Health Informatics (PhD)
Our PhD in Health Informatics will prepare scholars to discover and extend their scientific knowledge and advance the science and practice of health informatics.
The program is built around our core interdisciplinary specializations:
- design and structure of health information systems
- implementation and evaluation of health information systems
- health information systems applications
- health data science and analytics
- patient and equity-focused health technology interventions

Quick facts
Students in this program will:
- generate new knowledge through research and testing of theory in health informatics
- contribute to solutions that advance health informatics and health care in a culturally diverse society
- translate health informatics research findings into practice and policy across health care systems
- represent a health informatics perspective in research, practice, education and scholarly endeavours
- demonstrate leadership and management competencies in health informatics
- develop system evaluation and digital transformation plans
Find a supervisor
You may list a potential supervisor on your application, but this is not required.
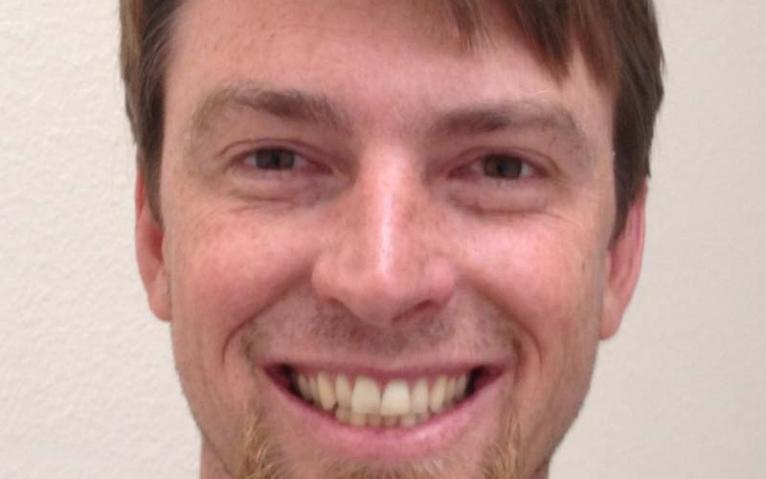
Abdul Roudsari
Professor Modelling and Simulation in healthcare; modelling methodology for health resource management; clinical decision support, machine learning and artificial intelligence – development and evaluation of decision support systems; evaluation methodologies with particular application in telemedicine. More recently my interests have developed into : Telemedicine technology, temporal representation and reasoning; utilisation of business intelligence in healthcare; shared decision-making, personalised health records and environmental sensing for health. Application area Chronic diseases.
Professor Data interoperability; Health database & data warehousing; AI & Data Mining application in healthcare, and e-health.
Andre Kushniruk
Director, Professor Usability of Health Information Systems; Human Factors in Healthcare; Clinical Informatics; Consumer informatics; Decision Support Systems; Healthcare Decision Making; Cognitive Informatics; AI in Healthcare; Evaluation methods; Healthcare System Design; Data Analytics and Visualization
Claudia Lai
Assistant Professor Digital Innovations that Promote Healthy Aging at home, Shared Decision Making, and Public Health; Community-Based Participatory Research; Digital Health Equity; Integrated Care; Learning Health Systems, Patient Portals
Dillon Chrimes
Assistant Teaching Professor Dr. Dillon Chrimes is currently not available to supervise graduate students.
Elizabeth Borycki
Professor Human Factors (Safety, Workflow and Usability); Design (User Interfaces, Heuristics and Guideline Development); Implementation Science (Technology Strategy, Implementation and Evaluation); Knowledge Management (Information Needs; Information Seeking; Decision Support Systems); Virtual Care (Mobile Health, Sensors, Medical Devices, Smart Homes, Telehealth); Data Science (Analytics, Dashboard Visualizations and AI); Clinical Informatics (ePrescribing, eMedRec, eMedication Administration Systems, Electronic Health Records); Nursing Informatics; Health Informatics (Professional Competency Development, Curriculum Design)
Helen Monkman
Assistant Professor, Undergraduate Advisor Human Factors; User Experience; Usability; Consumer Health Informatics; eHealth Literacy or Digital Health Literacy; Information Visualization.
Karen L. Courtney
Associate Professor, Graduate Advisor Areas of interest: Telehealth; m-Health; Information Technology Ethics; Community-based Informatics; Gerontechnology; Nursing Informatics; Health Services Research; Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD)
Simon Minshall
Assistant Teaching Professor, Health Terminology Standards Certificate Coordinator Simon Minshall is currently not available to supervise graduate students.
Show me program details
Providing you accurate admission requirements, application deadlines, tuition fee estimates and scholarships depends on your situation. Tell us about yourself:
I am a Canadian citizen or permanent resident International student
Show program details
Your program details
Application deadlines.
September 2025 entry – apply by January 15, 2025
Admission requirements
Program specific requirements.
- If you have a master’s degree in a field other than health informatics, you should apply to our MSc in Health Informatics program and indicate in your letter of intent that you are interested in applying to the PhD program in the future. Admission to the MSc program does not guarantee you future admission to the PhD program.
- Successful completion of a graduate level statistics course is required before you apply
As part of your application, you must submit:
- Three assessment reports. At least two should be from academics who can assess your capacity to conduct independent scholarly work and research.
- A curriculum vitae that summarizes your education background, employment history, professional/academic affiliations, and other achievements such as publications or awards.
- One or two sample publications or conference proceedings (if available). For each publication or proceeding, please include the full citation, indicate your percentage of contribution, your role and an electronic copy (preferably PDF).
- Thesis or research project (if available). Please provide an electronic copy (preferably PDF).
- Letter of intent summarizing why you are interested in earning the PhD in Health Informatics. Include your research interests and expectations of program in terms of personal and professional learning.
- Indicate if you have made contact with a faculty member regarding a possible supervisory arrangement. Having a prospective supervisor is not required.
- Successful completion of a graduate level statistics course is required before application.
- GRE scores must be submitted as part of the application.
Completion requirements
View the minimum course requirements for this program.
Funding & aid
Note : Co-op or assistantship is based on availability and not guaranteed.
All students are reviewed for graduate student funding annually. Funding is based on academic performance. We will consider students with a GPA of A- (7.0) or higher and adequate academic progress in the first year.
There is a maximum of two years of graduate student funding available from the school. Students on leave are not eligible for this funding.
You are encouraged to seek additional research funding opportunities through grants and additional financial assistance through university level awards, teaching assistantships and research assistantships.
- PhD students meeting the eligibility requirements will receive an entrance award.
- PhD students meeting the eligibility requirements and making adequate academic progress in the first year will be eligible for a second year of funding.
- Students who began in the MSc program and have successfully applied to PhD program will be considered for PhD first year funds after their successful admission to the PhD program. Example: A student applying in December 2019 and receiving admission to the PhD program would receive first year PhD funding beginning in September 2020. Eligibility criteria for MSc to PhD students is the same as PhD students.
Tuition & fees
Estimated minimum program cost*
* Based on an average program length. For a per term fee breakdown view the tuition fee estimator .
Estimated values determined by the tuition fee estimator shall not be binding to the University of Victoria.
Ready to apply?
You can start your online application to UVic by creating a new profile or using an existing one.
Apply now How to apply
Faculties & departments
- Faculty of Human and Social Development
- Health Information Science
Related programs
- Health Informatics (MSc)
- Nursing and Health Informatics Double Degree (MN + MSc)
- Health Terminology Standards (GCE)
Contact Sandra Boudewyn at [email protected] or 250-721-6459 .
< Back to Health Information Science overview
This website stores cookies on your computer. These cookies are used to collect information about how you interact with our website and allow us to remember your browser. We use this information to improve and customize your browsing experience, for analytics and metrics about our visitors both on this website and other media, and for marketing purposes. By using this website, you accept and agree to be bound by UVic’s Terms of Use and Protection of Privacy Policy . If you do not agree to the above, you must not use this website.
Study and Work in Health Informatics in Canada
Graduate Health Informatics Admission Requirements The prequisites required to become accepted in an graduate and/or post-graduate PhD program in Health Informatics.
What Health Informatics Students Learn Topics and concepts that are covered and the overall approach or focus taken in studying Health Informatics.
Research in Health Informatics Research areas, topics, interests projects in Health Informatics.
Career and Employment Opportunities in Health Informatics Professions or occupations available to graduates in Health Informatics and links to employment resources.
Copyright 2021 - Hecterra Publishing Inc. - Privacy Statement - Terms of Service

- Dean's Office
- Dean's Welcome
- FIMS Events
- EDID at FIMS
- FIMS Awards
Employment at FIMS
- Accessibility
- Mission & Goals
- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Certificates & Diplomas
- Legacy Programs
- Undergraduate Students
- Graduate Students
- Research News
- Research Spotlight
- Research in Action
- Lecture Series
- Student Research
- Fellowships & Chairs
- Participate in Research
- Research Funding & Support for Faculty
- Writing for The Conversation
- All Faculty
- Full-Time Faculty
- PhD Students
- All Personnel
- Retired Academic Personnel
- Alumni Newsletter
- FIMS Career Central
- Faculty Resources
- Future Students
- Current Students
- PhD Health Information Science
- MA Media Studies
- Master of Health Information Science (1 Year)
- Master of Health Information Science (2 Year)
- Master of Library & Information Science
- Master of Media in Journalism and Communication
- Learning Outcomes
- Program Structure
- Comprehensive Exam
- Thesis Supervision
- Collaborative Specialization
- Career Pathways
- Tuition & Finances
- Eugenia Canas Memorial Award in Health Equity
- How to Apply
- PhD Library & Information Science
- PhD Media Studies
Jointly hosted by

PhD in Health Information Science (PhD HIS)

Graduate studies in Health Information Science
Western’s Faculty of Information and Media Studies (FIMS) and Faculty of Health Sciences (FHS) offer three joint degrees: a PhD in Health Information Science, a one year, course-based Master of Health Information Science and a two year, thesis-based Master of Health Information Science. The PhD program is a research-intensive program designed for students who want to do independent, original research in health information science. The master's options are geared to either continued academic study, or entry into the job field.
Find out more about each program

Gain skills & knowledge in a rapidly expanding area of research
All three degree options provide students with fundamental knowledge in health and health care, including:
- Public health
- Health informatics and digital health
- Health policy and clinical health care
- Knowledge organization and management
- Knowledge translation
- Patient and professional information seeking behaviour
- Information ethics and policy
Meet our HIS students

Eliasu Yakubu
PhD HIS candidate.

Emily Porchak
MHIS candidate.

