Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples

How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.1 Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement
Learning objectives.
- Develop a strong, clear thesis statement with the proper elements.
- Revise your thesis statement.
Have you ever known a person who was not very good at telling stories? You probably had trouble following his train of thought as he jumped around from point to point, either being too brief in places that needed further explanation or providing too many details on a meaningless element. Maybe he told the end of the story first, then moved to the beginning and later added details to the middle. His ideas were probably scattered, and the story did not flow very well. When the story was over, you probably had many questions.
Just as a personal anecdote can be a disorganized mess, an essay can fall into the same trap of being out of order and confusing. That is why writers need a thesis statement to provide a specific focus for their essay and to organize what they are about to discuss in the body.
Just like a topic sentence summarizes a single paragraph, the thesis statement summarizes an entire essay. It tells the reader the point you want to make in your essay, while the essay itself supports that point. It is like a signpost that signals the essay’s destination. You should form your thesis before you begin to organize an essay, but you may find that it needs revision as the essay develops.

Elements of a Thesis Statement
For every essay you write, you must focus on a central idea. This idea stems from a topic you have chosen or been assigned or from a question your teacher has asked. It is not enough merely to discuss a general topic or simply answer a question with a yes or no. You have to form a specific opinion, and then articulate that into a controlling idea —the main idea upon which you build your thesis.
Remember that a thesis is not the topic itself, but rather your interpretation of the question or subject. For whatever topic your professor gives you, you must ask yourself, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful and confident.
A thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of your introduction. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an issue but rather dissects it.
A Strong Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement contains the following qualities.
Specificity. A thesis statement must concentrate on a specific area of a general topic. As you may recall, the creation of a thesis statement begins when you choose a broad subject and then narrow down its parts until you pinpoint a specific aspect of that topic. For example, health care is a broad topic, but a proper thesis statement would focus on a specific area of that topic, such as options for individuals without health care coverage.
Precision. A strong thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and to remain focused on the topic. If the specific topic is options for individuals without health care coverage, then your precise thesis statement must make an exact claim about it, such as that limited options exist for those who are uninsured by their employers. You must further pinpoint what you are going to discuss regarding these limited effects, such as whom they affect and what the cause is.
Ability to be argued. A thesis statement must present a relevant and specific argument. A factual statement often is not considered arguable. Be sure your thesis statement contains a point of view that can be supported with evidence.
Ability to be demonstrated. For any claim you make in your thesis, you must be able to provide reasons and examples for your opinion. You can rely on personal observations in order to do this, or you can consult outside sources to demonstrate that what you assert is valid. A worthy argument is backed by examples and details.
Forcefulness. A thesis statement that is forceful shows readers that you are, in fact, making an argument. The tone is assertive and takes a stance that others might oppose.
Confidence. In addition to using force in your thesis statement, you must also use confidence in your claim. Phrases such as I feel or I believe actually weaken the readers’ sense of your confidence because these phrases imply that you are the only person who feels the way you do. In other words, your stance has insufficient backing. Taking an authoritative stance on the matter persuades your readers to have faith in your argument and open their minds to what you have to say.
Even in a personal essay that allows the use of first person, your thesis should not contain phrases such as in my opinion or I believe . These statements reduce your credibility and weaken your argument. Your opinion is more convincing when you use a firm attitude.
On a separate sheet of paper, write a thesis statement for each of the following topics. Remember to make each statement specific, precise, demonstrable, forceful and confident.
- Texting while driving
- The legal drinking age in the United States
- Steroid use among professional athletes
Examples of Appropriate Thesis Statements
Each of the following thesis statements meets several of the following requirements:
- Specificity
- Ability to be argued
- Ability to be demonstrated
- Forcefulness
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxon in the play Fences symbolize the challenge of black males who lived through segregation and integration in the United States.
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration.
- Shakespeare’s use of dramatic irony in Romeo and Juliet spoils the outcome for the audience and weakens the plot.
- J. D. Salinger’s character in Catcher in the Rye , Holden Caulfield, is a confused rebel who voices his disgust with phonies, yet in an effort to protect himself, he acts like a phony on many occasions.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown.
- Exposing children from an early age to the dangers of drug abuse is a sure method of preventing future drug addicts.
- In today’s crumbling job market, a high school diploma is not significant enough education to land a stable, lucrative job.
You can find thesis statements in many places, such as in the news; in the opinions of friends, coworkers or teachers; and even in songs you hear on the radio. Become aware of thesis statements in everyday life by paying attention to people’s opinions and their reasons for those opinions. Pay attention to your own everyday thesis statements as well, as these can become material for future essays.
Now that you have read about the contents of a good thesis statement and have seen examples, take a look at the pitfalls to avoid when composing your own thesis:
A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of your subject or a description of what you will discuss in your essay.
Weak thesis statement: My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge.
A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side.
Weak thesis statement: Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end.
Weak thesis statement: Advertising companies use sex to sell their products.
A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad.
Weak thesis statement: The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging.
Read the following thesis statements. On a separate piece of paper, identify each as weak or strong. For those that are weak, list the reasons why. Then revise the weak statements so that they conform to the requirements of a strong thesis.
- The subject of this paper is my experience with ferrets as pets.
- The government must expand its funding for research on renewable energy resources in order to prepare for the impending end of oil.
- Edgar Allan Poe was a poet who lived in Baltimore during the nineteenth century.
- In this essay, I will give you lots of reasons why slot machines should not be legalized in Baltimore.
- Despite his promises during his campaign, President Kennedy took few executive measures to support civil rights legislation.
- Because many children’s toys have potential safety hazards that could lead to injury, it is clear that not all children’s toys are safe.
- My experience with young children has taught me that I want to be a disciplinary parent because I believe that a child without discipline can be a parent’s worst nightmare.
Writing at Work
Often in your career, you will need to ask your boss for something through an e-mail. Just as a thesis statement organizes an essay, it can also organize your e-mail request. While your e-mail will be shorter than an essay, using a thesis statement in your first paragraph quickly lets your boss know what you are asking for, why it is necessary, and what the benefits are. In short body paragraphs, you can provide the essential information needed to expand upon your request.
Thesis Statement Revision
Your thesis will probably change as you write, so you will need to modify it to reflect exactly what you have discussed in your essay. Remember from Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” that your thesis statement begins as a working thesis statement , an indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing.
Working thesis statements often become stronger as you gather information and form new opinions and reasons for those opinions. Revision helps you strengthen your thesis so that it matches what you have expressed in the body of the paper.
The best way to revise your thesis statement is to ask questions about it and then examine the answers to those questions. By challenging your own ideas and forming definite reasons for those ideas, you grow closer to a more precise point of view, which you can then incorporate into your thesis statement.
Ways to Revise Your Thesis
You can cut down on irrelevant aspects and revise your thesis by taking the following steps:
1. Pinpoint and replace all nonspecific words, such as people , everything , society , or life , with more precise words in order to reduce any vagueness.
Working thesis: Young people have to work hard to succeed in life.
Revised thesis: Recent college graduates must have discipline and persistence in order to find and maintain a stable job in which they can use and be appreciated for their talents.
The revised thesis makes a more specific statement about success and what it means to work hard. The original includes too broad a range of people and does not define exactly what success entails. By replacing those general words like people and work hard , the writer can better focus his or her research and gain more direction in his or her writing.
2. Clarify ideas that need explanation by asking yourself questions that narrow your thesis.
Working thesis: The welfare system is a joke.
Revised thesis: The welfare system keeps a socioeconomic class from gaining employment by alluring members of that class with unearned income, instead of programs to improve their education and skill sets.
A joke means many things to many people. Readers bring all sorts of backgrounds and perspectives to the reading process and would need clarification for a word so vague. This expression may also be too informal for the selected audience. By asking questions, the writer can devise a more precise and appropriate explanation for joke . The writer should ask himself or herself questions similar to the 5WH questions. (See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information on the 5WH questions.) By incorporating the answers to these questions into a thesis statement, the writer more accurately defines his or her stance, which will better guide the writing of the essay.
3. Replace any linking verbs with action verbs. Linking verbs are forms of the verb to be , a verb that simply states that a situation exists.
Working thesis: Kansas City schoolteachers are not paid enough.
Revised thesis: The Kansas City legislature cannot afford to pay its educators, resulting in job cuts and resignations in a district that sorely needs highly qualified and dedicated teachers.
