
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS
Published by Darrius Gripp Modified over 10 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS"— Presentation transcript:

The Internet.

The World Wide Web and the Internet MIS XLM.B Jack G. Zheng May 13 th 2008.

The Internet and the Web

Internet and WWW CS216. Open System Interconnection (OSI)

The Internet and the World Wide Web. Una DooneySlide 2Internet and WWW What is the Internet? This is the physical infrastructure or backbone of computers,

Introduction to Computer Administration. Computer Network - Basic Concepts Computer Networks Computer Networks Communication Model Communication Model.

The Internet As An Information Resource

Riso Digital Education Center1 Appendix05 RP(RP3105) Print (TCP/IP) (WindowsXP)

Searching & Saving Web Resources ADE100- Computer Literacy Lecture 23.

4.01 How Web Pages Work.

Computer networks SATISH MISHRA,PGT CS,KV TRIMULGHERRY.

What is the Internet? Internet: The Internet, in simplest terms, is the large group of millions of computers around the world that are all connected to.

Searching and Researching the World Wide: Emphasis on Christian Websites Developed from the book: Searching and Researching on the Internet and World Wide.

1 Networking A computer network is a collection of computing devices that are connected in various ways in order to communicate and share resources. The.

Lesson 19 Internet Basics.

Inside of a computer… What happens when you turn your computer on? What loads? Where are applications stored? How are do they run? In what form is information.

Chapter 5 Networks Communicating and Sharing Resources
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Networking

Connecting one computer to another computer creates a network.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies
AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Computer Networking PPT Presentation Templates With Samples and Examples

As your business continues to expand the number of users, desktops, laptops, peripherals (such as printers), smartphones and tablets connected to its computer network will equally increase, creating an ecosystem of computer networking. This resulting computer network plays an integral role for businesses in day to day operations.
From enabling data transmission, collaboration, and spread of information among stakeholders, clients, and employees, everything is communicated via networks adopted. With more and more such connections there is always a strain on organization systems leading to breaches in information, security and data. At the same time, the smooth functioning will be obstructed especially if your network or server is operating slower than usual.
This necessitates the need for robust implementation of computer networking that supports operation both locally and globally. Successful computer networking presentation in that scenario is one of the best ways for organizations to understand and implement the computer network architecture, troubleshoot issues, and create a robust infrastructure at all levels of organizations.
Check out our blog on the Top 7 Network Security Plan Templates to protect your network devices and systems.
But most organizations fail to do so due to lack of knowledge when it comes to dealing with complex networks, diverse systems, technologies and various protocols. If your business is also facing the same, it’s time to switch to SlideTeam’s Top Computer Networking PPT Presentation Templates. We bring you easy to edit, pre-made, content - friendly slides that address the essential components of a business network.
From fundamentals on network, network types, hub classification, monitoring devices, network topologies, to different types of threats and responsive security measures, our slides cover everything helping organizations to create efficient network structures.
So, what are you waiting for? Join us to explore our range of computer networking PPT Presentation Templates slides that are exclusively designed to help you organize and implement efficient network architecture within your workplaces.
Check out our blog on Top 10 Data Center Network Architecture Presentation to structurize your network effectively.
Template 1: Computer Networking Devices Powerpoint PPT Template Bundles
This PPT Slide depicts computer networking devices ranging from hub classification to switch organization, central router and bridge components, bridge stratification, gateway types, modems for decoding digital data and generating repeater signals, market snapshot, network management icons, and wifi network connections . This PPT Framework was created to provide IT professionals, students, and anybody else seeking a thorough grasp of different computer networking devices and their operations, with each component highlighted and displayed for easy reference. Download to learn how to keep your network running smoothly and reliably.

Template 2: Computer Networking Devices: Hub Classification
This presentation template presents a detailed description of hub devices used in computer networking systems to enable cost-effective deployment methodologies and facilitate network media connections. It discusses performance advantages, networks supported, ease of availability, and kinds such as active, passive, and intelligent hubs to help organizations make educated choices about their network architecture. After knowing the unique characteristics and benefits of each kind, businesses can make educated judgments about network management strategies. Download now so the firm can take full advantage of all available hub solutions!

DOWNLOAD NOW
Template 3: Computer Networking Devices: Switch Categorization
This PPT Layout features various kinds of switches, which are essential computer networking devices used by organizations to efficiently examine destination addresses and perform necessary checkpoints. It includes information such as managed switches with enhanced precision control and high-security levels, LAN switches that prevent packet overlap, and PoE switches that provide information and power transmission. This presentation template can assist organizations seeking to maximize network performance by efficiently inspecting destination addresses and performing checkpoints efficiently. Download to understand how switching categories helps businesses enhance network reliability.

Template 4: Computer Networking Devices: Major Parts of Router
This PPT Preset shows the many kinds of router systems used by corporations. Router systems are critical components of computer networking because they assist in isolating traffic, handling flow controls, and building effective administrative rules for businesses. Use this detailed presentation design to describe wireless devices for households and enterprises, as well as core routers that carry data across networks and fast, powerful routers, which make them best for improving any network infrastructure plan! Download today to guarantee that your business only employs high-quality technology for smooth communication and control!

DOWNLOAD NOW
Template 5: Computer Networking Devices: Types of Gateway
This presentation design describes the many kinds of gateway devices, which are essential components of computer networking devices that allow enterprises to consolidate internet access into a single device. They include unidirectional gateways like alerts and updates, bidirectional gateways like helpful feedback and replicating notifications, and functional gateways like voice-over trunk, cloud storage, internet-to-orbit communication capabilities, and prospective advantages. Understanding these devices and their characteristics of network management enables enterprises to improve communication operations while entirely using sophisticated network capabilities. Download now!