Danica Facca

Sandeep Dhaliwal

Tanaz Javan

Niharika Khanal

Amundeep Chaggar
Faculty of Information & Media Studies FIMS & Nursing Building, Room 2050 London, Ontario, Canada, N6A 5B9 Tel: 519-661-3720 Privacy | Web Standards | Terms of Use | Accessibility
FIMS Graduate Intranet
FIMS Faculty Resources
FIMS Events Calendar
FIMS Facebook Page

School of Graduate Studies
Health informatics, program overview.
The Institute of Health Policy, Management and Evaluation (IHPME) trains Canada’s future health leaders and researchers through its research and professional graduate degree programs and its involvement in a range of collaborative programs. Its unique interdisciplinary approach is ideally suited to today’s complex and rapidly changing health care landscape.
IHPME’s professional degree programs provide individuals with the knowledge, skills, and strategic perspective necessary to assume leadership roles in the health-care system. The faculty members are the foremost thinkers, researchers, and practitioners influencing our health-care system today. Students are exposed to the latest evidence-informed research, thinking, and practice in the Health Informatics program, leading to the Master of Health Informatics (MHI) degree.
The Master of Health Informatics (MHI) program offers in-depth knowledge Digital Health for the future leaders and policy-influencers of the future. The Program trains leaders capable of leading substantial change in the healthcare system and in influencing policy.
The MHI program curriculum enables graduates to design systems that serve the needs of multiple stakeholders, including patients, clinicians, developers, vendors and policymakers. It provides training on managing advanced health informatics tasks, building efficient systems, and shaping digital health policies. Advanced subjects such as information governance, interoperability, and cybersecurity are covered, in addition to the traditional topics of business analysis, knowledge management and data analytics. The program prepares students to enhance healthcare efficiency and patient experience. Real-world experiences and industry connections ensure our graduates are ready to lead in this ever-changing field.
As digitalization in the healthcare system accelerates, the MHI program evolves to meet emerging challenges. Regular course updates keep our curriculum relevant, reflecting the latest in digital health advancements. This adaptability prepares our students to be innovative leaders in health informatics.
Master of Health Informatics
Program description.
There are two options available to complete the MHI:
- Regular MHI option: This option is designed for individuals not currently in a health informatics profession and seeking a career in the field. Applicants to this option should not be employed full-time. The Regular MHI option is offered in person.
- Executive MHI option: This option is designed for individuals with at least five years of work experience in the healthcare sector and are interested in pursuing leadership positions and other career development. This program option enables students to continue professional employment and sustain career momentum while gaining specialized health informatics knowledge. The Executive MHI option is offered through online delivery. Students are required to be on campus for two residencies of 10 days each in February of Year 1 and February of Year 2
Quick Facts
The Master of Health Informatics (MHI) is a professional program which provides graduates with expertise in clinical information and communication technologies (ICTs) required to lead organizational and health system change. The MHI degree program prepares health informaticians to bridge the gaps between clinicians and ICT specialists.
- Regular MHI option: This is designed for individuals who are not currently in a health informatics profession and are seeking a career in the field. Applicants to this option should not be employed full-time. The Regular MHI option is offered in person.
- Executive MHI option: This is designed for individuals with at least five years of work experience in the health-care sector and are interested in pursuing leadership positions and other career development. This program option enables students to continue professional employment and sustain career momentum while gaining specialized health informatics knowledge. The Executive MHI option is offered through online delivery. Students are required to be on campus for two residencies of 10 days each in February of Year 1 and February of Year 2.
Regular MHI Option (Effective 2023-24)
Minimum admission requirements.
- Applicants are admitted under the General Regulations of the School of Graduate Studies. Applicants must also satisfy IHPME's additional admission requirements stated below.
- Appropriate bachelor's degree from a recognized university. Eligible undergraduate degrees include those in a health sciences or social sciences specialty, Regulated Health Professions in Ontario, or a computer science or information science specialty with the equivalent of a minimum mid-B average in the last academic year.
- Applicants whose primary language is not English and who graduated from a university where the language of instruction and examination was not English must demonstrate proficiency in English. See General Regulations section 4.3 for requirements.
Successful applicants normally have relevant professional experience as a health services professional (for example, manager or administrator) or health sciences/clinical practitioner with demonstrated basic literacy and/or programming skills in computer applications relevant to the health sector, or a computer or information technician within a health-care setting or health software vendor.
Program Requirements
Completion of 10.0 full-course equivalents (FCEs) as follows:
- Required coursework (7.5 FCEs)
Elective coursework (0.5 FCE)
- Students may elect to take up to 0.5 FCE on a Credit/No Credit (CR/NCR) basis. See the list of CR/NCR-eligible courses below.
A four-month, full-time practicum or field placement (MHI2005Y; 2.0 FCEs).
Degree requirements will be completed in 16 months across four consecutive sessions.
Students may elect to be assessed on a CR/NCR basis in courses marked by the symbol ⌘ up to a total of 0.5 FCE.
Required Courses
Practicum course, elective courses.
Students are encouraged to select an elective that allows them to focus on their individual areas of interest in health informatics. For this reason, the MHI program does not impose a selection of electives. Students are free to choose from all graduate courses across all disciplines at the University of Toronto. All selections are subject to approval in advance by the Program Director and the IHPME Chair.
Program Length
4 sessions full-time (typical registration sequence: F/W/S/F)
3 years full-time
Regular MHI Option (Effective 2024-25)
These requirements are effective from May 1, 2024.
Successful applicants normally have relevant professional experience as a health services professional (for example, manager or administrator) or health sciences/ clinical practitioner with demonstrated basic literacy and/or programming skills in computer applications relevant to the health sector, or a computer or information technician within a health-care setting or health software vendor.
Executive MHI Option (Effective 2023-24)
- Successful applicants normally have relevant professional experience (at least five years) as a health services professional (for example, manager or administrator) or health sciences/clinical practitioner with demonstrated basic literacy and/or programming skills in computer applications relevant to the health sector, or a computer or information technician within a health care setting or health software vendor.
- Successful applicants may be actively employed in a health informatics role or capacity.
- Elective coursework (1.0 FCE)
- A four-month, employer-sponsored or mentor-supervised Health Informatics Project (MHI2015Y; 1.5 FCEs).
- The Executive MHI degree requirements will be completed in 22 months across six consecutive sessions.
Students are encouraged to select two electives that allow them to focus on their individual areas of interest in health informatics. For this reason, the MHI program does not impose a selection of electives. Students are free to choose from all graduate courses across all disciplines at the University of Toronto. All selections are subject to approval in advance by the Program Director and the IHPME Chair.
6 sessions full-time (S/F/W/S/F/W)
Executive MHI Option (Effective 2024-25)
- The Executive MHI option is offered through online delivery. Students are required to be on campus for two residencies of 10 days each in February of Year 1 and February of Year 2.
- Medical Laboratory Science
- Kinesiology
- Technology-enriched Learning Environment (TELE)
- Allied Health Sciences
- Dean’s welcome
- Experiential learning
- Vision and mission statements
- Program maps and Course Hub
- Frequently asked questions
- Student testimonials
- Applying to our university
- Program maps
- Program handbook
- Learning environment
- Useful links
- Fitness and Health Promotion Bridge
- Vision, mission, values and goals
- MLSc Biosafety/Safety Manual
- Immunization requirements
- Pre-practicum requirements
- Vision, mission and program philosophy
- Nursing Program Office
- Health Administration
- How to apply
- Research projects
- Selection process
- Student clubs
- Graduate academic calendar
- Graduate program faculty research
- Important dates
- Adam Dubrowski
- Bernadette Murphy
- Brenda Gamble
- Carol D. Rodgers
- Caroline Barakat
- Connie Thurber
- Courtney Cross
- David Rudoler
- Donna Smeeton
- Efrosini Papaconstantinou
- Elita Partosoedarso
- Ellen Vogel
- Emma Bartfay
- Evelyn Moreau
- Fabiola Longo
- Ginny Brunton
- Heather Sprenger
- Helene-Marie Goulding
- Hilde Zitzelsberger
- Holly Jones-Taggart
- Janet McCabe
- Jennifer Abbass Dick
- JoAnne Arcand
- Joseph Gurgis
- Kerry Johnson
- Laura Banks
- Lavern Bourne
- Lori Livingston
- Manon Lemonde
- Meghann Lloyd
- Mikael Khan
- Mika Nonoyama
- Milly Ryan-Harshman
- Nancy Bergeron
- Nick La Delfa
- Nick Wattie
- Nooshin Khobzi Rotondi
- Otto Sanchez
- Paul Yielder
- Pierre Côté
- Robert Balogh
- Ruth Simpson
- Sarah Mavor
- Shilpa Dogra
- Toba Bryant
- Wally Bartfay
- Wendy Stanyon
- Research domains
- Research entities
- Institute for Disability and Rehabilitation Research
- 2018-2019 graduate research project information videos
- 2013-2014 graduate research projects information videos
- 2019-2020 graduate research project information videos
- Undergraduate student research
- Research summary 2018-2019
- Research summary 2015
- July 2015 Research Snapshot
- Research summary 2013-2014
- Guest lectures and podcasts
- Faculty research videos
- Faculty research snapshots
- Quick (Resource) links
We are thankful to be welcome on these lands in friendship. The lands we are situated on are covered by the Williams Treaties and are the traditional territory of the Mississaugas, a branch of the greater Anishinaabeg Nation, including Algonquin, Ojibway, Odawa and Pottawatomi. These lands remain home to many Indigenous nations and peoples.
We acknowledge this land out of respect for the Indigenous nations who have cared for Turtle Island, also called North America, from before the arrival of settler peoples until this day. Most importantly, we acknowledge that the history of these lands has been tainted by poor treatment and a lack of friendship with the First Nations who call them home.
This history is something we are all affected by because we are all treaty people in Canada. We all have a shared history to reflect on, and each of us is affected by this history in different ways. Our past defines our present, but if we move forward as friends and allies, then it does not have to define our future.
Learn more about Indigenous Education and Cultural Services
Health informatics
Education and research in our Health Informatics field will prepare you to identify, develop and manage health-care information systems that support health-care administration, management, policy, training, clinical management and clinical research. The Health Informatics program focuses on the effective use of health information and informatics technologies to improve health and health-care delivery.
You will work with cutting-edge researchers and learn about the latest approaches to health informatics. In Ontario Tech Uninversity's state-of-the-art health informatics laboratories, you will collaborate with leading researchers to employ the latest approaches in health informatics research.
Health Informatics Graduate Supervisors:
- Dr. Adam Dubrowski
- Dr. Fletcher Lu
- Dr. Carolyn McGregor

Master of Health Informatics
Advance your career as a health professional.
The Master of Health Informatics (MHI) program is designed for professionals with backgrounds in public health and/or health care who require more knowledge about computer science and health informatics.
Graduates can use this knowledge to identify, design and manage informatics solutions relevant to health and health systems.

Program overvew
- Designed for professionals with backgrounds in public health and/or health care: professionals who require more knowledge about computer science and health informatics in order to identify, design and manage informatics solutions relevant to health and health systems.
- You will learn from faculty who lead research in public health sciences and public health intervention design and evaluation.
- Through the experiential learning of a practicum position, you will experience what it is like to use the knowledge, tools, and skills learned in the MHI Program in a real public health setting.
- The MHI program is flexible for the working professional and is completed online as a part-time or full-time student.

Admission requirements

How to apply

Tuition costs

Living costs
Application deadline: february 1.
In order for an application to be considered, all required documentation, including academic references, must be submitted on or before this date. Please aim to apply by January 18 to allow adequate time to upload supporting documents and ensure that your referees are aware of this firm deadline.
NOTE: Due to the competitive nature of the professional programs at the University of Waterloo the ideal GPA for admission is based on the current pool of applicants and the previous years GPA cut-off. The minimum Graduate Studies application standard for admission is a CGPA of 3.0 or 75%. Successful applicants in the professional programs in 2020/2021 had an average GPA of 78%.
Course offerings and program sequence
The MHI program consists of 10 required courses (eight core courses, including the practicum course, and two electives).
Click on the links below to view the course offerings and program sequence for part- and full-time students. These sequences are subject to change but can be used as reference for planning your future terms.
Professional practicum
Gain work experience by completing a 420-hour professional practicum at a hospital, provincial or federal governmental agency or non-governmental organization. You will w ork closely with the Practicum Coordinator to find a meaningful practicum that will provide you with an opportunity to apply your knowledge and skills in a professional setting and to connect with future employers.
The practicum can be completed on a full-time basis over one term or part time over two terms.
Previous practicum sites and projects:
Learn more about the practicum →

During her practicum placement for her Master of Health Informatics program, Acrifa Fears worked for a software company where she worked on a project that utilized digital health technology to monitor patients post-sugery at home wile faciltating administration of care and communication between patient and the healthcare system. Learn more about her practicum experience →
Funding and awards
A variety of scholarships, assistantships, and other forms of financial aid are available for graduate students in any professional graduate program. Most of these awards are for full-time graduate students only.
Learn more about funding and awards for professional programs →
Frequently asked questions
We've compiled the answers to the most common questions about the MHI program . Read through for helpful information about admissions, the practicum and more.
Popular search terms:
No results found for “ ”.
Search another word or try popular search words.
Master of Health Informatics (MHI)
Advancing leadership and health informatics research in digital and AI technologies to drive organizational and system change within the healthcare sector.

MHI is one of Canada’s few graduate programs in the rapidly evolving field of health informatics with a strong focus on artificial intelligence (AI).
MHI learners bridge the gap between technology and the health information needs of clinicians, patients, administrators and policy-makers with information technology solutions that drive system change and improvement.

