- ćwiczenia z angielskiego
- konstrukcje gramatyczne i leksykalne
- mowa zależna
- ćwiczenie #2448

Mowa zależna – pytania (reported speech – questions): ćwiczenia
Intermediate.
- Mowa zależna ćwiczenia
- opis Mowa zależna
Choose the correct form to complete the reported questions. Remember about the sequence of tenses.
Wybierz właściwą formę, żeby uzupełnić pytania w mowie zależnej. pamiętaj o następstwie czasów..
A thief said: "Where's your money?" You report: "The thief asked me where I my money."
Someone in the street said: "What time is it?" You report: "A guy in the street asked me what the time ."
A guitarist said: "What chord are you playing there?" You report: "The guitarist asked me what chord ."
A smoker said: "Excuse me, mate, have you got a light?" You report: "Then he asked me if I a light."
A barman said: "We're closing soon. Any more orders?" You report: "The barman said the bar 1 soon and 2 us for our last orders."
A market trader said: "Would you like this bag in a different colour?" You report: "The stallholder 1 me a bag I 2 at in a different colour."
Your friend said: "Is that your dog in the river? You report: "My friend asked me 1 the dog in the river 2 3 ."
A mother said: "What do you want for lunch, Timmy?" You report: "She asked her son what he for lunch."
A butcher said: "Would you like me to cut the fat off this steak?" You report: "The butcher asked if I 1 the fat cut from the steak I 2 .
A man said: "Can you lend me ten pounds, please? You report: "I couldn't believe it when he me to lend him some money.
Opis gramatyki: Mowa zależna - tworzenie pytań | Reported speech lub wszystkie Mowa zależna ćwiczenia
Thank you, ang.pl
Thank you, ang.pl ~!! ٩(- ̮̮̃-̃)۶
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech
April 25, 2019 by Veerendra
CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English . Here we have given CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech.
1. There are two different ways in which we can report the words of a speaker : (a) Direct Speech or Direct Narration. (b) Indirect Speech or Indirect Narration.
2. (a) Direct Speech contains the actual words of the speaker ; as— Sarla said, “My father has a roaring business in Mumbai.” He said to me, “I am feeling unwell today.” In these sentences, actual words of the speaker are given within inverted commas without any change.
(b) Indirect Speech gives the substance of the speaker’s actual words and not the exact words spoken by him or her ; as— Sarla said that her father had a roaring business in Mumbai. He told me that he was feeling unwell that day.
3. The actual words of the speaker, given within ‘inverted commas’ are called the Reported Speech. In the same way, the Verb which introduces the Reported Speech is called the Reporting Verb. In the sentence above ‘said’ is the Reporting Verb and ‘My father has a roaring business in Mumbai’ is the Reported Speech. Reporting Verb and Reported Speech. Look at the following sentences : Radha says, “I shall finish my home-work today.” Sushma said to Pushpa, “Show me your dolls.” The verbs ‘says and said’ in the above sentences are ‘Reporting Verbs’. The exact words of the speaker given within the inverted commas are ‘Reported Speech’.
4. Here are some distinctive points regarding the Direct Speech and Indirect Speech : In the Direct Speech 1. The Reported Speech is put within Reported (Inverted) Commas. 2. The Reported Speech and the Reporting Verb are separated by a Comma. 3. The first word of the Reported Speech begins with a capital letter.
Transformation of Direct Speech into Indirect Speech
I. Rules for the Change of Tense
| Rule I. If the Reporting Verb is in the Present or Future Tense, the Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech does not change. |
Examples 1 Direct: Rajesh says, “She has brought lame to her family.” Indirect: Rajesh says that she has brought fame to her family. 2. Direct: ohit has said, “I cannot displease my friend.” Indirect: Rohit has said that he cannot displease his friend. 3. Direct: I shall say, “I went to Agra on Monday.” Indirect: I shall say that I went to Agra on Monday. 4. Direct: She will say, “I have sent him a present.” Indirect: She will say that she has sent him a present.
| Rule II. If the Reporting Verb is in the Past Tense, the tense of the verb in the Reported Speech must be changed into the corresponding Past Tense. |
Examples 1. Direct: I said, “I am speaking the truth.” Indirect: I said that I was speaking the truth. 2. Direct : The teacher said, “Boys fail because they do not study regularly.” Indirect: The teacher said that boys failed because they did not study regularly.
