- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Chapter 1: Real Numbers

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1- Real Numbers

NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers are provided here. These solutions are prepared by our expert faculty to help students in their board exam preparations. They solve and provide the NCERT Solutions for Maths to aid the students in solving the problems easily. They also focus on preparing the solutions in such a way that it is easy to understand for the students. A detailed and step-wise explanation is given for each question given in the exercises of NCERT books.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 10 Maths Chapter – 1 Real Numbers
Download most important questions for class 10 maths chapter – 1 real numbers.
Answers to the questions present in Real Numbers are given in the first chapter of Maths Solutions of NCERT Class 10. Here, students are introduced to several important concepts that will be useful for those who wish to pursue mathematics as a subject in their Class 11. Based on these solutions of Class 10 NCERT , students can prepare for their upcoming board exam. These solutions are helpful as they are in accordance with the CBSE Syllabus for 2023-24.
- Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
- Chapter 6 Triangles
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
- Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
- Chapter 10 Circles
- Chapter 11 Constructions
- Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 Statistics
- Chapter 15 Probability
- Exercise 1.1 Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Exercise 1.2 Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Exercise 1.3 Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Exercise 1.4 Chapter 1 Real Numbers
Download PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1- Real Numbers
carouselExampleControls111

Previous Next
Which is the best app for learning math?
This page covers all the chapter notes, and the solutions to the NCERT exercises for Class 10 math. However, if you wish to begin from the basics for this chapter, you can go through the visually appealing videos that are present in BYJU’S The Learning App for Class 10.
For math, the grade 10 BYJU’S The Learning App includes:
- 80+ math video lessons (1800+ minutes of content!)
- Comprehensive coverage of your school syllabus
- 50+ gamified interactive learning experiences
- Key questions
- Summary cards to revise formulae
- Practice tests
- 24 X 7 access to learning resources
BYJU’S The Learning App for grade 10 also covers Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Economics, Civics, History, and Geography.
Just Click here to know more about why BYJU’S The Learning App is the best app for learning math.
Access Answers to NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 – Real Numbers
Exercise 1.1 page: 7.
1. Use Euclid’s division algorithm to find the HCF of:
i. 135 and 225
ii. 196 and 38220
iii. 867 and 255
As you can see from the question, 225 is greater than 135. Therefore, by Euclid’s division algorithm, we have,
225 = 135 × 1 + 90
Now, remainder 90 ≠ 0, thus again using division lemma for 90, we get,
135 = 90 × 1 + 45
Again, 45 ≠ 0, repeating the above step for 45, we get,
90 = 45 × 2 + 0
The remainder is now zero, so our method stops here. Since, in the last step, the divisor is 45, therefore, HCF (225,135) = HCF (135, 90) = HCF (90, 45) = 45.
Hence, the HCF of 225 and 135 is 45.
In this given question, 38220>196, therefore the by applying Euclid’s division algorithm and taking 38220 as divisor, we get,
38220 = 196 × 195 + 0
We have already got the remainder as 0 here. Therefore, HCF(196, 38220) = 196.
Hence, the HCF of 196 and 38220 is 196.
As we know, 867 is greater than 255. Let us apply now Euclid’s division algorithm on 867, to get,
867 = 255 × 3 + 102
Remainder 102 ≠ 0, therefore taking 255 as divisor and applying the division lemma method, we get,
255 = 102 × 2 + 51
Again, 51 ≠ 0. Now 102 is the new divisor, so repeating the same step we get,
102 = 51 × 2 + 0
The remainder is now zero, so our procedure stops here. Since, in the last step, the divisor is 51, therefore, HCF (867,255) = HCF(255,102) = HCF(102,51) = 51.
Hence, the HCF of 867 and 255 is 51.
2. Show that any positive odd integer is of the form 6q + 1, or 6q + 3, or 6q + 5, where q is some integer.
Let a be any positive integer and b = 6. Then, by Euclid’s algorithm, a = 6q + r, for some integer q ≥ 0, and r = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, because 0≤r<6.
Now substituting the value of r, we get,
If r = 0, then a = 6q
Similarly, for r= 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5, the value of a is 6q+1, 6q+2, 6q+3, 6q+4 and 6q+5, respectively.
If a = 6q, 6q+2, 6q+4, then a is an even number and divisible by 2. A positive integer can be either even or odd Therefore, any positive odd integer is of the form of 6q+1, 6q+3 and 6q+5, where q is some integer.
3. An army contingent of 616 members is to march behind an army band of 32 members in a parade. The two groups are to march in the same number of columns. What is the maximum number of columns in which they can march?
Number of army contingent members = 616
Number of army band members = 32
If the two groups have to march in the same column, we have to find out the highest common factor between the two groups. HCF(616, 32), gives the maximum number of columns in which they can march.
By using Euclid’s algorithm to find their HCF, we get,
Since, 616>32, therefore,
616 = 32 × 19 + 8
Since, 8 ≠ 0, therefore, taking 32 as new divisor, we have,
32 = 8 × 4 + 0
Now we have got remainder as 0, therefore, HCF (616, 32) = 8.
Hence, the maximum number of columns in which they can march is 8.
4. Use Euclid’s division lemma to show that the square of any positive integer is either of the form 3m or 3m + 1 for some integer m.
Let x be any positive integer and y = 3.
By Euclid’s division algorithm, then,
x = 3q + r for some integer q≥0 and r = 0, 1, 2, as r ≥ 0 and r < 3.
Therefore, x = 3q, 3q+1 and 3q+2
Now as per the question given, by squaring both the sides, we get,
x 2 = (3q) 2 = 9q 2 = 3 × 3q 2
Let 3q 2 = m
Therefore, x 2 = 3m ……………………..(1)
x 2 = (3q + 1) 2 = (3q) 2 +1 2 +2×3q×1 = 9q 2 + 1 +6q = 3(3q 2 +2q) +1
Substitute, 3q 2 +2q = m, to get,
x 2 = 3m + 1 ……………………………. (2)