Template 6: Computer Network Powerpoint PPT Template Bundles
This PPT Slide covers a wide range of network kinds, critical components, main architectural categories, server visualizations, network topologies for data transmission, transmission mode categories, a network performance monitoring dashboard, models for software applications, interconnection open system interconnection types of software comparative analyses; challenges faced critical elements of network media security. The presentation slide is best used for IT professionals and students alike to enhance awareness of network complexities to facilitate improved decision-making and devise effective network management strategies. - a valuable resource! Download now.

Template 7: Types of Computer Network Security Software
This PPT Slide provides an overview of computer network security measures such as access control to applications and systems, antivirus detection of any harmful computer data-emitting malware programs, cloud security, which encompasses managing overall infrastructure security, firewalling to detect both incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent unauthorized network access, and sandboxing to scan for malware by opening files. This presentation design helps detect, prevent, and improve your understanding of network security. It illustrates how to secure digital assets best for both IT professionals and cybersecurity students alike. Download now.

Template 8: Computer Network Types for Connecting Devices
This presentation slide explains many computer networks that are often used to link devices, including virtual private networks offering private networks, wide area networks connecting computers over larger areas, local area networks connecting computers over shorter distances, personal area networks connecting devices in close proximity, and storage area networks. These networks enable users to access servers. It is crucial to comprehend how various networks improve accessibility and connection inside businesses! Get it today to maximize device connectivity on a variety of network types!

Template 9: Computer Network Internet Protocol Model Layers
This PPT Framework depicts an internet protocol model for computer networking layers, including the application layer, which communicates directly with software applications; the transport layer, which allows for end-to-end communication and data flow between hosts; and the network layer, which handles packet addresses and routines of data packets. And the data link layer, which regulates frame exchange between devices on the same network. This PPT Slide is used to get a basic grasp of computer networks as well as improve your technical talents! Download to manage data flow throughout the network.

Template 10: Computer Network Performance Monitoring Dashboard Template
This PPT Slide shows a dashboard that allows you to track and evaluate computer network configuration performance in real-time, giving you instant insights into the effectiveness of your network. These parameters, which help quickly identify network issues and ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction, include bandwidth, access rate, quality of calls, customer satisfaction calls, average server response time, regions, mean opinion score quality, and network quality metrics. Use this presentation slide to learn how to monitor and enhance network performance efficiently. Get it now.

DOWNLOAD NOW
Network Your Way to Success
Mastering computer networking presentations is becoming more critical in today's globalized environment. These top ten Top 10 Computer Networking Ppt Presentation Templates provide the optimal balance of style and content, allowing you to communicate complex concepts quickly. Regardless of your degree of expertise or understanding of networking principles, these templates give the visual help you need to boost your message and attract others.
Elevate your networking presentations to the next level with SlideTeam's expertly designed templates, and take them to the next level with these gorgeous, customized slides - your audience will appreciate you and the message will reverberate long after the slide stops! Visit SlideTeam now to obtain these gorgeous customized slides that may elevate an average presentation to remarkable levels that last long after the presentation is over!
Prepare your network infrastructure effectively with Top 10 Network Infrastructure Templates . Click to learn more.
Related posts:
- Top 10 Employee PIP Templates With Samples And Examples
- Top 10 Staff Analysis Templates With Examples And Samples
- Top 10 Data Assessment Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 7 Software Evaluation Criteria Templates with Examples and Samples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Cybersecurity Strategy Templates with Examples and Samples

Must-Have Emergency Evacuation Checklist Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


