Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples

What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
State-of-the-art literature review methodology: A six-step approach for knowledge synthesis
- Original Article
- Open access
- Published: 05 September 2022
- Volume 11 , pages 281–288, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Erin S. Barry ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0788-7153 1 , 2 ,
- Jerusalem Merkebu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3707-8920 3 &
- Lara Varpio ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1412-4341 3
28k Accesses
8 Citations
18 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Introduction
Researchers and practitioners rely on literature reviews to synthesize large bodies of knowledge. Many types of literature reviews have been developed, each targeting a specific purpose. However, these syntheses are hampered if the review type’s paradigmatic roots, methods, and markers of rigor are only vaguely understood. One literature review type whose methodology has yet to be elucidated is the state-of-the-art (SotA) review. If medical educators are to harness SotA reviews to generate knowledge syntheses, we must understand and articulate the paradigmatic roots of, and methods for, conducting SotA reviews.
We reviewed 940 articles published between 2014–2021 labeled as SotA reviews. We (a) identified all SotA methods-related resources, (b) examined the foundational principles and techniques underpinning the reviews, and (c) combined our findings to inductively analyze and articulate the philosophical foundations, process steps, and markers of rigor.
In the 940 articles reviewed, nearly all manuscripts (98%) lacked citations for how to conduct a SotA review. The term “state of the art” was used in 4 different ways. Analysis revealed that SotA articles are grounded in relativism and subjectivism.
This article provides a 6-step approach for conducting SotA reviews. SotA reviews offer an interpretive synthesis that describes: This is where we are now. This is how we got here. This is where we could be going. This chronologically rooted narrative synthesis provides a methodology for reviewing large bodies of literature to explore why and how our current knowledge has developed and to offer new research directions.
Similar content being viewed by others
How to use and assess qualitative research methods

Doing Reflexive Thematic Analysis

Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Literature reviews play a foundational role in scientific research; they support knowledge advancement by collecting, describing, analyzing, and integrating large bodies of information and data [ 1 , 2 ]. Indeed, as Snyder [ 3 ] argues, all scientific disciplines require literature reviews grounded in a methodology that is accurate and clearly reported. Many types of literature reviews have been developed, each with a unique purpose, distinct methods, and distinguishing characteristics of quality and rigor [ 4 , 5 ].
Each review type offers valuable insights if rigorously conducted [ 3 , 6 ]. Problematically, this is not consistently the case, and the consequences can be dire. Medical education’s policy makers and institutional leaders rely on knowledge syntheses to inform decision making [ 7 ]. Medical education curricula are shaped by these syntheses. Our accreditation standards are informed by these integrations. Our patient care is guided by these knowledge consolidations [ 8 ]. Clearly, it is important for knowledge syntheses to be held to the highest standards of rigor. And yet, that standard is not always maintained. Sometimes scholars fail to meet the review’s specified standards of rigor; other times the markers of rigor have never been explicitly articulated. While we can do little about the former, we can address the latter. One popular literature review type whose methodology has yet to be fully described, vetted, and justified is the state-of-the-art (SotA) review.
While many types of literature reviews amalgamate bodies of literature, SotA reviews offer something unique. By looking across the historical development of a body of knowledge, SotA reviews delves into questions like: Why did our knowledge evolve in this way? What other directions might our investigations have taken? What turning points in our thinking should we revisit to gain new insights? A SotA review—a form of narrative knowledge synthesis [ 5 , 9 ]—acknowledges that history reflects a series of decisions and then asks what different decisions might have been made.
SotA reviews are frequently used in many fields including the biomedical sciences [ 10 , 11 ], medicine [ 12 , 13 , 14 ], and engineering [ 15 , 16 ]. However, SotA reviews are rarely seen in medical education; indeed, a bibliometrics analysis of literature reviews published in 14 core medical education journals between 1999 and 2019 reported only 5 SotA reviews out of the 963 knowledge syntheses identified [ 17 ]. This is not to say that SotA reviews are absent; we suggest that they are often unlabeled. For instance, Schuwirth and van der Vleuten’s article “A history of assessment in medical education” [ 14 ] offers a temporally organized overview of the field’s evolving thinking about assessment. Similarly, McGaghie et al. published a chronologically structured review of simulation-based medical education research that “reviews and critically evaluates historical and contemporary research on simulation-based medical education” [ 18 , p. 50]. SotA reviews certainly have a place in medical education, even if that place is not explicitly signaled.
This lack of labeling is problematic since it conceals the purpose of, and work involved in, the SotA review synthesis. In a SotA review, the author(s) collects and analyzes the historical development of a field’s knowledge about a phenomenon, deconstructs how that understanding evolved, questions why it unfolded in specific ways, and posits new directions for research. Senior medical education scholars use SotA reviews to share their insights based on decades of work on a topic [ 14 , 18 ]; their junior counterparts use them to critique that history and propose new directions [ 19 ]. And yet, SotA reviews are generally not explicitly signaled in medical education. We suggest that at least two factors contribute to this problem. First, it may be that medical education scholars have yet to fully grasp the unique contributions SotA reviews provide. Second, the methodology and methods of SotA reviews are poorly reported making this form of knowledge synthesis appear to lack rigor. Both factors are rooted in the same foundational problem: insufficient clarity about SotA reviews. In this study, we describe SotA review methodology so that medical educators can explicitly use this form of knowledge synthesis to further advance the field.
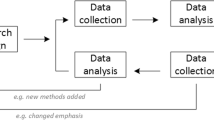
We developed a four-step research design to meet this goal, illustrated in Fig. 1 .
