Persuasive Essay Guide
Persuasive Essay About Covid19

How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid19 | Examples & Tips
11 min read

People also read
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing an Effective Persuasive Essay
200+ Persuasive Essay Topics to Help You Out
Learn How to Create a Persuasive Essay Outline
30+ Free Persuasive Essay Examples To Get You Started
Read Excellent Examples of Persuasive Essay About Gun Control
Crafting a Convincing Persuasive Essay About Abortion
Learn to Write Persuasive Essay About Business With Examples and Tips
Check Out 12 Persuasive Essay About Online Education Examples
Persuasive Essay About Smoking - Making a Powerful Argument with Examples
Are you looking to write a persuasive essay about the Covid-19 pandemic?
Writing a compelling and informative essay about this global crisis can be challenging. It requires researching the latest information, understanding the facts, and presenting your argument persuasively.
But don’t worry! with some guidance from experts, you’ll be able to write an effective and persuasive essay about Covid-19.
In this blog post, we’ll outline the basics of writing a persuasive essay . We’ll provide clear examples, helpful tips, and essential information for crafting your own persuasive piece on Covid-19.
Read on to get started on your essay.
- 1. Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 2. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid19
- 3. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Vaccine
- 4. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
- 5. Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
- 6. Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
- 7. Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 8. Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Here are the steps to help you write a persuasive essay on this topic, along with an example essay:
Step 1: Choose a Specific Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly state your position on a specific aspect of COVID-19. It should be debatable and clear. For example:
Step 2: Research and Gather Information
Collect reliable and up-to-date information from reputable sources to support your thesis statement. This may include statistics, expert opinions, and scientific studies. For instance:
- COVID-19 vaccination effectiveness data
- Information on vaccine mandates in different countries
- Expert statements from health organizations like the WHO or CDC
Step 3: Outline Your Essay
Create a clear and organized outline to structure your essay. A persuasive essay typically follows this structure:
- Introduction
- Background Information
- Body Paragraphs (with supporting evidence)
- Counterarguments (addressing opposing views)
Step 4: Write the Introduction
In the introduction, grab your reader's attention and present your thesis statement. For example:
Step 5: Provide Background Information
Offer context and background information to help your readers understand the issue better. For instance:
Step 6: Develop Body Paragraphs
Each body paragraph should present a single point or piece of evidence that supports your thesis statement. Use clear topic sentences, evidence, and analysis. Here's an example:
Step 7: Address Counterarguments
Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and refute them with strong counterarguments. This demonstrates that you've considered different perspectives. For example:
Step 8: Write the Conclusion
Summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement in the conclusion. End with a strong call to action or thought-provoking statement. For instance:
Step 9: Revise and Proofread
Edit your essay for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling errors. Ensure that your argument flows logically.
Step 10: Cite Your Sources
Include proper citations and a bibliography page to give credit to your sources.
Remember to adjust your approach and arguments based on your target audience and the specific angle you want to take in your persuasive essay about COVID-19.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid19
When writing a persuasive essay about the Covid-19 pandemic, it’s important to consider how you want to present your argument. To help you get started, here are some example essays for you to read:
Check out some more PDF examples below:
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Pandemic
Sample Of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 In The Philippines - Example
If you're in search of a compelling persuasive essay on business, don't miss out on our “ persuasive essay about business ” blog!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Vaccine
Covid19 vaccines are one of the ways to prevent the spread of Covid-19, but they have been a source of controversy. Different sides argue about the benefits or dangers of the new vaccines. Whatever your point of view is, writing a persuasive essay about it is a good way of organizing your thoughts and persuading others.
A persuasive essay about the Covid-19 vaccine could consider the benefits of getting vaccinated as well as the potential side effects.
Below are some examples of persuasive essays on getting vaccinated for Covid-19.
Covid19 Vaccine Persuasive Essay
Persuasive Essay on Covid Vaccines
Interested in thought-provoking discussions on abortion? Read our persuasive essay about abortion blog to eplore arguments!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
Covid19 has drastically changed the way people interact in schools, markets, and workplaces. In short, it has affected all aspects of life. However, people have started to learn to live with Covid19.
Writing a persuasive essay about it shouldn't be stressful. Read the sample essay below to get idea for your own essay about Covid19 integration.
Persuasive Essay About Working From Home During Covid19
Searching for the topic of Online Education? Our persuasive essay about online education is a must-read.
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
Covid-19 has been an ever-evolving issue, with new developments and discoveries being made on a daily basis.
Writing an argumentative essay about such an issue is both interesting and challenging. It allows you to evaluate different aspects of the pandemic, as well as consider potential solutions.
Here are some examples of argumentative essays on Covid19.
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 Sample
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 With Introduction Body and Conclusion
Looking for a persuasive take on the topic of smoking? You'll find it all related arguments in out Persuasive Essay About Smoking blog!
Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
Do you need to prepare a speech about Covid19 and need examples? We have them for you!
Persuasive speeches about Covid-19 can provide the audience with valuable insights on how to best handle the pandemic. They can be used to advocate for specific changes in policies or simply raise awareness about the virus.
Check out some examples of persuasive speeches on Covid-19:
Persuasive Speech About Covid-19 Example
Persuasive Speech About Vaccine For Covid-19
You can also read persuasive essay examples on other topics to master your persuasive techniques!
Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19 requires a thoughtful approach to present your arguments effectively.
Here are some tips to help you craft a compelling persuasive essay on this topic:
Choose a Specific Angle
Start by narrowing down your focus. COVID-19 is a broad topic, so selecting a specific aspect or issue related to it will make your essay more persuasive and manageable. For example, you could focus on vaccination, public health measures, the economic impact, or misinformation.
Provide Credible Sources
Support your arguments with credible sources such as scientific studies, government reports, and reputable news outlets. Reliable sources enhance the credibility of your essay.
Use Persuasive Language
Employ persuasive techniques, such as ethos (establishing credibility), pathos (appealing to emotions), and logos (using logic and evidence). Use vivid examples and anecdotes to make your points relatable.
Organize Your Essay
Structure your essay involves creating a persuasive essay outline and establishing a logical flow from one point to the next. Each paragraph should focus on a single point, and transitions between paragraphs should be smooth and logical.
Emphasize Benefits
Highlight the benefits of your proposed actions or viewpoints. Explain how your suggestions can improve public health, safety, or well-being. Make it clear why your audience should support your position.
Use Visuals -H3
Incorporate graphs, charts, and statistics when applicable. Visual aids can reinforce your arguments and make complex data more accessible to your readers.
Call to Action
End your essay with a strong call to action. Encourage your readers to take a specific step or consider your viewpoint. Make it clear what you want them to do or think after reading your essay.
Revise and Edit
Proofread your essay for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Make sure your arguments are well-structured and that your writing flows smoothly.
Seek Feedback
Have someone else read your essay to get feedback. They may offer valuable insights and help you identify areas where your persuasive techniques can be improved.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Here are some persuasive essay topics on COVID-19:
- The Importance of Vaccination Mandates for COVID-19 Control
- Balancing Public Health and Personal Freedom During a Pandemic
- The Economic Impact of Lockdowns vs. Public Health Benefits
- The Role of Misinformation in Fueling Vaccine Hesitancy
- Remote Learning vs. In-Person Education: What's Best for Students?
- The Ethics of Vaccine Distribution: Prioritizing Vulnerable Populations
- The Mental Health Crisis Amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic
- The Long-Term Effects of COVID-19 on Healthcare Systems
- Global Cooperation vs. Vaccine Nationalism in Fighting the Pandemic
- The Future of Telemedicine: Expanding Healthcare Access Post-COVID-19
In search of more inspiring topics for your next persuasive essay? Our persuasive essay topics blog has plenty of ideas!
To sum it up,
You have read good sample essays and got some helpful tips. You now have the tools you needed to write a persuasive essay about Covid-19. So don't let the doubts stop you, start writing!
If you need professional writing help, don't worry! We've got that for you as well.
MyPerfectWords.com is a professional persuasive essay writing service that can help you craft an excellent persuasive essay on Covid-19. Our experienced essay writer will create a well-structured, insightful paper in no time!
So don't hesitate and place your ' write my essay online ' request today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any ethical considerations when writing a persuasive essay about covid-19.
Yes, there are ethical considerations when writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19. It's essential to ensure the information is accurate, not contribute to misinformation, and be sensitive to the pandemic's impact on individuals and communities. Additionally, respecting diverse viewpoints and emphasizing public health benefits can promote ethical communication.
What impact does COVID-19 have on society?
The impact of COVID-19 on society is far-reaching. It has led to job and economic losses, an increase in stress and mental health disorders, and changes in education systems. It has also had a negative effect on social interactions, as people have been asked to limit their contact with others.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Answer Key
- SRMJEEE Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- JEE Advanced Registration
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET Courses List 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Covid 19 Essay in English
Essay on Covid -19: In a very short amount of time, coronavirus has spread globally. It has had an enormous impact on people's lives, economy, and societies all around the world, affecting every country. Governments have had to take severe measures to try and contain the pandemic. The virus has altered our way of life in many ways, including its effects on our health and our economy. Here are a few sample essays on ‘CoronaVirus’.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19
200 words essay on covid 19, 500 words essay on covid 19.

COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very short period of time. It has affected lives, economies and societies across the world, leaving no country untouched. The virus has caused governments to take drastic measures to try and contain it. From health implications to economic and social ramifications, COVID-19 impacted every part of our lives. It has been more than 2 years since the pandemic hit and the world is still recovering from its effects.
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, the world has been impacted in a number of ways. For one, the global economy has taken a hit as businesses have been forced to close their doors. This has led to widespread job losses and an increase in poverty levels around the world. Additionally, countries have had to impose strict travel restrictions in an attempt to contain the virus, which has resulted in a decrease in tourism and international trade. Furthermore, the pandemic has put immense pressure on healthcare systems globally, as hospitals have been overwhelmed with patients suffering from the virus. Lastly, the outbreak has led to a general feeling of anxiety and uncertainty, as people are fearful of contracting the disease.
My Experience of COVID-19
I still remember how abruptly colleges and schools shut down in March 2020. I was a college student at that time and I was under the impression that everything would go back to normal in a few weeks. I could not have been more wrong. The situation only got worse every week and the government had to impose a lockdown. There were so many restrictions in place. For example, we had to wear face masks whenever we left the house, and we could only go out for essential errands. Restaurants and shops were only allowed to operate at take-out capacity, and many businesses were shut down.
In the current scenario, coronavirus is dominating all aspects of our lives. The coronavirus pandemic has wreaked havoc upon people’s lives, altering the way we live and work in a very short amount of time. It has revolutionised how we think about health care, education, and even social interaction. This virus has had long-term implications on our society, including its impact on mental health, economic stability, and global politics. But we as individuals can help to mitigate these effects by taking personal responsibility to protect themselves and those around them from infection.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Education
The outbreak of coronavirus has had a significant impact on education systems around the world. In China, where the virus originated, all schools and universities were closed for several weeks in an effort to contain the spread of the disease. Many other countries have followed suit, either closing schools altogether or suspending classes for a period of time.
This has resulted in a major disruption to the education of millions of students. Some have been able to continue their studies online, but many have not had access to the internet or have not been able to afford the costs associated with it. This has led to a widening of the digital divide between those who can afford to continue their education online and those who cannot.
The closure of schools has also had a negative impact on the mental health of many students. With no face-to-face contact with friends and teachers, some students have felt isolated and anxious. This has been compounded by the worry and uncertainty surrounding the virus itself.
The situation with coronavirus has improved and schools have been reopened but students are still catching up with the gap of 2 years that the pandemic created. In the meantime, governments and educational institutions are working together to find ways to support students and ensure that they are able to continue their education despite these difficult circumstances.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Economy
The outbreak of the coronavirus has had a significant impact on the global economy. The virus, which originated in China, has spread to over two hundred countries, resulting in widespread panic and a decrease in global trade. As a result of the outbreak, many businesses have been forced to close their doors, leading to a rise in unemployment. In addition, the stock market has taken a severe hit.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Health
The effects that coronavirus has on one's health are still being studied and researched as the virus continues to spread throughout the world. However, some of the potential effects on health that have been observed thus far include respiratory problems, fever, and coughing. In severe cases, pneumonia, kidney failure, and death can occur. It is important for people who think they may have been exposed to the virus to seek medical attention immediately so that they can be treated properly and avoid any serious complications. There is no specific cure or treatment for coronavirus at this time, but there are ways to help ease symptoms and prevent the virus from spreading.
Applications for Admissions are open.

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

UPES School of Liberal Studies
Ranked #52 Among Universities in India by NIRF | Up to 30% Merit-based Scholarships | Lifetime placement assistance

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd
Enrol in PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd for JEE/NEET preparation

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
How to Write About Coronavirus in a College Essay
Students can share how they navigated life during the coronavirus pandemic in a full-length essay or an optional supplement.
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays

Getty Images
Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic.
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many – a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.
Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them – and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic – and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
10 Ways to Discover College Essay Ideas

Tags: students , colleges , college admissions , college applications , college search , Coronavirus
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Universities, the police and protests.
John J. Sloan III May 2, 2024

Biden Condemns Unrest on Campuses
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 2, 2024

How to Find a Mentor in College
Sarah Wood May 2, 2024

20 Beautiful College Campuses
Cole Claybourn May 1, 2024

Congress Comes Down on Campus Protests
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 1, 2024

University Leaders in Their Own Words
Laura Mannweiler May 1, 2024

Nationwide Campus Protests Escalate
Laura Mannweiler April 30, 2024

Best Colleges Surveys Are Out
Eric Brooks April 30, 2024

Questions to Ask on a College Visit
Sarah Wood April 30, 2024

Columbia Gives Ultimatum to Protesters
Lauren Camera April 29, 2024

I Thought We’d Learned Nothing From the Pandemic. I Wasn’t Seeing the Full Picture

M y first home had a back door that opened to a concrete patio with a giant crack down the middle. When my sister and I played, I made sure to stay on the same side of the divide as her, just in case. The 1988 film The Land Before Time was one of the first movies I ever saw, and the image of the earth splintering into pieces planted its roots in my brain. I believed that, even in my own backyard, I could easily become the tiny Triceratops separated from her family, on the other side of the chasm, as everything crumbled into chaos.
Some 30 years later, I marvel at the eerie, unexpected ways that cartoonish nightmare came to life – not just for me and my family, but for all of us. The landscape was already covered in fissures well before COVID-19 made its way across the planet, but the pandemic applied pressure, and the cracks broke wide open, separating us from each other physically and ideologically. Under the weight of the crisis, we scattered and landed on such different patches of earth we could barely see each other’s faces, even when we squinted. We disagreed viciously with each other, about how to respond, but also about what was true.
Recently, someone asked me if we’ve learned anything from the pandemic, and my first thought was a flat no. Nothing. There was a time when I thought it would be the very thing to draw us together and catapult us – as a capital “S” Society – into a kinder future. It’s surreal to remember those early days when people rallied together, sewing masks for health care workers during critical shortages and gathering on balconies in cities from Dallas to New York City to clap and sing songs like “Yellow Submarine.” It felt like a giant lightning bolt shot across the sky, and for one breath, we all saw something that had been hidden in the dark – the inherent vulnerability in being human or maybe our inescapable connectedness .
More from TIME
Read More: The Family Time the Pandemic Stole
But it turns out, it was just a flash. The goodwill vanished as quickly as it appeared. A couple of years later, people feel lied to, abandoned, and all on their own. I’ve felt my own curiosity shrinking, my willingness to reach out waning , my ability to keep my hands open dwindling. I look out across the landscape and see selfishness and rage, burnt earth and so many dead bodies. Game over. We lost. And if we’ve already lost, why try?
Still, the question kept nagging me. I wondered, am I seeing the full picture? What happens when we focus not on the collective society but at one face, one story at a time? I’m not asking for a bow to minimize the suffering – a pretty flourish to put on top and make the whole thing “worth it.” Yuck. That’s not what we need. But I wondered about deep, quiet growth. The kind we feel in our bodies, relationships, homes, places of work, neighborhoods.
Like a walkie-talkie message sent to my allies on the ground, I posted a call on my Instagram. What do you see? What do you hear? What feels possible? Is there life out here? Sprouting up among the rubble? I heard human voices calling back – reports of life, personal and specific. I heard one story at a time – stories of grief and distrust, fury and disappointment. Also gratitude. Discovery. Determination.
Among the most prevalent were the stories of self-revelation. Almost as if machines were given the chance to live as humans, people described blossoming into fuller selves. They listened to their bodies’ cues, recognized their desires and comforts, tuned into their gut instincts, and honored the intuition they hadn’t realized belonged to them. Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. “The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry myself have both shrunk and expanded,” she shared. “I don’t love myself very well with an audience.” Without the daily ritual of trying to pass as “normal” in public, Tamar, a queer mom in the Netherlands, realized she’s autistic. “I think the pandemic helped me to recognize the mask,” she wrote. “Not that unmasking is easy now. But at least I know it’s there.” In a time of widespread suffering that none of us could solve on our own, many tended to our internal wounds and misalignments, large and small, and found clarity.
Read More: A Tool for Staying Grounded in This Era of Constant Uncertainty
I wonder if this flourishing of self-awareness is at least partially responsible for the life alterations people pursued. The pandemic broke open our personal notions of work and pushed us to reevaluate things like time and money. Lucy, a disabled writer in the U.K., made the hard decision to leave her job as a journalist covering Westminster to write freelance about her beloved disability community. “This work feels important in a way nothing else has ever felt,” she wrote. “I don’t think I’d have realized this was what I should be doing without the pandemic.” And she wasn’t alone – many people changed jobs , moved, learned new skills and hobbies, became politically engaged.
Perhaps more than any other shifts, people described a significant reassessment of their relationships. They set boundaries, said no, had challenging conversations. They also reconnected, fell in love, and learned to trust. Jeanne, a quilter in Indiana, got to know relatives she wouldn’t have connected with if lockdowns hadn’t prompted weekly family Zooms. “We are all over the map as regards to our belief systems,” she emphasized, “but it is possible to love people you don’t see eye to eye with on every issue.” Anna, an anti-violence advocate in Maine, learned she could trust her new marriage: “Life was not a honeymoon. But we still chose to turn to each other with kindness and curiosity.” So many bonds forged and broken, strengthened and strained.
Instead of relying on default relationships or institutional structures, widespread recalibrations allowed for going off script and fortifying smaller communities. Mara from Idyllwild, Calif., described the tangible plan for care enacted in her town. “We started a mutual-aid group at the beginning of the pandemic,” she wrote, “and it grew so quickly before we knew it we were feeding 400 of the 4000 residents.” She didn’t pretend the conditions were ideal. In fact, she expressed immense frustration with our collective response to the pandemic. Even so, the local group rallied and continues to offer assistance to their community with help from donations and volunteers (many of whom were originally on the receiving end of support). “I’ve learned that people thrive when they feel their connection to others,” she wrote. Clare, a teacher from the U.K., voiced similar conviction as she described a giant scarf she’s woven out of ribbons, each representing a single person. The scarf is “a collection of stories, moments and wisdom we are sharing with each other,” she wrote. It now stretches well over 1,000 feet.
A few hours into reading the comments, I lay back on my bed, phone held against my chest. The room was quiet, but my internal world was lighting up with firefly flickers. What felt different? Surely part of it was receiving personal accounts of deep-rooted growth. And also, there was something to the mere act of asking and listening. Maybe it connected me to humans before battle cries. Maybe it was the chance to be in conversation with others who were also trying to understand – what is happening to us? Underneath it all, an undeniable thread remained; I saw people peering into the mess and narrating their findings onto the shared frequency. Every comment was like a flare into the sky. I’m here! And if the sky is full of flares, we aren’t alone.
I recognized my own pandemic discoveries – some minor, others massive. Like washing off thick eyeliner and mascara every night is more effort than it’s worth; I can transform the mundane into the magical with a bedsheet, a movie projector, and twinkle lights; my paralyzed body can mother an infant in ways I’d never seen modeled for me. I remembered disappointing, bewildering conversations within my own family of origin and our imperfect attempts to remain close while also seeing things so differently. I realized that every time I get the weekly invite to my virtual “Find the Mumsies” call, with a tiny group of moms living hundreds of miles apart, I’m being welcomed into a pocket of unexpected community. Even though we’ve never been in one room all together, I’ve felt an uncommon kind of solace in their now-familiar faces.
Hope is a slippery thing. I desperately want to hold onto it, but everywhere I look there are real, weighty reasons to despair. The pandemic marks a stretch on the timeline that tangles with a teetering democracy, a deteriorating planet , the loss of human rights that once felt unshakable . When the world is falling apart Land Before Time style, it can feel trite, sniffing out the beauty – useless, firing off flares to anyone looking for signs of life. But, while I’m under no delusions that if we just keep trudging forward we’ll find our own oasis of waterfalls and grassy meadows glistening in the sunshine beneath a heavenly chorus, I wonder if trivializing small acts of beauty, connection, and hope actually cuts us off from resources essential to our survival. The group of abandoned dinosaurs were keeping each other alive and making each other laugh well before they made it to their fantasy ending.
Read More: How Ice Cream Became My Own Personal Act of Resistance
After the monarch butterfly went on the endangered-species list, my friend and fellow writer Hannah Soyer sent me wildflower seeds to plant in my yard. A simple act of big hope – that I will actually plant them, that they will grow, that a monarch butterfly will receive nourishment from whatever blossoms are able to push their way through the dirt. There are so many ways that could fail. But maybe the outcome wasn’t exactly the point. Maybe hope is the dogged insistence – the stubborn defiance – to continue cultivating moments of beauty regardless. There is value in the planting apart from the harvest.
I can’t point out a single collective lesson from the pandemic. It’s hard to see any great “we.” Still, I see the faces in my moms’ group, making pancakes for their kids and popping on between strings of meetings while we try to figure out how to raise these small people in this chaotic world. I think of my friends on Instagram tending to the selves they discovered when no one was watching and the scarf of ribbons stretching the length of more than three football fields. I remember my family of three, holding hands on the way up the ramp to the library. These bits of growth and rings of support might not be loud or right on the surface, but that’s not the same thing as nothing. If we only cared about the bottom-line defeats or sweeping successes of the big picture, we’d never plant flowers at all.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Scenes From Pro-Palestinian Encampments Across U.S. Universities
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Why Your Breakfast Should Start with a Vegetable
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]

