop 4 SEN (grandmothers).
Social hierarchies
In addition to hierarchies relating to gender/position in the family such as grandmothers have decision making power, there was some mention of social hierarchies in Kaffrine, Senegal. For example, during times of food stress it was said that political groups distribute food and elected officials who choose the neighbourhoods in which the food will be distributed. Neighbourhood leaders then decide to whom the food is distributed, meaning there is a feeling that some people are being left out.
“ It’s political groups that come to distribute food or for political purposes…organizations that often come to distribute food aid, but in general it is always subject to a selection on the part of elected officials, in particular the neighbourhood leaders, who select the people they like and who leave the others ” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
Participants explained that during mealtimes, the family will share food from one large plate from which the father will eat first as a sign of respect and courtesy. Sometimes, children would also eat in their neighbour’s house to encourage them to eat.
“ Yes, it happens that we use that strategy so that children can eat. Note that children like to imitate so that’s why we [send them to the neighbour’s house]” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs)”.
Traditional beliefs about malnutrition
In Kaffrine, Senegal, some participants spoke of traditional beliefs relating to malnutrition, which are believed by fewer people these days. For example, uncovered food might attract bad spirits, and any person who eats it will become ill. There were a number of food taboos spoken of which were thought to have negative consequences for the baby, for example watermelon and grilled meat which were though to lead to birth complications and bleeding. Furthermore, cold water was thought to negatively impact the baby. Groups spoke of a tradition known as “bathie” in which traditional healers wash stunted children with smoke.
“ There are traditional practices called (Bathie) which are practiced by traditional healers. Parents are flexible about the practice of Bathie ” – Workshop 1 SEN (CHWs).
Causes of malnutrition and stunting were thought to be a lack of a balanced diet, lack of vitamin A, disease, intestinal worms, poor hygiene, socio-cultural issues such as non-compliance with food taboos, non-compliance with exclusive breastfeeding and close pregnancies. Malnutrition was also thought by some to be hereditary. Numerous signs of malnutrition were well known amongst the groups in Kaffrine. For example, signs of malnutrition were thought to be a big bloated belly, diarrhoea, oedema of the feet, anaemia, small limbs and hair loss as well as other symptoms such as red hair and a pale complexion. Despite this, malnutrition was thought to be hard to identify in Kaffrine as not all children will visit health centres, but mothers do try to take their babies heights and weights monthly. The groups were aware of the effect of poverty on the likelihood of stunting as impoverished parents cannot afford food. Furthermore, the groups mentioned that there is some stigma towards stunted children, and they can face mockery from other children although most local people feel pity and compassion towards them. Malnourished children are referred to as Khiibon or Lonpogne in the local language of Wolof.
“ It is poverty that is at the root of malnutrition, because parents do not have enough money [and] will have difficulty feeding their families well, so it is the situation of poverty that is the first explanatory factor of malnutrition here in Kaffrine” – Workshop 9 SEN (administrators).
“It can happen that some children are the victim of jokes for example of mockery from children of their same age, but not from adults and older ” – Workshop 9 SEN (administrators).
Pregnancy beliefs
In Kaffrine, Senegal, there were concerns around close pregnancies, and pregnancies in women who were too young, and for home births. Within the communities there was a stigma around close pregnancies, which prevented them from attending antenatal appointments. Similarly, there were superstitions around revealing early pregnancies, which again delayed attendance at health centres.
Groups acknowledged the role of good nutrition, and mentioned some forbidden foods such as salty foods, watermelon and grilled meat (which sometimes related back to a traditional belief that negative impacts would be felt in the pregnancy such as birth complications and bleeding). Similarly, drinking cold water was thought to negatively affect the baby. Beneficial foods mentioned included vegetables and meat, during pregnancy.
“ Often when a woman has close pregnancies, she can be ashamed, and this particularly delays the time of consultation” – Workshop 5 SEN (CHWs).
“Yes, there are things that are prohibited for pregnant women like salty foods” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
In Kaffrine, Senegal, some participants spoke of a traditional belief that if a pregnant woman consumes eggs then her baby might be overweight, or have problems learning how to talk. Despite this, mothers in Kaffrine said that they would be happy to accept eggs as a supplement, although if supplements are provided that require preparation (such as powdered supplements), they would be less likely to accept them.
“These restrictions are traditional, and more women no longer believe that eggs will cause a problem to the child. But if these eggs are brought by external bodies, we will hesitate to take it.” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
“They don’t eat eggs before the child starts speaking (the child only eats eggs when he starts talking). This is because it’s very heavy and can cause bloating and may also lead to intestinal problems.” – Workshop 4 SEN (grandmothers).
Other important topics – access to health services
For the participants in Kaffrine, Senegal, accessing health services was problematic, particularly for pre- and post-natal appointments, which faced frequent delays. Some women had access due to poor roads and chose to give birth at home. Access issues were further compounded by poverty and social factors, as procedures in hospitals can be costly, and women with close pregnancies (soon after an earlier one) can feel shame from society and hide their pregnancy.
“Women really have problems of lack of finances. There are social services in the hospital; but those services rarely attend to women without finances. Even when a child dies at birth they will require money to do the necessary procedure ” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
Creation of the culturally-informed protocols
Recommendations that comprise a culturally-informed protocol for intervention design in each locality are given in Table 3 .
The Major Cultural Themes, and specific Egg Intervention Themes drawn out from only 9–11 carefully planned group sessions in each country provided a rich set of recommendations towards a culturally-informed protocol for the localised design of a proposed Egg Intervention for both East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal. A culturally-informed protocol designed in this way comprises cultural insights which are worthy of consideration in local intervention design and should guide future stages of engagement and provide a platform from which good rapport and trust can be built between researchers and the community [ 16 ]. For example, in Kaffrine, Senegal, the early involvement of husbands and grandmothers is crucial, which reflects values around shared decision making within families that are noted to be more prevalent in LMICs, in contrast to individualistic values in HICs [ 16 , 39 ]. Similarly, due to strong religious values in both East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal, partnerships with Islamic leaders is likely to improve engagement. Past studies show the crucial role that religious leaders can play in determining social acceptability of interventions, particularly around taboo topics such as birth spacing [ 40 ].
The WVIS plus PEX:FGD method demonstrated here produced both broad cultural themes from shared values, which were in a concise and easy-to-understand format which could be readily communicated with the wider Action Against Stunting Hub, as well as life practices relevant to stunting in Kaffrine, Senegal and in East Lombok, Indonesia. Discussions of shared values during the WVIS main workshop provided useful cultural background within each community. PEX:FGD discussion uncovered numerous cultural factors within local life practices that could influence on the Egg Intervention engagement and acceptability. Combining themes from the WVIS workshop and PEX:FGDs allowed for specific recommendations to be made towards a culturally-informed protocol for the design of an Egg Intervention that included both broad cultural themes and specific Intervention insights (Table 3 ). For example, in Kaffrine, Senegal, to know that the husband’s authoritative family decision-making for health care (specific) is rooted in Islamic foundations (wider cultural) points to an Intervention Recommendation within the protocol, involving consultations with Islamic Leaders to lead community awareness targeting fathers. Similarly, in East Lombok, Indonesia the (specific) behaviour of breastfeeding for 2 years was underpinned by (wider cultural) shared values of living in Islam. This understanding of local values could prevent the imposition of culturally misaligned values, which Bernal and Adames (2017) caution against [ 17 ].
There are a number of interesting overlaps between values seen in the WVIS Frameworks and Narratives and the categories of Schwartz (1992) and The World Values Survey (2023) [ 41 , 42 ]. For example, in both Kaffrine, Senegal and East Lombok, Indonesia, strong religious values were found, and the groups spoke of the importance of practicing their religion with daily habits. This would align with traditional and conservation values [ 41 , 43 ]. Furthermore, in Kaffrine, Senegal participants often mentioned the importance of mutual aid within the community, and similar values of togetherness and respect in the community were found in East Lombok, Indonesia. These would seem to align with traditional, survival and conservation values [ 41 , 43 ]. However, the values mentioned by the groups in the WVIS workshops are far more specific, and it is possible that through asking what is most worthwhile, valuable and meaningful about their context, the participants are able to prioritise which aspects of their values are most salient to their daily lives. Grounded shared values such as these are generally neglected in Global Health Research, and values predominant in the Global North are often assumed to be universal [ 14 ]. Thus, by excluding the use of a predefined external framework, we minimized the risk of imposing our own ideas of values in the community, and increased the relevance, significance and local validity of the elicited information [ 28 ].
Participatory methods of engagement are an essential step in conducting Global Health Research but there is currently a paucity of specific guidance for implementing participatory methods in vulnerable communities [ 16 , 44 ]. In addition, there is acknowledgement in the literature that it is necessary to come into communities in LMICs without assumptions about their held values, and to use bottom-up participatory approaches to better understand local values [ 14 , 16 ]. The WVIS plus PEX:FGD methodology highlighted here exemplifies a method that is replicable in multiple country contexts [ 28 , 32 ] and can be used to crystallize local In Situ Shared Values which can be easily communicated to external researchers. Coupled with the specialised FGD (PEX:FGD), values-based perceptions of specific topics (in this case stunting) can be elicited leading to the creation of specific Culture-based recommendations. This therefore takes steps to answer the call by Memon and colleagues (2021) for the creation of cultural protocols ahead of conducting research in order to foster ethical research relationships [ 16 ]. We believe that the potential usefulness of the WVIS approach to guide engagement and inform intervention design is effectively demonstrated in this study and WVIS offers a method of making explicit local values in a novel and valuable way.
However, we acknowledge that our approach has several limitations. It has relied heavily on the local university researchers to debate and decide which participant stakeholder groups should be chosen, and although they did this in the context of the Whole Child approach, it would have been advantageous to have involved cultural researchers with a deeper understanding of cultural structures, to ensure sufficient opportunities for key cultural elements to emerge. This would have in particular strengthened the intervention design derived from the PEX:FGD data. For example, we retrospectively realised that our study could have been improved if grandmothers had been engaged in East Lombok. Understanding this limitation leads to suggestion for further work: to specifically investigate the overlap of this approach with disciplinary studies of culture, where social interactions and structures are taken into account via formal frameworks.
There are more minor limitations to note. For example, the WVIS approach can only be led by a trained and experienced facilitator: not all researchers can do this. A training programme is currently under development that could be made more widely available through online videos and a Handbook. Secondly, although the groups recruited do not need to be representative of the local population, the number recruited should be increased until theoretical saturation is achieved of the themes which emerge, which was not carried out in this study as we focussed on demonstrating the feasibility of the tool. Thirdly, there is a limit to the number of topics that can be explored in the PEX:FGDs within the timeframe of one focus group (depending on the stamina of the participants), and so if a wider range of topics need formative research, then more workshops are needed. Lastly, this work took place in a large, highly collaborative project involving expert researchers from local countries as well as international experts in WVIS : other teams may not have these resources. However, local researchers who train in WVIS could lead on their own (and in this Hub project such training was available).
The need for better understanding, acknowledgement and integration of local culture and shared values is increasing as the field of Global Health Research develops. This study demonstrates that the WVIS plus PEX:FGD shared values approach provides an efficient approach to contextualise and localise interventions, through eliciting and making communicable shared values and local life practices which can be used towards the formation of a culturally-informed protocols. Were this method to be used for intervention design in future, it is possible that more focus should be given to existing social structures and support systems and a greater variety of stakeholders should be engaged. This study thus contributes to the literature on methods to culturally adapt interventions. This could have significant implications for improving the uptake of nutrition interventions to reduce malnutrition through improved social acceptability, which could help progression towards the goal of Zero Hunger set within the SDGs. The transferability and generalisability of the WVIS plus PEX:FGD approach should now be investigated further in more diverse cultures and for providing formative research information for a wider range of research themes. Future studies could also focus on establishing its scaling and pragmatic usefulness as a route to conceptualising mechanisms of social acceptability, for example a mechanism may be that in communities with strong traditional religious values, social hierarchies involving religious leaders and fathers exist and their buy-in to the intervention is crucial to its social acceptability. Studies could also focus on the comparison or combination of WVIS plus PEX:FGD with other qualitative methods used for intervention design and implementation.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request [email protected], Orcid number 0000–0002–1811-4597. These include deidentified Frameworks of Shared Values and Accompanying Narrative from each Group; deidentified Hub Insight Statements of relevant themes.
World Health Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Driving commitment for nutrition within the UN Decade of Action on Nutrition: policy brief. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
Google Scholar
Victora CG, Christian P, Vidaletti LP, Gatica-Domínguez G, Menon P, Black RE. Revisiting maternal and child undernutrition in low-income and middle-income countries: variable progress towards an unfinished agenda. Lancet. 2021;397(10282):1388–99.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Aguayo VM, Nair R, Badgaiyan N, Krishna V. Determinants of stunting and poor linear growth in children under 2 years of age in India: an in-depth analysis of Maharashtra's comprehensive nutrition survey. Matern Child Nutr. 2016;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):121–40.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Beal T, Tumilowicz A, Sutrisna A, Izwardy D, Neufeld LM. A review of child stunting determinants in Indonesia. Matern Child Nutr. 2018;14(4):e12617.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hossain M, Choudhury N, Adib Binte Abdullah K, Mondal P, Jackson AA, Walson J, et al. Evidence-based approaches to childhood stunting in low and middle income countries: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child. 2017;102(10):903–9.
Brar S, Akseer N, Sall M, Conway K, Diouf I, Everett K, et al. Drivers of stunting reduction in Senegal: a country case study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(Suppl 2):860s–74s.
Heidkamp RA, Piwoz E, Gillespie S, Keats EC, D'Alimonte MR, Menon P, et al. Mobilising evidence, data, and resources to achieve global maternal and child undernutrition targets and the sustainable development goals: an agenda for action. Lancet. 2021;397(10282):1400–18.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Goudet SM, Bogin BA, Madise NJ, Griffiths PL. Nutritional interventions for preventing stunting in children (birth to 59 months) living in urban slums in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;6(6):Cd011695.
PubMed Google Scholar
Desai S, Misra M, Das A, Singh RJ, Sehgal M, Gram L, et al. Community interventions with women's groups to improve women's and children's health in India: a mixed-methods systematic review of effects, enablers and barriers. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(12)
Muraya KW, Jones C, Berkley JA, Molyneux S. Perceptions of childhood undernutrition among rural households on the Kenyan coast – a qualitative study. BMC Public Health. 2016;16(1):693.
Isler J, Sawadogo NH, Harling G, Bärnighausen T, Adam M, Sié A, et al. 'If he sees it with his own eyes, he will understand': how gender informed the content and delivery of a maternal nutrition intervention in Burkina Faso. Health Policy Plan. 2020;35(5):536–45.