Four-step research design process used for developing a State-of-the-Art literature review methodology
Step 1: Collect SotA articles
To build our initial corpus of articles reporting SotA reviews, we searched PubMed using the strategy (″state of the art review″[ti] OR ″state of the art review*″) and limiting our search to English articles published between 2014 and 2021. We strategically focused on PubMed, which includes MEDLINE, and is considered the National Library of Medicine’s premier database of biomedical literature and indexes health professions education and practice literature [ 20 ]. We limited our search to 2014–2021 to capture modern use of SotA reviews. Of the 960 articles identified, nine were excluded because they were duplicates, erratum, or corrigendum records; full text copies were unavailable for 11 records. All articles identified ( n = 940) constituted the corpus for analysis.
Step 2: Compile all methods-related resources
EB, JM, or LV independently reviewed the 940 full-text articles to identify all references to resources that explained, informed, described, or otherwise supported the methods used for conducting the SotA review. Articles that met our criteria were obtained for analysis.
To ensure comprehensive retrieval, we also searched Scopus and Web of Science. Additionally, to find resources not indexed by these academic databases, we searched Google (see Electronic Supplementary Material [ESM] for the search strategies used for each database). EB also reviewed the first 50 items retrieved from each search looking for additional relevant resources. None were identified. Via these strategies, nine articles were identified and added to the collection of methods-related resources for analysis.
Step 3: Extract data for analysis
In Step 3, we extracted three kinds of information from the 940 articles papers identified in Step 1. First, descriptive data on each article were compiled (i.e., year of publication and the academic domain targeted by the journal). Second, each article was examined and excerpts collected about how the term state-of-the-art review was used (i.e., as a label for a methodology in-and-of itself; as an adjective qualifying another type of literature review; as a term included in the paper’s title only; or in some other way). Finally, we extracted excerpts describing: the purposes and/or aims of the SotA review; the methodology informing and methods processes used to carry out the SotA review; outcomes of analyses; and markers of rigor for the SotA review.
Two researchers (EB and JM) coded 69 articles and an interrater reliability of 94.2% was achieved. Any discrepancies were discussed. Given the high interrater reliability, the two authors split the remaining articles and coded independently.
Step 4: Construct the SotA review methodology
The methods-related resources identified in Step 2 and the data extractions from Step 3 were inductively analyzed by LV and EB to identify statements and research processes that revealed the ontology (i.e., the nature of reality that was reflected) and the epistemology (i.e., the nature of knowledge) underpinning the descriptions of the reviews. These authors studied these data to determine if the synthesis adhered to an objectivist or a subjectivist orientation, and to synthesize the purposes realized in these papers.
To confirm these interpretations, LV and EB compared their ontology, epistemology, and purpose determinations against two expectations commonly required of objectivist synthesis methods (e.g., systematic reviews): an exhaustive search strategy and an appraisal of the quality of the research data. These expectations were considered indicators of a realist ontology and objectivist epistemology [ 21 ] (i.e., that a single correct understanding of the topic can be sought through objective data collection {e.g., systematic reviews [ 22 ]}). Conversely, the inverse of these expectations were considered indicators of a relativist ontology and subjectivist epistemology [ 21 ] (i.e., that no single correct understanding of the topic is available; there are multiple valid understandings that can be generated and so a subjective interpretation of the literature is sought {e.g., narrative reviews [ 9 ]}).
Once these interpretations were confirmed, LV and EB reviewed and consolidated the methods steps described in these data. Markers of rigor were then developed that aligned with the ontology, epistemology, and methods of SotA reviews.
Of the 940 articles identified in Step 1, 98% ( n = 923) lacked citations or other references to resources that explained, informed, or otherwise supported the SotA review process. Of the 17 articles that included supporting information, 16 cited Grant and Booth’s description [ 4 ] consisting of five sentences describing the overall purpose of SotA reviews, three sentences noting perceived strengths, and four sentences articulating perceived weaknesses. This resource provides no guidance on how to conduct a SotA review methodology nor markers of rigor. The one article not referencing Grant and Booth used “an adapted comparative effectiveness research search strategy that was adapted by a health sciences librarian” [ 23 , p. 381]. One website citation was listed in support of this strategy; however, the page was no longer available in summer 2021. We determined that the corpus was uninformed by a cardinal resource or a publicly available methodology description.
In Step 2 we identified nine resources [ 4 , 5 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ]; none described the methodology and/or processes of carrying out SotA reviews. Nor did they offer explicit descriptions of the ontology or epistemology underpinning SotA reviews. Instead, these resources provided short overview statements (none longer than one paragraph) about the review type [ 4 , 5 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ]. Thus, we determined that, to date, there are no available methodology papers describing how to conduct a SotA review.
Step 3 revealed that “state of the art” was used in 4 different ways across the 940 articles (see Fig. 2 for the frequency with which each was used). In 71% ( n = 665 articles), the phrase was used only in the title, abstract, and/or purpose statement of the article; the phrase did not appear elsewhere in the paper and no SotA methodology was discussed. Nine percent ( n = 84) used the phrase as an adjective to qualify another literature review type and so relied entirely on the methodology of a different knowledge synthesis approach (e.g., “a state of the art systematic review [ 29 ]”). In 5% ( n = 52) of the articles, the phrase was not used anywhere within the article; instead, “state of the art” was the type of article within a journal. In the remaining 15% ( n = 139), the phrase denoted a specific methodology (see ESM for all methodology articles). Via Step 4’s inductive analysis, the following foundational principles of SotA reviews were developed: (1) the ontology, (2) epistemology, and (3) purpose of SotA reviews.
