
Causal-Comparative Research Designs
Sep 05, 2014
230 likes | 896 Views
Causal-Comparative Research Designs. Causal-Comparative Research Method. The Study of Relationships between Variables Educational research is done to DESCRIBE educational phenomena or to EXPLORE relationships between phenomena

Share Presentation
- relationships
- academic achievement
- educational research
- research problem
- causal comparative study
- causal comparative research designs

Presentation Transcript
Causal-Comparative Research Method • The Study of Relationships between Variables • Educational research is done to DESCRIBE educational phenomena or to EXPLORE relationships between phenomena • The type of relationship of greatest interest to educators is that involving cause and effect • The discovery of cause-and-effect relationships is useful both for theory development and for educational improvement
Causal-Comparative Research Method • The Study of Relationships between Variables • Causal-comparative method is the simplest quantitative approach to exploring cause-and-effect relationships between phenomena • It involves a particular method of analyzing data to detect relationships between variables • The correlational method is another approach to achieve the same goal
Causal-Comparative Research Method • Advantages • AKA “ex post facto research” – causes are studied after they presumably have exerted their effect on another variable (e.g., administer a questionnaire to study the causes of high academic achievement) • Allows us to study cause-and-effect relationships under conditions where experimental manipulation is difficult or impossible • Many relationships can be studied in a single research study (refer to table 10.1)
Causal-Comparative Research Method • Disadvantages • Difficult to establish causality on the basis of the data collected • An observed relationship between variables A and B can mean that A causes B, B causes B, or a third variable C causes both A and B
Causal-Comparative Research Method Table 10.1 Academic Achievement and Extracurricular Participation of Employed and Nonemployed Students
Planning a Causal-Comparative Study • Statement of the Research Problem • Selecting a Defined Group • Selecting Comparison Groups • Data Collection • Data Analysis
Statement of the Research Problem • Speculate about the causes or effects of the phenomenon that interest you (i.e., based on previous research findings and theory, as well as your own observations of the phenomenon • After possible causes and effects have been identified, they should be incorporated into the statement of the research problem • Researcher should attempt to state and test alternative hypotheses about other factors that might explain observed differences between two groups • “Strong inference” vs. “shotgun approach”
Selecting a Defined Group • Define the group that possesses the characteristics one wishes to study • The definition should be precise so that the results of the study can be interpreted meaningfully
Selecting a Comparison Group • Once you have selected a group having the characteristic you wish to study, the next step is to select a group NOT having this characteristic, or having it to a lesser degree • The population from which the comparison sample is to be selected usually is defined so as to be similar to the characteristic-present group except for the variable being studied • Matching: used to equate two groups on one or more extraneous variable so that these extraneous variables do not confound study of causal relationships involving the variables of primary interest to the researcher • Extreme-groups method: involves selecting comparison groups that are at the two extremes of a score distribution on one variable
Data Collection • Standardized tests • Questionnaires • Interviews • Naturalistic observations
Data Analysis • Compute descriptive statistics for each comparison group in the study (e.g., group mean, stand deviation) • Conduct a test of statistical significance (choice of test depends research questions; t-test, ANOVA; MANOVA)
- More by User

Randomization and Comparative Designs
Randomization and Comparative Designs. Oncology Journal Club April 5, 2002. Comparative Designs. “Compare”: need more than one group Different types historical control two+ treatment groups treatment and placebo groups “Phase III”. Was this study comparative?.
245 views • 9 slides

Descriptive and Causal Research Designs
Descriptive and Causal Research Designs. Chapter 6. SLIDE 6-1. Classification of Descriptive Studies. Continuous Panel. Longitudinal. Discontinuous Panel. Descriptive Studies. Cross Sectional. Sample Survey. • allows turnover analysis if panel is continuous
625 views • 10 slides

Causal-Comparative Research
Causal-Comparative Research. Research that is interested in learning if there is a relationship between or among variables that is causal in nature ( i.e. does one variable cause a given outcome ). Causal-Comparative Research Characteristics. Is either retro spective or pro spective.
905 views • 4 slides

