
Work Life is Atlassian’s flagship publication dedicated to unleashing the potential of every team through real-life advice, inspiring stories, and thoughtful perspectives from leaders around the world.

Contributing Writer
Work Futurist

Senior Quantitative Researcher, People Insights
Principal Writer


How to build critical thinking skills for better decision-making
It’s simple in theory, but tougher in practice – here are five tips to get you started.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Have you heard the riddle about two coins that equal thirty cents, but one of them is not a nickel? What about the one where a surgeon says they can’t operate on their own son?
Those brain teasers tap into your critical thinking skills. But your ability to think critically isn’t just helpful for solving those random puzzles – it plays a big role in your career.
An impressive 81% of employers say critical thinking carries a lot of weight when they’re evaluating job candidates. It ranks as the top competency companies consider when hiring recent graduates (even ahead of communication ). Plus, once you’re hired, several studies show that critical thinking skills are highly correlated with better job performance.
So what exactly are critical thinking skills? And even more importantly, how do you build and improve them?
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to evaluate facts and information, remain objective, and make a sound decision about how to move forward.
Does that sound like how you approach every decision or problem? Not so fast. Critical thinking seems simple in theory but is much tougher in practice, which helps explain why 65% of employers say their organization has a need for more critical thinking.
In reality, critical thinking doesn’t come naturally to a lot of us. In order to do it well, you need to:
- Remain open-minded and inquisitive, rather than relying on assumptions or jumping to conclusions
- Ask questions and dig deep, rather than accepting information at face value
- Keep your own biases and perceptions in check to stay as objective as possible
- Rely on your emotional intelligence to fill in the blanks and gain a more well-rounded understanding of a situation
So, critical thinking isn’t just being intelligent or analytical. In many ways, it requires you to step outside of yourself, let go of your own preconceived notions, and approach a problem or situation with curiosity and fairness.
It’s a challenge, but it’s well worth it. Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems.
7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper
Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you’ll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions). But it’s better to think of critical thinking less as a distinct skill and more as a collection or category of skills.
To think critically, you’ll need to tap into a bunch of your other soft skills. Here are seven of the most important.
Open-mindedness
It’s important to kick off the critical thinking process with the idea that anything is possible. The more you’re able to set aside your own suspicions, beliefs, and agenda, the better prepared you are to approach the situation with the level of inquisitiveness you need.
That means not closing yourself off to any possibilities and allowing yourself the space to pull on every thread – yes, even the ones that seem totally implausible.
As Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D. writes in a piece for Psychology Today , “Even if an idea appears foolish, sometimes its consideration can lead to an intelligent, critically considered conclusion.” He goes on to compare the critical thinking process to brainstorming . Sometimes the “bad” ideas are what lay the foundation for the good ones.
Open-mindedness is challenging because it requires more effort and mental bandwidth than sticking with your own perceptions. Approaching problems or situations with true impartiality often means:
- Practicing self-regulation : Giving yourself a pause between when you feel something and when you actually react or take action.
- Challenging your own biases: Acknowledging your biases and seeking feedback are two powerful ways to get a broader understanding.
Critical thinking example
In a team meeting, your boss mentioned that your company newsletter signups have been decreasing and she wants to figure out why.
At first, you feel offended and defensive – it feels like she’s blaming you for the dip in subscribers. You recognize and rationalize that emotion before thinking about potential causes. You have a hunch about what’s happening, but you will explore all possibilities and contributions from your team members.
Observation
Observation is, of course, your ability to notice and process the details all around you (even the subtle or seemingly inconsequential ones). Critical thinking demands that you’re flexible and willing to go beyond surface-level information, and solid observation skills help you do that.
Your observations help you pick up on clues from a variety of sources and experiences, all of which help you draw a final conclusion. After all, sometimes it’s the most minuscule realization that leads you to the strongest conclusion.
Over the next week or so, you keep a close eye on your company’s website and newsletter analytics to see if numbers are in fact declining or if your boss’s concerns were just a fluke.
Critical thinking hinges on objectivity. And, to be objective, you need to base your judgments on the facts – which you collect through research. You’ll lean on your research skills to gather as much information as possible that’s relevant to your problem or situation.
Keep in mind that this isn’t just about the quantity of information – quality matters too. You want to find data and details from a variety of trusted sources to drill past the surface and build a deeper understanding of what’s happening.
You dig into your email and website analytics to identify trends in bounce rates, time on page, conversions, and more. You also review recent newsletters and email promotions to understand what customers have received, look through current customer feedback, and connect with your customer support team to learn what they’re hearing in their conversations with customers.
The critical thinking process is sort of like a treasure hunt – you’ll find some nuggets that are fundamental for your final conclusion and some that might be interesting but aren’t pertinent to the problem at hand.
That’s why you need analytical skills. They’re what help you separate the wheat from the chaff, prioritize information, identify trends or themes, and draw conclusions based on the most relevant and influential facts.
It’s easy to confuse analytical thinking with critical thinking itself, and it’s true there is a lot of overlap between the two. But analytical thinking is just a piece of critical thinking. It focuses strictly on the facts and data, while critical thinking incorporates other factors like emotions, opinions, and experiences.
As you analyze your research, you notice that one specific webpage has contributed to a significant decline in newsletter signups. While all of the other sources have stayed fairly steady with regard to conversions, that one has sharply decreased.
You decide to move on from your other hypotheses about newsletter quality and dig deeper into the analytics.
One of the traps of critical thinking is that it’s easy to feel like you’re never done. There’s always more information you could collect and more rabbit holes you could fall down.
But at some point, you need to accept that you’ve done your due diligence and make a decision about how to move forward. That’s where inference comes in. It’s your ability to look at the evidence and facts available to you and draw an informed conclusion based on those.
When you’re so focused on staying objective and pursuing all possibilities, inference can feel like the antithesis of critical thinking. But ultimately, it’s your inference skills that allow you to move out of the thinking process and onto the action steps.
You dig deeper into the analytics for the page that hasn’t been converting and notice that the sharp drop-off happened around the same time you switched email providers.
After looking more into the backend, you realize that the signup form on that page isn’t correctly connected to your newsletter platform. It seems like anybody who has signed up on that page hasn’t been fed to your email list.
Communication

3 ways to improve your communication skills at work
If and when you identify a solution or answer, you can’t keep it close to the vest. You’ll need to use your communication skills to share your findings with the relevant stakeholders – like your boss, team members, or anybody who needs to be involved in the next steps.
Your analysis skills will come in handy here too, as they’ll help you determine what information other people need to know so you can avoid bogging them down with unnecessary details.
In your next team meeting, you pull up the analytics and show your team the sharp drop-off as well as the missing connection between that page and your email platform. You ask the web team to reinstall and double-check that connection and you also ask a member of the marketing team to draft an apology email to the subscribers who were missed.
Problem-solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving are two more terms that are frequently confused. After all, when you think critically, you’re often doing so with the objective of solving a problem.
The best way to understand how problem-solving and critical thinking differ is to think of problem-solving as much more narrow. You’re focused on finding a solution.
In contrast, you can use critical thinking for a variety of use cases beyond solving a problem – like answering questions or identifying opportunities for improvement. Even so, within the critical thinking process, you’ll flex your problem-solving skills when it comes time to take action.
Once the fix is implemented, you monitor the analytics to see if subscribers continue to increase. If not (or if they increase at a slower rate than you anticipated), you’ll roll out some other tests like changing the CTA language or the placement of the subscribe form on the page.
5 ways to improve your critical thinking skills