An Introduction to Computer Networks - Second Edition
(6 reviews)
Peter Lars Dordal, Loyola University of Chicago
Copyright Year: 2014
Last Update: 2020
Publisher: Peter L Dordal
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Stuart Anderson, Adjunct Instructor, Norfolk State University on 11/13/23
The textbook is complete and thorough. The index correctly points to the material in the chapters. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The textbook is complete and thorough. The index correctly points to the material in the chapters.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The information in the book is accurate as it applies to networking concepts.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book's content is current.
Clarity rating: 4
The material is clear however, it does make assumptions about the reader's level of current knowledge about the material.
Consistency rating: 5
The material is consistent and flows in a good order.
Modularity rating: 4
The is very good in how the information is broken down into specific modules. Some modules need more information to make them more complete.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The information is organized in a fashion that allows future topics to build on the previous topics.
Interface rating: 5
There were no interface issues.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
There are no grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The test is inclusive of all cultures.
This is a good textbook for networking information. Some of the material could be explained in more detail to make it more of an introductory topic. A reader with networking experience would find this book a good reference, however, a reader new to the networks might find some of the material a bit light. As a network engineer, I found the information thorough and would work well with other networking material.
Reviewed by Terri Devlin, Instructor, Aims Community College on 7/23/19
Even though the title of the text is "An Introduction to Networking", the author seems to assume that the student or reader knows a lot about the subject matter and terminology. Topics and some definitions are presented, however the author does a... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
Even though the title of the text is "An Introduction to Networking", the author seems to assume that the student or reader knows a lot about the subject matter and terminology. Topics and some definitions are presented, however the author does a deep dive into the topic area quickly. This text would not be beneficial to students seeking CompTia Network + Certification because many of the terms and concepts tested in the certification exam are not covered in this text.
The author presents the material in an unbiased manner. Errors were not identified
Relevance/Longevity rating: 2
Out-of-date information was identified. The text is written in a manner that updates could be made in a straightforward manner.
Clarity rating: 2
The text was difficult to read because precise definitions and content were not provided. Other textbooks and internet sources were used to look up definitions and refresh understanding of technical terms and concepts
Consistency rating: 4
The terminology, framework, and chapter exercises followed a consistent approach.
The layout of the book is easy to understand and follow.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
The topics were organized in a logical fashion. It was a challenge to determine the network “big picture” and how the components fit into the picture. The topics make sense to people familiar with Networks. This text would be challenging to people new to Computer Network concepts.
Interface rating: 3
The text is free of navigation problems. The figures and tables were easily identified. An improvement could be made with providing better images or pictures.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The text was free of grammatical errors.
The text is appropriate for globally-based students.
Many computer concept textbooks have associated software that helps student learn topics and practice. Computer Networks is an area where practice helps students learn. This text did not have associated software available.
Reviewed by Audrey Styer, Instructor, CIS/CPS, Morton College on 12/21/18
This textbook provides a very comprehensive and in-depth introduction to computer networking. read more
This textbook provides a very comprehensive and in-depth introduction to computer networking.
All information presented is accurate.
This textbook is continually being updated to accommodate the ever-changing nature of computer networking.
Clarity rating: 5
Material is presented in a clear manner, but does require a prior basic understanding of computer networking.
Consistency of presentation and methodology is maintained throughout the text.
Modularity rating: 5
The chapters are well defined by topic
The material is presented in a logical manner that helps learners develop their understanding.
The PDF version is easy to read and navigate. The linked Table of Contents and Index make finding and moving to specific topics simple.
I found no grammatical errors.
This is not applicable to this topic.
The callout boxes provide a visual break for readers and increase learning with interesting facts and supporting information. Unfortunately, this textbook is too advanced for my undergraduate learners and does not map to CompTIA’s Network+ certification.
Reviewed by Sunho Lim, Assistant Professor, Texas Tech University on 3/27/18
The text covers all five layers (phy, link, net, trans, and app) and their associated algorithms and communication protocols in the network, and provides an effective index and/or golssary. read more
The text covers all five layers (phy, link, net, trans, and app) and their associated algorithms and communication protocols in the network, and provides an effective index and/or golssary.
The content is accurate and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
The most content is up-to-date and the text is written in a way to easily be updated. Since network technology is time-sensitive, some sections in the text should be updated.
The text is easy to read but some advanced sections (e.g., network simulator ns-2 and ns-3) would be challenging to read and understand technical terminology used.
The text is consistent in using terminology and framework.
The text is well divided into a set of sections. It is easy to selectively choose a section depending on the level of class or students.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics in the text are presented in a bottom-up way, but grouping sections in terms of layer would be great.
The text has an interface issue, such as some contents are displayed out of page or cut off.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 1
The text is not related to any culture.
The text is appropriate to both undergraduate to graduate students. A set of selective chapters can be used depending on the instructor. The text is good to use for a reference book.
Reviewed by Lisa Bain, Professor, Rhode Island College on 2/1/18
The book covers all the major topics required for a computer networking course. read more
The book covers all the major topics required for a computer networking course.
Yes, this book is accurate in the major areas that the reviewer read. The entire text was not reviewed.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
Yes, the book is up-to-date with the major concepts that do not change (e.g. TCP, IP, UDP) and also includes the latest standards for Wi-Fi. However, some networking technologies will need to be updated as advancements are made (e.g. newer Wi-Fi standards).
Yes, the text is clearly written. However, the content is very technical and would be challenging for a non-technical person to understand all aspects. It is very straight-forward and appropriate for a technical audience.
Yes, the book is consistent and uses the same technical terminology throughout.
Yes the book is very modular and provides many small sections within each chapter for specific topics.
The flow of the book is similar to other networking books in that is starts with an introduction then provides additional details in following chapters.
The interface in PDF is easy to navigate using the table of contents and embedded links.
Of the information read, no grammar errors were found.
This is not relative to this book.
This book would be appropriate for an instructor with a strong background in teaching networking and using a more technical approach.
Reviewed by Luke Osterritter, Adjunct Instructor, Penn State New Kensington on 2/1/18
This text does a great job of covering the basics of computer networks while also presenting in-depth information, as well as diving into some somewhat tangential, but important, areas (e.g. security). read more
This text does a great job of covering the basics of computer networks while also presenting in-depth information, as well as diving into some somewhat tangential, but important, areas (e.g. security).
There are some terms here that I have seen presented differently than I have learned them or encountered in industry, but nothing inaccurate.
It would seem that this book is kept rather up-to-date, though much of the content is so fundamental as to not have too much of an expiration date, even in this field.
