

Overleaf for LaTeX Theses & Dissertations: Home
- Using Templates on Overleaf
- Reference Managers and Overleaf
- Adding Tables, Images, and Graphs
Tips and tools for writing your LaTeX thesis or dissertation in Overleaf, including templates, managing references , and getting started guides.
Managing References
BibTeX is a file format used for lists of references for LaTeX documents. Many citation management tools support the ability to export and import lists of references in .bib format. Some reference management tools can generate BibTeX files of your library or folders for use in your LaTeX documents.
LaTeX on Wikibooks has a Bibliography Management page.
Find list of BibTeX styles available on Overleaf here
View a video tutorial on how to include a bibliography using BibTeX here
Collaborate with Overleaf
Collaboration tools
- One version of your project accessible to collaborators via a shared link or email invitation
- Easily select the level of access for collaborators (view, edit, or owner access)
- Real-time commenting speeds up the review process
- Tracked changes and full history view help to see contributions from collaborators
- Labels help to organize and compare different versions
- Chat in real time with collaborators right within the project
How to get started writing your thesis in LaTeX
Writing a thesis or dissertation in LaTeX can be challenging, but the end result is well worth it - nothing looks as good as a LaTeX-produced pdf, and for large documents it's a lot easier than fighting with formatting and cross-referencing in MS Word. Review this video from Overleaf to help you get started writing your thesis in LaTeX, using a standard thesis template from the Overleaf Gallery .
You can upload your own thesis template to the Overleaf Gallery if your university provides a set of LaTeX template files or you may find your university's thesis template already in the Overleaf Gallery.
This video assumes you've used LaTeX before and are familiar with the standard commands (see our other tutorial videos if not), and focuses on how to work with a large project split over multiple files.
Add Institutional Library contact info here.
Contact Overleaf or email [email protected]
5-part Guide on How to Write a Thesis in LaTeX
5-part LaTeX Thesis Writing Guide
Part 1: Basic Structure corresponding video
Part 2: Page Layout corresponding video
Part 3: Figures, Subfigures and Tables corresponding video
Part 4: Bibliographies with Biblatex corresponding video
Part 5: Customizing Your Title Page and Abstract corresponding video
ShareLaTeX Joins Overleaf!
Read more about Overleaf and ShareLaTeX joining forces here
Link your ORCiD ID
Link your ORCiD account to your Overleaf account.
See Overleaf news on our blog.
- Next: Using Templates on Overleaf >>
- Last Updated: May 18, 2021 1:57 PM
- URL: https://overleaf.libguides.com/Thesis
LaTeX-Tutorial.com
Bibliography in latex with bibtex/biblatex, learn how to create a bibliography with bibtex and biblatex in a few simple steps. create references / citations and autogenerate footnotes., creating a .bib file, using bibtex.
- Autogenerate footnotes with BibLaTeX
- BibTeX Format
BibTeX Styles
- New Post! Export Bibliographic Database (BibTeX) Entries from Online Databases
We have looked at many features of LaTeX so far and learned that many things are automated by LaTeX. There are functions to add a table of contents, lists of tables and figures and also several packages that allow us to generate a bibliography. I will describe how to use bibtex and biblatex (both external programs) to create the bibliography. At first we have to create a .bib file, which contains our bibliographic information.
A .bib file will contain the bibliographic information of our document. I will only give a simple example, since there are many tools to generate the entries automatically. I will not explain the structure of the file itself at this point, since i suggest using a bibtex generator (choose one from google). Our example will contain a single book and look like this:
If you don’t want to use a BibTeX generator or a reference management tool like Citavi (which generates BibTeX files automatically for you), you can find more examples of BibTeX formats here.
After creating the bibtex file, we have to tell LaTeX where to find our bibliographic database. For BibTeX this is not much different from printing the table of contents. We just need the commands \bibliography which tells LaTeX the location of our .bib file and \bibliographystyle which selects one of various bibliographic styles.