Beyond the buzzwords: Why interpersonal skills matter at work
Think critically about critical thinking and you’ll quickly realize that it’s not as instinctive as you’d like it to be. Fortunately, your critical thinking skills are learned competencies and not inherent gifts – and that means you can improve them. Here’s how:
- Practice active listening: Active listening helps you process and understand what other people share. That’s crucial as you aim to be open-minded and inquisitive.
- Ask open-ended questions: If your critical thinking process involves collecting feedback and opinions from others, ask open-ended questions (meaning, questions that can’t be answered with “yes” or “no”). Doing so will give you more valuable information and also prevent your own biases from influencing people’s input.
- Scrutinize your sources: Figuring out what to trust and prioritize is crucial for critical thinking. Boosting your media literacy and asking more questions will help you be more discerning about what to factor in. It’s hard to strike a balance between skepticism and open-mindedness, but approaching information with questions (rather than unquestioning trust) will help you draw better conclusions.
- Play a game: Remember those riddles we mentioned at the beginning? As trivial as they might seem, games and exercises like those can help you boost your critical thinking skills. There are plenty of critical thinking exercises you can do individually or as a team .
- Give yourself time: Research shows that rushed decisions are often regrettable ones. That’s likely because critical thinking takes time – you can’t do it under the wire. So, for big decisions or hairy problems, give yourself enough time and breathing room to work through the process. It’s hard enough to think critically without a countdown ticking in your brain.
Critical thinking really is critical
The ability to think critically is important, but it doesn’t come naturally to most of us. It’s just easier to stick with biases, assumptions, and surface-level information.
But that route often leads you to rash judgments, shaky conclusions, and disappointing decisions. So here’s a conclusion we can draw without any more noodling: Even if it is more demanding on your mental resources, critical thinking is well worth the effort.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
Critical Thinking, Decision Making, and Problem Solving
Cite this chapter.