Exception to Rule II (i) If there is a Universal Truth or Habitual fact in the Reported Speech, the Tense of the verb is never changed ; as— 1. Direct: He said, “Face is the index of mind.” Indirect: He said that face is the index of mind. 2. Direct: The teacher said. “The earth rotates round its axis.” Indirect: The teacher said that the earth rotates round its axis. 3. Direct: Horatius said, “Death comes sooner or later.” Indirect: Horatius said that death comes sooner or later.
(ii) The Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech does not change if the reported speech states a past historical fact ; as— 1. Direct: He said, “India became free on 15th August, 1947.” Indirect: He said that India became free on 15th August, 1947. 2. Direct: She said. “Her father lived at Lahore for ten years.” Indirect: She said that her father lived at Lahore for ten years.
(iii) If two such actions are given in the Reported Speech which take place at the same time, the Past Indefinite or Continuous Tense does not change. Direct: He said, “Mohan was singing a song while Gopal was playing on a flute.” Indirect: He said that Mohan was singing a song while Gopal was playing on a flute. Examples 1. Direct: She said, “I am a top-class singer.” Indirect: She said that she was a top-class singer. 2. Direct: We said, “He is writing a poem.” Indirect: We said that he was writing a poem. 3. Direct: He said, “It may rain tonight.” Indirect: He said that it might rain that night. 4. Direct: He said, “A devil ever remains a devil.” Indirect: He said that a devil ever remains a devil.
The future tense of the reported speech is changed as under : Future Indefinite—would/should Future Continuous—would/should be Future Perfect—would/should have Future Perfect Continuous—would/should have been
Examples 1. Direct: You said, “He is a very good athlete.” Indirect: You said that he was a very good athlete. 2. Direct: I said, “I have finished my work.” Indirect: I said that I had finished my work. 3. Direct: He said, “Her parents will pay a visit to Delhi.” Indirect: He said that her parents would pay a visit to Delhi.
Interrogative Sentences Conversion of Interrogative Sentences A From Direct Into Indirect
| 1. The Reporting Verb is changed, into ‘ask, enquire, inquire or demand etc. 2. No conjunction is used to introduce the Reported Speech if the question begins with (an interrogative) word ; such as—what, who, whose, which, when, where, why, how, whom etc. 3. If or whether is used to introduce the Reported Speech if the reported speech has no question word. 4. Change the questions into statements. Put full stop in place of mark of interrogation (?). |
Examples (a) Questions beginning with a Helping Verb 1. Direct: He said to her, “Shall I accompany you to Agra ?” Indirect: He asked her if he would (should) accompany her to Agra. 2. Direct: She said to him, “Had I been absenting myself from school for a month ?” Indirect: She asked him if she had been absenting herself from school for a month. 3. Direct: He said to us, “Has she been spinning since yesterday ?” Indirect: He asked us if she had been spinning since the previous day. 4. Direct: They said to you, “Shall we be going on picnic tomorrow ?” Indirect: They asked you if they would be going on picnic the next day. 5. Direct: I said to her, “Will you have ironed your clothes ?” Indirect: I asked her if she would have ironed her clothes.
(b) Sentences having ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ 1. Direct: “Are there any more files ?” He asked. “Yes, sir,” said the peon. Indirect: He asked the peon if there were any more files. The peon replied respectfully in affirmative. 2. Direct: The teacher said to Lila. “Did you break the window pane ?” “No, sir.” said Lila, “I did not.” Indirect: The teacher asked Lila if she had broken the window pane. Lila replied respect¬fully and refused it (to have done it). 3. Direct: “If you find my answers satisfactory, will you give me five rupees ?” said the astrologer. “No.” replied the customer. Indirect: The astrologer asked the customer whether he would give him five rupees if he found his answers satisfactory. The customer replied in negative. 4. Direct: I said to him. “Do you want to go to Chandigarh ?” He said, “No, sir.” Indirect: I asked him if he wanted to go to Chandigarh and respectfully he replied in negative. 5. Direct: He said to me, “Does Mohan still play ?” I said, “Yes, sir.” Indirect: He asked me if Mohan still played and I replied in positive.
