Identity Theme in There There Literary Analysis Essay Example
Characters in “There There” struggle with finding their identity and people today struggle with it too. “There There” is about different characters who are trying to figure out their true Indian identity. All these perspectives are led up to the characters coming together to honor the past traditions that they lost with the powwow. Just as the characters were starting to find their identity, they were interrupted by a shooting, which sent people screaming and running out of the stadium. This situation makes them come together and put away their differences. According to the characters in there There being an Indian today means connecting with their ancestry and culture while addressing hardships they are facing with their present day indenity.
Dene Oxendene makes videos to make room for people to talk about what being Indian means to them at the same time trying to find the missing part of himself. “There is real Passion there, and rage, and that’s part of what I’m bringing to the project because I feel that way too” (Orange, 40). He is bringing the hardships that he has faced into the project. Using that he can find out what he is in the process. Dene Oxendene is trying to discover what he thinks being Indian means to him through hearing other people’s stories about what being Indian means to them.
Orvil Red-Feather learns about being Indian by watching hours of powwow videos on YouTube because Opal will not l tell them anything because of what she faced during her childhood. “Virtually everything about being Indian he’d learned virtually from watching hours and hours of powwow footage… on YouTube.” (Orange, 121). He had to teach himself by watching hours of video on YouTube because opal prohibited Orvil from engaging with his Indian identity. “it’s important that he dress like an Indian, dance like an Indian, even if it is an act, even if he feels like fraud.” Even though Orvil feels like he does not belong, he cannot give up because he has not found that missing part of his identity. The hardship that Orvil is facing is that Opal does not want Orvil to experience the same trouble she had to deal with when she was younger, and now Orvil feels disconnected from the past and that will stop him from creating a present-day identity as an urban Indian. He tries to teach himself by watching videos about his Indian culture.
Edwin black knows so many things about his ancestor culture but, cannot relate to his own identity. "The problem with Indigenous art in general is that it's stuck in the past"(Orange, 77). Edwin uses music from the past to learn so much about identity of his ancestry/ culture but struggles to connect to his own identity as an urban Indian because the music is from his ancestors that were taken from their land and put in city, that makes it hard for Edwin to what it means to be Indian to him. Edwin knows a lot about his culture from the past, but his hardship is trying to connect the past, but trying to figure out what it means to be Indian today to him,
In conclusion, according to the characters that are in “there there” being Indian today means trying to connect with the past culture and bring it alive in the present at the same time dealing with the hardships that come with them. These are some of the characters in “there there” and this is what Indian means to them, there are so many more characters that have different meanings about being Indian, but they all relate back trying to connect with past culture to create present day identity. Their ancestor past identity has been erased because they had to move to the city away from homelands, that is way it is hard for the characters to find their true Indian identity. This information is helpful and relates because the whole book talks about identity of urban Indian and how the characters find their identity as an Indian with history.

Related Samples
- A Farewell to Arms Literary Analysis Essay Example
- Literary Analysis of 'The Things They Carried' by Tim O'Brien
- Carver Briggs Character Analysis in Goodbye Days by Jeff Zentner
- Should To Kill A Mockingbird Be Taught In Schools Essay Example
- Symbols In The Glass Castle
- How to Read Nonfiction Like a Professor by Thomas Foster Book Review
- The American Dream in The Great Gatsby (Book Analysis)
- The Effect of War on the Soldier (All Quiet on the Western Front Essay Example)
- Essay Sample on Kissing in Vietnamese by Ocean Vuong
- A Comparison Of The Holocaust In The Books Of Maus And Night
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers
There There
By tommy orange, there there essay questions.
Analyze the prologue of There There in terms of both form and content. Why might Tommy Orange have chosen to begin his novel with this type of prologue?
The choice to begin a novel with a critical essay is a bold one. However, in this case, it is necessary: Orange cannot rely on the general public's knowledge of the historical context and political analysis that the narrator provides in the prologue. The prologue effectively situates the novel's characters' trials in their historical context, showing that they are all shaped by the legacy of colonialism.
What might be the reason Tommy Orange writes from the perspective of so many different characters? What effect does this formal decision have on the experience of reading the novel, especially in Part IV?
The plethora of perspectives that shape There There acts as a formal mechanism through which Orange can push back on the stereotypes that reduce so much of the Native community to sameness. Through many different characters' voices, he shows that the community is diverse. However, the numerous character perspectives also allow Orange to develop coherent themes over the course of many different storylines and show the breadth and commonality of some of the issues that the community faces. In Part IV specifically, when the violence breaks out, the use of many different voices increases the feeling of chaos and commotion for readers, making their reading experience mirror the characters' experience at the powwow.
What is the role of the matriarchal/grandmother figure in There There ? Discuss the gender roles that appear in the novel.
There are several strong matriarchs in There There. Many of the male characters have a strong female relative whom they love and respect. For the Red Feather boys, this is Opal; for Calvin, Maggie; for Octavio, Josefina; for Tony, Maxine. These male characters all rely and depend on these women for advice, guidance, and sometimes material support as well. It is the men, not the women, who are typically the perpetrators of violence. For example, only men are involved in the plot to rob the powwow. Women, in contrast, suffer for this violence—whether as intentional victims of abusive husbands and violent partners or as accidental victims of wayward bullets.
What are some of the ways in which different characters in the novel tell their stories? What, if anything, is the novel's overall message about storytelling?
The characters of There There give voice to their stories in different ways. Some do so through cultural expression; Orvil, for example, learns traditional dance. When he dons regalia, he feels connected to his culture. Thomas, too, finds his voice when he drums and sings at the powwow. This act of expression, however, is not explicitly about connecting to his culture, but rather about feeling a void and reaching peace that he usually requires alcohol for. These are just two examples of characters finding expression as a means of empowerment. Stories, the novel seems to suggest, can provide an antidote to the pain and loss created by years of colonial displacement as well as the contemporary problems that characters face.
What does the city of Oakland represent? What is the relationship between the depiction of Oakland in the novel and the novel's depiction of Native history?
In Orange's There There, the city of Oakland represents the importance, but also the precarity, of home. The city that Orange depicts is undergoing an active process of change at the hands of young white people, who are bringing gentrification to poorer and crime-ridden neighborhoods. As Gertrude Stein said about her home in Oakland, the process of change has made it so that "there is no there there" anymore. One of the characters, Dene, draws the direct link between this process of change and the process of displacement that pushed Native people off their lands over the past several centuries. Just as Oakland is rapidly gentrifying, in indigenous America, "there is no there there" anymore.

There There Questions and Answers
The Question and Answer section for There There is a great resource to ask questions, find answers, and discuss the novel.
How does Tommy Orange’s novel There There illustrate a coming-of-age story in certain parts, and what is the significance of this for you?
I think coming of age stories are about finding one's authenticity. Throughout the novel, characters struggle with the perceived authenticity of their Native identity. For some, this manifests in physical appearance: Dene, for example, worries...
boat analogy
Several different tropes may be used throughout the book, so it's not clear which particular boat trope the novel The Oranges refers to. However, in general, the boat metaphor is often used as a metaphor for life and the journey we are on.
How do the characters in There There navigate this modern form of identity of "Urban Indian" alongside their ancestral roots?
Throughout the novel, characters struggle with the perceived authenticity of their Native identity. For some, this manifests in physical appearance: Dene, for example, worries that the Native panelist for his grant application interview won't...
Study Guide for There There
There There study guide contains a biography of Tommy Orange, literature essays, quiz questions, major themes, characters, and a full summary and analysis.
- About There There
- There There Summary
- Character List
Essays for There There
There There essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of There There by Tommy Orange.
- The Indigenous Struggle Towards Self-Realization in 'There There'
- Mimetic Characterization in There, There

There There
Tommy orange, everything you need for every book you read..
In the weeks leading up to the Big Oakland Powwow, a disparate but interconnected group of urban Native Americans living in Oakland prepare for the festivities, working through the losses and traumas they’ve suffered both in their own lifetimes and through the inheritance of an overwhelmingly painful cultural legacy of violence and racism. Among the attendees of the powwow are the lost and insecure Tony Loneman , a young man whose shame over having a face marked by fetal alcohol syndrome leads to his involvement in a scheme to rob the powwow; Octavio Gomez , a drug dealer and the mastermind behind the scheme; and Dene Oxendene , who’s hoping to honor his recently deceased uncle’s legacy by collecting the stories of other Native Americans living in Oakland for a documentary film. Also present are Opal Viola Victoria Bear Shield , her half-sister Jacquie Red Feather , and Jacquie’s culturally adrift grandchildren Orvil , Lony , and Loother , who all struggle to understand one another, and the complicated cultural tradition they’re a part of. Interwoven with these central stories are the tales of a number of other individuals who are interconnected in unlikely and amazing ways—though they are often unaware of the deep ties, both cultural and familial, which bind them to one another.
As the powwow nears, Octavio plots with Calvin Johnson , Calvin’s brother Charles , and Charles’s friend Carlos —along with Tony Loneman, who Octavio hopes will take the fall for the crime—about how to steal tens of thousands of dollars in cash prizes from the powwow. Calvin, who is on the powwow committee, provides the group with valuable inside information.
Jacquie, who attends a professional conference in Albuquerque while struggling to maintain an eleven-day sobriety streak, reconnects with Harvey , the father of the child she gave up for adoption long ago, and agrees to travel with him to Oakland to attend the powwow. Meanwhile, Dene Oxendene secures a grant to support his storytelling project, and begins collecting on film the stories of Native Americans living in Oakland. He joins the powwow committee so that he can set up a storytelling booth at the big event, and looks forward to realizing his uncle Lucas ’s dream.
Fourteen-year-old Orvil Red Feather, who has taught himself Native dance by watching YouTube videos after a lifetime of being forbidden to learn about “Indianing” by his great-aunt Opal, prepares to enter a dance competition at the powwow with the help of his brothers Loother and Lony—and also discovers, disturbingly and intriguingly, that a lump in his leg seems to be leaking spider ’s legs. Meanwhile, Edwin Black joins the powwow committee after securing an internship at the Indian Center in an attempt to temper his internet addiction, reconnect with his Native roots, and perhaps even meet his birth father, Harvey, at the powwow. The adopted-at-birth Blue , another member of the powwow committee, reflects on the abuse she suffered at the hands of her ex-husband, Paul —and how far she’s come as a Native community organizer over the years in spite of the cultural isolation which marked her privileged youth.
At the powwow, everyone arrives hoping for a chance to shine, to make some money, and to connect with far-flung or long-lost friends and family. Orvil joins a group of dancers in a Grand Entry showcase, and is reminded of the spiritual power of dance and community when one of the dancers gives a rousing speech. Thomas Frank , the recently fired alcoholic janitor at the Indian Center, is given a chance to redeem himself through music as he participates in a drumming group led by the kindly Bobby Big Medicine . Edwin meets Harvey (his birth father), and Blue recognizes his friend Jacquie as her birth mother, though she’s too shy and shell-shocked to say anything. Elsewhere, Tony Loneman dons traditional regalia and heads to the powwow on a busy BART train , feeling a sense of purpose—however misplaced—for the first time in his life.
Daniel Gonzales , Octavio’s teenage cousin, used his 3-D printer to create several plastic guns and sold them to Octavio—and now plans to watch the robbery unfold by flying his high-tech drone over the coliseum. When the robbery goes bad and Carlos attempts to steal the bounty for himself, the robbers begin exchanging fire. As the shootout grows bloodier and bloodier, several innocent powwow attendees are caught in the crossfire—Orvil and Edwin are wounded, but with the help of their friends and family make it to a nearby hospital, while Calvin, Charles, Thomas, coliseum employee Bill Davis , and Tony Loneman die in the massacre. As Tony lies on the ground dying after putting an end to the shooting by killing Charles, he feels he is at last free from the bodily prison which bound him for years. He hears birds singing overhead as his consciousness dims.

There There
81 pages • 2 hours read
A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides with detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, and more. For select classroom titles, we also provide Teaching Guides with discussion and quiz questions to prompt student engagement.
Chapter Summaries & Analyses
Character Analysis
Symbols & Motifs
Important Quotes
Essay Topics
Discussion Questions
The young men who rob the powwow do so for a variety of reasons. Using their narrative sections as a guide, explore the historical and sociocultural reasons that cause each to participate in this violent act.
Orange presents multiple examples of how people relate to their Indigenous identity . Using clear evidence from the text, examine at least two characters: one who navigates their identity in a healthy way and one who does so in an unhealthy manner.
The prologue and interlude sections offer a break in narration style from the rest of the novel. What purpose do these sections serve in the larger arc of the novel?

Don't Miss Out!
Access Study Guide Now
Featured Collections
Historical Fiction
View Collection
2.5 Writing Process: Thinking Critically about How Identity Is Constructed Through Writing
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain the importance of communication in various cultural, language, and rhetorical situations.
- Implement a variety of drafting strategies to demonstrate the connection between language and social justice.
- Apply the composition processes and tools as a means to discover and reconsider ideas.
- Participate in the collaborative and social aspects of writing processes.
- Give and act on productive feedback to works in progress.
Now it’s your turn to join this cultural conversation. As you write, keep your audience in mind as well as the principles of inclusivity and anti-racism that you have learned about. Consider how you can share your personal experiences, ideas, and beliefs in a way that is inclusive of all and shows sensitivity to the culture of your readers.
Summary of Assignment: Cultural Artifact
Choose an artifact that symbolizes something about a culture to which you belong. This might be a physical object that you have, or it may be a metaphorical object, such as Du Bois’s color line or veil, that represents something larger about your culture. Write approximately 350–700 words describing it, using sensory detail and explaining its meaning both to you personally and within your culture. To begin your thinking, view this TEDx Talk for a discussion of cultural artifacts and narrative led by artist David Bailey.
Another Lens 1. Choose a space that is important to a cultural community to which you belong. While visiting this space, conduct an hour-long observation. Respond in writing to these items: Describe the space in detail. What do you see permanently affixed in the space? What activity is going on? How is the space currently used? What is the atmosphere? How are you feeling while conducting your observation? Then, do some brief research on the space (using the Internet, the library, or campus archives), and answer these questions: What is the history of the space? When was it established, and under what circumstances? How has this space been used in the past? What is your response or reaction to this history? Then write a passage in which you highlight a unique feature of the space and your cultural relationship to it.
Another Lens 2. Considering Du Bois’s theory of double consciousness, explore the ways in which you may experience competing identities or competing cultures in your own life. What experiences have you had or witnessed where language clashed with or supported your identity or culture? What happened? How did others react? How did you react? What insight does your experience offer on this discussion of rhetoric and the power of language to define, shape, and change or give birth to identity or culture?
Quick Launch: Joining the Dialogue
You may choose to use journaling to develop your language use and voice. Journaling, or keeping a written record of your thoughts and ideas, can clarify your thoughts and emotions, help you better understand your values, and increase your creativity. The following two journaling techniques should help you get started.
Character Sketch and Captured Moment
Because your cultural artifact may be tied to a person, a character sketch might help you think about its significance. A character sketch is a brief description of a real or fictional person—in this case, likely someone you know or even yourself. In it, you describe the character’s personality, physical traits, habits, history, relationships, and ties to the cultural artifact. You may include research about the character to introduce readers to them. Use the following format if you need more guidance:
Character Sketch
- Anecdote about the character
- Most important traits
- Physical appearance
- Ties to cultural artifact
A character sketch of your grandmother might read as follows.
student sample text My first memory of Nonna materializes in the kitchen, where we are baking Swedish cookies together. She carefully shows me how to measure ingredients, stirring with her hand over mine in her deep “cookie-making” bowl. Nonna is a slight woman with a big heart full of kindness. She teaches me many skills, both in and out of the kitchen, that I still use today. Some have proven to be life lessons. She never met a stranger she didn’t like and often said it takes more effort to be unkind than kind. Because of Nonna, the Swedish cookie has become a metaphor for my life. The ingredients of one’s life make up an identity, and the combination is always delicious. end student sample text
Another journaling technique is to record a captured moment through the examination of a cultural artifact. This exercise lets you use an artifact as a means to look at an event in your life and create a written piece that captures its importance, emotion, or meaning. Select an artifact and an experience. Think about what they mean to you. What do you remember, and why? Then go deeper. Analyze the long-term meaning of it in your life. Try to recreate the artifact and then the experience in your mind, and relive the sensations you experienced in the moment.
Choose the Artifact
Begin your assignment by choosing your artifact. You may take inspiration from W. E. B. Du Bois’s image of the veil in the annotated sample in the previous section. Or, going back to the beginning of this chapter and Sequoyah ’s syllabary, you may choose to take inspiration from something linguistic, an expression or a way of talking that is associated with your culture. You may choose an artifact that, like the veil, has metaphorical significance. Or you may choose a more tangible artifact, such as a religious symbol, a traditional clothing item, or any number of objects related to your chosen culture.
Once you have chosen your artifact, do a prewriting exercise called a freewrite . In this activity, set a time limit (say, 10 minutes), and write whatever comes to mind about your object within that time. Don’t worry about organization, flow, grammar, punctuation, or whether your writing is “good”; just write. This exercise not only gets your creative juices flowing but also allows you to put pen to paper and opens your mind to what may be subconscious thoughts about the object as it relates to culture.
Next, it is time to take a more refined approach to planning your writing. Think back to The Digital World: Building on What You Already Know to Respond Critically , which addresses the different purposes for writing. To help shape your writing use a separate sheet of paper to answer the questions in Table 2.1 .
Drafting: Critical Context
In your writing, try to incorporate and respond to the current cultural climate. Context is information that helps readers understand the cultural factors that affect your ideas, actions, and thoughts. Context helps build the relationship between you as a writer and your audience, providing clarity and meaning. For example, Du Bois’s veil means very little until readers understand the deep racial divide that existed during his lifetime, including Jim Crow laws , segregation , and violent crimes committed against his fellow Black Americans.
Cultural Context
Sharing cultural context helps your readers understand elements of culture they may be unfamiliar with. Consider what background information you need to provide, especially information that is integral to readers’ understanding of the traditions, beliefs, and actions that relate to your artifact. Essentially, you will need to close the gap between your own culture and that of your readers.
Armed with your freewrite and your answers to the questions as a starting place, create your first draft. As you write, embed cultural context and explain the significance of your artifact in a way that is relatable and meaningful to your audience. Like Du Bois, try to use figurative language, such as similes or personification, in your description, and include the relevant sensory elements of the artifact: its appearance, taste, smell, sound, and feel. See Print or Textual Analysis: What You Read for definitions and examples of some figurative language, or consult this site . Consider using a graphic organizer like Figure 2.6 as a guide. Add more outer circles if needed, and be mindful of writing in a way that it is accessible and inclusive.
Remember that your first draft is just a starting point. The most important thing is to get your ideas on paper. This draft can be considered a test of sorts—one that determines what should and should not appear in the final paper.
Consider the following sensory description of Broadway in New York, written by British novelist Charles Dickens (1812–1870) in his book American Notes for General Circulation (1842). What does Dickens, as a British observer, note about this street in America? How does he use language to convey what he sees, hears, and smells? In what ways does he use language to convey a British viewpoint?
public domain text Warm weather! The sun strikes upon our heads at this open window, as though its rays were concentrated through a burning-glass; but the day is in its zenith, and the season an unusual one. Was there ever such a sunny street as this Broadway! The pavement stones are polished with the tread of feet until they shine again; the red bricks of the houses might be yet in the dry, hot kilns; and the roofs of those omnibuses look as though, if water were poured on them, they would hiss and smoke, and smell like half-quenched fires. No stint of omnibuses here! Half-a-dozen have gone by within as many minutes. Plenty of hackney cabs and coaches too; gigs, phaetons, large-wheeled tilburies, and private carriages—rather of a clumsy make, and not very different from the public vehicles, but built for the heavy roads beyond the city pavement. . . . [C]oachmen . . . in straw hats, black hats, white hats, glazed caps, fur caps; in coats of drab, black, brown, green, blue, nankeen, striped jean and linen; and there, in that one instance (look while it passes, or it will be too late), in suits of livery. Some southern republican that, who puts his blacks in uniform, and swells with Sultan pomp and power. Yonder, where that phaeton with the well-clipped pair of grays has stopped—standing at their heads now—is a Yorkshire groom, who has not been very long in these parts, and looks sorrowfully round for a companion pair of top-boots, which he may traverse the city half a year without meeting. Heaven save the ladies, how they dress! We have seen more colours in these ten minutes, than we should have seen elsewhere, in as many days. What various parasols! what rainbow silks and satins! what pinking of thin stockings, and pinching of thin shoes, and fluttering of ribbons and silk tassels, and display of rich cloaks with gaudy hoods and linings! The young gentlemen are fond, you see, of turning down their shirt-collars and cultivating their whiskers, especially under the chin; but they cannot approach the ladies in their dress or bearing, being, to say the truth, humanity of quite another sort. Byrons of the desk and counter, pass on, and let us see what kind of men those are behind ye: those two labourers in holiday clothes, of whom one carries in his hand a crumpled scrap of paper from which he tries to spell out a hard name, while the other looks about for it on all the doors and windows. end public domain text
Now, how might Dickens go on to provide context and make connections between British and American cultures so that readers understand both more keenly? Although American Notes is generally critical of the United States, this description creates a positive mood, as if Dickens recognizes something of home during his visit to Broadway—a cultural artifact. This recognition suggests that moments of unexpected joy can create connections between cultures.
Peer Review:
One of the most helpful parts of the writing process can be soliciting input from a peer reviewer. This input will be particularly helpful for this assignment if the peer reviewer is not a member of the culture you are writing about. An outsider’s view will help you determine whether you have included appropriate cultural context. Peer reviewers can use the following sentence starters to provide feedback.
- One piece of your writing I found meaningful was ________.
- Something new I learned about your culture is ________; you explained this well by ________.
- Something I was confused by was ________; I don’t understand this because ________.
- A major point that I think needs more detail or explanation is ________.
- In my opinion, the purpose of your paper is ________.
- To me, it seems that your audience is ________.
- I would describe the voice of your piece as ________.
- I think you could better build cultural context by ________.
Writing is a recursive process; you will push forward, step back, and repeat steps multiple times as your ideas develop and change. As you reread, you may want to add, delete, reorder, or otherwise change your draft. This response is natural. You may need to return to the brainstorming process to mine for new ideas or organizational principles.
As you reread and prepare for revisions, focus on the voice you have used. If a friend were to read your draft, could they “hear” you in it? If not, work on revising to create a more natural cadence and tone. Another area of focus should be to explain cultural context and build cultural bridges. Use your peer reviewer’s feedback to develop a piece that will be meaningful to your audience.
While describing your artifact is likely a deeply personal endeavor, an important part of writing is to consider your audience. Composition offers a unique opportunity to build and share cultural understanding. One way to achieve this goal is by using anti-racist and inclusive language. Try to view your composition from outside of your own experience.
- Is any language or are any ideas harmful or offensive to other cultures?
- Are you using the language of preference for a specified group?
- Can people of various abilities read and understand your writing?
One overarching strategy you can use for anti-racist revision is to constantly question commonly used words and phrases. For example, the word Eskimo is a European term used to describe people living in the Arctic without regard for differentiation. The term was later used to describe a popular frozen treat known as an Eskimo pie . Today, the term is considered offensive to Inuit communities—Indigenous people living in Alaska, Canada, and Greenland. You can also make yourself aware of the evolving preferences for language use. For example, the term Negro gave way to African American , which is now giving way to the term Black . Finally, consider the use of the word see , for example, to mean “to understand”: Do you see what I mean? Is the use of see in this way inclusive of a visually impaired person who may be reading your text? To start, determine one or two places to include anti-racist or inclusive language or ideas in your writing, and build those into your piece.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/2-5-writing-process-thinking-critically-about-how-identity-is-constructed-through-writing
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- TUTORING & TEST PREP
- TALK TO AN ADVISOR
Fostering Inclusivity in College Counseling
Recent posts, subscribe here, more expert advice, let's get existential: how to write a college essay about identity.

