

10 Feasibility study and business plan differences you should know
by Naiyer Jawaid | Nov 8, 2021 | Development , Real Estate | 5 comments

Feasibility study and business plan differences are subtle. In this post we will discuss 10 differences will help you to evaluate and differentiate between a feasibility study and a business plan.
Do you know what is a feasibility report? Do you know what is a business plan? Can you easily differentiate between a feasibility report and a business plan?
It’s easy! Just read out through the article and it will all be easy.
Let’s start by learning about a feasibility report:
A feasibility study is a formal document that assist in the identification and investigation of a proposed project. We can identify the project's weaknesses and strengths with the support of a feasibility study report, which saves us time and energy. We can determine whether the suggested idea will be lucrative and practicable in the future.
Before investing in a project, it is critical to determine if the project will be beneficial in the long run. The organization also needs to know how much the project will cost. Overall, a feasibility analysis indicates whether the firm should invest or continue with the project.

You should also like to read When to do feasibility study?
Now let us learn about business plan:
A business plan is a formal document that contains the goals/ objective of the business, the time in which the goal will be completed and the strategies that can be adopted to reach the specific goal.
A business plan is a necessary document for every new firm to have in place before it can begin operations. Writing a credible business plan is typically a requirement for banks and venture capital companies before contemplating granting funding to new enterprises.
It is not a smart idea to operate without a business strategy. In fact, very few businesses can survive for long without one. There are many more advantages to developing and keeping to a strong business plan, such as the ability to think through ideas without investing too much money and, eventually, losing money. Business plans are used by start-ups to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
A feasibility study is used to assess if a business or a concept is viable. After the business opportunity has been identified, the business strategy is produced. “A feasibility study is carried out with the goal of determining the workability and profitability of a company venture. A feasibility study is conducted before any money is committed in a new business endeavour to see whether it is worth the time, effort, and resources.

Similarities between a Feasibility study and a business plan
It's essential to analyse the similarities between a feasibility study and a business plan because they're both implemented altogether in same ways to help you build a lucrative company. The following are some of the similarities between the two documents:
Time: Both the reports are completed before the business begins and can be repeated afterwards to decide the next stages for new concepts.
Input: Both Feasibility report and the Business plan include input from a variety of people or departments with a variety of talents.
Format: Both report formats incorporate other documents that are gathered in order to create the report.
Components: Examining the target market, market circumstances, and financial expenses are some of the topics examined.
Use: Both may be displayed to potential investors and can assist the organization's management in making choices.
Organizations uses a business plan and a feasibility study as analytical and decision-making tools.
Although the three tools can be used in conjunction with one another in decision-making processes, they each have their own strengths and weaknesses, and they appear to target and address separate processes.
You might also like to read How to write a feasibility study report?

Now let us evaluate the difference between feasibility report and a business report-
- A feasibility study is conducted to determine the viability and profitability of a business endeavour. A feasibility study is conducted before any money is committed in a new business endeavour to see whether it is worth the time, effort, and resources.
A business plan, on the other hand, is created only when it has been determined that a business opportunity exists and that the endeavour is about to begin.
- A feasibility report is the first step and after that a business plan is made to be implemented, without feasibility report a business plan cannot be made.
- A feasibility study contains computations, research, and projected financial forecasts for a company possibility. A business plan, on the other hand, is mostly comprised of tactics and strategies to be applied to establish and expand the company.
- A feasibility study is concerned with the viability of a business concept, but a business plan is concerned with the development and sustainability of a company.
- A feasibility report informs the entrepreneur about the profit potential of a company concept or opportunity, whereas a business plan assists the entrepreneur in raising the necessary start-up cash from investors.
- Key components of a feasibility study and a business plan
| Title page | Executive summary |
| Table of contents | Company summary |
| Executive summary | Market analysis |
| Market feasibility | Management team |
| Technical feasibility | Sales strategies |
| Financial feasibility | Funding |
| Organizational feasibility | Revenue projections |
| Conclusion | Appendix |
| Appendix and reference pages |
- A business plan does not include the description of the sales methods used, such as distribution agreements, strategic alliances, and the amount of involvement with partners, as well as the payment terms, warranties, and other customer support.
But a feasibility report includes all the sales methods, strategies, alliances to payment and customer support.
- Feasibility report contains:
- Assists in cost estimation, describe the production site, required inputs, and sourcing region.
- Physical description of the factory, including machine, capacity, warehouse, and supply chain, is necessary.
- Indicate if the area used for production is rented or owned. This will have an impact on the financial forecast.
- Information regarding the manufacturer's capacity, order details, price, and so on, if manufacturing is outsourced. To aid in cost estimation, describe the production site, needed inputs, and sourcing location.
- A physical description of the factory, including machine, capacity, warehouse, and supply chain, is necessary.
But a business plan does not contain anything related to production and operations, but a business plan contains all the information related to management.
- A poorly written business plan – poor projections, strategies, analysis, business model, and environmental factors, among other things – can be easily adjusted during business operations, but this cannot be said of a feasibility study because an incorrect conclusion in a feasibility study can be costly — it could mean launching a venture with little chance of survival or approving a proposal that wastes the company's human and financial resources.
- A business plan presume that a company will prosper and lays out the procedures needed to get there. Those in charge of conducting a feasibility study should not have any predetermined notions regarding the likelihood of success. They must maintain as much objectivity as possible. They do research and allow the facts to lead to the study's conclusion. If the study concludes that the idea is viable, some of the findings, such as market size predictions, may be incorporated in the company's business plan.
You should also read What is land development feasibility study?
These 10 differences will help you to evaluate and differentiate between a feasibility study and a business plan.
Feasibility study may appear to be like the business plan in many respects. "A feasibility study may easily be transformed to a business plan” but it is crucial to remember that the feasibility study is completed prior to the endeavor. The business plan should be thought of in terms of growth and sustainability, whereas the feasibility study should be thought of in terms of concept viability.
This is all you need to know and understand about feasibility study and business plan.
Get ready to apply your knowledge in the real words with lots of success.
You might also like to explore below external contents on feasibility study :
- What Is a Feasibility Study? – Types & Benefits
- Best 8 Property Management Software
- FEASIBILITY STUDIES & BUSINESS PLANS
Hope you enjoyed this post on feasibility study , let me know what you think in the comment section below.
Are you someone involved with real estate feasibility?
We are excited to launch the next generation of real estate feasibility software to help you manage your development projects with ease.
Register now for a free trail license!
This is a very good piece of writing. When you have a concept for a company but want to be sure it’s a good idea, you do a feasibility study.
It was very helpful. Thank you so much!
Appropriately timed! A company’s future operations are laid out in great detail in the company’s business plan. Once you’ve done your feasibility study, you’ll know whether or not the proposal has merit. The next step is to lay out your goals, whether financial and otherwise, as well as the strategies you want to use to attain them and the organisational structure you envision.
Prior to the company opening, both are undertaken, and may be repeated again in the future to identify the next steps on new ideas that may arise.
Great Content.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Follow Us On
Latest Posts

We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
Back to Business Plans
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on February 27, 2023 Updated on December 11, 2023

A business plan and a business proposal are similar documents. In fact, in some cases the terms can be used interchangeably, such as when both aim to attract investment.
But generally speaking, a business proposal tends to have broader scope, and this handy guide lays out precisely how these two common terms differ.
| Feature | Business Plan | Business Proposal |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Outlines a company's mission, vision, and means to achieve its goals. | Proposes a specific project or solution to a client or potential partner. |
| Audience | Investors, stakeholders, financial institutions, and internal team. | Potential clients, partners, or businesses. |
| Content | Executive Summary Company Description/Overview Products/Services Offered Market Analysis Marketing and Sales Strategies Operations and Management Financial Plan Appendices | Introduction Problem Statement Proposed Solution Pricing Timeline Terms and Conditions Conclusion |
| Duration | Generally, long-term. Speaks to the company's overall direction. | Usually short-term, addressing a specific project or need. |
| Focus | Comprehensive view of the business, including strategies, resources, and financial projections. | Focuses on a particular problem or need and the solution the company offers. |
| Use | To guide the company's direction and attract investments or loans. | To secure a contract, partnership, or client engagement. |
| Update Frequency | Periodically, as the company evolves or when significant changes occur in the market or industry. | As needed for different clients or projects. |
| Format | More detailed and structured. May have appendices with additional information. | Typically more concise, tailored to the client or project. |
- What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a detailed document laying out how the business will function and develop in its first few years. The key is the “plan” part of the name, as it will specify how you will launch, gain customers, operate, make money, and, with any luck, expand.
Yet what many first-time business owners seem to forget is that a business plan is not a static document. The initial version is based largely on assumptions, supported by research. But as you run your business you’ll learn what works and what does not and make endless tweaks to your plan.
Thus, creating a business plan is not a one-time action – it’s a dynamic and continuous process of crafting and adapting your vision and strategy.
Components of a Business Plan
A business plan is generally much more detailed and broader than a business proposal, and has several elements :
- Executive Summary
- Company Description/Overview
- Products or Services Offered
- Market Analysis
- Marketing and Sales Strategies
- Operations and Management
- Financial Plan
- What is a Business Proposal?
A business proposal is created in connection to a specific business deal being offered by one party to another. As mentioned, when you take a business plan to an investor, you’re proposing a business relationship, so in this case a business plan and a business proposal are much the same.
But a business proposal could also be for others purposes, including:
- Bringing on a partner
- Proposing a management contract to a person you want to hire
- Proposing a business relationship with a potential customer
- Proposing a partnership with another company
- Suggesting a deal to a member of your board of directors
A business proposal may offer specific terms for the potential relationship, or it may be just about the benefits the relationship will bring, with terms to be negotiated later. Essentially, it’s a sales tool to get people or companies to do business with you in some way.
Business proposals can be structured in various ways, but usually, they’ll include a summary of what your company can offer, a scope of the work to be done together, and sometimes, a price quote or a proposed structure of the business relationship.
Clearly, a business plan and a business proposal are similar – and can even be one and the same. At the same time, they can also serve very different purposes. Unlike a business plan, a business proposal can have a variety of aims and thus does not have a “one size fits all” structure.
Whichever one you need, be sure to take your time with the research and writing so your business has the best chance for success.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.
Crafting the Perfect Business Plan: A Deep Dive with Upmetrics’ Vinay Kevadiya
Carolyn Young
Published on October 13, 2023
In the first segment of our conversation with Vinay Kevadiya, the visionary behind Upmetrics, we explored the platform’s origins and itsunique ...

LivePlan Software Review
Published on September 15, 2023
When you’re starting a business, a business plan is essential whether you’re going to obtain financing or not. Creating a business plan helpsyou ...

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix?
Published on September 13, 2023
Launching a business involves countless tasks, and one of the crucial early hurdles is writing a business plan. Many entrepreneurs who aren’tlooki ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.

Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
The terms “business plan” and “business proposal” are sometimes used interchangeably, however, they are very different. The main difference between a business plan and a business proposal is that a business plan documents your growth strategy while a business proposal is a specific ask for someone to take an action you desire (e.g., buy your product/service, invest in your company, partner with you, etc.).
In this article, we will define a business plan and a business proposal and give you examples of when each is appropriate for you to use.
What is a Business Plan?

Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
Business Plan Structure
Typically, the business plan structure contains the following 10 components:
- Executive Summary
- Business Description & Overview
- Market Research & Analysis
- Customer Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Strategy & Plan
- Operations Plan
- Management Team
- Financial Projections & Plan
It is recommended that a business plan is updated annually to adjust for changes in the industry trends and the business itself.
What is a Business Proposal?

