- Member login
- Pre-algebra lessons
- Pre-algebra word problems
- Algebra lessons
- Algebra word problems
- Algebra proofs
- Advanced algebra
- Geometry lessons
- Geometry word problems
- Geometry proofs
- Trigonometry lessons
- Consumer math
- Baseball math
- Math for nurses
- Statistics made easy
- High school physics
- Basic mathematics store
- SAT Math Prep
- Math skills by grade level
- Ask an expert
- Other websites
- K-12 worksheets
- Worksheets generator
- Algebra worksheets
- Geometry worksheets
- Free math problem solver
- Pre-algebra calculators
- Algebra Calculators
- Geometry Calculators
- Math puzzles
- Math tricks

Kinetic energy problems
When solving kinetic energy problems, you may be asked to find 3 variables. These variables are the kinetic energy, the mass, or the speed.
Problem # 1:
Suppose a car has 3000 Joules of kinetic energy. What will be its kinetic energy if the speed is doubled? What if the speed is tripled?
We already proved in kinetic energy lesson that whenever the speed is doubled, the kinetic energy is quadrupled or four times as big.
4 × 3000 = 12000
Therefore, the kinetic energy is going to be 12000 joules.
Let v be the speed of a moving object. Let speed = 3v after the speed is tripled.
9 × 3000 = 27000
Therefore, the kinetic energy is going to be 27000 joules.
Problem # 2:
Calculate the kinetic energy of a 10 kg object moving with a speed of 5 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy again when the speed is doubled.
Tricky kinetic energy problems
Problem # 3:
Suppose a rat and a rhino are running with the same kinetic energy. Which one do you think is going faster?
The only tricky and hard part is to use the kinetic energy formula to solve for v.
Multiply both sides by 2
Problem # 4:
The kinetic energy of an object is 8 times bigger than the mass. Is it possible to get speed of the object?
Think carefully and try to solve this problem yourself.
Potential energy
Applied math
Calculators.
100 Tough Algebra Word Problems. If you can solve these problems with no help, you must be a genius!

Recommended
About me :: Privacy policy :: Disclaimer :: Donate Careers in mathematics
Copyright © 2008-2021. Basic-mathematics.com. All right reserved
- My Storyboards
Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheets
Customize energy worksheets.
If you're assigning this to your students, copy the worksheet to your account and save. When creating an assignment, just select it as a template!
Enhancing Learning with Worksheets: Teaching Potential and Kinetic Energy
In the dynamic world of science education, finding effective methods to teach complex concepts is essential for fostering student understanding and engagement. One such intricate topic is the interplay and difference between kinetic and potential energy. These concepts play a vital role in our understanding of the physical world and are fundamental to comprehending various natural phenomena.
Understanding Potential and Kinetic Energy
Potential energy is the stored energy an object possesses due to its position or configuration, while kinetic refers to the energy of motion an object gains from its velocity. These two forms are closely related and often transform from one to the other as objects move in their environments.
Worksheet Ideas
- Definitions Match: Provide a list of energy-related terms and their definitions. Ask your class to match each term with its correct explanation. Answers can be included as a helpful resource for students to verify their solutions.
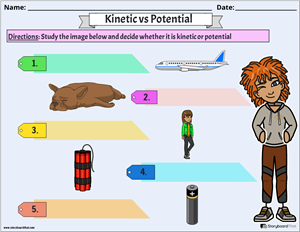
- Kinetic vs Potential Energy Worksheet: Present a mix of images or descriptions of objects in motion and at rest. Students can label each example with the correct type as potential or kinetic. Activities like these encourage active participation, reinforce understanding, and provide practical application of the concepts, fostering a deeper grasp of the interplay between these two essential forms.
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Roller Coaster Worksheet: Offer a roller coaster diagram at different points along the track. Students identify and calculate the potential and kinetic energy at each point.
- Kinetic and Potential Quiz Worksheet: Present a series of statements related to kinetic and potential energy. Students determine if each statement is true or false and describe why they chose their answer.
- Kinetic and Potential Energy Transformation Worksheet: Create a flowchart, or force diagram, depicting the transformation between potential and kinetic forms in various scenarios, specifically when work is done on an object to cause movement. Students complete the flowchart with labels and arrows.
- Flow Diagram: Offer a diagram illustrating a specific energy flow, such as the process of energy production in a power plant. Students label the diagram with the correct stages and types of energy involved.