The complexity of managing COVID-19: How important is good governance?
- Download the essay
Subscribe to Global Connection
Alaka m. basu , amb alaka m. basu professor, department of global development - cornell university, senior fellow - united nations foundation kaushik basu , and kaushik basu nonresident senior fellow - global economy and development @kaushikcbasu jose maria u. tapia jmut jose maria u. tapia student - cornell university.
November 17, 2020
- 13 min read
This essay is part of “ Reimagining the global economy: Building back better in a post-COVID-19 world ,” a collection of 12 essays presenting new ideas to guide policies and shape debates in a post-COVID-19 world.
The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed the inadequacy of public health systems worldwide, casting a shadow that we could not have imagined even a year ago. As the fog of confusion lifts and we begin to understand the rudiments of how the virus behaves, the end of the pandemic is nowhere in sight. The number of cases and the deaths continue to rise. The latter breached the 1 million mark a few weeks ago and it looks likely now that, in terms of severity, this pandemic will surpass the Asian Flu of 1957-58 and the Hong Kong Flu of 1968-69.
Moreover, a parallel problem may well exceed the direct death toll from the virus. We are referring to the growing economic crises globally, and the prospect that these may hit emerging economies especially hard.
The economic fall-out is not entirely the direct outcome of the COVID-19 pandemic but a result of how we have responded to it—what measures governments took and how ordinary people, workers, and firms reacted to the crisis. The government activism to contain the virus that we saw this time exceeds that in previous such crises, which may have dampened the spread of the COVID-19 but has extracted a toll from the economy.
This essay takes stock of the policies adopted by governments in emerging economies, and what effect these governance strategies may have had, and then speculates about what the future is likely to look like and what we may do here on.
Nations that build walls to keep out goods, people and talent will get out-competed by other nations in the product market.
It is becoming clear that the scramble among several emerging economies to imitate and outdo European and North American countries was a mistake. We get a glimpse of this by considering two nations continents apart, the economies of which have been among the hardest hit in the world, namely, Peru and India. During the second quarter of 2020, Peru saw an annual growth of -30.2 percent and India -23.9 percent. From the global Q2 data that have emerged thus far, Peru and India are among the four slowest growing economies in the world. Along with U.K and Tunisia these are the only nations that lost more than 20 percent of their GDP. 1
COVID-19-related mortality statistics, and, in particular, the Crude Mortality Rate (CMR), however imperfect, are the most telling indicator of the comparative scale of the pandemic in different countries. At first glance, from the end of October 2020, Peru, with 1039 COVID-19 deaths per million population looks bad by any standard and much worse than India with 88. Peru’s CMR is currently among the highest reported globally.
However, both Peru and India need to be placed in regional perspective. For reasons that are likely to do with the history of past diseases, there are striking regional differences in the lethality of the virus (Figure 11.1). South America is worse hit than any other world region, and Asia and Africa seem to have got it relatively lightly, in contrast to Europe and America. The stark regional difference cries out for more epidemiological analysis. But even as we await that, these are differences that cannot be ignored.
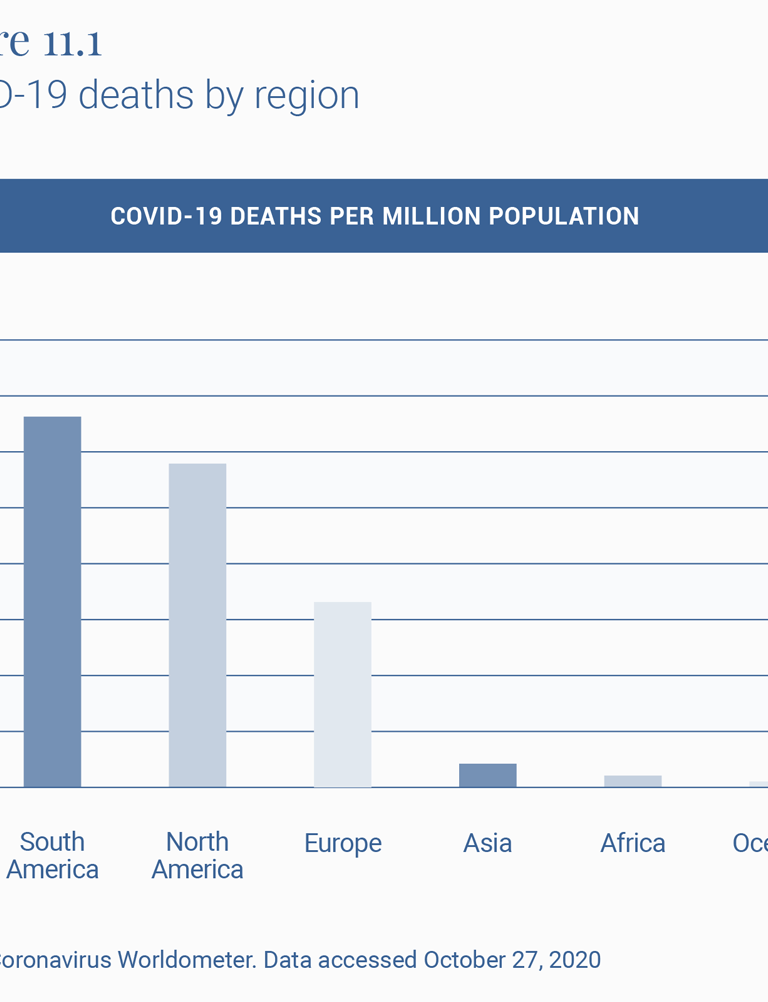
To understand the effect of policy interventions, it is therefore important to look at how these countries fare within their own regions, which have had similar histories of illnesses and viruses (Figure 11.2). Both Peru and India do much worse than the neighbors with whom they largely share their social, economic, ecological and demographic features. Peru’s COVID-19 mortality rate per million population, or CMR, of 1039 is ahead of the second highest, Brazil at 749, and almost twice that of Argentina at 679.
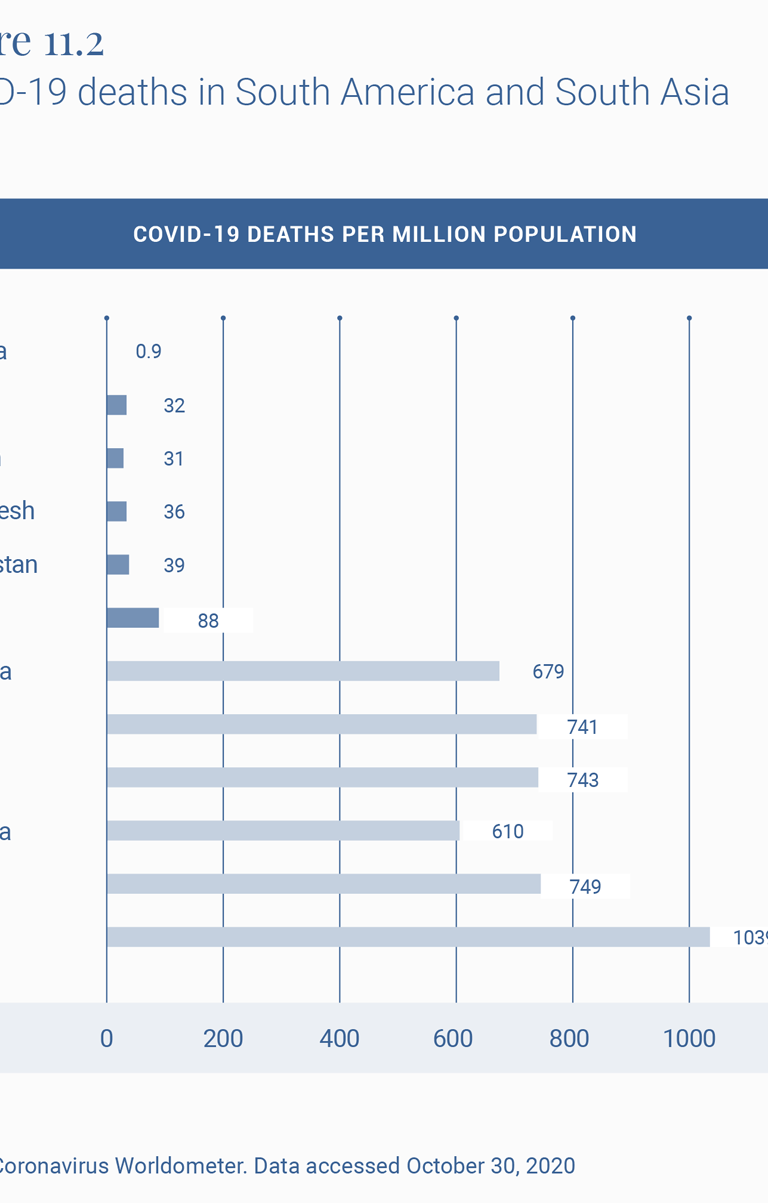
Similarly, India at 88 compares well with Europe and the U.S., as does virtually all of Asia and Africa, but is doing much worse than its neighbors, with the second worst country in the region, Afghanistan, experiencing less than half the death rate of India.
The official Indian statement that up to 78,000 deaths 2 were averted by the lockdown has been criticized 3 for its assumptions. A more reasonable exercise is to estimate the excess deaths experienced by a country that breaks away from the pattern of its regional neighbors. So, for example, if India had experienced Afghanistan’s COVID-19 mortality rate, it would by now have had 54,112 deaths. And if it had the rate reported by Bangladesh, it would have had 49,950 deaths from COVID-19 today. In other words, more than half its current toll of some 122,099 COVID-19 deaths would have been avoided if it had experienced the same virus hit as its neighbors.
What might explain this outlier experience of COVID-19 CMRs and economic downslide in India and Peru? If the regional background conditions are broadly similar, one is left to ask if it is in fact the policy response that differed markedly and might account for these relatively poor outcomes.
Peru and India have performed poorly in terms of GDP growth rate in Q2 2020 among the countries displayed in Table 2, and given that both these countries are often treated as case studies of strong governance, this draws attention to the fact that there may be a dissonance between strong governance and good governance.
The turnaround for India has been especially surprising, given that until a few years ago it was among the three fastest growing economies in the world. The slowdown began in 2016, though the sharp downturn, sharper than virtually all other countries, occurred after the lockdown.
On the COVID-19 policy front, both India and Peru have become known for what the Oxford University’s COVID Policy Tracker 4 calls the “stringency” of the government’s response to the epidemic. At 8 pm on March 24, 2020, the Indian government announced, with four hours’ notice, a complete nationwide shutdown. Virtually all movement outside the perimeter of one’s home was officially sought to be brought to a standstill. Naturally, as described in several papers, such as that of Ray and Subramanian, 5 this meant that most economic life also came to a sudden standstill, which in turn meant that hundreds of millions of workers in the informal, as well as more marginally formal sectors, lost their livelihoods.
In addition, tens of millions of these workers, being migrant workers in places far-flung from their original homes, also lost their temporary homes and their savings with these lost livelihoods, so that the only safe space that beckoned them was their place of origin in small towns and villages often hundreds of miles away from their places of work.
After a few weeks of precarious living in their migrant destinations, they set off, on foot since trains and buses had been stopped, for these towns and villages, creating a “lockdown and scatter” that spread the virus from the city to the town and the town to the village. Indeed, “lockdown” is a bit of a misnomer for what happened in India, since over 20 million people did exactly the opposite of what one does in a lockdown. Thus India had a strange combination of lockdown some and scatter the rest, like in no other country. They spilled out and scattered in ways they would otherwise not do. It is not surprising that the infection, which was marginally present in rural areas (23 percent in April), now makes up some 54 percent of all cases in India. 6
In Peru too, the lockdown was sudden, nationwide, long drawn out and stringent. 7 Jobs were lost, financial aid was difficult to disburse, migrant workers were forced to return home, and the virus has now spread to all parts of the country with death rates from it surpassing almost every other part of the world.
As an aside, to think about ways of implementing lockdowns that are less stringent and geographically as well as functionally less total, an example from yet another continent is instructive. Ethiopia, with a COVID-19 death rate of 13 per million population seems to have bettered the already relatively low African rate of 31 in Table 1. 8
We hope that human beings will emerge from this crisis more aware of the problems of sustainability.
The way forward
We next move from the immediate crisis to the medium term. Where is the world headed and how should we deal with the new world? Arguably, that two sectors that will emerge larger and stronger in the post-pandemic world are: digital technology and outsourcing, and healthcare and pharmaceuticals.
The last 9 months of the pandemic have been a huge training ground for people in the use of digital technology—Zoom, WebEx, digital finance, and many others. This learning-by-doing exercise is likely to give a big boost to outsourcing, which has the potential to help countries like India, the Philippines, and South Africa.
Globalization may see a short-run retreat but, we believe, it will come back with a vengeance. Nations that build walls to keep out goods, people and talent will get out-competed by other nations in the product market. This realization will make most countries reverse their knee-jerk anti-globalization; and the ones that do not will cease to be important global players. Either way, globalization will be back on track and with a much greater amount of outsourcing.
To return, more critically this time, to our earlier aside on Ethiopia, its historical and contemporary record on tampering with internet connectivity 9 in an attempt to muzzle inter-ethnic tensions and political dissent will not serve it well in such a post-pandemic scenario. This is a useful reminder for all emerging market economies.
We hope that human beings will emerge from this crisis more aware of the problems of sustainability. This could divert some demand from luxury goods to better health, and what is best described as “creative consumption”: art, music, and culture. 10 The former will mean much larger healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors.
But to take advantage of these new opportunities, nations will need to navigate the current predicament so that they have a viable economy once the pandemic passes. Thus it is important to be able to control the pandemic while keeping the economy open. There is some emerging literature 11 on this, but much more is needed. This is a governance challenge of a kind rarely faced, because the pandemic has disrupted normal markets and there is need, at least in the short run, for governments to step in to fill the caveat.
Emerging economies will have to devise novel governance strategies for doing this double duty of tamping down on new infections without strident controls on economic behavior and without blindly imitating Europe and America.
Here is an example. One interesting opportunity amidst this chaos is to tap into the “resource” of those who have already had COVID-19 and are immune, even if only in the short-term—we still have no definitive evidence on the length of acquired immunity. These people can be offered a high salary to work in sectors that require physical interaction with others. This will help keep supply chains unbroken. Normally, the market would have on its own caused such a salary increase but in this case, the main benefit of marshaling this labor force is on the aggregate economy and GDP and therefore is a classic case of positive externality, which the free market does not adequately reward. It is more a challenge of governance. As with most economic policy, this will need careful research and design before being implemented. We have to be aware that a policy like this will come with its risk of bribery and corruption. There is also the moral hazard challenge of poor people choosing to get COVID-19 in order to qualify for these special jobs. Safeguards will be needed against these risks. But we believe that any government that succeeds in implementing an intelligently-designed intervention to draw on this huge, under-utilized resource can have a big, positive impact on the economy 12 .
This is just one idea. We must innovate in different ways to survive the crisis and then have the ability to navigate the new world that will emerge, hopefully in the not too distant future.
Related Content
Emiliana Vegas, Rebecca Winthrop
Homi Kharas, John W. McArthur
Anthony F. Pipa, Max Bouchet
Note: We are grateful for financial support from Cornell University’s Hatfield Fund for the research associated with this paper. We also wish to express our gratitude to Homi Kharas for many suggestions and David Batcheck for generous editorial help.
- “GDP Annual Growth Rate – Forecast 2020-2022,” Trading Economics, https://tradingeconomics.com/forecast/gdp-annual-growth-rate.
- “Government Cites Various Statistical Models, Says Averted Between 1.4 Million-2.9 Million Cases Due To Lockdown,” Business World, May 23, 2020, www.businessworld.in/article/Government-Cites-Various-Statistical-Models-Says-Averted-Between-1-4-million-2-9-million-Cases-Due-To-Lockdown/23-05-2020-193002/.
- Suvrat Raju, “Did the Indian lockdown avert deaths?” medRxiv , July 5, 2020, https://europepmc.org/article/ppr/ppr183813#A1.
- “COVID Policy Tracker,” Oxford University, https://github.com/OxCGRT/covid-policy-tracker t.
- Debraj Ray and S. Subramanian, “India’s Lockdown: An Interim Report,” NBER Working Paper, May 2020, https://www.nber.org/papers/w27282.
- Gopika Gopakumar and Shayan Ghosh, “Rural recovery could slow down as cases rise, says Ghosh,” Mint, August 19, 2020, https://www.livemint.com/news/india/rural-recovery-could-slow-down-as-cases-rise-says-ghosh-11597801644015.html.
- Pierina Pighi Bel and Jake Horton, “Coronavirus: What’s happening in Peru?,” BBC, July 9, 2020, https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-53150808.
- “No lockdown, few ventilators, but Ethiopia is beating Covid-19,” Financial Times, May 27, 2020, https://www.ft.com/content/7c6327ca-a00b-11ea-b65d-489c67b0d85d.
- Cara Anna, “Ethiopia enters 3rd week of internet shutdown after unrest,” Washington Post, July 14, 2020, https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/africa/ethiopia-enters-3rd-week-of-internet-shutdown-after-unrest/2020/07/14/4699c400-c5d6-11ea-a825-8722004e4150_story.html.
- Patrick Kabanda, The Creative Wealth of Nations: Can the Arts Advance Development? (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2018).
- Guanlin Li et al, “Disease-dependent interaction policies to support health and economic outcomes during the COVID-19 epidemic,” medRxiv, August 2020, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.08.24.20180752v3.
- For helpful discussion concerning this idea, we are grateful to Turab Hussain, Daksh Walia and Mehr-un-Nisa, during a seminar of South Asian Economics Students’ Meet (SAESM).
Global Economy and Development
Paula Ingabire
May 2, 2024
The Brookings Institution, Washington DC
10:30 am - 12:00 pm EDT
Anwar Aridi, Jeong-Dong Lee
May 1, 2024
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 04 June 2021
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: an overview of systematic reviews
- Israel Júnior Borges do Nascimento 1 , 2 ,
- Dónal P. O’Mathúna 3 , 4 ,
- Thilo Caspar von Groote 5 ,
- Hebatullah Mohamed Abdulazeem 6 ,
- Ishanka Weerasekara 7 , 8 ,
- Ana Marusic 9 ,
- Livia Puljak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8467-6061 10 ,
- Vinicius Tassoni Civile 11 ,
- Irena Zakarija-Grkovic 9 ,
- Tina Poklepovic Pericic 9 ,
- Alvaro Nagib Atallah 11 ,
- Santino Filoso 12 ,
- Nicola Luigi Bragazzi 13 &
- Milena Soriano Marcolino 1
On behalf of the International Network of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (InterNetCOVID-19)
BMC Infectious Diseases volume 21 , Article number: 525 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
16k Accesses
29 Citations
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
Navigating the rapidly growing body of scientific literature on the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic is challenging, and ongoing critical appraisal of this output is essential. We aimed to summarize and critically appraise systematic reviews of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in humans that were available at the beginning of the pandemic.
Nine databases (Medline, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, Web of Sciences, PDQ-Evidence, WHO’s Global Research, LILACS, and Epistemonikos) were searched from December 1, 2019, to March 24, 2020. Systematic reviews analyzing primary studies of COVID-19 were included. Two authors independently undertook screening, selection, extraction (data on clinical symptoms, prevalence, pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, diagnostic test assessment, laboratory, and radiological findings), and quality assessment (AMSTAR 2). A meta-analysis was performed of the prevalence of clinical outcomes.
Eighteen systematic reviews were included; one was empty (did not identify any relevant study). Using AMSTAR 2, confidence in the results of all 18 reviews was rated as “critically low”. Identified symptoms of COVID-19 were (range values of point estimates): fever (82–95%), cough with or without sputum (58–72%), dyspnea (26–59%), myalgia or muscle fatigue (29–51%), sore throat (10–13%), headache (8–12%) and gastrointestinal complaints (5–9%). Severe symptoms were more common in men. Elevated C-reactive protein and lactate dehydrogenase, and slightly elevated aspartate and alanine aminotransferase, were commonly described. Thrombocytopenia and elevated levels of procalcitonin and cardiac troponin I were associated with severe disease. A frequent finding on chest imaging was uni- or bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacity. A single review investigated the impact of medication (chloroquine) but found no verifiable clinical data. All-cause mortality ranged from 0.3 to 13.9%.
Conclusions
In this overview of systematic reviews, we analyzed evidence from the first 18 systematic reviews that were published after the emergence of COVID-19. However, confidence in the results of all reviews was “critically low”. Thus, systematic reviews that were published early on in the pandemic were of questionable usefulness. Even during public health emergencies, studies and systematic reviews should adhere to established methodological standards.
Peer Review reports
The spread of the “Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus 2” (SARS-CoV-2), the causal agent of COVID-19, was characterized as a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) in March 2020 and has triggered an international public health emergency [ 1 ]. The numbers of confirmed cases and deaths due to COVID-19 are rapidly escalating, counting in millions [ 2 ], causing massive economic strain, and escalating healthcare and public health expenses [ 3 , 4 ].
The research community has responded by publishing an impressive number of scientific reports related to COVID-19. The world was alerted to the new disease at the beginning of 2020 [ 1 ], and by mid-March 2020, more than 2000 articles had been published on COVID-19 in scholarly journals, with 25% of them containing original data [ 5 ]. The living map of COVID-19 evidence, curated by the Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre), contained more than 40,000 records by February 2021 [ 6 ]. More than 100,000 records on PubMed were labeled as “SARS-CoV-2 literature, sequence, and clinical content” by February 2021 [ 7 ].
Due to publication speed, the research community has voiced concerns regarding the quality and reproducibility of evidence produced during the COVID-19 pandemic, warning of the potential damaging approach of “publish first, retract later” [ 8 ]. It appears that these concerns are not unfounded, as it has been reported that COVID-19 articles were overrepresented in the pool of retracted articles in 2020 [ 9 ]. These concerns about inadequate evidence are of major importance because they can lead to poor clinical practice and inappropriate policies [ 10 ].
Systematic reviews are a cornerstone of today’s evidence-informed decision-making. By synthesizing all relevant evidence regarding a particular topic, systematic reviews reflect the current scientific knowledge. Systematic reviews are considered to be at the highest level in the hierarchy of evidence and should be used to make informed decisions. However, with high numbers of systematic reviews of different scope and methodological quality being published, overviews of multiple systematic reviews that assess their methodological quality are essential [ 11 , 12 , 13 ]. An overview of systematic reviews helps identify and organize the literature and highlights areas of priority in decision-making.
In this overview of systematic reviews, we aimed to summarize and critically appraise systematic reviews of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in humans that were available at the beginning of the pandemic.
Methodology
Research question.
This overview’s primary objective was to summarize and critically appraise systematic reviews that assessed any type of primary clinical data from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. Our research question was purposefully broad because we wanted to analyze as many systematic reviews as possible that were available early following the COVID-19 outbreak.
Study design
We conducted an overview of systematic reviews. The idea for this overview originated in a protocol for a systematic review submitted to PROSPERO (CRD42020170623), which indicated a plan to conduct an overview.
Overviews of systematic reviews use explicit and systematic methods for searching and identifying multiple systematic reviews addressing related research questions in the same field to extract and analyze evidence across important outcomes. Overviews of systematic reviews are in principle similar to systematic reviews of interventions, but the unit of analysis is a systematic review [ 14 , 15 , 16 ].
We used the overview methodology instead of other evidence synthesis methods to allow us to collate and appraise multiple systematic reviews on this topic, and to extract and analyze their results across relevant topics [ 17 ]. The overview and meta-analysis of systematic reviews allowed us to investigate the methodological quality of included studies, summarize results, and identify specific areas of available or limited evidence, thereby strengthening the current understanding of this novel disease and guiding future research [ 13 ].
A reporting guideline for overviews of reviews is currently under development, i.e., Preferred Reporting Items for Overviews of Reviews (PRIOR) [ 18 ]. As the PRIOR checklist is still not published, this study was reported following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2009 statement [ 19 ]. The methodology used in this review was adapted from the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions and also followed established methodological considerations for analyzing existing systematic reviews [ 14 ].