Zaidi S, Das JK, Khan GN, Najmi R, Shah MM, Soofi SB. Food supplements to reduce stunting in Pakistan: a process evaluation of community dynamics shaping uptake. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1046.
Wight D, Plummer M, Ross D. The need to promote behaviour change at the cultural level: one factor explaining the limited impact of the MEMA kwa Vijana adolescent sexual health intervention in rural Tanzania. A process evaluation. BMC Public Health. 2012;12(1):788.
Aubel J, Chibanda D. The neglect of culture in global health research and practice. BMJ Glob Health. 2022;7(9):e009914.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Myser C. Defining "global health ethics": offering a research agenda for more bioethics and multidisciplinary contributions-from the global south and beyond the health sciences-to enrich global health and global health ethics initiatives. J Bioeth Inq. 2015;12(1):5–10.
Memon R, Asif M, Khoso AB, Tofique S, Kiran T, Chaudhry N, et al. Recognising values and engaging communities across cultures: towards developing a cultural protocol for researchers. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):47.
Bernal G, Adames C. Cultural adaptations: conceptual, ethical, contextual, and methodological issues for working with Ethnocultural and majority-world populations. Prev Sci. 2017;18(6):681–8.
Glickman SW, McHutchison JG, Peterson ED, Cairns CB, Harrington RA, Califf RM, et al. Ethical and scientific implications of the globalization of clinical research. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(8):816–23.
King KF, Kolopack P, Merritt MW, Lavery JV. Community engagement and the human infrastructure of global health research. BMC Med Ethics. 2014;15(1):84.
Horton R. Offline: is global health neocolonialist? Lancet. 2013;382(9906):1690.
Article Google Scholar
Woodward EN, Matthieu MM, Uchendu US, Rogal S, Kirchner JE. The health equity implementation framework: proposal and preliminary study of hepatitis C virus treatment. Implement Sci. 2019;14(1):26.
The Pūtaiora Writing Group. Te Ara Tika Guidelines for Māori research ethics: A framework for researchers and ethics committee members. Health Research Council of New Zealand. (no date). Online, Accessed 5 th May 2023. Available from: http://www.hrc.govt.nz/sites/default/files/2019-06/Resource%20Library%20PDF%20-%20Te%20Ara%20Tika%20Guidelines%20for%20Maori%20Research%20Ethics.pdf
Pelto GH, Armar-Klemesu M, Siekmann J, Schofield D. The focused ethnographic study 'assessing the behavioral and local market environment for improving the diets of infants and young children 6 to 23 months old' and its use in three countries. Matern Child Nutr. 2013;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):35–46.
Bentley ME, Johnson SL, Wasser H, Creed-Kanashiro H, Shroff M, Fernandez Rao S, et al. Formative research methods for designing culturally appropriate, integrated child nutrition and development interventions: an overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014;1308:54–67.
Kodish S, Aburto N, Dibari F, Brieger W, Agostinho SP, Gittelsohn J. Informing a behavior change communication strategy: formative research findings from the scaling up nutrition movement in Mozambique. Food Nutr Bull. 2015;36(3):354–70.
Mattes RD, Rowe SB, Ohlhorst SD, Brown AW, Hoffman DJ, Liska DJ, et al. Valuing the diversity of research methods to advance nutrition science. Adv Nutr. 2022;13(4):1324–93.
Robert RC, Bartolini RM, Creed-Kanashiro HM, Verney SA. Using formative research to design context-specific animal source food and multiple micronutrient powder interventions to improve the consumption of micronutrients by infants and young children in Tanzania, Kenya, Bangladesh and Pakistan. Matern Child Nutr. 2021;17(2):e13084.
Sethamo OA, Masika RJ, Harder MK. Understanding the role of crystallizing local shared values in fostering effective community engagement in adaptation planning in Botswana. Clim Dev. 2020;12(5):448–56.
Odii EC, Ebido CC, Harder MK. A values-based approach for generating localized social indicators for use in sustainability assessment and decision-making: test case of brownfield soft reuse in Nigeria. Sci Total Environ. 2020;711:135045.
Podger D, Piggot G, Zahradnik M, Janoušková S, Velasco I, Hak T, et al. The earth charter and the ESDinds initiative: developing indicators and assessment tools for civil society organisations to examine the values dimensions of sustainability projects. J Educ Sustain Dev. 2010;4(2):297–305.
Odii BC, Huang Y, Bouvrie N, Harder MK. Cycles of meaning-making crystallization in the WeValue InSitu process as clear contributions towards transformative learning. J Clean Prod. 2021;304:127024.
Huang Y, Wu W, Xue Y, Harder MK. Perceptions of climate change impacts on city life in Shanghai: through the lens of shared values. Cleaner Prod Lett. 2022;3:100018.
Action Against Stunting Hub. UKRI GCRF action against stunting: alleviating child undernutrition, globally. 2020. URL: https://actionagainststunting.org/ [Accessed 15/08/2022].
UNICEF. Nutrition country profiles . 2010. URL: https://data.unicef.org/resources/nutrition-country-profiles/ [Accessed 10/05/2023].
Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory. 2nd ed. London: SAGE; 2014.
Noblit GW, Hare RD, Hare RD. Meta-ethnography: synthesizing qualitative studies: sage; 1988.
Stelle I, McDonagh LK, Hossain I, Kalea AZ, Pereira DIA. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1140.
Muraya KW, Jones C, Berkley JA, Molyneux S. "If it's issues to do with nutrition…I can decide…": gendered decision-making in joining community-based child nutrition interventions within rural coastal Kenya. Health Policy Plan. 2017;32(suppl_5):v31–v9.
Aubel J. Grandmothers — a neglected family resource for saving newborn lives. BMJ Glob Health. 2021;6(2):e003808.
Egeh AA, Dugsieh O, Erlandsson K, Osman F. The views of Somali religious leaders on birth spacing - a qualitative study. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2019;20:27–31.
Schwartz SH. Universals in the content and structure of values: Theoretical advances and empirical tests in 20 countries. Advances in experimental social psychology. 25: Elsevier; 1992. p. 1–65.
World Values Survey Association. Findings and insights, 2020 [Available from: https://www.worldvaluessurvey.org/WVSContents.jsp .]
Inglehart R, Welzel C. Value change and the persistence of cultural traditions. Modernization, cultural change, and democracy: the human development sequence. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2005. p. 48–76.
Glandon D, Paina L, Alonge O, Peters DH, Bennett S. 10 best resources for community engagement in implementation research. Health Policy Plan. 2017;32(10):1457–65.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank the Hub PI, Claire Heffernan, for feedback on a late draft of the manuscript.
The Action Against Stunting Hub is funded by the Medical Research Council through the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) Global Challenges Research Fund (GCRF), Grant No.: MR/S01313X/1.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Values & Sustainability Research Group, School of Architecture, Technology and Engineering, University of Brighton, Brighton, UK
Annabel J. Chapman, Mahsa Firoozmand & Marie K. Harder
Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
Chike C. Ebido, Rahel Neh Tening, Yanyan Huang & Marie K. Harder
Department of Zoology and Environmental Biology, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Nigeria
Chike C. Ebido
Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Université Cheikh Anta Diop (UCAD), Dakar, Senegal
Ndèye Marème Sougou
Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta, Indonesia
Risatianti Kolopaking
Southeast Asian Ministers of Education Organization Regional Centre for Food and Nutrition (SEAMEO RECFON) Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
Risatianti Kolopaking & Rita Anggorowati
International Research Laboratory (IRL 3189) Environnement santé et sociétés/CNRS/UCAD, Dakar, Senegal
Amadou H. Diallo
Department of Medical Records and Health Information, Faculty of Health and Technology, Universitas Bandung, Bandung, Indonesia
Rita Anggorowati
Laboratory of Cultural Anthropology, IFAN, Université Cheikh Anta Diop (UCAD), Dakar, Senegal
Fatou B. Dial & Cheikh El Hadji Abdoulaye Niang
School of Education, Languages and Linguistics, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Portsmouth, Portsmouth, UK
Jessica Massonnié
Department of Learning and Leadership, IOE, UCL’s Faculty of Education and Society, University College London, London, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MKH formulated the initial research question and study design. AJC developed the specific research question. Data collection in Senegal involved CCE, NMS, AHD, FBD, RNT, CEHAN and JM. Data collection in Indonesia involved RA, RK, YH and MKH. Cultural interpretation in Senegal Involved AHD, FBD, NMS, RNT and JM. Analysis involved AJC and MF. AJC and MKH wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Marie K. Harder .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and has been approved by the Ethics Review Board of the University of Brighton, and national ethics committees for research in Indonesia and Senegal. Informed consent was obtained in the local vernacular language, Bahasa, French or Wolof. Participants retained a copy of the informed consent document for reference.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Chapman, A.J., Ebido, C.C., Tening, R.N. et al. Creating culturally-informed protocols for a stunting intervention using a situated values-based approach ( WeValue InSitu ): a double case study in Indonesia and Senegal. BMC Public Health 24 , 987 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18485-y
Download citation
Received : 27 September 2023
Accepted : 29 March 2024
Published : 09 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18485-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Health intervention
- Shared values
- Culturally-informed protocol
- Cultural factors
- WeValue InSitu
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Main Navigation
/prod01/channel_8/media/scu-dep/current-students/images/Coffs-harbour_student-group_20220616_33.jpg)
- Accept offer and enrol
- Current Students
Personalise your experience
Did you mean..., diploma of arts and social sciences, art/science collaboration wins waterhouse natural science art prize, unit of study busn6008 strategy and case analysis (online) (2025).
Future students: 1300 854 556 [email protected]
Current students: [email protected]
updated - DO NOT REMOVE THIS LINE 6:05 AM on Fri, 12 April
Show me unit information for year
Unit snapshot.
PG Coursework Unit
Credit points
Faculty & college.
Faculty of Business, Law and Arts
Anti-requisites
BUSN6005 - Strategy and Case Analysis
Unit description
Examines the key principles of strategic management, with particular focus on the strategy process and its individual components – analysis, choice, action and evaluation. This unit makes use of the case analysis method so that students can apply their understanding to real-world problems across a range of professional contexts.
Unit content
Part 1 – Strategy Development
- Outside-in: Strategy as positioning, Porter’s 5-forces and positional matrix, PESTEL
- Inside-out: Resource-based view of strategy, VIRO/VIRN, developing resources/capabilities
- Emergent view of strategy, experiments, strategy innovation, the three views and bringing them together
Part 2 – Strategic Analysis and Fit
- Analysis models and frameworks such as McKinsey7-Ss, MIT90s, CAGE, and how to use them
- Fit and sustainability, strategy-structure-processes, Miles and Snow, structural options
Part 3 – Strategy Implementation
- Strategy implementation and organisational change
Availabilities
Learning outcomes.
Unit Learning Outcomes express learning achievement in terms of what a student should know, understand and be able to do on completion of a unit. These outcomes are aligned with the graduate attributes . The unit learning outcomes and graduate attributes are also the basis of evaluating prior learning.
On completion of this unit, students should be able to:
demonstrate an understanding of strategic management tools, frameworks and processes
apply strategic management theories to the analysis of real-world case studies
critique the strategic management approach of a contemporary organisation
apply a formal strategy process to diagnose and address a strategic business problem.
Teaching and assessment
Scu online (term), prescribed learning resources.
- Prescribed text information is not currently available.
- Prescribed resources/equipment information is not currently available.
Prescribed Learning Resources may change in future Teaching Periods.
Fee information
Commonwealth Supported courses For information regarding Student Contribution Amounts please visit the Student Contribution Amounts .
Fee paying courses For postgraduate or undergraduate full-fee paying courses please check Domestic Postgraduate Fees OR Domestic Undergraduate Fees .
International
Please check the international course and fee list to determine the relevant fees.
Courses that offer this unit
Graduate diploma of information technology management (2024), graduate diploma of information technology management (2025), graduate diploma of project management (2024), graduate diploma of project management (2025), master of business administration (2025), master of business administration (2024), master of information technology management (2024), master of information technology management (2025), master of project management (2025), master of project management (2024), any questions we'd love to help.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Case Study: How Aggressively Should a Bank Pursue AI?
- Thomas H. Davenport
- George Westerman

A Malaysia-based CEO weighs the risks and potential benefits of turning a traditional bank into an AI-first institution.
Siti Rahman, the CEO of Malaysia-based NVF Bank, faces a pivotal decision. Her head of AI innovation, a recent recruit from Google, has a bold plan. It requires a substantial investment but aims to transform the traditional bank into an AI-first institution, substantially reducing head count and the number of branches. The bank’s CFO worries they are chasing the next hype cycle and cautions against valuing efficiency above all else. Siti must weigh the bank’s mixed history with AI, the resistance to losing the human touch in banking services, and the risks of falling behind in technology against the need for a prudent, incremental approach to innovation.
Two experts offer advice: Noemie Ellezam-Danielo, the chief digital and AI strategy at Société Générale, and Sastry Durvasula, the chief information and client services officer at TIAA.
Siti Rahman, the CEO of Malaysia-headquartered NVF Bank, hurried through the corridors of the university’s computer engineering department. She had directed her driver to the wrong building—thinking of her usual talent-recruitment appearances in the finance department—and now she was running late. As she approached the room, she could hear her head of AI innovation, Michael Lim, who had joined NVF from Google 18 months earlier, breaking the ice with the students. “You know, NVF used to stand for Never Very Fast,” he said to a few giggles. “But the bank is crawling into the 21st century.”
- Thomas H. Davenport is the President’s Distinguished Professor of Information Technology and Management at Babson College, a visiting scholar at the MIT Initiative on the Digital Economy, and a senior adviser to Deloitte’s AI practice. He is a coauthor of All-in on AI: How Smart Companies Win Big with Artificial Intelligence (Harvard Business Review Press, 2023).
- George Westerman is a senior lecturer at MIT Sloan School of Management and a coauthor of Leading Digital (HBR Press, 2014).