By using this code, we will obtain something like this:

I named my .bib file lesson7a1.bib, note that I did not enter the .bib extension. For the style, I’ve choosen the ieeetr style, which is very common for my subject, but there are many more styles available. Which will change the way our references look like. The ieeetr style will mark citations with successive numbers such as [1] in this example. If I choose the style to apalike instead, i will get the following result:

Most editors will let you select, to run bibtex automatically on compilation. In TeXworks (MiKTeX) for example, this should be selected by default.
If you use a different editor, it can be necessary to execute the bibtex command manually. In a command prompt/shell simply run:
It is necessary to execute the pdflatex command, before the bibtex command, to tell bibtex what literature we cited in our paper. Afterwards the .bib file will be translated into the proper output for out references section. The next two steps merge the reference section with our LaTeX document and then assign successive numbers in the last step.
Autogenerate footnotes in \(\LaTeX\) using BibLaTeX
The abilities of BibTeX are limited to basic styles as depicted in the examples shown above. Sometimes it is necessary to cite all literature in footnotes and maintaining all of them by hand can be a frustrating task. At this point BibLaTeX kicks in and does the work for us. The syntax varies a bit from the first document. We now have to include the biblatex package and use the \autocite and \printbibliography command. It is crucial to move the \bibliography{lesson7a1} statement to the preamble of our document:
The \autocite command generates the footnotes and we can enter a page number in the brackets \autocite[1]{DUMMY:1} will generate a footnote like this:
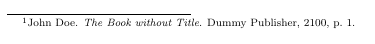
For BibLaTeX we have to choose the citation style on package inclusion with:
The backend=bibtex part makes sure to use BibTeX instead of Biber as our backend, since Biber fails to work in some editors like TeXworks. It took me a while to figure out how to generate footnotes automatically, because the sources I found on the internet, didn’t mention this at all.
BibTeX Formats
This is not meant to be a comprehensive list of BibTeX formats, but rather give you an idea of how to cite various sources properly. If you’re interested in an extensive overview of all BibTeX formats, I suggest you to check out the resources on Wikibooks.
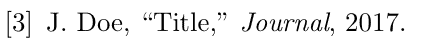
Inbook (specific pages)
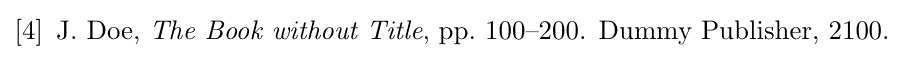
This is a list of the formats that I have most commonly used. If you think some important format is missing here, please let me know.
Here’s a quick overview of some popular styles to use with BibTeX.

I’m trying to keep this list updated with other commonly used styles. If you’re missing something here, please let me know.
- Generate a bibliography with BibTeX and BibLaTeX
- First define a .bib file using: \bibliography{BIB_FILE_NAME} (do not add .bib)
- For BibTeX put the \bibliography statement in your document , for BibLaTeX in the preamble
- BibTeX uses the \bibliographystyle command to set the citation style
- BibLaTeX chooses the style as an option like: \usepackage[backend=bibtex, style=verbose-trad2]{biblatex}
- BibTeX uses the \cite command, while BibLaTeX uses the \autocite command
- The \autocite command takes the page number as an option: \autocite[NUM]{}
Next Lesson: 08 Footnotes
- Basic remarks
- Bitmap fonts
- Page layout
Bibliography
- Footnote citing
Tips on Writing a Thesis in LaTeX

A typical scientific document contains a number of references, and this leads to the problem of organizing and presentation of the references in the document. The problem can be subdivided into several parts: store of the reference information, later retrieval of this information while preparing the document, and presentation (formatting) of the reference information in the document and in the bibliography according to a particular format.
A widely-used approach to deal with references in LaTeX documents is to employ BibTeX reference management software. In BibTeX reference information is stored in format-independent plain text file(s) (usually with .bib extension), which can be modified with almost any text editor. Such a text file contains BibTeX entries , and each entry, formed by several text lines, has
- unique ID or key , needed to identify and refer to the particular entry, for instance Author2001 ;
- entry type , which can be article , book , thesis , etc.;
- entry fields (such as year , publisher , journal , etc.), corresponding to the particular type.
Here is an example of the article type entry from the .bib file I used while typesetting thesis:
The command \bibliography { reference_list } placed before \begin { document } is used to specify a plain text input file ( reference_list.bib here) containing information on references.
