

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the complete ib extended essay guide: examples, topics, and ideas.
International Baccalaureate (IB)

IB students around the globe fear writing the Extended Essay, but it doesn't have to be a source of stress! In this article, I'll get you excited about writing your Extended Essay and provide you with the resources you need to get an A on it.
If you're reading this article, I'm going to assume you're an IB student getting ready to write your Extended Essay. If you're looking at this as a potential future IB student, I recommend reading our introductory IB articles first, including our guide to what the IB program is and our full coverage of the IB curriculum .
IB Extended Essay: Why Should You Trust My Advice?
I myself am a recipient of an IB Diploma, and I happened to receive an A on my IB Extended Essay. Don't believe me? The proof is in the IBO pudding:
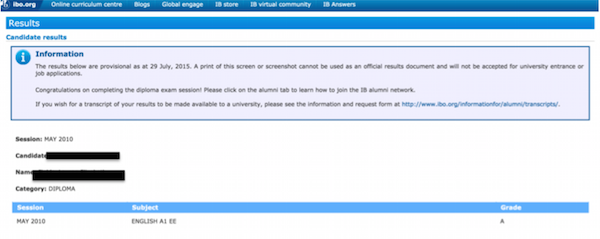
If you're confused by what this report means, EE is short for Extended Essay , and English A1 is the subject that my Extended Essay topic coordinated with. In layman's terms, my IB Diploma was graded in May 2010, I wrote my Extended Essay in the English A1 category, and I received an A grade on it.
What Is the Extended Essay in the IB Diploma Programme?
The IB Extended Essay, or EE , is a mini-thesis you write under the supervision of an IB advisor (an IB teacher at your school), which counts toward your IB Diploma (learn more about the major IB Diploma requirements in our guide) . I will explain exactly how the EE affects your Diploma later in this article.
For the Extended Essay, you will choose a research question as a topic, conduct the research independently, then write an essay on your findings . The essay itself is a long one—although there's a cap of 4,000 words, most successful essays get very close to this limit.
Keep in mind that the IB requires this essay to be a "formal piece of academic writing," meaning you'll have to do outside research and cite additional sources.
The IB Extended Essay must include the following:
- A title page
- Contents page
- Introduction
- Body of the essay
- References and bibliography
Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories , or IB subject groups, which are as follows:
- Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
Once you figure out your category and have identified a potential research topic, it's time to pick your advisor, who is normally an IB teacher at your school (though you can also find one online ). This person will help direct your research, and they'll conduct the reflection sessions you'll have to do as part of your Extended Essay.
As of 2018, the IB requires a "reflection process" as part of your EE supervision process. To fulfill this requirement, you have to meet at least three times with your supervisor in what the IB calls "reflection sessions." These meetings are not only mandatory but are also part of the formal assessment of the EE and your research methods.
According to the IB, the purpose of these meetings is to "provide an opportunity for students to reflect on their engagement with the research process." Basically, these meetings give your supervisor the opportunity to offer feedback, push you to think differently, and encourage you to evaluate your research process.
The final reflection session is called the viva voce, and it's a short 10- to 15-minute interview between you and your advisor. This happens at the very end of the EE process, and it's designed to help your advisor write their report, which factors into your EE grade.
Here are the topics covered in your viva voce :
- A check on plagiarism and malpractice
- Your reflection on your project's successes and difficulties
- Your reflection on what you've learned during the EE process
Your completed Extended Essay, along with your supervisor's report, will then be sent to the IB to be graded. We'll cover the assessment criteria in just a moment.

We'll help you learn how to have those "lightbulb" moments...even on test day!
What Should You Write About in Your IB Extended Essay?
You can technically write about anything, so long as it falls within one of the approved categories listed above.
It's best to choose a topic that matches one of the IB courses , (such as Theatre, Film, Spanish, French, Math, Biology, etc.), which shouldn't be difficult because there are so many class subjects.
Here is a range of sample topics with the attached extended essay:
- Biology: The Effect of Age and Gender on the Photoreceptor Cells in the Human Retina
- Chemistry: How Does Reflux Time Affect the Yield and Purity of Ethyl Aminobenzoate (Benzocaine), and How Effective is Recrystallisation as a Purification Technique for This Compound?
- English: An Exploration of Jane Austen's Use of the Outdoors in Emma
- Geography: The Effect of Location on the Educational Attainment of Indigenous Secondary Students in Queensland, Australia
- Math: Alhazen's Billiard Problem
- Visual Arts: Can Luc Tuymans Be Classified as a Political Painter?
You can see from how varied the topics are that you have a lot of freedom when it comes to picking a topic . So how do you pick when the options are limitless?

How to Write a Stellar IB Extended Essay: 6 Essential Tips
Below are six key tips to keep in mind as you work on your Extended Essay for the IB DP. Follow these and you're sure to get an A!
#1: Write About Something You Enjoy
You can't expect to write a compelling essay if you're not a fan of the topic on which you're writing. For example, I just love British theatre and ended up writing my Extended Essay on a revolution in post-WWII British theatre. (Yes, I'm definitely a #TheatreNerd.)
I really encourage anyone who pursues an IB Diploma to take the Extended Essay seriously. I was fortunate enough to receive a full-tuition merit scholarship to USC's School of Dramatic Arts program. In my interview for the scholarship, I spoke passionately about my Extended Essay; thus, I genuinely think my Extended Essay helped me get my scholarship.
But how do you find a topic you're passionate about? Start by thinking about which classes you enjoy the most and why . Do you like math classes because you like to solve problems? Or do you enjoy English because you like to analyze literary texts?
Keep in mind that there's no right or wrong answer when it comes to choosing your Extended Essay topic. You're not more likely to get high marks because you're writing about science, just like you're not doomed to failure because you've chosen to tackle the social sciences. The quality of what you produce—not the field you choose to research within—will determine your grade.
Once you've figured out your category, you should brainstorm more specific topics by putting pen to paper . What was your favorite chapter you learned in that class? Was it astrophysics or mechanics? What did you like about that specific chapter? Is there something you want to learn more about? I recommend spending a few hours on this type of brainstorming.
One last note: if you're truly stumped on what to research, pick a topic that will help you in your future major or career . That way you can use your Extended Essay as a talking point in your college essays (and it will prepare you for your studies to come too!).
#2: Select a Topic That Is Neither Too Broad nor Too Narrow
There's a fine line between broad and narrow. You need to write about something specific, but not so specific that you can't write 4,000 words on it.
You can't write about WWII because that would be a book's worth of material. You also don't want to write about what type of soup prisoners of war received behind enemy lines, because you probably won’t be able to come up with 4,000 words of material about it. However, you could possibly write about how the conditions in German POW camps—and the rations provided—were directly affected by the Nazis' successes and failures on the front, including the use of captured factories and prison labor in Eastern Europe to increase production. WWII military history might be a little overdone, but you get my point.
If you're really stuck trying to pinpoint a not-too-broad-or-too-narrow topic, I suggest trying to brainstorm a topic that uses a comparison. Once you begin looking through the list of sample essays below, you'll notice that many use comparisons to formulate their main arguments.
I also used a comparison in my EE, contrasting Harold Pinter's Party Time with John Osborne's Look Back in Anger in order to show a transition in British theatre. Topics with comparisons of two to three plays, books, and so on tend to be the sweet spot. You can analyze each item and then compare them with one another after doing some in-depth analysis of each individually. The ways these items compare and contrast will end up forming the thesis of your essay!
When choosing a comparative topic, the key is that the comparison should be significant. I compared two plays to illustrate the transition in British theatre, but you could compare the ways different regional dialects affect people's job prospects or how different temperatures may or may not affect the mating patterns of lightning bugs. The point here is that comparisons not only help you limit your topic, but they also help you build your argument.
Comparisons are not the only way to get a grade-A EE, though. If after brainstorming, you pick a non-comparison-based topic and are still unsure whether your topic is too broad or narrow, spend about 30 minutes doing some basic research and see how much material is out there.
If there are more than 1,000 books, articles, or documentaries out there on that exact topic, it may be too broad. But if there are only two books that have any connection to your topic, it may be too narrow. If you're still unsure, ask your advisor—it's what they're there for! Speaking of advisors...

Don't get stuck with a narrow topic!
#3: Choose an Advisor Who Is Familiar With Your Topic
If you're not certain of who you would like to be your advisor, create a list of your top three choices. Next, write down the pros and cons of each possibility (I know this sounds tedious, but it really helps!).
For example, Mr. Green is my favorite teacher and we get along really well, but he teaches English. For my EE, I want to conduct an experiment that compares the efficiency of American electric cars with foreign electric cars.
I had Ms. White a year ago. She teaches physics and enjoyed having me in her class. Unlike Mr. Green, Ms. White could help me design my experiment.
Based on my topic and what I need from my advisor, Ms. White would be a better fit for me than would Mr. Green (even though I like him a lot).
The moral of my story is this: do not just ask your favorite teacher to be your advisor . They might be a hindrance to you if they teach another subject. For example, I would not recommend asking your biology teacher to guide you in writing an English literature-based EE.
There can, of course, be exceptions to this rule. If you have a teacher who's passionate and knowledgeable about your topic (as my English teacher was about my theatre topic), you could ask that instructor. Consider all your options before you do this. There was no theatre teacher at my high school, so I couldn't find a theatre-specific advisor, but I chose the next best thing.
Before you approach a teacher to serve as your advisor, check with your high school to see what requirements they have for this process. Some IB high schools require your IB Extended Essay advisor to sign an Agreement Form , for instance.
Make sure that you ask your IB coordinator whether there is any required paperwork to fill out. If your school needs a specific form signed, bring it with you when you ask your teacher to be your EE advisor.
#4: Pick an Advisor Who Will Push You to Be Your Best
Some teachers might just take on students because they have to and aren't very passionate about reading drafts, only giving you minimal feedback. Choose a teacher who will take the time to read several drafts of your essay and give you extensive notes. I would not have gotten my A without being pushed to make my Extended Essay draft better.
Ask a teacher that you have experience with through class or an extracurricular activity. Do not ask a teacher that you have absolutely no connection to. If a teacher already knows you, that means they already know your strengths and weaknesses, so they know what to look for, where you need to improve, and how to encourage your best work.
Also, don't forget that your supervisor's assessment is part of your overall EE score . If you're meeting with someone who pushes you to do better—and you actually take their advice—they'll have more impressive things to say about you than a supervisor who doesn't know you well and isn't heavily involved in your research process.
Be aware that the IB only allows advisors to make suggestions and give constructive criticism. Your teacher cannot actually help you write your EE. The IB recommends that the supervisor spends approximately two to three hours in total with the candidate discussing the EE.
#5: Make Sure Your Essay Has a Clear Structure and Flow
The IB likes structure. Your EE needs a clear introduction (which should be one to two double-spaced pages), research question/focus (i.e., what you're investigating), a body, and a conclusion (about one double-spaced page). An essay with unclear organization will be graded poorly.
The body of your EE should make up the bulk of the essay. It should be about eight to 18 pages long (again, depending on your topic). Your body can be split into multiple parts. For example, if you were doing a comparison, you might have one third of your body as Novel A Analysis, another third as Novel B Analysis, and the final third as your comparison of Novels A and B.
If you're conducting an experiment or analyzing data, such as in this EE , your EE body should have a clear structure that aligns with the scientific method ; you should state the research question, discuss your method, present the data, analyze the data, explain any uncertainties, and draw a conclusion and/or evaluate the success of the experiment.
#6: Start Writing Sooner Rather Than Later!
You will not be able to crank out a 4,000-word essay in just a week and get an A on it. You'll be reading many, many articles (and, depending on your topic, possibly books and plays as well!). As such, it's imperative that you start your research as soon as possible.
Each school has a slightly different deadline for the Extended Essay. Some schools want them as soon as November of your senior year; others will take them as late as February. Your school will tell you what your deadline is. If they haven't mentioned it by February of your junior year, ask your IB coordinator about it.
Some high schools will provide you with a timeline of when you need to come up with a topic, when you need to meet with your advisor, and when certain drafts are due. Not all schools do this. Ask your IB coordinator if you are unsure whether you are on a specific timeline.
Below is my recommended EE timeline. While it's earlier than most schools, it'll save you a ton of heartache (trust me, I remember how hard this process was!):
- January/February of Junior Year: Come up with your final research topic (or at least your top three options).
- February of Junior Year: Approach a teacher about being your EE advisor. If they decline, keep asking others until you find one. See my notes above on how to pick an EE advisor.
- April/May of Junior Year: Submit an outline of your EE and a bibliography of potential research sources (I recommend at least seven to 10) to your EE advisor. Meet with your EE advisor to discuss your outline.
- Summer Between Junior and Senior Year: Complete your first full draft over the summer between your junior and senior year. I know, I know—no one wants to work during the summer, but trust me—this will save you so much stress come fall when you are busy with college applications and other internal assessments for your IB classes. You will want to have this first full draft done because you will want to complete a couple of draft cycles as you likely won't be able to get everything you want to say into 4,000 articulate words on the first attempt. Try to get this first draft into the best possible shape so you don't have to work on too many revisions during the school year on top of your homework, college applications, and extracurriculars.
- August/September of Senior Year: Turn in your first draft of your EE to your advisor and receive feedback. Work on incorporating their feedback into your essay. If they have a lot of suggestions for improvement, ask if they will read one more draft before the final draft.
- September/October of Senior Year: Submit the second draft of your EE to your advisor (if necessary) and look at their feedback. Work on creating the best possible final draft.
- November-February of Senior Year: Schedule your viva voce. Submit two copies of your final draft to your school to be sent off to the IB. You likely will not get your grade until after you graduate.
Remember that in the middle of these milestones, you'll need to schedule two other reflection sessions with your advisor . (Your teachers will actually take notes on these sessions on a form like this one , which then gets submitted to the IB.)
I recommend doing them when you get feedback on your drafts, but these meetings will ultimately be up to your supervisor. Just don't forget to do them!