When you’re a teenager, you’re probably too busy to sit down and think about your own identity. No one exactly assigns you “introspection time” as homework (though, if you’re my student, this has very likely happened). So when you start working on your college essays, it might be the first time you truly start thinking about how you can express who you are in a way that will help a group of strangers understand something about you. Let’s be honest—it feels like a lot of pressure to sum up your identity in 250 words or less. But we’re here to help.
There are many different types of application essays you’ll need to write, as my colleague Annie so perfectly laid out here . But we’re going to talk about one type in particular: the essays about identity and diversity. These are powerful college essays that give admissions officers an opportunity to glimpse into your daily life and understand your unique experiences. For some students, though, these essays can be daunting to think about and write.
Ever wonder why colleges are asking these questions? Well, the simple answer is that they want to get to know you more. Aside from your academic interests, your activities, and your accomplishments in the classroom, there really isn’t that much space to talk about things like your ethnic background, religion, gender identity, or local community. And these are things colleges want to know about you, too!
How Do You Write a Good Identity and Diversity Essay?
Before you start writing, let’s define a few terms you might run into while drafting your college essays about identity and diversity.
Who are you? I know what you’re thinking—it’s way too early in the morning to get this existential. I hear you. But let’s break this down. Identity is made up of many qualities: personality, culture, ethnic or racial background, sexual orientation, gender, physical ability, and linguistic background, among others. Maybe you identify really strongly with the religion on Mom’s side of the family, but not Dad’s. Maybe you speak a language not typical of folks from your culture. Maybe you have recently come into your gender identity and finally feel like yourself. Why is that identity important to the way you define who you are? Think of it like this: If you’ve met someone new, and your goal is to help them get to know you in the shortest amount of time possible, how would you be able to accomplish this? What’s your tagline? That’s how you’ll want to tackle this type of college essay.
Diversity
One individual person can’t be diverse. But when a college is referring to diversity, they’re usually looking to their student body and asking how you, as an individual with your own identity, can add to their diversity. What experiences have you had in your life that might help you make the student body more diverse? Have you dealt with dyslexia and come to terms with how best to learn, keeping your abilities in mind? If so, how can you contribute to other students who might learn differently? Did you grow up as the oldest of 10 siblings and have to take care of them on a daily basis? What kind of responsibilities did you have and how did that influence you? These don’t need to be visible qualities. The goal of the diversity college essay is to understand how these identifying factors can help you contribute to a school in a way they haven’t seen before.
Let’s define community. You may associate it with the city or neighborhood you live in. But a community doesn’t have to be geographical. It doesn’t even have to be formal. Community can come from that sense of connection you have with like-minded people. It can be built with people you’ve shared experiences with. So, when we think of community in this sense, we could be thinking about the community that exists within your apartment complex. We could be thinking about the youth group at your mosque. We could be thinking about your little group of artists within your science and tech magnet school. Think about what communities you are a part of, and be prepared to talk about your place within them.
You might think that these questions are only being asked by small liberal arts schools—but that’s not true. Bigger schools and colleges also want to get to know all of the thousands of students they’re bringing to campus as part of their class.
.png?width=600&height=200&name=Blog%20CTAs%20(8).png)
Big Name Colleges that Care About Diversity
To give you a glimpse of the variety, here are a few examples of college essays where these identity and diversity may come into play:
University of Michigan
“Everyone belongs to many different communities and/or groups defined by (among other things) shared geography, religion, ethnicity, income, cuisine, interest, race, ideology, or intellectual heritage. Choose one of the communities to which you belong, and describe that community and your place within it.”
University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill
“Expand on an aspect of your identity (for example, your religion, culture, race, sexual or gender identity, affinity group, etc.). How has this aspect of your identity shaped your life experiences thus far?”
Pomona College
“Tell us about an experience when you dealt with disagreement or conflict around different perspectives within a community.”
Sarah Lawrence College
“Sarah Lawrence College's community places strong value in inclusion and diversity. In 250-500 words, tell us about what you value in a community and how your perspective, lived experiences, or beliefs might contribute to your College community.”
Remember what these colleges are trying to understand: who you are and what has influenced you to become the person you are today (identity), where you come from (community), and how you might be able to add to the diversity of their college campus. Once you really get to the core and understand the intent of these types of college essays, you’ll absolutely be able to write in an earnest and genuine way. We say this frequently at Collegewise, but it’s worth repeating here, especially when it comes to essays about identity and diversity. Just be yourself.
About Us: With more than twenty years of experience, Collegewise counselors and tutors are at the forefront of the ever-evolving admissions landscape. Our work has always centered on you: the student. And just like we’ve always done, we look for ways for you to be your best self - whether it’s in the classroom, in your applications or in the right-fit college environment. Our range of tools include counseling , test prep , academic tutoring , and essay management, all with the support of our proprietary platform , leading to a 4x higher than average admissions rates.
Recommended Articles

College applications without essays: do they exist?

5 College Essay Examples & What to Avoid

How to Write a College Transfer Essay
Subscribe to email updates.
- Tutoring & Test Prep
- Our Counselors
© 2024 Collegewise. All Rights Reserved. Privacy

Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, how do i write a college essay about my identity.
My identity has played a big role in my life, and I want to write about it in my college essay. How can I approach this topic in a way that showcases who I am without sounding cliché or overly dramatic? Thanks for any suggestions!
Hello! I'm glad to see that you're considering writing about your identity, as it's an important part of who you are. To avoid sounding cliché or overly dramatic, there are a few tips I'd like to share with you.
First, focus on specific experiences or moments that have shaped your identity. Instead of making general statements, think about the events in your life that have had a significant impact on you and what you learned from them. This will help you tell a unique story that only you can tell.
Second, don't be afraid to be vulnerable. Sharing your personal thoughts and feelings can make your essay more engaging and relatable. For example, my child wrote about their experience as an immigrant, discussing the challenges they faced in adapting to a new culture and how it shaped their perspective on life.
Third, use vivid language and descriptive details to paint a picture for your reader. This will make your essay more memorable and allow your reader to connect with your story on a deeper level. For example, instead of just saying 'I felt out of place,' describe the physical and emotional sensations you experienced in that moment.
Finally, make sure to tie your identity back to your goals, values, or aspirations. Show how your identity has influenced your choices and what you hope to accomplish in the future. This will give your essay a sense of purpose and demonstrate your growth as an individual.
I hope these tips help you craft a compelling essay that showcases your unique identity. Best of luck with your college applications!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
How to Write a Cultural Identity Essay With Tips and Examples
11 December 2023
last updated
Writing a cultural identity essay is an exciting academic exercise that allows students to develop and utilize critical thinking, reflective, and analytical skills. Unlike a standard essay, this type of paper requires learners to use first-person language throughout. In essence, a cultural identity essay is about writers and what makes them identify with a particular cultural orientation. When writing a cultural identity essay, authors should choose a specific identity and focus on it throughout their texts. Moreover, they should reflect and brainstorm, use the “show, not tell” method, utilize transitions to create a natural flow, and proofread their papers to eliminate mistakes and errors. Hence, students need to learn how to write a cultural identity essay to provide high-quality papers to their readers.
Definition of a Cultural Identity Essay
Students undertake different writing exercises in the learning environment to develop their critical thinking, reflective, and analytical skills. Basically, one of these exercises is academic writing , and among different types of essays that students write is a cultural identity essay. In this case, it is a type of essay where authors write about their culture, which entails exploring and explaining the significance of their cultural identity. Moreover, there are numerous topics that instructors may require students to write about in a cultural identity essay. For example, some of these essay topics fall under different disciplines, such as religion, socio-economic status, family, education, ethnicity, and business. In essence, the defining features of a cultural identity essay are what aspects make authors know that they are writing in this type of essay. In turn, these features include language, nationality, gender, history, upbringing, and religion, among many others.

Differences Between a Cultural Identity Essay and Other Papers
Generally, a cultural identity essay is similar to a standard essay regarding an essay structure and an essay outline . However, the point of difference is the topic. While standard essays, such as argumentative, persuasive, and informative essays, require learners to use third-person language, such a paper requires them to use first-person language. In this case, when writing a cultural identity essay, authors should use the word “I” throughout to show the audience that they are writing from their perspective. Indeed, this aspect is the primary objective of a cultural identity essay – to give the writer’s perspective concerning their culture. Besides, another point of difference between a cultural identity essay and other papers is that the former does not require writers to utilize external sources but to write from a personal viewpoint.
List of Possible Examples of Cultural Identity Essay Topics
1. cultural identity and socialization in a learning environment.
Here, a cultural identity essay prompt may require students to discuss the significance of culture in education, focusing on cultural identity and socialization. As such, this topic requires writers to reflect on how culture influences behavior in a learning environment.
2. The Impact of Culture Change on Family
Here, this prompt may require students to explore and discuss how culture impacts a family unit. Moreover, the theme is a family, and the students’ mission would be to explain how culture in all its dynamics affects families in diverse settings.
3. The Role of Language in Building a Cultural Identity
Here, instructions may require students to explore and explain the significance of language in cultural identity. Hence, writers should focus on explaining the place of culture in the sociology discipline, focusing on the connection between language and cultural identity.
4. The Significance of Culture in a Globalized Economy
Here, a cultural identity essay topic may require students to explore and discuss how culture affects individuals and businesses in today’s connected world. Also, the students’ task would be to explain how culture, in all its dynamics, such as language, is essential in business for individuals and enterprises.
5. How Culture Influences Relations in the Workplace
Here, an essay prompt may require students to explore and explain how culture, in all its dynamics, affects or influences social relations at the workplace. In turn, the task of writers, for example, would be to focus on how Human Resource (HR) departments can use culture to enrich workplace relations.
6. The Place of Culture in Individuals’ Self-Concept
Here, an analysis of a theme may require students to reflect on how their cultural orientation has affected their self-concept. Moreover, the student’s task would be to discuss how culture and its dynamics enable individuals to build a strong or weak understanding of themselves.
7. The Importance of Cultural Orientation in a Multicultural Environment
Here, assignment instructions may require students to explore and discuss how their cultural orientation enables them to operate in a culturally diverse environment, such as a school or workplace. In this case, the student’s task would be to explain how cultural characteristics, such as language and religion, facilitate or hamper social competency in a multicultural setting.
8. How Global Conflicts Disturb Cultural Identity for Refugees
Here, this example of a cultural identity topic may require students to explore and explain how conflicts in today’s world, such as civil unrest, affect the cultural identity of those who flee to foreign countries. Also, the student’s task would be to explain how one’s culture is affected in a new environment with totally different cultural dynamics.
9. The Challenges of Acculturation
Here, a cultural identity essay prompt may require students to explore and explain the challenges that individuals face in identifying with the dominant culture. In particular, the student’s task would be to explain the significance of the dominant culture and what those from other cultures that try to identify with it must confront.
10. Host Country Culture and Multinational Enterprises
Here, this prompt sample may require students to explore and explain how a host country’s culture affects expatriates working for multinational corporations. Besides, the students’ task would be to show how one’s culture defines their behaviors and how that can be affected in a new environment with new cultural characteristics.
11. Compare and Contrast Native Culture and Dominant Culture in the United States
Here, such instructions require students to explain specific areas of similarity and difference between the Native culture and the dominant culture. In turn, the students’ task would be to define the Native culture and the dominant culture and help the audience to understand whether they mean the same thing. Hence, whether they do or do not, students should elaborate.
12. The Objective of Acculturation
Here, this example of a cultural identity essay topic requires students to explore and explain why people prefer to identify with the dominant culture. Moreover, the students’ task would be to note the advantages of the dominant culture over others and the opportunities that one may access to identify with this dominant culture.
13. The Challenges That the LGBTQ Community Faces in the Modern World
Here, essay prompt instructions require students to explore and discuss the challenges that lesbians, gays, bisexuals, and transgender people face in their normal day-to-day activities. In this case, the students’ task would be to explain the uniqueness of the LGBTQ community and how stereotyping makes their lives miserable in an environment where people are intolerant of different personalities and viewpoints.
14. Dangers of Cultural Intolerance in the Health Care System
Here, instructions may require students to explore and discuss how nurses that are intolerant to cultural differences may jeopardize patients’ lives.
15. Advantages and Disadvantages of Acculturation
Here, a cultural identity essay prompt requires students to discuss the pros and cons of identifying with the dominant culture.
How Students Know if They Write a Cultural Identity Essay
The defining features of a cultural identity essay give students the indication that they need to write this kind of essay. Basically, when learners read instructions regarding their essay topics they need to write about, they should identify one or several defining elements. In turn, these elements include language, nationality, religion, ethnicity, and gender.
Structure of a Cultural Identity Essay
As stated previously, the primary point of similarity between a cultural identity essay and standard papers is an essay structure and an essay outline. Basically, this structure and outline comprise of three main sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. Like in all other essays, writing a cultural identity essay requires students to address specific issues, which are, in essence, the defining characteristics of the essay’s structure and outline.
I. Introduction and Its Defining Characteristics
The introduction is the first paragraph of a cultural identity essay. Here, students introduce themselves to the audience, giving a brief background of their cultural identity. Moreover, rules of academic writing dictate that this part should not exceed 10 percent of the entire paper. In this case, writers should be brief and concise. Then, the most prominent component of this section is a thesis, a statement that appears at the end of an introduction paragraph and whose objective is to indicate the writer’s mission. In summary, the introduction part’s defining features are the writer’s background and thesis statement . In turn, the former gives a hint about a writer, and the latter provides the audience with insight into the writer’s objective in writing a cultural identity essay.
The body of a cultural identity essay is the most significant section of a paper and takes the largest part. Generally, writers use several paragraphs to advance different arguments to explain specific concepts. In a cultural identity essay, writers can use different paragraphs to explain important aspects of their cultural identity. Nonetheless, what determines the number of paragraphs and the content of each is a paper topic. Also, the most prominent defining features of a cultural identity essay’s body are paragraphs, with each advancing a unique concept about the writer’s cultural identity. In turn, paragraphs are where writers provide real-life experiences and other personal anecdotes that help the audience to develop a deeper understanding of authors from a cultural perspective.
III. Conclusion
The conclusion part is the last section of a cultural identity essay. In particular, writers restate a thesis statement and summarize the main points from body paragraphs. Moreover, authors provide concluding remarks about a topic, which is mostly an objective personal opinion. In summary, the conclusion part’s defining features are a restatement of a thesis, a summary of the main points, and the writer’s final thoughts about a topic.
Outline Template for a Cultural Identity Essay
I. Introduction
A. Hook statement/sentence. B. Background information. C. A thesis statement that covers the main ideas from 1 to X in one sentence.
II. Body Paragraphs
A. Idea 1 B. Idea 2 … X. Idea X
A. Restating a thesis statement. B. Summary of the main points from A to X. C. Final thoughts.
An Example of a Cultural Identity Essay
Topic: Identifying as a Naturalist
I. Introduction Sample in a Cultural Identity Essay
The period of birth marks the beginning of one’s identity, with culture playing a significant role. However, from the stage of adolescence going forward, individuals begin to recognize and understand their cultural makeup. In my case, I have come to discover my love for nature, an aspect that I believe has made me a naturalist both in belief and action.
II. Examples of Body Paragraphs in a Cultural Identity Essay
A. idea 1: parents.
Parents play a critical role in shaping the cultural and personal identity of their children. In my case, it is my mother who has instilled in me a love for nature. Although I may not say exactly when this love started, I can only reason that since it was ingrained in me since childhood, it has developed gradually.
B. Idea 2: Naturalism
Today, naturalism defines my interactions with people and the environment. In short, I can say it shapes my worldview. As a lover of nature herself, my mother had this habit of taking me outdoors when I was a toddler. I have seen family photographs of my mother walking through parks and forests holding my hand. What is noticeable in these pictures besides my mother and me is the tree cover that gives the setting such a lovely sight. Moreover, I can now understand why I seem more conversant with the names and species of flowers, trees, and birds than my siblings- my mother was the influence. In turn, my siblings and friends make a joke that I have developed a strong love for nature to the point of identifying myself with the environment. Hence, the basis for this argument is my love for the green color, where even my clothes and toys are mostly green.
III. Conclusion Sample of a Cultural Identity Essay
Naturally, human beings behave in line with their cultural background and orientation. Basically, this behavior is what determines or reflects their cultural identity. In turn, my intense love for nature underscores my naturalist identity. While I may not tell the stage in life when I assumed this identity, I know my mother has played a significant role in shaping it, and this is since childhood.
Summing Up on How to Write a Good Cultural Identity Essay
Like any standard paper, writing a cultural identity essay allows students to build essential skills, such as critical thinking, reflective, and analytical skills. In this case, the essence of a paper is to provide the writer’s cultural identity, background, or orientation. Therefore, in order to learn how to write a good cultural identity essay, students should master the following tips:
- Decide where to focus. Culture is a broad topic, and deciding what to focus on is essential in producing a cultural identity essay. For example, one may have several cultural identities, and addressing all may lead to inconclusive explanations.
- Reflect and brainstorm. Given the close link between one’s cultural identity and personal experiences, learners need to reflect on experiences that would provide the audience with an accurate picture of their cultural identity.
- Adopt the “Show, not tell” approach by providing vivid details about one’s experiences. Using personal anecdotes may be effective in accomplishing this objective.
- Use transitions , such as “therefore,” “thus,” ” additionally,” and “furthermore,” to enhance a natural and logical flow throughout the essay.
- Stay personal by using first-person language to describe one’s background and experiences.
- Proofread a cultural identity essay to eliminate spelling and grammatical mistakes and other notable errors, such as an inconsistent life storyline.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles
How to cite a dsm-5 in apa 7 and 6: guidelines with examples, how to cite an encyclopedia in mla 9: the main rules with examples.