I believe the text is clear in most cases. However, I do feel many of the topics become very in-depth, very fast. It would be nice to have some concepts factored out to their basics early in the chapters, then expounded upon later.
The text does not appear to have any major inconsistencies.
When viewing online, the table of contents makes the content very browsable. However, when viewing in PDF, the large amount of subheadings for any one chapter can be a bit tough to navigate.
As the author notes, there isn't much agreement in how to present this topic, and it can be very difficult to explain one portion without referencing another topic that may not have been presented. I think factoring out some basics and explaining them up front, as this book has done, is a clever way of handling this.
I did not encounter any issues with the text interface.
I did not see any obvious grammatical errors.
This book is very matter-of-fact, with little in the way of irreverence. Likewise, there isn't much to work with here to be proactively inclusive. I think it works to be somewhat inert in this manner.
Overall, I think that this book is a great resource to have given its open availability. It's not the simplest book, so using this in a first level class or in a more general IT, CS, or survey course will take some shepherding on the part of the instructor. The comprehensiveness does suggest to me that this might be able to fill two courses worth of content, as well. It would be nice to have some of the information factored out, with some of the highlights available as lecture materials. On its own though, I feel this would be a strong resource to use in a computer networking course.
Table of Contents
- 1 An Overview of Networks
- 3 Other LANs
- 6 Abstract Sliding Windows
- 7 IP version 4
- 8 IP version 6
- 9 Routing-Update Algorithms
- 10 Large-Scale IP Routing
- 11 UDP Transport
- 12 TCP Transport
- 13 TCP Reno and Congestion Management
- 14 Dynamics of TCP Reno
- 15 Newer TCP Implementations
- 16 Network Simulations: ns-2
- 17 The ns-3 Network Simulator
- 19 Queuing and Scheduling
- 20 Quality of Service
- 21 Network Management and SNMP
- 22 Security
- 23 Bibliography
- 24 Selected Solutions
Ancillary Material
- Peter L Dordal
About the Book
An Introduction to Computer Networks is a free and open general-purpose computer-networking textbook, complete with diagrams and exercises.It covers the LAN, internetworking and transport layers, focusing primarily on TCP/IP. Particular attention is paid to congestion; other special topics include queuing, real-time traffic, network management, security and the ns simulator.
The book is suitable as the primary text for an undergraduate or introductory graduate course in computer networking, as a supplemental text for a wide variety of network-related courses, and as a reference work.
About the Contributors
Peter Lars Dordal is an associate professor within the Department of Computer Science at Loyola University of Chicago. His research interests are in programming languages and computer networks.
Contribute to this Page
- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
Basics of Computer Networking
Computer networking is a cornerstone of modern technology, enabling the interconnected systems that power the Internet, business communications, and everyday digital interactions. Understanding the fundamentals of computer networking is essential for anyone involved in technology, from enthusiasts to professionals. This article will explore the basics of computer networking, including network types, components, protocols, and essential services like the Domain Name System (DNS).
.jpg)
Computer Networking
What is a Computer Network?
A computer network is a collection of interconnected devices that share resources and information. These devices can include computers, servers, printers, and other hardware. Networks allow for the efficient exchange of data, enabling various applications such as email, file sharing, and internet browsing.
How Does a Computer Network Work?
Basics building blocks of a Computer network are Nodes and Links. A Network Node can be illustrated as Equipment for Data Communication like a Modem, Router, etc., or Equipment of a Data Terminal like connecting two computers or more. Link in Computer Networks can be defined as wires or cables or free space of wireless networks.
The working of Computer Networks can be simply defined as rules or protocols which help in sending and receiving data via the links which allow Computer networks to communicate. Each device has an IP Address, that helps in identifying a device.
Basic Terminologies of Computer Networks
- Network: A network is a collection of computers and devices that are connected together to enable communication and data exchange.
- Nodes: Nodes are devices that are connected to a network. These can include computers, Servers, Printers, Routers, Switches , and other devices.
- Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules and standards that govern how data is transmitted over a network. Examples of protocols include TCP/IP , HTTP , and FTP .
- Topology: Network topology refers to the physical and logical arrangement of nodes on a network. The common network topologies include bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree.
- Service Provider Networks: These types of Networks give permission to take Network Capacity and Functionality on lease from the Provider. Service Provider Networks include Wireless Communications, Data Carriers, etc.
- IP Address : An IP address is a unique numerical identifier that is assigned to every device on a network. IP addresses are used to identify devices and enable communication between them.
- DNS: The Domain Name System (DNS) is a protocol that is used to translate human-readable domain names (such as www.google.com) into IP addresses that computers can understand.
- Firewall: A firewall is a security device that is used to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls are used to protect networks from unauthorized access and other security threats.
Types of Enterprise Computer Networks
- LAN: A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that covers a small area, such as an office or a home. LANs are typically used to connect computers and other devices within a building or a campus.
- WAN: A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that covers a large geographic area, such as a city, country, or even the entire world. WANs are used to connect LANs together and are typically used for long-distance communication.
- Cloud Networks: Cloud Networks can be visualized with a Wide Area Network (WAN) as they can be hosted on public or private cloud service providers and cloud networks are available if there is a demand. Cloud Networks consist of Virtual Routers, Firewalls, etc.
These are just a few basic concepts of computer networking. Networking is a vast and complex field, and there are many more concepts and technologies involved in building and maintaining networks. Now we are going to discuss some more concepts on Computer Networking.
- Open system: A system that is connected to the network and is ready for communication.
- Closed system: A system that is not connected to the network and can’t be communicated with.
Types of Computer Network Architecture
Computer Network falls under these broad Categories:
- Client-Server Architecture: Client-Server Architecture is a type of Computer Network Architecture in which Nodes can be Servers or Clients. Here, the server node can manage the Client Node Behaviour.
- Peer-to-Peer Architecture: In P2P (Peer-to-Peer) Architecture , there is not any concept of a Central Server. Each device is free for working as either client or server.
Network Devices
An interconnection of multiple devices, also known as hosts, that are connected using multiple paths for the purpose of sending/receiving data or media. Computer networks can also include multiple devices/mediums which help in the communication between two different devices; these are known as Network devices and include things such as routers, switches, hubs, and bridges.
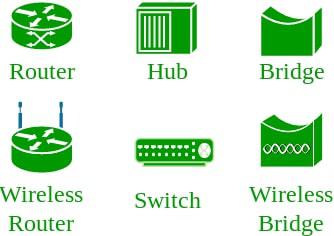
Network Topology
The Network Topology is the layout arrangement of the different devices in a network. Common examples include Bus, Star, Mesh, Ring, and Daisy chain.
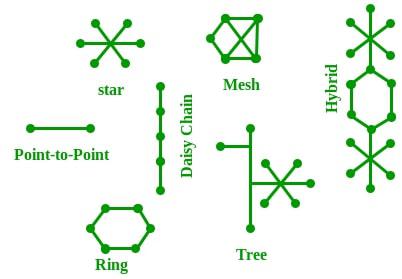
OSI Model
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection . It is a reference model that specifies standards for communications protocols and also the functionalities of each layer. The OSI has been developed by the International Organization For Standardization and it is 7 layer architecture. Each layer of OSI has different functions and each layer has to follow different protocols. The 7 layers are as follows:
- Physical Layer
- Data link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
Network Protocols
A protocol is a set of rules or algorithms which define the way how two entities can communicate across the network and there exists a different protocol defined at each layer of the OSI model. A few such protocols are TCP, IP, UDP, ARP, DHCP, FTP, and so on.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Function: The foundational protocol suite of the internet, enabling reliable communication.
Components:
TCP: Ensures data is delivered reliably and in order.
IP: Routes data packets to their destination based on IP addresses.

Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and HTTPS
Function: The protocols used for transmitting web pages.
HTTP: Unsecured communication.
HTTPS: Secured communication using SSL/TLS encryption.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Function: Protocol for sending email.
Components: Works with other protocols like POP3 and IMAP for email retrieval.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Function: Protocol for transferring files between computers.
Components: Includes commands for uploading, downloading, and managing files on a remote server.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Function: Automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network.
Components: Reduces manual configuration and IP address conflicts.
Domain Name System (DNS)
Function: Translates human-friendly domain names into IP addresses.
Components: Ensures seamless navigation on the internet.
Unique Identifiers of Network
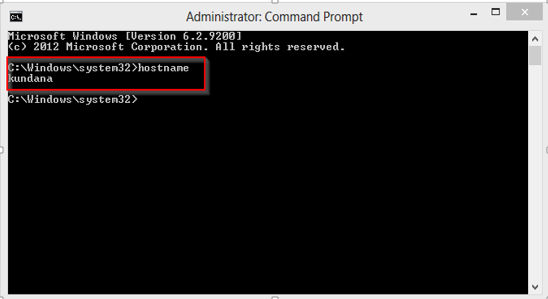
Hostname: Each device in the network is associated with a unique device name known as Hostname. Type “hostname” in the command prompt(Administrator Mode) and press ‘Enter’, this displays the hostname of your machine.
IP Address (Internet Protocol address): Also known as the Logical Address, the IP Address is the network address of the system across the network. To identify each device in the world-wide-web, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) assigns an IPV4 (Version 4) address as a unique identifier to each device on the Internet. The length of an IPv4 address is 32 bits, hence, we have 2 32 IP addresses available. The length of an IPv6 address is 128 bits.
In Windows Type “ipconfig” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this gives us the IP address of the device. For Linux, Type “ifconfig” in the terminal and press ‘Enter’ this gives us the IP address of the device.
MAC Address (Media Access Control address): Also known as physical address, the MAC Address is the unique identifier of each host and is associated with its NIC (Network Interface Card) . A MAC address is assigned to the NIC at the time of manufacturing. The length of the MAC address is: 12-nibble/ 6 bytes/ 48 bits Type “ipconfig/all” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this gives us the MAC address.
Port: A port can be referred to as a logical channel through which data can be sent/received to an application. Any host may have multiple applications running, and each of these applications is identified using the port number on which they are running.
A port number is a 16-bit integer, hence, we have 2 16 ports available which are categorized as shown below:
| Well known Ports | 0 – 1023 |
| Registered Ports | 1024 – 49151 |
| Ephemeral Ports | 49152 – 65535 |
Number of ports: 65,536 Range: 0 – 65535 Type “ netstat -a ” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this lists all the ports being used.
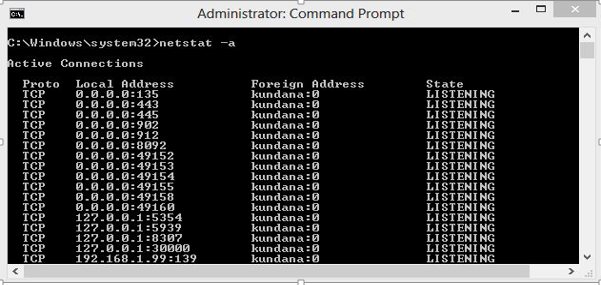
List of Ports
Socket: The unique combination of IP address and Port number together is termed a Socket.
Other Related Concepts
DNS Server: DNS stands for Domain Name System . DNS is basically a server that translates web addresses or URLs (ex: www.google.com) into their corresponding IP addresses. We don’t have to remember all the IP addresses of each and every website. The command ‘ nslookup ’ gives you the IP address of the domain you are looking for. This also provides information on our DNS Server. \
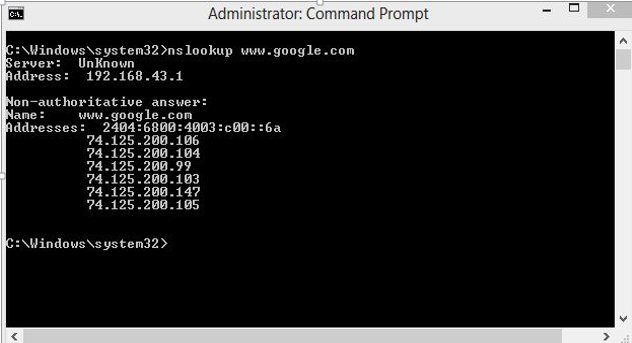
Domain IP Address
ARP: ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol . It is used to convert an IP address to its corresponding physical address(i.e., MAC Address). ARP is used by the Data Link Layer to identify the MAC address of the Receiver’s machine.
RARP: RARP stands for Reverse Address Resolution Protocol . As the name suggests, it provides the IP address of the device given a physical address as input. But RARP has become obsolete since the time DHCP has come into the picture.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a critical component of computer networking. It converts easily recognizable domain names, such as www.example.com, into numerical IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network.
How DNS Works?
User Input: When a user enters a domain name in a browser, the system needs to find its IP address.
DNS Query: The user’s device sends a DNS query to the DNS resolver.
Resolver Request: The DNS resolver checks its cache for the IP address. If not found, it forwards the request to the root DNS server.
Root DNS Server: The root DNS server provides the address of the TLD (Top-Level Domain) server for the specific domain extension (e.g., .com).
TLD DNS Server: The TLD server directs the resolver to the authoritative DNS server for the actual domain.
Authoritative DNS Server: The authoritative DNS server knows the IP address for the domain and provides it to the resolver.
Response to User: The resolver stores the IP address in its cache and sends it to the user’s device.
Access Website : With the IP address, the user’s device can access the desired website.
DNS works efficiently, translating user-friendly domain names into IP addresses, allowing seamless navigation on the internet.
Network Security
Ensuring the security of a network is crucial to protect data and resources from unauthorized access and attacks. Key aspects of network security include:
Firewalls: Devices or software that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules.
Encryption: The process of encoding data to prevent unauthorized access. Commonly used in VPNs, HTTPS, and secure email.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Tools that monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and potential threats.
Access Control: Mechanisms that restrict access to network resources based on user identity and role.
Regular Updates and Patching: Keeping software and hardware up to date to protect against vulnerabilities.
Understanding the basics of computer networking is essential in today’s interconnected world. Networks enable the seamless exchange of information, support countless applications, and underpin the functionality of the internet. From different types of networks and their components to protocols and security measures, a solid grasp of these concepts is foundational for anyone working in or with technology. As technology evolves, so too will the complexity and capabilities of computer networks, making continuous learning and adaptation crucial.
Basics of Computer Networking – FAQs
What is an ip address.
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique identifier assigned to each device on a network. It allows devices to locate and communicate with each other. There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 (e.g., 192.168.1.1) and IPv6 (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
What is a firewall?
A firewall is a network security device or software that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. It acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks like the internet.
What is the difference between TCP and UDP?
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): A connection-oriented protocol that ensures reliable and ordered delivery of data. It is used for applications where data integrity is critical, like web browsing and email. UDP (User Datagram Protocol): A connectionless protocol that does not guarantee delivery or order. It is used for applications where speed is more important than reliability, like streaming and gaming.
What is DNS?
DNS (Domain Name System) is a system that translates human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network.
What is a subnet mask?
A subnet mask is used in IP addressing to divide the network into sub-networks, or subnets. It helps determine which portion of an IP address is the network address and which part is the host address.
What is NAT (Network Address Translation)?
NAT is a method used by routers to translate private IP addresses within a local network to a public IP address before sending data over the internet. This helps to conserve IP addresses and add a layer of security by hiding internal network addresses.
What is a MAC address?
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface card (NIC) for communication on a physical network segment. It is a hardware address that is unique to each network device.
What is bandwidth?
Bandwidth refers to the maximum rate of data transfer across a network or internet connection in a given amount of time. It is usually measured in bits per second (bps).
What is latency in networking?
Latency is the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination across a network. It is usually measured in milliseconds (ms) and can affect the performance of networked applications.
What is VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
A VPN is a secure connection that allows users to access a private network over the public internet. It encrypts the data traffic and helps maintain privacy and security.
What is a proxy server?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between a user’s device and the internet. It can be used for purposes such as improving security, filtering content, or bypassing geographical restrictions.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Best Twitch Extensions for 2024: Top Tools for Viewers and Streamers
- Discord Emojis List 2024: Copy and Paste
- Best Adblockers for Twitch TV: Enjoy Ad-Free Streaming in 2024
- PS4 vs. PS5: Which PlayStation Should You Buy in 2024?
- Full Stack Developer Roadmap [2024 Updated]
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Introduction to Computer Networking
Sep 03, 2014
580 likes | 953 Views
Introduction to Computer Networking. Definition. Network Any interconnected group or system. Multiple computers and other devices connected together to share information. (nodes). History. 1957 USSR launches Sputnik, first artificial earth satellite 1958
Share Presentation
- network segments
- data packet
- computer networking
- connects network segments
- wide area network wan