In terms of what you are asking from them, it can be anything that involves funds and time on their end including cash investment, product development assistance, and even employees if they have applicable skill sets.
Business Proposal Structure
An invited business proposal is written in response to an RFP. A request for proposal (RFP) is a document that invites potential suppliers to submit business proposals. How to write a business proposal depends on the format requested and the questions included in the RFP.
The following are the components that usually make up a business proposal:
- Brief description of your company’s services/products as the proposed solution to the goals of the RFP
- Reiteration of the scope of the particular project
- Responses to questions asked in the RFP
- Cost of the project, including drafting services, materials, tools, labor, delivery and other expenses
An unsolicited business proposal is essentially the same format, but it will solicit the client’s business while anticipating the clients’ concerns and issues. A business proposal is more of a marketing document than an offer because it attempts to persuade the potential client to do business by demonstrating your value proposition and a call to action.
So, What’s the Difference Between a Business Proposal vs. a Business Plan?
In a business proposal, company representatives typically work with the customer to tailor a business proposition that is attractive to both parties. This usually comes in the form of a written document detailing the services and cost associated with fulfilling an offer or request but can also include electronic contracts.
In contrast, a business plan is a description of your company on the executive and operational levels aimed at investors for raising financial support or other stakeholders in order to facilitate long-term growth. For example, an investor will want to know about how different departments within your business interact with one another, while somebody who will be implementing your product probably only needs more limited information such as design specs because they are not going into production themselves.
A business proposal may provide you with more details of the project, but it does not include information about your company’s operations or future plans.
Examples of Business Plans vs. Business Proposals
- When you give a potential investor your business plan which includes all sorts of information about how we will achieve your goals together as well as the amount of money it’s going to take. The business proposal is for them to write you a check in return for interest/principal payments or a percentage of your company.
- You might be getting partners involved in your business who will help with product development and distribution. You are offering them a business proposal to work together. However, they may request to see your business plan to better understand your goals, potential profitability, and how you plan to reach these goals before deciding to work with you.
- Your existing business has been so successful that you decide to outsource the social media marketing efforts to a freelancer to free up more of your time. The freelancer would provide a business proposal stating their terms and conditions along with the agreed-upon pay arrangement for their services. This change in organizational structure may be noted in your business plan to demonstrate expansion and financial stability to continue growth.
- In your business plan , one of your goals is to grow your client base by 5% each month. You identify potential clients in need of your services or products and send an unsolicited business proposal to demonstrate how your products or services can benefit them in order to develop a new prospective client list.
The business plan is a roadmap for your company’s present and future, while the business proposal has to do with what you are asking someone else for money. Applying this difference into practice can be difficult at times because business plans are often marketed as business proposals. However, it is important to be able to identify the difference between a business plan and business proposal in order to maximize their effectiveness and importance with potential investors or partners.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Business Plan and Proposal: Everything You Need to Know
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. A business plan is a document that clearly spells out how a business intends to realize its objectives and goals, while a business proposal is a sales document that a business entity uses to request a contract from a client.
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
A business plan and a business proposal are different from each other by content, goals, writing style, and structure. The major difference between both is that a business plan is a document that presents facts, while a business proposal is a request for a deal and a quotation of prices.
A Business Plan
You can think of a business plan as the documentation of a company's grand vision. Business plans are naturally tactical. It's like stating where and when you want to start, when you want to get to the next point in view, and how you intend to accomplish that progress. A business plan includes descriptions of how the business is intended to run, the details of financial goals, possible business rivalry, marketing strategy, executive summary, and other factors that affect a company's planned business growth.
A business plan is particularly effective in making potential investors interested in a company (especially a startup company that's yet to make a name in its industry). Additionally, a business plan can provide an idea of what a company requires for professionals such as attorneys, accountants, and potential employees. A business plan distinctly describes the scope of the business, and in so doing, clears your thoughts as a business owner.
The business plan should be honestly made because it's the outline of the company's vision. It indicates whether or not the business goals of the company are realistically achievable. Experts say an effective business plan would take approximately six weeks of thorough research and groundwork to create. In other words, you typically can't create an effective business plan in one day, present it to potential investors the next day, and achieve desired results.
A Business Proposal
A business proposal goes to a prospective client directly from an established business. It's an attempt to sell a business entity's service or product to a client, and not an attempt to sell the business itself. Also, a business proposal isn't an estimate. Though costs and certain other details will be provided in the business proposal, an estimate is a lot more unofficial and simply a provision to skim over the costs. It doesn't present the entire picture.
Basically, business proposals show a particular idea, such as a new, profitable undertaking. The proposal is intended to get investors to support the particular business endeavor being suggested. For instance, a well-known eatery chain may wish to extend its business to a nearby state. Such an eatery would have to compose a business proposal in order to get the financial support of its target investors.
Though the business proposal provides an overview of what the company does (similar to a business plan), its major objective is to provide the details of the suggested business idea, including providing answers in advance for any concerns that could be raised by potential investors.
Components of a Business Plan
Basically, a business plan has three components: business model description, sales tactics, and financial goals. However, more elaborately, it has the following sections of information:
- Executive summary
- Description of products and services
- Industry analysis (analysis of possible business rivalry)
- Marketing strategy
- Operating plan
- Structure of leadership
- Internal analysis
- Built-out plan
- Introduction of management
- Financial goals (deliberations on monetary concerns, and how to address them and achieve expected results).
Solicited vs. Unsolicited Business Proposals
A solicited business proposal, when presented in response to a request for proposal (RFP), should be in the format requested by the client in their RFP. The same format may or may not be used for an unsolicited business proposal. Its purpose is to suggest and develop a business idea. Therefore, it's recommended to use the same format or some other format that's well-known in the field of endeavor.
An unsolicited business proposal offers a business entity the flexibility to choose what structure they deem appropriate. However, the proposal is expected to meet industry standards, no matter what format is used. For instance, it should emphasize major areas of interest, be thoroughly researched, offer a proposition of value, and feature a call to action.
If you need help with a business plan and proposal, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Business Proposal Ideas
- Comparison Between Business Proposal and Business Plan
- Business Contract Proposal
- Business Proposal Introduction
- How To Write A Business Proposal
- Writing A Contract Proposal
- LLC Business Plan Template
- Sample of a Good Business Plan
- Service Business Plan
- How to Contact Companies for Business

Business Plan vs Proposal: An In-Depth Comparison

Explore the distinguishing factors and circumstances that make a Business Plan or Business Proposal more fitting for driving success and growth in your enterprise. Gain insights into the purpose, audience, and strategic value of each document, and learn when it’s best to utilize a Business Plan or pitch with a Business Proposal.
Table of Contents
What is the Main Difference Between a Business Plan and a Business Proposal?
The main difference between a Business Plan and a Business Proposal is that a business plan is a formal document that outlines the company’s goals, strategies, market analysis, financial needs, and projections for the future, aimed at providing a roadmap for the business’s success and often used to secure funding or guide the management team. On the other hand, a business proposal is a tailored document created to pitch a specific product, service, or solution to a potential client or partner, detailing how the business can fulfill a particular need or solve a specific problem for the recipient, often with the goal of initiating a transaction or project.
Understanding Business Plans and Business Proposals
A Business Plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s objectives, strategies, market analysis, financial forecasts, and operational structures. It primarily serves as an internal roadmap for the company’s strategic direction and helps to attract investors by showcasing the company’s potential for growth and profit. Business plans are often developed during the foundational stages of a company and updated periodically to guide the company through different stages of growth.
A Business Proposal , on the other hand, is a targeted pitch provided to a specific client or partner to convince them to do business with you. Unlike a business plan, a business proposal is not a broad overview of the entire company. Instead, it is a customized suggestion that outlines how your business can solve a particular problem or meet a specific need of the prospective client. The proposal highlights the benefits of selecting your company’s products or services and typically includes pricing, terms, and conditions for a potential engagement or project.
Key Differences between a Business Plan and a Business Proposal
- Purpose : A business plan is primarily used for strategic planning and securing investment, while a business proposal is aimed at winning a specific contract or project.
- Audience : The audience for a business plan is typically potential investors, stakeholders, or company management. On the other hand, the business proposal is directed towards a specific client or partner.
- Focus : A business plan covers the entire company’s goals and operations, whereas a business proposal targets a specific offering for the client.
- Details : While business plans include detailed financial projections and market analysis, business proposals focus on how your company can meet the client’s needs and the costs associated with your proposition.
- Frequency : Business plans are created infrequently, often at startup or significant growth stages, while business proposals are generated as needed when pursuing new business opportunities.
- Structure : Business plans have a standard structure, including an executive summary, company overview, products/services, and financials, whereas proposals are tailored to the client’s request.
- Standardization : Business plans tend to follow a similar format from one to the next, while proposals are highly customized to align with the potential client’s requirements.
- Duration : The time horizon in a business plan can span several years, reflecting long-term planning, but a business proposal typically concerns the timeframe for a specific project or service offering.
Key Similarities between a Business Plan and a Business Proposal
- Strategic Elements : Both documents outline strategic approaches, whether for the company as a whole or a specific project.
- Research : Thorough market research is essential in creating either a business plan or a business proposal to ensure feasibility and competitiveness .
- Objective Setting : Each document includes clear objectives that the company wishes to achieve, be it long-term company goals or objectives of a contract.
- Persuasive Nature : Both are meant to be persuasive documents that convince the reader to invest in the company or to hire the company for services/products.
- Professional Presentation : A business plan and a business proposal should both be presented in a professional manner, well-organized and free of errors, to make the best impression.
- Financial Information : Financial aspects are crucial in both; while a business plan may have more comprehensive financial projections, a proposal should still outline costs and pricing models.
- Action Plan : Action steps or milestones are outlined in both to guide the intended strategy into practical steps or to give the prospective client a clear timeline for project completion.
Advantages of a Business Plan Over a Business Proposal
- Clarity and focus : A business plan provides a clear roadmap for your company , detailing your objectives, strategies, and financial projections. It enables you to stay focused on your long-term goals and the steps required to reach them.
- Risk assessment : It allows for a thorough risk assessment, helping you foresee potential challenges and devise strategies to mitigate them.
- Investor attraction : A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and lenders as it showcases the viability and profitability of your business idea.
- Strategic planning : The business plan acts as a strategic planning tool, helping you to align your short-term and long-term goals with the overall vision of the business.
- Operational guidance : It provides detailed operational guidance, outlining day-to-day activities, management responsibilities, and the organizational structure.
- Performance tracking : By setting benchmarks and performance metrics, a business plan makes it easier to track progress and measure success over time.
- Market analysis : A business plan includes an extensive market analysis, offering insights into your target market, competition, and market trends, which are crucial for making informed decisions.
Disadvantages of a Business Plan Compared to a Business Proposal
- Inflexibility : A business plan can be quite rigid, with a focus on long-term strategies and projections that might not adapt well to rapid changes in the market.
- Time-consuming : Preparing a comprehensive business plan requires a significant amount of time and effort, potentially diverting resources from immediate business opportunities.
- Outdated information : A business plan might quickly become outdated if the market or the company’s circumstances change, requiring frequent revisions.
- Cost : The production of a business plan can be costly, especially if it necessitates the expertise of consultants or outside advisers.
- Overemphasis on planning : There’s a risk of over-planning and under-executing, where too much time is spent on creating the perfect business plan instead of taking action.
- Complexity : A business plan’s complexity might be intimidating or overwhelming for small business owners who may prefer the simplicity and directness of a business proposal.
- Less tailored : While a business proposal is often customized to the needs and interests of a specific client or investor, a business plan is a broader document that may not address specific concerns or questions from potential stakeholders.
Advantages of a Business Proposal Over a Business Plan
- Focus on Specificity : A business proposal is usually tailored to a specific client or project, which means it’s highly targeted and practical. This specificity allows the business to directly address the client’s needs and provide a customized solution that a general business plan cannot offer.
- Rapid Execution : Proposals tend to be shorter and more concise, which allows for quicker evaluation and a faster start on the project. Businesses can get to work immediately after the proposal is accepted, shortening the time from planning to action.
- Persuasive Element : A business proposal aims to persuade a particular client or investor to buy into the idea, product, or service. This persuasive nature means that proposals often focus on benefits and competitive advantages, potentially leading to a higher success rate in securing funding or partnership.
- Adaptability : Since a proposal is typically for a particular client or project, it can be easily adjusted for different opportunities or audiences without reworking an entire business plan. This adaptability makes it more versatile in responding to market changes.
- Ease of Preparation : A business proposal can be less daunting to create than a full-blown business plan as it generally does not require as much market analysis and financial forecasting. It allows the business to focus on the immediate opportunity rather than extensive strategic planning.
- Potential for Immediate Feedback : When you present a business proposal, you often do so in a setting that allows for immediate questions and feedback. This gives you the chance to quickly address concerns, modify your offer, and improve the chances of an agreement.
- Enhanced Relationship Building : Crafting a proposal requires understanding the client’s needs and objectives deeply, often leading to stronger client-business relationships. This rapport can be beneficial for both future business and referrals.
Disadvantages of a Business Proposal When Compared to a Business Plan
- Lack of Long-term Vision : A business proposal is often focused on the immediate project and may not outline the long-term strategic direction of the company as comprehensively as a business plan would.
- Limited Scope : Proposals generally address specific aspects of a business’s operations rather than providing a complete picture. This narrow focus might overlook broader opportunities or challenges that a business plan would typically account for.
- Missed Detail : While business proposals are succinct, the brevity can sometimes result in the omission of important details that would be standard in a business plan, such as thorough market analysis or full financial projections.
- Potential Dependency : If a company relies too much on individual proposals for direction, it might find itself without a cohesive strategy which a business plan is designed to provide. This can lead to a reactive rather than proactive business approach.
- Risk of Assuming Knowledge : Proposals may assume that the reader has a certain level of understanding about the company or product, which can be a risky assumption if the reader is new to the business or its offerings.
- Need for Customization : Each business proposal needs to be customized for its intended audience, which can be resource-intensive when dealing with multiple prospects or regular tender submissions.
- Limited Investor Appeal : Investors often prefer to understand the comprehensive strategy and the broader financial implications of a business, something a focused business proposal may fail to communicate in comparison to a detailed business plan.
Situations When a Business Plan Is Preferable to a Business Proposal
- Establishing Clear Direction : When a new business is just starting out, laying out a comprehensive business plan is crucial for establishing a clear direction and objectives for the business. It serves as a roadmap for where the owners want to take the company and how they plan to get there.
- Securing Funding from Investors : A business plan is generally required for entrepreneurs seeking investment or loans. It presents detailed financial projections, market analysis, and business strategies that are essential to convince investors or banks to finance the venture.
- Long-term Strategic Planning : For setting long-term goals and defining the vision of the business, a business plan is more appropriate because it takes a broader view of the business’s place in the market and its growth strategy over the coming years.
- Developing Comprehensive Financial Projections : A business plan includes detailed financial forecasts that cover multiple years. This level of detail is necessary for stakeholders to understand the financial trajectory and potential of the company .
Situations When a Business Proposal Is Preferable to a Business Plan
- Responding to Specific Client Requests : A business proposal is tailored to the needs and specifications of a potential client or partner. When a business wants to offer solutions to another company’s problem, a proposal is best suited for outlining how it will meet those specific needs.
- Competitive Bidding Situations : When entering a bid to win a contract, a business proposal is more advantageous as it focuses on why the business is the best fit for the project, detailing its approach, unique benefits, and value proposition.
- Establishing Partnership Agreements : If a company is looking to form a collaboration or partnership, a business proposal lays out the terms and benefits of the partnership, which is more specific than the broader scope of a business plan.
- Project-driven Opportunities : For businesses that operate on a project-by-project basis, such as construction or consulting, business proposals are the better tool. They provide prospective clients with a detailed breakdown of the objectives, strategies, and costs for each unique project.
What components should be included in a business plan?
- Executive Summary : An overview of the business and its strategy
- Company Description : Legal establishment, history, start-up plans, etc.
- Market Analysis : Industry, market and competitor research
- Organization and Management : Business and management structure
- Service or Product Line : Description of what you’re selling
- Marketing and Sales Strategies : How you’ll attract and retain customers
- Funding Request : Your current funding requirements
- Financial Projections : Balance sheets, cash flow statements, and income statement forecasts
- Appendix : An optional section that includes résumés, permits, and other legal documents
How often should a business plan be revised?
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more frequently if there are significant changes in the market, the business model, or if new challenges or opportunities arise .
In what scenarios is a business proposal unnecessary?
A business proposal may not be necessary when transactions are straightforward and do not require detailed explanations, such as standard retail sales or when there is already an established relationship with the client based on trust and familiarity.
Can a business proposal lead to a long-term relationship with a client?
Absolutely. If a proposal leads to a successful project and client satisfaction, it can serve as the foundation for a long-term business relationship and future projects or collaborations.
What is an unsolicited business proposal?
An unsolicited business proposal is one that is offered without an explicit request from the potential client. It often reflects the proposer’s initiative to identify potential needs of the recipient and offer solutions to unaddressed challenges.
How can you make a business proposal stand out?
To make a business proposal stand out, it should clearly articulate the unique value proposition, be tailored to the client’s specific needs, contain compelling and concise content, and demonstrate a deep understanding of the client’s industry and challenges.
Are there any legal considerations when drafting a business proposal?
Yes, a business proposal should ensure that all claims and statements are truthful and that no proprietary or confidential information is disclosed without permission. Additionally, the terms and conditions should be clearly outlined to avoid any misunderstandings, and if accepted, it can be the basis for a legally binding contract.
Business Plan vs Proposal Summary
The decision between a Business Plan and a Business Proposal hinges on the specific requirements, goals, and context of your enterprise. A Business Plan lays the foundation for your company’s long-term strategy, risk mitigation, and operational guidance, with an expansive view of the business’s aims and the means to attract investors. Conversely, a Business Proposal concentrates on the immediacy of client-specific projects, presenting a tailored solution with a persuasive edge to secure contracts and foster client relationships swiftly.
| Aspect | Business Plan | Business Proposal |
|---|---|---|
| A formal document outlining a company’s strategic direction, goals, and requirements. | A customized document designed to pitch a product or service to a potential client. | |
| Used for strategic planning, securing investment, and internal guidance. | Aimed at winning a specific contract or project by addressing a client’s needs. | |
| Potential investors, stakeholders, and company management. | Specific clients or partners with particular needs or requests. | |
| Broad, covering all areas of the business including long-term goals and operations. | Specific to an offering that aligns with the client’s issue or challenge. | |
| In-depth market analysis, financial projections, strategies, and organizational details. | Customized solutions, benefits, pricing, and terms for a prospective engagement. | |
| Prepared infrequently, at startup or significant growth stages. | Generated as needed when seeking new business or responding to RFPs. | |
| Standardized with sections like executive summary, market analysis, and financials. | Custom-tailored to the client’s request, often varying in structure. | |
| Long-term outlook, often spanning multiple years. | Focused on a specific project or service timeframe. | |
| Follows a consistent format for different uses. | Highly customized to the potential client’s requirements. | |
| May seem inflexible due to its long-term and broad nature. | Adaptable and specific to client or project needs. | |
| Provides a thorough business model and can attract investors with detailed planning. | Directly addresses a client’s needs and can initiate business quickly. | |
| Can be time-consuming, costly, and may require frequent updating. | Lacks long-term strategic details and may depend excessively on the prospects. | |
| When establishing a new business, seeking funding, and defining long-term strategy. | When targeting a client request, competitive bidding, and project-specific opportunities. | |
| Both outline strategic approaches, require research, set clear objectives, are persuasive in nature, and include financial information and action plans. |
About The Author
Hidayat Rizvi
Related posts.