Partner Center
Why is nutrient cycling in food systems so limited? A case study from the North-Netherlands region
- Original Article
- Open access
- Published: 12 April 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Durk W. Tamsma ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3748-6660 1 ,
- Corina E. van Middelaar ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6835-998X 2 ,
- Imke J. M. de Boer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0675-7528 2 ,
- Johannes Kros ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1354-4990 3 ,
- Martin K. van Ittersum ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8611-6781 1 &
- Antonius G. T. Schut ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7512-728X 1
Identifying pathways to circular agriculture requires a profound understanding of nutrient flows and losses throughout the food system, and of interactions between biophysical conditions, land use, food production and food consumption. We quantified nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) flows of the food system of the North-Netherlands (NN) region and of its 30 subregions varying in biophysical and socio-economic conditions. The food system included agriculture, food processing, consumption, and waste processing. Nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), phosphorus use efficiency (PUE) and the nutrient cycling counts were calculated. Results show a low NUE (25%) and PUE (59%) of the food system. External inputs were used to maintain high yields and production. Nutrient cycling was very limited with losses from agriculture ranging from 143 to 465 kg N ha −1 y −1 and 4 to 11 kg P ha −1 y −1 . Food system losses ranged from 181 to 480 kg N ha −1 y −1 and from 7 to 31 kg P ha −1 y −1 and varied with biophysical conditions, population density and farming systems. Large losses were associated with livestock farming and farming on drained peat soils. Food system efficiency was strongly associated with the utilization of produce. We conclude that increasing circularity requires tailoring of agriculture to local biophysical conditions and food system redesign to facilitate nutrient recycling. Steps towards circularity in NN include: matching livestock production to feed supply from residual flows and lands unsuitable for food crops, diversifying crop production to better match local demand and increasing waste recovery.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Today’s food system has a significant impact on the planet (Crippa et al. 2021 ; Mueller et al. 2012 ; Pereira et al. 2010 ). Currently food systems heavily rely on external resources including energy, mined nutrients and chemicals (Kuokkanen et al. 2017 ). Various factors enhance this input dependency. The disconnection of food production and consumption leads to losses of nutrients in the system from urban areas. On-farm and regional specialization in agriculture with de-coupled crop and livestock production (Garrett et al. 2020 ; Martin et al. 2016 ; Schut et al. 2021 ) has resulted in inefficient use of nutrients (Tan et al. 2022 ) with manure excess in areas of intensive livestock production (Bai et al. 2022 ; de Vries et al. 2021 ). Furthermore, the utilization of less suitable soils for intensive agriculture comes with substantial nutrient losses and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, the latter in particular from degradation of organic soils (Crippa et al. 2021 ). The theory of circular agriculture provides a guideline to resolve several of these issues and is increasingly seen as an important means for a sustainable food future.
The concept of circularity has been applied to agriculture (de Boer and van Ittersum 2018 ), food systems (Jurgilevich et al. 2016 ) and the biobased economy (Muscat et al. 2021 ). Muscat et al. ( 2021 ) argue that the foremost principle of circular agriculture is to safeguard the health of (agro)ecosystems by not exceeding the regenerative capacity of natural resources. In addition, they emphasize the importance of efficient resource use by avoiding non-essential products and residual flows of essential products, prioritizing biomass use for human needs, and by recycling of unavoidable residual flows. Finally, they propose that the external energy requirement of the system can be decreased by working with nature and by maximising the utility of materials and recycling (Bergen et al. 2001 ; Muscat et al. 2021 ). By following these principles of circularity, food systems could in theory transition from a linear extract-consume-discard system to a more circular one in which resource loops are closed to prevent depletion of mineral and fossil resources and reduce emissions to the air, water and soil (Muscat et al. 2021 ).
Circularity of resource flows in the food system requires a food systems lens to quantify and eventually optimize flows between food system components in order to minimize resource use and environmental impacts at the level of the entire food system. This goes beyond resource use efficiency of individual agricultural sectors or production chains. Circular food systems also require spatial reconfiguration of production to enhance re-coupling of nutrient flows with limited biomass transport and to stay within local environmental carrying capacities (Bai et al. 2022 ; Koppelmäki et al. 2021 ). Furthermore, production may need to be coupled to food demand on more local or regional scales to limit nutrient imbalances between regions and to minimize energy use and GHG emissions from transportation. However, the feasibility of recoupling nutrient flows locally is strongly tied to the local biophysical production conditions which determine the suitability for and efficiency of food production. The scale at which striving for circularity in food systems is feasible is therefore determined by the biophysical context affecting the ability to produce food, but also by the processing capacity of agricultural products, food demand and the availability of consumer waste.
Several studies have quantified biomass and/or nutrient flows at farm (de Vries et al. 2018 ; Schröder et al. 2003 ), regional (Hanserud et al. 2016 ; Le Noë et al. 2017 ; Theobald et al. 2016 ; Vingerhoets et al. 2023 ), national (van Selm et al. 2022 ) or global (Crippa et al. 2021 ; Willett et al. 2019 ) levels with the aim of more circular resource use. However, such studies either focus on the entire food system with a subnational region as the smallest spatial unit, or on agriculture in its local context but with limited attention for the complexity of agriculture as part of the food system. Hence, it is still poorly understood how the biophysical production environment, type and productivity of production systems and local food demand interact with nutrient flows, losses and circularity of the food system.
To improve our understanding of these interrelationships, the objective of this study was twofold. First, we aimed to quantify nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) flows and to evaluate differences in efficiency between subsystems of the food system and between subregions within the ‘North-Netherlands’ (NN); and second to benchmark the circularity of the current food system and provide a deeper understanding of nutrient cycling, losses and inefficiencies in this highly specialized, food exporting region. We compared four subregions that strongly differed in soil type as a proxy for the biophysical conditions, production volumes of crop- and animal products as an indicator of specialization and population as a proxy for consumption. Three subregions had suitable sandy- and clay soils. Of these Achtkarspelen was characterized by predominantly intensive husbandry and low population density, Veendam-Pekela by arable farming and low population density and Assen by mixed farming and high population density. Subregion de Fryske Marren was characterized by predominantly peat soils with dairy farming and a low population density. Nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and phosphorus use efficiency (PUE) were evaluated at subsystem level and for the entire food system. A cycling count indicator (van Loon et al. 2023 ) was used to evaluate the degree of nutrient recycling in the current food system and to identify opportunities to enhance circular resource use. We hypothesized that subregional differences in indicators of efficiency and circularity of the food system are directly linked to the biophysical characteristics of the production environment and associated agricultural specialization and to local food demand and thus to import and export.
A mass flow analysis was conducted to quantify nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) flows in the food system of the North Netherlands region and of constituent subregions for the years 2015–2019. Total flows and losses as well as nutrient use efficiency and the nutrient cycling count of the current food system were calculated.
Delineation of case study
Region description.
The North Netherlands (NN) region covers an area of 8,292 km 2 land and includes the provinces of Friesland, Groningen, and Drenthe with in total 1,7 million inhabitants. The population density of 216 inhabitants km −2 is much lower than the Dutch average of 517 inhabitants km −2 , yet is still far above the EU27 average of 118 inhabitants km −2 (CBS 2020 ; EUROSTAT 2021 ). However, NN is relatively land abundant with 0.31 ha of cultivated land per capita, which includes cropland, grassland, and horticulture (CBS 2022a , b ). This is way more than the 0.06 ha cultivated land per capita for the Netherlands and 0.22 ha cultivated land per capita for the EU27 (The World Bank 2020 ), highlighting the role of NN as a food producing region. About 70% of the land in NN is used for agriculture, including 45% for livestock farming and 19% for cropping (CBS 2018 , 2022b ). Main crops are: winter and spring wheat, barley, sugar beets and seed, ware and starch potatoes. The livestock sector consists mainly of dairy cattle with a smaller number of pig and poultry farms (Smit et al. 2017 ). Horticulture takes up about 1% of total agricultural land (Smit et al. 2017 ). There is an ongoing trend of specialization and increasing farm size, in line with wider European trends (Schut et al. 2021 ; Smit et al. 2017 ). The NN is a strong exporting region producing for the EU and world markets (CBS 2016 ). The region includes a wide variety of bio-physical conditions, with different soil types and ground water levels. NN is an important region for biodiversity conservation, and supports large populations of migratory birds (Reneerkens et al. 2005 ) and has unique habitats for various animal and plant species (Aptroot et al. 2012 ; Peeters and Reemer 2003 ). It also borders the Wadden sea, the largest tidal flats in the world that provide a unique habitat for numerous species (Wortelboer 2010 ).
We divided NN into 30 constituent subregions that contrasted in predominant soil type, agricultural specialization and population density (Fig. 1 ). Soil type was chosen as a proxy for variations in the biophysical production environment, as it is the most important determinant of the suitability for and the nutrient efficiency of the production of different crops in the region. Agricultural specialization determines what is produced, processed and exported from a subregion. Variation in population density is directly related to consumption and the availability of recyclable consumer waste. These proxies for the biophysical environment, specialization and consumption together give insight in the potential for and possible pathways to circularity in a local or regional food system.
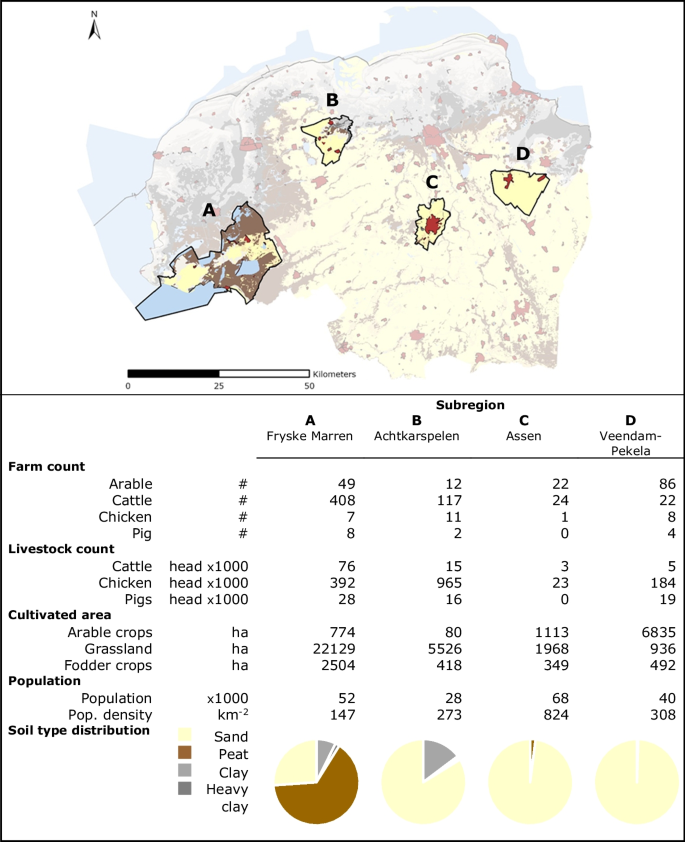
Map and summary statistics of four subregions in North Netherlands (NN). These subregions illustrate the local contrasts in soil types, agricultural specialization and population density found within the region. The presented statistics include farm- and livestock counts (CBS 2022b ), the cultivated area of arable and feed crops (CBS 2022b ) and population density (CBS 2022a ) and are average values for the years 2015–2019. The pie charts show the ratio between different soil types in each subregion
Definition of the food system and substance flow model
This case study focused on the food system within mainland NN. The subsystems included were: agriculture, food- and feed processing, (human) consumption and waste processing. A substance flow model was developed to analyse annual nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in- and outflows of the system, including flows within and between the different subsystems (Supplementary Material; Fig. S1 ). The selection of flows was based on earlier studies on comparable food systems (Smit et al. 2010 ; van der Wiel et al. 2020 , 2021 ) and adapted to region-specific conditions. Where possible, flows were quantified by using publicly available data from national databases and research reports. Important sources included Statistics Netherlands (CBS), the Dutch Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management (Rijkswaterstaat), the National Institute for Health and the Environment (RIVM) and the INITIATOR (Integrated Nutrient ImpacT Assessment Tool On a Regional scale) model developed by Wageningen Environmental Research. Gaps in the data were filled through interviews with experts from the region. Data was collected for the municipality level. Average data from the years 2015–2019 was used where possible to account for temporal variation. As the 2015–2019 period coincided with a reorganisation of municipalities in NN, the spatial entities changed. Therefore, subregions were created by merging municipalities to the level at which data was available for all years, creating the smallest possible spatial entities. For several flows no data was available at the subregional spatial level, most notably trade data for food and feed. In these cases a feed and food balance approach was used to estimate imports and exports (van der Wiel et al. 2021 ). Agricultural products were assumed to be processed in the subregion of origin, since flows of agricultural products to centralized processing facilities could not be tracked. Thus the systems presented here for NN and each subregion represent the food systems flows that are associated with the food production and consumption in NN and in each respective subregion.
Calculation of flows
A complete overview of all flows, their main data sources and calculation is given in the Supplementary Material (Fig. S1 ; Table S1 ). The entire calculation procedure has been made available online (DOI: https://doi.org/10.4121/8899e893-c68a-4fe1-813e-6af228eb0ef1 ). Below we provide an outline of the calculation procedure for the main components in the food system.
Agriculture
Agriculture was restricted to arable crop and livestock production, (greenhouse) horticulture was excluded. Livestock included dairy and beef cattle, pigs, poultry, and sheep. Livestock from hobby farms were excluded as these were not included in the agricultural census.
Most internal flows in the subsystem agriculture were calculated using the INITIATOR model (de Vries et al. 2023 ; Kros et al. 2019 ). INITIATOR calculates spatially explicit N, P and C fluxes in agriculture, including the supply of N, P and C in the form of fertilizer, animal manure, deposition and N fixation, the N and P discharge by the crop and the emissions of methane (CH 4 ), ammonia (NH 3 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and nitrogen oxides (NO x ) to the atmosphere. The model uses detailed spatial data that largely came from available national datasets, such as the geographically explicit agricultural census data, including crop type, cropping area, livestock numbers and housing type at farms. INITIATOR was used to calculate manure excretion on farm level as well as gaseous N losses from animal housing and manure storage. Manure was distributed over the fields of the farm, up to the legal application limit for animal manure per hectare. Any excess manure was initially divided over the agricultural area within each (aggregated) municipality. Any remaining excess was subsequently exported to regions of NN with a manure shortage, i.e. where more manure could be applied within the legal limit. Similarly, if the legal application limit was not reached, manure was imported from other regions of the Netherlands with excess manure. In the Netherlands, legislation enforces that excess manure needs to be exported as manure or in processed form to farmers in manure deficient areas who get rewarded for manure application on cropland. Gaps between effective N and P applied with animal manure and the legal total effective application limits were assumed to be filled up with artificial fertilizers and compost. This is a reasonable assumption, because fertilizer inputs are cheap relative to product prices in the Netherlands and farmers utilize the entire application norm (Langeveld et al. 2007 ; Reijneveld et al. 2010 ). In addition N and P inputs from atmospheric deposition were taken into account. The INITIATOR soil module was used to calculate the amounts of nitrogen fixation and decomposition of organic matter as well as crop uptake and losses from manure storage, fertilizer application, leaching, runoff and denitrification per hectare. Loss fractions differed between soil types and groundwater levels (de Vries et al. 2023 ).