The early bird DOES get the worm!
How Is the IB Extended Essay Graded?
Extended Essays are graded by examiners appointed by the IB on a scale of 0 to 34 . You'll be graded on five criteria, each with its own set of points. You can learn more about how EE scoring works by reading the IB guide to extended essays .
- Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
- Criterion B: Knowledge and Understanding (6 points maximum)
- Criterion C: Critical Thinking (12 points maximum)
- Criterion D: Presentation (4 points maximum)
- Criterion E: Engagement (6 points maximum)
How well you do on each of these criteria will determine the final letter grade you get for your EE. You must earn at least a D to be eligible to receive your IB Diploma.
Although each criterion has a point value, the IB explicitly states that graders are not converting point totals into grades; instead, they're using qualitative grade descriptors to determine the final grade of your Extended Essay . Grade descriptors are on pages 102-103 of this document .
Here's a rough estimate of how these different point values translate to letter grades based on previous scoring methods for the EE. This is just an estimate —you should read and understand the grade descriptors so you know exactly what the scorers are looking for.
Here is the breakdown of EE scores (from the May 2021 bulletin):
How Does the Extended Essay Grade Affect Your IB Diploma?
The Extended Essay grade is combined with your TOK (Theory of Knowledge) grade to determine how many points you get toward your IB Diploma.
To learn about Theory of Knowledge or how many points you need to receive an IB Diploma, read our complete guide to the IB program and our guide to the IB Diploma requirements .
This diagram shows how the two scores are combined to determine how many points you receive for your IB diploma (3 being the most, 0 being the least). In order to get your IB Diploma, you have to earn 24 points across both categories (the TOK and EE). The highest score anyone can earn is 45 points.
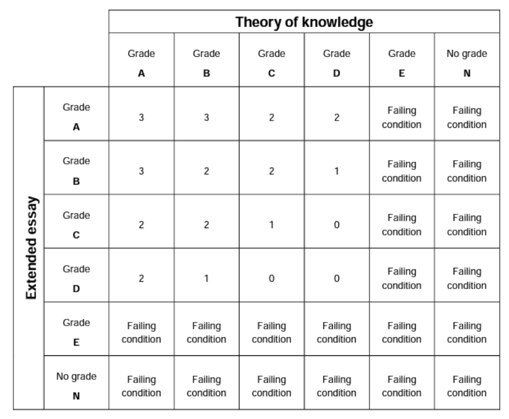
Let's say you get an A on your EE and a B on TOK. You will get 3 points toward your Diploma. As of 2014, a student who scores an E on either the extended essay or TOK essay will not be eligible to receive an IB Diploma .
Prior to the class of 2010, a Diploma candidate could receive a failing grade in either the Extended Essay or Theory of Knowledge and still be awarded a Diploma, but this is no longer true.
Figuring out how you're assessed can be a little tricky. Luckily, the IB breaks everything down here in this document . (The assessment information begins on page 219.)
40+ Sample Extended Essays for the IB Diploma Programme
In case you want a little more guidance on how to get an A on your EE, here are over 40 excellent (grade A) sample extended essays for your reading pleasure. Essays are grouped by IB subject.
- Business Management 1
- Chemistry 1
- Chemistry 2
- Chemistry 3
- Chemistry 4
- Chemistry 5
- Chemistry 6
- Chemistry 7
- Computer Science 1
- Economics 1
- Design Technology 1
- Design Technology 2
- Environmental Systems and Societies 1
- Geography 1
- Geography 2
- Geography 3
- Geography 4
- Geography 5
- Geography 6
- Literature and Performance 1
- Mathematics 1
- Mathematics 2
- Mathematics 3
- Mathematics 4
- Mathematics 5
- Philosophy 1
- Philosophy 2
- Philosophy 3
- Philosophy 4
- Philosophy 5
- Psychology 1
- Psychology 2
- Psychology 3
- Psychology 4
- Psychology 5
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 1
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 2
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 3
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 1
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 2
- Visual Arts 1
- Visual Arts 2
- Visual Arts 3
- Visual Arts 4
- Visual Arts 5
- World Religion 1
- World Religion 2
- World Religion 3

What's Next?
Trying to figure out what extracurriculars you should do? Learn more about participating in the Science Olympiad , starting a club , doing volunteer work , and joining Student Government .
Studying for the SAT? Check out our expert study guide to the SAT . Taking the SAT in a month or so? Learn how to cram effectively for this important test .
Not sure where you want to go to college? Read our guide to finding your target school . Also, determine your target SAT score or target ACT score .
Want to improve your SAT score by 160 points or your ACT score by 4 points? We've written a guide for each test about the top 5 strategies you must be using to have a shot at improving your score. Download it for free now:

As an SAT/ACT tutor, Dora has guided many students to test prep success. She loves watching students succeed and is committed to helping you get there. Dora received a full-tuition merit based scholarship to University of Southern California. She graduated magna cum laude and scored in the 99th percentile on the ACT. She is also passionate about acting, writing, and photography.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
What Is an IB Extended Essay and How to Write It?
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
The IB extended essay is a paper of up to 4,000 words that is required for students enrolled in the International Baccalaureate (IB) diploma program. The extended essay allows students to engage in independent research on a topic within one of the available subject areas.
The extended essay should be an original piece of academic writing that demonstrates the following student's abilities:
- Formulating a research question
- Conductig independent investigation
- Presenting key findings in a scholarly format.
Check out this article by StudyCrumb to discover how to write an IB extendend essay properly. We will give you a complete writing guide and critical tips you need for this essay type.
IB Extended Essay: What Is It?
An extended essay is independent research. Usually students choose a topic in consultation with a mentor. It is an integral part of the International Baccalaureate (IB) degree program. This means that you won't receive a degree without a successfully written paper. It requires 4,000-word study on a chosen narrow topic. To get a high score, you should meet all required structure and formatting standards. This is the result of approximately 40 working hours. Its purpose is giving you the opportunity to try independent research writing. It's approved that these skills are critical for student success at university. The following sections explain how to write an extended article with examples. So keep reading!
Choosing a Mentor for Extended Essay
IB extended essay guidelines require supervisor meetings, totaling 3-5 hours. They include three critical reflections. A mentor won't write a paper instead of you but can help adjust it. So it is important to consult with them, but no one will proofread or correct actual research for you. In general, initially treat an essay as an exclusively individual work. So your role and contribution are maximal.
Extended Essay Outline
Let's take a look at how to write an extended essay outline. In this part, you organize yourself so that your work develops your idea. So we especially recommend you work out this step with your teacher. You can also find any outline example for essay . In your short sketch, plan a roadmap for your thoughts. Think through and prepare a summary of each paragraph. Then, expand annotation of each section with a couple more supporting evidence. Explain how specific examples illustrate key points. Make it more significant by using different opinions on general issues.
Extended Essay: Getting Started
After you chose an extended essay topic and made an outline, it's time to start your research. Start with a complete Table of Contents and make a choice of a research question. Select the subject in which you feel most confident and which is most interesting for you. For example, if at school you are interested in natural science, focus on that. If you have difficulties choosing a research question, rely on our essay topic generator .
Extended Essay Introduction
In the introduction of an extended essay, present a thesis statement. But do it in such a way that your readers understand the importance of your research. State research question clearly. That is the central question that you are trying to answer while writing. Even your score depends on how you develop your particular research question. Therefore, it is essential to draw it up correctly. Gather all relevant information from relevant sources. Explain why this is worth exploring. Then provide a research plan, which you will disclose further.
Extended Essay Methodology
In accordance with extended essay guidelines, it's mandatory to choose and clearly state a methodological approach. So, it will be apparent to your examiner how you answered your research question. Include your collection methods and tools you use for collection and analysis. Your strategies can be experimental or descriptive, quantitative or qualitative. Research collection tools include observations, questionnaires, interviews, or background knowledge.
Extended Essay Main Body
Well, here we come to the most voluminous part of the extended essay for IB! In every essay body paragraph , you reveal your research question and discuss your topic. Provide all details of your academic study. But stay focused and do it without dubious ideas. Use different sources of information to provide supporting arguments and substantial evidence. This will impress professors. For this section, 3 main paragraphs are enough. Discuss each idea or argument in a separate paragraph. You can even use supporting quotes where appropriate. But don't overcomplicate. Make your extended essay easy to read and logical. It's critical to stay concise, so if you aren't sure how to make your text readable, use our tool to get a readbility test . Following the plan you outlined earlier is very important. Analyze each fact before including it in your writing. And don't write unnecessary information.
Extended Essay Conclusion
Now let's move on to the final part of IB extended essay guidelines. In conclusion, focus on summarizing the main points you have made. No new ideas or information can be introduced in this part. Use conclusion as your last chance to impress your readers. Reframe your own strong thesis. Here you must show all key points. Do not repeat absolutely every argument. Better try to make this part unique. This will show that you have a clear understanding of the topic you have chosen. And even more professional will be recommendations of new areas for future research. One good paragraph may be enough here. Although in some cases, two or three paragraphs may be required.
Extended Essay Bibliography & Appendices
To write an impressive extended essay, you should focus on appropriate information. You must create a separate page for bibliography with all sources you used. Tip from us: start writing this page with the first quote you use. Don't write this part last or postpone. In turn, appendices are not an essential section. Examiners will not pay much attention to this part. Therefore, include all information directly related to analysis and argumentation in the main body. Include raw data in the appendix only if it is really urgently needed. Moreover, it is better not to refer to appendices in text itself. This can disrupt the narrative of the essay.
Extended Essay Examples
We have prepared a good example of an extended essay. You can check it by downloading it for free. You can use it as a template. However, pay attention that your paper is required to be unique. Don't be afraid to present all the skills you gained during your IB.
Final Thoughts on IB Extended Essay
In this article, we presented detailed IB extended essay guidelines. An extended essay is a daunting academic challenge to write. It is a research paper with a deep thematic analysis of information. But we have described several practical and straightforward tips. Therefore, we are sure that you will succeed!
If topics seem too complex, turn to our top essay writers. They will accomplish any IB assignment in the best way your professor can evaluate it!