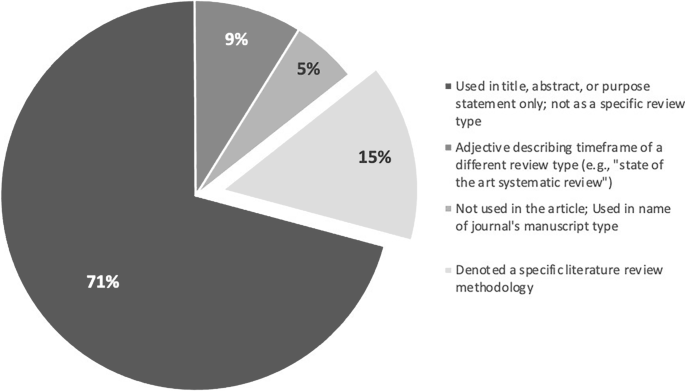
Four ways the term “state of the art” is used in the corpus and how frequently each is used
Ontology of SotA reviews: Relativism
SotA reviews rest on four propositions:
The literature addressing a phenomenon offers multiple perspectives on that topic (i.e., different groups of researchers may hold differing opinions and/or interpretations of data about a phenomenon).
The reality of the phenomenon itself cannot be completely perceived or understood (i.e., due to limitations [e.g., the capabilities of current technologies, a research team’s disciplinary orientation] we can only perceive a limited part of the phenomenon).
The reality of the phenomenon is a subjective and inter-subjective construction (i.e., what we understand about a phenomenon is built by individuals and so their individual subjectivities shape that understanding).
The context in which the review was conducted informs the review (e.g., a SotA review of literature about gender identity and sexual function will be synthesized differently by researchers in the domain of gender studies than by scholars working in sex reassignment surgery).
As these propositions suggest, SotA scholars bring their experiences, expectations, research purposes, and social (including academic) orientations to bear on the synthesis work. In other words, a SotA review synthesizes the literature based on a specific orientation to the topic being addressed. For instance, a SotA review written by senior scholars who are experts in the field of medical education may reflect on the turning points that have shaped the way our field has evolved the modern practices of learner assessment, noting how the nature of the problem of assessment has moved: it was first a measurement problem, then a problem that embraced human judgment but needed assessment expertise, and now a whole system problem that is to be addressed from an integrated—not a reductionist—perspective [ 12 ]. However, if other scholars were to examine this same history from a technological orientation, learner assessment could be framed as historically constricted by the media available through which to conduct assessment, pointing to how artificial intelligence is laying the foundation for the next wave of assessment in medical education [ 30 ].
Given these foundational propositions, SotA reviews are steeped in a relativist ontology—i.e., reality is socially and experientially informed and constructed, and so no single objective truth exists. Researchers’ interpretations reflect their conceptualization of the literature—a conceptualization that could change over time and that could conflict with the understandings of others.
Epistemology of SotA reviews: Subjectivism
SotA reviews embrace subjectivism. The knowledge generated through the review is value-dependent, growing out of the subjective interpretations of the researcher(s) who conducted the synthesis. The SotA review generates an interpretation of the data that is informed by the expertise, experiences, and social contexts of the researcher(s). Furthermore, the knowledge developed through SotA reviews is shaped by the historical point in time when the review was conducted. SotA reviews are thus steeped in the perspective that knowledge is shaped by individuals and their community, and is a synthesis that will change over time.
Purpose of SotA reviews
SotA reviews create a subjectively informed summary of modern thinking about a topic. As a chronologically ordered synthesis, SotA reviews describe the history of turning points in researchers’ understanding of a phenomenon to contextualize a description of modern scientific thinking on the topic. The review presents an argument about how the literature could be interpreted; it is not a definitive statement about how the literature should or must be interpreted. A SotA review explores: the pivotal points shaping the historical development of a topic, the factors that informed those changes in understanding, and the ways of thinking about and studying the topic that could inform the generation of further insights. In other words, the purpose of SotA reviews is to create a three-part argument: This is where we are now in our understanding of this topic. This is how we got here. This is where we could go next.
The SotA methodology
Based on study findings and analyses, we constructed a six-stage SotA review methodology. This six-stage approach is summarized and guiding questions are offered in Tab. 1 .
Stage 1: Determine initial research question and field of inquiry
In Stage 1, the researcher(s) creates an initial description of the topic to be summarized and so must determine what field of knowledge (and/or practice) the search will address. Knowledge developed through the SotA review process is shaped by the context informing it; thus, knowing the domain in which the review will be conducted is part of the review’s foundational work.
Stage 2: Determine timeframe
This stage involves determining the period of time that will be defined as SotA for the topic being summarized. The researcher(s) should engage in a broad-scope overview of the literature, reading across the range of literature available to develop insights into the historical development of knowledge on the topic, including the turning points that shape the current ways of thinking about a topic. Understanding the full body of literature is required to decide the dates or events that demarcate the timeframe of now in the first of the SotA’s three-part argument: where we are now . Stage 2 is complete when the researcher(s) can explicitly justify why a specific year or event is the right moment to mark the beginning of state-of-the-art thinking about the topic being summarized.
Stage 3: Finalize research question(s) to reflect timeframe
Based on the insights developed in Stage 2, the researcher(s) will likely need to revise their initial description of the topic to be summarized. The formal research question(s) framing the SotA review are finalized in Stage 3. The revised description of the topic, the research question(s), and the justification for the timeline start year must be reported in the review article. These are markers of rigor and prerequisites for moving to Stage 4.