The crop offtake of kg N ha −1 and kg P ha −1 and crop area obtained from INITIATOR were multiplied to obtain production per subregion. Crops in INITIATOR output were grouped into: potatoes, sugar beet, wheat, other cereals, grass, silage maize and miscellaneous crops. We segregated the production of crop groups into individual crops by estimating for each subregion the production ratio between each crop in a group. To this aim crop areas and yields from (CBS 2022b ) and crop nutrient content obtained from experimental studies in the Netherlands were multiplied to provide N and P production per crop (de Ruijter et al. 2020 ; Ehlert et al. 2009 ). The total mass of N and P in consumed feed was calculated using the average fodder and feed concentrate consumption per animal per feed group reported by (CBS 2019 ) and the livestock numbers from the agricultural census (CBS 2022b ). It was assumed that all fodder was produced in the region. In most cases the production of fodder crops did not exactly match the calculated consumption by livestock. Such discrepancies were resolved by adjusting the grass nutrient content, as this was a major source of uncertainty. The feed concentrate requirement was filled with residual flows from the processing and waste processing industries and supplemented with feed imports if needed (see Sects. 2.2.3 and 2.2.5). Animal production was calculated by multiplying livestock numbers by production per animal and the N and P content of various animal products (CBS 2019 ). Nutrient balances were maintained, i.e. nutrients in feed supply exactly matched offtake with animal products and excreta.
Food processing
Food processing included processing of raw products from agriculture in each subregion and NN only. The fraction of each raw crop and animal product that was processed was derived from literature (Supplementary Material; Table S1 ). The remaining produce was assumed to be consumed in unprocessed form. Crop and animal products were converted into food products and residual flows using transfer coefficients (TCs). TCs were derived either directly from processing industries in the region or from Dutch sectorial sources (Supplementary Material; Table S1 ). The most common application of each residual flow was obtained from industry reports or directly from processing companies. Applications of processing output were grouped as: food, livestock feed, soil amendment and other flows that left the food system. In case flows had multiple applications a best-case scenario was assumed where application as livestock feed was preferred over application to soil, which in turn was preferred over applications outside the food system. Food, feed, and soil amendments that were not exported were designated as inputs to consumption and agriculture respectively (see 2.2.5). We assumed that seed potatoes and non-food cash crops (e.g. fiber hemp) were exported as whole products from the region without further processing. Losses from processing to the environment were not quantified because of data limitations.
Food consumption
Consumption included the food consumption of the human population in the region, excluding their pets and recreational animals. Food consumption was calculated from regional and municipal demographic data (CBS 2022a ) and consumption per capita. Per capita consumption of products in different food groups was derived from the Dutch Food Consumption Survey (van Rossum et al. 2020 ). An overview of food groups is given in (van Rossum et al. 2020 ). One average diet was assumed for the entire population, based on the average diet of males and females between the ages of 1 and 79, weighed by the population composition of NN (van Rossum et al. 2020 ). The N and P contents per food item were obtained from the Dutch Food Composition Database and averaged for all products in a food group (RIVM 2021 ). The amount of food waste was estimated based on the food waste survey by (CREM Waste Management 2017 ). Human body mass changes were ignored, and it was therefore assumed that all consumed N and P in food was excreted.
Waste processing
Waste processing included organic waste arising from the food system only, thus including food waste and human excreta but excluding garden waste. All human excreta were assumed to be treated at a typical communal wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), since 99.7% of Dutch households is connected to the communal sewer (Oosterom and Hermans 2013 ). N and P from human excreta were allocated to sludge, emissions to the air and to surface water (Rijkswaterstaat 2019 ; WSBD 2018 ). In the Netherlands nutrients are currently not recovered from sludge in any significant quantity and were therefore considered lost from the system (Regelink et al. 2017 ). Food waste went to incineration, landfilling, livestock feed, composting or anaerobic digestion in ratios derived from (Soethoudt and Vollebregt 2020 ). All incinerated and landfilled food waste was considered lost from the food system. Compost, digestate and livestock feed were returned to agriculture.
Retail: Food and feed import- and export
A net balance approach was used to estimate food and feed imports and exports at subregional and at NN regional level. Livestock N and P requirements were met with local roughage and co-products from processing industries and waste processing and were supplemented with feed imports. Local food demand for each food group was filled with produce from the subregion or NN region and supplemented with food imports. Consumed horticulture products were part of the food imports, as horticulture was not included in this study due to its small acreage in the region. Products that were produced but not consumed were assumed to be exported. Summed totals of import and export were used to calculate the net import/export balance over all food groups. This is an approach that determines the highest possible degree of local consumption rather than actual local consumption, used to compensate for the lack of trade data at the sub-national level. Losses from retail were ignored as losses from supermarkets in the Netherlands are estimated at only 1.7% (CBL 2020 ).
Data reliability
Data uncertainty was accounted for using the approach of (van der Wiel et al. 2021 ). An uncertainty level was assigned to each flow based on the type of data source, as most sources did not provide uncertainty estimates. Flows were assigned the uncertainty level of the most uncertain data source used in their calculation, rather than the propagated uncertainty of all variables (van der Wiel et al. 2021 ). The level of aggregation of source data differed substantially between flows, meaning that uncertainty propagation would disproportionally affect flows based on less aggregated data. Each uncertainty level was associated with a relative uncertainty interval as specified by (van der Wiel et al. 2021 ) (Table 1 ). Subsequently, uncertainty ranges were calculated by multiplying each flow by their respective relative uncertainty interval. Flows in the subsystem agriculture were assigned the uncertainty level nearest to the uncertainties reported for each flow by (de Vries et al. 2003 ) and N losses were assigned the highest uncertainty level as the fate of N in the environment is not well documented. The uncertainty estimates of all flows can be found in the Supplementary Material (Table S1 ).
All flows, balances and indicators were computed for the NN region and for each subregion. Flows were expressed in megagram per year (Mg y −1 ) and converted to kilogramme per hectare of agricultural land per year (kg ha −1 y −1 ), using the total area used for agriculture in a (sub)region. Checks were done to ensure the law of mass conservation was observed. This was done for each subsystem and for the whole food system. The use efficiencies (UE) for N (NUE) and P (PUE) were determined for the whole food system and for each subsystem:
For NUE and PUE output and input are the N or P flows out of and into the respective (sub)system, excluding losses. An overview of the most important inputs and outputs into the system and subsystems is given in Fig. 2 . For example, inputs into subsystem livestock are feed from waste processing, feed from food processing, feed import and feed crops. Outputs of livestock are animal products and excreted manure with losses all resulting from manure storage. A complete overview of all individual flows is given in the Supplementary Material (Fig. S1 ). All flows with a purpose outside the food system or outside the (sub)region were considered outputs, thus including food exports, manure export (in the case of any excess) and residual flows of food processing, but excluding landfilled food waste which was considered a loss. To assess the effects of the assumption that manure is a useful export product, we also calculated UEs excluding manure export as useful output, as excess manure is of limited value compared to food exports. In this case excess manure was counted as a loss. Furthermore, we estimated the externalized losses from the production of feed imports, by dividing the amount of imported feed by the production efficiency of feed crops in NN. Depletion of N and P in the soil was counted as an input to the system and accumulation as an output.
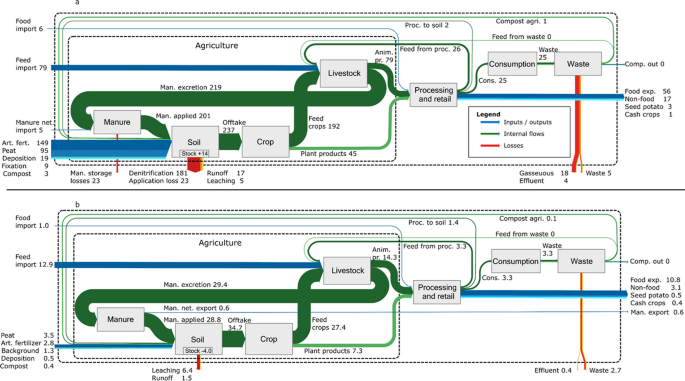
Nitrogen (panel a.) and phosphorus (panel b.) flows in the North Netherlands food system expressed in kilograms per hectare of agricultural land per year (kg ha −1 y. −1 ). System in- and outputs are shown in blue where inputs enter the system (and each subsystem) from the left, outputs leave from the right. Internal flows are shown in green and losses are shown as red arrows leaving the (sub)system from the bottom. Values are averages for the period 2015–2019. Note that all (sub)system balances are 0, which may appear differently in this figure due to rounding. The unrounded numbers for each flow are given in the Supplementary Material (Fig. S2 )
To assess the recycling of nutrients within the food system, we determined the cycle count indicator (CyCt) for nitrogen (CyCt N ) and phosphorus (CyCt P ) (van Loon et al. 2023 ). The CyCt quantifies the average number of times that inputs are cycled through the food system before being removed from the system as outputs or losses. It is defined as:
where A is the fraction of inputs that is removed from the food system per cycle and (1-A) indicates the fraction of inputs retained in the system after each cycle.
The flows, UE and CyCt of N and P in the NN region were compared to studies on regional nutrient flows to contextualize our results and thereby provided the baseline for subregional food system flows.
Nutrient flows in North Netherlands food system
In total, 99% of imported N and 96% of imported P went to agriculture and the rest was captured in imported food (Fig. 2 ). The largest N inputs were artificial fertilizer (41%), mineralisation of organic peat soils (26%) and imported animal feed (22%). The largest P inputs were imported animal feed (48%), soil stock change due to lowered yearly application limits (15%), mineralisation of organic peat soils (13%) and artificial fertilizer (10%). The main system outputs were the export of food, non-food biomass from processing and the production and export of seed potatoes. About 91% of N losses and 72% of P losses were from agriculture. The NUE and PUE were respectively 0.25 and 0.59 for the food system compared to 0.36 and 0.74 for agriculture (Table 2 ).
The largest flows in the food system were associated with agriculture (Fig. 2 ), as NN region is a net production region. Total crop offtake was 237 kg N ha −1 y −1 and 35 kg P ha −1 y −1 , of which 81% was in fodder, and 19% in food and feed crops for processing. The combined production of plant and animal products for processing and human consumption was 124 kg N ha −1 y −1 and 22 kg P ha −1 y −1 . Of this, 36% of N and 34% of P were in plant products and 64% of N and 66% of P in animal products. Losses from agriculture were the largest of the food system, with the majority of N losses being lost from the soil via denitrification (72%), fertilizer application losses consisting mainly of NH 3 (9%), runoff (7%) and leaching (2%). The remaining 9% was lost from manure storage, predominantly as NH 3 . P was only lost from the soil via leaching (76%) and runoff (24%). In total, 81% of harvested N and 79% of P was directly fed to livestock. Losses were largest in the subsystem soil. Hence, a large proportion of losses from agriculture can to attributed to feed production. Of all livestock feed 26% of N and 30% of P was imported from outside the region. The losses during the production of imported feed were not included in this analysis. Including such losses would increase the N and P losses associated to animal production even further.
Processing and retail
Of the total production of crop- and animal products in the region about 60% of N and P ended up in food products, 23% was returned to agriculture as feed or soil amendment and 14% ended up in products not used in the food system (Fig. 2 ). A substantial part of the flows leaving the food system was offal, of which a large part is used in the production of pet feed. Smaller flows leaving the system included seed potatoes, non-food cash crops and non-food/feed products of animal origin (Supplementary Material; Fig. S2 ). Losses from processing could not be accounted for due to a lack of data. However, 14% of N and P going into processing ended up in non-food products, that left the food system and were essentially lost. For instance, offal from animal carcases is processed into pet feed and is eventually excreted by pets and generally not recovered. The generation of non-food flows thus indicates an inefficiency in the use of food crops that could (partly) have been used to feed the human population.
Only 25% of N and 18% of P of locally produced food products was consumed within the region, with the rest being exported. This means that 75% of N losses and 82% of P losses from agriculture and food processing could be attributed to the production of food exports, when assuming uniform losses per kg of N and P across crops and animal products. As animal products made up a large share of exports, the percentage of losses associated with export is likely higher.
Consumption and waste
About 24% of N and 30% of P in purchased food was imported from outside the NN food system (Fig. 2 ). Of purchased food, 91% of N and 93% of P was consumed and ultimately disposed in wastewater. The remaining 9% of N and 7% of P was food waste, which is in line with the 10% reported by (Yahia and Mourad ( 2020 ) for European consumers.
Nitrogen in wastewater was lost as N 2 (64%) or N 2 O (1%). About 19% ended up in sewage sludge and 16% was lost to surface water. Phosphorus in wastewater went to sludge (86%) and to surface water (14%). Sludge is usually dried and burned or landfilled, and N and P in sludge was a loss from the system.
Food waste was either burned (35% of N and 40% of P) or composted (30% of N and 27% of P), digested (22% of N and 9% of P), landfilled (3% of N and 3% of P) or used as livestock feed (2% of N and 21% of P). Only compost, digestate and feed from waste were returned to the system, with the rest effectively being lost.
Subregional variation in specialization, soil type and N balances of agriculture
Within NN there is spatial heterogeneity in soil types (Fig. 3 ; panel a), population density (Fig. 3 ; panel b) and agricultural specialization, represented by the fraction of produced N in crop products (Fig. 3 .; panel d). Most areas dominated by sandy soils have a mixture of specialized crop and livestock farms. The eastern part of the region with sandy soils, with some oligotrophic peat residues that were left after peat excavation, is largely specialized in crop production. The fertile clay soils near the coast that were reclaimed from the sea are used by specialized crop farmers (light grey in Fig. 3 ; panel a), whereas the areas with heavy clay soils further inland (dark grey in Fig. 3 ; panel a) are dominated by dairy farmers. The south-(western) part of the region that is dominated by peat soils is largely livestock-oriented, specifically toward dairy farming. The spatially segregated specialized crop and livestock production in the northern part of the region is not distinguishable on these maps due to low spatial resolution of the available data, thus showing a ratio of crop to animal production close to 50%. Patterns of specialization largely follow patterns of soil type and groundwater levels. Urban centres are relatively small and population densities are diluted by low population density in the rest of the subregion.