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

Extended essay
The extended essay is an independent, self-directed piece of research, finishing with a 4,000-word paper.
One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students.
Read about the extended essay in greater detail.
You can also read about how the IB sets deadlines for the extended essay , find examples of extended essay titles from previous DP students and learn about the world studies extended essay .
Learn more about the extended essay in a DP workshop for teachers .
DP subject briefs
Find out about what each subject offers within the Diploma Programme (DP).
Our DP subject briefs—for both standard and higher level—contain information about core requirements, aims and assessment.
- Explore the DP subject briefs

We use cookies on this site. By continuing to use this website, you consent to our use of these cookies. Read more about cookies
Guide to the IB Extended Essay in 2024
January 24, 2024

If you’re an International Baccalaureate student getting ready to write your IB Extended Essay, you might be experiencing some very understandable trepidation. But have no fear—we’re here to help you understand what’s required of you, how to plan ahead (IB extended essay topics), and how you’ll be graded (IB extended essay rubric). Keep reading for a good dose of preparation and confidence before you begin the journey. In this article, we’ll cover:
What is the IB Extended Essay?
The ib extended essay—required content, ib extended essay topics.
IB Extended Essay—Sample Essays
IB Extended Essay Tips
Ib extended essay rubric, ib extended essay—more resources.
The IB Extended Essay is a 4,000-word paper that asks you to immerse yourself in research and academic writing. A required part of the IB program, the Extended Essay is a chance to dig deep into a topic that fascinates you.
Although it’s no small task, the IB Extended Essay is an opportunity to gain practical research and writing skills that will come in handy again in college. As you write, you’ll learn how to:
- Identify credible sources
- Formulate a research question and limit your scope of research
- Communicate ideas to an audience
- Develop a well-supported argument
The IB Extended Essay is largely an independent, self-directed project, but don’t worry—the IB program doesn’t throw you into the deep end. You do get to select a mentor (usually a teacher at your school) to help guide you through the process. As you write, you’ll be required to meet with your mentor three times. As part of your final evaluation, your mentor will interview you in a final reflection section called a viva voce . During the viva voce, your mentor will check for plagiarism and malpractice, ask you to reflect on challenges and difficulties, and prompt you to discuss what you’ve learned through the research and writing process. Your mentor will then generate a report that factors into your final grade.
Your final essay must include the following:
- Contents page
- Introduction
- Body of the essay
- References and bibliography
For this essay, it will be up to you to generate a topic; the International Baccalaureate does not provide prompts. However, your essay will need to fit within one of six provided subject areas . You’ll choose from the following list of IB Extended Essay Topics:
- Language and literature
- Language acquisition
- Individuals and societies
- Mathematics
IB Extended Essay Topics (Continued)
At a glance, the subject areas might look limited, but the topics you can choose to write about are actually wide-ranging. The “Individuals and societies” category includes social science topics like economics, history, world religions, and philosophy. And, if you’re leaning toward “Science,” you can choose from classic subjects such as biology, chemistry, and physics, or related topics like environmental systems or health science, among others.
The IB also offers a special “World Studies” option for students interested in researching global issues. This subject would allow you to center your writing on global issues such as migration, global health, cultural exchange, or climate change.
Wondering what an outstanding IB Extended Essay looks like? The International Baccalaureate provides quite a few sample student essays online . Here are five essays that earned A grades.
Language and literature: An exploration of an aspect of the narrative voice in Vladimir Nabokov’s Lolita
Environmental Systems and Societies: The economic impact of the 1995 reintroduction of grey wolves to Yellowstone National Park
Psychology: To what extent do social networking sites (SNS) usage lead to experience of anxiety in adolescents?
Music: Composition techniques in the 1st movement of Johannes Brahms’s Symphony No. 2, Op. 73
Business Management: Corporate Culture at Oracle
1) Pick something you’re passionate about
As you can see from the titles above, the IB Extended Essay is a great place to delve into a niche topic that fascinates you. Since you’ll be spending many months on this essay, you’ll want to pick a topic you genuinely enjoy spending time learning about. It’s also smart to choose something you’ve already learned about in your IB classes so that you have a strong foundation of knowledge to start with. In music class, do you love pondering why music makes us feel a certain way? Maybe an essay about music theory will keep your gears turning. Do you come alive trying to solve seemingly impossible problems in physics class? Now’s your chance to put those equations into action.
Since this essay is all about your academic interests, it’s also a good idea to pick a topic that’s relevant to what you plan to study in college. Selecting a relevant topic will provide you with significant exposure to the field and will also give you something meaningful to talk about in your college admissions essays.
2) Limit your scope
What’s the meaning of life? Why do wars happen? What is time? Some questions are just way too big to answer, and your IB Extended Essay is not a good place to tackle expansive, philosophical questions. Instead, think of this essay as a place to investigate one piece of a big question. If, let’s say, you’re generally interested in what helps women reach positions of leadership in business, this is a good place to examine how one or a few companies approach this issue. Or, if you’re interested in studying what inspires surrealist painters, you’ll want to pick one or a few painters to research, likely all from the same time period. For both these topics, you’d need a whole textbook to tackle the full question, but limiting your scope will make it much easier to write a clear and cohesive 4,000 words.
On the other hand, it’s possible to narrow your focus too much. It would be impossible, for example, to write 4,000 words about a single sentence in a novel. Make sure you talk about scope early and often with your mentor. Together, you can find the perfect Goldilocks scope for your project that’s not too big and not too small.
3) Choose a good mentor
Speaking of mentors, choosing wisely will help you enormously as you embark on your IB Extended Essay. You’ll want to make sure you choose someone with existing knowledge in your research topic. Your English teacher may be able to give you great writing advice, for example, but they won’t be able to guide your research and scope if you’re writing about marine animals or modern dance.
Before you approach a teacher, make sure you have at least one topic idea (or even a few ideas) in mind so that you can make sure they’ll be a good fit to supervise your project. When you meet with them, find out what their mentorship style is like. Make sure they’ll have time to read several drafts of your essays, meet with you a few times, and give you feedback. Some IB schools will require your IB Extended Essay mentor to sign an agreement form too, so make sure you find out what paperwork is required in advance.
4) Get organized, way organized
The IB Extended Essay is not something you can crank out the night before it’s due. The essay is meant to be a substantive, in-depth, thoughtful, and thoroughly researched analysis, and Rome simply isn’t built in a day. This might be the longest paper you’ve written to date, and this project might require more research than you’ve been asked to do before. Timelines vary by school, but you’ll likely spend between eight months and a year working on your IB Extended Essay. So, how will you pull it all off? For these 8-12 months, organization will be your guiding light. We recommend you:
- Get started early. If your essay is due November of your senior year, start generating topic ideas during your junior year right after winter break.
- Create a long-view schedule for yourself. What will you accomplish each month of your process?
- Give yourself deadlines. Once you choose a mentor, suggest 2-3 draft deadline dates so that you will be held accountable throughout the writing process.
- Find a note-taking system that works for you. You’ll be reading many articles and books and it’s hard to keep track of all your sources. Create a document or spreadsheet where you keep track of the sources you’ve found and check them off as you read. As you finish reading a text, type up important quotes and a few notes explaining how it connects to your topic and to your other texts.
5)Write a messy first draft
Writing never comes out perfect the first time, even for New York Times bestselling authors and the most experienced researchers. In your first draft, give yourself permission to get all your thoughts out, no matter how unstructured or rambling they are. Call this your brainstorming draft. When you’re ready to revisit it, see what patterns emerge, what common ideas you can group together, what beginning buds of ideas you can make bloom into full-fledged analysis.
6) Communicate for an audience
When you’re used to producing writing that only your teacher reads, it can be hard to remember to write for an audience. But at the end of the day, writing is communication , and the best writing is clear and thorough communication that anyone could pick up and read. For your IB Extended Essay, you’ll want to remember that many people will be reading your final essay, and not all of them will be experts in the niche topic you choose to study. Ask yourself: how can I explain my research to an audience who doesn’t already agree with my analysis?
To communicate to an audience, you’ll want to:
- Provide lots of general background information on your topic.
- Don’t assume your reader is familiar with your sources. Introduce them as if they’re guest speakers about to walk up to a podium and deliver a lecture.
- After including quotes, facts, and figures, be sure to explain what those sources mean in your own words and how they connect to your bigger-picture argument.
- Don’t assume your arguments are self-evident. In this essay, communicating for an audience means supplying ongoing interpretation and analysis, even if it feels like you’re explaining the obvious. Your reader isn’t on your research journey with you, so your points might not be so obvious to your reader.
Although your IB Extended Essay provides a report that factors into your grade, your essay will also be assessed by external examiners the IB. Per the IB Extended Essay Rubric , essays are graded on a scale from 0 to 34 based on 5 different criteria:
- Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
- Criterion B: Knowledge and Understanding (6 points maximum)
- Criterion C: Critical Thinking (12 points maximum)
- Criterion D: Presentation (4 points maximum)
- Criterion E: Engagement (6 points maximum)
As you can see, Critical Thinking is the most significant rubric category. This means that the IB wants to see you arrive at your own unique analysis of your topic, drawing connections between sources and data, and making well-supported arguments. This means they want a lot of you: your ideas, your interpretations, your thoughts. Make sure you emphasize that in your essay, but of course don’t forget the other categories.
The score a student receives corresponds to a letter grade scale that is slightly different than what we’re accustomed to in the U.S. Here’s the letter grade to numerical score breakdown:
You must earn a D or higher to receive your IB Diploma. To learn more about the different criteria included in the IB Extended Essay Rubric, you can explore the IB’s full guide to the Extended Essay .
We hope you found our look at the IB extended essay rubric and IB extended essay topics to be helpful. Ready to dive into research? You may want to read our 10 Expert Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension before you hit the books.
And if you’re a high school student in the process of mapping out your pathway to college, take a look at a few other useful guides:
- IB vs AP—Which Classes are Best for College Admission?
- How to Earn College Credit in High School
- High School Course Requirements for College Admission
- SAT Score Calculator
- ACT Score Calculator
- High School Success

Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Sign Up Now

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Write an Extended Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
by Antony W
October 10, 2023