Approval of a research ethics committee was not necessary as the study analyzed only publicly available articles.
Eligibility criteria
Systematic reviews were included if they analyzed primary data from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 as confirmed by RT-PCR or another pre-specified diagnostic technique. Eligible reviews covered all topics related to COVID-19 including, but not limited to, those that reported clinical symptoms, diagnostic methods, therapeutic interventions, laboratory findings, or radiological results. Both full manuscripts and abbreviated versions, such as letters, were eligible.
No restrictions were imposed on the design of the primary studies included within the systematic reviews, the last search date, whether the review included meta-analyses or language. Reviews related to SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses were eligible, but from those reviews, we analyzed only data related to SARS-CoV-2.
No consensus definition exists for a systematic review [ 20 ], and debates continue about the defining characteristics of a systematic review [ 21 ]. Cochrane’s guidance for overviews of reviews recommends setting pre-established criteria for making decisions around inclusion [ 14 ]. That is supported by a recent scoping review about guidance for overviews of systematic reviews [ 22 ].
Thus, for this study, we defined a systematic review as a research report which searched for primary research studies on a specific topic using an explicit search strategy, had a detailed description of the methods with explicit inclusion criteria provided, and provided a summary of the included studies either in narrative or quantitative format (such as a meta-analysis). Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews were considered eligible for inclusion, with or without meta-analysis, and regardless of the study design, language restriction and methodology of the included primary studies. To be eligible for inclusion, reviews had to be clearly analyzing data related to SARS-CoV-2 (associated or not with other viruses). We excluded narrative reviews without those characteristics as these are less likely to be replicable and are more prone to bias.
Scoping reviews and rapid reviews were eligible for inclusion in this overview if they met our pre-defined inclusion criteria noted above. We included reviews that addressed SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses if they reported separate data regarding SARS-CoV-2.
Information sources
Nine databases were searched for eligible records published between December 1, 2019, and March 24, 2020: Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews via Cochrane Library, PubMed, EMBASE, CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), Web of Sciences, LILACS (Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature), PDQ-Evidence, WHO’s Global Research on Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19), and Epistemonikos.
The comprehensive search strategy for each database is provided in Additional file 1 and was designed and conducted in collaboration with an information specialist. All retrieved records were primarily processed in EndNote, where duplicates were removed, and records were then imported into the Covidence platform [ 23 ]. In addition to database searches, we screened reference lists of reviews included after screening records retrieved via databases.
Study selection
All searches, screening of titles and abstracts, and record selection, were performed independently by two investigators using the Covidence platform [ 23 ]. Articles deemed potentially eligible were retrieved for full-text screening carried out independently by two investigators. Discrepancies at all stages were resolved by consensus. During the screening, records published in languages other than English were translated by a native/fluent speaker.
Data collection process
We custom designed a data extraction table for this study, which was piloted by two authors independently. Data extraction was performed independently by two authors. Conflicts were resolved by consensus or by consulting a third researcher.
We extracted the following data: article identification data (authors’ name and journal of publication), search period, number of databases searched, population or settings considered, main results and outcomes observed, and number of participants. From Web of Science (Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA), we extracted journal rank (quartile) and Journal Impact Factor (JIF).
We categorized the following as primary outcomes: all-cause mortality, need for and length of mechanical ventilation, length of hospitalization (in days), admission to intensive care unit (yes/no), and length of stay in the intensive care unit.
The following outcomes were categorized as exploratory: diagnostic methods used for detection of the virus, male to female ratio, clinical symptoms, pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, laboratory findings (full blood count, liver enzymes, C-reactive protein, d-dimer, albumin, lipid profile, serum electrolytes, blood vitamin levels, glucose levels, and any other important biomarkers), and radiological findings (using radiography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound).
We also collected data on reporting guidelines and requirements for the publication of systematic reviews and meta-analyses from journal websites where included reviews were published.
Quality assessment in individual reviews
Two researchers independently assessed the reviews’ quality using the “A MeaSurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews 2 (AMSTAR 2)”. We acknowledge that the AMSTAR 2 was created as “a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomized or non-randomized studies of healthcare interventions, or both” [ 24 ]. However, since AMSTAR 2 was designed for systematic reviews of intervention trials, and we included additional types of systematic reviews, we adjusted some AMSTAR 2 ratings and reported these in Additional file 2 .
Adherence to each item was rated as follows: yes, partial yes, no, or not applicable (such as when a meta-analysis was not conducted). The overall confidence in the results of the review is rated as “critically low”, “low”, “moderate” or “high”, according to the AMSTAR 2 guidance based on seven critical domains, which are items 2, 4, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15 as defined by AMSTAR 2 authors [ 24 ]. We reported our adherence ratings for transparency of our decision with accompanying explanations, for each item, in each included review.
One of the included systematic reviews was conducted by some members of this author team [ 25 ]. This review was initially assessed independently by two authors who were not co-authors of that review to prevent the risk of bias in assessing this study.
Synthesis of results
For data synthesis, we prepared a table summarizing each systematic review. Graphs illustrating the mortality rate and clinical symptoms were created. We then prepared a narrative summary of the methods, findings, study strengths, and limitations.
For analysis of the prevalence of clinical outcomes, we extracted data on the number of events and the total number of patients to perform proportional meta-analysis using RStudio© software, with the “meta” package (version 4.9–6), using the “metaprop” function for reviews that did not perform a meta-analysis, excluding case studies because of the absence of variance. For reviews that did not perform a meta-analysis, we presented pooled results of proportions with their respective confidence intervals (95%) by the inverse variance method with a random-effects model, using the DerSimonian-Laird estimator for τ 2 . We adjusted data using Freeman-Tukey double arcosen transformation. Confidence intervals were calculated using the Clopper-Pearson method for individual studies. We created forest plots using the RStudio© software, with the “metafor” package (version 2.1–0) and “forest” function.
Managing overlapping systematic reviews
Some of the included systematic reviews that address the same or similar research questions may include the same primary studies in overviews. Including such overlapping reviews may introduce bias when outcome data from the same primary study are included in the analyses of an overview multiple times. Thus, in summaries of evidence, multiple-counting of the same outcome data will give data from some primary studies too much influence [ 14 ]. In this overview, we did not exclude overlapping systematic reviews because, according to Cochrane’s guidance, it may be appropriate to include all relevant reviews’ results if the purpose of the overview is to present and describe the current body of evidence on a topic [ 14 ]. To avoid any bias in summary estimates associated with overlapping reviews, we generated forest plots showing data from individual systematic reviews, but the results were not pooled because some primary studies were included in multiple reviews.
Our search retrieved 1063 publications, of which 175 were duplicates. Most publications were excluded after the title and abstract analysis ( n = 860). Among the 28 studies selected for full-text screening, 10 were excluded for the reasons described in Additional file 3 , and 18 were included in the final analysis (Fig. 1 ) [ 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ]. Reference list screening did not retrieve any additional systematic reviews.
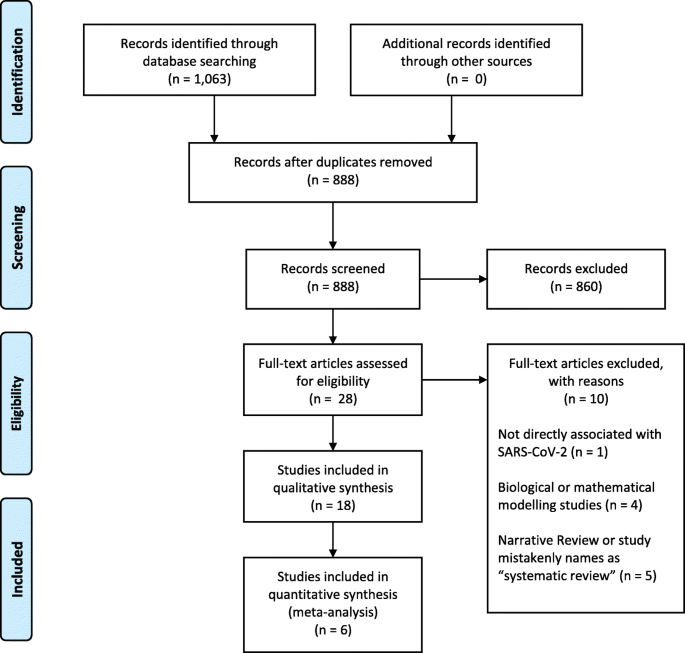
PRISMA flow diagram
Characteristics of included reviews
Summary features of 18 systematic reviews are presented in Table 1 . They were published in 14 different journals. Only four of these journals had specific requirements for systematic reviews (with or without meta-analysis): European Journal of Internal Medicine, Journal of Clinical Medicine, Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Clinical Research in Cardiology . Two journals reported that they published only invited reviews ( Journal of Medical Virology and Clinica Chimica Acta ). Three systematic reviews in our study were published as letters; one was labeled as a scoping review and another as a rapid review (Table 2 ).
All reviews were published in English, in first quartile (Q1) journals, with JIF ranging from 1.692 to 6.062. One review was empty, meaning that its search did not identify any relevant studies; i.e., no primary studies were included [ 36 ]. The remaining 17 reviews included 269 unique studies; the majority ( N = 211; 78%) were included in only a single review included in our study (range: 1 to 12). Primary studies included in the reviews were published between December 2019 and March 18, 2020, and comprised case reports, case series, cohorts, and other observational studies. We found only one review that included randomized clinical trials [ 38 ]. In the included reviews, systematic literature searches were performed from 2019 (entire year) up to March 9, 2020. Ten systematic reviews included meta-analyses. The list of primary studies found in the included systematic reviews is shown in Additional file 4 , as well as the number of reviews in which each primary study was included.
Population and study designs
Most of the reviews analyzed data from patients with COVID-19 who developed pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), or any other correlated complication. One review aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of using surgical masks on preventing transmission of the virus [ 36 ], one review was focused on pediatric patients [ 34 ], and one review investigated COVID-19 in pregnant women [ 37 ]. Most reviews assessed clinical symptoms, laboratory findings, or radiological results.
Systematic review findings
The summary of findings from individual reviews is shown in Table 2 . Overall, all-cause mortality ranged from 0.3 to 13.9% (Fig. 2 ).
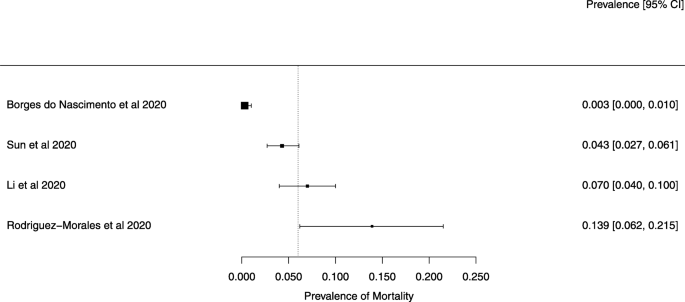
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of mortality
Clinical symptoms
Seven reviews described the main clinical manifestations of COVID-19 [ 26 , 28 , 29 , 34 , 35 , 39 , 41 ]. Three of them provided only a narrative discussion of symptoms [ 26 , 34 , 35 ]. In the reviews that performed a statistical analysis of the incidence of different clinical symptoms, symptoms in patients with COVID-19 were (range values of point estimates): fever (82–95%), cough with or without sputum (58–72%), dyspnea (26–59%), myalgia or muscle fatigue (29–51%), sore throat (10–13%), headache (8–12%), gastrointestinal disorders, such as diarrhea, nausea or vomiting (5.0–9.0%), and others (including, in one study only: dizziness 12.1%) (Figs. 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 and 9 ). Three reviews assessed cough with and without sputum together; only one review assessed sputum production itself (28.5%).
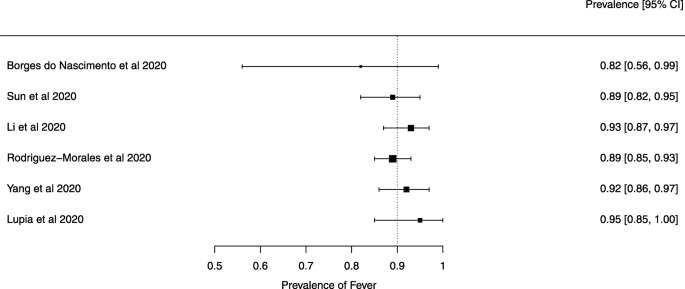
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of fever
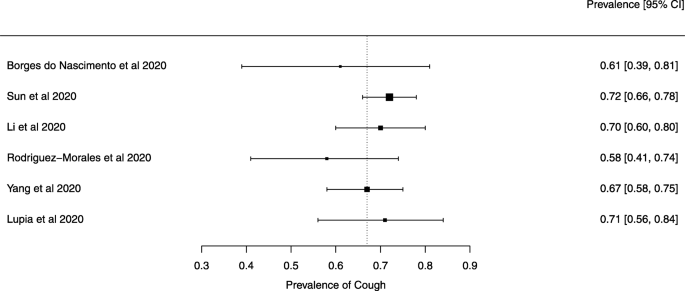
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of cough
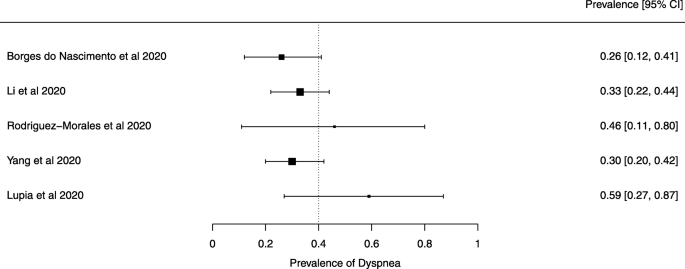
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of dyspnea
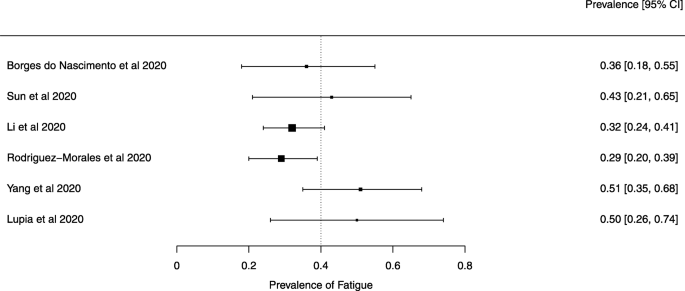
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of fatigue or myalgia
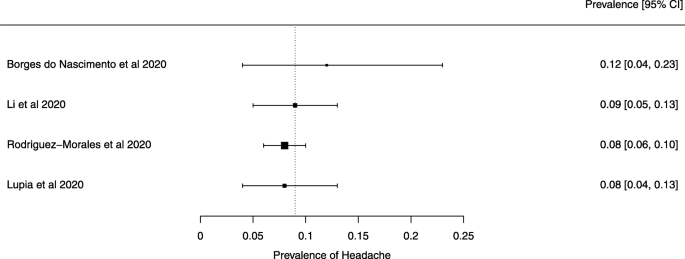
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of headache
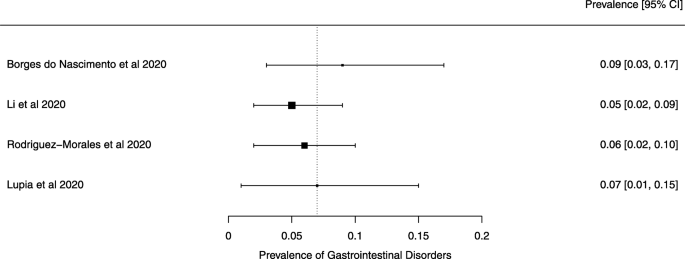
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of gastrointestinal disorders
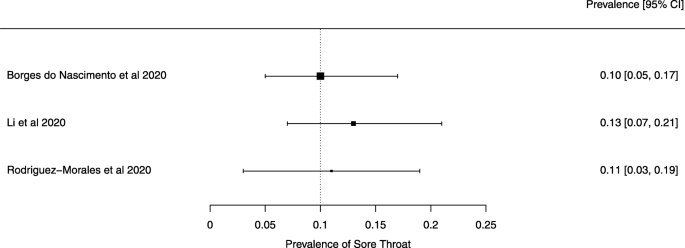
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of sore throat
Diagnostic aspects
Three reviews described methodologies, protocols, and tools used for establishing the diagnosis of COVID-19 [ 26 , 34 , 38 ]. The use of respiratory swabs (nasal or pharyngeal) or blood specimens to assess the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid using RT-PCR assays was the most commonly used diagnostic method mentioned in the included studies. These diagnostic tests have been widely used, but their precise sensitivity and specificity remain unknown. One review included a Chinese study with clinical diagnosis with no confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 infection (patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 if they presented with at least two symptoms suggestive of COVID-19, together with laboratory and chest radiography abnormalities) [ 34 ].
Therapeutic possibilities
Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions (supportive therapies) used in treating patients with COVID-19 were reported in five reviews [ 25 , 27 , 34 , 35 , 38 ]. Antivirals used empirically for COVID-19 treatment were reported in seven reviews [ 25 , 27 , 34 , 35 , 37 , 38 , 41 ]; most commonly used were protease inhibitors (lopinavir, ritonavir, darunavir), nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (tenofovir), nucleotide analogs (remdesivir, galidesivir, ganciclovir), and neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir). Umifenovir, a membrane fusion inhibitor, was investigated in two studies [ 25 , 35 ]. Possible supportive interventions analyzed were different types of oxygen supplementation and breathing support (invasive or non-invasive ventilation) [ 25 ]. The use of antibiotics, both empirically and to treat secondary pneumonia, was reported in six studies [ 25 , 26 , 27 , 34 , 35 , 38 ]. One review specifically assessed evidence on the efficacy and safety of the anti-malaria drug chloroquine [ 27 ]. It identified 23 ongoing trials investigating the potential of chloroquine as a therapeutic option for COVID-19, but no verifiable clinical outcomes data. The use of mesenchymal stem cells, antifungals, and glucocorticoids were described in four reviews [ 25 , 34 , 35 , 38 ].
Laboratory and radiological findings
Of the 18 reviews included in this overview, eight analyzed laboratory parameters in patients with COVID-19 [ 25 , 29 , 30 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 39 ]; elevated C-reactive protein levels, associated with lymphocytopenia, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, as well as slightly elevated aspartate and alanine aminotransferase (AST, ALT) were commonly described in those eight reviews. Lippi et al. assessed cardiac troponin I (cTnI) [ 25 ], procalcitonin [ 32 ], and platelet count [ 33 ] in COVID-19 patients. Elevated levels of procalcitonin [ 32 ] and cTnI [ 30 ] were more likely to be associated with a severe disease course (requiring intensive care unit admission and intubation). Furthermore, thrombocytopenia was frequently observed in patients with complicated COVID-19 infections [ 33 ].
Chest imaging (chest radiography and/or computed tomography) features were assessed in six reviews, all of which described a frequent pattern of local or bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacity [ 25 , 34 , 35 , 39 , 40 , 41 ]. Those six reviews showed that septal thickening, bronchiectasis, pleural and cardiac effusions, halo signs, and pneumothorax were observed in patients suffering from COVID-19.
Quality of evidence in individual systematic reviews
Table 3 shows the detailed results of the quality assessment of 18 systematic reviews, including the assessment of individual items and summary assessment. A detailed explanation for each decision in each review is available in Additional file 5 .
Using AMSTAR 2 criteria, confidence in the results of all 18 reviews was rated as “critically low” (Table 3 ). Common methodological drawbacks were: omission of prospective protocol submission or publication; use of inappropriate search strategy: lack of independent and dual literature screening and data-extraction (or methodology unclear); absence of an explanation for heterogeneity among the studies included; lack of reasons for study exclusion (or rationale unclear).
Risk of bias assessment, based on a reported methodological tool, and quality of evidence appraisal, in line with the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) method, were reported only in one review [ 25 ]. Five reviews presented a table summarizing bias, using various risk of bias tools [ 25 , 29 , 39 , 40 , 41 ]. One review analyzed “study quality” [ 37 ]. One review mentioned the risk of bias assessment in the methodology but did not provide any related analysis [ 28 ].
This overview of systematic reviews analyzed the first 18 systematic reviews published after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, up to March 24, 2020, with primary studies involving more than 60,000 patients. Using AMSTAR-2, we judged that our confidence in all those reviews was “critically low”. Ten reviews included meta-analyses. The reviews presented data on clinical manifestations, laboratory and radiological findings, and interventions. We found no systematic reviews on the utility of diagnostic tests.
Symptoms were reported in seven reviews; most of the patients had a fever, cough, dyspnea, myalgia or muscle fatigue, and gastrointestinal disorders such as diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting. Olfactory dysfunction (anosmia or dysosmia) has been described in patients infected with COVID-19 [ 43 ]; however, this was not reported in any of the reviews included in this overview. During the SARS outbreak in 2002, there were reports of impairment of the sense of smell associated with the disease [ 44 , 45 ].
The reported mortality rates ranged from 0.3 to 14% in the included reviews. Mortality estimates are influenced by the transmissibility rate (basic reproduction number), availability of diagnostic tools, notification policies, asymptomatic presentations of the disease, resources for disease prevention and control, and treatment facilities; variability in the mortality rate fits the pattern of emerging infectious diseases [ 46 ]. Furthermore, the reported cases did not consider asymptomatic cases, mild cases where individuals have not sought medical treatment, and the fact that many countries had limited access to diagnostic tests or have implemented testing policies later than the others. Considering the lack of reviews assessing diagnostic testing (sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of RT-PCT or immunoglobulin tests), and the preponderance of studies that assessed only symptomatic individuals, considerable imprecision around the calculated mortality rates existed in the early stage of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Few reviews included treatment data. Those reviews described studies considered to be at a very low level of evidence: usually small, retrospective studies with very heterogeneous populations. Seven reviews analyzed laboratory parameters; those reviews could have been useful for clinicians who attend patients suspected of COVID-19 in emergency services worldwide, such as assessing which patients need to be reassessed more frequently.
All systematic reviews scored poorly on the AMSTAR 2 critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews. Most of the original studies included in the reviews were case series and case reports, impacting the quality of evidence. Such evidence has major implications for clinical practice and the use of these reviews in evidence-based practice and policy. Clinicians, patients, and policymakers can only have the highest confidence in systematic review findings if high-quality systematic review methodologies are employed. The urgent need for information during a pandemic does not justify poor quality reporting.
We acknowledge that there are numerous challenges associated with analyzing COVID-19 data during a pandemic [ 47 ]. High-quality evidence syntheses are needed for decision-making, but each type of evidence syntheses is associated with its inherent challenges.
The creation of classic systematic reviews requires considerable time and effort; with massive research output, they quickly become outdated, and preparing updated versions also requires considerable time. A recent study showed that updates of non-Cochrane systematic reviews are published a median of 5 years after the publication of the previous version [ 48 ].
Authors may register a review and then abandon it [ 49 ], but the existence of a public record that is not updated may lead other authors to believe that the review is still ongoing. A quarter of Cochrane review protocols remains unpublished as completed systematic reviews 8 years after protocol publication [ 50 ].
Rapid reviews can be used to summarize the evidence, but they involve methodological sacrifices and simplifications to produce information promptly, with inconsistent methodological approaches [ 51 ]. However, rapid reviews are justified in times of public health emergencies, and even Cochrane has resorted to publishing rapid reviews in response to the COVID-19 crisis [ 52 ]. Rapid reviews were eligible for inclusion in this overview, but only one of the 18 reviews included in this study was labeled as a rapid review.
