

Essay on Environmental Sustainability
Students are often asked to write an essay on Environmental Sustainability in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Environmental Sustainability
Understanding environmental sustainability.
Environmental sustainability is about making decisions that do not harm the environment. It’s about preserving nature for future generations.
Importance of Environmental Sustainability
Our survival depends on the environment. If we don’t sustain it, we risk losing resources like water and air. It’s crucial for our health and economy.
Ways to Achieve Sustainability
We can achieve sustainability by reducing waste, recycling, and using renewable energy. It’s about changing our lifestyles to protect the environment.
Environmental sustainability is crucial for our future. We all need to play our part to ensure our planet remains healthy.
Also check:
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Environmental Sustainability
250 Words Essay on Environmental Sustainability
Introduction to environmental sustainability.
Environmental sustainability is an integral aspect of our existence, intertwined with the notion of preserving the natural world for future generations. It encapsulates the concept of stewardship, wherein we are responsible for managing the Earth’s resources responsibly and efficiently.
The Imperative of Sustainable Practices
The current environmental crisis, characterized by climate change, deforestation, and biodiversity loss, underscores the urgency of sustainable practices. These practices aim to minimize the environmental footprint by reducing waste, conserving energy, and promoting recycling. They are not merely an ethical obligation, but a necessity for human survival.
Role of Innovation in Sustainability
Innovation plays a pivotal role in environmental sustainability. Technological advancements like renewable energy, green architecture, and waste management systems pave the way for a sustainable future. They provide practical solutions to environmental problems, enabling us to balance economic growth with ecological preservation.
Individual Responsibility and Collective Action
Environmental sustainability demands individual responsibility and collective action. Each of us can contribute by adopting sustainable lifestyles, such as minimizing waste, conserving water, and reducing energy consumption. Collective action, on the other hand, involves policy changes, corporate responsibility, and international cooperation.
In conclusion, environmental sustainability is a multidimensional concept, involving the careful management of natural resources, innovative technologies, and concerted human effort. As stewards of the Earth, we must strive to ensure the sustainability of our planet for future generations.
500 Words Essay on Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability is a concept that has grown in prominence as the world grapples with the effects of climate change. It refers to the practice of using resources in a way that preserves the environment for future generations. This includes reducing waste, promoting renewable energy, and maintaining biodiversity.
The Importance of Environmental Sustainability
The significance of environmental sustainability cannot be overstated. As the world’s population continues to grow, so does the demand for resources. This increased demand, coupled with unsustainable practices, has led to environmental degradation, loss of biodiversity, and climate change. By practicing environmental sustainability, we can help ensure that future generations inherit a planet that is as rich and diverse as the one we enjoy today.
Principles of Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability is underpinned by several key principles. First, we must recognize the finite nature of our planet’s resources and strive to use them sparingly. Second, we must work towards reducing waste and promoting recycling. Third, we must strive to reduce our carbon footprint and promote renewable energy. Lastly, we must value and protect our biodiversity, recognizing the intrinsic worth of all living things.
Challenges to Environmental Sustainability
Despite its importance, achieving environmental sustainability is not without its challenges. There is often a conflict between economic development and environmental protection, with many arguing that the latter hampers the former. Additionally, there is a lack of awareness and understanding about environmental issues, leading to apathy and inaction. Lastly, there is a lack of political will to implement and enforce environmental regulations.
Role of Individuals and Institutions in Promoting Environmental Sustainability
Individuals and institutions have a crucial role to play in promoting environmental sustainability. Individuals can make a difference by making sustainable choices in their daily lives, such as reducing waste, recycling, and choosing renewable energy. Institutions, on the other hand, can implement sustainable practices in their operations and advocate for environmental sustainability at the policy level.
In conclusion, environmental sustainability is not just a buzzword; it is a necessity for our survival and the survival of future generations. It requires a collective effort from individuals, institutions, and governments alike. By understanding the importance of environmental sustainability and the principles that underpin it, we can all play a part in preserving our planet for future generations.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Environmental Issues
- Essay on Environmental Hygiene
- Essay on Environmental Hazards
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Environmental Sustainability, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 572
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
The implication of sustainability is the inherent potential for tolerance. In the context of human life, the implication of sustainability is maintaining a fair well-being on a long term basis with regard to the dimensions of environmental, social as well as economic perspectives (Bell, 2003, 115-156). The idea of stewardship in addition to managing the utility of resources in a responsible manner is encompassed in the issues of sustainability. Sustainability has an ecological dimension which addresses the diversity of biological systems and the maintenance of their productivity which is a significant precondition for the well-being of people.
The maintenance of healthy environments as well as ecosystems is a source of important goods as well as services to the human kind as well as the rest of the organisms. Human influence to the ecosystem is an issue that requires proper management. One important approach to achieve this end is through the management of the environment. The achievement of this is facilitated by information accessible from the fields of conservation biology, environmental science as well as earth science. Resources consumption is another alternative approach in management of ecosystem (Gottfried, 2004, 97-106).
Human beings should strive towards a sustainable living which is achievable through restricting human activities within the natural or environmental system while at the same time avoiding acts that can inflict harm to others. This relates to the determination of appropriate sources of food, energy, cloths among other products. Sustainability through recycling has positively impacted on the habits of majority people and this has been reflected on the positive impact on worldwide climate change.
Recycle for Environmental Sustainability
A positive impact on global climate change is achieved through recycling (Hiss, 1990, 167). The starting point is the local retailer who is encouraged to avail more products that can be recycled. Buying products along with their containers whose materials can be recycled has been a significant step towards promotion of recycled product market. Paper products such as the toilet papers should have a percentage of about 50% materials that have already been recycled. Products from companies which use chlorine in the process of bleaching paper products results to the creation of dioxin waste and therefore are deliberately avoided.
Enacting and Implementing a New Method of Environmental Sustainability
The use of organic foods offers the most reliable solution of eating sustainably. This is an important direction to take in an attempt of achieving environmental sustainability because of a variety of reasons. The local and seasoned foods are associated with several benefits in addition making a positive impact on global climate change. The amount of energy that is allied to the emissions of carbon dioxide arising from the systems of growth as well as transportation of food products is significantly reduced. The economy is supported from the local level and there is a reconnection of the cycles of nature as time progresses. Eating locally takes account of choosing the types of food closed to the living locality and this is an implication of sustainability. It reduces the time period between harvesting of the food product or its processing to the time of its consumption. A lot of nutrients are lost when a certain food product takes significantly long time between the time of its harvesting to the time of its consumption
Works Cited
Bell, Simon & Morse, Stephen. Measuring Sustainability. London: Earthscan Pub. Ltd., 2003.
Gottfried, David. Greed to Green. CA: Worldbuild Pub., 2004. >>http://www.lincolngreenbydesign.com/resources/bibliography.php<<
Hiss, Tony. The Experience of Place. NY: Alfred A. Knopf, 1990.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Apple on the Job Training Program, Essay Example
Cost-Effective OJT Program, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Climate Change
- Policy & Economics
- Biodiversity
- Conservation
Get focused newsletters especially designed to be concise and easy to digest
- ESSENTIAL BRIEFING 3 times weekly
- TOP STORY ROUNDUP Once a week
- MONTHLY OVERVIEW Once a month
- Enter your email *
Explainer: What Is Sustainability and Why Is it Important?
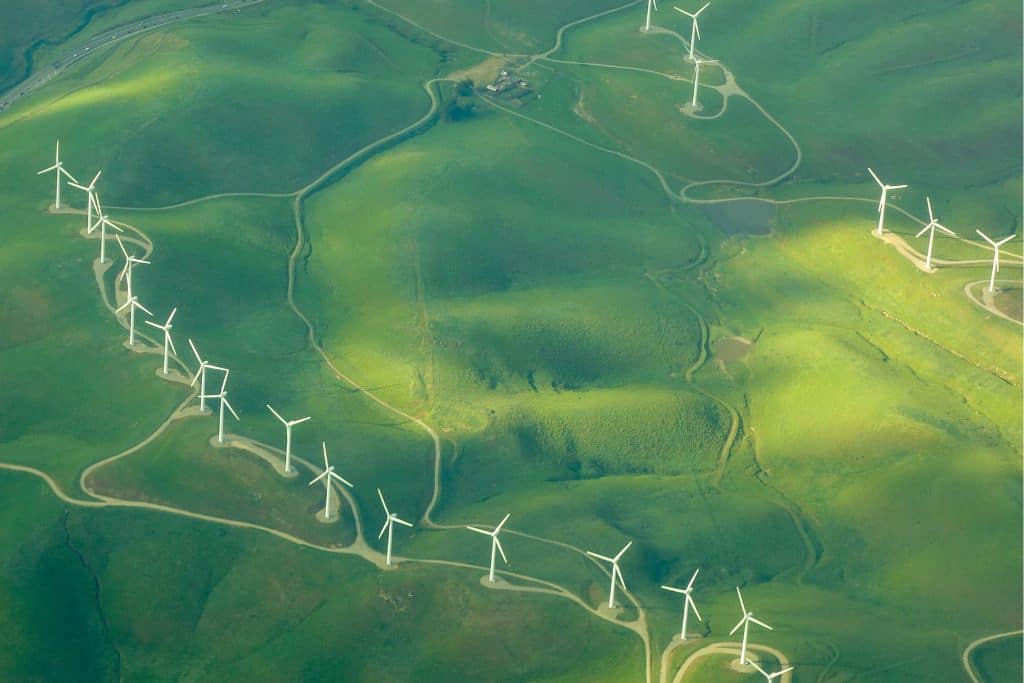