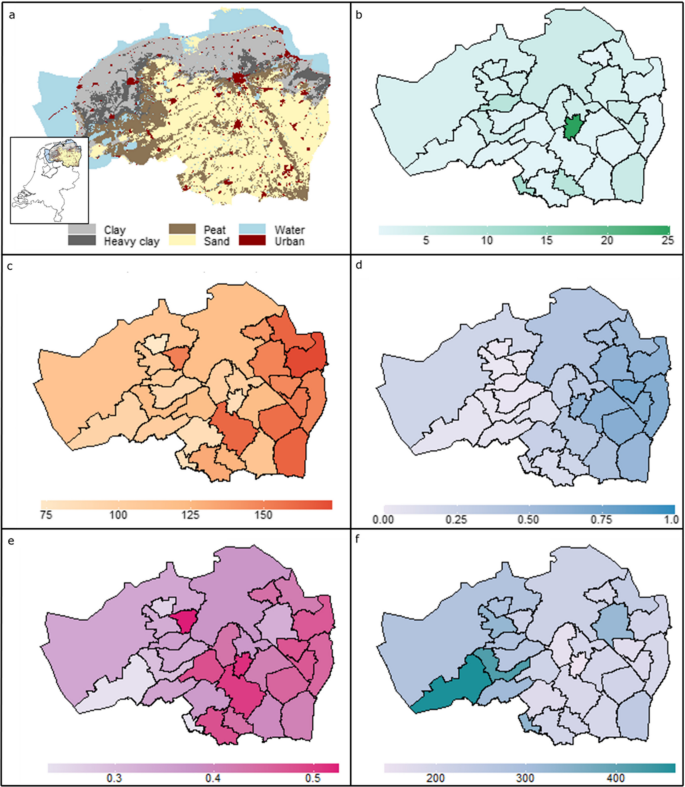
Maps of soil types and urban areas ( a. ), population density ( b. ), total N yield of crop and animal products ( c. ), proportion of N yield in crop products ( d. ), nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of agriculture ( e. ) and nitrogen losses from agriculture ( f. ) per subregion in NN
The maps of NUE (Fig. 3 ; panel e) and losses (Fig. 3 ; panel f) show a similar pattern as specialization (Fig. 3 ; panel c). The highest NUEs and lowest losses were found in the eastern parts, whilst NUE was lower and losses were higher in the southern part of the region. In the cropping regions higher production levels of agricultural products (excl. feed) were achieved (Fig. 3 ; panels c and d) with lower losses (and less inputs). Most subregions with predominantly animal production had lower NUE and higher losses per hectare. However, there were several outliers to this pattern, which are explained below. The spatial correlation between soil type and NUE and losses was less clear than that between specialization and NUE. The exception was that losses on the south-western peat soils were notably higher than in the rest of the region.
Comparing nutrient flows in contrasting subregions
The N balances of the food system of four selected subregions, contrasting in specialization, soil type and population density are shown in Fig. 4 and NUE and PUE values of their subsystems in Table 2 . Additionally, an overview of N flows in the food systems of these subregions is given in the Supplementary Material (Fig. S3 ). These balances and flows are used to explain the patterns observed for NUE and PUE and specialization and soil type, as well as exceptions to patterns.
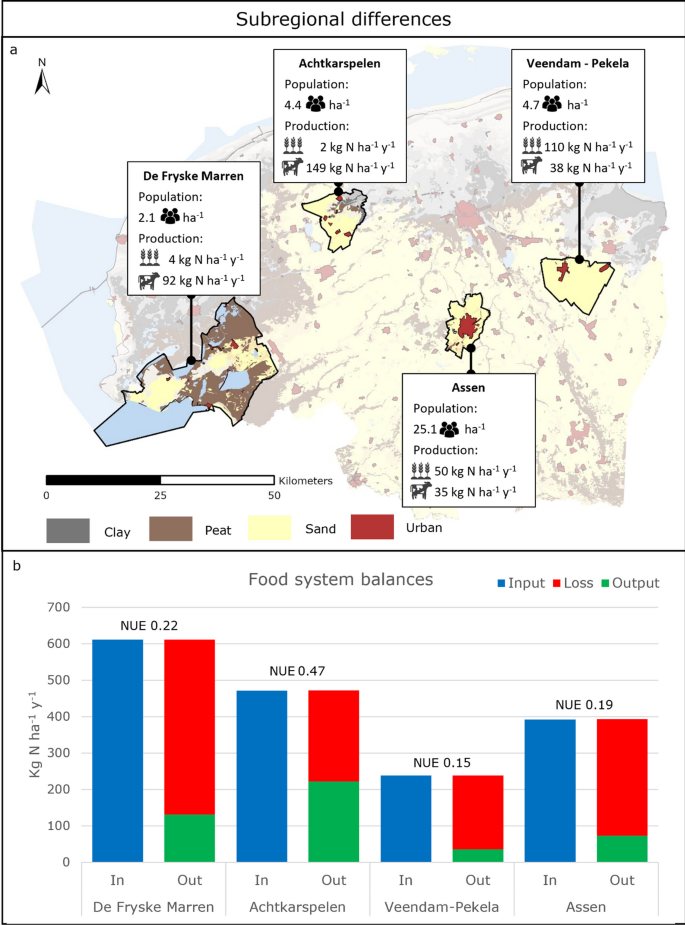
Overview of contrasting subregions in north-Netherlands (NN), varying in soil type, specialization, and population density ( a. ) and their respective food system N balances and nitrogen use efficiencies (NUE) ( b. ). Food system losses were especially large in areas of dairy farming on peat soils ( Fryske Marren ) and in more urbanized areas where losses were large from both agriculture and consumer waste ( Assen ). Intensive animal production had lower losses inside the region ( Achtkarspelen ), as losses from the production of imported feed and utilization of exported manure took place outside the region. Including such losses would drastically reduce the NUE. Arable farming was associated with higher yields per hectare and smaller losses, but as a large share of nutrients in crop products was processed into livestock feed, the food system NUE and outputs in areas dominated by arable farming were very low ( Veendam-Pekela )
De Fryske Marren
De Fryske marren is located on peat soil and is strongly specialized in dairy production (Fig. 4 ). There was a substantial input from decomposing peat of 335 kg N ha −1 y −1 . Agriculture in De Fryske Marren had an NUE of 0.23 and a PUE of 0.68, slightly lower than the average NUE of 0.36 and PUE of 0.74 for the NN region (Table 2 ). Losses from agriculture were 465 kg N ha −1 y −1 , 86% higher than the regional average of 250 kg N ha −1 y −1 . Production was 96 kg N ha −1 y −1 , 23% lower than the regional average of 124 kg N ha −1 y −1 . The excess N was mostly lost to the air via denitrification. De Fryske Marren also had a high feed self-sufficiency, as local feed production met 77% of demand. The losses associated with feed production were thus largely internalized. Of the N in harvested plant material, 99% was in fodder. As the largest part of consumed feed was converted into manure and not into food products, food production was low despite the large inputs and losses.
Achtkarspelen
Achtkarspelen is located on sandy soil (Fig. 4 ) and had the highest intensity of animal production in the region including landless poultry and pork production, yielding 149 kg N ha −1 y −1 in animal source food products, which was 89% higher than the regional average. The total production including crops was 151 kg N ha −1 y −1 , which was 22% above the regional average. At the same time, the NUE of agriculture of 0.53 and PUE of 0.88 were among the highest of all subregions (Table 2 ). Losses from agriculture were 219 kg N ha −1 y −1 , which was 13% lower than the regional average.
The apparently high efficiency of animal production in this subregion resulted from the externalization of some main sources of losses, i.e. feed production and manure application. Achtkarspelen had the largest feed imports and manure exports per hectare of all subregions (Supplementary Material; Fig. S2 ). About 40% of feed was imported from outside the subregion, thus externalizing a large part of the losses associated with growing feed crops. Also, manure export made up about a third of system output, but manure is of much lower utility than food products and its utilization causes losses elsewhere. Excluding manure export as system output reduced the NUE of this subregion from 0.53 to 0.38 and the PUE from 0.88 to 0.55 (Table 2 ). Also including the losses related to the production of imported feed would further reduce the efficiency (to about NUE 0.25).
Veendam-Pekela
Veendam-Pekela is situated on sandy soils with mostly arable farming of especially starch potatoes along with substantial areas of sugar beets and cereals (Fig. 4 ). The NUE of agriculture in Veendam-Pekela was 0.47 and the PUE 0.90, which was higher than the NUE of 0.36 and PUE of 0.74 for the NN region (Table 2 ). Losses were 169 kg N ha −1 y −1 , 32% lower than the regional average. Production was 147 kg N ha −1 y −1 , which was 19% higher than the regional average. About 74% of N outputs were in plant products and 26% in animal products. Starch potatoes and sugar beets are processed into starch and sugar products which mostly consist of carbohydrates, whilst most of the nutrients in the raw products end up in non-edible residual flows. Therefore only 27% of total N production ended up in food products; the other part was used for animal feed (58%), soil amendment (9%) or left the food system in non-food products (9%). Therefore, whilst the NUE and PUE of agriculture and productivity were higher than average, food export was lower than in less productive subregions as a large proportion of produce ended up in non-food flows. This resulted in an NUE of only 0.15 and PUE of 0.60 on food system level (Table 2 ).
With 25 persons ha −1 Assen is the subregion with the highest population density in the NN region (Fig. 4 ). Consumers purchased 188 kg N ha −1 y −1 in food, of which 87% was imported from outside the subregion. The largest leak of the system was consumer waste processing (178 kg N ha −1 y −1 ) rather than agriculture (143 kg N ha −1 y −1 ). The NUE of agriculture was 0.51 compared to 0.05 for waste processing (Table 2 ). The PUE of agriculture was 0.74, compared to 0.04 for waste processing. Therefore, subregions with higher population density generally had a lower food system NUE and PUE. However, per kg N in produced food products, 4.0 kg N ha −1 y −1 was lost from agriculture, while of each kg N in purchased food products 0.9 kg N ha −1 y −1 was lost after waste(water) processing. Thus, per kg N in food products losses from agriculture still outweighed losses from consumption. Even if all N lost through consumer waste in this urban subregion were returned to agriculture, it would not be sufficient to replace current inputs to agriculture. Agriculture in turn did not provide sufficient food to feed the local population.
Current circularity in NN and subregions
Nutrient cycling was very low in the food systems of NN and its subregions (Table 2 ), indicating that hardly any N inputs were recycled through the system. All calculated CyCt values were < 0.03, indicating that the vast bulk of N and P inputs did not complete a full cycle through the food system. This resulted from very little re-use of nutrients after consumption and large losses and exports from the system. Subregions with a high production to consumption ratio scored worse on the circularity indicator. Nutrients in exported food were lost from the region and not returned as recycled system inputs and therefore reduced the cycling count.
Nutrient flows and efficiencies varied strongly between subsystems and subregions. At system level NUE varied most strongly with agricultural specialization and soil type, whilst PUE varied most strongly with population density. The cycling count was very low for both N and P in all subregions, indicating that the current system heavily depends on external inputs with large losses from the system.
Nutrient dynamics of the food system and its subsystems
Food system performance in this export oriented region was mainly determined by the performance of the subsystem agriculture. The very limited recovery from consumer waste had an insignificant impact on the NN region as these flows were relatively small (Geertjes et al. 2016 ; Soethoudt and Timmermans 2013 ). The NUE of the current food system in the NN region was 0.25, which equals the NUE for the Netherlands (Erisman et al. 2018 ) and is higher than the reported NUE value (0.18) for Europe (Leip et al. 2022 ). The relatively high PUE of 0.59 was mostly due to small P surpluses in agriculture when compared to other regions (Einarsson et al. 2020 ) and partly due to the legacy of historically applied P (Sattari et al. 2012 ).
The low NUE (0.36) of the agriculture subsystem mainly resulted from the low N conversion efficiency of livestock, the cultivation of feed crops and mineralisation of peat soils. This NUE was lower than the 0.43 reported by CBS for agriculture in the Netherlands (CBS 2022c ). The lower NUE found here was mainly the result of counting the additional inputs provided by peat soil, which are usually omitted. In peatlands large nutrient surpluses were found. Strongly reducing application limits for peatlands would improve NUE, reduce N 2 O emission and limit P saturation of peatlands without production loss.
The cycle count (CyCt) of the NN food system was only 0.0069 for N and 0.0091 for P. These figures were lower than the CyCt of 0.02 found by van Loon et al. ( 2023 ) for the highly linear food system in the Flanders region (Belgium). The lower values for NN can be explained by larger inputs and larger losses per hectare in NN and especially by a larger share of products leaving the region in exports. Of all inputs into the subsystem agriculture only 7% of N was recycled from the NN food system. A similarly strong dependency on nutrient imports has also been reported in other regions with intensive agriculture (Chowdhury et al. 2018 ; Le Noë et al. 2018 ; Papangelou and Mathijs 2021 ). Increasing the CyCt and reducing the dependency on nutrient imports can be achieved by reducing exports and reducing losses, as the CyCt counts the proportion that remains in the system but does not distinguish between losses and useful flows that leave the system.
Differences in nutrient flows between subregions
Variation with soil type: large losses from organic soils.
Nutrient flows and losses varied substantially with soil type. Losses from peat soils were higher than from clay and sandy soils and consequently, UE and CyCt were low in subregions with mainly peat soils (Fig. 3 ; panels a. and f.). Groundwater tables in areas of peat soils in NL are typically lowered to facilitate intensive agriculture. The resulting aerobic conditions strongly enhance the mineralisation rate of organic matter stored in peat soils, estimated here at 335 kg N ha −1 y −1 and 38 kg P ha −1 y −1 for a subregion dominated by peat soils. Similar rates were found for one test site in the Netherlands (Pijlman et al. 2020 ), though most estimates for the Netherlands are somewhat lower, i.e. ca. 250 kg ha −1 y −1 (Pijlman et al. 2020 ; Vellinga and André 1999 ). Peat soils also receive substantial inputs of N and P from applications of animal manures and artificial fertilizers, resulting in a comparatively large surplus of 465 kg N ha −1 y −1 and 11 kg P ha −1 y −1 . Most of the N surplus is eventually lost through denitrification with a substantial amount of N 2 O (Velthof et al. 2009 ). The oxidation of peat soils is also one of the largest sources of GHGs from agriculture worldwide (Leifeld and Menichetti 2018 ; Lin et al. 2022 ; Tiemeyer et al. 2016 ). Peat soils in the Netherlands are frequently P saturated (Schoumans and Chardon 2015 ), which increases the potential risk of P leaching to water bodies (Lin et al. 2022 ; Schrier-Uijl et al. 2014 ).The large differences in NUE and PUE between soil types suggest that prioritizing the use of most suitable soils for agriculture will substantially increase efficiency and reduce losses from agriculture (Muscat et al. 2021 ; Netherlands Scientific Council for Government Policy 1992 ).