- John Heywood 2
Part of the book series: Synthesis Lectures on Engineering ((SLE))
95 Accesses
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Polya, G. (1957). How to Solve it, 2nd ed., Garden City, Doubleday Anchor. 71
MATH Google Scholar
Red, W. E. (1981). Problem solving and beginning engineering students. Engineering Education, 72(2), pp. 167–170. 71
Google Scholar
Rosati, P. A. (1987). Practising a problem solving strategy with computer tutorials. International Journal of Applied Engineering Education, 3(1), pp. 49–53. 71
Woods, D. R. et al. (1997). Developing problem solving skills: The McMaster problem solving program. Journal of Engineering Education, 86(2), pp. 75–91. 71, 79
Article Google Scholar
Fuller, M. and G. Kardos (1980). Structure and process in problem solving in J. Lubkin (Ed.), The Teaching of Problem Solving in Engineering and Related Fields. Washington, DC, ASEE. 71
Wales, C. E. and R. A. Stager (1986). Series of papers in issues, 5, 6, 7, and 8 in volume 62 in Engineering Education. 71
Maslow (i) makes a distinction between primary and secondary needs. The primary needs are basic, such as water, food, sex, lactation, urination, defecation, heat avoidance and cold avoidance. The secondary needs vary from person to person. They are ranked hierarchically in the sense that the primary needs have to be met before the secondary needs can be met. 71
D’Amour, G. and C. A. Wales (1977). Improving problem solving skills through a course in guided design. Engineering Education, February, pp. 381–384. Wales, C. E. and R. A. Stager (1986) issues 5, 6, 7, and 8 of Vol 62 of Engineering Education, contain a series of articles on guided design. 72
Wales, C. E., Nardi, A. H., and R. A. Stager (1986). Professional Decision Making. Mor-ganstown, WV, Center for Guided Design, West Virginia University. 72
Heywood, L. (2008). Instructional and Curriculum Leadership. Towards Inquiry Oriented Schools. Dublin. Original Writing for the National Association of Principals and Deputies. See also Heywood, J. (1996). An approach to teaching decision making skills using an engineering heuristic. ASEE/IEEE Proceedings Frontiers in Education Conference, 1, pp. 67–73. 72, 82
Luchins asked pupils in his research group to obtain specified amounts of water from three jars filled to different levels (capacity). He showed them first two problems which involved all three jars. In a further nine problems, the subjects mainly used the three-jar solution, to solve the problem when two jar solutions were possible. The “set” interfered with their problem solving. Subsequently Luchins divided another group into two subgroups. The first sub-group worked through the problem in the usual way, using the three jar solution. The second sub-group were told to think more carefully about how to solve the problems. Given that instruction, the majority of students in the second sub-group moved to the more simple solution using two jars. 73
Luchins, A. S. (1942). Mechanization in problems solving: The effect of “Einstellung.” Psychological Monographs, no 248.
The quotations in this paragraph come from Heywood (2008) [10]. More details of Ly-don’s plan, which was made available to future classes will also be found in that reference. 73, 75
Larkin, J. H. (1979). Processing information for effective problem solving. Engineering Education, 70(3), pp. 285–288. 73
Marton, F., Hounsell, D., and N. J. Entwistle (Eds.), (1984). The Experience of Learning. Edinburgh. Scottish Academic Press. 73
Cowan, J. (1998). One Becoming an Innovative University Teacher. Reflection in Action. Buckingham. SRHE/Open University Press. 73
McCracken, W. M. and W. C. Newstetter (2001). Text to diagram to symbol. Representational transformations in problem solving. ASEE/IEEE Proceedings Frontiers in Education Conference, F2G-13 to 17. 75
Cajander, A., Daniels, M., and B. R. Komsky (2011). Development of professional competencies in engineering education. ASEE/IEEE Proceedings Frontiers in Education Conference, S1C-1 to 5. 76
A recent review of critical thinking will be found in, Cooney, E., Alfrey, H., and S. Owens (2017). Critical thinking in engineering and technology. A review. Proceedings Annual Conference of the American Society for Engineering Education. Paper 1110. 76
Pascarella, E. T. and P. T. Terenzini (2005). How College Affects Students. A Third Decade, vol 2, San Fransisco. Josey Bass. 77
Kaupp, J. A., Frank, B. M., and A. S.-Y. Chen (2013). Investigating the impact of model eliciting activities on the development of critical thinking. Proceedings of Annual Conference of the American Society for Engineering Education. Paper 6432. 77
Lin, Y., Shahhosseini, A. M., and M. A. Badar (2017). Assessing conceptual mapping based active learning for advancing engineering diagnostic skills. Proceedings Annual Conference of the American Society for Engineering Education. Session T149. 77
The Joint Matriculation Board published each year reports of how the candidates performed in each of the questions. One comment on a question in engineering science was published by Carter, Heywood and Kelly (i). It illustrates just how difficult it is to design such questions. The report reads: “The figure (not shown here) represents some of the more important parts of a single bar, 1 kw radiant electric fire. Discuss the purpose of these components and suggest a suitable material for each. (Base your discussion on the function each part has to fulfil and requisite physical properties). Discuss the other factors that a manufacturer would consider in producing the components from particular materials. Describe and suggest materials for other parts which you believe will be necessary for satisfactory use of the fire, but which has not been indicated in the sketch.” 77 The examiners published comment on the answers was: “This was the most popular question and the most badly done. Only one of the two candidates calculated the resistance required for the element. Candidates tended not to answer the questions asked. E.g., they did not state the function of each of the parts of the fire and materials were often suggested without reasons. Candidates stated factors the manufacturer should consider, without discussion. The question was answered on the whole in too facile a number.” In (i) they expanded on this type of question as follows, “Although this type of question suffered from superficiality of response it was retained in similar form as a component of the examination for six years. However, significant attempts were made to direct candidates’ answers into more detailed engineering analyses of the problems set, by the requiring statements relevant, for example, to improved safety and efficiency, broadening the range of use or versatility of the device, and by specifying more closely, the parameters which were of most importance, e.g., electrical, mechanical, thermal or optical properties. Although this further guidance was given, the Examiners’ reports continued to indicate that a significant proportion of the candidates’ answers were superficial, and that the necessary skills for attempting such questions were not being fully developed by the curriculum study as hoped. In the seventh year, therefore, this type ofquestion was modified to consider not engineering devices, but engineering situations, and the methods of achieving solutions under a variety of constraints. Thus, in the next examination a question was set about the design of a technician’s preparation room and the modifications to the design which would be necessary by imposition of a 50% reduction in available finance after the first design stage. The topic was deliberately chosen to lie within the familiarity and experience of the candidates; logical argument and judgement about possible alternative solutions were required from the candidate. The realities of life were introduced into the question through economic constraints and the skills of evaluation and judgement were tested. This type of question is generally, most difficult to assess but with experience the examiners are readily able to evaluate the cogent and relevant arguments and detect the simplistic and facile. Since the introduction ofthis type ofquestion, there have been many excellent answers and there have been some signs ofa general improvement in the candidates’ engineering reasoning, synthesis and evaluative ability.” (i) Carter, G., Heywood, J., and D. T. Kelly (1986). Case Study in Curriculum Assessment. GCE Engineering Science (Advanced). Manchester. Roundthorn Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Trinity College Dublin-University of Dublin, Ireland
John Heywood
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Heywood, J. (2018). Critical Thinking, Decision Making, and Problem Solving. In: Empowering Professional Teaching in Engineering. Synthesis Lectures on Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-79382-0_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-79382-0_6
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-79381-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-79382-0
eBook Packages : Synthesis Collection of Technology (R0) eBColl Synthesis Collection 8
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
SLO campus power outage. Classes starting at 8:45 AM and earlier cancelled today. Next update by 8:15am
- Cuesta College Home
- Current Students
- Student Success Centers
Study Guides
- Critical Thinking
Decision-making and Problem-solving
Appreciate the complexities involved in decision-making & problem solving.
Develop evidence to support views
Analyze situations carefully
Discuss subjects in an organized way
Predict the consequences of actions
Weigh alternatives
Generate and organize ideas
Form and apply concepts
Design systematic plans of action
A 5-Step Problem-Solving Strategy
Specify the problem – a first step to solving a problem is to identify it as specifically as possible. It involves evaluating the present state and determining how it differs from the goal state.
Analyze the problem – analyzing the problem involves learning as much as you can about it. It may be necessary to look beyond the obvious, surface situation, to stretch your imagination and reach for more creative options.
seek other perspectives
be flexible in your analysis
consider various strands of impact
brainstorm about all possibilities and implications
research problems for which you lack complete information. Get help.
Formulate possible solutions – identify a wide range of possible solutions.
try to think of all possible solutions
be creative
consider similar problems and how you have solved them
Evaluate possible solutions – weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. Think through each solution and consider how, when, and where you could accomplish each. Consider both immediate and long-term results. Mapping your solutions can be helpful at this stage.
Choose a solution – consider 3 factors:
compatibility with your priorities
amount of risk
practicality
Keys to Problem Solving
Think aloud – problem solving is a cognitive, mental process. Thinking aloud or talking yourself through the steps of problem solving is useful. Hearing yourself think can facilitate the process.
Allow time for ideas to "gel" or consolidate. If time permits, give yourself time for solutions to develop. Distance from a problem can allow you to clear your mind and get a new perspective.
Talk about the problem – describing the problem to someone else and talking about it can often make a problem become more clear and defined so that a new solution will surface.
Decision Making Strategies
Decision making is a process of identifying and evaluating choices. We make numerous decisions every day and our decisions may range from routine, every-day types of decisions to those decisions which will have far reaching impacts. The types of decisions we make are routine, impulsive, and reasoned. Deciding what to eat for breakfast is a routine decision; deciding to do or buy something at the last minute is considered an impulsive decision; and choosing your college major is, hopefully, a reasoned decision. College coursework often requires you to make the latter, or reasoned decisions.
Decision making has much in common with problem solving. In problem solving you identify and evaluate solution paths; in decision making you make a similar discovery and evaluation of alternatives. The crux of decision making, then, is the careful identification and evaluation of alternatives. As you weigh alternatives, use the following suggestions:
Consider the outcome each is likely to produce, in both the short term and the long term.
Compare alternatives based on how easily you can accomplish each.
Evaluate possible negative side effects each may produce.
Consider the risk involved in each.
Be creative, original; don't eliminate alternatives because you have not heard or used them before.
An important part of decision making is to predict both short-term and long-term outcomes for each alternative. You may find that while an alternative seems most desirable at the present, it may pose problems or complications over a longer time period.
- Uses of Critical Thinking
- Critically Evaluating the Logic and Validity of Information
- Recognizing Propaganda Techniques and Errors of Faulty Logic
- Developing the Ability to Analyze Historical and Contemporary Information
- Recognize and Value Various Viewpoints
- Appreciating the Complexities Involved in Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
- Being a Responsible Critical Thinker & Collaborating with Others
- Suggestions
- Read the Textbook
- When to Take Notes
- 10 Steps to Tests
- Studying for Exams
- Test-Taking Errors
- Test Anxiety
- Objective Tests
- Essay Tests
- The Reading Process
- Levels of Comprehension
- Strengthen Your Reading Comprehension
- Reading Rate
- How to Read a Textbook
- Organizational Patterns of a Paragraph
- Topics, Main Ideas, and Support
- Inferences and Conclusions
- Interpreting What You Read
- Concentrating and Remembering
- Converting Words into Pictures
- Spelling and the Dictionary
- Eight Essential Spelling Rules
- Exceptions to the Rules
- Motivation and Goal Setting
- Effective Studying
- Time Management
- Listening and Note-Taking
- Memory and Learning Styles
- Textbook Reading Strategies
- Memory Tips
- Test-Taking Strategies
- The First Step
- Study System
- Maximize Comprehension
- Different Reading Modes
- Paragraph Patterns
- An Effective Strategy
- Finding the Main Idea
- Read a Medical Text
- Read in the Sciences
- Read University Level
- Textbook Study Strategies
- The Origin of Words
- Using a Dictionary
- Interpreting a Dictionary Entry
- Structure Analysis
- Common Roots
- Word Relationships
- Using Word Relationships
- Context Clues
- The Importance of Reading
- Vocabulary Analogies
- Guide to Talking with Instructors
- Writing Help
Jamil Hellu's "Face to Face" Exhibition Opens at Miossi Art Gallery
Cuesta college hosts 3rd annual awareness gallery for students, dual enrollment program leads ca in student participation.