Recognized by Canada’s Vector Institute , MHI focuses on areas of policy, management and evaluation, and system leadership to best prepare the healthcare sector for downstream AI and health information technology-based change.
Scholarship recipients become part of the Vector Institute’s community of renowned researchers, major Canadian companies, and AI startups solving high-impact problems. Recipients receive support for their education, and an affiliation with Vector can open high-quality career options through Vector’s networking & career events, Digital Talent Hub and professional development.
Vector will be holding webinars for prospective students in February 2024. Please review this page and sign up to hear from Vector directly on registration details for these webinars and other information on the scholarship.
MHI – Master of Health Informatics
MHI Application Deadline: January 6, 2024 (strongly recommended), accepting applications until March 1, 2024 *to be considered for Vector, applications must be submitted by Jan 6, 2024
Explore MHI
Emhi – executive master of health informatics.
EMHI Application Deadline: January 6, 2024 (strongly recommended), accepting applications until March 1, 2024 *to be considered for Vector, applications must be submitted by Jan 6, 2024
Explore EMHI
Program highlights.

Lead Change
Advance your project management, critical thinking, and leadership skills through MHI’s innovative curriculum that equips graduates to meet the rising demands for professional competencies in the field.

Gain Real-World Experience
Apply program learnings to real-world healthcare problems through practicum placements and workplace projects.

Make Connections
Expand your professional network and career prospects by making connections with MHI’s extensive and influential community of health informatics leaders in Canada and beyond.
Health Informatics Career Opportunities

MHI’s partnerships with leading health and industry organizations offer unparalleled networking opportunities that can help accelerate your career.
Graduates working in the domain of Health/Clinical Informatics
48% EMHI 56% MHI
Graduates working in the domain of Project Management
25% EMHI 56% MHI
Graduates working in the domain of Leadership/Management
40% EMHI 31% MHI
Master of Health Informatics (MHI) in Action

Women in AI Canada Hackathon 2022
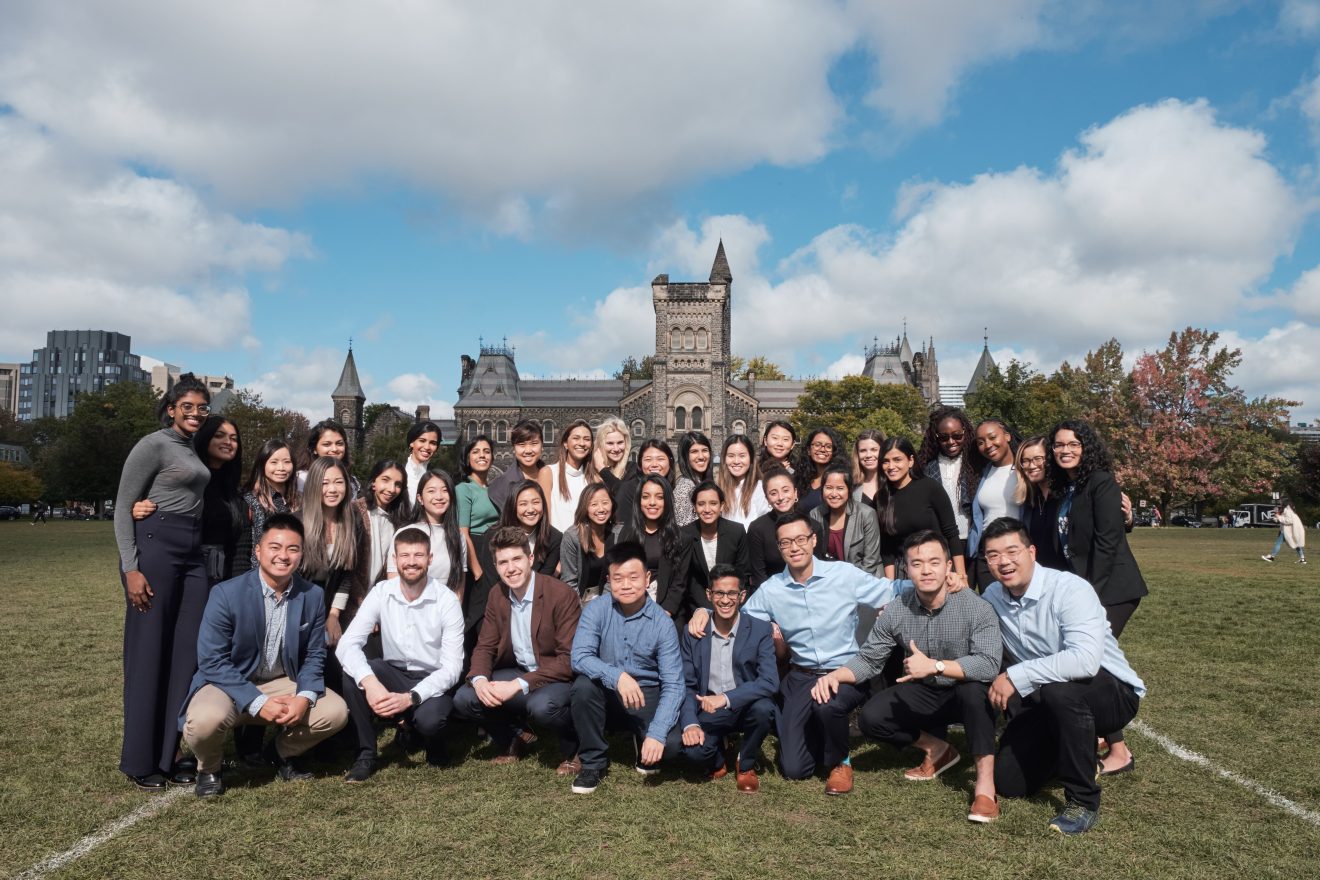

MHI Class of 2021
Picture taken in 2019
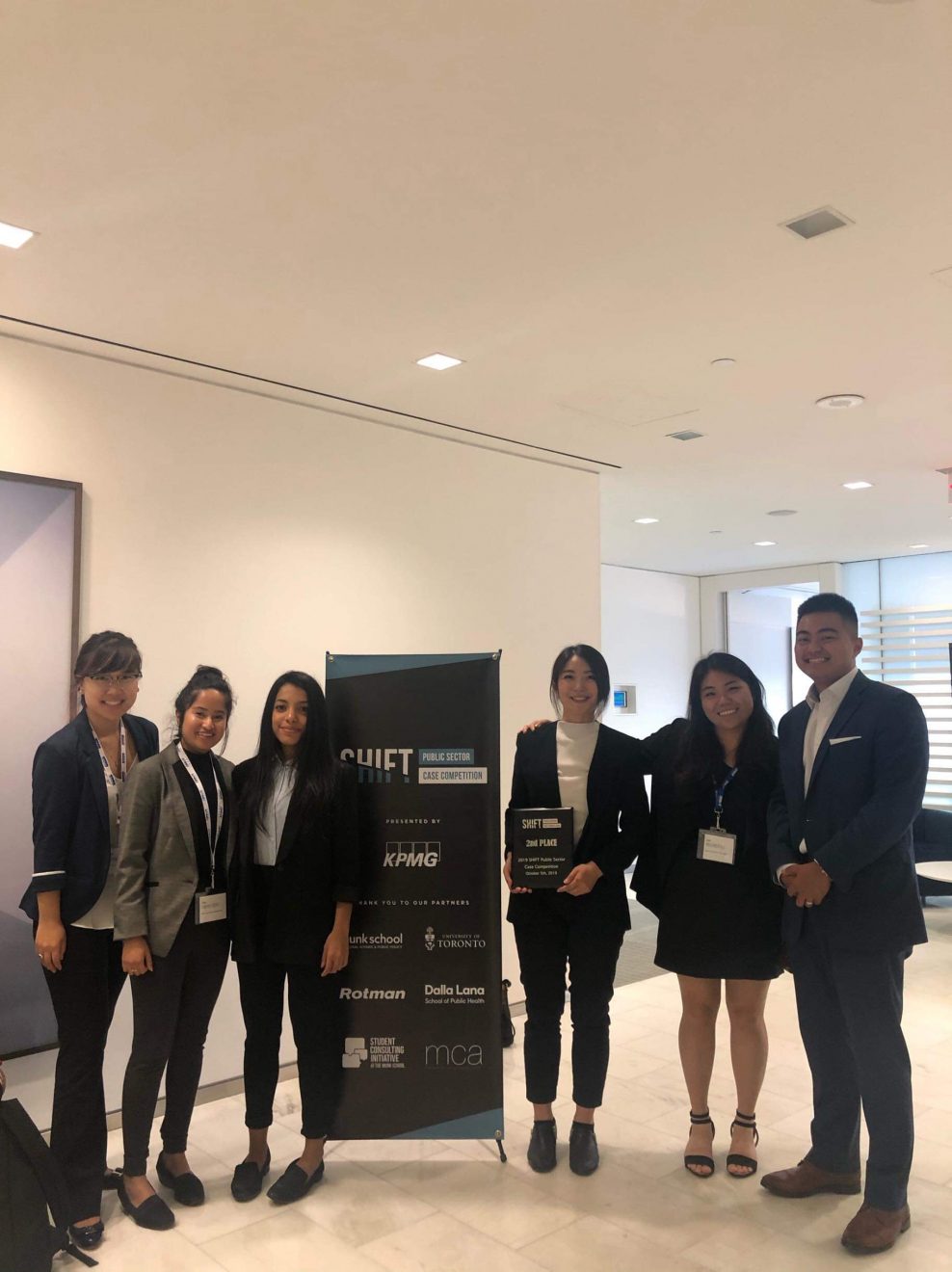

MHI Cohort at SHIFT Case Competition hosted by KPMG 2019
Reanne Li (third from the right) pictured with 2nd place winning plaque

MHI at Hacking Health Hamilton Hackathon 2019

MHI at GMCA Case Competition 2019

Master of Health Informatics ( MHI) Halloween Party 2019
People from mhi.

Accepting students Find by research interest or program

Graduate Students
Get the latest student theses

Administrative Staff
Get the help you are looking for
Latest Alumni Stories

Emerald Liang
Emerald Liang shares how MHI provides a deeper understanding of the impact technology can have in healthcare.

Eunice Leung
Eunice Leung shares how MHI provides a greater perspective for what technology and informatics can bring to healthcare.

Claudia Lee
Claudia Lee shares how she gained knowledge from industry experts and established connections with faculty, peers, and the broader IHPME community.