The linking verb in this working thesis statement is the word are . Linking verbs often make thesis statements weak because they do not express action. Rather, they connect words and phrases to the second half of the sentence. Readers might wonder, “Why are they not paid enough?” But this statement does not compel them to ask many more questions. The writer should ask himself or herself questions in order to replace the linking verb with an action verb, thus forming a stronger thesis statement, one that takes a more definitive stance on the issue:
- Who is not paying the teachers enough?
- What is considered “enough”?
- What is the problem?
- What are the results
4. Omit any general claims that are hard to support.
Working thesis: Today’s teenage girls are too sexualized.
Revised thesis: Teenage girls who are captivated by the sexual images on MTV are conditioned to believe that a woman’s worth depends on her sensuality, a feeling that harms their self-esteem and behavior.
It is true that some young women in today’s society are more sexualized than in the past, but that is not true for all girls. Many girls have strict parents, dress appropriately, and do not engage in sexual activity while in middle school and high school. The writer of this thesis should ask the following questions:
- Which teenage girls?
- What constitutes “too” sexualized?
- Why are they behaving that way?
- Where does this behavior show up?
- What are the repercussions?
In the first section of Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , you determined your purpose for writing and your audience. You then completed a freewriting exercise about an event you recently experienced and chose a general topic to write about. Using that general topic, you then narrowed it down by answering the 5WH questions. After you answered these questions, you chose one of the three methods of prewriting and gathered possible supporting points for your working thesis statement.
Now, on a separate sheet of paper, write down your working thesis statement. Identify any weaknesses in this sentence and revise the statement to reflect the elements of a strong thesis statement. Make sure it is specific, precise, arguable, demonstrable, forceful, and confident.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
In your career you may have to write a project proposal that focuses on a particular problem in your company, such as reinforcing the tardiness policy. The proposal would aim to fix the problem; using a thesis statement would clearly state the boundaries of the problem and tell the goals of the project. After writing the proposal, you may find that the thesis needs revision to reflect exactly what is expressed in the body. Using the techniques from this chapter would apply to revising that thesis.
Key Takeaways
- Proper essays require a thesis statement to provide a specific focus and suggest how the essay will be organized.
- A thesis statement is your interpretation of the subject, not the topic itself.
- A strong thesis is specific, precise, forceful, confident, and is able to be demonstrated.
- A strong thesis challenges readers with a point of view that can be debated and can be supported with evidence.
- A weak thesis is simply a declaration of your topic or contains an obvious fact that cannot be argued.
- Depending on your topic, it may or may not be appropriate to use first person point of view.
- Revise your thesis by ensuring all words are specific, all ideas are exact, and all verbs express action.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.1: Thesis Statements - simple and complex
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 225928
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
TOPIC VERSUS THESIS?
The subject you are writing about is the topic. Add your opinion to a topic to create a thesis.
Topic + opinion = thesis
Add the significance to make a more complex thesis:
Topic + opinion + so what? = thesis
WHAT IS A THESIS?
The thesis is the main point of an essay, a focused, arguable statement which allows the reader to make predictions about the reading.
WHAT ARE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF AN EFFECTIVE THESIS?
- The language is clear , straight-forward and can’t be misunderstood.
- It is contestable and arguable. Ask yourself: Could someone disagree? The answer should be yes.
- It is concentrated on a focused point: not too broad and not too narrow, but the right size for the assignment.
- It is complex and delves into the larger significance or impact.
- It is compelling and draws in your readers’ interest and makes them want to read more to see how you prove your claim.
- It is directly connected to the prompt/question/assignment for the essay.
A THESIS IS NOT:
Why use a thesis.
- It allows the reader to make predictions about the reading.
- It guides the writer to stay focused on the main idea of the essay.
- It generates thought, evidence and analysis.
- What am I trying to accomplish in this essay?
- What do I want to convince my reader of?
HOW DO I KNOW IT'S A THESIS?
TOPIC + OPINION = THESIS
A thesis is TOPIC + OPINION so you need to make sure that opinion in present or else it is not a thesis statement. The opinion is what makes a thesis arguable and it provides the purpose and focus for the paper: to convince your reader of that opinion.
Locating the Opinion in a Thesis: When you look for the opinion in a thesis, ask yourself: What is the writer’s attitude towards the topic? For example, in the sentence “Backpacking in the mountains last year was an exciting experience,” the topic is “backpacking” and the opinion is that this trip was “exciting.” Another person on the same trip might have had a different attitude and may have found the trip boring or exhausting. “Exciting” reveals the writer’s attitude and also indicates what the essay with this thesis statement will be focused on: demonstrating why it was “exciting.” This thesis statement limits the writer’s focus and clearly tells the reader what the essay will be about.
Practice: Topic and Opinion of a thesis
Put a box around the TOPIC and underline the OPINION words below. If there are no opinion words, it is not a thesis :
- The subject of unwarranted fears, most bats are harmless and highly beneficial.
- Vigorous exercise is a good way to reduce the effects of stress on the body.
- Buffalo and Toronto differ in four major ways.
- Developing color film is more complicated than developing black and white.
- In this essay I will discuss abortion.
- Television is destroying the unity of the modern family.
- In her essay, Erlich shows that there is a balance of community and isolation in her hometown.
Put a box around the TOPIC and underline the OPINION words below:
- The subject of unwarranted fears, most bats are harmless and highly beneficial .
- In this essay I will discuss abortion (no opinion words—not a thesis)
- In her essay, Erlich shows that there is a balance of community and isolation in her hometown .
HOW DO I KNOW IT'S A COMPLEX THESIS?
TOPIC + OPINION + SO WHAT? = COMPLEX THESIS
A complex thesis is TOPIC + OPINION + SO WHAT? To form an arguable thesis, add opinion to a topic, and to make a more complex thesis, add “so what?” So what is the larger significance, the implications, and/or the outcomes of what you are arguing?
Practice: List the thesis topic and opinion
Below are student-created thesis statements about non-fiction texts. For each thesis, list the TOPIC, the OPINION and the “SO WHAT?”
THESIS STATEMENTS ON NON-FICTION TEXTS:
(1) In Field Notes from a Catastrophe, Elizabeth Kolbert seeks to use the evidence she has collected across her years of worldwide travel to show how we should best address climate change. Kolbert uses the island of Samsø to support her case for the mass implementation of alternative energy sources, but she does not point out the many cons that come with the use of alternative energy sources that are wind, biofuels, and solar which is reason enough to refrain from attempts at a greater implementation of them until problems of space, waste, and cost are addressed. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________ (2) In her book Field Notes from a Catastrophe , Elizabeth Kolbert argues that everybody needs to work on ending humans’ carbon emissions to prevent catastrophic climate change on our planet. However, at this point, catastrophic climate change in inevitable, so instead we need to focus our efforts on researching ways to make the new climates survivable. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________
(3) T.V Reed in his book The Art of Protest, argues that environmentalism has been coded as a “white issue.” If those raising the awareness are perceived as largely white and well-off preaching to and within the same demographic, the probability of those most impacted, namely the poor communities of color who disproportionately suffer environmental hazards and toxic dumps, having a voice is dismal, so meaningful change will not occur. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________ (4) In The Art of Protest , T.V. Reed in his chapter “Singing Civil Rights,” says that music during the time of the Civil Rights Movement soulfully spoke about the oppressions of racism against blacks in America. Nowadays, Hip-Hop is one of the main driving forces keeping the conversation going about the continued inequalities that blacks suffer, and this is particularly important in an age of rising police brutality targeted at black men. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________ (5) In I Am Malala, Malala Yousafzai shows how education can be used to combat terrorism in Pakistan because when people become more educated, they can more confidently self-advocate and are less susceptible to being falsely seduced by empty propaganda, so if the country follows Malala’s lead, it can rid itself of the Taliban influence. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________
(6) Malala Yousafzai’s story, as told in her book I am Malala , is powerful and her cause is admirable but her idea that education combats terrorism is simplistic and glosses over the importance of the geopolitical situation Pakistan finds itself in. Education in this environment is no guarantee of deradicalization and may even work to galvanize their cause. In a political context of postcolonial exploitation where foreign governments actively try to destabilize the country and fund extremist groups, education will just make more effective terrorists. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________ (7) In Anthony Swofford’s Jarhead , we see a military culture of toxic masculinity—where relationships with women are transactional, showing emotional sensitivity is weakness, and violence is the preferred method of conflict resolution. This phenomenon is systemic in all branches of the military and is the catalyst for the extensive number of sexual harassment cases, rape, and high rates of suicide for service members. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________ (8) In Jarhead, Anthony Swofford described how the soldier’s first amendment rights are suspended once they sign the military contract. This silencing ensures that the Marines continue to follow orders from the “top” without any objections, and this control ensures that the interests of the rich and powerful are protected while the rights of the soldiers as U.S. citizens are violated, and this enables war for profit to continue. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________
(1) Topic : greater implementation of alternative energy sources Opinion: problems with alternative energy are not satisfactorily solved So What? wider implementation of alternative energy could worsen current problems of space, waste and cost
(2) Topic : catastrophic climate change Opinion: catastrophic climate change is inevitable So What? need to refocus efforts from reducing carbon emissions to adaptation and survival
(3) Topic : only whites leading environment movement Opinion: non-whites most impacted but no voice So What? no change
(4) Topic : music conveying black oppression Opinion: today hip-hop conveys on-going black oppression So What? importantly exposes rise in police brutality targeting black men
(5) Topic : education to combat terrorism in Pakistan Opinion: more education leads to people self-advocating and not being tricked by propaganda So What? Pakistan can rid itself of Taliban
(6) Topic : education to combat terrorism in Pakistan Opinion: foreign countries are actively trying to destabilize Pakistan and are funding extremists So What? education will make more effective terrorists
(7) Topic : military culture of toxic masculinity Opinion: toxic masculinity is systemic in all branches of military So What? leads to sexual harassment, rape and suicide
(8) Topic : freedom of speech of soldiers suspended Opinion: silence allows the rich and powerful to use soldiers as they like So What? allows war for profit to continue
Practice: List the "topic", "opinion" and "so what"?