(c) Questions beginning with Interrogative Words 1. Direct: He said to me. “Whom does she want to contact ?” Indirect: He asked me whom she wanted to contact. 2. Direct: They said to her, “Whose house are you purchasing ?” Indirect: They asked her whose house she was purchasing. 3. Direct: You said to him “Why are you making mischief ?” Indirect: You asked him why he was making mischief. 4. Direct: They said to us, “How have you solved this sum ?” Indirect: They asked us how we had solved that sum. 5. Direct: We said to them, “Who has misguided you ?” Indirect: We asked them who had misguided them.
(d) Questions beginning with modal auxiliaries 1. Direct: I said to him, “May Sunita come in to discuss with you something ?” Indirect: I asked him if Sunita might come in to discuss with him something. 2. Direct: The traveller said to me, “Can you tell me the way to the nearest inn ?” Indirect: The traveller asked me if I could tell him the way to the nearest inn. 3. Direct: He said to me. “Must I leave for Mumbai tomorrow ?” Indirect: He asked me if he had to leave for Mumbai the next day. 4. Direct: I said to her, “Could you give me your notes ?” Indirect: I asked her if she could give me her notes. 5. Direct: I said to him, “Need I go to him ?” Indirect: I asked him if I had to go to him.
Exercise 1 (Solved)
Convert the following sentences into Indirect Speech : 1. He said to her. “Do you want to go home ?” 2. He said to you. “Where are you going ?“ 3. I said to him, “What brings you here ?” 4. You said to us, “How do you solve this sum ?” 5. She said to me, “How are you getting on with your studies ?” 6. I said to my friend, “Have you been to England ?”
Convert the following sentences into Indirect Speech : 1. She said to me, “Who taught you English ?” 2. He said to his mother, “Why did you not wash my school dress ?” 3. The mother said to the child, “Did you have your breakfast ?” 4. Anil said to his sister, “How did you fare in the interview ?” 5. The policeman asked me, “Had the thief stolen your watch ?” Answers: I. 1. He asked her if she wanted to go home. 2. He asked you where you were going. 3. I asked him what brought him there. 4. You asked us how we solved that sum. 5. She asked me how I was getting on with my studies. 6. I asked my friend if he had been to England.
II. 1. She asked me who had taught me English. 2. He asked his mother why tehe had not washed his school dress. 3. The mother asked the child if he had his breakfast. 4. Anil asked his sister how she had fared in the interview. 5. The policeman asked me if the thief had stolen my watch.
Exercise 2 (Solved)
Change the following into indirect speech : 1. He said to me, “I have often told you not to play with me.” 2. They wrote, “It is time we thought about settling this matter.” 3. The teacher promised. “If you come to school tomorrow, I will explain it.” 4. “What do you want ?” he said to her. 5. He said, “How’s your father ?” 6. “Don’t you know the way home ?” asked I. 7. “Do you really come from China ?” said the prince. 8. “Sit down, boys,” said the teacher. 9. “Run away, children,” said the mother. Answers: 1. He told me that he had often told me not to play with him. 2. They wrote that it was time they thought about settling the matter. 3. The teacher promised to me that he would explain it if I went to school the following day. 4. He asked her what she wanted. 5. He enquired about my father. 6. I asked if he did not know the way home. 7. The Prince asked him if he really came from China. 8. The teacher asked the boys to sit down. 9. The mother asked the children to run away.