Farmer vs Businessman: A Detailed Comparative Analysis of Two Vital Roles

Salesman vs Businessman: Comprehensive Analysis for Aspiring Professionals


Difference Between Business Improvement and Business Process Reengineering

Difference Between Indian and American Business Culture
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Important Links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Social Networks
- hidayat.rizvi.1
- @HidayatRizvi
- hidayat_rizvi_2000
- hidayat-rizvi-b0788b10
HidayatRizvi.com © 2024. All Rights Reserved
Get a free consultation, enter your contact details and i will get in touch, send a message. i will respond quickly, try quickbooks free for 30 days, get started with quickbooks in 30 minutes*., *based on a survey of small businesses using quickbook online conducted september 2018..

- Contact sales
- Start free trial
Project Planning: How to Make a Project Plan
This guide is brought to you by projectmanager, the project planning software trusted by 35,000+ users worldwide. make a project plan in minutes.
What Is a Project Plan?
How to create a project plan, project planning phase, what is project planning software, benefits of online project planning software, must-have project planning software features, project planning terms, project planning steps, how to create a project plan with projectmanager, what is the purpose of a project management plan, the elements of a project plan, how long does the project planning phase take, techniques for the project planning process, how to manage your project plan.
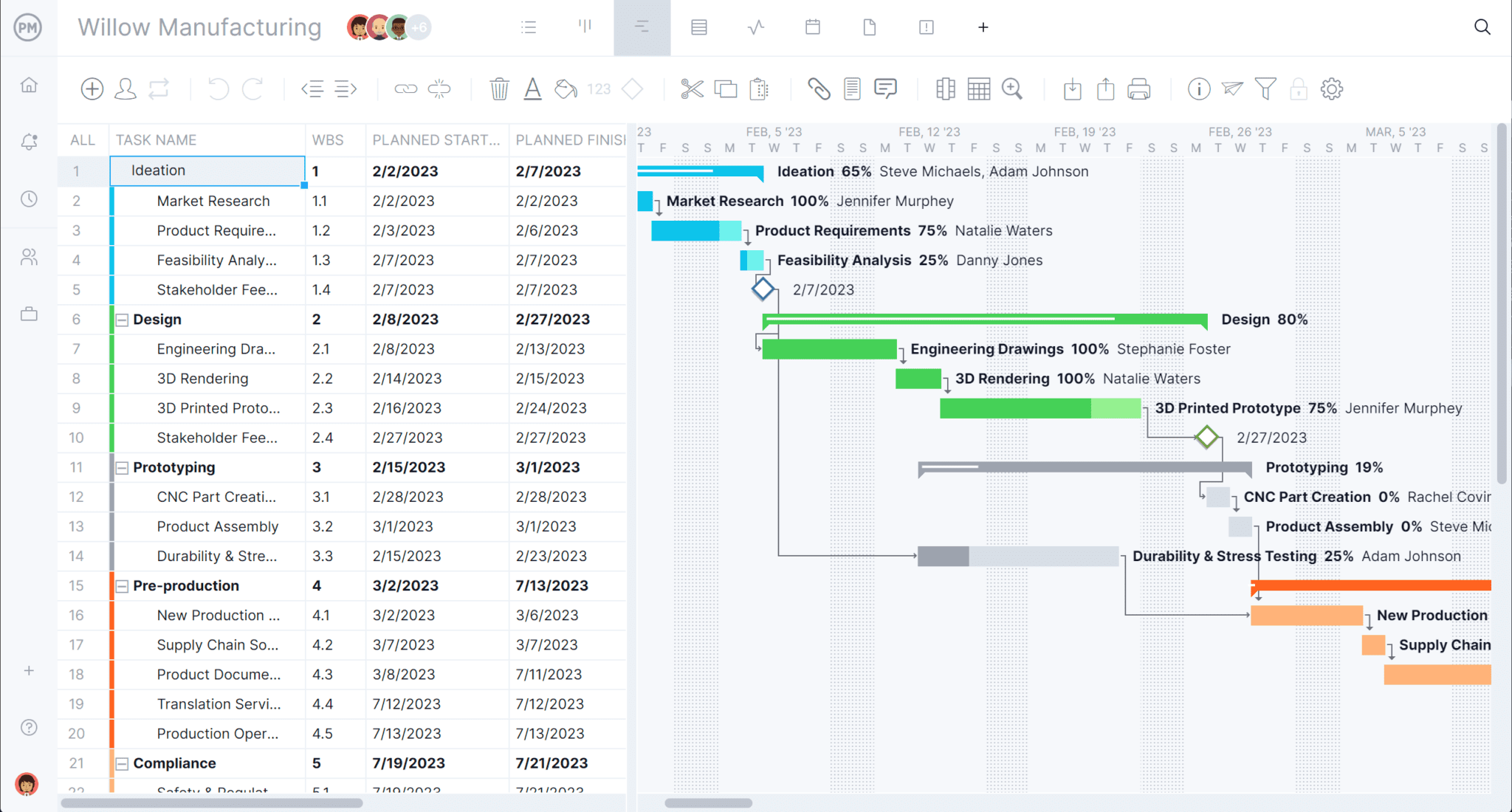
A project plan is a series of formal documents that define the execution and control stages of a project. The plan includes considerations for risk management, resource management and communications, while also addressing scope, cost and schedule baselines. Project planning software is used by project managers to ensure that their plans are thorough and robust.
ProjectManager allows you to make detailed project plans with online Gantt charts that have task dependencies, resource hours, labor costs, milestones, the critical path and more. Plus, your team can execute the plan in any of our five project views, while you track progress along the way with dashboards. Start today for free.
The project plan, also called project management plan, answers the who, what, where, why, how and when of the project—it’s more than a Gantt chart with tasks and due dates. The purpose of a project plan is to guide the execution and control project phases.
As mentioned above, a project plan consists of the following documents:
- Project Charter : Provides a general overview of the project. It describes the project’s reasons, goals, objectives, constraints, stakeholders, among other aspects.
- Statement of Work : A statement of work (SOW) defines the project’s scope, schedule, deliverables, milestones, and tasks.
- Work Breakdown Structure : Breaks down the project scope into the project phases, subprojects, deliverables, and work packages that lead to your final deliverable.
- Project Plan : The project plan document is divided in sections to cover the following: scope management, quality management, risk assessment, resource management, stakeholder management, schedule management and the change management plan.
This guide aims to give you all the information and resources you need to create a project plan and get it approved by your customers and stakeholders. Let’s start with the basics of writing a project plan.