References can be "cited" during editing the LaTeX document using, for example, \cite { key } command, and later at the document compilation step LaTeX input files must be processed with LaTeX and BibTeX .
The most popular approaches to indicate a reference appearing in the text can be classified as "numeric" and "author–year". The former uses sequential number of a reference in the document
while "author–year" is based on the extended reference information and may appear like this:
Each indication has particular advantages and drawbacks. For example, numeric is more compact (i.e., require less space in a text line), and a group of references can be "compressed" into a range in the case they have sequential numbering (i.e., [1,2,3,5] will be shown as [1–3,5]). On the other hand, author–year indication shows more information on the cited document (typically, first one or two author names, and a year of a publication), but requires more space compared to the numeric one. The space consumed by reference may become important if your document has high density of references (and you care about in-line space "wasted" by references :).
In my thesis I have decided to use "numeric" indication, but contrary to the example above reference numbers appear in the text as a footnote: reference number by itself has script size ,
and each number has associated script-sized text at the bottom of the page (where the reference appeared) containing extended information on the cited reference:
This citation scheme improves in-line space saving compared to the plain numeric indication due to the reduced size of numbers, and at the same time allows the reader to see what exactly was cited without looking in the bibliography (which is typically located at the end of a document or chapter). The drawback of the footnote citation scheme follows from the space consumed at the bottom of the page: if there are too many citations on the page, footnote text will occupy a lot of space. For example:
To create citations in my thesis, I employed the biblatex package, which is one of the most notable packages I have used with LaTeX. The package provides a highly customizable interface for the creation and edit of the presentation of bibliographic data in the document. Compared to the plain BibTeX, biblatex enables relatively easy customization of the appearance of bibliographic data. Below I provide customizations I used to modify the default biblatex output. The detailed description of the biblatex commands is available in the package documentation .
The two basic commands to enable biblatex and output citation list are
While preparing the thesis I activated biblatex with the following options compiling the document using biblatex with the options below will need custom-numeric-comp.bbx and custom-numeric-comp.cbx files (see next sections, "Biblatex customization" and "Footnote citation") :
Option hyperref=true was specified to transform various citation elements (like citation number, page number where citation appears, hyperlink to the web page where cited document can be found, etc.) into clickable hyperlinks. This option requires hyperref package (see also notes on hyperref ).
With options url=false,isbn=false I disabled printing the URLs and ISBNs in the bibliography.
Back references
Option backref=true enables generation of the back references to the citation, which are usually number(s) of the page where citation appears:
The back reference text preceding the page number ("see p.") can be modified using the following command:
Just a note on the back references. When you are reading a .pdf document, encounter a reference, and click on it, .pdf viewer will change view to the record of this reference in the bibliography. Now, if you want to return to the main text and continue reading, you may find it difficult to do using back reference when the reference was cited on several pages (back reference will contain several page numbers and you have to bear in mind the original page number you came to the bibliography), and a good solution here is to use " Alt + ← " instead of the back reference itself. On the other hand, back references are useful to indicate how often and where a particular reference was cited in the document.
Citation style
Option style=custom-numeric-comp determines the citation style. As seen from its name, the chosen citation style uses numbers ( numeric ) to indicate citations in text, and consequent numbers are compressed ( comp ) into a range: [1,2,3,5] is printed as [1–3,5]. Above it was mentioned that I used footnote version of the standard biblatex numeric-comp style — as a result, each citation has i) its number typeset as superscript, and ii) short and extended reference information located at the bottom of the page ("footnote text") and in the bibliography, respectively:
Option citereset=chapter defines biblatex behavior for the reference footnote text in a typical situation when a citation appears several times in the document: footnote text for the particular citation is printed only once per document chapter ( citereset=chapter ), where chapter is defined according to the LaTeX sectioning commands . In my thesis a typical chapter includes about 20 pages, and I assumed citereset=chapter to be quite acceptable. However, one of my colleagues was confused by such a rule for printing the footnote text (i.e., he did not get the logic behind the rule until I have explained it). I was thinking about resetting footnote text as "once-per-page" (not "once-per-chapter") but decided to avoid this due to high density of the references in my thesis. If you are interested in such a behavior some useful information can be found here .