Below are student-created thesis statements about fiction texts. For each thesis, list the TOPIC, the OPINION and the “SO WHAT?”
THESIS STATEMENTS ON FICTION TEXTS: POETRY
(1) Before the abolition of slavery in 1865, Frances Ellen Watkins Harper, fashioned her poem “Bury Me in a Free Land” to sharpen the glaring contradiction between the most cherished American value of freedom, and its antithesis expressed in the enslavement and brutalization of African Americans. Harper thereby forces her readers to come to terms with their own hypocrisy as Americans to hasten the demise of slavery. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________ (2) In the different stanzas in her poem “Bury Me in a Free Land,” Frances Ellen Watkins Harper, gives graphic snapshots depicting the horrors of slavery: blacks sold like animals on the auction block, escaped blacks being hunted down, blacks being whipped and beaten bloody, black babies being taken from mothers. Unfortunately, African-Americans living in the “land of the free” today still suffer many of these same forms of injustice as their labor continues to be exploited, as they suffer higher rates of profiling and murder, and as their families continue to be torn apart due to mass incarceration. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________
THESIS STATEMENTS ON FICTION TEXTS: Short Stories
(3) In Zora Neale Hurston’s short story “Sweat,” Sykes, a black man living in the Jim Crow South, constantly feels the need to assert his masculinity over Delia through acts of abuse and adultery in order to make up for insecurities resulting from his failure to fulfill the traditional male roles of provider and protector. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________ (4) In her short story “Sweat,” Zora Neale Hurston makes her reader feel empathy for the main character Delia, a hardworking woman who endures years of mental and physical abuse from her husband. Through helping her reader care about Delia, Hurston enables her reader to feel the triple burden of oppression of being black, female and poor in America. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________
THESIS STATEMENTS ON FICTION TEXTS: Plays (Drama)
(5) Yusef’s wife, Anbara, writes revolutionary articles in the play Tennis in Nablus by Ismail Khalidi highlighting women’s empowerment and support as absolutely essential for the success of any movement or revolution that aspires toward real change. Khalidi uses symbolism and imagery to demonstrate that a primary reason for the failure of the Palestinian nation to escape the abuse of their British oppressors was because of their refusal to empower the most deeply oppressed members of their own society, their women. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________ (6) In his play Tennis in Nablus , Ismail Khalidi creates an emotional connection for his audience to the struggle of the Palestinians in their revolt against the British in the 1930s by describing a division within a family and using it as a metaphor for the divisive impact of colonization in Palestine then and afterwards. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________
THESIS STATEMENTS ON FICTION TEXTS: Novels
(7) In Reading Lolita in Tehran , Azar Nafisi demonstrates how literature is not only powerful enough to become a threat against oppressive regimes, but that it also emotionally liberates those who are covertly standing against the oppressive government. By studying Vladimir Nabokov’s novel Lolita in their secret book club, Nafisi and her students were able to relate to Lolita’s struggle but also reject being passive victims, which inspires the students to silently resist their oppressive government. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________ (8) In Azar Nafisi's novel, Reading Lolita in Tehran, she incorporates the classic American novel The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald in conjunction with telling the history of and her experiences in the Islamic Republic of Tehran to demonstrate how reconstructing and living in the past only dooms the future. TOPIC: _________________________________________________________________________ OPINION: _______________________________________________________________________ SO WHAT? ______________________________________________________________________
(1) Topic : American values of freedom versus slavery Opinion: American values of freedom contradict slavery So What? coming to terms with this hypocrisy hastens the end of slavery
(2) Topic : treatment of African-Americans during slavery versus now Opinion: the ways blacks suffered during slavery can still be seen today So What? African-Americans are still not truly free
(3) Topic : Sykes’ abuse of Delia Opinion: abuse results from need to assert masculinity So What? need to assert masculinity results from failure to be provider and protector. Implied: racism has emasculated, disempowered and embittered Sykes
(4) Topic : empathy for Delia Opinion: Hurston makes her reader feel empathy for Delia So What? empathy will lead to understanding the oppression resulting from race, gender, and class
(5) Topic : Palestinian revolt against the British Opinion: women are essential to revolution and real change So What? Palestinian revolt failed due to not empowering their own women
(6) Topic : Palestinian revolt against the British Opinion: emotional connection is made through divided family So What? divided family a metaphor for Palestine then and after
(7) Topic : Nafisi’s use of Lolita Opinion: Lolita helped the women to reject being passive victims So What? inspires silent resistance to government
(8) Topic : Nafisi’s use of The Great Gatsby Opinion: Nafisi uses The Great Gatsby to comment on the Islamic Republic So What? shows reconstructing and living in past dooms the future
Thesis Statements
What is a thesis statement.
A thesis statement argues an analytical idea. It is your own interpretation that you intend to back up with textual evidence; this is your reason and motivation for writing.
A strategy for crafting a thesis statement:
1. answer the "how" or "why":.
A thesis statement must be specific not only about the main idea, but how or why that main idea is logical or meaningful.
Weak Thesis Statement : Students should spend their free period time in the lounge.
- This is a main idea, but it does not explain how or why it makes sense.
Strong Thesis Statement: Students should spend their free period time in the lounge because students can socialize by interacting with other students in the open and free space.
- This is a main idea with a reason that explains why it’s a logical idea.
2. Experiment with structure:
Once you have clarified a specific main idea and why or how it makes sense, you can fool around with the structure of the sentence. Below are structural variations on that same strong thesis statement:
- Since free period time is for socializing, students should spend their free period time in the lounge because it’s the best place in the school for students to interact with each other.
- While the library is also a place where students socialize, the lounge is the best place for students to spend their free period time since an open and free space for students to interact in a non-academic setting.
3. Use a complex sentence:
Complex sentences , like the ones written above, work well for thesis statements. A complex sentence has more than one clause: a dependent clause and an independent clause.
An independent clause can stand on its own as a full sentence: Students should spend their free period time in the lounge.
A dependent clause cannot stand alone as a complete sentence; it always clarifies the independent idea:
- Since free period time is for socializing,
- Because it’s the best place in the school for students to interact with each other,
Below are some examples of complex sentence structures that can work for your thesis statement:
Examples of effective thesis statements
- By empathizing with the struggle some individuals face to feel free, Scout is able to surpass her initial misjudgments of others and recognize that each person deserves respect.
- Since Holden lacks self-confidence and is dissatisfied with who he is as an individual, he is unable to form meaningful relationships with other adults.
- Although Mr. Hundert has strong morals, he does not consistently act on his beliefs and thus fails to instill a sense of morality in his students.