In this guide, you’ll learn how to write an Extended Essay that not only explores a research issue comprehensively but also earns top grades.
To write a good Extended Essay, choose a topic you’re interested in, develop a specific research question, do your research, and structure your essay. Plan your writing process, schedule meetings with your supervisor, write the essay, and proofread before submitting.
An alternative way to write an Extended Essay is to seek for professional academic writing help online.
At Help for Assessment, we offer the best EE writing service online and this writing assistance can go a long way to get your Extended Essay written on time.
To be clear, an Extended Essay isn’t an assignment you should fail unless you purposely intend to do so. A good way to write an EE on any subject is to develop a solid structure and then follow it from start to finish.
How to Write an Extended Essay Step-by-Step
To write a comprehensive Extended Essay on any subject within the 40 hours:
1. Choose a Topic
The first step to write an EE is to choose an Extended Essay topic to explore.
Unfortunately, you can’t scrape a good topic off a book or ask a friend in your IB class to share their thoughts. You have to brainstorm and do some preliminary research to find an interesting topic to work on.
You don’t have to spend so many hours looking for a topic for your EE.
First, determine what your passion outside the classroom is. Then, come up with a list of potential topics that you can explore based on the subject of your choice.
As you do your topic hunting, you might discover that you have an interest in more than one topic.
We recommend that you choose the most interesting of all topic, particularly the one tied to an area you’ve always wanted to explore.
Also, make sure the topic allows you to have something original to write in the essay.
Should the topic be one that doesn’t allow you to share ideas beyond what’s obvious, drop it and look for something else.
2. Research Your Topic
Researching your topic will help to inform your essay in the writing stage. If you do the research right, the structure, case study, and the experiments will easily fit on their own.
To do your research more effectively:
- Start by reading the EE guidelines for the subject you’d like to explore. Doing so will help you determine whether you need primary sources, secondary research, or a combination of both.
- Determine if you have to collect data from someone else, look for facts, create your own data, or use other people’s opinion.
- Check with your supervisor how recent your research should be.
- Conduct your research based on the subject, the topic you selected, and the suggestions from your supervisor.
Note that you may have to search multiple sources to identify the most relevant information for your Extended Essay.
You want to make sure your bibliography is detailed enough to show that you have invested enough time to research your topic.
3. Develop a Research Question
You need to develop a clear and concise research question that gives your intended reader a clear focus of the essay.
The Extended Essay Guide requires that your research question be precise, and it doesn’t necessarily have to be in the form of a question. In addition, your research question should be something worth asking.
If the research issue you’ve developed is concise, detailed, specific, and linked to the topic you would like to explore in 4,000 words, you’re set to start writing the Extended Essay.
4. Structure and Plan Your EE
Your Extended Essay should feature the following format:
- Your research question
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Bibliography
- 3 Reflections
Use this outline in the order provided to organize your research and write the Extended Essay.
5. Consult Your Supervisor
One of the advantages of being in an IB program is that you can always choose someone to guide you through the Extended Essay reflection process .
It could be a teacher you're comfortable with or a fellow student.
Ensure you make good use of them by consulting them with your research so they can tell you whether you're on the right path.
6 Write Your First and Last Draft
Once you're comfortable that you've done comprehensive research, use your outline to write your first draft.
Don't worry about grammar or punctuation.
Just give life to your outline; then afterward, you can use this first draft to write the official extended essay you will submit.
7. Proofread and Edit Your Work
When your final extended essay is ready, edit and proofread for grammatical errors or any other errors you may not have noticed while rewriting it from your first draft.
If possible, have your supervisor go through it as well before submission.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. how long does it take to write an extended essay.
IB requires you to write your Extended Essay within 40 hours.
That’s enough time to start and complete the writing process if you start working on the EE as early as right now.
2. When Should I Write an EE?
The right approach to tackle an Extended Essay assignment is to start early. Instead of waiting to write a last minute essay , start right away so that you have ample time to do the work.
Keep in mind that time management is critical to your success.
Once you’ve selected a topic for your Extended Essay assignment, the next task should be to create a schedule you can work with.
Determine how much time you’re willing and able to assign to your research process , break the task into small sections that you can manage, and then assign each section a realistic deadline.
3. How Do You Structure an Extended Essay?
Your Extended Essay must feature your research question, a cover page, table of contents, an introduction, the main body, a conclusion, a bibliography, and 3 reflections.
It’s possible to feel stuck as you continue to work on your Extended Essay, but your supervisor will be there to help you during the reflection sessions.
During these sessions, your supervisor will evaluate your research question, look at your structure and writing plan, and comment on your first draft.
Remember, you have 40 hours to work on the essay, which should be enough to get the assignment completed on time.
Should you feel stuck in the writing process, you can reach out to the IB team at Help for Assessment and we’ll be happy to help.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
What is the IB Program Extended Essay?
Why is the ib extended essay important, writing the extended essay, how can i choose a topic, how can i best prepare for the extended essay, final thoughts.
Published November 26, 2023
The Ultimate Guide to IB Extended Essays

High School Sophomore from West Virginia, Avid Classics Enthusiast, Marketing Intern and Blog Writer at Knowt :)
For high school students taking part in the International Baccalaureate (IB) program, the Extended Essay is a substantial academic endeavor that deserves careful consideration. Not doing well on this essay might lose you your IB diploma. It represents an opportunity to dive deeply into a subject of personal interest, showcasing not only one's research and writing abilities but also a commitment to scholarly exploration. In this article, we'll provide a comprehensive understanding of what the essay entails, its significance within the program, the sequential stages involved in its completion, and how students can effectively navigate this substantial academic challenge. Whether you are embarking on this intellectual journey or seeking to gain insight into this fundamental component of the IB curriculum, our guide intends to shed light on the purpose, process, and educational impact of the essay in a formal and informative manner.
The IB Extended Essay is a rigorous independent research project at the heart of the IB Diploma Programme. It challenges high school students to dive into a chosen subject of personal interest in a structured and scholarly manner. The Extended Essay requires students to engage in extensive research, develop a clear research question or hypothesis, and produce a substantial written essay of up to 4,000 words. This endeavor is designed to cultivate essential skills, including critical thinking, research methodology, and effective communication, while encouraging students to explore their passions and pursue academic excellence. The Extended Essay not only serves as a capstone achievement in the programbut also provides a valuable opportunity for students to develop the intellectual independence and research skills needed for success in higher education and beyond.
The IB Extended Essay holds paramount significance within the International Baccalaureate (IB) program for several compelling reasons. Firstly, it fosters intellectual independence and critical thinking, as students are tasked with formulating their research questions, conducting thorough investigations, and presenting their findings in a scholarly manner. This process not only hones their research skills but also nurtures a passion for academic inquiry. Additionally, the Extended Essay equips students with valuable research methodologies, analytical abilities, and effective communication skills, all of which are indispensable for success in higher education and future careers. Furthermore, it offers an opportunity for students to explore their interests deeply, cultivating a lifelong love for learning. Ultimately, the Extended Essay is not merely an academic exercise but a transformative experience that prepares students for the challenges of university studies and instills a sense of intellectual curiosity and rigor that extends far beyond their academic journey.
Topic Selection: Begin by selecting a subject area and a specific topic that genuinely interests you. Ensure that it aligns with one of the approved IB subject areas and is sufficiently focused.
Formulate a Research Question: Develop a clear and concise research question or hypothesis that will serve as the central focus of your essay. Ensure that your question is researchable and open to investigation.
Conduct In-Depth Research: Dive into extensive research, gathering a variety of sources relevant to your topic. This includes books, academic articles, primary sources, and data, if applicable. Keep detailed notes and organize your sources systematically.
Create an Outline: Outline the structure of your essay, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Establish a logical flow for your arguments and evidence. You can use Knowt's AI to help structure your essay as well!
Write the First Draft: Begin writing your essay based on your outline. Ensure that your arguments are well-structured, supported by evidence, and directly related to your research question. Adhere to the word limit and proper citation style.
Revise and Refine: Review your first draft critically. Check for clarity, coherence, and conciseness in your writing. Revise and refine your arguments, and make sure your essay flows smoothly.
Seek Feedback: Share your draft with teachers, peers, or mentors for constructive feedback. Consider their suggestions and make necessary revisions.
Finalize Your Essay: After incorporating feedback, finalize your essay, paying meticulous attention to grammar, spelling, and formatting. Ensure that your citations and bibliography follow the prescribed citation style.
Abstract and Table of Contents: Write a clear and concise abstract that summarizes your essay's key points. Create a table of contents to provide readers with a roadmap of your essay's structure.
Proofread: Proofread your essay carefully to eliminate any errors or inconsistencies. Consider seeking assistance from a trusted proofreader to catch any overlooked mistakes.
Submit Your Essay: Submit your final essay to your IB coordinator, adhering to the submission deadline and any specific formatting requirements.
Reflect on the Process: Take time to reflect on your journey, the challenges you encountered, and the skills you developed. Consider how your research contributed to your understanding of the subject.
Looking over your subject matter, or notes, to see if there is a particular part of the class that you would like to explore further is one way to start. Look for a subject that you find particularly interesting and would like to explore further. You will be spending quite a bit of time with your research topic, so make sure it is something you enjoy! If your notes are not very detailed and need more information, check out these free IB resources , which include study guides and notes from HL Latin to SL Biology to HL/SL Computer Science . We have it all.
Preparing effectively for the IB Extended Essay involves a combination of careful planning and consistent effort. Start by selecting a topic that genuinely interests you, as passion for your subject matter will sustain your motivation throughout the project. Next, create a detailed timeline that outlines specific milestones, research periods, and writing deadlines to ensure you stay on track. Familiarize yourself with the Extended Essay guide from various IB resources and assessment criteria to understand what is expected. Seek guidance and feedback from your EE supervisor and teachers, and don't hesitate to ask questions when you encounter challenges. Prioritize thorough research, utilize credible sources, and keep meticulous notes to ease the writing process. Stay organized, manage your time wisely, and allocate dedicated study sessions for your EE. Finally, embrace revisions and feedback as opportunities for improvement and consider seeking external guidance or resources if needed. With careful planning, dedication, and a proactive approach to research and writing, you'll be well-prepared to excel in your Extended Essay project.
Overall, the IB Extended Essay is an exciting journey that invites you to explore your interests deeply and cultivate a genuine passion for learning. It's a chance to take your academic skills to the next level, fostering critical thinking, research prowess, and effective communication—all of which will serve you well in future endeavors. Embrace this opportunity with enthusiasm, knowing that your dedication and curiosity will lead you to discoveries beyond the confines of your essay. While the path may have its challenges, remember that with determination and support, you can not only succeed but also find fulfillment in the pursuit of knowledge. So, embark on this adventure with confidence, for the Extended Essay is your platform to make a meaningful contribution to the world of ideas and scholarship. Your journey is bound to be rewarding, and your growth as a student and thinker, truly remarkable.

Everything You Need To Get A 7 in IB Theatre
Hey there! This article is all about our tips for how to study for the IB Theatre exam to get a solid 7. I'll break down the tricks, and IB Theatre test prep so with the right strategies and IB Theatre resources, nailing the exam is totally doable! Free IB Theatre Resources!! Hey, no worries if you're in a last-minute cramming session for IB Theatre! We totally get it, and trust me, we've all been there too! So, if you're wondering how to ace the IB Theatre exam when you're running out of time, here are some awesome resources and IB Theatre exam tips created by fellow students that will help y...

Everything You Need to Get a 7 on IB Economics
Hey there! This article is all about our tips for how to study for the IB Economics exam to get a solid 7. I'll break down the tricks, and IB Economics test prep so with the right strategies and IB Economics resources, nailing the exam is totally doable! Free IB Economics Resources!! Hey, no worries if you're in a last-minute cramming session for IB Economics! We totally get it, and trust me, we've all been there too! So, if you're wondering how to ace the IB Economics exam when you're running out of time, here are some awesome resources and IB Economics exam tips created by fellow students th...

Everything You Need to Get a 7 on IB Computer Science
Hey there! This article is all about our tips for how to study for the IB Computer Science exam to get a solid 7. I'll break down the tricks, and IB Computer Science test prep so with the right strategies and IB Computer Science resources, nailing the exam is totally doable! Free IB Computer Science resources Hey, no worries if you're in a last-minute cramming session for IB Computer Science! We totally get it, and trust me, we've all been there too! So, if you're wondering how to ace the IB Computer Science exam when you're running out of time, here are some awesome resources and IB Computer ...