Number of displayed author names
Options maxcitenames=3 and maxbibnames=100 limit number of authors of the cited document to be printed in the document body and in the bibliography, respectively. If the number of authors exceeds maxcite(bib)names , the author list is truncated according to biblatex settings, and usually printed as "Author1 et al." In my case I have very short authors lists in the footnote text (document body) to reduce space occupied by footnote citations,
and virtually all authors are displayed in the bibliography:
I note that I have prepared my thesis with biblatex v. 0.9a (19.03.2010), while this on-line document was prepared and tested on biblatex v. 1.6 (29.07.2011). Options maxcitenames and maxbibnames were not available in v. 0.9a, and the described biblatex behavior (with maxcitenames=3 and maxbibnames=100 ) was obtained using maxnames=3 while loading the biblatex package, and maxnames=100 while printing the bibliography, i.e.
The next section continues the discussion of the biblatex customization.
- KU Libraries
- Subject & Course Guides
- KU Thesis and Dissertation Formatting
- LaTeX/BibTeX Support
KU Thesis and Dissertation Formatting: LaTeX/BibTeX Support
- Formatting Specifics
- Title and Acceptance Pages
- Fonts and Spacing
- Page Numbering
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures
- Rotating Charts or Tables
- Working with Footnotes
- Converting to PDF
- Embedding Fonts
- Completed KU Dissertations & Theses
- About: Survey of Earned Doctorates
- Copyright and ETD Release Form
- Resources for KUMC Students
- Thesis/Dissertation Filenames
Are You a LaTeX/BibTeX User?
LaTeX/BibTeX Templates
Under "Support for Formatting Theses and Dissertations", there are some handy LaTeX thesis and dissertation templates:
- https://graduate.ku.edu/etd-formatting-and-working-multimedia-files
LaTeX/ BibTeX Libguide
Do you have a general question about how to use LaTeX? Here is a link to the KU libguide:
- https://guides.lib.ku.edu/LaTeX/BibTeX
- << Previous: Thesis/Dissertation Filenames
- Last Updated: Aug 25, 2023 10:49 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.ku.edu/etd
LaTeX Resources for Graduate Students: Formatting of theses and dissertations
- BibTeX reference format
- BibTeX command
- LaTeX bibliography file
- LaTeX editors and compilers
- Sample LaTeX file with bibliography
- Sample LaTeX file without bibliography
- Formatting of theses and dissertations
Formatting and structure
The Cornell Graduate School has become increasingly flexible about the formatting of theses and dissertations. There now are only seven core requirements . For the structure of theses and dissertations here is a list of required and recommended sections .
Latex template
Among the available thesis and dissertation templates provided by the Graduate School is also a LaTeX template (ZIP archive). This template has been uploaded to Overleaf and placed in the Cornell template directory . This template contains a small fix to avoid an error message about \ifpdf .
- << Previous: Sample LaTeX file without bibliography
- Last Updated: Oct 25, 2022 5:12 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/latex

- Register Forgot password
BibTeX Style Examples
Next: drawing in latex with tikz.


BibTeX mastersthesis template
The mastersthesis entry type is intended to be used for a Master's thesis.
Minimal template
Minimal template with required fields only for a BibTeX mastersthesis entry.
Full template
Full template including required and optional fields for a BibTeX mastersthesis entry.
No Search Results
How to Write a Thesis in LaTeX (Part 1): Basic Structure
Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | Part 4 | Part 5
Author: Josh Cassidy (August 2013)
This five-part series of articles uses a combination of video and textual descriptions to teach the basics of writing a thesis using LaTeX. These tutorials were first published on the original ShareLateX blog site during August 2013; consequently, today's editor interface (Overleaf) has changed considerably due to the development of ShareLaTeX and the subsequent merger of ShareLaTeX and Overleaf. However, much of the content is still relevant and teaches you some basic LaTeX—skills and expertise that will apply across all platforms.