x 2 = (3q + 2) 2 = (3q) 2 +2 2 +2×3q×2 = 9q 2 + 4 + 12q = 3 (3q 2 + 4q + 1)+1
Again, substitute, 3q 2 +4q+1 = m, to get,
x 2 = 3m + 1…………………………… (3)
Hence, from equation 1, 2 and 3, we can say that the square of any positive integer is either of the form 3m or 3m + 1 for some integer m.
5. Use Euclid’s division lemma to show that the cube of any positive integer is of the form 9m, 9m + 1 or 9m + 8.
x = 3q+r, where q≥0 and r = 0, 1, 2, as r ≥ 0 and r < 3.
Therefore, putting the value of r, we get,
Now, by taking the cube of all the three above expressions, we get,
Case (i): When r = 0, then,
x 2 = (3q) 3 = 27q 3 = 9(3q 3 )= 9m; where m = 3q 3
Case (ii): When r = 1, then,
x 3 = (3q+1) 3 = (3q) 3 +1 3 +3×3q×1(3q+1) = 27q 3 +1+27q 2 +9q
Taking 9 as common factor, we get,
x 3 = 9(3q 3 +3q 2 +q)+1
Putting = m, we get,
Putting (3q 3 +3q 2+ q) = m, we get ,
Case (iii): When r = 2, then,
x 3 = (3q+2) 3 = (3q) 3 +2 3 +3×3q×2(3q+2) = 27q 3 +54q 2 +36q+8
x 3 =9(3q 3 +6q 2 +4q)+8
Putting (3q 3 +6q 2 +4q) = m, we get ,
Therefore, from all the three cases explained above, it is proved that the cube of any positive integer is of the form 9m, 9m + 1 or 9m + 8.
Exercise 1.2 Page: 11
1. Express each number as a product of its prime factors:
By taking the LCM of 140, we will get the product of its prime factor.
Therefore, 140 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 7 × 1 = 2 2 ×5×7
By Taking the LCM of 156, we will get the product of its prime factor.
Hence, 156 = 2 × 2 × 13 × 3 × 1 = 2 2 × 13 × 3
By taking the LCM of 3825, we will get the product of its prime factor.
Hence, 3825 = 3 × 3 × 5 × 5 × 17 × 1 = 3 2 ×5 2 ×17
By Taking the LCM of 5005, we will get the product of its prime factor.
Hence, 5005 = 5 × 7 × 11 × 13 × 1 = 5 × 7 × 11 × 13
By taking the LCM of 7429, we will get the product of its prime factor.
Hence, 7429 = 17 × 19 × 23 × 1 = 17 × 19 × 23
2. Find the LCM and HCF of the following pairs of integers and verify that LCM × HCF = product of the two numbers.
(i) 26 and 91
(ii) 510 and 92
(iii) 336 and 54
Expressing 26 and 91 as product of its prime factors, we get,
26 = 2 × 13 × 1
91 = 7 × 13 × 1
Therefore, LCM (26, 91) = 2 × 7 × 13 × 1 = 182
And HCF (26, 91) = 13
Verification
Now, product of 26 and 91 = 26 × 91 = 2366
And product of LCM and HCF = 182 × 13 = 2366
Hence, LCM × HCF = product of the 26 and 91.
Expressing 510 and 92 as product of its prime factors, we get,
510 = 2 × 3 × 17 × 5 × 1
92 = 2 × 2 × 23 × 1
Therefore, LCM(510, 92) = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 × 17 × 23 = 23460
And HCF (510, 92) = 2
Now, product of 510 and 92 = 510 × 92 = 46920
And Product of LCM and HCF = 23460 × 2 = 46920
Hence, LCM × HCF = product of the 510 and 92.
Expressing 336 and 54 as product of its prime factors, we get,
336 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 7 × 3 × 1
54 = 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 1
Therefore, LCM(336, 54) = = 3024
And HCF(336, 54) = 2×3 = 6
Now, product of 336 and 54 = 336 × 54 = 18,144
And product of LCM and HCF = 3024 × 6 = 18,144
Hence, LCM × HCF = product of the 336 and 54.
3. Find the LCM and HCF of the following integers by applying the prime factorisation method.
(i) 12, 15 and 21
(ii) 17, 23 and 29
(iii) 8, 9 and 25
Writing the product of prime factors for all the three numbers, we get,
HCF(12,15,21) = 3
LCM(12,15,21) = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 × 7 = 420
HCF(17,23,29) = 1
LCM(17,23,29) = 17 × 23 × 29 = 11339
HCF(8,9,25)=1
LCM(8,9,25) = 2×2×2×3×3×5×5 = 1800
4. Given that HCF (306, 657) = 9, find LCM (306, 657).
Solution: As we know that,
HCF×LCM=Product of the two given numbers
9 × LCM = 306 × 657
LCM = (306×657)/9 = 22338
Hence, LCM(306,657) = 22338
5. Check whether 6 n can end with the digit 0 for any natural number n.
Solution: If the number 6 n ends with the digit zero (0), then it should be divisible by 5, as we know any number with unit place as 0 or 5 is divisible by 5.
Prime factorization of 6 n = (2×3) n
Therefore, the prime factorization of 6 n doesn’t contain prime number 5.
Hence, it is clear that for any natural number n, 6 n is not divisible by 5, and thus it proves that 6 n cannot end with the digit 0 for any natural number n.
6. Explain why 7 × 11 × 13 + 13 and 7 × 6 × 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 + 5 are composite numbers.
Solution: By the definition of composite number, we know, if a number is composite, then it means it has factors other than 1 and itself. Therefore, for the given expression;
7 × 11 × 13 + 13
Taking 13 as common factor, we get,
=13(7×11×1+1) = 13(77+1) = 13×78 = 13×3×2×13
Hence, 7 × 11 × 13 + 13 is a composite number.
Now let’s take the other number,
7 × 6 × 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 + 5
Taking 5 as a common factor, we get,
=5(7×6×4×3×2×1+1) = 5(1008+1) = 5×1009
Hence, 7 × 6 × 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 + 5 is a composite number.
7. There is a circular path around a sports field. Sonia takes 18 minutes to drive one round of the field, while Ravi takes 12 minutes for the same. Suppose they both start at the same point and at the same time, and go in the same direction. After how many minutes will they meet again at the starting point?
Solution: Since, Both Sonia and Ravi move in the same direction and at the same time, the method to find the time when they will be meeting again at the starting point is LCM of 18 and 12.
Therefore, LCM(18,12) = 2×3×3×2×1=36
Hence, Sonia and Ravi will meet again at the starting point after 36 minutes.
Exercise 1.3 Page: 14
1. Prove that √ 5 is irrational.
Solutions: Let us assume, that √ 5 is rational number.
i.e. √ 5 = x/y (where, x and y are co-primes)
Squaring both the sides, we get,
(y √ 5) 2 = x 2
⇒5y 2 = x 2 ……………………………….. (1)
Thus, x 2 is divisible by 5, so x is also divisible by 5.
Let us say, x = 5k, for some value of k and substituting the value of x in equation (1), we get,
5y 2 = (5k) 2
⇒y 2 = 5k 2
is divisible by 5 it means y is divisible by 5.
Clearly, x and y are not co-primes. Thus, our assumption about √ 5 is rational is incorrect.
Hence, √ 5 is an irrational number.
2. Prove that 3 + 2√5 + is irrational.
Solutions: Let us assume 3 + 2 √ 5 is rational.
Then we can find co-prime x and y (y ≠ 0) such that 3 + 2√5 = x/y
Rearranging, we get,
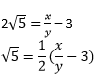
Since, x and y are integers, thus,