It seems like nowadays, the term ‘sustainable’ is used all around us – from food packaging to clothing companies and even tourism. In fact, ‘sustainability’ was one of the most-searched terms in fashion in 2019, and Google searches for the term have been on the rise, illustrating the public’s growing interest in the topic. But what is sustainability exactly and why is it so important?
What Is Sustainability
The go-to definition when discussing sustainability is “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”. And though you may have heard this before, many people do not know the origins of this definition in particular. In 1987, the United Nations Brundtland Commission published this particular definition of sustainability in the Brundtland report , which called for a strategy that united development and the environment. Over the years, alternative definitions have emerged, but the Brundtland report’s 1980s take on the explanation is still commonly used.
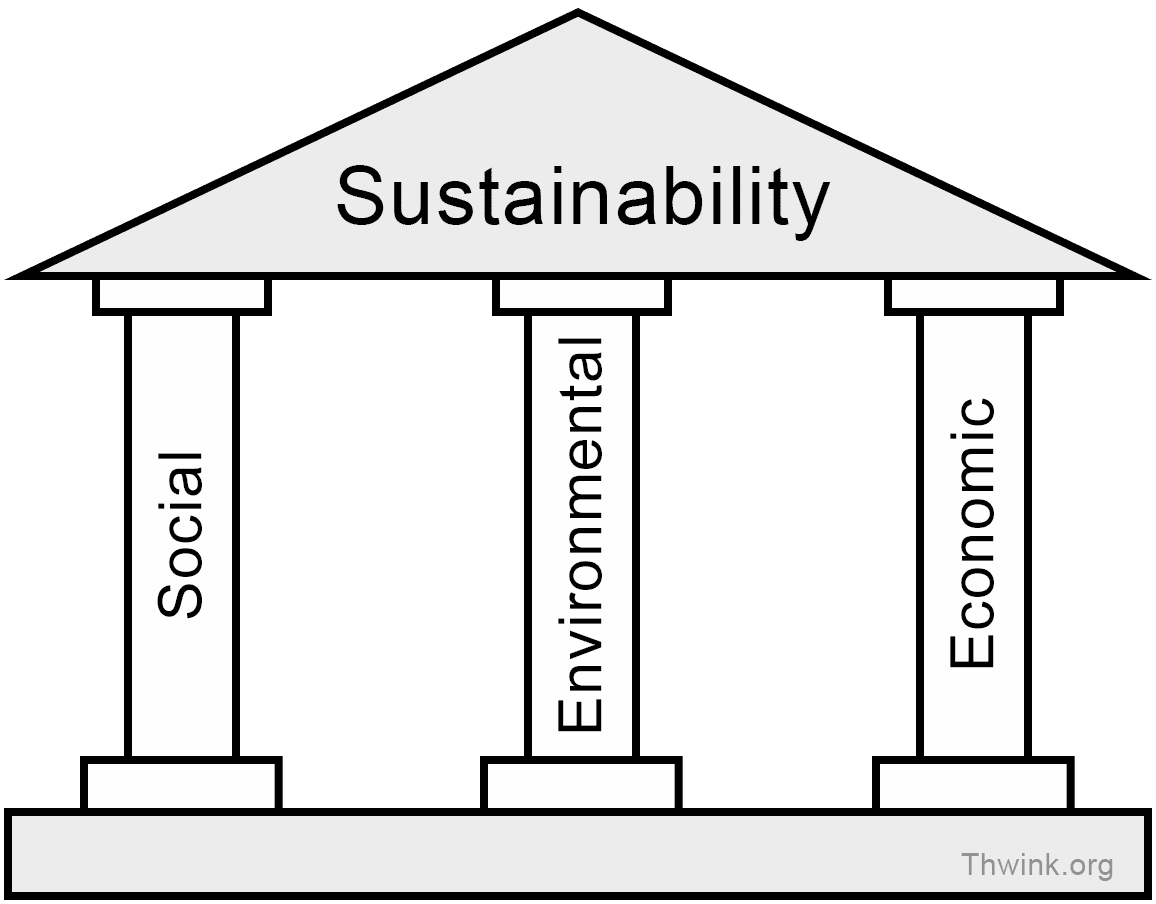
The ‘ Three Pillars of Sustainability’ is another popular framework used to describe what sustainable development is. This tool conveys that sustainability consists of environmental, social, and economic factors that are vital when discussing the topic:
- Environmental sustainability is perhaps the most obvious of the three pillars, as it symbolises the importance of things like natural resources and biodiversity to support life on Earth.
- Social sustainability places importance on social structures, well-being, and harmony; all factors that poverty, wars, and injustices can affect.
- Economic sustainability describes the ability of an economy to grow. This is especially important in today’s societies, at a time when many sustainable initiatives require financing and a strong economic rationale.
In order to find solutions to ongoing sustainability issues, it is imperative that we consider all three pillars.
You might also like: We Need Sustainable Food Packaging Now. Here’s Why.
What Are the Planetary Boundaries And How Do They Relate to Sustainability?
The concept of planetary boundaries (PB) is focussed on nine aspects that humanity needs in order to thrive in the future. This idea was developed in 2009 by the Stockholm Resilience Centre and other groups: “ We propose a new approach to global sustainability in which we define planetary boundaries within which we expect that humanity can operate safely. Transgressing one or more […] may be deleterious or even catastrophic due to the risk of crossing .”
At the time when this new concept was introduced, scientists believed that humanity had already transgressed three boundaries, and was rapidly approaching several others. In 2022, a re-assessment of the PBs by fourteen scientists concluded that humanity had transgressed additional boundaries, relating to freshwater and environmental pollutants in particular.

The PBs have been widely cited in sustainability literature over the last decade, and provide an illustrative tool to track and evaluate how we are depleting the Earth’s valuable ecosystem services and precious systems. Though the tool is mainly environmentally focused, it has informed various policies and practices, including the World Business Council on Sustainable Development’s Action 2020 Strategy. In turn, this has had a knock-on effect on social and economic aspects of global policy and governance, including “financial investment, food, textiles, building, technology and household goods sectors”.
You might also like: Sustainable Alternatives to Fast Fashion
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
In 2015, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development was adopted by the UN Member States. One of the most well-known elements of this were the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) which set out various goals that the international community must work together to achieve – ranging from environmental and social to economic issues.

We cannot discuss the SDGs without first acknowledging their predecessor – the eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) – set out in September 2000. These goals ranged from halving extreme poverty to halting the spread of HIV/AIDS. By the end of the 15-year cycle of the MDGs in 2015, the UN established an even more ambitious set of goals – the SDGs – to enter into force on 1 January 2016. While not all of the MDGs were met globally, significant progress was made in several areas.
The SDGs have been continually monitored and provide key benchmarks for us to understand how sustainability is being achieved worldwide. Overview reports are regularly published and comment on the nuances that significant events bring to achieving the SDGs (like the COVID-19 pandemic, for example). You can read the 2022 SDG Report here .
You might also like: Why the Sustainable Development Goals for 2030 Are More Important Than Ever
Why Is Sustainability Important?
So far, we’ve discussed the different ways that sustainability is defined and the tools and metrics we have developed on a global scale to measure our impact on the environment, societies, and economies worldwide. But why is sustainability important?
Here are a few reasons, although the list could go on for a lot longer:
- Sustainability joins social, environmental, and economic issues together throughout global discussions, ensuring that key elements do not get left behind. Focusing on aspects other than the environment alone ensures a fairer, more equitable discussion (as long as a diverse range of players is at the table).
- Sustainability opens up new conversations between a range of people with diverse skills and thought processes – for example scientists, sociologists, and economists all have key skills to enable humanity to thrive and sustain the Earth.
- The SDGs are an impactful way to evaluate our progress and have encouraged key ideas and strategies to flourish while remaining realistic about the next steps and improvements.
This story is funded by readers like you
Our non-profit newsroom provides climate coverage free of charge and advertising. Your one-off or monthly donations play a crucial role in supporting our operations, expanding our reach, and maintaining our editorial independence.
About EO | Mission Statement | Impact & Reach | Write for us

Top 7 Smart Cities in the World in 2024

The Green Dilemma: Can AI Fulfil Its Potential Without Harming the Environment?

How Does Overpopulation Affect Sustainability? Challenges and Solutions
Hand-picked stories weekly or monthly. We promise, no spam!
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Boost this article By donating us $100, $50 or subscribe to Boosting $10/month – we can get this article and others in front of tens of thousands of specially targeted readers. This targeted Boosting – helps us to reach wider audiences – aiming to convince the unconvinced, to inform the uninformed, to enlighten the dogmatic.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction of Sustainability, Sustainable Development, and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
What is sustainability.
Sustainability is a well-known and frequently used term of the 21st century. How often do you see or hear the word? Have you ever stopped to really think about what exactly does sustainability mean and where did the term originate from?
A quick Google search for ‘what is sustainability’ yields over 1.9 billion results. Sustainability is widely defined as ‘the ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level’. Embedded in most definitions of sustainability are concerns for the environment, social equity, and economic prosperity(1). Most definitions look to avoid the depletion of natural resources to maintain an ecological balance. Sustainability in the context of the environment looks at the activities required to balance social, economic, and environmental needs to maintain ecosystem services at a suitable level. It is generally accepted, the goals of sustainability are related to the need for the conservation of natural capital and ecosystem services, with a shift to a less resource-intensive future [1] .
While to most, the concept of sustainability is a relatively new idea, sustainability has a long history of use and meaning. The practice of sustainability has been utilized by various cultures for thousands of years, with the term sustainability first used in the 1700’s. Sustainability comes from the practice of nachhaltigkeit , translated to mean ‘sustained yield’ in English, a term coined in 1713 by German foresters [2] . Sustained yield refers to the practice of taking only enough trees to allow forests to naturally regenerate well into the future. The concept of sustained yield broadened to include the conservation of plants, animals, and other food necessities, eventually moving beyond the forestry discourse but still mainly confined to research and science.
It was not until the 1970’s that the concept of sustainability became more widely used. In January 1972, the journal the Ecologist published the Blueprint for Survival , a series of science papers calling for better management of natural resources and modification of consumptive lifestyles of western civilizations. That same year, a global think-tank published the report Limits to Growth , where a definition was given to the term sustainable. For the first time in the literature, sustainable was defined to mean without sudden and uncontrolled collapse and capable of satisfying the basic material requirements of all its people (2). Then later that year the United Nations (UN) world conference on human environment was held Stockholm, Sweden to address the global the growing environmental crisis. The term sustainable development was introduced into the discourse. As evidenced at the UN Conference, the environment was being neglected and not in balance with economic development.
Through the 1980’s, the concept of sustainability became more mainstream. In 1987, former Norwegian Prime Minister Gro Harlem Brundtland, as chairwoman of what was then the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED) released a Report, widely known as the Brundtland’s Commission, Our Common Future . The report emphasized the importance that development should consider social, environmental, and economic aspects to ensure the sustainability of all human societies. Her main concern was that development had to meet “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” [3] . This concept went on to become the most widely used definition of sustainability although in the context of sustainable development.
Although sustainability and sustainable development both consider the environment, society, and economies with a future timeframe, the two terms have very different meanings and should not be used interchangeably. Sustainability looks at the activities required to protect the environment as our base for survival while balancing social, cultural, and economic needs. It is generally accepted that the goals of sustainability are related to the need to conserve our natural world with a shift away from the resource-intensive current way of living 1 .
What is Sustainable Development?
We learned that sustainability is the process of living within the limits of available physical, natural, and social resources in ways that allow all living things, not only humans to thrive well into the future.
Sustainable development is a process that creates growth and progress through the addition of physical, economic, environmental, and social components to improve quality of life without damaging the resources of the environment. Simply put, sustainable development is a way for people to use resources without the resources running out 3 .
As previously discussed, the concept of sustainable development arrived in 1987 by the Brundtland Commission “Our Common Future”, the document that defined sustainable development as an approach designed to meet the needs of the present [generation] without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs 3 . This definition incorporated the understanding that economic growth is required to provide societies with the necessities of life such as clean water and food, while acknowledging the dilemma of environmental degradation that often coincides with economic development.
In 1992 the UN conference on the environment and development, informally known as the Earth Summit, or the Rio Conference took place in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The conference promoted the idea of ecological sustainable development and in order to achieve it you had to consider social development (communities). From the mid 1990’s, different strategies were developed to try to work out what sustainability means in practice, how do we get that middle area where the environment, economics, and social development are achieved at the same time. Governments alone can not achieve sustainable development. Governments can set regulations and determine infrastructure needs but they don’t tend to have long-term goals in mind, they tend to focus on election cycles which are typically about 4 to 8 years. The market economies (goods and services) timeframe is usually only about 4 months to a year. Sustainability is about long-term solutions. The market economies and governments can not effectively do this. If the community is not driving the will for a better more sustainable future, sustainable development will be difficult to achieve. As we previously discussed, the Brundtland Commission’s definition has become a widely used definition for sustainable development and sustainability and has therefore come with many challenges, including confusion over meaning, interpretations, and misinformation.
Recognizing some of the key challenges with the implementation of sustainable development and the quest for achieving a balance between the environment and economies, the role of people and societies were formally added into the equation for sustainable development in 2005 at the UN World Summit on Social Development. The three pillars of sustainability became widely known and currently used today:
(Click on the “?” icons below for more information):
This updated model for sustainable development recognizes that in order to meet the needs of current and future generations you have to consider the three pillars or the 3P’s (people, planet, prosperity), and they all need to be working together at the same. The key being all at the same time, or simultaneously.
Integrating the short-term and long-term needs with a focus on future generations, will require social development, environmental protection, and economic prosperity working in unison. Being able to incorporate sustainability into your day to day activities, this is what will create change.
The United Nations and the Path to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
History of the un.
Direct Source
The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945 after the Second World War by 51 countries committed to maintaining international peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations, and promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights.
Due to its unique international character, and the powers vested in its founding Charter, the Organization can take action on a wide range of issues and provide a forum for its 193 Member States to express their views, through the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council and other bodies and committees.
The work of the United Nations reaches every corner of the globe. Although best known for peacekeeping, peace-building, conflict prevention and humanitarian assistance, there are many other ways the United Nations and its System (specialized agencies, funds, and programmes) affect our lives and make the world a better place. The Organization works on a broad range of fundamental issues, from sustainable development, environment and refugees protection, disaster relief, counter terrorism, disarmament and non-proliferation, to promoting democracy, human rights, gender equality and the advancement of women, governance, economic and social development and international health, clearing landmines, expanding food production, and more, in order to achieve its goals and coordinate efforts for a safer world for this and future generations.
The UN has 4 main purposes:
- To keep peace throughout the world;
- To develop friendly relations among nations;
- To help nations work together to improve the lives of poor people, to conquer hunger, disease, and illiteracy, and to encourage respect for each other’s rights and freedoms;
- To be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations to achieve these goals
Pathway to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
In 2015, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development was adopted by 193 United Nations (UN) Member States. The 2030 Agenda is centered on the 17 SDGs which are underpinned by the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). The MDGs were developed in 2000 to end poverty and hunger, fight inequality and injustice, advance climate change action, create sustainable consumption and production, and promote peace and prosperity for all. One major change between the MDGs versus the SDGs is that for the SDGs, all countries are now involved. The MDGs only applied to developing countries. Another difference is that each country has set their own goals and priorities for achieving the SDGs. International collaboration to advance the SDG Agenda remains a critical component. The 17 SD goals, with their 169 targets, and over 230 indicators work together at the local and international level to help promote a shared global framework to achieve a fair, equitable, and sustainable future for all. Currently, all countries and international organizations are working on the achievement of the UN 2030 Agenda serving as the basis for better economic development that is environmentally low impact, socially just, and economically efficient and fair.
Pathway to the SDGs
Comprehension Questions
Recommended reading.
- Sustainable Development Solutions Network. (2021). Sustainable Development Report 2021: The Decade of Action for the Sustainable Development Goals .
Additional Readings
- Brundtland G, Khalid M. 1987. UN Brundtland commission report. Our Common Future . 41-59.
- Kidd C. V. 1992. The evolution of sustainability . Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Ethics , 5(1), 1-26.
- Baker, J., Dupont, D., & Vasseur, L. (2021). Exploring Canadian Ramsar Sites Ecosystem Governance and Sustainability. Wetlands, 41(1), 1-11. ↵
- Grober, U. (2007). Deep roots-a conceptual history of sustainable development (Nachhaltigkeit) . ↵
- United Nations. (2021). 1987 Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future (page 41) . ↵
Introduction to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Copyright © by Jocelyn Baker is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