Alex Gao shares the value of MHI’s emphasis on combining theory and practice.
Latest News

Public Trust Crucial for Use of Administrative Health Data in Identifying Future Health Risks
March 6, 2024
Faculty / Research

Master’s students awarded prestigious Vector Scholarship in Artificial Intelligence
June 2, 2023
Awards / Students

IHPME Team Leads Work on World Bank Report
May 30, 2023
Faculty / Research / Students

Research and Impact Day 2023: Event Recap
May 19, 2023

Research and Impact Day 2023
March 22, 2023
Education / Faculty / Research / Students

2023 International Women’s Day
March 8, 2023
Research / Students
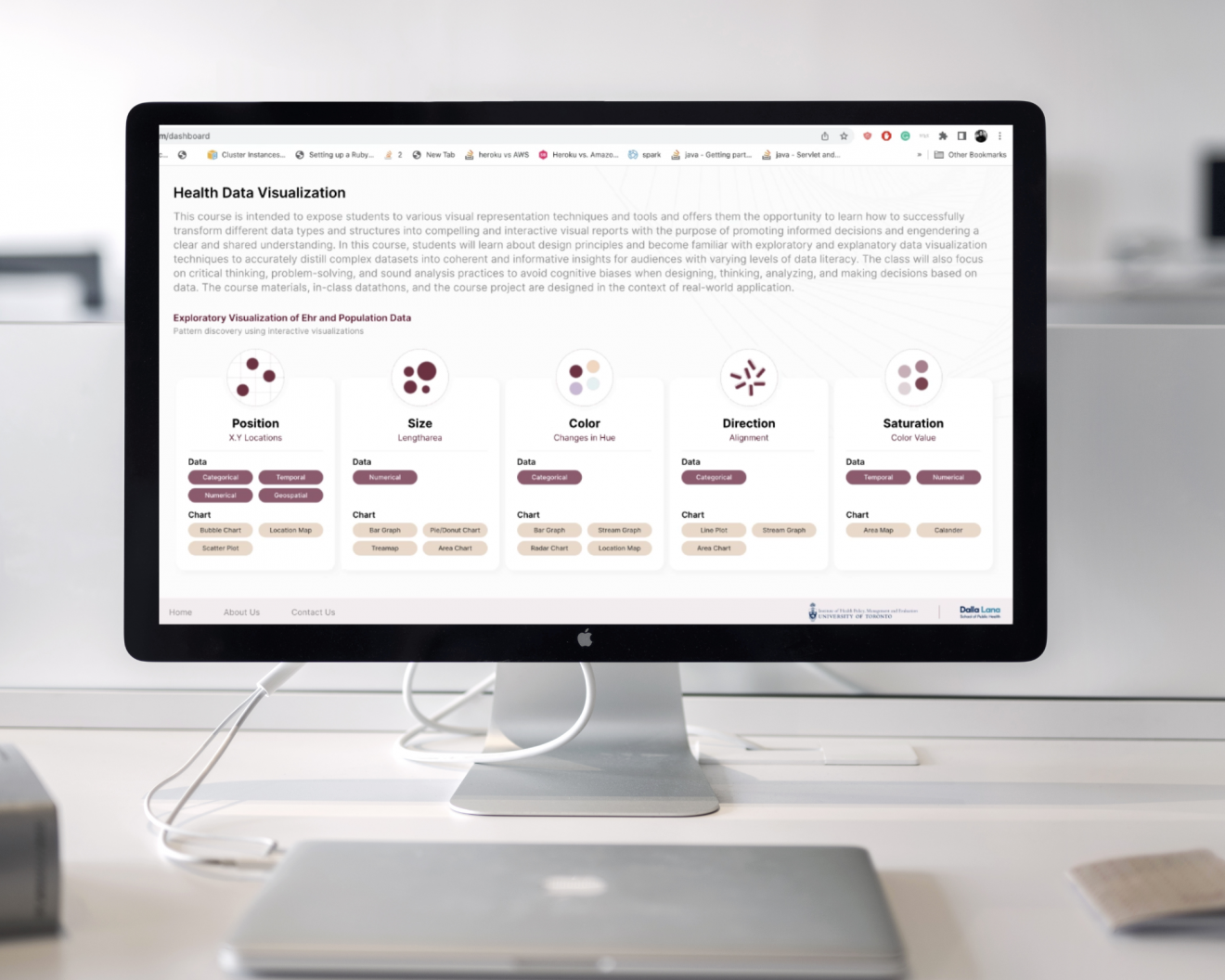
HIVE Lab at IHPME Leads to Improved Storytelling
February 28, 2023

Dr. Julia Zarb Retires from the University of Toronto
December 16, 2022

Dr. Aviv Shachak elected fellow of the International Academy of Health Sciences Informatics
June 7, 2021

Giving back – alumni return as mentors to support growth and networking in Master of Health Informatics program
November 7, 2019
Upcoming Events
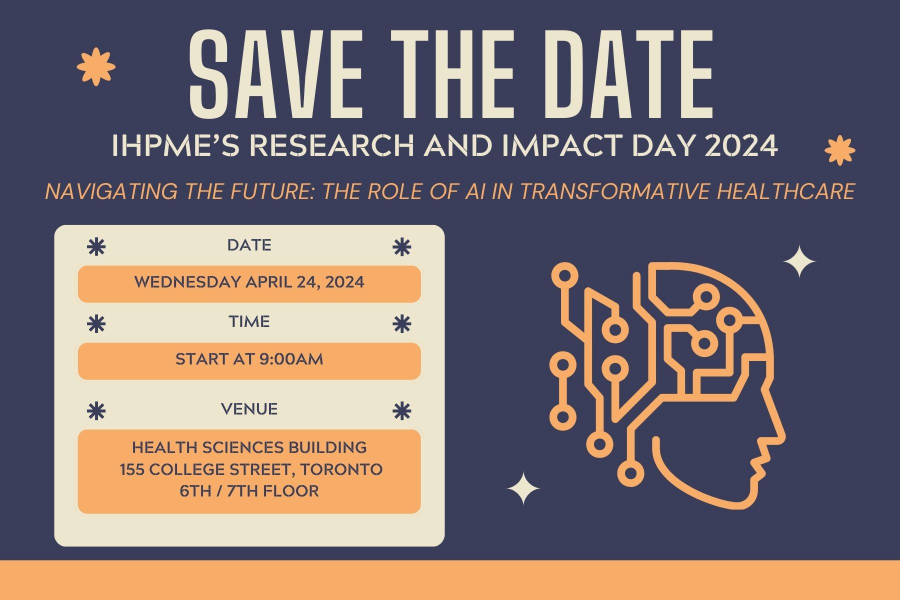
Research and Impact Day 2024
Apr 24, 2024 from 9am (EDT)
155 College Street 6th/7th Floor
IHPME-GSU Events
Join us on Socials
Connect with the master of health informatics (mhi) community.
Join a thriving network of MHI alumni and students who share research, events, news and job postings in the field.
- LinkedIn Page
- LinkedIn Group
Learn More About IHPME’s Master of Health Informatics (MHI)
Mhi program director.
Karim Keshavjee Email Address: karim.keshavjee@utoronto.ca
Graduate Administrator
Zoe Downie-Ross Phone Number: (416) 946-3486 Email Address: ihpme.grad.admin@utoronto.ca
Coordinates student records, graduate funding, and student-related awards.
Graduate Admissions
Christina Lopez Email Address: ihpme.admissions@utoronto.ca
Manages admissions and responds to all related inquiries.
Graduate Assistant
Nadia Ismail Phone Number: (416) 946-4100 Email Address: ihpme.grad.assist@utoronto.ca
Coordinates various graduate initiatives including defences, student events, and graduation.
MHI Program Assistant
Aileen O’Dowd Email Address: ihpme.mhi.program@utoronto.ca
Manages the MHI courses including enrolment, grades, and access to Quercus. For admissions inquiries contact ihpme.admissions@utoronto.ca .
Graduate Placements
Christina Lopez Phone Number: (416) 978-1108 Email Address: ihpme.placements@utoronto.ca
Coordinates details involving student placement and experiential learning

- Doctor of Philosophy in Bioinformatics (PhD)
- Graduate School
- Prospective Students
- Graduate Degree Programs
Canadian Immigration Updates
Applicants to Master’s and Doctoral degrees are not affected by the recently announced cap on study permits. Review more details
Go to programs search
The Doctor of Philosophy in Bioinformatics (PhD)is an interdisciplinary program that combines the application of computer technology to the management and analysis of biological data. The result is that computers are being used to organize data generated from experiments into databases, develop new algorithms and software, and use this software for the interpretation and analysis of the data into meaningful biological information. For the past ten years, our PhD program has been training students to organize, visualize, analyze and interpret biological data. Students have access to world renowned bioinformaticians at the University of British Columbia, Simon Fraser University and the BC Cancer Agency, and have exposure to the latest technologies to develop their skills.
Strategic Program Objectives:
- To build on British Columbia's reputation and excellence in bioinformatics.
- To integrate bioinformatics into basic biology to further current research excellence in other life science sectors of the province.
- To foster collaborations locally, nationally and internationally.
For specific program requirements, please refer to the departmental program website
What makes the program unique?
The Bioinformatics PhD program integrates academic centres in computer science, statistics, molecular biology and biotechnology, with translational groups at hospitals and at the clinical interface. The innovative partnership among the University of British Columbia, Simon Fraser University and the BC Cancer Agency allows students' access to experts in the field of bioinformatics, and exposure to original research and opportunities to complete significant practical work on real bioinformatics problems. Internships allow student mobility between Canadian and international universities, institutions and industries to further enhance collaborations among Canadian high-technology research groups in both the private and public sectors.
I chose UBC because I love the UBC research environment and the lifestyle that living in BC affords.