Ideally, COVID-19 evidence would be continually summarized in a series of high-quality living systematic reviews, types of evidence synthesis defined as “ a systematic review which is continually updated, incorporating relevant new evidence as it becomes available ” [ 53 ]. However, conducting living systematic reviews requires considerable resources, calling into question the sustainability of such evidence synthesis over long periods [ 54 ].
Research reports about COVID-19 will contribute to research waste if they are poorly designed, poorly reported, or simply not necessary. In principle, systematic reviews should help reduce research waste as they usually provide recommendations for further research that is needed or may advise that sufficient evidence exists on a particular topic [ 55 ]. However, systematic reviews can also contribute to growing research waste when they are not needed, or poorly conducted and reported. Our present study clearly shows that most of the systematic reviews that were published early on in the COVID-19 pandemic could be categorized as research waste, as our confidence in their results is critically low.
Our study has some limitations. One is that for AMSTAR 2 assessment we relied on information available in publications; we did not attempt to contact study authors for clarifications or additional data. In three reviews, the methodological quality appraisal was challenging because they were published as letters, or labeled as rapid communications. As a result, various details about their review process were not included, leading to AMSTAR 2 questions being answered as “not reported”, resulting in low confidence scores. Full manuscripts might have provided additional information that could have led to higher confidence in the results. In other words, low scores could reflect incomplete reporting, not necessarily low-quality review methods. To make their review available more rapidly and more concisely, the authors may have omitted methodological details. A general issue during a crisis is that speed and completeness must be balanced. However, maintaining high standards requires proper resourcing and commitment to ensure that the users of systematic reviews can have high confidence in the results.
Furthermore, we used adjusted AMSTAR 2 scoring, as the tool was designed for critical appraisal of reviews of interventions. Some reviews may have received lower scores than actually warranted in spite of these adjustments.
Another limitation of our study may be the inclusion of multiple overlapping reviews, as some included reviews included the same primary studies. According to the Cochrane Handbook, including overlapping reviews may be appropriate when the review’s aim is “ to present and describe the current body of systematic review evidence on a topic ” [ 12 ], which was our aim. To avoid bias with summarizing evidence from overlapping reviews, we presented the forest plots without summary estimates. The forest plots serve to inform readers about the effect sizes for outcomes that were reported in each review.
Several authors from this study have contributed to one of the reviews identified [ 25 ]. To reduce the risk of any bias, two authors who did not co-author the review in question initially assessed its quality and limitations.
Finally, we note that the systematic reviews included in our overview may have had issues that our analysis did not identify because we did not analyze their primary studies to verify the accuracy of the data and information they presented. We give two examples to substantiate this possibility. Lovato et al. wrote a commentary on the review of Sun et al. [ 41 ], in which they criticized the authors’ conclusion that sore throat is rare in COVID-19 patients [ 56 ]. Lovato et al. highlighted that multiple studies included in Sun et al. did not accurately describe participants’ clinical presentations, warning that only three studies clearly reported data on sore throat [ 56 ].
In another example, Leung [ 57 ] warned about the review of Li, L.Q. et al. [ 29 ]: “ it is possible that this statistic was computed using overlapped samples, therefore some patients were double counted ”. Li et al. responded to Leung that it is uncertain whether the data overlapped, as they used data from published articles and did not have access to the original data; they also reported that they requested original data and that they plan to re-do their analyses once they receive them; they also urged readers to treat the data with caution [ 58 ]. This points to the evolving nature of evidence during a crisis.
Our study’s strength is that this overview adds to the current knowledge by providing a comprehensive summary of all the evidence synthesis about COVID-19 available early after the onset of the pandemic. This overview followed strict methodological criteria, including a comprehensive and sensitive search strategy and a standard tool for methodological appraisal of systematic reviews.
In conclusion, in this overview of systematic reviews, we analyzed evidence from the first 18 systematic reviews that were published after the emergence of COVID-19. However, confidence in the results of all the reviews was “critically low”. Thus, systematic reviews that were published early on in the pandemic could be categorized as research waste. Even during public health emergencies, studies and systematic reviews should adhere to established methodological standards to provide patients, clinicians, and decision-makers trustworthy evidence.
Availability of data and materials
All data collected and analyzed within this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
World Health Organization. Timeline - COVID-19: Available at: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline . Accessed 1 June 2021.
COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). Available at: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Anzai A, Kobayashi T, Linton NM, Kinoshita R, Hayashi K, Suzuki A, et al. Assessing the Impact of Reduced Travel on Exportation Dynamics of Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19). J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):601.
Chinazzi M, Davis JT, Ajelli M, Gioannini C, Litvinova M, Merler S, et al. The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Science. 2020;368(6489):395–400. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba9757 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Fidahic M, Nujic D, Runjic R, Civljak M, Markotic F, Lovric Makaric Z, et al. Research methodology and characteristics of journal articles with original data, preprint articles and registered clinical trial protocols about COVID-19. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20(1):161. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-020-01047-2 .
EPPI Centre . COVID-19: a living systematic map of the evidence. Available at: http://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Projects/DepartmentofHealthandSocialCare/Publishedreviews/COVID-19Livingsystematicmapoftheevidence/tabid/3765/Default.aspx . Accessed 1 June 2021.
NCBI SARS-CoV-2 Resources. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sars-cov-2/ . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Gustot T. Quality and reproducibility during the COVID-19 pandemic. JHEP Rep. 2020;2(4):100141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100141 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kodvanj, I., et al., Publishing of COVID-19 Preprints in Peer-reviewed Journals, Preprinting Trends, Public Discussion and Quality Issues. Preprint article. bioRxiv 2020.11.23.394577; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.23.394577 .
Dobler CC. Poor quality research and clinical practice during COVID-19. Breathe (Sheff). 2020;16(2):200112. https://doi.org/10.1183/20734735.0112-2020 .
Article Google Scholar
Bastian H, Glasziou P, Chalmers I. Seventy-five trials and eleven systematic reviews a day: how will we ever keep up? PLoS Med. 2010;7(9):e1000326. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000326 .
Lunny C, Brennan SE, McDonald S, McKenzie JE. Toward a comprehensive evidence map of overview of systematic review methods: paper 1-purpose, eligibility, search and data extraction. Syst Rev. 2017;6(1):231. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0617-1 .
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Becker LA, Pieper D, Hartling L. Chapter V: Overviews of Reviews. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). Cochrane. 2020. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). Cochrane. 2020; Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Newton AS, Scott SD, Hartling L. The impact of different inclusion decisions on the comprehensiveness and complexity of overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-018-0914-3 .
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Newton AS, Scott SD, Hartling L. A decision tool to help researchers make decisions about including systematic reviews in overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-018-0768-8 .
Hunt H, Pollock A, Campbell P, Estcourt L, Brunton G. An introduction to overviews of reviews: planning a relevant research question and objective for an overview. Syst Rev. 2018;7(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-018-0695-8 .
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Pieper D, Tricco AC, Gates M, Gates A, et al. Preferred reporting items for overviews of reviews (PRIOR): a protocol for development of a reporting guideline for overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):335. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-019-1252-9 .
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Open Med. 2009;3(3):e123–30.
Krnic Martinic M, Pieper D, Glatt A, Puljak L. Definition of a systematic review used in overviews of systematic reviews, meta-epidemiological studies and textbooks. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):203. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-019-0855-0 .
Puljak L. If there is only one author or only one database was searched, a study should not be called a systematic review. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;91:4–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.08.002 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gates M, Gates A, Guitard S, Pollock M, Hartling L. Guidance for overviews of reviews continues to accumulate, but important challenges remain: a scoping review. Syst Rev. 2020;9(1):254. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-020-01509-0 .
Covidence - systematic review software. Available at: https://www.covidence.org/ . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017;358:j4008.
Borges do Nascimento IJ, et al. Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19) in Humans: A Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med. 2020;9(4):941.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Adhikari SP, Meng S, Wu YJ, Mao YP, Ye RX, Wang QZ, et al. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-020-00646-x .
Cortegiani A, Ingoglia G, Ippolito M, Giarratano A, Einav S. A systematic review on the efficacy and safety of chloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19. J Crit Care. 2020;57:279–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.03.005 .
Li B, Yang J, Zhao F, Zhi L, Wang X, Liu L, et al. Prevalence and impact of cardiovascular metabolic diseases on COVID-19 in China. Clin Res Cardiol. 2020;109(5):531–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-020-01626-9 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Li LQ, Huang T, Wang YQ, Wang ZP, Liang Y, Huang TB, et al. COVID-19 patients’ clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92(6):577–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25757 .
Lippi G, Lavie CJ, Sanchis-Gomar F. Cardiac troponin I in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): evidence from a meta-analysis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63(3):390–1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2020.03.001 .
Lippi G, Henry BM. Active smoking is not associated with severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Eur J Intern Med. 2020;75:107–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2020.03.014 .
Lippi G, Plebani M. Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;505:190–1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.004 .
Lippi G, Plebani M, Henry BM. Thrombocytopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: a meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;506:145–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.022 .
Ludvigsson JF. Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults. Acta Paediatr. 2020;109(6):1088–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.15270 .
Lupia T, Scabini S, Mornese Pinna S, di Perri G, de Rosa FG, Corcione S. 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak: a new challenge. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020;21:22–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2020.02.021 .
Marasinghe, K.M., A systematic review investigating the effectiveness of face mask use in limiting the spread of COVID-19 among medically not diagnosed individuals: shedding light on current recommendations provided to individuals not medically diagnosed with COVID-19. Research Square. Preprint article. doi : https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-16701/v1 . 2020 .
Mullins E, Evans D, Viner RM, O’Brien P, Morris E. Coronavirus in pregnancy and delivery: rapid review. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2020;55(5):586–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.22014 .
Pang J, Wang MX, Ang IYH, Tan SHX, Lewis RF, Chen JIP, et al. Potential Rapid Diagnostics, Vaccine and Therapeutics for 2019 Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV): a systematic review. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):623.
Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Cardona-Ospina JA, Gutiérrez-Ocampo E, Villamizar-Peña R, Holguin-Rivera Y, Escalera-Antezana JP, et al. Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020;34:101623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101623 .
Salehi S, Abedi A, Balakrishnan S, Gholamrezanezhad A. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review of imaging findings in 919 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;215(1):87–93. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.23034 .
Sun P, Qie S, Liu Z, Ren J, Li K, Xi J. Clinical characteristics of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a single arm meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92(6):612–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25735 .
Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, Pu K, Chen Z, Guo Q, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;94:91–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017 .
Bassetti M, Vena A, Giacobbe DR. The novel Chinese coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections: challenges for fighting the storm. Eur J Clin Investig. 2020;50(3):e13209. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.13209 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Hwang CS. Olfactory neuropathy in severe acute respiratory syndrome: report of a case. Acta Neurol Taiwanica. 2006;15(1):26–8.
Google Scholar
Suzuki M, Saito K, Min WP, Vladau C, Toida K, Itoh H, et al. Identification of viruses in patients with postviral olfactory dysfunction. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(2):272–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000249922.37381.1e .
Rajgor DD, Lee MH, Archuleta S, Bagdasarian N, Quek SC. The many estimates of the COVID-19 case fatality rate. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(7):776–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30244-9 .
Wolkewitz M, Puljak L. Methodological challenges of analysing COVID-19 data during the pandemic. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20(1):81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-020-00972-6 .
Rombey T, Lochner V, Puljak L, Könsgen N, Mathes T, Pieper D. Epidemiology and reporting characteristics of non-Cochrane updates of systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study. Res Synth Methods. 2020;11(3):471–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1409 .
Runjic E, Rombey T, Pieper D, Puljak L. Half of systematic reviews about pain registered in PROSPERO were not published and the majority had inaccurate status. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019;116:114–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.08.010 .
Runjic E, Behmen D, Pieper D, Mathes T, Tricco AC, Moher D, et al. Following Cochrane review protocols to completion 10 years later: a retrospective cohort study and author survey. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019;111:41–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.03.006 .
Tricco AC, Antony J, Zarin W, Strifler L, Ghassemi M, Ivory J, et al. A scoping review of rapid review methods. BMC Med. 2015;13(1):224. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-015-0465-6 .
COVID-19 Rapid Reviews: Cochrane’s response so far. Available at: https://training.cochrane.org/resource/covid-19-rapid-reviews-cochrane-response-so-far . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Cochrane. Living systematic reviews. Available at: https://community.cochrane.org/review-production/production-resources/living-systematic-reviews . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Millard T, Synnot A, Elliott J, Green S, McDonald S, Turner T. Feasibility and acceptability of living systematic reviews: results from a mixed-methods evaluation. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):325. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-019-1248-5 .
Babic A, Poklepovic Pericic T, Pieper D, Puljak L. How to decide whether a systematic review is stable and not in need of updating: analysis of Cochrane reviews. Res Synth Methods. 2020;11(6):884–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1451 .
Lovato A, Rossettini G, de Filippis C. Sore throat in COVID-19: comment on “clinical characteristics of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a single arm meta-analysis”. J Med Virol. 2020;92(7):714–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25815 .
Leung C. Comment on Li et al: COVID-19 patients’ clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92(9):1431–2. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25912 .
Li LQ, Huang T, Wang YQ, Wang ZP, Liang Y, Huang TB, et al. Response to Char’s comment: comment on Li et al: COVID-19 patients’ clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92(9):1433. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25924 .
Download references
Acknowledgments
We thank Catherine Henderson DPhil from Swanscoe Communications for pro bono medical writing and editing support. We acknowledge support from the Covidence Team, specifically Anneliese Arno. We thank the whole International Network of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (InterNetCOVID-19) for their commitment and involvement. Members of the InterNetCOVID-19 are listed in Additional file 6 . We thank Pavel Cerny and Roger Crosthwaite for guiding the team supervisor (IJBN) on human resources management.
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University Hospital and School of Medicine, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil
Israel Júnior Borges do Nascimento & Milena Soriano Marcolino
Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA
Israel Júnior Borges do Nascimento
Helene Fuld Health Trust National Institute for Evidence-based Practice in Nursing and Healthcare, College of Nursing, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
Dónal P. O’Mathúna
School of Nursing, Psychotherapy and Community Health, Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Department of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care and Pain Medicine, University of Münster, Münster, Germany
Thilo Caspar von Groote
Department of Sport and Health Science, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany
Hebatullah Mohamed Abdulazeem
School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Health and Medicine, The University of Newcastle, Callaghan, Australia
Ishanka Weerasekara
Department of Physiotherapy, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, University of Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka
Cochrane Croatia, University of Split, School of Medicine, Split, Croatia
Ana Marusic, Irena Zakarija-Grkovic & Tina Poklepovic Pericic
Center for Evidence-Based Medicine and Health Care, Catholic University of Croatia, Ilica 242, 10000, Zagreb, Croatia
Livia Puljak
Cochrane Brazil, Evidence-Based Health Program, Universidade Federal de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
Vinicius Tassoni Civile & Alvaro Nagib Atallah
Yorkville University, Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada
Santino Filoso
Laboratory for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (LIAM), Department of Mathematics and Statistics, York University, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Nicola Luigi Bragazzi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
IJBN conceived the research idea and worked as a project coordinator. DPOM, TCVG, HMA, IW, AM, LP, VTC, IZG, TPP, ANA, SF, NLB and MSM were involved in data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and initial draft writing. All authors revised the manuscript critically for the content. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Livia Puljak .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not required as data was based on published studies.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: appendix 1..
Search strategies used in the study.
Additional file 2: Appendix 2.
Adjusted scoring of AMSTAR 2 used in this study for systematic reviews of studies that did not analyze interventions.
Additional file 3: Appendix 3.
List of excluded studies, with reasons.
Additional file 4: Appendix 4.
Table of overlapping studies, containing the list of primary studies included, their visual overlap in individual systematic reviews, and the number in how many reviews each primary study was included.
Additional file 5: Appendix 5.
A detailed explanation of AMSTAR scoring for each item in each review.
Additional file 6: Appendix 6.
List of members and affiliates of International Network of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (InterNetCOVID-19).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Borges do Nascimento, I.J., O’Mathúna, D.P., von Groote, T.C. et al. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: an overview of systematic reviews. BMC Infect Dis 21 , 525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06214-4
Download citation
Received : 12 April 2020
Accepted : 19 May 2021
Published : 04 June 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06214-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Coronavirus
- Evidence-based medicine
- Infectious diseases
BMC Infectious Diseases
ISSN: 1471-2334
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
current events conversation
What Students Are Saying About Living Through a Pandemic
Teenage comments in response to our recent writing prompts, and an invitation to join the ongoing conversation.