Photo by Trent Parke/Magnum
You are a network
You cannot be reduced to a body, a mind or a particular social role. an emerging theory of selfhood gets this complexity.
by Kathleen Wallace + BIO
Who am I? We all ask ourselves this question, and many like it. Is my identity determined by my DNA or am I product of how I’m raised? Can I change, and if so, how much? Is my identity just one thing, or can I have more than one? Since its beginning, philosophy has grappled with these questions, which are important to how we make choices and how we interact with the world around us. Socrates thought that self-understanding was essential to knowing how to live, and how to live well with oneself and with others. Self-determination depends on self-knowledge, on knowledge of others and of the world around you. Even forms of government are grounded in how we understand ourselves and human nature. So the question ‘Who am I?’ has far-reaching implications.
Many philosophers, at least in the West, have sought to identify the invariable or essential conditions of being a self. A widely taken approach is what’s known as a psychological continuity view of the self, where the self is a consciousness with self-awareness and personal memories. Sometimes these approaches frame the self as a combination of mind and body, as René Descartes did, or as primarily or solely consciousness. John Locke’s prince/pauper thought experiment, wherein a prince’s consciousness and all his memories are transferred into the body of a cobbler, is an illustration of the idea that personhood goes with consciousness. Philosophers have devised numerous subsequent thought experiments – involving personality transfers, split brains and teleporters – to explore the psychological approach. Contemporary philosophers in the ‘animalist’ camp are critical of the psychological approach, and argue that selves are essentially human biological organisms. ( Aristotle might also be closer to this approach than to the purely psychological.) Both psychological and animalist approaches are ‘container’ frameworks, positing the body as a container of psychological functions or the bounded location of bodily functions.
All these approaches reflect philosophers’ concern to focus on what the distinguishing or definitional characteristic of a self is, the thing that will pick out a self and nothing else, and that will identify selves as selves, regardless of their particular differences. On the psychological view, a self is a personal consciousness. On the animalist view, a self is a human organism or animal. This has tended to lead to a somewhat one-dimensional and simplified view of what a self is, leaving out social, cultural and interpersonal traits that are also distinctive of selves and are often what people would regard as central to their self-identity. Just as selves have different personal memories and self-awareness, they can have different social and interpersonal relations, cultural backgrounds and personalities. The latter are variable in their specificity, but are just as important to being a self as biology, memory and self-awareness.
Recognising the influence of these factors, some philosophers have pushed against such reductive approaches and argued for a framework that recognises the complexity and multidimensionality of persons. The network self view emerges from this trend. It began in the later 20th century and has continued in the 21st, when philosophers started to move toward a broader understanding of selves. Some philosophers propose narrative and anthropological views of selves. Communitarian and feminist philosophers argue for relational views that recognise the social embeddedness, relatedness and intersectionality of selves. According to relational views, social relations and identities are fundamental to understanding who persons are.
Social identities are traits of selves in virtue of membership in communities (local, professional, ethnic, religious, political), or in virtue of social categories (such as race, gender, class, political affiliation) or interpersonal relations (such as being a spouse, sibling, parent, friend, neighbour). These views imply that it’s not only embodiment and not only memory or consciousness of social relations but the relations themselves that also matter to who the self is. What philosophers call ‘4E views’ of cognition – for embodied, embedded, enactive and extended cognition – are also a move in the direction of a more relational, less ‘container’, view of the self. Relational views signal a paradigm shift from a reductive approach to one that seeks to recognise the complexity of the self. The network self view further develops this line of thought and says that the self is relational through and through, consisting not only of social but also physical, genetic, psychological, emotional and biological relations that together form a network self. The self also changes over time, acquiring and losing traits in virtue of new social locations and relations, even as it continues as that one self.
H ow do you self-identify? You probably have many aspects to yourself and would resist being reduced to or stereotyped as any one of them. But you might still identify yourself in terms of your heritage, ethnicity, race, religion: identities that are often prominent in identity politics. You might identify yourself in terms of other social and personal relationships and characteristics – ‘I’m Mary’s sister.’ ‘I’m a music-lover.’ ‘I’m Emily’s thesis advisor.’ ‘I’m a Chicagoan.’ Or you might identify personality characteristics: ‘I’m an extrovert’; or commitments: ‘I care about the environment.’ ‘I’m honest.’ You might identify yourself comparatively: ‘I’m the tallest person in my family’; or in terms of one’s political beliefs or affiliations: ‘I’m an independent’; or temporally: ‘I’m the person who lived down the hall from you in college,’ or ‘I’m getting married next year.’ Some of these are more important than others, some are fleeting. The point is that who you are is more complex than any one of your identities. Thinking of the self as a network is a way to conceptualise this complexity and fluidity.
Let’s take a concrete example. Consider Lindsey: she is spouse, mother, novelist, English speaker, Irish Catholic, feminist, professor of philosophy, automobile driver, psychobiological organism, introverted, fearful of heights, left-handed, carrier of Huntington’s disease (HD), resident of New York City. This is not an exhaustive set, just a selection of traits or identities. Traits are related to one another to form a network of traits. Lindsey is an inclusive network, a plurality of traits related to one another. The overall character – the integrity – of a self is constituted by the unique interrelatedness of its particular relational traits, psychobiological, social, political, cultural, linguistic and physical.
Figure 1 below is based on an approach to modelling ecological networks; the nodes represent traits, and the lines are relations between traits (without specifying the kind of relation).
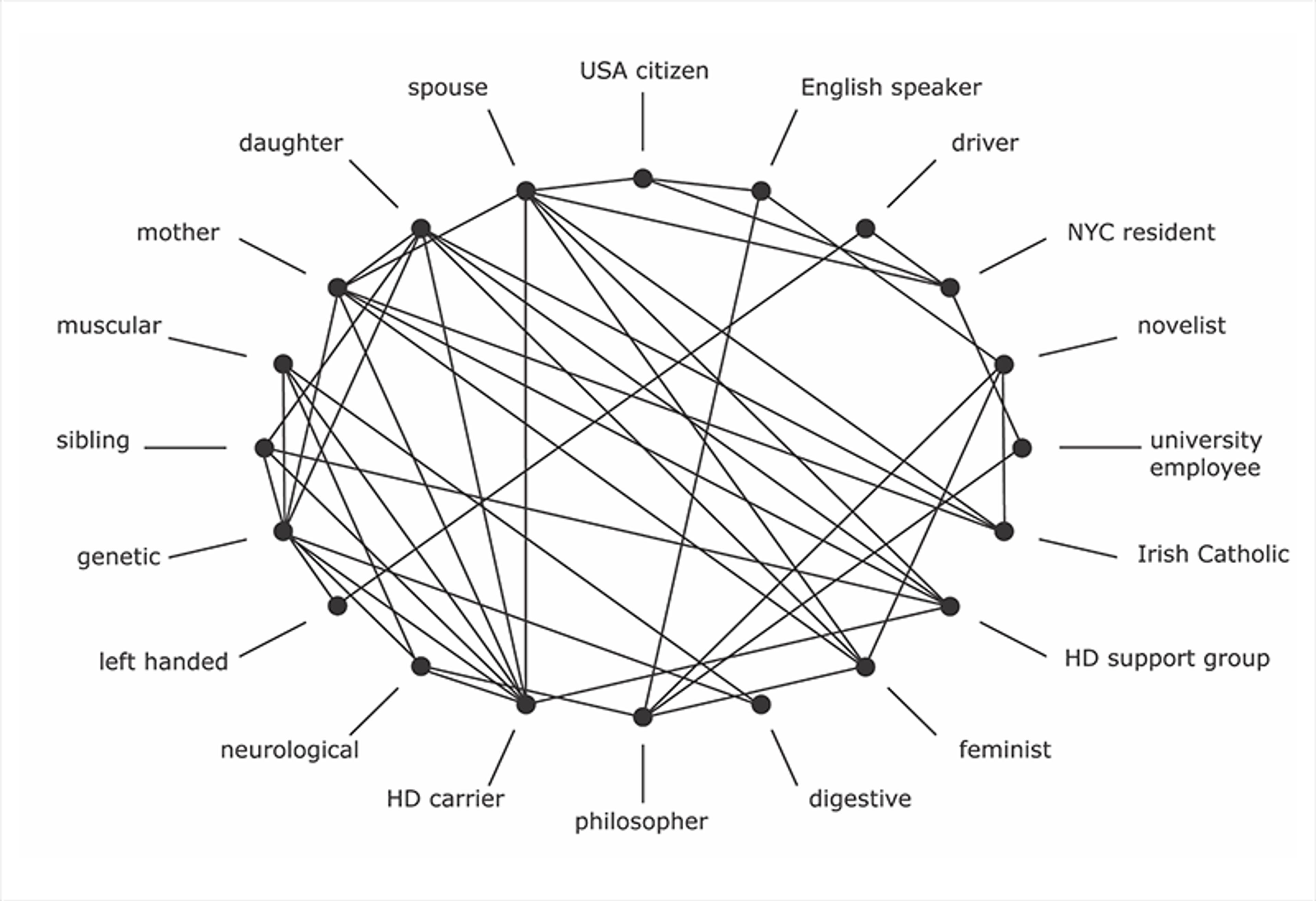
We notice right away the complex interrelatedness among Lindsey’s traits. We can also see that some traits seem to be clustered, that is, related more to some traits than to others. Just as a body is a highly complex, organised network of organismic and molecular systems, the self is a highly organised network. Traits of the self can organise into clusters or hubs, such as a body cluster, a family cluster, a social cluster. There might be other clusters, but keeping it to a few is sufficient to illustrate the idea. A second approximation, Figure 2 below, captures the clustering idea.
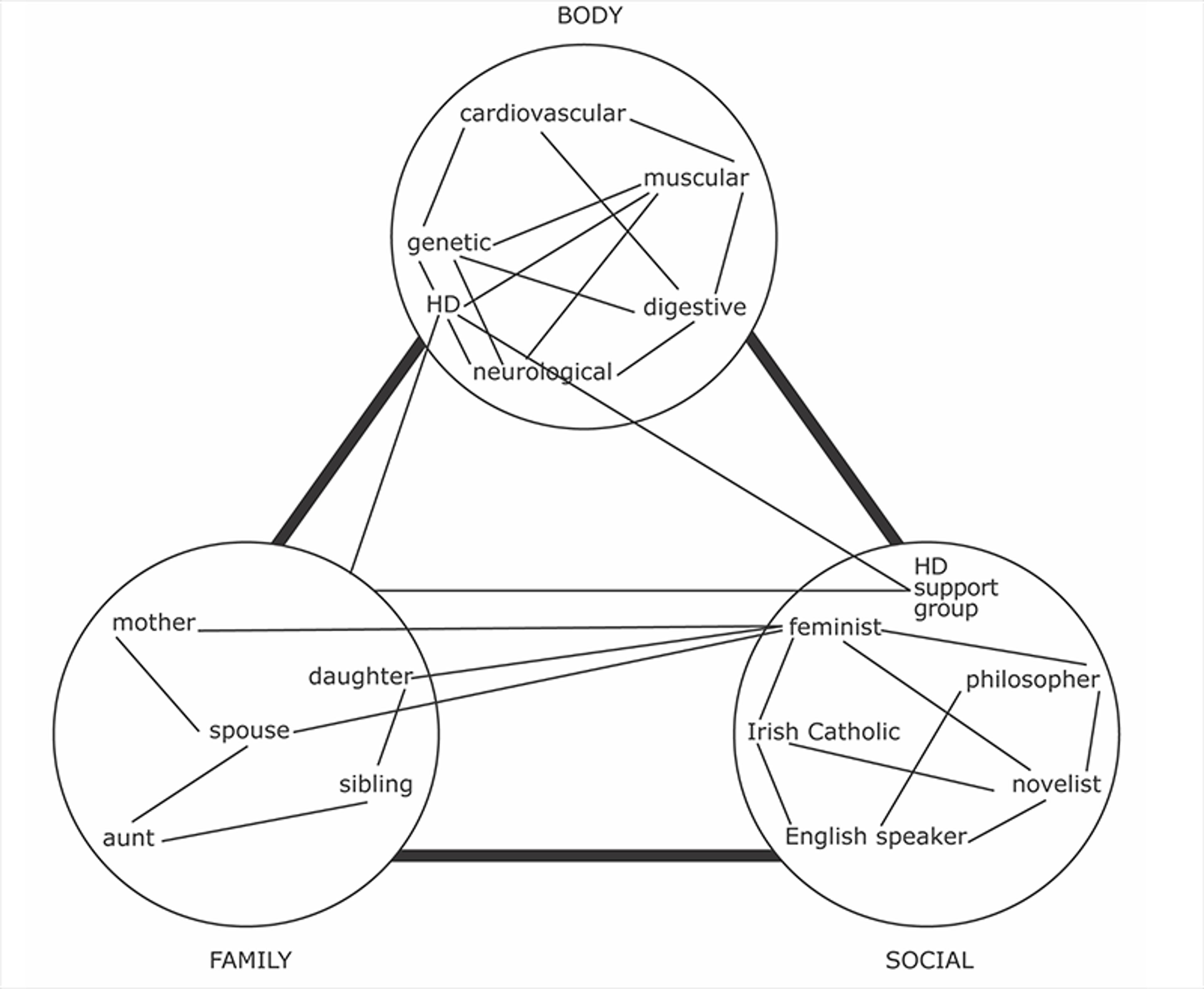
Figures 1 and 2 (both from my book , The Network Self ) are simplifications of the bodily, personal and social relations that make up the self. Traits can be closely clustered, but they also cross over and intersect with traits in other hubs or clusters. For instance, a genetic trait – ‘Huntington’s disease carrier’ (HD in figures 1 and 2) – is related to biological, family and social traits. If the carrier status is known, there are also psychological and social relations to other carriers and to familial and medical communities. Clusters or sub-networks are not isolated, or self-enclosed hubs, and might regroup as the self develops.
Sometimes her experience might be fractured, as when others take one of her identities as defining all of her
Some traits might be more dominant than others. Being a spouse might be strongly relevant to who Lindsey is, whereas being an aunt weakly relevant. Some traits might be more salient in some contexts than others. In Lindsey’s neighbourhood, being a parent might be more salient than being a philosopher, whereas at the university being a philosopher is more prominent.
Lindsey can have a holistic experience of her multifaceted, interconnected network identity. Sometimes, though, her experience might be fractured, as when others take one of her identities as defining all of her. Suppose that, in an employment context, she isn’t promoted, earns a lower salary or isn’t considered for a job because of her gender. Discrimination is when an identity – race, gender, ethnicity – becomes the way in which someone is identified by others, and therefore might experience herself as reduced or objectified. It is the inappropriate, arbitrary or unfair salience of a trait in a context.
Lindsey might feel conflict or tension between her identities. She might not want to be reduced to or stereotyped by any one identity. She might feel the need to dissimulate, suppress or conceal some identity, as well as associated feelings and beliefs. She might feel that some of these are not essential to who she really is. But even if some are less important than others, and some are strongly relevant to who she is and identifies as, they’re all still interconnected ways in which Lindsey is.
F igures 1 and 2 above represent the network self, Lindsey, at a cross-section of time, say at early to mid-adulthood. What about the changeableness and fluidity of the self? What about other stages of Lindsey’s life? Lindsey-at-age-five is not a spouse or a mother, and future stages of Lindsey might include different traits and relations too: she might divorce or change careers or undergo a gender identity transformation. The network self is also a process .
It might seem strange at first to think of yourself as a process. You might think that processes are just a series of events, and your self feels more substantial than that. Maybe you think of yourself as an entity that’s distinct from relations, that change is something that happens to an unchangeable core that is you. You’d be in good company if you do. There’s a long history in philosophy going back to Aristotle arguing for a distinction between a substance and its properties, between substance and relations, and between entities and events.
However, the idea that the self is a network and a process is more plausible than you might think. Paradigmatic substances, such as the body, are systems of networks that are in constant process even when we don’t see that at a macro level: cells are replaced, hair and nails grow, food is digested, cellular and molecular processes are ongoing as long as the body is alive. Consciousness or the stream of awareness itself is in constant flux. Psychological dispositions or attitudes might be subject to variation in expression and occurrence. They’re not fixed and invariable, even when they’re somewhat settled aspects of a self. Social traits evolve. For example, Lindsey-as-daughter develops and changes. Lindsey-as-mother is not only related to her current traits, but also to her own past, in how she experienced being a daughter. Many past experiences and relations have shaped how she is now. New beliefs and attitudes might be acquired and old ones revised. There’s constancy, too, as traits don’t all change at the same pace and maybe some don’t change at all. But the temporal spread, so to speak, of the self means that how a self as a whole is at any time is a cumulative upshot of what it’s been and how it’s projecting itself forward.
Anchoring and transformation, sameness and change: the cumulative network is both-and , not either-or
Rather than an underlying, unchanging substance that acquires and loses properties, we’re making a paradigm shift to seeing the self as a process, as a cumulative network with a changeable integrity. A cumulative network has structure and organisation, as many natural processes do, whether we think of biological developments, physical processes or social processes. Think of this constancy and structure as stages of the self overlapping with, or mapping on to, one another. For Lindsey, being a sibling overlaps from Lindsey-at-six to the death of the sibling; being a spouse overlaps from Lindsey-at-30 to the end of the marriage. Moreover, even if her sibling dies, or her marriage crumbles, sibling and spouse would still be traits of Lindsey’s history – a history that belongs to her and shapes the structure of the cumulative network.
If the self is its history, does that mean it can’t really change much? What about someone who wants to be liberated from her past, or from her present circumstances? Someone who emigrates or flees family and friends to start a new life or undergoes a radical transformation doesn’t cease to have been who they were. Indeed, experiences of conversion or transformation are of that self, the one who is converting, transforming, emigrating. Similarly, imagine the experience of regret or renunciation. You did something that you now regret, that you would never do again, that you feel was an expression of yourself when you were very different from who you are now. Still, regret makes sense only if you’re the person who in the past acted in some way. When you regret, renounce and apologise, you acknowledge your changed self as continuous with and owning your own past as the author of the act. Anchoring and transformation, continuity and liberation, sameness and change: the cumulative network is both-and , not either-or .
Transformation can happen to a self or it can be chosen. It can be positive or negative. It can be liberating or diminishing. Take a chosen transformation. Lindsey undergoes a gender transformation, and becomes Paul. Paul doesn’t cease to have been Lindsey, the self who experienced a mismatch between assigned gender and his own sense of self-identification, even though Paul might prefer his history as Lindsey to be a nonpublic dimension of himself. The cumulative network now known as Paul still retains many traits – biological, genetic, familial, social, psychological – of its prior configuration as Lindsey, and is shaped by the history of having been Lindsey. Or consider the immigrant. She doesn’t cease to be the self whose history includes having been a resident and citizen of another country.
T he network self is changeable but continuous as it maps on to a new phase of the self. Some traits become relevant in new ways. Some might cease to be relevant in the present while remaining part of the self’s history. There’s no prescribed path for the self. The self is a cumulative network because its history persists, even if there are many aspects of its history that a self disavows going forward or even if the way in which its history is relevant changes. Recognising that the self is a cumulative network allows us to account for why radical transformation is of a self and not, literally, a different self.
Now imagine a transformation that’s not chosen but that happens to someone: for example, to a parent with Alzheimer’s disease. They are still parent, citizen, spouse, former professor. They are still their history; they are still that person undergoing debilitating change. The same is true of the person who experiences dramatic physical change, someone such as the actor Christopher Reeve who had quadriplegia after an accident, or the physicist Stephen Hawking whose capacities were severely compromised by ALS (motor neuron disease). Each was still parent, citizen, spouse, actor/scientist and former athlete. The parent with dementia experiences loss of memory, and of psychological and cognitive capacities, a diminishment in a subset of her network. The person with quadriplegia or ALS experiences loss of motor capacities, a bodily diminishment. Each undoubtedly leads to alteration in social traits and depends on extensive support from others to sustain themselves as selves.
Sometimes people say that the person with dementia who doesn’t know themselves or others anymore isn’t really the same person that they were, or maybe isn’t even a person at all. This reflects an appeal to the psychological view – that persons are essentially consciousness. But seeing the self as a network takes a different view. The integrity of the self is broader than personal memory and consciousness. A diminished self might still have many of its traits, however that self’s history might be constituted in particular.
Plato, long before Freud, recognised that self-knowledge is a hard-won and provisional achievement
The poignant account ‘Still Gloria’ (2017) by the Canadian bioethicist Françoise Baylis of her mother’s Alzheimer’s reflects this perspective. When visiting her mother, Baylis helps to sustain the integrity of Gloria’s self even when Gloria can no longer do that for herself. But she’s still herself. Does that mean that self-knowledge isn’t important? Of course not. Gloria’s diminished capacities are a contraction of her self, and might be a version of what happens in some degree for an ageing self who experiences a weakening of capacities. And there’s a lesson here for any self: none of us is completely transparent to ourselves. This isn’t a new idea; even Plato, long before Freud, recognised that there were unconscious desires, and that self-knowledge is a hard-won and provisional achievement. The process of self-questioning and self-discovery is ongoing through life because we don’t have fixed and immutable identities: our identity is multiple, complex and fluid.
This means that others don’t know us perfectly either. When people try to fix someone’s identity as one particular characteristic, it can lead to misunderstanding, stereotyping, discrimination. Our currently polarised rhetoric seems to do just that – to lock people into narrow categories: ‘white’, ‘Black’, ‘Christian’, ‘Muslim’, ‘conservative’, ‘progressive’. But selves are much more complex and rich. Seeing ourselves as a network is a fertile way to understand our complexity. Perhaps it could even help break the rigid and reductive stereotyping that dominates current cultural and political discourse, and cultivate more productive communication. We might not understand ourselves or others perfectly, but we often have overlapping identities and perspectives. Rather than seeing our multiple identities as separating us from one another, we should see them as bases for communication and understanding, even if partial. Lindsey is a white woman philosopher. Her identity as a philosopher is shared with other philosophers (men, women, white, not white). At the same time, she might share an identity as a woman philosopher with other women philosophers whose experiences as philosophers have been shaped by being women. Sometimes communication is more difficult than others, as when some identities are ideologically rejected, or seem so different that communication can’t get off the ground. But the multiple identities of the network self provide a basis for the possibility of common ground.
How else might the network self contribute to practical, living concerns? One of the most important contributors to our sense of wellbeing is the sense of being in control of our own lives, of being self-directing. You might worry that the multiplicity of the network self means that it’s determined by other factors and can’t be self -determining. The thought might be that freedom and self-determination start with a clean slate, with a self that has no characteristics, social relations, preferences or capabilities that would predetermine it. But such a self would lack resources for giving itself direction. Such a being would be buffeted by external forces rather than realising its own potentialities and making its own choices. That would be randomness, not self-determination. In contrast, rather than limiting the self, the network view sees the multiple identities as resources for a self that’s actively setting its own direction and making choices for itself. Lindsey might prioritise career over parenthood for a period of time, she might commit to finishing her novel, setting philosophical work aside. Nothing prevents a network self from freely choosing a direction or forging new ones. Self-determination expresses the self. It’s rooted in self-understanding.
The network self view envisions an enriched self and multiple possibilities for self-determination, rather than prescribing a particular way that selves ought to be. That doesn’t mean that a self doesn’t have responsibilities to and for others. Some responsibilities might be inherited, though many are chosen. That’s part of the fabric of living with others. Selves are not only ‘networked’, that is, in social networks, but are themselves networks. By embracing the complexity and fluidity of selves, we come to a better understanding of who we are and how to live well with ourselves and with one another.
To read more about the self, visit Psyche , a digital magazine from Aeon that illuminates the human condition through psychology, philosophical understanding and the arts.