Angela McLaughlin

Program Structure
The major requirement for the Ph.D. is completion of a research dissertation meeting the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies requirements. There are no specific course requirements for the Ph.D. degree program apart from the dissertation. However, the student's Ph.D. dissertation committee has the prerogative to impose course requirements where course deficiencies are perceived.
All doctoral students are required to successfully complete a comprehensive examination, which consists of an oral and written component within the first 36 months of study. All students are required to present a Bioinformatics graduate program seminar upon completion of their program, and before their dissertation defense.
A student's committee for the doctorate will consist of the dissertation supervisor and three others. The supervisor and at least one other member must be members of the Bioinformatics graduate program.
Quick Facts
Program enquiries, admission information & requirements, program instructions.
Students must secure a supervisor before they can be admitted into the program. As well, they must meet the minimum admission requirements set out by Graduate and Post-doctoral Studies at UBC.
1) Check Eligibility
Minimum academic requirements.
The Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies establishes the minimum admission requirements common to all applicants, usually a minimum overall average in the B+ range (76% at UBC). The graduate program that you are applying to may have additional requirements. Please review the specific requirements for applicants with credentials from institutions in:
- Canada or the United States
- International countries other than the United States
Each program may set higher academic minimum requirements. Please review the program website carefully to understand the program requirements. Meeting the minimum requirements does not guarantee admission as it is a competitive process.
English Language Test
Applicants from a university outside Canada in which English is not the primary language of instruction must provide results of an English language proficiency examination as part of their application. Tests must have been taken within the last 24 months at the time of submission of your application.
Minimum requirements for the two most common English language proficiency tests to apply to this program are listed below:
TOEFL: Test of English as a Foreign Language - internet-based
Overall score requirement : 100
IELTS: International English Language Testing System
Overall score requirement : 7.0
Other Test Scores
Some programs require additional test scores such as the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or the Graduate Management Test (GMAT). The requirements for this program are:
The GRE is not required.
Prior degree, course and other requirements
Prior degree requirements.
Students admitted to the Ph.D. degree program normally possess an M.Sc. degree in Bioinformatics or a related area, with clear evidence of research ability or potential.
Document Requirements
CV, Official transcripts, three letters of reference, Official English exam scores (if required)
2) Meet Deadlines
January 2025 intake, application open date, canadian applicants, international applicants, may 2025 intake, september 2025 intake, deadline explanations.
Deadline to submit online application. No changes can be made to the application after submission.
Deadline to upload scans of official transcripts through the applicant portal in support of a submitted application. Information for accessing the applicant portal will be provided after submitting an online application for admission.
Deadline for the referees identified in the application for admission to submit references. See Letters of Reference for more information.
3) Prepare Application
Transcripts.
All applicants have to submit transcripts from all past post-secondary study. Document submission requirements depend on whether your institution of study is within Canada or outside of Canada.
Letters of Reference
A minimum of three references are required for application to graduate programs at UBC. References should be requested from individuals who are prepared to provide a report on your academic ability and qualifications.
Statement of Interest
Many programs require a statement of interest , sometimes called a "statement of intent", "description of research interests" or something similar.
Supervision
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
Instructions regarding thesis supervisor contact for Doctor of Philosophy in Bioinformatics (PhD)
Citizenship verification.
Permanent Residents of Canada must provide a clear photocopy of both sides of the Permanent Resident card.
4) Apply Online
All applicants must complete an online application form and pay the application fee to be considered for admission to UBC.
Research Information
Program components.
Students who secure an NSERC-CREATE scholarship will undertake a 3-4 month internship that may be local, within Canada or at an international University or Institution.
Research Facilities
Bioinformatics faculty are spread throughout the UBC campus, as well as off-campus at the BC Cancer Research Centre or hospital research labs and Institutions.
Tuition & Financial Support
Financial support.
Applicants to UBC have access to a variety of funding options, including merit-based (i.e. based on your academic performance) and need-based (i.e. based on your financial situation) opportunities.
Program Funding Packages
All students accepted by a faculty member and enrolled in the program will be paid a minimum stipend of $24,300/year.
Average Funding
- 9 students received Teaching Assistantships. Average TA funding based on 9 students was $10,203.
- 20 students received Research Assistantships. Average RA funding based on 20 students was $24,220.
- 2 students received Academic Assistantships. Average AA funding based on 2 students was $3,698.
- 30 students received internal awards. Average internal award funding based on 30 students was $9,330.
- 5 students received external awards. Average external award funding based on 5 students was $20,667.
Scholarships & awards (merit-based funding)
All applicants are encouraged to review the awards listing to identify potential opportunities to fund their graduate education. The database lists merit-based scholarships and awards and allows for filtering by various criteria, such as domestic vs. international or degree level.
Graduate Research Assistantships (GRA)
Many professors are able to provide Research Assistantships (GRA) from their research grants to support full-time graduate students studying under their supervision. The duties constitute part of the student's graduate degree requirements. A Graduate Research Assistantship is considered a form of fellowship for a period of graduate study and is therefore not covered by a collective agreement. Stipends vary widely, and are dependent on the field of study and the type of research grant from which the assistantship is being funded.
Graduate Teaching Assistantships (GTA)
Graduate programs may have Teaching Assistantships available for registered full-time graduate students. Full teaching assistantships involve 12 hours work per week in preparation, lecturing, or laboratory instruction although many graduate programs offer partial TA appointments at less than 12 hours per week. Teaching assistantship rates are set by collective bargaining between the University and the Teaching Assistants' Union .
Graduate Academic Assistantships (GAA)
Academic Assistantships are employment opportunities to perform work that is relevant to the university or to an individual faculty member, but not to support the student’s graduate research and thesis. Wages are considered regular earnings and when paid monthly, include vacation pay.
Financial aid (need-based funding)
Canadian and US applicants may qualify for governmental loans to finance their studies. Please review eligibility and types of loans .
All students may be able to access private sector or bank loans.
Foreign government scholarships
Many foreign governments provide support to their citizens in pursuing education abroad. International applicants should check the various governmental resources in their home country, such as the Department of Education, for available scholarships.
Working while studying
The possibility to pursue work to supplement income may depend on the demands the program has on students. It should be carefully weighed if work leads to prolonged program durations or whether work placements can be meaningfully embedded into a program.
International students enrolled as full-time students with a valid study permit can work on campus for unlimited hours and work off-campus for no more than 20 hours a week.
A good starting point to explore student jobs is the UBC Work Learn program or a Co-Op placement .
Tax credits and RRSP withdrawals
Students with taxable income in Canada may be able to claim federal or provincial tax credits.
Canadian residents with RRSP accounts may be able to use the Lifelong Learning Plan (LLP) which allows students to withdraw amounts from their registered retirement savings plan (RRSPs) to finance full-time training or education for themselves or their partner.
Please review Filing taxes in Canada on the student services website for more information.
Cost Estimator
Applicants have access to the cost estimator to develop a financial plan that takes into account various income sources and expenses.
Career Outcomes
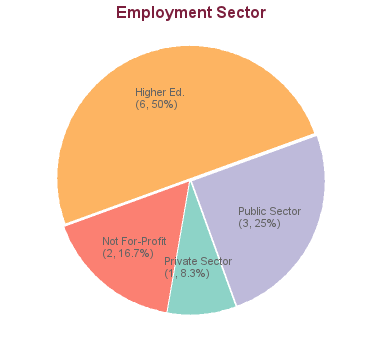
12 students graduated between 2005 and 2013. Of these, career information was obtained for 12 alumni (based on research conducted between Feb-May 2016):
Sample Employers in Higher Education
Sample employers outside higher education, sample job titles outside higher education, phd career outcome survey, career options.
As biological datasets increase exponentially in both size and complexity, bioinformatics tools have central importance in fields and industries ranging from environmental management, forestry, aquaculture, and biofuels to personalized medicine, drug development, preventative medicine and gene therapy. Individuals who can analyuze and interpret large data sets or "big data" are highly sought after by both public and private sector employers. Academic positions at Universities are widely available in all fields of study.
Ph.D. graduates from the program have gone on to pursue post-doctoral studies at Stanford, Harvard school of Medicine, Max Delbruck Centre in Berlin, Broad Institute at MIT and Harvard, Ontario Cancer Institute, Howard Hughes Medical Institute in Santa Cruz, and locally at UBC and SFU. One graduate is an assistant professor at Simon Fraser University and another is an assistant professor at the University of Dalhousie in Halifax, NS.
Alumni on Success

Benjamin Good
Job Title Assistant Professor
Employer The Scripps Research Institute
Enrolment, Duration & Other Stats
These statistics show data for the Doctor of Philosophy in Bioinformatics (PhD). Data are separated for each degree program combination. You may view data for other degree options in the respective program profile.
ENROLMENT DATA
Completion rates & times.
- Research Supervisors
Advice and insights from UBC Faculty on reaching out to supervisors
These videos contain some general advice from faculty across UBC on finding and reaching out to a supervisor. They are not program specific.

This list shows faculty members with full supervisory privileges who are affiliated with this program. It is not a comprehensive list of all potential supervisors as faculty from other programs or faculty members without full supervisory privileges can request approvals to supervise graduate students in this program.
- Accili, Eric (molecular mechanisms responsible for cellular pacemaking behavior )
- Adams, Keith (Molecular evolution, genome evolution, and gene expression)
- Aparicio, Samuel (Breast cancer, genome sequencing )
- Bashashati Saghezchi, Ali (Bioinformatics; Medical and biomedical engineering; Artificial Intelligence; Computational Pathology; Cancer Genomics; Computational Biology; Digital Pathology; Image Processing; Machine Learning; Ovarian Cancer; Signal Processing; Multi-modal Learning)
- Birol, Inanc (bioinformatics, computational biology, genomics, transcriptome analysis, next generation sequencing, cancer, Bioinformatics, sequence assembly, transcriptomics, gene regulation networks, high throughput informatics for big data)
- Bohlmann, Joerg (plant biochemistry, forestry genomics, forest health, conifers, poplar, bark beetle, mountain pine beetle, natural products, secondary metabolites, terpenes, floral scent, grapevine, Conifer genomics Forest health genomics Mountain pine beetle, fungus, pine interactions and genomics Chemical ecology of conifer, insect interactions)
- Bouchard-Cote, Alexandre (machine/statistical learning; mathematical side of the subject as well as in applications in linguistics and biology)
- Brooks-Wilson, Angela (Bioinformatics; Clinical oncology; Genetic medicine; Genomics; cancer families; cancer genetics; genetic susceptibility; human genetics; longevity; Super seniors)
- Brown, Carolyn Janet (Bioinformatics; Clinical oncology; Genetic medicine; Genomics; Health counselling; Applied Genetics; Chromosomes: Structure / Organization; DNA methylation; Epigenetic control of gene expression; Gene Regulation and Expression; Genes escaping X-chromosome inactivation; Long non-coding RNAs; X-chromosome inactivation; XIST RNA)
- Carlsten, Christopher (Environment and Respiratory Diseases)
- Cembrowski, Mark Steven (Molecular neuroscience; Mathematical modelling and simulation; Mechanisms of memory in the brain; Anxiety; Big Data; Bioinformatics; Cell types; Computation; CRISPR-Cas9; Fear; Genetics; modeling; Neural circuits; neuroscience; Neuroscience of memory; PTSD; RNAseq)
- Cherkasov, Artem (Drug design; Bioinformatics, Molecular modeling; Proteomics; Artificial intelligence; Antibiotics )
- Cohen Freue, Gabriela (statistical genomics (focus in proteomics), robust estimation and inference, linear models with endogeneity )
- Collins, Colin (translational genomics where mathematics, genomics, computer science, and clinical science converge in diagnostics and therapeutics)
- Condon, Anne (Algorithms; Molecular Programming)
- Coombs, Daniel (Mathematical biology; Cellular immunology; Complex physical systems; Epidemiology (except nutritional and veterinary epidemiology); Cell Signaling and Infectious and Immune Diseases; Cell biophysics; Disease models; Epidemiology; Immune cell signalling; Mathematics)
- Daley, Denise (Bioinformatics; Asthma; Complex Trait Genetics; Epigenetics; gene-gene and gene-environment interactions; Genetic Diseases; genetic epidemiology; Genetics of Aging; statistical genetics; Susceptibility Genes)
- Dao Duc, Khanh (Genomics; Mathematical biology; Neurocognitive patterns and neural networks; Agricultural spatial analysis and modelling; combine mathematical,computational and statistical tools to study fundamental biological processes; regulation and determinants of gene expression and translation; Machine Learning for Biological Imaging and Microscopy; Database development and management; Biological and Artificial Neural Networks for geometric representation)
- de Boer, Carl (Gene regulation)
- Dennis, Jessica (Bioinformatics; Genetic medicine; Administrative health data; Complex Trait Genetics; Electronic health records; Epidemiology; genetic epidemiology; Genetics of Neurological and Psychiatric Diseases; Machine Learning; Mental Health and Psychopathology in Children and Youth; Precision Health; statistical genetics)
- Ding, Jiarui (Bioinformatics; Basic medicine and life sciences; Computational Biology; Machine Learning; Probabilistic Deep Learning; single-cell genomics; visualization; Cancer biology; Computational Immunology; Food Allergy; neuroscience)
- Eaves, Constance Jean (Normal and leukemic stem cells, normal and malignant breast stem cells)
- Finlay, B Brett (Infectious agents, bacteria, microbial infections and how humans react to it)
- Frangou, Sophia (the study of the human brain in health and disease)
- Friedman, Jan Marshall (Other clinical medicine; Genetic medicine; Genomics; Health counselling; Application of whole genome sequencing to diagnose genetic disease; Birth defects epidemiology; Clinical genomics; Developmental Genetics; Genetics and Heredity; Neurofibromatosis)
Doctoral Citations
Sample thesis submissions.
- Machine learning for antimicrobial peptide discovery and design
- The gut microbiome in pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis
- Development and application of consensus hit-calling protocols for the virtual screening of ‘undruggable’ and difficult drug targets
- Phylogenetic methods for estimating human immunodeficiency virus 1 proviral integration dates
- Finding the functional consequences of genetic risk loci on gene expression and DNA methylation by integrating contextual information
- Transcriptome assembly and visualization for RNA-sequencing data
- Epigenetic dysregulation in lymphoid leukemias
- Deciphering non-coding driver mutations in prostate cancer
- Advancing our understanding of genome regulation via optimization of stem cell differentiation and interpretable deep learning : [supplementary material]
- Advancing our understanding of genome regulation via optimization of stem cell differentiation and interpretable deep learning
- Linking function and phylogeny in microbiomes using TreeSAPP
- Annotation of complex genomes for comparative genomics
- Identifying predictive gene expression signatures of sepsis severity
Related Programs
Same specialization.
- Master of Science in Bioinformatics (MSc)
Further Information
Specialization.
Bioinformatics combines computational and biological disciplines.
UBC Calendar
Program website, faculty overview, academic unit, program identifier, classification, supervisor search.
Departments/Programs may update graduate degree program details through the Faculty & Staff portal. To update contact details for application inquiries, please use this form .
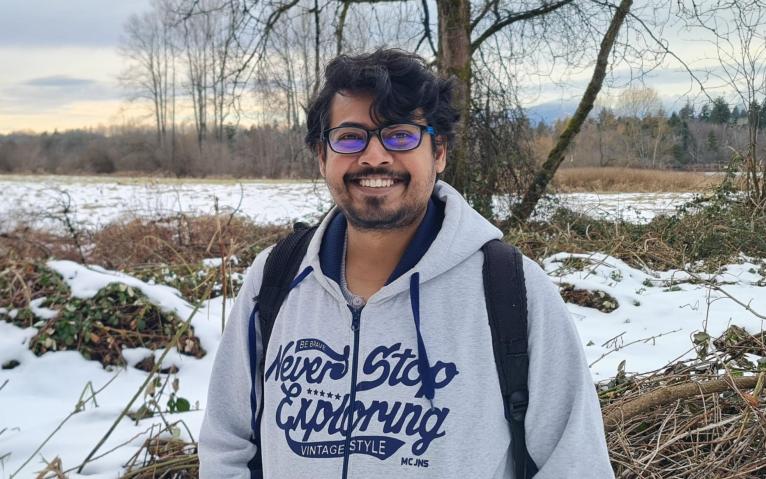