By The Learning Network
The rapidly-developing coronavirus crisis is dominating global headlines and altering life as we know it. Many schools worldwide have closed. In the United States alone, 55 million students are rapidly adjusting to learning and socializing remotely, spending more time with family, and sacrificing comfort and convenience for the greater good.
For this week’s roundup of student comments on our writing prompts , it was only fitting to ask teenagers to react to various dimensions of this unprecedented situation: how the coronavirus outbreak is affecting their daily lives, how we can all help one another during the crisis and what thoughts or stories the term “social distancing” conjures for them.
Every week, we shout out new schools who have commented on our writing prompts. This week, perhaps because of many districts’ move to remote online learning, we had nearly 90 new classes join us from around the world. Welcome to the conversation to students from:
Academy of St. Elizabeth; Abilene, Tex.; Alabama; Anna High School, Tex.; Arlington, Va.; Austria-Hungary; Baltimore, Md.; Bellingham, Wash.; Ben Lippen School; Bloomington, Ind.; Branham High School, San Jose, Calif.; Boston; Buffalo High School, Wyo.; Camdenton, Mo.; Cincinnati, Ohio; Collierville, Tenn.; Dawson High School, Tex.; Denmark; Desert Vista High School; Doylestown, Penn.; Dublin, Calif.; Dunkirk, N.Y. ; Eleanor Murray Fallon Middle School; Elmhurst, Ill.; Fairfax, Va.; Framingham, Mass.; Frederick, Md.; Hartford, Conn.; Jefferson, N.J.; Kantonschule Uster, Switzerland; Laconia, N.H.; Las Vegas; Lashon Academy; Lebanon, N.H.; Ledyard High School; Leuzinger High School; Livonia, Mich.; Manistee Middle School; Miami, Fla.; Melrose High School; Milton Hershey School, Hershey, Penn.; Milwaukee; Montreal; Naguabo, Puerto Rico; Nebraska; Nessacus Regional Middle School; New Rochelle, N.Y.; Newport, Ky.; Newton, Mass.; North Stanly High School; Oakland, Calif.; Papillion Middle School; Polaris Expeditionary Learning School; Pomona, Calif.; Portsmouth, N.H.; Pueblo, Colo.; Reading, Mass.; Redmond Wash.; Richland, Wash.; Richmond Hill Ontario; Ridgeley, W.Va.; Rockford, Mich.; Rovereto, Italy; Salem, Mass.; Scottsdale, Ariz.; Seattle, Wash.; Sequoyah School Pasadena; Shackelford Junior High, Arlington, Tex.; South El Monte High School; Sugar Grove, Ill.; St. Louis, Mo.; Timberview High School; Topsfield, Mass.; Valley Stream North High School; Vienna, Va.; Waupun, Wis.; Wauwatosa, Wis.; Wenatchee, Wash.; Westborough Mass.; White Oak Middle School, Ohio; and Winter Park High School.
We’re so glad to have you here! Now, on to this week’s comments.
Please note: Student comments have been lightly edited for length, but otherwise appear as they were originally submitted.
How Is the Coronavirus Outbreak Affecting Your Life?
The coronavirus has changed how we work, play and learn : Schools are closing, sports leagues have been canceled, and many people have been asked to work from home.
We asked students how their lives have changed since the onset of this pandemic. They told us about all the things they miss, what it’s like to learn online, and how they’re dealing with the uncertainty. But, they also pointed out the things that have brought them joy and peace amid the chaos.
Life as we know it, upended
Yesterday my school district announced that our school would be closed until May 5. Upon receiving the email, I immediately contacted my friends to share our responses. To most of my friends and me, this news was no surprise. Already finishing week one of quarantine, I find myself in a state of pessimism in regards to life in the midst of a pandemic. My days have blurred into Google Classroom assignments, hobby seeking, aimless searching on Netflix, and on exceptionally boring days, existential contemplation.
The dichotomy of chance freedom from school and yet the discombobulated feelings of helplessness and loneliness plague my time home alone. My parents are yet working and as an only child, I try my best to stay sane with blasting music and shows. Other times I call my friends to pass the time doing school assignments. Even then, schoolwork seems increasingly pointless.
With most of my classes being APs, the recent CollegeBoard update for the 2020 AP exams was a blow to my educational motivation. I am naturally a driven, passionate learner with intense intellectual curiosity. But in the midst of this chaos, I can’t help feeling like all the assignments from my classes are just busywork. I manage to stay afloat, keeping in mind that everyone is doing their best. Despite no ostensible end in sight, I hope this quarantine brings out the best in me, in society, and in nature.
— Brenda Kim, Valencia High School
The struggles (and joys) of distance learning
Although we do have online school now, it is not the same. Working from home is worse as I don’t care to admit, my work habits from home are not the best. I am easily able to procrastinate at home and having class in bed is not the best idea. Plus, I can no longer get the one on one help teachers provide if needed.
— larisa, california
The coronavirus affected me because now having to do school virtually is kinda hard because I don’t have much of a good wi-fi, and its nerve-racking to know about what we’re gonna do about the tests we have to take in order to pass because I do care about graduating, and going to next grade in order to keep going to finally graduate school and get my diploma I just hope this virus doesn’t affect anything else besides school.
— julien phillips, texas
I personally have to do 2-3 hours of work a day instead of the usual 8 hours (including homework), and it feels more tiring somehow. I’m in the comfort of my home all the time, but have to do this for a few hours, and it feels much more monotonous than 8 hours in a classroom, and that’s what everybody has been doing for a lot of their life.
But in that sense, it also feels a lot calmer not being around people constantly, having anxiety and autism. The people in classrooms are insane. It didn’t affect my life negatively by much, but it really makes me think. If the school system were like this in the near future, I think it would be much more sustainable, in many ways.
— Alexen, Lawrence, Massachusetts
I never understood how much social interaction I experienced at school until the end of the first week of my self quarantine. I had been trapped in my house with my family for about 5 days at that point, when my AP Language and Composition class had a Zoom conference. I had done them for other classes so I wasn’t exactly excited for the opportunity. It was just another zoom lecture.
As it turned out, it wasn’t a lecture, it was a conversation. It was a discussion about our last current events assignment that I didn’t know I desperately needed. The conversation was explosive. Differing opinions flew left and right, people brought their cats to join in the fun, family members popped in and out of the frames, and the controlled chaos felt incredible. I relished in the opportunity to argue and challenge their opinions. I didn’t even realize how isolated I was feeling until I was able to talk to them in a creative and intellectual setting once again.
— Yaffa Segal, New Rochelle High School
Finding new ways to socialize
Finding new ways to stay social has been essential, and recently, my friends and I all drove our cars to a large parking lot, parked more than 6 feet apart from each other, sat in our trunks, talked and enjoyed each other’s company for over an hour and a half. This was crucial in keeping our sanity. We missed each other and being in the presence of people other than our family; however, we were sure to maintain our distance and continue social distancing. We did not touch anything new and we stayed more than 6 feet apart from each other speaking about the adjustments we have been making and the ways we have been coping with all of the changes we are experiencing.
— Carly Rieger, New Rochelle High School
…[T]his “corona-cation” has given me a lot of time to reflect, and while I haven’t seen my friends in person for a week and half, I feel closer to them than ever. We’ve FaceTimed almost every day and we play some of our favorite group games; Psych and PhotoRoulette are two apps I highly recommend to have fun from the comfort of everyone’s homes.
Because my mom has a weak immune system, I’ve been quarantined since the moment my school closed, so social distancing has been a little more than 6 feet for me. However, my friends did make me a care package filled with my favorite candy and a puzzle which my family completed in a week.
— Jessica Griffin, Glenbard West HS Glen Ellyn, IL
Mourning canceled events
To say that this virus has completely changed my day to day living would just be an understatement. I went from having things to do from 7:20am to 8:45pm every week day to absolutely nothing. The whole month of March was going to be booked as well. I had activities such as the Wilmington Marathon that I work at and the Masters Swim meet that I was going to volunteer for. Then I had a club swim meet but everything got canceled. Everything that I was looking forward to just came to a halt and nothing is going to be postponed, just canceled.
— Ellen Phillips, Hoggard
As a High School senior, this quarantine has seemed to just chop off the fun part of our senior year. We had made it so far, and were so close to getting to experience all of the exciting events and traditions set aside for seniors. This includes our graduation, prom (which is a seniors only event at my school), senior picnic, theme weeks, and much more.
— Cesar, Los Angeles
Like many other students involved in their school theatre programs, I was severely affected by the closing of schools due the growing pandemic. My theatre company had been rehearsing our play for months and in an instant, we were no longer allowed to work on our show. The Texas UIL One-Act Play Contest was postponed because of the coronavirus, and while it is a reasonable action, it left an army of theatre students with nothing to do but vent through memes, TikTok, and other forms of social media. These coping mechanisms helped me, as well as my fellow company members, process the reality that after all the hard work we put in, we may never get to perform for an audience.
— Ryan C, Dawson High School
Living with mental, emotional and financial strain
The coronavirus is having a pretty significant impact on me. Physically, it’s reducing my daily physical activity to the point where the most exercise I get is walking around my house and dancing around my room to songs that make me feel like I’m not in the middle of a pandemic. Emotionally, it has also been very straining. My mom is a substitute teacher and she is out of work for the rest of the school year with no pay. I myself am missing my closest friends a lot right now, and feel lonely often.
— Sela Jasim, Branham High School
I struggle a lot with mental health. I have had depression and ptsd, as well as anxiety for years. Seeing people outside of my family is what keeps me sane, especially those closest to me. Having to FaceTime my therapist is weird and scary. Things are so different now, and I’m slowly losing motivation. My thoughts recently have been “don’t think about it” when I think of how long this could possibly last. I am scared for my grandparents, who live across the country. I feel like I haven’t spent enough time with them and I’m losing my chance. Everything is weird. I can’t find a better way to describe it without being negative. This is a really strange time and I don’t like it. I’m trying my hardest to stay positive but that has never been one of my strong suits.
— Caileigh Robinson, Bellingham, Washington
My mom is a nurse so she has to face the virus, in fact today she is at work, her unit is also the unit that will be taking care of coronavirus patients. My whole family is very afraid that she will get very sick.
— Maddie H., Maryland
Appreciating the good
Although we are going through a horrific time filled with all kinds of uncertainty, we are given the opportunity to spend more time with our loved family and learn more about ourselves to a broader extent while also strengthening our mental mindset. I can’t stress the amount of frustration I have to return to class and my everyday routine however, I’ve learned to become stronger mentality while also becoming creative on how I live my life without being surrounded by tons of people everyday.
— anthony naranjo, Los Angeles
Although I could list all the negatives that come with Covid-19, being a junior in high school, this quarantine has been a really nice calm break from a life that seemed to never stop. A break from 35 hour school weeks along with 15 hours worth of work, being able to sit down and do hobbies I missed is something I am really appreciating.
— Ella Fredrikson, Glenbard West, Glen Ellyn, IL
An upside to these past weeks of quarantine is being able to see my usually busy family more, especially my father. I’ve had more talks and laughs with my family the last few days than I’ve had in the past couple of months, which helped lighten such a stressful time in my opinion.
— Marlin Flores, Classical High School
Several months before the outbreak my mom randomly asked me what would I study if I could choose anything, not for a grade, not for any credit. Now, because of corona, I am learning Greek with my father! He can’t travel for work now and doesn’t attend meetings as frequently, so he is at home too.
— Lily, Seoul, Korea
How Can We Help One Another During the Coronavirus Outbreak?
In a series of recent Times articles , authors wrote about the need for solidarity and generosity in this time of fear and anxiety and the need for Americans to make sacrifices to ensure their safety and that of others in their community.
So we asked students what they and their friends, family and community could do to help and look out for one another during the coronavirus outbreak. Here is what they said:
Help your neighbors, especially the sick and elderly.
There are so many things we can do to help each other during this pandemic. Use gloves when you go shopping or are in public, masks if you think that it would be best for you, those who have more wiggle room financially can help out others who don’t have that same wiggle room financially and who are now struggling, buy groceries for those who can’t afford it or are at risk if they were to go out in public. Donate if you can, and help the elderly or those who desperately need it, and for goodness sake wash your hands and (for all that need to hear the reminder) SOCIAL DISTANCING IS A FRIEND. Social distancing is proven to help drastically, so please, social distance.
— Dakodah, Camdenton, MO
As a person, we have the ability to help our friends, families, elders, people with illnesses in our community and people with high risks of getting the virus. We can accomplish this by simply observing who may need help with shopping, for groceries or clothes, with yard work, or any kind of outside work that is done where there are rooms full of people, such as going to the bank. As a younger person and a person with a low risk of getting the virus, I have the capability to walk to places and go in and out of buildings with a smaller chance of getting the virus as compared to one of my elder neighbors. My friends and I can go around the neighborhood and see who needs help during this hard time, whether I have to give them money or food to help them out.
— Adrianna P, New York
Many elderly people in my vicinity suffer from chronic conditions and illnesses and there are others who often live alone. Going to the grocery store or the pharmacy can also be hassle for many. Due to the recent pandemic, people are stocking up necessities however, some people are not being practical and overstock, not leaving anything for others. Fights are breaking out in grocery stores and this is a dangerous situation to put the elderly in.
— Sydney, B
In our American society we tend to be very individualistic. This pandemic has truly proved that point as people do not care for other but themselves. During this time we should consider not only ourselves but the people in need, which are the elderly and young children. Instead of hoarding all the food share some with a neighbor or an old person that doesn’t quite have the ability to run around store to store grabbing what they can. Make sure when you feel ill or if a family member feels ill to stay contained in your home. If this is not an option you could always take your ideas to social media, posting ways to stay clean and making sure we support the people who need it.
— Marley Gutierrez, Pomona, CA
Stay connected.
We could help one another just by the simple ways of: texting your friends every now and then and keep them in check and give them positive reinforcements; call your far away family and report to them on how you are doing and make sure that they are doing OK as well; help elders that are not safe to go out by running errands for them.
— Xammy Yang, California
It’s really important for everyone to stay in contact with others. Be open to talking to people you don’t necessarily talk to all the time just so you can fulfill your own social requirements. It’s also important to listen to others and take into account their feelings. We are all in a time of stress and anxiety about the unknown and we have to just go with the flow and wait it out. I’m stressed about possibly missing milestones in my life, like prom and graduation, but there are others suffering. We all just need to be prepared, stay healthy, and reach out to others.
— Elysia P., Glenbard West HS, Glen Ellyn, IL
Stay apart.
The most important thing one can do during this time of uncertainty is to protect oneself, that is how one can protect others. By practicing social distancing, the risk of spreading germs or disease is reduced. From within one’s home, much can be done. Keeping in touch with close friends and family, donating money and food to those in need and not hoarding or stockpiling too much are all things one could do to support one’s community. Every little thing counts.
— Francheska M-Q, Valley Stream North
Honestly, as boring as it sounds, staying home is the best way we can help against the coronavirus. The second best in my opinion would be spreading the word and encouraging others to wash their hands often and to not go in large groups. Our number one priority should be protecting the elderly and people more vulnerable to getting the disease, or more likely for it to be fatal. If I were to get the virus, my chances of death would be very low, but I would be most worried about accidentally passing on the virus to an elderly person who might not be so lucky. Staying home, clean, and avoiding large groups is the safest and best way for us to help in efforts against the coronavirus.
— Christian Cammack, Hoggard High School In Wilmington, NC
Stay informed.
During this time of crisis, seeking accurate information should remain people’s main focus. Reading articles from trusted sources such as the CDC and New York Times rather than sensationalized media that spreads false rumors for attention will improve reactions to this scary situation because it has the potential to reduce panic and allow people to find ways proven to slow the spread of the virus.
— Argelina J., NY
Donate to those in need.
We can help one another during the virus break by doing online donations to people who need it the most, not taking supplies that you know you don’t need, and/or offering online support for those who have relatives that have the virus and want someone to talk to. We, as a community, can keep distance and update each other on the constant updating news.
— Marisa Mohan<3, NY
… donate food to food banks or homeless shelters. Food is even more of a necessity right now, so it is crucial that everyone has what they need because some people get their food from school or from work, which isn’t available at the moment. Finally, even if we feel we’re healthy and we’re not afraid to get the Coronavirus, it is very vital to participate in social distancing because it will help society overall.
— Bridget McBride, Glenbard West HS, Glen Ellyn, IL
Encourage positivity.
In my opinion, we should all do our best to help and encourage each other with healthy habits and staying positive. Too many people are worried about the coronavirus. What will happen because of this is more stress and anxiety. In turn, this leads to people stocking up on products and taking resources from other people who need them. As long as we all contribute and help one another, we will be able to keep things under control.
— Mieko, CA
Learn lessons for future preparedness.
I believe that this horrible trouble we are all put into is teaching our younger generations such as me, to be prepared when these unexpected events happen. We can help the elders and take care of them because if we don’t prepare next time then we will struggle to survive if the coronavirus becomes a long term thing. This situation is also bringing our communities together, or at least teaching us to. We can learn to share resources that maybe we have to much of. Just a couple days ago, my grandma had ran out of cleaning supplies and she didn’t have a working car at the time. My family and I decided to give her some of our extra supplies since we stocked up on so much. I believe that we can definitely use this time to help our minds grow and learn new things.
— Becky Alonso, CA
Things we shouldn’t do
“Desperate times call for desperate measures.” -Hippocrates This quote describes my opinion of the COVID-19 crisis. Our communities must make sacrifices in order to overcome the trials we are facing. Instead of describing what we should do, I am going to shortly convey examples of what our local communities shouldn’t do. We shouldn’t panic. Panic causes the nervous system to spark and will create unsettling emotions that will produce nothing helpful for the situation at hand. We shouldn’t buy abundant amounts of resources unless instructed to. Please be considerate towards these people because they probably are struggling a lot more than you at the moment. We should be mindful of others. I am not saying we have to interact with everyone (DO NOT DO THAT), but I am saying we should be kind when we do interact.
— Adrianna Waterford, Bloomington, IN
What Story Could This Image Tell?
In our Picture Prompt, “ Social Distancing, ” we asked students to write memoirs and poems inspired by the illustration above, or tell a short story from the perspective of one of the people pictured. In prose and poetry, they expressed a range of responses to the pandemic , from fear, panic and anxiety to resilience and hope.
Creative short stories
From the perspective of the Binocular guy:
I thought social distancing would be great, no one would bother me or interrupt my work. But actually doing it makes me realize that those things, those pains in my neck that would annoy me, are the things I miss the most. I miss the smell of Phyllis’s choking perfume. I miss Michael pacing around the office. I miss the way that Pam would bite her pen when she was focusing. I miss people. Now that I’m alone in my apartment, I hunger for human interaction. I have taken to staring out the window at people walking past and imagining the conversations they have. Oh how I wish to be a part of them, but I can’t risk going outside. I thought my window would cure my loneliness, but it has only made it worse. Social distancing has hurt me more than any virus could.
— Andrew B., Abilene
It’s another day in the city. Car horns honking, people scurrying over town, and there I am. No, not that person or the other. In the upper left corner. Do you see me? Yes, you found me! The only creature not on a screen. I have never understood why they sit there and look at their own devices. I enjoy sitting on the roof and looking at others. People watching is my favorite, but the only thing that most people are watching is a tiny screen. Everyone is wrapped up in their circumstances. Sick in bed with their computer, walking down the stairs with a device. But I’ll be here, waiting for someone to notice me — just the dog on the rooftop.
— Hope Heinrichs, Hoggard High School in Wilmington, NC
Opening to short story for the homeless man:
It’s so cold out today. My blanket is the only that is keeping me partially warm. Before today, my HELP sign got me a few dimes. That way I could buy some food. But today, the streets are empty. The only people passing by either have masks covering their face or run past me with their hands full of food and supplies. I wonder what’s going on?
— Ariel S., Los Angeles
Cold: That’s all he feels as he’s reclining on a random door.
Scared: That’s what he wants to avoid feeling as he sees people coughing around him.
Alone: That’s what he is as he wanders from place to place, looking for somewhere to spend the night.
Worried: That the door’s owner might make him leave his only sanctuary.
Pity: That’s the emotion he evokes on the few that are brave enough to wander the streets.
Remorse: That’s the emotion that the passersby show when they refuse to stop to help.
Cold: That’s all he feels as he realizes that he has no one.
— Laura Arbona, Hoggard High School in Wilmington, NC
Memoirs in the time of coronavirus
Trapped. The walls are closing in. Someone coughs from outside, I immediately close the blinds and clorox the window. The television is on loud. The person on the other end of the line of dad’s phone is obviously deaf because dad is yelling into our end. In line for the computer, I have been waiting for two hours.
— Allison Coble, Hoggard High School
It all began with just one human. After days there where more and more infected people and everything started to be different. We all thought it isn’t that bad and China is the only one who suffers but we were absolutely wrong … Now there are too much cities which are in quarantine and there are about 16 thousand deaths. I’m scared. And I can#t do anything than staying at home and pray. I often watch videos and try to distract myself. When people ask me what has changed I can say: Everything. The human has changed. The human attitude has changed. Just everything. It’s not surprising for me if you can’t find toilet paper or water. The people are going crazy because of this virus. They know that they can be in danger fast if they just make one false decision. In this time we all have our anxiety. Either we are scared of being infected or we are scared that a loved one is infected.
— jana.hhg, Germany
This pic remind to me that we live in this period. Under from the outbreak of pandemic’s coronavirus, we stop to go out in order to avoid each social contact. So, we stay our home every day, all day. Most of the people stop working regularly and they work from home. The schools and other utilities are closed down and remain still open grocery stores and services for essential products. The whole world is in quarantine. Our effort to be uninfected is captured from this pic.
— Joanna, Greece
This photo shows that even in a time where socializing is not advising, humans are naturally social and are still coexisting in this time of distancing. The way the artist drew this made me feel a sense of separation but also togetherness at the same time, which is similar to the way I feel now. We’re all living our different lives with different situations and yet, we’re all somewhat connected.
— Ella Shynett, Hoggard High School in Wilmington, NC
Its Day 3 of quarantine and its starting to hit. This picture shows us how people are pretty much keeping as much distance away from people as possible. They’re still living their lives normally, just alone. But at my house it’s anything but normal. Every time I touch a light switch, my mom swoops in and wipes it down with a Clorox wipe. When I have to itch my nose, my mom screams at me. But I know deep down she’s just trying to keep me and my sister safe from the virus. She mainly wants to protect my grandma, who is very vulnerable at this time. Its gonna take some time to adjust to this type of living, not seeing friends in person for weeks, or just going to starbucks. But I know that it will all pass in no time and we can go back to living our normal lives. I actually can’t wait for school to start for once.
— Dean, Glenbard West Highschool
Stuck inside with nothing to do I’m really bored can’t think of anything at all :/. All I can do is homework woohoo Cant see my friends all I can do is call Trying to get it all done before its due With this virus I sadly can’t even go to the mall Thinking of you and you and you Can’t wait to go back to school and walk the fourth grade hall!
— Isabella V Grade 4, Jefferson Township, NJ
Poem by The Lady Running With Toilet Paper:
TP TP Why do people have to hoard it It’s the coronavirus, not diarrhea Don’t’ jack up the prices, I can’t afford it One pack, that’s it It’s all I could find To those hoarding the toilet paper You make me lose my hope in mankind
As I rush down the vacant street I pass by some stores Some open, some closed As I scramble past the doors No one seems to be coughing But I can feel it in the air A dull creeping paranoia Assembling into a scare
Up the stairs I make sure to not touch anything Don’t forget to use your elbows Don’t touch the key ring In through the door, drop the TP, wash my hands Wipe down the counter, wipe down the door Make sure to cancel any plans
Sit in solitude Turn on the TV and watch the news All I’m able to think is, “Oh god we’re screwed!”
— Ellinor Jonasson, Minnesota
Is social distancing impractical, when we live at such close proximity, drink tea with the neighbors, or buy food from the Deli,
You could choose to be stubborn, and get frustrated from being indoors, or you could be compliant, And watch the birds soar,
In the end it’s our choice where we decide to look, The dirty wall to the left, or the canvas on the right,
— Saharsh Satheesh, Collierville High School, Tennessee
Students’ Essays on Infectious Disease Prevention, COVID-19 Published Nationwide
As part of the BIO 173: Global Change and Infectious Disease course, Professor Fred Cohan assigns students to write an essay persuading others to prevent future and mitigate present infectious diseases. If students submit their essay to a news outlet—and it’s published—Cohan awards them with extra credit.
As a result of this assignment, more than 25 students have had their work published in newspapers across the United States. Many of these essays cite and applaud the University’s Keep Wes Safe campaign and its COVID-19 testing protocols.
Cohan, professor of biology and Huffington Foundation Professor in the College of the Environment (COE), began teaching the Global Change and Infectious Disease course in 2009, when the COE was established. “I wanted very much to contribute a course to what I saw as a real game-changer in Wesleyan’s interest in the environment. The course is about all the ways that human demands on the environment have brought us infectious diseases, over past millennia and in the present, and why our environmental disturbances will continue to bring us infections into the future.”
Over the years, Cohan learned that he can sustainably teach about 170 students every year without running out of interested students. This fall, he had 207. Although he didn’t change the overall structure of his course to accommodate COVID-19 topics, he did add material on the current pandemic to various sections of the course.
“I wouldn’t say that the population of the class increased tremendously as a result of COVID-19, but I think the enthusiasm of the students for the material has increased substantially,” he said.
To accommodate online learning, Cohan shaved off 15 minutes from his normal 80-minute lectures to allow for discussion sections, led by Cohan and teaching assistants. “While the lectures mostly dealt with biology, the discussions focused on how changes in behavior and policy can solve the infectious disease problems brought by human disturbance of the environment,” he said.
Based on student responses to an introspective exam question, Cohan learned that many students enjoyed a new hope that we could each contribute to fighting infectious disease. “They discovered that the solution to infectious disease is not entirely a waiting game for the right technologies to come along,” he said. “Many enjoyed learning about fighting infectious disease from a moral and social perspective. And especially, the students enjoyed learning about the ‘socialism of the microbe,’ how preventing and curing others’ infections will prevent others’ infections from becoming our own. The students enjoyed seeing how this idea can drive both domestic and international health policies.”
A sampling of the published student essays are below:
Alexander Giummo ’22 and Mike Dunderdale’s ’23 op-ed titled “ A National Testing Proposal: Let’s Fight Back Against COVID-19 ” was published in the Journal Inquirer in Manchester, Conn.
They wrote: “With an expansive and increased testing plan for U.S. citizens, those who are COVID-positive could limit the number of contacts they have, and this would also help to enable more effective contact tracing. Testing could also allow for the return of some ‘normal’ events, such as small social gatherings, sports, and in-person class and work schedules.
“We propose a national testing strategy in line with the one that has kept Wesleyan students safe this year. The plan would require a strong push by the federal government to fund the initiative, but it is vital to successful containment of the virus.
“Twice a week, all people living in the U.S. should report to a local testing site staffed with professionals where the anterior nasal swab Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test, used by Wesleyan and supported by the Broad Institute, would be implemented.”
Kalyani Mohan ’22 and Kalli Jackson ’22 penned an essay titled “ Where Public Health Meets Politics: COVID-19 in the United States ,” which was published in Wesleyan’s Arcadia Political Review .
They wrote: “While the U.S. would certainly benefit from a strengthened pandemic response team and structural changes to public health systems, that alone isn’t enough, as American society is immensely stratified, socially and culturally. The politicization of the COVID-19 pandemic shows that individualism, libertarianism and capitalism are deeply ingrained in American culture, to the extent that Americans often blind to the fact community welfare can be equivalent to personal welfare. Pandemics are multifaceted, and preventing them requires not just a cultural shift but an emotional one amongst the American people, one guided by empathy—towards other people, different communities and the planet. Politics should be a tool, not a weapon against its people.”
Sydnee Goyer ’21 and Marcel Thompson’s ’22 essay “ This Flu Season Will Be Decisive in the Fight Against COVID-19 ” also was published in Arcadia Political Review .
“With winter approaching all around the Northern Hemisphere, people are preparing for what has already been named a “twindemic,” meaning the joint threat of the coronavirus and the seasonal flu,” they wrote. “While it is known that seasonal vaccinations reduce the risk of getting the flu by up to 60% and also reduce the severity of the illness after the contamination, additional research has been conducted in order to know whether or not flu shots could reduce the risk of people getting COVID-19. In addition to the flu shot, it is essential that people remain vigilant in maintaining proper social distancing, washing your hands thoroughly, and continuing to wear masks in public spaces.”
An op-ed titled “ The Pandemic Has Shown Us How Workplace Culture Needs to Change ,” written by Adam Hickey ’22 and George Fuss ’21, was published in Park City, Utah’s The Park Record .
They wrote: “One review of academic surveys (most of which were conducted in the United States) conducted in 2019 found that between 35% and 97% of respondents in those surveys reported having attended work while they were ill, often because of workplace culture or policy which generated pressure to do so. Choosing to ignore sickness and return to the workplace while one is ill puts colleagues at risk, regardless of the perceived severity of your own illness; COVID-19 is an overbearing reminder that a disease that may cause mild, even cold-like symptoms for some can still carry fatal consequences for others.
“A mandatory paid sick leave policy for every worker, ideally across the globe, would allow essential workers to return to work when necessary while still providing enough wiggle room for economically impoverished employees to take time off without going broke if they believe they’ve contracted an illness so as not to infect the rest of their workplace and the public at large.”