Get your free
Project Plan Template
Use this free Project Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Your project plan is essential to the success of any project. Without one, your project may be susceptible to common project management issues such as missed deadlines, scope creep and cost overrun. While writing a project plan is somewhat labor intensive up front, the effort will pay dividends throughout the project life cycle.
The basic outline of any project plan can be summarized in these five steps:
- Define your project’s stakeholders, scope, quality baseline, deliverables, milestones, success criteria and requirements. Create a project charter, work breakdown structure (WBS) and a statement of work (SOW) .
- Identify risks and assign deliverables to your team members, who will perform the tasks required and monitor the risks associated with them.
- Organize your project team (customers, stakeholders, teams, ad hoc members, and so on), and define their roles and responsibilities.
- List the necessary project resources , such as personnel, equipment, salaries, and materials, then estimate their cost.
- Develop change management procedures and forms.
- Create a communication plan , schedule, budget and other guiding documents for the project.
Each of the steps to write a project plan explained above correspond to the 5 project phases, which we will outline in the next section.
What Are the 5 Phases of the Project Life Cycle?
Any project , whether big or small, has the potential to be very complex. It’s much easier to break down all the necessary inclusions for a project plan by viewing your project in terms of phases. The Project Management Institute , within the Project Management Book of Knowledge (PMBOK), have identified the following 5 phases of a project:
- Initiation: The start of a project, in which goals and objectives are defined through a business case and the practicality of the project is determined by a feasibility study.
- Planning: During the project planning phase, the scope of the project is defined by a work breakdown structure (WBS) and the project methodology to manage the project is decided on. Costs, quality and resources are estimated, and a project schedule with milestones and task dependencies is identified. The main deliverable of this phase is your project plan.
- Execution: The project deliverables are completed during this phase. Usually, this phase begins with a kick-off meeting and is followed by regular team meetings and status reports while the project is being worked on.
- Monitoring & Controlling: This phase is performed in tandem with the project execution phase. Progress and performance metrics are measured to keep progress on the project aligned with the project plan.
- Closure: The project is completed when the stakeholder receives the final deliverable. Resources are released, contracts are signed off on and, ideally, there will be an evaluation of the successes and failures.
Free Project Plan Template
Address all aspects of your project plan with this free project plan template for Word . This in-depth template will guide you through every phase of the project, as well as all the elements you need to outline for a proper document. Download your template today.
We’ve created also created other project planning templates to help you create all the different documents that make up a project plan, like the project schedule, project budget or resource plan.
Now that we’ve learned how to make a project plan, and identified the stages of the project management life cycle, we need to emphasize on the importance of the project planning phase.
The project planning process is critical for any kind of project because this is where you create all the documents that will guide how you’ll execute your project plan and how you’ll control risks and any issues that might occur. These documents, which are part of the project management plan, cover all the details of your project without exception.
There are project plan templates out there that can help you organize your tasks and begin the project planning process—but we here at ProjectManager recommend the use of project planning software. The feature set is far more robust and integrated with every project phase compared to an Excel project plan template, and is a great way to ensure your actual progress stays aligned with your planned progress.
Once you write a project plan, it’s time for implementation . Watch the video below to see how project planning software helps organize a project’s tasks, resources and costs.
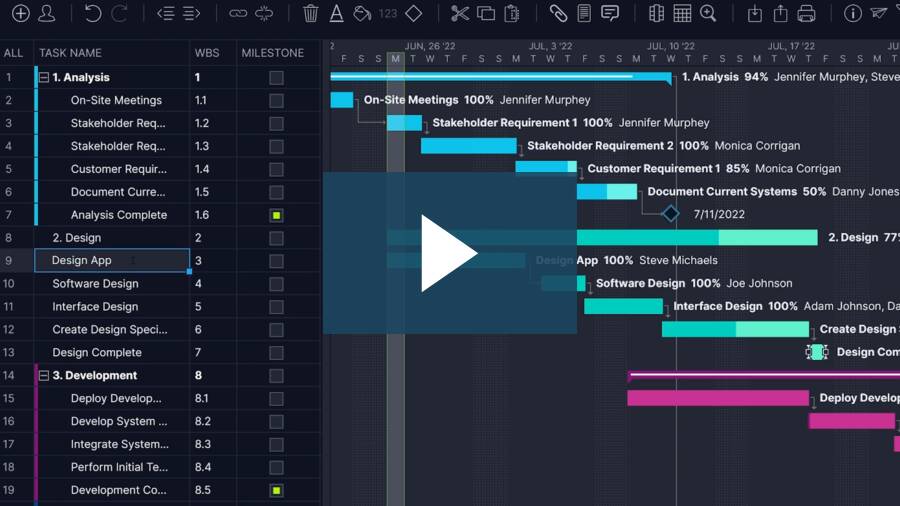
Project planning tools has become an invaluable tool for project managers in recent years, as it provides them the ability to maintain and automate the components we outlined above. Project planning software is a great tool to facilitate project management processes such as schedule development, team management, cost estimation, resource allocation and risk monitoring.
Beyond that, planning software also allows managers to monitor and track their plan as it moves through the execution phase of the project. These features include dashboards, for a high-level view of the project’s progress and performance, and in-depth reports that can be used to communicate with stakeholders.
Project planning software comes in all different sizes and shapes. There are some that focus on a single aspect, and others that offer a suite of planning features that can be used in each one of the project planning steps. What’s right for your project depends on your specific needs, but in general terms, project planning software is a much more powerful tool than project planning templates .
Related: 20 Must-Have Project Management Excel Templates
Online project planning software is highly flexible and adaptable to your team’s style of work. It has features that are designed to assist you throughout your project planning process.
Before the rise of planning software, project managers would typically have to keep up with a disjointed collection of documents, excel spreadsheets and so on. Savvy managers, however, make use of the project management tools available to them to automate what they can, and streamline what they can’t.
Some of the time-saving benefits of project planning software include the following.
- Organize, prioritize and assign tasks
- Plan and schedule milestones and task dependencies
- Monitor progress, costs and resources
- Collaborate with team
- Share project plans with team and stakeholders
- Generate reports on plans
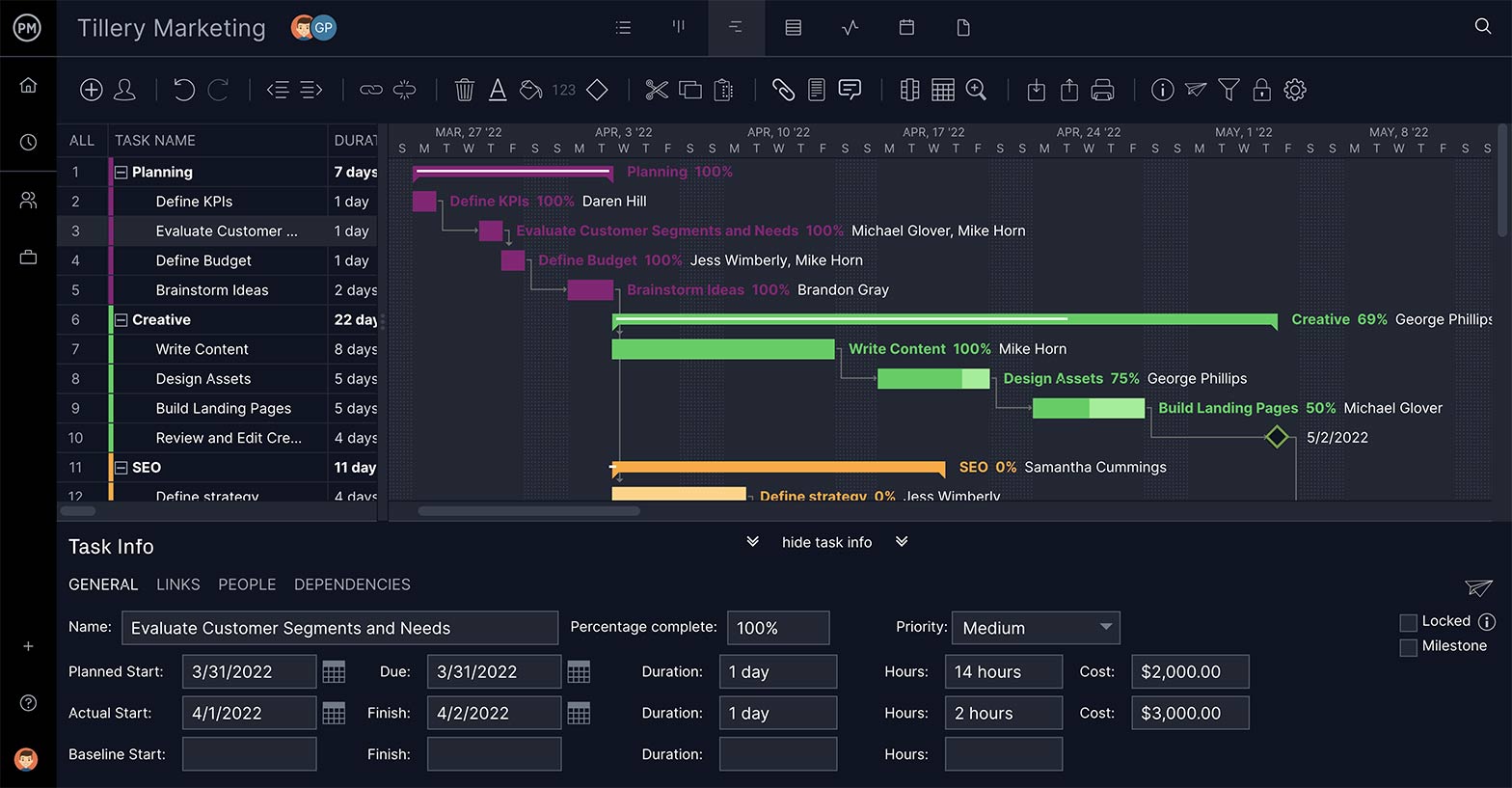
Gantt Charts for Superior Planning
A Gantt chart is the most essential tool for the project planning process. Organize tasks, add their duration and they automatically populate a project timeline . Set milestones to break the larger project into manageable phases, and link task dependencies to avoid bottlenecks later in the project.
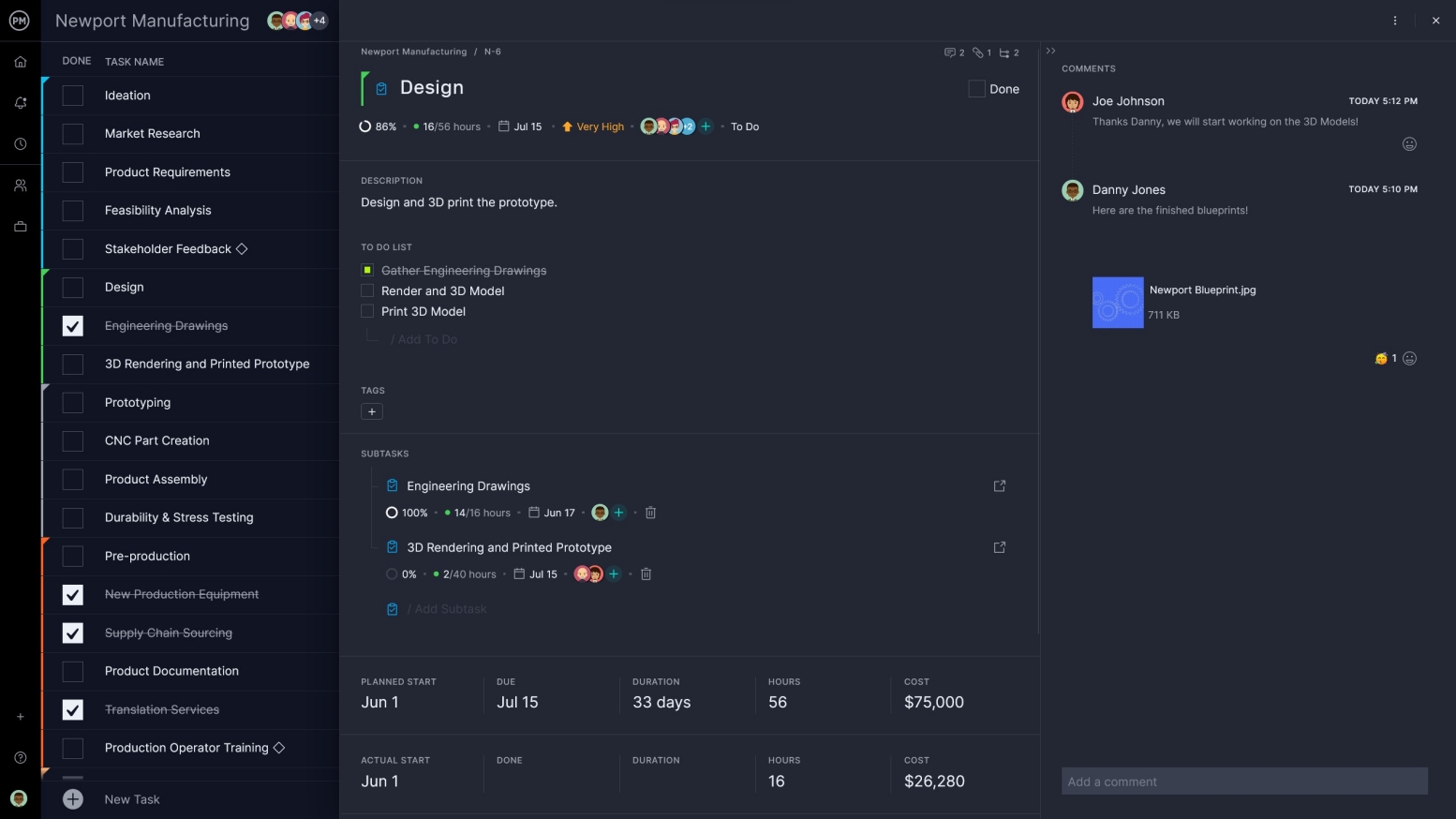
Get More Than a To-Do List
When planning a project, you need more than a to-do list. Seek out a planning software with a task list feature that lets you set priority levels, filters and collaborate. It’s a big plus if you can also make personal task lists that are private to manage your own work.
Use Kanban for Workflows
Workflows ensure proper execution of your plan, and no feature does this better than kanban boards. Customize boards to match your workflow and drag and drop cards as teams get their work done. See what work needs to be done and keep the focus on productivity with this feature.
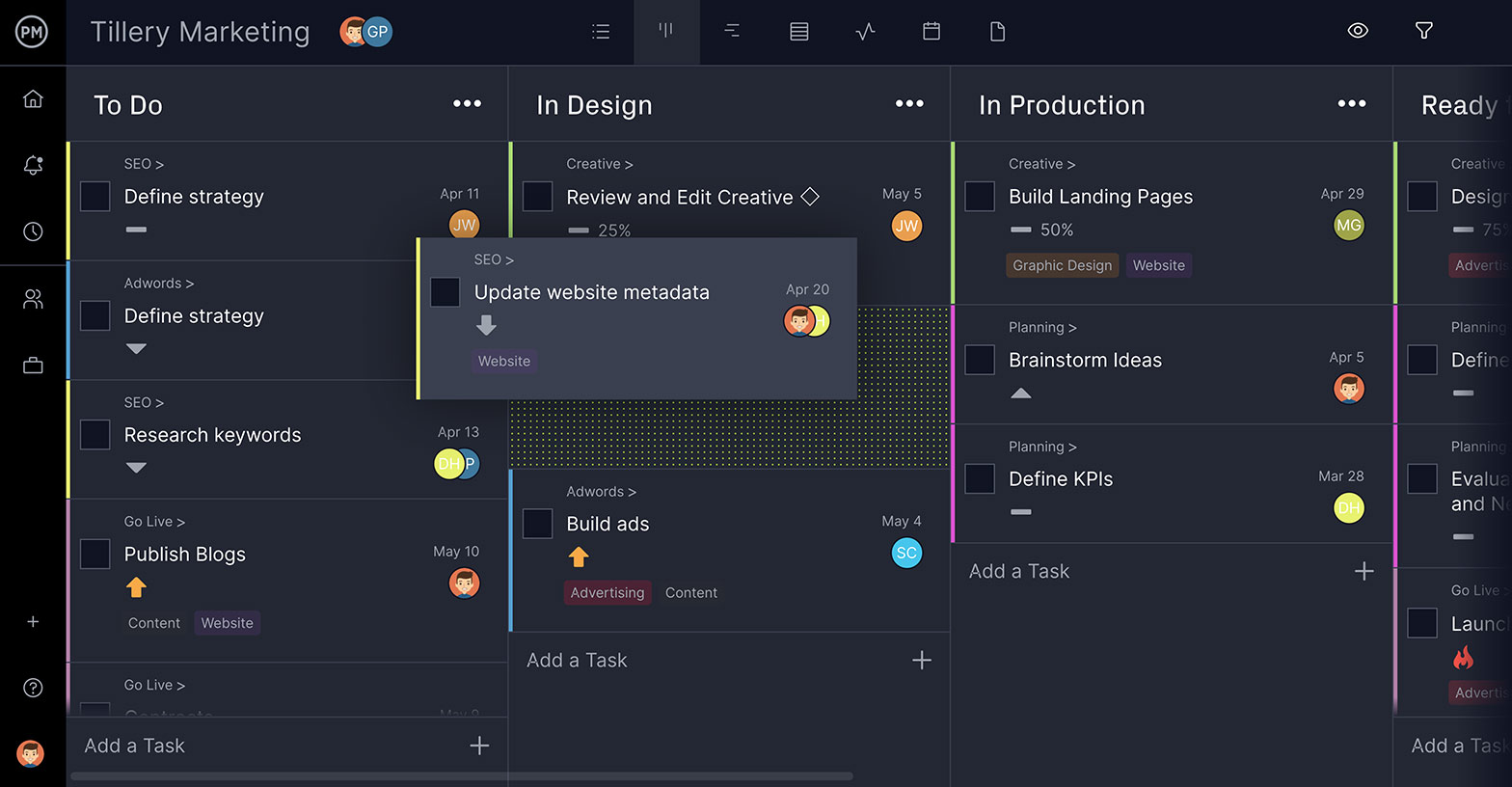
Be Able to Track Progress
A dashboard can keep your project plan on track. Try and find a dashboard that’s synced with your planning tools, so everything updates automatically. It will make reporting easier too.