Psychiatry and psychotherapy
The therapist who hated me
Going to a child psychoanalyst four times a week for three years was bad enough. Reading what she wrote about me was worse
Michael Bacon

Consciousness and altered states
A reader’s guide to microdosing
How to use small doses of psychedelics to lift your mood, enhance your focus, and fire your creativity
Tunde Aideyan

The scourge of lookism
It is time to take seriously the painful consequences of appearance discrimination in the workplace
Andrew Mason

Thinkers and theories
Our tools shape our selves
For Bernard Stiegler, a visionary philosopher of our digital age, technics is the defining feature of human experience
Bryan Norton
Family life
A patchwork family
After my marriage failed, I strove to create a new family – one made beautiful by the loving way it’s stitched together

The cell is not a factory
Scientific narratives project social hierarchies onto nature. That’s why we need better metaphors to describe cellular life
Charudatta Navare
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Why Identity Matters and How It Shapes Us
Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SanjanaGupta-d217a6bfa3094955b3361e021f77fcca.jpg)
Dr. Sabrina Romanoff, PsyD, is a licensed clinical psychologist and a professor at Yeshiva University’s clinical psychology doctoral program.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SabrinaRomanoffPhoto2-7320d6c6ffcc48ba87e1bad8cae3f79b.jpg)
Verywell / Zoe Hansen
Defining Identity
- What Makes Up a Person's Identity?
Identity Development Across the Lifespan
The importance of identity, tips for reflecting on your identity.
Your identity is a set of physical, mental, emotional, social, and interpersonal characteristics that are unique to you.
It encapsulates your core personal values and your beliefs about the world, says Asfia Qaadir , DO, a child and adolescent psychiatrist at PrairieCare.
In this article, we explore the concept of identity, its importance, factors that contribute to its development , and some strategies that can help you reflect upon your identity.
Your identity gives you your sense of self. It is a set of traits that distinguishes you from other people, because while you might have some things in common with others, no one else has the exact same combination of traits as you.
Your identity also gives you a sense of continuity, i.e. the feeling that you are the same person you were two years ago and you will be the same person two days from now.
Asfia Qaadir, DO, Psychiatrist
Your identity plays an important role in how you treat others and how you carry yourself in the world.
What Makes Up a Person's Identity?
These are some of the factors that can contribute to your identity:
- Physical appearance
- Physical sensations
- Emotional traits
- Life experiences
- Genetics
- Health conditions
- Nationality
- Race
- Social community
- Peer group
- Political environment
- Spirituality
- Sexuality
- Personality
- Beliefs
- Finances
We all have layers and dimensions that contribute to who we are and how we express our identity.
All of these factors interact together and influence you in unique and complex ways, shaping who you are. Identity formation is a subjective and deeply personal experience.
Identity development is a lifelong process that begins in childhood, starts to solidify in adolescence, and continues through adulthood.
Childhood is when we first start to develop a self-concept and form an identity.
As children, we are highly dependent on our families for our physical and emotional needs. Our early interactions with family members play a critical role in the formation of our identities.
During this stage, we learn about our families and communities, and what values are important to them, says Dr. Qaadir.
The information and values we absorb in childhood are like little seeds that are planted years before we can really intentionally reflect upon them as adults, says Dr. Qaadir.
Traumatic or abusive experiences during childhood can disrupt identity formation and have lasting effects on the psyche.
Adolescence
Adolescence is a critical period of identity formation.
As teenagers, we start to intentionally develop a sense of self based on how the values we’re learning show up in our relationships with ourselves, our friends, family members, and in different scenarios that challenge us, Dr. Qaadir explains.
Adolescence is a time of discovering ourselves, learning to express ourselves, figuring out where we fit in socially (and where we don’t), developing relationships, and pursuing interests, says Dr. Qaadir.
This is the period where we start to become independent and form life goals. It can also be a period of storm and stress , as we experience mood disruptions, challenge authority figures, and take risks as we try to work out who we are.
As adults, we begin building our public or professional identities and deepen our personal relationships, says Dr. Qaadir.
These stages are not set in stone, rather they are fluid, and we get the rest of our lives to continue experiencing life and evolving our identities, says Dr. Qaadir.
Having a strong sense of identity is important because it:
- Creates self-awareness: A strong sense of identity can give you a deep sense of awareness of who you are as a person. It can help you understand your likes, dislikes, actions, motivations, and relationships.
- Provides direction and motivation: Having a strong sense of identity can give you a clear understanding of your values and interests, which can help provide clarity, direction, and motivation when it comes to setting goals and working toward them.
- Enables healthy relationships: When you know and accept yourself, you can form meaningful connections with people who appreciate and respect you for who you are. A strong sense of identity also helps you communicate effectively, establish healthy boundaries, and engage in authentic and fulfilling interactions.
- Keeps you grounded: Our identities give us roots when things around us feel chaotic or uncertain, says Dr. Qaadir. “Our roots keep us grounded and help us remember what truly matters at the end of the day.”
- Improves decision-making: Understanding yourself well can help you make choices that are consistent with your values, beliefs, and long-term goals. This clarity reduces confusion, indecision, and the tendency to conform to others' expectations, which may lead to poor decision-making .
- Fosters community participation: Identity is often shaped by cultural, social, political, spiritual, and historical contexts. Having a strong sense of identity allows you to understand, appreciate, and take pride in your cultural heritage. This can empower you to participate actively in society, express your unique perspective, and contribute to positive societal change.
On the other hand, a weak sense of identity can make it more difficult to ground yourself emotionally in times of stress and more confusing when you’re trying to navigate major life decisions, says Dr. Qaadir.
Dr. Qaadir suggests some strategies that can help you reflect on your identity:
- Art: Art is an incredible medium that can help you process and reflect on your identity. It can help you express yourself in creative and unique ways.
- Reading: Reading peoples’ stories through narrative is an excellent way to broaden your horizons, determine how you feel about the world around you, and reflect on your place in it.
- Journaling: Journaling can also be very useful for self-reflection . It can help you understand your feelings and motivations better.
- Conversation: Conversations with people can expose you to diverse perspectives, and help you form and represent your own.
- Nature: Being in nature can give you a chance to reflect undisturbed. Spending time in nature often has a way of putting things in perspective.
- Relationships: You can especially strengthen your sense of identity through the relationships around you. It is valuable to surround yourself with people who reflect your core values but may be different from you in other aspects of identity such as personality styles, cultural backgrounds, passions, professions, or spiritual paths because that provides perspective and learning from others.
American Psychological Association. Identity .
Pfeifer JH, Berkman ET. The development of self and identity in adolescence: neural evidence and implications for a value-based choice perspective on motivated behavior . Child Dev Perspect . 2018;12(3):158-164. doi:10.1111/cdep.12279
Hasanah U, Susanti H, Panjaitan RU. Family experience in facilitating adolescents during self-identity development . BMC Nurs . 2019;18(Suppl 1):35. doi:10.1186/s12912-019-0358-7
Dereboy Ç, Şahin Demirkapı E, et al. The relationship between childhood traumas, identity development, difficulties in emotion regulation and psychopathology . Turk Psikiyatri Derg . 2018;29(4):269-278.
Branje S, de Moor EL, Spitzer J, Becht AI. Dynamics of identity development in adolescence: a decade in review . J Res Adolesc . 2021;31(4):908-927. doi:10.1111/jora.12678
Stirrups R. The storm and stress in the adolescent brain . The Lancet Neurology . 2018;17(5):404. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30112-1
Fitzgerald A. Professional identity: A concept analysis . Nurs Forum . 2020;55(3):447-472. doi:10.1111/nuf.12450
National Institute of Standards and Technology. Identity .
By Sanjana Gupta Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.

How to Write an Essay about Your Identity

If you’re looking for a simple way to write an essay about your identity, then you’ve found the perfect tutorial!
Writing an essay about your identity can be a great way to highlight who you are as a person and explore your values, experiences, and characteristics. So, in this tutorial, I will show you how to write such an essay in five simple steps effectively. We’ll also work on a sample essay so you can see how to put these steps into practice.
Let’s get started!