Short term classes available now.
Register Today!
- Open training
- Team training
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving for Effective Decision-Making
Personal effectiveness.
An Essential Competency In Today’s Workplace
Mastering critical thinking and problem-solving skills can help you make better decisions or recommendations- an essential competency in today’s knowledge workplaces. Critical thinking helps you to examine and improve thought processes, ask the right questions, challenge assumptions and consider varying viewpoints. Effective problem-solving helps you to properly identify and systematically work through a problem in a comprehensive manner, ensuring clarity when it comes time to make decisions or recommendations.
This course will demonstrate how critical thinking, problem-solving and decision-making work optimally together, and will provide hands-on practice with tools that you can apply to your everyday workday tasks, big or small.
Learning outcomes
By the end of this workshop, you will be able to:
- Define critical thinking and identify your critical thinking styles
- Work through the critical thinking process to build, analyze and evaluate varying viewpoints
- Improve key critical thinking skills, including active listening and questioning
- Analyze context and information to clearly understand and identify a problem
- Apply problem solving steps and tools
- Identify appropriate solutions using specific approaches
- Select the best technique for making decisions
- Avoid common decision-making mistakes
Workshop topics
Maximizing the Power of Your Brain
- Critical thinking and problem-solving the key to effective decision making
- The Iceberg Principle and the Understanding-Resolution Ration
Critical Thinking
- Definition of a Critical Thinker
- Critical thinking behaviours: active listening, probing, Empty Your Bucket
- Identify and evaluate issues and viewpoints
- The 3 C’s: context, credibility, and consistency
- Critical thinking worksheet- practice it!
- Problem Solving
- The problem-solving process- various models
- Obstacles and counterproductive approaches
- Problem-solving techniques for groups and individuals
- Applying a problem-solving model to a workplace scenario
Decision Making
- Individual and collective decision-making traps
- How to choose: criteria, goals and vision-based decision-making
- Individual and group decision-making tools and techniques
- Decision-making – practical application to a workplace scenario

Prerequisites
There are no prerequisites for this course
Who should attend this course?
Anyone who is required to problem solve on the job or make important project, department or organizational decisions or recommendations
Does this course address your competency development needs?
This workshop addresses:
- Achievement and Results Oriented
- Adaptability and Flexibility
- Analytical Thinking
- Change Management and Leadership
- Creative Thinking
- Decision Making and Decisiveness
- Engagement and Motivation
- Impact and Influence
- Innovation and Initiative
- Self Confidence and Self Esteem
- Strategic Thinking
- Teamwork and Cooperation
- Working with Others
To learn more about core competencies, click here .
$ 595 plus tax
Choose my session
- Instructor: Barbara Odenwald
The advantages of team sessions
- Learn and grow together as a team
- Location and time of your choice
- Sessions can be customized to fit your objectives
- Surprisingly cost effective
Submit your interest
Questions? Let us help
Participant reviews.
“Awesome course, very happy my supervisor signed me up. I look forward to implementing knowledge gained wherever possible in my current role. It will be beneficial in the future as well, should I move to a different role. Thank you!” –Past participant
“I enjoyed how this course was not a large group of people, so discussions and activities were easier and we can hear from everyone in the group. The instructor provided reasonable break periods throughout the course.” –Past participant
“This course really helps bring your sense of awareness and the way you will look at a situation, and how critical thinking can help you make better decisions.” –Past participant
Trusted by Clientele across Canada as a Top Corporate Training Company
Welcome to our new website.
We appreciate your patience as we add the finishing touches. In the meantime, go and explore!
Cookie Usage Disclaimer: This website uses cookies to enhance your browsing experience. By continuing to use this site, you consent to our use of cookies. For more information, please review our Privacy Policy .
Hello! We'd love to hear from you!
Complete the form below or reach us at: [email protected] , or 613-234-2020
Contact details
To help you.
- I wish to subscribe to PMC Training content.
More From Forbes
13 Easy Steps To Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
With the sheer volume of information that we’re bombarded with on a daily basis – and with the pervasiveness of fake news and social media bubbles – the ability to look at evidence, evaluate the trustworthiness of a source, and think critically is becoming more important than ever. This is why, for me, critical thinking is one of the most vital skills to cultivate for future success.
Critical thinking isn’t about being constantly negative or critical of everything. It’s about objectivity and having an open, inquisitive mind. To think critically is to analyze issues based on hard evidence (as opposed to personal opinions, biases, etc.) in order to build a thorough understanding of what’s really going on. And from this place of thorough understanding, you can make better decisions and solve problems more effectively.
To put it another way, critical thinking means arriving at your own carefully considered conclusions instead of taking information at face value. Here are 13 ways you can cultivate this precious skill:
1. Always vet new information with a cautious eye. Whether it’s an article someone has shared online or data that’s related to your job, always vet the information you're presented with. Good questions to ask here include, "Is this information complete and up to date?” “What evidence is being presented to support the argument?” and “Whose voice is missing here?”
2. Look at where the information has come from. Is the source trustworthy? What is their motivation for presenting this information? For example, are they trying to sell you something or get you to take a certain action (like vote for them)?
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
3. Consider more than one point of view. Everyone has their own opinions and motivations – even highly intelligent people making reasonable-sounding arguments have personal opinions and biases that shape their thinking. So, when someone presents you with information, consider whether there are other sides to the story.
4. Practice active listening. Listen carefully to what others are telling you, and try to build a clear picture of their perspective. Empathy is a really useful skill here since putting yourself in another person's shoes can help you understand where they're coming from and what they might want. Try to listen without judgment – remember, critical thinking is about keeping an open mind.
5. Gather additional information where needed. Whenever you identify gaps in the information or data, do your own research to fill those gaps. The next few steps will help you do this objectively…
6. Ask lots of open-ended questions. Curiosity is a key trait of critical thinkers, so channel your inner child and ask lots of "who," "what," and "why" questions.
7. Find your own reputable sources of information, such as established news sites, nonprofit organizations, and education institutes. Try to avoid anonymous sources or sources with an ax to grind or a product to sell. Also, be sure to check when the information was published. An older source may be unintentionally offering up wrong information just because events have moved on since it was published; corroborate the info with a more recent source.
8. Try not to get your news from social media. And if you do see something on social media that grabs your interest, check the accuracy of the story (via reputable sources of information, as above) before you share it.
9. Learn to spot fake news. It's not always easy to spot false or misleading content, but a good rule of thumb is to look at the language, emotion, and tone of the piece. Is it using emotionally charged language, for instance, and trying to get you to feel a certain way? Also, look at the sources of facts, figures, images, and quotes. A legit news story will clearly state its sources.
10. Learn to spot biased information. Like fake news, biased information may seek to appeal more to your emotions than logic and/or present a limited view of the topic. So ask yourself, “Is there more to this topic than what’s being presented here?” Do your own reading around the topic to establish the full picture.
11. Question your own biases, too. Everyone has biases, and there’s no point pretending otherwise. The trick is to think objectively about your likes and dislikes, preferences, and beliefs, and consider how these might affect your thinking.
12. Form your own opinions. Remember, critical thinking is about thinking independently. So once you’ve assessed all the information, form your own conclusions about it.
13. Continue to work on your critical thinking skills. I recommend looking at online learning platforms such as Udemy and Coursera for courses on general critical thinking skills, as well as courses on specific subjects like cognitive biases.
Read more about critical thinking and other essential skills in my new book, Future Skills: The 20 Skills & Competencies Everyone Needs To Succeed In A Digital World . Written for anyone who wants to surf the wave of digital transformation – rather than be drowned by it – the book explores why these vital future skills matter and how to develop them.
- Editorial Standards
- Forbes Accolades
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Critical Thinking and Decision-Making - Decision-Making Strategies
Critical thinking and decision-making -, decision-making strategies, critical thinking and decision-making decision-making strategies.