Steps to Make a Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet
- Define Learning Objectives: Clearly outline the objectives of your kinetic and potential energy worksheet. Identify the specific concepts and skills you want your class to grasp, such as understanding the relationship between these different types.
- Choose Relevant Content: Select content that aligns with your learning objectives. Include examples, scenarios, and real-life situations that demonstrate the concepts of kinetic and potential energy in various contexts.
- Craft Engaging Questions: Develop a variety of engaging questions that prompt critical thinking and application. Incorporate different question types, such as multiple-choice, short answer, and problem-solving questions, to cater to diverse learning styles.
- Include Visual Aids: Enhance comprehension by incorporating diagrams, graphs, and illustrations. Visual aids make abstract ideas more concrete and accessible to learners.
- Progressive Complexity: Structure the worksheet with a gradual increase in complexity. Start with foundational questions that introduce basic concepts and then progress to more challenging scenarios that require deeper analysis.
- Real-World Scenarios: Integrate real-world scenarios, such as creating a potential and kinetic roller coaster worksheet, to illustrate the transformation between kinetic and potential energy. This adds relevance and makes the concepts relatable.
- Provide a Potential Vs Kinetic Energy Worksheet Answer Key: Offer an answer key for your kinetic and potential worksheet as a separate resource. This allows educators to verify correctness and provides a valuable tool for student self-assessment and review. Not only does including a kinetic and potential energy worksheet answer key empower learners to gauge their progress and accuracy, but it also encourages independent learning, fosters self-confidence, and enables them to address any misconceptions they might have about energy transformations.
- Review and Refine: Before finalizing, review the worksheet to ensure it aligns with your learning objectives, features relevant keywords, and effectively engages your class. Make necessary revisions to enhance clarity and effectiveness.
More Storyboard That Resources and Printables
- Science Lab Worksheet
- Introduction to Energy
- Different Types of Energy
- Scientific Observation Worksheet
How to Make a Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheet
Choose one of the premade templates.
We have lots of templates to choose from. Take a look at our example for inspiration!
Click on "Copy Template"
Once you do this, you will be directed to the storyboard creator.
Give Your Worksheet a Name!
Be sure to call it something related to the topic so that you can easily find it in the future.
Edit Your Worksheet
This is where you will include directions, specific images, and make any aesthetic changes that you would like. The options are endless!
Click "Save and Exit"
When you are finished, click this button in the lower right hand corner to exit your storyboard.
From here you can print, download as a PDF, attach it to an assignment and use it digitally, and more!
Happy Creating!
Frequently Asked Questions about Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheets
Why is understanding kinetic and potential energy important.
Understanding these concepts helps explain various phenomena, from simple motions like falling objects to complex systems like mechanical devices and natural processes.
How can I teach kinetic and potential energy to students creatively using worksheets?
Teaching kinetic and potential energy creatively using worksheets can be achieved through interactive approaches. Design worksheets that encourage students to create comic strips illustrating energy conversions, solve puzzles matching scenarios with transformations, or participate in energy-themed treasure hunts. Interactive diagrams, word searches, and riddles can also engage students while reinforcing concepts. Utilize storyboard or flipbook formats to visually represent energy changes, and incorporate cut-and-paste activities for hands-on learning. These creative potential and kinetic energy worksheet strategies blend education with enjoyment, enhancing students' understanding and retention of kinetic and potential energy concepts.
Can kinetic and potential energy worksheets be used for cross-curricular learning?
Yes, kinetic and potential energy worksheets can be effectively used for cross-curricular learning. Beyond physics, these concepts have applications in various subjects. In mathematics, students can calculate energy values and graph transformations. Art can involve creating visual representations, while language arts can incorporate energy concepts into writing. Physical education can explore energy in sports, and engineering can relate energy to design. Historical, geographical, environmental, economic, and music aspects can all be linked to energy, making cross-curricular integration a means to enhance students' interdisciplinary skills and real-world connections.

Pricing for Schools & Districts
Limited Time
- 5 Teachers for One Year
- 1 Hour of Virtual PD
30 Day Money Back Guarantee • New Customers Only • Full Price After Introductory Offer • Access is for 1 Calendar Year

- Thousands of images
- Custom layouts, scenes, characters
- And so much more!!
Create a Storyboard
Introductory School Offer
30 Day Money Back Guarantee. New Customers Only. Full Price After Introductory Offer. Access is for 1 Calendar Year
Generating a Quote
This is usually pretty quick :)
Quote Sent!