- Although Myrtle initially embodies the glimpse of possibility and vitality in the Valley of Ashes, her desperate attempts to appear wealthy through Tom coupled with her exaggerated death highlight Fitzgerald's resentment toward the dismal reality of the American Dream.
- Since Achebe explores the complexity and dignity of the Igbo tribe's religion and culture, he combats the image of Africans as a crude and savage people.

Thesis Sentence
Ai generator.

Embarking on academic writing or preparing a pivotal argument for your essay? The heart of your piece lies in its thesis sentence . A succinct, powerful statement, the thesis guides readers, setting the tone for what’s to come. Discover prime examples, expert writing strategies, and invaluable tips to make your thesis stand out in a sea of academic prose.
What is the Thesis Sentence? – Definition
In simple terms, a thesis sentence is a one or two-sentence statement in an essay or research paper that precisely expresses the main idea or argument. It provides readers with an overview of the topic and the author’s stance on it, effectively laying the groundwork for the entire piece.
What is the best Example of a Thesis Sentence?
A standout thesis sentence offers clarity and a definitive perspective. For instance, if writing about the impact of social media on youth, a strong thesis might be: “Social media has a profound, often detrimental, effect on the mental well-being of today’s youth, as evidenced by rising rates of anxiety and decreased attention spans.” This statement not only presents a clear position but also hints at the evidence that the writer might use to support this claim.
100 Thesis Sentence Examples

Size: 145 KB
Crafting the ideal thesis sentence can elevate your essay or paper, presenting your argument in a clear and compelling manner. To provide you with inspiration and guidance, we’ve curated a collection of 100 exemplary thesis sentences. These samples, spanning various topics and disciplines, demonstrate the potential of a well-constructed thesis to anchor your work and captivate your audience.
- Electric vehicles have the potential to drastically reduce carbon emissions, leading us toward a sustainable future.
- Online education offers unparalleled flexibility but lacks the personal touch of traditional classroom settings.
- Globalization brings economic growth; however, it also exacerbates income inequalities within countries.
- Artificial intelligence poses both opportunities for efficiency and ethical dilemmas in decision-making processes.
- Childhood obesity is a growing concern, directly linked to sedentary lifestyles and processed food consumption.
- Mental health awareness needs greater emphasis in schools to combat rising cases of student depression.
- Space exploration provides not just scientific advancement but also unifies humanity in exploration.
- Modern architecture reflects a blend of functionality and aesthetics, representing societal values.
- Organic farming promises a sustainable solution to the environmental crises caused by conventional agricultural practices.
- Music therapy can play a pivotal role in the rehabilitation of patients with neurological disorders.
- Virtual reality transforms not only gaming but also medical training and therapy.
- Renewable energy sources are the key to addressing the looming global energy crisis.
- Animal testing is an ethically contentious issue, with alternatives emerging in recent scientific advancements.
- Social media platforms influence public opinion more powerfully than traditional media.
- Remote work culture has its merits in work-life balance but can erode team cohesion.
- Digital currencies represent the future of trade, though they introduce new regulatory challenges.
- Youth sports contribute not only to physical health but also to discipline and teamwork skills.
- Urban green spaces are essential for mental health, biodiversity, and counteracting pollution in cities.
- E-commerce has revolutionized shopping, yet it poses challenges to brick-and-mortar stores and local economies.
- Cultural exchange programs promote global unity and understanding, dismantling stereotypes.
- Preservation of indigenous languages is crucial for maintaining cultural heritage and diversity.
- The gig economy provides flexibility for workers but often lacks job security and benefits.
- Online privacy is endangered by the rise of data breaches and surveillance capitalism.
- Children’s exposure to screens impacts cognitive development and necessitates stricter parental controls.
- Nuclear energy remains a double-edged sword: a potent energy source but with disposal concerns.
- Modern tourism threatens historical sites but boosts local economies.
- Adopting pets from shelters can help reduce the stray animal crisis and promotes humane treatment.
- Mindfulness meditation reduces stress levels and has potential applications in clinical therapy.
- Fast fashion contributes to environmental degradation, advocating for sustainable consumption.
- Artificial sweeteners , while calorie-free, may have unforeseen health impacts.
- Urban farming holds the promise of food sustainability in densely populated cities.
- Mandatory voting laws could increase political participation but question voluntary democratic engagement.
- Homeschooling offers personalized education but might limit social interactions.
- Antibiotic resistance is a burgeoning global crisis spurred by over-prescription and misuse.
- Gender-neutral parenting challenges traditional norms and fosters an inclusive environment.
- Augmented reality will reshape education, making it more interactive and immersive.
- Binge-watching culture is reshaping entertainment consumption and impacts mental health.
- Marine conservation zones protect biodiversity and ensure sustainable fishing practices.
- Intermittent fasting has health benefits beyond weight loss, including cognitive and cardiac improvements.
- Digital detox retreats answer the modern need to disconnect and recharge mentally.
- Museums in the digital age must evolve to remain relevant and engage younger generations.
- Public transport investments reduce urban congestion and carbon footprints.
- Plant-based diets mitigate environmental degradation and promote holistic health.
- Consumer data collection straddles the line between business intelligence and privacy invasion.
- Urban vertical gardens can revolutionize urban agriculture and combat pollution.
- Telemedicine is revolutionizing healthcare access, especially in remote areas.
- Biodegradable packaging is the future of sustainability in the retail industry.
- Microfinancing empowers grassroots entrepreneurs, especially in developing countries.
- Language learning apps are democratizing education but cannot replace traditional methods entirely.
- Carpooling and ride-sharing reduce urban emissions and promote a shared economy.
- Theaters in the digital age face challenges from streaming platforms but offer a unique experience.
- 3D printing will revolutionize manufacturing, reducing waste and speeding production.
- Sleep’s role is underestimated in cognitive function and overall health.
- Ocean cleanup initiatives combat the plastic crisis but require global cooperation.
- Gamified learning platforms enhance student engagement and retention.
- Blockchain technology offers secure data management but is energy-consuming and requires widespread adoption.
- Historical fiction novels blend factual events with imaginative storytelling, enhancing both education and entertainment.
- Zero waste initiatives promote sustainable living, combating the throwaway culture of modern society.
- Telecommuting benefits the environment and worker satisfaction, but challenges team dynamics.
- Green architecture is the intersection of design and sustainability, making it vital for future urban planning.
- Astronomical tourism opens the wonders of the universe but requires careful management to protect natural nightscapes.
- The rise of abooks redefines reading, making literature accessible in our multitasking age.
- Gene editing techniques hold promise for medical breakthroughs, yet they introduce ethical dilemmas.
- Agroforestry practices enhance biodiversity, soil health, and offer economic benefits to farmers.
- Veganism goes beyond diet; it’s an ethical stance against animal exploitation.
- Cloud computing streamlines data storage but introduces security concerns.
- Holistic medicine integrates mind and body healing, challenging conventional medical paradigms.
- Subscription-based business models resonate with modern consumers, ensuring steady revenue for businesses.
- Cultural immersion travel deepens understanding, combating shallow tourist experiences.
- Biometrics is revolutionizing security, yet poses personal privacy risks.
- Freelance economies offer freedom and flexibility, contrasting the stability of traditional job markets.
- Biodiversity conservation is essential for ecosystem stability and the survival of humanity.
- Mental health days acknowledge the importance of psychological well-being in the workplace.
- Solar power technology is rapidly advancing, making it a feasible replacement for fossil fuels.
- Civic education is crucial in fostering informed and active citizens in democracies.
- Edible insect consumption addresses food sustainability and introduces new culinary experiences.
- Urban beekeeping supports declining bee populations and promotes local food production.
- Mobile health apps enhance personal health management but require stringent data protection measures.
- Trade school education is equally valuable as traditional college degrees, offering practical skills.
- Elderly care robots alleviate human caregiver burdens but prompt questions about emotional connections.
- Second language acquisition enriches cognitive abilities and cultural understanding.
- Craftsmanship in the digital age celebrates hands-on creation amidst automated mass production.
- Ocean wave energy conversion is a promising, untapped sustainable energy resource.
- Diverse representation in media is essential for societal inclusivity and combating stereotypes.
- Microplastics in water sources pose severe environmental and health concerns.
- Fair trade products support ethical consumerism and uplift marginalized producers.
- Hybrid learning models combine online and offline methods, optimizing educational outcomes.
- Multi-generational households foster family bonding but present unique challenges.