Critical Thinking and Decision-Making: Decision-Making Strategies
Lesson 3: decision-making strategies.
/en/problem-solving-and-decision-making/why-is-it-so-hard-to-make-decisions/content/
How do you usually make decisions?
There are lots of ways to make a decision . For example, you could flip a coin. You could trust your gut and do what you think is right. Or you could avoid thinking about it at all, and just make a choice at random—for better or for worse.
That's probably OK for small decisions, but what about more important ones? It's better to think carefully about your options and consider the many paths you could take.
With the right tools, you can learn to do this objectively , so you can make decisions you feel good about. We're going to cover several strategies that can help.
Watch the video below to learn more about decision-making strategies.
Making decisions objectively
The first step to making any decision is simple: Identify the problem . As an example, say you're trying to choose between two apartments. One is cheaper but farther away from work. The other is closer—and nicer!—but much more expensive.
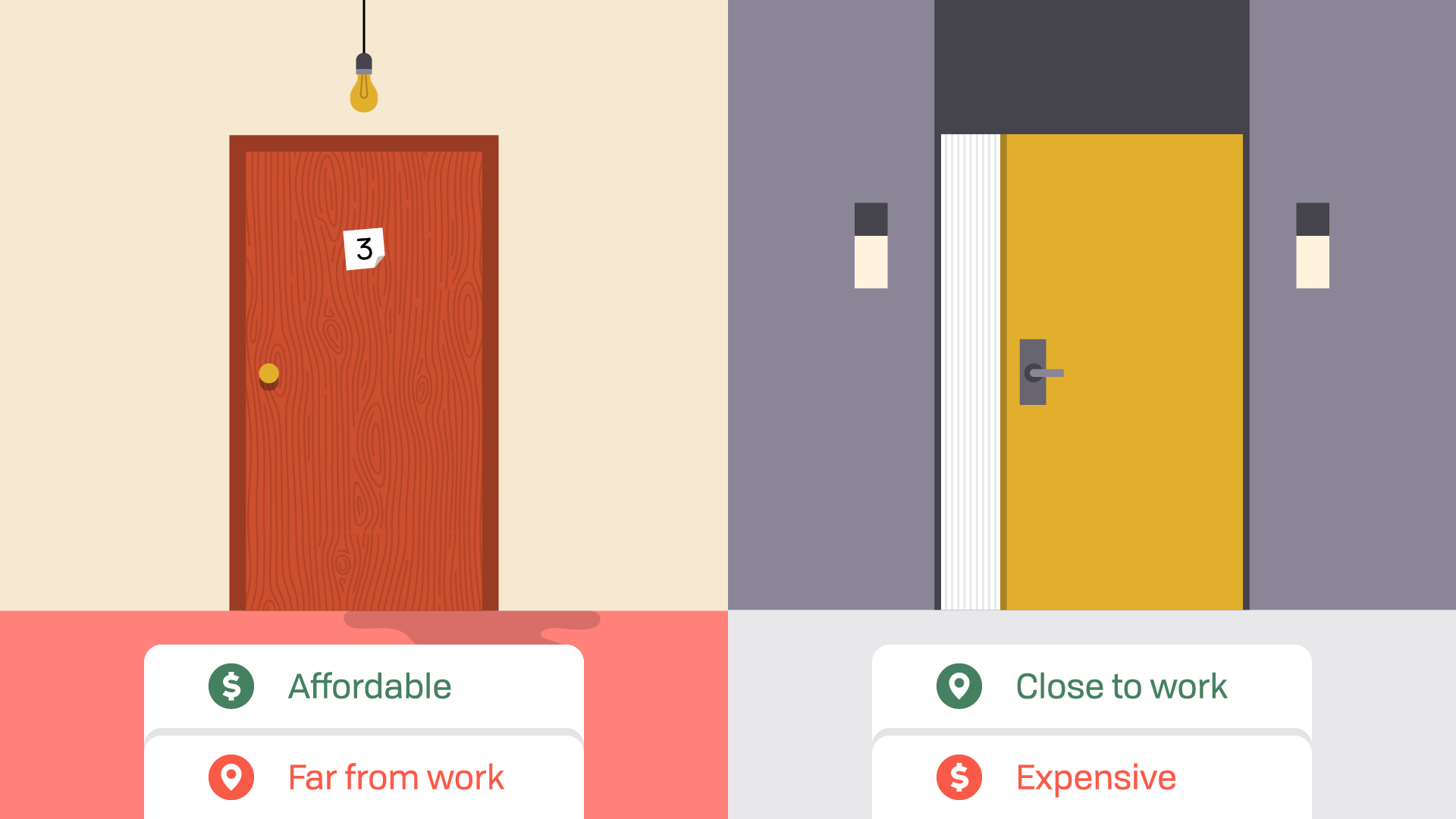
Which one would you choose? Depending on what you value, you probably have some idea. This initial response, the one tied to your instincts and emotions , is perfectly valid; however, you should also try to look at your options rationally .
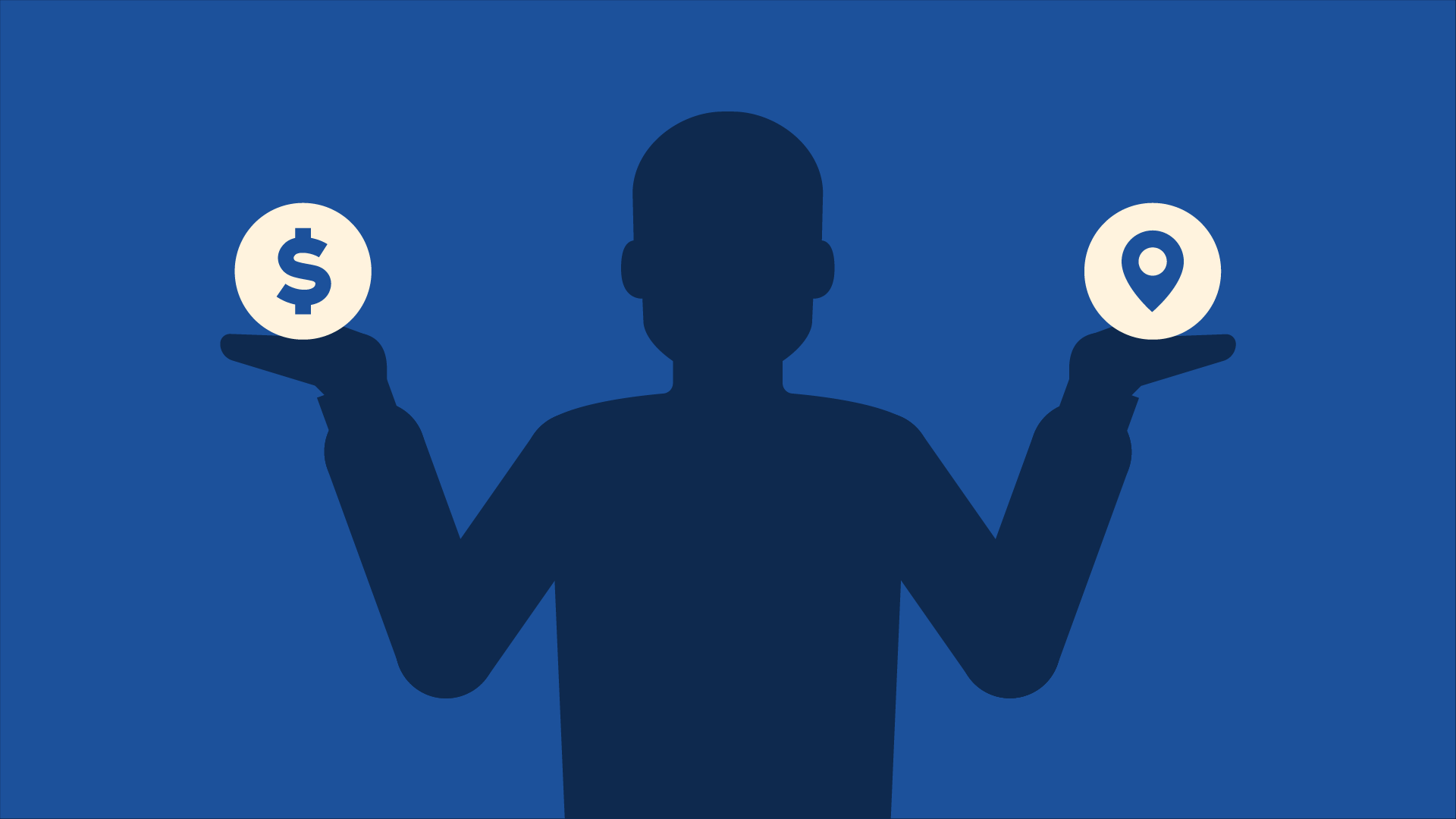

