

Why Is Electrical Safety Important: A Comprehensive Explanation
Why Is Electrical Safety Important: Every year, nearly 1,000 deaths are caused by electrical accidents in the home, underscoring the critical question: Why is electrical safety important? It is not just about safeguarding property; it’s about protecting lives.
According to the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI), electrical fires cause approximately $1.3 billion in property damage annually. This alarming statistic emphasizes the necessity of understanding and adhering to safety guidelines.
Why Is Electrical Safety Important in Everyday Life?
Definition and Importance of Electrical Safety Have you ever wondered, “Why is electrical safety important?” It’s like the superhero of your household, guarding against unseen perils. Electrical safety refers to the practice of using electricity in a way that doesn’t put anyone at risk. Simple, right? Yet, a shocking number of accidents happen every year.
Statistics Related to Electrical Accidents Let’s not beat around the bush – nearly 1,000 deaths occur annually from electrical-related accidents in the U.S. alone. That’s more people than can fit in most coffee shops, even during the peak morning rush!
How It Relates to House Renting Now, if you’re renting a house, these numbers aren’t just statistics – they could be about your next-door neighbor or even you! Ensuring electrical safety means knowing the condition of the house’s wiring, outlets, and appliances. In fact, understanding this facet of safety can make your home a haven, not a hazard. Learn more about electrical safety in rental homes from our expert guide .
External Perspective But don’t just take our word for it. Check out this detailed explanation of why electrical safety is vital from our friends across the pond.
Common Electrical Hazards
Types of Electrical Hazards Here’s where things get really electrifying (pun intended!). From frayed wires looking like they’ve had a bad hair day to overloaded circuits acting like a buffet line on Thanksgiving – these are real hazards, folks. They are just waiting to ruin your day.
| Hazard | Examples |
|---|---|
| Faulty Wiring | Exposed wires, damaged insulation |
| Overloaded Circuits | Tripped circuit breakers, flickering lights |
| Misused Extension Cords | Daisy chaining, improper storage |
| Electrical Appliances | Malfunctioning toasters, overheating chargers |
| Water Contact | Wet hands near outlets, wet appliances |
Real-life Examples and Scenarios Take the example of Joe, who thought using a fork to get his toast out was a bright idea. Spoiler alert: It wasn’t. Or Suzy, who believed daisy-chaining extension cords was a fun, flower-themed game. Guess what? It’s not fun, and it’s definitely not a game.
Preventative Measures But fear not, dear reader. For every peril, there’s a preventative measure. Joe could’ve used a fork made of wood or plastic (something not conductive), and Suzy should’ve read the safety instructions that came with those cords. Prevention is simple:

- Know Your Stuff : Read instructions and safety labels.
- Inspect Regularly : A wire looking worse for wear? Replace it.
- Use Common Sense : If it seems like a bad idea, it probably is.
Linking to Prevention Guidelines Intrigued? Get the full scoop on electrical safety importance and electrical hazard prevention from those who know it best.
Tips for Ensuring Electrical Safety at Home
Safe Usage of Appliances Plug it, unplug it, but don’t hug it! Appliances are our friends, but only when we use them safely. Whether it’s a toaster or a hairdryer, remember:
- Read the manual : It’s not just for decoration!
- Turn off before unplugging : This isn’t a thrill ride.
Importance of Proper Wiring and Outlets Why is electrical safety important? Ask about your wires and outlets. Faulty wiring is like a sneaky ninja, lying in wait. Ensure professional installation and regular check-ups to keep those ninjas at bay.
Child Safety Concerns and Solutions Kids and electricity mix as well as cats and water. Here’s how to keep the little ones safe:

- Use outlet covers : They’re like helmets for your plugs.
- Educate about dangers : Or, how not to learn the electric slide.
For a More In-Depth Look Curious for more? Dive into our detailed guide on appliance safety here .
A Broader Perspective Not convinced? Maybe the professionals will sway you. Here’s what the experts have to say on the importance of electrical safety at home .
Electrical Safety in the Workplace
Regulations and Standards It’s not all fun and games at work, especially when it comes to electricity. Regulations are like the referees of the workplace, ensuring everything is fair and square. Key things to remember:
- Follow OSHA guidelines : They’re not just for show!
- Know your local regulations : Ignorance isn’t bliss here.
Best Practices for Employee Safety Employee safety isn’t a perk; it’s a necessity. Best practices aren’t best guesses; they’re grounded in reality. Tips to follow:
- Regular training : Knowledge beats guesswork.
- Clear communication : Talk isn’t cheap; it’s essential.
Importance of Regular Inspections Inspections are like dental check-ups for your workplace – a bit tedious, but utterly essential. Regular inspections help:
- Identify potential risks : Before they bite!
- Ensure compliance : It’s not just a buzzword.
Further Insights from the Pros Want to dig deeper? Here’s an expert take on the importance of electrical safety in the workplace .

Electrical Safety Training and Education
Availability and Importance of Training Why is electrical safety important? You wouldn’t send a knight into battle without armor, so why deal with electricity without proper training?
- It’s a necessity, not a luxury : Without training, a socket is a roulette wheel.
- Professional and personal : Whether at work or at home, safety training is essential.
Resources for Online and Offline Learning Want to be a Jedi of electrical safety? Here are some resources:
- Online platforms : YouTube isn’t just for cat videos; find tutorials there!
- Offline classes : Sometimes, face-to-face beats screen-to-screen.
- Professional courses : Invest in yourself; it pays the best interest.
Further Reading For those hungry for more, check out our comprehensive guide on electrical safety courses .
Expert Insights Still not enough? Here’s a professional’s take on why electrical safety training is so crucial .
The Global Perspective on Electrical Safety
International Standards and Regulations
| Region | Standard | Description |
|---|---|---|
| USA | NEC (National Electrical Code) | Regulates electrical installations and safety |
| Europe | IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) | Harmonized safety standards across countries |
| Asia | Local Regulations | Varies by country, focusing on regional needs |
Electricity doesn’t stop at borders, and neither do safety standards.
- IEC, ISO, NEC : Acronyms that save lives.
- Harmonized standards : Like an orchestra, but less musical and more life-saving.
How Different Countries Approach Electrical Safety Different strokes for different folks, but the goal is the same: safety first.
Linking to Global Initiatives and Forums Want to connect with other safety enthusiasts? There are forums and platforms where you can share and learn:
- Global safety conferences : Like Comic-Con, but with fewer capes.
- Online communities : Facebook isn’t just for vacation photos.
A Professional Perspective Thinking globally? Here’s what a global safety expert has to say about the importance of electrical safety across the globe .
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is electrical safety important in house renting.
Electrical safety is vital in house renting to protect tenants and properties from electrical hazards, including shocks, fires, and other related accidents.
What are some common electrical safety tips?
Some common electrical safety tips include:
- Using the right type of outlets and plugs
- Regularly checking for exposed wires or faulty equipment
- Avoiding overloading circuits
How can renters ensure electrical safety?
Renters can ensure electrical safety by:
- Hiring professionals for electrical repairs
- Following guidelines provided by landlords or property managers
- Educating themselves on basic electrical safety practices
What consequences can arise from neglecting electrical safety?
Neglecting electrical safety can lead to serious consequences such as:
- Electrical shocks or burns
- Fires causing property damage
- Legal liabilities for landlords
How often should electrical systems be inspected?
Electrical systems should be inspected at least once every five years by a qualified electrician to ensure continued safety.
What resources are available for learning more about electrical safety?
Resources available for learning about electrical safety include:
- Local electrical authorities
- Online tutorials and videos
- Professional electricians offering consultation services
Understanding why electrical safety is important in the context of house renting is paramount. Not only does it preserve the property’s integrity, but it also protects the lives of those living within it. Equip yourself with the knowledge and tools needed to safeguard your home against potential electrical hazards.
Thank you for reading!
Electrical Safety and Hazards of Electricity Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Bibliography
Electrical Safety is a part of industrial safety programs aimed to protect workers and outside environment from threats and risks. The electrical safety regulation involves congressional legislation stating the need to protect health, safety, and the environment; setting goals for improvements in the present condition; and establishing the commissions to deal with the day-to-day problems of actually achieving the goals. Once established, the new agencies attempt to settle quickly into full-blown and efficient administrative processes. While the legislation provided guidelines as to why the agency should proceed, it usually does specify the method or process of regulation.
Electricity is dangerous for a human causing death and health hazards. If a current runs through a human body it burns the flesh and causes the shock. In its turn, shock leads to heart attack and heart failure. One-tenth of an ampere may prove death if it passes through the main part of the body. “Of all the skin layers, keratin exhibits the highest resistance to the passage of electricity” (Cadick et al 2005, p. 1.20).
For instance, the 110 volts is enough to be fatal. in industrial setting, electricity is dangerous because it causes rapid heating and expansion of sap vapors in case of fire. In current, “electrons move because they push on each other to spread apart. When more electrons are in one place than another, those in the crowded area push harder than those in the emptier area, so electrons move from the former to the latter. Resistance is modeled as a blocking process in which “imperfections” in the material act as obstacles in the electrons’ paths” (McCutchen 1999, p. 259).
In industrial settings, electricity is dangerous because of high voltage and metal constructions used in many plants and factories. “Employees who work around electricity don’t survive on luck. Worse is the fact that having a near death accident doesn’t “feel” lucky to most” (Cadick et al 2005, p. 8.14). The regulation of worker safety goes toward specifying equipment. The Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 is enacted to reverse the rising trend of worker accidents during the 1960s. When the act became law, the secretary of labor set the first safety standards based on equipment specifications arrive at over the previous two decades by industry health associations and nonprofit safety organizations (Viscusi 2000).
Today, electrical safety issues contain extremely detailed specifications of the physical conditions of production, ranging from the cleanliness of the working area to the position and size of mesh screens over moving machinery. The goals are to set in terms of improving health and safety across the country, EPA, NHTSA, and OSHA regulations evolved away from performance to setting out and partially enforcing detailed equipment specifications (Viscusi 2000).
Because standard setting has been litigious and prolonged, the existing set of rules has not been complete. But these regulations when available and applied to the individual plant have proven to be extremely detailed and inflexible. When they have not fit, the only way to resolve an all-or-nothing confrontation has been to postpone application. in utility and industrial settings, ”electricity is conducted along copper wires in power generation, transmission, and distribution” (Cadick et al 2005, p. 11.8).
By controlling equipment and production processes, the agencies regulating electrical safety have had some impact on industry costs and prices. Electrical safety concerns logically fall into four basic categories: product design standards, installation standards, safety-related maintenance information and usage instructions “(Cadick et al 2005, p. 6.16). The impact is realized by the companies in higher equipment costs and reduced equipment options. This, in turn, increases the long-run, and increases the short-run, costs of production. Behavior modification approaches to workplace safety invoke a domino model, such that reinforcement strategies affect safe behavior, which in turn affects accident rates.
Following Patterson (1999), the simplest form of event sequence model accords less attention to causes and more attention to the outcomes leading up to an accident. The nuance here is that an accident is a process, rather than a single discrete event. Patterson (1999) conceptualizes the accident process as a hazard buildup cycle. At first, the workplace is safe with no uncontrolled hazards. As people start to work, however, tools are left out in work spaces, and different people enter the work space to do different things with different tools and equipment. People and objects move around and make opportunities to bump into each other.
Eventually hazards accumulate to a critical level when an accident occurs. Notice that there is a entropy concept implicit in the hazard buildup view of an accident process. For instance, in industrial settings: “whenever possible, safety grounds are applied to create a zone of equal potential around the employee. This means that the voltage is equal on all components within reach of the employee” (Cadick et al 2005, p. 2.84).
An intervention based on the hazard buildup cycle would emphasize training for good factory housekeeping. Other possible forms of training would center on the best use of tools, and procedures that would minimize the acceleration of the hazard buildup. Workers should learn to recognize the buildup cycle, and to spontaneously intervene by reorganizing their work spaces for a safer outcome (Viscusi 2000). The intervention essentially kick-starts a self-organization process for all workers. Entropy, having increased unto chaos, now causes the system to self-organize into a state where there is less internal entropy, and a more controlled transferral of energy into the work environment.
The concept of electrical safety climate was first expressed by Zohar (1980 cited Patterson 1999), who was investigating the safety practices, and workers’ views of those safety practices, that distinguished factories with good safety performance from those with poor performance. Attitudes toward the organization’s safety program and its effectiveness, worker training, availability of needed tools and personal protection equipment, and the foreman’s attentiveness to rule violations, all served to distinguish high and low performing groups (Viscusi 2000). The set of survey questions, taken together denoted a climate for safety.
The concept of climate was similar in principle to the organizational climate concepts, except that climate was viewed with respect to a more limited set of objectives or issues. The introduction of an organizational construct was justified because the measurements distinguished organizations rather than individuals (Patterson 1999).
Electrical workers and inspectors operate with a variety of notions of compliance. Full compliance is a standard set of conditions which they are aiming towards: this will usually be at least the legal or administrative definition of compliance, and it may represent a standard above the legal minimum. Inspectors may also operate with temporary definitions of compliance, that is a state of affairs which is less than full compliance but which is tolerated for a fixed period, until such time as they consider it reasonable for a state of full compliance to have been achieved (Cadick et al 2005).
Both of these are positive definitions, to the extent that they emphasize the degree to which something measures up to the required standard. When inspectors are wanting to emphasize the negative aspects of a situation they talked in terms of non-compliance. The definition, achievement, and maintenance of compliance is a process which continues for as long as a business is in operation and known about by the regulatory authorities. But while the activities regulated by inspectors are continuous, inspectors’ visits to these sites are ‘momentary’ and sometimes infrequent (Patterson 1999).
They therefore make decisions from ‘snapshots’ of activity, and with the benefit of varying levels of training, guidance, and experience. Issues of compliance therefore emerge in different contexts and settings and the meanings they take on are molded accordingly. It may take inspectors a long time to become familiar with some very large and complex organizations, a task which may be made more difficult by reorganizations.
For instance, British Railways is perhaps a good example, since its national organization was differentiated both on a regional basis and according to specialisms such as civil engineering, mechanical and electrical engineering, signals and telecommunications, and operations (Patterson 1999). Not only was this a complicated organization in itself but it was not a static organization. Each of the parts might be reorganized, leaving members of the RI with the problem of not knowing whom to contact, especially if jobs were awkwardly defined. However, some inspectors felt that reorganizations could help them if individual managers became responsible for larger areas, as inspectors would then need to contact fewer managers to effect improvements across a greater area.
In industrial settings, the environmental hazard parameters can be thought of as background and trigger variables, respectively. The relationship between hazards and accidents is thought to be linear in the sense of the Patterson (1999) hazard buildup process. Other evidence suggests that the electrical safety is actually a log-linear relationship, such that hazards are more closely related to the log of accidents rates, rather than to accident rates directly (Parkhurst and Niebur 2002).
Variables that represent sources of stress, which in turn affect performance, are thought to cause a sharp inflection of risk over a short amount of time when the background hazard level is sufficiently strong. Risk inflection, which is greatest when anxiety and stress are high, safety management is poor, and group size is small. Good safety management is thought to produce only a relatively low. Safety management is a control mechanism both in real circumstances and as a bifurcating effect in the model. Tests of the cusp model in two situations showed that the model provides a good description of the accident process and affords a variety of qualitative recommendations that an organization can use to enhance its safety performance (McCutchen 1999).
In sum, electricity is dangerous because it causes deaths and injuries if the workers are not protected and safety measures are not kept. Behavior modification programs, which selectively reward desired safety responses and censure undesirable behaviors, rank among the most effective means of controlling accidents, as long as the contingencies of reinforcement center on rewarding the desired behavior to a greater extent than on punishing undesirable behavior. Their chief limitations are, however, that they require constant monitoring by the agencies delivering the rewards, and only a narrow set of behaviors can be targeted effectively within a specific program. Also, they tend to view targeted behaviors in isolation, rather than as results of a complex system process. Sometimes those limitations are not problems, of course, but sometimes they are.
- Cadick, J., Capelli_M., Neitzel, D. K. Electrical Safety Handbook . McGraw-Hill Professional; 3 edition, 2005.
- McCutchen, D. Making Their Own Connections: Students’ Understanding of Multiple Models in Basic Electricity. Cognition and Instruction , 17, 1999. 249-259.
- Patterson, W. Transforming Electricity: The Coming Generation of Change . Earthscan Ltd, 1999.
- Parkhurst, D. J., Niebur, E., Variable-Resolution Displays: A Theoretical, Practical, and Behavioral Evaluation. Human Factors , 44, 2002, p. 611.
- Viscusi, K. Corporate Risk Analysis: A Reckless Act? Stanford Law Review , 52, 2000, pp. 547-597.
- Electricity Hazards for Human Body
- Airbags' History, Working Principles, Usefulness
- “Safety, Accidents, and Investigations: Be Prepared for the Unexpected” by Robert Battles
- The Electrical Safety Attitudes and Behaviors
- Utilitarianism in Food Safety Management
- Bhopal Gas Incident of 1984: Ethical Issues
- Deepwater Horizon Oil Rig Explosion in 2010
- Hazard Preparedness and Mitigation for Miami, Florida
- Draft Disaster/Emergency Plan for the Qatar Civil Defence Department’s Response to Stadium Disaster
- The Ras Laffan Emergency and Safety College: Fire Safety Management Plan
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, August 16). Electrical Safety and Hazards of Electricity. https://ivypanda.com/essays/electrical-safety-and-hazards-of-electricity/
"Electrical Safety and Hazards of Electricity." IvyPanda , 16 Aug. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/electrical-safety-and-hazards-of-electricity/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Electrical Safety and Hazards of Electricity'. 16 August.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Electrical Safety and Hazards of Electricity." August 16, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/electrical-safety-and-hazards-of-electricity/.
1. IvyPanda . "Electrical Safety and Hazards of Electricity." August 16, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/electrical-safety-and-hazards-of-electricity/.
IvyPanda . "Electrical Safety and Hazards of Electricity." August 16, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/electrical-safety-and-hazards-of-electricity/.
Introducing Smart Electrical Management

Your cart is empty
Product added to cart
Why is Electrical Safety Important: Understanding the Risks and Precautions
Electrical safety is of paramount importance in both residential and commercial settings. Every year, accidents involving electricity lead to serious injuries, fatalities, and extensive property damage. These incidents often stem from a lack of knowledge about electrical hazards and failure to adhere to safety practices. We must prioritize electrical safety to protect ourselves, our families, and our colleagues from the dangers associated with improper handling of electrical devices and systems.
Understanding and managing the inherent risks of electricity is crucial for the creation of a safe living and working environment. Comprehensive safety regulations and standards have been established to guide us in protecting individuals from electric shocks, burns, and other related injuries. Adherence to these guidelines through proper training and the use of protective measures is essential. We also need to ensure that the tools and equipment we use are maintained and handled correctly to prevent hazardous situations.
Key Takeaways
- Electrical safety is critical to prevent injuries, fatalities, and property damage.
- Adherence to safety standards and proper training is necessary for managing risks.
- Regular maintenance and correct handling of tools and equipment enhance safety.
Understanding Electrical Hazards
Electrical safety is crucial because hazards associated with electricity can lead to serious accidents and injuries. We must be aware of the various sources and forms of these hazards to create a safe environment .
Sources of Electrical Hazards
Electrical hazards originate from various sources, often involving high voltages, faulty wiring, or inadequate safety measures. For example, exposed electrical parts, inadequate wiring, and overloaded circuits are common origins of these dangers. To illustrate:
- Exposed electrical parts : Items such as live wires, which may be accidentally touched, posing a risk for shock or burns.
- Inadequate wiring : An improperly sized wire for the current can lead to overheating and potential fires.
- Overloaded circuits : Placing too much load on a circuit can cause overheating, which may result in a fire hazard.
Common Electrical Injuries
When we encounter electrical hazards , several types of injuries can occur, including electric shocks , burns, and the severe effects of arc flash. Below are the common injuries:
- Electric shock : Caused when current passes through the body, potentially disturbing heart rhythm or causing muscle spasms.
- Burns : These could be thermal burns from heat generated by an electric arc or contact burns from touching overheated equipment.
- Arc flash : A dangerous release of energy caused by an electric arc, which can lead to severe burns and even blindness.
By understanding these hazards and injuries, we can take appropriate measures to safeguard against them and reduce the risk of electrical accidents .
Importance of Electrical Safety Training
We understand the necessity of electrical safety training as a crucial aspect of maintaining a secure workplace. Our focus on comprehensive training ensures that workers are well-prepared to navigate the risks associated with electrical systems.
Reducing Workplace Accidents
Through rigorous electrical safety training , we strive to significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents in the workplace. Our statistics show that trained individuals are less prone to mishaps , making training a vital investment.
- Preventative Measures : Employees learn to identify and rectify potential hazards early on.
- Emergency Protocols : Our training includes clear instructions on handling emergencies, thereby mitigating adverse situations.
Developing Best Practices
We build upon foundational knowledge to instill best practices among our workers, ensuring safety becomes a routine part of their technical repertoire.
- Standard Procedures : Comprehensive guidelines for everyday tasks to minimize risk.
- Continuous Learning : Encourage additional training and apprenticeship opportunities to keep skills sharp.
Our dedication to online and in-person training options allows flexibility for our team to remain at the forefront of electrical training and safety standards.
Comprehensive Safety Regulations and Standards
Electrical safety is paramount, and we observe stringent regulations and standards to protect both personnel and infrastructure from hazards. Our compliance with these measures ensures a workplace that is both safe and efficient.
Role of OSHA in Safety
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a pivotal role in assuring safe and healthful working conditions. OSHA's standards are designed to minimize electrical risks and are enforceable under law. We adhere to these regulations to not only avoid legal consequences but to maintain a safe environment for our employees. OSHA guidelines are comprehensive, encompassing recommendations for:
- Proper installation and maintenance of equipment
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Employee training and certification
Compliance with these regulations is both a legal requirement and a moral imperative for us. It ensures that the risk of accidents and injuries is significantly reduced.
NFPA Guidelines
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) is responsible for creating standards for fire safety , which includes electrical safety. The NFPA’s guidelines, particularly the NFPA 70E, focus on:
- Electrical safety requirements for employee workplaces
- Safe work practices
- Maintenance requirements
These guidelines serve as a benchmark for our safety protocols. Our strict adherence to the NFPA’s standards ensures that we minimize the potential for electrical fires and related hazards. By following these nationally recognized guidelines, we provide an environment that prioritizes the safety of our operations and personnel.
Protective Measures and Equipment
In this section, we'll examine the crucial roles of personal protective equipment and the importance of regular maintenance and inspections in ensuring electrical safety.
Use of Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is our first line of defense against electrical hazards, especially when working in environments with potential electrical risks. The selection of appropriate PPE is guided by the level of voltage encountered and the type of operation being performed. Below is a list of key items and their uses:
- Insulated Gloves : Provide essential hand protection from electric shock and burns.
- Safety Glasses : Shield eyes from sparks and flying debris.
- Flame-Resistant Clothing : Mitigates the risk of burns from arc flashes.
- Dielectric Footwear : Prevents ground faults by insulating feet from the ground.
- Face Shields : Protect the face from electrical arcs and flashes.
- Ear Plugs/Ear Muffs : Protect hearing against the noise during the operation of certain high-voltage equipment.
Using lockout/tagout procedures ensures machinery is properly shut down and inoperable during maintenance or repair, preventing accidental energization.
Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance and inspections are mandatory for preventing electrical accidents. We rely on structured protocols for assessing and maintaining equipment, which often includes the following steps:
Visual Inspections : Ensuring there are no frayed wires, loose connections, or signs of wear.
Testing : Using appropriate tools to check for proper operation and grounding. A routine testing schedule is non-negotiable.
Documentation : Keeping detailed records of inspections and maintenance activities aids in tracking equipment condition and ensures compliance with safety regulations.
Repairs : Timely addressing of identified issues minimizes risk and maintains the integrity of the electrical safety equipment.
Through diligent adherence to these procedures, we can significantly reduce electrical incidents, maintaining a safe working environment for all.
Leave a comment
More than just a guarantee, 100% free quotes.
Zero cost to receive an estimate for your building.
100% Guarantee
(All pilot projects) If you're not happy with the service you don't pay.
24/7 Video Training
Forget how to do something? Goto https://youtube.com/@circuitiq
Customer Support
1-888-956-2283 or [email protected]
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.

11 Important Principles Of Electrical Safety
Electrical safety is of paramount importance in all industries that deal with electricity. This includes construction sites, manufacturing plants, offices, and even homes. The importance of electrical safety cannot be overstated, as electrical accidents can cause serious injury or even death. In this blog, we will discuss the principles of electrical safety and why it is so important. Whether you are an electrician, an engineer, or just someone who wants to stay safe around electricity, this blog will provide you with valuable information to help you avoid electrical accidents and stay safe.
Why Is Electrical Safety Important?
Electrical safety refers to the measures taken to minimize the risk of injury or death due to electric shock, electrocution, fires, or explosions resulting from the use of electricity. It involves understanding the hazards associated with electricity , identifying potential risks, and implementing preventive measures to reduce or eliminate those risks.
The importance of electrical safety cannot be overstated. Electricity is a powerful force that can cause serious injuries or even death if not handled properly. Electric shock can result in burns, respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and other life-threatening conditions. In addition, electrical faults can cause fires and explosions, leading to property damage and loss of life.
Electrical safety is critical in all industries that use electricity, including construction, manufacturing, and healthcare. Employers are responsible for ensuring that their employees are trained to recognize electrical hazards and follow safe work practices. It is also important for individuals to understand electrical safety when working with electricity at home, whether it is changing a light bulb or installing new electrical outlets.
Electrical safety is vital to protect individuals from the dangers of electricity. It is important to understand the principles of electrical safety and to take necessary precautions to prevent accidents and injuries. By following safe work practices and maintaining electrical equipment properly, we can reduce the risk of electrical accidents and create a safer working and living environment.
Electrical Safety Principles
Electrical safety is crucial to prevent accidents, injuries, and property damage caused by electrical hazards. Here are some key principles of electrical safety:
1. Understand The Basics Of Electricity
Understanding the basics of electricity is a crucial first step in ensuring electrical safety. By being knowledgeable about the fundamental concepts of electricity, individuals can better identify potential hazards and take appropriate safety measures to prevent accidents and injuries.
Key concepts include:
- Voltage: Voltage, also known as electric potential difference, is the force that pushes electric charge through a conductor. It is measured in volts (V) and is often compared to water pressure in a pipe. Higher voltage means a higher potential for electrical hazards.
- Current: Electric current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire. It is measured in amperes (A) and can be compared to the flow of water through a pipe. Higher currents can generate more heat and pose a greater risk of electrocution or fire.
- Resistance: Resistance is a property of materials that opposes the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms (Ω) and can be compared to the narrowing of a water pipe, restricting the flow of water. Materials with high resistance, like insulators, impede the flow of electric current, while materials with low resistance, like conductors, allow the flow of electric current.
- Electrical circuits: An electrical circuit is a closed loop through which electric current flows. It consists of a power source (e.g., a battery or generator), conductors (wires), a load (an electrical device, such as a light bulb or motor), and a return path to the power source. Circuits can be designed in series, parallel, or a combination of both.
By comprehending these basic concepts, individuals can better understand how electrical systems work, recognize potential hazards, and apply appropriate safety measures to reduce the risk of electrical accidents.

2. Insulate conductors
Insulating conductors is a critical principle of electrical safety, as it helps prevent accidental contact with live wires, reducing the risk of electrical shock, burns, and short circuits. Proper insulation ensures that electrical current is contained within the conductors, minimizing the potential for accidents and injuries.
Key considerations for insulating conductors include:
- Select appropriate insulation materials: Insulation materials should be non-conductive, such as plastic, rubber, or other similar materials. These materials prevent the flow of electrical current, ensuring that the live conductors remain isolated from surrounding objects and people.
- Inspect insulation regularly: Insulation can deteriorate over time, becoming less effective or even exposing live conductors. Regularly inspect the insulation on electrical wires and equipment for signs of wear or damage, and replace it as necessary.
- Use insulated tools: When working with electrical equipment, use insulated tools with non-conductive handles to reduce the risk of accidental contact with live conductors .
- Guard against environmental factors: Insulation should be chosen based on the specific environment in which the conductor will be used. For example, outdoor conductors should have insulation that can withstand exposure to sunlight, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, while conductors in industrial settings may require insulation resistant to chemicals or other harsh conditions.
- Comply with regulations and standards: Ensure that the insulation used on conductors complies with local regulations and industry standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) or the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards.
By properly insulating conductors, you can significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents and injuries, creating a safer environment for both workers and equipment.
3. Proper Grounding
Proper grounding is a fundamental principle of electrical safety, as it helps protect people and equipment from electrical faults and provides a safe path for current to flow in the event of a fault. Grounding minimizes the risk of electrical shock, equipment damage, and fires by directing excess current away from people and sensitive components.
Key aspects of proper grounding include:
- Grounding conductors: Electrical systems should have a grounding conductor connected to a grounding electrode, such as a metal water pipe or a ground rod. This conductor creates a low-resistance path for fault current to flow safely to the earth, preventing hazardous voltage levels on equipment and reducing the risk of electrical shock.
- Grounded outlets: Use grounded (three-prong) outlets for all electrical devices, especially those with metal casings or high power consumption. The third prong connects to the grounding conductor, providing additional protection against electrical faults.
- Ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs): Install GFCIs in areas where water and electricity are in close proximity, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor outlets. GFCIs monitor the flow of current and quickly trip the circuit if they detect a ground fault, reducing the risk of electrical shock.
- Equipment grounding: Ensure that all metal parts of electrical equipment are properly grounded. This includes the metal enclosures of devices, such as motors, transformers, and control panels, as well as any conductive materials that could become energized during a fault.
- Regular inspections and maintenance: Periodically inspect your grounding system for proper connections, corrosion, or other signs of damage. Regular maintenance helps ensure that the grounding system remains effective in protecting against electrical hazards.
- Compliance with regulations and standards: Follow local regulations and industry standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) or International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, for proper grounding practices and requirements.
By implementing proper grounding techniques and regularly inspecting and maintaining your grounding system, you can significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents, protect valuable equipment, and ensure a safer environment for both workers and equipment.

4. Circuit Protection
Circuit protection is a vital principle of electrical safety, as it safeguards electrical systems from damage caused by overloads, short circuits, and ground faults. By implementing appropriate circuit protection devices, you can prevent equipment damage, minimize fire risks, and reduce the potential for electrical shock.
Key aspects of circuit protection include:
- Fuses: Fuses are designed to protect electrical circuits by melting a metal filament when the current exceeds a specified rating. Once the fuse is blown, it must be replaced to restore the electrical circuit. Fuses come in various types and ratings, depending on the specific application.
- Circuit breakers: Circuit breakers are automatic switches that detect an overload or short circuit and interrupt the flow of current by tripping the switch. Unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset after the fault has been corrected, making them a reusable protection method. Circuit breakers come in different types, such as thermal, magnetic, or a combination of both.
- Ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs): GFCIs are specialized devices designed to protect against ground faults by constantly monitoring the flow of current in a circuit. If the GFCI detects an imbalance in the current flow, indicating a potential ground fault, it quickly trips the circuit, cutting off the power supply. GFCIs are commonly used in areas with increased risk of electric shock, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor outlets.
- Arc-fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs): AFCIs protect against arc faults, which can occur when damaged or worn wiring creates a high-temperature electrical discharge. Arc faults can lead to fires, so AFCIs are designed to detect these events and interrupt the circuit, preventing potential hazards.
- Proper sizing and selection: Choose the appropriate circuit protection devices based on the specific electrical system and equipment requirements. Ensure that the devices are rated according to the system’s voltage and current specifications, and follow local regulations and industry standards for proper installation.
By incorporating effective circuit protection measures, you can enhance electrical safety, protect valuable equipment, and reduce the likelihood of electrical accidents and fires.
5. Maintain Safe Distances
Maintaining safe distances is a key principle of electrical safety, as it helps prevent accidental contact with live conductors, electrical equipment, and energized systems. By keeping an appropriate distance from electrical hazards, individuals can reduce the risk of electrical shock, arc flash incidents, and other accidents.
Important aspects of maintaining safe distances include:
- Approach boundaries: Understand and adhere to the defined approach boundaries for electrical systems, which may include limited, restricted, and prohibited approach boundaries. These boundaries are established based on the voltage level and potential hazards associated with the electrical equipment.
- Clearance distances: Observe the minimum clearance distances specified for electrical installations, such as overhead power lines or electrical substations. These distances are designed to prevent accidental contact with energized conductors and reduce the risk of electrical shock or electrocution.
- Arc flash boundaries: Be aware of arc flash boundaries, which indicate the distance at which an arc flash can cause severe burns or injuries. Workers should avoid crossing these boundaries without proper personal protective equipment (PPE) and training.
- Safe work practices: Follow safe work practices when working around electrical equipment, such as maintaining a safe distance from energized components, using insulated tools, and avoiding contact with conductive materials.
- Exclusion zones: Establish and enforce exclusion zones around electrical work areas, where only qualified personnel with the necessary PPE and training are allowed to enter. This helps minimize the risk of untrained individuals coming into contact with electrical hazards.
- Use of barriers and warning signs: Install physical barriers, such as guardrails or covers, and post warning signs to indicate the presence of electrical hazards and remind individuals to maintain a safe distance.
- Training and awareness: Ensure that all workers are adequately trained in electrical safety, including the importance of maintaining safe distances from electrical hazards and the appropriate approach boundaries for specific tasks and equipment.
By maintaining safe distances from electrical hazards and following established approach boundaries, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents and create a safer environment for both workers and equipment.

6. Use Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is also a key principle of electrical safety, as it provides a crucial line of defense for individuals working with or around electricity. By wearing suitable PPE, workers can minimize the risk of injury from electrical hazards such as shocks, burns, and arc flashes.
Essential PPE for electrical safety includes:
- Insulated gloves: Insulated gloves, made from materials like rubber, provide protection against electrical shock by creating a barrier between the worker and live conductors. These gloves should be rated for the specific voltage level being worked on and should be inspected regularly for signs of wear or damage.
- Safety glasses or goggles: Eye protection is essential when working with electricity, as it helps prevent injuries from flying debris, sparks, or intense light produced during electrical work. Safety glasses or goggles should be worn at all times when working on or near electrical equipment.
- Face shields: Face shields protect the face from burns and other injuries caused by electrical arcs, explosions, or flash hazards. They should be used in conjunction with safety glasses or goggles for complete eye and face protection.
- Flame-resistant clothing: Flame-resistant (FR) clothing is designed to resist ignition and minimize the spread of flames, providing protection against burns caused by arc flashes or electrical fires. Workers should wear FR clothing that meets industry standards, such as those established by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) .
- Insulated footwear: Insulated footwear, made from non-conductive materials, can help protect workers from electrical shock by reducing the flow of current through the body. Electrical hazard (EH) rated shoes or boots are recommended for those working in environments with potential electrical hazards.
- Dielectric hard hats: Dielectric hard hats, made from non-conductive materials, protect the head from electrical shock and falling objects. These hard hats should meet relevant safety standards and be used in conjunction with other PPE to ensure complete protection.
- Protective hearing equipment: In some cases, electrical work may involve loud noises that can damage hearing. Workers should use earplugs or earmuffs to protect their hearing when working in high-noise environments.
By selecting and using appropriate PPE, workers can significantly reduce the risk of injury from electrical hazards and ensure a safer working environment. Remember to inspect, maintain, and replace PPE as needed to ensure its effectiveness.
7. Follow Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Following Lockout/Tagout procedures is an essential principle of electrical safety, as it ensures that electrical equipment and systems are de-energized and cannot be accidentally re-energized during maintenance, repair, or other work activities. This practice helps prevent injuries and fatalities caused by unexpected energization, the release of stored energy, or the start-up of equipment.
Key elements of Lockout/Tagout procedures include:
- Develop a Lockout/Tagout program: Establish a comprehensive Lockout/Tagout program within your organization, outlining specific procedures, responsibilities, and requirements for equipment and personnel.
- Identify energy sources: Before working on electrical equipment, identify all energy sources, such as electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, and stored energy, and ensure they are properly isolated and controlled.
- Shut down equipment: Using the established shutdown procedure, typically switching off the power and disconnecting the equipment from the energy source.
- Isolate energy sources: Physically isolate the energy sources by disconnecting, blocking, or otherwise preventing energy flow to the equipment. This may involve unplugging devices, opening circuit breakers, or closing valves.
- Apply Lockout/Tagout devices: Attach lockout devices, such as padlocks, to the energy-isolating mechanisms to prevent the equipment from being re-energized. Attach warning tags to inform others that the equipment is locked out and should not be operated.
- Verify de-energization: Test the equipment to ensure it has been successfully de-energized and that there is no residual or stored energy. Use appropriate testing instruments, such as voltage testers, to confirm the absence of electrical energy.
- Perform the required work: Once the equipment is de-energized and locked out, perform maintenance, repair, or other work activities.
- Restore equipment to service: After completing the work, follow established procedures for removing Lockout/Tagout devices, re-energizing the equipment, and returning it to service. This process should involve verifying that all workers are clear of the equipment and that all tools and materials have been removed.
By adhering to proper Lockout/Tagout procedures, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries related to unexpected equipment energization and ensure a safer work environment for all personnel involved.

8. Properly Maintain Electrical Equipment
Properly maintaining electrical equipment is also an essential principle of electrical safety, as it ensures that devices and systems operate safely and efficiently. Regular maintenance can help prevent electrical hazards, such as short circuits, overloads, and fires, by identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate.
Key aspects of properly maintaining electrical equipment include:
- Scheduled maintenance: Develop a schedule for all electrical equipment, including inspections, testing, and servicing. Regular maintenance schedules can help identify issues early and prevent unexpected equipment failure or hazards.
- Visual inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections of electrical equipment, looking for signs of wear, damage, or overheating. Check for loose connections, frayed or damaged wiring, and any signs of corrosion.
- Testing and calibration: Periodically test and calibrate electrical equipment to ensure it functions correctly and within specified tolerances. This may include testing circuit breakers, GFCIs, and other protective devices to ensure they operate as intended.
- Cleaning and servicing: Clean electrical equipment to remove dust, dirt, and debris, which can cause overheating or reduced performance. Perform routine servicing tasks, such as lubricating moving parts or replacing worn components, as needed.
- Repair and replacement: Promptly repair or replace damaged electrical equipment to prevent further deterioration or hazards. Always use the correct replacement parts and follow the manufacturer’s repair guidelines.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain accurate records of all maintenance activities, including inspections, testing, repairs, and replacements. This documentation can help track the performance and condition of electrical equipment over time and support effective maintenance planning.
- Training and awareness: Ensure that individuals responsible for maintaining electrical equipment are adequately trained and aware of the potential hazards, best practices, and relevant regulations and standards related to electrical safety.
By properly maintaining electrical equipment and regularly inspecting and servicing devices, you can minimize the risk of electrical accidents, improve equipment performance, and extend the life of your electrical systems.
9. Avoid Overloading Circuits
Avoiding circuit overloads is also a crucial principle of electrical safety, as overloads can cause excessive heat, damage to electrical equipment, and even fires. By ensuring that electrical circuits are not overloaded, you can maintain a safe environment and minimize the risk of electrical accidents.
Key guidelines for avoiding circuit overloads include:
- Know the circuit’s capacity: Familiarize yourself with the capacity of each circuit in your home or workplace. The circuit’s capacity, typically expressed in amperes (A), determines the maximum amount of electrical current it can safely handle.
- Calculate the load: Add up the total electrical load of all devices connected to a single circuit, taking into account their wattage (W) and voltage (V). Ensure that the total load does not exceed the circuit’s capacity.
- Use the 80% rule: As a safety measure, avoiding exceeding 80% of the circuit’s capacity is recommended. This helps account for potential variations in electrical demand and provides a margin of safety against overloads.
- Distribute the load: Avoid plugging too many devices into a single outlet or circuit. Distribute high-power appliances and devices across multiple circuits to prevent overloading.
- Avoid extension cord overuse: While extension cords can be useful in certain situations, overusing them can contribute to circuit overload. Do not plug multiple high-power devices into a single extension cord; avoid connecting multiple extension cords.
- Use surge protectors: Surge protectors can help protect your devices from voltage spikes and overloads. Choose a surge protector with an appropriate capacity for your connecting devices, and ensure it’s properly grounded.
- Regular maintenance and inspection: Inspect your electrical system, including wiring, outlets, and circuit breakers, for signs of wear or damage. Regular maintenance can help identify potential issues before they lead to overloads or other hazards.
By following these guidelines and being mindful of the electrical load on your circuits, you can effectively avoid overloading and reduce the risk of electrical accidents and fires.
10. Be Aware Of Environmental Factors
Being aware of environmental factors is also a critical principle of electrical safety, as certain conditions can increase the risk of electrical hazards or affect the performance of electrical equipment. Individuals can take appropriate precautions and maintain a safer work environment by understanding how environmental factors influence electrical safety.
Key environmental factors to consider include:
- Moisture and humidity: Moisture and high humidity can increase the risk of electrical shock, as water is a conductor of electricity. Always exercise caution when working near water or damp environments, and use GFCIs to protect against ground faults. Additionally, ensure that electrical equipment is rated for wet or damp locations.
- Dust and debris: Accumulating dust and debris on or around electrical equipment can cause overheating, reduced performance, or even fires. Regularly clean electrical equipment and enclosures to prevent buildup, and consider using dust-tight enclosures in particularly dusty environments.
- Temperature extremes: Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can affect the performance and lifespan of electrical equipment. Ensure that equipment is rated for the specific environmental conditions it will be exposed to, and consider using temperature controls or insulation to maintain safe operating conditions.
- Corrosive or hazardous environments: Certain environments, such as those with high levels of corrosive gases, chemicals, or airborne particles, can cause damage to electrical equipment and increase the risk of electrical hazards. Use equipment rated for use in hazardous or corrosive environments, and follow proper maintenance procedures to minimize potential risks.
- Space constraints: Limited space around electrical equipment can restrict proper airflow, leading to overheating and reduced performance. Ensure that equipment has adequate clearance for cooling and is not obstructed by other objects or materials.
- Vibration and mechanical stress: Excessive vibration or mechanical stress can cause damage to electrical equipment, such as loose connections or component failures. Ensure that equipment is securely mounted and protected from excessive vibration or stress.
- Lightning and surge protection: Electrical equipment can be damaged by voltage surges caused by lightning strikes or other power disturbances. Implement appropriate surge protection measures, such as surge protectors or lightning arresters, to protect equipment and minimize the risk of damage.
By being aware of environmental factors and taking appropriate precautions, individuals can effectively manage the risks associated with various conditions and maintain a safer work environment when dealing with electrical equipment and systems.

11. Training And Awareness
Effective training and awareness are essential components of electrical safety, as they equip individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills to work safely with or around electricity. This principle emphasizes the importance of proper education in identifying potential hazards, understanding best practices, and avoiding accidents.
Key aspects of training and awareness include:
- Safety training: Workers who interact with electrical equipment, systems, or devices should receive comprehensive safety training that covers relevant topics, such as the basics of electricity, hazard identification, risk assessment, safe work practices, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Regular updates and refreshers: To maintain a high level of electrical safety awareness, training should be updated regularly, and refresher courses provided to ensure workers know the latest safety standards, best practices, and technological advancements.
- Safety culture: Promoting a strong safety culture within an organization encourages employees to prioritize safety, adhere to established procedures, and proactively identify and report potential hazards. This mindset helps create an environment where electrical safety is ingrained in the daily work routine.
- Hazard communication: Clear and effective communication is crucial for electrical safety. This includes the proper labelling of electrical equipment, the use of warning signs, and the sharing of information about potential hazards among team members.
- Emergency response: Training should also cover emergency response procedures in an electrical incident, such as administering first aid, using fire extinguishers, and evacuating the area. This knowledge can be vital in mitigating the consequences of an accident and ensuring the safety of all individuals involved.
By prioritizing training and awareness, organizations can ensure that employees are well-equipped to work safely with electricity, minimize risks, and prevent accidents, thus contributing to a safer work environment.
Understanding and implementing the important principles of electrical safety is essential for ensuring a secure and hazard-free environment when working with or around electricity. By focusing on these key principles, including understanding the basics of electricity, adhering to proper installation and maintenance practices, using appropriate personal protective equipment, and being aware of environmental factors, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents, injuries, and equipment damage.
Creating a culture of electrical safety within your organization requires ongoing training, awareness, and a commitment to best practices. Both employers and employees must take these principles seriously and prioritize safety above all else. By doing so, you can create a safer work environment for everyone involved, protect valuable equipment, and minimize the likelihood of costly and dangerous electrical incidents. Electrical safety is not just a one-time effort but an ongoing responsibility that requires diligence, knowledge, and a proactive approach.
- Sign up for free
- SafetyCulture
- Electrical Hazards
Protect Your Workplace from Electrical Hazards
Learn more about electrical hazards in the workplace and how to practice electrical safety to mitigate risks

What are Electrical Hazards?
Electrical hazards refer to the potential dangers and risks that are associated with electrical systems. The main electrical hazards when working with electricity include:
- electrocution,
- electric shock;
- and other serious injuries.
In extreme cases, they can even lead to fires or explosions, posing a threat to life, property, and the overall safety of a place and its occupants.
Why It’s Important to Know About These Hazards
Working around electricity can be very safe on the job site when workers properly identify and control hazards. But, inadequate training, lack of experience, and failure to recognize potential hazards could result in electric shock or death.
The construction industry is most in danger from electrical hazards, accounting for 52% of all electrical fatalities in the US workplace . Most of these incidents and fatalities were caused by direct worker contact with overhead power lines and contact with machines, tools, and hand-carried metallic objects. So how do we protect ourselves against these dangers?
One of the best ways to protect yourself against these dangers is through awareness. Knowing the potential risks associated with electricity allows you to take precautions to prevent electrical accidents and fatalities. Having this knowledge can also help you spot the signs of electrical hazards immediately for prompt action, thereby contributing to the overall safety of the workplace .
Causes of Electrical Hazards
Electrical hazards, while dangerous, can be prevented when you’re aware of the factors that contribute to them. Here’s a list of the most common causes of electrical hazards to watch out for:
- Insufficient insulation – Over time, electrical insulation can deteriorate due to wear and tear, rodents, or exposure to moisture. This degradation can lead to exposed wires and increase the risk of electric shock or short circuits.
- Circuit breaker failure – If the circuit breaker fails to trip during an overload, it loses its protective functioning, further increasing the risk of electrical hazards.
- Damaged electrical appliances – Loose connections, frayed wires, or cracked insulation can result in electrical malfunctions.
- Improper use of extension cords – Practices like daisy chaining and overloading can cause overheating and ignite electrical fires.
- Inadequate maintenance – Failing to regularly inspect electrical systems, ignoring warning signs, or bypassing safety procedures can trigger severe electrical hazards over time.
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
Electrical Hazards Examples
Electrocution is one of the most common hazards across construction sites according to OSHA . Identifying electrical hazards can help raise awareness of the risks, their severity, and how they can harm workers.
In this section, learn about common electrical hazards in the workplace and electrical safety tips to prevent them:
- Overhead power lines
- Damaged tools and equipment
- Inadequate wiring and overloaded circuits
- Exposed electrical parts
- Improper grounding
- Damaged insulation
- Wet conditions
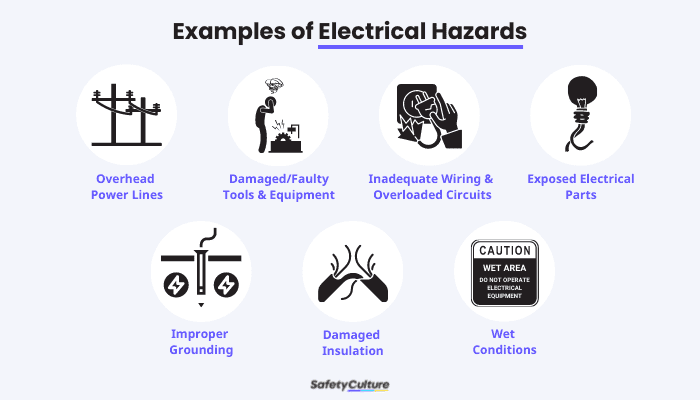
Examples of Electrical Hazards
Overhead Power Lines
Overhead powered and energized electrical lines have high voltages which can cause major burns and electrocution to workers. Remember to maintain a minimum distance of 10 feet from overhead power lines and nearby equipment. Conduct site surveys to ensure that nothing is stored under overhead power lines.
In addition, safety barriers and signs must be installed to warn nearby non-electrical workers of the hazards present in the area.
Damaged Tools and Equipment
Exposure to damaged electrical tools and equipment can be very dangerous. Do not fix anything unless you are qualified to do so. Thoroughly check for cracks, cuts, or abrasions on cables, wires, and cords. In case of any defects, have them repaired or replaced.
Aside from this, Lock Out Tag Out (LOTO) procedures should be performed at all times before commencing electrical maintenance and repairs. LOTO procedures are there to protect all workers on a worksite.
Inadequate Wiring and Overloaded Circuits
Using wires of inappropriate size for the current can cause overheating and electrical fires to occur. To prevent this, use the correct wire suitable for the operation and the electrical load to work on. Use the correct extension cord designed for heavy-duty use.
Make sure to not overload an outlet and use proper circuit breakers. Perform regular fire risk assessments to identify areas at risk of bad wiring and circuits.
Exposed Electrical Parts
Examples of exposed electrical parts include temporary lighting, open power distribution units, and detached insulation parts on electrical cords. These hazards can cause potential shocks and burns. Secure these items with proper guarding mechanisms and always check for any exposed parts to be repaired immediately.
Improper Grounding
The most common OSHA electrical violation is the improper grounding of equipment. Proper grounding can eliminate unwanted voltage and reduce the risk of electrocution. Never remove the metallic ground pin as it is responsible for returning unwanted voltage to the ground.
Damaged Insulation
Defective or inadequate insulation is a hazard. Be aware of damaged insulation and report it immediately. Turn off all power sources before replacing damaged insulation and never attempt to cover them with electrical tape.
Wet Conditions
Never operate electrical equipment in wet locations. Water greatly increases the risk of electrocution especially if the equipment has damaged insulation. Have a qualified electrician inspect electrical equipment that has gotten wet before energizing it.
Preventing Hazards Through Electrical Inspections
Electrical inspections are an essential preventive measure to avoid electrical hazards in the workplace. This procedure helps detect and address potential hazards, reducing the risk of electrical injuries and contributing to a safer working environment. Failure to conduct these inspections regularly can also lead to accidents caused by electric shock or even death.
So how do these inspections aid in preventing electrical hazards? Here’s a quick overview to help you get started:
- Assessing the condition of electrical equipment – During an electrical inspection, a property’s electrical equipment undergoes quality and safety checks to ensure that they are in working condition before being operated.
- Detecting electrical hazards – Regular electrical inspections allow electricians to identify faulty wiring, damaged cords, or malfunctioning equipment and carry out the necessary repairs or replacements.
- Ensuring compliance with safety codes – These inspections are conducted by electrical servicing companies to make sure that a property follows electrical safety laws and regulations.
- Evaluating electrical safety procedures – Electrical inspections provide an overall assessment of the worksite, training provided, and equipment used. These results allow you to identify and bridge any gaps in safety procedures.
- Recommending corrective actions – After completing the inspection, inspectors provide recommendations on areas for improvement based on the identified risks and noncompliances. These can range from repairs and replacements to upgrades and safety training.
Create Your Own Electrical Hazard Safety Checklist
Eliminate manual tasks and streamline your operations.
Set the Tone for Safety with Electrical Hazards Safety Training
Electrical safety training is a must for personal safety, accident prevention, and regulatory compliance. It equips workers with the necessary skills to minimize risks and safeguard themselves against electrical hazards in various workplace settings.
Don’t let your team’s electrical hazards safety training turn into another tedious activity that they just want to get over with. With the help of training courses on the SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) platform, you can give them an engaging training experience while making sure that they learn everything they need to work safely and effectively.
And here’s the best part: most of these Training courses are designed to be editable! Feel free to add your own content or branding to make the training look and sound just like you.
Equip Inspectors With an Electrical App That Simplifies Their Work
Why use safetyculture.
Traditionally, electrical inspectors document their findings and observations manually on paper. Further, they have to go back to the office, review all results, and create an Electrical Certificate of Compliance (CoC) if the client’s property has been proven to be compliant. This cumbersome process makes critical data susceptible to damage and loss, in addition to the storage and organization issues it presents.
SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) , the world’s leading electrical inspection software, can solve this problem by converting paper forms into digital ones. This mobile-first solution makes the inspection process more efficient and systematic to help save invaluable time, boost productivity, improve communication, and upgrade operational efficiency.
The convenience of using the SafetyCulture inspection app on a handheld device can solve traditional paper form issues and more, as follows:
- Convert paper forms into digital templates , customize existing checklists from the Public Library , or create them from scratch .
- Record your observations and complete inspections from a mobile device, even when offline .
- Capture and annotate photo evidence for documentation and review.
- Generate a comprehensive inspection report in PDF, Word, CSV, or Web format.
- Issue electronic CoCs with clients and personnel within the organization.
- Assign corrective actions , with detailed notes and photos, to relevant personnel.
- Enhance safety measures against electrical hazards using data and insights from the Analytics dashboard.
- Schedule electrical inspections and be alerted of their completion or lack thereof.
- Relay safety reminders and policy updates across the organization via Heads Up .
- Keep workers informed about potential electrical hazards in their line of work using mobile-ready training courses.
FAQs About Electrical Hazards
Who is at risk of electrical hazards.
Engineers, electricians, and overhead line workers, both contractors and subcontractors are at the top of the list of professionals who are most exposed to electrical hazards. Common tasks that put these workers at risk include electrical installation and repairs, testing of fixtures and equipment, and inspection and maintenance activities.
People who are indirectly working with electricity like office workers are also exposed to electrical hazards.
What are electrical hazard areas?
According to the National Electrical Code , electrical hazard areas are specific places or environments with an increased risk of electrical hazards. These hazardous locations typically have conditions or equipment that pose potential dangers to workers, such as:
- Chemical plants
- Oil refineries
- Gas stations
- Laboratories
How often should electrical equipment be inspected and tested?
Electrical equipment should be checked regularly to make sure that they are working properly and are safe to use. Testing intervals, however, may vary depending on various factors such as the type of equipment, its intended use, the manufacturer’s recommendations, and the working environment they are utilized or exposed to.
For instance, some equipment may require quarterly or biannual check-ups. OSHA also recommends that all electrical equipment be inspected at least once every year.
What are the warning signs of faulty electrical equipment?
Faulty electrical equipment can put individuals at risk if they’re not found and resolved swiftly. Here are a few signs that could warn you if your electrical equipment is defective:
- Visibly damaged wiring
- Scorching or discoloration around outlets or switches
- Flickering or dimming lights
- Buzzing or crackling sounds
- Persistent burning odors
- Hot outlets or switches
- Frequent tripping of circuit breakers

Jona Tarlengco
Related articles

- HVAC System Components
Learn about the essential parts and functions of HVAC systems. Discover how each component works together to maintain comfort and efficiency.
- Find out more

- RoHS Compliance
Explore the significance of RoHS compliance and discover the steps and best practices to achieve compliance, upholding operational excellence and sustainability goals.

- Electrical Safety Training
Build and improve a culture of safety in your organization, especially among employees involved in electrical work, by conducting electrical safety training.
Related pages
- Electrical Training Software
- Electrician App
- Fire Alarm Inspection Software
- Food Waste Management Software
- Construction Waste Management Software
- Electrical Safety Toolbox Talk
- Electrical Safety
- Electrical Work Permit Checklist
- Electrical Risk Assessment Template
- Electrical Installation Condition Report
- Electrical Inspection Checklists
- Foodborne Illness Complaint Form

Deputy Managing Director & Principal Electrical Consultant
BEng CEng (Hons) MIET
Paul Hopton
Paul is a senior engineering manager and chartered electrical engineer with significant experience in operations, maintenance, engineering and project management gained in the Oil and Gas/Chemical/Steel Industries and the Military.
Following service in the RAF as a Flight Simulator Technician, Paul joined DuPont, during his time there he graduated in electrical engineering and soon became chartered and a member of the IET. Paul later joined BG Group as a maintenance and operations engineer at one of the UK’s largest gas storage facilities. One to further his career, Paul joined Millennium Chemicals at a Titanium Dioxide top tier COMAH site, he was their I&E Maintenance Superintendent until he was attracted back to the gas storage business under Centrica ownership, as their Electrical Technical Authority.
Paul more recently worked for Tata Steel Europe’s corporate engineering function as their lead on electrical asset integrity, writing and implemented 15 safety critical company standards and guides including Arc Flash Risk Management; Safety Instrumented Systems Design and Fire System Design.

Why is electrical safety important
Identify electrical safety hazards.
You cannot smell, hear, or see electricity, so making sure you have the right systems in place to manage this hazardous energy is critical to the wellbeing of your employees and your Company.
There are two major hazards of electricity:
- Electric Shock
Electrical safety is important because hazards such as arc flash and shock can result in death if you are exposed to them. Fortunately, the likelihood of this occurring is relatively low. However, the control measures that prevent these hazards require careful management, attention to detail and technical competence.
Injuries that can result from electric shock are as follows:
- Cardiac arrest due to the electrical effect on the heart
- Muscle, nerve, and tissue destruction from a current passing through the body
- Thermal burns from contact with the electrical source
- Falling or injury after contact with electricity
Injuries that can result from Arc Flash are as follows:
- Burns from the high temperatures produced by the arc
- Blindness from the ultra-violet light produced by the arc
- Hearing loss caused by the pressure wave from the arc blast
Comply with Electrical Safety Legislation
Not surprisingly there is legislation in place that aims to regulate these hazards. The three main ones are:

- employers have towards employees and members of the public
- employees have to themselves and to each other certain self-employed have towards themselves and others
- The Electricity at Work Regulations – Expand on the rules regarding electrical safety in teh Health and Safety at Work Act 1974. Employers are given duties and resonsibilites to make sure that all work activity that uses or may be affected by electricity is done safely, and that all foreseeable risks are assessed and minimised as much as possible.
- Management of Health & Safety at Work Regulations 1999 – Employers are required to undertake an assessment of the risks to the health and safety of their employees and other people who may be affected by their work activity.
Managing Electrical Risk is Important
We will now try to answer the question: What should you have in place to manage electrical risk?
In a nutshell, it is important have an Electrical Safety Management System in place. What does that consist of, you may ask? It depends upon the size of your organisation, but let us assume you are a large company, you should have something like the following in place:
1. Electrical Safety Rules – including training, compliance, and auditing. 2. Electrical Safety Instructions typically these may cover subjects such as:
3. Electrical Permit System – typically:
4. electrical authorisation system – you should have different levels of authorisation for electrical personnel that limits what work they can do. you may have several different levels of authorisation such as:.

Electrical Risk Self
Achieving compliance with legislation.
Within each category there can also be different levels of authorisation dependent upon the competency required to undertake certain tasks.
1. Electrical Competency Management System :
This should describe how you manage electrical competence, from recruitment through to technical competence requirements for each electrical role within your organisation.
2. Organisational arrangements:
This should describe who is responsible for electrical safety and how your organisation is set up to manage electrical safety, including individual roles and responsibilities.
We have helped many Companies put their Electrical Safety arrangements in order. If you feel like you might need some help, contact us today.
Latest News
Electrical Safety news

BS7671 Amendment 2 – What Do We Think Will Change?
Compliance Director, Andrew Linley, discusses the possible changes being released through Amendment 2 to BS 7671.
Arc Flash news

When Is Arc Flash Protection Required?
Paul Hopton, Deputy Managing Director and Principal Electrical Consultant, discusses when Arc Flash Protection is required, carrying out Risk Assessments to determine the requirement and suitable competency of those involved.

Arc Flash Protection Boundary Distances
Compliance Director, Andy Linley, discusses Arc Flash Boundary distances, what they are and factors affecting them.
Receive the latest news & updates from ESUK.
Essay Curve
Essay on Electrical Safety – 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words

Essay on Electrical Safety: Electricity is a powerful and essential resource in our modern world, but it can also be extremely dangerous if not handled properly. In this essay, we will explore the importance of electrical safety and the potential risks associated with electrical hazards. From understanding the basics of electricity to implementing safety measures in our homes and workplaces, it is crucial to prioritize electrical safety to prevent accidents and protect ourselves and others from harm.
Table of Contents
Electrical Safety Essay Writing Tips
1. Introduction: Start your essay by introducing the importance of electrical safety in our daily lives. Mention how electricity is an essential part of modern society, but it can also be dangerous if not handled properly.
2. Define electrical safety: Define what electrical safety means and why it is important. Explain that electrical safety refers to the practices and precautions taken to prevent accidents and injuries related to electricity.
3. Common electrical hazards: Discuss some common electrical hazards that people may encounter in their daily lives, such as faulty wiring, overloaded circuits, and damaged electrical appliances.
4. Tips for electrical safety: Provide a list of practical tips for ensuring electrical safety at home and in the workplace. This may include:
– Always hire a qualified electrician for electrical work – Avoid overloading outlets and power strips – Keep electrical cords away from water and heat sources – Regularly inspect electrical appliances for damage – Use ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens – Teach children about electrical safety and keep them away from electrical hazards
5. Importance of electrical safety training: Highlight the importance of providing electrical safety training to individuals who work with electricity or in environments where electrical hazards are present. Emphasize that proper training can prevent accidents and save lives.
6. Consequences of electrical accidents: Discuss the potential consequences of not following electrical safety practices, such as electric shocks, burns, fires, and even death. Stress the importance of taking electrical safety seriously to avoid these risks.
7. Conclusion: Summarize the key points of your essay and reiterate the importance of practicing electrical safety in all aspects of life. Encourage readers to prioritize electrical safety and take necessary precautions to prevent accidents and injuries related to electricity.
Essay on Electrical Safety in 10 Lines – Examples
1. Electrical safety is important to prevent accidents and injuries caused by electricity. 2. Always unplug appliances before cleaning or servicing them to avoid electric shocks. 3. Do not overload electrical outlets or use damaged cords or plugs to prevent fires. 4. Keep electrical appliances away from water to avoid the risk of electric shock. 5. Use ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in areas where water is present, such as bathrooms and kitchens. 6. Do not touch electrical appliances with wet hands to prevent electric shocks. 7. Make sure all electrical work is done by a qualified electrician to ensure safety. 8. Teach children about electrical safety and the dangers of playing with electrical outlets or cords. 9. Install smoke detectors and carbon monoxide detectors to alert you to potential electrical hazards. 10. Regularly inspect and maintain electrical systems in your home or workplace to prevent accidents.
Sample Essay on Electrical Safety in 100-180 Words
Electrical safety is of utmost importance in any setting, whether it be at home, in the workplace, or in public spaces. Failure to follow proper safety precautions when dealing with electricity can result in serious injuries or even death.
To ensure electrical safety, it is important to always use equipment that is in good condition and properly maintained. Avoid overloading outlets or extension cords, as this can lead to overheating and fires. Make sure to unplug appliances when not in use and never touch electrical appliances with wet hands.
It is also crucial to have a qualified electrician perform any repairs or installations to avoid the risk of electrical shock. Additionally, always turn off the power supply before working on any electrical equipment.
By following these simple guidelines and being aware of potential hazards, we can prevent accidents and ensure the safety of ourselves and those around us. Remember, when it comes to electricity, safety should always come first.
Short Essay on Electrical Safety in 200-500 Words
Electrical safety is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe and hazard-free environment in both residential and commercial settings. Electricity is a powerful and essential source of energy that powers our daily lives, but it can also be extremely dangerous if not handled properly. From electrical shocks to fires, the risks associated with electricity are numerous and can have serious consequences.
One of the most important aspects of electrical safety is proper installation and maintenance of electrical systems. Faulty wiring, overloaded circuits, and outdated electrical equipment can all increase the risk of electrical hazards. It is essential to have a qualified electrician inspect and maintain electrical systems regularly to ensure they are up to code and functioning properly. This can help prevent electrical fires, shocks, and other accidents that may result from faulty wiring or equipment.
Another key aspect of electrical safety is proper handling of electrical appliances and devices. It is important to always follow manufacturer instructions and safety guidelines when using electrical equipment to prevent accidents. This includes avoiding overloading circuits, using extension cords properly, and keeping electrical appliances away from water sources to prevent electrical shocks.
In addition to proper installation and maintenance of electrical systems, it is important to be aware of potential electrical hazards and take precautions to prevent accidents. This includes keeping electrical cords and wires away from heat sources, sharp objects, and high-traffic areas to prevent damage and reduce the risk of electrical fires. It is also important to use ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in areas where water is present, such as kitchens and bathrooms, to prevent electrical shocks.
Furthermore, it is important to educate yourself and others about electrical safety practices to prevent accidents and injuries. This includes teaching children about the dangers of electricity and how to safely use electrical appliances and devices. It is also important to have a plan in place in case of an electrical emergency, such as knowing how to shut off power to the affected area and having a fire extinguisher on hand in case of an electrical fire.
In conclusion, electrical safety is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe and hazard-free environment in both residential and commercial settings. By following proper installation and maintenance practices, handling electrical appliances and devices safely, being aware of potential hazards, and educating yourself and others about electrical safety practices, you can help prevent accidents and injuries related to electricity. Remember, when it comes to electricity, safety should always be the top priority.
Essay on Electrical Safety in 1000-1500 Words
Electrical safety is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe environment in both residential and commercial settings. Electricity is a powerful force that can cause serious harm if not handled properly. In this essay, we will discuss the importance of electrical safety, common hazards to be aware of, and best practices for preventing accidents and injuries.
One of the main reasons why electrical safety is so important is because electricity is a silent killer. Unlike other hazards that may be more visible or easily detectable, electricity can be present without any obvious signs. This makes it crucial to always be vigilant and take precautions when working with or around electrical systems.
There are several common hazards that can pose a risk to electrical safety. One of the most common hazards is faulty wiring. Over time, wiring can become worn or damaged, leading to potential electrical fires or shocks. It is important to regularly inspect wiring and replace any damaged or outdated components to prevent accidents.
Another common hazard is overloading electrical circuits. When too many devices are plugged into a single outlet or circuit, it can cause overheating and potentially start a fire. It is important to use power strips and surge protectors to distribute the load evenly and avoid overloading circuits.
Water is also a major hazard when it comes to electrical safety. Water is a conductor of electricity, so any contact with water can lead to electric shocks or short circuits. It is important to keep electrical appliances away from water sources and to never use them with wet hands.
In addition to these common hazards, there are also specific safety measures that should be taken when working with electricity. One of the most important safety practices is to always turn off the power before working on any electrical system. This can prevent accidental shocks or fires while performing maintenance or repairs.
It is also important to use the right tools and equipment when working with electricity. Insulated gloves, goggles, and other protective gear can help prevent injuries in case of an accident. Additionally, using tools that are specifically designed for electrical work can help ensure that the job is done safely and efficiently.
Regular maintenance and inspections are also key components of electrical safety. By regularly checking wiring, outlets, and appliances for signs of wear or damage, you can prevent potential hazards before they become serious issues. It is also important to have a qualified electrician inspect your electrical systems on a regular basis to ensure that everything is up to code and functioning properly.
In conclusion, electrical safety is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe environment in both residential and commercial settings. By being aware of common hazards, following best practices, and taking necessary precautions, you can prevent accidents and injuries related to electricity. Remember to always turn off the power before working on electrical systems, use the right tools and equipment, and regularly inspect and maintain your electrical systems to ensure a safe and hazard-free environment.
Related Essays
Essay on A Visit To A Fair – 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Value of Games And Sports – Essay in 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Essay on Importance of Teacher – 100, 200, 500, 1000 Words
Essay on A Visit To A Museum – 100, 200, 500, 1000 Words
Essay on Effect of Social Media On Youth
Essay on Shri Guru Nanak Dev Ji – Short & Long Essay Examples
Essay on Nuclear Family – Short Essay & Long Essay upto 1500 Words
Essay on Anudeep Durishetty – 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Essay on Non Violence – Samples, 10 Lines to 1500 Words
Covid 19 Responsive School – Essay in 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Safety Officer
- Safety Quiz
- Interview Q/A
- Online Exam
- Download PPT
- Get Certificate Online
- HSE Web Story
- NEBOSH IDIP
- Fire Engineering
- Basic Safety
- Construction Safety
- Workplace Safety
- Fire Safety
- Crane Safety
- Work At Height
- Excavation Safety
Electrical Safety
- Confined Space
- Noise Safety
- Vibration Safety
- Scaffolding
- Radiography
- HSE Calculations & Formulas
- Safety Slogan
- Tool Box Talk
- HSE Documentation
- HSE Training
- Risk Assessment
- Safety Audit
- Accident Investigation
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

Table of Contents
Electrical Safety: Protecting Lives and Property
Electricity powers our modern world, but it also poses significant hazards if not handled with care. From electric shock to fires and arc flashes, the risks associated with electrical systems are real and potentially life-threatening. In this article, we’ll delve into the importance of electrical safety and explore practical measures to prevent accidents and injuries.
Introduction to Electrical Safety
Importance of electrical safety.
Electrical safety is paramount in both residential and commercial settings. Neglecting safety protocols can result in severe injuries, property damage, and even fatalities. By understanding and adhering to safety guidelines, individuals can protect themselves, their families, and their assets from electrical hazards.

Common Electrical Hazards
Electricity can pose various hazards, including electric shock, electrical fires, and arc flashes. These dangers underscore the critical need for vigilance and proactive safety measures.
Understanding Electrical Hazards
Electric shock.
Electric shock occurs when the body comes into contact with an electric current. The severity of the shock depends on factors such as voltage, current, and duration of exposure. Even low-voltage shocks can be dangerous, causing muscle contractions, burns, and cardiac arrest.
Electrical Fires
Faulty wiring, overloaded circuits, and malfunctioning appliances can lead to electrical fires. These fires spread quickly and can engulf entire buildings if not promptly extinguished. Prevention and early detection are essential in mitigating the risk of electrical fires.
Arc Flashes
An arc flash is a sudden release of energy due to an electrical fault, resulting in an explosive discharge of intense heat and light. Arc flashes can cause severe burns, vision impairment, and even death. Proper safety protocols and protective equipment are crucial in minimizing the risk of arc flash incidents.
Preventing Electric Shock
Inspecting electrical cords and outlets.
Regularly inspecting electrical cords and outlets for signs of wear or damage can help prevent electric shock accidents. Replace damaged cords and outlets promptly to eliminate potential hazards.
Using Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs)
GFCIs are electrical safety devices designed to protect against electric shock by quickly shutting off power in the event of a ground fault. Install GFCIs in areas prone to moisture, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor spaces.
Avoiding Water Near Electrical Appliances
Water and electricity are a dangerous combination. Keep electrical appliances away from water sources and ensure hands are dry when handling them. Never operate electrical devices with wet hands.
Preventing Electrical Fires
Proper use of extension cords.
Extension cords should be used temporarily and never as a permanent solution for powering appliances or devices. Avoid running cords under carpets or rugs, as this can cause overheating and increase the risk of fire.
Avoiding Overloading Circuits
Overloading circuits by connecting too many appliances to a single outlet can lead to overheating and electrical fires. Distribute electrical loads evenly across multiple outlets and circuits to prevent overload.
Regular Maintenance of Electrical Systems
Regular maintenance, including inspection of wiring, panels, and appliances, can identify potential fire hazards before they escalate. Schedule professional inspections and address any issues promptly to ensure the safety of your electrical system.
Protection Against Arc Flashes
Arc flash hazard analysis.
Conducting an arc flash hazard analysis can help identify potential risks and develop appropriate safety measures. Assessing equipment, operating conditions, and protective measures is essential in mitigating the risk of arc flashes.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Workers exposed to arc flash hazards must wear appropriate PPE, including flame-resistant clothing, face shields, and insulated gloves. Providing and maintaining quality PPE is crucial in safeguarding employees against arc flash injuries.
Training and Awareness
Education and training are key components of arc flash prevention. Ensure workers understand the risks associated with arc flashes and are trained to recognize warning signs and respond appropriately in the event of an incident.
Safety Measures for Electrical Appliances
Checking for damage before use.
Inspect electrical appliances for damage or defects before each use. Frayed cords, loose plugs, and exposed wires pose significant safety hazards and should be repaired or replaced immediately.
Unplugging Appliances When Not in Use
When not in use, unplug electrical appliances to prevent them from consuming standby power and reduce the risk of electrical fires. This practice also extends the lifespan of appliances and reduces energy costs.
Using Appliances According to Manufacturer Instructions
Follow manufacturer instructions for proper use and maintenance of electrical appliances. Overlooking safety guidelines can compromise performance and increase the likelihood of accidents.
Safety Guidelines for Electrical Work
Hiring qualified electricians.
Electrical work should be performed by licensed and experienced professionals to ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations. Hiring qualified electricians minimizes the risk of electrical accidents and ensures work is done safely and effectively.
Following Safety Protocols and Standards
Adhering to established safety protocols and standards is essential when performing electrical work. This includes using appropriate tools and equipment, following lockout/tagout procedures, and implementing proper grounding techniques.
Using Insulated Tools and Equipment
Insulated tools and equipment protect workers from electrical shock and arc flash hazards by preventing direct contact with live electrical components. Inspect tools regularly and replace any damaged or worn-out items.
Safety in Wet or Damp Environments
Installing appropriate electrical outlets.
Install ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in areas where water is present, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor spaces. GFCIs help prevent electric shock by quickly cutting off power in the event of a ground fault.
Using Weatherproof Covers for Outdoor Outlets
Outdoor electrical outlets should be equipped with weatherproof covers to protect against moisture and debris. Regularly inspect covers for damage and replace them as needed to maintain safety.
Using Portable GFCIs in Wet Areas
When working in wet or damp environments, use portable GFCIs to provide additional protection against electric shock. These devices are easy to install and provide an extra layer of safety for workers.
Educating Children about Electrical Safety
Teaching basic safety rules.
Educate children about basic electrical safety rules, such as not playing with electrical outlets or cords and never touching electrical appliances with wet hands. Reinforce these rules through regular discussions and demonstrations.
Keeping Electrical Devices out of Reach
Store electrical devices, such as hairdryers, curling irons, and power tools, out of reach of young children to prevent accidents and injuries. Use outlet covers and cord organizers to minimize accessibility.
Supervising Children around Electrical Appliances
Supervise children closely when they are near electrical appliances or outlets, especially in potentially hazardous areas like kitchens and bathrooms. Teach children to respect electricity and avoid dangerous behaviors.
Emergency Preparedness
Creating an emergency plan.
Develop an emergency plan that includes procedures for responding to electrical emergencies, such as fires, shocks, or power outages. Ensure all family members are familiar with the plan and know how to evacuate safely if necessary.
Knowing How to Shut off Electricity
Identify the location of the main electrical panel and learn how to shut off electricity in the event of an emergency. Label circuit breakers or fuses clearly to facilitate quick and easy access during an emergency.
Having a First Aid Kit and Fire Extinguisher
Keep a well-stocked first aid kit and fire extinguisher in your home or workplace to deal with electrical emergencies effectively. Train family members or employees on how to use these lifesaving tools safely.
Workplace Electrical Safety
Osha regulations and compliance.
Employers must comply with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations to ensure a safe working environment for employees. OSHA standards cover various aspects of electrical safety, including equipment maintenance, training, and hazard communication.
Workplace Safety Training
Provide comprehensive training to employees on electrical safety practices, including hazard recognition, proper use of PPE, and emergency procedures. Regular training sessions and refresher courses help reinforce safety protocols and reduce the risk of workplace accidents.
Reporting and Addressing Hazards
Encourage employees to report electrical hazards promptly and take immediate action to address them. Conduct regular inspections and maintenance to identify and correct potential safety issues before they escalate into serious incidents.
Electrical Safety in Construction Sites
Risk assessment and planning.
Conduct a thorough risk assessment of construction sites to identify electrical hazards and develop appropriate safety measures. Implement a comprehensive safety plan that addresses equipment, procedures, and personnel training.
Proper Use of Temporary Power Systems
Temporary power systems used on construction sites should be installed and maintained according to safety standards and regulations. Avoid overloading circuits and ensure proper grounding to minimize the risk of electrical accidents.
Implementing Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Implement lockout/tagout procedures to control hazardous energy during construction activities. This involves isolating electrical sources, securing them with locks or tags, and verifying that they are de-energized before performing maintenance or repairs.
Electrical Safety in the Healthcare Industry
Safe use of medical devices.
Healthcare facilities must adhere to strict safety protocols when using medical devices powered by electricity. Regular maintenance and testing of equipment are essential to ensure reliability and patient safety.
Grounding and Isolation of Equipment
Proper grounding and isolation of electrical equipment are critical in healthcare settings to prevent electric shock and equipment malfunction. Implementing redundant safety measures and conducting regular inspections help mitigate the risk of electrical hazards.
Training Healthcare Staff on Electrical Safety
Provide comprehensive training to healthcare staff on electrical safety procedures, including proper use of medical devices, handling of electrical emergencies, and infection control measures. Regular drills and simulations help prepare staff for real-life scenarios.
The Role of Technology in Electrical Safety
Advancements in circuit protection devices.
Technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated circuit protection devices, such as arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs). These devices provide enhanced safety features and help prevent electrical fires and shocks.
Smart Home Technology for Monitoring Electrical Systems
Smart home technology enables homeowners to monitor and control their electrical systems remotely, reducing the risk of accidents and improving energy efficiency. Features such as real-time alerts and automated shut-off mechanisms enhance safety and convenience.
Remote Diagnostics and Maintenance
Remote diagnostics and maintenance capabilities allow electricians to identify and address electrical issues without being physically present on-site. This minimizes downtime, reduces costs, and improves overall system reliability.
Electrical safety is a shared responsibility that requires vigilance, knowledge, and proactive measures. By understanding the risks associated with electricity and implementing appropriate safety measures, individuals and organizations can prevent accidents, protect lives, and safeguard property. Remember, when it comes to electrical safety, it’s better to be safe than sorry.
Electrical Grounding: Unraveling the Importance and Essential Techniques
Electrical Cord Management: Safeguarding Against Overloading and Tripping Hazards
Electrical Cord Safety: Inspection and Replacement Guidelines
Electrical Safety: Hazards and GFCI Purpose
Electrical Safety for Non-Electricians: Building Basic Awareness and Precautions
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are the most common causes of electrical fires?
- Electrical fires are often caused by faulty wiring, overloaded circuits, and malfunctioning appliances.
2. How can I protect my home from electrical hazards?
- Inspect electrical cords and outlets regularly, use GFCIs in wet areas, and avoid overloading circuits to minimize the risk of electrical accidents.
3. Why is it important to hire qualified electricians for electrical work?
- Qualified electricians have the training and expertise to perform electrical work safely and effectively, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring compliance with regulations.
4. What should I do in case of an electrical emergency?
- In case of an electrical emergency, such as a fire or electric shock, evacuate the area immediately and call emergency services. If safe to do so, shut off electricity at the main panel.
5. How often should I test my smoke alarms and GFCIs?
- Test smoke alarms and GFCIs monthly to ensure they are functioning correctly. Replace batteries in smoke alarms and test GFCIs by pressing the “test” button regularly.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
National electrical safety month, 6 golden rules of electrical safety, 20 electrical safety rules, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Popular Posts
Top 15 best safety slogan in hindi, easy nebosh igc exam questions and answers, hse engineer job vacancy : urgent requirement, 25 safety officer interview questions (with sample answers), top 25 best hindi safety slogan in 2024, 10 essential safety officer tips every workplace needs to know, industrial safety, safety officer & safety engineer, work at height | hazards | control measures, very important slip trip and fall hazards, personal fall arrest system, latest post, how to become a safety officer in 3 steps, hse/safety engineer (kwd 1125) and hse/safety officer (kwd 600) urgent recruitment..., why safety officers could go to jail, which safety officer course is best, 80 safety officer/supervisor and 35 work permit receiver urgently required for..., (nebosh) the national examination board in occupational safety and health, 03 safety officer jobs vacancy in saudi arabia: oil and gas..., 03 safety officer urgently required for saudi arabia: online interview, 05 hse officers urgently required in saudi arabia, 06 safety officer and safety engineer urgently required for oil and....

Electrical safety in the 21st century
It isn’t breaking news that electrical professionals face potential hazards every day. While safety is constantly top of mind, the industry puts the spotlight on it every May to increase public awareness and reinforce its importance to electrical professionals.
Organizations like the International Association of Electrical Inspectors (IAEI) have made it their mission over the last century to educate and inform those in the electrical field on the best safety practices so they can keep themselves and the general public safe from the hazards of the electricity that powers our lives.
What do the numbers say about how the industry is doing regarding safety? Let’s take a look at the reality of the situation.
The Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) has compiled statistics on electrical fatalities and injuries for the years 2003–2017. The construction industry is by far the most exposed to electrical fatalities with 54 percent of all electrical deaths occurring in that industry.
The organization reported the most fatalities took place in 2004 (254)with the lowest recorded in 2015 (134). Things seem to have swung in a positive direction by the end of the reporting period with ESFI documenting an 11 percent drop in fatal electrical injuries between 2016 and 2017, charting 136 fatalities in 2017. It was noted that 5 percent of electrical injuries in 2017 were fatal.
Of the electrical fatalities during 2010, 98 percent died of electrocution; 63 percent were constructing, repairing, or cleaning something at the time of death; 34 percent died on industrial premises, 28 percent at a private residence, and nearly 12 percent on a street or highway, according to ESFI.
As for injuries, they topped out in 2005 with 2,950 injuries recorded and saw a low of 1,640 injuries in 2016. However, the organization found a 35 percent increase in electrical injuries between 2016 and 2017, with 2,210 charted.
“A total of 42,882 occupational fatalities occurred [years 2003–2010] from all causes, and 1,738 of those were due to contact with electric current,” according to ESFI.org. “The construction industry had the highest number of electrical fatalities [849] …. Just five occupations in the construction trades—electricians, construction laborers, roofers, painters, and carpenters—experienced more than 32 percent of all electrical fatalities [with] electrical power line installers and repairers about 8 percent, and tree trimmers about 5 percent.”
Safety trends and training
Safety is becoming more important for all industries, and this trend is leading the way for improvements in every working environment.
“There is a heightened awareness that a safe workplace is important to all workers, and workplaces, roles, and associated hazards vary for electrical workers,” said Donny Cook, chief electrical inspector for Shelby County, Alabama.
The goal of any safety program is always to reduce incidents, and in 2019, trainers are seeing the fruits of their labors.
“As safety awareness has continued to increase, the number of incidents has decreased,” said Dave Scheuerman, technical training manager for Littelfuse, Inc., who specializes in arc-flash training. “We have noticed that there is more of an emphasis on conducting arc-flash assessments, and as a result, [organizations have] an increase in knowledge of which equipment is dangerous within their facility. That being said, there are still many facilities that have not yet conducted an arc-flash hazard assessment in the last few years, or at all.”
During a 2019 arc-flash safety web training, a poll question asked participants how long it had been since an arc-flash analysis was done in their facility. Of those responding, 34.5 percent answered “never.” Scheuerman pointed out that the latest edition of NFPA 70E, Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace, requires these studies at least every five years.
“So, our efforts continue to make users more aware of the potential dangers. With such information, facilities will be able to make more educated decisions on how to improve their electrical safety and react better to electrical safety concerns,” Scheuerman said.
NFPA 70E details “requirements for safe work practices to protect personnel by reducing exposure to major electrical hazards. Originally developed at OSHA’s request, NFPA 70E helps companies and employees avoid workplace injuries and fatalities due to shock, electrocution, arc-flash, and arc-blast, and assists in complying with OSHA 1910 Subpart S and OSHA 1926 Subpart K,” according to NFPA.org.
Many safety trainers are focusing on NFPA 70E training. Cook said the IAEI Central Alabama Division hosted an eight-hour NFPA 70E training program in February. Scheuerman said his organization is focusing on it too.
“Much of our current safety training efforts involve the utilization of the NFPA 70E Hierarchy of Controls …. The five levels shown in the pyramid [elimination, substitution, engineering controls, administrative controls, and PPE] provide users with important guidance on how best to protect their workers and themselves,” Scheuerman said. “Everyone is trying to mitigate risks and increase safety. Now that NFPA 70E has introduced the Hierarchy of Control pyramid, it is all about getting to the top of the pyramid and removing the hazard.”
The future of training
Over the last few years, Cook said he has noticed training being offered outside of the industrial environment with general training readily available and needed, and specific training in many areas of the industry in high demand.
“I will be working with industry to develop more focused and specific training for various tasks associated with different jobs,” Cook said. “It is necessary to raise awareness for all electrical industry professionals, and then provide specific training based on normal work tasks. When limited training is developed, industry must make it clear the limitations of that specific training.”
Scheuerman and his team will continue educating on the dangers of arc-flashes. He said the National Electric Code (NEC) does not require arc-flash relays in all low-voltage applications—only in 1,200 amperes and above.
“It is critical to continue educating users on the potential dangers of shock, arc-flash, and arc-blast hazards, and some of the effective methods to mitigate accordingly,” Scheuerman said. “If more people are aware of their dangers, then more people will be likely to incorporate adequate protection. Ideally, they will seek prevention above protection.”
Future training may be shocking (pun intended). While most education for the last two decades has focused on arc-flashes, electric shock is more common but less talked about.
“There are four times more shock incidents than arc-flash incidents,” Scheuerman said. “So, in the next couple of years, we expect there to be a deeper discussion on how to prevent shock hazards from occurring. Some of these changes will be in the form of new products and technologies, but much of it will again come back to training and education of the workers and other users. Proper prevention will make us all safer from the hazards that can be so damaging, let alone deadly.”
With many cities and states in North America going green, solar and wind safety training will also take center stage. These alternative energy systems use direct current (DC) systems instead of alternating current (AC), but most existing standards only cover AC systems.
“Industry-wide efforts are already underway to develop similar guidelines for DC—efforts that will likely quicken as the trends toward the use of alternative energy continues to grow globally,” Scheuerman said. “Another change we have seen includes all solar rooftop installations are required to have rapid shutdown systems for first responders to reduce shock hazards according to NEC 690.12. These regulations get tighter and stricter as time goes forward.”
Are you wearing protection?
Everyone in the electrical industry is familiar with personal protective equipment (PPE)—also known as wearables.
“In the safety world, ‘wearables’ can include ‘smart’ personal protective equipment, glasses with heads-up displays, and hard hats with sensors. What most of these devices have in common is they give safety professionals and other employees a set of watchful eyes to help ensure the health and well-being of the workforce, particularly lone workers,” reported Safety + Health magazine in February 2019. “To some workers, however, these watchful eyes may be perceived as prying eyes. That’s why experts say it’s important to lay down the groundwork and gain the trust of employees before turning to these new-wave devices.”
While PPE is a last line of defense against safety hazards, safety experts will tell you that it shouldn’t be the only defense.
“It’s critical to understand that, although you’re on a good path, you still may be only halfway there. It’s also important to make sure your workforce understands that they’re still not ready to work on or near live electrical equipment until they don other important PPE to protect their head and face, as well as rubber electrical gloves and leather protectors to protect against shock,” said Mike Enright in Occupational Health & Safety in March 2019.
While relying on PPE has been the norm for many years, a new trend of designing-in safety is emerging in the electrical industry. Scheuerman told participants in a web training that “simply relying on PPE to protect workers is, in reality, the least effective means of mitigating arc-flash hazards.”
The wear and tear on PPE can also become quite costly for companies.
“The cost of equipment can add up,” Richard Dale, associate product manager industrial business unit for Littelfuse, Inc. told a web training class. “You’ll need to replace [suits] more often. Gloves can cost up to $70 per pair and need to be replaced every 6 months.”
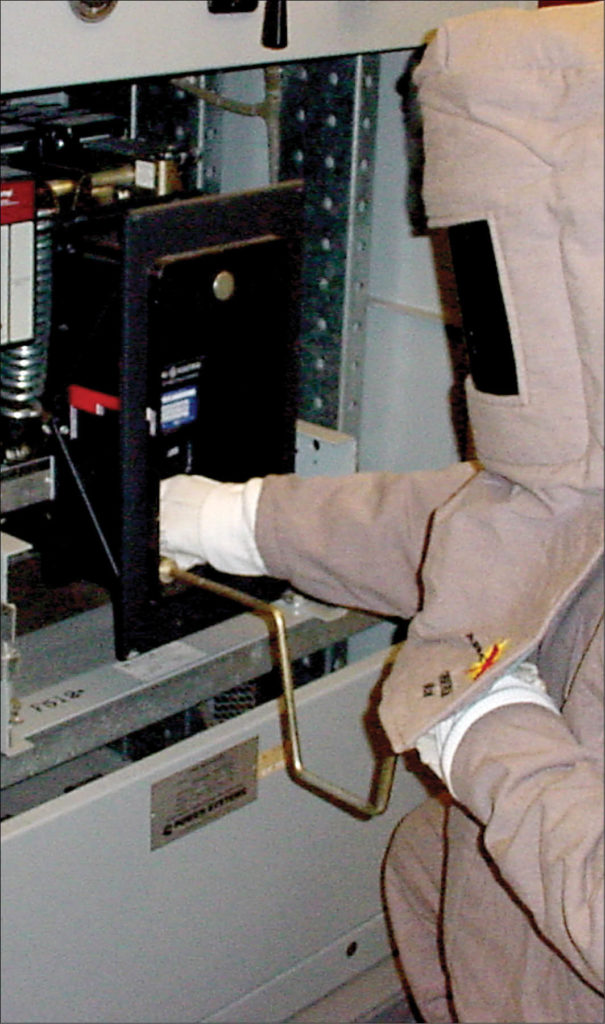

Assess your safety habits
Here are a few questions to ask when assessing electrical safety within the workplace:
- Is there justification for working on the equipment while energized? If yes, does the installer or inspector wear the proper personal protective equipment (PPE) while performing that task?
- Is the level of PPE equipment to be worn understood by the installer/inspector?
- Does the employer know that installers or inspectors work on equipment while it is energized? Does the employer understand OSHA regulations about working on energized equipment?
- Are panelboard covers removed when the panelboard is energized? If yes, is PPE worn while performing that task?
- Do the electrical workers know the difference between a curable burn and a burn that is not curable?
- Does the worker understand the definition of the term “qualified person” in Article 100 of NFPA 70E or CSA Z462? Are they considered a “qualified person,” and do they know the limits of their qualifications?
A good indication that more training is needed is if all or most of the answers to these questions are no. Several organizations provide information and safety training in these areas (including IAEI). In addition to education and training, organizational and individual awareness of hazards and the protective measures needed to avoid the risks are also important. It is imperative that electrical workers understand the necessity of respecting the power and danger of electricity.
Technology for safety
Technology is changing the way we live our lives, and even how we get our electricity. There are many devices being developed every day to help electrical professionals stay safe while doing their jobs. A trend in the industry is reducing the arc-flash risk or eliminate it altogether. One option on the market is Bluetooth-enabled overload relays.
“[These relays feature] ethernet capabilities that allow users to communicate with it directly using their smartphone or tablet,” Scheuerman said. “For example, users can see real-time voltage or current and recent fault information without having to be right at the panel. They can be on the floor monitoring how a motor is operating, instead of having to be across the room at the control panel retrieving data. This is a considerable advancement for safety as it prevents people from having to open the panels unnecessarily.”
Opening panel doors can significantly increase the chances of an operator being exposed to a potential arc-flash hazard. “The ability to check settings from the safety of a smartphone or tablet means that workers no longer have to go on-site and put themselves at risk by opening the cabinet doors, unless it is necessary and, preferably, de-energized,” Scheuerman said.
Other devices on the market for utilities are develop by LIneVision. The company—a spinoff of Genscape and founded in May 2018—provides non-contact monitoring of transmission lines with more than 5,000 lines being monitored worldwide. The real-time transmission line monitoring company uses advanced sensors and analytics to improve capacity, reliability, and safety of lines.
“One of the things we do is unlock additional capacity on existing transmission lines. The way we do that is by monitoring the back of the lines,” said LineVision CEO Hudson Gilmer. “By monitoring it, we can unlock 15 to 40 percent of additional capacity on existing lines. The way we do this is through non-contact sensors on towers.”
Gilmer said this is safer for electrical professionals because no live line work is involved. This system allows continuous monitoring of the transmission lines and detects clearance violations [lines that are sagging too low], storm damage, and ice on lines.
“All this is done remotely without having to send crews out to do inspections,” Gilmer said. “This [product] is extending that situational awareness to the back of the grid, the high voltage transmission lines.”
The technology allows utilities to do condition-based asset health monitoring, predict the remaining asset life of a conductor, and help utilities predict repair and replacement of lines.
“In 5 to 10 years, every transmission line should be monitored,” Gilmer said. “We’re building a business to keep driving down the costs of these systems. We really want to help utilities get the benefits of monitoring on all their lines.”
Safety first is always a good idea, but especially so in the electrical industry. The job you do as an electrical professional is so essential to the business of everyday life. When you are safe, you ensure the safety of everyone who uses electricity.

Air-Conditioning Equipment Installations

Basic three-phase power measurements explained

Safety in Marinas

Find Us on Socials
Electrically safe work practices — nfpa 70e basics.
Pre-Wired and Modular systems can save substantial time and money over traditional hard-wired methods.
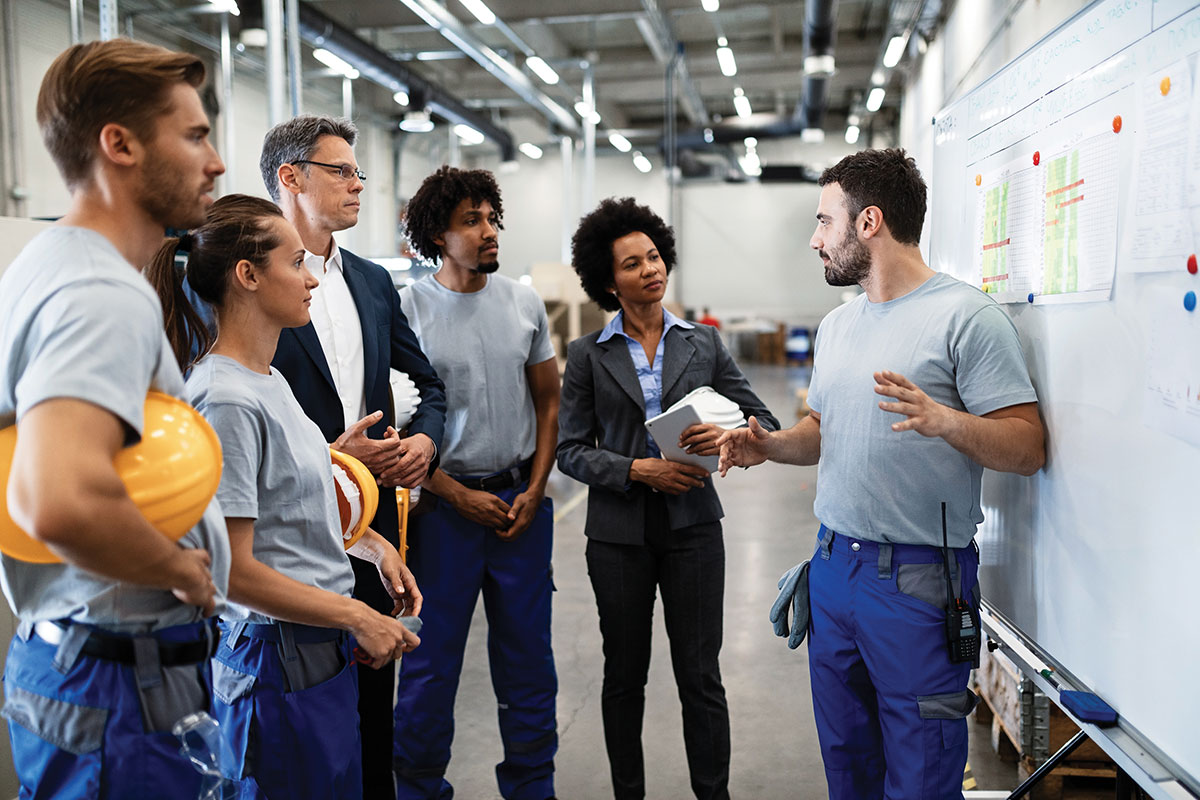

Workforce Development and its Role in Electrical Safety
A change in overall workforce development will occur when more states make programs like these a requirement of licensure within their state.
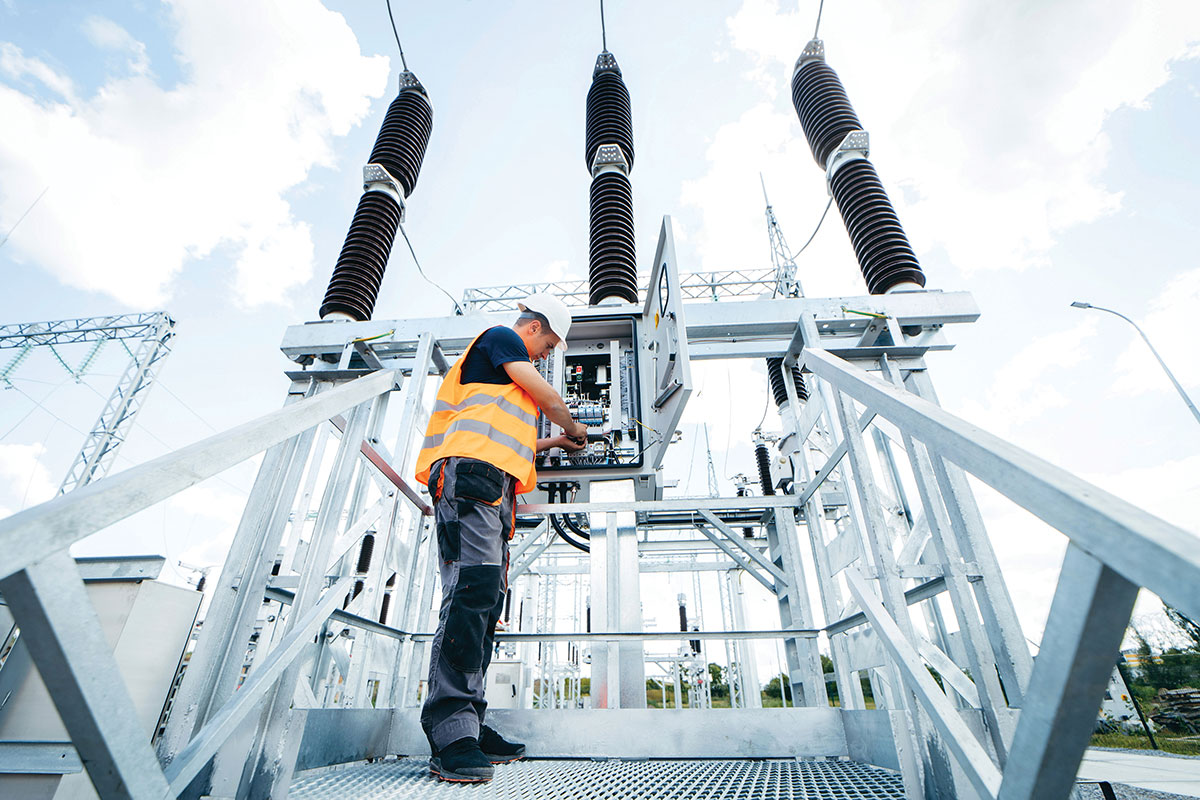

EFCOG Best Practice #240 — Electrical Utility Risk Assessment
Electrical utility tasks involve high hazard activities where the risk is often undefined. This DOE best practice can be used as a guide for other type of projects.
- Motor Efficiency Calculator

- 209.527.2800

- The Importance Of Electrical Safety

An industrial building requires a lot of power for machinery, tools and systems. Since electricity is common in industrial work, it’s easy to forget the potential dangers of using it.
Keeping your workers safe when working with electricity is crucial, so it pays to stay up to date on electrical safety equipment and practices.
Why Electrical Safety Is Important
Electrical safety matters because electricity is powerful and potentially harmful. Mishandled electricity can cause serious injury or death, so keeping electricians safe at work requires use of the proper techniques.
Make sure your employees have electrical safety training. This knowledge enables workers to make smart decisions when working with electricity. Training also prevents incident-related costs for your business.
It’s an employer’s responsibility to train their workers. If insufficient training causes an accident, the employer could be held accountable, so be sure your workers are familiar with these key electrical safety tips for industrial work:
- Exercise caution: Always use caution when working with electrical gear. Assume that you’re working with live, energized wires and act accordingly.
- Check for electrical current: Before touching a wire or metal surface, use a multimeter to see if it has an electrical current.
- Secure electrical cords: Tape extension cords around the work site to the floor or wall — hanging cords can fall and hurt someone, and laying them loosely can be a tripping hazard.
- Be mindful of conductive materials: Know which materials are conductive and don’t use them around high-voltage equipment.
- Inspect cords and electrical connections: Regularly examine cords and connections like outlets and plugs for signs of wear and damage. If you find issues, replace the component immediately.
- Wear personal protective equipment (PPE): Wear PPE like safety glasses, insulated gloves and a hard hat when using electrical items.
IRISS Thermo Clip™ Series
How can you stay safe during electrical work.
Another way you can stay safe during electrical work is using a Thermo Clip™ from IRISS. This tool is a visual over-temperature indicator that identifies overheated wires entering or exiting a power source or power control device.
The clips attach to any wire size from 17 AWG to 750 MCM and circuits rated 36 kVAC (600 VDC). The clip has patented thermochromic technology that will change its color if the wire’s heat exceeds its thermal rating.
The Thermo Clip™ easily identifies problems and helps you correct issues early. These cost-effective, easy-to-use clips prevent equipment failure, downtime and injury.
- IRISS Thermo Clip™ Series Specifications & Additional Information

Get Electrical Safety Training and Equipment From Industrial Electrical Company
Industrial Electrical Company (IEC) offers industrial training services for electrical workers in the Central Valley of California and western Nevada. We provide industry-standard electrical safety and compliance training on-site, off-site and online. IEC is also proud to sell the Thermo Clip™ Series and other products from IRISS .
Order today to put the IRISS Thermo Clip™ to work in your facility or contact us to start electrical training for your team.

Get in Touch With Our Experts
Our motor shop is located right in the Central Valley and can complete any job from total welding services to custom modifications. To learn more about our services, classes and products, contact us online today.
- Network Sites:
- Technical Articles
- Market Insights

- Or sign in with
- iHeartRadio

- The Importance of Electrical Safety
Join our Engineering Community! Sign-in with:
- Direct Current (DC)
Electrical Safety
- Physiological Effects of Electricity
- Shock Current Path
- Ohm’s Law (again!)
- Safe Practices
- Emergency Response
- Common Sources of Hazard
- Safe Circuit Design
- Safe Meter Usage
- Electric Shock Data
With this lesson, I hope to avoid a common mistake found in electronics textbooks of either ignoring or not covering with sufficient detail the subject of electrical safety. I assume that whoever reads this book has at least a passing interest in actually working with electricity, and as such the topic of safety is of paramount importance. Those authors, editors, and publishers who fail to incorporate this subject into their introductory texts are depriving the reader of life-saving information.
As an instructor of industrial electronics, I spend a full week with my students reviewing the theoretical and practical aspects of safe work practices. The same textbooks I found lacking in technical clarity, I also found lacking in coverage of electrical safety. Hence, the creation of this chapter. Its placement after the first two chapters is intentional: in order for the concepts of electrical safety to make the most sense, some foundational knowledge of electricity is necessary.
Another benefit of including a detailed lesson on electrical safety is the practical context it sets for basic concepts of voltage, current, resistance , and circuit design. The more relevant a technical topic can be made, the more likely a student will be to pay attention and comprehend. And what could be more relevant than application to your own personal safety? Also, with electrical power being such an everyday presence in modern life, almost anyone can relate to the illustrations given in such a lesson. Have you ever wondered why birds don’t get shocked while resting on power lines? Read on and find out!
RELATED WORKSHEET:
- Voltage, Current, and Resistance Worksheet
- Back to Index
- Textbook Index
Lessons in Electric Circuits
Volumes », chapters ».
- 1 Basic Concepts Of Electricity
- 2 Ohm's Law
Pages »
- 4 Scientific Notation And Metric Prefixes
- 5 Series And Parallel Circuits
- 6 Divider Circuits And Kirchhoff's Laws
- 7 Series-parallel Combination Circuits
- 8 DC Metering Circuits
- 9 Electrical Instrumentation Signals
- 10 DC Network Analysis
- 11 Batteries And Power Systems
- 12 Physics Of Conductors And Insulators
- 13 Capacitors
- 14 Magnetism and Electromagnetism
- 15 Inductors
- 16 RC and L/R Time Constants
- 17 Contributor List
- Alternating Current (AC)
- Semiconductors
- Digital Circuits
- EE Reference
- DIY Electronics Projects
- Advanced Textbooks Practical Guide to Radio-Frequency Analysis and Design
- Designing Analog Chips
Related Content
- The Importance of the ISO 26262 Automotive Safety Standard: New Sensors from ams
- Schneider Electric Safety Modules | Tech Chat
- The Importance of Complex Conjugates
- The Importance of Usability When Designing Hardware: Lessons Learned from Developing ProtoBricks
- New Transceivers Illustrate the Importance of Electrical Fast Transient (EFT) Immunity
- Looking for Good Waves: The Importance of Signal Integrity in High-Speed PCB Design
You May Also Like

A Quick Guide to the EV Charging Business
In Partnership with Future Electronics

Frequency Response of the MOSFET Common-Source Amplifier
by Nicholas St. John

Simulating the Short-Circuit Power Dissipation of a CMOS Inverter
by Robert Keim

Solutions Guide to Temperature Sensing

Arm Unveils ‘Best Generation of Neoverse Technology Yet’
by Jake Hertz

Welcome Back
Don't have an AAC account? Create one now .
Forgot your password? Click here .

1-866-777-1360 M-F 6am - 4pm PST Mon-Fri, 06:00 - 16:00 (UTC-8)
Get Catalog | Get Free Samples
Why is electrical safety important?
Other Questions/Answers
- Agricultural Labeling (43)
- Ammonia Pipe Marking (15)
- Arc Flash (22)
- Barcoding (36)
- Continuous Improvement (16)
- Crane Safety (21)
- Electrical Safety (63)
- Emergency Evacuation (27)
- Equipment Labeling (5)
- Facility Efficiency (23)
- Facility Marking (8)
- Fire Safety (37)
- Floor Marking (33)
- Forklift Safety (24)
- Hazcom (50)
- Healthcare (26)
- Kaizen (33)
- Kanban (24)
- Labeling (5)
- Lean Manufacturing (86)
- Lockout Tagout (22)
- Military Equipment (4)
- Mining Safety (8)
- Organized Workplace (13)
- Pharmaceutical Labeling (30)
- Pipe Marking (32)
- Rack Labeling (11)
- Regulations & Compliance (33)
- Safety Signs (32)
- Six Sigma (48)
- Social Distancing (81)
- Solar Panel Labeling (5)
- Spill Cleanup (18)
- Tool Organization (25)
- Transportation (36)
- Valve Tag (19)
- Wire Marking (36)
- Workplace Safety (81)

Workplace safety is something that every company needs to make a top priority. There are many types of hazards that exist, and in general they are all just covered under the generic topic of workplace safety. Interestingly, electrical safety is often addressed separately by many businesses. Some people wonder why electrical safety is so important, and why it gets so much attention. There are many statistics and facts that can provide some insights into what makes electrical safety stand out when it comes to the efforts that are made to improve safety.
Electrical Safety Facts
The following are some interesting, and often unsettling, facts about electrical safety in the workplace .
- High Incident Rates – In a survey 97% of professional electricians have reported that they have been shocked or otherwise injured while on the job. While most of these were minor shocks, this illustrates just how often they take place.
- Workplace Fatalities – Electrocutions ranks as the fourth most common cause of workplace deaths.
- Disabling Injuries – Electrocutions are also responsible for a large number of employees becoming disabled each year. On average 3600 people are disabled in this way each year.
- Medical Costs – The medical costs related to a serious electrical burn can be over $4 million and take many years.
- Total Costs – Medical costs aren’t the only expense associated with electricity related incidents. These incidents can cause fires, damage to equipment, and more. In just one year, electric incidents cost $14.6 billion to American facilities.
Electrical Safety is Unique
As you can see from the statistics above, electrical safety a priority in the workplace is very important. In addition, hazards related to electricity are often quite different than other types of workplace dangers. Finally, electrical hazards are not something that the average person has much experience with, which is why it is critical that they are given at least basic electrical safety training so they know how to avoid accidents or injuries. While it is true that all workplace safety is important, electrical safety needs to be treated differently to ensure the safety of everyone in the facility.
Similar Questions
- Why is Electrical Panel Labeling Important?
- What electrical safety training should I provide?
- What are the basics of electrical safety?
- What are electrical safety measures?
- What are electrical safety risks in the office?
- What are electrical safety audits?
- How often should electrical safety training be offered?
- How does electrical shock occur and how can it be prevented?
- How can visual communication improve electrical safety?
Additional Resources
- Arc Flash and Electrical Safety
- Improving Workplace Electrical Safety
- 10 Essential Steps for Electrical Safety
- OSHA Facts [Updated Statistics 2019]
- Electrical Wire Colors
View all Electrical Safety Q&A
Free E-Book
Wire Marking
Learn how to manage wires and cables to improve electrical safety.
Download now ›
Electrical Panel Labeling
- 10 Steps for Electrical Safety
- Electrical Safety Signs
- What is an Electric Arc?
- NFPA 70E: Standard for Electrical Safety
- National Electrical Code (NEC)
- Electrical Safety Products
- Electrical Safety Questions and Answers
- What Levels of Voltage are Lethal?
- More Electrical Safety Resources
Helpful Resources
Oops, something went wrong. Please try again.
You are now logged in!
- SUBCONTRACTORS
- Subcontractors
- Electrical Safety in the News
- What Is Electrical Work?
- Electrical Safety Program
- Electrical Safety Principles
- What is “Exposed”?
- What is a QEW?
- Qualified Electrical Worker (QEW)
- Field Guides
- Emergency Response
- How to Obtain LOTO Supplies
- Request LOTO Tags
- Request LOTO Assistance
- Sign Up for Training
- Lockout / Tagout Program – Pub 3000, Ch 18
- Cord and Plug
- LOTO Procedure Inspection (Quickbase)
- Absent Person LOTO Lock Removal Form
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedure Template
- Request Repair Assistance
- Request Inspections
- Request Labels (Surveyors)
- For Surveyors
- For Inspectors
- ESO/ESA Training
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Presentations
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedure Database User Guide
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Permit Database User Guide
- EESP Inspection Database User Guide
- Reference Standards
- Lessons Learned
- Electrical Safety Articles
- Safety Alerts
- Electrical AHJ Delegation Letters
- Electrical Safety Committee
- Distribution System Status
Electricity behaves the same no matter what country you are in. It doesn’t matter whether you are in the Americas or Europe, Asia or Africa. It also doesn’t matter whether you are an electrician, a researcher, an engineer, or even an office worker who performs occasional household repairs. If you make contact with a hazardous live circuit part, your life will be at risk. In this sense, mere compliance to local national regulations matters less than understanding basic electrical safety principles. This page in particular is intentionally written without any regulatory or compliance language.
Principle 1: Work only on dead equipment whenever possible
Working on live electrical equipment can be extremely hazardous. Most installations and repairs can and should be performed dead, not live. This is a changed expectation that grew out of a recognition that too many workers were getting killed or seriously hurt by working on or near live electrical equipment. It used to be a job expectation for electricians to perform live installations and repairs. Not anymore! We have learned, the hard way, that taking the time to properly shut down equipment in order to work dead not only saves lives, but also time and money in the long run. Employers who ask their employees to make live repairs often do not understand the risk involved to their people or to their business. Working live should only be done as a last resort and where working dead in not possible, such as for some types of testing and troubleshooting.
Principle 2: Lock it out to prevent reenergization
A fundamental aspect of working dead, along with Principle #3, is to control the sources of hazardous energy. Without proper control, the equipment could be inadvertently reenergized while people are working on it. This could be devastating. A fundamental best practice in electrical safety is to padlock the isolation switch or breaker to maintain the isolation throughout the entire duration of work. This process is called Lockout, or Lockout/Tagout (LOTO).
Many countries and employers have highly developed Control of Hazardous Energy programs that define when and how to lock out equipment. A solid lockout policy will require individual locks for each employee and written lockout procedures when more than one isolation point is required. Each individual is responsible for locking out and protecting their own life. Conversely, an employer is also responsible for implementing an effective lockout policy.
Principle 3: Test it before you touch
Hazardous voltage cannot be detected by a human sense before it is too late. Do not rely on the noise going away, or the lights going off. It could still be live. Do not rely on your own knowledge either. Most people who get a shock are surprised: they were 100% convinced that the circuit was dead. However, they didn’t perform a test to verify.
A proper test for absence of voltage, sometimes called a Zero Voltage Verification (ZVV), is always conducted with a contact multimeter or similar voltage tester. In order to verify the meter is in proper working order, the meter must be checked on a known live source BEFORE AND AFTER the zero voltage measurement. This is called the LIVE-DEAD-LIVE procedure. Remember, even a bad meter can read zero voltage, so you have to prove your meter is working.
Principle 4: Ensure you have the proper qualifications
Electrical safety requires a fairly solid technical understanding. Various countries and local administrations define qualified in different manners. This could be licensing, completion of an apprenticeship, formal education, on the job training, or a combination of all of these. Ultimately, one thing matters: are you competent enough to work on the system to recognize the hazards? Do you know which parts are/could be live, and to what voltage? Can you recognize when things are wrong? Can you follow a circuit diagram to help in your troubleshooting efforts? Do you know how to properly select the right tools and personal protective equipment (PPE) necessary for the task? Finally, do you have the hands-on experience and body positioning techniques to keep you safe?
A properly qualified person should be able to reply YES to these questions, and be comfortable doing so. Conversely, every qualified person should also be aware of their own limitations. Nobody knows everything, and sometimes we need to seek out assistance from someone with a different skill set or level of knowledge.
What’s missing? What about PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)?
Wearing proper PPE is of course necessary when working on equipment that is or could potentially be energized. This can include shock protection and/or arc flash protection. However, PPE is the LAST line of defense. It is never acceptable to just put people into PPE and sent them to work. PPE will instead be specified after a proper analysis of the job scope and of the hazards involved. A good risk assessment will identify ways to eliminate or reduce risk such that PPE is not always necessary.
- What is “Hazardous”?
- What is “Exposed”?
- What to Look for During a Walk-through
- AHJ Approval Process for QEWs
- QEW Electrical Safety Training
- How to Obtain Electrical PPE/Tools
- AED Location Map
- Electrical Injury Emergency Response
A U.S. Department of Energy National Laboratory Managed by the University of California
Questions & Comments Privacy & Security Notice
- google plus
Solutions for
Educator & Staff Training
Improve compliance and deliver critical professional development with online courses and management system
Safety & Compliance
Inclusive Instruction & Interventions
Diversity & Inclusion
School Bus Driver
Cybersecurity Awareness
Facilities Maintenance
Child Sexual Abuse Prevention
Student Safety & Wellness Program NEW
Student Safety & Wellness Program
Keep students safe and healthy with safety, well-being, and social and emotional learning courses and lessons
Substance Misuse Prevention Courses
Mental Health & Well-Being Courses
Healthy Relationships Courses
Personal & Community Safety Courses
Career Readiness & Life Skills NEW
Professional Growth Management
Integrated software to manage and track evaluations and professional development and deliver online training
Professional Development Management
Evaluations Management
Anonymous Reporting & Safety Communications
Empower your school community to ask for help to improve school safety and prevent crises before they occur
Incident & EHS Management
Streamline safety incident reporting and management to improve safety, reduce risk, and increase compliance
Career & Technical Education NEW
Career and Technical Education Solutions
Maximize Student Outcomes with Our All-in-One Work-Based Learning Platform and CTE Courses.
Vector Pathways NEW
CTE Training Courses NEW
Higher Education
Student Training
Increase safety, well-being, and belonging with proven-effective training on critical prevention topics
Sexual Assault Prevention
Alcohol & Drug Misuse Prevention
Diversity, Inclusion, & Belonging
Wellness & Safety
Career & Personal Development NEW
Fraternity & Sorority Life
Faculty & Staff Training
Create a safe, healthy, and welcoming campus environment and improve compliance with online training courses
Harassment, Discrimination, & Sexual Assault Prevention
IT & Campus Security
Health & Safety
Human Resources & Workforce Management
Environmental Health & Facilities Management
Campus Climate Surveys
Simplify VAWA compliance with easy, scalable survey deployment, tracking, and reporting
Empower your faculty, staff, and students to take an active role in protecting themselves and others
Manufacturing
Safety Training NEW
Safety Training
Elevate performance and productivity while reducing risk across your entire organization with online training.
MSHA Training
Industrial Skills Training NEW
Industrial Skills Training
Close skills gap, maximize production, and drive consistency with online training
Core Industrial Skills
Preventive Maintenance
Electrical Maintenance
Continuous Improvement
Power Generation
Paper Manufacturing Training
Enhance worker expertise and problem-solving skills while ensuring optimal production efficiency.
HR & Compliance
Provide role-specific knowledge, develop skills, and improve employee retention with career development training.
Professional Development NEW
DEI Training NEW
Anti Harassment Training NEW
Learning Management System (LMS)
Assign, track, and report role-based skills and compliance training for the entire workforce
Competency Assessments NEW
Learning Paths NEW
EHS Management
Track, Analyze, Report Health and Safety Activities and Data for the Industrial Workforce
Incident Management
Inspections & Audits
Real-TIme Safety Metrics and Reports
Behavior-Based Safety
Hazard Reporting
Job Safety Analysis
SDS & Chemical Management
Safety Communication
Enhance the safety for the industrial workforce with two-way risk communications, tools, and resources
Fire Departments
Training Management
A training management system tailored for the fire service--track all training, EMS recerts, skill evaluations, ISO, and more in one place
Training Management System
Skill Evaluations
Firefighter Continuing Education
Online EMS Recertification Training
Fire Academy Automation
Fire Standards and Training
Crew Shift Scheduling
Simplify 24/7 staffing and give firefighters the convenience of accepting callbacks and shifts from a mobile device
Checks & Inventory Management
Streamline truck checks, PPE inspections, controlled substance tracking, and equipment maintenance with a convenient mobile app
Controlled Substance Tracking
Exposure and Critical Incident Monitoring NEW
Exposure and Critical Incident Monitoring
Document exposures and critical incidents and protect your personnels’ mental and physical wellness
Training Management and Recertification
A training management system tailored for EMS services—EMS online courses for recerts, mobile-enabled skill evaluations, and more
EMS Skill Evaluations
EMS Shift Scheduling
Simplify 24/7 staffing and give medics the convenience of managing their schedules from a mobile device
Inventory Management
Streamline vehicle checks, controlled substance tracking, and equipment maintenance with a convenient mobile app
Wellness Monitoring & Exposure Tracking NEW
Wellness Monitoring & Exposure Tracking
Law Enforcement
Training and FTO Management
Increase performance, reduce risk, and ensure compliance with a training management system tailored for your FTO/PTO and in-service training
Training Management System & FTO
Law Enforcement Online Training
Academy Automation
POST and Regulatory Management
Early Intervention & Performance Management
Equip leaders with a tool for performance management and early intervention that helps build positive agency culture
Officer Shift Scheduling
Simplify 24/7 staffing and give officers the convenience of managing their schedules from a mobile device
Asset Mangagement & Inspections
Streamline equipment checks and vehicle maintenance to ensure everything is working correctly and serviced regularly
Energy Skills Training
Empower your team with skills and safety training to ensure compliance and continuous advancement.
Track, analyze, report health and safety activities and data for the industrial workforce
Lone Worker Safety
Enhance lone worker safety with two way risk communications, tools, and resources
Federal Training Management
Lower training costs and increase readiness with a unified system designed for high-risk, complex training and compliance operations.
Military Training Management
Increase mission-readiness and operational efficiency with a unified system that optimizes military training and certification operations.
Local Government Training Management
Technology to train, prepare, and retain your people
Fire Marshall Training & Compliance
Improve fire service certification and renewal operations to ensure compliance and a get a comprehensive single source of truth.
Elevate fire academy training with automation software, enhancing efficiency and compliance.
POST Training & Compliance
Streamline your training and standards operations to ensure compliance and put an end to siloed data.
Law Enforcement Academy Automation
Modernize law enforcement training with automation software that optimizing processes and centralizes academy information in one system.
Simplify incident reporting to OSHA and reduce risk with detailed investigation management.
Architecture, Engineering & Construction
Ensure licensed professionals receive compliance and CE training via online courses and learning management.
Online Continuing Education
Keep AEC staff licensed in all 50 states for 100+ certifications with online training
Architecture
Engineering
Construction
Project Management
Drive organizational success with training that grows skills and aligns with the latest codes and standards
Heath & Safety
Construction and Trades
Track, Analyze, Report Health and Safety Activities and Data for AEC Worksites
Inspections and Audits
Real-Time Safety Metrics and Reports
Enhance AEC workforce safety with two-way risk communications, tools, and resources
Anti-Money Laundering Training
Reduce risk in casino operations with Title 31 and Anti-Money Laundering training compliance
Employee Training
Deliver our leading AML and casino-specific online courses to stay compliant with national and state standards
Streamline training operations, increase employee effectiveness, and reduce liability with our LMS for casinos
Simplify incident reporting to OSHA and reduce risk with detailed investigation management
Employee Scheduling
Equip your employees with a mobile app to manage their schedules and simplify your 24/7 staff scheduling

Industrial Manufacturing
Chemical Processing
Pulp & Paper
Food & Beverage NEW
Utilities NEW
Renewables NEW
Distribution & Logistics
Distribution & Warehousing NEW
Public Safety
EMS Agencies
911 Emergency Communications
State Government - Fire Departments
State Government - Law Enforcement
Local Government
Architecture & Engineering
Facilities Management
Course Center
Success Stories
Speak to an Expert

Resource Center
Expert insights to boost training
Resource type
Course Catalogs
Whitepapers/Guides
Product Brochures
Acquisitions
Vector Cares
Executive Team
Industry Honors

Elevate Training, Elevate Success
Firefighter
See All Industrial Courses
See All AEC Courses
See All Facilities Courses
See All Casino Courses

Why is Electrical Safety Training Important?
July 16, 2018
Resource : blog industry : multiple industries tags : safety , vector ehs management.
Training employees to work safely around electrical hazards is a critical requirement for maintaining worker safety. Electricity is a serious workplace hazard that can result in serious injuries and even fatalities if your workers are not properly trained.
According to the Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries, exposure to electricity was the cause of 136 work-related deaths in 2017 . In response to these dangers of electricity, OSHA requires organizations to train employees to protect them from electrocution, shocks, arc flash, explosions, and fires.
It is important you know OSHA's electrical safety training requirements for employees, and what work they are able to perform with this training. You should also consider providing additional training to further mitigate the risks that come with electrical hazards.
OSHA's Electrical Standard Requirements
As outlined in OSHA’s electrical safety standards , affected workplaces must offer comprehensive safety training on the best work practices when around electrical hazards.
Because of the potential for workplace accidents and injuries , OSHA states that only “qualified” workers can perform maintenance and repairs of electrical equipment. These qualified workers must be fully trained to identify exposed live electrical parts and their voltage, and know exactly what procedures to follow when they work on exposed live parts or are close enough to be at risk.
Your company must document which electrical training employees have received and demonstrated an understanding of the course material. We recommend using online training tracking software to easily meet these requirements. Such software not only offers a high return on investment for employee training , but can offer training certificates when employees pass a course.
Workers that are “non-qualified” to perform maintenance on electrical equipment also must be trained in electrical safety if they could be exposed to electrical hazards while on the job. At a minimum, employees need to be trained in the skills and techniques necessary to recognize exposed live parts, determine the voltage of such parts, and the corresponding clearance distances.
NFPA 70E Certification Training
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) developed the NFPA 70E Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace originally at the request of OSHA. As such, following the NFPA 70E standard will assist you in complying with OSHA's 1910 Subpart S and 1926 Subpart K electrical safety standards.
However, becoming NFPA 70E certified is NOT required to comply with OSHA's standards. Rather, passing NFPA 70E training is a guaranteed way to comply with OSHA's standards, and as such has become an industry-recognized proof of competence.
Training programs and courses that consist of NFPA 70E material, but do not offer an NFPA 70E certification, will still qualify your employees for electrical work.
The Benefit of Additional Electrical Training
Due to the severity of risk from electrical work, safety training should not stop at meeting OSHA's requirements.
Many organizations in especially high-risk industries provide additional training on top of what is required in OSHA's standards. In addition to electricians and others in the construction industry, employees in mass transit, utility, industrial goods manufacturing, and mechanic repair positions have historically been at high risk of injury due to exposure to electricity.
Recurring training sessions can help mitigate the dangers of electricity in these industries, by keeping workers up-to-date with best practices and information.
Ensuring workers are educated about the types of electrical injuries, how they can occur, proper protection required, and lockout/tagout procedures is essential to maintaining a safe work environment. It can also cut down on costly OSHA citations, as improper lockout/tagout practices are in OSHA’s most frequently violated standards .
We recommend you follow a safety training guide to keep track of which electrical training is required, and which can provide additional benefits.
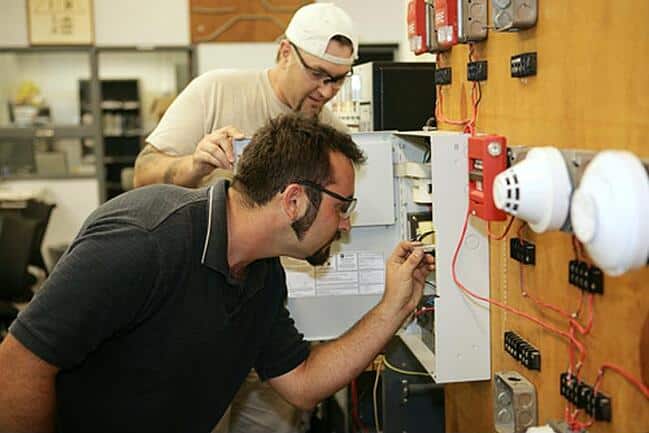

Key Electrical Safety Training Topics & Tools
To meet OSHA's training requirements for electrical safety, there are certain topics that must be included in your training program. Vector Solutions' training content catalog offers numerous online courses to meet OSHA standards including:
- Electrical Safety (General)
- Electrical Safety in Hazmat Environments
- Electrical Safety in the Laboratory
- Electrocution Hazards in Construction Part I and Part II
- Lock Out / Tag Out
While it is important employees take these classes as needed, keeping record of which employees have taken which courses can be a hassle. This is especially true when using an Excel spreadsheet, as it is all to easy for records to be edited or deleted without realizing it.
To stay on top of your electrical training needs, you should be using training management software designed specifically to help you track your employees' training. This will allow you to easily keep track and even schedule electrical safety training to ensure employees are being trained and retrained on electrical safety as needed. Such software will even alert you and employees when they are overdue for their training.
It's time to stop stressing about the various hazards of electrical work. Contact us to learn more about providing online electrical safety training to your workforce, and keep your workers safe.
Blog June 11 2024 -->
A breakdown of the 4 steps of a…, blog march 23 2021 -->, how to buy ehs management software, blog december 8 2020 -->, introduction to vector ehs safety management software, want to know more, reach out and a vector solutions representative will respond back to help answer any questions you might have..
- Advanced search
- Peer review
- Record : found
- Abstract : found
- Poster : found
IMPORTANCE OF ELECTRICAL SAFETY MEASURES IN EVERY WORKPLACE

- Download PDF
- Review article
- Invite someone to review
Abstract
Safety is a vital trait that must be ensued in all activities of human life. However, life without electricity will be unimaginable, Similarly, electricity constitutes a larger part of workplace hazard such as electrocution, electric shock, explosions or fire causing burns. So, Electrical Safety requires adequate attention while planning, designing, installing, operating and maintaining electrical equipment and installations in any workplace. This paper examines various types of hazard related to electrical services in any workplace and necessary safety measures were suggested as stated in all the standard regulatory bodies to reduce future occurrence and also to boost energy efficiency.
Author and article information
Affiliations, author notes, author information.
This work has been published open access under Creative Commons Attribution License CC BY 4.0 , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Conditions, terms of use and publishing policy can be found at www.scienceopen.com .
Okoye Cletus Uche, Adelakun Najeem Olawale. Design and Evaluation of Electrical Services for an Energy Efficient Home. 2019. Zenodo. [ Cross Ref ]
Comment on this article

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Ensuring electrical safety means knowing the condition of the house's wiring, outlets, and appliances. In fact, understanding this facet of safety can make your home a haven, not a hazard. Learn more about electrical safety in rental homes from our expert guide. External Perspective. But don't just take our word for it.
Electrical safety is a general practice for workers exposed to handling and maintaining electrically powered equipment. It's a set of guidelines they follow to mitigate electrical hazards and prevent their dangerous effects in case of an incident. Failure to adhere to electrical safety can lead to accidents, near misses, or even fatalities.
Main text. Electricity is dangerous for a human causing death and health hazards. If a current runs through a human body it burns the flesh and causes the shock. In its turn, shock leads to heart attack and heart failure. One-tenth of an ampere may prove death if it passes through the main part of the body.
Electrical safety is critical to prevent injuries, fatalities, and property damage. Adherence to safety standards and proper training is necessary for managing risks. Regular maintenance and correct handling of tools and equipment enhance safety. is crucial because hazards associated with electricity can lead to serious accidents and injuries.
7. Follow Lockout/Tagout Procedures. Following Lockout/Tagout procedures is an essential principle of electrical safety, as it ensures that electrical equipment and systems are de-energized and cannot be accidentally re-energized during maintenance, repair, or other work activities.
Electrical hazards refer to the potential dangers and risks that are associated with electrical systems. The main electrical hazards when working with electricity include: burns, electrocution, arc flash, electric shock; and other serious injuries. In extreme cases, they can even lead to fires or explosions, posing a threat to life, property ...
Electric Shock. Arc Flash. Electrical safety is important because hazards such as arc flash and shock can result in death if you are exposed to them. Fortunately, the likelihood of this occurring is relatively low. However, the control measures that prevent these hazards require careful management, attention to detail and technical competence.
Electrical Safety Essay Writing Tips. 1. Introduction: Start your essay by introducing the importance of electrical safety in our daily lives. Mention how electricity is an essential part of modern society, but it can also be dangerous if not handled properly. 2. Define electrical safety: Define what electrical safety means and why it is important.
Electrical safety is a shared responsibility that requires vigilance, knowledge, and proactive measures. By understanding the risks associated with electricity and implementing appropriate safety measures, individuals and organizations can prevent accidents, protect lives, and safeguard property.
Another benefit of including a detailed lesson on electrical safety is the practical context it sets for basic concepts of voltage, current, resistance, and circuit design. The more relevant a technical topic can be made, the more likely a student will be to pay attention and comprehend. And what could be more relevant than application to your ...
Some basic electrical safety tips include the following: Avoid using devices with frayed or damaged cords or plugs; these items should be discarded, as they are likely to cause a fire or ...
The Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) has compiled statistics on electrical fatalities and injuries for the years 2003-2017. The construction industry is by far the most exposed to electrical fatalities with 54 percent of all electrical deaths occurring in that industry. The organization reported the most fatalities took place ...
Why Electrical Safety Is Important. Electrical safety matters because electricity is powerful and potentially harmful. Mishandled electricity can cause serious injury or death, so keeping electricians safe at work requires use of the proper techniques. Make sure your employees have electrical safety training.
The Importance of Electrical Safety. PDF Version. With this lesson, I hope to avoid a common mistake found in electronics textbooks of either ignoring or not covering with sufficient detail the subject of electrical safety. I assume that whoever reads this book has at least a passing interest in actually working with electricity, and as such ...
Electrical Safety is Unique. As you can see from the statistics ...
The following table demonstrates the importance of electrical safety. 97% of all electricians have been shocked or injured on the job. Approximately 30,000 workers receive electrical shocks yearly. Over 3600 disabling electrical contact injuries occur annually. Electrocutions are the 4th leading cause of traumatic occupational fatalities.
Electrical safety is important for all workers, but it should be a major concern for the electrical maintenance worker. It is important that you be able to recognize electrical hazards and know how to protect yourself. Prevention is the best way to avoid electric shock, arc, and blast injuries. If you understand and respect electricity, always ...
Five Principles of Electrical Safety. Electricity behaves the same no matter what country you are in. It doesn't matter whether you are in the Americas or Europe, Asia or Africa. It also doesn't matter whether you are an electrician, a researcher, an engineer, or even an office worker who performs occasional household repairs. If you make contact with a hazardous live circuit part, your ...
life without electricity will be unimaginable, Similarly, electricity constitutes a. larger part of workplace hazard such as electrocution, electric shock, explosions. or fire causing burns. So ...
Training employees to work safely around electrical hazards is a critical requirement for maintaining worker safety. Electricity is a serious workplace hazard that can result in serious injuries and even fatalities if your workers are not properly trained. According to the Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries, exposure to electricity was the ...
Safety is a vital trait that must be ensued in all activities of human life. However, life without electricity will be unimaginable, Similarly, electricity constitutes a larger part of workplace hazard such as electrocution, electric shock, explosions or fire causing burns. So, Electrical Safety requires adequate attention while planning ...
Safety Precaution means to strictly follow the. prescribed rules for safety of self, working personnel and. tools to conduct electrical work, otherwise possibilit y of. electric shock or hazards ...
Interestingly, electrical safety is often addressed separately by many businesses. Some people wonder why electrical safety is so important, and why it gets so much attention. There are many statistics and facts that can provide some insights into what makes electrical safety stand out when it comes to the efforts that are made to improve safety.