Step 1. Plan the word count for your essay’s paragraphs.
Doing this first step is important if you want to make things simpler for you while writing an essay. You’ll get to know exactly how many words each paragraph will have, which makes the process quicker.
Note that essays have three parts you must include:
- The introductory paragraph
- Three body paragraphs
- The concluding paragraph
For example, suppose you need a 300-word paragraph. How would you distribute 300 words across five paragraphs? Here’s a simple way to do that:

That’s all you need for your essay — short introductory and concluding paragraphs and three concise body paragraphs.
Step 2. Select your main idea and supporting points.
You need to come up with a central idea that will give you a frame of reference for the rest of your essay. To do this, you can first consider what your identity is. Then, determine what shapes this identity.
For example, are you an artist? Maybe you’re imaginative and creative! Do you have a unique perspective on things? Do you like expressing yourself visually?
Or maybe, you’re a doctor? Do you have extensive knowledge and expertise in the field of medicine? Do you possess strong problem-solving and critical-thinking skills?
Whatever they are, you will use them as your basis — your essay’s thesis .
For our sample essay, we can use this as our main idea: “My identity as an educator has been shaped by my faith, parenthood, and my inborn creativity.”
Next, we will use the Power of Three to divide this main idea into three supporting points.

The Power of Three is a three-part structure that helps you produce your body paragraphs.
Let’s see how it works for our sample essay. In this case, we will use three things that could shape someone’s identity as an educator:
- My faith is an integral part of my identity.
- Parenthood has had a significant impact on my identity.
- Creativity has been a part of my identity for as long as I can remember.
Now we have what we need to start writing our essay. Let’s go to the next step!
Step 3. Write the introductory paragraph.
To write an introductory paragraph , you can follow the diagram below:

First, you need an introduction — an opening sentence that briefly sets the essay’s context. Next, you will include your thesis and three supporting points.
Here’s an example:
Introductory Paragraph
“Different factors, including beliefs, experiences, and innate qualities, shape our identities. For me, my identity as an educator has been shaped by my faith, parenthood, and my inborn creativity. My faith guides my values and principles in teaching. My experiences as a parent have also helped me develop empathy and understanding toward my students. And my inborn creativity allows me to come up with innovative ways to present lessons, engage my students, and foster a positive learning environment.”
As you can tell, the introductory paragraph proceeds from general to specific , starting from the introduction, followed by the thesis and three supporting points.
Step 4. Write the body paragraphs.
Our essay will contain three body paragraphs that expound our supporting points. Here’s how to structure a body paragraph in any essay:

Body paragraphs start with a topic sentence that briefly summarizes the entire paragraph. Next, you will explain and illustrate your point using example/s .
Paragraph 1
“My faith is an integral part of my identity. My faith guides me in creating a safe and positive learning environment for my students. I strive to make my classroom a safe space where my students feel welcomed and valued. I model kindness and compassion, which I hope inspires and encourages my students to treat each other with the same level of respect and understanding.”
Note that the topic sentence gives context to the entire body paragraph. The following sentences explain the supporting point, and the rest illustrates it with an example.
Paragraph 2
“Parenthood has had a significant impact on my identity as an educator. It has taught me to approach teaching with compassion and empathy. As a parent, I learned that everyone has unique needs and struggles that require understanding and, if possible, a personalized approach to teaching. I apply this principle in my classroom by taking the time to get to know my students and understand their personal learning styles and circumstances. I schedule one-on-one meetings with students and offer them encouragement and resources to help those struggling to catch up.”
Paragraph 3
“Creativity has always been a part of my identity, especially as an educator. It is essential in creating engaging learning experiences for my students. I constantly look for fun and innovative ways to present lessons that will help them foster a love for learning. I incorporate hands-on activities and projects in my lessons to challenge my students creatively and critically about the material. For example, when I taught animal classification last academic year, I organized a field trip to a local zoo where the students observed and learned firsthand about the animals and ecosystems they were studying.”
Like paragraph 1, body paragraphs 2 and 3 follow the exact same structure outlined in the diagram above. It proceeds from the topic sentence to the explanation and example.
Excellent! Now we’re ready for the final step.
Step 5. Write the concluding paragraph.
The most time-proven way to write a concluding paragraph for any essay is to simply paraphrase all the points you’ve already mentioned in the introductory paragraph. Don’t copy and paste it! Instead, you can check your introductory paragraph and write the concluding paragraph based on it.
Let’s try this method to write the concluding paragraph in our sample essay:
“A combination of our beliefs, experiences, and characteristics shape our identities. As an educator, my identity has been shaped by my faith, parenthood, and creativity. My faith guides me in modeling important values in my classroom. Parenthood has taught me to approach teaching with empathy. And my creativity enables me to present material in innovative and engaging ways, which helps foster a love for learning in my students.”
We only restated the points in the introductory paragraph but used different words. Doing so makes writing the concluding paragraph pretty quick and simple.
And now we’re done! I hope you find this tutorial helpful.
Now it’s time for you to write your essay about your identity!
Tutor Phil is an e-learning professional who helps adult learners finish their degrees by teaching them academic writing skills.
Recent Posts
How to Write a 300 Word Essay - Simple Tutorial
https://youtu.be/qXST2gJbkhw If you need to write a 300-word essay, you’ve come to the right place. I’m Tutor Phil, and in this tutorial I’ll guide you through the process step by...
Essay Writing for Beginners: 6-Step Guide with Examples
https://youtu.be/w6yanrc1a_g If you need to write an essay, whether for a college course or to pass a writing test, this guide will take you through the process step-by-step. Even if you have...
Cultural Identity Essay
27 August, 2020
12 minutes read
Author: Elizabeth Brown
No matter where you study, composing essays of any type and complexity is a critical component in any studying program. Most likely, you have already been assigned the task to write a cultural identity essay, which is an essay that has to do a lot with your personality and cultural background. In essence, writing a cultural identity essay is fundamental for providing the reader with an understanding of who you are and which outlook you have. This may include the topics of religion, traditions, ethnicity, race, and so on. So, what shall you do to compose a winning cultural identity essay?

Cultural Identity Paper: Definitions, Goals & Topics

Before starting off with a cultural identity essay, it is fundamental to uncover what is particular about this type of paper. First and foremost, it will be rather logical to begin with giving a general and straightforward definition of a cultural identity essay. In essence, cultural identity essay implies outlining the role of the culture in defining your outlook, shaping your personality, points of view regarding a multitude of matters, and forming your qualities and beliefs. Given a simpler definition, a cultural identity essay requires you to write about how culture has influenced your personality and yourself in general. So in this kind of essay you as a narrator need to give an understanding of who you are, which strengths you have, and what your solid life position is.
Yet, the goal of a cultural identity essay is not strictly limited to describing who you are and merely outlining your biography. Instead, this type of essay pursues specific objectives, achieving which is a perfect indicator of how high-quality your essay is. Initially, the primary goal implies outlining your cultural focus and why it makes you peculiar. For instance, if you are a french adolescent living in Canada, you may describe what is so special about it: traditions of the community, beliefs, opinions, approaches. Basically, you may talk about the principles of the society as well as its beliefs that made you become the person you are today.
So far, cultural identity is a rather broad topic, so you will likely have a multitude of fascinating ideas for your paper. For instance, some of the most attention-grabbing topics for a personal cultural identity essay are:
- Memorable traditions of your community
- A cultural event that has influenced your personality
- Influential people in your community
- Locations and places that tell a lot about your culture and identity
Cultural Identity Essay Structure
As you might have already guessed, composing an essay on cultural identity might turn out to be fascinating but somewhat challenging. Even though the spectrum of topics is rather broad, the question of how to create the most appropriate and appealing structure remains open.
Like any other kind of an academic essay, a cultural identity essay must compose of three parts: introduction, body, and concluding remarks. Let’s take a more detailed look at each of the components:
Introduction
Starting to write an essay is most likely one of the most time-consuming and mind-challenging procedures. Therefore, you can postpone writing your introduction and approach it right after you finish body paragraphs. Nevertheless, you should think of a suitable topic as well as come up with an explicit thesis. At the beginning of the introduction section, give some hints regarding the matter you are going to discuss. You have to mention your thesis statement after you have briefly guided the reader through the topic. You can also think of indicating some vital information about yourself, which is, of course, relevant to the topic you selected.
Your main body should reveal your ideas and arguments. Most likely, it will consist of 3-5 paragraphs that are more or less equal in size. What you have to keep in mind to compose a sound ‘my cultural identity essay’ is the argumentation. In particular, always remember to reveal an argument and back it up with evidence in each body paragraph. And, of course, try to stick to the topic and make sure that you answer the overall question that you stated in your topic. Besides, always keep your thesis statement in mind: make sure that none of its components is left without your attention and argumentation.
Conclusion
Finally, after you are all finished with body paragraphs and introduction, briefly summarize all the points in your final remarks section. Paraphrase what you have already revealed in the main body, and make sure you logically lead the reader to the overall argument. Indicate your cultural identity once again and draw a bottom line regarding how your culture has influenced your personality.
Best Tips For Writing Cultural Identity Essay
Writing a ‘cultural identity essay about myself’ might be somewhat challenging at first. However, you will no longer struggle if you take a couple of plain tips into consideration. Following the tips below will give you some sound and reasonable cultural identity essay ideas as well as make the writing process much more pleasant:
- Start off by creating an outline. The reason why most students struggle with creating a cultural identity essay lies behind a weak structure. The best way to organize your ideas and let them flow logically is to come up with a helpful outline. Having a reference to build on is incredibly useful, and it allows your essay to look polished.
- Remember to write about yourself. The task of a cultural identity essay implies not focusing on your culture per se, but to talk about how it shaped your personality. So, switch your focus to describing who you are and what your attitudes and positions are.
- Think of the most fundamental cultural aspects. Needless to say, you first need to come up with a couple of ideas to be based upon in your paper. So, brainstorm all the possible ideas and try to decide which of them deserve the most attention. In essence, try to determine which of the aspects affected your personality the most.
- Edit and proofread before submitting your paper. Of course, the content and the coherence of your essay’s structure play a crucial role. But the grammatical correctness matters a lot too. Even if you are a native speaker, you may still make accidental errors in the text. To avoid the situation when unintentional mistakes spoil the impression from your essay, always double check your cultural identity essay.
A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

Speak Your Truth: Sharing Your Identity in College Essays

Written by Sara Calvert-Kubrom on September 21st, 2023
- college applications ,
- race-neutral admissions ,
- writing college essays ,
- Most college essays, including the main Common Application essay and University of California Personal Insight Questions, invite broad reflection on experiences which can be linked to student identity.
- Some colleges invite students to share more through supplemental essays specific to their applications. Many colleges changed these essays this year to signal their institutional values and assess student readiness to engage with difference in college. Inside Higher Ed has a helpful article with examples of these prompts.
- Many applications have an additional information section where students can share any important context about their experiences. Although I encourage students to be concise (this isn’t an extra essay!), and to avoid being redundant with information provided elsewhere, this can be a fantastic area to utilize if a student wants to share important elements of who they are without having to use the main essay for this purpose.
- Activities lists might feature identity-based clubs, organizations, and initiatives.
Find out what you can expect from our partnership and view our variety of flexible services .

amet, adipisicing elit sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt?
Follow these pre-application steps to help your student stay on track for admissions success., related resources.

Read | Posted on November 17th, 2023
Are Optional College Essays Really Optional?

Read | Posted on November 6th, 2023
4 Tips for Writing the University of California Essays

Read | Posted on March 14th, 2023
What You Can Do Before Senior Year to Prepare for Essay Writing
Browse categories.
- Applying For Financial Aid
- Choosing The Right College
- College Admissions Consulting
- College Applications
- College Coach Mentionables: News & Events
- College Entrance Exams
- College Essays
- College Loan Advice
- College Visits
- Finding Scholarships
- How To Pay For College
- Meet a College Finance Expert
- Meet An Admissions Counselor
- Uncategorized
Interested?
Call 877-402-6224 or complete the form for information on getting your student started with one of our experts.