Comparing your options
Start by comparing them. There are several ways to do this. For example, you could list all the factors that you're considering—things like price, location, and other amenities—then choose the one thing that's most important to you. With that in mind, which option comes out on top?

Creating a points system
You could go one step further and create a points system . Take that same list and turn it into a scorecard for each option.
In this example, it means the first apartment would score high on affordable rent (let's say a 10), but much lower on location . The other apartment would score about the opposite in the same categories.
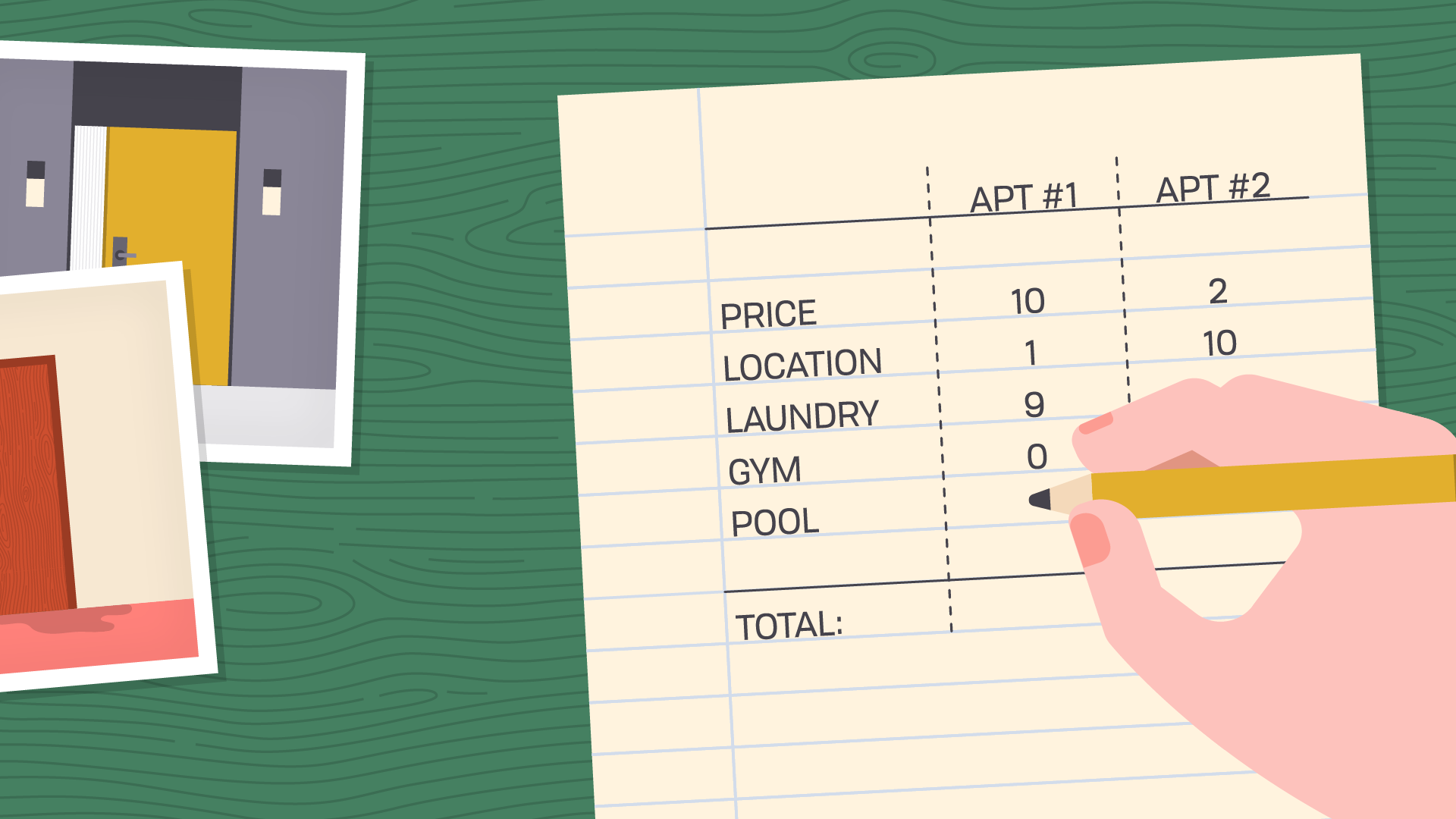
Keep going down the list until you've scored every item, being as objective as you can. Then add up the totals, and see if you have a winner.
Identifying pros and cons
Looking at it another way, you could evaluate one option at a time using a list of pros and cons. It sounds simple, but sometimes it helps to write these things down.