Nutrient use efficiency of agriculture is strongly associated with specialization
Spatial patterns of NUE, PUE and losses from agriculture largely matched patterns of specialization. In subregions more specialized in crop production the inputs were generally lower, but N and P yields were higher. Losses from animal production were substantial and resulted from losses in the field for feed crop production, manure storage and manure application. The efficiency of e.g., dairy fed mostly with local roughage was low (NUE 0.23). The N and P efficiency of intensive animal husbandry systems fed on imported feeds was much higher, i.e., up to NUEs of 0.53 and PUEs of 0.88. In this case losses during the production of imported feed and application of exported manure took place outside the subregion’s borders and are externalised. Externalizing losses may give a false sense of efficiency of the production systems in question (Quemada et al. 2020 ; Schröder et al. 2011 ). When accounting for the external losses that result from manure application elsewhere, the NUE of 0.25 of these subregions was similar to that of subregions with more local feed production, congruent with an NUE of 23% for pig farms (Quemada et al. 2020 ).
The apparently high NUE and PUE of agriculture in subregions specialised in crop production do not account for the larger losses at food system level. For example Veendam-Pekela mainly produces food crops for the processing industry, predominantly starch potato and sugar beet. During processing most nutrients in these crops end up in residual flows that are used as feed and for non-food purposes. Yet, animal food derived from these food crops comes with a substantially larger loss per kg food than food crops: only around 27% of N and 33% of P of nutrients in feed crops is converted into edible food. The rest of the N and P is recycled via manure with associated losses elsewhere. Hence, at system level the UE is much lower. Sectors should therefore be evaluated in a food system context to account for such externalized losses (van Loon et al. 2023 ).
Low efficiency and large losses from urban areas
Population density was negatively associated with UE and CyCt of the food system, as the UE of waste treatment was lower than that of agriculture and processing. For PUE this effect was stronger than for NUE, as relatively little P was lost from agriculture (PUE 0.74) whilst from waste processing most P was lost (PUE 0.04). The NUE for the subsystem waste processing was 0.05, still much lower than the NUE of 0.36 of the subsystem agriculture. Subregion Assen was the only subregion with a net-consumption, i.e., more food was consumed than produced. In this subregion, only 13% of the N that was consumed came from local products. This means recycling of N from consumer waste into agriculture also adds some external N to the farming system. However, about 49% of N going into agriculture is lost in agriculture and another part ends up as non-food product flows after processing. This means that even in a region with net food import, recycling consumer waste can only replace a very limited part of agricultural N inputs. Recycling P from waste processing to agriculture strongly reduces losses in the system, as the main P losses were from consumer waste whilst P losses from the agriculture subsystem were relatively small. Recycling the nutrients from waste flows requires the adoption of technologies for resource recovery into the waste management system, that until now has been geared toward pollution prevention rather than resource recovery (Coppens et al. 2016 ; Verger et al. 2018 ).
Towards circularity in NN
Improving circularity in nn.
The circularity of food systems can be improved by avoiding non-essential products and residual flows of essential products, prioritizing biomass use for human consumption, repurposing residual flows and minimizing energy use (Muscat et al. 2021 ). Applying these principles to the food system of NN could provide benefits to the environment (IFA 2022 ; Struik and Kuyper 2017 ) and human health (van Selm et al. 2021 ), but may also have other consequences. First, nutrient inputs would need to be reduced and internal cycling enhanced by limiting the currently large losses and by re-using residual flows. This could increase the currently low NUE (0.25) and PUE (0.59) of the food system. Reducing losses requires more efficient farming methods and technologies to recover unavoidable urban waste. Food exports should be limited, to maintain a neutral regional nutrient balance. Where possible, nutrients must also be recovered from non-food flows with applications outside the food system such as pet feed or biobased building materials. Second, limiting feed imports would mean that a higher share of the feed that is used in the region must be produced locally, preferably from land unsuitable for food crops and from residual flows from the food system. In NN heavy clay soils that are currently used as grasslands may be unsuited for cropping. Peat soils are not suitable for circular intensive agriculture, including feed production, as oxidation and associated N emissions from peat soils can only be restricted by restoring and maintaining high groundwater tables (Lin et al. 2022 ; Schrier-Uijl et al. 2014 ). Safeguarding peat soils would therefore limit their agricultural use to systems suited to wet conditions (Lin et al. 2022 ; Offermanns et al. 2023 ; Schoumans and Chardon 2015 ). The possible production of additional feed from available recyclable flows that are not yet used is very limited when compared to current feed imports. Therefore, adhering to the principles of circularity would strongly reduce current livestock production in NN. Third, to meet most of the food demand with food produced in NN requires that rotations are diversified and include more crop types, consequently diversifying current narrow crop rotations. Diversification of crop rotations has additional benefits, including reduced nutrient leaching (Nemecek et al. 2015 ), increased resilience to biotic and abiotic stress (Degani et al. 2019 ) and increased productivity (Mudgal et al. 2010 ). Lastly, a more local food production may lower energy use by reducing the need for transportation. However, there are trade-offs: local production may be less efficient and lead to larger losses (Schulte-Uebbing and De Vries 2021 ), more energy use and higher GHG emissions in agriculture when more land is needed for cultivation. In subregions with sandy and suitable clay soils for cropping it may be possible to provide a full diet locally, yet in subregions dominated by peat and heavy clay soils only few crops can be grown. In subregions with plenty suitable land but low population density, the exploitation of good soils would be limited by the availability of residual flows as circular inputs. Therefore, closing nutrient loops in NN on the subregional level is probably not feasible.
Consequences of circularity in NN
A more circular food system will have economic consequences for a strongly export-oriented region like NN. Required changes will affect exports (and associated inflow of foreign currency) and the income of farmers, but will at the same time reduce environmental costs that are currently not accounted for. Reducing food export to improve circularity in NN would affect food importing regions, including the nearby Randstad metropolitan area (with larger cities including Amsterdam) with insufficient suitable land. Reduced food production in exporting regions might affect food availability in food importing regions in the short term (Mayer et al. 2015 ; van Berkum 2021 ) when this cannot be compensated elsewhere. However, it can also be argued that maintaining the current system compromises global food security due to the strong food-feed competition of current intensive animal production systems (Mottet et al. 2017 ; Muscat et al. 2021 ). Increasing food security with limited environmental impact and reduced land requirements per person requires a shift towards more plant-based diets (Leip et al. 2022 ). Regardless of dietary composition, some regions may not have the capacity to produce enough food to fulfil local demand in a sustainable way (Schulte-Uebbing and De Vries 2021 ). For example, there is not much suitable soil for food crops in the Randstad area, located in a region with mostly peat soils unsuitable for most crops. In other areas, crop production may be less efficient than in NN. Shifting production to such an area is likely to lead to large losses with large impacts in those regions, and consequently increase resource use and GHG emissions at national or global level (Leifeld and Menichetti 2018 ; Tiemeyer et al. 2016 ). Hence a strict application principles of circularity may thus be detrimental for efficiency at larger scales. A circular food system at the appropriate scale increases the options to produce food where it can be done most efficiently (Billen et al. 2018 ), where the optimum scale is determined by trade-offs between the efficiency of production and use of recycled biomass flows including associated transport requirements. These environmental and socio-economic trade-offs of circularity on various scales and with varying land use intensities are still poorly understood (Koppelmäki et al. 2021 ; Muscat et al. 2020 ). Our study shows that integrating knowledge of the local context and the food system will be key for proper planning of circular systems with limited losses at larger geographical scales, such as the Netherlands including the Randstad metropolitan area.
Quantification of nutrient flows as a prerequisite for circular agriculture
The first step towards circularity is a clear understanding of nutrient flows in the current food system, by using the best available data. Yet, we acknowledge data limitations encountered for the NN region. Nutrient flows are currently poorly monitored, at both the farm and regional scales. Nutrient emissions from food processing and waste processing facilities were not readily available. Some of the most important flows in the food system, such as livestock feed composition and origin of ingredients, are currently unavailable (Koppelmäki et al. 2021 ; van der Wiel et al. 2021 ). We recommend open access of existing data sources and for regular sampling of nutrient contents of farm inputs and produce and of all processing flows including waste. This would also provide key insights in crop nutrient offtakes and hence direct options to improve soil nutrient management and reduce losses in the agricultural system in a local context (Silva et al. 2021 ; Sylvester-Bradley et al. 2022 ).
Large differences in flows and efficiencies between subregions with different soil types, specialization, and population density were found. In food system studies not accounting for the local context, such differences are masked. We also found that the efficiency of subsystems in the food system and specialized subregions within the region differ strongly. Food system efficiency strongly depends on how flows are utilized in the system. If flows are not utilized efficiently, food system efficiency will be very low, even though the efficiency of individual subsystems may be high. Hence, to improve efficiency and circularity, a food system lens is required to better tailor the agricultural system to local biophysical conditions and regional food demand. Follow-up research will be needed to address the question what a circular food system would look like in practice, or at what scale such systems should operate.
In the current NN food system the NUE and PUE were low and nutrient recycling was extremely limited with a cycling count close to zero. The system depends heavily on feed and fertilizer imports. A large proportion of the losses can be attributed to production for export. There is little scope to improve nutrient cycling by utilizing unused residues as these residual flows are small compared to the losses from the system. We conclude that reducing losses would therefore require substantial changes to the current food system, especially to the subsystem agriculture. Important steps towards circularity in production-oriented regions such as NN include: matching livestock production with the potential feed supply from residual flows and lands unsuitable for food crops, diversification of crop production to better match local demand and the adoption of technologies to facilitate recovery of nutrients from (consumer) waste. In more urbanized regions where consumption exceeds production, dietary change and the adoption of technologies for nutrient recovery from waste will be most important.
Aptroot A, Herk KV, Sparrius L (2012) Basisrapport voor de Rode Lijst Korstmossen. Buxbaumiella 92:1–117
Google Scholar
Bai Z, Fan X, Jin X, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Oenema O, Velthof G, Hu C, Ma L (2022) Relocate 10 billion livestock to reduce harmful nitrogen pollution exposure for 90% of China’s population. Nat Food 3(2):152–160. https://doi.org/10.1038/S43016-021-00453-Z
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bergen SD, Bolton SM, Fridley JL (2001) Design principles for ecological engineering. Ecol Eng 18(2):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8574(01)00078-7
Article Google Scholar
Billen G, Lassaletta L, Garnier J, Noë J Le, Aguilera E, Sanz-Cobeña A (2018) Opening to distant markets or local reconnection of agro-food systems? Environmental consequences at regional and global scales. Agroecosyst Divers Reconciling Contemp Agric Environ Qual 391–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811050-8.00025-X
CBL (2020) Nederlandse supermarkten maken voedselverspilling inzichtelijk. https://www.cbl.nl/nederlandse-supermarkten-maken-voedselverspilling-inzichtelijk/ . Accessed 14 Oct 2022
CBS (2016) Export buiten EU groot in Friesland en Noord-Brabant. https://www.cbs.nl/nl-nl/nieuws/2016/14/export-buiten-eu-groot-in-friesland-en-noord-brabant . Accessed 23 Jan 2023
CBS (2018) Bodemgebruik; uitgebreide gebruiksvorm, per gemeente. https://www.cbs.nl/nl-nl/cijfers/detail/70262ned . Accessed 23 Feb 2023
CBS (2019) Dierlijke mest en mineralen 1990–2018. Centraal Bureau voor de Statistiek, p 127. https://www.cbs.nl/nl-nl/publicatie/2019/49/dierlijke-mest-en-mineralen-2018
CBS (2020) Regionale kerncijfers Nederland. https://opendata.cbs.nl/statline/#/CBS/nl/dataset/70072ned/table?dl=4BA5F . Accessed 9 Feb 2021
CBS (2022a) Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand. https://opendata.cbs.nl/statline/#/CBS/nl/dataset/37230NED/table?fromstatweb . Accessed 25 Feb 2023
CBS (2022b) Landbouw; gewassen, dieren en grondgebruik naar gemeente. https://opendata.cbs.nl/#/CBS/nl/dataset/80781ned/table . Accessed 25 Feb 2023
CBS (2022c) Mineralenbalans landbouw. https://opendata.cbs.nl/#/CBS/nl/dataset/83475NED/table . Accessed 25 Apr 2023
Chowdhury RB, Moore GA, Weatherley AJ (2018) A multi-year phosphorus flow analysis of a key agricultural region in Australia to identify options for sustainable management. Agric Syst 161(December 2016):42–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2017.12.005
Coppens J, Meers E, Boon N, Buysse J, Vlaeminck SE (2016) Follow the N and P road: High-resolution nutrient flow analysis of the Flanders region as precursor for sustainable resource management. Resour Conserv Recycl 115(2016):9–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.08.006
CREM Waste Management (2017) Bepaling voedselverspilling in huishoudelijk afval Nederland 2016. https://www.voedingscentrum.nl/Assets/Uploads/voedingscentrum/Documents/Professionals/Pers/Persmappen/Verspilling%202017/Voedselverspilling%20via%20Huishoudelijk%20afval%202016_sorteeranalyse%20(CREMWM).pdf
Crippa M, Solazzo E, Guizzardi D, Monforti-Ferrario F, Tubiello FN, Leip A (2021) Food systems are responsible for a third of global anthropogenic GHG emissions. Nat Food 2(3):198–209. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00225-9
de Boer IJM, van Ittersum MK (2018) Circularity in agricultural production. Wageningen University and Research. https://edepot.wur.nl/470625
de Ruijter FJ, van Dijk W, van Geel WCA, Holshof G, Postma R, Wilting P (2020) Actualisatie van stikstof- en fosfaatgehalten van akkerbouwgewassen met een groot areaal (Rapport / Stichting Wageningen Research, Wageningen Plant Research (WPR), Business unit Agrosysteemkunde; No. WPR-957). Wageningen Plant Research. https://doi.org/10.18174/520624
de Vries W, Kros J, Oenema O, de Klein J (2003) Uncertainties in the fate of nitrogen II: A quantitative assessment of the uncertainties in major nitrogen fluxes in the Netherlands. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 66(1):71–102. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023354109910
de Vries W, Kros J, Voogd JCH, van Duijvendijk K, Ros GH (2018) Kansen voor het sluiten van de mineralenbalansen in Noord-Nederland: Effecten op regionale schaal en bedrijfsschaal. (Wageningen Environmental Research rapport; No. 2925), Wageningen Environmental Research. https://doi.org/10.18174/467746
de Vries W, Kros J, Voogd JC, Ros GH (2023) Integrated assessment of agricultural practices on large scale losses of ammonia, greenhouse gases, nutrients and heavy metals to air and water. Sci Total Environ 857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159220