Therefore, √ 5 is also a rational number. But this contradicts the fact that √ 5 is irrational.
So, we conclude that 3 + 2 √ 5 is irrational.
3. Prove that the following are irrationals:
(iii) 6 + √ 2
Let us assume 1/√2 is rational.
Then we can find co-prime x and y (y ≠ 0) such that 1/√2 = x/y
Since, x and y are integers, thus, √2 is a rational number, which contradicts the fact that √2 is irrational.
Hence, we can conclude that 1/√2 is irrational.
Let us assume 7√5 is a rational number.
Then we can find co-prime a and b (b ≠ 0) such that 7√5 = x/y
Since, x and y are integers, thus, √5 is a rational number, which contradicts the fact that √5 is irrational.
Hence, we can conclude that 7√5 is irrational.
Let us assume 6 +√2 is a rational number.
Then we can find co-primes x and y (y ≠ 0) such that 6 +√2 = x/y⋅
√2 = (x/y) – 6
Since, x and y are integers, thus (x/y) – 6 is a rational number and therefore, √2 is rational. This contradicts the fact that √2 is an irrational number.
Hence, we can conclude that 6 +√2 is irrational.
Exercise 1.4 Page: 17
1. Without actually performing the long division, state whether the following rational numbers will have a terminating decimal expansion or a non-terminating repeating decimal expansion:
(i) 13/3125 (ii) 17/8 (iii) 64/455 (iv) 15/1600 (v) 29/343 (vi) 23/(2 3 5 2 ) (vii) 129/(2 2 5 7 7 5 ) (viii) 6/15 (ix) 35/50 (x) 77/210
Note: If the denominator has only factors of 2 and 5 or in the form of 2 m ×5 n then it has terminating decimal expansion.
If the denominator has factors other than 2 and 5 then it has a non-terminating decimal expansion.
(i) 13/3125
Factorizing the denominator, we get,
3125 = 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 = 5 5
Since, the denominator has only 5 as its factor, 13/3125 has a terminating decimal expansion.
8 = 2×2×2 = 2 3
Since, the denominator has only 2 as its factor, 17/8 has a terminating decimal expansion.
(iii) 64/455
455 = 5×7×13
Since, the denominator is not in the form of 2 m × 5 n , thus 64/455 has a non-terminating decimal expansion.
(iv) 15/ 1600
1600 = 2 6 ×5 2
Since, the denominator is in the form of 2 m × 5 n , thus 15/1600 has a terminating decimal expansion.
343 = 7×7×7 = 7 3 Since, the denominator is not in the form of 2 m × 5 n thus 29/343 has a non-terminating decimal expansion.
(vi)23/(2 3 5 2 )
Clearly, the denominator is in the form of 2 m × 5 n .
Hence, 23/ (2 3 5 2 ) has a terminating decimal expansion.
(vii) 129/(2 2 5 7 7 5 )
As you can see, the denominator is not in the form of 2 m × 5 n .
Hence, 129/ (2 2 5 7 7 5 ) has a non-terminating decimal expansion.
(viii) 6/15
Since, the denominator has only 5 as its factor, thus, 6/15 has a terminating decimal expansion.
35/50 = 7/10
Factorising the denominator, we get,
Since, the denominator is in the form of 2 m × 5 n thus, 35/50 has a terminating decimal expansion.
77/210 = (7× 11)/ (30 × 7) = 11/30
30 = 2 × 3 × 5
As you can see, the denominator is not in the form of 2 m × 5 n .Hence, 77/210 has a non-terminating decimal expansion.
2. Write down the decimal expansions of those rational numbers in Question 1 above which have terminating decimal expansions.

13/3125 = 0.00416
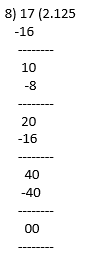
17/8 = 2.125
(iii) 64/455 has a non terminating decimal expansion
(iv)15/ 1600

15/1600 = 0.009375
(v) 29/ 343 has a non terminating decimal expansion
(vi)23/ (2 3 5 2 ) = 23/(8×25)= 23/200

23/ (2 3 5 2 ) = 0.115
(vii) 129/ (2 2 5 7 7 5 ) has a non terminating decimal expansion
(viii) 6/15 = 2/5