Thanks for signing up as a global citizen. In order to create your account we need you to provide your email address. You can check out our Privacy Policy to see how we safeguard and use the information you provide us with. If your Facebook account does not have an attached e-mail address, you'll need to add that before you can sign up.
This account has been deactivated.
Please contact us at [email protected] if you would like to re-activate your account.
Climate change is the most urgent issue affecting the whole planet right now. It has been described as the defining human development issue of our generation.
Climate change-related hazards are ongoing and increasing. They pose a serious threat to the achievement of the MDGs as they have the potential to reverse years of development gains. Tackling the climate is a need for justice: developing countries have 98% of the seriously affected and 99% of all deaths from weather-related disasters, along with over 90% of the total economic losses, while the 50 Least Developed Countries contribute less than 1% of global carbon emissions.
Climate change and global poverty must be combated simultaneously. 75% of the world’s poor live in rural areas and largely depend on natural resources for their livelihoods and income. They suffer the most from natural disasters due to poor infrastructure and systems that are not equipped to deal with the drastic impact of major catastrophes such as the 2004 tsunami or Haiti earthquake.
Projected impacts from climate change include the following:
Decline in agricultural productivity : The areas suitable for agriculture, the length of growing seasons and the yield potential of food staples are all projected to decline. Some African countries could see agricultural yields decrease by 50% by 2050 and crop net revenues could fall by as much as 90% by 2100.
Increased water stress: Changing climate patterns will have important implications for water availability in Africa. By 2020, an additional 75-250 million people in Africa are projected to be exposed to increased water stress due to climate change.
Rising sea levels : Across the globe, sea levels could rise rapidly with accelerated ice sheet disintegration. In Africa, highly productive ecosystems, which form the basis for important economic activities such as tourism and fisheries, are located in coastal zones. In total, 70 million people and 30% of the Africa's coastal infrastructure could face the risk of coastal flooding by 2080 because of rising sea levels.
Risks to human health: Climate change will affect human health through variables such as changes in temperature, exposure to natural disasters, access to food and air quality. Previously malaria-free highland areas in Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda and Burundi could experience modest incursions of malaria by the 2050s, with conditions for transmission becoming highly suitable by the 2080s. In total, an additional 260-320 million people worldwide could be living in malaria-infested areas by 2080.
Threats to ecosystems and biodiversity : Changes induced by climate change are likely to result in species range shifts and changes in tree productivity, adding further stress to forest ecosystems. Studies predict that 25-40% of mammal species such as zebra could become endangered or extinct by 2080.
Global efforts are key to ensure environmental sustainability. Industrialized countries are historically responsible for the bulk of green house gas emissions. However, meaningful reductions in emissions today can only be achieved through an approach that includes emerging markets. In addition, developing regions like sub-Saharan Africa, must be enabled to embark on a low carbon growth path as they continue to grow their economic base and energy supply and demand. Industrialized countries have an obligation to support Africa and other regions in this endeavor. Moreover, it is in their interest to do so as climate change impacts will be felt throughout the world. Developing and emerging countries have signaled they would agree to a global climate deal if they are supported. In addition, there are untapped opportunities for partnering with sub-Saharan Africa to stem further declines. Africa's vast rainforests and natural resources could be invested in through re-forestation and agro-forestry programs to provide sustainable livelihoods and carbon storage/sequestration.
by Jared Levy, Austin Peck VOICE OVER RECORDING Margarita Mix, Hollywood VERY SPECIAL THANKS TO: Cody Irizarry, Jane Rosenthal, Nancy Lefkowitz
Defend the Planet
Introduction to the importance of environmental sustainability
Oct. 15, 2012
Introductory essay
Written by the educators who created Climate Change, a brief look at the key facts, tough questions and big ideas in their field. Begin this TED Study with a fascinating read that gives context and clarity to the material.
The greenhouse effect has been detected, and it is changing our climate now. James Hansen, June 24, 1988
The drought that crippled much of the U.S. and Canada in 1988-89 was the costliest natural disaster in U.S. history prior to Hurricane Katrina. It spawned dust storms in the Midwest and forest fires in Yellowstone National Park. That summer, thousands died during an intense heat wave.
It was against this backdrop, on a 101-degree day in the nation's capital, that NASA scientist James Hansen delivered his landmark testimony to the Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee. The next day, The New York Times ran a headline that read "Global Warming Has Begun, Expert Warns." Coverage of Hansen's testimony by the Times and other national and global media organizations transformed climate change from a relatively obscure scientific topic to one that people began to discuss over dinner, in the pub, at school and at work.
It remained newsworthy over the rest of that pivotal year. Days after Hansen's testimony, the World Meteorological Association (WMO) hosted a conference called "Our Changing Atmosphere," one of the earliest international climate change gatherings. 300 scientists and policy makers representing 46 countries attended. Participants called upon countries to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 20 percent or more by 2005, and by the end of the year the WMO and the United Nations Environment Program had established the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously became one of the first world leaders to talk about climate change in a speech delivered that September to the Royal Society. "For generations, we have assumed that the efforts of mankind would leave the fundamental equilibrium of the world's systems and atmosphere stable," remarked Thatcher. "But it is possible that… we have unwittingly begun a massive experiment with the system of this planet itself." In this speech and others she gave during the remainder of her tenure, Thatcher advocated for expanded climate research and for policies that would safeguard the environment and promote sustainable development.
As global public awareness of the issue grew in the 1980s and beyond, the science and its significance were vigorously debated. Is there credible evidence that climate change is real? If it's real, when and how will we feel its effects? If it's real, what should be done, and who should do it? (Thatcher herself reversed position many years later, calling climate change "the doomsters' favorite subject" predicated on science that is "extremely obscure" and leading to "worldwide, supra-national socialism.")
Climate change is still hotly contested and the debate is often shrill, with skeptics branded as "climate deniers" and activists derisively labeled "warmists." Tensions are palpable, as when nearly 800 NGO representatives walked out of the 2013 international climate negotiations in Poland.
How has climate change become so politicized? It requires us to tackle thorny ethical and economic dilemmas, like how the least developed nations will cope with the effects of climate change and who should help them. It highlights serious structural issues like how to reckon with entrenched carbon-based industry interests and the connected yet complex resistances to decarbonization efforts. It calls for global governmental collaboration on an unprecedented scale. Atmospheric chemist Rachel Pike comments, "It goes, of course, to the top of our sky, but it goes to the bottom of the ocean, to every corner of the globe. It's every nation, every people. It's political, it's economic, it requires debate; it's scientific, it's engineering. It's the biggest problem you could ever imagine." It's no surprise, then, that climate change prompts a range of individual psychological and collective societal responses—avoidance, fatalism, denial, paralysis and wishful thinking, to name a few.
It's also not surprising that the scientific evidence is contested, given that the indicators of climate change -- like changing precipitation patterns over decadal time scales -- may be difficult for ordinary citizens to detect, and given what's at stake once we acknowledge that those indicators are correct. Initially -- and even today, despite the fact that we've reached the gold standard for scientific certainty -- some have questioned the quantity and quality of the evidence, feeding the public's perception that the science is half-baked. In reality, by the time Hansen delivered his congressional testimony in 1988, he'd been researching the relationship between atmospheric components and temperature since the 1960s, building upon a line of scientific inquiry stretching back at least a century.
A crash course on climate science
During the previous century, French physicist Joseph Fourier (1821) and Irish physicist John Tyndall (1861) described the Earth's natural "greenhouse effect" whereby water vapor and other gases in the atmosphere regulate the planet's surface temperatures. By the end of the 1800s, Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius had made the prediction that industrialized coal-burning would intensify the natural greenhouse effect. Remarkably, when Arrhenius calculated the quantitative effects on temperature his results were relatively close to what's predicted by modern climate change models.
In the 1930s, British engineer and citizen scientist Guy Callendar demonstrated that global temperatures were rising, using data from more than 140 weather stations around the world. Callendar argued that rising CO2 levels were to blame, but his hypothesis failed to gain widespread acceptance in the scientific community. Two decades later, American researcher Gilbert Plass analyzed the infrared absorption of various gases and created the early computational models suggesting that a 3- to 4-degree rise in temperature would result from doubling the concentration of atmospheric CO2. For the scientists aware of Plass's work, Dave Keeling's findings a few years later were undoubtedly unsettling: the American geochemist provided the first unequivocal proof that atmospheric CO2 levels were increasing, based on analysis of atmospheric samples he collected at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii.
Many scientists assumed that the world's oceans would absorb the extra atmospheric CO2 that human industry was producing, until American oceanographer Roger Revelle and chemist Hans Suess demonstrated otherwise. The authors of a 1957 National Academy of Sciences climatology report quoted Revelle: "In consuming our fossil fuels at a prodigious rate, our civilization is conducting a grandiose scientific experiment."
Revelle's subsequent testimony before a Congressional committee helped put climate change on the radar of elected officials. In 1965, a presidential advisory panel warned that the greenhouse effect was a "real concern," and the U.S. government's engagement deepened when Nixon established the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in 1970. Political and scientific interest in climate change grew during the ‘70s, culminating in the First World Climate Conference sponsored by the WMO in 1979. The Second World Climate Conference a decade later paved the way for the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in 1992, where the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was launched and the groundwork laid for subsequent international climate change negotiations.
The challenge of communicating climate change
The task of translating climate research for policymakers and the general public has been hampered by multiple definitions of climate change within and outside of the scientific community. As Roger Pielke Jr. argued in his 2005 article " Misdefining climate change: Consequences for science and action ," definitions used by the UNFCCC, IPCC and others profoundly influence public opinion and the range of probable policy choices. Additionally, the conflation of "climate change," "global warming" and "the greenhouse effect" in news coverage has fueled public confusion about how to diagnose and treat the problem. For our purposes here, "climate change" is any change in climate over time due to natural variability or as a result of human activity. This is consistent with the IPCC's use of the term.
Rachel Pike's comment that it's the "biggest problem you could ever imagine" reminds us that climate change is a dense and multifaceted issue. There are facets of climate science and policy where convergent agreement dominates, while in other areas, contentious disagreement has generated worthwhile debate and discussion. The media's conflation of these diverse dimensions into one sweeping issue has contributed to confusion and created a breeding ground for manipulation from outlier viewpoints to inadvertently or deliberately skew public opinion.
It's important that we critically assess who ‘speaks for climate change' and understand their agendas. To the extent that their claims are flatly reported, or that in the name of fairness and balance speakers are frequently placed on equal footing irrespective of their expertise, individuals and organizations have become empowered to speak with authority through mass media. This skews how citizens and policy makers understand climate change issues, the stakes involved and the spectrum of possible actions to take. Cognizant of this, in 2013 the L.A. Times announced it would no longer print letters from climate change detractors. L.A. Times letters editor Paul Thornton wrote, "Simply put, I do my best to keep errors of fact off the letters page; when one does run, a correction is published. Saying "there's no sign humans have caused climate change" is not stating an opinion, it's asserting a factual inaccuracy."
About this TED Studies collection
While poorly communicated information can hamper the ability to make important decisions related to climate change causes and consequences, accurate and engaging information accessed through these TED Talks gives you power: power to understand, power to share your understanding with others, and power to take action.
Here we'll consider the environment as our planet's renewable and non-renewable natural resources, and a support system for the quantity, quality and sustainability of human activities. We'll see science as a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge, sorting through the unceasing flow of human experience. We'll explore policy as guides for decision making about human management of environment, articulating the principles, intentions, and mandates about who gets what, when and how. And we'll contemplate values as systems of conduct and broad preferences (individual to societal) concerning the morality of outcomes.
We begin with three modules that center our considerations on the climate science. First, through science journalist Lee Hotz's TED Talk, we explore the evidence that the climate is changing. Next, photographer James Balog contributes additional compelling, visible, measurable documentation of certain climate change effects. Balog's talk also highlights critical elements of the certainty/uncertainty debate that has dogged the issue. Third, through the TED Talk by climate scientist James Hansen, we explore the convergent agreement in the scientific community that humans contribute to contemporary climate change.
We continue with three modules exploring the politics of taking action through mitigation, adaptation and cross-cutting market-based, risk-reduction regulatory measures. We start with a TED Talk from former United States Vice President Al Gore, who calls for various ways to reduce our emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere (mitigation). Next, we turn to the TED Talk by environmental lawyer Vicki Arroyo, who suggests ways in which human communities can reduce their vulnerability to climate change and increase resilience (adaptation). Then we consider cross-cutting, often market-based risk reduction efforts by way of a TED Talk from journalist Naomi Klein. Her talk opens a space where we can critically evaluate climate risk reduction endeavors such as the market-based cap and trade proposals that are considered an essential tool by some, and merely a shell game by others.
We finish with two modules that focus our attention on important values and ethics questions. First, former UK Prime Minister Gordon Brown challenges us to build a stronger global society by cutting carbon emissions in a way that is beneficial and equitable to all nations. Finally we turn to sustainabily strategist Johan Rockström's TED Talk about how nine ‘planetary boundaries' (which include climate change) can usefully guide ecosystem and environmental protection for future generations.
Let's begin with a look at the scientific evidence that's being unearthed at" the South Pole; science journalist Lee Hotz takes us there via his TED Talk "Inside an Antarctic time machine."