Get Transparency Into Teams
For a plan to go smoothly, you have to know what your team is working on. Find a way to balance your team’s availability with the project schedule. Workload features that map out resource allocation and holidays can be a big help here.
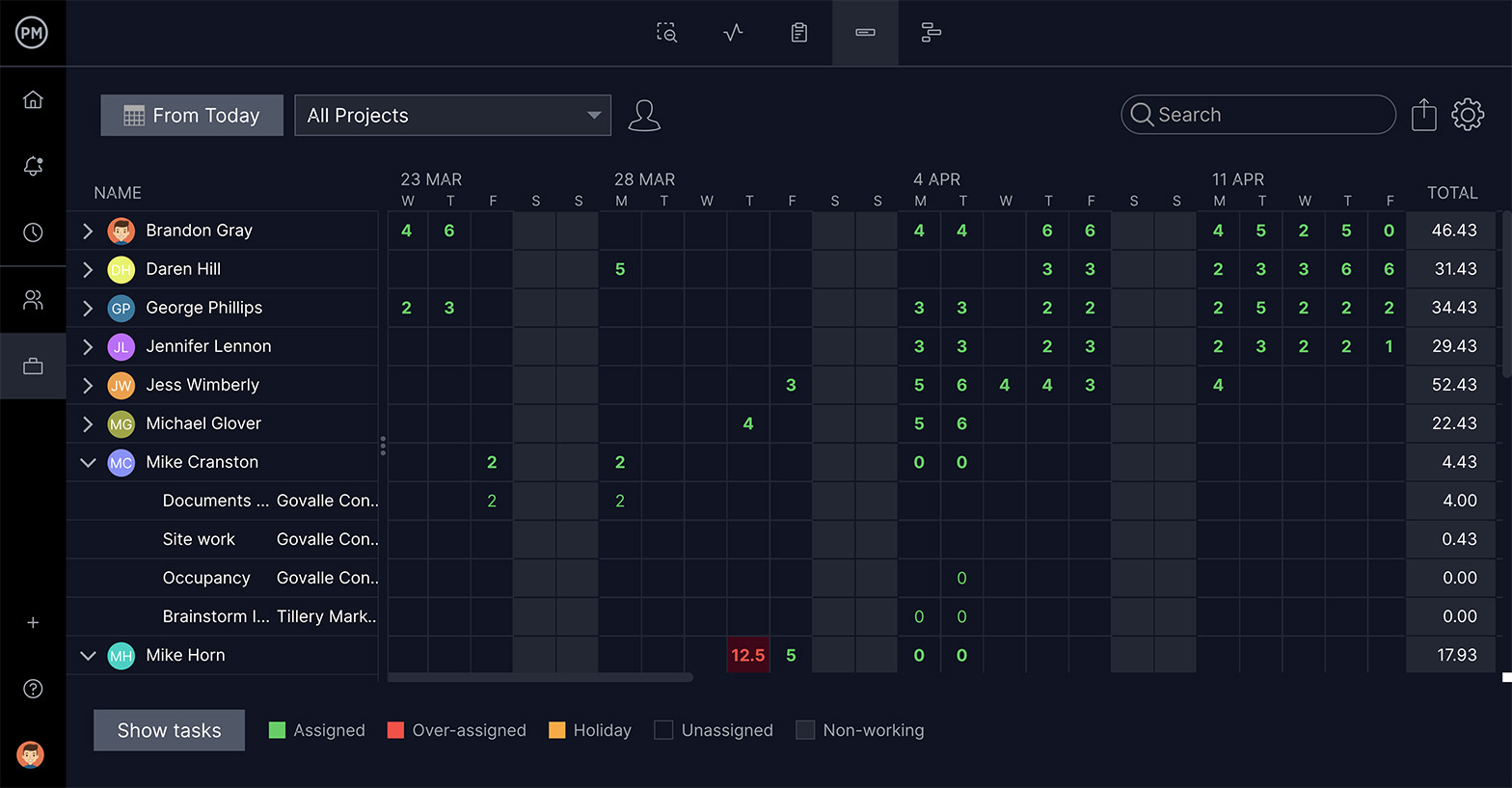
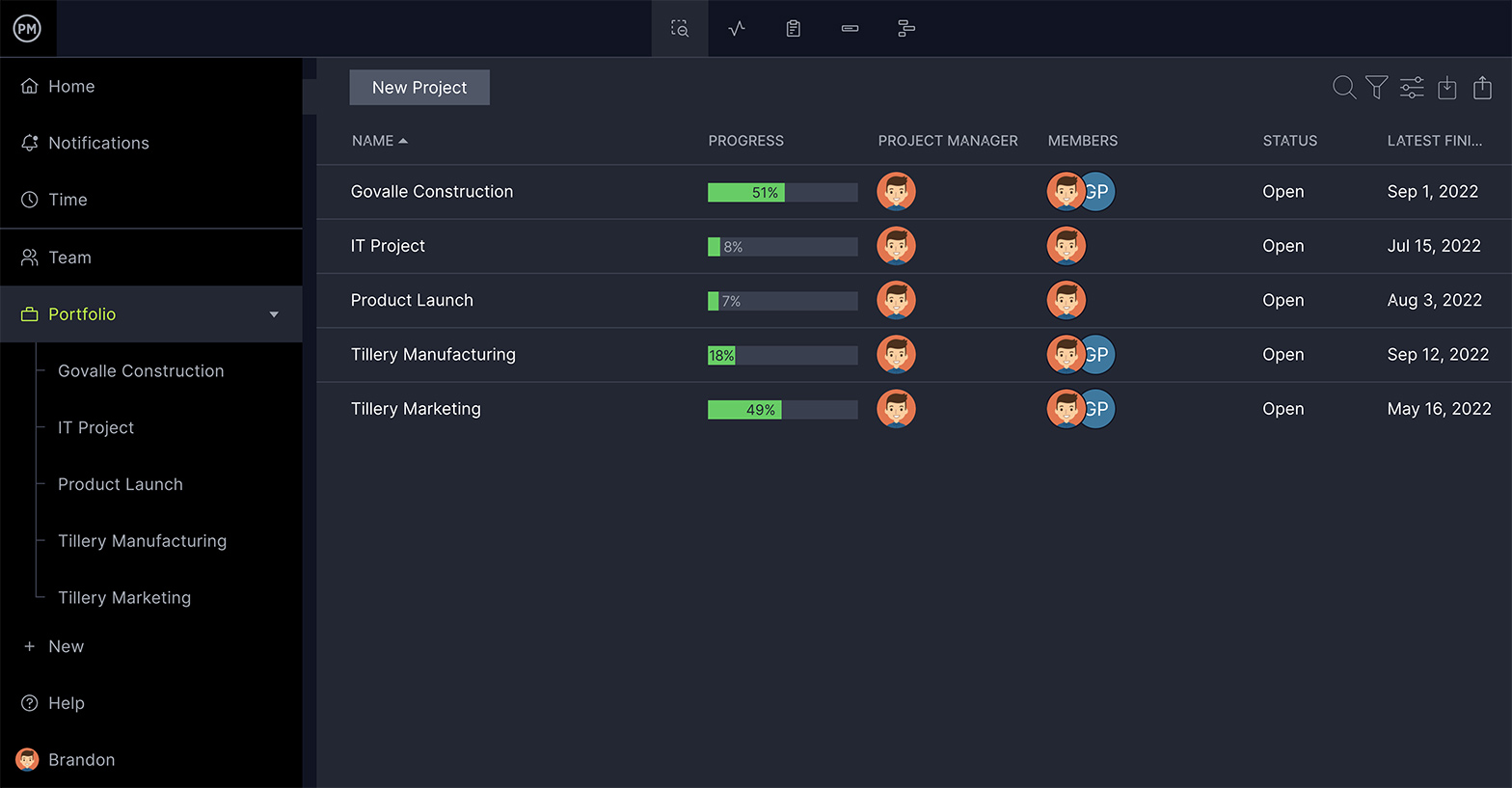
Be Able to Manage Multiple Projects
Rarely do you need to only focus on one project at a time. Give yourself the flexibility to manage multiple projects at once in the same tool. A roadmap feature that maps all of your projects on one timeline can be a lifesaver.
Before we dive into how to create a project plan, it helps to be familiar with some of the terms that you’ll run across. Here is a list of general terms you’ll encounter in this guide.
- Deliverable: The results of a project, such as a product, service, report, etc.
- Stakeholder: Anyone with a vested interest in the project—project manager, project sponsor, team members, customers, etc.
- Tasks: Small jobs that lead to the final deliverable.
- Milestone: The end of one project phase, and the beginning of the next.
- Resources: Anything you need to complete the project, such as personnel, supplies, materials, tools, people and more.
- Budget: Estimate of total cost related to completing a project.
- Tracking & Monitoring: Collecting project data, and making sure it reflects the results you planned for.
The project planning process is critical for the success of your project, and as a project manager, you have to think about all the elements that make up your project management plan such as work, time, resources and risks.
Now, we’re going to take you through the main project planning steps :
- Outline the business case
- Meet with key stakeholders
- Define project scope
- Assemble a project team
- Determine a project budget
- Set project goals & objectives
- Outline project deliverables
- Create a project schedule
- Assign tasks to your team members
- Do a risk analysis
- Create your project plan
- Report your progress
By following these project planning steps, you’ll clarify what you need to achieve, work out the processes you need to get there and develop an action plan for how you are going to take this project plan outline forward.
1. Outline the Business Case
If you have a project, there’s a reason for it—that’s your business case . The business case outlines reasons why the project is being initiated, its benefits and the return on investment. If there’s a problem that is being solved, then that problem is outlined here. The business case will be presented to those who make decisions at your organization, explaining what has to be done, and how, along with a feasibility study to assess the practicality of the project. If approved, you have a project.
2. Meet with Key Stakeholders
Every project has stakeholders , those who have a vested interest in the project. From the ones who profit from it, to the project team members who are responsible for its success. Therefore, any project manager must identify who these key stakeholders are during the project planning process, from customers to regulators. Meeting with them is crucial to get a better picture of what the project management plan should include and what is expected from the final deliverable.
3. Define Project Scope
It refers to the work required to accomplish the project objectives and generate the required deliverables. The project scope should be defined and organized by a work breakdown structure (WBS). Therefore, the project scope includes what you must do in the project (deliverables, sub deliverables, work packages, action items ), but also what is nonessential. The latter is important for the project plan, because knowing what isn’t high priority helps to avoid scope creep ; that is, using valuable resources for something that isn’t key to your project’s success.
4. Assemble a Project Team
You’ll need a capable project team to help you create your project plan and execute it successfully. It’s advisable to gather a diverse group of experienced professionals to build a multi-disciplinary team that sees your project management plan from different perspectives.
5. Determine a Project Budget
Once you define your project scope, you’ll have a task list that must be completed to deliver your project successfully. To do so, you’ll need resources such as equipment, materials, human capital, and of course, money. Your project budget will pay for all this. The first step to create a project budget is to estimate the costs associated with each task. Once you have those estimated costs, you can establish a cost baseline , which is the base for your project budget.
6. Set Project Goals & Objectives
Goals and objectives are different things when it comes to planning a project. Goals are the results you want to achieve, and are usually broad. Objectives , on the other hand, are more specific; measurable actions that must be taken to reach your goal. When creating a project plan, the goals and objectives naturally spring from the business case, but in this stage, you go into further detail. In a sense, you’re fine-tuning the goals set forth in the business case and creating tasks that are clearly defined. These goals and objectives are collected in a project charter , which you’ll use throughout the project life cycle.
7. Outline Project Deliverables
A project can have numerous deliverables. A deliverable can be a good, service or result that is needed to complete a task, process, phase, subproject or project. For example, the final deliverable is the reason for the project, and once this deliverable is produced, the project is completed. As defined in the project scope, a project consists of subprojects, phases, work packages, activities and tasks, and each of these components can have a deliverable. The first thing to do is determine what the final deliverable is, and how you will know that the quality meets your stakeholder’s expectations. As for the other deliverables in the project, they must also be identified and someone on the team must be accountable for their successful completion.
8. Create a Project Schedule
The project schedule is what everything hangs on. From your tasks to your budget , it’s all defined by time. Schedules are made up by collecting all the tasks needed to reach your final deliverable, and setting them on a project timeline that ends at your deadline. This can make for an unruly job ahead, which is why schedules are broken into phases, indicated by milestones , which mark the end of one project phase and the beginning of the next.
9. Assign Tasks to Your Team Members
The plan is set, but it still exists in the abstract until you take the tasks on your schedule and begin assigning them out to your team members. Their roles and responsibilities must be clearly defined, so they know what to do. Then, when you assign them tasks from your plan, they should be clear, with directions and any related documentation they will need to execute the tasks.
10. Do a Risk Analysis
Every project has some level of risk . There are several types of risk such as scope risk, technical risks and schedule risk, among others. Even if your project plan is thorough, internal and external factors can impact your project’s time, cost and scope (triple constraint). Therefore, you need to regard your planning as flexible. There are many ways to prepare for risk, such as developing a change management plan, but for now, the most important thing to do is to track your progress throughout the execution phase by using project status reports and/or project planning software to monitor risk.
11. Create your Project Plan
As discussed above, a project management plan is a document that’s made of several elements. Before we get into a detailed explanation of each of them, it’s important to understand that you should include them all to have a solid project plan. The components that you’ll need might vary depending on your project, but in general terms, you’ll need these main documents to create your project management plan:
- Project charter
- Project schedule
- Project budget
- Project scope statement
- Risk management plan
- Change management plan
- Cost management plan
- Resource management plan
- Stakeholder management plan
12. Report Your Progress
Your ultimate goal is to ensure a successful project for your stakeholders. They’re invested, and will not be satisfied twiddling their thumbs without looking at project status reports to track progress. By constructing a work breakdown structure (WBS) during the project planning phase you can break down the project for them so that they understand how your project plan will be executed. Keeping stakeholders informed is important to manage their expectations and ensure that they’re satisfied. Having regular planning meetings where you present progress reports are a great way to show them that everything is moving forward as planned and to field any questions or concerns they might have. Your stakeholder management plan will specify how you’ll engage stakeholders in the project.
Project planning software is a tool that helps to plan, organize and manage the schedule and resources needed to complete a project. ProjectManager is an award-winning project management software that organizes projects from planning to completion. Sign up for a free 30-day trial and follow along to build a thorough project plan that covers every detail.
1. List Your Tasks for the Plan
Tasks are the building blocks of any project and the start of any plan is identifying all the tasks that lead to your final deliverable.
Open the tool to add your tasks on the Gantt chart or one of the other multiple project views. You can import a task list from any spreadsheet or use one of our templates to get started.
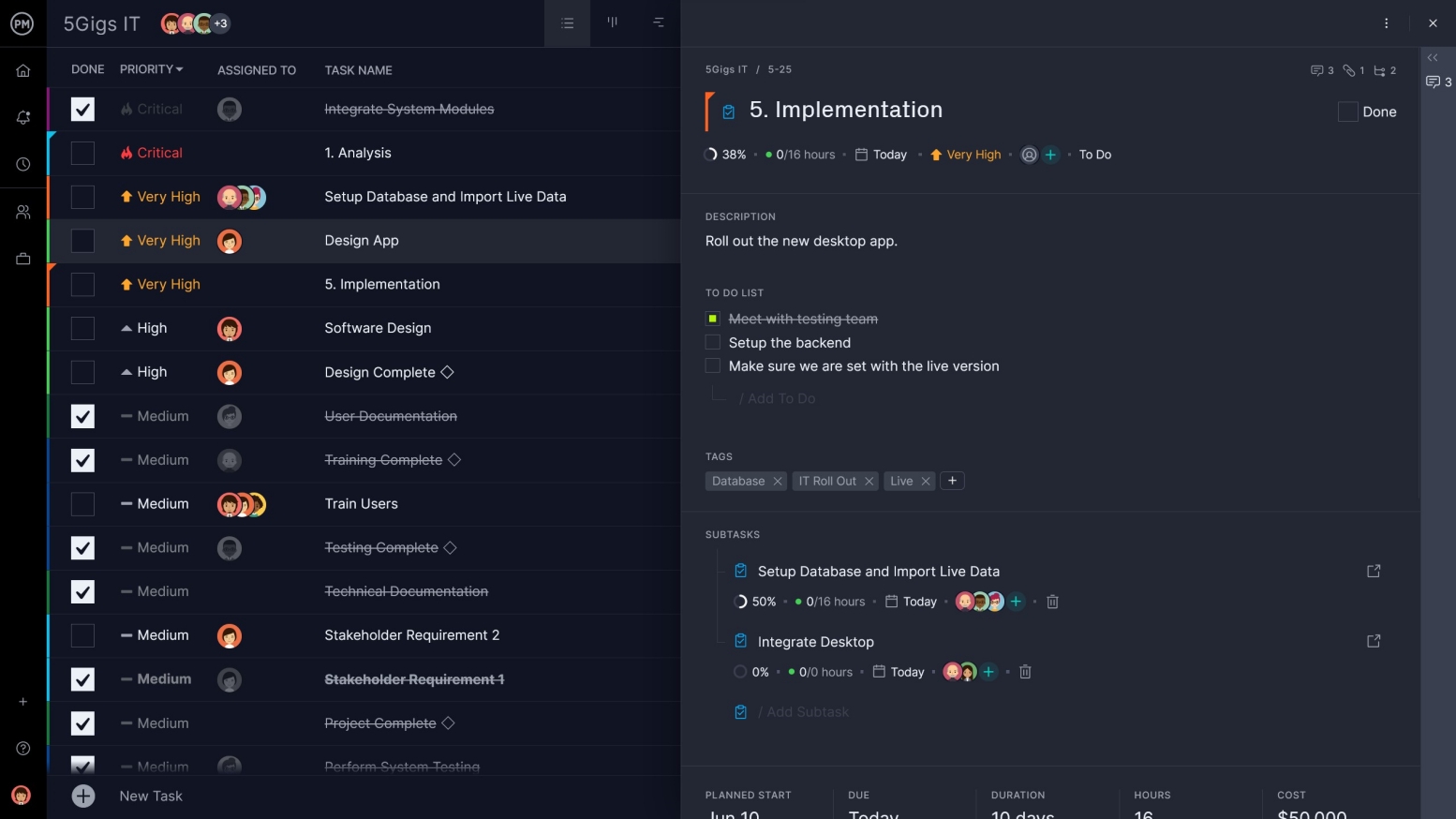
2. Add Duration and Costs to Tasks
Every task has an estimated duration, which is the time it will take to complete it. They will also require a certain amount of funding, which needs to be collected to formulate your plan.
Add the start and end dates for each task in the Gantt and they populate a project timeline, so you can see the whole project laid out in one place. There’s also a column for task costs.
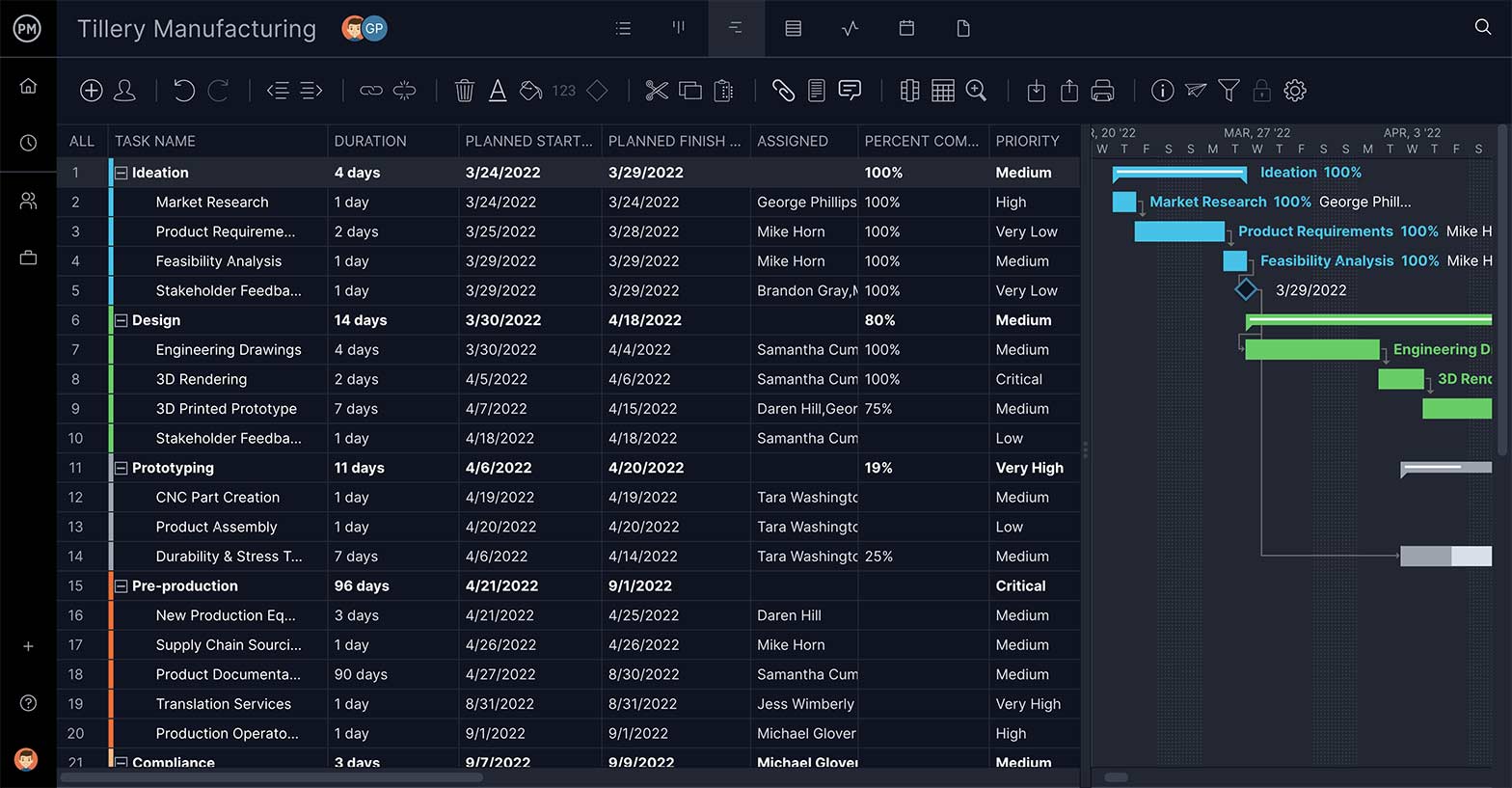
3. Link Dependent Tasks
Tasks are not always separate from one another. Often one cannot start or stop until another has started or stopped. That’s called a task dependency and needs to be noted in your plan.
Link dependent tasks by dragging one to the other. A dotted line indicates that they’re linked, so you stay aware of the fact and can avoid bottlenecks later in the project.
4. Set Milestones & Baseline
A milestone indicates the end of one phase and the beginning of another, which helps with tracking and morale. The baseline sets your plan so you can compare it to actual progress.
There is a filter on the Gantt that automatically sets the baseline, so you can use it to track your actual progress against the plan. The baseline can also be locked with a click.
5. Onboard Team & Assign
Getting the team and the tool together is how a project plan becomes actualized. The easier and seamless this transition, the faster you’ll get to work on the project.
Invite your team from the software and it generates an email with a link. Once they follow that link, they’re in and have access to the tools they need to manage their tasks.
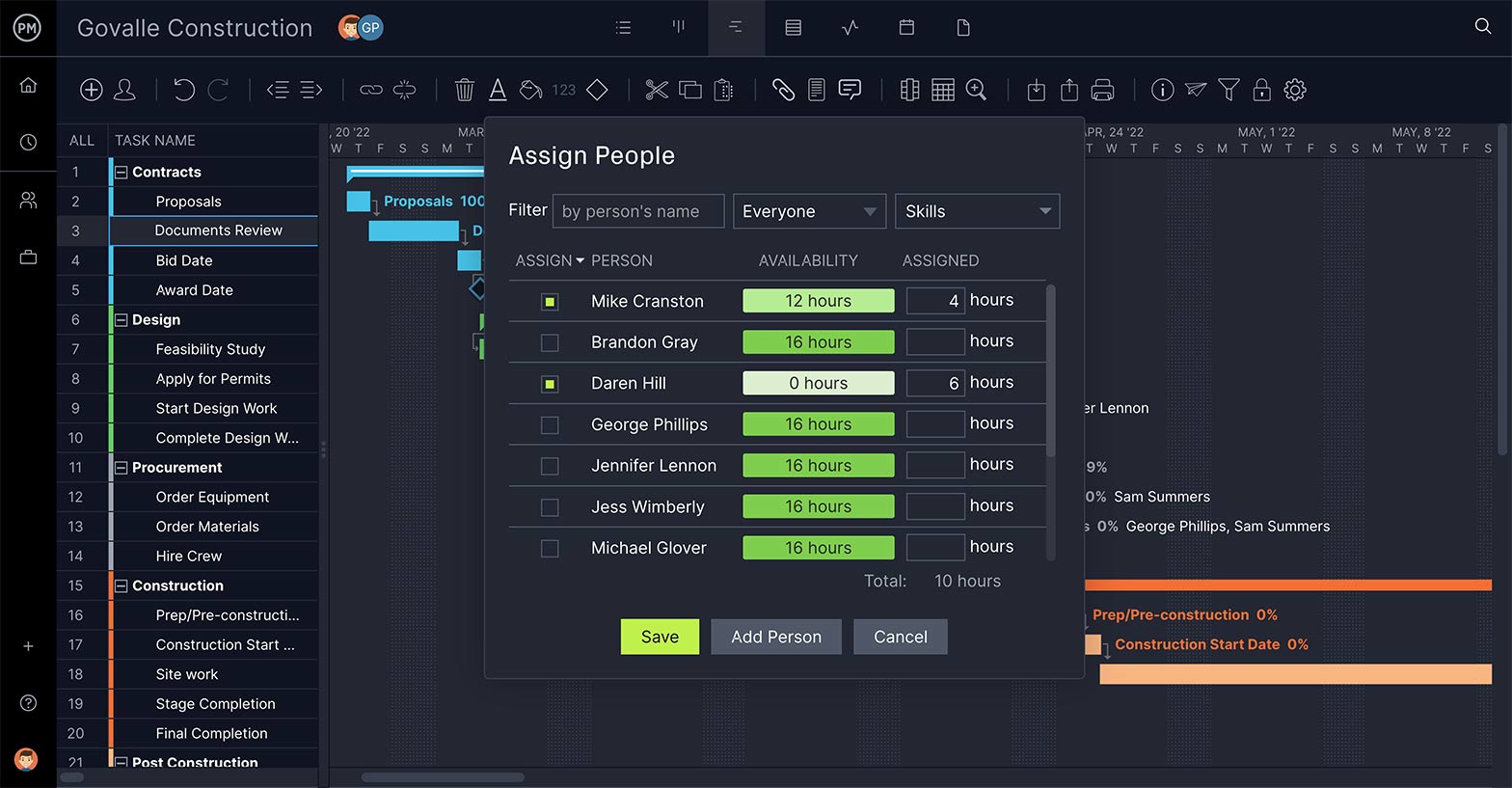
6. Monitor Progress & Report to Stakeholders
Keeping track of your progress and then updating stakeholders is both how you stay on track and manage your stakeholders’ expectations.
See progress as it happens on our real-time dashboard, which calculates data and displays it over six project metrics. Reports can be filtered and shared for a deep dive into those numbers.