Presentation Transcript
Definition • Network • Any interconnected group or system. • Multiple computers and other devices connected together to share information. (nodes)
History • 1957 • USSR launches Sputnik, first artificial earth satellite • 1958 • US forms the ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) for their military to have an edge on science and technology
History • 1962 • Paul Baran invented Packet Switching – breaking digital messages into bite-size chunks which can easily be sent to computer • 1969 • A four node computer system called Arpanet was developed • First electronic message was sent
History • 1971 • Arpanet now has 15 nodes • First email was sent to a group of computers • 1972 • Arpanet has now 37 nodes
History • 1976 • Queen Elizabeth of England sends her first email • Early 1980s • The military set up their own network and named it MILNET
History • Mid 1980s • Network of linked computers are growing… around 50,000 nodes • It linked universities and research laboratories • 1982 • It was then called the INTERNET
Benefits • File sharing • Hardware sharing • Program sharing • User communication • Multiplayer gaming
Considerations • Money • Future Growth • Cable Type • Cable Length
Networking Models • Client/Server • Two computers – Clients & Servers • Clients are usually computer workstations sitting on the desks of employees in an organization • Servers are usually more powerful computers and are held in a central location/s within an organization
Network Servers • Servers are computers that perform services for other computers on the network • LANs and WANs usually have File Servers and Login Servers • The Internet has other types of servers such as Web Servers and Mail Servers.
Networking Models • Peer-to-Peer (P2P) • Only workstations are connected to each other • Much simpler to set up than Client/Server Networks • Lack some of the advantages normally associated with networks (Central Management) • Set up among with few computers within an office or single room
Networking Models • Local Area Network (LAN) • A network contained within one building or site • Wide Area Network (WAN) • A network that spans several sites across a city, country or even the world • A Client/Server may be a LAN or WAN, but a P2P network can only be a LAN.
Data Packets • When a workstation wishes to send data, it encloses the data in a 'packet' containing a 'header' and a 'trailer' • The header and trailer contain information for the destination computer.
Data Packets • When a data packet is put onto the network by a workstation, each computer on the network examines the packet to see who it is intended for. • The packet quickly dissipates if it is not recognized, allowing other packets to be sent. • The rate at which packets can be sent is called the Bandwidth
Data Packets • Data packets are transmitted between computers on the network either as • Electrical signals in electric wires • Light signals in fiber optic cables • Electromagnetic waves through space
Electrical Cables • Electrical cables are the usual means of connecting the computers in a LAN and in a WAN on one site. • Cables can either be coaxial cables or twisted pair cables.
Coaxial Cables • Coaxial cables have a copper wire running through the middle encased in plastic insulation. • The plastic insulation is itself encased in a metal braid (copper mesh) which is covered by an outer layer of plastic insulator.
Coaxial Cables
Coaxial Cables • The electrical signals run through the central wire and the metal braid acts as both an earth and as a shield against electromagnetic interference. • Coaxial cables are connected to devices by means of a special plug with a bayonet connection. This is called a BNC plug.
Twisted Pair Cables • Twisted pair cables come in two types • Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) • Shielded Twisted Pair (STP).
Twisted Pair Cables • UTP cables have pairs of insulated copper wires twisted round each other to cancel out electromagnetic interference. • STP cable wires have a metal cover encasing the twisted pairs, shielding them further from outside electromagnetic interference.
Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted Pair Cable
RJ-45 Connector
Fiber Optic Cables • Fiber optic cable is often used to connect several buildings within a site. • Fiber optic cables are more expensive than electrical cables • But have higher bandwidths and can transmit over longer distances.
Fiber Optic Cables • Fiber optic cables have a thin strand of glass in the center that carries the light pulses initially put into it by means of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
Fiber Optic Cables • The central strand is encased in glass shield of lower density than the central strand – ensures that the light signal is kept within the central strand by total internal reflection.
Fiber Optic Cables • The glass cladding may then be surrounded by strengthening wires and a plastic outer cover.
Fiber Optic Cables
Network Interface Card • All computers within a network need to be physically connected to the network. • This is achieved by a Network Interface Card or Ethernet Cards which transmits and receives the data packets. • A Network Interface Card has one or more sockets for network cables and the type of socket depends on the type of network it will be used in.
Network Interface Card
Network Hub • A device for connecting multiple twisted pair or fiber optic Ethernet devices together, making them act as a single segment
Network Switch • Is a computer networking device that connects network segments. It often referred to as an intelligent hub or switching hub.
Switch Hub Router
Router • A computer networking device that forwards data packet across an internetwork toward their destinations, through a process known as routing. • Filter out traffic according to their protocols.
Backbone • A backbone is a larger transmission line that carries data gathered from smaller lines that interconnect with it.
Backbone • At local level, a backbone is a line or set of lines that LANs connect to for a WAN connection. • On the Internet, a backbone is a set of paths that local or regional networks connect to for long-distance interconnection.
Gateway • A gateway is hardware or software that provides a bridge between two otherwise incompatible networks. • Once a gateway is established then data can flow seamlessly between the network segments. • Software routers are sometimes referred to as gateways.
Network Cabinet
- More by User
CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication
CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. Data Link Layer Part II – Sliding Window Protocols . Part 2 - Topics. Sliding Window Protocols Go Back N Sliding Window Protocol Selective Repeat Sliding Window Protocol. Data Frame Transmission.
1.08k views • 42 slides
CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. Theoretical Basis of Data Communication. Topics. Analog/Digital Signals Time and Frequency Domains Bandwidth and Channel Capacity Data Communication Measurements. Signals.
828 views • 48 slides