Inside an Antarctic time machine
Relevant talks.

James Balog
Time-lapse proof of extreme ice loss.

James Hansen
Why i must speak out about climate change.

New thinking on the climate crisis

Vicki Arroyo
Let's prepare for our new climate.

Naomi Klein
Addicted to risk.

Gordon Brown
Global ethic vs. national interest.

Johan Rockström
Let the environment guide our development.
What Is Environmentally Sustainable Society Essay
What is environmentally sustainable society? What does it compose of and how does it grow economically? Find all the answers in this environmental sustainability essay example!
Introduction
- Environmentally sustainable society

Works Cited
The environment is an essential component of human life in their daily life. An environmentally sustainable society meets the needs of the individuals in society without causing the destruction of natural resources and protects it for the future generation. Environmentalists are people who advocate for an environmentally sustainable society. Environmentalists emphasize the importance of the environment and seek to influence political processes to include policies that protect natural resources. The following is a discussion on how an environmentally sustainable society can be achieved.
Environmentally Sustainable Society
An environmentally sustainable society can be achieved if the natural resources are taken care of by the present generation to mind future generations. The purpose is to ensure that there is continuity of the people in the society. The environment to sustain society can be achieved if policies that advocate for the protection of the environment are enacted.
To sustain society, the environment should be conserved, refurbished, and improved. Major concerns are environmental pollution, land, ecology, biodiversity, and ethics concerning the environment. The political environmentalist actively campaigns about conservation of the environment. The lobby and support education concerning the preservation and improvement of natural resources. They emphasize that individual behavior should be geared towards the preservation of the environment.
Environmental conservation initiatives will make society come up with schemes to protects and sustain the environment for future societies. Such initiatives will lead to renewable energy as an alternative to sources of fuel that are harmful to the environment. Alternatives to electrical energy are sort (Costa and Kahn 1).
Environmental movements are effective in forming initiatives that maintain society by sustaining the environment. The movements have fewer followers than other ideologies. The curriculum has been introduced in some of the education systems to incorporate policies that are relevant to the preservation of the environment and society. The movements emphasize human rights, health concerns, and ecology, which are necessary for the well being of every individual in society.
To achieve an environmentally sustainable society, the oppression of minority societies should be halted. The minorities have been oppressed, where industrial waste has been dumped close to their neighborhood. Other injustices have been in the form of industries polluting water and polluting air, affecting the societies living close to the industries. Other organizations have made weak infrastructure that has collapsed and injured members of the society. Others have been exposed to chemical toxins that have been carelessly handled by major institutions. To overcome the injustices and oppression of the members of society, environmental movements suggest that the implementation of policies that protect people and the environment should be fastened.
To attain an environmentally sustainable society, the progress of the society should be taken care of in relation to the environment. The needs of the society should be met to elongate their life and to enable them live a fulfilling life with health. The society needs to access safe and clean water for consumption. They also need a supply of food to sustain them. Protecting the environment will ensure that present and future generations can acquire safe water and food. Children are entitled to a safe environment. The society should reduce factors that may lead to infant mortality (McCarthy 1).
In line with Dunlap and McCright (1), environmentalists argue that human beings are responsible for the changes in environment. They also argue that the power to restore the environment is in their hands. Instead of viewing the future as a time where the inevitable will happen, the society should take action to restore the environment. Since global warming is viewed as a threat, the human society can do what the environmentalists recommend. Environmentalists recommend that people plant trees and protect natural habitats of plants and animals.
Political supporters of natural environment have introduced national parks and national forests. Government’s protection of the forest and ecology ensures that the ecosystem balance is maintained. It also shows commitment of the government to the continuity of its people. Regulations on the environment play a major role in environmentally sustainable society.
Prevention of war is essential. War affects the environment and the society. War causes destruction of the environment and infrastructure. What is more is that human being lives are lost. Changes that foster peace are necessary to enable people live productive lives and cause positive change to the environment.
Environmentalism views other form of economic system as destructive to the environment that the society it protects depends on. Economic ideologies that seek to increase productivity and revenue by utilizing industrial technology with harmful emissions and pollution to the environment are discouraged. The scientific evidence on environmental change has made more environmentalists to emphasize the need to rehabilitate natural resources. Scientific evidence points at destruction of atmosphere, different forms of pollution and health problems as evidence.
Other concerns of the environmentalist are the ability to provide food for the increasing population against the challenges of climate changes. The state has a responsibility of protecting its citizens against starvation by implementing policies and schemes that will enable production of food. Protecting the environment will benefit the entire human race on earth.
The environment is important to the human society. An environmentally sustainable society can be achieved if the society conserves and improves the natural resources. Environmentalists seek to influence policy making to conserve the environment. The major concerns of the environmentalists are the change in climate, environmental pollution, biodiversity, ecosystem, preservation of land and environmental ethics.
To sustain the society the environment should be protected for present and future generations. Environmental movements make proposals on the best ways of conserving the environment. There are initiatives to change to alternative energy sources and provide safe environment for the society. Oppression of the minority communities by exposing them to industrial waste and garbage is discouraged. Policies that enhance security and safety of water and food are adopted. Industrial emissions and chemicals that contaminate the environment are dejected. Curriculum in schools includes environmental studies which encourage environmental conservation.
The public is also given information on the environment. Evidence from scientists emphasizes the need for environmental conservation. Peace and the well being of society are encouraged. Human health is also up help if environmentally sustainable society is pursued. Planting of trees, protecting the existing ecosystem and other natural resources is the emphases that will help the society attain sustainability of the society.
Costa, Dora & Kahn, Mathew. Energy conservation “nudges” and environmentalist ideology: Evidence from a randomized residential electricity field experiment , 2010. Web.
Dunlap, Riley and McCright, Aaron. A Widening Gap: Republican and Democratic Views on Climate Change , 2008. Web.
McCarthy, John. Progress and Its Sustainability.” Sustainability of Human Progress , 2010. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 31). What Is Environmentally Sustainable Society Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/environmentally-sustainable-society/
"What Is Environmentally Sustainable Society Essay." IvyPanda , 31 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/environmentally-sustainable-society/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'What Is Environmentally Sustainable Society Essay'. 31 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "What Is Environmentally Sustainable Society Essay." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/environmentally-sustainable-society/.
1. IvyPanda . "What Is Environmentally Sustainable Society Essay." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/environmentally-sustainable-society/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "What Is Environmentally Sustainable Society Essay." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/environmentally-sustainable-society/.
- Natural Gas and Environmentalists Views
- Soil Ecology and Restoration Science
- Environmental Conditions in Tunnels Towards Environmentally Sustainable Future
- Ecology Issues: Rainforest Conservation
- Energy Use and Conservation
- “Eco-Warriors” by Rik Scarce
- Animal Liberation vs. Environmentalism
- Building a School in the Polluted Environment
- An Introduction Towards a Sustainable Future
- Ecology of Commerce: Green Taxes
- Environmental Sustainability Understanding
- Environmental Geology and Sustainability
- Global Warming as Environmental Injustice
- Sustainable vs. Unsustainable Development
- Carbon Credit and Amazon Carbon Project
Sustainability Essay: How to Write a Great Report
The art of crafting a sustainability essay is a profound endeavor that transcends boundaries. This comprehensive guide is not limited to students alone because sustainability reports may be necessary in any sphere. It extends its reach to business managers, environmental activists, policymakers, and anyone seeking to make a positive impact on the world. As the global call for sustainability grows louder, your essay can be a powerful tool to inspire change and contribute to the larger vision of a sustainable future. Let’s explore the key elements, essential tips, and real-life examples to create a compelling and influential sustainability report.