Mohit Pandey
Prior to joining UBC for my Ph.D., I was working in deep learning applications in late-stage drug discovery - particularly with large clinical trials. I had a chance to talk with my supervisor before coming to UBC. He made me realize how even early-stage drug discovery can benefit from advances in...
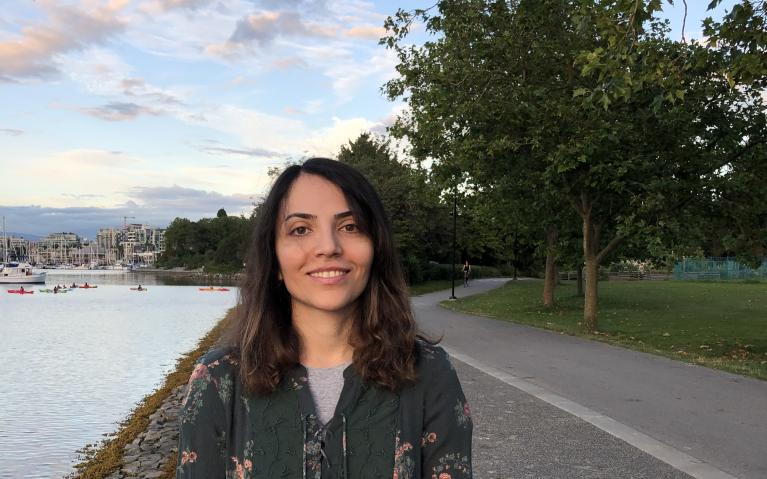

Faeze Keshavarz
I strongly believe that UBC provides a lot of resources and opportunities to students. The most valuable resource to me has undoubtedly been the chance to learn from some of the best and most experienced researchers and scientists in my field. The opportunity to collaborate with other scientists...
Curious about life in Vancouver?
Find out how Vancouver enhances your graduate student experience—from the beautiful mountains and city landscapes, to the arts and culture scene, we have it all. Study-life balance at its best!
- Why Grad School at UBC?
- Application & Admission
- Info Sessions
- Research Projects
- Indigenous Students
- International Students
- Tuition, Fees & Cost of Living
- Newly Admitted
- Student Status & Classification
- Student Responsibilities
- Supervision & Advising
- Managing your Program
- Health, Wellbeing and Safety
- Professional Development
- Dissertation & Thesis Preparation
- Final Doctoral Exam
- Final Dissertation & Thesis Submission
- Life in Vancouver
- Vancouver Campus
- Graduate Student Spaces
- Graduate Life Centre
- Life as a Grad Student
- Graduate Student Ambassadors
- Meet our Students
- Award Opportunities
- Award Guidelines
- Minimum Funding Policy for PhD Students
- Killam Awards & Fellowships
- Policies & Procedures
- Information for Supervisors
- Dean's Message
- Leadership Team
- Strategic Plan & Priorities
- Vision & Mission
- Equity, Diversity & Inclusion
- Initiatives, Plans & Reports
- Graduate Education Analysis & Research
- Media Enquiries
- Newsletters
- Giving to Graduate Studies
Strategic Priorities
- Strategic Plan 2019-2024
- Improving Student Funding
- Promoting Excellence in Graduate Programs
- Enhancing Graduate Supervision
- Advancing Indigenous Inclusion
- Supporting Student Development and Success
- Reimagining Graduate Education
- Enriching the Student Experience
Initiatives
- Public Scholars Initiative
- 3 Minute Thesis (3MT)
- PhD Career Outcomes
- Great Supervisor Week
Spring Open House: We can't wait to welcome you on-campus on Saturday, April 13, from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. Find all the details here .
Health Informatics Program (Postgraduate) (T402)