Introduction to Computer Networking. Networks, Devices, Bandwidth MM Clements. Last Week …………. Shared Ethernet needed rules to avoid collisions on the network - CSMA/ CD Switched Ethernet does not allow for collisions so CSMA/ CD not needed Implemented for backward compatibility
664 views • 28 slides

Introduction to Computer Networking. Wireless Network. Wired Network. Hybrid Network. Direct Connect. Powerline Network. Basics (pcmag.com).
582 views • 39 slides

Introduction to computer networking
Introduction to computer networking. Objective: To be acquainted with: The definitions of networking Network topology Network peripherals, hardware and software. Definitions. 1.1 Network Definition
733 views • 50 slides

CS 313 Introduction to Computer Networking Telecommunication
2. Topics. IntroductionError CorrectionError Detection. . 3. Introduction. Transmission impairments (errors)Attenuation Loss of energy as signal propagatesDelay DistortionComponents travel at different speedsNoiseUnwanted energy from other sources. 4. Attenuation, distortion, and noise. .
316 views • 24 slides

Computer Networking Course Introduction
Computer Networking Course Introduction. Dr Sandra I. Woolley. Content. Course Summary The Recommended Text Course Structure, Content and Assessment Recommended Software. The Course Summary. The Recommended Text. Communication Networks A. Leon-Garcia & I. Widjaja McGraw-Hill
273 views • 14 slides

CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. Introduction. Topics. Introduction Metric Units Network Hardware Network Software Reference Models Example Networks Standards and Standards Organizations. Introduction. First two decades of computing
1.69k views • 125 slides

Introduction to Computer Networking: Trends and Issues
Introduction to Computer Networking: Trends and Issues. Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 [email protected] A talk given to“CS 131R: Computer Science I” Class October 4, 2011 These slides are available on-line at: http://www1.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/talks/cs13111.htm.
534 views • 31 slides