- Westbourne Voices
- Awards and Affiliations
- Virtual Tour
- Admissions Overview
- School Admissions Process
- Nursery Admissions Process
- International Student Admissions
- Visits & Open Days
- Welcome to Nursery
- Nursery Life
- Nursery Curriculum
- Nursery Sessions
- Nursery Fees and Applications
- Stepping up to Prep School
- Welcome to Prep School
- Prep Academic Curriculum
- Prep Co-Curricular
- Prep School Case Studies
- Stepping up to Senior School
- Welcome to Senior School
- GCSE Subjects
- Senior Co-curricular
- Stepping Up to Sixth Form
- Welcome to Sixth Form
- IB Subjects
- IB Inner Core
- Oxbridge and Russell Group
- Careers Guidance
- Super Curriculum
- Sixth Form Case Studies
- Westbourne Life
- Welcome to Boarding
- Boarding Options
- Boarding Life
- Boarding FAQs
- Boarding Case Studies
- Future Leaders Lab
- School Uniform
- School Transport
- Visiting Information

How To Write The Extended Essay (With Topics and Examples)
This comprehensive guide navigates through every aspect of the EE, from selecting a topic and developing a research question to conducting in-depth research and writing a compelling essay. It offers practical strategies, insights, and tips to help students craft a piece of work that not only meets the rigorous standards of the IB but also reflects their academic passion and curiosity. Join us as we explore the keys to success in the Extended Essay, preparing you for an intellectually rewarding experience.
Posted: 13th February 2024
Section jump links:
Section 1: Understanding the IB Extended Essay
Section 2: the importance of the extended essay, section 3: selecting a topic, section 4: developing your research question, section 5: research methodology and theoretical frameworks, section 6: evaluating sources and data, section 7: integrating evidence and analysis, section 8: writing and structuring the extended essay, section 9: reflection and the rppf, section 10: the significance of academic discipline in the ee, section 11: good practice in extended essay writing, section 12: managing the extended essay process, section 13: collaboration and feedback, section 14: avoiding plagiarism, section 15: emphasising original thought, section 16: final presentation and viva voce, section 17: beyond the extended essay, what is the ib extended essay.
The International Baccalaureate (IB) Extended Essay (EE) is a cornerstone of the IB Diploma Programme . It’s an independent, self-directed piece of research, culminating in a 4,000-word paper. This project offers students an opportunity to investigate a topic of their own choice, bridging the gap between classwork and the kind of research required at the university level.
Key Objectives and the Role of the EE in the IB Curriculum
The Extended Essay has several key objectives:
- To provide students with the chance to engage in an in-depth study of a question of interest within a chosen subject.
- To develop research, thinking, self-management, and communication skills.
- To introduce students to the excitement and challenges of academic research.
The EE plays a critical role in the IB curriculum by:
- Encouraging intellectual discovery and creativity.
- Facilitating academic growth and personal development through research and writing.
- Preparing students for the rigours of higher education.
Extended Essay Word Count and Requirements
The EE has a maximum word count of 4,000 words. This does not include the abstract, contents page, bibliography, or footnotes (which must be used sparingly). Here are some essential requirements:
- Research Question: Your essay must be focused on a clear, concise research question. You should aim to provide a comprehensive answer to this question through your research and writing.
- Subject : The EE can be written in one of the student’s six chosen subjects for the IB diploma or in a subject recognized by the IB.
- Supervision : Each student is assigned a supervisor (usually a teacher in their school) who provides guidance and support throughout the research and writing process.
- Assessment: The essay is externally assessed by the IB, contributing up to three points towards the total score for the IB diploma, depending on the grade achieved and the performance in the Theory of Knowledge course.
The Extended Essay is not just an academic requirement but a unique opportunity to explore a topic of personal interest in depth. This can be an incredibly rewarding experience, providing valuable skills and insights that will serve you well in your future academic and professional endeavours.

The EE is more than just a requirement for the IB Diploma. It’s an essential part of the IB experience , offering profound benefits for students. Let’s explore why the EE holds such significance.

Academic and Personal Development Benefits
Skill enhancement:.
The EE fosters a range of academic skills crucial for success in higher education and beyond. It teaches students how to:
- Conduct comprehensive research
- Develop a coherent argument
- Write extensively on a subject
- Manage time effectively
Personal Growth:
Beyond academic prowess, the EE encourages personal development. Students learn to:
- Pursue their interests deeply
- Overcome challenges independently
- Reflect on their learning process
- Enhance their curiosity and creativity
Contribution to University Admissions
Standout applications:.
The EE can be a significant advantage in university applications . It demonstrates a student’s ability to undertake serious research projects and commit to an intensive academic task. Universities value this dedication, seeing it as indicative of a student’s readiness for undergraduate studies.
Showcase of Skills:
The EE allows students to showcase their research, writing, and analytical skills. It provides concrete evidence of their academic abilities and their capacity to engage deeply with a topic of interest.
Skill Development: Research, Writing, and Critical Thinking
Research Skills:
Students learn to navigate academic literature, evaluate sources, and gather relevant data. This process sharpens their research skills, laying a solid foundation for future academic endeavours.
Writing Skills:
Crafting a 4,000-word essay challenges students to express their ideas clearly and persuasively. It hones their writing skills, teaching them the art of structured and focused academic writing.
Critical Thinking:
The EE encourages students to analyse information critically, assess arguments, and develop their viewpoints. This critical engagement fosters a sophisticated level of thought, beneficial in both academic and real-world contexts.
In conclusion, the Extended Essay is a pivotal element of the IB Diploma Programme. It’s an invaluable opportunity for intellectual and personal growth, preparing students for the challenges of higher education and beyond. With its emphasis on independent research and writing, the EE equips students with the skills and confidence to navigate their future academic journeys successfully.

Choosing a topic for your Extended Essay is the first step in a journey towards developing a deep understanding of a specific area of interest. It’s crucial to select a topic that is not only academically viable but also personally engaging. Here’s how to navigate this critical phase.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Your EE Topic
Interest and passion:.
Select a topic that fascinates you. Your interest will sustain motivation over the months of research and writing.
Availability of Resources:
Ensure there are enough resources available on your chosen topic. Access to libraries, databases, and experts in the field is essential for comprehensive research.
Scope and Focus:
The topic should be narrow enough to allow for in-depth study yet broad enough to find sufficient research material. Balancing specificity with resource availability is key.
IB Subject Areas:
Your topic must align with one of the subjects you are studying in the IB Diploma Programme or an approved subject area. Familiarity with the subject’s methodology and criteria is crucial for success.
How to Align Your Interests with the IB Subjects
Explore the syllabus:.
Review the syllabus of your IB subjects to identify topics that interest you. This can provide a framework for your EE.
Consult with Teachers:
Teachers can offer insights into feasible topics that align with the IB criteria and offer guidance on how to approach them.
Consider Interdisciplinary Topics:
Some of the most engaging EEs explore the intersection between different subjects. If this interests you, ensure your approach meets the criteria for an interdisciplinary essay under the IB’s World Studies EE option.
Extended Essay Topics: Examples Across Various Disciplines
- Sciences: How does the introduction of non-native plant species affect biodiversity in your local ecosystem?
- History : What was the impact of Winston Churchill’s leadership on Britain’s role in World War II?
- English: How does the use of unreliable narrators influence the reader’s perception in Ian McEwan’s novels?
- Mathematics: Investigating the application of the Fibonacci sequence in predicting stock market movements.
- Visual Arts: Exploring the influence of Japanese art on Claude Monet’s painting style.
Selecting the right topic is foundational to your EE journey. It shapes your research direction, influences your engagement with the essay, and ultimately contributes to the satisfaction and success of your EE experience. Take your time, consult widely, and choose a topic that you are eager to explore in depth.

Crafting a focused and clear research question is a pivotal element of your Extended Essay. This question not only guides your research but also frames your essay’s entire structure. It’s the question to which your essay will provide an answer, and as such, it requires thoughtful consideration and precision.
A well-developed research question should be specific, relevant, and challenging. It should invite analysis, discussion, and the exploration of significant academic literature. Here’s a deeper look into formulating a robust research question for your EE.
Characteristics of a Strong Research Question
The hallmark of a strong research question is its specificity. It shouldn’t be too broad, as this could lead to a superficial treatment of the topic.
Conversely, a question that’s too narrow might not allow for comprehensive exploration or significant discussion. Finding a balance is key. The question should also be focused on a particular aspect of a subject area, enabling in-depth analysis within the word count limit.
Another important characteristic is the question’s alignment with available resources. Before finalising your question, ensure that you have access to sufficient data and scholarly research to support your investigation. This might involve preliminary searches in academic databases, libraries, or consultation with your supervisor.
Tips for Refining Your Research Question
Start by brainstorming broad topic areas that interest you. Once you’ve identified a general area of interest, begin narrowing down by asking yourself specific questions about the topic. What aspects of this topic are unexplored or underexplored? What specific angle can I take that will make my research unique?
It’s also beneficial to review past EEs or academic journals for inspiration. Seeing how others have structured their research questions can provide valuable insight into crafting your own. However, ensure your question remains original and tailored to your interests.
Examples of Effective Research Questions
To give you an idea of what a well-formulated research question looks like, here are a few examples:
- Biology: How does the concentration of a specific nutrient affect the growth rate of plant species X in a hydroponic setup compared to soil-based growth?
- History: To what extent did the public speeches of Martin Luther King Jr. influence the public’s perception of the Civil Rights Movement in the United States between 1963 and 1968?
- Economics: How significant is the impact of recent economic policies on small businesses in [specific location] during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- English Literature: How does the use of magical realism in Gabriel García Márquez’s ‘One Hundred Years of Solitude’ reflect the political and social issues of post-colonial Latin America?
Developing your research question is an iterative process. It may evolve as you delve deeper into your research. Be open to refining your question based on the information you discover and discussions with your supervisor. A well-crafted research question will not only guide your research effectively but also engage your interest throughout the writing process, leading to a more meaningful and insightful Extended Essay.

A critical component of your Extended Essay is selecting an appropriate research methodology and theoretical framework. These elements are foundational to conducting your research and crafting your argument, influencing how you collect, analyse, and interpret data.
Understanding Research Methodologies
Research methodology refers to the systematic approach you take to investigate your research question. It encompasses the methods and procedures you use to collect and analyse data. Your chosen methodology should align with the nature of your research question and the objectives of your essay.
In the sciences, for example, your methodology might involve experiments, observations, or simulations to gather empirical data. In the humanities, you may lean towards content analysis, comparative analysis, or historical investigation, relying on textual or archival sources.
Selecting the right methodology is crucial. It should provide a clear path to answering your research question, considering the resources available and the scope of your essay. It’s also important to justify your choice of methodology in your essay, explaining why it’s appropriate for your research question and how it will help you achieve your objectives.
Applying Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks provide a lens through which your research is conducted and interpreted. They offer a structured way to understand and analyse your findings, grounding your study in existing knowledge and theories.
Choosing a theoretical framework involves identifying relevant theories, models, or concepts that apply to your topic. For instance, if you’re exploring media representation of gender, you might utilise feminist theory as a framework to analyse your findings. In economics, you might apply game theory to understand competitive behaviours in a market.
The framework should guide your analysis, providing a coherent basis for interpreting your data. It helps to structure your argument, offering a deeper insight into the significance of your findings within the broader academic discourse.
Integrating Methodology and Frameworks into Your Research
Successfully integrating your chosen methodology and theoretical framework involves a few key steps:
- Clarify the Scope: Ensure your research question, methodology, and theoretical framework align in scope and focus. They should work together seamlessly to guide your research.
- Justify Your Choices: Explain the rationale behind your chosen methodology and framework. Discuss why they are suitable for your research question and how they will support your investigation.
- Apply Consistently: Use your methodology and framework consistently throughout your research and analysis. This consistency strengthens the coherence and academic rigour of your essay.
Reflecting on these components during the planning stage can enhance the quality of your research and the clarity of your argument. Your methodology and theoretical framework are not just academic requirements; they’re tools that shape the direction and depth of your inquiry, enabling a more structured and insightful exploration of your topic.