de Vries W, Schulte-Uebbing L, Kros H, Voogd JC, Louwagie G (2021) Spatially explicit boundaries for agricultural nitrogen inputs in the European Union to meet air and water quality targets. Sci Total Environ 786:147283. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.147283
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Degani E, Leigh SG, Barber HM, Jones HE, Lukac M, Sutton P, Potts SG (2019) Crop rotations in a climate change scenario: short-term effects of crop diversity on resilience and ecosystem service provision under drought. Agric Ecosyst Environ 285(May). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2019.106625
Ehlert PAI, Dekker PHM, van der Schoot JR, Visschers R, van Middelkoop JC, van der Maas MP, Pronk AA, van Dam AM (2009) Fosforgehalten en fosfaatafvoercijfers van landbouwgewassen. Alterra Rep 1773:125
Einarsson R, Pitulia D, Cederberg C (2020) Subnational nutrient budgets to monitor environmental risks in EU agriculture: calculating phosphorus budgets for 243 EU28 regions using public data. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-020-10064-y
Erisman JW, Leach A, Bleeker A, Atwell B, Cattaneo L, Galloway J (2018) An integrated approach to a nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) indicator for the food production-consumption chain. Sustainability 10(4):1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10040925
EUROSTAT (2021) Population density. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/tps00003/default/bar?lang=en . Accessed 9 Feb 2021
Garrett RD, Ryschawy J, Bell LW, Cortner O, Ferreira J, Garik AVN, Gil JDB, Klerkx L, Moraine M, Peterson CA, Dos Reis JC, Valentim JF (2020) Drivers of decoupling and recoupling of crop and livestock systems at farm and territorial scales. Ecol Soc 25(1):24. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-11412-250124
Geertjes K, Baas K, Verschuren S, Kaashoek R, Graveland C (2016) Stikstof in afvalwater en slib. Centraal Bureau voor de Statistiek. https://www.cbs.nl/-/media/_pdf/2016/12/stikstof-in-afvalwater.pdf
Hanserud OS, Brod E, Øgaard AF, Müller DB, Brattebø H (2016) A multi-regional soil phosphorus balance for exploring secondary fertilizer potential: the case of Norway. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 104(3):307–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-015-9721-6
Article CAS Google Scholar
IFA (2022) Reducing emissions from fertilizer use. https://www.systemiq.earth/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Fertilizer_Report_Final.pdf . Accessed 23 Jan 2023
Jurgilevich A, Birge T, Kentala-Lehtonen J, Korhonen-Kurki K, Pietikäinen J, Saikku L, Schösler H (2016) Transition towards circular economy in the food system. Sustainability 8(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010069
Koppelmäki K, Helenius J, Schulte RPO (2021) Nested circularity in food systems: A Nordic case study on connecting biomass, nutrient and energy flows from field scale to continent. Resour Conserv Recycl 164:105218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105218
Kros H, van Os J, Voogd JC, Groenendijk P, van Bruggen C, te Molder R, Ros G (2019) Ruimtelijke allocatie van mesttoediening en ammoniakemissie: beschrijving mestverdelingsmodule INITIATOR versie 5. (Wageningen Environmental Research rapport; No. 2939). Wageningen Environmental Research. https://doi.org/10.18174/474513
Kuokkanen A, Mikkilä M, Kuisma M, Kahiluoto H, Linnanen L (2017) The need for policy to address the food system lock-in: A case study of the Finnish context. J Clean Prod 140:933–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.171
Langeveld JWA, Verhagen A, Neeteson JJ, van Keulen H, Conijn JG, Schils RLM, Oenema J (2007) Evaluating farm performance using agri-environmental indicators: Recent experiences for nitrogen management in The Netherlands. J Environ Manage 82(3):363–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.11.021
Le Noë J, Billen G, Esculier F, Garnier J (2018) Long-term socioecological trajectories of agro-food systems revealed by N and P flows in French regions from 1852 to 2014. Agr Ecosyst Environ 265:132–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.06.006
Le Noë J, Billen G, Garnier J, Barcelo D (2017) How the structure of agro-food systems shapes nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon fluxes: The generalized representation of agro-food system applied at the regional scale in France-NC-ND license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ). Sci Total Environ 586:42–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.040
Leifeld J, Menichetti L (2018) The underappreciated potential of peatlands in global climate change mitigation strategies. Nat Commun 9(1071). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03406-6
Leip A, Caldeira C, Corrado S, Hutchings NJ, Lesschen JP, Schaap M, de Vries W, Westhoek H, van Grinsven HJM (2022) Halving nitrogen waste in the European Union food systems requires both dietary shifts and farm level actions. Glob Food Sec 35:100648. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GFS.2022.100648
Lin F, Zuo H, Ma X, Ma L (2022) Comprehensive assessment of nitrous oxide emissions and mitigation potentials across European peatlands. Environ Pollut 301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119041
Martin G, Moraine M, Ryschawy J, Magne MA, Asai M, Sarthou JP, Duru M, Therond O (2016) Crop–livestock integration beyond the farm level: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 36(3):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13593-016-0390-X
Mayer A, Schaffartzik A, Haas W, Sepulveda AR (2015) Patterns of global biomass trade - Implications for food sovereignty and socio-environmental conflicts. EJOLT Report (20):106. https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.1442.5128
Mottet A, de Haan C, Falcucci A, Tempio G, Opio C, Gerber P (2017) Livestock: on our plates or eating at our table? A new analysis of the feed/food debate. Glob Food Sec 14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2017.01.001
Mudgal S, Lavelle P, Cachia F, Somogyi D, Majewski EF, Laurence Bechini L, Debaeke P (2010) Environmental impacts of different crop rotations in the European Union (ENV.B.1/ETU/2009/0026). European Commission - DG ENV. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363884907_Environmental_impacts_of_crop_rotations_in_the_EU
Mueller ND, Gerber JS, Johnston M, Ray DK, Ramankutty N, Foley JA (2012) Closing yield gaps through nutrient and water management. Nature 490(7419):254–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11420
Muscat A, de Olde EM, de Boer IJM, Ripoll-Bosch R (2020) The battle for biomass: a systematic review of food-feed-fuel competition. Glob Food Sec 25(September):100330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2019.100330
Muscat A, de Olde EM, Ripoll-Bosch R, Van Zanten HHE, Metze TAP, Termeer CJAM, van Ittersum MK, de Boer IJM (2021) Principles, drivers and opportunities of a circular bioeconomy. Nat Food 2(8):561–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00340-7
Nemecek T, Hayer F, Bonnin E, Carrouée B, Schneider A, Vivier C (2015) Designing eco-efficient crop rotations using life cycle assessment of crop combinations. Eur J Agron 65:40–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2015.01.005
Netherlands Scientific Council for Government Policy (1992) Ground for choices: four perspectives for the rural areas in the European Community. Sdu uitgeverij.
Offermanns L, Tiemeyer B, Dettmann U, Rüffer J, Düvel D, Vogel I, Brümmer C (2023) High greenhouse gas emissions after grassland renewal on bog peat soil. Agric For Meteorol 331(October 2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2023.109309
Oosterom E, Hermans R (2013) Riolering in beeld benchmark rioleringszorg 2013. Stichting Rioned. https://www.riool.net/documents/20182/326834/Riolering+in+Beeld+2013/691bd284-0772-4c3f-8a29-1e08b1af0237
Papangelou A, Mathijs E (2021) Assessing agro-food system circularity using nutrient flows and budgets. J Environ Manag 288. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2021.112383
Peeters TMJ, Reemer M (2003) Bedreigde en verdwenen bijen van Nederland (Apidae S.L.). Basisrapport met voorstel voor de Rode Lijst (EIS2003–02). – European Invertebrate Survey - Nederland, Leiden. https://repository.naturalis.nl/pub/220052
Pereira HM, Leadley PW, Proença V, Alkemade R, Scharlemann JPW, Fernandez-Manjarrés JF, Araújo MB, Balvanera P, Biggs R, Cheung WWL, Chini L, Cooper HD, Gilman EL, Guénette S, Hurtt GC, Huntington HP, Mace GM, Oberdorff T, Revenga C, … Walpole M (2010) Scenarios for global biodiversity in the 21st century. Science 330(6010):1496–1501. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1196624
Pijlman J, Holshof G, van den Berg W, Ros GH, Erisman JW, van Eekeren N (2020) Soil nitrogen supply of peat grasslands estimated by degree days and soil organic matter content. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 117(3):351–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-020-10071-z
Quemada M, Lassaletta L, Jensen LS, Godinot O, Brentrup F, Buckley C, Foray S, Hvid SK, Oenema J, Richards KG, Oenema O (2020) Exploring nitrogen indicators of farm performance among farm types across several European case studies. Agric Syst 177. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AGSY.2019.102689
Regelink I, Ehlert P, Römkens P (2017) Perspectieven voor de afzet van (fosfaat-verarmd) zuiveringsslib naar de landbouw. (Wageningen Environmental Research rapport; No. 2819). Wageningen Environmental Research. https://doi.org/10.18174/420057
Reijneveld JA, Ehlert PAI, Termorshuizen AJ, Oenema O (2010) Changes in the soil phosphorus status of agricultural land in the Netherlands during the 20th century. Soil Use Manag 26(4):399–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1475-2743.2010.00290.X
Reneerkens J, Piersma T, Spaans B (2005) De Waddenzee als kruispunt van vogeltrekwegen; Literatuurstudie naar de kansen en bedreigingen van wadvogels in internationaal perspectief (NIOZ-REPORT 2005–4; Issues 2005–4). Koninklijk Nederlands Instituut voor Onderzoek der Zee. https://www.commissiemer.nl/docs/mer/p15/p1543/1543-83literatuurstudie.pdf
Rijkswaterstaat (2019) Effluenten RWZI’s (gemeten stoffen). https://www.emissieregistratie.nl/
RIVM (2021) NEVO-online versie 2021/7.0. https://nevo-online.rivm.nl/ . Accessed 12 Dec 2022
Sattari SZ, Bouwman AF, Giller KE, Van Ittersum MK (2012) Residual soil phosphorus as the missing piece in the global phosphorus crisis puzzle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(16):6348–6353. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1113675109/-/DCSUPPLEMENTAL/PNAS.201113675SI.PDF
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Schoumans OF, Chardon WJ (2015) Phosphate saturation degree and accumulation of phosphate in various soil types in The Netherlands. Geoderma 237:325–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.08.015
Schrier-Uijl AP, Kroon PS, Hendriks DMD, Hensen A, Van Huissteden J, Berendse F, Veenendaal EM (2014) Agricultural peatlands: towards a greenhouse gas sink - A synthesis of a Dutch landscape study. Biogeosciences 11(16):4559–4576. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-4559-2014
Schröder JJ, Aarts HFM, Ten Berge HFM, Van Keulen H, Neeteson JJ (2003) An evaluation of whole-farm nitrogen balances and related indices for efficient nitrogen use. Eur J Agron 20(1–2):33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1161-0301(03)00070-4
Schröder JJ, Smit AL, Cordell D, Rosemarin A (2011) Improved phosphorus use efficiency in agriculture: a key requirement for its sustainable use. Chemosphere 84(6):822–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.01.065
Schulte-Uebbing L, De Vries W (2021) Reconciling food production and environmental boundaries for nitrogen in the European Union. Sci Total Environ 786:147427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147427
Schut AGT, Cooledge EC, Moraine M, Van De Ven GWJ, Jones, DL, Chadwick DR (2021) Reintegration of crop-livestock systems in Europe: an overview. Front Agric Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.15302/J-FASE-2020373
Silva JV, van Ittersum MK, ten Berge HFM, Spätjens L, Tenreiro TR, Anten NPR, Reidsma P (2021) Agronomic analysis of nitrogen performance indicators in intensive arable cropping systems: An appraisal of big data from commercial farms. Field Crops Res 269(May). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108176
Smit AL, Van Middelkoop JC, Van Dijk W, Van Reuler H, De Buck AJ (2010) A quantification of phosphorus flows in the Netherlands through agricultural production, industrial processing and households. (Rapport / Plant Research International 364) - 55. Wageningen: Plant Research International. https://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wurpubs/402102
Smit AB, Jager JH, Van der Meer RW, Verhoog D, Vogelzang TA, Dolman M, Kros H (2017) De Noord-Nederlandse agrosector en agrocluster in beeld. https://edepot.wur.nl/414084
Soethoudt H, Timmermans T (2013) Monitor Voedselverspilling: mid-term rapportage (Food & Biobased Research 1372). Wageningen UR Food & Biobased Research. https://www.wur.nl/upload_mm/e/2/d/ab1ed91f-5884-4ee4-ab50-e0e204a96877_2013-05-13%20Rapport%20monitor%20Voedselverspilling.pdf
Soethoudt H, Vollebregt M (2020) Monitor Voedselverspilling: update 2009–2018: Hoeveel kilo gaat er in Nederland verloren? (Rapport / Wageningen Food & Biobased Research; No. 2050). Wageningen Food & Biobased Research. https://doi.org/10.18174/522604
Struik PC, Kuyper TW (2017) Sustainable intensification in agriculture: the richer shade of green. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 37(5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-017-0445-7
Sylvester-Bradley R, Roques S, Baxter C, Kendall S (2022) Nutrient harvests : the essential yardstick to transform crop nutrition. In: IFS Proceedings 874. International Fertiliser Society. https://fertiliser-society.org/store/nutrient-harvests-the-essential-yardstick-to-transform-crop-nutrition/
Tan M, Hou Y, Zhang L, Shi S, Long W, Ma Y, Zhang T, Oenema O (2022) Nutrient use efficiency of intensive dairy farms in China – Current situation and analyses of options for improvement. Agric Syst 203(September):103495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2022.103495
The World Bank (2020) Arable land (hectares per person) - European Union. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/AG.LND.ARBL.HA.PC?locations=EU . Accessed 25 Apr 2023
Theobald TFH, Schipper M, Kern J (2016) Regional phosphorus flows Berlin-Brandenburg phosphorus flows in Berlin-Brandenburg, a regional flow analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl 112:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.04.008
Tiemeyer B, Albiac Borraz E, Augustin J, Bechtold M, Beetz S, Beyer C, Drösler M, Ebli M, Eickenscheidt T, Fiedler S, Förster C, Freibauer A, Giebels M, Glatzel S, Heinichen J, Hoffmann M, Höper H, Jurasinski G, Leiber-Sauheitl K, … Zeitz J (2016) High emissions of greenhouse gases from grasslands on peat and other organic soils. Glob Change Biol 22(12):4134–4149. https://doi.org/10.1111/GCB.13303
van Berkum S (2021) How trade can drive inclusive and sustainable food system outcomes in food deficit low-income countries. Food Secur 13(6):1541–1554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-021-01218-z
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
van der Wiel BZ, Weijma J, van Middelaar CE, Kleinke M, Buisman CJN, Wichern F (2020) Restoring nutrient circularity: A review of nutrient stock and flow analyses of local agro-food-waste systems. Resour Conserv Recycl X 3(August):100014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcrx.2019.100014
van der Wiel BZ, Weijma J, van Middelaar CE, Kleinke M, Buisman CJN, Wichern F (2021) Restoring nutrient circularity in a nutrient-saturated area in Germany requires systemic change. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 121(2–3):209–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-021-10172-3
van Loon MP, Vonk WJ, Hijbeek R, van Ittersum MK, ten Berge HFM (2023) Circularity indicators and their relation with nutrient use efficiency in agriculture and food systems. Agric Syst 207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103610
van Rossum CTM, Buurma-Rethans EJM, Dinnissen CS, Beukers MH, Brants HAM, Dekkers ALM, Ocké MC (2020) The diet of the Dutch - Results of the Dutch National Food Consumption Survey 2012–2016 (RIVM report 2020–0083). National Institute for Public Health and the Environment. https://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/2020-0083.pdf
van Selm B, Frehner A, de Boer IJM, van Hal O, Hijbeek R, van Ittersum MK, Talsma EF, Lesschen JP, Hendriks CMJ, Herrero M, van Zanten HHE (2022) Circularity in animal production requires a change in the EAT-Lancet diet in Europe. Nat Food 3(1):66–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00425-3
van Selm B, Frehner A, van Hal O (2021) The compatibility of animal-sourced food and circularity in healthy European diets. Res Square 1–15. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-147410/v1 License:
Vellinga THV, André G (1999) Sixty years of Dutch nitrogen fertiliser experiments, an overview of the effects of soil type, fertiliser input, management and developments in time. Neth J Agric Sci 47:215–241
Velthof GL, Oudendag D, Witzke HP, Asman WAH, Klimont Z, Oenema O (2009) Integrated assessment of nitrogen losses from agriculture in EU-27 using MITERRA-EUROPE. J Environ Qual 38(2):402–417. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2008.0108
Verger Y, Petit C, Barles S, Billen G, Garnier J, Esculier F, Maugis P (2018) A N, P, C, and water flows metabolism study in a peri-urban territory in France: the case-study of the Saclay plateau. Resour Conserv Recycl 137(April):200–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.06.007
Vingerhoets R, Spiller M, De Backer J, Adriaens A, Vlaeminck SE, Meers E, Moreira MT (2023) Detailed nitrogen and phosphorus flow analysis, nutrient use efficiency and circularity in the agri-food system of a livestock-intensive region. J Clean Prod 410:137278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137278
Willett W, Rockström J, Loken B, Springmann M, Lang T, Vermeulen S, Garnett T, Tilman D, DeClerck F, Wood A, Jonell M, Clark M, Gordon LJ, Fanzo J, Hawkes C, Zurayk R, Rivera JA, De Vries W, Majele Sibanda L, … Murray CJL (2019) Food in the Anthropocene: the EAT–Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet 393(10170):447–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31788-4
Wortelboer FG (2010) Natuurkwaliteit en biodiversiteit van de Nederlandse zoute wateren (50040216/2010). Planbureau voor de Leefomgeving. https://www.pbl.nl/publicaties/natuurkwaliteit-en-biodiversiteit-van-de-nederlandse-zoute-wateren
WSBD (2018) Zuiveringsspiegel 2018. Waterschap Brabantse Delta. https://simcms.brabantsedelta.nl/_flysystem/media/zuiveringsspiegel_2018_-_waterschap_brabantse_delta.pdf
Yahia EM, Mourad M (2020) Preventing food losses and waste to achieve food security and sustainability, 1st edn. Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing, pp 341–366. https://doi.org/10.19103/as.2019.0053.14
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Dutch Research Council (NWO) Green III program (Grant number GROEN.2019.001) with co-funding from the Dutch Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality; Rabobank; Agrifirm Noord-West Europa; and Meststoffen Nederland. The authors express their gratitude to all supporting parties.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Plant Production Systems Group, Wageningen University & Research, Wageningen, the Netherlands
Durk W. Tamsma, Martin K. van Ittersum & Antonius G. T. Schut
Animal Production Systems Group, Wageningen University & Research, Wageningen, the Netherlands
Corina E. van Middelaar & Imke J. M. de Boer
Wageningen Environmental Research, Wageningen, the Netherlands
Johannes Kros
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Durk W. Tamsma, Corina E. van Middelaar, Imke J.M. de Boer, Martin K. van Ittersum and Antonius G.T. Schut wrote the main manuscript and contributed to the study design. Durk W. Tamsma prepared the figures. Durk W. Tamsma and Johannes Kros collected the data. Durk W. Tamsma and Antonius G.T. Schut prepared R scripts and analyzed the data. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Durk W. Tamsma .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (PDF 1.43 MB)
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Tamsma, D.W., van Middelaar, C.E., de Boer, I.J.M. et al. Why is nutrient cycling in food systems so limited? A case study from the North-Netherlands region. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-024-10352-x
Download citation
Received : 22 May 2023
Accepted : 12 March 2024
Published : 12 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-024-10352-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Food system
- Circular agriculture
- Nutrient use efficiency
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Separation Anxiety Dog
An unconventional approach to separation anxiety.
Expand your tools by learning different nuances of the SA training protocol
"An Unconventional Approach to Separation Anxiety"
Are you familiar with the CSAT approach to separation anxiety cases? If you are, and have been implementing it with your own separation anxiety clients I'm sure that you have found that this approach has a high rate of success, and I hope that you are feeling great about helping so many dogs and their families to successfully overcome this challenge. This approach is wonderful, and I personally implement it all the time and have lots of success doing so.
During my journey as a Certified Separation Anxiety Trainer I have realized more and more how all dogs benefit from a balance between predictability and flexibility. How beneficial is each of these parts of the puzzle, and in which amount will depend on each dog, and finding the right combination of both will ultimately set the dog (and us) up for success.
For the dogs who benefit from predictability over flexibility, the conventional training protocol can prove to be challenging, and it can lead to inconsistencies in the progress. Dogs who count steps, who learn that getting up makes the guardian come back earlier and earlier, or for the ones who just have a hard time grasping not knowing exactly when the guardian will return, an unconventional and more predictable protocol can make all the difference!
During this 90-min webinar we will discuss a specific case study where we successfully implemented an unconventional approach to separation anxiety within the same frame of the desensitization protocol that you are already familiar with. And where increasing predictability, among other things (always considering an integrative approach) was a game changer that got us from a 3-min absence where we had been stuck for over a year to a current 45-min absence duration.
If you would like to expand your knowledge about how to implement different nuances of the classic separation anxiety training model depending on what is more beneficial for each dog, this webinar is for you!
It is recommended to be familiar with the CSAT separation anxiety desensitization protocol before taking this webinar.
This webinar was live on Wednesday, June the 22nd at 2pm EST, and included a 60-min lecture plus 30-min of Q&A. You can now watch it ON DEMAND.

ACCESS ON DEMAND
Access now and have access to the recording for one year
What is included?
60-min lecture (recording)
30-min Q&A (recording)
One year access to the webinar recording
1.5 CEUs for CCPDT, 1.5 CEUs for IAABC and KPA
- Get 7 Days Free
University of Phoenix and Manpower Release Case Study on Building Skills Pathway for Employees
Alliance efforts were previously recognized with Excellence in Academic Partnerships Award by Chief Learning Officer
University of Phoenix and ManpowerGroup (Manpower), the employment agency dedicated to enriching people's lives with meaningful employment and development opportunities for more than 60 years, have issued a case study highlighting their academic alliance as a successful collaboration on an upskilling program. The case study provides a closer look at University of Phoenix alliance with Manpower on the shared efforts to support Manpower associates in gaining new skills and expanding career opportunities.
“The labor market continues to lean on the effectiveness of data-informed approaches to identifying and addressing skills gaps in the workforce,” states Jay Titus, vice president and general manager of Workforce Solutions Group at University of Phoenix. “We are impressed with Manpower’s dedication to identifying and addressing skill and career opportunities for their associates, and we are proud of how our highly collaborative approach to helping address talent skills gaps has been effective for them.”
According to a 2023 study conducted by Manpower, global talent shortages reached a 15-year high with 75% of U.S. employers reporting difficulty finding appropriately skilled talent. And findings from the University of Phoenix Career Institute® Career Optimism Index ® point to the opportunity for employers to invest in skilling with 70% of American workers indicating they would be more likely to stay with their employer if their company gave them more opportunities to apply new skills.
University of Phoenix Workforce Solutions Group offers companies across diverse industries as well as community colleges tailored learning and career pathways to recruit, upskill, reskill, and retain their workforce in an affordable and timely manner. Their flexible solutions are aligned to workplace needs and feature live support, career guidance and support tools, education programs, learning pathways, and credit options, including certificates, workshops, single courses, degree programs, or any combination of these tools.
The case study shares insights on this approach to workforce development through the Manpower Acceleration Program, designed in a collaborative approach in which University of Phoenix created short, skill-focused classes that prepared Manpower associates to pursue career opportunities. Graduates from the program receive certificates of achievement and one college credit that can be applied to a University of Phoenix degree. More than 2,500 Manpower associates have completed courses in accounts receivable/payable, contact center/customer service, contact center team leadership, help desk, human resources, project management, and warehouse/production leadership. Participants can pursue a degree in business, health care, technology, criminal justice, human services, communications or sciences.
“Our MyPath program was built to help our Associates reach for new and meaningful opportunities in their career progression,” stated Nimo Shah, Director, MyPath ManpowerGroup. “Our team worked closely with University of Phoenix to create this talent development solution, and we are pleased to share more on how this defined a successful pathway for our Associates to gain new skills.”
The alliance was recently recognized with the 2023 Chief Learning Officer (CLO) Learning in Practice Award in the category, Excellence in Academic Partnerships. The CLO Learning in Practice Awards honor learning and development leaders for their work in designing and delivering exemplary employee development programs.
University of Phoenix's commitment to career-minded learning is evident through its innovative skills-tagged curriculum and digital badging model to meet working adult learners’ need to demonstrate skills attainment for workplace relevancy . The University has issued over 450,000 badges since September 2021, for skills obtained in undergraduate, graduate, and professional development courses. Currently, 100% of the University’s associate, bachelor’s and master’s programs open for new enrollment are now skills mapped.
Read the Manpower and University of Phoenix case study here .
About University of Phoenix
University of Phoenix innovates to help working adults enhance their careers and develop skills in a rapidly changing world. Flexible schedules, relevant courses, interactive learning, skills-mapped curriculum for our bachelor’s and master’s degree programs and a Career Services for Life® commitment help students more effectively pursue career and personal aspirations while balancing their busy lives. For more information, visit phoenix.edu .
Sharla Hooper University of Phoenix [email protected]
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20240410159586/en/
Market Updates
Magnificent no more apple and tesla stocks are weighing on the market, what’s happening in the markets this week, what hot inflation and delayed rate cuts mean for investors, these 4 charts show plunging expectations for fed rate cuts, march cpi report: why is inflation still so sticky, forecasts for march cpi report show more mixed signals on inflation, 5 dirt-cheap stocks to buy in april, markets brief: what fewer rate cuts could mean for stock valuations, stock picks, citigroup earnings: laser focus on expenses needed to achieve long-term targets, wells fargo earnings: net interest income guidance unchanged and trading revenue strong, the best chinese stocks to buy, the role of market movements in your portfolio, going into earnings, is netflix stock a buy, a sell, or fairly valued, jpmorgan earnings: bumper profits driven by strong net interest income and trading revenue, 3 cheap stocks to watch in the fight over sports streaming, blackrock earnings: market gains make up for weaker inflows as firm hits record aum, sponsor center.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table.
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically ...
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
It's been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students.
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
Unlike case study or ethnography, when researchers use a narrative approach, they are focused on the participants' stories. Liamputtong (2009) outlines five steps for conducting data analysis within the narrative approach (this type of analysis is referred to as narrative analysis), and it primarily deals with data collected from a narrative ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
to use a case study in our research, this does not mean the selection of a method, but rather a selection of what will be explored (ibid., p. 301). An individual case
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
In this study, we adopted a descriptive case study approach to answer our research questions as the case study method is considered suitable for exploring and providing an in-depth understanding ...
Authors sometimes use incongruent methods of data collection and analysis or use the case study as a default when other methodologies do not fit. 9,10 Despite these criticisms, case study methodology is becoming more common as a viable approach for HSR. 11 An abundance of articles and textbooks are available to guide researchers through case ...
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business ...
Case studies are often used in the exploratory phase of research to gather qualitative data. They can also be used to create, support, or refute a hypothesis and guide future research. For instance, a marketing professional might conduct a case study to discover why a viral ad campaign was so successful.
Origins and definitions. French sociologist Frederic Le Play (1806-1882) is associated with the origin of the case study approach (Hamel et al., 1993).Using a purposive sample of working class families and fieldwork methods of observation and individual interview, he sought a contextualised and in-depth understanding of their individual experiences.
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table 5 ), the ...
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows: • Select the topic and the deadline of your case study. • Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the writing process you struggle with. • Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
Study setting. This research was exploratory rather than explanatory in nature. The emphasis was on demonstrating the usefulness of the WeValue InSitu (WVIS) approach to develop culturally-informed protocols of practical use in intervention design, in different cultural sites.This study was set within a broader shared-values workstream within the UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub project [].
In the current study, we focused on adolescent substance use initiation of heavy drinking, cannabis use, and hard drug use. This measurement approach offers a broader assessment of risk than focusing on only one substance and allows us to capture escalation to polysubstance initiation, an area of research that is relatively lacking in the ...
Examines the key principles of strategic management, with particular focus on the strategy process and its individual components - analysis, choice, action and evaluation. This unit makes use of the case analysis method so that students can apply their understanding to real-world problems across a range of professional contexts.
Siti Rahman, the CEO of Malaysia-based NVF Bank, faces a pivotal decision. Her head of AI innovation, a recent recruit from Google, has a bold plan. It requires a substantial investment but aims ...
Identifying pathways to circular agriculture requires a profound understanding of nutrient flows and losses throughout the food system, and of interactions between biophysical conditions, land use, food production and food consumption. We quantified nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) flows of the food system of the North-Netherlands (NN) region and of its 30 subregions varying in biophysical and ...
On this 90-min webinar we will discuss a specific case study where an unconventional, more predictable approach to separation anxiety as a nuance of the conventional SA desensitization protocol was highly successful, and a game changer. On this 90-min webinar we will discuss a specific case study where an unconventional, more predictable ...
The case study shares insights on this approach to workforce development through the Manpower Acceleration Program, designed in a collaborative approach in which University of Phoenix created ...