Exercise 3 (Solved)
The following passage has not been edited. There is an error in each line. Write the error along with the correction. Do not forget to underline the error. Her mother said that you must go straight to (a) your grandmother. There was a wolf (b) _______ in the wood through which she are (c) _______ going. But if she keep the road, he (d) _______ will not do any harm. The mother (e) _______ asked her to do as she tells her. (f) _______ Answers: (a) you—she (b) your—her (c) are—was (d) keep—kept (e) will—would (f) tells—had told
Exercise 4 (For Practice)
Police told Maninder that he is entitled (a) _______ to have a solicitor present. He denies (b) _______ that he knows anyone by the name of (c) _______ Surinder. Maninder confirmed that he has been (d) _______ in the vicinity of the factory last Monday. (e) _______ However, he said that he is visiting his mother. (f) _______ He maintains that he is innocent. (g) _______
Exercise 5 (For Practice)
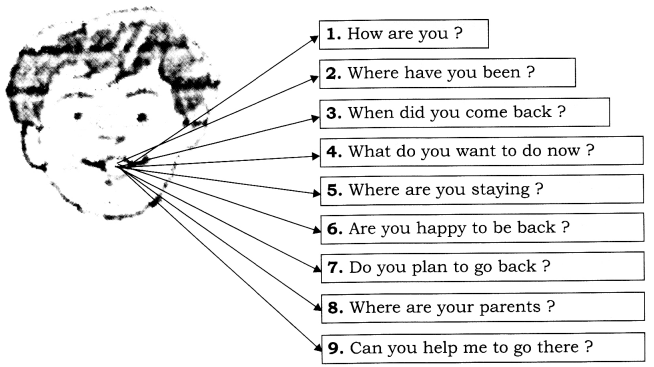
Exercise 6 (For Practice)
Each of the pair of sentences given below is a dialogue between a man and a woman. Change each pair into one simple sentence. Complete the answers. The first one has been done as an example. Question 1. “Shall we get married ?” “Yes, let us.” Answer: They decided to get married.
Question 2. “Please help me”. “O.K.” Answer: She agreed
Question 3. “May I help you ?” “No, thanks.” Answer: He offered
Question 4. “Let’s meet after the class.” “O.K. fine.” Answer: They arranged
Question 5. “What’s your name ?” “I won’t tell you”. Answer: She refused
Question 6. “I have stood first.” “Congratulations”. Answer: She congratulated
Multiple Choice Questions Exercise 1
Read the dialogues given below and then complete the report by choosing the correct options from the ones given below the dialogue : 1. Judge: Why don’t you speak the truth ? Witness: I have spoken only the truth. Judge: Were you really present at the scene ? Witness: Yes, sir.
The judge asked the witness (a) ……… the truth. The witness replied that (b) ……….. only the truth. At this the judge asked (c) ………….. at the scene. The witness replied in positive. (a) (i)why don’t you speak (ii) why didn’t he speak (iii) why you didn’t speak (iv) why he did not speak
(b) (i) he had spoken (ii) I have spoken (iii) I had spoken (iv) he has spoken
(c) (i) if you are really present (ii) that you were really present (iii) if he was really present (iv) that he was really present
2. Mother: What is the matter ? Son: Grandfather has shot a policeman. Mother: Why ? Son: He was a deserter. Mother asked the son (a) ………… The son replied (b) …………. a policeman. The mother demanded (c) ………… To this the son replied that he was a deserter. (a) (i) that what is the matter (ii) what is the matter (iii) what the matter was (iv) if what was the matter
(b) (i) that the grandfather has shot (ii) that Grandfather had shot (iii) if grandfather had shot (iv) why Grandfather had shot
(c) (i) why (ii) why Grandfather has shot (iii) that why grandfather had shot (iv) why Grandfather had shot
3. Merchant: How much have you collected ? Accountant: Twenty thousand in cash and the balance on paper. Merchant: Where have you deposited the cash ? The Merchant asked the accountant (a) …………. collected. The accountant replied (b) …………. and the balance on paper. Then the merchant wanted to know (c) …………. . (a) (i) how much you have (ii) how much have you (iii) how much had he (iv) how much he had
(b)(i) that I have collected twenty thousand in cash (ii) that he has collected twenty thousand in cash (iii) that he had collected twenty thousand in cash (iv) he had collected twenty thousand in cash
(c)(i) where have you deposited the cash (ii) where he had deposited the cash (iii) where had he deposited the cash (iv) where the cash had been deposited
4. Son: How are you feeling now? Father: Much better, son. Son: Are you taking the medicines regularly? Father: Yes, my dear. The son asked his father (a) …………. then. The father replied that (b) …………. much better. The son further asked (c) …………. the medicines regularly. The father replied in affirmative. (a) (i) that how he was feeling (ii) how he was feeling (iii) how you are feeling (iv) how was he feeling