7. Adjust Plan As Needed
No plan remains the same throughout a project. Things happen and changes are demanded. Therefore, being able to edit your plan easily is key to the project planning process.
Edit your plan on the Gantt by a simple drag and drop. Move the old date to the new date and not only is that task fixed, but any impacted tasks are also updated automatically.
ProjectManager is an award-winning software that helps managers plan and helps teams get organized. Gantt charts control all aspects of your project plan from scheduling to assigning tasks and even monitoring progress. Multiple project views provide transparency into workflow and give everyone the tools they need to be at their best.
Ready to make your plan? Try ProjectManager today with this free 30-day trial.
The project manager is responsible for producing the project plan, and while you can’t make up all the content yourself, you’ll be the one banging the keys to type it all out. Use templates where you can to save time. Download our free project plan template and write your plan in double-quick time!
The purpose of a project management plan is to serve as a guide for the execution and control phases. The project plan provides all the information necessary for the execution phase such as the project’s goals, objectives, scope of work, milestones, risks and resources. Then, this information helps project managers monitor and control the progress of the project.
We plan at the beginning to save time later. A good project plan means that you don’t have to worry about whether the project participants are going to be available on the right dates—because you’ve planned for them to be. You don’t have to worry about how to pay those invoices—you’ve planned your financial process. You don’t have to worry about whether everyone agrees on what a quality outcome looks like—you’ve already planned what quality measures you are going to use.
A good project plan sets out the processes that everyone is expected to follow, so it avoids a lot of headaches later. For example, if you specify that estimates are going to be worked out by subject matter experts based on their judgement, and that’s approved, later no one can complain that they wanted you to use a different estimating technique. They’ve known the deal since the start.
Project plans are also really helpful for monitoring progress. You can go back to them and check what you said you were going to do and how, comparing it to what you are actually doing. This gives you a good reality check and enables you to change course if you need to, bringing the project back on track.
Tools like dashboards can help you make sure that your project is proceeding according to plan. ProjectManager has a real-time dashboard that updates automatically whenever tasks are updated.
The project planning process already discussed only scratches the surface of what is a deep well of practices created to control your project. They start with dialogue — speaking to stakeholders, teams, et al.
The deliverable for your planning phase is a document called the project plan. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) – Fifth Edition says that the project plan is made up of lots of subsidiary plans. These include:
- A project scope statement to define all the tasks and deliverables that are needed to complete the project
- A risk management plan for dealing with project risk including the processes for logging and tracking risks
- A change management plan to manage any changes that will be made to the project plan
- A cost management plan for managing costs and the budgeting elements of the project including any procurements or supplier engagements you might have
- A resource management plan for managing the material resources such as equipment and the human resources on the team both in terms of availability and skills
- A stakeholder management plan setting out who is going to receive messages about the project, when and in what format
- A quality plan that specifies the quality targets for the project
That’s a lot of documentation.
In reality, it’s rare that you’ll produce these as individual documents. What you need is a project plan that talks about the important elements of each of these. There’s no point creating a big document that sets out exactly how your business works anyway. If you already have a structured risk management process , then don’t waste time writing it all down again in your project plan.
Your project management plan needs to include enough information to make sure that you know exactly what processes and procedures need to be followed and who needs to be involved. Get your project plan approved by your stakeholders, your project sponsor and your team so there are no surprises later. As explained above, project planning charts and techniques such as Gantt charts, CPM, WBS or PERT can help you create your project plan.
This is hard to answer. It’s going to take longer to plan the moon landing than a new dating app.
The best way to estimate how long your project planning phase will take is to look at similar projects that have happened before, and see how long it took them to plan. Talk to the project manager as well, if you can, because they’ll have a view on whether that length of time was enough or not!
It’s easy to see how long other projects took if you have a project management tool that archives your old project schedules and makes the data available to everyone who needs it. You can then search for similar projects and study their schedules in detail.
A project plan is all about working out what to do and how to do it, so you need to get a lot of people involved. There are several good tools and project planning techniques for getting information from other people including:
- One-to-one meetings or interviews
- Surveys or customer focus groups to gather and validate requirements.
You should also arm yourself with a task management tool , like a list or a kanban board. They are incredibly useful for noting down important things that should be in your project plan. Kanban board software can help structure your plan by writing down the key headings and then moving them around as required until you have a flow that looks right.