Email Sent to
Kinetic & Potential Energy Practice Worksheets

- Google Apps™ ,
- Easel Activity Frequently assigned
What educators are saying
Also included in.

Description
Review Kinetic and Potential Energy with this easy to use and check worksheet covering identifying points and solving equations.
This resource includes 5 pages of student practice.
- 3 pages where students identify points (highest amount of kinetic energy, potential energy is decreasing, etc.)
- 2 pages where students will solve using the kinetic and potential energy equations
Who is this resource for?
This resource can be used by classroom teachers, tutors, and parents of students in grades 6-9. It provides a variety of practice covering the mentioned topics.
How Can I Use this Resource?
- Emergency Sub Plans
- An independent work station in a set of stations
- Differentiation – Assign this practice as reteaching for students who have yet to show mastery.
- Creation of Independent Work Packet for students who are not able to be present for direct instruction.
- Extension activity for early finishers or for students who show a special interest in the topic
- Use as a square on a Choice Board
- Interactive Notebooks: Print 2 pages in one and cut apart. Glue mini pages into notebooks with room for annotations on the side
- Interactive Notebooks: Print entire PDF as a mini booklet and add to notebooks using these simple instructions.
What's Included?
Purchase includes a printable PDF file in color. On page 2 of this resource you will find a link to a student friendly Google Slide version of this file. You will be able to copy this file and use it with Google Classroom or any other paperless initiative.
Please take a look at the preview file to see more of this resource.
This is an Easel Resource Too!
We know you're busy, so this resource has already been prepped for use in Easel by TPT. That means that in the Easel Activity, all non-student pages have been removed and answer boxes have been added where they're needed. You can assign this resource to your students as a fillable PDF just seconds after purchasing, with no extra steps on your end.
More questions?
Email me at [email protected] .
More on Energy:
- Energy One Pager
- Kinetic vs. Potential Energy Google Slides Presentation
- Kinetic vs. Potential Energy Guided Reading
- Forms of Energy Presentation
- Kinetic vs. Potential Energy Virtual Lab
- Matter & Energy Guided Practice
- Forms of Energy Color by Number
- Energy Guided Practice
- Energy Transformations Presentation
- Energy Forms & Transformations Quiz
To stay updated on sales and new products, please follow my store:
My TpT Store
Connect and chat with me!
My Facebook Page
On Pinterest
Questions & Answers
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

GCSE Physics Worksheets Kinetic Energy Calculations w solutions
Subject: Physics
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
19 September 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Based on Ek = (1/2)mv^2
Over 15 questions each to solve for E, m, and v. Answersheet included.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
- Physics Class-11th Notes
- Physics Formulas
- Physics Symbol
- Application of Physics
- Class 8 Science
- Class 9 Science
- Class 10 Science
- Class 11 Science
- Class 12 Science
- Class 8 Study Material
- Class 9 Study Material
- Class 10 Study Material
- Class 11 Study Material
- Class 12 Study Material
Practice Problems on Kinetic Energy
When work is done by a force on an object. It acquires energy, it can be any form. Energy can take on many forms and can be converted from one form to another form. Potential energy, electric potential energy, kinetic energy, etc. are some examples of different types of energy. Kinetic energy comes when the object starts moving. This energy is due to motion. Although this energy is due to motion, this energy is not created. It is usually converted from one type of energy to another type. Let’s look at this concept in detail.
Kinetic Energy
If an object is stationary, and we want to put that object into motion. We need to apply force. Any type of acceleration requires some force. When this force is applied, work is done on the object. When the work is done on an object, this means energy is getting transferred to the object is one form or another. Force can be removed once the object is in motion, but till the time force was applied on the object. The work that was done during that time is converted into energy.
Kinetic energy is the energy an object acquires by virtue of its motion.
This energy can be transferred from one object to another. For example, a moving ball hitting a stationary ball might cause the other ball to move. In this situation, some kinetic energy of the ball is transferred to another ball.
Formula of Kinetic Energy
To calculate the kinetic energy of the object, let’s consider a scenario where a force F, is acting on an object of mass M. In this case, the object starts moving with the acceleration “a” and covers a distance of “d”.
Work done in this case will be,
The acceleration “a” can be replaced using an equation of motion.
v 2 = u 2 + 2a.d
⇒v 2 – u 2 = 2a.d
⇒ [Tex]\frac{v^2 – u^2}{2a}[/Tex] = d
Substituting the value of “d” in the equation,
⇒ W = [Tex]m.d.\frac{v^2 – u^2}{2d}[/Tex]
⇒W = [Tex]m.\frac{v^2 – u^2}{2}[/Tex]
⇒W = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}m(v^2 – u^2)[/Tex]
So, this whole work done is converted into the K.E of the object.