(ix) 35/50 = 7/10
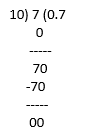
35/50 = 0.7
(x) 77/210 has a non-terminating decimal expansion.
3. The following real numbers have decimal expansions as given below. In each case, decide whether they are rational or not. If they are rational, and of the form, p q what can you say about the prime factors of q?
(i) 43.123456789
(ii) 0.120120012000120000. . .
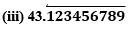
Since it has a terminating decimal expansion, it is a rational number in the form of p/q and q has factors of 2 and 5 only.
Since, it has non-terminating and non- repeating decimal expansion, it is an irrational number.
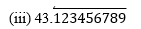
Since it has non-terminating but repeating decimal expansion, it is a rational number in the form of p/q and q has factors other than 2 and 5.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 – Real Numbers
Real Number is one of the important topics in Maths, and it has a weightage of 6 marks in Class 10 (Unit – Number Systems) Maths board exams. The average number of questions asked in this chapter is usually 3. Three questions were asked from this chapter in the previous year board examination (2018).
- One out of three questions in part A (1 mark).
- One out of three questions in part B (2 marks).
- One out of three questions in part C (3 marks).
This chapter talks about
- Euclid’s Division Algorithm
- The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
- Revisiting Rational & Irrational Numbers
- Decimal Expansions
List of Exercises in Class 10 Maths Chapter 1: Exercise 1.1 Solutions 5 Questions ( 4 long, 1 short) Exercise 1.2 Solutions 7 Questions ( 4 long, 3 short) Exercise 1.3 Solutions 3 Questions ( 3 short) Exercise 1.4 Solutions 3 Questions ( 3 short)
Real Numbers is introduced in Class 9, and this is discussed in further detail in Class 10. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers provides the answers to the questions present in this chapter. The chapter discusses real numbers and their applications. The divisibility of integers using Euclid’s division algorithm says that any positive integer a can be divided by another positive integer b such that the remainder will be smaller than b. On the other hand, The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic works on the multiplication of positive integers.
The chapter starts with the introduction of real numbers in section 1.1, followed by two very important topics in sections 1.2 and 1.3
- Euclid’s Division Algorithm – It includes 5 questions based on Theorem 1.1 – Euclid’s Division Lemma.
- The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic – Explore the applications of this topic which talks about the multiplication of positive integers, through solutions of the 7 problems in Exercise 1.2.
Next, it discusses the following topics, which were introduced in Class 9.
- Revisiting Rational & Irrational Numbers – In this, the solutions for 3 problems in Exercise 1.3 are given, which also use the topic in the last Exercise 1.2.
- Decimal Expansions – It explores when the decimal expansion of a rational number is terminating and when it is recurring. It includes a total of 3 problems with sub-parts in Exercise 1.4
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1- Real Numbers
- These NCERT Solutions help you solve and revise the updated CBSE syllabus of Class 10 for 2023-24.
- After going through the stepwise solutions given by our subject expert teachers, you will be able to score more marks.
- It follows NCERT guidelines which help in preparing the students competently.
- It contains all the important questions from the examination point of view.
Disclaimer –
Dropped Topics –
1.2 Euclid’s division lemma 1.5 Revisiting rational numbers and their decimal Expansions
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1
What are the main topics covered in the ncert solutions for class 10 maths chapter 1, how many exercises are there in ncert solutions for class 10 maths chapter 1, are ncert solutions for class 10 maths chapter 1 important from the exam point of view, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It’s helping a lot in tenth Thanks byjus
Byju’s is quite helpful for giving a clear knowledge to new students of promoted class. The best study materials are published in the website make students to succeed.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Main Topics Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Tests 10th Maths Chapter 1 Question wise Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 MCQ Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Assignments
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1
Learning Class 10 Maths Chapter 1, Real Numbers, effectively requires a systematic approach and a clear understanding of the concepts involved. Here are some steps and strategies to help you learn this chapter.
Get here the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers all exercises in Hindi and English medium revised and modified for session 2024-25. The solution of chapter 1 class 10th mathematics is updated according to NCERT textbooks published for 2024-25 CBSE exams.
Euclid’s Division Lemma states that for any two positive integers a and b, there exist unique integers q and r such that: a = bq + r, where 0 ≤ r < b. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic states that every positive integer greater than 1 can be expressed as a product of prime numbers in a unique way, up to the order of factors.
| Class: 10 | Mathematics |
| Chapter: 1 | Real Numbers |
| Number of Exercises: | 2 (Only Two) |
| Content: | NCERT Exercises Solutions and Tests |
| Academic Session: | Year 2024-25 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Methods for proving the irrationality of certain numbers, such as the square root of a prime number, are discussed. Understanding decimal expansions of real numbers. Terminating decimals and recurring decimals. Rationalization is the process of converting an irrational number into a rational one by multiplying or dividing by a suitable number.

According to rationalised syllabus for academic session 2024-25, only two exercises are in chapter 1. The exercise 1.1 deleted and exercise 1.2 become the exercise 1.1. Similarly exercise 1.3 become exercise 1.2 and exercises 1.4 is also deleted. The course structure of class 10 mathematics chapter 1 is given below: Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic – statements after reviewing work done earlier and after illustrating and motivating through examples, Proofs of irrationality of √2, √3, √5.
>> Total Number of Exercises: 2 >> Total Marks in Board Exam: 6 >> Number of Periods needed: 15
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1, titled Real Numbers, is an important chapter that lays the foundation for understanding various mathematical concepts. The main points covered in this chapter include introduction to Real Numbers. Real numbers are a set of numbers that includes all rational and irrational numbers. Real numbers can be represented on the number line.
Utilize online resources like video tutorials, educational websites like Tiwari Academy, and interactive quizzes to reinforce your understanding of the chapter. As you progress, practice solving sample papers or past year question papers. This will help you become familiar with the exam pattern and time management. Periodically test your knowledge by attempting self-assessment quizzes or problems from the chapter. This will help you gauge your progress.
In class 10 Maths Chapter we will learn about understanding square numbers and their properties. Finding the square root of a number using prime factorization. Real numbers are used in various mathematical applications, such as finding the distance between two points in coordinate geometry.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers
The chapter provides numerous examples and practice problems to reinforce the concepts discussed. These are the main points covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 1, Real Numbers. It serves as the building block for further mathematical concepts and is essential for a solid foundation in mathematics. Get here topic wise NCERT Solutions for 10th Mathematics chapter 1 all exercises in Hindi and English medium. Students can take help of videos for solving questions of each exercise.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Solutions for CBSE Board
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.2
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Solutions for State Boards
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.3
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.4
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 NCERT Book
- Class 10 Mathematics NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
10th Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Solutions
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 1 Express each number as a product of its prime factors: (i) 140 (ii) 156 (iii) 3825 (iv) 5005 (v) 7429 The step by step solutions of each part is given here with practice questions>. You can discuss with us Part (i) , Part (ii) , Part (iii) , Part (iv) , and Part (v) to learn more about the solution.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 2 Find the LCM and HCF of the following pairs of integers and verify that LCM × HCF = product of the two numbers. (i) 26 and 91 (ii) 510 and 92 (iii) 336 and 54. Get the solution of question 2 and discuss Part (i) , Part (ii) and Part (iii) with us along with assignments and other doubts for more clarification.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 3 Find the LCM and HCF of the following integers by applying the prime factorisation method. (i) 12, 15 and 21 (ii) 17, 23 and 29 (iii) 8, 9 and 25. Discuss with part one , two and three in detail and get worksheets to understand the solution in simple way.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 4 Given that HCF (306, 657) = 9, find LCM (306, 657). The solution of this question is very simple and usually asked in MCQ type questions. For more revision , please write to us .
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 5 Check whether 6ⁿ can end with the digit 0 for any natural number n. The solution of question 5 is similar to the example given in textbook. Discuss with us and Practice here more questions based on question 5.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 6 Explain why 7 × 11 × 13 + 13 and 7 × 6 × 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 + 5 are composite numbers. Extra questions for practice based on the solution of question 6 are given here to download. Put your view to discuss with us.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Question 7 There is a circular path around a sports field. Sonia takes 18 minutes to drive one round of the field, while Ravi takes 12 minutes for the same. Suppose they both start at the same point and at the same time, and go in the same direction. After how many minutes will they meet again at the starting point? Question number 7 is important for exams. Get here the solution and practice assignments with answers for revision.
10th Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.2 Solutions
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.2 Question 1 Prove that √5 is irrational. To understand the solution of question 1, student need to practice assignments and discuss the explanation in depth.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.2 Question 2 Prove that 3 + 2√5 is irrational. Get here the assignments and practice questions based on the solution of question 2. If still there is any doubt, please visit to discussion forum.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.2 Question 3 Prove that the following are irrationals: (i) 1/√2 (ii) 7√5 (iii) 6 + √2 The solution of question 3 is similar to question 1 and 2. Get more practice to learn the concepts in better way. Discuss in detail here.
Use number lines and diagrams to visualize concepts like decimal expansions and the placement of real numbers on the number line. Visual aids can help make abstract concepts more concrete. Don’t hesitate to ask your teacher or a classmate for help if you encounter difficulties. Sometimes, discussing problems with others can provide valuable insights. Maintain a study schedule and allocate specific time slots for learning and practicing this chapter. Consistency is key.
Download App for Class 4