Language and Identity Essay
Introduction.
- Language and Gender
- Language and Racial Identity
- Language and Social Status
Works Cited
Language serves as a vital means of expression, facilitating communication and interaction. It’s not merely a tool for conveying thoughts but is intrinsically linked with an individual’s identity. The question arises: How is language profoundly intertwined with identity?
Individuals, each with their unique characteristics, employ language to express their distinctions or commonalities. In particular, language can be a unifying force for people belonging to a specific social group, highlighting the bond between language and identity from the beginning.
An individual’s identity is not fixed; it varies depending on the situation, purpose, and context. When people find themselves in new environments, they often reshape their identities to adapt. This adaptability underscores the need to explore how environmental changes can redefine the link between language and identity.
Language can also indicate a person’s social status, race, nationality, or gender. Typically, members of a specific group share a common language, reinforcing their unity. This shared linguistic experience solidifies group identity and fosters a sense of belonging through shared experiences and ease of communication.
In this language and identity essay, we explore the dynamic interplay between these two concepts, exploring how they mutually influence and define each other.
Language and Identity: Gender
The intersection of language and gender identity reveals distinct patterns. Across various cultures, gender-based variations in speech are prevalent. Historically, linguistic differences have been observed in how women and men communicate. These differences often stem from the divergent social statuses of men and women, significantly influencing their manner of speaking. Power dynamics and societal roles of subordination between genders typically manifest in their vocabulary choices.
In many societies, there is an expectation for women to use more refined and polite language compared to men. Such cultural norms frequently discourage women from using profanity or obscene language. In these contexts, women often occupy a subordinate position, with their social liberties being more restricted than men’s. This disparity can increase insecurity, uncertainty, and a lack of confidence among women (Talbot 35). Consequently, the use of language within a society can indicate the level of social freedom and gender equality. The linguistic choices of men and women are integral to the discourse on language and identity. Those are not merely reflections of individual preferences but norms deeply embedded in societal structures and expectations. Gendered language norms, as explored in educational settings, not only shape communication styles but also reinforce gender stereotypes and roles, perpetuating inequality. Thus, studying language about gender identity, a key component in teacher education programs, provides critical insights into the broader societal dynamics and power relations that govern gender interactions.
Language and Identity: Race
The intricate relationship between language and racial or ethnic identity is undeniable. An individual’s history shapes their language, leading to those with similar racial backgrounds often using similar languages for communication. One’s mother tongue, acquired at birth, is a fundamental aspect of racial identity, providing a crucial sense of belonging, especially in early life.
In many households, a specific language is used for family communication. This habitual use of a language fosters an association with affection and intimacy, setting it apart from the language used in public settings. For example, Hispanic families living in America often identify Spanish as a critical component of their racial identity.
Consequently, while they might use English in public spaces, they prefer Spanish for intimate conversations with friends and family. Spanish allows for expressing emotions and thoughts in ways that might be more challenging in English (Talbot 173). Speaking a particular language can create a bond among its speakers, delineating an ‘us versus them’ dynamic with those who do not say it.
However, this practice can also lead to social isolation for minorities who speak a different language than the majority. They may struggle to relate to those who do not speak their native language or express themselves in the dominant public language. Even in monolingual societies, people often resort to a distinct language or dialect within their close social circles, aiding in more apparent emotional expression.
The narrative “Aria” by Richard Rodriguez illustrates the role of language as a marker of racial identity. Rodriguez recounts how Spanish, the sole language spoken at home, influenced his upbringing in California, where English was the norm. This use of Spanish fostered a warm, familial environment.
This language choice created a comfortable and inviting atmosphere at home, but it also labeled English speakers as “flos gringos” – the others (Rodriguez 134). While Spanish strengthened familial bonds and provided a sense of identity, it simultaneously isolated the family socially, limiting their interactions to Spanish-speaking relatives.
The exclusive use of Spanish at home adversely affected Rodriguez and his siblings’ educational progress. A shift occurred when nuns from their school intervened, prompting the family to start using English at home. This change markedly improved their social interactions. However, over time, Rodriguez lost proficiency in Spanish, leading his relatives to call him “pocho derogatorily” – a term for someone who has lost their identity (Rodriguez 137). To his relatives, speaking Spanish was a crucial element of their identity. “Aria” underscores the significance of language in racial identity. Despite assimilating into American society, Rodriguez experienced a nostalgic connection to his heritage whenever he heard Spanish spoken, indicating its enduring link to his racial identity.
Language and Identity: Social Status
The social status of individuals often manifests in their speech patterns. Educational attainment significantly influences language proficiency, as those from higher social classes typically access better education. This access equips them with the skills to use language effectively in communication.
People from various social backgrounds tend to exhibit distinct dialects. These dialectic variations reflect their diverse social experiences. Grammatical differences are not the only distinguishing factors; phonological and phonetic variations are also prevalent, leading to distinct accents among different social statuses. Therefore, the linguistic divide between social classes acts as both a consequence and a reinforcer of social stratification, mirroring the complexities of societal hierarchies. This phenomenon underscores the intricate relationship between language use and social identity, where speech patterns become markers of social positioning and mobility.
During the nineteenth century, slavery was a prevalent institution in America. Slaves were relegated to the lowest social echelon. Slave owners were intent on preserving this hierarchy, deeming it improper for slaves to acquire literacy skills. The ability to read and write was seen as a potential elevation of the slaves’ intellectual status, which could threaten the established order. Thus, the enforced illiteracy of slaves perpetuated their subjugation and created a linguistic divide between them and their masters (Jones and Christensen 45). In modern times, every society exhibits some form of social stratification. This concept refers to the structured ranking of social classes within a societal hierarchy. Their relative social distances influence the linguistic impact between social groups. Language changes in a higher social class might have little to no effect on the language used by lower social classes. Conversely, social groups closely aligned in status may share similar linguistic traits.
Language is integral in facilitating effective communication between two parties. However, its efficiency largely depends on both parties’ language understanding. As such, language can be a tool for enhancing or impeding communication. Individuals need to understand the nuances of words within the specific language used.
Misinterpretation of language can lead to incorrect perceptions of the message being conveyed. This issue often arises because some words may have varied meanings depending on the context. Therefore, the speaker must assess the listener’s ability to comprehend the information, which should be a central consideration in the communication process (Tan 142). This ensures that the intended message is accurately understood.
Language has two main functions. It helps communicate and gives a group of people a sense of identity and pride. People usually identify themselves with a specific language. Various groups use jargon that is only comprehensible to people within the group.
Language may show the social status, gender, and race of an individual. People who belong to different social statuses usually use other languages. In addition, different genders use different language vocabularies. A study on the language vocabulary of different genders may help determine a society’s social freedom. Language is a source of racial identity. People usually use a specific language when communicating with people from their race. The use of this language creates racial identity.
Jones, Malinda E., and Ann E. Christensen. “Learning to Read.” Constructing Strong Foundations of Early Literacy . Routledge, 2022. 33-46.
Talbot, Mary, ed. Language and Power in The Modern World . Edinburgh University Press, 2019.
Rodriguez, Richard. “Aria.” The Blair Reader: Exploring Issues and Ideas . Ed. Laurie G. Kirszner and Stephen R. Mandell. Ontario: Pearson Education Canada, 2007, pp. 133-139.
Tan, Amy “Mother Tongue.” The Blair Reader: Exploring Issues and Ideas . Ed. Laurie G. Kirszner and Stephen R. Mandell. Ontario: Pearson Education Canada, 2007, pp. 140-144.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 1). Language and Identity Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/
"Language and Identity Essay." IvyPanda , 1 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Language and Identity Essay'. 1 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Language and Identity Essay." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/.
1. IvyPanda . "Language and Identity Essay." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Language and Identity Essay." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/.
- "Gangstas" by Richard Rodriguez
- Richard Rodriguez’s Essay “The Achievement of Desire”: Interpretation and Commentary
- Euthanasia: Philosophical Issues at Stake in Rodriguez
- Richard Rodriguez’s Writing Style
- Richard Rodriguez’s Opinion on Migration and the American Dream
- Blaxicans and Other Reinvented Americans’
- Comparison of the Educational Articles by R. Rodriguez and M. Pratt
- Opinion About the Course and the Author Richard Rodriguez
- Embarking on Research by Rau, Gao and Wu (2006) and by Rodriguez, Ooms and Montanez (2008)
- The Achievement of Desire
- Sarah Baartman Discussion
- Sarah Baartman: A Victim of Discrimination
- Evidence of Racism in the American Schools
- Analysis on Religion, Racism and Family Conflicts
- Race, Inclusion, Exclusion, and Segregation
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Race and Ethnicity — Cultural Identity
Essays on Cultural Identity
What makes a good cultural identity essay topics.
When it comes to writing a cultural identity essay, choosing the right topic is crucial. A good essay topic should be thought-provoking, unique, and relevant to today's society. It should also allow for in-depth exploration and analysis. In this section, we will discuss What Makes a Good cultural identity essay topic and provide recommendations on how to brainstorm and choose an essay topic.
When brainstorming essay topics, it's important to consider your own interests and experiences. Reflect on your own cultural background and think about topics that resonate with you personally. Additionally, consider current events and societal issues that are relevant to cultural identity. This can help you choose a topic that is both timely and impactful.
Another important factor to consider when choosing a cultural identity essay topic is the level of complexity and depth it offers. A good essay topic should allow for meaningful exploration and analysis, rather than just surface-level discussion. Look for topics that are multi-dimensional and can be approached from various angles.
In addition, consider the potential impact of the topic. A good cultural identity essay topic should have significance and relevance beyond just the individual writer. It should be able to engage readers and provoke thoughtful discussion.
Overall, a good cultural identity essay topic should be personal, relevant, complex, and impactful. It should allow for in-depth exploration and analysis, and resonate with both the writer and the reader.
Best Cultural Identity Essay Topics
- The impact of globalization on cultural identity
- The role of language in shaping cultural identity
- Cultural appropriation in the fashion industry
- The influence of social media on cultural identity
- The interplay between religion and cultural identity
- The portrayal of cultural identity in literature and film
- The significance of traditional food in cultural identity
- The impact of immigration on cultural identity
- The evolution of cultural identity in the digital age
- The intersection of gender and cultural identity
- The role of education in shaping cultural identity
- The representation of cultural identity in art and music
- The impact of colonialism on cultural identity
- The influence of technology on cultural identity
- The role of family in shaping cultural identity
- The impact of cultural identity on mental health
- The relationship between cultural identity and national identity
- The significance of cultural festivals in shaping identity
- The impact of cultural identity on social justice movements
- The portrayal of cultural identity in the media
Cultural Identity essay topics Prompts
- Imagine a world where cultural identity is completely fluid and constantly changing. How would this impact society and individual experiences?
- Write about a time when you felt a strong connection to your cultural identity. What was the experience like, and how did it shape your sense of self?
- Consider the role of language in shaping cultural identity. How does language influence the way we perceive ourselves and others?
- Explore the concept of cultural hybridity and its impact on individual and collective identity.
- Reflect on the ways in which cultural identity can be both a source of pride and a source of conflict. How can individuals navigate these complexities in today's world?
Choosing a cultural identity essay topic is an important step in the writing process. By considering your own experiences, the complexity of the topic, and its potential impact, you can choose a topic that is both engaging and meaningful. With the recommendations and list of topics provided in this article, you are well-equipped to begin your exploration of cultural identity through writing.
The Significance of Cultural Identity
Everyday use: thesis statement, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Joanne Hyppolite's Dyaspora
I am proud of my cultural identity, the importance of cultural identity and socialization in education, cultural identity and the importance of preserving culture, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Cultural Identity of an Indonesian Immigrant
I am proud to be mexican, my cultural identity: who i am, cultural identity in city of clowns by daniel alarcón, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Impact of Globalization to Cultural Identity
A topic of cultural identity in gene yang’s american born chinese, the theme of sruggling with cultural identity: the inheritance of loss by karen desi, the connection of food and identity, unique culture of nicaragua, egypt, mexico, and united states: understanding cultural similarities and differences, analyzing cultural systems through a sociologist perspective, benefits of cross-culture awareness, understanding the significance of personal identity, the role of student life in the identity formation, a shared national identity of britain in the period 1830-1951, puerto rican identity in the united states, the culture of canada, the national and cultural identity in children's films toy story 3 and spirited away, experiencing different cultures: my personal experience, living in the czech republic, the role of cultural norm in formulating a person’s identity, african music as a part of social and cultural context, complexities of cultural identity in frozen river, relation of cultural industries and cultural heritage.
Cultural identity is a part of a person's identity, or their self-conception and self-perception, and is related to nationality, ethnicity, religion, social class, generation, locality or any kind of social group that has its own distinct culture.
There are three pieces that make up a person's cultural identity, these are cultural knowledge, category label, and social connections.
1. Schwartz, S. J., Zamboanga, B. L., & Weisskirch, R. S. (2008). Broadening the study of the self: Integrating the study of personal identity and cultural identity. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 2(2), 635-651. (https://compass.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1751-9004.2008.00077.x) 2. Hall, S. (1989). Cultural identity and cinematic representation. Framework: The Journal of Cinema and Media, (36), 68-81. (https://www.jstor.org/stable/44111666) 3. Bhugra, D. (2004). Migration, distress and cultural identity. British medical bulletin, 69(1), 129-141. (https://academic.oup.com/bmb/article/69/1/129/523340) 4. Jo Hatch, M., & Schultz, M. (1997). Relations between organizational culture, identity and image. European Journal of marketing, 31(5/6), 356-365. (https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/eb060636/full/html) 5. Lucy, S. (2007). Ethnic and cultural identities. In Archaeology of Identity (pp. 96-119). Routledge. (https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9780203087572-10/ethnic-cultural-identities-sam-lucy) 6. Karst, K. L. (1985). Paths to belonging: The constitution and cultural identity. NCL Rev., 64, 303. (https://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/nclr64&div=21&id=&page=) 7. Otcu, B. (2010). Heritage language maintenance and cultural identity formation: The case of a Turkish Saturday school in New York City. Heritage Language Journal, 7(2), 273-298. (https://brill.com/view/journals/hlj/7/2/article-p273_6.xml) 8. Schachter, E. P. (2005). Context and identity formation: A theoretical analysis and a case study. Journal of Adolescent Research, 20(3), 375-395. (https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0743558405275172) 9. Hall, S., & Ghazoul, F. (2012). Cultural identity and diaspora. Alif: Journal of Comparative Poetics, (32), 257-258. (https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA302403835&sid=googleScholar&v=2.1&it=r&linkaccess=abs&issn=11108673&p=AONE&sw=w&userGroupName=anon%7E81809ec)
Relevant topics
- American Identity
- Indigenous People
- Intercultural Communication
- Mexican American
- Physical Appearance
- African American
- Social Justice
- Effects of Social Media
- Sex, Gender and Sexuality
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Constructing Writer Identity: Self-Representation
- First Online: 15 February 2023
Cite this chapter

- Hiroe Kobayashi 22 &
- Carol Rinnert 23
Part of the book series: Multilingual Education ((MULT,volume 42))
293 Accesses
Developing writers often struggle with one kind of interactional metadiscourse, which conveys images of the writer’s identity directly to readers, known as self-representation (Hyland, Stance and voice in written academic genres. Palgrave Macmillan, London, pp 134–150, 2012). In this chapter, we explore how writers project their writer identity by referring to themselves in their texts. In English, such self-representation is best seen in first-person pronouns, whereas in Japanese, pronouns are optional and much less frequent. However, in both languages, first-person opinion qualifiers (such as “I believe …”) serve the function of representing the writer’s attitude toward the opinion expressed. Our analysis first examines the use of six functions of first-person pronouns (Tang, John, Engl Specific Purposes 1:523–539, 1999) in 82 English essays. We then compare first-person opinion qualifiers in 82 Japanese and 66 English argumentation essays. The findings reveal complex patterns of changing self-representation across groups and languages. Overall, the use of pronouns in English moves from personal (“I”), to more objective (third-person or impersonal), to more reader-inclusive (“we”). Dominant opinion qualifiers in both languages change from affective (“I like/want”) to self-reflective (“I think”), later adding performative (“I agree”) and non-use of a first-person qualifier, suggesting a gradual development in the writers’ stance toward the given issue from personal to more objective, nuanced, and implicit.
- Writer self-reference across languages
- Functions of first-person pronouns
- English/Japanese first-person opinion qualifiers
- Implicit and nuanced position statements
- Constructing writer self-image
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
We found a statistically significant difference among the groups according to one-way ANOVA tests for first-person pronouns ( F = 10.473, df = 5, p = .000) and for combined first- and second-person ( F = 13.449, df = 5, p = .000). Post-hoc Scheffé tests showed significant differences in first-person frequencies between the Novices and Experienced Group 2 ( p = .000), Group 3 ( p = .044), and the North Americans ( p = .000), as well as significant differences in the combined pronoun frequencies between the Novices and all other groups (ranging from p = .000 to.024) except Returnees, and between the Returnees and Experienced Group 2 ( p = .004), Group 3 ( p = .046), and North Americans ( p = .000).
We can speculate that the Returnees may have learned to address their classmates with “you” in discussions and debates in their overseas classes, and then transferred this practice into their writing.
In fact, there were no instances of this category in Tang and John’s ( 1999 ) data either, which they attributed to the fact that their writing task assigned did not involve collecting and analyzing empirical data.
On reflection, we realize that some of these personal perspectives might have fit Tang and John’s ( 1999 ) “originator” category, but we tended to limit that category to original opinions, rather than personal observations. For example, we put “ I cannot imagine anyone who would rather live alone or in a nursing home than with his or her own family.” (NA-8) under “personal” perspective, whereas it might have been categorized under “originator” in Tang and John’s study.
The term “performative verb” may be considered controversial in current Speech Act theory, with “declarative verb” being the preferred term for the same function (linguist Susumu Kubo, personal communication, April 17, 2022). Nevertheless, we decided to keep the term “performative” to avoid possible confusion with the traditional grammar term “declarative” (vs. “interrogative”) sentence.
The view of “ to omou ” and “ to kangaeru ” as offering a personal opinion can also be supported from a linguistic perspective. Japanese writers sometimes make the first person explicit together with the particle “ wa ” when they use one of these phrasal verbs, like “ watakushi-wa hitori tabi no hō ga ii to omou/kangaeru ” ( I think that it is better to travel alone). The function of the particle “ wa ” is complex and is understood to have at least two main functions in Japanese: As a topic marker, meaning “about myself” or “regarding myself”; and to limit the subject of the verb to exclude other possibilities, which can be considered a contrastive function, similar to one of the functions of strong stress in spoken English. Thus, using “ watakushi-wa ” (“I” plus the particle) explicitly in a position statement can make it clear that that the opinion is the writer’s own, not anyone else’s.
The use of first-person pronouns in English academic writing is still controversial among L1 English writing teachers, and the advice given to writers is not always consistent. In fact, some English composition teachers and materials advise students not to use “I think” when expressing their opinions in their essays, either because it is unnecessary or because it is too informal. For example, one textbook advises against using such phrases as “I think” and “In my opinion” because the whole essay represents the writer’s own perspective (Baldwin et al., 2007 ). This kind of instructional advice may dissuade some writers from using both “I think” and “I believe” in their formal English writing.
Baldwin, P., Gillotte-Tropp, H., Goen-Salter, S., & Wong, J. M. (2007). Composing for success: A student’s guide to reading and writing . Pearson Custom Publishing.
Google Scholar
Bereiter, C., & Scardamalia, M. (1987). The psychology of written composition . Lawrence Erlbaum.
Biber, D. (1988). Variation across speech and writing . Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Burgess, A., & Ivanič, R. (2010). Writing and being written: Issues of identity across timescales. Written Communication, 27 (2), 228–255.
Article Google Scholar
Casanave, C. P. (2002). Writing games: Multicultural case studies of academic literacy practices in higher education . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Charles, M. (2006). The construction of stance in reporting clauses: A cross-disciplinary study of theses. Applied Linguistics, 27 (3), 492–518.
Daijisen . (1998). [Japanese dictionary]. Shogakkan.
Hirvela, A., & Belcher, D. (2001). Coming back to voice: The multiple voices and identities of mature multilingual writers. Journal of Second Language Writing, 10 , 83–106.
Honda, K. (1972). Nihongo no sakubun gijutsu [Japanese composition skills]. Asahi Shimbun Press.
Hyland, K. (1996). Writing without conviction? Hedging in scientific research articles. Applied Linguistics, 17 (4), 433–454.
Hyland, K. (2002). What do they mean? Questions in academic writing. Text & Talk, 22 (4). https://doi.org/10.1515/text.2002.021
Hyland, K. (2012). Undergraduate understandings: Stance and voice in final year reports. In K. Hyland & C. Sancho Guinda (Eds.), Stance and voice in written academic genres (pp. 134–150). Palgrave Macmillan.
Chapter Google Scholar
Hyland, K. (2015). Genre, discipline and identity. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 19 , 32–43.
Hyland, K., & Milton, J. (1997). Qualification and certainty in L1 and L2 students’ writing. Journal of Second Language Writing, 6 , 183–205.
Ivanič, R. (1998). Writing and identity: The discoursal construction of identity in academic writing . John Benjamins Press.
Ivanič, R., & Camps, D. (2001). I am how I sound: Voice as self-representation in L2 writing. Journal of Second Language Writing, 10 , 3–33.
Johnson, D. (1992). Compliments and politeness in peer-review texts. Applied Linguistics, 13 , 51–71.
Jorden, E. H., & Noda, M. (1987). Japanese: The spoken language . Yale Language Press.
Joseph, J. E. (2004). Language and identity: National, ethnic, religious . Palgrave Macmillan.
Kellogg, R. T. (2008). Training writing skills: A cognitive development perspective. Journal of Writing Research, 1 (1), 1–26.
Kobayashi, H., & Rinnert, C. (2002). High school student perceptions of first language literacy instruction: Implications for second language writing. Journal of Second Language Writing, 11 , 91–116.
Kobayashi, H., & Rinnert, C. (2012). Understanding L2 writing development from a multicompetence perspective: Dynamic repertoires of knowledge and text construction. In R. M. Manchón (Ed.), L2 writing development: Multiple perspectives (pp. 101–134). De Gruyter Mouton.
Kobayashi, H., & Rinnert, C. (2013). L1/L2/L3 writing development: Longitudinal case study of a Japanese multicompetent writer. Journal of Second Language Writing, 22 , 4–33.
Kōjien . (1998). [Japanese dictionary] (5th ed.). Iwanami Shoten.
Lee, J. J., & Deakin, L. (2016). Interactions in L1 and L2 undergraduate student writing: Interactional metadiscourse in successful and less-successful argumentative essays. Journal of Second Language Writing, 33 , 21–34.
LoCastro, V. (2000). Evidence of accommodation to L2 pragmatic norms in peer review tasks of Japanese learners of English. JALT Journal, 22 (2), 245–270.
Matsuda, P. (2015). Identity in written discourse. Annual Review of Applied Linguistics, 35 , 140–159.
Matsuda, P. K., & Jeffery, J. (2012). Voice in student essays. In K. Hyland & C. Sancho Guinda (Eds.), Stance and voice in written academic genres (pp. 151–165). Palgrave Macmillan.
Matsuda, P. K., & Tardy, C. M. (2007). Voice in academic writing: The rhetorical construction of author identity in blind manuscript review. English for Specific Purposes, 26 , 235–249.
Mizutani, N. (1985). Nichiei hikaku: Hanashi kotoba no bumpō [Japanese-English comparison: Grammar for spoken language]. Kuroshio Shuppan.
Murata, K. (2011). Voices from the unvoiced: A comparative study of hidden values and attitudes in opinion-giving. Language and Intercultural Communication, 11 , 6–25.
Netsu, M., & LoCastro, V. (1997). Opinion-giving and point of view in discussion tasks. Proceedings of the 8th conference on second language research in Japan , pp. 136–153.
Nogami, Y. (2020). Identity and pragmatic language use: A study on Japanese ELF users. De Gruyter Mouton.
Norton, B. (2000). Identity and language learning . Pearson Education.
Norton, B., & McKinney, C. (2011). An identity approach to second language acquisition. In D. Atkinson (Ed.), Alternative approaches to second language acquisition (pp. 73–94). Routledge.
Ohno, S. (1999). Nihongo renshuu cho. [Japanese language exercise book]. Iwanami Shoten.
Rahtu, T. (2015). Multifunctional roles of the first person singular in academic texts. In S. Starch, C. Jones, & A. Maiorani (Eds.), Meaning making in text (pp. 31–50). Palgrave Macmillan.
Rambo, R. (2012). English composition 1: Formal writing voice . Retrieved December 10, 2016, from http://www2.ivcc.edu/rambo/tip_formal_writing_voice.htm
Rinnert, C., Kobayashi, H., & Katayama, A. (2015). Argumentation text construction by Japanese as a foreign language writers: A dynamic view of transfer. The Modern Language Journal, 99 , 213–245.
Staples, S., & Reppen, R. (2016). Understanding first-year L2 writing: A lexico-grammatical analysis across L1s, genres, and language ratings. Journal of Second Language Writing, 32 , 17–35.
Takahashi, T., & Beebe, L. M. (1993). Cross-linguistic influence in the speech act of correction. In G. Kasper & S. Blum-Kulka (Eds.), Interlanguage pragmatics (pp. 138–160). Oxford University.
Tang, R., & John, S. (1999). The “I” in identity: Exploring writer identity in student academic writing through the first person pronoun. English for Specific Purposes, 18 (Supplement 1), 523–539.
Tardy, C. M. (2012a). A rhetorical genre theory perspective on L2 writing development. In R. M. Manchón (Ed.), L2 writing development: Multiple perspectives (pp. 165–190). De Gruyter Mouton.
Tardy, C. M. (2012b). Current conceptions of voice. In K. Hyland & C. Sancho Guinda (Eds.), Stance and voice in written academic genres (pp. 34–48). Palgrave Macmillan.
Zhao, C. G. (2013). Measuring authorial voice strength in L2 argumentative writing: The development and validation of an analytic rubric. Language Testing, 30 (2), 201–230.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University, Higashi Hiroshima, Japan
Hiroe Kobayashi
Faculty of International Studies, Hiroshima City University, Hiroshima, Japan
Carol Rinnert
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Kobayashi, H., Rinnert, C. (2023). Constructing Writer Identity: Self-Representation. In: Developing Multilingual Writing. Multilingual Education, vol 42. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12045-9_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12045-9_4
Published : 15 February 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-12044-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-12045-9
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Plan Your Visit
- Group Visits
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Accessibility Options
- Sweet Home Café
- Museum Store
- Museum Maps
- Our Mobile App
- Search the Collection
- Exhibitions
- Initiatives
- Museum Centers
- Publications
- Digital Resource Guide
- The Searchable Museum
- Freedmen's Bureau Search Portal
- Early Childhood
- Talking About Race
- Digital Learning
- Strategic Partnerships
- Ways to Give
- Internships & Fellowships
- Today at the Museum
- Upcoming Events
- Ongoing Tours & Activities
- Past Events
- Host an Event at NMAAHC
- About the Museum
- The Building
- Meet Our Curators
- Founding Donors
- Corporate Leadership Councils
- NMAAHC Annual Reports
A New African American Identity: The Harlem Renaissance