- Urban rewilding projects revitalize natural habitats in cityscapes, supporting biodiversity.
- Digital art forms elevate traditional art through technology, yet spark debates on authenticity.
- Food forest initiatives enhance sustainable agriculture, merging productivity with ecosystem health.
- Biophilic design in offices boosts worker productivity and well-being.
- Rainwater harvesting is a sustainable solution to global water scarcity issues.
- Paperless offices reduce environmental impact and increase organizational efficiency.
- Drama therapy offers transformative healing, using performance as a therapeutic tool.
- Ethical AI development balances technological advancement with humane considerations.
- Micro-adventures encourage local exploration, redefining the concept of travel.
- Refurbishing old buildings preserves historical heritage and is environmentally responsible.
- Inclusive toy designs reflect diverse societies, promoting acceptance from a young age.
- Afforestation projects combat deforestation, sequester carbon, and restore habitats.
Thesis Sentence Examples for Essay
Crafting an engaging thesis statement for an essay is crucial. It provides clarity, introduces the main topic, and sets the essay’s tone. This concise yet impactful statement is what keeps readers invested, guiding them through the content.
- Climatic changes influence biodiversity, challenging ecosystems worldwide.
- Digital currencies have revolutionized the global financial system, making transactions more transparent.
- Remote working is a viable alternative to traditional office environments, promoting flexibility.
- Ancient civilizations left imprints on modern cultures, influencing art, politics, and philosophy.
- E-learning platforms provide democratized education, making knowledge accessible to all.
- Artificial intelligence is redefining industries, enhancing efficiency, and customer experiences.
- Organic farming supports sustainable agriculture, providing healthier produce options.
- Sports and physical activities contribute to improved mental health and overall well-being.
- Alternative energy sources are the key to addressing global warming and ensuring sustainable energy.
- The role of media is pivotal in shaping public opinion, especially in this digital age.
Thesis Sentence Examples for High School
High school essays require precise thesis statements, laying the foundation for budding scholars to express their arguments. A strong thesis guides readers, ensuring they grasp the main idea being conveyed.
- Uniforms in schools promote equality among students, reducing social discriminations.
- Extracurricular activities enhance the overall development of high school students.
- Advanced technology has reshaped classroom dynamics, promoting interactive learning.
- Peer pressure in high schools plays a significant role in shaping teenagers’ personalities.
- Summer vacations provide students with a break, enhancing productivity during academic years.
- Counseling sessions in schools benefit students, addressing their emotional and academic needs.
- School libraries encourage reading habits, supporting comprehensive learning.
- Health education should be a mandatory part of the high school curriculum.
- Bullying in schools affects students’ mental health, necessitating strict preventive measures.
- Homework assignments reinforce classroom teachings, ensuring better understanding.
Thesis Sentence Starter Examples
Kickstarting an essay with a compelling thesis statement ensures the reader’s instant engagement. These starter thesis examples set the stage for detailed arguments and discussions.
- Given the rising pollution, eco-friendly vehicles are the need of the hour.
- In the realm of literature, Shakespeare’s works stand unmatched in their depth.
- Considering the health benefits, regular exercise should be a daily routine for everyone.
- Amidst technological advancements, preserving privacy is paramount.
- With the surge in online communication, face-to-face interactions remain invaluable.
- Observing the economic patterns, sustainable business models prove more beneficial long-term.
- Facing the challenge of global warming, renewable energy sources become indispensable.
- Through centuries of art evolution, Renaissance art holds a special place in history.
- Given the prevalence of mental health issues, therapy and counseling are essential services.
- In light of recent events, community building becomes vital for societal progress.
How do you start a thesis sentence?
A thesis sentence serves as the cornerstone of an essay, offering a concise summary of the main idea or claim. Crafting an impactful thesis sentence requires precision and clarity. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you start:
- Understand the Question: Before diving in, understand the essay prompt or research question thoroughly. Knowing the question helps you tailor the thesis effectively.
- Brainstorm: Jot down initial ideas that come to mind. This rough list can be refined later.
- Narrow Down: Ensure your thesis focuses on a specific aspect instead of being overly broad. For instance, instead of “Eating vegetables is good,” specify why and how, like “Eating leafy greens aids digestion due to their high fiber content.”
- Take a Stand: A thesis isn’t just a statement; it often presents an argument. Make sure you’re presenting a perspective or an opinion.
- Be Clear and Concise: Avoid jargon and complicated sentences. Keep it direct and to the point.
- Avoid Clichés and Generalizations: Using worn-out phrases or overly generalized statements weakens your thesis.
- Ensure it’s Debatable: An effective thesis often presents an argument that could be challenged. For instance, “Social media affects mental health” is more debatable than “The earth revolves around the sun.”
- Revise and Refine: After drafting, revisit your thesis. Can it be clearer or more concise? Does it thoroughly represent what your essay will discuss?
- Seek Feedback: Sharing your thesis with peers or mentors can provide valuable insights.
- Position Appropriately: Typically, the thesis is placed at the end of the introduction, setting the stage for the rest of the essay.
What is a thesis sentence in an essay?
A thesis sentence, often referred to as a thesis statement, is a single sentence in an essay (usually appearing in the introduction) that encapsulates the essay’s main idea, argument, or focus. It offers readers a lens through which they can understand the purpose and direction of the essay.
Characteristics of a Thesis Sentence:
- Specificity: It pinpoints the main topic of your essay, avoiding vague generalizations.
- Assertiveness: It takes a clear stance or position on the topic.
- Relevance: It sets the tone and direction for the entire essay, ensuring that readers know what to expect.
- Debatable Nature: Good thesis sentences can be argued, offering a perspective or viewpoint on a subject.
- Clarity: It’s articulated in clear and straightforward language.
- Conciseness: It’s typically just one or two sentences long, no matter how complex the topic might be.
- Guide for the Reader: Think of it as a map or guidepost for your readers, giving them a clear idea of what the essay will discuss.
For instance, in an essay about the effects of technology on communication, a thesis sentence might be, “While modern technology has many benefits, its overuse has led to decreased face-to-face communication, leading to feelings of isolation in individuals.” This statement provides a clear position and direction for the essay.
How do you write a Thesis Sentence? – Step by Step Guide
Crafting a compelling thesis sentence is crucial, as it sets the tone and direction for the entirety of your essay or research paper. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure your thesis sentence is effective and impactful:
- Research Your Topic: Before you can form an opinion or argument, you need to have a clear understanding of your topic. Dive into trusted resources and gather information.
- Understand the Prompt: If you’re writing an essay based on a prompt, make sure you fully grasp what’s being asked.
- Brainstorm Ideas: Note down any thoughts, perspectives, or arguments related to your topic. This brainstorming can form the foundation of your thesis.
- Narrow Your Focus: A good thesis is specific and to the point. Narrow down your topic to a specific aspect that you want to focus on.
- Formulate an Opinion: Your thesis should not just state a fact. It should convey an opinion or take a stance on an issue.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Avoid complex jargon or overly long sentences. Your thesis should be understandable to a broad audience.
- Ensure It’s Debatable: Your thesis should present a claim or argument that others could reasonably dispute.
- Position Properly: Typically, your thesis sentence should be placed at the end of your essay’s introductory paragraph.
- Revise and Refine: Don’t hesitate to revisit and tweak your thesis as your essay evolves. Sometimes, as you write and explore your topic further, your thesis might need adjustment.
- Seek Feedback: Have peers or instructors review your thesis sentence. They might offer invaluable insights or ways to strengthen it.
Tips for Using Thesis Sentences
- Stay Consistent: Ensure that your essay remains consistent with your thesis. Each paragraph should contribute to or elaborate on the argument or claim you’ve made.
- Avoid Generalizations: Phrases like “Everyone knows,” “Since the beginning of time,” or “All people think” tend to weaken your thesis. Stick to specifics.
- Steer Clear of Clichés: Originality strengthens your thesis. Relying on clichéd phrases or ideas can dilute its impact.
- Stay Flexible: As you delve deeper into writing your essay, you might find more relevant points that can make your thesis even stronger. Don’t be rigid; be ready to adjust your thesis if needed.
- Use Strong Language: Words like “might,” “maybe,” “perhaps,” can make your thesis sound uncertain. Choose assertive language to convey confidence in your argument.
- Support Your Thesis: Throughout your essay, continuously provide evidence and examples that back up the claim made in your thesis.