Stage 4: Develop search strategy to find relevant articles
In Stage 4, the researcher(s) develops a search strategy to identify the literature that will be included in the SotA review. The researcher(s) needs to determine which literature databases contain articles from the domain of interest. Because the review describes how we got here , the review must include literature that predates the state-of-the-art timeframe, determined in Stage 2, to offer this historical perspective.
Developing the search strategy will be an iterative process of testing and revising the search strategy to enable the researcher(s) to capture the breadth of literature required to meet the SotA review purposes. A librarian should be consulted since their expertise can expedite the search processes and ensure that relevant resources are identified. The search strategy must be reported (e.g., in the manuscript itself or in a supplemental file) so that others may replicate the process if they so choose (e.g., to construct a different SotA review [and possible different interpretations] of the same literature). This too is a marker of rigor for SotA reviews: the search strategies informing the identification of literature must be reported.
Stage 5: Analyses
The literature analysis undertaken will reflect the subjective insights of the researcher(s); however, the foundational premises of inductive research should inform the analysis process. Therefore, the researcher(s) should begin by reading the articles in the corpus to become familiar with the literature. This familiarization work includes: noting similarities across articles, observing ways-of-thinking that have shaped current understandings of the topic, remarking on assumptions underpinning changes in understandings, identifying important decision points in the evolution of understanding, and taking notice of gaps and assumptions in current knowledge.
The researcher(s) can then generate premises for the state-of-the-art understanding of the history that gave rise to modern thinking, of the current body of knowledge, and of potential future directions for research. In this stage of the analysis, the researcher(s) should document the articles that support or contradict their premises, noting any collections of authors or schools of thinking that have dominated the literature, searching for marginalized points of view, and studying the factors that contributed to the dominance of particular ways of thinking. The researcher(s) should also observe historical decision points that could be revisited. Theory can be incorporated at this stage to help shape insights and understandings. It should be highlighted that not all corpus articles will be used in the SotA review; instead, the researcher(s) will sample across the corpus to construct a timeline that represents the seminal moments of the historical development of knowledge.
Next, the researcher(s) should verify the thoroughness and strength of their interpretations. To do this, the researcher(s) can select different articles included in the corpus and examine if those articles reflect the premises the researcher(s) set out. The researcher(s) may also seek out contradictory interpretations in the literature to be sure their summary refutes these positions. The goal of this verification work is not to engage in a triangulation process to ensure objectivity; instead, this process helps the researcher(s) ensure the interpretations made in the SotA review represent the articles being synthesized and respond to the interpretations offered by others. This is another marker of rigor for SotA reviews: the authors should engage in and report how they considered and accounted for differing interpretations of the literature, and how they verified the thoroughness of their interpretations.
Stage 6: Reflexivity
Given the relativist subjectivism of a SotA review, it is important that the manuscript offer insights into the subjectivity of the researcher(s). This reflexivity description should articulate how the subjectivity of the researcher(s) informed interpretations of the data. These reflections will also influence the suggested directions offered in the last part of the SotA three-part argument: where we could go next. This is the last marker of rigor for SotA reviews: researcher reflexivity must be considered and reported.
SotA reviews have much to offer our field since they provide information on the historical progression of medical education’s understanding of a topic, the turning points that guided that understanding, and the potential next directions for future research. Those future directions may question the soundness of turning points and prior decisions, and thereby offer new paths of investigation. Since we were unable to find a description of the SotA review methodology, we inductively developed a description of the methodology—including its paradigmatic roots, the processes to be followed, and the markers of rigor—so that scholars can harness the unique affordances of this type of knowledge synthesis.
Given their chronology- and turning point-based orientation, SotA reviews are inherently different from other types of knowledge synthesis. For example, systematic reviews focus on specific research questions that are narrow in scope [ 32 , 33 ]; in contrast, SotA reviews present a broader historical overview of knowledge development and the decisions that gave rise to our modern understandings. Scoping reviews focus on mapping the present state of knowledge about a phenomenon including, for example, the data that are currently available, the nature of that data, and the gaps in knowledge [ 34 , 35 ]; conversely, SotA reviews offer interpretations of the historical progression of knowledge relating to a phenomenon centered on significant shifts that occurred during that history. SotA reviews focus on the turning points in the history of knowledge development to suggest how different decisions could give rise to new insights. Critical reviews draw on literature outside of the domain of focus to see if external literature can offer new ways of thinking about the phenomenon of interest (e.g., drawing on insights from insects’ swarm intelligence to better understand healthcare team adaptation [ 36 ]). SotA reviews focus on one domain’s body of literature to construct a timeline of knowledge development, demarcating where we are now, demonstrating how this understanding came to be via different turning points, and offering new research directions. Certainly, SotA reviews offer a unique kind of knowledge synthesis.
Our six-stage process for conducting these reviews reflects the subjectivist relativism that underpins the methodology. It aligns with the requirements proposed by others [ 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ], what has been written about SotA reviews [ 4 , 5 ], and the current body of published SotA reviews. In contrast to existing guidance [ 4 , 5 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ], our description offers a detailed reporting of the ontology, epistemology, and methodology processes for conducting the SotA review.
This explicit methodology description is essential since many academic journals list SotA reviews as an accepted type of literature review. For instance, Educational Research Review [ 24 ], the American Academy of Pediatrics [ 25 ], and Thorax all lists SotA reviews as one of the types of knowledge syntheses they accept [ 27 ]. However, while SotA reviews are valued by academia, guidelines or specific methodology descriptions for researchers to follow when conducting this type of knowledge synthesis are conspicuously absent. If academics in general, and medical education more specifically, are to take advantage of the insights that SotA reviews can offer, we need to rigorously engage in this synthesis work; to do that, we need clear descriptions of the methodology underpinning this review. This article offers such a description. We hope that more medical educators will conduct SotA reviews to generate insights that will contribute to further advancing our field’s research and scholarship.