Program Description
Tuition & fees.
- Admission Requirements
- Program Outcomes
Program Overview
Health Informatics is a one-year graduate certificate program for healthcare and information systems professionals currently employed or with experience in healthcare or technology, or who have an interest in the advancement of IT in healthcare.
We aim to accommodate busy schedules with evening and weekend classes; however, some courses are scheduled during daytime hours. See the Full Description section for more details.
Full Description
The landscape of healthcare is undergoing a remarkable transformation thanks to the evolution of information and communication technologies. This shift is revolutionizing the way we access and share information, all aimed at enhancing patient care.
Our Health Informatics one-year graduate certificate program brings together professionals from both health-related and IT sectors to shape you into a health informatics specialist, ready to tackle the challenges of current and future healthcare systems. If you're a professional in IT, healthcare, or related areas, and dream of being a health informatician/analyst, or if you're a practitioner wanting to level up your game with formal education, this intensive program is for you.
Throughout the program, our team of health informatics/business system analyst pros and faculty will guide you through developing critical skills and competencies in these areas:
- healthcare systems, technologies, and trends
- electronic medical records (EMRs)
- ethical, professional, legal, and policy implications of health information systems technologies and health information standards
- problem identification and analysis
- documenting and analyzing healthcare organization, health user, and solution requirements
- process, workflow, and system/solution modelling
- project management
- technical writing
- leadership and management
- business and system analysis techniques and core professional competencies such as analytical thinking and problem solving, communication and facilitation, and collaborative skills
The Health Informatics program is all about diving deep into the world of health informatics. What makes this graduate certificate program stand out? It's all about hands-on experience and application. You'll immerse yourself in health informatics and analysis through case studies, industry projects, and practical work experience. As you develop innovative solutions, you'll emerge from this program with skills that prepare you for the real-life demands of your career.
Upon graduation, you'll have the essential skills and competencies needed for professional certification programs in Health Informatics and Project Management.
Here are some skills you'll be able to show off after completing this program:
- Formulate change strategies to implement health information systems technologies (HIST) within the healthcare setting.
- Apply business and system analysis techniques to evaluate the effectiveness of health information systems technologies within a health-related setting.
- Design and protoype web and mobile health apps.
- Integrate relevant standards and professional, ethical, and legislative requirements with health information system technologies.
- Design training and education for the effective use of HIST.
- Configure all aspects of an EMR used by physicians in outpatient settings and multidisciplinary clinics.
Hands-On Experience With A Commercial EMR
We've partnered with Arya Health, the maker of AryaEHR, a commercially available EMR, to give you hands-on practical experience with an EMR that physicians use across Canada. This means you'll graduate with EMR experience on your resume, giving you a competitive edge in the marketplace. George Brown College is the only College that offers this valuable experience. Find out more on AryaEHR's website .
IIBA Academic Membership
Academic Membership in the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA) offers colleges and universities that have Business Analyst curriculums and care about advancing the BA profession within their student population the opportunity to participate in IIBA membership and benefit from IIBA’s other products and services. The Academic recognition programs offer the students of Business Analyst-related programs the opportunity to receive recognition from the IIBA.
New - Graduates Prepared to Write the IIBA Entry Certification in Business Analysis (TIM) Designation (ECBA)
Students who successfully graduate from this program will be prepared to write the IIBA Entry Certification of Business Analysis designation from the International Institute of Business Analysis. This professional designation recognizes the student’s theoretical understanding of the Business Analyst Body of Knowledge (BABOK), as well as the context of business analysis applied across industries.
Learn more about the Entry Certification in Business Analysis ( www.iiba.org ).
Technology Requirements
This program requires you to have access to a personal laptop with the following specifications:
- Screen 13-inch minimum
- Webcam + mic
- 256 GB SSD Hard Drive (512 GB SSD is better)
- Quad-core i7 2.4GHz or better
- 2 TB (minimum) external hard drive
- Consistent access to a reliable high-speed internet connection (minimum 10 Mbs download speed recommended)
Program Delivery
Note on program delivery: Most courses take place in the evening and on weekends; however, some courses may take place from 2 PM - 6 PM on weekdays.
Your Field Education Options
In semester 3, students complete a Work Integrated Project, or qualified students are eligible for co-op. Learn more about how to qualify, apply, and important dates for co-op on the Centre for Arts, Design & Information Technology Experiential Learning page.
Career & Postgraduate Study Opportunities
Career options.
Upon completion of the program, you'll have the skills needed for positions such as:
- project/program coordinator
- service desk analyst
- product analyst
- apps analyst
- testing analyst
- privacy co-ordinator
- training co-ordinator
- clinical informatics co-ordinator
- data co-ordinator
- junior business analyst
Required Courses
PRINTABLE CURRICULUM PLANNER 2024-2025
Program Learning Outcomes
The graduate has reliably demonstrated the ability to:
- Assess organizational requirements for health information system technologies (HIST).
- Formulate strategies for the selection and implementation of HIST.
- Design and deliver educational/training strategies for end-users.
- Evaluate the impact of HIST on business/clinical processes, and on health services delivery.
Domestic Tuition
International tuition, additional costs.
* Amounts listed are the estimated total of tuition, materials, student service and ancillary fees for the first two semesters of programs starting in Fall 2023 . Fees are subject to change for programs starting in Fall 2024 and at later dates. This fee does not include books, which are to be purchased by the student separately.
** Amounts listed are the estimated total of tuition, materials, student service and ancillary fees for the first two semesters of programs starting in Fall 2024 . Tuition fees are subject to board approval. Material, student service and ancillary fees are estimated based on prior years. All fees are subject to change without notice. This fee does not include books, which are to be purchased by the student separately.
‡ Semester 3 fees will consist of a flat fee of $500 for co-op placement or for the work-integrated project, fees are to be paid separately, both of which are not included in the total above.
- International Students
Visit the International Fees and Related Costs page for more information.
Financial Assistance
This program is approved for OSAP funding, provided the applicant meets OSAP eligibility criteria.
Disclaimer: The information contained in this website is subject to change without notice. It should not be viewed as a representation, offer or warranty. Students are responsible for verifying George Brown College fee requirements.
- Minimum two-year diploma or bachelor's degree* in Health Sciences or related field from an accredited institution.
- Minimum three-year diploma in Information Technology* or related field from an accredited institution.
- Minimum one year of work experience as a health-care professional or an IT professional, or equivalent (resumé required).
Candidates will be accepted based on the combination of relevant education and work experience.
* Please note that domestic applicants who are submitting international transcripts require a Canadian equivalency evaluation. This can be obtained through ICAS (International Credential Assessment Service) at icascanada.ca or WES (World Education Services) at wes.org/ca .
English Language Proficiency
Applicants with international transcripts who do not provide English language proficiency test results must test at the college level in the George Brown College English assessment to be considered for admission.
Please visit English Proficiency for more details.
Course exemptions
College or university credits may qualify you for course exemptions. Please visit Transfer Guide for more information.
Visit the International Admissions page for more information regarding country specific admission requirements.
- How to Apply
Domestic students should apply through Ontario Colleges.
Visit the How to Apply page for more information on how and when to apply.
International students should apply through the George Brown College Online Application System .
School of Computer Technology
Phone: 416-415-5000, ext. 4287 Email: [email protected]
The office hours are: Monday, Tuesday, Thursday and Friday: 9 – 6 p.m. Wednesday: 9 – 4 p.m.
Program Co-ordinator: Dr. Thérèse Bernier Email: [email protected] Phone: 416-415-5000 x 3744 Office hours: Monday, 2-5 P.M.
For more information about George Brown College, you may also call the Contact Centre at 416-415-2000 or long distance 1-800-265-2002.
Contact one of our international recruitment representatives specializing by country of origin by either booking a virtual meeting or submitting an inquiry. For more information visit the International Contact Us page
Visit Our Campus
The Health Informatics program is offered through our School of Computer Technology from our Casa Loma Campus at 146 Kendal Avenue . Sign up for an information session or campus tour to learn more about George Brown College and the program. You can also explore our virtual tour.
This program is geared toward health care and information systems professionals currently employed or with experience in a health care or technology environment, or who have an interest in the advancement of information technologies in the health care delivery sector.
Efforts are made towards evening and weekend classes; however, some courses are scheduled during daytime hours. See Full Description section for further information.
The evolution of information and communication technologies is transforming the healthcare system and creating new ways of accessing and exchanging information. These changes endeavour to benefit patient care. These technological changes also impact the health care sector. Healthcare and information systems professionals currently employed or with experience in a healthcare or technology environment, or who have an interest in the advancement of information technologies in the healthcare delivery sector, will be interested in this program.
The Health Informatics graduate certificate program brings together professionals in health-related and information technology sectors to develop specialists in health informatics who can respond to the current and emerging needs of health care systems. This intensive program is designed for IT, health care or related professionals who aspire to enter into a health informatician/analyst role, or practitioners who wish to enhance their experience with formal education. As a student in this program, you will be engaged and supported by a team of health informatician/business system analyst professionals and faculty in developing critical skills and competencies in the areas of:
- health care systems, technologies and trends
- ethical, professional, legal and policy implications of health information systems technologies and health information standards
- documenting and analyzing health-care organization, health-user and solution requirements
- process, workflow and system/solution modelling
The Health Informatics program provides breadth and depth of applied knowledge in the field of health informatics. A key characteristic that sets this graduate certificate program apart is the applied nature of the curriculum. Students will be immersed in the process of health informatics/analysis through case studies, industry projects and practical work experience, and will be responsible for developing solutions. The uniqueness of this program is in creating graduates with work-ready skills built through applied, hands-on experience.
Graduates of the program will have acquired knowledge, skills and competencies relevant to professional certification programs in Health Informatics and Project Management.
Graduates will be able to:
- Formulate change strategies to implement appropriate health information systems technologies (HIST) within the health-care setting.
- Integrate relevant standards and professional, ethical and legislative requirements with the appropriate health information system technologies.
Hands-On Experience With A Commercial Emr
Arya Health, the maker of AryaEHR, a commercially available EMR, has partnered with the George Brown College Health Informatics program to give students hands-on practical experience with an EMR in use by physicians across Canada. Students will graduate having EMR experience on their resume, giving them a competitive edge in the marketplace. George Brown College is the only College that offers this valuable experience. Find out more on AryaEHR's website .
IIBA ACADEMIC MEMBERSHIP
New – graduates prepared to write the iiba entry certification in business analysis (tm) designation (ecba)..
Students who successfully graduate from the program will be prepared to write the IIBA Entry Certification of Business Analysis designation from the International Institute of Business Analysis. This professional designation recognizes the student’s theoretical understanding of the Business Analyst Body of Knowledge (BABOK), as well as the context of business analysis applied across industries.
This program requires students to have access to a personal laptop with the following specifications:
Note on program delivery: Most courses are offered in the evening and week-ends. Some courses may be scheduled 2pm-6pm on weekdays.
Upon completion of the program, graduates will be able to meet the requirements for positions such as:
PRINTABLE CURRICULUM PLANNER 2023-2024
* Amounts listed are the total of tuition, materials, student service and ancillary fees for the first two semesters of programs starting in Fall 2022 . Fees are subject to change for programs starting in Fall 2023 and at later dates.
** Amounts listed are the total of tuition, materials, student service and ancillary fees for the first two semesters of programs starting in Fall 2023. Fees are subject to change for programs starting in Fall 2024 and at later dates.
Program Co-ordinator: Dr. Thérèse Bernier Email: [email protected] Phone: 416-415-5000 x 3744 Office hours: Monday, 2 – 5 p.m.
Land acknowledgement
Learn more about our land acknowledgment
- Arts, Design & Information Technology
- Community Services & Early Childhood
- Construction & Engineering Technologies
- Health Sciences
- Hospitality & Culinary Arts
- Preparatory & Liberal Studies
- Alumni Stories
- Achievements
- Connected to Employers
- College Advising
- Experiential Learning
- FAQ – Guidance Counsellors
- Campus Tours
- Information Sessions
- Online Tours & Information Sessions
- Virtual Tour
- Student Life
- Study and Work Abroad
- Transfer Agreements & Opportunities
- Courses eligible for transfer
- Course-to-Course Equivalency Database
- Transferring Credits Into GBC
- Transferring Credits to Another institution
- Transferring Credits within GBC
- Entry Advising
- Information sessions and workshops
- Appointments
- Program Availability
- Program Requirements
- English Proficiency
- Mature Students
- Admission & Placement Assessments
- College Policies
- CHOICES: Explore your Post-Secondary Options
- Academic Upgrading – Study On‑Campus
- Academic Upgrading (Online) - ACE Distance
- Academic Upgrading for Deaf & Hard‑of‑Hearing (Study On‑Campus)
- Academic Upgrading for Deaf & Hard‑of‑Hearing Adults (Online)
- Degree Preparation: University Level (U‑Level) Bridging Programs
- Mature Student Assessment Prep (MSAP)
- Placement Test Assessment Prep (PTAP)
- Academic Upgrading FAQ
- Advanced Standing
- Prior Learning Assessment and Recognition (PLAR)
- Tuition fees and costs
- Awards and Scholarships
- Canada Learning Bond
- External Loans
- How to Pay for College
- Tuition Payment Plan
- Work Study Program
- Contact Financial Aid
- Career Coach
- Contact Admissions
- Spring 2024 Delivery
- Winter 2024 Delivery
- Program Finder
- Program Comparison
- International-Eligible Programs
- Apprenticeship Programs
- Better Jobs Ontario
- Bridging Programs
- Continuing Education
- Degree Programs
- English as a Second Language (ESL) Programs
- Online Programs
- Postgraduate Programs
- Pre-Programs
- Course Outlines Search
- 2024-2025 Program Viewbook
- 2024-2025 Degree Program Viewbook
- Academic Centres & Schools
- Ask George Brown
- Campus Bookstore
- Computer Store
- Athletics & Recreation
- Black Student Success Network (BSSN)
- Experience Record
- Recreational Sports
- Student Association
- Student Clubs
- Student Life Volunteer Squad
- Study & Work Abroad
- Campuses & Locations
- How to Get Your Student ID Online
- How to Use Your Student ID Card
- Replacing Lost Student ID Card
- Your Digital GBC ID
- Policies, Terms & Conditions
- Important Dates
- Academic Records
- Contact Office of the Registrar
- Financial Aid
- Graduation & Convocation
- Registration Information
- Tuition Tax Receipts
- Academic Program Orientations
- Before You Start
- Navigating your first 30 days
- Orientation Events Calendar
- Transitioning Semesters
- About Clinical Pre-Placement Office
- Additional requirements
- Announcements
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Deadline Dates
- Flu Shot vaccine
- ParaMed Placement Pass
- Prerequisite Health Forms by Program
- Webinar Schedules
- Spring 2024 Registration
- Register for Electives
- Registration FAQ
- Accessible Learning Services
- Anti-Racism, Equity and Human Rights Services
- Career Services & Job Posting
- Child Care Centres
- Counselling
- Deaf & Hard of Hearing Services
- First Year Experience
- Food and Drink
- Gym & Fitness Classes
- Housing Information
- Indigenous Initiatives
- Library Learning Commons (LLC)
- Locker Rentals
- Office of Student Conduct & Support
- Reflection Rooms
- Safewalk Program
- Sexual Violence Resources
- Staying Healthy Off-Campus
- Student Residence
- Student Success Hub
- Tutoring & Learning Centre (TLC)
- Where to Eat on Campus
- Welcome & Information Desks
- Entry Advising Services
- AppsAnywhere
- Brightspace Support
- Email Support
- Gartner Access
- Mobile Apps
- Office 365 & OneDrive
- Protecting your computer and devices from malware
- Resetting Your Password
- Tech Support
- Zoom Support
- International Viewbooks
- Life with George Brown
- Withdrawal & Refund Policy
- Refund Process policies
- International Student Advisors Contact
- Permits & Visas
- Scholarships
- Download the iCent App
- Study Abroad
- Outbound Exchange Opportunities
- Inbound Exchange Opportunities
- Work-Integrated Learning Abroad
- International Pathways to Further Study
- Cultural Intelligence Certificate Program
- Tuition Fees and Related Costs
- International Partners
- Information for Agents
- Contact International
- Accessibility
- AODA Accessibility Training for Employees
- College AODA Policies
- College AODA Reports
- Planning for Accessible Event
- Anti-Racism
- Freedom of Expression
- Freedom of Information and Protection of Privacy (FIPPA)
- Human Rights
- Say My Name
- Sexual Harassment and Sexual Violence Policy, Prevention and Support
- Student Self-Identification Survey
- Employee Resources
- Contact Archives
- Casa Loma Campus
- St. James Campus
- Waterfront Campus
- Toronto Metropolitan University Location
- Sunnybrook Location
- Fashion Exchange
- Young Centre for the Performing Arts
- The George Student Residence
- College History
- Alumni Relations
- Retirees' Association
- Seniors' Association
- Contact information
- Annual Reports
- Board of Governors
- College Council
- Labour Negotiations at George Brown College
- Master Campus Plan
- President Dr. Gervan Fearon – video messages
- Senior Leadership Team
- GBC Foundation
- Temporary & Contract
- Why Work at George Brown
- Health & Safety Guidelines for Contractors
- How to Support George Brown
- Food Court Social
- Government Relations
- Health, Safety & Wellness
- GBC in the Media
- Information for Media
- News & Announcements
- Social Media Hub
- Thought Leadership
- Developing New Programs
- Program Review
- Curriculum Support Resources
- Office of Research & Innovation
- Anti–Spam Commitment
- Freedom of Expression policy
- Privacy Policy
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Socially Responsible Procurement
- Procurement Supply Chain Code of Ethics
- Contact & Security Locations
- Emergency Call Boxes
- Emergency Preparedness & Guidelines
- Health Emergency Business Continuity Plan (CEP)
- Emergency Procedures
- Flyers, Pamphlets, and Informational Materials
- In Case of Emergency
- Public Safety and Security Forms
- Winter weather guide
- Institutional Research & Planning
- Strategic Project Portfolio Management
- Strategic and Operational Planning
- LEAD Values
- Sustainability Plan 2022
- Sustainability Guidelines
- The Story of Recycling
- Waste Management and Recycling
- What can I do?
- Work Shift Podcast
- Current Students
- Parents & Guidance Counsellors
- Industry Partners
- Job Seekers
- Services for the Public
- Brightspace (D2L)
- College Email
- Emergency information
- MyGBC Student Portal
- Password Reset
- Technical Support
- Contact George Brown
- Campuses and Locations
- Centre & School Directory
- 24/7 Urgent Support
- On-Campus Emergency & Security
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
- Departments
Language selection
- Search and menus
Health Services and Policy Research Doctoral Training Programs in Canada
Table 1 is an inventory of university-based health services and policy research (and related) doctoral training programs in Canada. A HSPR doctoral training program is defined as a program that is authorized to award a degree, concentration or specialization in HSPR or a related field, such as health economics, health technology assessment, health services organization and management, health services outcomes and evaluation, etc.). *Related assets are doctoral training programs in related fields, like public policy, epidemiology, and biostatistics that do not indicate a specialization or concentration in HSPR. Table 1 was compiled based on a 2014 analysis of Canada’s assets and resources in HSPR (full report is available upon request), a 2016 search of university websites in all provinces and territories across the country, and validation with key informant experts. It is possible that some programs were missed and that the list is comprehensive but not exhaustive.
- Support Dal
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Family & Friends
- Agricultural Campus (Truro)
- Halifax Campuses
- Campus Maps
- Brightspace
Dalhousie University
Digital innovation mdi.
- Faculty of Computer Science
- Program details
- Career Development
- Graduate life
- Certificate in Health Informatics
- Certificate in Digital Business
- Certificate in Data Science