- Reiterate Your Thesis: In your conclusion, restate your thesis (though not verbatim) to remind readers of your main argument as you wrap up your essay.
Remember, your thesis sentence is the backbone of your essay. It sets the tone, direction, and foundation upon which the rest of your arguments and points will be built. Crafting it with care will set the stage for a compelling and well-structured essay.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Complex Sentence: Definition, Explanation, Types And Examples

Allison Bressmer

There are four categories of sentences: simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex. Each type of sentence has its own essential ingredients.
For the complex sentence , those ingredients are an independent clause and at least one dependent clause .
As you continue reading, I’ll show you how you can mix those two ingredients (the independent and dependent clauses) in different ways to whip up complex sentences.
What are Complex Sentences?
What are independent and dependent clauses, how to create complex sentences, what’s the difference between complex and compound sentences, what’s the difference between complex and compound-complex sentences.
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and a dependent clause. Here’s an example of a complex sentence:
Because my pizza was cold, I put it in the microwave.
This sentence has an independent clause (“I put it in the microwave”) and a dependent clause (“Because my pizza was cold”) so it’s a complex sentence.
Before we get further into examples of complex sentences, let’s do a quick refresher on clauses.
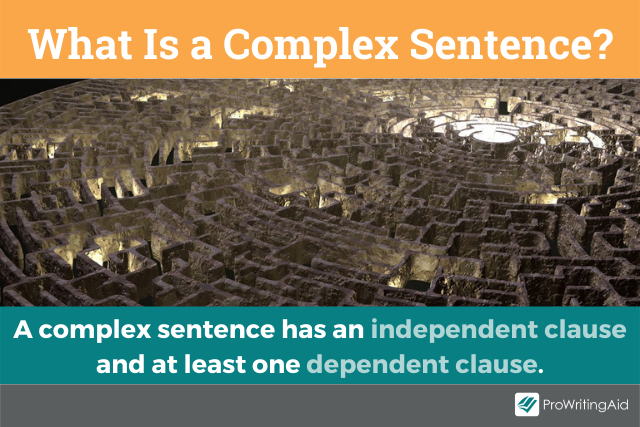
A clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a verb.
The difference between independent and dependent clauses is this: an independent clause can stand alone as a sentence and a dependent clause cannot.
What Is an Independent Clause?
An independent clause is a simple sentence. Those two terms, independent clause and simple sentence , mean the same thing.
An independent clause includes a subject and a verb , and expresses a complete thought— just like a simple sentence does.
An independent clause makes sense on its own. In these examples, the subjects and verbs are in bold.
- I had a rough start to my birthday today.
- I slept through my alarm.
- My boss was angry about my subsequent late arrival.
- Someone stole my lunch from the office fridge!
- No one even brought a cake to celebrate my birthday.

What Is A Dependent Clause?
A dependent clause also contains a subject and a verb , but does not express a complete thought .
It depends on connection to an independent clause to make sense. Another name for a dependent clause is subordinate clause.
A dependent clause often starts with a subordinating conjunction , a word which establishes a relationship between the information in the subordinating clause and the independent clause it is connected to.
These relationships include cause/effect, time, place, condition, comparison, and concession.
In these examples of dependent clauses, the subjects and verbs are in bold, and the subordinating conjunctions are highlighted.
- Because I left work late
- Since it was dark when I got back to my house
- While I was careful to observe my surroundings
- As soon as I opened the door
Did you notice the difference between these examples and the independent clauses?
With the independent clauses, we know what’s happening by the end of the sentence. This poor person, let’s call her Joanne, has had a lousy day.
With the dependent clauses, we are “left hanging,” and it seems as if Joanne’s day may have gotten even worse!
I wish we could find out if she at least got home safely on her forgotten birthday!

Actually, I think I have a solution. We can use those dependent clauses as one of the ingredients in our about-to-be-created complex sentences. Then we’ll get the complete story.
Complex sentences include an independent and at least one dependent clause.
Though the dependent clause cannot stand alone as a sentence, it does add to the meaning of the independent clause.
In a complex sentence, the independent and dependent clauses can be put together in a variety of ways. For example:
Dependent followed by independent: In this format, put a comma after the dependent clause.
- Because I left work late, I just wanted to get home and relax.
(The dependent clause tells us why Joanne wanted to get home)
Independent followed by dependent: In this format, no comma is needed.
- I was feeling extra stressed and tired since it was dark when I got back to my house.
(The dependent clause tells us why Joanne was extra stressed and tired)
Dependent both before and after independent: In this format, a comma is required after the first dependent clause.
- While I was careful to observe my surroundings, I almost tripped walking up to my door since I couldn’t see in the darkness.
(The dependent clause establishes a relationship of contrast with the independent clause)
Two dependents followed by an independent clause: In this format, put a comma after each dependent clause.
- As soon as I opened the door, and after I had kicked off my shoes, I had a sense that someone was in my house.
(The dependent clauses tell us when Joanne experienced that sense)
Do you see how those ingredients work together to create a complete thought?
While the independent clause doesn’t need the dependent clause to survive as a sentence, the dependent clause adds to the meaning of that dependent clause.
Here are a couple more examples to let you know what ultimately happened at the end of Joanne’s lousy day.
Take notice of their respective structures—the order of the independent (IC) and dependent clauses (DC), and where the commas (if needed) appear.
- I continued to walk down the hallway even though I was quite scared. (IC-DC)
- After letting out what I thought was an intimidating yell, I was greeted by five of my close friends yelling “Surprise!” (DC, IC)
- We all had a good laugh because of my lame attempt to scare away the “bad guys.” (IC-DC)
- Since my friends gifted me with a lovely surprise and chocolate cake, even though my birthday started out terribly, it ended in the best way possible. (DC, DC, IC)
Happy Birthday Joanne! To celebrate, I’ll show you one more way to structure a complex sentence.
Using A Dependent Clause to Interrupt an Independent Clause in a Complex Sentence
All the examples so far have shown complex sentences that include an independent clause and a dependent clause placed one after the other in one order or another.
But sometimes, a dependent clause can be put right in the middle of an independent clause. In this format, the dependent clause should be surrounded with commas.
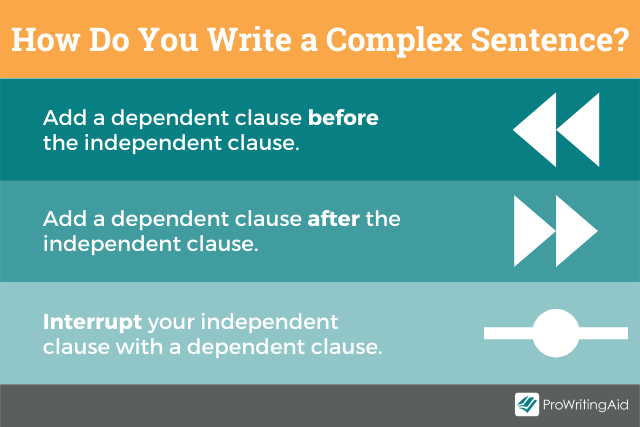
In these examples, the dependent clause is in bold. If you remove it from the sentence, you’re left with an independent clause.
- The dog, because he was so friendly , was adopted quickly.
- The meal, even though it was exceptional , was expensive.
- The students, whatever their skill levels , all showed improvement.
While a complex sentence includes an independent and at least one dependent clause, a compound sentence includes two independent clauses.
In a compound sentence, the independent clauses can either be joined with a semicolon or with a comma + coordinating conjunction combination.
Examples of Compound Sentences Using Semicolons
A semicolon has the combined power of both a period and a comma. It is strong enough to create a stop—a distinction—between two independent clauses, but is more gentle than a period.
The semicolon doesn’t create a full stop; it maintains a connection between the clauses, which is where you see its comma function.
You would use a semicolon when your independent clauses are closely related and you don’t want to create a full stop between them.
- I took a walk today ; the fresh autumn air was invigorating.
- The leaves created a rainbow of colors ; the foliage was enchanting.
- I returned home feeling both calm and energized ; the beauty of nature is truly special.
Examples of Compound Sentences Using Coordinating Conjunctions + Comma
Coordinating conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses that are of equal value, such as two independent clauses.
Each of those clauses can stand on its own as a sentence.
The seven coordinating conjunctions are and, but, or, nor, so, yet, for.
A coordinating conjunction + comma combination has the power to connect—to hold together—two independent clauses.