(b) (i) I am feeling (ii) I was feeling (iii) he is feeling (iv) he was feeling
(c) (i) if you are taking (ii) if he is taking (iii) that he was taking (iv) if he was taking
5. Ram: Do you shave every day? Mohan: Yes. Don’t you? Ram: No. I shave only once a week Ram asked Mohan (a) …………. everyday. Mohan replied in positive and asked (b) …………. the same. Ram agreed that he didn’t and said (c) …………. only once a week. (a) (i) do you shave (ii) did he shave (iii) if he shaved (iv) that if he shaved
(b) (i) don’t you (ii) you don’t (iii) if you don’t (iv) if he didn’t
(c) (i) I shave (ii) that he shaved (iii) if he shaved (iv) if I shaved
6. Sue: What is it dear? Johnsy: The leaves. Sue: Are you counting the leaves? Johnsy: Yes. Sue asked Johnsy (a) …………. Johnsy replied that (b) …………. Sue further asked (c) …………. the leaves. Johnsy replied in positive. (a) (i) what it is (ii) what is it (iii) what is was (iv) what was it
(b) (i) that it was the leaves (ii) it is leaves (iii) that it are leaves (iv) that it had leaves
(c) (i) are you counting (ii) that she was counting (iii) was she counting (iv) if she was counting Answers: 1. (a) (iv) why he did not speak (b) (i) he had spoken (c)(iii) if he was really present 2. (a) (iii) what the matter was (b)(ii) that Grandfather had shot (c) (iv) why Grandfather had shot 3. (a) (iv) how much he had (b) (iii) that he had collected twenty thousand in cash (c) (ii) where he had deposited the cash 4. (a) (ii) how he was feeling (b) (iv) he was feeling (c) (iv) if he was taking 5. (a) (iii) if he shaved (b) (iv) if he didn’t (c) (ii) that he shaved 6. (a) (iii) what is was (b)(i) that it was the leaves (c) (iv) if she was counting
We hope the CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.

Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
Klasa 8 Angielski Reported speech
Przykłady z naszej społeczności, liczba wyników dla zapytania „klasa 8 angielski reported speech”: 10 000+.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Mowa zależna – Reported speech. Mowy zależnej używamy, kiedy chcemy zrelacjonować czyjąś wypowiedź, a nie przytoczyć ją dosłownie. W języku angielskim połączona jest z następstwem czasów. Następstwo czasów, to zastępowanie czasów ich przeszłymi odpowiednikami.
Choose the correct form to complete the reported questions. Remember about the sequence of tenses.
Mowa zależna - Reported Speech – Ćwiczenia i testy interaktywne z języka angielskiego. Polecenie: Choose the correct answers to report the sentences in the past. Remember about the sequence of tenses.
Reported speech - mowa zależna quiz for 8th grade students. Find other quizzes for English and more on Quizizz for free!
Mowa zależna – pytania (reported speech – questions): ćwiczenia. Choose the correct form to complete the reported questions. Remember about the sequence of tenses. Wybierz właściwą formę, żeby uzupełnić pytania w mowie zależnej. Pamiętaj o następstwie czasów.
CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech. 1. There are two different ways in which we can report the words of a speaker : (a) Direct Speech or Direct Narration. (b) Indirect Speech or Indirect Narration. 2. (a) Direct Speech contains the actual words of the speaker ; as— Sarla said, “My father has a roaring business in Mumbai.”
Reported speech jest dość skomplikowanym zagadnieniem. Jeżeli zapomnieliście lub nie pamiętacie na czym polega przekształcenie zdań w mowę zależną, konieczni...
REPORTED SPEECH 1.Przepisz zdania stosując mowę zależną. Pamiętaj o następstwie czasów. 1. „My parents live in Liverpool.” Ann said ..... 2. „We will buy the books.” They said ..... 3.
Reported speech - Mowa zależna w języku angielskim. 'Co on powiedział?' OK English. 8.75K subscribers. Subscribed. 342. 16K views 5 years ago. Mowa zależna to skomplikowany temat. Przede...
Klasa 8 Angielski Reported speech. Przykłady z naszej społeczności. Liczba wyników dla zapytania „klasa 8 angielski reported speech”: 10 000+. New Horizons - B2 - Grammar - Lesson 20 - Introduction Połącz w pary. autor: Bertrandantonyt. Dorośli Angielski English Reported Speech. New Horizons - B1 - Grammar - Lesson 20 - Practice 2 Odwracanie kart.