In the journey of crafting an Extended Essay (EE), the ability to critically evaluate sources and data stands as a fundamental skill. This evaluation is crucial in establishing the credibility and reliability of the information that forms the backbone of your research. Understanding how to discern the quality and relevance of your sources ensures that your EE is built on a solid foundation of trustworthy information.
Criteria for Selecting Credible and Relevant Sources
Authority: Consider the source’s authorship. Look for works by experts in the field, academic institutions, or reputable organisations. The author’s qualifications and affiliations can significantly impact the reliability of the information.
Accuracy: The information should be supported by evidence, referenced appropriately, and free from factual errors. Reliable sources often undergo a peer-review process, ensuring that the content is scrutinised and validated by other experts in the field.
Currency: The relevance of information can diminish over time, especially in fields that evolve rapidly, such as science and technology. Ensure that the sources you use are up-to-date, reflecting the latest research and developments.
Purpose: Understand the purpose behind the information. Is it to inform, persuade, entertain, or sell? Recognising the intent can help you assess potential biases, which is particularly important when dealing with controversial topics.
Techniques for Evaluating the Reliability and Validity of Data
Cross-Verification: Cross-check information across multiple sources to verify its accuracy and reliability. Consistency among various sources can be a good indicator of the information’s validity.
Statistical Analysis: When dealing with numerical data, consider its statistical significance and the methodology used in its collection. Reliable data should be gathered using sound scientific methods and accurately represent the population or phenomena studied.
Source Evaluation Tools: Utilise tools and checklists designed to evaluate the credibility of sources. These can provide a structured approach to assessing the quality of your research materials.
Incorporating Primary vs. Secondary Sources Effectively
Primary Sources: These are firsthand accounts or direct evidence concerning the topic you’re researching. They include interviews, surveys, experiments, and historical documents. Primary sources offer original insights and data, allowing for a deeper and more personal engagement with your subject.
Secondary Sources: These sources analyse, interpret, or summarise information from primary sources. They include textbooks, articles, and reviews. Secondary sources can provide context, background, and a broader perspective on your topic.
Balancing primary and secondary sources enriches your research, providing both the raw data and the interpretations that help frame your analysis. By rigorously evaluating sources and data, you ensure that your Extended Essay rests on a foundation of credible and relevant information, enhancing the depth and rigour of your investigation.

The heart of a compelling Extended Essay (EE) lies in the seamless integration of evidence and analysis. This integration not only supports and substantiates your arguments but also demonstrates your ability to critically engage with your research topic. Here’s how to weave evidence and analysis together in a way that enhances the strength and persuasiveness of your EE.
Strategies for Integrating Evidence Seamlessly into Your Argument
Directly Link Evidence to Your Thesis: Every piece of evidence you include should directly support or relate to your thesis statement. This ensures that all the information contributes to building your argument coherently.
Use Evidence to Illustrate Points: Utilise examples, data, quotes, and case studies as concrete evidence to illustrate your points. This makes abstract concepts more tangible and convincing to the reader.
Analyse, Don’t Just Present: For every piece of evidence, provide analysis and interpretation. Explain how it supports your argument, what it demonstrates, and its implications for your research question.
Balancing Descriptive and Analytical Writing
Avoid Over-Description: While some description is necessary to set the context, avoid dedicating too much space to merely describing your evidence. The focus should be on analysis.
Develop a Critical Voice: Cultivate a critical approach to your evidence. This means evaluating its reliability, considering its limitations, and discussing its relevance to your argument.
Synthesise Information: Aim to synthesise evidence from multiple sources to support your points. This demonstrates comprehensive understanding and the ability to draw connections across your research.
How to Critically Analyse Sources and Data Within Your Essay
Question the Source: Consider the source’s origin, purpose, and potential bias. How might these factors influence the information presented?
Evaluate Methodology: If the evidence comes from a study or experiment, evaluate the methodology used. Is it sound and appropriate for the research question?
Consider the Broader Context: Place your evidence within the broader scholarly conversation on your topic. How does it fit with, challenge, or expand existing knowledge?
By thoughtfully integrating evidence and providing in-depth analysis, you can create a nuanced and compelling EE that goes beyond mere description to offer original insights into your topic. This approach not only strengthens your argument but also showcases your critical thinking and analytical skills, essential qualities for success in the IB Diploma Programme and beyond.
The Extended Essay presents an opportunity for IB students to engage deeply with a topic of their choice. However, to effectively communicate your research and insights, your essay must be well-structured and clearly written.
This section provides guidance on how to write and structure your EE, ensuring your work is coherent, persuasive, and academically rigorous.
Outline of the Extended Essay Structure
A well-organised structure is crucial for the readability and coherence of your EE. Typically, an Extended Essay includes the following components:
- Title Page: Displays the essay title, research question, subject the essay is registered in, and word count.
- Abstract: A concise summary of the essay, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusion (Note: For essays submitted in 2018 and forward, the IB no longer requires an abstract, so check the most current guidelines).
- Contents Page: Lists the sections and subsections of your essay with page numbers.
- Introduction: Introduces the research question and your essay’s purpose, outlining the scope of the investigation.
- Body : The main section of your essay, divided into clearly titled subsections, each addressing specific aspects of the research question. It’s where you present your argument, supported by evidence.
- Conclusion: Summarises the findings, discusses the implications, and reflects on the research’s limitations and potential areas for further study.
- References/Bibliography: Lists all sources used in the essay in a consistent format, following the chosen citation style.
- Appendices: (If necessary) Contains supplementary material that is relevant to the research but not essential to its explanation.
Detailed Breakdown of Each Section
Introduction:
The introduction sets the stage for your research. It should clearly state your research question and explain the significance of the topic. Briefly outline the theoretical framework and methodology, and provide an overview of the essay’s structure.
The body is the heart of your essay. It should be logically organised to build your argument step by step. Each paragraph should start with a clear topic sentence, followed by evidence and analysis. Use subheadings to divide the sections thematically or methodologically, ensuring each part contributes to answering the research question.
- Developing Arguments: Present and critique different perspectives, systematically leading the reader through your analytical process.
- Using Evidence: Incorporate relevant data, quotes, and examples to support your arguments. Ensure all sources are appropriately cited.
- Analysis and Discussion: Go beyond describing your findings; analyse and interpret them in the context of your research question and theoretical framework.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should not introduce new information. Instead, it should synthesise your findings, highlighting how they contribute to understanding the research question. Reflect on the research process, acknowledging any limitations and suggesting areas for further investigation.
Importance of Coherence and Logical Flow
Maintaining coherence and a logical flow throughout your EE is essential. Transition sentences between paragraphs and sections can help link ideas smoothly, guiding the reader through your argument. A coherent structure ensures that your essay is accessible and persuasive, making a strong impression on the reader.
A well-written and structured EE is a testament to your understanding of the research process and your ability to communicate complex ideas effectively. By adhering to a clear structure and focusing on coherence and logical progression, you can craft an essay that is engaging, insightful, and academically rigorous.

A unique and integral component of the IB Extended Essay (EE) process is the Reflections on Planning and Progress Form (RPPF). The RPPF serves as a personal and academic exploration tool, guiding students through the planning, research, and writing phases of their EE. It encourages students to reflect on their learning journey, documenting insights gained, challenges encountered, and the evolution of their thinking.
The Role of Reflection in the EE Process
Reflection is at the heart of the EE, enabling students to engage critically with their own learning processes. It helps in:
- Self-Assessment: Encouraging students to consider their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Skill Development: Facilitating a deeper understanding of the research and writing skills developed during the EE process.
- Critical Thinking: Promoting an evaluative approach to the research process, allowing students to make informed decisions about their methodologies, sources, and arguments.
How to Effectively Complete the RPPF
Completing the RPPF involves three formal reflection sessions, which are crucial milestones in the EE journey:
- Initial Reflection: Focuses on the selection of the topic and formulation of the research question. Students should discuss their motivations, initial ideas, and anticipated challenges.
- Interim Reflection: Occurs midway through the process. Students reflect on the progress made, adjustments to their research plan, and any challenges they’ve faced. It’s an opportunity to reassess the direction of the EE and make necessary modifications.
- Final Reflection: After completing the EE, students reflect on their overall experience, the skills they’ve developed, and the knowledge they’ve gained. This reflection should also consider the impact of the research process on their personal and academic growth.
In each reflection, students should be honest and critical, providing insights into their learning journey. The reflections are not just about documenting successes but also about understanding the learning process, including setbacks and how they were overcome.
Examples of Reflective Questions and Insightful Responses
Initial reflection:.
Question: “What excites me about my chosen topic?”
Insightful Response: Discuss the personal or academic interest in the topic, any prior knowledge, and what you hope to discover through your research.
Interim Reflection:
Question: “What challenges have I encountered in my research, and how have I addressed them?”
Insightful Response: Describe specific obstacles, such as difficulty accessing resources or refining the research question, and the strategies employed to overcome them.
Final Reflection:
Question: “How has my understanding of the topic evolved through the research process?”
Insightful Response: Reflect on how the research challenged or confirmed initial assumptions and what was learned about the topic and the research process itself.
The RPPF is not just a formal requirement but a valuable component of the EE that enriches the student’s learning experience. By fostering reflection, the RPPF helps students to articulate their journey, offering insights into the complexities of research and the personal growth that accompanies the creation of an extended academic work.

The Extended Essay allows students to explore a topic of interest within the framework of an IB subject. The choice of academic discipline not only shapes the content and focus of the essay but also influences the methodologies and theoretical frameworks that students may employ. Understanding and adhering to the conventions and requirements of the chosen discipline is crucial for the success of the EE.
Adhering to Disciplinary Conventions and Guidelines
Each academic discipline has its own set of conventions regarding research methodologies, writing styles, and citation formats. For example, a science EE might require empirical research and quantitative analysis, whereas an essay in the humanities might focus on qualitative analysis and critical interpretation of texts.
Key considerations include:
- Methodology: The choice of methodology should align with disciplinary norms. Science EEs might involve experiments, whereas essays in history might rely on primary source analysis.
- Structure: While the basic structure of the EE remains consistent across subjects, the presentation of arguments and evidence might vary. Essays in the arts and humanities might follow a thematic structure, while those in the sciences might be organised around experimental findings.
- Citation Style: Different disciplines prefer specific citation styles. For instance, APA might be favoured in psychology, while MLA is commonly used in literature essays. Adhering to the appropriate style is crucial for academic integrity.
How Different Disciplines Influence the Approach to Research and Writing
The academic discipline not only dictates the formal aspects of the EE but also influences the approach to research and writing. For instance, an EE in Visual Arts would require a different analytical lens compared to an EE in Economics. The former might analyse the impact of cultural contexts on artistic expressions, while the latter could evaluate economic theories through case studies.
Disciplinary perspectives also affect:
- Argumentation : The way arguments are constructed and evidenced can differ. In the sciences, arguments are often built around data and logical reasoning, while in the humanities, they might be more interpretative, drawing on various theoretical perspectives.
- Critical Engagement: The extent and nature of critical engagement with sources can vary. In subjects like History or English, a critical analysis of diverse interpretations is fundamental, whereas in the Sciences, the focus might be on empirical evidence and hypothesis testing.
Examples of Disciplinary Perspectives in Extended Essay Examples
- Biology EE: An investigation into the effects of environmental changes on local biodiversity, employing scientific methods for data collection and analysis.
- Economics EE: An analysis of the impact of a specific economic policy on a local economy, using economic theories and models to interpret data.
- English Literature EE: A comparative study of the theme of alienation in two novels, using literary theories to explore the authors’ narrative techniques.
Understanding the significance of academic discipline in the EE ensures that students approach their research with the appropriate methodologies and analytical frameworks. It encourages respect for the depth and breadth of the subject area, contributing to a more nuanced and informed exploration of the chosen topic.