Introduction to computer networking. Distributed Algorithms Class Recitation. Ex. 1 - PIF Revisited. Given the PIF algorithm: Init: l N ( l )0; m 0; p 0 Upon receipt of MSG s ( l ) N ( l )1 if m =0 then p1 send MSG s to all l N -{ l } m 1
271 views • 14 slides

Introduction to computer networking. Internet: the global communications network. Internet. Text, audio, image and video: multimedia communications in the Internet.
1.47k views • 132 slides

Introduction to Computer Networking: Trends and Issues. Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 [email protected] A talk given in “CS 131: Computer Science I” Class October 4, 2010 These slides are available on-line at:
1.02k views • 26 slides
CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. DSL, Cable, and Mobile Telephone System. Topics. Digital Subscriber Line Cable Mobile Telephone System. Digital Subscriber Lines. Bandwidth versus distanced over category 3 UTP for DSL. Digital Subscriber Lines.
499 views • 33 slides
CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. Data Link Layer Part II – Sliding Window Protocols. Part 2 - Topics. Sliding Window Protocols Go Back N Sliding Window Protocol Selective Repeat Sliding Window Protocol. Data Frame Transmission.
569 views • 42 slides
Introduction to computer networking. Objectives To be acquainted with: The definitions of networking Network topology Network peripherals, hardware and software Network setup for Windows and Linux OS. Definitions. Network Definition
657 views • 50 slides

CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. Chapter 5 Network Layer. Topics. Design Issues Routing Algorithms Congestion Control Internetworking. Position of network layer. Network Layer Design Issues. Store-and-Forward Packet Switching
751 views • 73 slides

CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. Local Area Networks. Topics. LANs - IEEE Project 802 Ethernet Data Link Layer Switching. Figure 12-1. LAN Compared with the OSI Model. Figure 12-2. Project 802. Ethernet. Ethernet Cabling Manchester Encoding
517 views • 50 slides

CSCI411 Introduction to Computer Networking
CSCI411 Introduction to Computer Networking. Today – General Overview. Introduce basic concepts and vocabulary Networking overview Internet: What is the internet Architecture Layers. What is a Network?.
580 views • 56 slides
493 views • 48 slides

CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. Error Correction/Detection. Topics. Introduction Error Correction Error Detection. Introduction. Transmission impairments (errors) Attenuation Loss of energy as signal propagates Delay Distortion
321 views • 30 slides
CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. Data Link Layer Part I – Designing Issues and Elementary Protocols. Topics. Introduction Framing Error Control Flow Control Elementary Data Link Protocols. Introduction.
353 views • 33 slides

CS412 Introduction to Computer Networking & Telecommunication. Medium Access Control Sublayer. Topics. Introduction Channel Allocation Problem Multiple Access Protocols CDMA. Introduction. Broadcast networks Key issue: who gets to use the channel when there is competition Referred to as
384 views • 37 slides
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Fundamentals of computer networking
Learn the fundamental principles of computer networking to prepare you for the Azure admin and developer learning paths.
Learning objectives
In this module, you will:
- List the different network protocols and network standards.
- List the different network types and topologies.
- List the different types of network devices used in a network.
- Describe network communication principles like TCP/IP, DNS, and ports.
- Describe how these core components map to Azure networking.
Prerequisites
- Introduction min
- Network types and topologies to use when you design a network min
- Types of network devices to use when you build a network min
- Network protocols to use when you implement a network min
- IP address standards and services min
- Summary min
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

Computer Networks
Subject: Computing
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
7 September 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

You will find a complete Unit of work on Computer Networks for KS3. This includes presentations, worksheets and homeworks.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
25 The Internet is a global network of computer networks utilizing a suite of protocols called TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) that supports interconnection of a number of different computer networks Information Technology Center. 26 The Internet covers large, international Wide Area Networks (WAN's) as well as ...
nection on a single computer, as well. A network requires one computer to act as the server, waiting patiently for an incoming connec. ion from another computer, the client.Server-side applications set up a soc. et that listens to a particular port. The server socket is an integer identifier associated with a local IP address, and a the port ...
ndamentals - ReinventionThe Internet is co. Growth over time and technology trends drive upheavals in Internet. design and usage. Today's Internet is different from yesterday's. And tomorrow's will be different again. But the fundamentals remain the same. entals - Reinvention (2)Many billions of Int. 5B+ on Cell Networks.
Template 2: Computer Networking Devices: Hub Classification. This presentation template presents a detailed description of hub devices used in computer networking systems to enable cost-effective deployment methodologies and facilitate network media connections. It discusses performance advantages, networks supported, ease of availability, and kinds such as active, passive, and intelligent ...
An Introduction to Computer Networks - Second Edition
380 likes | 858 Views. Introduction to Computer Network. Dr. Rania R Ziedan. Agenda. Introduction Network types Network topology Network connection models OSI model. Computer network. A collection of computing devices that are connected in various ways in order to communicate and share resources or files. Download Presentation.
CONTENTS Preface 3 Second Edition. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 Licensing ...
Networking Fundamentals
Introduction to Computer Networks: Slides
Computer network
The Basics of Computer Networking.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document provides an overview of computer networking concepts. It defines what a computer network is and describes the three main types: wide area networks (WANs), local area networks (LANs), and peer-to-peer networks.
Basics of Computer Networking
Introduction to computer networking
Introduction to Computer Networking. Definition. Network Any interconnected group or system. Multiple computers and other devices connected together to share information. (nodes). History. 1957 USSR launches Sputnik, first artificial earth satellite 1958. Download Presentation. network.
Fundamentals of computer networking - Training
Give your computer network presentations a professional touch with a computer network PowerPoint template. Whether you're an IT professional, a student studying networking, or a business owner presenting your network infrastructure, these templates will help you deliver your message with clarity and style. With a range of customizable slides ...
You will find a complete Unit of work on Computer Networks for KS3. This includes presentations, worksheets and homeworks.