Writing an Essay about Sustainability: What to Include?
These are the core elements of any essay about sustainability:
Defining Sustainability
At the heart of every sustainability essay lies the core definition of sustainability. To create a meaningful impact, your introduction must encompass a holistic understanding of the term. Explain how sustainability involves balancing environmental, social, and economic considerations to ensure the well-being of both present and future generations. Acknowledge that sustainable practices promote harmony between humanity and the planet, fostering resilience and longevity in our interconnected ecosystem.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
When you write a sustainability report, align it with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to give it a global context. These 17 goals serve as a compass to guide nations and organizations toward a more sustainable path. If you are writing about a specific issue, demonstrate how it relates to one or more SDGs, emphasizing its relevance and impact on broader sustainable development efforts.
Research and Data
A compelling sustainability essay requires a robust foundation of research and data. Cite credible sources to support your claims and recommendations. For instance, if you are writing about renewable energy, include statistical evidence showcasing the growth of renewable energy adoption and its positive effects on reducing carbon emissions. Use case studies and real-world examples to back your arguments, making your essay both informative and persuasive.
If you struggle with researching proper data and statistics, you can resort to online essay service for help in this issue. CustomWritings is one of such writing services. It offers online help for any type of report or essay. Professional writers can help you in conducting research to find actual data about sustainability.
Stakeholder Analysis
Recognize that sustainability is a collaborative effort involving various stakeholders. Address the perspectives and interests of governments, businesses, communities, NGOs, and individuals. Analyzing diverse viewpoints allows your essay to present a comprehensive and inclusive approach to tackling sustainability challenges.
Environmental Sustainability
Dedicate a substantial portion of your essay to discussing environmental sustainability. It is the cornerstone of the broader sustainability framework. Elaborate on the pressing issues of climate change, deforestation, pollution, and biodiversity loss. Introduce innovative solutions such as sustainable agriculture, green urban planning, and circular economy practices. Provide tangible examples of how businesses have successfully integrated sustainable practices into their operations, reducing their carbon footprint and contributing to a healthier planet.
Social Sustainability
Address the social dimension of sustainability in your essay. Discuss the importance of social equity, inclusivity, and community engagement. Highlight initiatives that promote education, healthcare, and poverty alleviation. It ensures that no one is alone in the journey towards sustainability. For instance, you can showcase how microfinance programs have empowered women in rural areas, leading to better economic and social outcomes.
Economic Sustainability
Explain the integral role of economic sustainability in the sustainability essay. Emphasize the need for responsible and ethical business practices that prioritize long-term benefits over short-term gains. Discuss how the circular economy model can foster economic growth while minimizing waste generation and resource depletion. Back your arguments with success stories of companies that have embraced sustainable business practices and thrived in the market.
Main Tips to Write a Sustainability Essay
The following are the vital tips on how to write a sustainability essay properly:
- Clear and concise language. While sustainability is a multifaceted topic, use clear and concise language to convey your ideas effectively. Avoid jargon and complex terminology that might alienate readers. Instead, focus on presenting complex concepts in a manner accessible to a broader audience of your essay on sustainability.
- Engaging introduction. Begin your sustainability essay with an engaging introduction that captivates readers' attention. Draw them in with a compelling narrative, an intriguing fact, or a quote from a prominent sustainability advocate. By generating interest from the outset, you encourage readers to delve deeper into your essay.
- Structured body paragraphs. Organize your sustainability essay into well-structured body paragraphs, each dedicated to a specific theme or sub-topic. Utilize subheadings within these paragraphs to create a clear and logical flow of information. This approach allows readers to navigate through the essay with ease and focus on key aspects of sustainability.
- Incorporate visuals. Incorporate visual aids such as charts, graphs, infographics, and images to enhance the visual appeal of your sustainability essay. Visual representations of data and information make complex concepts more understandable and memorable.
- Addressing counter arguments. Anticipate potential counterarguments to your sustainability proposals and address them with well-reasoned responses. By demonstrating a thoughtful consideration of opposing viewpoints, you strengthen the validity of your essay and showcase your critical thinking skills.
- Real-life examples . Enrich your sustainability essay with real-life examples of successful sustainability initiatives from different sectors. These examples offer tangible evidence of the impact of sustainable practices and inspire readers to envision their potential in their own lives or organizations.
- The significance of sustainable development. In your sustainability essay, emphasize the broader significance of sustainable development. Discuss how the interplay between environmental, social, and economic aspects influences the achievement of a sustainable future. Address the implications of sustainability on a global scale, underscoring the collective responsibility of individuals, businesses, and governments.
- In the conclusion of your sustainability essay, reiterate the core messages and highlight the urgency of embracing sustainable practices. Encourage readers to take concrete actions, both big and small, to contribute to sustainability efforts. Inspire a sense of hope and determination, emphasizing that collective efforts can lead to a brighter, more sustainable future for generations to come.
Let’s Sum It Up!
Writing a sustainability essay is not merely an academic exercise but an opportunity to contribute actively to a cause that affects us all. By incorporating essential elements, engaging examples, and practical tips into your essay, you can amplify its impact and foster a deeper understanding of sustainability issues. Whether you are an individual, a business manager, or a policymaker, your essay holds the potential to drive transformative change and shape a more sustainable world. Let us join hands and embark on this journey of sustainability, where every word written and every action taken brings us closer to a greener, more equitable future.
Continue reading here: Students and Sustainability: Shaping an Eco-Friendly Campus
Was this article helpful?
Related Posts
- What Evergreen Plants Grow Well in Shade?
- Sea World Killer Whale Lives Up to its Name; Attacks and Kills Trainer
- How Can Future Oil Spills Be Prevented
- Top 5 Car Companies That are Helping the Environment
- Copenhagen Becomes First Scandinavian City with a Mandatory Green Roof Policy
- Toothpaste and its Impact on the Environment
Readers' Questions
How to write a sustainability statement?
Writing a sustainability statement involves three key steps: assessing your organization's environmental impact, setting goals and targets, and communicating your commitment to sustainability. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you write a sustainability statement: Assess environmental impact: Begin by evaluating the environmental impact of your organization's operations, products, and services. Consider factors such as energy use, waste generation, greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, and supply chain practices. Identify areas where you can make improvements to minimize negative effects. Set goals and targets: Based on your environmental impact assessment, set specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals and targets. These should address areas where your organization can reduce its environmental footprint or improve sustainability practices. Examples may include reducing energy consumption by a certain percentage, increasing recycling rates, or sourcing sustainable materials. Craft the statement: Once your goals and targets are established, start drafting your sustainability statement. Here's a framework to follow: a. Introduction: Begin with a concise introduction, stating your organization's name and its commitment to sustainability. b. Values and principles: Outline the key values and principles that guide your organization's sustainability efforts. This could include a commitment to conserving resources, reducing waste, promoting social responsibility, or supporting local communities. c. Goals and targets: Clearly articulate the specific goals and targets you have set for your organization. Provide details on what you aim to achieve, why these goals are important, and how you plan to measure your progress. d. Actions taken: Describe the actions your organization has already taken to address sustainability or reduce its environmental impact. Highlight any initiatives, projects, or practices currently underway that demonstrate your commitment to sustainability. e. Stakeholder engagement: Emphasize the importance of engaging with key stakeholders such as employees, customers, suppliers, and local communities to promote sustainability and gather feedback. Discuss any collaborative efforts or partnerships you have established. f. Continuous improvement: Emphasize your commitment to continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and revising your sustainability practices, as well as seeking new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. g. Conclusion: Wrap up with a strong statement summarizing your dedication to sustainability and the positive impact you aim to make. Review and finalize: After writing the statement, review it for clarity and accuracy. Engage relevant stakeholders within your organization to gather their input and make any necessary revisions. Ensure that the final statement aligns with your organization's values and long-term objectives. Communicate and share: Share your sustainability statement with both internal and external stakeholders. Publish it on your organization's website, include it in annual reports, and promote it through various communication channels to raise awareness about your commitment to sustainability. You can also consider obtaining external certifications or voluntary sustainability reporting to enhance credibility. Remember that your sustainability statement should be transparent, honest, and action-oriented, reflecting your organization's genuine commitment to sustainable practices.
12.4 Annotated Student Sample: "Healthy Diets from Sustainable Sources Can Save the Earth" by Lily Tran
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Analyze how writers use evidence in research writing.
- Analyze the ways a writer incorporates sources into research writing, while retaining their own voice.
- Explain the use of headings as organizational tools in research writing.
- Analyze how writers use evidence to address counterarguments when writing a research essay.
Introduction
In this argumentative research essay for a first-year composition class, student Lily Tran creates a solid, focused argument and supports it with researched evidence. Throughout the essay, she uses this evidence to support cause-and-effect and problem-solution reasoning, make strong appeals, and develop her ethos on the topic.
Living by Their Own Words
Food as change.
public domain text For the human race to have a sustainable future, massive changes in the way food is produced, processed, and distributed are necessary on a global scale. end public domain text
annotated text Purpose. Lily Tran refers to what she sees as the general purpose for writing this paper: the problem of current global practices in food production, processing, and distribution. By presenting the “problem,” she immediately prepares readers for her proposed solution. end annotated text
public domain text The required changes will affect nearly all aspects of life, including not only world hunger but also health and welfare, land use and habitats, water quality and availability, energy use and production, greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, economics, and even cultural and social values. These changes may not be popular, but they are imperative. The human race must turn to sustainable food systems that provide healthy diets with minimal environmental impact—and starting now. end public domain text
annotated text Thesis. Leading up to this clear, declarative thesis statement are key points on which Tran will expand later. In doing this, she presents some foundational evidence that connects the problem to the proposed solution. end annotated text
THE COMING FOOD CRISIS
public domain text The world population has been rising exponentially in modern history. From 1 billion in 1804, it doubled to approximately 2 billion by 1927, then doubled again to approximately 4 billion in 1974. By 2019, it had nearly doubled again, rising to 7.7 billion (“World Population by Year”). It has been projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050 (Berners-Lee et al.). At the same time, the average life span also has been increasing. These situations have led to severe stress on the environment, particularly in the demands for food. It has been estimated, for example, that by 2050, milk production will increase 58 percent and meat production 73 percent (Chai et al.). end public domain text
annotated text Evidence. In this first supporting paragraph, Tran uses numerical evidence from several sources. This numerical data as evidence helps establish the projection of population growth. By beginning with such evidence, Tran underscores the severity of the situation. end annotated text
public domain text Theoretically, the planet can produce enough food for everyone, but human activities have endangered this capability through unsustainable practices. Currently, agriculture produces 10–23 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions. Greenhouse gases—the most common being carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor— trap heat in the atmosphere, reradiate it, and send it back to Earth again. Heat trapped in the atmosphere is a problem because it causes unnatural global warming as well as air pollution, extreme weather conditions, and respiratory diseases. end public domain text
annotated text Audience. With her audience in mind, Tran briefly explains the problem of greenhouse gases and global warming. end annotated text
public domain text It has been estimated that global greenhouse gas emissions will increase by as much as 150 percent by 2030 (Chai et al.). Transportation also has a negative effect on the environment when foods are shipped around the world. As Joseph Poore of the University of Oxford commented, “It’s essential to be mindful about everything we consume: air-transported fruit and veg can create more greenhouse gas emissions per kilogram than poultry meat, for example” (qtd. in Gray). end public domain text
annotated text Transition. By beginning this paragraph with her own transition of ideas, Tran establishes control over the organization and development of ideas. Thus, she retains her sources as supports and does not allow them to dominate her essay. end annotated text
public domain text Current practices have affected the nutritional value of foods. Concentrated animal-feeding operations, intended to increase production, have had the side effect of decreasing nutritional content in animal protein and increasing saturated fat. One study found that an intensively raised chicken in 2017 contained only one-sixth of the amount of omega-3 fatty acid, an essential nutrient, that was in a chicken in 1970. Today the majority of calories in chicken come from fat rather than protein (World Wildlife Fund). end public domain text
annotated text Example. By focusing on an example (chicken), Tran uses specific research data to develop the nuance of the argument. end annotated text
public domain text Current policies such as government subsidies that divert food to biofuels are counterproductive to the goal of achieving adequate global nutrition. Some trade policies allow “dumping” of below-cost, subsidized foods on developing countries that should instead be enabled to protect their farmers and meet their own nutritional needs (Sierra Club). Too often, agriculture’s objectives are geared toward maximizing quantities produced per acre rather than optimizing output of critical nutritional needs and protection of the environment. end public domain text
AREAS OF CONCERN
Hunger and nutrition.
annotated text Headings and Subheadings. Throughout the essay, Tran has created headings and subheadings to help organize her argument and clarify it for readers. end annotated text
public domain text More than 820 million people around the world do not have enough to eat. At the same time, about a third of all grains and almost two-thirds of all soybeans, maize, and barley crops are fed to animals (Barnard). According to the World Health Organization, 462 million adults are underweight, 47 million children under 5 years of age are underweight for their height, 14.3 million are severely underweight for their height, and 144 million are stunted (“Malnutrition”). About 45 percent of mortality among children under 5 is linked to undernutrition. These deaths occur mainly in low- and middle-income countries where, in stark contrast, the rate of childhood obesity is rising. Globally, 1.9 billion adults and 38.3 million children are overweight or obese (“Obesity”). Undernutrition and obesity can be found in the same household, largely a result of eating energy-dense foods that are high in fat and sugars. The global impact of malnutrition, which includes both undernutrition and obesity, has lasting developmental, economic, social, and medical consequences. end public domain text
public domain text In 2019, Berners-Lee et al. published the results of their quantitative analysis of global and regional food supply. They determined that significant changes are needed on four fronts: end public domain text
Food production must be sufficient, in quantity and quality, to feed the global population without unacceptable environmental impacts. Food distribution must be sufficiently efficient so that a diverse range of foods containing adequate nutrition is available to all, again without unacceptable environmental impacts. Socio-economic conditions must be sufficiently equitable so that all consumers can access the quantity and range of foods needed for a healthy diet. Consumers need to be able to make informed and rational choices so that they consume a healthy and environmentally sustainable diet (10).
annotated text Block Quote. The writer has chosen to present important evidence as a direct quotation, using the correct format for direct quotations longer than four lines. See Section Editing Focus: Integrating Sources and Quotations for more information about block quotes. end annotated text