Writing an Extended Essay involves more than just conducting research and presenting findings; it requires careful planning, effective engagement with your supervisor, and a critical approach to your sources. Here are some best practices to help you navigate the EE writing process successfully.
Time Management and Planning
Time management is crucial in the EE process. The project spans several months, so it’s essential to break down the work into manageable stages. Create a timeline early in the process, including key milestones such as completing the research, drafting sections, and finalising the essay. Allocate time for unexpected challenges and ensure you have buffer periods for revision and feedback.
Planning Tips:
- Set Goals: Establish clear, achievable goals for each phase of your EE journey.
- Use Tools: Leverage planning tools or software to organise your tasks and deadlines.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review your progress against your plan and adjust as necessary.
Engaging with Supervisors Effectively:Your supervisor is a valuable resource throughout the EE process. They can provide guidance on your research question, methodology, and essay structure, as well as feedback on your drafts.
Maximising Supervisor Engagement:
- Prepare for Meetings: Come to each meeting with specific questions or sections of your essay you want feedback on.
- Be Open to Feedback: Constructive criticism is essential for improvement. Listen to your supervisor’s suggestions and consider how to incorporate them into your work.
- Communicate Regularly: Keep your supervisor informed of your progress and any challenges you encounter.
Critical Engagement with Sources
A critical approach to the sources you use is fundamental to a high-quality EE. Evaluate the reliability, relevance, and bias of your sources to ensure your essay is grounded in credible evidence.
Strategies for Source Evaluation:
- Source Variety: Use a range of sources, including academic journals, books, and reputable online resources, to provide a balanced perspective on your topic.
- Critical Analysis : Don’t just summarise sources. Analyse their arguments, identify limitations, and consider how they contribute to your research question.
- Citation and Paraphrasing: Accurately cite all sources to avoid plagiarism. When paraphrasing, ensure you’re genuinely rephrasing ideas in your own words while still crediting the original author.
Good practice in EE writing is not just about adhering to academic standards; it’s about engaging deeply with your topic, embracing the research process, and developing skills that will serve you well in your academic and professional future. By managing your time effectively, leveraging the support of your supervisor, and critically engaging with sources, you can craft an EE that is not only academically rigorous but also personally rewarding.

Successfully navigating the Extended Essay process requires more than just academic skill; it demands effective project management. This encompasses planning, organising, and executing your EE from initial conception to final submission. Here are strategies to help you manage the EE process, ensuring a smooth journey and a rewarding outcome.
Planning and Time Management Strategies Specific to the EE
Develop a Detailed Plan: Start by breaking down the EE process into stages: topic selection, research, drafting, and revising. Assign deadlines to each stage based on the final submission date, allowing extra time for unforeseen delays.
Use a Calendar or Planner: Keep track of deadlines, meetings with your supervisor, and other important dates. Digital tools can be particularly useful, offering reminders and helping you stay organised.
Set Regular Milestones: Milestones offer checkpoints to assess your progress. These could be completing the research phase, finishing a first draft, or finalising your citations. Celebrate these achievements to stay motivated.
Milestones and Checklists to Keep You on Track
Create Checklists: For each phase of the EE process, develop a checklist of tasks. This could include conducting initial research, writing specific sections of the essay, or completing rounds of revision.
Regular Progress Reviews: Schedule weekly or bi-weekly reviews of your progress against your plan. Adjust your plan as needed based on these reviews.
Stay Flexible: Be prepared to adapt your plan. Research might take longer than expected, or you might decide to change your focus slightly after discussing with your supervisor.
Dealing with Challenges and Setbacks During the EE Journey
Anticipate Potential Issues: Think ahead about what might go wrong and how you would address it. Having contingency plans can reduce stress and keep you on track.
Seek Support When Needed: Don’t hesitate to reach out to your supervisor, peers, or other mentors if you encounter obstacles. They can offer advice, support, and perspective.
Maintain a Positive Attitude: Challenges are part of the learning process. View setbacks as opportunities to improve your problem-solving and resilience skills.
Managing the EE process effectively is about more than just completing a requirement for the IB Diploma; it’s an exercise in self-management and personal growth. By carefully planning your work, setting and celebrating milestones, and being prepared to tackle challenges, you can navigate the EE process with confidence and achieve a result that reflects your hard work and dedication.

Mastering the art of collaboration and effectively incorporating feedback are pivotal aspects of crafting a high-calibre Extended Essay (EE). These processes enrich your work, offering new perspectives and insights that can significantly enhance the depth and quality of your research and writing. Let’s delve into how to navigate these collaborative interactions and integrate feedback productively.
Effective Collaboration with Your Supervisor
Your supervisor is a key ally in your EE journey, providing guidance, support, and expert insight into your chosen topic. Building a productive relationship with your supervisor involves clear communication, active engagement, and receptiveness to their advice.
- Prepare for Meetings: Maximise the value of your meetings by preparing questions and topics for discussion. This shows initiative and helps you focus on areas where you need the most guidance.
- Be Open to Suggestions: Your supervisor brings a wealth of experience and knowledge. Being open to their suggestions can unlock new avenues of inquiry and refine your research focus.
- Follow Up: After meetings, review the guidance provided and take action. Following up on suggestions and demonstrating progress is key to a fruitful collaboration.
Incorporating Feedback Constructively
Feedback is a gift, offering you fresh eyes on your work and highlighting areas for improvement. Whether it comes from your supervisor, peers, or other mentors, constructive feedback is instrumental in elevating the quality of your EE.
- Critically Evaluate Feedback: Not all feedback will be equally applicable or helpful. Assess suggestions critically and decide which ones align with your research goals and vision for your EE.
- Implement Changes Thoughtfully: When integrating feedback, do so thoughtfully and systematically. Consider how each piece of advice enhances your argument or strengthens your analysis.
- Maintain Your Own Voice: While it’s important to consider feedback, your EE should ultimately reflect your ideas, analysis, and voice. Balance the input from others with your own scholarly insights.
Balancing Independent Research with Guidance
Navigating the balance between independent research and the guidance received is a delicate aspect of the EE process. While the EE is your project, drawing on the expertise and feedback of others can significantly enhance its depth and scope.
- Value Independence: Embrace the opportunity to conduct independent research, making your EE a true reflection of your interests and intellectual curiosity.
- Seek Guidance Wisely: Utilise your supervisor and other resources judiciously. They can provide clarity, offer new perspectives, and help you navigate complex aspects of your research.
- Synthesise Input: Integrate the guidance and feedback you receive in a way that complements your research, ensuring that your EE remains a coherent and cohesive piece of scholarly work.
The interplay between collaboration, feedback, and independent research is central to the EE process. By engaging effectively with your supervisor, thoughtfully incorporating feedback, and maintaining a balance between guidance and your own scholarly pursuits, you can craft an EE that is not only academically rigorous but also a true testament to your growth as a learner.
Plagiarism is a critical concern in academic writing, including the Extended Essay. It involves using someone else’s work without proper acknowledgment, which can compromise the integrity of your essay and result in severe penalties. Understanding what constitutes plagiarism and how to avoid it is essential for maintaining academic honesty and ensuring the credibility of your research.
Understanding What Constitutes Plagiarism
Plagiarism can take many forms, from directly copying text without quotation marks to paraphrasing someone else’s ideas without proper citation. It also includes using images, charts, or data without acknowledging the source. Even unintentional plagiarism, where sources are not deliberately misrepresented but are inadequately cited, can have serious consequences.
How to Properly Cite Sources and Paraphrase
Citing Sources : Every time you use someone else’s words, ideas, or data, you must cite the source. This not only includes quotes and paraphrases but also data, images, and charts. Familiarise yourself with the citation style recommended for your subject area, whether it be APA, MLA, Chicago, or another, and apply it consistently throughout your essay.
Paraphrasing: Paraphrasing involves rewording someone else’s ideas in your own words. It’s essential to do more than just change a few words around; you need to completely rewrite the concept, ensuring you still cite the original source. Good paraphrasing demonstrates your understanding of the material and integrates it seamlessly into your argument.
Using Plagiarism Detection Tools
Many schools and students use plagiarism detection tools to check the originality of their work before submission. These tools compare your essay against a vast database of published material and other student submissions to identify any matches. Utilising these tools can help you identify areas of your essay that need better paraphrasing or citation.
Avoiding plagiarism in the EE involves diligent research, careful writing, and thorough citation. It’s about respecting the intellectual property of others while demonstrating your own understanding and analysis of the topic. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your EE is both original and academically honest, reflecting the hard work and integrity that define the IB learner profile.

In the Extended Essay, showcasing original thought is not just encouraged; it’s a cornerstone of what makes an EE stand out. Originality in this context means more than just avoiding plagiarism; it involves presenting unique perspectives, developing novel arguments, or exploring new areas within a subject. Here’s how you can emphasise original thought in your EE.
The Value of Originality and Creativity
Originality and creativity in the EE demonstrate your ability to think independently and engage critically with your subject. It shows that you’re not just capable of summarising existing knowledge but also contributing to the conversation in your discipline. This level of engagement is what the IB looks for in assessing the EE, as it reflects a deeper understanding and application of the subject matter.
Balancing Academic Rigour with Personal Voice and Analysis
While it’s important to ground your EE in academic research and follow disciplinary conventions, finding a balance with your personal voice and analysis is key to originality. Here are ways to achieve this balance:
- Personal Insight : Inject your essay with your insights, interpretations, and conclusions based on the research. This personal engagement with the topic distinguishes your EE from a mere literature review.
- Critical Analysis: Go beyond describing what others have said. Critique the arguments, identify gaps in the research, and propose new ways of understanding the subject.
- Innovative Approach: Consider addressing less explored aspects of your topic or applying theories and methodologies from other disciplines to bring fresh perspectives.
Strategies for Developing and Showcasing Original Thought
Question Assumptions: Start by questioning the prevailing assumptions or widely held beliefs in your subject area. This critical stance can open up avenues for original analysis.
Interdisciplinary Connections: Drawing connections between different disciplines can reveal new insights and approaches that enrich your essay.
Reflect on Your Learning: Use the insights gained from your coursework and personal interests to inform your approach. Often, your unique educational and life experiences can inspire original perspectives.
Emphasising original thought in your EE is about striking a balance between demonstrating your mastery of the subject and pushing beyond the boundaries of existing knowledge. It involves a blend of thorough research, critical thinking, and creative engagement with the topic. By fostering a unique perspective and injecting your personal voice into your analysis, you can create an EE that is not only academically rigorous but also distinctly yours, leaving a lasting impression on your readers.

The culmination of the Extended Essay process includes the final presentation and the Viva Voce, a concluding interview between the student and their supervisor. These components serve not only as a summation of your EE journey but also as an opportunity to reflect on your learning and the skills you’ve developed. Understanding the significance and how to prepare for these elements is crucial for a successful EE completion.
Preparing for the Final Presentation
The final presentation is an opportunity to share the highlights of your EE journey, including your research question, methodology, key findings, and any challenges you overcame. It’s a moment to showcase the depth of your research and the personal growth you experienced throughout the process.
Key Elements to Include:
- Overview of Your Research: Briefly summarise your research question and why you chose it, highlighting your methodology and the scope of your investigation.
- Significant Findings: Share the key insights and discoveries you made during your research. This is a chance to underscore the original contributions of your EE.
- Challenges and Solutions : Discuss any significant obstacles you faced and how you addressed them. Reflecting on these challenges shows your problem-solving skills and resilience.
- Reflections on the Process: Share what you’ve learned about yourself as a learner, the skills you’ve developed, and how the EE has impacted your academic and personal growth.
Tips for a Successful Viva Voce
The Viva Voce is a short interview with your supervisor after you’ve submitted your EE. It’s an integral part of the reflection process, allowing you to discuss the successes and challenges of your research journey.
To Prepare for the Viva Voce:
- Review Your EE: Be familiar with your essay’s content, as you’ll discuss your work in detail. Be ready to explain your research decisions and reflect on your learning process.
- Anticipate Questions: Your supervisor might ask about how you selected your topic, the development of your research question, your approach to research and writing, and the skills you’ve developed.
- Reflect on Your Learning: Think about the entire EE process, including what you learned, how you’ve grown, and how the experience might influence your future academic or career goals.
How the Viva Voce Contributes to Your Overall EE Assessment
While the Viva Voce doesn’t directly affect your EE grade, it plays a crucial role in the holistic assessment of your IB Diploma. It demonstrates the authenticity of your work and your engagement with the EE process, providing insights into your approach, dedication, and intellectual growth.
The final presentation and Viva Voce are essential milestones that mark the completion of your EE journey. They offer a platform to reflect on the challenges you’ve navigated, the knowledge you’ve gained, and the skills you’ve honed. Preparing thoroughly for these elements ensures you can confidently articulate your research journey, showcasing the depth of your inquiry and your development as an IB learner.

The journey through the Extended Essay is more than an academic exercise; it’s a transformative experience that equips IB Diploma students with skills and insights that extend far beyond the programme.
Reflecting on how the EE prepares you for future academic and professional endeavours can highlight the lasting value of this rigorous project.
How the Skills Developed During the EE Can Benefit You in Future Academic and Professional Endeavours
Research and Analytical Skills: The EE demands a high level of research and analysis, teaching students how to gather, assess, and interpret data. These skills are invaluable in higher education and many professional fields, where evidence-based decision-making is crucial.
Critical Thinking: Crafting an EE requires students to evaluate sources critically, consider multiple perspectives, and develop well-reasoned arguments. This ability to think critically is highly sought after in both academia and the workplace.
Project Management: Completing an EE involves planning, organisation, time management, and problem-solving. Managing such a long-term project successfully can boost your confidence in handling complex tasks and projects in the future.
Communication: Writing the EE enhances your ability to communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively, a skill that is essential in any professional setting. Additionally, the final presentation and Viva Voce develop your verbal communication and presentation skills.
Examples of How the EE Has Helped Alumni in Their Post-IB Journeys
Many IB alumni attribute their success in university and their careers to the foundation laid by their EE experience. For instance, alumni often report that the EE made the transition to university-level research and writing much smoother. Others have found that the skills developed through the EE, such as critical thinking and project management, have set them apart in job interviews and workplace projects.
Encouragement to View the EE as a Stepping Stone to Lifelong Learning
The EE is not just a requirement for the IB Diploma; it’s an introduction to a lifelong journey of inquiry and discovery. It encourages a mindset of curiosity and a habit of continuous learning that can enrich both your personal and professional life. Viewing the EE through this lens can transform it from a daunting task into an exciting opportunity to explore your passions and develop essential skills for the future.
The Extended Essay is a hallmark of the IB Diploma Programme, embodying the essence of inquiry, critical thinking, and scholarly engagement. From selecting a topic and formulating a research question to conducting in-depth research and presenting findings, the EE challenges students to transcend the boundaries of traditional learning, fostering skills and insights that extend far beyond the confines of the classroom.
This comprehensive guide has navigated the critical aspects of the EE process, offering strategies for managing time, engaging with supervisors, and ensuring academic integrity. It has underscored the importance of original thought, the role of academic discipline, and the value of reflection, aiming to equip students with the tools they need to succeed in this rigorous academic endeavour.
The Extended Essay is a testament to your dedication, intellectual curiosity, and academic prowess. Embrace this opportunity to shine, to explore, and to make your mark on the world of knowledge.
How can we help?
The Extended Essay Step by Step Guide 5: Structure and Planning

When it comes to writing a brilliant first draft of your Extended Essay, or any essay, I fully believe that a solid structure is one of the surest guarantees of success there is. It’s the skeleton of the essay that makes it into a fully formed being instead of a pile of jelly. And the best way to make sure you have a skeleton instead of just gelatine (is that a rhyme?) is to create a plan or outline.
We’ve talked about how to choose a topic , go about your research , and pin down a research question. So now we’re going to address how you can take all of that work and turn it into a concrete plan. It’s all about organising your ideas so that they are as clear as possible. After you’ve done this, writing the essay will be about simply filling in the gaps!
Preparing to construct your Extended Essay Outline
Know your destination.
Although your research question should already suggest what you are aiming to achieve in the essay, your conclusion needs to take this a step further. It can’t just be the same as your introduction but in different words (as tempting as that option is!). Everything in your essay should take the reader on a journey to this conclusion. It should help progress your argument so that we get closer with every paragraph.
If you’re now realising that you don’t know your destination, take the time to figure this out before you start writing. The results of a Science experiment will make it pretty obvious, but even in more subjective subjects such as English, History and World Studies you need to decide what conclusion your research points towards.
My advice to you, if you simply aren’t sure, is to follow your instincts. Think about how your evidence has affected what you personally think about the topic. Chances are it will have convinced you of something. For a reminder of different types of essay conclusions, there are some useful summaries in this article.

Define your ideas
Take a moment to free your mind from all the details, facts, quotes and data. Go back to the essence of your essay, which is the argument you are trying to make. Without using your research to speak for itself, identify all the different ideas you want to include, and the things you want to say.
For example, you might have evidence that Virginia Woolf uses imagery of flowers frequently throughout Mrs Dalloway , but what does this actually mean in the context of your question? The idea behind it might relate more to her affinity with nature, or the parallels she draws between flowers and people.
Exercise 2: write down all the ideas you want to include in your essay. Don’t worry about an order yet. Focus instead of getting all of your ‘points’ written down somewhere. Not only is this likely to help your organise your thoughts, but it will also mean you can refer back to it later to make sure you haven’t forgotten one of your favourite ideas! This can take the form of a mind map, a list, a Word Doc. Do whatever feels easiest, because chances are this is what will help your ideas flow naturally.
Filter your evidence
I can 99% guarantee you that you won’t be able to use all the research you have done. A lot of it will be:
- Irrelevant to the question
- Repetition of what you already have
- Not quite right for your line of argument
THEREFORE it is important that you filter your evidence so that you only have the best examples and information.
Use your research question as your starting point and your conclusion sentence (the one you wrote earlier) as the end point. It is your job to make sure that every piece of research is part of a bridge between the two. Absolutely every quote, fact or piece of data that you include should actively answer your question. If it doesn’t, don’t include it.
Exercise 3: First, highlight the clearest, most informative research that you have gathered. Next, take all of these pieces of research, and write a short, one-sentence summary next to each one, describing how it relates to your question. Use your own words. You will hopefully start finding that they are backing up some of the points you know you want to include.
Constructing your Extended Essay Outline
There are different techniques you can use to structure an essay. Because the Extended Essay is much longer than what most of you will be used to, I strongly recommend using a particular technique or process to do this. Below are some examples, and you should do whatever works best for you.
The Bullet-Point Outline:
You know this one. It’s the most classic example of how to structure an essay and the one most of you have probably tried before. The trick with this one is to start small and expand outwards afterwards.
- Summarise each paragraph into one line that defines the idea or sub-topic behind it.
- Evidence, data or a quote
- How the example relates to the idea you are trying to convey
- Expand your paragraph bullet points by adding in other ideas or points that are directly relevant to the overall idea behind it
The Post-it Note Outline:
I’m defining this as anything that involves you breaking down your paragraphs into defined pieces. Post-it notes, cards, and scraps of paper are the most common examples. This option is brilliant if you struggle coming up with an order for your ideas straight away. Instead it lets you play around with all the different parts of your essay as you go, until you have put them in the best possible order.

If you like the idea of this process but can’t stand the idea of lots of physical pieces of paper, there are some apps that perform a similar function such as Gingko or Evernote .
The Spreadsheet Outline:
For the structure nuts among you. The beauty of this is that it lets you easily compare paragraphs in terms of length and content by breaking each one down into clear sections. You can choose how exactly you format it, but it might look like this:
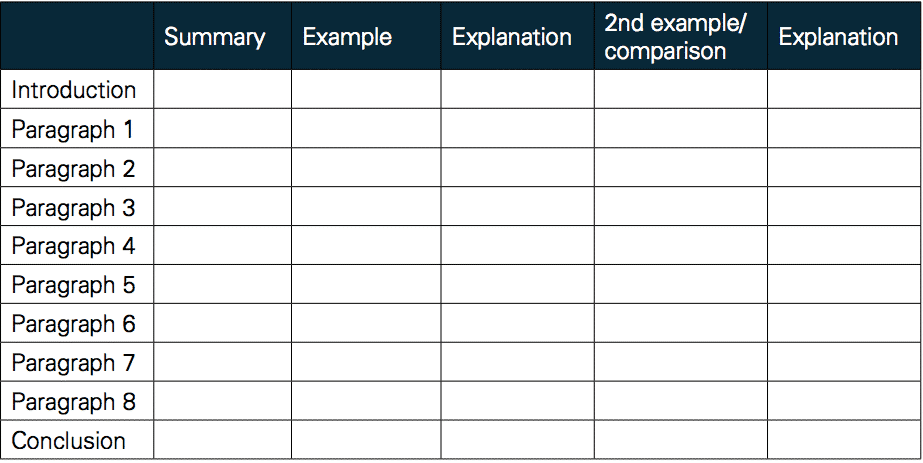
As with the post-it version it is super easy to use this method to change the order of your paragraphs. You can also tailor the columns depending on what categories are most relevant to you. If you want to go a step further you can even colour code your sheet, for example according to 1st hand data or 2nd hand data, or close analysis and thematic analysis.
The key is to have a view of the bigger picture of your essay. How you go about it is up to you!
Read Part 6 – How to write it!
Share article links
Related Articles

- IB - Understanding It
- Most Popular
- Plan for Success
- Revision Skills
Top 5 Essentials for Studying Biology
Every group of subjects in the IB has its own set of challenges, and no one strategy will fit every class. So this week, let’s talk about the essentials for studying good ol’ Biology during the IB! 1. Draw diagrams One of the benefits of studying biology is that most topics we learn are […]

- IB Extended Essay
How to Write an Extended Essay Proposal
The first ‘official’ step in the Extended Essay process is often writing a proposal. This can seem intimidating at first, but it’s a really helpful thing to write. It’s a great way to get an overview of the steps along the EE journey and it helps you get started – which can be one of […]

How to Write an Extended Essay Proposal – Part 2
This week we’re continuing our “How to Write an Extended Essay Proposal” series. Check out the first part of this series here for a rundown of the different sections that your proposal should include. Here we’ll take a look at a few common problems people encounter when writing their proposal. Problem 1: “I don’t have […]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For the Extended Essay, you will choose a research question as a topic, conduct the research independently, then write an essay on your findings. The essay itself is a long one—although there's a cap of 4,000 words, most successful essays get very close to this limit.
To write an impressive extended essay, you should focus on appropriate information. You must create a separate page for bibliography with all sources you used. Tip from us: start writing this page with the first quote you use. Don't write this part last or postpone. In turn, appendices are not an essential section.
The extended essay is an independent, self-directed piece of research, finishing with a 4,000-word paper. One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students. Read about the extended essay in greater detail. You can also read about how the IB sets deadlines for ...
Just write. No one will see it but you. Exercise 2: Pick one of the three options above and try it: write your favourite ‘piece’ of the essay first, write as much as you can by hand in one writing sprint, or lose the grammar and just get the ideas down in the right order. 3. Perfect Your Extended Essay Language.
10 Steps to Writing an IB Extended Essay. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write an extended essay, from research question to complete essay. 1. Define the Topic and Draft the Research Question. 2. Create a Timeline. 3. Research sources and expand knowledge about the topic. 4.
IB Extended Essay Rubric. Although your IB Extended Essay provides a report that factors into your grade, your essay will also be assessed by external examiners the IB. Per the IB Extended Essay Rubric, essays are graded on a scale from 0 to 34 based on 5 different criteria: Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
To write a comprehensive Extended Essay on any subject within the 40 hours: 1. Choose a Topic. The first step to write an EE is to choose an Extended Essay topic to explore. Unfortunately, you can’t scrape a good topic off a book or ask a friend in your IB class to share their thoughts.
The IB Extended Essay is a rigorous independent research project at the heart of the IB Diploma Programme. It challenges high school students to dive into a chosen subject of personal interest in a structured and scholarly manner. The Extended Essay requires students to engage in extensive research, develop a clear research question or ...
The Extended Essay has several key objectives: To provide students with the chance to engage in an in-depth study of a question of interest within a chosen subject. To develop research, thinking, self-management, and communication skills. To introduce students to the excitement and challenges of academic research.
The idea behind it might relate more to her affinity with nature, or the parallels she draws between flowers and people. Exercise 2: write down all the ideas you want to include in your essay. Don’t worry about an order yet. Focus instead of getting all of your ‘points’ written down somewhere.