A comma alone isn’t enough and produces an error called a comma splice.
In each of the following examples, the coordinating conjunction + comma combination is in bold.
- I ordered a salad ,but I really wanted a big bowl of spaghetti.
- The spaghetti smelled so good ,and I can’t stop thinking about it.
- I’m going back to that restaurant ,so I can order what I really want.
A compound sentence, unlike a complex sentence, only includes independent clauses. It does not include any dependent clauses.
The compound-complex sentence includes at least two independent clauses (remember: the complex sentence only has one) and one or more dependent clauses.
Examples of Compound-Complex Sentences
In these examples, the independent clauses are in bold.
- After I ordered my spaghetti, I felt happy , and I couldn’t wait to sit down and eat !
- I think I could eat pasta every day , even though I probably shouldn’t, and I would enjoy every bite .
- Because I want to eat healthy and since I’ve satisfied my craving, I’ll get back to salad tomorrow, but I’ll probably be back for more spaghetti before too long!
How Complex Sentences Help Your Writing
Adding variety to your sentence structure is important to good writing. If you rely too much on one style of sentence, your work will become monotonous and take on a droning effect. No one wants that!
By understanding how complex sentences work, you can add them to your work with confidence.
And if you need a boost for your confidence while you’re still practicing, run your work through ProWritingAid’s Sentence Structure Report.
It will help you see where your sentence structure may be repetitive and offer suggestions for how to add some variety.
Although the example below provides some really interesting details, the structure is repetitive, in fact, all the sentences start with a subject.
Including complex and varied sentence structures is essential if you want to keep your reader's attention.
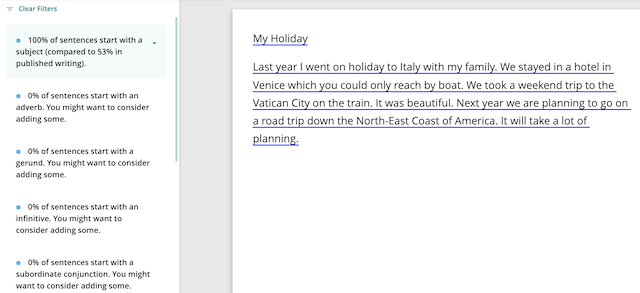
Try the Sentence Structure report with a free ProWritingAid account.
As a writer, it’s important to understand the tools of your trade. Sentence structure is one of those tools.
Take the time to notice how other writers use simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences in their work.
Observe and learn as you read and then be inspired!
Are you prepared to write your novel? Download this free book now:

The Novel-Writing Training Plan
So you are ready to write your novel. excellent. but are you prepared the last thing you want when you sit down to write your first draft is to lose momentum., this guide helps you work out your narrative arc, plan out your key plot points, flesh out your characters, and begin to build your world..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Allison Bressmer is a professor of freshman composition and critical reading at a community college and a freelance writer. If she isn’t writing or teaching, you’ll likely find her reading a book or listening to a podcast while happily sipping a semi-sweet iced tea or happy-houring with friends. She lives in New York with her family. Connect at linkedin.com/in/allisonbressmer.
Most Popular
12 days ago
How to Use Apostrophes
Alot or a lot.
11 days ago
Damnit or Dammit: How You Should Be Writing
What is a complex sentence.

Ever tried to build a piece of IKEA furniture without a manual? That’s what writing can feel like if you don’t understand complex sentences. But if you do know how to use them, your writing transforms from basic assembly instructions to a symphony of ideas. Let’s see how all this works. And we promise, no Allen wrenches are required.
What is a Complex Sentence?
We all know from the early days of schooling that a few words together make sentences. They’re the building blocks of our communication, much like the tiny Lego pieces that hold our grand constructions together. Sentences come in different flavors: simple, compound, and complex, each with its characteristics. They can express statements, questions, exclamations, or commands, each performing distinct functions in communication.
A complex sentence is made up of one independent clause and at least one dependent clause. The independent clause is a complete thought that can stand alone, while the dependent clause, though related, cannot exist separately and needs the independent clause to make sense.
So, how do you spot these tasty sentences? Look for sentences that have a main clause and one or more subordinate clauses. Subordinate clauses often start with words like “because,” “although,” “since,” “if,” “when,” and “while.” For example:

Other ways to identify a complex sentence is by relative pronouns and punctuation. Pronouns like “which”, “that”, “who”, “whom”, “whose” introduce clauses that modify nouns, and a comma often separates the dependent clause from the independent clause if the dependent clause comes first.
Get all your complex sentences checked for punctuation
When to use complex sentences vs simple sentences.
Complex sentences are your best friend when you want to show the relationship between ideas, add depth to your writing, and convey more information. They allow the writer to connect ideas elegantly and emphasize certain points over others. They are perfect for explanations, descriptions, and showing cause and effect. Use them to:
| Context | Example | Details |
| Provide detailed explanations | “She stayed up late because she had to finish her project.” | Complex sentences can help you elaborate on the reasons behind actions, providing a fuller picture for your reader. |
| Show cause and effect | “He missed the bus since he woke up late.” | These sentences clearly demonstrate the relationship between events, making it easier for readers to understand the sequence and connection between actions. |
| Add depth to descriptions | “The campus feels peaceful when the sun sets and the lights begin to glow softly in the evening.” | By combining descriptive elements, complex sentences can create vivid imagery and a more immersive experience for the reader. |
| Contrast ideas | “Although the library is often crowded, it remains the best place to study because of its quiet zones and resources.” | Using complex sentences allows you to present contrasting ideas within a single sentence, highlighting differences and nuances. |
| Explain conditions | “If you complete your assignments on time, you can enjoy the weekend without stress.” | Conditional statements help to explain potential outcomes based on certain conditions, adding clarity to your writing. |
| Illustrate relationships between actions | “While she listens to music, she completes her homework more efficiently.” | These sentences can show how different actions are related, often indicating that one activity influences or happens simultaneously with another. |
However, try not to overuse them. In certain types of writing, like instructions or action scenes, shorter sentences might work better to maintain clarity and pace. Simple sentences make instructions easier to follow and action scenes remain dynamic and fast-paced.
- Action Scenes : “She ran to the door. She opened it quickly.”
Simple sentences are effective in action scenes because they create a fast-paced, dynamic flow that mirrors the urgency and rapid progression of events. They allow the reader to follow the action easily without getting bogged down by complex structures.
2. Instructions : “Press the button. Wait for the light to turn green.”
When giving instructions, simplicity is key to prevent confusion. Simple sentences break down tasks into clear, manageable steps, making it easier for the reader to follow along and execute the instructions correctly.
3. Conveying Urgency: “Call 911. Stay calm.”
In emergencies or situations requiring immediate action, simple sentences deliver the message quickly and unambiguously, ensuring that the reader understands exactly what needs to be done without delay.
4. Highlighting Key Points: “Study hard. Get good grades.”
When you want to emphasize important points or principles, simple sentences can make your message more impactful and memorable by stripping away any unnecessary words.
5. Introducing New Concepts: “Photosynthesis is a process. Plants use it to make food.”
When introducing new or complex concepts, starting with simple sentences helps to build a foundational understanding before delving into more intricate details. This approach ensures that the reader grasps the basics before moving on to more complex explanations.
6. Summarizing Information: “Exercise regularly. Eat a balanced diet.”
Simple sentences are excellent for summarizing key takeaways or providing concise advice. They distill information into its most essential elements, making it easy for the reader to remember and apply.
7. Creating Dramatic Effect: “The lights went out. Silence filled the room.”
In narrative writing, simple sentences can be used to create dramatic pauses or build suspense, allowing the reader to feel the intensity of the moment.
How to Make Complex Sentences
Creating complex sentences depends on the context and style of your writing. But first of all, it requires an understanding of a few important grammar concepts that often work together in a team when it comes to this type of sentence. They are independent clauses, dependent clauses, and subordinating conjunctions.
- An independent clause is like an adult who can live on their own. It expresses a complete thought and can stand alone as a sentence.
- A dependent clause , on the other hand, is like a teenager who still needs support. It cannot be used on its own and needs to be connected to an independent clause.
- Subordinating conjunctions are the glue that holds complex sentences together. They introduce dependent clauses and show the relationship between the dependent and independent clauses. Common subordinating conjunctions include “although,” “because,” “since,” “unless,” “while,” and “if.”