Cooper HM. Organizing knowledge syntheses: a taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowl Soc. 1988;1:104.
Google Scholar
Badger D, Nursten J, Williams P, Woodward M. Should all literature reviews be systematic? Eval Res Educ. 2000;14:220–30.
Article Google Scholar
Snyder H. Literature review as a research methodology: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2019;104:333–9.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Info Libr J. 2009;26:91–108.
Sutton A, Clowes M, Preston L, Booth A. Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Info Libr J. 2019;36:202–22.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Prisma Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097.
Tricco AC, Langlois E, Straus SE, World Health Organization, Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research. Rapid reviews to strengthen health policy and systems: a practical guide. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017.
Jackson R, Feder G. Guidelines for clinical guidelines: a simple, pragmatic strategy for guideline development. Br Med J. 1998;317:427–8.
Greenhalgh T, Thorne S, Malterud K. Time to challenge the spurious hierarchy of systematic over narrative reviews? Eur J Clin Invest. 2018;48:e12931.
Bach QV, Chen WH. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of microalgae via thermogravimetric analysis (TGA): a state-of-the-art review. Bioresour Technol. 2017;246:88–100.
Garofalo C, Milanović V, Cardinali F, Aquilanti L, Clementi F, Osimani A. Current knowledge on the microbiota of edible insects intended for human consumption: a state-of-the-art review. Food Res Int. 2019;125:108527.
Carbone S, Dixon DL, Buckley LF, Abbate A. Glucose-lowering therapies for cardiovascular risk reduction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: state-of-the-art review. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018;93:1629–47.
Hofkens PJ, Verrijcken A, Merveille K, et al. Common pitfalls and tips and tricks to get the most out of your transpulmonary thermodilution device: results of a survey and state-of-the-art review. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2015;47:89–116.
Schuwirth LW, van der Vleuten CP. A history of assessment in medical education. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2020;25:1045–56.
Arena A, Prete F, Rambaldi E, et al. Nanostructured zirconia-based ceramics and composites in dentistry: a state-of-the-art review. Nanomaterials. 2019;9:1393.
Bahraminasab M, Farahmand F. State of the art review on design and manufacture of hybrid biomedical materials: hip and knee prostheses. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2017;231:785–813.
Maggio LA, Costello JA, Norton C, Driessen EW, Artino AR Jr. Knowledge syntheses in medical education: a bibliometric analysis. Perspect Med Educ. 2021;10:79–87.
McGaghie WC, Issenberg SB, Petrusa ER, Scalese RJ. A critical review of simulation-based medical education research: 2003–2009. Med Educ. 2010;44:50–63.
Krishnan DG, Keloth AV, Ubedulla S. Pros and cons of simulation in medical education: a review. Education. 2017;3:84–7.
National Library of Medicine. MEDLINE: overview. 2021. https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medline/medline_overview.html . Accessed 17 Dec 2021.
Bergman E, de Feijter J, Frambach J, et al. AM last page: a guide to research paradigms relevant to medical education. Acad Med. 2012;87:545.
Maggio LA, Samuel A, Stellrecht E. Systematic reviews in medical education. J Grad Med Educ. 2022;14:171–5.
Bandari J, Wessel CB, Jacobs BL. Comparative effectiveness in urology: a state of the art review utilizing a systematic approach. Curr Opin Urol. 2017;27:380–94.
Elsevier. A guide for writing scholarly articles or reviews for the educational research review. 2010. https://www.elsevier.com/__data/promis_misc/edurevReviewPaperWriting.pdf . Accessed 3 Mar 2020.
American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics author guidelines. 2020. https://pediatrics.aappublications.org/page/author-guidelines . Accessed 3 Mar 2020.
Journal of the American College of Cardiology. JACC instructions for authors. 2020. https://www.jacc.org/pb-assets/documents/author-instructions-jacc-1598995793940.pdf . Accessed 3 Mar 2020.
Thorax. Authors. 2020. https://thorax.bmj.com/pages/authors/ . Accessed 3 Mar 2020.
Berven S, Carl A. State of the art review. Spine Deform. 2019;7:381.
Ilardi CR, Chieffi S, Iachini T, Iavarone A. Neuropsychology of posteromedial parietal cortex and conversion factors from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease: systematic search and state-of-the-art review. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022;34:289–307.
Chan KS, Zary N. Applications and challenges of implementing artificial intelligence in medical education: integrative review. JMIR Med Educ. 2019;5:e13930.
World Health Organization. Framework for action on interprofessional education and collaborative practice. 2010. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/framework-for-action-on-interprofessional-education-collaborative-practice . Accessed July 1 2021.
Hammersley M. On ‘systematic’ reviews of research literatures: a ‘narrative’ response to Evans & Benefield. Br Educ Res J. 2001;27:543–54.
Chen F, Lui AM, Martinelli SM. A systematic review of the effectiveness of flipped classrooms in medical education. Med Educ. 2017;51:585–97.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8:19–32.
Matsas B, Goralnick E, Bass M, Barnett E, Nagle B, Sullivan E. Leadership development in US undergraduate medical education: a scoping review of curricular content and competency frameworks. Acad Med. 2022;97:899–908.