Women’s cross country team members and classmates Jane Hollander ’23 and Sara Greene ’23 wrote a sports-themed essay titled “ This Season, High School Winter Sports Aren’t Worth the Risk ,” which was published in Tap into Scotch Plains/Fanwood , based in Scotch Plains, N.J. Their essay focused on the risks high school sports pose on student-athletes, their families, and the greater community.
“We don’t propose cutting off sports entirely— rather, we need to be realistic about the levels at which athletes should be participating. There are ways to make practices safer,” they wrote. “At [Wesleyan], we began the season in ‘cohorts,’ so the amount of people exposed to one another would be smaller. For non-contact sports, social distancing can be easily implemented, and for others, teams can focus on drills, strength and conditioning workouts, and skill-building exercises. Racing sports such as swim and track can compete virtually, comparing times with other schools, and team sports can focus their competition on intra-team scrimmages. These changes can allow for the continuation of a sense of normalcy and team camaraderie without the exposure to students from different geographic areas in confined, indoor spaces.”
Brook Guiffre ’23 and Maddie Clarke’s ’22 op-ed titled “ On the Pandemic ” was published in Hometown Weekly, based in Medfield, Mass.
“The first case of COVID-19 in the United States was recorded on January 20th, 2020. For the next month and a half, the U.S. continued operating normally, while many other countries began their lockdown,” they wrote. “One month later, on February 29th, 2020, the federal government approved a national testing program, but it was too little too late. The U.S. was already in pandemic mode, and completely unprepared. Frontline workers lacked access to N-95 masks, infected patients struggled to get tested, and national leaders informed the public that COVID-19 was nothing more than the common flu. Ultimately, this unpreparedness led to thousands of avoidable deaths and long-term changes to daily life. With the risk of novel infectious diseases emerging in the future being high, it is imperative that the U.S. learn from its failure and better prepare for future pandemics now. By strengthening our public health response and re-establishing government organizations specialized in disease control, we have the ability to prevent more years spent masked and six feet apart.”
In addition, their other essay, “ On Mass Extinction ,” was also published by Hometown Weekly .
“The sixth mass extinction—which scientists have coined as the Holocene Extinction—is upon us. According to the United Nations, around one million plant and animal species are currently in danger of extinction, and many more within the next decade. While other extinctions have occurred in Earth’s history, none have occurred at such a rapid rate,” they wrote. “For the sake of both biodiversity and infectious diseases, it is in our best interest to stop pushing this Holocene Extinction further.”
An essay titled “ Learning from Our Mistakes: How to Protect Ourselves and Our Communities from Diseases ,” written by Nicole Veru ’21 and Zoe Darmon ’21, was published in My Hometown Bronxville, based in Bronxville, N.Y.
“We can protect ourselves and others from future infectious diseases by ensuring that we are vaccinated,” they wrote. “Vaccines have high levels of success if enough people get them. Due to vaccines, society is no longer ravaged by childhood diseases such as mumps, rubella, measles, and smallpox. We have been able to eradicate diseases through vaccines; smallpox, one of the world’s most consequential diseases, was eradicated from the world in the 1970s.
“In 2000, the U.S. was nearly free of measles, yet, due to hesitations by anti-vaxxers, there continues to be cases. From 2000–2015 there were over 18 measles outbreaks in the U.S. This is because unless a disease is completely eradicated, there will be a new generation susceptible.
“Although vaccines are not 100% effective at preventing infection, if we continue to get vaccinated, we protect ourselves and those around us. If enough people are vaccinated, societies can develop herd immunity. The amount of people vaccinated to obtain herd immunity depends on the disease, but if this fraction is obtained, the spread of disease is contained. Through herd immunity, we protect those who may not be able to get vaccinated, such as people who are immunocompromised and the tiny portion of people for whom the vaccine is not effective.”
Dhruvi Rana ’22 and Bryce Gillis ’22 co-authored an op-ed titled “ We Must Educate Those Who Remain Skeptical of the Dangers of COVID-19 ,” which was published in Rhode Island Central .
“As Rhode Island enters the winter season, temperatures are beginning to drop and many studies have demonstrated that colder weather and lower humidity are correlated with higher transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19,” they wrote. “By simply talking or breathing, we release respiratory droplets and aerosols (tiny fluid particles which could carry the coronavirus pathogen), which can remain in the air for minutes to hours.
“In order to establish herd immunity in the US, we must educate those who remain skeptical of the dangers of COVID-19. Whether community-driven or state-funded, educational campaigns are needed to ensure that everyone fully comprehends how severe COVID-19 is and the significance of airborne transmission. While we await a vaccine, it is necessary now more than ever that we social distance, avoid crowds, and wear masks, given that colder temperatures will likely yield increased transmission of the virus.”
Danielle Rinaldi ’21 and Verónica Matos Socorro ’21 published their op-ed titled “ Community Forum: How Mask-Wearing Demands a Cultural Reset ” in the Ewing Observer , based in Lawrence, N.J.
“In their own attempt to change personal behavior during the pandemic, Wesleyan University has mandated mask-wearing in almost every facet of campus life,” they wrote. “As members of our community, we must recognize that mask-wearing is something we are all responsible and accountable for, not only because it is a form of protection for us, but just as important for others as well. However, it seems as though both Covid fatigue and complacency are dominating the mindsets of Americans, leading to even more unwillingness to mask up. Ultimately, it is inevitable that this pandemic will not be the last in our lifespan due to global warming creating irreversible losses in biodiversity. As a result, it is imperative that we adopt the norm of mask-wearing now and undergo a culture shift of the abandonment of an individualistic mindset, and instead, create a society that prioritizes taking care of others for the benefit of all.”