This time, it's OK to be subjective —certain factors can and should carry more weight than others. It's how you feel about them that counts, so be honest about what these things mean to you.
Thinking about the consequences
Imagining possible outcomes might give you some perspective on the decision. Say you're thinking about adopting a dog. What do you think the consequences might be in a month? In a year? How about several years from now?

Making decisions can be a roller coaster ride, especially when there are long-term consequences to think about. We can't see into the future, but we can try to be prepared.
Other mental tricks
At this point, it's normal to feel overwhelmed, even stuck. With so much to consider, how do you know you're making the right choice? There are a couple more techniques that can help you fire up your brain and trick it into thinking differently . Try these the next time you need a mental reset.
The two-minute diversion
Distract yourself with a two-minute activity that you find moderately difficult . Maybe you like playing mobile games, or solving math problems for fun—whatever works for you (we won't judge).

Believe it or not, you'll continue to process the decision unconsciously , according to brain imaging research by Carnegie Mellon University. This brief window of time helps you internalize important details, so you can make better, more insightful decisions.

Thinking in third person
Sometimes it helps to step outside yourself and pretend you're helping someone else . Studies show we're able to think more objectively in third person —that's why it's easier to give advice than it is to receive it.
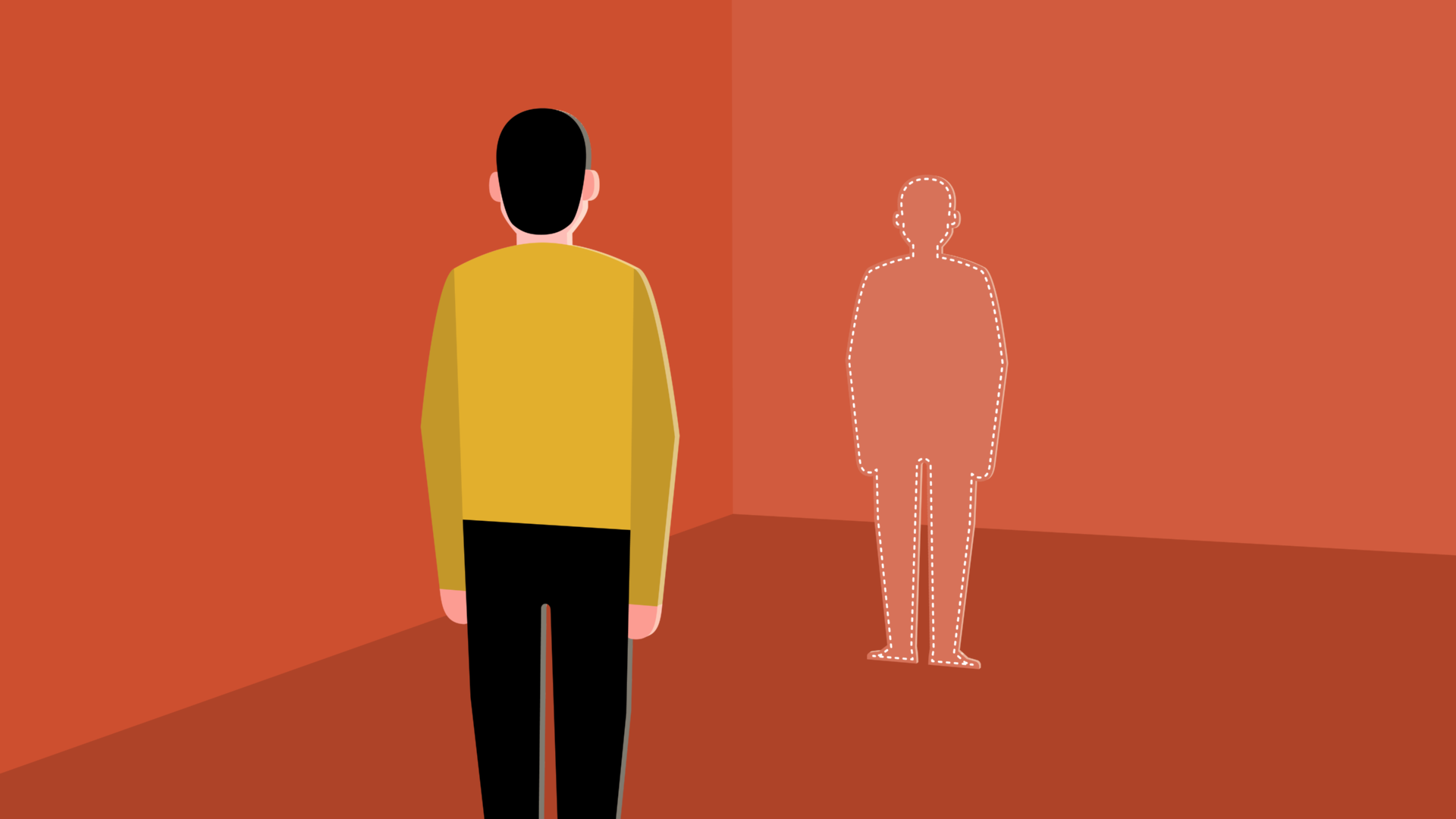

If a friend or family member were struggling with the same decision, what questions would you ask them? What compromises would you suggest?

Really think about it. Adopting a different point of view might help you see the situation in an entirely new way.

Making decisions with confidence
Making decisions isn't like taking a test. There are no right or wrong answers, per se—it just depends on the situation.