In case, initial velocity u = 0,
K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/Tex]
One can also say, the network work done on the system is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object.
Note: 1. Kinetic energy depends on the velocity of the object squared. This means, when th velocity of the object is doubled, its kinetic energy becomes four times. 2. K.E must always have zero or positive values. 3. Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, and it is expressed in Joules.
Sample Problems
Question 1: A ball has a mass of 2Kg, suppose it travels at 10m/s. Find the kinetic energy possessed by it.
Answer:
Given: m = 2Kg, and v = 10m/s The KE is given by, K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/Tex] K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/Tex] ⇒ K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}(2)(10)^2[/Tex] ⇒ K.E = 100J
Question 2: A ball has a mass of 10Kg, suppose it travels at 100m/s. Find the kinetic energy possessed by it.
Given: m = 10Kg, and v = 100m/s The KE is given by, K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/Tex] K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/Tex] ⇒ K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}(10)(100)^2[/Tex] ⇒ K.E = 50000J
Question 3: A spaceship has a mass of 20000Kg, suppose it travels at 10m/s. Find the kinetic energy possessed by it.
Given: m = 20000Kg, and v = 10m/s The KE is given by, K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/Tex] K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/Tex] ⇒ K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}(20000)(10)^2[/Tex] ⇒ K.E = 10 6 J
Question 4: Work done by a force on a moving object is 100J. It was traveling at a speed of 2 m/s. Find the new speed of the object if the mass of the object is 2Kg.
Answer: Given: W = 100J Work done by the force is equal to the change in kinetic energy. W = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}m(v^2 – u^2)[/Tex] Given, u = 2 m/s and v = ?, m = 2kg. Plugging the values in the given equation, W = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}m(v^2 – u^2)[/Tex] ⇒ [Tex]100 = \frac{1}{2}(2)(v^2 – 2^2)[/Tex] ⇒ [Tex]100 = v^2 – 2^2 \\ = 104 = v^2 \\ = v = \sqrt{104} \text{ m/s}[/Tex] [Tex]v = \sqrt{104} \text{ m/s}[/Tex]
Question 5: Work done by a force on a moving object is -50J. It was traveling at a speed of 10m/s. Find the new speed of the object if the mass of the object is 2Kg.
Given: W = -50J Work done by the force is equal to the change in kinetic energy. W = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}m(v^2 – u^2)[/Tex] Given, u = 10m/s and v = ? . m = 2kg. Plugging the values in the given equation, W = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}m(v^2 – u^2)[/Tex] ⇒ [Tex]-50 = \frac{1}{2}(2)(v^2 – 10^2)[/Tex] ⇒ [Tex]-50 = v^2 – 10^2 \\ = 50 = v^2 \\ = v = \sqrt{50} \\ = v = 5\sqrt{2} \text{ m/s}[/Tex] The speed is decreased because the work done was negative. This means that the force was acting opposite to the block and velocity was decreased.
Question 6: Suppose a 1000Kg was traveling at a speed of 10m/s. Now, this mass transfers all its energy to a mass of 10Kg. What will be the velocity of the 10Kg mass after being hit by it?
KE is given by the formula, K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2 [/Tex] KE of the heavier object M = 1000Kg and v = 10m/s K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2 [/Tex] ⇒ K.E = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}(1000)(10)^2[/Tex] ⇒K.E = 50,000J Now this energy is transferred to another ball. m = 10Kg and v = ? 50,000 = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}(10)v^2[/Tex] ⇒ 10,000 = v 2 ⇒ v = 100 m/s
Question 7: Suppose a 10Kg mass was traveling at a speed of 100m/s. Now, this mass transfers all its energy to a mass of 20Kg. What will be the velocity of the 20Kg mass after being hit by it?
To find the velocity of the 20 kg mass after being hit by the 10 kg mass, we use the principle of conservation of momentum. According to the conservation of momentum, the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision, assuming no external forces are acting on the system. m 1 = 10kg v 1 = 100m/s m 2 =20kg v 2 = ? The total momentum before the collision (P initial) is : = m 1 x v 1 = 10 x 100 = 1000 Kgm/s According to the conservation of momentum: P initial = P final m 1 x v 1 = m 2 x v 2 10 x 100 = 20 x v 2 1000 = 20 x v 2 v 2 = 1000/20 = 50m/s So, the velocity of the 20 kg mass after being hit by the 10 kg mass is 50m/s.