The complete chapter of 10th Maths chapter 1 is divided in four main parts. The explanation of each part with video explanation is given below. Start by reading the chapter thoroughly and grasp the basic definitions and concepts. Ensure that you understand the definitions of real numbers, Euclid’s Division Lemma, and the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. Take concise notes while reading the chapter. Write down key formulas, definitions, and important points. These notes will be helpful for quick revision.
Learn here how to find the prime factorization of numbers. This skill is essential for various aspects of number theory. Practice finding the prime factorization of different numbers. Practice working with terminating and recurring decimals. Solve problems that involve decimal expansions of real numbers. Familiarize yourself with methods for rationalizing irrational numbers, especially square roots. Practice these techniques with different examples. Remember that learning mathematics often requires patience and persistence. Take your time to understand each concept thoroughly before moving on to the next. By following these steps and strategies, you can effectively learn Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Main Topics Mathematics is best learned through practice. Solve a variety of problems related to real numbers, including examples from your textbook and additional practice questions. Pay attention to different types of questions, such as finding HCF, LCM, prime factorization, and working with decimal expansions.
| Topics | Detail about the Topics |
|---|---|
| Topic: 1 | |
| Topic: 2 | |
| Topic: 3 | |
| Topic: 4 |
10th Maths Chapter 1 Practice Test Papers
Euclid’s Division Lemma is a fundamental concept in this chapter. Make sure you understand how it works and can apply it to solve problems related to divisibility and remainders. There are four exercises in chapter 1 covering all the four topics on Real Numbers. Students can practice well using the 6 question papers given below. It will help to prepare the chapter for CBSE exams also.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Tests with Answers
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Test 1
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Test 2
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Test 3
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Test 4
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Test 5
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Test 6
- Download More Assignments with Solution

The word algorithm come from the name of the name of the 9th century Persian mathematician al-Khwarizmi. The word ‘algebra’ is derived from a book, he wrote, called Hisab al-jabr w’al-muqabala.
An equivalent version of Fundamental theorem of Arithmetic was probably first recorded as Proposition 14 of Book IX in Euclid’s Elements, before it came to be known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
However, the first correct proof was given by Carl Friedrich Gauss in his al-Khwarizmi. Carl Friedrich Gauss is often referred to as the ‘Prince of Mathematicians’ and is considered one of the three greatest mathematicians of all time, along with Archimedes and Newton. He has made fundamental contributions to both mathematics and science. Learn here how to make class 10 Maths chapter 1 easy to learn.
How many exercises are there in class 10 Maths chapter 1 Real numbers?
Now there are only 2 exercises in class 10 chapter 1 (Real numbers): In first exercise (Ex 1.1), there are 5 questions. In second exercise (Ex 1.2), there are 7 questions. So, there are in all 18 questions in class 10 chapter 1 (Real numbers). There are in all 11 examples in class 10 chapter 1 (Real numbers).
- Examples 1,2,3,4 are based on Ex 1.1.
- Examples 5,6,7,8 are based on Ex 1.2.
Are there any Theorems or Algorithm in 10th Maths chapter 1?
Yes, there are 7 Theorems and 1 Algorithm in class 10 chapter 1 (Real numbers). First exercise (Ex 1.1) is based on Theorem 1.1 (Euclid’s Division Lemma) and Euclid’s Division algorithm. Theorem 1.2 (Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic) is used in second exercise (Ex 1.2).
What are the Important questions from Maths class 10 chapter 1 Real numbers?
Important questions from Maths class 10 chapter 1:
- In first exercise (Ex 1.1), all questions are important.
- In second exercise (Ex 1.2), Q2, 4, 5, 7 are important.
Which topics students should recall before starting class 10 Maths chapter 1?
Students should recall some topics of class 9 chapter 1 (Number systems). Topics :
- Types of numbers (Natural number, Whole number, Integers, Rational numbers, Irrational numbers and Real numbers).
- Decimal expansion of Rational numbers (Terminating and Non-terminating recurring) and Irrational numbers (Non-terminating non-recurring).
- HCF (Highest Common Factor) and LCM (Lowest/Least Common Multiple).
- And some other topics like Meaning of Dividend, Divisor, Quotient and Remainder, Prime numbers, Composite numbers, Factors.
Chapter 2: Polynomials »

Shikhar Tiwari
Having graduated from Electronics and Communication Engineering from AKTU – Noida, India, in 2021, working for Tiwari Academy as a content writer and reviewer. My main focus is to provide an easy to understand methods in all subjects specially mathematics and making study material with step by step explanation.
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 1 Class 10 Real Numbers
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for NCERT 2023-2024 Book.
Answers to all exercise questions and examples are solved for Chapter 1 Class 10 Real numbers. Solutions of all these NCERT Questions are explained in a step-by-step easy to understand manner
In this chapter, we will study
- What is a Real Number
- What is Euclid's Division Lemma , and
- How to find HCF (Highest Common Factor) using Euclid's Division Algorithm
- Then, we study Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which is basically Prime Factorisation
- And find HCF and LCM using Prime Factorisation
- We also use the formula of HCF and LCM of two numbers a and b HCF × LCM = a × b
- Then, we see what is an Irrational Number
- and Prove numbers irrational (Like Prove √ 2, √ 3 irrational)
- We revise our concepts about Decimal Expansion (Terminating, Non-Terminating Repeating, Non Terminating Non Repeating)
- And find out Decimal Expansion of numbers without performing long division
Click on an NCERT Exercise below to get started.
Or you can also check the Concepts from the concept Wise. The chapter is divided into concepts, and first each concept is explained. And then, the questions of the concept is solved, from easy to difficult. This is the Teachoo way of learning.
You can check the concepts by clicking on a link below Concept Wise.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?

Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers
March 31, 2019 by Veerendra
Get here Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers . These NCERT Solutions for Class 10 of Maths subject includes detailed answers of all the questions in Chapter 1 – Class 10 Real Numbers provided in NCERT Book which is prescribed for class 10 in schools.
Resource: National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) Solutions Class: 10th Class Subject: Maths Chapter: Chapter 1 – Real Numbers
- No of Exercises – 4 (Contains 17 Questions)
- Class 10 Real Numbers Ex 1.1 – 4 Questions Based on Euclid’s division lemma
- Class 10 Real Numbers Ex 1.2 – 7 Questions Based on Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, LCM and HCF
- Class 10 Real Numbers Ex 1.3 – 3 Questions Based on Rational and Irrational Numbers
- Class 10 Real Numbers Ex 1.4 – 3 Questions Based in which you have to expand fractions into decimals and write decimals in their fraction form.
Real Numbers Class 10 Ex 1.1

(iii) Given numbers are 867 and 255 On applying Euclid’s division algorithm, we have 867 = 255 x 3 + 102 Since the remainder 102 ≠ 0, so again we apply Euclid’s division algorithm to 255 and 102. to get 255 = 102 x 2 + 51 Since the remainder 51 ≠ 0, so again we apply Euclid’s division algorithm to 102 and 51, to get 102 = 51 x 2 + 0 We find the remainder is 0 and the divisor is 51 ∴ The HCF of 867 and 255 is 51. Alternatively: (iii) 867 and 255 Step 1: Since 867 > 255, apply Euclid’s division lemma, to a =867 and b=255 to find q and r such that 867 = 255q + r, 0 ≤ r<255 On dividing 867 by 255 we get quotient as 3 and remainder as 102 i.e 867 = 255 x 3 + 102
Step 2: Since remainder 102 ≠ 0, we apply the division lemma to a=255 and b= 102 to find whole numbers q and r such that 255 = 102q + r where 0 ≤ r<102 On dividing 255 by 102 we get quotient as 2 and remainder as 51 i.e 255 = 102 x 2 + 51
Step 3: Again remainder 51 is non zero, so we apply the division lemma to a=102 and b= 51 to find whole numbers q and r such that 102 = 51 q + r where 0 r < 51 On dividing 102 by 51 quotient is 2 and remainder is 0 i.e 102 = 51 x 2 + 0 Since the remainder is zero, the divisor at this stage is the HCF Since the divisor at this stage is 51,therefore, HCF of 867 and 255 is 51.
Concept Insight: To crack such problem remember to apply Euclid’s division Lemma which states that “Given positive integers a and b, there exist unique integers q and r satisfying a = bq + r, where 0 ≤ r < b” in the correct order. Here, a > b. Euclid’s algorithm works since Dividing ‘a’ by ‘b’, replacing ‘b’ by ‘r’ and ‘a’ by ‘b’ and repeating the process of division till remainder 0 is reached, gives a number which divides a and b exactly. i.e HCF(a,b) =HCF(b,r) Note that do not find the HCF using prime factorization in this question when the method is specified and do not skip steps.

Concept Insight: In order to solve such problems Euclid’s division lemma is applied to two integers a and b the integer b must be taken in accordance with what is to be proved, for example here the integer b was taken 6 because a must be of the form 6q + 1, 6q + 3, 6q + 5. Basic definition of even and odd numbers and the fact that addition and, multiplication of integers is always an integer are applicable here.

Question 5: Use Euclid’s division lemma to show that the cube of any positive integer is of the form 9m, 9m + 1 or 9m + 8. Solution:

Thus, the cube of any positive integer is of the form 9m, 9m + 1 or 9m + 8.
Alternatively:
Let a be a positive integer, q be the quotient and r be the remainder. Dividing a by 3 using the Euclid’s Division Algorithm, we have, a = 3q + r, where 0 ≤ r < 3 Putting r = 0, 1 and 2, we get: a = 3q, a = 3q + 1 and a = 3q + 2 If a = 3q, then a 3 = 27q 3 = 9(3q 3 ) = 9m. (Assuming m = 3q 3 .) If a = 3q + 1, then a 3 = (3q + l) 3 = 27q 3 + 9q(3q + 1) + 1 = 9(3q 3 + 3q 2 + q) + 1 = 9m + 1, (Assuming m = 3q 3 + 3q 2 + q) If a = 3q + 2, then a 3 = (3q + 2) 3 = 27q 3 + 18q(3q + 2) + (2) 3 = 9(3q 3 + 6q 2 + 4q) + 8 = 9m + 8, (Assuming m – 3q 3 + 6q 2 + 4q) Hence, a 3 is of the form 9m, 9m + 1 or 9m + 8.
Real Numbers Class 10 Ex 1.2

Question 7: There is a circular path around a sports field. Sonia takes 18 minutes to drive one round of the field, while Ravi takes 12 minutes for the same. Suppose they both start at the same point and at the same time, and go in the same direction. After how many minutes will they meet again at the starting point? Solution: Method 1:

Therefore, both Sonia and Ravi will meet again at the starting point after 36 minutes.
Real Numbers Class 10 Ex 1.3
Question 1. Prove that √5 is irrational. Solution: Let us assume that is rational. ∴ There exists co-prime integers a and b (b ≠ 0) such that √5 = \(\frac { a }{ b }\) ⇒ √5b= 0 Squaring on both sides, we get 5b 2 = a 2 …… (i) ⇒ 5 divides a 2 ⇒ 5 divides a So, we can write a = 5c for some integer c. From (i) and (ii) 5b 2 = 25c 2 ⇒ b 2 = 5c 2 ⇒ 5 divides b 2 ⇒ 5 divides b ∴ 5 is a common factor of a and b. But this contradicts the fact that a and b are co-primes. This contradiction has arisen because of our incorrect assumption that √5 is rational. Hence, √5 is irrational. Alternatively: Let √5 = \(\frac { p }{ q }\) be a rational number, where p and q are co-primes and q ≠ 0. Then, √5q = p => 5q 2 =p 2 ⇒ p 2 – Sq 2 … (i) Since 5 divides p 2 , so it will divide p also. Let p = 5r Then p 2 – 25r 2 [Squaring both sides] ⇒ 5q 2 = 25r 2 [From(i)] ⇒ q 2 = 5r 2 Since 5 divides q 2 , so it will divide q also. Thus, 5 is a common factor of both p and q. This contradicts our assumption that √5 is rational. Hence, √5 is irrational. Hence, proved.