Cristancho SM. On collective self-healing and traces: How can swarm intelligence help us think differently about team adaptation? Med Educ. 2021;55:441–7.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Rhonda Allard for her help with the literature review and compiling all available articles. We also want to thank the PME editors who offered excellent development and refinement suggestions that greatly improved this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Anesthesiology, F. Edward Hébert School of Medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, MD, USA
Erin S. Barry
School of Health Professions Education (SHE), Maastricht University, Maastricht, The Netherlands
Department of Medicine, F. Edward Hébert School of Medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, MD, USA
Jerusalem Merkebu & Lara Varpio
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Erin S. Barry .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
E.S. Barry, J. Merkebu and L. Varpio declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
The opinions and assertions contained in this article are solely those of the authors and are not to be construed as reflecting the views of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, the Department of Defense, or the Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine.
Supplementary Information
40037_2022_725_moesm1_esm.docx.
For information regarding the search strategy to develop the corpus and search strategy for confirming capture of any available State of the Art review methodology descriptions. Additionally, a list of the methodology articles found through the search strategy/corpus is included
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Barry, E.S., Merkebu, J. & Varpio, L. State-of-the-art literature review methodology: A six-step approach for knowledge synthesis. Perspect Med Educ 11 , 281–288 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40037-022-00725-9
Download citation
Received : 03 December 2021
Revised : 25 July 2022
Accepted : 27 July 2022
Published : 05 September 2022
Issue Date : October 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40037-022-00725-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- State-of-the-art literature review
- Literature review
- Literature review methodology
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Research Methods: Literature Reviews
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Literature Reviews
- Scoping Reviews
- Systematic Reviews
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Persuasive Arguments
- Subject Specific Methodology
A literature review involves researching, reading, analyzing, evaluating, and summarizing scholarly literature (typically journals and articles) about a specific topic. The results of a literature review may be an entire report or article OR may be part of a article, thesis, dissertation, or grant proposal. A literature review helps the author learn about the history and nature of their topic, and identify research gaps and problems.
Steps & Elements
Problem formulation
- Determine your topic and its components by asking a question
- Research: locate literature related to your topic to identify the gap(s) that can be addressed
- Read: read the articles or other sources of information
- Analyze: assess the findings for relevancy
- Evaluating: determine how the article are relevant to your research and what are the key findings
- Synthesis: write about the key findings and how it is relevant to your research
Elements of a Literature Review
- Summarize subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with objectives of the review
- Divide works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, those offering alternative theories entirely)
- Explain how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others
- Conclude which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of an area of research
Writing a Literature Review Resources
- How to Write a Literature Review From the Wesleyan University Library
- Write a Literature Review From the University of California Santa Cruz Library. A Brief overview of a literature review, includes a list of stages for writing a lit review.
- Literature Reviews From the University of North Carolina Writing Center. Detailed information about writing a literature review.
- Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach Cronin, P., Ryan, F., & Coughan, M. (2008). Undertaking a literature review: A step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing, 17(1), p.38-43
Literature Review Tutorial
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Scoping Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 12:00 PM
- URL: https://guides.auraria.edu/researchmethods
1100 Lawrence Street Denver, CO 80204 303-315-7700 Ask Us Directions
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley Open Access Collection

An overview of methodological approaches in systematic reviews
Prabhakar veginadu.
1 Department of Rural Clinical Sciences, La Trobe Rural Health School, La Trobe University, Bendigo Victoria, Australia
Hanny Calache
2 Lincoln International Institute for Rural Health, University of Lincoln, Brayford Pool, Lincoln UK
Akshaya Pandian
3 Department of Orthodontics, Saveetha Dental College, Chennai Tamil Nadu, India
Mohd Masood
Associated data.
APPENDIX B: List of excluded studies with detailed reasons for exclusion
APPENDIX C: Quality assessment of included reviews using AMSTAR 2
The aim of this overview is to identify and collate evidence from existing published systematic review (SR) articles evaluating various methodological approaches used at each stage of an SR.
The search was conducted in five electronic databases from inception to November 2020 and updated in February 2022: MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science Core Collection, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and APA PsycINFO. Title and abstract screening were performed in two stages by one reviewer, supported by a second reviewer. Full‐text screening, data extraction, and quality appraisal were performed by two reviewers independently. The quality of the included SRs was assessed using the AMSTAR 2 checklist.
The search retrieved 41,556 unique citations, of which 9 SRs were deemed eligible for inclusion in final synthesis. Included SRs evaluated 24 unique methodological approaches used for defining the review scope and eligibility, literature search, screening, data extraction, and quality appraisal in the SR process. Limited evidence supports the following (a) searching multiple resources (electronic databases, handsearching, and reference lists) to identify relevant literature; (b) excluding non‐English, gray, and unpublished literature, and (c) use of text‐mining approaches during title and abstract screening.
The overview identified limited SR‐level evidence on various methodological approaches currently employed during five of the seven fundamental steps in the SR process, as well as some methodological modifications currently used in expedited SRs. Overall, findings of this overview highlight the dearth of published SRs focused on SR methodologies and this warrants future work in this area.