Question 8: Suppose a 10Kg block was kept at 20m height. Now, this block is dropped. Find out the velocity of the block just before it hits the ground.
The block of 10Kg is kept at a height of 20m. The potential energy of the block will be, P.E = mgh Here m = 10, g = 10m/s 2 and h = 20m. P.E = mgh ⇒ P.E = (10)(10)(20) ⇒ P.E = 2000J Now, this energy is converted completely into KE. KE = PE ⇒2000 = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/Tex] Given m = 10Kg, ⇒2000 = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}10v^2[/Tex] ⇒400 = v 2 v = 20m/s
Question 9: Suppose a rock of 100Kg was kept at 80m height. Now, this block is dropped. Find out the velocity of the block just before it hits the ground.
The block of 10Kg is kept at a height of 80m. The potential energy of the block will be, P.E = mgh Here m = 100, g = 10m/s 2 and h = 80m. P.E = mgh ⇒ P.E = (100)(10)(80) ⇒ P.E = 80000J Now, this energy is converted completely into KE. KE = PE ⇒80000 = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/Tex] Given m = 100Kg, ⇒80000 = [Tex]\frac{1}{2}100v^2[/Tex] ⇒1600 = v 2 v = 40m/s
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Learning
- School Physics
- Physics-Class-11
- How to Underline in Discord
- How to Block Someone on Discord
- How to Report Someone on Discord
- How to add Bots to Discord Servers
- 15 Most Important Aptitude Topics For Placements [2024]
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Kinetic Energy Practice Problems 1. What is the Kinetic Energy of a 150 kg object that is moving with a speed of 15 m/s? KE = ½ mv2 KE = ? m = 150kg v = 15m/s KE = ½ (150kg) (15 m/s)2 KE = ½ (150kg)(225) KE = 16875J 2. An object has a kinetic energy of 25 J and a mass of 34 kg , how fast is the object moving? KE = ½ mv2
Show all of your math when answering the problems below. Write directly on this page. 1. A 1 kg rock is at a height of 100 meters. a. What is the rock's gravitational potential energy at 100 meters high? b. Calculate the rock's gravitational potential energy at 50 m, 20 m, 1 m, and 0 m high. Put the answers in the data table below.
KE = mass x velocity2. PE = m (mass) x g (gravity) x h (height) On Earth, gravity (g) = 9.8 m/s2, so in the formula substitute 9.8 for gravity. 7. You serve a volleyball with a mass of 2 kg. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 30 m/s. The ball has kinetic energy. Calculate it.
Kinetic Energy Practice Problems. Kinetic Energy Practice Problems. 1. What is the Kinetic Energy of a 150 kg object that is moving with a speed of 15 m/s? 2. An object has a kinetic energy of 25 J and a mass of 34 kg , how fast is the object moving? 3. An object moving with a speed of 35 m/s and has a kinetic energy of 1500 J, what is the mass ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy Practice Problems Solve the following problems and show your work! 1. A car has a mass of 2,000 kg and is traveling at 28 meters per second. What is the car's kinetic energy? 2. When a golf ball is hit, it travels at 41 meters per second. The mass of a golf ball is 0.045 kg. What is the kinetic energy of the golf ...
POTENTIAL ENERGY: LAW OF CONCERVATION OF MATTER. ENERGY TRANSFORMATION. KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY WORKSHEET. Potential energy: PE = mgh Kinetic energy: KE = 1/2 m v2 Total mechanical energy: ME = PE + KE. Practice problems: 1. A baby carriage is sitting at the top of a hill that is 21 m high. The carriage with the baby weighs 12 Kg.
Potential energy (PE) is the capacity or potential of an object to do work. An object acquires this type of force when it is in a position to either move or do some work. As soon as the movement starts, the PE changes form. PE depends on an object's position relative to other things and the forces they exert on each other.
What is its kinetic energy? 2. The kinetic energy of a 20.0 N droid is 5.00 x 102 J. What is the speed of the droid? 3. A 10.0 N lightsaber is accelerated from rest at a rate of 2.5 m/s2. What is the kinetic energy of the lightsaber after it has accelerated over a distance of 15.0 m. 4. A 1200.0 N Wookie jumps off a cliff on Earth.