public domain text Among their findings, they singled out, in particular, the practice of using human-edible crops to produce meat, dairy, and fish for the human table. Currently 34 percent of human-edible crops are fed to animals, a practice that reduces calorie and protein supplies. They state in their report, “If society continues on a ‘business-as-usual’ dietary trajectory, a 119% increase in edible crops grown will be required by 2050” (1). Future food production and distribution must be transformed into systems that are nutritionally adequate, environmentally sound, and economically affordable. end public domain text
Land and Water Use
public domain text Agriculture occupies 40 percent of Earth’s ice-free land mass (Barnard). While the net area used for producing food has been fairly constant since the mid-20th century, the locations have shifted significantly. Temperate regions of North America, Europe, and Russia have lost agricultural land to other uses, while in the tropics, agricultural land has expanded, mainly as a result of clearing forests and burning biomass (Willett et al.). Seventy percent of the rainforest that has been cut down is being used to graze livestock (Münter). Agricultural use of water is of critical concern both quantitatively and qualitatively. Agriculture accounts for about 70 percent of freshwater use, making it “the world’s largest water-consuming sector” (Barnard). Meat, dairy, and egg production causes water pollution, as liquid wastes flow into rivers and to the ocean (World Wildlife Fund and Knorr Foods). According to the Hertwich et al., “the impacts related to these activities are unlikely to be reduced, but rather enhanced, in a business-as-usual scenario for the future” (13). end public domain text
annotated text Statistical Data. To develop her points related to land and water use, Tran presents specific statistical data throughout this section. Notice that she has chosen only the needed words of these key points to ensure that she controls the development of the supporting point and does not overuse borrowed source material. end annotated text
annotated text Defining Terms. Aware of her audience, Tran defines monocropping , a term that may be unfamiliar. end annotated text
public domain text Earth’s resources and ability to absorb pollution are limited, and many current agricultural practices undermine these capacities. Among these unsustainable practices are monocropping [growing a single crop year after year on the same land], concentrated animal-feeding operations, and overdependence on manufactured pesticides and fertilizers (Hamilton). Such practices deplete the soil, dramatically increase energy use, reduce pollinator populations, and lead to the collapse of resource supplies. One study found that producing one gram of beef for human consumption requires 42 times more land, 2 times more water, and 4 times more nitrogen than staple crops. It also creates 3 times more greenhouse gas emissions (Chai et al.). The EAT– Lancet Commission calls for “halting expansion of new agricultural land at the expense of natural ecosystems . . . strict protections on intact ecosystems, suspending concessions for logging in protected areas, or conversion of remaining intact ecosystems, particularly peatlands and forest areas” (Willett et al. 481). The Commission also calls for land-use zoning, regulations prohibiting land clearing, and incentives for protecting natural areas, including forests. end public domain text
annotated text Synthesis. The paragraphs above and below this comment show how Tran has synthesized content from several sources to help establish and reinforce key supports of her essay . end annotated text
Greenhouse Gas and Climate Change
public domain text Climate change is heavily affected by two factors: greenhouse gas emissions and carbon sequestration. In nature, the two remain in balance; for example, most animals exhale carbon dioxide, and most plants capture carbon dioxide. Carbon is also captured, or sequestered, by soil and water, especially oceans, in what are called “sinks.” Human activities have skewed this balance over the past two centuries. The shift in land use, which exploits land, water, and fossil energy, has caused increased greenhouse-gas emissions, which in turn accelerate climate change. end public domain text
public domain text Global food systems are threatened by climate change because farmers depend on relatively stable climate systems to plan for production and harvest. Yet food production is responsible for up to 30 percent of greenhouse gas emissions (Barnard). While soil can be a highly effective means of carbon sequestration, agricultural soils have lost much of their effectiveness from overgrazing, erosion, overuse of chemical fertilizer, and excess tilling. Hamilton reports that the world’s cultivated and grazed soils have lost 50 to 70 percent of their ability to accumulate and store carbon. As a result, “billions of tons of carbon have been released into the atmosphere.” end public domain text
annotated text Direct Quotation and Paraphrase. While Tran has paraphrased some content of this source borrowing, because of the specificity and impact of the number— “billions of tons of carbon”—she has chosen to use the author’s original words. As she has done elsewhere in the essay, she has indicated these as directly borrowed words by placing them within quotation marks. See Section 12.5 for more about paraphrasing. end annotated text
public domain text While carbon sequestration has been falling, greenhouse gas emissions have been increasing as a result of the production, transport, processing, storage, waste disposal, and other life stages of food production. Agriculture alone is responsible for fully 10 to 12 percent of global emissions, and that figure is estimated to rise by up to 150 percent of current levels by 2030 (Chai et al.). Münter reports that “more greenhouse gas emissions are produced by growing livestock for meat than all the planes, trains, ships, cars, trucks, and all forms of fossil fuel-based transportation combined” (5). Additional greenhouse gases, methane and nitrous oxide, are produced by the decomposition of organic wastes. Methane has 25 times and nitrous oxide has nearly 300 times the global warming potential of carbon dioxide (Curnow). Agricultural and food production systems must be reformed to shift agriculture from greenhouse gas source to sink. end public domain text
Social and Cultural Values
public domain text As the Sierra Club has pointed out, agriculture is inherently cultural: all systems of food production have “the capacity to generate . . . economic benefits and ecological capital” as well as “a sense of meaning and connection to natural resources.” Yet this connection is more evident in some cultures and less so in others. Wealthy countries built on a consumer culture emphasize excess consumption. One result of this attitude is that in 2014, Americans discarded the equivalent of $165 billion worth of food. Much of this waste ended up rotting in landfills, comprised the single largest component of U.S. municipal solid waste, and contributed a substantial portion of U.S. methane emissions (Sierra Club). In low- and middle-income countries, food waste tends to occur in early production stages because of poor scheduling of harvests, improper handling of produce, or lack of market access (Willett et al.). The recent “America First” philosophy has encouraged prioritizing the economic welfare of one nation to the detriment of global welfare and sustainability. end public domain text
annotated text Synthesis and Response to Claims. Here, as in subsequent sections, while still relying heavily on facts and content from borrowed sources, Tran provides her synthesized understanding of the information by responding to key points. end annotated text
public domain text In response to claims that a vegetarian diet is a necessary component of sustainable food production and consumption, Lusk and Norwood determined the importance of meat in a consumer’s diet. Their study indicated that meat is the most valuable food category to consumers, and “humans derive great pleasure from consuming beef, pork, and poultry” (120). Currently only 4 percent of Americans are vegetarians, and it would be difficult to convince consumers to change their eating habits. Purdy adds “there’s the issue of philosophy. A lot of vegans aren’t in the business of avoiding animal products for the sake of land sustainability. Many would prefer to just leave animal husbandry out of food altogether.” end public domain text
public domain text At the same time, consumers expect ready availability of the foods they desire, regardless of health implications or sustainability of sources. Unhealthy and unsustainable foods are heavily marketed. Out-of-season produce is imported year-round, increasing carbon emissions from air transportation. Highly processed and packaged convenience foods are nutritionally inferior and waste both energy and packaging materials. Serving sizes are larger than necessary, contributing to overconsumption and obesity. Snack food vending machines are ubiquitous in schools and public buildings. What is needed is a widespread attitude shift toward reducing waste, choosing local fruits and vegetables that are in season, and paying attention to how foods are grown and transported. end public domain text
annotated text Thesis Restated. Restating her thesis, Tran ends this section by advocating for a change in attitude to bring about sustainability. end annotated text
DISSENTING OPINIONS
annotated text Counterclaims . Tran uses equally strong research to present the counterargument. Presenting both sides by addressing objections is important in constructing a clear, well-reasoned argument. Writers should use as much rigor in finding research-based evidence to counter the opposition as they do to develop their argument. end annotated text
public domain text Transformation of the food production system faces resistance for a number of reasons, most of which dispute the need for plant-based diets. Historically, meat has been considered integral to athletes’ diets and thus has caused many consumers to believe meat is necessary for a healthy diet. Lynch et al. examined the impact of plant-based diets on human physical health, environmental sustainability, and exercise performance capacity. The results show “it is unlikely that plant-based diets provide advantages, but do not suffer from disadvantages, compared to omnivorous diets for strength, anaerobic, or aerobic exercise performance” (1). end public domain text
public domain text A second objection addresses the claim that land use for animal-based food production contributes to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions and is inefficient in terms of nutrient delivery. Berners-Lee et al. point out that animal nutrition from grass, pasture, and silage comes partially from land that cannot be used for other purposes, such as producing food directly edible by humans or for other ecosystem services such as biofuel production. Consequently, nutritional losses from such land use do not fully translate into losses of human-available nutrients (3). end public domain text
annotated text Paraphrase. Tran has paraphrased the information as support. Though she still cites the source, she has changed the words to her own, most likely to condense a larger amount of original text or to make it more accessible. end annotated text
public domain text While this objection may be correct, it does not address the fact that natural carbon sinks are being destroyed to increase agricultural land and, therefore, increase greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere. end public domain text
public domain text Another significant dissenting opinion is that transforming food production will place hardships on farmers and others employed in the food industry. Farmers and ranchers make a major investment in their own operations. At the same time, they support jobs in related industries, as consumers of farm machinery, customers at local businesses, and suppliers for other industries such as food processing (Schulz). Sparks reports that “livestock farmers are being unfairly ‘demonized’ by vegans and environmental advocates” and argues that while farming includes both costs and benefits, the costs receive much more attention than the benefits. end public domain text
FUTURE GENERATIONS
public domain text The EAT– Lancet Commission calls for a transformation in the global food system, implementing different core processes and feedback. This transformation will not happen unless there is “widespread, multi-sector, multilevel action to change what food is eaten, how it is produced, and its effects on the environment and health, while providing healthy diets for the global population” (Willett et al. 476). System changes will require global efforts coordinated across all levels and will require governments, the private sector, and civil society to share a common vision and goals. Scientific modeling indicates 10 billion people could indeed be fed a healthy and sustainable diet. end public domain text
annotated text Conclusion. While still using research-based sources as evidence in the concluding section, Tran finishes with her own words, restating her thesis. end annotated text
public domain text For the human race to have a sustainable future, massive changes in the way food is produced, processed, and distributed are necessary on a global scale. The required changes will affect nearly all aspects of life, including not only world hunger but also health and welfare, land use and habitats, water quality and availability, energy use and production, greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, economics, and even cultural and social values. These changes may not be popular, but they are imperative. They are also achievable. The human race must turn to sustainable food systems that provide healthy diets with minimal environmental impact, starting now. end public domain text
annotated text Sources. Note two important aspects of the sources chosen: 1) They represent a range of perspectives, and 2) They are all quite current. When exploring a contemporary topic, it is important to avoid research that is out of date. end annotated text
Works Cited
Barnard, Neal. “How Eating More Plants Can Save Lives and the Planet.” Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine , 24 Jan. 2019, www.pcrm.org/news/blog/how-eating-more-plants-can-save-lives-and-planet. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Berners-Lee, M., et al. “Current Global Food Production Is Sufficient to Meet Human Nutritional Needs in 2050 Provided There Is Radical Societal Adaptation.” Elementa: Science of the Anthropocene , vol. 6, no. 52, 2018, doi:10.1525/elementa.310. Accessed 7 Dec. 2020.
Chai, Bingli Clark, et al. “Which Diet Has the Least Environmental Impact on Our Planet? A Systematic Review of Vegan, Vegetarian and Omnivorous Diets.” Sustainability , vol. 11, no. 15, 2019, doi: underline 10.3390/su11154110 end underline . Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Curnow, Mandy. “Managing Manure to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions.” Government of Western Australia, Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development, 2 Nov. 2020, www.agric.wa.gov.au/climate-change/managing-manure-reduce-greenhouse-gas-emissions. Accessed 9 Dec. 2020.
Gray, Richard. “Why the Vegan Diet Is Not Always Green.” BBC , 13 Feb. 2020, www.bbc.com/future/article/20200211-why-the-vegan-diet-is-not-always-green. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Hamilton, Bruce. “Food and Our Climate.” Sierra Club, 2014, www.sierraclub.org/compass/2014/10/food-and-our-climate. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Hertwich. Edgar G., et al. Assessing the Environmental Impacts of Consumption and Production. United Nations Environment Programme, 2010, www.resourcepanel.org/reports/assessing-environmental-impacts-consumption-and-production.
Lusk, Jayson L., and F. Bailey Norwood. “Some Economic Benefits and Costs of Vegetarianism.” Agricultural and Resource Economics Review , vol. 38, no. 2, 2009, pp. 109-24, doi: 10.1017/S1068280500003142. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Lynch Heidi, et al. “Plant-Based Diets: Considerations for Environmental Impact, Protein Quality, and Exercise Performance.” Nutrients, vol. 10, no. 12, 2018, doi:10.3390/nu10121841. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Münter, Leilani. “Why a Plant-Based Diet Will Save the World.” Health and the Environment. Disruptive Women in Health Care & the United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2012, archive.epa.gov/womenandgirls/web/pdf/1016healththeenvironmentebook.pdf.
Purdy, Chase. “Being Vegan Isn’t as Good for Humanity as You Think.” Quartz , 4 Aug. 2016, qz.com/749443/being-vegan-isnt-as-environmentally-friendly-as-you-think/. Accessed 7 Dec. 2020.
Schulz, Lee. “Would a Sudden Loss of the Meat and Dairy Industry, and All the Ripple Effects, Destroy the Economy?” Iowa State U Department of Economics, www.econ.iastate.edu/node/691. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Sierra Club. “Agriculture and Food.” Sierra Club, 28 Feb. 2015, www.sierraclub.org/policy/agriculture/food. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Sparks, Hannah. “Veganism Won’t Save the World from Environmental Ruin, Researchers Warn.” New York Post , 29 Nov. 2019, nypost.com/2019/11/29/veganism-wont-save-the-world-from-environmental-ruin-researchers-warn/. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Willett, Walter, et al. “Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT– Lancet Commission on Healthy Diets from Sustainable Food Systems.” The Lancet, vol. 393, no. 10170, 2019. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31788-4. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
World Health Organization. “Malnutrition.” World Health Organization, 1 Apr. 2020, www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malnutrition. Accessed 8 Dec. 2020.
World Health Organization. “Obesity and Overweight.” World Health Organization, 1 Apr. 2020, www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight. Accessed 8 Dec. 2020.
World Wildlife Fund. Appetite for Destruction: Summary Report. World Wildlife Fund, 2017, www.wwf.org.uk/sites/default/files/2017-10/WWF_AppetiteForDestruction_Summary_Report_SignOff.pdf.
World Wildlife Fund and Knorr Foods. Future Fifty Foods. World Wildlife Fund, 2019, www.wwf.org.uk/sites/default/files/2019-02/Knorr_Future_50_Report_FINAL_Online.pdf.
“World Population by Year.” Worldometer , www.worldometers.info/world-population/world-population-by-year/. Accessed 8 Dec. 2020.
Discussion Questions
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/12-4-annotated-student-sample-healthy-diets-from-sustainable-sources-can-save-the-earth-by-lily-tran
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Environmental Sustainability
Essays on Environmental Sustainability
History of electric cars, incorporating population education in schools, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Futura Bar Research Paper
Global assembly line analysis, leading change: essential traits for success, media stereotypes of haiti, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Reflection Paper on Guest Speaker
Solar city case study, ethical ethics of costco, evolution of electric cars, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Lorax Discussion Questions
Essay on wind energy, swot analysis: new belgium brewing company, united parcel service airlines: a case study, balancing wind wolf: environmental benefits and wildlife impacts, summary of novella carpenter's urban farm, wind energy: a sustainable and viable source for the future, my vision for america, argumentative essay on solar energy, topics in this category.
- Wind Energy
- Alternative Energy
- Solar Energy
- Sustainability
- Fossil Fuels
- Renewable Energy
Popular Categories
- Environmental Protection
- Environment Problems
- Human Impact
- Earth & Nature

Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Book Title: Introduction to Environmental Sciences and Sustainability
Author: Emily P. Harris

Download this book
- Digital PDF
- Common Cartridge (LTI Links)
Book Description: Introduction to Environmental Sciences and Sustainability is a college-level Open Educational Resource (OER) that focuses on the most relevant environmental science issues and addresses ways to incorporate sustainable practices. This resource is targeted at environmental science students.
Book Information
Book description.
Introduction to Environmental Sciences and Sustainability is a college-level Open Educational Resource (OER) that focuses on the most relevant environmental science issues and addresses ways to incorporate sustainable practices. The text is designed for an introductory-level college science course. Topics include the fundamentals of ecology, biodiversity, pollution, climate change, food production, human population growth, and incorporating sustainable approaches in our communities, economies, and environments. This resource is targeted at environmental science students.
Students can print a PDF copy of this text as a hard copy (at the student’s expense). Electronic copies of a PDF or the ebook are available through UWF’s Library Pressbook.
Contributors: Chasidy Hobbs, M.S. and Kwame Owusu-Daaku, Ph.D
Book Source
This book is a cloned version of Environmental Biology by Matthew R. Fisher, published using Pressbooks by Open Oregon Educational Resources under a CC BY (Attribution) license. It may differ from the original.
Introduction to Environmental Sciences and Sustainability Copyright © 2023 by Emily P. Harris is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Earth Sciences, Geography, Environment, Planning
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Environmental science
Course: ap®︎/college environmental science > unit 4, introduction to sustainability.
- Intro to sustainable practices
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
Video transcript
Essay On Sustainable Development
500 words essay on sustainable development.
Sustainable development is basically an action plan which helps us to achieve sustainability in any activity which makes use of the resource. Moreover, it also demands immediate and intergenerational replication. Through essay on sustainable development, we will help you understand the concept and its advantages.
Through sustainable development, we formulate organising principles which help to sustain the limited resources essential to provide for the needs of our future generations. As a result, they will be able to lead a content life on the planet .

What is Sustainable Development?
The World Commission on Environment and Development popularized this concept in 1987. Their report defines the idea as a “development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.”
In other words, they aimed to prevent the stripping the natural world of resources which the future generations will require. As we all know that usually, one particular need drives development. Consequently, the wider future impacts are not considered.
As a result, a lot of damage happens due to this type of approach. Thus, the longer we continue to pursue unsustainable development, the more severe will the consequences be. One of the most common is climate change which is being debated widely worldwide.
In fact, climate change is already wreaking havoc on our surroundings. So, the need of the hour is sustainable development. We must ask ourselves, must we leave a scorched planet with an ailing environment for our future generations?
In order to undo the mess created by us, we must follow sustainable development. This will help us promote a more social, environmental and economical thinking. Most importantly, it is not that difficult to attain this.
We must see that world as a system which connects space, and time. Basically, it helps you understand that water pollution in South Africa will ultimately impact water quality in India. Similarly, it is the case for other things as well.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Measures to Practice Sustainable Development
There are many measures to take up for practising sustainable development. To begin with, it is important to ensure clean and hygienic living and working conditions for the people.
Next, sponsoring research on environmental issues which pertains to regions. Further, ensuring safety against known and proven industrial hazards. It is also important to find economical methods to salvage dangerous industrial wastes.
Most importantly, we must encourage afforestation . Including environmental education as part of the school and college curriculum will also help. Similarly, it is essential to socialize and humanize all environmental issues.
Further, we must encourage uses of non-conventional sources of energy, especially solar energy. Looking for substitutes for proven dangerous materials on the basis of local resources and needs will help. Likewise, we must produce environment-friendly products.
It is also essential to popularize the use of organic fertilizers and other biotechniques. Finally, the key is environmental management which must be monitored and ensure accountability.
Conclusion of Essay on Sustainable Development
To sum it up, sustainable development continuously seeks to achieve social and economic progress in ways which will not exhaust the Earth’s finite natural resources. Thus, we must all develop ways to meet these needs so that our future generations can inherit a healthier and greener planet.
FAQ on Essay on Sustainable Development
Question 1: State two measures we can take for sustainable development.
Answer 1: The first measure we can take is by finding economical methods for salvaging hazardous industrial wastes. Next, we must encourage afforestation.
Question 2: What is the aim of sustainable development?
Answer 2 : The aim of sustainable development is to maximise human well-being or quality of life without having to risk the life support system.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Sustainable Development: Samples in 250, 300 and 500 Words
- Updated on
- Nov 18, 2023