1. INTRODUCTION
Evidence synthesis is a prerequisite for knowledge translation. 1 A well conducted systematic review (SR), often in conjunction with meta‐analyses (MA) when appropriate, is considered the “gold standard” of methods for synthesizing evidence related to a topic of interest. 2 The central strength of an SR is the transparency of the methods used to systematically search, appraise, and synthesize the available evidence. 3 Several guidelines, developed by various organizations, are available for the conduct of an SR; 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 among these, Cochrane is considered a pioneer in developing rigorous and highly structured methodology for the conduct of SRs. 8 The guidelines developed by these organizations outline seven fundamental steps required in SR process: defining the scope of the review and eligibility criteria, literature searching and retrieval, selecting eligible studies, extracting relevant data, assessing risk of bias (RoB) in included studies, synthesizing results, and assessing certainty of evidence (CoE) and presenting findings. 4 , 5 , 6 , 7
The methodological rigor involved in an SR can require a significant amount of time and resource, which may not always be available. 9 As a result, there has been a proliferation of modifications made to the traditional SR process, such as refining, shortening, bypassing, or omitting one or more steps, 10 , 11 for example, limits on the number and type of databases searched, limits on publication date, language, and types of studies included, and limiting to one reviewer for screening and selection of studies, as opposed to two or more reviewers. 10 , 11 These methodological modifications are made to accommodate the needs of and resource constraints of the reviewers and stakeholders (e.g., organizations, policymakers, health care professionals, and other knowledge users). While such modifications are considered time and resource efficient, they may introduce bias in the review process reducing their usefulness. 5
Substantial research has been conducted examining various approaches used in the standardized SR methodology and their impact on the validity of SR results. There are a number of published reviews examining the approaches or modifications corresponding to single 12 , 13 or multiple steps 14 involved in an SR. However, there is yet to be a comprehensive summary of the SR‐level evidence for all the seven fundamental steps in an SR. Such a holistic evidence synthesis will provide an empirical basis to confirm the validity of current accepted practices in the conduct of SRs. Furthermore, sometimes there is a balance that needs to be achieved between the resource availability and the need to synthesize the evidence in the best way possible, given the constraints. This evidence base will also inform the choice of modifications to be made to the SR methods, as well as the potential impact of these modifications on the SR results. An overview is considered the choice of approach for summarizing existing evidence on a broad topic, directing the reader to evidence, or highlighting the gaps in evidence, where the evidence is derived exclusively from SRs. 15 Therefore, for this review, an overview approach was used to (a) identify and collate evidence from existing published SR articles evaluating various methodological approaches employed in each of the seven fundamental steps of an SR and (b) highlight both the gaps in the current research and the potential areas for future research on the methods employed in SRs.
An a priori protocol was developed for this overview but was not registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), as the review was primarily methodological in nature and did not meet PROSPERO eligibility criteria for registration. The protocol is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. This overview was conducted based on the guidelines for the conduct of overviews as outlined in The Cochrane Handbook. 15 Reporting followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta‐analyses (PRISMA) statement. 3
2.1. Eligibility criteria
Only published SRs, with or without associated MA, were included in this overview. We adopted the defining characteristics of SRs from The Cochrane Handbook. 5 According to The Cochrane Handbook, a review was considered systematic if it satisfied the following criteria: (a) clearly states the objectives and eligibility criteria for study inclusion; (b) provides reproducible methodology; (c) includes a systematic search to identify all eligible studies; (d) reports assessment of validity of findings of included studies (e.g., RoB assessment of the included studies); (e) systematically presents all the characteristics or findings of the included studies. 5 Reviews that did not meet all of the above criteria were not considered a SR for this study and were excluded. MA‐only articles were included if it was mentioned that the MA was based on an SR.
SRs and/or MA of primary studies evaluating methodological approaches used in defining review scope and study eligibility, literature search, study selection, data extraction, RoB assessment, data synthesis, and CoE assessment and reporting were included. The methodological approaches examined in these SRs and/or MA can also be related to the substeps or elements of these steps; for example, applying limits on date or type of publication are the elements of literature search. Included SRs examined or compared various aspects of a method or methods, and the associated factors, including but not limited to: precision or effectiveness; accuracy or reliability; impact on the SR and/or MA results; reproducibility of an SR steps or bias occurred; time and/or resource efficiency. SRs assessing the methodological quality of SRs (e.g., adherence to reporting guidelines), evaluating techniques for building search strategies or the use of specific database filters (e.g., use of Boolean operators or search filters for randomized controlled trials), examining various tools used for RoB or CoE assessment (e.g., ROBINS vs. Cochrane RoB tool), or evaluating statistical techniques used in meta‐analyses were excluded. 14
2.2. Search
The search for published SRs was performed on the following scientific databases initially from inception to third week of November 2020 and updated in the last week of February 2022: MEDLINE (via Ovid), Embase (via Ovid), Web of Science Core Collection, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and American Psychological Association (APA) PsycINFO. Search was restricted to English language publications. Following the objectives of this study, study design filters within databases were used to restrict the search to SRs and MA, where available. The reference lists of included SRs were also searched for potentially relevant publications.
The search terms included keywords, truncations, and subject headings for the key concepts in the review question: SRs and/or MA, methods, and evaluation. Some of the terms were adopted from the search strategy used in a previous review by Robson et al., which reviewed primary studies on methodological approaches used in study selection, data extraction, and quality appraisal steps of SR process. 14 Individual search strategies were developed for respective databases by combining the search terms using appropriate proximity and Boolean operators, along with the related subject headings in order to identify SRs and/or MA. 16 , 17 A senior librarian was consulted in the design of the search terms and strategy. Appendix A presents the detailed search strategies for all five databases.
2.3. Study selection and data extraction
Title and abstract screening of references were performed in three steps. First, one reviewer (PV) screened all the titles and excluded obviously irrelevant citations, for example, articles on topics not related to SRs, non‐SR publications (such as randomized controlled trials, observational studies, scoping reviews, etc.). Next, from the remaining citations, a random sample of 200 titles and abstracts were screened against the predefined eligibility criteria by two reviewers (PV and MM), independently, in duplicate. Discrepancies were discussed and resolved by consensus. This step ensured that the responses of the two reviewers were calibrated for consistency in the application of the eligibility criteria in the screening process. Finally, all the remaining titles and abstracts were reviewed by a single “calibrated” reviewer (PV) to identify potential full‐text records. Full‐text screening was performed by at least two authors independently (PV screened all the records, and duplicate assessment was conducted by MM, HC, or MG), with discrepancies resolved via discussions or by consulting a third reviewer.