Now you know the elements and the structure of complex sentences. All you need to do is to practice. Mastering complex sentences is an invaluable skill for any writer. By understanding how to use independent and dependent clauses along with subordinating conjunctions, you can add depth and clarity to your writing. Complex sentences help you convey complicated ideas, show relationships between concepts, and create a more engaging and sophisticated narrative. Practice incorporating complex sentences into your writing to enhance your communication and captivate your readers with your command of language.
Why are complex sentences important?
Complex sentences are important because they allow writers to show the relationship between ideas, add detail, and convey more information in a single sentence. They make writing more engaging and nuanced.
What are some common subordinating conjunctions?
Some common subordinating conjunctions include because, although, since, if, when, while, even though, unless, and as soon as.
Can a complex sentence start with a dependent clause?
Yes, a complex sentence can start with a dependent clause. For example, “Although it was raining, we went for a walk.” In this case, the dependent clause “Although it was raining” comes first, followed by the independent clause “we went for a walk.”
How can I practice writing complex sentences?
You can practice writing complex sentences by combining simple sentences using subordinating conjunctions, expanding your ideas with additional details, and reading examples of complex sentences in well-written articles or books. Writing exercises that focus on sentence combining can also be helpful.
What is the difference between a complex sentence and a compound sentence?
A complex sentence contains one independent clause and at least one dependent clause, while a compound sentence contains two or more independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction (e.g., and, but, or) or a semicolon. For example, “She finished her assignment, and she went to bed” is a compound sentence, whereas “Although she was tired, she finished her assignment before going to bed” is a complex sentence.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from Grammar Guides

Remember Me
Is English your native language ? Yes No
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
Compound-Complex Sentence
Explanation.
The COMPOUND-COMPLEX SENTENCE is composed of at least three sets of subjects and verbs (clauses), at least two independent and one dependent. This more advanced structure allows the writer to show relationships between multiple ideas. You might think of this as a sort of verbal equation:
(Subordinating Word + S V ), S V+ S V . (dependent clause), independent clause/independent clause
When they observed fossils and rock strata, ancient humans puzzled about them, but no one understood their significance.*
The equation can be organized in other ways as well; the dependent clause may modify the second independent clause, and then it would come as close to that as possible, which would put it at the end of the equation:
S V+ S V (Subordinating Word + S V ). independent clause/independentclause dependent clause
Aristotle, Avicenna, and Leonardo da Vinci speculated about geology; however, fully-formed theories were n’t developed until the eighteenth century, when Abraham Werner and James Hutton devised theories at about the same time.
Or, it might modify the first independent clause and be most logically placed nearest that, or right in the middle:
SV (Subordinating Word + SV) /SV. independent clause dependent clause independent clause.
Werner’s theory hypothesizes that all Earth’s rocks were deposited in a global flood, so it is often referred to as the Neptunist theory.
Added to this flexibility is the fact that a compound-complex sentence might contain more than three clauses:
(Subordinating Word + SV), SV(Relative Pronoun + V)(Subordinating word + SV)/SV (Subordinating Word + S(subordinating word +SV)V). (dependent) independent (dependent)(dependent)/independent (dependent within dependent).
Although some of Werner’s terminology is occasionally used by geologists today, the Neptunist theory has been supplanted by James Hutton’s Plutonist theory, which suggests that all rocks are being constantly reformed by heat in the Earth’s core; in fact, Hutton is often considered the father of modern geology, since most of the ideas that he formulated have proven to be correct.
Holy Cats! Whew! For the most part, you will seldom run into a situation where you need to construct such a dense and chewy sentence, but it's good to know how to build more advanced sentence structures so that you can connect ideas for your reader, and also so you can vary your sentence structure. Let’s practice on something a little less convoluted.
Here are three related sentences:
1) During the Cambrian Era, none of the continents existed as we know them today. (complex sentence)
2) Sea level was much higher. (simple sentence)
3) Very little water was tied up in ice. (simple sentence)
While it is acceptable to leave these three sentences separate, the reader has no hint of the relationships between them. The two main points seem to be about the continents and the sea level, so let’s connect them with a coordinating conjunction:
1) During the Cambrian Era, none of the continents existed as we know them today, and sea level was much higher.
2) Very little water was tied up in ice.
The final sentence helps explain why the sea level was much higher, so it makes sense to attach that to the compound sentence with a subordinating conjunction, like this:
1) During the Cambrian Era, none of the continents existed as we know them today, and sea level was much higher because very little water was tied up in ice.
*All examples based on information from “Geological Time Scale.” Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation. 26 March 2015. Web. 31 March 2015.
Learn more about " Complex Sentences " by reviewing the handout.
Learn more about " Compound Sentences " by reviewing the handout.
We’re Sorry!
This website is unavailable in your location.
It appears you are attempting to access this website from a country outside of the United States, therefore access cannot be granted at this time.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Complex Sentence Thesis Formula is a structured approach to crafting thesis statements that incorporate intricate ideas within a single sentence. It involves constructing a thesis statement using a complex sentence structure, which includes one main clause (the claim) and one or more subordinate clauses (the reasons or supporting points).
Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don't use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences. Contentious: Your thesis shouldn't be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
•A strong thesis statement makes a complex and unique argument that someone could reasonably object to; the rest of the essay should then defend that argument. » For instance, "Andrew Carnegie was extremely wealthy" is not a sufficiently insightful the- ... sentences in a thesis driven essay; always refer to your assignment or sample ...
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
Where does a Thesis Statement go? Your thesis should be stated somewhere in the opening paragraphs of your paper, most often as the last sentence of the introduction. Often, a thesis will be one sentence, but for complex subjects, you may find it more effective to break the thesis statement into two sentences.
Also remember that each paragraph, while part of the whole essay, needs a definite shape of its own. That shape is: A claim (topic sentence) in support of your argument. The evidence (mostly textual) in support of that claim. Your analysis of that evidence and how it relates back to your thesis. Without this part of the paragraph, you expect ...
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
A thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of your introduction. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an ...
THESIS STATEMENTS ON NON-FICTION TEXTS: (1) In Field Notes from a Catastrophe, Elizabeth Kolbert seeks to use the evidence she has collected across her years of worldwide travel to show how we should best address climate change. Kolbert uses the island of Samsø to support her case for the mass implementation of alternative energy sources, but ...
Complex sentences, like the ones written above, work well for thesis statements.A complex sentence has more than one clause: a dependent clause and an independent clause. An independent clause can stand on its own as a full sentence: Students should spend their free period time in the lounge.. A dependent clause cannot stand alone as a complete sentence; it always clarifies the independent idea:
After the topic sentence, include any evidence in this body paragraph, such as a quotation, statistic, or data point, that supports this first point. Explain what the evidence means. Show the reader how this entire paragraph connects back to the thesis statement. Paragraph #2. Possible topic sentence for Paragraph #2:
100 Thesis Sentence Examples. Details. File Format. PDF. Size: 145 KB. Download. Crafting the ideal thesis sentence can elevate your essay or paper, presenting your argument in a clear and compelling manner. To provide you with inspiration and guidance, we've curated a collection of 100 exemplary thesis sentences.
Here's an example of a complex sentence: Because my pizza was cold, I put it in the microwave. This sentence has an independent clause ("I put it in the microwave") and a dependent clause ("Because my pizza was cold") so it's a complex sentence. Before we get further into examples of complex sentences, let's do a quick refresher ...
3. Conveying Urgency: "Call 911. Stay calm.". In emergencies or situations requiring immediate action, simple sentences deliver the message quickly and unambiguously, ensuring that the reader understands exactly what needs to be done without delay. 4. Highlighting Key Points: "Study hard.
Here are three related sentences: 1) During the Cambrian Era, none of the continents existed as we know them today.(complex sentence) 2)Sea levelwas much higher.(simple sentence) 3) Very little water was tied up in ice.(simple sentence) While it is acceptable to leave these three sentences separate, the reader has no hint of the relationships ...
Compound-complex sentence. A compound-complex sentence consists of at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause. There are many ways to put together a compound-complex sentence. You can tell that it's a compound-complex sentence by getting rid of the conjunctions and looking at each clause.
See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Learn how to properly connect independent and dependent clauses to write complex sentences.
DEKALB COUNTY, Ga. — The DeKalb County Police Department is investigating a homicide that occurred at an apartment complex. Police say they responded to Peachtree Creek Circle just after 6 p.m ...