Finally, you’ll need an online project management system to store your project management plan in. Make sure that everyone in the team can access the latest version of the project plan.
Your project plan is not a document written in stone. You should be referring back to it and making changes to it as often as you need to. Parts of it, like your project schedule, will change almost daily. Other parts, like your procurement plans and cost management processes, won’t change at all during the life of your project.
The important thing to remember is that if your project management plan isn’t working for you, think about what you can do to change it. It’s there to guide your project management, not restrict you from doing the right thing. If you need to review how you manage work and project resources, then go back and review it. Make the changes you need, get the plan approved again and share it with the team.
How To Make a Project Plan When You Don’t Have All the Answers
Yes, this happens–most of the time! It’s rare to have all the information at the beginning of a project. Most managers want you to dive in and get started, but you might not have the luxury of knowing all the details.
That’s OK; we have techniques to help deal with uncertainty.
First is the project assumption. You use these to put caveats on your plan and to document the things that you assume to be true at this point in time. For example:
- We assume that the resources will be available.
- We assume that the required funding is available.
- We assume that the colors requested will be in line with the company brand and that Marketing sign off is not required.
You get the picture. Then, if the design team comes back and says that they want the product to be a totally new palette of colors and that Marketing has to approve that, you are justified in saying that you’ll have to change the timescales on the schedule to make that possible.
You planned based on an assumption (that everyone agreed to, because you got the document approved) and that assumption turned out not to be true.
Next Steps for Project Planning
The most important thing to remember is that you shouldn’t rush the project planning process. Done properly, project planning takes time. And it’s worth doing it properly because if you don’t, we guarantee that you will hit problems later on as people won’t understand what they are supposed to do and why.
Great planning sets you up for success. It gives you the confidence of knowing that you’ve got all your processes, tools and systems in place to deliver the perfect result.
Now that you’ve learned all about project planning, it’s time to take action. Sign up for a free 30-day trial of ProjectManager and start planning your project today!
Start My Free Trial
Project Planning Resources
- Best Project Planner Tools: Apps, Software & Templates
- Best Project Planning Software of 2024 (Free & Paid)
- 25 of the Best Planning Quotes
- 3 Best Planner Apps for Mac in 2024
- 3 Best Project Management Charts for Project Planning
- Project Management Trends
- How to Create a Project Roadmap (Example Included)
- What Is Aggregate Planning? Strategies & Tips
- What Is Rolling Wave Planning?
- How to Create a Project Execution Plan (PEP) – Free Template Included
- Sample Project Plan For Your Next Project
- Operational Planning: How to Make an Operations Plan
- Project Planning Software
- Gantt Chart Software
- Project Scheduling Software
- Work Breakdown Structure Software
- Project Timeline Software
- Resource Planning Software
- Free Project Planning Templates
- Free Project Management Templates
- Project Proposal Template
- Project Charter Template
- Project Timeline Template
- Implementation Plan Template
- Work Plan Template
- Action Plan Template
Start your free 30-day trial
Deliver faster, collaborate better, innovate more effectively — without the high prices and months-long implementation and extensive training required by other products.
Difference Between a Business Plan & a Business Proposal
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Why Create a Business Plan?
How to rescind a business letter, 6 types of business plans.
- How to Create a New Business Plan
- How to Conclude a Business Plan
A business plan and a business proposal are very different documents, with different purposes and goals. A business plan is a factual broad description of a company on the executive and operational level. A business proposal is a focused sales document intended to describe how a company will approach a project, state the value of the project to the client and solicit the client's business. A business plan is a written presentation of fact. A business proposal is a quote and call to action.
Reasons for a Business Plan
A business plan documents your vision for your business and how you intend to achieve that vision. It contains financial projections of what the business will cost to develop and operate plus an estimation of the revenues to be generated. Its purpose is to provide a reasonably detailed explanation of your business for use by potential investors, suppliers, prospective employees, accountants, attorneys and other people who need a quick but comprehensive understanding of what your company does and its potential for success. The primary reason for a business plan is to record and convey information.
Reasons for a Business Proposal
Proposals may be unsolicited business ideas presented to a potential customer or partner, or they may be answers to requests for proposal submitted to your company by a potential client. They are limited in scope to a particular project or need. A business proposal also generally has a specific audience. The primary reason for a business proposal is to solicit or develop a business opportunity.
Business Plan Structure
A business plan has three elements: description of the business model, the marketing model and financial projections. It consists of informative sections, including the executive summary, business description, marketing model, analysis of industry competition, build-out plan, operations plan, introduction of management, and a discussion of financial issues and projection of results. It is introduced by an executive summary, which can be a dense abstract or a longer marketing tool to attract interest in the business plan. The business plan is an informational document designed to factually display your company's operations and potential.
Business Proposal Structure
A business proposal written in response to a Request for Proposal (RFP) should follow the format requested in the RFP. Generally, this involves a quick description of your company's services and products that are relevant to the goals of the RFP, a reiteration of the scope of work, answers to specific questions posed in the RFP and a quote detailing materials, tools, labor, delivery and other elements of the cost of the project.
An unsolicited business proposal intended to create and develop a business opportunity follows essentially the same format but anticipates questions the potential client might have. A proposal is more of a marketing document, designed to convince the audience to do business by presenting a value proposition and a call to action.
- Entrepreneur: An Introduction to Business Plans
- Forbes: The Difference Between a Business Plan and Planning
Victoria Duff specializes in entrepreneurial subjects, drawing on her experience as an acclaimed start-up facilitator, venture catalyst and investor relations manager. Since 1995 she has written many articles for e-zines and was a regular columnist for "Digital Coast Reporter" and "Developments Magazine." She holds a Bachelor of Arts in public administration from the University of California at Berkeley.
Related Articles
5 types of business documents, what does a business plan consist of, the importance of a business plan, what is the relationship between the business plan, marketing plan & sales plan, examples of business feasibility reports, the differences between a business plan & business model, reasons to convert a pdf to microsoft word, what are the six elements of a business plan, mission statement vs. executive summary, most popular.
- 1 5 Types of Business Documents
- 2 What Does a Business Plan Consist Of?
- 3 The Importance of a Business Plan
- 4 What Is the Relationship Between the Business Plan, Marketing Plan & Sales Plan?
Difference Between a Business Plan and a Business Proposal