With the end of the Civil War in 1865, hundreds of thousands of African Americans newly freed from the yoke of slavery in the South began to dream of fuller participation in American society, including political empowerment, equal economic opportunity, and economic and cultural self-determination.
Unfortunately, by the late 1870s, that dream was largely dead, as white supremacy was quickly restored to the Reconstruction South. White lawmakers on state and local levels passed strict racial segregation laws known as “Jim Crow laws” that made African Americans second-class citizens. While a small number of African Americans were able to become landowners, most were exploited as sharecroppers, a system designed to keep them poor and powerless. Hate groups like the Ku Klux Klan (KKK) perpetrated lynchings and conducted campaigns of terror and intimidation to keep African Americans from voting or exercising other fundamental rights.
With booming economies across the North and Midwest offering industrial jobs for workers of every race, many African Americans realized their hopes for a better standard of living—and a more racially tolerant environment—lay outside the South. By the turn of the 20th century, the Great Migration was underway as hundreds of thousands of African Americans relocated to cities like Chicago, Los Angeles, Detroit, Philadelphia, and New York. The Harlem section of Manhattan, which covers just three square miles, drew nearly 175,000 African Americans, giving the neighborhood the largest concentration of black people in the world. Harlem became a destination for African Americans of all backgrounds. From unskilled laborers to an educated middle-class, they shared common experiences of slavery, emancipation, and racial oppression, as well as a determination to forge a new identity as free people.
The Great Migration drew to Harlem some of the greatest minds and brightest talents of the day, an astonishing array of African American artists and scholars. Between the end of World War I and the mid-1930s, they produced one of the most significant eras of cultural expression in the nation’s history—the Harlem Renaissance. Yet this cultural explosion also occurred in Cleveland, Los Angeles and many cities shaped by the great migration. Alain Locke, a Harvard-educated writer, critic, and teacher who became known as the “dean” of the Harlem Renaissance, described it as a “spiritual coming of age” in which African Americans transformed “social disillusionment to race pride.”
The Harlem Renaissance encompassed poetry and prose, painting and sculpture, jazz and swing, opera and dance. What united these diverse art forms was their realistic presentation of what it meant to be black in America, what writer Langston Hughes called an “expression of our individual dark-skinned selves,” as well as a new militancy in asserting their civil and political rights.
Among the Renaissance’s most significant contributors were intellectuals W.E.B. Du Bois, Marcus Garvey, Cyril Briggs, and Walter Francis White; electrifying performers Josephine Baker and Paul Robeson; writers and poets Zora Neale Hurston, Effie Lee Newsome, Countee Cullen; visual artists Aaron Douglas and Augusta Savage; and an extraordinary list of legendary musicians, including Louis Armstrong, Count Basie, Eubie Blake, Cab Calloway, Duke Ellington, Billie Holiday, Ivie Anderson, Josephine Baker, Fats Waller, Jelly Roll Morton, and countless others.

Josaphine Baker
At the height of the movement, Harlem was the epicenter of American culture. The neighborhood bustled with African American-owned and run publishing houses and newspapers, music companies, playhouses, nightclubs, and cabarets. The literature, music, and fashion they created defined culture and “cool” for blacks and white alike, in America and around the world.
As the 1920s came to a close, so did the Harlem Renaissance. Its heyday was cut short largely due to the Stock Market Crash of 1929 and resulting Great Depression, which hurt African American-owned businesses and publications and made less financial support for the arts available from patrons, foundations, and theatrical organizations.
However, the Harlem Renaissance’s impact on America was indelible. The movement brought notice to the great works of African American art, and inspired and influenced future generations of African American artists and intellectuals. The self-portrait of African American life, identity, and culture that emerged from Harlem was transmitted to the world at large, challenging the racist and disparaging stereotypes of the Jim Crow South. In doing so, it radically redefined how people of other races viewed African Americans and understood the African American experience.
Most importantly, the Harlem Renaissance instilled in African Americans across the country a new spirit of self-determination and pride, a new social consciousness, and a new commitment to political activism, all of which would provide a foundation for the Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s. In doing so, it validated the beliefs of its founders and leaders like Alain Locke and Langston Hughes that art could be a vehicle to improve the lives of the African Americans.

Gallery Modal
Subtitle here for the credits modal..
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Indian government ordered killings in Pakistan, intelligence officials claim
Allegations of up to 20 assassinations since 2020 follow Canada’s accusation of Delhi role in murders of dissidents
The Indian government assassinated individuals in Pakistan as part of a wider strategy to eliminate terrorists living on foreign soil, according to Indian and Pakistani intelligence operatives who spoke to the Guardian.
Interviews with intelligence officials in both countries, as well as documents shared by Pakistani investigators, shed new light on how India’s foreign intelligence agency allegedly began to carry out assassinations abroad as part of an emboldened approach to national security after 2019. The agency, the Research & Analysis Wing (Raw), is directly controlled by the office of India’s prime minister, Narendra Modi, who is running for a third term in office in elections later this month.
The accounts appear to give further weight to allegations that Delhi has implemented a policy of targeting those it considers hostile to India. While the new allegations refer to individuals charged with serious and violent terror offences, India has also been accused publicly by Washington and Ottawa of involvement in the murders of dissident figures including a Sikh activist in Canada and of a botched assassination attempt on another Sikh in the US last year.
The fresh claims relate to almost 20 killings since 2020, carried out by unknown gunmen in Pakistan. While India has previously been unofficially linked to the deaths, this is the first time Indian intelligence personnel have discussed the alleged operations in Pakistan, and detailed documentation has been seen alleging Raw’s direct involvement in the assassinations.
The allegations also suggest that Sikh separatists in the Khalistan movement were targeted as part of these Indian foreign operations, both in Pakistan and the west.
According to Pakistani investigators, these deaths were orchestrated by Indian intelligence sleeper-cells mostly operating out of the United Arab Emirates. The rise in killings in 2023 was credited to the increased activity of these cells, which are accused of paying millions of rupees to local criminals or poor Pakistanis to carry out the assassinations. Indian agents also allegedly recruited jihadists to carry out the shootings, making them believe they were killing “infidels”.

According to two Indian intelligence officers, the spy agency’s shift to focusing on dissidents abroad was triggered by the Pulwama attack in 2019 , when a suicide bomber targeted a military convoy in Indian-administered Kashmir, killing 40 paramilitary personnel. The Pakistan-based terror group Jaish-e-Mohammed claimed responsibility.
Modi was running for a second term at the time and was brought back to power in the aftermath of the attack.
“After Pulwama, the approach changed to target the elements outside the country before they are able to launch an attack or create any disturbance,” one Indian intelligence operative said. “We could not stop the attacks because ultimately their safe havens were in Pakistan, so we had to get to the source.”
To conduct such operations “needed approval from the highest level of government”, he added.
The officer said India had drawn inspiration from intelligence agencies such as Israel’s the Mossad and Russia’s KGB, which have been linked to extrajudicial killings on foreign soil. He also said the killing of the Saudi journalist and dissident Jamal Khashoggi, who was murdered in 2018 in the Saudi embassy, had been directly cited by Raw officials.
“It was a few months after the killing of Jamal Khashoggi that there was a debate among the top brass of intelligence in the prime minister’s office about how something can be learned from the case. One senior officer said in a meeting that if Saudis can do this, why not us?” he recounted.
“What the Saudis did was very effective. You not only get rid of your enemy but send a chilling message, a warning to the people working against you. Every intelligence agency has been doing this. Our country cannot be strong without exerting power over our enemies.”
Senior officials from two separate Pakistani intelligence agencies said they suspected India’s involvement in up to 20 killings since 2020. They pointed to evidence relating to previously undisclosed inquiries into seven of the cases – including witness testimonies, arrest records, financial statements, WhatsApp messages and passports – which investigators say showcase in detail the operations conducted by Indian spies to assassinate targets on Pakistani soil. The Guardian has seen the documents but they could not be independently verified.

The intelligence sources claimed that targeted assassinations increased significantly in 2023, accusing India of involvement in the suspected deaths of about 15 people, most of whom were shot at close range by unknown gunmen.
In a response to the Guardian, India’s ministry of external affairs denied all the allegations, reiterating an earlier statement that they were “false and malicious anti-India propaganda”. The ministry emphasised a previous denial made by India’s foreign minister, Subrahmanyam Jaishankar, that targeted killings in other countries were “not the government of India’s policy”.
In the killing of Zahid Akhund , an alias for the convicted Kashmiri terrorist Zahoor Mistry who was involved in the deadly hijacking of an Air India flight, the Pakistani documents say a Raw handler allegedly paid for information on Akhund’s movements and location over a period of months. She then allegedly contacted him directly, pretending to be a journalist who wanted to interview a terrorist, in order to confirm his identity.
“Are you Zahid? I am a journalist from the New York Post,” read messages in the dossier shown to the Guardian. Zahid is said to have responded: “For what u r messaging me?”
Millions of rupees were then allegedly paid to Afghan nationals to carry out the shooting in Karachi in March 2022. They fled over the border but their handlers were later arrested by Pakistani security agencies .
According to the evidence gathered by Pakistan, the killings were regularly coordinated out of the UAE, where Raw established sleeper cells that would separately arrange different parts of the operation and recruit the killers.
Investigators alleged that millions of rupees would often be paid to criminals or impoverished locals to carry out the murders, with documents claiming that payments were mostly done via Dubai. Meetings of Raw handlers overseeing the killings are also said to have taken also place in Nepal, the Maldives and Mauritius.
“This policy of Indian agents organising killings in Pakistan hasn’t been developed overnight,” said a Pakistani official. “We believe they have worked for around two years to establish these sleeper cells in the UAE who are mostly organising the executions. After that, we began witnessing many killings.”

In the case of Shahid Latif , the commander of Jaish-e-Mohammed and one of India’s most notorious militants, several attempts were allegedly made to kill him. In the end, the documents claim, it was an illiterate 20-year-old Pakistani who carried out the assassination in Pakistan in October, allegedly recruited by Raw in the UAE, where he was working for a minimal salary in an Amazon packing warehouse.
Pakistani investigators found that the man had allegedly been paid 1.5m Pakistani rupees (£4,000) by an undercover Indian agent to track down Latif and later was promised 15m Pakistani rupees and his own catering company in the UAE if he carried out the killing. The young man shot Latif dead in a mosque in Sialkot but was arrested soon after, along with accomplices.
The killings of Bashir Ahmad Peer , commander of the militant outfit Hizbul Mujahideen, and Saleem Rehmani, who was on India’s most-wanted list, were also allegedly planned out of the UAE, with transaction receipts from Dubai appearing to show payments of millions of rupees to the killers. Rehmani’s death had previously been reported as the result of a suspected armed robbery .
Analysts believe Pakistani authorities have been reluctant to publicly acknowledge the killings as most of the targets are known terrorists and associates of outlawed militant groups that Islamabad has long denied sheltering.
In most cases, public information about their deaths has been scant. However, Pakistani agencies showed evidence they had conducted investigations and arrests behind closed doors.
The figures given to the Guardian match up with those collated by analysts who have been tracking unclaimed militant killings in Pakistan. Ajay Sahni, the executive director of the Institute for Conflict Management in Delhi, said his organisation had documented 20 suspicious fatalities in Pakistan by unknown attackers since 2020, though two had been claimed by local militant groups. He emphasised that because of Pakistan’s refusal to publicly investigate the cases – or even acknowledge that these individuals had been living in their jurisdiction – “we have no way of knowing the cause”.
“If you look at the numbers, there is clearly a shift in intent by someone or other,” said Sahni. “It would be in Pakistan’s interest to say this has been done by India. Equally, one of the legitimate lines of inquiry would be possible involvement of the Indian agencies.”
Pakistan’s foreign secretary, Muhammad Syrus Sajjad Qazi, publicly acknowledged two of the killings in a press conference in January, where he accused India of carrying out a “sophisticated and sinister” campaign of “extraterritorial and extrajudicial killings” in Pakistan.
Islamabad’s accusations were met with scepticism by others, due to the longstanding animosity between the two neighbouring countries who have gone to war four times and have often made unsubstantiated accusations against the other.
For decades India has accused Pakistan of bankrolling a violent militant insurgency in the disputed region of Indian-administered Kashmir and of giving a safe haven to terrorists. In the early 2000s, India was hit by successive terrorist attacks orchestrated by Pakistan-based Islamist militant groups, including the 2006 Mumbai train blasts , which killed more than 160 people, and the 2008 Mumbai bombings , which killed 172 people.
Both countries are known to have carried out cross-border intelligence operations, including small bomb blasts. However, analysts and Pakistani officials described the alleged systematic targeted killings of dissidents by Indian agents on Pakistani soil since 2020 as “new and unprecedented”.
The majority of those allegedly killed by Raw in Pakistan in the past three years have been individuals associated with militant groups such as Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed, and in several cases have convictions or proven links to some of India’s deadliest terrorist incidents, which have killed hundreds of people. Others were seen to be “handlers” of Kashmiri militants who helped coordinate attacks and spread information from afar.
According to one of the Indian intelligence officers, the Pulwama attack in 2019 prompted fears that militant groups in Pakistan were planning a repeat of attacks such as the 2008 Mumbai bombings.
“The previous approach had been to foil terrorist attacks,” he said. “But while we were able to make significant progress in bringing the terrorist numbers down in Kashmir, the problem was the handlers in Pakistan. We could not just wait for another Mumbai or an attack on parliament when we are aware that the planners were still operating in Pakistan.”
In September, the Canadian prime minister, Justin Trudeau, told parliament there were “credible allegations” that Indian agents had orchestrated the killing of Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a prominent Sikh activist who was gunned down in Vancouver. Weeks later, the US Department of Justice released an indictment vividly detailing how an Indian agent had attempted to recruit a hitman in New York to kill another Sikh activist, later named as Gurpatwant Singh Pannun.

Both men had been major advocates of the Khalistan movement , which seeks to create an independent Sikh state and is illegal in India. India denied any involvement in the killing of Nijjar, while according to a recent report , India’s own investigation into the Pannun plot concluded that it had been carried out by a rogue agent who was no longer working for Raw.
According to one Indian intelligence official, Delhi recently ordered the suspension of targeted killings in Pakistan after Canada and the US went public with their allegations. No suspicious killings have taken place so far this year.
Two Indian operatives separately confirmed that diaspora Khalistani activists had become a focus of India’s foreign operations after hundreds of thousands of farmers, mostly Sikhs from Punjab, descended on Delhi to protest against new farm laws. The protest ultimately forced the government into a rare policy U-turn, which was seen as an embarrassment .
The suspicion in Delhi was that firebrand Sikh activists living abroad, particularly those in Canada, the US and the UK, were fuelling the farmers’ protests and stirring up international support through their strong global networks. It stoked fears that these activists could be a destabilising force and were capable of reviving Khalistani militancy in India.
“Places were raided and people were arrested in Punjab, but things were actually being controlled from places like Canada,” said one of the Indian intelligence operatives. “Like other intelligence agencies, we had to deal with it.”
In the UK, Sikhs in the West Midlands were issued “threat to life” warnings, amid growing concern about the safety of separatist campaigners who Sikhs claim are being targeted by the Indian government.

Before the US and Canadian cases, a high-profile Khalistani leader, Paramjit Singh Panjwar , was shot dead in Lahore last May. Pakistani investigators claimed they had warned Panjwar that his life was in danger a month before he was killed and said another Khalistani activist living in Pakistan has also faced threats to his life.
Panjwar’s assassination is among those alleged to have been carried out by Indian operatives using what Pakistani agencies described as the “religious method”. According to the documents, Indian agents used social media to infiltrate networks of Islamic State (IS) and units connected to the Taliban, where they recruited and groomed Pakistani Islamist radicals to carry out hit jobs on Indian dissidents by telling them they were carrying out “sacred killings” of “infidels”.
These agents allegedly sought help from former IS fighters from the Indian state of Kerala – who had travelled to Afghanistan to fight for IS but surrendered after 2019 and were brought back through diplomatic channels – to get access to these jihadist networks.
According to an investigation by the Pakistani agencies, Panjwar’s killer, who was later caught, allegedly thought he was working on the instructions of the Pakistan Taliban affiliate Badri 313 Battalion and had to prove himself by killing an enemy of Islam.
The killing of Riyaz Ahmad , a top Lashkar-e-Taiba commander, in September last year was allegedly carried out by Raw in a similar manner. His killer, Pakistan believes, was recruited through a Telegram channel for those who wanted to fight for IS, and which had been infiltrated by Raw agents.
They have claimed the assassin was Muhammad Abdullah, a 20-year-old from Lahore. He allegedly told Pakistani investigators he was promised he would be sent to Afghanistan to fight for IS if he passed the test of killing an “infidel” in Pakistan, with Ahmed presented as the target. Abdullah shot and killed Ahmed during early morning prayers at a mosque in Rawalkot, but was later arrested by Pakistani authorities.
Walter Ladwig, a political scientist at King’s College London, said the alleged shift in strategy was in line with Modi’s more aggressive approach to foreign policy and that just as western states have been accused of extrajudicial killings abroad in the name of national security, there were those in Delhi who felt “India reserves the right to do the same”.
Daniel Markey, a senior adviser on south Asia at the United States Institute of Peace, said: “In terms of India’s involvement, it all kind of adds up. It’s utterly consistent with this framing of India having arrived on the world stage. Being willing to take this kind of action against perceived threats has been interpreted, at least by some Indians, as a marker of great power status.”
The allegations of extrajudicial killings, which would violate international law, could raise difficult questions for western countries that have pursued an increasingly close strategic and economic relationship with Modi and his Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata party (BJP) government, including pushing for intelligence-sharing agreements.
A former senior Raw official who served before Modi’s premiership denied that extrajudicial killings were part of the agency’s remit. He confirmed that nothing would be done without the knowledge of the national security adviser, who would then report it to the prime minister, and on occasion they would report directly to the prime minister. “I could not do anything without their approval,” he said.
The former Raw official claimed that the killings were more likely to have been carried out by Pakistan themselves, a view that has been echoed by others in India.
Pakistani agencies denied this, pointing to a list of more than two dozen dissidents living in Pakistan to whom they had recently issued direct warnings of threats to their lives and instructed them to go into hiding. Three individuals in Pakistan said they had been given these warnings. They claimed others who had not heeded the threats and continued their normal routines were now dead.
- South and central Asia
Most viewed
What is the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse?

It almost time! Millions of Americans across the country Monday are preparing to witness the once-in-a-lifetime total solar eclipse as it passes over portions of Mexico, the United States and Canada.
It's a sight to behold and people have now long been eagerly awaiting what will be their only chance until 2044 to witness totality, whereby the moon will completely block the sun's disc, ushering in uncharacteristic darkness.
That being said, many are curious on what makes the solar eclipse special and how is it different from a lunar eclipse.
The total solar eclipse is today: Get the latest forecast and everything you need to know
What is an eclipse?
An eclipse occurs when any celestial object like a moon or a planet passes between two other bodies, obscuring the view of objects like the sun, according to NASA .
What is a solar eclipse?
A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon comes in between the Earth and the sun, blocking its light from reaching our planet, leading to a period of darkness lasting several minutes. The resulting "totality," whereby observers can see the outermost layer of the sun's atmosphere, known as the corona, presents a spectacular sight for viewers and confuses animals – causing nocturnal creatures to stir and bird and insects to fall silent.
Partial eclipses, when some part of the sun remains visible, are the most common, making total eclipses a rare sight.
What is a lunar eclipse?
A total lunar eclipse occurs when the moon and the sun are on exact opposite sides of Earth. When this happens, Earth blocks the sunlight that normally reaches the moon. Instead of that sunlight hitting the moon’s surface, Earth's shadow falls on it.
Lunar eclipses are often also referred to the "blood moon" because when the Earth's shadow covers the moon, it often produces a red color. The coloration happens because a bit of reddish sunlight still reaches the moon's surface, even though it's in Earth's shadow.
Difference between lunar eclipse and solar eclipse
The major difference between the two eclipses is in the positioning of the sun, the moon and the Earth and the longevity of the phenomenon, according to NASA.
A lunar eclipse can last for a few hours, while a solar eclipse lasts only a few minutes. Solar eclipses also rarely occur, while lunar eclipses are comparatively more frequent. While at least two partial lunar eclipses happen every year, total lunar eclipses are still rare, says NASA.
Another major difference between the two is that for lunar eclipses, no special glasses or gizmos are needed to view the spectacle and one can directly stare at the moon. However, for solar eclipses, it is pertinent to wear proper viewing glasses and take the necessary safety precautions because the powerful rays of the sun can burn and damage your retinas.
Contributing: Eric Lagatta, Doyle Rice, USA TODAY
Advertisement
What Solar Eclipse-Gazing Has Looked Like for the Past 2 Centuries
Millions of people on Monday will continue the tradition of experiencing and capturing solar eclipses, a pursuit that has spawned a lot of unusual gear.
- Share full article

By Sarah Eckinger
- April 8, 2024
For centuries, people have been clamoring to glimpse solar eclipses. From astronomers with custom-built photographic equipment to groups huddled together with special glasses, this spectacle has captivated the human imagination.
Creating a Permanent Record
In 1860, Warren de la Rue captured what many sources describe as the first photograph of a total solar eclipse . He took it in Rivabellosa, Spain, with an instrument known as the Kew Photoheliograph . This combination of a telescope and camera was specifically built to photograph the sun.
Forty years later, Nevil Maskelyne, a magician and an astronomy enthusiast, filmed a total solar eclipse in North Carolina. The footage was lost, however, and only released in 2019 after it was rediscovered in the Royal Astronomical Society’s archives.

Telescopic Vision
For scientists and astronomers, eclipses provide an opportunity not only to view the moon’s umbra and gaze at the sun’s corona, but also to make observations that further their studies. Many observatories, or friendly neighbors with a telescope, also make their instruments available to the public during eclipses.
Fredrik Hjalmar Johansen, Fridtjof Nansen and Sigurd Scott Hansen observing a solar eclipse while on a polar expedition in 1894 .
Women from Wellesley College in Massachusetts and their professor tested out equipment ahead of their eclipse trip (to “catch old Sol in the act,” as the original New York Times article phrased it) to New London, Conn., in 1922.
A group from Swarthmore College in Pennsylvania traveled to Yerbaniz, Mexico, in 1923, with telescopes and a 65-foot camera to observe the sun’s corona .
Dr. J.J. Nassau, director of the Warner and Swasey Observatory at Case School of Applied Science in Cleveland, prepared to head to Douglas Hill, Maine, to study an eclipse in 1932. An entire freight car was required to transport the institution’s equipment.
Visitors viewed a solar eclipse at an observatory in Berlin in the mid-1930s.
A family set up two telescopes in Bar Harbor, Maine, in 1963. The two children placed stones on the base to help steady them.
An astronomer examined equipment for an eclipse in a desert in Mauritania in June 1973. We credit the hot climate for his choice in outfit.
Indirect Light
If you see people on Monday sprinting to your local park clutching pieces of paper, or with a cardboard box of their head, they are probably planning to reflect or project images of the solar eclipse onto a surface.
Cynthia Goulakos demonstrated a safe way to view a solar eclipse , with two pieces of cardboard to create a reflection of the shadowed sun, in Lowell, Mass., in 1970.
Another popular option is to create a pinhole camera. This woman did so in Central Park in 1963 by using a paper cup with a small hole in the bottom and a twin-lens reflex camera.
Amateur astronomers viewed a partial eclipse, projected from a telescope onto a screen, from atop the Empire State Building in 1967 .
Back in Central Park, in 1970, Irving Schwartz and his wife reflected an eclipse onto a piece of paper by holding binoculars on the edge of a garbage basket.
Children in Denver in 1979 used cardboard viewing boxes and pieces of paper with small pinholes to view projections of a partial eclipse.
A crowd gathered around a basin of water dyed with dark ink, waiting for the reflection of a solar eclipse to appear, in Hanoi, Vietnam, in 1995.
Staring at the Sun (or, How Not to Burn Your Retinas)
Eclipse-gazers have used different methods to protect their eyes throughout the years, some safer than others .
In 1927, women gathered at a window in a building in London to watch a total eclipse through smoked glass. This was popularized in France in the 1700s , but fell out of favor when physicians began writing papers on children whose vision was damaged.
Another trend was to use a strip of exposed photographic film, as seen below in Sydney, Australia, in 1948 and in Turkana, Kenya, in 1963. This method, which was even suggested by The Times in 1979 , has since been declared unsafe.
Solar eclipse glasses are a popular and safe way to view the event ( if you use models compliant with international safety standards ). Over the years there have been various styles, including these large hand-held options found in West Palm Beach, Fla., in 1979.
Parents and children watched a partial eclipse through their eclipse glasses in Tokyo in 1981.
Slimmer, more colorful options were used in Nabusimake, Colombia, in 1998.
In France in 1999.
And in Iran and England in 1999.
And the best way to see the eclipse? With family and friends at a watch party, like this one in Isalo National Park in Madagascar in 2001.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
AT&T says a data breach leaked millions of customers’ information online. Were you affected?
FILE - The sign in front of an AT&T retail store is seen in Miami, July 18, 2019. The theft of sensitive information belonging to millions of AT&T’s current and former customers has been recently discovered online, the telecommunications giant said Saturday, March 30, 2024. In an announcement addressing the data breach, AT&T said that a dataset found on the dark web contains information including some Social Security numbers and passcodes for about 7.6 million current account holders and 65.4 million former account holders. (AP Photo/Lynne Sladky, File)
- Copy Link copied
NEW YORK (AP) — The theft of sensitive information belonging to millions of AT&T’s current and former customers has been recently discovered online, the telecommunications giant said this weekend.
In a Saturday announcement addressing the data breach, AT&T said that a dataset found on the “dark web” contains information including some Social Security numbers and passcodes for about 7.6 million current account holders and 65.4 million former account holders.
Whether the data “originated from AT&T or one of its vendors” is still unknown, the Dallas-based company noted — adding that it had launched an investigation into the incident. AT&T has also begun notifying customers whose personal information was compromised.
Here’s what you need to know.
WHAT INFORMATION WAS COMPROMISED IN THIS BREACH?
Although varying by each customer and account, AT&T says that information involved in this breach included Social Security numbers and passcodes — which, unlike passwords, are numerical PINS that are typically four digits long.
Full names, email addresses, mailing address, phone numbers, dates of birth and AT&T account numbers may have also been compromised. The impacted data is from 2019 or earlier and does not appear to include financial information or call history, the company said.
HOW DO I KNOW IF I WAS AFFECTED?
Consumers impacted by this breach should be receiving an email or letter directly from AT&T about the incident. The email notices began going out on Saturday, an AT&T spokesperson confirmed to The Associated Press.
WHAT ACTION HAS AT&T TAKEN?
Beyond these notifications, AT&T said that it had already reset the passcodes of current users. The company added that it would pay for credit monitoring services where applicable.
AT&T also said that it “launched a robust investigation” with internal and external cybersecurity experts to investigate the situation further.
HAS AT&T SEEN DATA BREACHES LIKE THIS BEFORE?
AT&T has seen several data breaches that range in size and impact over the years .
While the company says the data in this latest breach surfaced on a hacking forum nearly two weeks ago, it closely resembles a similar breach that surfaced in 2021 but which AT&T never acknowledged, cybersecurity researcher Troy Hunt told the AP Saturday.
“If they assess this and they made the wrong call on it, and we’ve had a course of years pass without them being able to notify impacted customers,” then it’s likely the company will soon face class action lawsuits, said Hunt, founder of an Australia-based website that warns people when their personal information has been exposed.
A spokesperson for AT&T declined to comment further when asked about these similarities Sunday.
HOW CAN I PROTECT MYSELF GOING FORWARD?
Avoiding data breaches entirely can be tricky in our ever-digitized world, but consumers can take some steps to help protect themselves going forward.
The basics include creating hard-to-guess passwords and using multifactor authentication when possible. If you receive a notice about a breach, it’s good idea to change your password and monitor account activity for any suspicious transactions. You’ll also want to visit a company’s official website for reliable contact information — as scammers sometimes try to take advantage of news like data breaches to gain your trust through look-alike phishing emails or phone calls.
In addition, the Federal Trade Commission notes that nationwide credit bureaus — such as Equifax, Experian and TransUnion — offer free credit freezes and fraud alerts that consumers can set up to help protect themselves from identity theft and other malicious activity.
AP Reporter Matt O’Brien contributed to this report from Providence, Rhode Island.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The characters who make up the cast of Tommy Orange's novel There There are wildly different—but they all share a tense relationship to the intersection of their cultural identity as Native Americans and their personal identities. Orvil Red Feather, Blue, and Edwin Black are each shown worrying that they are not "Native enough," or are Native in the wrong ways—and must reconcile what ...
There, There by Tommy Orange Essay bri sanchez october 2021 identity is huge topic that we as society do not take seriously enough. most people believe that ... Tommy Orange writes about indigenous people in his book titled "There, There" and their struggles with living in today's society and tells them in many different perspectives to ...
Start an essay Ask a question ... the characters of There There are united by their struggles in identity. Characters like Blue, Orvil, Edwin, Calvin, and Thomas grew up separated from their ...
Orange's novel is about the experience of urban Indians: every one of his characters has grown up in a city—specifically, Oakland—rather than a reservation. The novel thus challenges the stereotype afflicting white America that depicts Native life as solely revolving around the reservation. Tony, for example, loves to ride his bicycle ...
The main themes of There There are coming to terms with identity, the effect of the past on the present and future, and the power of culture to unite. Coming to terms with identity: The novel's ...
There There by Tommy Orange Questions and Topics for Discussion. 1. The prologue of There There provides a historical overview of how Native populations were systematically stripped of their identity, their rights, their land, and, in some cases, their very existence by colonialist forces in America. How did reading this section make you feel?
3. 📌Published: 18 June 2022. Characters in "There There" struggle with finding their identity and people today struggle with it too. "There There" is about different characters who are trying to figure out their true Indian identity. All these perspectives are led up to the characters coming together to honor the past traditions that ...
There There Essay Questions. 1. Analyze the prologue of There There in terms of both form and content. Why might Tommy Orange have chosen to begin his novel with this type of prologue? The choice to begin a novel with a critical essay is a bold one. However, in this case, it is necessary: Orange cannot rely on the general public's knowledge of ...
There There Summary. In the weeks leading up to the Big Oakland Powwow, a disparate but interconnected group of urban Native Americans living in Oakland prepare for the festivities, working through the losses and traumas they've suffered both in their own lifetimes and through the inheritance of an overwhelmingly painful cultural legacy of ...
Essay Topics. 1. The young men who rob the powwow do so for a variety of reasons. Using their narrative sections as a guide, explore the historical and sociocultural reasons that cause each to participate in this violent act. 2.
2.2 Identity Trailblazer: Cathy Park Hong; 2.3 Glance at the Issues: Oppression and Reclamation; 2.4 Annotated Sample Reading from The Souls of Black Folk by W. E. B. Du Bois; 2.5 Writing Process: Thinking Critically about How Identity Is Constructed Through Writing; 2.6 Evaluation: Antiracism and Inclusivity; 2.7 Spotlight on … Variations of ...
Identity is made up of many qualities: personality, culture, ethnic or racial background, sexual orientation, gender, physical ability, and linguistic background, among others. Maybe you identify really strongly with the religion on Mom's side of the family, but not Dad's. Maybe you speak a language not typical of folks from your culture.
I'm glad to see that you're considering writing about your identity, as it's an important part of who you are. To avoid sounding cliché or overly dramatic, there are a few tips I'd like to share with you. First, focus on specific experiences or moments that have shaped your identity. Instead of making general statements, think about the events ...
Here, a cultural identity essay prompt may require students to discuss the significance of culture in education, focusing on cultural identity and socialization. As such, this topic requires writers to reflect on how culture influences behavior in a learning environment. 2. The Impact of Culture Change on Family.
Just as a body is a highly complex, organised network of organismic and molecular systems, the self is a highly organised network. Traits of the self can organise into clusters or hubs, such as a body cluster, a family cluster, a social cluster. There might be other clusters, but keeping it to a few is sufficient to illustrate the idea.
The Importance of Identity. Having a strong sense of identity is important because it: Creates self-awareness: A strong sense of identity can give you a deep sense of awareness of who you are as a person. It can help you understand your likes, dislikes, actions, motivations, and relationships. Provides direction and motivation: Having a strong ...
That's all you need for your essay — short introductory and concluding paragraphs and three concise body paragraphs. Step 2. Select your main idea and supporting points. You need to come up with a central idea that will give you a frame of reference for the rest of your essay.
Сultural Identity Essay Examples. First and foremost, a cultural identity essay is the one where you share your vision of the world and personality. Below is an example that you might consider when writing your next cultural identity essay. I was born in Italy to a German family. My mother comes from the capital of Germany - Berlin, while my ...
Once students start working on applications, there are several places identity may come forward in their materials: Most college essays, including the main Common Application essay and University of California Personal Insight Questions, invite broad reflection on experiences which can be linked to student identity.
The intricate relationship between language and racial or ethnic identity is undeniable. An individual's history shapes their language, leading to those with similar racial backgrounds often using similar languages for communication. One's mother tongue, acquired at birth, is a fundamental aspect of racial identity, providing a crucial ...
6 pages / 2536 words. Frozen River reflects the complexities of cultural identities in America by showing us many examples of privilege, hard times, problems, racism, prejudice and alliance. It shows us different perspectives on multiple problems. In the time and society that the movie was taken place in shows...
Aims. In this chapter we focus on how writers' explicit self-representation in their texts contributes to constructing their identities. To do this, we examine two aspects of self-representation in the writers' essays: (1) functions of first-person pronouns, and (2) use of first-person opinion qualifiers.
The Great Migration drew to Harlem some of the greatest minds and brightest talents of the day, an astonishing array of African American artists and scholars. Between the end of World War I and the mid-1930s, they produced one of the most significant eras of cultural expression in the nation's history—the Harlem Renaissance. Yet this cultural explosion also occurred in Cleveland, Los ...
Forrester's Top Trends In IoT Security In 2024 report provides insights into nine trends defining the current landscape and future direction of IoT security. The study found that 34% of ...
Allegations of up to 20 assassinations since 2020 follow Canada's accusation of Delhi role in murders of dissidents
Meanwhile, there was a partial mediating effect of self-directed learning ability between professional identity and burnout (-0.24, 95% CI = -0.30, -0.20). Conclusions. Nursing educators should emphasize on developing effective strategies to improve nursing students' professional identity and self-directed learning ability to prevent or reduce ...
The major difference between the two eclipses is in the positioning of the sun, the moon and the Earth and the longevity of the phenomenon, according to NASA. A lunar eclipse can last for a few ...
Eclipse-gazers have used different methods to protect their eyes throughout the years, some safer than others. In 1927, women gathered at a window in a building in London to watch a total eclipse ...
NEW YORK (AP) — The theft of sensitive information belonging to millions of AT&T's current and former customers has been recently discovered online, the telecommunications giant said this weekend.. In a Saturday announcement addressing the data breach, AT&T said that a dataset found on the "dark web" contains information including some Social Security numbers and passcodes for about 7. ...