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY WORKSHEET Name:_____KEY_____ Determine whether the objects in the following problems have kinetic or potential energy. Then choose the correct formula to use: KE = 1/2 m v2 OR PE = mgh = F w h 1. You serve a volleyball with a mass of 2.1 kg. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 30 m/s. The ball has
KE = 196 j. At what height is an object that weighs 490 N if its potential energy is 4900 N-m? 10 m. A motorbike has 4500 j of KE and is traveling at 15 m/s. What is its mass? 45 kg. Some practice with energy. Formulas - (Kinetic Energy) KE = (MV^2)/2 (Gravitational Potential Energy) GPE = WH (Weight) W = 9.8M (Mass) M = W/9.8 These….
This worksheet provides basic problems for calculating kinetic energy, using mass and velocity.•Problem solving steps and answers are provided on a separate page for teachers.•Aimed at Grade 7-8 students...
9v 2 2. K = 9. mv 2 2. The 9 that you see means that the kinetic energy is multiplied by 9. 9 × 3000 = 27000. Therefore, the kinetic energy is going to be 27000 joules. Problem # 2: Calculate the kinetic energy of a 10 kg object moving with a speed of 5 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy again when the speed is doubled.
For each problem, write the formula used, show your work, & write your answer with correct units. Example: An 80kg man is jogging at a rate of 4m/s. He has kinetic energy. Calculate it: Kinetic Energy = ½ x mass x velocity2 Kinetic Energy = ½ x 80kg x (4m/s)2 Kinetic Energy = ½ x 80 x 16 Kinetic Energy = 40 x 16 Kinetic Energy = 640 J 1. You ...
Solution: The total energy of the cart is expressed by the sum of its potential energy and its kinetic energy. Potential energy of an object in a gravitational field is expressed by the formula. PE = mgh. where. PE is the potential energy. m is the mass of the object. g is the acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s 2.
Kinetic energy calculations. A scaffolded worksheet to allow students to practice using the equation for kinetic energy. Each section gets more challenging with steps to build confidence before moving on to rearranging equations, changing prefixes, using multi-step calculations. to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Kinetic and Potential Energy Transformation Worksheet: Create a flowchart, or force diagram, depicting the transformation between potential and kinetic forms in various scenarios, specifically when work is done on an object to cause movement. Students complete the flowchart with labels and arrows.
Zip. A 2-page worksheet product designed to help upper middle school and lower high school students review to the topic of solving gravitational potential energy (GPE=mgh) and kinetic energy (KE=1/2MV2) calculations through a set of 10 word problems.Product Contents:Pages 1-2 - GPE and KE Word Problems:Formulas for GPE and KE4 leveled word ...
10. Ping Pong Catapult. With the Ping Pong Catapult lesson, students experiment with the Ping Pong Catapult to explore potential and kinetic energy by launching ping pong balls. (There are multiple student projects that use the Ping Pong Catapult and might also be useful in your classroom exploration.) 11.
Review Kinetic and Potential Energy with this easy to use and check worksheet covering identifying points and solving equations. This resource includes 5 pages of student practice. 3 pages where students identify points (highest amount of kinetic energy, potential energy is decreasing, etc.) 2 pages where students will solve using the kinetic ...
The potential energy of a 550 kg missile flying at 800 meters is. 4. Multiple Choice. 5. Multiple Choice. A ball that has a mass of 3kg and has a potential energy of 5,000 J is how high in the air. 6. Multiple Choice. A soccer ball has a gravitational potential energy of 80%.
If the mass of an object is halved and its speed is doubled, the kinetic energy is doubled. 5. Solution : Formula for kinetic energy. K.E = (1/2)mv 2. When the kinetic energy is doubled, let us assume that the velocity has to be increased by the factor 'x'. 2K.E = (1/2)m (xv) 2. 2K.E = (1/2)mx 2 v 2. 2K.E = x 2 (1/2)mv 2.
Based on Ek = (1/2)mv^2 Over 15 questions each to solve for E, m, and v. Answersheet included.
Note: 1. Kinetic energy depends on the velocity of the object squared. This means, when th velocity of the object is doubled, its kinetic energy becomes four times. 2. K.E must always have zero or positive values. 3. Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, and it is expressed in Joules. Sample Problems.
If this problem persists, tell us. Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. Donate or volunteer today! Site Navigation. About. News; Impact; Our team; Our interns; Our content specialists; Our leadership; Our supporters; Our contributors; Our finances; Careers;