Real Numbers Class 10 Ex 1.4

Question 2. Write down the decimal expansions of those rational numbers in the question 1, which have terminating decimal expansions. Solution:

Class 10 Real Numbers Summary
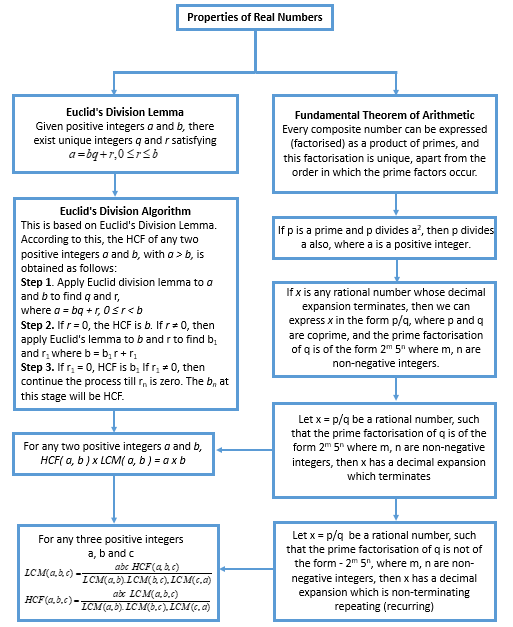
We have studied the following points: 1. Euclid’s Division Lemma: Given positive integers a and b, there exist whole numbers q and r satisfying a = bq + r where 0 = r = b. 2. Euclid’s Division Algorithm: According to this, which is based on Euclid’s division lemma, the HCF of any two positive integers a and b with a > b is obtained as follows: Step 1 Apply the division lemma to find q and r where a = bq + r, O = r < b. Step 2 If r = 0, the HCF is b . If r? 0 apply Euclid Lemma to b and r Step 3 Continue the process until the remainder is zero. The divisor at this stage will be HCF (a, b). Also HCF (a, b) = HCF (b, r) 3. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: Every composite number can be expressed (factorized) as a product of primes and this factorization is unique, apart from the order in which the prime factors occur.
4. If p is a prime and p divides a 2 , then p divides a also, where a is a positive integer.
5. If x is any rational number whose decimal expansion terminates, then we can express x in the form p/q, where p and q are coprime, and the prime factorisation of q is of the form 2 m 5 n where m, n are non-negative integers.
6. Let x = p/q be a rational number, such that the prime factorisation of q is of the form 2 m 5 n where m, n are non-negative integers, then x has a decimal expansion which terminates
7. Let x = p/q be a rational number, such that the prime factorisation of q is not of the form – 2 m 5 n , where m, n are non-negative integers, then x has a decimal expansion which is non-terminating repeating (recurring)
8. To Prove √3 Rational Number.
Class 10 Maths Real numbers Mind Map
Euclid’s division lemma.
For given any two positive integers a and b, there exist unique integers q and r satisfying a = bq + r, 0 ≤ r < b Lemma : A lemma is a proven statement used for proving another statement.
Euclid’s Division Algorithm
Euclid’s division algorithm is a technique to compute the Highest Common Factor (HCF) of two given positive integers. To get HCF of two positive integers c and d, c > d following steps are to be followed:
(i) Apply Euclid’s division lemma to c and d to get whole numbers q and r such that c = dq + r, 0 ≤ r < d. (ii) If r = 0, then d is HCF of c and d. If r ≠ 0. apply division lemma to d and r. (iii) Continue the process till the remainder is zero. The divisor at this stage will be the required HCF.
Note: (i) Euclid’s division lemma and algorithm are so closely interlinked that people often call former as the division algorithm also. (ii) Euclid’s division algorithm is stated for only +ve integers but it can be extended for all integers except zero.
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic

HCF and LCM of Three Numbers
Note: For three positive integers a, b and c HCF (a, b, c) × LCM (a, b, c) ≠ a × b × c
Irrational Numbers
Number which is not a rational number or whose decimal expansion is non-terminating and non-repeating Note: (i) The sum or difference of a rational and an irrational number is irrational, e.g., 2 + √2 is irrational, 2 – √3 is irrational. (ii) The product and quotient of a non-zero rational and irrational number is irrational, e.g., 5 × √2 is irrational \(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{3}\) is irrational
Rational Numbers and Their Decimal Expansion
(i) If denominator of a rational number is of the form 2 n 5 m , where n, m are non-negative integers then x has decimal expansion which terminates. (ii) If decimal expansion of rational number terminates then its denominator has prime factorisation of the form 2 n 5 m , where n, m are non-negative integers. (iii) If denominator of a rational number is not of the form 2 n 5 m , where n and m are non-negative integers then the rational number has decimal expansion which is non-terminating repeating. Thus we conclude that the decimal expansion of every rational number is either terminating or non-terminating repeating.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
- Chapter 6 Triangles
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
- Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
- Chapter 10 Circles
- Chapter 11 Constructions
- Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 Statistics
- Chapter 15 Probability
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers
NCERT solutions for class 10 maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers encompasses essential concepts around real numbers such as Euclid’s division lemma, Prime Numbers, Composite Numbers, Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, HCF, and LCM by Prime Factorization Method, and Irrational Numbers. Real numbers are the combination of rational and irrational numbers. They are denoted by the symbol "R" and can be both positive and negative. NCERT solutions class 10 maths Chapter 1 will help cover all the relevant concepts of real numbers as it has significant applications in real life. Kids also learn about important facts such as the use of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic in proving the irrationality of many of the numbers and exploring when exactly the decimal expansion of a rational number is terminating and when it is non terminating. As numbers form the foundation of Mathematics , understanding the basics is a must.
In this chapter, students will also learn how to represent the real numbers on a number line and the process of successive magnification, which is used to represent a decimal expansion on a number line . The lesson combines certain concepts that kids have come across in previous classes with newer complicated topics to give them a holistic understanding of real numbers and their application. The Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 can be found in the pdf format below and also you can find some of these in the exercises given below.
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.3
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.4
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 PDF
Mathematics presents us with a variety of numbers and real numbers are one of them. In order to understand higher mathematics, it makes sense to first take a look at the number system in detail which has been achieved in this book. An interesting aspect of the NCERT book is that it details some historical notes, cutting the monotony of studies. Further, the solutions have certain tips and tricks to help a child streamline his process of learning. The links for NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths available for free PDF download are given below:
☛ Download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers
NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Download PDF