Causal-Comparative Research. July 23, 2001 EAF 410. What is it?. Associational Differences between/among groups Categorical data Differences already exist Ex post facto Much research in medicine & sociology. What are the effects of teacher gender on student behavior
688 views • 25 slides

Causal-Comparative Research. Chapter Sixteen. Steps Involved in Causal-Comparative Research. Problem Formulation The first step is to identify and define the particular phenomena of interest and consider possible causes Sample
2.03k views • 24 slides

CAUSAL-COMPARATIVE RESEARCH
CAUSAL-COMPARATIVE RESEARCH. LIYANA BT AHMAD AFIP 2010439958. OVERVIEW. Description Characteristics Procedure Sample Data Analysis Example of topics Example of research utilizing the methodology. DESCRIPTION. It is a quantitative research
638 views • 12 slides

Research Designs
Research Designs. By: Fatma & Wenshan . Agenda. A quick review on research methods Short break Research on instructional strategies Activity Implication for research approaches Significant research finding in the last five years Likely development in the next five years.
641 views • 38 slides

Educational Research: Causal-Comparative Studies
Educational Research: Causal-Comparative Studies. Nasih Jaber Ali 25-10-2011. The basic steps of research. Scientific and disciplined inquiry is an orderly process, involving: Recognition and identification of a topic to be studied (“ problem ”)
978 views • 33 slides

Exploratory, Descriptive, and Causal Research Designs
Exploratory, Descriptive, and Causal Research Designs. Chapter 3, Student Edition. Learning Objectives. Describe the major emphasis of each of the three basic types of research design Describe the key characteristics and basic uses of exploratory research
1.98k views • 17 slides

Experimental vs. Causal-Comparative Studies
Experimental vs. Causal-Comparative Studies. Topic 3. Experimental Study. Study where treatments are given to observe their effects Treatments – input or stimulus given by the researcher Not useful when a study would be physically, ethically, legally, or financially impossible. Demographics.
365 views • 16 slides

CAUSAL-COMPARATIVE
CAUSAL-COMPARATIVE. CAUSAL-COMPARATIVE. investigators attempt to determine the cause or consequences of differences that already exist between or among groups of individuals
778 views • 17 slides

Exploratory, Descriptive, and Causal Research Designs. Chapter 3. Research Designs. Three types Exploratory Descriptive Causal. Source: evolvedmarketingconcepts.com. Exploratory Research. Purposes Diagnosing a situation Screening alternatives Discovering new ideas Produce hypotheses
531 views • 10 slides

Educational Research: Causal-Comparative Studies. EDU 8603 Educational Research Richard M. Jacobs, OSA, Ph.D. Research. The systematic application of a family of methods employed to provide trustworthy information about problems.
865 views • 64 slides

Experimental and Causal-Comparative Designs
Experimental and Causal-Comparative Designs. Purpose. Examine the possible influences that one factor or condition may have on another factor or condition cause-and-effect relationships ideally, by controlling all factors except those whose possible effects are the focus of investigation.
776 views • 62 slides

Research Designs. Types of Research. Quantitative - Uses data numbers– statistics Can be descriptive Can be experimental/correlational Qualitative – Uses data narrative descriptive ethnographic. DESCRIPTIVE. Quantitative - survey studies Qualitative - observational research
766 views • 31 slides

Correlational Designs Causal Modeling Quasi-Experimental Designs
Correlational Designs Causal Modeling Quasi-Experimental Designs. Quasi means “seeming like.” Quasi-experiments superficially resemble experiments, but lack their required manipulation of antecedent conditions and/or random assignment to conditions.
1.26k views • 30 slides

Comparative Research
Comparative Research. Comparative Research. General All research is comparative Terms of comparative social science Comparative Research Proper (Ragin) Goals/Advantages Characteristics Comparative Methods Method of Agreement (Mill) Method of Difference (Mill)
1.56k views • 24 slides