Table of contents
It’s natural to get confused between a business proposal and a business plan if you are planning to turn your idea into reality. While business proposals and plans may sound similar on the surface, they have differences — such as distinct purposes and formats.
A business plan describes your business goals, strategies, and financial projections. A business proposal, on the other hand, proposes a specific solution to a problem or opportunity and helps you persuade the relevant stakeholder to invest in your business.
However, writing a business proposal or a business plan can be challenging, especially if you are confused about their purpose. In this blog, we will explain the difference between a business plan and a business proposal and its major components.
Business Plan
A business plan tells the investors how you plan to ship your product to enough people to clock revenue. It’s about the strategies that will make you the first buck.
A business plan keeps your team on the same page — you can use it as a guiding light. It can help you track the progress of your business, give you a roadmap, and help you make decisions about your business’s future.
Plus, it can be helpful when it comes to pitching your business idea to a third party, for example, when seeking a loan.
Components of a Business Plan
A business plan is majorly divided into three sections, which include an executive summary, a sales and marketing strategy, and a financial plan.
An executive summary is a brief, clear, and compelling overview of your business. It is usually the first section of the document, and it contains the most important information, such as your strengths.
These can be further broken down into the following sections:
- Description of products and services, including mission, vision, and objectives of the business
- Target market
- Competitive advantage
- Industry and Competitor Analysis
- Marketing strategy
- Operating plan
- Team structure and qualifications
- Internal business analysis
- Management introduction
- Financial analysis
- Cash flow statement or sales forecast
- Break-even analysis
Business Proposal
A business proposal is a separate written document that outlines a specific business opportunity, project, or idea and presents it to potential clients.
It intends to persuade them to take action, such as accepting a business deal or entering into a partnership, thereby helping you get new customers or partners.
A business proposal should be customized to the needs and interests of the receiver. A generic proposal will rarely help you meet your business goals.
At the same time, ensure your proposal is well-organized, persuasive, and creative. Check out these free business proposal templates to impress your clients.
Solicited and Unsolicited Business Proposals
Proposals are solicited from you, or you send them on your initiative.
You write a solicited proposal in response to a prospect’s or customer’s request for a product. They may ask you verbally, or they may issue a written request for proposals (RFP). A solicited business proposal contains a detailed description of the product, service, or solution that you offer to solve the customer's problem or need. It’s generally easier to write because you know what the customer wants or expects.
But if you’re writing the proposal on your own, which is the case with unsolicited business proposals, then you’re convincing the receiver to work with you or buy from you. Such proposals are often challenging to write because you have to convince them they have a problem and you have a solution.
Components of a Business Proposal
The following are the key components of a business proposal :
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Problem statement
- Scope of work
- Benefits of Return on Investment (ROI)
- Call to Action (CTA)
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
While a business plan outlines your goals and explains how you will achieve them, a proposal sells your product to potential customers.
In the following table, we have summarized the main differences between a business plan and a business proposal:

Streamline the proposal creation process
To wrap up, a business proposal is a document that pitches your products or services to a potential client, while a business plan outlines your goals, strategies, and financial projections for your business.
With business management software like Cone, you can easily streamline and automate your proposal creation while ensuring your proposals are bespoke and customized. Sign up for free and experience the seamless proposal creation process for yourself. While you’re at it, check out other business proposals and management resources we have for you.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business plan is a formal document that contains the goals/ objective of the business, the time in which the goal will be completed and the strategies that can be adopted to reach the specific goal. A business plan is a necessary document for every new firm to have in place before it can begin operations.
Unravel the differences between a business plan and a proposal. Delve into their purposes, structures, and when to use each in your entrepreneurial journey.
The main difference between a business plan and a business proposal is that a business plan documents your growth strategy while a business proposal is a specific ask for someone to take an action you desire (e.g., buy your product/service, invest in your company, partner with you, etc.).
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it plans to achieve them. Business plans are valuable to both startup and established companies.
The difference between a business case and a business plan also derives from the fact that the business case usually refers to a project and one aspect of the business, whereas the business plan presents a detailed plan of action for the entire organisation over several years.
A business plan is a document that clearly spells out how a business intends to realize its objectives and goals, while a business proposal is a sales document that a business entity uses to request a contract from a client. Business Plan vs. Business Proposal.
Purpose: A business plan is primarily used for strategic planning and securing investment, while a business proposal is aimed at winning a specific contract or project. Audience : The audience for a business plan is typically potential investors, stakeholders, or company management.
Learn more. The project plan, also called project management plan, answers the who, what, where, why, how and when of the project—it’s more than a Gantt chart with tasks and due dates. The purpose of a project plan is to guide the execution and control project phases. As mentioned above, a project plan consists of the following documents:
A business plan and a business proposal are very different documents, with different purposes and goals. A business plan is a factual broad description of a company on the executive...
A business plan describes your business goals, strategies, and financial projections. A business proposal, on the other hand, proposes a specific solution to a problem or opportunity and helps you persuade the relevant stakeholder to invest in your business.