Shayna Dollinger ’22 and Hayley Lipson ’21 wrote an essay titled “ My Pandemic Year in College Has Brought Pride and Purpose. ” Dollinger submitted the piece, rewritten in first person, to Jewish News of Northern California . Read more about Dollinger’s publication in this News @ Wesleyan article .
“I lay in the dead grass, a 6-by-6-foot square all to myself. I cheer for my best friend, who is on the stage constructed at the bottom of Foss hill, dancing with her Bollywood dance group. Masks cover their ordinarily smiling faces as their bodies move in sync. Looking around at friends and classmates, each in their own 6-by-6 world, I feel an overwhelming sense of normalcy.
“One of the ways in which Wesleyan has prevented outbreaks on campus is by holding safe, socially distanced events that students want to attend. By giving us places to be and things to do on the weekends, we are discouraged from breaking rules and causing outbreaks at ‘super-spreader’ events.”
An op-ed written by Luna Mac-Williams ’22 and Daëlle Coriolan ’24 titled “ Collectivist Practices to Combat COVID-19 ” was published in the Wesleyan Argus .
“We are embroiled in a global pandemic that disproportionately affects poor communities of color, and in the midst of a higher cultural consciousness of systemic inequities,” they wrote. “A cultural shift to center collectivist thought and action not only would prove helpful in disease prevention, but also belongs in conversation with the Black Lives Matter movement. Collectivist models of thinking effectively target the needs of vulnerable populations including the sick, the disenfranchised, the systematically marginalized. Collectivist systems provide care, decentering the capitalist, individualist system, and focusing on how communities can work to be self-sufficient and uplift our own neighbors.”
An essay written by Maria Noto ’21 , titled “ U.S. Individualism Has Deadly Consequences ,” is published in the Oneonta Daily Star , based in Oneonta, N.Y.
She wrote, “When analyzing the cultures of certain East Asian countries, several differences stand out. For instance, when people are sick and during the cold and flu season, many East Asian cultures, including South Korea, use mask-wearing. What is considered a threat to freedom by some Americans is a preventive action and community obligation in this example. This, along with many other cultural differences, is insightful in understanding their ability to contain the virus.
“These differences are deeply seeded in the values of a culture. However, there is hope for the U.S. and other individualistic cultures in recognizing and adopting these community-centered approaches. Our mindset needs to be revolutionized with the help of federal and local assistance: mandating masks, passing another stimulus package, contact tracing, etc… However, these measures will be unsuccessful unless everyone participates for the good of a community.”
A published op-ed by Madison Szabo ’23 , Caitlyn Ferrante ’23 ran in the Two Rivers Times . The piece is titled “ Anxiety and Aspiration: Analyzing the Politicization of the Pandemic .”
John Lee ’21 and Taylor Goodman-Leong ’21 have published their op-ed titled “ Reassessing the media’s approach to COVID-19 ” in Weekly Monday Cafe 24 (Page 2).
An essay by Eleanor Raab ’21 and Elizabeth Nefferdorf ’22 titled “ Preventing the Next Epidemic ” was published in The Almanac .
- Keep Wes Safe
- student publications
- Teaching during the pandemic
Related Articles
Faculty Achievements in Academic Year 2023-24
Wesleyan Senior Studies Texas Book Challenges
At WesFest, Admitted Students Share Opinions on Diversity of Thought, Open Curriculum
Previous matesan's new book explores political violence, islamist mobilization in egypt and indonesia, next students launch fun, interactive virtual program for school-aged kids.
- Newsletters
Site search
- Israel-Hamas war
- Home Planet
- 2024 election
- Supreme Court
- TikTok’s fate
- All explainers
- Future Perfect
Filed under:
Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus
Artists, novelists, critics, and essayists are writing the first draft of history.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/66606035/1207638131.jpg.0.jpg)
The world is grappling with an invisible, deadly enemy, trying to understand how to live with the threat posed by a virus . For some writers, the only way forward is to put pen to paper, trying to conceptualize and document what it feels like to continue living as countries are under lockdown and regular life seems to have ground to a halt.
So as the coronavirus pandemic has stretched around the world, it’s sparked a crop of diary entries and essays that describe how life has changed. Novelists, critics, artists, and journalists have put words to the feelings many are experiencing. The result is a first draft of how we’ll someday remember this time, filled with uncertainty and pain and fear as well as small moments of hope and humanity.
At the New York Review of Books, Ali Bhutto writes that in Karachi, Pakistan, the government-imposed curfew due to the virus is “eerily reminiscent of past military clampdowns”:
Beneath the quiet calm lies a sense that society has been unhinged and that the usual rules no longer apply. Small groups of pedestrians look on from the shadows, like an audience watching a spectacle slowly unfolding. People pause on street corners and in the shade of trees, under the watchful gaze of the paramilitary forces and the police.
His essay concludes with the sobering note that “in the minds of many, Covid-19 is just another life-threatening hazard in a city that stumbles from one crisis to another.”
Writing from Chattanooga, novelist Jamie Quatro documents the mixed ways her neighbors have been responding to the threat, and the frustration of conflicting direction, or no direction at all, from local, state, and federal leaders:
Whiplash, trying to keep up with who’s ordering what. We’re already experiencing enough chaos without this back-and-forth. Why didn’t the federal government issue a nationwide shelter-in-place at the get-go, the way other countries did? What happens when one state’s shelter-in-place ends, while others continue? Do states still under quarantine close their borders? We are still one nation, not fifty individual countries. Right?
Award-winning photojournalist Alessio Mamo, quarantined with his partner Marta in Sicily after she tested positive for the virus, accompanies his photographs in the Guardian of their confinement with a reflection on being confined :
The doctors asked me to take a second test, but again I tested negative. Perhaps I’m immune? The days dragged on in my apartment, in black and white, like my photos. Sometimes we tried to smile, imagining that I was asymptomatic, because I was the virus. Our smiles seemed to bring good news. My mother left hospital, but I won’t be able to see her for weeks. Marta started breathing well again, and so did I. I would have liked to photograph my country in the midst of this emergency, the battles that the doctors wage on the frontline, the hospitals pushed to their limits, Italy on its knees fighting an invisible enemy. That enemy, a day in March, knocked on my door instead.
In the New York Times Magazine, deputy editor Jessica Lustig writes with devastating clarity about her family’s life in Brooklyn while her husband battled the virus, weeks before most people began taking the threat seriously:
At the door of the clinic, we stand looking out at two older women chatting outside the doorway, oblivious. Do I wave them away? Call out that they should get far away, go home, wash their hands, stay inside? Instead we just stand there, awkwardly, until they move on. Only then do we step outside to begin the long three-block walk home. I point out the early magnolia, the forsythia. T says he is cold. The untrimmed hairs on his neck, under his beard, are white. The few people walking past us on the sidewalk don’t know that we are visitors from the future. A vision, a premonition, a walking visitation. This will be them: Either T, in the mask, or — if they’re lucky — me, tending to him.
Essayist Leslie Jamison writes in the New York Review of Books about being shut away alone in her New York City apartment with her 2-year-old daughter since she became sick:
The virus. Its sinewy, intimate name. What does it feel like in my body today? Shivering under blankets. A hot itch behind the eyes. Three sweatshirts in the middle of the day. My daughter trying to pull another blanket over my body with her tiny arms. An ache in the muscles that somehow makes it hard to lie still. This loss of taste has become a kind of sensory quarantine. It’s as if the quarantine keeps inching closer and closer to my insides. First I lost the touch of other bodies; then I lost the air; now I’ve lost the taste of bananas. Nothing about any of these losses is particularly unique. I’ve made a schedule so I won’t go insane with the toddler. Five days ago, I wrote Walk/Adventure! on it, next to a cut-out illustration of a tiger—as if we’d see tigers on our walks. It was good to keep possibility alive.
At Literary Hub, novelist Heidi Pitlor writes about the elastic nature of time during her family’s quarantine in Massachusetts:
During a shutdown, the things that mark our days—commuting to work, sending our kids to school, having a drink with friends—vanish and time takes on a flat, seamless quality. Without some self-imposed structure, it’s easy to feel a little untethered. A friend recently posted on Facebook: “For those who have lost track, today is Blursday the fortyteenth of Maprilay.” ... Giving shape to time is especially important now, when the future is so shapeless. We do not know whether the virus will continue to rage for weeks or months or, lord help us, on and off for years. We do not know when we will feel safe again. And so many of us, minus those who are gifted at compartmentalization or denial, remain largely captive to fear. We may stay this way if we do not create at least the illusion of movement in our lives, our long days spent with ourselves or partners or families.
Novelist Lauren Groff writes at the New York Review of Books about trying to escape the prison of her fears while sequestered at home in Gainesville, Florida:
Some people have imaginations sparked only by what they can see; I blame this blinkered empiricism for the parks overwhelmed with people, the bars, until a few nights ago, thickly thronged. My imagination is the opposite. I fear everything invisible to me. From the enclosure of my house, I am afraid of the suffering that isn’t present before me, the people running out of money and food or drowning in the fluid in their lungs, the deaths of health-care workers now growing ill while performing their duties. I fear the federal government, which the right wing has so—intentionally—weakened that not only is it insufficient to help its people, it is actively standing in help’s way. I fear we won’t sufficiently punish the right. I fear leaving the house and spreading the disease. I fear what this time of fear is doing to my children, their imaginations, and their souls.
At ArtForum , Berlin-based critic and writer Kristian Vistrup Madsen reflects on martinis, melancholia, and Finnish artist Jaakko Pallasvuo’s 2018 graphic novel Retreat , in which three young people exile themselves in the woods:
In melancholia, the shape of what is ending, and its temporality, is sprawling and incomprehensible. The ambivalence makes it hard to bear. The world of Retreat is rendered in lush pink and purple watercolors, which dissolve into wild and messy abstractions. In apocalypse, the divisions established in genesis bleed back out. My own Corona-retreat is similarly soft, color-field like, each day a blurred succession of quarantinis, YouTube–yoga, and televized press conferences. As restrictions mount, so does abstraction. For now, I’m still rooting for love to save the world.
At the Paris Review , Matt Levin writes about reading Virginia Woolf’s novel The Waves during quarantine:
A retreat, a quarantine, a sickness—they simultaneously distort and clarify, curtail and expand. It is an ideal state in which to read literature with a reputation for difficulty and inaccessibility, those hermetic books shorn of the handholds of conventional plot or characterization or description. A novel like Virginia Woolf’s The Waves is perfect for the state of interiority induced by quarantine—a story of three men and three women, meeting after the death of a mutual friend, told entirely in the overlapping internal monologues of the six, interspersed only with sections of pure, achingly beautiful descriptions of the natural world, a day’s procession and recession of light and waves. The novel is, in my mind’s eye, a perfectly spherical object. It is translucent and shimmering and infinitely fragile, prone to shatter at the slightest disturbance. It is not a book that can be read in snatches on the subway—it demands total absorption. Though it revels in a stark emotional nakedness, the book remains aloof, remote in its own deep self-absorption.
In an essay for the Financial Times, novelist Arundhati Roy writes with anger about Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s anemic response to the threat, but also offers a glimmer of hope for the future:
Historically, pandemics have forced humans to break with the past and imagine their world anew. This one is no different. It is a portal, a gateway between one world and the next. We can choose to walk through it, dragging the carcasses of our prejudice and hatred, our avarice, our data banks and dead ideas, our dead rivers and smoky skies behind us. Or we can walk through lightly, with little luggage, ready to imagine another world. And ready to fight for it.
From Boston, Nora Caplan-Bricker writes in The Point about the strange contraction of space under quarantine, in which a friend in Beirut is as close as the one around the corner in the same city:
It’s a nice illusion—nice to feel like we’re in it together, even if my real world has shrunk to one person, my husband, who sits with his laptop in the other room. It’s nice in the same way as reading those essays that reframe social distancing as solidarity. “We must begin to see the negative space as clearly as the positive, to know what we don’t do is also brilliant and full of love,” the poet Anne Boyer wrote on March 10th, the day that Massachusetts declared a state of emergency. If you squint, you could almost make sense of this quarantine as an effort to flatten, along with the curve, the distinctions we make between our bonds with others. Right now, I care for my neighbor in the same way I demonstrate love for my mother: in all instances, I stay away. And in moments this month, I have loved strangers with an intensity that is new to me. On March 14th, the Saturday night after the end of life as we knew it, I went out with my dog and found the street silent: no lines for restaurants, no children on bicycles, no couples strolling with little cups of ice cream. It had taken the combined will of thousands of people to deliver such a sudden and complete emptiness. I felt so grateful, and so bereft.
And on his own website, musician and artist David Byrne writes about rediscovering the value of working for collective good , saying that “what is happening now is an opportunity to learn how to change our behavior”:
In emergencies, citizens can suddenly cooperate and collaborate. Change can happen. We’re going to need to work together as the effects of climate change ramp up. In order for capitalism to survive in any form, we will have to be a little more socialist. Here is an opportunity for us to see things differently — to see that we really are all connected — and adjust our behavior accordingly. Are we willing to do this? Is this moment an opportunity to see how truly interdependent we all are? To live in a world that is different and better than the one we live in now? We might be too far down the road to test every asymptomatic person, but a change in our mindsets, in how we view our neighbors, could lay the groundwork for the collective action we’ll need to deal with other global crises. The time to see how connected we all are is now.
The portrait these writers paint of a world under quarantine is multifaceted. Our worlds have contracted to the confines of our homes, and yet in some ways we’re more connected than ever to one another. We feel fear and boredom, anger and gratitude, frustration and strange peace. Uncertainty drives us to find metaphors and images that will let us wrap our minds around what is happening.
Yet there’s no single “what” that is happening. Everyone is contending with the pandemic and its effects from different places and in different ways. Reading others’ experiences — even the most frightening ones — can help alleviate the loneliness and dread, a little, and remind us that what we’re going through is both unique and shared by all.
Will you support Vox today?
We believe that everyone deserves to understand the world that they live in. That kind of knowledge helps create better citizens, neighbors, friends, parents, and stewards of this planet. Producing deeply researched, explanatory journalism takes resources. You can support this mission by making a financial gift to Vox today. Will you join us?
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
Next Up In Culture
Sign up for the newsletter today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
Thanks for signing up!
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.