Focus on taking the time to think about your options and what you hope to achieve so you can feel confident about the choices you make. It's not as easy as flipping a coin, but it's worth the extra effort.

/en/problem-solving-and-decision-making/using-brain-teasers-to-build-critical-thinking-skills/content/

- Kindle Store
- Kindle eBooks
- Education & Teaching
Promotions apply when you purchase
These promotions will be applied to this item:
Some promotions may be combined; others are not eligible to be combined with other offers. For details, please see the Terms & Conditions associated with these promotions.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Critical Thinking: Master Systematic Problem Solving, Strategic Decision Making, Analytical Reasoning, and Identifying Logical Fallacies to Make Better Choices Kindle Edition
Think Smarter Learn How to Make Better Decisions
In Critical Thinking: Think Smarter , you’ll discover proven techniques and strategies to sharpen your analytical thinking, strengthen your problem-solving skills, identify logical fallacies, and improve communication.
Critical thinking allows you to evaluate situations clearly and rationally, helping you understand underlying causes, question assumptions, and explore solutions. Utilizing logic provides structure to your thinking process, enabling you to analyze problems methodically and make sound, reasoned decisions. Problem-solving is the practical application of these skills, empowering you to overcome challenges and implement effective solutions. This book provides you with practical tools to make sound decisions confidently in your work and personal life.
What you’ll gain from this book:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Learn how to make well-informed decisions with clarity and ease, even in complex situations.
- Effective Problem-Solving Strategies: Uncover innovative solutions and overcome obstacles with confidence, no matter how challenging.
- Mastering Bias and Misinformation: Develop the skills to identify reliable sources, challenge assumptions, and distinguish fact from fiction in today’s information-saturated world.
- Strengthened Analytical Skills: Utilize strategies to evaluate arguments critically and spot logical fallacies, boosting your strategic thinking and reasoning.
- Improved Communication and Persuasion: Express your thoughts more clearly and persuasively, leading to better understanding and stronger interpersonal relationships.
- Empowerment and Self-Confidence: As you progress, you’ll feel more empowered and self-assured, making decisions based on sound judgment and easily navigating complexities.
And much more!
Critical Thinking: Thinking Smarter is your key to becoming an empowered, strategic thinker. Start learning and applying the principles of critical thinking today and unlock the ability to thrive personally and professionally. Make a great decision, scroll up and add this to your cart!
- Print length 149 pages
- Language English
- Publication date October 18, 2024
- File size 334 KB
- Page Flip Enabled
- Word Wise Enabled
- Enhanced typesetting Enabled
- See all details
Product details
- ASIN : B0DKB6BK6L
- Publication date : October 18, 2024
- Language : English
- File size : 334 KB
- Simultaneous device usage : Unlimited
- Text-to-Speech : Enabled
- Screen Reader : Supported
- Enhanced typesetting : Enabled
- X-Ray : Not Enabled
- Word Wise : Enabled
- Print length : 149 pages
- #206 in Education Problem Solving
- #1,315 in Business Decision-Making
- #2,073 in Personal Success in Business
Customer reviews
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 5 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 4 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 3 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 2 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
- 5 star 4 star 3 star 2 star 1 star 1 star 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
No customer reviews
Report an issue.
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Registry & Gift List
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking enhances decision-making, problem-solving and communication abilities by fostering logical reasoning, analytical skills and an open mindset. It enables individuals to overcome ...
Definition. Simply put, critical thinking is the act of deliberately analyzing information so that you can make better judgements and decisions. It involves using things like logic, reasoning, and creativity, to draw conclusions and generally understand things better. This may sound like a pretty broad definition, and that's because critical ...
Problem-solving. Critical thinking and problem-solving are two more terms that are frequently confused. After all, when you think critically, you're often doing so with the objective of solving a problem. The best way to understand how problem-solving and critical thinking differ is to think of problem-solving as much more narrow.
Critical thinking is a crucial skill that enhances your ability to navigate the complexities of life. By mastering the six main types of critical thinking skills—analysis, interpretation, inference, evaluation, problem-solving, and decision making—you can make better decisions, solve problems efficiently, and become a more effective ...
Decision-Making Strategies arrow_forward_ios Learn some simple strategies for making decisions more easily. 4 Using Brain Teasers to Build Critical Thinking Skills arrow_forward_ios Learn about how brainteasers work and how they can help you improve your critical thinking skills.
Critical thinking can significantly enhance your problem-solving and decision-making skills. You make better-quality decisions, come up with more innovative solutions, and enjoy faster outcomes. Some benefits of critical thinking include: clear understanding of problems or situations.
The "set" interfered with their problem solving. Subsequently Luchins divided another group into two subgroups. The first sub-group worked through the problem in the usual way, using the three jar solution. The second sub-group were told to think more carefully about how to solve the problems.
Critical thinking. This is a mode of thinking, compared to problem-solving, which is a set of solution-oriented strategies. Since critical thinking strengthens your reasoning, it makes it easier to learn new skills, including problem-solving. Working on your critical thinking can also help you understand yourself better, including your value ...
Decision making is a process of identifying and evaluating choices. We make numerous decisions every day and our decisions may range from routine, every-day types of decisions to those decisions which will have far reaching impacts. The types of decisions we make are routine, impulsive, and reasoned. Deciding what to eat for breakfast is a ...
Mastering critical thinking and problem-solving skills can help you make better decisions or recommendations- an essential competency in today's knowledge wor. ... This course will demonstrate how critical thinking, problem-solving and decision-making work optimally together, and will provide hands-on practice with tools that you can apply to ...
This one-day class offers tools and techniques for sharpening the "gray cells" of the brain for clearer thinking and more effective decision-making. Participants will learn how to manage cognitive biases that interfere with reasoning and decision making, identify and avoid poor reasoning and persuasion techniques, and make decisions avoiding ...
Try to listen without judgment - remember, critical thinking is about keeping an open mind. 5. Gather additional information where needed. Whenever you identify gaps in the information or data ...
Making decisions objectively. The first step to making any decision is simple: Identify the problem. As an example, say you're trying to choose between two apartments. One is cheaper but farther away from work. The other is closer—and nicer!—but much more expensive.
Critical thinking is an essential element in decision-making, which involves choices, and problem-solving, which requires analysis. Decision-making A free flow of ideas is essential to problem-solving and decision-making because it helps prevent preconceived ideas from controlling the process. Many decisions in healthcare are arrived at by group or
Problem-solving and decision-making in a complex world In the age of algorithms and information overload, critical-thinking skills are essential to stay relevant in business. As processes, jobs and entire industries become digitised, it will be vital to capitalise on human advantage by practising strategic self-reflection and asking the right ...
Think Smarter Learn How to Make Better Decisions. In Critical Thinking: Think Smarter, you'll discover proven techniques and strategies to sharpen your analytical thinking, strengthen your problem-solving skills, identify logical fallacies, and improve communication.. Critical thinking allows you to evaluate situations clearly and rationally, helping you understand underlying causes ...