Your thesis could be the longest and most complicated document you'll ever write, which is why it's such a good idea to use L a T e X instead of a common word processor. L a T e X makes tasks that are difficult and awkward in word processors, far simpler.
When writing something like a thesis its worth splitting up the document into multiple .tex files. It's also wise to organise the project using folders; therefore, we'll create two new folders, one for all the images used in the project and one for all the .tex files making up the main body of the thesis.

- 1 The preamble
- 2 The frontmatter
- 3 The main body
- 4 The endmatter
- 5 All articles in this series
The preamble
In this example, the main.tex file is the root document and is the .tex file that will draw the whole document together. The first thing we need to choose is a document class. The article class isn't designed for writing long documents (such as a thesis) so we'll choose the report class, but we could also choose the book class.
We can also change the font size by adding square brackets into the \documentclass command and specifying the size—we'll choose 12pt. Let's also prepare the document for images by loading the graphicx package. We'll also need to tell L a T e X where to look for the images using the \graphicspath command, as we're storing them in a separate folder.
The start of our preamble now looks like this:
Now we can finish off the preamble by filling in the title, author and date information. To create the simplest title page we can add the thesis title, institution name and institution logo all into the \title command; for example:
This isn't the best way to alter the title page so we'll look at more elaborate ways of customising title pages later on in the series, but this will suffice for now.
This is what the \maketitle command now produces for us:

The frontmatter
After the title page we need to add in an abstract, dedication, declaration and acknowledgements section. We can add each of these in on separate pages using unnumbered chapters. To do this we use the \chapter command and add an asterisk. After these sections we'll add a table of contents using the \tableofcontents command:
The main body
Now for the main body of the document. In this example we will add-in five chapters, one of which will be an introduction and another will be a conclusion. However, instead of just composing these chapters in the main .tex file, we'll create a separate .tex file for each chapter in the chapters folder. We can then fill in these chapters with text remembering to split them up into sections and subsections.

Then to add these chapters into the document, we use the \input command in the root document. Remember to add in chapters/ before the file name so that L a T e X knows where to find it.
The endmatter
We will now add in an appendix at the end of the document. To do this we use the \appendix command to tell L a T e X that what follows are appendices. Again We'll write the appendix in a separate file and then input it.
If we now compile the document, all our chapters will be added to the document and the table of contents will be automatically generated.

Now we have a basic structure for a thesis set up. In the next post I will show you how to change the page layout and add headers.
All articles in this series
- Part 1: Basic Structure ;
- Part 2: Page Layout ;
- Part 3: Figures, Subfigures and Tables ;
- Part 4: Bibliographies with BibLaTeX ;
- Part 5: Customising Your Title Page and Abstract .
- Documentation Home
- Learn LaTeX in 30 minutes
Overleaf guides
- Creating a document in Overleaf
- Uploading a project
- Copying a project
- Creating a project from a template
- Using the Overleaf project menu
- Including images in Overleaf
- Exporting your work from Overleaf
- Working offline in Overleaf
- Using Track Changes in Overleaf
- Using bibliographies in Overleaf
- Sharing your work with others
- Using the History feature
- Debugging Compilation timeout errors
- How-to guides
- Guide to Overleaf’s premium features
LaTeX Basics
- Creating your first LaTeX document
- Choosing a LaTeX Compiler
- Paragraphs and new lines
- Bold, italics and underlining
Mathematics
- Mathematical expressions
- Subscripts and superscripts
- Brackets and Parentheses
- Fractions and Binomials
- Aligning equations
- Spacing in math mode
- Integrals, sums and limits
- Display style in math mode
- List of Greek letters and math symbols
- Mathematical fonts
- Using the Symbol Palette in Overleaf
Figures and tables
- Inserting Images
- Positioning Images and Tables
- Lists of Tables and Figures
- Drawing Diagrams Directly in LaTeX
- TikZ package
References and Citations
- Bibliography management with bibtex
- Bibliography management with natbib
- Bibliography management with biblatex
- Bibtex bibliography styles
- Natbib bibliography styles
- Natbib citation styles
- Biblatex bibliography styles
- Biblatex citation styles
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using polyglossia and fontspec
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using babel and fontspec
- International language support
- Quotations and quotation marks
Document structure
- Sections and chapters
- Table of contents
- Cross referencing sections, equations and floats
- Nomenclatures
- Management in a large project
- Multi-file LaTeX projects
- Lengths in L a T e X
- Headers and footers
- Page numbering
- Paragraph formatting
- Line breaks and blank spaces
- Text alignment
- Page size and margins
- Single sided and double sided documents
- Multiple columns
- Code listing
- Code Highlighting with minted
- Using colours in LaTeX
- Margin notes
- Font sizes, families, and styles
- Font typefaces
- Supporting modern fonts with X Ǝ L a T e X
Presentations
- Environments
Field specific
- Theorems and proofs
- Chemistry formulae
- Feynman diagrams
- Molecular orbital diagrams
- Chess notation
- Knitting patterns
- CircuiTikz package
- Pgfplots package
- Typesetting exams in LaTeX
- Attribute Value Matrices
Class files
- Understanding packages and class files
- List of packages and class files
- Writing your own package
- Writing your own class
Advanced TeX/LaTeX
- In-depth technical articles on TeX/LaTeX
Have you checked our knowledge base ?