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers
With the aid of the easily available links above, students will get to explore real numbers with a variety of examples and problems. It is essential to read the theorems and explanations first before moving on to the solved examples and exercise questions. Kids should make it a point to periodically revise these links as some questions can prove to be confusing. Thus, if not given ample time to study students might not be able to recall concepts when required. The exercise-wise analysis of NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers is given below :
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.1 - 5 Questions
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.2 - 7 Questions
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.3 - 3 Questions
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.4 - 3 Questions
Topics Covered : The topics covered in Class 10 maths NCERT solutions Chapter 1 are Euclid’s division algorithm , the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic , revision of Irrational Numbers & Rational Numbers , Prime Numbers , Composite Numbers , HCF , and LCM by Prime Factorization, as well as proving if a number is rational or irrational. All the questions related to these topics are discussed in detail in the NCERT solutions.
Total Questions : Class 10 maths chapter 1 Real Numbers consists of 18 key questions, of which 10 are easy, 5 are moderate, and 3 are complicated sums. By solving the problems, students can cover all the topics of this chapter and prepare for their board exams.
List of Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1
NCERT solutions Class 10 maths chapter 1 covers the formulas based on the properties of real numbers and their theorems. These formulas will help the students solve questions accurately and quickly. They are not just helpful for class 10, but higher-level mathematics as well. Apart from these, it is necessary for kids to remember certain points related to a particular category of numbers . For example, the decimal expansion of an irrational number is non-terminating and non-repeating. Let us go through some of the formulas and properties covered in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers:
- Commutative Property: m + n = n + m
- Associative Property: m + (n + r) = (m + n) + r
- Euclid’s Division Lemma: [a=bq+r,0≤r<b]
Important Questions for Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 |
|---|
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.2 |
|---|
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.3 |
|---|
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.4 |
|---|
Video Solutions for Class 10 Maths NCERT Chapter 1
| NCERT Video Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 | |
|---|---|
| Video Solutions for Class 10 Maths Exercise 1.1 | |
| Video Solutions for Class 10 Maths Exercise 1.2 | |
| Video Solutions for Class 10 Maths Exercise 1.3 | |
| Video Solutions for Class 10 Maths Exercise 1.4 | |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1
Why are ncert solutions class 10 maths chapter 1 vital for scoring well.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 deals with real numbers and their concepts which strengthens the student’s theoretical and practical knowledge. This chapter helps kids understand the divisibility and multiplication of integers through concepts like Euclid’s Division Lemma and the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. These concepts have deep and significant applications as well as carry a good weightage in board exams. Thus, the NCERT solutions class 10 Maths Chapter 1 is vital for the students to score well.
Do I Need to Practice all Questions Given in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Real Numbers?
We have a total of 18 questions in NCERT solutions class 10 maths Real Numbers which are in various formats. Some of the questions related to topics like LCM and HCF, prime factorization, need a step-wise approach. Euclid’s Division Lemma is one topic that requires regular practice. Since all the questions cover a variety of topics, you must practice each and every question of this chapter.
What are the Important Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1?
The important sub-topics covered in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 are Euclid’s Division Lemma and the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. Euclid’s Division Lemma helps students calculate the HCF of two positive integers while the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic is useful in finding the HCF and LCM of two positive integers. Students can practice questions related to both topics in order to get a crystal-clear understanding of the subject matter.
How Many Questions are there in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers?
There are a total of 18 well-researched questions in the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real numbers. These 18 questions are accurately placed to match the context of the theory. They are divided into 4 exemplar exercises. The 18 questions are further segregated into long answers, moderate level, and easy ones. Students can allocate sufficient time to each of these subcategories to gain mastery of this topic.
What are the Important Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1?
The important formulas mentioned in the NCERT Solutions class 10 maths chapter 1 are the properties of real numbers like commutative and distributive properties, the equation for Euclid’s Lemma, and its proof. These formulas have frequent applications in the chapter and are very easy to remember. Therefore, students must read the theory and understand the derivation of these formulas.
Why Should I Practice NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Real Numbers Chapter 1?
Consistent practice can do wonders. NCERT Solutions helps the students to be confident and solidify their mathematical knowledge. Understanding concepts like rational numbers, irrational numbers, HCF, LCM will assist the kids in preparing for higher classes. Hence, practicing the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Real Numbers Chapter 1 is essential for 10th-grade students.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers Assignments and Worksheets with solutions and answers updated for academic session 2024-25. All the chapter is divided into 4 assignments taking easy, average, and difficult questions.
We have provided below the largest collection of CBSE NCERT Assignments for Class 10 Real Numbers which can be downloaded by you for free. These free assignments cover all Class 10 Real Numbers important questions and answers and have been designed based on the latest CBSE NCERT Books and Syllabus. You can click on the links below to download ...
In real numbers for Class 10, we will learn about Euclid’s division algorithm, the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, methods of finding LCM, HCF and the complete explanation of rational and irrational numbers.
Solution: Let x be any positive integer and y = 3. By Euclid’s division algorithm; x =3q + r (for some integer q ≥ 0 and r = 0, 1, 2 as r ≥ 0 and r < 3) Therefore, x = 3q, 3q + 1 and 3q + 2. As per the given question, if we take the square on both the sides, we get; x 2 = (3q) 2 = 9q 2 = 3.3q 2. Let 3q 2 = m. Therefore, x 2 = 3m …………………. (1)
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers: Download PDF for Free and study offline. Clear doubts on Real Numbers of Class 10 Maths and excel in your exam. Register at BYJU'S for NCERT Solutions!
Get here the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers all exercises in Hindi and English medium revised and modified for session 2024-25. The solution of chapter 1 class 10th mathematics is updated according to NCERT textbooks published for 2024-25 CBSE exams.
Answers to all exercise questions and examples are solved for Chapter 1 Class 10 Real numbers. Solutions of all these NCERT Questions are explained in a step-by-step easy to understand manner. In this chapter, we will study. What is a Real Number. What is Euclid's Division Lemma, and.
Class 10 Maths Real Numbers. Rational numbers and irrational numbers are taken together form the set of real numbers. The set of real numbers is denoted by R. Thus every real number is either a rational number or an irrational number. In either case, it has a non–terminating decimal representation.
These NCERT Solutions for Class 10 of Maths subject includes detailed answers of all the questions in Chapter 1 – Class 10 Real Numbers provided in NCERT Book which is prescribed for class 10 in schools.
NCERT solutions for class 10 maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers encompasses essential concepts around real numbers such as Euclid’s division lemma, Prime Numbers, Composite Numbers, Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, HCF, and LCM by Prime Factorization Method, and Irrational Numbers.