EDU 702 Research Methodology ( CAUSAL COMPARATIVE ) Lecturer:
EDU 702 Research Methodology ( CAUSAL COMPARATIVE ) Lecturer: Prof. Madya Dr. Izaham Shah Ismail Presented by: SANIAH BT. HASSAN - 2010912919 NOOR AZURA BT. BAHARUDIN - 2010530931
424 views • 24 slides

Correlational and Causal Comparative Research
Correlational and Causal Comparative Research. Definition and Purpose . Correlational research involves the collection of data to determine the extent to which two (or more) variables are related. If a relationship exists, we say that the two variables covary in some non-random way.
723 views • 37 slides

Causal Comparative Research: Purpose
Causal Comparative Research: Purpose. Attempts to determine cause and effect not as powerful as experimental designs Alleged cause and effect have already occurred and are being examined after the fact (e.g., ex post facto)
874 views • 15 slides

Sampling, Causal Research
Sampling, Causal Research. Market Intelligence Julie Edell Britton Session 6 September 5, 2009. Today’s Agenda. Announcements Sampling Sampling Error Milan Food Case WSJ/Harris Interactive Survey Causal Research – Experiments Pre-experimental Designs True Experiments
321 views • 31 slides

Correlational and Causal-Comparative Designs
Correlational and Causal-Comparative Designs. SPED 8671 Shawnee Wakeman. Review of types of variables. Categorical variables Also called nominal, discrete, dichotomous Ordinal (rank order) variables Continuous variables Subtypes: Interval (no true zero; but equal intervals)
296 views • 27 slides

Comparative Research
Ai generator.

Although not everyone would agree, comparing is not always bad. Comparing things can also give you a handful of benefits. For instance, there are times in our life where we feel lost. You may not be getting the job that you want or have the sexy body that you have been aiming for a long time now. Then, you happen to cross path with an old friend of yours, who happened to get the job that you always wanted. This scenario may put your self-esteem down, knowing that this friend got what you want, while you didn’t. Or you can choose to look at your friend as an example that your desire is actually attainable. Come up with a plan to achieve your personal development goal . Perhaps, ask for tips from this person or from the people who inspire you. According to the article posted in brit.co , licensed master social worker and therapist Kimberly Hershenson said that comparing yourself to someone successful can be an excellent self-motivation to work on your goals.
Aside from self-improvement, as a researcher, you should know that comparison is an essential method in scientific studies, such as experimental research and descriptive research . Through this method, you can uncover the relationship between two or more variables of your project in the form of comparative analysis .
What is Comparative Research?
Aiming to compare two or more variables of an experiment project, experts usually apply comparative research examples in social sciences to compare countries and cultures across a particular area or the entire world. Despite its proven effectiveness, you should keep it in mind that some states have different disciplines in sharing data. Thus, it would help if you consider the affecting factors in gathering specific information.
Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods in Comparative Studies
In comparing variables, the statistical and mathematical data collection, and analysis that quantitative research methodology naturally uses to uncover the correlational connection of the variables, can be essential. Additionally, since quantitative research requires a specific research question, this method can help you can quickly come up with one particular comparative research question.
The goal of comparative research is drawing a solution out of the similarities and differences between the focused variables. Through non-experimental or qualitative research , you can include this type of research method in your comparative research design.
13+ Comparative Research Examples
Know more about comparative research by going over the following examples. You can download these zipped documents in PDF and MS Word formats.
1. Comparative Research Report Template