Message sent! Our team will review it and reply by email.
Guide to BibTeX Type MasterThesis
BibTeX is a reference management tool that is commonly used in LaTeX documents. The “masterthesis” BibTeX type is used for master’s theses. In this guide, we will explain the required and optional fields for the “masterthesis” BibTeX type.
Need a simple solution for managing your BibTeX entries? Explore CiteDrive!
- Web-based, modern reference management
- Collaborate and share with fellow researchers
- Integration with Overleaf
- Comprehensive BibTeX/BibLaTeX support
- Save articles and websites directly from your browser
- Search for new articles from a database of tens of millions of references
Required Fields
The “masterthesis” BibTeX type requires the following fields:
- author : The author of the thesis.
- title : The title of the thesis.
- school : The name of the institution that awarded the degree.
- year : The year the degree was awarded.
Optional Fields
In addition to the required fields, the “masterthesis” BibTeX type also has a number of optional fields that can be used to provide additional information. These fields include:
- type : The type of the thesis, such as “Master’s thesis”.
- address : The location of the institution.
- month : The month the thesis was submitted.
- note : Any additional information about the thesis.
Here is an example of how to use the “masterthesis” BibTeX type:
In this example, the BibTeX entry defines a master’s thesis authored by Jane Doe titled “A Study of Example”. The degree was awarded in 2022 by the University of Example, and the thesis was submitted in June in Example City, CA. The type of the thesis is specified as “Master’s thesis”, and a note is included that provides a URL for the thesis.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
By default, this thebibliography environment is a numbered list with labels [1], [2] and so forth. If the document class used is article, \begin{thebibliography} automatically inserts a numberless section heading with \refname (default value: References).If the document class is book or report, then a numberless chapter heading with \bibname (default value: Bibliography) is inserted instead.
BibTeX template files for @phdthesis: • author • title • school • year. The quick BibTeX guide All you ever need to know about ... The phdthesis entry type is intended to be used for a PhD thesis. Minimal template. Minimal template with required fields only for a BibTeX phdthesis entry. @phdthesis {citekey, author = "", title ...
Define a new bibstring diplomathesis and give it a useful replacement text. diplomathesis = {diploma thesis}, author = {Dagobert Duck}, title = {Seashells as Currency after the Brexit}, type = {diplomathesis}, % mathesis and phdthesis work here. institution = {University of Ducktown}, year = {2019}, The known strings are.
In the previous post we looked at using images and tables in our thesis. In this post we are going to look at adding a bibliography to our thesis. To do this we are going to use the biblatex package.This involves creating a list of sources in a separate file called a .bib file.. The Bib File
In this example, the BibTeX entry defines a PhD thesis authored by John Smith titled "An Analysis of Example". The degree was awarded in 2022 by the University of Example, and the thesis was submitted in June in Example City, CA. The type of the thesis is specified as "PhD thesis", and a note is included that provides a URL for the thesis.