Need help? Connect with an advisor.
We have dedicated academic advisors ready to assist you at [email protected] .
The Certificate in Health Informatics aims to train students in the world of health informatics, giving you the skills to develop and use information technology to create a better healthcare system .
Health informaticians work in an interdisciplinary environment incorporating computer science, medicine, health, nursing and business knowledge to improve healthcare and health outcomes.
Program overview
Customize your degree.
Although all MDI students follow a required program outline , you can create your own degree with a wide variety of elective options that support the Certificate in Health Informatics.
Two of the following courses:
Assigned by the graduate committee based on academic background and goals.
DGIN 5100 Foundations in Web Technologies
This hands-on course examines the technologies and infrastructure required to support digital innovation. The course examines the major components of the information technology infrastructure, such as networks, databases and data warehouses, electronic payment, security, and human-computer interfaces. The course covers key web concepts and skills for designing, creating and maintaining websites, such as Grid Theory, HTML5, CSS, JavaScript, AJAX theory, PHP, SQL and NoSQL databases. Other principles such as Web Accessibility, Usability and User eXperience, as well as best security practices, are explored in detail through a combination of lectures, in-class examples, individual lab work and assignments, and a final group project.
DGIN 5200 Foundations in Business
The overall aim of this course is to develop a high-level understanding of the dynamics of innovation, the distribution and outcomes of the strategic management of innovation and the relationships that are important in developing high-impact organizations.
DGIN 5300 Law, Policy, and Ethics in Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies—such as digital media, the “internet of things”, artificial intelligence (AI), and financial tech—are playing an increasingly central role in how individuals live and interact with each other; how businesses innovate and create new opportunities; and how governments function and serve their populations. But the unrestrained development and use of these technologies can raise complex legal, policy, and ethical challenges. This course offers students an introduction to foundational legal, policy, and ethical issues raised by emerging technologies in a variety of contexts, with special consideration for digital innovation and commerce. On completion, students will be able to better identify, understand, and critically assess these issues and also more effectively manage and resolve them in the course of the professional pursuits.
DGIN 5400 Statistics for Health Informatics
This course covers essential statistical methods for medical research. Topics include descriptive analysis techniques and basic principles of statistical inference for comparison of means, proportions and investigation of relationships between variables using regression mod-eling techniques. Students will also become familiar with nonparametric tests and power and sample size calculations.
The following core course:
Dgin 5201 digital transformation.
This core digital innovation course focuses on the design and management of digital innovation projects for both public sector and private sector organizations. Specifically, this course provides students with knowledge and skills to initiate and execute digital innovation and transformation projects in existing organizations or new start-ups.
One of the following core courses:
Dgin 5001 – capstone in digital innovation.
This course requires students to apply principles of Digital Innovation (DI) holistically to a concrete problem. In the context of a multidisciplinary team, students are expected to apply Di processes, develop negotiation and collaborative skills.
DGIN 5002 – Research Methods
This class will provide Master of Digital Innovation thesis students with an understanding of the principles of empirical science as they relate to computer science related research. The goal is for the student to determine the research methods most appropriate for their research area and to be able to design simple to moderately complicated research studies. The course covers both quantitative and qualitative research issues and will provide a practical introduction to the statistics through hand-on tutorials. In addition, this course will provide the basis for critical reading of research findings in the literature and students will gain experience with scientific writing. This course will teach students how to assess the validity of other researchers’ articles, and at the same time, enable students to validate their own research.
All health informatics students complete the following electives:
Hinf 6101 health information flow and use.
This course tracks the flow and use of health information in relation to population and individual health needs, including its generation, collection, movement, storage and use in various settings. The course includes a discussion of health and health information, and of the measurement of health and health services processes.
HINF 6110 Health Information Systems and Issues
A course about health infostructures and their strengths and weaknesses. Students will learn about how such structures operate, the issues they generate, their impact on the health of populations and their impact on the flow and use of information. Particular attention will be paid to ethical and practical health informatics issues.
HINF 6230 Knowledge Management for Health Informatics
The goal of this course is to characterize healthcare knowledge and to examine the technical issues related to the development and deployment of knowledge management solutions for managing healthcare knowledge to support three main activities: Clinical decision support, practitioner and patient education, and health administration. At the conclusion of the course, students will be able to (a) identify the presence (or lack) of healthcare knowledge within a healthcare enterprise; (b) capture it using various knowledge representation formalisms; and (c) utilize it via new or existing knowledge management infrastructures to impact the delivery the healthcare.
Your choice of two elective courses from the following:
Hinf 6020 research methods.
This course explores the logic and principles of research design, measurement, and data collection. The course offers a range of methodological issues and methods, including experimental and quasi-experimental designs, survey research and sampling, measurement, and qualitative methods.
HINF 6102 Health Information Standards and Use
This seminar course discusses technical and philosophical issues related to the capture and use of information. Issues include nomenclature; the reliability and accuracy of coding schema; interoperability; and, ISO/CEN, HL7 and Infoway standards development. Student projects will track the flow and use of information for hospital, community and public health purposes.
HINF 6210 Databases and Data Mining for Health Informatics
Health organizations collect massive amount of data to support clinical decision-making, outcome measurement, policy setting, administration and research. This course provides a conceptual understanding of various data mining algorithms and introduces healthcare-related data mining strategies to facilitate the mining of real-life healthcare data to provide data-driven healthcare decision-support services.
DGIN 5401 Operationalized Machine Learning in Healthcare
This course provides a broad overview of machine learning and machine learning operations in healthcare contexts. We begin by studying how healthcare data is unique, and how machine learning methods have been applied to clinical and medical tasks. We focus on various graphical, deep learning, time-series, and transfer learning models and unique aspects of their application in healthcare. We cover concepts of fairness, privacy, trust, explainability, and other human factors. We discuss implementation techniques, including ‘MLOps’ for healthcare, and opportunities for real-world deployment. Much of the course will be seminar-based, including guest lectures and descriptions of research papers. Students will choose and complete a commensurate research project. The course expects and requires a familiarity with programming and core concepts in data mining or data science. It is strongly recommended that Master of Digital Innovation students take this in their final semester.
Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3H 4R2 1-902-494-2211 Agricultural Campus Truro, Nova Scotia, Canada B2N 5E3 1-902-893-6600
- Campus Directory
- Student Career Services
- Employment with Dalhousie
- For Parents
- For Employers
- Media Centre
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3H 4R2 1.902.494.2211
- Skip to main content

- All countries /
- North America /
- Computer Science and IT /
- Computer Science /
- Health Informatics
10 Universities in Canada offering Health Informatics degrees and courses
More Information
Are you looking for Health Informatics courses? Here you can find course providers offering full-time, part-time, online or distance learning options.
You've reached your limit of 10 Favourites
Confederation College
George brown college, fleming college.

Centennial College

Southern Alberta Institute of Technology (SAIT)

Sault College

University of Regina
THE World Ranking: 801

University of Victoria
THE World Ranking: 351

Dalhousie University
THE World Ranking: 301

University of Toronto
THE World Ranking: 21
There are more Health Informatics courses available in North America
- British Columbia
- Nova Scotia
- Saskatchewan
- Study level:
- All study levels
- Postgraduate
- Undergraduate
- Career based/Vocational
- Study mode:
- Online/Distance
Filter your results
Tell us about you.
- Nationality Select country Select country
- My current qualification is from Select country Yes No Select country Select country
- Current qualification {0} is not applicable for the study level you selected below. Qualification Qualification
- Grade type (only one grade type for your qualification) Grade type Grade type
- My score (current or expected) Please select Please select Please select Please select Please select Please select
Tell us your preferences
- Subject Health Informatics
Qualification
- Destination Canada
- Study options
- Annual tuition fees
Subject areas
Destination.
- The UConn School of Business has grown to become one of the most comprehensive business schools in the country.
- NEW: Want to study in your home country for a foreign qualification? Find out more about cross-border study!


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
PhD in Health Informatics. We are no longer accepting applications for the MSc or PhD programs for September 2024 entry. The next application entry term is September 2025 with an application deadline of January 15, 2025. We expect admission decisions for Sept. 2024 applications will be available in late March/early April 2024.
Our PhD in Health Informatics will prepare scholars to discover and extend their scientific knowledge and advance the science and practice of health informatics. The program is built around our core interdisciplinary specializations: design and structure of health information systems. implementation and evaluation of health information systems.
Study and Work in Health Informatics in Canada. The prequisites required to become accepted in an graduate and/or post-graduate PhD program in Health Informatics. Topics and concepts that are covered and the overall approach or focus taken in studying Health Informatics. Research areas, topics, interests projects in Health Informatics.
HIS General Inquiries [email protected] 519-661-4017 FIMS Graduate Student Services 519-661-4017 FHS Dean's Office 519-661-2111 ext. 88918 Jointly hosted by PhD in Health Information Science (PhD HIS)
Health Informatics. Home; Programs; Health Informatics; Program Overview. The Institute of Health Policy, Management and Evaluation (IHPME) trains Canada's future health leaders and researchers through its research and professional graduate degree programs and its involvement in a range of collaborative programs.
The Health Informatics program focuses on the effective use of health information and informatics technologies to improve health and health-care delivery. You will work with cutting-edge researchers and learn about the latest approaches to health informatics. In Ontario Tech Uninversity's state-of-the-art health informatics laboratories, you ...
PhD studentsin the School of Public Health Sciences can pursue a designated field to exemplify an area of expertise within their broader program. Fields include epidemiology and biostatistics, health evaluation, health informatics, health and environment, global health, aging and health and work and health . The University of Waterloo's unique ...
Students in the Health Informatics stream will develop strategies to actively participate in multidisciplinary collaborations with diverse groups (e.g., patients, clinicians, health care managers, computer scientists, engineers) and will learn to assess and deploy the latest in computing and informatics systems to support efficient health care ...
The MHI program is flexible for the working professional and is completed online as a part-time or full-time student. Offered online. The Master of Health Informatics program provides flexibility for the working professional and can be completed in 16 months to four years. It also features a four-month professional experience component.
Master of Health Informatics (MHI) Advancing leadership and health informatics research in digital and AI technologies to drive organizational and system change within the healthcare sector. MHI is one of Canada's few graduate programs in the rapidly evolving field of health informatics with a strong focus on artificial intelligence (AI).
The Doctor of Philosophy in Bioinformatics (PhD)is an interdisciplinary program that combines the application of computer technology to the management and analysis of biological data. The result is that computers are being used to organize data generated from experiments into databases, develop new algorithms and software, and use this software for the interpretation and analysis of the data ...
Health Informatics is a one-year graduate certificate program for healthcare and information systems professionals currently employed or with experience in ... Health Informatics program to give students hands-on practical experience with an EMR in use by physicians across Canada. Students will graduate having EMR experience on their resume ...
8 Universities in Canada offering postgraduate Health Informatics degrees and courses. Plan your studies abroad now. You are currently browsing our site with content tailored to students in your country
Overview. Table 1 is an inventory of university-based health services and policy research (and related) doctoral training programs in Canada. A HSPR doctoral training program is defined as a program that is authorized to award a degree, concentration or specialization in HSPR or a related field, such as health economics, health technology ...
We offer a PhD in Health Informatics program at University of Victoria, British Columbia which will prepare scholars to discover and extend their scientific knowledge and advance the science and practice of health informatics. University of Victoria. Victoria , Canada. Top 2% worldwide. Studyportals University Meta Ranking.
[email protected]. The Certificate in Health Informatics aims to train students in the world of health informatics, giving you the skills to develop and use information technology to create a better healthcare system . Health informaticians work in an interdisciplinary environment incorporating computer science, medicine, health, nursing and ...
Health Information Science. Health Information Science. Health Informatics Technology (Fast-Track) (Online) This page shows a selection of the available Masters programmes in Canada. If you're interested in studying a Health Informatics degree in Canada you can view all 17 Masters programmes.
Depending on the university or college offering Masters in Health Informatics in Canada, the total program costs between 13,195-45,830 CAD (7.96-27.65 lakhs INR). Masters in Health Informatics in Canada is also available as an Ontario Graduate Certificate program, which usually takes 2-3 semesters to complete.
Southern Alberta Institute of Technology (SAIT) Canada. View 1 Health Informatics courses. 44725. Views. 740. Favourites.
The PhD program is designed for students seeking the highest level of advanced training in the area of health informatics. Students take a sequence of core courses in health informatics, computing, and biostatistics, and electives in technical and health science areas, and pursue one of four tracks: Data Science and Informatics for Learning Health Systems; Clinical Informatics; Translational ...