On 3rd August 2023, the Indian Government released its Net zero emissions target policy to reduce its carbon footprints. To achieve the sustainable development goals (SDG) , as specified by the UN, India is determined for its long-term low-carbon development strategy. Selfishly pursuing modernization, humans have frequently compromised with the requirements of a more sustainable environment.
As a result, the increased environmental depletion is evident with the prevalence of deforestation, pollution, greenhouse gases, climate change etc. To combat these challenges, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change launched the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) in 2019. The objective was to improve air quality in 131 cities in 24 States/UTs by engaging multiple stakeholders.
‘Development is not real until and unless it is sustainable development.’ – Ban Ki-Moon
The concept of Sustainable Development in India has even greater relevance due to the controversy surrounding the big dams and mega projects and related long-term growth. Since it is quite a frequently asked topic in school tests as well as competitive exams , we are here to help you understand what this concept means as well as the mantras to drafting a well-written essay on Sustainable Development with format and examples.
This Blog Includes:
What is sustainable development, 250-300 words essay on sustainable development, 300 words essay on sustainable development, 500 words essay on sustainable development, introduction, conclusion of sustainable development essay, importance of sustainable development, examples of sustainable development.
As the term simply explains, Sustainable Development aims to bring a balance between meeting the requirements of what the present demands while not overlooking the needs of future generations. It acknowledges nature’s requirements along with the human’s aim to work towards the development of different aspects of the world. It aims to efficiently utilise resources while also meticulously planning the accomplishment of immediate as well as long-term goals for human beings, the planet as well and future generations. In the present time, the need for Sustainable Development is not only for the survival of mankind but also for its future protection.
Looking for ideas to incorporate in your Essay on Sustainable Development? Read our blog on Energy Management – Find Your Sustainable Career Path and find out!
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 250-300 words:
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 300 + words:

Must Read: Article Writing
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 500 + words:

Essay Format
Before drafting an essay on Sustainable Development, students need to get familiarised with the format of essay writing, to know how to structure the essay on a given topic. Take a look at the following pointers which elaborate upon the format of a 300-350 word essay.
Introduction (50-60 words) In the introduction, students must introduce or provide an overview of the given topic, i.e. highlighting and adding recent instances and questions related to sustainable development. Body of Content (100-150 words) The area of the content after the introduction can be explained in detail about why sustainable development is important, its objectives and highlighting the efforts made by the government and various institutions towards it. Conclusion (30-40 words) In the essay on Sustainable Development, you must add a conclusion wrapping up the content in about 2-3 lines, either with an optimistic touch to it or just summarizing what has been talked about above.
How to write the introduction of a sustainable development essay? To begin with your essay on sustainable development, you must mention the following points:
- What is sustainable development?
- What does sustainable development focus on?
- Why is it useful for the environment?
How to write the conclusion of a sustainable development essay? To conclude your essay on sustainable development, mention why it has become the need of the hour. Wrap up all the key points you have mentioned in your essay and provide some important suggestions to implement sustainable development.
The importance of sustainable development is that it meets the needs of the present generations without compromising on the needs of the coming future generations. Sustainable development teaches us to use our resources in the correct manner. Listed below are some points which tell us the importance of sustainable development.
- Focuses on Sustainable Agricultural Methods – Sustainable development is important because it takes care of the needs of future generations and makes sure that the increasing population does not put a burden on Mother Earth. It promotes agricultural techniques such as crop rotation and effective seeding techniques.
- Manages Stabilizing the Climate – We are facing the problem of climate change due to the excessive use of fossil fuels and the killing of the natural habitat of animals. Sustainable development plays a major role in preventing climate change by developing practices that are sustainable. It promotes reducing the use of fossil fuels which release greenhouse gases that destroy the atmosphere.
- Provides Important Human Needs – Sustainable development promotes the idea of saving for future generations and making sure that resources are allocated to everybody. It is based on the principle of developing an infrastructure that is can be sustained for a long period of time.
- Sustain Biodiversity – If the process of sustainable development is followed, the home and habitat of all other living animals will not be depleted. As sustainable development focuses on preserving the ecosystem it automatically helps in sustaining and preserving biodiversity.
- Financial Stability – As sustainable development promises steady development the economies of countries can become stronger by using renewable sources of energy as compared to using fossil fuels, of which there is only a particular amount on our planet.
Mentioned below are some important examples of sustainable development. Have a look:
- Wind Energy – Wind energy is an easily available resource. It is also a free resource. It is a renewable source of energy and the energy which can be produced by harnessing the power of wind will be beneficial for everyone. Windmills can produce energy which can be used to our benefit. It can be a helpful source of reducing the cost of grid power and is a fine example of sustainable development.
- Solar Energy – Solar energy is also a source of energy which is readily available and there is no limit to it. Solar energy is being used to replace and do many things which were first being done by using non-renewable sources of energy. Solar water heaters are a good example. It is cost-effective and sustainable at the same time.
- Crop Rotation – To increase the potential of growth of gardening land, crop rotation is an ideal and sustainable way. It is rid of any chemicals and reduces the chances of disease in the soil. This form of sustainable development is beneficial to both commercial farmers and home gardeners.
- Efficient Water Fixtures – The installation of hand and head showers in our toilets which are efficient and do not waste or leak water is a method of conserving water. Water is essential for us and conserving every drop is important. Spending less time under the shower is also a way of sustainable development and conserving water.
- Sustainable Forestry – This is an amazing way of sustainable development where the timber trees that are cut by factories are replaced by another tree. A new tree is planted in place of the one which was cut down. This way, soil erosion is prevented and we have hope of having a better, greener future.
Related Articles
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015. These include: No Poverty Zero Hunger Good Health and Well-being Quality Education Gender Equality Clean Water and Sanitation Affordable and Clean Energy Decent Work and Economic Growth Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure Reduced Inequality Sustainable Cities and Communities Responsible Consumption and Production Climate Action Life Below Water Life on Land Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions Partnerships for the Goals
The SDGs are designed to address a wide range of global challenges, such as eradicating extreme poverty globally, achieving food security, focusing on promoting good health and well-being, inclusive and equitable quality education, etc.
India is ranked #111 in the Sustainable Development Goal Index 2023 with a score of 63.45.
Hence, we hope that this blog helped you understand the key features of an essay on sustainable development. If you are interested in Environmental studies and planning to pursue sustainable tourism courses , take the assistance of Leverage Edu ’s AI-based tool to browse through a plethora of programs available in this specialised field across the globe and find the best course and university combination that fits your interests, preferences and aspirations. Call us immediately at 1800 57 2000 for a free 30-minute counselling session
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
Thanks a lot for this important essay.
NICELY AND WRITTEN WITH CLARITY TO CONCEIVE THE CONCEPTS BEHIND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.
Thankyou so much!

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500 Words Essay on Environmental Sustainability Introduction to Environmental Sustainability. Environmental sustainability is a concept that has grown in prominence as the world grapples with the effects of climate change. It refers to the practice of using resources in a way that preserves the environment for future generations.
The implication of sustainability is the inherent potential for tolerance. In the context of human life, the implication of sustainability is maintaining a fair well-being on a long term basis with regard to the dimensions of environmental, social as well as economic perspectives (Bell, 2003, 115-156). The idea of stewardship in addition to ...
Olawunmi Ibraheem Cosc 110 Environmental Sustainability in the United State Professor Timothy Oladunni 4/27/17 Environmental sustainability is the rates of renewable resource harvest, pollution creation, and non-renewable resource depletion that can be continued indefinitely. If they cannot be continued indefinitely then they are not ...
Environmental sustainability is perhaps the most obvious of the three pillars, as it symbolises the importance of things like natural resources and biodiversity to support life on Earth.; Social sustainability places importance on social structures, well-being, and harmony; all factors that poverty, wars, and injustices can affect.; Economic sustainability describes the ability of an economy ...
Sustainable development is a process that creates growth and progress through the addition of physical, economic, environmental, and social components to improve quality of life without damaging the resources of the environment. Simply put, sustainable development is a way for people to use resources without the resources running out 3.
Water Science School (WSS). (2018). Pharmaceuticals in water. USGS. Web. This essay, "Environmental Sustainability on a Global Scale" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper. However, you must cite it accordingly .
Introduction to the importance of environmental sustainability. Climate change is the most urgent issue affecting the whole planet right now. Climate change-related hazards are ongoing and increasing. They pose a serious threat to the achievement of the MDGs as they have the potential to reverse years of development gains.
The greenhouse effect has been detected, and it is changing our climate now. James Hansen, June 24, 1988. The drought that crippled much of the U.S. and Canada in 1988-89 was the costliest natural disaster in U.S. history prior to Hurricane Katrina. It spawned dust storms in the Midwest and forest fires in Yellowstone National Park.
The environment is an essential component of human life in their daily life. An environmentally sustainable society meets the needs of the individuals in society without causing the destruction of natural resources and protects it for the future generation. Environmentalists are people who advocate for an environmentally sustainable society.
Engaging introduction. Begin your sustainability essay with an engaging introduction that captivates readers' attention. Draw them in with a compelling narrative, an intriguing fact, or a quote from a prominent sustainability advocate. By generating interest from the outset, you encourage readers to delve deeper into your essay. Structured body ...
Social sustainability is the ability of a society to uphold universal human rights and meet people's basic needs, such as healthcare, education, and transportation. Healthy communities ensure personal, labour, and cultural rights are respected and all people are protected from discrimination. Economic sustainability is the ability of human ...
1. Introduction. This chapter will provide the reader with a background in sustainability and its numerous definitions. It also will talk about the history of sustainability, and when that term first started being used. It goes in depth into the "pillars" of sustainability and what each of those means. Finally, it will talk about what a ...
Analyze how writers use evidence to address counterarguments when writing a research essay. Introduction. In this argumentative research essay for a first-year composition class, student Lily Tran creates a solid, focused argument and supports it with researched evidence. ... environmental sustainability, and exercise performance capacity. The ...
Environmental Sustainability in the United States ecognizing the need for more fuel-efficient and environmentally sustainable practices, a growing number of public and private sector organizations are taking the lead in making it a priority to develop and implement these initiatives in recent years. One public sector organization in the United States that is modeling the way for others is the ...
Writing an environmental sustainability essay, it's only natural to seek help online as it's a challenging matter that requires statistical data and full understanding of the environmental challenges that come along. ... Studying this sample, you will see that there is always an introduction to the topic that narrows things down by focusing ...
sustainability, the long-term viability of a community, set of social institutions, or societal practice.In general, sustainability is understood as a form of intergenerational ethics in which the environmental and economic actions taken by present persons do not diminish the opportunities of future persons to enjoy similar levels of wealth, utility, or welfare.
Introduction. Chapter 1: Introduction to Environmental Science and Sustainability. 1.1 The Earth, Humans, and the Environment. 1.2 The Process of Science. 1.3 Environment and Sustainability. 1.4 Environmental Ethics. 1.5 Environmental Justice and Indigenous Struggles. 1.6 Chapter Resources. Chapter 2: Matter, Energy, and Life.
Sustainability refers to humans living on Earth and their use of resources without depletion of the resources for future generations. Environmental indicators that can guide humans to sustainability include biological diversity, food production, average global surface temperatures and CO2 concentrations, human population, and resource depletion ...
concept of sustainable development within the international legal framework in gen-eral, and the climate change regime in particular. It argues that sustainable devel-opment should primarily be seen as a normative concept, closely linked to an idea of environmental justice that incorporates the interests not only of present humans
1. Introduction. The concept of sustainable development has become a reference for scientific research on the environment and has acquired a paradigm character for development (Alvarado-Herrera et al., 2017; Gore, 2015) since its appearance in the Brundtland Report in 1987 (WCED, 1987).Since the Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit, the concept has become hegemonic and has been incorporated in ...
The essays included in this special edition attempt to place these tensions into new and emerging contextual "workings" within and against one another—among financial/economic determinants and environmental imperatives; across science, social science, and humanities disciplinary boundaries; and in reconfiguring qualitative and quantitative research methodologies and findings, to propose ...
500 Words Essay on Sustainable Development. Sustainable development is basically an action plan which helps us to achieve sustainability in any activity which makes use of the resource. Moreover, it also demands immediate and intergenerational replication. Through essay on sustainable development, we will help you understand the concept and its ...
Essay on Sustainable Development: Samples in 250, 300 and 500 Words. On 3rd August 2023, the Indian Government released its Net zero emissions target policy to reduce its carbon footprints. To achieve the sustainable development goals (SDG), as specified by the UN, India is determined for its long-term low-carbon development strategy.