- Google Docs
Size: 113 KB

2. Business Comparative Research Template

Size: 69 KB
3. Comparative Market Research Template

Size: 172 KB
4. Comparative Research Strategies Example

5. Comparative Research in Anthropology Example

Size: 192 KB
6. Sample Comparative Research Example

Size: 516 KB
7. Comparative Area Research Example

8. Comparative Research on Women’s Emplyment Example

Size: 290 KB
9. Basic Comparative Research Example

Size: 19 KB
10. Comparative Research in Medical Treatments Example

11. Comparative Research in Education Example

Size: 455 KB
12. Formal Comparative Research Example

Size: 244 KB
13. Comparative Research Designs Example

Size: 259 KB
14. Casual Comparative Research in DOC

Best Practices in Writing an Essay for Comparative Research in Visual Arts
If you are going to write an essay for a comparative research examples paper, this section is for you. You must know that there are inevitable mistakes that students do in essay writing . To avoid those mistakes, follow the following pointers.
1. Compare the Artworks Not the Artists
One of the mistakes that students do when writing a comparative essay is comparing the artists instead of artworks. Unless your instructor asked you to write a biographical essay, focus your writing on the works of the artists that you choose.
2. Consult to Your Instructor
There is broad coverage of information that you can find on the internet for your project. Some students, however, prefer choosing the images randomly. In doing so, you may not create a successful comparative study. Therefore, we recommend you to discuss your selections with your teacher.
3. Avoid Redundancy
It is common for the students to repeat the ideas that they have listed in the comparison part. Keep it in mind that the spaces for this activity have limitations. Thus, it is crucial to reserve each space for more thoroughly debated ideas.
4. Be Minimal
Unless instructed, it would be practical if you only include a few items(artworks). In this way, you can focus on developing well-argued information for your study.
5. Master the Assessment Method and the Goals of the Project
We get it. You are doing this project because your instructor told you so. However, you can make your study more valuable by understanding the goals of doing the project. Know how you can apply this new learning. You should also know the criteria that your teachers use to assess your output. It will give you a chance to maximize the grade that you can get from this project.
Comparing things is one way to know what to improve in various aspects. Whether you are aiming to attain a personal goal or attempting to find a solution to a certain task, you can accomplish it by knowing how to conduct a comparative study. Use this content as a tool to expand your knowledge about this research methodology .
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTML5 video
Causal-Comparative Research Designs
Published by Tre Everage Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Causal-Comparative Research Designs"— Presentation transcript:

Educational Research: Causal-Comparative Studies
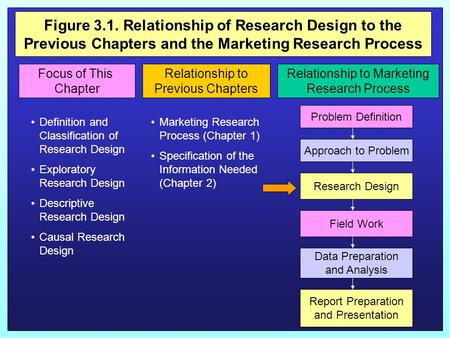
Figure 3.1. Relationship of Research Design to the Previous Chapters and the Marketing Research Process Figure 3.1Relationship to the Previous Chapter.

© LOUIS COHEN, LAWRENCE MANION & KEITH MORRISON

Chapter 2: Nonexperimental Research Approaches This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited.

Unit 2: Research Methods in Psychology

Causal-Comparative Research

Experimental Methods What is an experiment? Manipulation of one or more variables by the experimenter to determine the effect of this manipulation on another.

Chapter 1 Conducting & Reading Research Baumgartner et al Chapter 1 Nature and Purpose of Research.

Causal Comparative Research: Purpose

Survey Research & Understanding Statistics

6-1 Chapter Six DESIGN STRATEGIES. 6-2 What is Research Design? A plan for selecting the sources and types of information used to answer research questions.

Correlational and Causal Comparative Research

DESIGNING, CONDUCTING, ANALYZING & INTERPRETING DESCRIPTIVE RESEARCH CHAPTERS 7 & 11 Kristina Feldner.

Experimental vs. Causal-Comparative Studies Topic 3.

McGraw-Hill © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Causal-Comparative Research Chapter Sixteen.

The Research Design.

Chapter 8 Experimental Research

Chapter Three Chapter Three.

Research Methods Purpose: To Reach a Specific Goal Describe a phenomenon Predict future or past behavior Control current or future behavior and thinking.

Chapter 2: The Research Enterprise in Psychology
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Demystifying the research process: understanding a descriptive comparative research design
- Pediatric Nursing 37(4):188-9
- 37(4):188-9

- Villanova University
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
No full-text available
To read the full-text of this research, you can request a copy directly from the author.

- Karen Joy A. Masepequeña
- Jay Ric L. Pangalaya

- Perzeus Lhey D. Villahermosa
- July M. Villaren
- Alberto Sarte
- Jennisa E Baroro

- Liezel Maravilla

- ( Corresponding
- Ali 1 Bylieva

- Rocelyn A Camino
- Rosalie N Darunday
- Honey Claire B Gallando
- Zainal Abidin

- Univers Access Inform Soc

- Kawther Sacor I. Abdulhalim

- Hong-va Leong

- Lemuel Perez

- Mary Kris Maranga
- Novie Jane Maranga
- Charlene Mae Tautu-An

- Bliss Ann Marie V. Nene
- Kenn Carlo A. Delao
- , Abeguel M. Vargas

- Arlene A. Matawaran
- Elvin B. Rodriguez
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Experimental and Causal-Comparative Designs. Experimental and Causal-Comparative Designs. Purpose. Examine the possible influences that one factor or condition may have on another factor or condition cause-and-effect relationships ideally, by controlling all factors except those whose possible effects are the focus of investigation.
5 Terms of comparative social research Observation: One characteristic of one case Description: representation of all relevant features/aspects of a case Classification: Grouping of cases along one (and only one ) feature. Each case can be attributed to one class only. Ex: Classification of voters according to their party preference: Labour voters, Con Voters, LibDem Voters Typology: Grouping ...
An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: ... Causal-Comparative Research Designs. Causal-Comparative Research Designs. Causal-Comparative Research Method. The Study of Relationships between Variables Educational research is done to DESCRIBE educational phenomena or to EXPLORE relationships between phenomena.
A causal-comparative study is a study in which the researcher attempts to determine the cause, or reason, for pre-existing differences in groups of individuals called an "ex post facto" study because both the effect and the hypothetized cause have already occurred and must be studied in retrospect. 3 The aim of causal-comparative research ...
Causal-Comparative Research Designs. Causal-Comparative Research Method. The Study of Relationships between Variables Educational research is done to DESCRIBE educational phenomena or to EXPLORE relationships between phenomena Slideshow 3972969 by halima. ... An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: ...
Identify causal-comparative research topics, and describe the basic causal-comparative design. 2 Chapter 9: Causal-Comparative Research Objectives Identify and describe three types of control procedures that can be used in a causal-comparative study, and explain why the results of causal-comparative studies must be interpreted very ...
The goal of comparative research is drawing a solution out of the similarities and differences between the focused variables. Through non-experimental or qualitative research, you can include this type of research method in your comparative research design. 13+ Comparative Research Examples. Know more about comparative research by going over ...
Kaiser Health News, Feb. 1, 2010 The administration, releasing its 2011 budget request to Congress on Monday, proposed spending $286 million on comparative effectiveness research overseen by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The agency got $21 million for such research in its current fiscal-year budget, and an additional $300 ...
2 Introduction to Causal-Comparative Research A causal-comparative study is a study in which the researcher attempts to determine the cause, or reason, for pre-existing differences in groups of individuals called an "ex post facto" study because both the effect and the hypothetized cause have already occurred and must be studied in retrospect.
Portfolio Activity #8 Mini-proposal 3. Briefly describe a causal-comparative research project relevant to one of your identified research topics. In small groups discuss your mini-proposal ideas and be prepared to share your discussions with the rest of the class. 4.
3 Causal-Comparative Research Method The Study of Relationships between Variables Causal-comparative method is the simplest quantitative approach to exploring cause-and-effect relationships between phenomena It involves a particular method of analyzing data to detect relationships between variables The correlational method is another approach to achieve the same goal
Descriptive-comparative research is a quantitative research design that aims to describe the differences between groups in a population without manipulating the independent variable (Mary Ann ...
Corso di Comparative Research Designs and Methods - Prof. Berg Schlosser Dirk Vai al corso http://bit.ly/2F8WrDzExplore comparative analysis and its importan...
Comparative research in communication and media studies is conventionally understood as the contrast among different macro-level units, such as world regions, countries, sub-national regions, social milieus, language areas and cultural thickenings, at one point or more points in time. ... Adjusting Research Designs to Account for Effects of ...