Introduction. When it comes to bibliography-management packages, there are three main options in LaTeX: bibtex, natbib and biblatex. This article explains how to use the biblatex package, to manage and format the bibliography in a LaTeX document.biblatex is a modern option for processing bibliography information, provides an easier and more flexible interface and a better language localization ...
BibTeX is a file format used for lists of references for LaTeX documents. Many citation management tools support the ability to export and import lists of references in .bib format. Some reference management tools can generate BibTeX files of your library or folders for use in your LaTeX documents. LaTeX on Wikibooks has a Bibliography ...
Generating the Bibliography and References. The bibliography and list of references are generated by running BibTeX. To generate the bibliography, load the file thesisbib.tex into your editor, then run BibTeX on it. If each chapter has its own list of references, you will need to run BibTeX on each chapter to update its list of references.
Summary. Generate a bibliography with BibTeX and BibLaTeX. First define a .bib file using: \bibliography {BIB_FILE_NAME} (do not add .bib) For BibTeX put the \bibliography statement in your document, for BibLaTeX in the preamble. BibTeX uses the \bibliographystyle command to set the citation style.
Such a text file contains BibTeX entries, and each entry, formed by several text lines, has. unique ID or key, needed to identify and refer to the particular entry, for instance Author2001; entry type, which can be article, book, thesis, etc.; entry fields (such as year, publisher, journal, etc.), corresponding to the particular type.
KU Thesis and Dissertation Formatting: LaTeX/BibTeX Support Information for University of Kansas graduate students on required content order, page numbering, creating headings, formatting table of contents, adding captions, creating a table of figures and embedding fonts for theses and dissertations.
The 14 BibTeX entry types. Possibly the most difficult aspect of using BibTeX to manage bibliographies is deciding what entry type to use for a reference source. We list all the 14 BibTeX entry types including their description on when to use. article. An article from a journal, magazine, newspaper, or periodical.
BibTeX reference format; BibTeX command; LaTeX bibliography file; LaTeX editors and compilers; Sample LaTeX file with bibliography; ... Among the available thesis and dissertation templates provided by the Graduate School is also a LaTeX template (ZIP archive).
BibTeX Style Examples. Next: Drawing in LaTeX with TikZ. In the following section you see how different bibtex styles look in the resulting PDF. The style is defined in the \bibliographystyle { style } command where style is to be replaced with one of the following styles (e.g. alpha, etc.).
BibTeX template files for @mastersthesis: • author • title • school • year. The quick BibTeX guide All you ever need to know about ... BibTeX Format Templates. BibTeX mastersthesis template. The mastersthesis entry type is intended to be used for a Master's thesis. Minimal template. Minimal template with required fields only for a ...
The preamble. In this example, the main.tex file is the root document and is the .tex file that will draw the whole document together. The first thing we need to choose is a document class. The article class isn't designed for writing long documents (such as a thesis) so we'll choose the report class, but we could also choose the book class.. We can also change the font size by adding square ...
Information and discussion about BiBTeX - the bibliography tool for LaTeX documents. 1 post • Page 1 of 1. ... LaTeXTemplates_masters-doctoral-thesis_v2.5. Post by zimbodel » Wed Apr 10, 2024 12:58 pm . I am using the LaTeX Template masters/doctoral thesis package It can be downloaded from the web as LaTeXTemplates_masters-doctoral-thesis_v2 ...
In addition to the required fields, the "masterthesis" BibTeX type also has a number of optional fields that can be used to provide additional information. These fields include: type: The type of the thesis, such as "Master's thesis". address: The location of the institution. month: The month the thesis was submitted.
My bibliography at the end of the paper gets wrong. I'm using abntcite.sty. Here goes the code: @masterthesis{Filho2016Automatic, author = {Silva{ }Filho, P. F. F.}, institution = {Dissertação (Mestrado) - ITA}, pages = 159, school = {Dissertação (Mestrado) - ITA}, title = {Automatic Landmark Recognition in aerial images for the autonomous ...
23. Use @master s thesis (with an s after master) instead of @masterthesis (which doesn't exist and probably defaults to some other type), then school will appear. The entry type @unpublished doesn't support school, so I'd suggest using note instead, as is recommended in the biblatex documentation: