
25 Media Literacy Examples

Media literacy refers to the ability to approach media sources with a critical and discerning eye.
In an era of new media where there are few gatekeepers to media production and dissemination, it’s increasingly important for everyone from students to pundits to journalists to be media literate.
Examples of media literacy include the ability to identify scholarly from non-scholarly sources, critique author motivations, and understand logical fallacies used by media sources to develop falsifiable arguments.
To be more media literate, I give my students the CRAAP framework and 21 examples of how to use it, which are outlined below.
Media Literacy and the CRAAP Framework
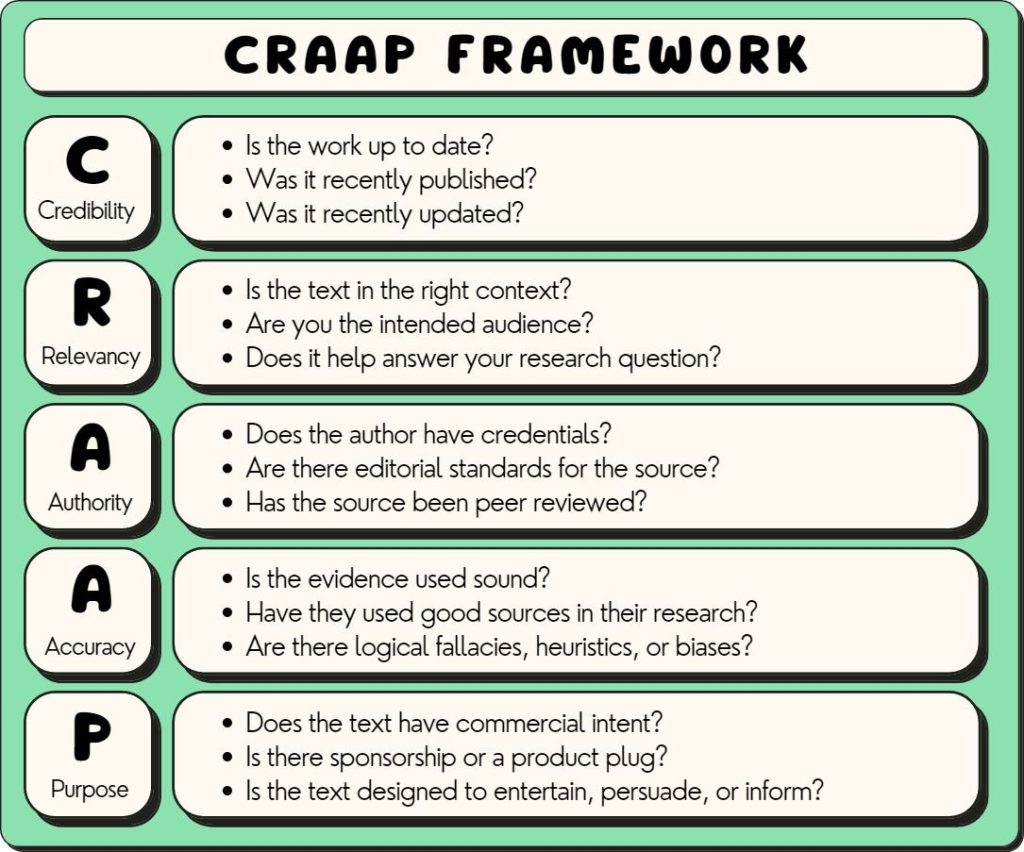
The CRAAP framework is a framework for critiquing media. It provides five broad themes of media critique:
Currency: Check whether the work is current (recently written) or recently updated. Discern whether currency is important. At times, you may want to use old texts!
Relevancy : A text may be good, but irrelevant. You may not be the intended audience or the text may be being used out of context.
Authority: If an author is a topical expert, the content may be more implicitly trustworthy. There are several ways to check for the authority of a text, outlined later in this article.
Accuracy : Use your analytical skills critical thinking skills, and fact checking to discern if the content is accurate.
Purpose: Discern what the author’s purpose is . Sometimes, a text is designed to persuade, which may affect how biased it is.
Below, I’ll break down these five broad themes into 21 examples of media literacy questions you can use to critique media texts.
Media Literacy Examples
Below are 21 examples of ways you can check to see if a media source is reliable.
1. Checking the Age of the Source (Currency)
- If the information is time sensitive, you may need the newest possible sources.
- Universities tend to prefer students cite texts that are less than 10 years old.
- If the source is old, you may need to check newer sources to see if the information has changed.
- Evergreen topics (topics that do not change) may be old but still relevant.
- Remember that the newness of a source doesn’t tell you everything. It may be new, but inaccurate.
2. Finding Seminal Sources (Currency)
- Sources may be old but still worth using. For example, a seminal source such as a philosopher’s original text or the Bible may be worth examining if it remains relevant.
- New sources might provide up to date or culturally relevant critiques of seminal sources.
3. Identifying Update Dates (Currency)
- If a text is older but recently updated, it may still present the newest facts and analysis.
4. Discerning Intended Audience (Relevance)
- A source may be discussing the topic you are interested in, but it may be targeted at children or a Sub-Section of the population so the information is not directly relevant to you.
5. Discerning Context (Relevance)
- Sometimes something can appear relevant but be out of context. A statistic about divorce rates may appear relevant until you realize it is about divorces in Indonesia and you live in Brazil.
- Ensure all quotes are contextualized so you aren’t reading something that is being quoted out of context.
6. Checking the Type of Source – Primary vs Secondary (Relevance)
- A primary source will generally be more authoritative than a secondary source. The farther removed an article is from the original source, the less accuracy we can presume it has.
7. Checking the Author’s Credentials (Authority)
- Journalists are expected to adhere to journalistic ethics, especially if they are employed by respected media organizations.
- Academics are similarly expected to adhere to standards in which they are trained.
- If the author has first hand experience we may consider them to be more authoritative.
8. Checking the Author’s Expertise (Authority)
- If the author is a credentialed practitioner in the field in which they are discussing, we may find them more trustworthy.
- A person may be an authority, but they should also be an authority in their field. I have a PhD in Education. I have no business writing articles about chemistry!
- Appeals to authority may be a way to shield inaccurate information (known as the appeal to authority fallacy ). Be sure to keep a critical eye even if the author is credentialed, or a credentialed expert has been cited.
9. Checking the Publisher (Authority)
- Authority is also established by quality and respected publishers. If you are on a news website with a clearly posted editorial policy, it may be more authoritative than someone’s blog.
- Universities with .edu domains will be more respected publishers than most .com websites.
10. Checking for Gatekeepers (Authority)
- Gatekeepers include editors, peer reviewers, and publishing houses. These gatekeepers can prevent the publication of low quality or inaccurate content.
- Social media like twitter and blogs do not have gatekeepers, which can lower the reliability.
11. Checking for Peer Review (Authority)
- Peer review occurs when another respectable source reads, reviews, and fact checks the content. This helps ensure high quality .
- Double blind review refers to reviews made by anonymous experts who do not know the author of the original content. Double blind review is one of the highest standards of quality for academic sources.
12. Checking Images (Authority)
- Original images, rather than stock photos or other people’s images, can be used as proof that the person has first hand knowledge. For example, a product review might be more highly regarded if there are pictures of the reviewer actually using the product.
13. Checking the Reference List (Accuracy)
- Citation of sources helps readers to fact-check for accuracy of content. It also helps ensure transparency .
- If the sources cited are respected, primary sources, or from academic texts, the references will be more reliable.
14. Checking the Evidence Used (Accuracy)
- Citation of evidence, such as data and first-person quotes, can help demonstrate accuracy of data.
15. Checking for Author Biases (Accuracy)
- Media literate readers keep their eye out for bias in writing. There are many types of bias, such as cultural, political, and framing bias.
- Authors may cherry-pick data to help support their views, so keep an eye on the sources used and check their bias as well.
16. Reflecting on Personal Biases (Accuracy)
- Ensure you read texts from a variety of sources to avoid falling into confirmation bias by only reading texts that support your views.
17. Being Aware of Fallacies (Accuracy)
- Read the arguments made by authors and keep an eye on the use of logic and reason. Authors may use logical fallacies and heuristics that readers should critically analyze.
18. Checking for Spelling and Grammar (Accuracy)
- Many librarians will recommend checking a source’s spelling and grammar with the assumption that poor spelling and grammar is a sign of low quality content. While this may demonstrate poor editorial standards, beware of falling into a fallacy: the spelling may be bad, but the content may be good.
19. Independently Fact-Checking (Accuracy)
- Fact check dubious claims by triangulating against other sources, including sources from other media outlets with different potential biases.
20. Checking for Inclusion of Multiple Perspectives (Accuracy)
- An article that explores multiple perspectives, competing perspectives, and weaknesses in their own arguments, demonstrate reflectiveness that may demonstrate reliable and responsible reporting.
21. Checking for Right of Reply
- A text that is critical of someone but has approached them for comment or given them right of reply may be respected for their journalistic ethics.
22. Checking for Persuasive Intent (Purpose)
- Reflect on whether the text aims to be objective or persuasive. If the text is arguing for a particular point of view, then it may not be presenting the full story.
23. Checking for Commercial Intent (Purpose)
- If the source is trying to sell a product or service, it may have financial interests that make it biased.
24. Checking for Entertainment Intent (Purpose)
- A source designed to entertain my be more willing to bend the truth or may engage in hyperbole, exaggeration, or sarcasm.
25. Checking for Content Sponsorship (Authority)
- If an article or video is sponsored, it may be less likely to be critical of the sponsor, which may lower the source’s authority.
Other Considerations
26. have you considered source diversity.
- If you are reading multiple sources, ensure you are engaging with a diversity of authors. This may include diversity of: publications, political biases, genders, social classes, races, and so on. Diversity of social positions may demonstrate diversity of perspectives.
Media literacy is increasingly necessary in an era of new and social media . But it is required no matter the medium – newspaper, website, YouTube video, blog, tweet, or anything in between.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Common Sense Media
Movie & TV reviews for parents
- For Parents
- For Educators
- Our Work and Impact
Or browse by category:
- Get the app
- Movie Reviews
- Best Movie Lists
- Best Movies on Netflix, Disney+, and More
Common Sense Selections for Movies

50 Modern Movies All Kids Should Watch Before They're 12

- Best TV Lists
- Best TV Shows on Netflix, Disney+, and More
- Common Sense Selections for TV
- Video Reviews of TV Shows

Best Kids' Shows on Disney+

Best Kids' TV Shows on Netflix
- Book Reviews
- Best Book Lists
- Common Sense Selections for Books

8 Tips for Getting Kids Hooked on Books

50 Books All Kids Should Read Before They're 12
- Game Reviews
- Best Game Lists
Common Sense Selections for Games
- Video Reviews of Games

Nintendo Switch Games for Family Fun

- Podcast Reviews
- Best Podcast Lists
Common Sense Selections for Podcasts

Parents' Guide to Podcasts

- App Reviews
- Best App Lists

Social Networking for Teens

Gun-Free Action Game Apps

Reviews for AI Apps and Tools
- YouTube Channel Reviews
- YouTube Kids Channels by Topic

Parents' Ultimate Guide to YouTube Kids

YouTube Kids Channels for Gamers
- Preschoolers (2-4)
- Little Kids (5-7)
- Big Kids (8-9)
- Pre-Teens (10-12)
- Teens (13+)
- Screen Time
- Social Media
- Online Safety
- Identity and Community

Explaining the News to Our Kids
- Family Tech Planners
- Digital Skills
- All Articles
- Latino Culture
- Black Voices
- Asian Stories
- Native Narratives
- LGBTQ+ Pride
- Best of Diverse Representation List

Celebrating Black History Month


Movies and TV Shows with Arab Leads

Celebrate Hip-Hop's 50th Anniversary

What is media literacy, and why is it important?
The word "literacy" usually describes the ability to read and write. Reading literacy and media literacy have a lot in common. Reading starts with recognizing letters. Pretty soon, readers can identify words -- and, most importantly, understand what those words mean. Readers then become writers. With more experience, readers and writers develop strong literacy skills. ( Learn specifically about news literacy .)
Media literacy is the ability to identify different types of media and understand the messages they're sending. Kids take in a huge amount of information from a wide array of sources, far beyond the traditional media (TV, radio, newspapers, and magazines) of most parents' youth. There are text messages, memes, viral videos, social media, video games, advertising, and more. But all media shares one thing: Someone created it. And it was created for a reason. Understanding that reason is the basis of media literacy. ( Learn how to use movies and TV to teach media literacy. )
The digital age has made it easy for anyone to create media . We don't always know who created something, why they made it, and whether it's credible. This makes media literacy tricky to learn and teach. Nonetheless, media literacy is an essential skill in the digital age.
Specifically, it helps kids:
Learn to think critically. As kids evaluate media, they decide whether the messages make sense, why certain information was included, what wasn't included, and what the key ideas are. They learn to use examples to support their opinions. Then they can make up their own minds about the information based on knowledge they already have.
Become a smart consumer of products and information. Media literacy helps kids learn how to determine whether something is credible. It also helps them determine the "persuasive intent" of advertising and resist the techniques marketers use to sell products.
Recognize point of view. Every creator has a perspective. Identifying an author's point of view helps kids appreciate different perspectives. It also helps put information in the context of what they already know -- or think they know.
Create media responsibly. Recognizing your own point of view, saying what you want to say how you want to say it, and understanding that your messages have an impact is key to effective communication.
Identify the role of media in our culture. From celebrity gossip to magazine covers to memes, media is telling us something, shaping our understanding of the world, and even compelling us to act or think in certain ways.
Understand the author's goal. What does the author want you to take away from a piece of media? Is it purely informative, is it trying to change your mind, or is it introducing you to new ideas you've never heard of? When kids understand what type of influence something has, they can make informed choices.
When teaching your kids media literacy , it's not so important for parents to tell kids whether something is "right." In fact, the process is more of an exchange of ideas. You'll probably end up learning as much from your kids as they learn from you.
Media literacy includes asking specific questions and backing up your opinions with examples. Following media-literacy steps allows you to learn for yourself what a given piece of media is, why it was made, and what you want to think about it.
Teaching kids media literacy as a sit-down lesson is not very effective; it's better incorporated into everyday activities . For example:
- With little kids, you can discuss things they're familiar with but may not pay much attention to. Examples include cereal commercials, food wrappers, and toy packages.
- With older kids, you can talk through media they enjoy and interact with. These include such things as YouTube videos , viral memes from the internet, and ads for video games.
Here are the key questions to ask when teaching kids media literacy :
- Who created this? Was it a company? Was it an individual? (If so, who?) Was it a comedian? Was it an artist? Was it an anonymous source? Why do you think that?
- Why did they make it? Was it to inform you of something that happened in the world (for example, a news story)? Was it to change your mind or behavior (an opinion essay or a how-to)? Was it to make you laugh (a funny meme)? Was it to get you to buy something (an ad)? Why do you think that?
- Who is the message for? Is it for kids? Grown-ups? Girls? Boys? People who share a particular interest? Why do you think that?
- What techniques are being used to make this message credible or believable? Does it have statistics from a reputable source? Does it contain quotes from a subject expert? Does it have an authoritative-sounding voice-over? Is there direct evidence of the assertions its making? Why do you think that?
- What details were left out, and why? Is the information balanced with different views -- or does it present only one side? Do you need more information to fully understand the message? Why do you think that?
- How did the message make you feel? Do you think others might feel the same way? Would everyone feel the same, or would certain people disagree with you? Why do you think that?
- As kids become more aware of and exposed to news and current events , you can apply media-literacy steps to radio, TV, and online information.
Common Sense Media offers the largest, most trusted library of independent age-based ratings and reviews. Our timely parenting advice supports families as they navigate the challenges and possibilities of raising kids in the digital age.
Media Literacy Essays
Media view of victimization: “a tale of two femicides – and media bias.”, the sensationalism of current news media, media literacy and ways it has evolved, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail

Media Literacy
What is media Literacy?
Media literacy is the ability to understand, analyse, and create media messages. It is an evolving skill set that teachers and students must frequently encounter in the classroom, as the environments in which we consume and create media constantly change and become more complex.
Becoming media literate and teaching media literacy to students involves understanding how media messages are constructed and the techniques used to convey information and ideas.
Most importantly, it includes evaluating the credibility and reliability of media sources, recognising bias and disinformation, and understanding the impact media can have on individuals and society.
We have never lived in an era where it has been so easy to create and consume media and share it with the world as it is today; as such, we should be more enlightened about the purpose and intent of the messages being presented. Becoming media literate has never been more important as the validity and credibility of news, facts and opinions are more challenging to determine.
Students who are media literate are better equipped to critically analyze the information they receive and make informed decisions about what they believe and how they engage with media.
As teachers, it is crucial to integrate media literacy into all curriculum areas so students understand media reaches and influences us in many ways.
What skills are required to become media literate?
Becoming media literate is a process of critical thinking , healthy scepticism and understanding the factors that drive and influence the media itself. For this to occur, we have broken down these broad skills into individual components that students and teachers need to understand more deeply.
- How to analyse media messages : This involves teaching students the techniques used to inform, entertain, and persuade an audience and helping them understand the messages being conveyed.
- How to evaluate a source: When students can determine the credibility and reliability of media sources, they will make far wiser evaluations of the message and purpose of the content they consume.
- Understanding the impact of the media: What influence does the media have upon individuals, groups, and society? Teaching students why we should embrace freedom of speech and the search for truth above all else is essential. Students who understand the chaos of controlled and corrupt media approach it with a healthy level of scepticism and respect.
- Understanding how media is produced: By understanding the complexity and simplicity of producing various forms of media and sharing them with an audience, students can better determine if the media message they are consuming has been created by an agenda-driven machine or an expert in the field on a given topic.
- Knowing the difference between fact and opinion: It may seem simplistic and obvious, but when students can quickly identify if a statement is an absolute verified fact that has weight and credibility versus an opinion, it completely changes how that message is received. If students cannot separate these two areas, we educators have significantly failed them.
- Recognizing media manipulation: As terrible as it may seem, there are tens of thousands of people devoting their lives to producing propaganda, advertising, or disinformation for profit, persuasion and power every single day. Make it clear to all students that not all media should be trusted and that constant disinformation will be presented to them throughout their lives.
- Identifying and Understanding Bias: When students understand that all media has a purpose for being created and may frequently contain some degree of bias, they will look beyond simply what they are being told and ask why this message is being shared.
- Digital Literacy Skills and Media Creation: Navigating the media requires a basic understanding of technology and digital media. Providing students with the skills to effectively use technology and digital media to access, analyze, and create media messages moves them from consumers to creators with a practical and ethical understanding of the impact that their media messages can have.
TEACHING STUDENTS TO NAVIGATE THE “DISINFORMATION ERA”
Never before has it been so easy for someone, anyone, to create a message and share it with hundreds of millions of people, and even more concerning is that it has never been easier for governments to control that flow of information within their borders so that they control the narrative on every news story, and to the bend and erase history at will. We see this in action today in countries such as North Korea, China and Russia.
Disinformation is the spread of false or misleading information, often intended to control public opinion or promote a specific agenda. This problem has become increasingly prevalent in recent years and has driven a sharp rise in wild conspiracy theories, scams, and radicalization. It is essential that students are taught to navigate this complex digital landscape and identify credible sources of information.
The information era of the early 2000s has doubled down on its capacity to share and consume information through digital technology and has taken an unfortunate turn in recent years to create an information superhighway leading to a complex system of facts, opinions, bias, hatred and outright lies that are becoming increasingly difficult to navigate, especially for those who have grown up knowing nothing else but consuming their news through YouTube, Social media and the weight of opinion from social influencers outranks that of experts and proven research.
How did we get here?
The answer to that question is complex, but three critical turning points have driven us to the point at which we find ourselves.
1: The ease of content creation: This point has been covered well enough, but when anyone with the literacy skills of a child can use tools such as artificial intelligence to write a flawless 2000-word article or create a 10-minute video explaining in the style of a professional news outlet and share it with millions of people via social media via paid promotion for well under $100 this marks a clear turning point in the way we consume and create media.
To create and deliver content at this level of quality and scale only a decade earlier would have cost thousands of dollars and required far more checks and balances.
2: Algorithms determining what we consume: In the same way in which Spotify and Netflix determine what shows and music we should listen to based upon what we like, and thumbs down and so on, social media drives our consumption of news and information in the same way.
The primary intent of social media is to keep users on the platform for as long as possible regardless of what we are doing: watching videos, liking photos, or sharing posts. It doesn’t matter as long as our eyeballs remain on their platform. This allows social media outlets such as Facebook, TikTok and Instagram to sell advertising and generate billions of dollars of revenue each month.
So just as you might prefer Beiber over Beethoven on your music playlists, computer-driven algorithms will increase music that has more in common with your tastes and then remove those that do not. Undeniably, these algorithms are practical and helpful in ensuring your wants and needs are often met.
But wait; what if those algorithms effectively removed some of the most fantastic music we have ever heard? Music that might provide insight into new cultural areas puts us in a completely different headspace or opens our eyes to how other generations of music shaped the music we listen to today. What a shallow pool of musical tastes we would quickly swim in as our playlists blend into the same 100 songs we listen to all the time. Sound familiar?
So if we transfer that process of algorithms feeding us our musical tastes into how social media feeds us news and events, it is not hard to see how our biases, likes and dislikes can be quickly targeted and capitalized upon in the same way.
The more significant problem here is that if you are interested in news articles revolving around science and technology, for example, not only will you find your news feed packed with these stories exclusively with news stories of this nature, but other news events will be removed.
3: Welcome to the Algorithmic “Rabbit Hole”
The third and final act explaining how we got here is the most interesting, and we can use it as a metaphor from the story Alice in Wonderland, where she enters the rabbit hole and is transported to a surreal state of being that is both disturbing and delightful.
The “YouTube” rabbit hole is a phenomenon that demonstrates this process most effectively; how we start innocently viewing videos on a specific topic, such as “NBA highlights from the 90s”, that within 10 – 12 videos will evolve into a new stream of “recommended content” exposing “NBA Scandals”, that then leads to “Celebrity Conspiracy theories” to videos focussed on (Insert topic here) full of foul language, wild opinions, conspiracies and flat out lies.
So what is happening here, and why?
If we remember that the sole focus is to keep you on the platform so that advertising can be sold, the algorithm also knows that you will quickly tire of the same content no matter what it is. As such, it needs to provide alternate content that is in a similar vein that might also be more contentious and packed full of user feedback and comments that will create a higher level of engagement.
Effectively the algorithm needs to keep upping the “sugar, or dosage”, leading creators to create more contentious and hyperbolic even radicalized content as the race for your attention span continues to evolve. All the while, that balanced understanding of any topic is pushed to the side and eventually completely removed in favour of your new and more extreme and niche areas of interest. And this is not a healthy place for anyone to exist, especially those who are blind to the process that led them here.
This leads creators to create more wild and contentious content to draw an audience, and the cycle is repeated.
Conscious and state-controlled disinformation
Until now, we have been referring to companies using technologies to keep users engaged and persuade them to consume particular information streams for financial gain. Still, it did not take long for authoritarian countries to use this same technology to generate propaganda, erase history and sway public opinion within their own borders and those of their ideological rivals.
The big difference here is we are moving at scale from a backyard operation of disinformation to an environment in which state-sponsored projects where money, time and resources are unlimited and the capacity to create chaos on a global scale dramatically increases. Effectively enabling the process of weaponising disinformation.
Why bother trying to invade your enemy when you can far more easily create chaos and revolution amongst their own citizens in relative obscurity?
Ironically, it is the countries that value free and open media that are at the most significant risk of falling victim to disinformation attacks as there is little capacity to filter, censor and control the flow of information within social media as opposed to autocratic nations have removed the technical pathways and human rights of free press and free speech within their own borders.
A Complete Teaching Unit on Fake News

Digital and social media have completely redefined the media landscape, making it difficult for students to identify FACTS AND OPINIONS covering:
Teach them to FIGHT FAKE NEWS with this COMPLETE 42 PAGE UNIT. No preparation is required,

Media Literacy Teaching Strategies
Media literacy has become essential in the digital age, enabling individuals to navigate the vast information landscape and critically analyze media messages. Educators must equip students with the tools and knowledge necessary to become media-literate citizens. This article will explore practical strategies for teaching media literacy in the classroom, providing teachers with practical approaches to empower students to decipher and engage with media content.
In this article, we will approach the principles of media literacy from five perspectives and provide three practical examples of media literacy lessons in the classroom.
1: Build a Foundation of Media Literacy Early On
Teaching media literacy from an early age is paramount for several reasons.
Firstly, starting early allows educators to develop critical thinking skills in students . By introducing media literacy concepts and practices at a young age, students learn to question, analyze, and evaluate media content. They become more discerning consumers who can distinguish between reliable and unreliable information. Early exposure to media literacy enables students to understand the persuasive techniques, biases, and manipulative strategies employed in media, empowering them to make informed decisions about the information they encounter.
Secondly, with the pervasive presence of digital media in children’s lives, early media literacy education helps students navigate the digital landscape responsibly. Young children are increasingly exposed to online platforms, social media, and digital content. By teaching them media literacy skills, educators can guide students to critically evaluate the reliability of online information, identify potential risks and dangers, and understand the consequences of their digital actions.
Early exposure to media literacy aids in developing digital citizenship skills, enabling students to protect their privacy, engage in respectful online communication, and become critical consumers of digital content.
Moreover, early media literacy education is vital in countering misinformation and fake news. In the internet age, misinformation spreads rapidly, and young minds can be particularly vulnerable to its influence. By introducing students to fact-checking techniques, teaching them to identify credible sources, and instilling critical evaluation skills, educators empower students to actively debunk falsehoods and discern the authenticity of information.
Teaching students about media literacy from an early age is essential for fostering critical thinking skills, navigating the digital landscape responsibly, and countering misinformation. By equipping students with media literacy skills, educators empower them to become active and discerning participants in the media ecosystem.
Digital and social media have completely redefined the media landscape, making it difficult for students to identify FACTS AND OPINIONS covering:
- Radicalization
- Social Media, algorithms and technology
- Research Skills
- Fact-Checking beyond Google and Alexa
2: Promote Active Media Consumption
Encourage students to engage with media content rather than passively consume it actively. Teach them to question the sources, intentions, and biases behind the information they encounter. Encourage critical thinking by asking open-ended questions and facilitating discussions. Assign media analysis projects where students evaluate the credibility and reliability of different sources.
Let’s look at three strategies for promoting active media consumption in students.
Media Analysis and Discussion: Engage students in media analysis activities that encourage critical thinking and discussion. Give them various media examples, such as news articles, advertisements, videos, or social media posts. Guide them to identify the main message, purpose, intended audience, and persuasive techniques employed in each media piece.
Encourage students to question the credibility of the sources, evaluate the evidence provided, and consider any biases or stereotypes present. Facilitate group discussions where students can share their insights, challenge each other’s perspectives, and develop their analytical skills.
Fact-Checking and Verification: Teach students how to fact-check and verify the information they encounter in media. Introduce them to reliable fact-checking websites and tools, such as Snopes, FactCheck.org , or Google’s Fact Check Explorer.
Guide students through evaluating sources, cross-referencing information, and verifying claims made in media content. Encourage students to question the accuracy and reliability of information before accepting it as true. Provide real-world examples of misinformation or fake news stories and engage students in hands-on activities where they can fact-check and debunk false claims.
Media Creation and Critique: Encourage students to become active creators of media content and engage in self-reflection and critique.
Assign projects where students create media artifacts, such as videos, podcasts, or blog posts, focusing on a specific topic or theme. During creation, emphasize the importance of ethical media production, accurate representation, and responsible storytelling. After students complete their creations, facilitate peer feedback sessions where they can provide constructive criticism, discuss the impact of their media choices, and reflect on how their biases and perspectives may have influenced their work.
By incorporating these three approaches into media literacy education, educators can foster active media consumption skills in students. Students will develop the ability to critically analyze media messages, fact-check information, and engage responsibly with the media they encounter.
3: Develop Digital Literacy Skills
Equipping students with digital literacy skills is essential in today’s digital landscape. Teach them to navigate online platforms responsibly, evaluate websites for credibility, and protect their privacy. Introduce them to fact-checking websites and tools that can help them verify information. Discuss the ethical considerations surrounding online content creation, including copyright and plagiarism.
Here are three strategies to enhance your student’s digital literacy skills.
Digital Research and Information Literacy: Teach students how to conduct effective online research and evaluate the credibility and reliability of digital sources. Introduce them to various search strategies, such as using appropriate keywords and advanced search operators, to find relevant and trustworthy information. Guide students in critically evaluating websites, considering factors such as authorship, domain authority, date of publication, and potential biases. Provide them with practical exercises where they can analyze and compare different sources of information on a specific topic. Emphasize the importance of citing sources and avoiding plagiarism in their digital research.
Digital Communication and Collaboration: Teach students effective digital communication and collaboration skills. Guide them in using appropriate language and etiquette in online communication, whether through email, discussion forums, or social media platforms. Discuss the importance of considering the audience and context when communicating online and the potential implications of their digital footprint.
Foster opportunities for collaborative digital projects, where students can learn to work together virtually, use digital collaboration tools, and engage in respectful and effective online teamwork. Emphasize the importance of clear and concise digital communication, active listening, and constructive feedback.
Educators can help students develop essential digital literacy skills by implementing these three strategies. Students will become adept at conducting effective online research, evaluating the credibility of digital sources, protecting their online privacy and security, and engaging in responsible digital communication and collaboration. These skills are vital for their success in the digital age and empower them to navigate the digital landscape with confidence and discernment.
4: Address Bias and Stereotypes in the Media
Guide students in identifying and challenging bias and stereotypes present in media. Teach them to recognize how media influences societal perceptions and impacts diverse communities. Provide examples of media representations that reinforce stereotypes and facilitate discussions on how these representations can perpetuate inequality and discrimination. Encourage students to seek out alternative narratives and diverse voices.
Here are three strategies for teaching this in the classroom.
Media Analysis and Deconstruction: Engage students in critical media analysis and deconstruction activities to identify and challenge bias and stereotypes. Select media examples, such as advertisements, news articles, TV shows, or movies, that contain explicit or implicit biases or reinforce stereotypes.
Guide students to analyze the language, visuals, representations, and portrayals in the media content. Encourage them to question the underlying assumptions, stereotypes, and biases present. Facilitate discussions where students can express their observations, share alternative perspectives, and explore the potential consequences of these biases and stereotypes. Encourage them to critically reflect on how media influences societal perceptions and impacts diverse communities.
Undertake Media Representation Projects: Assign projects that involve creating media representations that challenge bias and stereotypes. Ask students to create their own advertisements, news articles, videos, or other media artifacts that counter prevailing stereotypes and promote inclusive representations.
Provide guidelines and prompts that encourage students to think critically about the messages they want to convey and the impact they want to make. Emphasize the importance of accurately and respectfully representing different social, cultural, and ethnic groups. Encourage students to collaborate and share their creations, discussing the intentions and impact of their media representations.
Promote Diverse Media Consumption: Encourage students to actively seek out and consume media content from diverse sources and perspectives. Introduce them to media outlets, books, films, and online platforms prioritising diverse voices and challenging stereotypes. Provide recommendations and resources that showcase alternative narratives and perspectives.
Guide students in critically evaluating the diversity of media they consume and discussing the representations they encounter. Encourage them to question the absence or underrepresentation of certain groups and to explore media that provides more balanced and inclusive portrayals. Facilitate discussions where students can share their findings, insights, and reflections on the importance of diverse media consumption.
By incorporating these strategies into media literacy education, educators can effectively address bias and stereotypes in media. Students will develop the skills to critically analyze and challenge biased representations, actively create media promoting inclusivity, and seek out diverse media content. This empowers students to become more discerning consumers, critical thinkers, and advocates for media representations that reflect the diversity and richness of our society.
5: Embed Media Literacy Across the Curriculum
Integrate a media literacy curriculum across various subjects beyond traditional media studies. Show students how media literacy skills relate to science, history, literature, and other disciplines. For example, in a history class, students can analyze primary sources or examine the portrayal of historical events in films. By connecting media literacy to different subjects, students understand its universal applicability.
Embed Media Analysis and Content Creation into all subject areas: Integrate media analysis and creation activities across different subjects to enhance critical thinking and communication skills. For example, in English language arts, analyze media representations in literature or explore the persuasive techniques used in advertising.
In social studies, analyze historical documentaries or discuss the portrayal of different cultures and societies in media. In science, examine the portrayal of scientific concepts in popular media or evaluate the accuracy of scientific claims in news articles.
Encourage students to create media artifacts demonstrating their understanding of the subject, such as videos, podcasts, infographics, or written articles. Students gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter by integrating media literacy into various subjects while developing critical media analysis and media creation skills.
Create Collaborative Media Projects: Implement collaborative media projects that span multiple subjects, promoting interdisciplinary learning. Design projects that require students to research, analyze, and create media content related to a specific topic.
For example, students could collaborate on a digital storytelling project that combines historical research, creative writing, and digital media production. Students could create multimedia presentations or documentaries integrating scientific research, data analysis, and visual communication skills. By working together on these projects, students develop a comprehensive understanding of the topic, enhance their media literacy skills, and learn the value of collaboration and teamwork.
Promote the pursuit of Media Ethics and Digital Citizenship Discussions: Incorporate discussions on media ethics and digital citizenship into various subjects to foster responsible media consumption and online behaviour. Dedicate class time to explore topics such as media bias, fake news, online privacy, cyberbullying, or the responsible use of social media. Engage students in critical conversations about the ethical considerations of media production and consumption.
Provide opportunities for students to share their perspectives, debate relevant issues, and develop strategies for responsible digital engagement. By addressing media ethics and digital citizenship in different subjects, students comprehensively understand their responsibilities as media consumers and producers.
Educators can seamlessly integrate media literacy across all curriculum areas by employing these strategies. Students will develop critical thinking, creativity, communication, and digital citizenship skills, enabling them to navigate and engage with media in various academic contexts effectively.
Bonus tip for teaching media literacy: Stay Updated and Adapt:
Media landscapes and technologies evolve rapidly, so educators need to stay updated and adapt their teaching strategies accordingly. Stay informed about emerging media trends, new platforms, and changing media consumption patterns. Continuously refine your teaching methods to align with the ever-changing media landscape.
Teaching media literacy is essential for equipping students with the critical thinking skills to navigate the complex media environment. By starting early, promoting active consumption, developing digital literacy, fostering collaboration, addressing bias and stereotypes, incorporating media literacy across subjects, and staying updated, educators can empower students to become discerning consumers and active media content creators.
By implementing these strategies, educators play a pivotal role in shaping informed and engaged citizens who can confidently navigate the media landscape.
As educators, let us seize the opportunity to cultivate media literacy skills in our students, enabling them to analyze, evaluate, and create media content responsibly and effectively.

- About Media@LSE
- Policy briefs
- COVID 19 pandemic
- Public Service Media
- Internet Governance
- Children and the Media
- Media representation
- 20th Anniversary
Sonia Livingstone
October 25th, 2018, media literacy: what are the challenges and how can we move towards a solution.
1 comment | 86 shares
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes

Last time I wrote about media literacy, I was glad to observe that, as the media increasingly mediate everything in society, there is growing emphasis on the importance of ensuring that people have the media literacy not only to engage with the media but to engage with society through the media . But I was also frustrated at some of the superficial hand-waving from policy makers towards media literacy and media education, seemingly without understanding what is involved or what the challenges are.
Silver bullet solution?
In our ever-more complex media and information environment, media literacy is being hailed as a silver bullet solution – hopefully to be dealt with by one-shot awareness-raising campaigns delivered by brand-promoting CSR departments, or by issuing vaguely-phrased high-handed injunctions to the (apparently unhearing and otherwise preoccupied) Department of Education. The motivation is rarely pedagogic but, rather, more the policy of ‘last resort.’
So, in the face of multiple problems of hate speech, or cyberbullying, or hacked YouTube content, or fake news etc., we are witnessing urgent calls to manage the media environment better – especially, to regulate the internet. But in the face of clashes of positive and negative rights, regulatory difficulties, powerful global companies and short-termist political expediency, this call in turn quickly morphs into a call for the supposedly ‘softer’ solution of educating the internet-using public.
Let me be clear. I am 100% in favour of educating the public. I have devoted years to arguing for more and better media literacy. In this digital age, I believe media literacy’s time has come, and its advocates should grab the opportunity with both hands and advance the cause with all their energy.
But energy and enthusiasm are most effectively expended when the challenges to be met are properly recognised. So let me set these out, as I see them, lest our energies are wasted and the window of opportunity is lost.
First, three educational challenges
- Investment . Make no mistake: education is an expensive solution in terms of time, effort and infrastructure. It needs a pedagogy, teacher training, curriculum resources, mechanisms for audit and assessment. To manage schools, governments devote an entire ministry to achieve this – yet they are simultaneously heavily criticised for their failures, and yet constantly under siege to solve yet more of society’s pressing ills.
- Reaching adults not in education or training is an even larger challenge, rarely met in any area of demand. So who is responsible, and who are or should be the agents of change? The answers will vary by country, culture and purpose. But they should be identified so that the actions of civil society, public services such as libraries, industry and other private actors can be coordinated.
- Exacerbating inequalities . We like to think of education as a democratising mechanism, because everyone has the right to school and training. But research consistently shows that education affects life outcomes differentially, advantaging the already-advantaged and failing sufficiently to benefit the less-advantaged, especially the so-called “hard to reach.” What proportion of media literacy resources are provided equivalently to all (risking exacerbating inequality) and what proportion are targeted at those who most need them? (I don’t know the answer, but someone should know it).
Then there’s the challenges of the digital
- Mission creep . As more and more of our lives are mediated – work, education, information, civic participation, social relationships and more – the scope of media literacy grows commensurately. Just today, in my Twitter feed, I read exhortations to ensure that people:
– Understand how black-boxed automated systems make potentially discriminator decisions
– Distinguish the intent and credibility signalling behind mis- and dis-information to tackle “fake news”
– Identify when a potential abuser is using their smart home technology to spy on them
– Weigh the privacy implications when they use public services in smart cities
It is, therefore, vital to set some priorities.
- Legibility . As I’ve observed before: we cannot teach what is unlearnable, and people cannot learn to be literate in what is illegible. We cannot teach people data literacy without transparency, or what to trust without authoritative markers of authenticity and expertise. So people’s media literacy depends on how their digital environment has been designed and regulated.
- Postponing the positives . The rapid pace of socio-technological innovation means everyone is scrambling to keep up, and just battling with the new harms popping up unexpectedly is extremely demanding. The result is that attention to the “ hygiene factors ” in the digital environment dominates efforts – so that media literacy risks being limited to safety and security. Our bigger ambitions for mediated learning, creativity, collaboration and participation get endlessly postponed in the process, especially for children and young people.
For the media literacy community itself, there’s some very real challenges of expertise and sustainability. These may be dull, or even invisible, to those calling for the silver bullet solution. But they matter.
- Capacity and sustainability . The media literacy world comprises many small, enthusiastic, even idealistic initiatives, often based on a few people with remarkably little by way of sustained funding or infrastructure. The media literacy world is a bit like a start-up culture without the venture capitalists. We can talk a good story, but there’s always a risk of losing what’s been gained and having to start over.
- Evidence and evaluation . When you look closely at the evidence cited in this field, it’s not as robust or precise as one would like. Even setting aside the now tiresome debate over definitions of media literacy, the difficulties of measurement remain. Perhaps for the lack of agreed measures, there’s more evidence of outputs than outcomes, of short term reach rather than long term improvements. There’s remarkably few independent evaluations of what works. Compare media literacy interventions to other kinds of educational interventions – where’s the randomised control trials, the systematic evidence reviews, the targeted attention to specific subgroups of the population, the costed assessments of benefit relative to investment?
Last but certainly not least, there’s the politics of media literacy
- “Responsibilising” the individual. In policy talk especially, the call for media literacy and education to solve the problems of digital platforms tends, however inadvertently, to task the individual with dealing with the explosion of complexities, problems and possibilities of our digital society. In a policy field where governments fear they lack the power to take on the big platforms, it is the individual who must wise up, becoming media-savvy, rise to the challenge. Since, of course, the individual can hardly succeed where governments cannot, the politics of media literacy risks not only burdening but also blaming the individual for the problems of the digital environment.
As Ioanna Noula recently put it , “by emphasising kindness and ethics, these approaches also undermine the value of conflict and dissent for the advancement of democracy” and they “decontextualize” citizenship such that “ the attentions of concerned adults and youth alike are turned away from the social conditions that make young people vulnerable.” So instead of empowered media-literate citizens exercising their communicative entitlements , the emphasis becomes one of dutiful citizens, as part of a moralising discourse.
How can we turn things around?
I’ll make three suggestions, to end on a positive:
Before advocating for media literacy as part of a solution to the latest socio-technological ill, let’s take a holistic approach. This means, let’s get really clear what the problem is, and identify what role media or digital technologies play in that problem – if any! We might even ask for a “ theory of change ” to clarify how the different components of a potential solution are expected to work together. And, getting ambitious now, what about a responsible organisation – whether local, national or international – tasked with coordinating all these actions and evaluating the outcomes?
Then let’s figure out all the other players, so that we can articulate which part of the solution media literacy may provide, and what others will contribute – regulators, policy makers, civil society organisations, the media themselves – thereby avoiding the insidious tendency for the whole problem to get dumped at the feet of media educators. We might further expect – demand – that the other players should embed media literacy expectations into their very DNA, so that all organisations shaping the digital environment share the task of explaining their operation to the public and providing user-friendly mechanisms of accountability.
Last, let’s take the questions of value, empowerment and politics seriously. What does good look like? Is it dutiful citizens being kind to each other online, behaving nicely in an orderly fashion? Or is it deliberating, debating, even conflicting citizens? Citizens who express themselves through digital media, organise through digital media, protest to the authorities and insist on being heard? I think it should be the latter, not least because our societies are increasingly divided, angry and dis-empowered. It’s time that people are heard, and it’s time for the digital environment to live up to its democratizing promise. But this requires change on behalf of the policy makers. We should not only ask whether people trust media, or trust the government. We should also ask whether the media trusts the people and treats them with respect. And whether governments and related authorities and civic bodies trust the people, treat them with respect, and hear what they say.
This article gives the views of the author, and not the position of the LSE Media Policy Project nor of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
About the author

Sonia Livingstone OBE is Professor of Social Psychology in the Department of Media and Communications at LSE. Taking a comparative, critical and contextual approach, her research examines how the changing conditions of mediation are reshaping everyday practices and possibilities for action. She has published twenty books on media audiences, media literacy and media regulation, with a particular focus on the opportunities and risks of digital media use in the everyday lives of children and young people. Her most recent book is The class: living and learning in the digital age (2016, with Julian Sefton-Green). Sonia has advised the UK government, European Commission, European Parliament, Council of Europe and other national and international organisations on children’s rights, risks and safety in the digital age. She was awarded the title of Officer of the Order of the British Empire (OBE) in 2014 'for services to children and child internet safety.' Sonia Livingstone is a fellow of the Academy of Social Sciences, the British Psychological Society, the Royal Society for the Arts and fellow and past President of the International Communication Association (ICA). She has been visiting professor at the Universities of Bergen, Copenhagen, Harvard, Illinois, Milan, Oslo, Paris II, Pennsylvania, and Stockholm, and is on the editorial board of several leading journals. She is on the Executive Board of the UK Council for Child Internet Safety, is a member of the Internet Watch Foundation’s Ethics Committee, is an Expert Advisor to the Council of Europe, and was recently Special Advisor to the House of Lords’ Select Committee on Communications, among other roles. Sonia has received many awards and honours, including honorary doctorates from the University of Montreal, Université Panthéon Assas, the Erasmus University of Rotterdam, the University of the Basque Country, and the University of Copenhagen. She is currently leading the project Global Kids Online (with UNICEF Office of Research-Innocenti and EU Kids Online), researching children’s understanding of digital privacy (funded by the Information Commissioner’s Office) and writing a book with Alicia Blum-Ross called ‘Parenting for a Digital Future (Oxford University Press), among other research, impact and writing projects. Sonia is chairing LSE’s Truth, Trust and Technology Commission in 2017-2018, and participates in the European Commission-funded research networks, DigiLitEY and MakEY. She runs a blog called www.parenting.digital and contributes to the LSE’s Media Policy Project blog. Follow her on Twitter @Livingstone_S
There’s a funny thing about media literacy, and that is that media have crept their way into everyone’s daily life. A young person knows who’s a friend and who’s not and media have a lot to do with that…. Isn’t media literacy also: discussing daily life and the latest news wit peers and teacher and trying to reach a common goal: making the world a better, more liveable place? PS I’m a schoollibrarian in Amsterdam, Holland and for me media literacy also means also informing teachers about books that tell about worldwide digital developments, like The raod to Unfreedom by Timoty Snyder, not exactly hopeful information, but it’s better to know than not to know.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Related Posts

Education for digital citizenship is in vogue, but is it dominated by a new commercial landscape?
October 18th, 2018.

The vital role of measuring impact in media literacy initiatives
July 19th, 2022.

The citizen interest – still a thorny problem for Ofcom
November 3rd, 2014.

Two parallel realities: a media literacy contradiction?
December 17th, 2019.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Adv Med Educ Prof
- v.3(1); 2015 Jan
Impact of media literacy education on knowledge and behavioral intention of adolescents in dealing with media messages according to Stages of Change
Narjes geraee.
1 Department of health education and promotion, School of Health, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran;
MOHAMMAD HOSSEIN KAVEH
Davod shojaeizadeh.
2 Department of health education and promotion, School of Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran;
HAMID REZA TABATABAEE
3 Department of epidemiology, School of Health, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran
Introduction : Mass media influence the health behaviors of adolescents. Evidence shows that traditional strategies such as censorship or limitation are no longer efficient; therefore, teaching media literacy is the best way to protect adolescents from harmful effects. The aim of this pilot study was to evaluate the effects of a media literacy training program on knowledge and behavioral intention of a sample of female students according to the stages of change in dealing with media messages.
Methods : The study was conducted based on a pre-test and post-test control group design. Some 198 female students including 101 in the intervention group and 97 in the control group participated in this study. The educational program was run using interactive teaching-learning techniques. Data collection was performed using a validated and reliable self-administered questionnaire in three phases including a pre-test, post-test, 1 and post-test, 2. The research data was analyzed through SPSS statistical software, version 14 using both descriptive and inferential statistics.
Results : The results of the study showed a significant increase (p=0.001) in the intervention group’s knowledge mean scores after the training program. On the other hand, the difference was not significant in the control group (p=0.200). A considerable percentage of the participants, in the intervention and control groups, were in pre contemplation and contemplation stages in the pre-test (64 and 61, respectively). After the intervention, however, a significant improvement (p=0.001) was observed in the intervention group’s stages of change compared to that in the control group. The distribution of the control group students regarding the stages of change was similar to that in the pre-test.
Conclusion : The study findings revealed that the planned education programs are efficient to improve the adolescents’ knowledge and behavioral intention in dealing with mass media messages.
Introduction
The main feature of the 21st century is media-saturated culture and provision and ease of access to different types of media for everybody, particularly children and adolescents ( 1 - 4 ).
In general, mass media are the result of the people’s need to satisfy such requirements as gaining news and information, entertainment, and socialization. However, the media are not the mirror of reality and their content is not always complete, accurate, and unbiased ( 5 , 6 ).
Nowadays, in addition to consuming the old media, such as TV, children and adolescents also spend a lot of time on new types of media ( 7 , 8 ). Thus, concerns for the adolescents are increasing in this regard. Some issues related to these concerns include the effect of the media on violence, violent behaviors, and crimes ( 9 , 10 ), sexual relationships ( 11 ), educational performance ( 12 ), body image ( 13 ), diet, increasing prevalence of obesity and being involved in sedentary activities ( 14 ), drug abuse and smoking ( 15 ), alcohol abuse ( 16 ), food preferences ( 17 ), and change in the conversational language structure ( 5 ).
Some media authorities believe that such problems can be solved through limitation and censorship. However, censorship and limitation are not desirable responses to the concerns about the mass media and their effects on the children and adolescents ( 18 ).
General health specialists have also made use of various strategies for adjusting the effects of the media on health. Up to now, such approaches as regulation of the media contents, limitation of the children’s media consumption, and social marketing, have been utilized to address the problem ( 7 ).
Since government laws and regulations and changing the media contents are not appropriate strategies for monitoring media consumption and, at the same time, reduction of the adolescents’ exposure to the media is not always practical, parents feel concerned about their children’s media utilization, because children mostly use the media at home. Therefore, parents’ role, as well as the children’s perception, should be taken into account in directing children’s media consumption ( 19 - 21 ). Nevertheless, studies have shown that in the Iranian society, parents do not highly interfere in their children’s watching TV and using computer games, Internet, and other media ( 22 ). Thus, cognitive and motivational backgrounds should be created in the adolescents so that they react toward the media content as well as function spontaneously. One of the important ways to achieve this aim is training the children and adolescents on media literacy.
Many organizations, such as American Academy of Pediatrics, Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Office of National Drug Control Policy, UNESCO, European Commission, and European Parliament and a lot of media organizations, such as Center for Media Literacy (CML), Association for Media Literacy (AML), and National Association for Media Literacy Education (NAMLE), have strong statements regarding media literacy ( 8 , 21 ).
Media literacy is defined as the “ability to understand, analyze, evaluate, and create media messages”. Media literacy training increases the individuals’ doubt about the media content ( 23 ). After all, existence of the individuals with high media literacy leads to increase in the media quality because such individuals require more realistic messages of higher quality ( 5 ).
Evidence shows that the interventions which have been based on the theoretical concepts are more effective in comparison to those which have been based on behavior. Moreover, considerable effectiveness of the interventions requires new methodologies and state of the art in order to repeat and develop findings ( 24 ).
Up to now, various change theories have been developed, providing frameworks for interventions to help people gain positive healthy behaviors. Overall, individual beliefs and purposes are the main elements of two main theories on changes in health-oriented behaviors: Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) and Transtheoretical Model (TTM) ( 25 ).
Transtheoretical model has been defined as a framework which aims to direct the content and scheduling of the designed interventions for improving and facilitating healthy behaviors ( 24 ).
In general, transtheoretical model consists of four constructs: 1- stages of change: temporal readiness for behavior modification, 2- decisional balance: relative importance of perceived advantages and disadvantages of change, 3- situational self-efficacy: trust in the individual capability for behavioral change in positive social and emotional situations, and 4- processes of change: behavioral and experimental strategies people employ in order to improve through the stages ( 26 , 27 ).
“Stages of change” is the main construct of the transtheoretical model. This model considers behavioral changes as a process rather than a dichotomous phenomenon ( 28 ). “Stages of change” is an important construct because it is the representative of time dimension. In the past, behavioral change was considered as a separate event; for instance, quitting smoking, alcohol, or overeating ( 26 ). On the other hand, the transtheoretical model assumes change as a dynamic phenomenon which is created over time and due to movement through several distinct stages. Besides, the individuals should make multiple attempts for behavior change in order to achieve complete success ( 26 , 29 , 30 ).
As mentioned above, in the stages of change model, individuals should move through several stages in order to change their behavior. Each stage is a distinct point in the individuals’ readiness for change and it is assumed that they should do a set of activities in a certain period of time in order to move on to the next stage ( 25 ).
In spite of the increasing trend of growth of the mass media in Iran, unfortunately no attempts have been made in this regard. Considering this gap, performing educational, as well as research activities, seems to be essential in our country. Therefore, the present study aims to describe the mean score of knowledge and the distribution of behavioral intention of a sample of Iranian female students in exposure to media messages, regarding the stages of change before and after receiving media literacy training.
As media literacy training has not been executed in Iran up to now, this study was conducted as a pilot study, using a randomized, controlled, and educational trial design. The study participants included 198 female students in four state secondary schools in Shiraz, Iran. The students were selected through random sampling. After all, a sample of 198 students was determined for the study with 101 in the intervention and 97 in the control group.
The study data were collected, using a questionnaire which was completed by both groups in three phases including before, immediately and one month after the training program. The content validity of the questionnaire was approved, using the ideas of 5 experts of the field. The questionnaire consisted of two parts: the first including the Knowledge questions with 7 case-based, essay-type, open-ended questions which were calculated using the analytical scoring method. The overall scores ranged from 0 to 5. Twenty percent of questionnaires were randomly selected and the knowledge construct was scored by two independent raters, and 78 percent agreement was achieved between raters. In this study, knowledge implied the ability to remember the information about the effects of media messages and different possible reactions toward them, the techniques utilized in creating the media messages, surface and hidden meanings of the messages and different possible interpretations. The students’ stages of change were assessed by describing a correct situation regarding appropriately and critically dealing with media messages, and posing a question about the conformity of the students’ present behavior to that situation. In this way, the students who mentioned that they had not even thought about it were categorized in the “pre contemplation” group, while those who stated that they had thought about the situation but had not done anything about it were classified in the “contemplation” group. In addition, the students who said that they had talked to the informed individuals and had planned to do something were put in the “preparation” category. Finally, the students who claimed that they had acted properly for almost one month were classified in the “act” category and those who stated that they had acted properly for more than 6 months were categorized in the “maintenance” group.
The training program was conducted in 3 sessions using active teaching/learning methods and the students were also provided with booklets.
Since most of the students in both groups, after the initial analyses, were found to be in the pre contemplation stage, the training strategies were focused on increasing the students’ awareness of the media on the adolescents’ health, different possible reactions toward the media, correct reaction to the media, and the outcomes of having active, critical reactions to the media messages in the students’ present and future lives.
Statistical Analysis
The collected data were analyzed through SPSS statistical software, version 14. As K-S Test showed that the distribution of the data was not normal, non-parametric tests such as Mann Whitney and Friedman were used.
The students of the two groups were similar regarding age, sex, and kind of school. The pre-test analyses revealed no significant difference between the two groups regarding knowledge score (p=0.2). The mean score of students’ knowledge in the intervention group, being 0.67±0.42 in the pre-test, increased to 3.15±1.13 in the first post-test. Their mean score of knowledge was 2.87±0.89 in the second post-test. The mean score of knowledge in the control group remained relatively the same through the three phases. Using Freidman and Wilcoxon test, we found that the changes in knowledge mean scores within and between the study groups were statistically significant (p=0.001) (Table.1).
Knowledge mean scores in the groups before and after the training program
The results of Chi-square test showed no significant difference (χ 2 =0.78, df=3, p=0.8) between the two groups regarding their frequency distribution according to their intentional behavior status based on the stages of change. Most of the students in both groups were in the pre contemplation stage (64.35% in the intervention and 62.88% in the control group) and a small number of students were in the maintenance stage (2.97% in the intervention and 2.06% in the control group).
After the intervention, 62.37% and 12.87% of the intervention group students were in the preparation and action stages in the first post-test, and 56.43 and 9.90 in the second post-test, respectively. In the control group, on the other hand, the frequency distribution of the students regarding the stages of change in the post-tests were similar to the pre-test and more than half of the students were still in the pre contemplation stage
The statistical analysis showed significant improvement of the intervention group students regarding the stages of change (p=0.001). However, no significant difference was observed in the frequency distribution of the control group students regarding the stages of change before and after the intervention ( Table 2 ).
Frequency distribution of the students regarding the stages of change before and after the educational intervention
* Statistical test was performed after merging the two last groups (action & maintenance)
The present study investigated the effectiveness of a training program based on the “stages of change” construct of the transtheoretical model, designed in order to improve the knowledge and behavioral intention of the students in exposure to media messages. The study findings revealed the effectiveness of the training program in improving the intervention group students for having an active, critical reaction toward the media messages.
Knowledge is often considered as a prerequisite and predisposing factor to behavioral change. Knowledge is considered as an essential attribute of behavior, and higher rates of knowledge are correlated with higher rates of positive behavior.
Evidence, on the other hand, shows the efficacy of planned educational interventions in knowledge enhancement to facilitate acquiring desired behaviors ( 31 ).
The low levels of students’ knowledge about media literacy, as detected in the pre-test phase of this study, imply the lack of related educational programs in our country and students’ need for such essential programs.
Therefore, the significant increase in knowledge mean score of the intervention group in both phases after the training program is in favor of the efficacy of such programs in improving students’ knowledge about media.
This finding is in line with a large number of studies about media literacy trainings. For instance, Kupersmidt and Scull concluded that even a one-day workshop on media literacy education was effective on the participants’ knowledge of media literacy ( 2 ).
According to the study results concerning the stages of change, a considerable percentage of the participants were in precontemplation and contemplation stages regarding having an active reaction in exposure to media messages in the pre-test. After the intervention, however, a significant improvement was observed in the intervention group’s stages of change in comparison to that in the control group.
Kupersmidt and Scull performed a study and showed a significant reduction in the behavioral intention for alcohol and tobacco abuse in the students who had participated in media literacy training program ( 32 ).
Furthermore, based on the studies by TQ, Tein et al. (2010) and Kupersmidt et al. (2011) to evaluate the adolescents’ media literacy and its relationship with smoking, alcohol abuse, and their future vulnerability, having media literacy was accompanied by less drug and alcohol abuse ( 33 , 34 ).
“Stages of change” construct of the transtheoretical model is based on the assumption that training can improve the individuals’ development through the stages. In this model, each stage represents how much the training has been accepted by the individuals and how effective it has been ( 35 ). Moreover, the participants should perform appropriate tasks at the right time in order to move on to the next stage. This implies that the individuals need special strategies, called the processes of change, in each stage ( 36 ).
According to this model, the individuals in the pre contemplation stage need information about the dangers of their present behavior, while those in the following stages require practical recommendations regarding how to change their behavior ( 35 ). Thus, processes such as awareness increasing should be applied in order to help the individuals move from the pre contemplation to the contemplation stage ( 26 ).
The findings of the current study showed that using awareness increasing strategies regarding daily media consumption, negative effects of the media, and different possible reactions toward them led to a significant improvement in the intervention group students’ development from pre contemplation to contemplation and preparation stages.
It has been assumed that moving through the stages is related to the factors associated with each particular behavior. Therefore, identification and measurement of the effective factors in moving through the stages, including motivation for change, self-confidence, self-efficacy, and social support, can also be beneficial in designing more influential interventions ( 37 ).
In conclusion, the low levels of students’ knowledge about media literacy and their distributions at precontemplation and contemplation stages at pre-test, showed the lack of any sufficient educational programs in Iranian schools. This study revealed the adolescents' need for a theory-based Media Literacy education program.
Ethical aspects of the study
As there was no obligation to mention the name on the questionnaires, and students were assured that their responses will be confidential and also the data were analyzed collectively, therefore there was no need to fill the consent form.
Acknowledgment
This manuscript was extracted from the thesis of the first author (grant No. 6354).The authors therefore thank the vice-chancellery of research and technology at Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran, for the financial support. We also acknowledge the sincere contribution of administrators, teachers, and specially students who participated in this study.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Examples >
- Essay Topics
Essays on Media Literacy
9 samples on this topic
The array of written assignments you might be tasked with while studying Media Literacy is stunning. If some are too challenging, an expertly crafted sample Media Literacy piece on a related subject might lead you out of a dead end. This is when you will definitely acknowledge WowEssays.com ever-expanding directory of Media Literacy essay samples meant to ignite your writing enthusiasm.
Our directory of free college paper samples showcases the most vivid instances of top-notch writing on Media Literacy and related topics. Not only can they help you develop an interesting and fresh topic, but also exhibit the effective use of the best Media Literacy writing practices and content organization techniques. Also, keep in mind that you can use them as a source of dependable sources and factual or statistical data processed by real masters of their craft with solid academic experience in the Media Literacy field.
Alternatively, you can take advantage of effective write my essay assistance, when our experts deliver a unique model essay on Media Literacy tailored to your individual specifications!
Free Media Literacy Question & Answer: Top-Quality Sample To Follow
Sample research paper on wid iii assignment.
December 11, 16
Free Effects Of Mass Media Paper Essay Sample
Major Developments In Mass Media Over The Last Century
Example Of Adolescent Girls And Media Essay
Adolescent Girls and the Media
Example Of Research Paper On Media Violence And Its Affect On Children
How television affects communication in minors: research proposal you might want to emulate, television censorship essay example, women in negative advertising research paper.
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Sexualized Culture and its Effects on Hyper Sexuality Disorder
This essay about the intersection of hypersexualized culture and Hypersexuality Disorder explores how pervasive sexual imagery in media and advertising may influence psychological health and societal norms. It discusses the characteristics of Hypersexuality Disorder, marked by uncontrollable sexual impulses that disrupt personal and social functioning. The essay examines the potential roles of media in normalizing risky sexual behaviors and exacerbating feelings of inadequacy, which may lead to or intensify hypersexual behaviors. Furthermore, it suggests strategies for addressing these cultural impacts, including promoting media literacy and educational programs on healthy sexual development. Overall, the essay argues for a nuanced understanding of the relationship between cultural factors and sexual health disorders, emphasizing the need for comprehensive research and dialogue in managing the implications of a sexualized society.
How it works
In recent decades, the pervasive reach of sexualized imagery in media and advertising has raised important questions about its impact on societal norms and individual psychological health. One significant area of concern is the potential link between a hypersexualized culture and the prevalence of Hypersexuality Disorder, a condition characterized by excessive preoccupations with sexual fantasies, urges, or behaviors that are difficult to control, causing distress or impairment in personal, family, or social functions.
Hypersexuality Disorder, often referred to in the media and popular culture as sex addiction, involves persistent and escalating patterns of sexual behavior despite negative consequences to one’s health, relationships, and responsibilities.
The condition is not just about having a high libido but is a recognized psychological disorder that requires a nuanced understanding and clinical approach.
The rise of a sexualized culture can be seen in the way products are marketed, the normalization of pornography, and the portrayal of sexuality in films and television. These cultural products do not just reflect societal attitudes towards sex; they also shape them. For young people growing up in an environment saturated with sexual imagery and messages, the line between normal sexual development and the risk of developing unhealthy sexual habits can become blurred.
The media’s role in exacerbating hypersexual behavior is complex. On one hand, the accessibility and ubiquity of sexually explicit material may lower the threshold for sexual activity and potentially normalize excessive or risky sexual behaviors. On the other hand, the portrayal of sexuality as a primary aspect of attractiveness and success could pressure individuals to conform to these standards, possibly fueling feelings of inadequacy and leading to compulsive sexual behaviors as a way to validate self-worth or manage stress and anxiety.
Clinically, the treatment for Hypersexuality Disorder involves a variety of approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, which helps individuals understand and manage their thoughts and behaviors, and pharmacotherapy to address underlying or associated psychological issues such as depression or anxiety disorders. A critical component of therapy is also exploring how cultural influences and personal experiences shape one’s sexual attitudes and behaviors.
Socially, addressing the impacts of a sexualized culture requires a broader societal effort. This includes promoting media literacy to help individuals critically assess and understand the media they consume. It also involves fostering environments that support healthy sexual development, where sexuality is respected but not exploited. Educational programs that discuss the psychological, emotional, and physical aspects of sexuality could help mitigate the impact of hypersexualized media.
In conclusion, while a direct causation link between sexualized culture and Hypersexuality Disorder has not been definitively established, the correlation suggests that cultural factors do play a role in the manifestation and exacerbation of the disorder. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing effective interventions and supports for those affected. As society continues to evolve its views on sexuality, ongoing dialogue and research are essential to navigate the complex interplay between cultural trends and individual health.
Remember, this essay is a starting point for inspiration and further research. For more personalized assistance and to ensure your essay meets all academic standards, consider reaching out to professionals at [EduBirdie](https://edubirdie.com/?utm_source=chatgpt&utm_medium=answer&utm_campaign=essayhelper).
Cite this page
Sexualized Culture And Its Effects On Hyper Sexuality Disorder. (2024, Apr 22). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/sexualized-culture-and-its-effects-on-hyper-sexuality-disorder/
"Sexualized Culture And Its Effects On Hyper Sexuality Disorder." PapersOwl.com , 22 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/sexualized-culture-and-its-effects-on-hyper-sexuality-disorder/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Sexualized Culture And Its Effects On Hyper Sexuality Disorder . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/sexualized-culture-and-its-effects-on-hyper-sexuality-disorder/ [Accessed: 22 Apr. 2024]
"Sexualized Culture And Its Effects On Hyper Sexuality Disorder." PapersOwl.com, Apr 22, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/sexualized-culture-and-its-effects-on-hyper-sexuality-disorder/
"Sexualized Culture And Its Effects On Hyper Sexuality Disorder," PapersOwl.com , 22-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/sexualized-culture-and-its-effects-on-hyper-sexuality-disorder/. [Accessed: 22-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Sexualized Culture And Its Effects On Hyper Sexuality Disorder . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/sexualized-culture-and-its-effects-on-hyper-sexuality-disorder/ [Accessed: 22-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
NPR defends its journalism after senior editor says it has lost the public's trust

David Folkenflik

NPR is defending its journalism and integrity after a senior editor wrote an essay accusing it of losing the public's trust. Saul Loeb/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
NPR is defending its journalism and integrity after a senior editor wrote an essay accusing it of losing the public's trust.
NPR's top news executive defended its journalism and its commitment to reflecting a diverse array of views on Tuesday after a senior NPR editor wrote a broad critique of how the network has covered some of the most important stories of the age.
"An open-minded spirit no longer exists within NPR, and now, predictably, we don't have an audience that reflects America," writes Uri Berliner.
A strategic emphasis on diversity and inclusion on the basis of race, ethnicity and sexual orientation, promoted by NPR's former CEO, John Lansing, has fed "the absence of viewpoint diversity," Berliner writes.
NPR's chief news executive, Edith Chapin, wrote in a memo to staff Tuesday afternoon that she and the news leadership team strongly reject Berliner's assessment.
"We're proud to stand behind the exceptional work that our desks and shows do to cover a wide range of challenging stories," she wrote. "We believe that inclusion — among our staff, with our sourcing, and in our overall coverage — is critical to telling the nuanced stories of this country and our world."

NPR names tech executive Katherine Maher to lead in turbulent era
She added, "None of our work is above scrutiny or critique. We must have vigorous discussions in the newsroom about how we serve the public as a whole."
A spokesperson for NPR said Chapin, who also serves as the network's chief content officer, would have no further comment.
Praised by NPR's critics
Berliner is a senior editor on NPR's Business Desk. (Disclosure: I, too, am part of the Business Desk, and Berliner has edited many of my past stories. He did not see any version of this article or participate in its preparation before it was posted publicly.)
Berliner's essay , titled "I've Been at NPR for 25 years. Here's How We Lost America's Trust," was published by The Free Press, a website that has welcomed journalists who have concluded that mainstream news outlets have become reflexively liberal.
Berliner writes that as a Subaru-driving, Sarah Lawrence College graduate who "was raised by a lesbian peace activist mother ," he fits the mold of a loyal NPR fan.
Yet Berliner says NPR's news coverage has fallen short on some of the most controversial stories of recent years, from the question of whether former President Donald Trump colluded with Russia in the 2016 election, to the origins of the virus that causes COVID-19, to the significance and provenance of emails leaked from a laptop owned by Hunter Biden weeks before the 2020 election. In addition, he blasted NPR's coverage of the Israel-Hamas conflict.
On each of these stories, Berliner asserts, NPR has suffered from groupthink due to too little diversity of viewpoints in the newsroom.
The essay ricocheted Tuesday around conservative media , with some labeling Berliner a whistleblower . Others picked it up on social media, including Elon Musk, who has lambasted NPR for leaving his social media site, X. (Musk emailed another NPR reporter a link to Berliner's article with a gibe that the reporter was a "quisling" — a World War II reference to someone who collaborates with the enemy.)
When asked for further comment late Tuesday, Berliner declined, saying the essay spoke for itself.
The arguments he raises — and counters — have percolated across U.S. newsrooms in recent years. The #MeToo sexual harassment scandals of 2016 and 2017 forced newsrooms to listen to and heed more junior colleagues. The social justice movement prompted by the killing of George Floyd in 2020 inspired a reckoning in many places. Newsroom leaders often appeared to stand on shaky ground.
Leaders at many newsrooms, including top editors at The New York Times and the Los Angeles Times , lost their jobs. Legendary Washington Post Executive Editor Martin Baron wrote in his memoir that he feared his bonds with the staff were "frayed beyond repair," especially over the degree of self-expression his journalists expected to exert on social media, before he decided to step down in early 2021.
Since then, Baron and others — including leaders of some of these newsrooms — have suggested that the pendulum has swung too far.

Author Interviews
Legendary editor marty baron describes his 'collision of power' with trump and bezos.
New York Times publisher A.G. Sulzberger warned last year against journalists embracing a stance of what he calls "one-side-ism": "where journalists are demonstrating that they're on the side of the righteous."
"I really think that that can create blind spots and echo chambers," he said.
Internal arguments at The Times over the strength of its reporting on accusations that Hamas engaged in sexual assaults as part of a strategy for its Oct. 7 attack on Israel erupted publicly . The paper conducted an investigation to determine the source of a leak over a planned episode of the paper's podcast The Daily on the subject, which months later has not been released. The newsroom guild accused the paper of "targeted interrogation" of journalists of Middle Eastern descent.
Heated pushback in NPR's newsroom
Given Berliner's account of private conversations, several NPR journalists question whether they can now trust him with unguarded assessments about stories in real time. Others express frustration that he had not sought out comment in advance of publication. Berliner acknowledged to me that for this story, he did not seek NPR's approval to publish the piece, nor did he give the network advance notice.
Some of Berliner's NPR colleagues are responding heatedly. Fernando Alfonso, a senior supervising editor for digital news, wrote that he wholeheartedly rejected Berliner's critique of the coverage of the Israel-Hamas conflict, for which NPR's journalists, like their peers, periodically put themselves at risk.
Alfonso also took issue with Berliner's concern over the focus on diversity at NPR.
"As a person of color who has often worked in newsrooms with little to no people who look like me, the efforts NPR has made to diversify its workforce and its sources are unique and appropriate given the news industry's long-standing lack of diversity," Alfonso says. "These efforts should be celebrated and not denigrated as Uri has done."
After this story was first published, Berliner contested Alfonso's characterization, saying his criticism of NPR is about the lack of diversity of viewpoints, not its diversity itself.
"I never criticized NPR's priority of achieving a more diverse workforce in terms of race, ethnicity and sexual orientation. I have not 'denigrated' NPR's newsroom diversity goals," Berliner said. "That's wrong."
Questions of diversity
Under former CEO John Lansing, NPR made increasing diversity, both of its staff and its audience, its "North Star" mission. Berliner says in the essay that NPR failed to consider broader diversity of viewpoint, noting, "In D.C., where NPR is headquartered and many of us live, I found 87 registered Democrats working in editorial positions and zero Republicans."
Berliner cited audience estimates that suggested a concurrent falloff in listening by Republicans. (The number of people listening to NPR broadcasts and terrestrial radio broadly has declined since the start of the pandemic.)
Former NPR vice president for news and ombudsman Jeffrey Dvorkin tweeted , "I know Uri. He's not wrong."
Others questioned Berliner's logic. "This probably gets causality somewhat backward," tweeted Semafor Washington editor Jordan Weissmann . "I'd guess that a lot of NPR listeners who voted for [Mitt] Romney have changed how they identify politically."
Similarly, Nieman Lab founder Joshua Benton suggested the rise of Trump alienated many NPR-appreciating Republicans from the GOP.
In recent years, NPR has greatly enhanced the percentage of people of color in its workforce and its executive ranks. Four out of 10 staffers are people of color; nearly half of NPR's leadership team identifies as Black, Asian or Latino.
"The philosophy is: Do you want to serve all of America and make sure it sounds like all of America, or not?" Lansing, who stepped down last month, says in response to Berliner's piece. "I'd welcome the argument against that."
"On radio, we were really lagging in our representation of an audience that makes us look like what America looks like today," Lansing says. The U.S. looks and sounds a lot different than it did in 1971, when NPR's first show was broadcast, Lansing says.
A network spokesperson says new NPR CEO Katherine Maher supports Chapin and her response to Berliner's critique.
The spokesperson says that Maher "believes that it's a healthy thing for a public service newsroom to engage in rigorous consideration of the needs of our audiences, including where we serve our mission well and where we can serve it better."
Disclosure: This story was reported and written by NPR Media Correspondent David Folkenflik and edited by Deputy Business Editor Emily Kopp and Managing Editor Gerry Holmes. Under NPR's protocol for reporting on itself, no NPR corporate official or news executive reviewed this story before it was posted publicly.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
NPR in Turmoil After It Is Accused of Liberal Bias
An essay from an editor at the broadcaster has generated a firestorm of criticism about the network on social media, especially among conservatives.

By Benjamin Mullin and Katie Robertson
NPR is facing both internal tumult and a fusillade of attacks by prominent conservatives this week after a senior editor publicly claimed the broadcaster had allowed liberal bias to affect its coverage, risking its trust with audiences.
Uri Berliner, a senior business editor who has worked at NPR for 25 years, wrote in an essay published Tuesday by The Free Press, a popular Substack publication, that “people at every level of NPR have comfortably coalesced around the progressive worldview.”
Mr. Berliner, a Peabody Award-winning journalist, castigated NPR for what he said was a litany of journalistic missteps around coverage of several major news events, including the origins of Covid-19 and the war in Gaza. He also said the internal culture at NPR had placed race and identity as “paramount in nearly every aspect of the workplace.”
Mr. Berliner’s essay has ignited a firestorm of criticism of NPR on social media, especially among conservatives who have long accused the network of political bias in its reporting. Former President Donald J. Trump took to his social media platform, Truth Social, to argue that NPR’s government funding should be rescinded, an argument he has made in the past.
NPR has forcefully pushed back on Mr. Berliner’s accusations and the criticism.
“We’re proud to stand behind the exceptional work that our desks and shows do to cover a wide range of challenging stories,” Edith Chapin, the organization’s editor in chief, said in an email to staff on Tuesday. “We believe that inclusion — among our staff, with our sourcing, and in our overall coverage — is critical to telling the nuanced stories of this country and our world.” Some other NPR journalists also criticized the essay publicly, including Eric Deggans, its TV critic, who faulted Mr. Berliner for not giving NPR an opportunity to comment on the piece.
In an interview on Thursday, Mr. Berliner expressed no regrets about publishing the essay, saying he loved NPR and hoped to make it better by airing criticisms that have gone unheeded by leaders for years. He called NPR a “national trust” that people rely on for fair reporting and superb storytelling.
“I decided to go out and publish it in hopes that something would change, and that we get a broader conversation going about how the news is covered,” Mr. Berliner said.
He said he had not been disciplined by managers, though he said he had received a note from his supervisor reminding him that NPR requires employees to clear speaking appearances and media requests with standards and media relations. He said he didn’t run his remarks to The New York Times by network spokespeople.
When the hosts of NPR’s biggest shows, including “Morning Edition” and “All Things Considered,” convened on Wednesday afternoon for a long-scheduled meet-and-greet with the network’s new chief executive, Katherine Maher , conversation soon turned to Mr. Berliner’s essay, according to two people with knowledge of the meeting. During the lunch, Ms. Chapin told the hosts that she didn’t want Mr. Berliner to become a “martyr,” the people said.
Mr. Berliner’s essay also sent critical Slack messages whizzing through some of the same employee affinity groups focused on racial and sexual identity that he cited in his essay. In one group, several staff members disputed Mr. Berliner’s points about a lack of ideological diversity and said efforts to recruit more people of color would make NPR’s journalism better.
On Wednesday, staff members from “Morning Edition” convened to discuss the fallout from Mr. Berliner’s essay. During the meeting, an NPR producer took issue with Mr. Berliner’s argument for why NPR’s listenership has fallen off, describing a variety of factors that have contributed to the change.
Mr. Berliner’s remarks prompted vehement pushback from several news executives. Tony Cavin, NPR’s managing editor of standards and practices, said in an interview that he rejected all of Mr. Berliner’s claims of unfairness, adding that his remarks would probably make it harder for NPR journalists to do their jobs.
“The next time one of our people calls up a Republican congressman or something and tries to get an answer from them, they may well say, ‘Oh, I read these stories, you guys aren’t fair, so I’m not going to talk to you,’” Mr. Cavin said.
Some journalists have defended Mr. Berliner’s essay. Jeffrey A. Dvorkin, NPR’s former ombudsman, said Mr. Berliner was “not wrong” on social media. Chuck Holmes, a former managing editor at NPR, called Mr. Berliner’s essay “brave” on Facebook.
Mr. Berliner’s criticism was the latest salvo within NPR, which is no stranger to internal division. In October, Mr. Berliner took part in a lengthy debate over whether NPR should defer to language proposed by the Arab and Middle Eastern Journalists Association while covering the conflict in Gaza.
“We don’t need to rely on an advocacy group’s guidance,” Mr. Berliner wrote, according to a copy of the email exchange viewed by The Times. “Our job is to seek out the facts and report them.” The debate didn’t change NPR’s language guidance, which is made by editors who weren’t part of the discussion. And in a statement on Thursday, the Arab and Middle Eastern Journalists Association said it is a professional association for journalists, not a political advocacy group.
Mr. Berliner’s public criticism has highlighted broader concerns within NPR about the public broadcaster’s mission amid continued financial struggles. Last year, NPR cut 10 percent of its staff and canceled four podcasts, including the popular “Invisibilia,” as it tried to make up for a $30 million budget shortfall. Listeners have drifted away from traditional radio to podcasts, and the advertising market has been unsteady.
In his essay, Mr. Berliner laid some of the blame at the feet of NPR’s former chief executive, John Lansing, who said he was retiring at the end of last year after four years in the role. He was replaced by Ms. Maher, who started on March 25.
During a meeting with employees in her first week, Ms. Maher was asked what she thought about decisions to give a platform to political figures like Ronna McDaniel, the former Republican Party chair whose position as a political analyst at NBC News became untenable after an on-air revolt from hosts who criticized her efforts to undermine the 2020 election.
“I think that this conversation has been one that does not have an easy answer,” Ms. Maher responded.
Benjamin Mullin reports on the major companies behind news and entertainment. Contact Ben securely on Signal at +1 530-961-3223 or email at [email protected] . More about Benjamin Mullin
Katie Robertson covers the media industry for The Times. Email: [email protected] More about Katie Robertson
Home — Essay Samples — Information Science and Technology — Digital Literacy — The Value of Being a Media and Information Literate Individual
The Value of Being a Media and Information Literate Individual
- Categories: Digital Literacy
About this sample

Words: 654 |
Published: Sep 1, 2023
Words: 654 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Information Science and Technology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1474 words
1 pages / 594 words
2 pages / 985 words
4 pages / 1802 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Digital Literacy
In our increasingly interconnected world, where technology is deeply woven into the fabric of our daily lives, the specter of computer threats looms large. From malware attacks to hacking and data breaches, the digital landscape [...]
In an era dominated by information and communication technologies, the importance of media literacy has never been more profound. As individuals interact with an array of media platforms and consume a deluge of information [...]
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, the importance of media and information literacy cannot be overstated. As we are inundated with an overwhelming amount of information from various sources, the ability to critically [...]
Warschauer, M. (2018). Digital literacy and digital literacies: Policy, pedagogy and research considerations for education. Nordic Journal of Digital Literacy, 13(1), 2-19. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/00220411011066763
Morphological Image Processing is an important tool in the Digital Image processing, since that science can rigorously quantify many aspects of the geometrical structure of the way that agrees with the human intuition and [...]
With the passage of time, educators and parents have focused on literacy skills such as reading writing, and spelling and have worked very hard on developing these abilities for their children. Therefore, they are not happy with [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essays.io ️ Media Literacy, Essay Example from students accepted to Harvard, Stanford, and other elite schools. ... Related Essay Samples & Examples. Voting as a Civic Responsibility, Essay Example. Voting is a process whereby individuals, such as an electorate or gathering, come together to make a choice or convey an opinion, typically after ...
Media Literacy Examples. Below are 21 examples of ways you can check to see if a media source is reliable. 1. Checking the Age of the Source (Currency) If the information is time sensitive, you may need the newest possible sources. Universities tend to prefer students cite texts that are less than 10 years old.
This essay delves into the significance of media literacy in an age where media messages permeate every facet of our lives. By critically understanding and evaluating media content, individuals can become informed consumers and responsible contributors to the digital landscape.
Media literacy is the ability to identify different types of media and understand the messages they're sending. Kids take in a huge amount of information from a wide array of sources, far beyond the traditional media (TV, radio, newspapers, and magazines) of most parents' youth. There are text messages, memes, viral videos, social media, video ...
Media literacy encompasses a range of competencies that enable individuals to engage with media content critically and intelligently. In a landscape where media messages can shape perceptions, influence behavior, and even shape societal norms, media literacy serves as a defense against manipulation and misinformation.
New Media Literacy Essay. first used, 'literacy' had a very traditional meaning: the ability to read and write ("Literacy," 2011). Being literate was the norm, it was required for all and it distinguished race and class. However, as times change and culture emerges and grows, people acquire new knowledge, such as technology, that can ...
Introduction to the Problem The widespread usage of smartphones and other digital devices has enhanced the necessity of media literacy as a life skill. A media-literate individual can critically assess and interpret media messages, understand the media's role in society, and produce media material with integrity. Students can learn to ...
Media Literacy Thinking About Media. PAGES 6 WORDS 2186. In fact, this is something that Obama discusses openly in his book, Dreams of My Father. In that book, Obama discusses the fact that his stepfather is Muslim and how he believes his stepfather's religion helped shape the man that he is. However, that book, written before Obama came into ...
1: Build a Foundation of Media Literacy Early On. Teaching media literacy from an early age is paramount for several reasons. Firstly, starting early allows educators to develop critical thinking skills in students. By introducing media literacy concepts and practices at a young age, students learn to question, analyze, and evaluate media content.
As governments seek to tackle a variety of problems of the digital age, media (or digital) literacy is often cited as the solution, partly because it is far less controversial than attempting to regulate the internet. LSE Professor Sonia Livingstone, chair of the LSE Commission on Truth, Trust and Technology, stresses the complexity of the challenges involved in improving media literacy, and ...
Media Literacy - Free Essay Examples and Topic Ideas. Media literacy is the ability to critically analyze and evaluate media messages in order to understand how they are constructed, their motives and the impact they have on individuals and society as a whole. It is about being able to decode the information presented in different forms of ...
In honor of Media Literacy Week 2020, the National Association for Media Literacy Education (NAMLE) is focusing on five components of media literacy: Access, Analyze, Evaluate, Create, and Act. In this lesson, students will explore these five elements through engagement with Pulitzer Center news stories. Objectives: Students will be able to... Describe what it means for a story to be under ...
Media literacy is the ability to analyze and evaluate different types of media and the messages they are sending. In today's world, media is a part of our everyday lives. Nonetheless, many people ...
Incorporating media literacy education into the curriculum can take various forms, from dedicated courses to integrating media literacy concepts into existing subjects such as language arts, social studies, and science. These approaches enable students to develop media literacy skills organically as they engage with various subjects.
Essay On Media Literacy. Type of paper: Essay. Topic: Media, Family, Parents, Father, United States, Mass Media, Gay, Campbell. Pages: 2. Words: 400. Published: 03/30/2023. In the modern world, media is an important tool of communication that forms a message and sends it to a wide audience for analysis and interpretation.
The media landscape has undergone an unprecedented revolution in recent decades, becoming an integral and omnipresent part of modern society. In this comprehensive essay, we delve into the multifaceted role of media and its profound impact on individuals and communities worldwide. Media, encompassing various forms such as television, radio ...
Media literacy is defined as the "ability to understand, analyze, evaluate, and create media messages". ... The students were selected through random sampling. After all, a sample of 198 students was determined for the study with 101 in the intervention and 97 in the control group. ... of the field. The questionnaire consisted of two parts ...
Essays on Media Literacy. 9 samples on this topic. The array of written assignments you might be tasked with while studying Media Literacy is stunning. If some are too challenging, an expertly crafted sample Media Literacy piece on a related subject might lead you out of a dead end.
In conclusion, the importance of media and information literacy is paramount in our digital age. It equips individuals with the skills to critically assess media content, differentiate between credible and unreliable sources, and make informed decisions. Media literacy fosters critical thinking, safeguards against misinformation, and promotes ...
Pages: 2 (1063 words) Views: 939. Grade: 5. Download. In the present time, technology is already playing a big role in our society. From the small details and months of delivering messages, we are now in the era where we can already send and receive messages in a second. Within importance of media and information literacy essay this topic will ...
The essay examines the potential roles of media in normalizing risky sexual behaviors and exacerbating feelings of inadequacy, which may lead to or intensify hypersexual behaviors. Furthermore, it suggests strategies for addressing these cultural impacts, including promoting media literacy and educational programs on healthy sexual development.
In conclusion, the value of being a media and information literate individual is a hallmark of a well-rounded and empowered citizen in the digital age. Media literacy equips individuals with the critical skills needed to navigate the complex information landscape, engage in informed civic participation, enhance critical thinking, and practice ...
NPR defends its journalism after senior editor says it has lost the public's trust. NPR is defending its journalism and integrity after a senior editor wrote an essay accusing it of losing the ...
An essay from an editor at the broadcaster has generated a firestorm of criticism about the network on social media, especially among conservatives. By Benjamin Mullin and Katie Robertson NPR is ...
Moreover, media and information literacy plays a pivotal role in fostering media literacy education guides students in understanding the power dynamics at play within media content. By recognizing the influence of media ownership, cultural perspectives, and political interests on the content presented, individuals can engage with media more ...