What the backlash to student protests over Gaza is really about

The lessons from colleges that didn’t call the police

Should humans get their own geologic era?

The longshot plan to end the war in Gaza and bring peace to the Middle East

Drake vs. everyone, explained
Where billions of cicadas will emerge this spring (and over the next decade), in one map
- Skip to main content
- Skip to FDA Search
- Skip to in this section menu
- Skip to footer links

The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Search
- Menu
- News & Events
- Speeches by FDA Officials
- Remarks by Commissioner Stephen Hahn, M.D. — The COVID-19 Pandemic — Finding Solutions, Applying Lessons Learned - 06/01/2020
Speech | Virtual
Event Title Remarks by Commissioner Stephen Hahn, M.D. — The COVID-19 Pandemic — Finding Solutions, Applying Lessons Learned June 1, 2020
The COVID-19 Pandemic — Finding Solutions, Applying Lessons Learned
(Remarks as prepared for delivery. The text and video of this speech are slightly, though not substantively different from the version presented by Dr. Hahn on June 1 to the Alliance for a Stronger FDA, via audio broadcast only. Because of evolving scheduling challenges, it was not clear whether Dr. Hahn would be able to present the speech live and so it was recorded by video earlier. Ultimately, he did give the speech live to the Alliance, but only via an audio link. Given the minimal changes in the live version, we are posting the video version and the accompanying text.)
One of the most frustrating challenges each of us can face is the inability to control the events that affect our lives. Often, we are thrust into situations not of our own making. It’s no surprise that one of the most familiar adages concerns the best laid plans of mice and men going awry.
And yet, to borrow another often-used saying, necessity is the mother of invention. History teaches us that crises often lead to accelerated change and innovations and new discoveries.
This dynamic has been on my mind a great deal recently. It wasn’t too long ago – last December, to be exact -- that I had the distinction of being confirmed as the 24th Commissioner of the Food and Drug Administration.
This is the greatest honor of my life. I have long cherished the critical role the FDA plays in protecting and promoting the public health, and I’ve relied on the Agency’s expertise throughout my professional life.
So, I eagerly embraced my new responsibilities and the chance to make a real difference in public health. I was especially conscious that we live in a time of extraordinary scientific achievement, especially in oncology, with unprecedented opportunities to help make the lives of American patients and consumers healthier and safer.
I quickly immersed myself in the Agency’s broad and complex responsibilities, seizing every opportunity to learn about the FDA, both those areas with which I’d previously had minimum involvement, such as food policy, and those with which I had more familiarity, like cancer treatments and innovative clinical trial design.
I began to work with, and learn from, the agency’s extraordinary leadership team. I learned very quickly that the principles that have guided me throughout my life, such as my commitment to relying only on the best medical science and most rigorous data in support of advancing innovation and discovery, and my fundamental belief in promoting integrity and transparency in the scientific process, are the same principles that guide the FDA in both science and regulation.
So, I was in the midst of transitioning from being Chief Medical Executive at MD Anderson Cancer Center to being Commissioner of FDA when our entire world was turned upside down with the appearance of the novel COVID-19 coronavirus.
I certainly did not anticipate a public health emergency of this magnitude when I joined the agency. And I could not have imagined how significantly my new role would change and be shaped by this pandemic. I definitely could not have known that discussions about personal protective equipment (or PPE) or face masks or nasal swabs would be central to my work as Commissioner.
One thing was apparent: I would need to manage this evolving situation even as I was still learning about FDA.
From the very start I knew that even in a crisis situation – or perhaps especially because we are in a crisis situation – it is imperative that we maintain FDA’s high standards for evaluating products and making sure that the benefits outweigh potential harms.
To maintain our standard, I pledged to myself and emphasized to my new colleagues at FDA that our decisions would always be rooted in science. Having spent my entire career as a physician and scientist caring for patients with cancer, I’ve always valued highly a commitment to good data and sound science. I feel comfortable working with the scientists at FDA because I know they not only share that value, that commitment, but that they will tolerate nothing less. So, it was critical to me, as the pandemic escalated that this be reinforced as the guidepost for all of our decisions.
It may have been trial by fire, but I have the good fortune to work with an enormous number of talented individuals and teams who are helping guide us through this crisis. Every day they show extraordinary expertise, commitment, and resilience.
I also was able to call on many from outside the agency, including former FDA leaders as well as colleagues from the medical community.
What struck me was the uniformity of their advice. Those who formerly worked at FDA urged me to rely upon the FDA staff, many of whom have the experience to help manage a pandemic. My friends from outside the agency urged that we move quickly to make decisions, set direction and to be transparent about what we are doing. I have tried to follow all of this excellent advice.
Protecting the Food Supply
Since this crisis and the actions of the FDA have evolved so rapidly, let me summarize what we have done. I am confident that the FDA has measured up to this unprecedented challenge.
I want to start with the first word in the FDA’s name – food. Most of us take food safety for granted. But it takes a lot of hard work to maintain a safe food supply. This was true even before the COVID-19 pandemic but is especially challenging during an ongoing international crisis.
During the pandemic, through the collaboration of the FDA, the food industry and our federal and state partners, we have been able to maintain the safety of the nation’s food supply. Our Coordinated Outbreak Response and Evaluation team remained on the job, monitoring for signs of foodborne illness outbreaks and prepared to take action when needed.
And along with our federal partners, including CDC and USDA, we also have provided best practices for food workers, industry, and consumers on how to stay safe and keep food safe.
Diagnosing and Developing Treatments
On the medical side, we immediately committed to facilitating efforts to develop diagnostic tests, treatments and vaccines for the disease. We have helped facilitate increases in our national testing capacity, have helped ensure continued access to necessary medical products, and have sought to prevent the sale of fraudulent products.
If there’s one thing that’s been reaffirmed during this crisis, it’s the essential role of medical devices, including diagnostics, to countering this pandemic.
From the earliest days of our response, we worked to ensure that we had the essential medical devices, including personal protective equipment, to help treat those who are ill and to ensure that health care workers and others on the front line are properly protected.
To be sure, there were bumps along the road, but today we have an adequate supply of the devices that have been in unprecedented high demand such as PPE, ventilators, and others.
We’ve reviewed and issued emergency use authorizations for medical devices for COVID-19 at an incredibly fast pace.
And we’ve worked closely with many companies that don’t regularly make medical products but wanted to pitch in by making hand sanitizer, ventilators, or PPE.
There was a special focus on the development and availability of accurate and reliable COVID-19 tests. We need to know who has the disease and who has had it. This is essential if we are to understand this virus and return to a more normal lifestyle.
Since January, we’ve worked with hundreds of test developers, many of whom have submitted emergency use authorization requests to FDA for tests that detect the virus or antibodies to the virus.
As you have seen reported, early in the crisis we provided regulatory flexibility for developers with validated tests as outlined in our policies because public health needs dictated that we do as much testing as possible. But as the process has matured, we have helped increase the number of authorized tests, and we have adapted some of our policies to best serve the public need.
Today, if evidence arises that raises questions about a particular test’s reliability, we will take appropriate action to protect consumers from inaccurate tests. This is a dynamic process that is continually being informed by new data and evidence.
We’ve used a similar dynamic process in the search for therapeutic treatments and vaccines.
We are working closely with partners throughout the government and academia, and with drug and vaccine developers to explore, expedite, and incentivize the development of these products.
More than 90 drugs are being studied, and FDA is actively working with numerous vaccine sponsors, including three sponsors who have announced they have vaccine candidates that are now in clinical trials in the U.S. More than 144 clinical trials have been initiated for therapeutic agents, with hundreds more in the pipeline. We don’t have a cure or vaccine yet, but we’re on our way, at unprecedented speed.
Ultimately, of course, the way we’ll eventually defeat this virus is with a vaccine. FDA is working closely to provide technical assistance to federal partners, vaccine developers, researchers, manufacturers, and experts across the globe and exploring all possible options to advance the most efficient and timely development of vaccines, while at the same time maintaining regulatory independence.
Communicating and Educating
There is much more to do going forward, and that includes research, exploration and discovery, and communicating what we know.
As the country starts to reopen, it’s essential that the public understands what they need to do to continue to protect themselves. There has been a proliferation of information, and misinformation, on the internet and in other sources. Consumers need to understand that this virus is still with us and that we, as individuals and communities working together, need to take steps to continue to contain its spread.
The FDA has an important part to play in communicating public information to all populations in the U.S. FDA has increased outreach by developing and disseminating COVID-19 health education materials for consumers in multiple languages to diverse communities and the public overall. Everyone should have a clear understanding of why hand-washing and social distancing remain essential. Consumers need to think about how to shop for food safely. People need to know when to call their doctors and when to ask about getting tested. Health care professionals need to know how to manage their patients in this new environment, and how best to apply telemedicine, the use of which is rapidly accelerating.
I want the FDA to serve as a national resource for the public and health care community. I regard educating the public and providing accurate, reliable, up-to-date information as not just an Agency priority, but one of my own personal responsibilities as Commissioner. I will be out in public and in the media talking about how individuals can help us contain and conquer this virus.
I believe my personal experience with being self-quarantined will make me a better communicator. Being quarantined for 14 days in May was certainly no fun, but because we at FDA were already functioning very effectively virtually, I was able to continue to be fully engaged, and provide direction and leadership. And it made me even more focused on making sure consumers have all the information they need about self-protection.
We now need to look forward. A major strength of the FDA is not just in our response to a crisis, but in our ability to learn from the work we do and apply that experience in the future.
As this pandemic evolved, it was clear that some FDA processes needed to be adjusted to accommodate the urgency of the pandemic. I think the entire FDA team has now seen first-hand that we need to look at some of our processes and policies. I have instructed my staff to identify the lessons learned from this pandemic and what adjustments may be needed, not just to manage this or future emergencies, but to make FDA itself more efficient in carrying out our regulatory responsibilities.
I am committed to making sure that some of the lessons learned from managing this pandemic will lead to permanent improvements at the FDA in processes and policies.
For example, in facilitating the development of new treatments, we streamlined some of our processes.
We have taken a fresh look at how clinical trials should be designed and conducted. In a pandemic we knew we needed to get answers more quickly. For instance, early on, the FDA, National Institutes of Health, and industry worked together to facilitate the implementation of a “master protocol” that can be used in multiple clinical trials and allows for the study of more than one promising new drug for COVID-19 at a time. And we have used expanded access to meet the needs of patients who are not eligible or who are unable to participate in randomized clinical trials.
Many of the permanent changes that we will implement really represent an acceleration of where we were headed before. For example, the concept of decentralized clinical trials, in which trial procedures are conducted near the patient’s home and through use of local health care providers or local laboratories has been discussed before, and laid the foundation for some of the trials for COVID-19 products.
Another area where our pre-COVID work has informed our response to the pandemic involves the use of Real World Evidence (RWE).
In recent years, the agency has taken steps to leverage modern, rigorous analyses of real-world data—such as data from electronic health records, insurance claims, patient registries and lab results.
As the pandemic brought an urgency to these efforts, the FDA advanced collaborations with public and private partners to collect and analyze a variety of real-world data sources, using our Sentinel system and other resources.
Evaluation of real-world data has the potential to provide a wealth of rapid, actionable information to better understand disease symptoms, describe and measure immunity, and use available medical product supplies to help mitigate potential shortages. These data can also inform ongoing work to evaluate potential therapies, vaccines or diagnostics for COVID-19. The more experience we have with real world evidence, the more confidence we will have in using it for product decisions.
I mention real world evidence, but in reality, we have so many examples of how lessons learned from the pandemic will affect FDA in the future.
To the extent that the innovations and adaptations we implemented during the pandemic crisis worked and would be appropriate to implement outside of a pandemic situation, we will incorporate them into standard FDA procedures. And to the extent that we identified unnecessary barriers, we will remove them. This is one of my top priorities. Permanent change where needed will take place, and will make FDA an even stronger agency.
As I mentioned before, anything that enables quicker reviews and authorizations we will seek to make permanent.
But make no mistake. We will not cut corners on safety or effectiveness. I said this before, and I say it again. Good science as the basis for decision making has been a hallmark of my career, and is a value that I hold deeply. The American public must have confidence in the products regulated by the FDA.
Speed is important, but so are safety, accuracy and effectiveness.
FDA’s commitment to good science and rigorous data is unwavering, even as we look at how we can learn from this pandemic.
I am hopeful that this is a once-in-a-lifetime experience for all of us. An unprecedented historic event that has required an unprecedented response from us and everyone around the world.
That said, I am pleased that throughout this crisis the rest of the FDA’s work has continued, with relatively few interruptions. New drugs and devices have been authorized. Our food safety surveillance has adapted and our outbreak response resources have been maintained. Our oversight of tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, has gone on. The Agency has measured up to the challenge in all ways.
And we are well positioned as we move into a new phase, that is, transitioning back to what has come to be known as the “new normal.” Our staff has done a phenomenal job of adapting to this new normal. And I am confident that they are ready to deal with any additional upcoming challenges.
I will close with something I’ve seen reaffirmed time and time again over the past few months. That is the essential role that the FDA plays in consumer protection and beyond in advancing public health.
Before coming to the FDA, I had heard about the extraordinary dedication of the agency’s workforce. Working side by side with my colleagues in response to this pandemic, I’ve seen that characterization validated over and over.
It is my great honor to serve with so many highly skilled and committed professionals. And the American people can be assured that this agency is working around the clock for them, doing whatever is necessary to fulfill our mission to protect and promote the health of the American public.
I encourage you all to stay safe, aware, and focused as we continue to respond to the challenges of this public health emergency.

COMMENTS
rodaranches. report flag outlined. Answer: COVID-19 is a pandemic. Thousands of people are being affected and millions of people are being infected. We can't go outside and play, school is closed and we can't visit family and friends. The novel coronavirus has caused many loved ones to be mourned and missed.
Whatever your point of view is, writing a persuasive essay about it is a good way of organizing your thoughts and persuading others. A persuasive essay about the Covid-19 vaccine could consider the benefits of getting vaccinated as well as the potential side effects. Below are some examples of persuasive essays on getting vaccinated for Covid-19.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19. COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very ...
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App ...
Nearly every 100 years, humans collectively face a pandemic crisis. After the Spanish flu, now the world is in the grip of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). First detected in 2019 in the Chinese city of Wuhan, COVID-19 causes severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Despite the initial evidence indicating a zoonotic origin, the contagion ...
Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. "The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry ...
Publishing Opportunity: Submit your final essay to our Student Editorial Contest, open to middle school and high school students ages 10-19, until April 21. Please be sure to read all the rules ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed the inadequacy of public health systems worldwide, casting a shadow that we could not have imagined even a year ago. As the fog of confusion lifts and we begin to ...
Navigating the rapidly growing body of scientific literature on the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic is challenging, and ongoing critical appraisal of this output is essential. We aimed to summarize and critically appraise systematic reviews of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in humans that were available at the beginning of the pandemic. Nine databases (Medline, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, Web of ...
March 26, 2020. The rapidly-developing coronavirus crisis is dominating global headlines and altering life as we know it. Many schools worldwide have closed. In the United States alone, 55 million ...
The COVID-19 pandemic is far from over and could yet evolve in unanticipated ways, but one of its most important lessons is already clear: preparation and early execution are essential in ...
My alarm sounds at 8:15 a.m. I open my eyes and take a deep breath. I wiggle my toes and move my legs. I do this religiously every morning. Today, marks day 74 of staying at home. My mornings are ...
Kalyani Mohan '22 and Kalli Jackson '22 penned an essay titled " Where Public Health Meets Politics: COVID-19 in the United States ," which was published in Wesleyan's Arcadia Political Review. They wrote: "While the U.S. would certainly benefit from a strengthened pandemic response team and structural changes to public health ...
The days dragged on in my apartment, in black and white, like my photos. Sometimes we tried to smile, imagining that I was asymptomatic, because I was the virus. Our smiles seemed to bring good ...
This article outlines and gives a complete overview of SARS-CoV-2, including its pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and precautions. This article also provides the current scenario of the pandemic worldwide, since new findings are rapidly evolving and can help the readers in upgrading their knowledge about the COVID-19.
1. Introduction. The outbreak of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as the largest global pandemic ever experienced [].Experts have proposed that social lockdown will lead to improvements such as controlling the increase in the number of infected individuals and preventing a huge burden on the healthcare system [, , ].Governments of many countries across the world have ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on individuals, societies, and economies worldwide. Its multifaceted nature presents a wealth of topics suitable for academic exploration. This essay provides guidance on developing engaging and insightful essay topics related to COVID-19, offering a comprehensive range of perspectives to choose from.
Remarks by Commissioner Stephen Hahn, M.D., given electronically (by audio) to the Alliance for a Stronger FDA, on June 1, 2020, and recorded May 30, on video, at the HHS broadcast studio
25 October 2022. Vaccines save millions of lives each year. The development of safe and effective COVID-19 vaccines are a crucial step in helping us get back to doing more of the things we enjoy with the people we love. We've gathered the latest expert information to answer some of the most common questions about COVID-19 vaccines.