Data related to review characteristics, results, key findings, and conclusions were extracted by at least two reviewers independently (PV performed data extraction for all the reviews and duplicate extraction was performed by AP, HC, or MG).
2.4. Quality assessment of included reviews
The quality assessment of the included SRs was performed using the AMSTAR 2 (A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews). The tool consists of a 16‐item checklist addressing critical and noncritical domains. 18 For the purpose of this study, the domain related to MA was reclassified from critical to noncritical, as SRs with and without MA were included. The other six critical domains were used according to the tool guidelines. 18 Two reviewers (PV and AP) independently responded to each of the 16 items in the checklist with either “yes,” “partial yes,” or “no.” Based on the interpretations of the critical and noncritical domains, the overall quality of the review was rated as high, moderate, low, or critically low. 18 Disagreements were resolved through discussion or by consulting a third reviewer.
2.5. Data synthesis
To provide an understandable summary of existing evidence syntheses, characteristics of the methods evaluated in the included SRs were examined and key findings were categorized and presented based on the corresponding step in the SR process. The categories of key elements within each step were discussed and agreed by the authors. Results of the included reviews were tabulated and summarized descriptively, along with a discussion on any overlap in the primary studies. 15 No quantitative analyses of the data were performed.
From 41,556 unique citations identified through literature search, 50 full‐text records were reviewed, and nine systematic reviews 14 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 were deemed eligible for inclusion. The flow of studies through the screening process is presented in Figure 1 . A list of excluded studies with reasons can be found in Appendix B .

Study selection flowchart
3.1. Characteristics of included reviews
Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of included SRs. The majority of the included reviews (six of nine) were published after 2010. 14 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 Four of the nine included SRs were Cochrane reviews. 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 The number of databases searched in the reviews ranged from 2 to 14, 2 reviews searched gray literature sources, 24 , 25 and 7 reviews included a supplementary search strategy to identify relevant literature. 14 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 26 Three of the included SRs (all Cochrane reviews) included an integrated MA. 20 , 21 , 23
Characteristics of included studies
SR = systematic review; MA = meta‐analysis; RCT = randomized controlled trial; CCT = controlled clinical trial; N/R = not reported.
The included SRs evaluated 24 unique methodological approaches (26 in total) used across five steps in the SR process; 8 SRs evaluated 6 approaches, 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 while 1 review evaluated 18 approaches. 14 Exclusion of gray or unpublished literature 21 , 26 and blinding of reviewers for RoB assessment 14 , 23 were evaluated in two reviews each. Included SRs evaluated methods used in five different steps in the SR process, including methods used in defining the scope of review ( n = 3), literature search ( n = 3), study selection ( n = 2), data extraction ( n = 1), and RoB assessment ( n = 2) (Table 2 ).
Summary of findings from review evaluating systematic review methods
There was some overlap in the primary studies evaluated in the included SRs on the same topics: Schmucker et al. 26 and Hopewell et al. 21 ( n = 4), Hopewell et al. 20 and Crumley et al. 19 ( n = 30), and Robson et al. 14 and Morissette et al. 23 ( n = 4). There were no conflicting results between any of the identified SRs on the same topic.
3.2. Methodological quality of included reviews
Overall, the quality of the included reviews was assessed as moderate at best (Table 2 ). The most common critical weakness in the reviews was failure to provide justification for excluding individual studies (four reviews). Detailed quality assessment is provided in Appendix C .
3.3. Evidence on systematic review methods
3.3.1. methods for defining review scope and eligibility.
Two SRs investigated the effect of excluding data obtained from gray or unpublished sources on the pooled effect estimates of MA. 21 , 26 Hopewell et al. 21 reviewed five studies that compared the impact of gray literature on the results of a cohort of MA of RCTs in health care interventions. Gray literature was defined as information published in “print or electronic sources not controlled by commercial or academic publishers.” Findings showed an overall greater treatment effect for published trials than trials reported in gray literature. In a more recent review, Schmucker et al. 26 addressed similar objectives, by investigating gray and unpublished data in medicine. In addition to gray literature, defined similar to the previous review by Hopewell et al., the authors also evaluated unpublished data—defined as “supplemental unpublished data related to published trials, data obtained from the Food and Drug Administration or other regulatory websites or postmarketing analyses hidden from the public.” The review found that in majority of the MA, excluding gray literature had little or no effect on the pooled effect estimates. The evidence was limited to conclude if the data from gray and unpublished literature had an impact on the conclusions of MA. 26
Morrison et al. 24 examined five studies measuring the effect of excluding non‐English language RCTs on the summary treatment effects of SR‐based MA in various fields of conventional medicine. Although none of the included studies reported major difference in the treatment effect estimates between English only and non‐English inclusive MA, the review found inconsistent evidence regarding the methodological and reporting quality of English and non‐English trials. 24 As such, there might be a risk of introducing “language bias” when excluding non‐English language RCTs. The authors also noted that the numbers of non‐English trials vary across medical specialties, as does the impact of these trials on MA results. Based on these findings, Morrison et al. 24 conclude that literature searches must include non‐English studies when resources and time are available to minimize the risk of introducing “language bias.”
3.3.2. Methods for searching studies
Crumley et al. 19 analyzed recall (also referred to as “sensitivity” by some researchers; defined as “percentage of relevant studies identified by the search”) and precision (defined as “percentage of studies identified by the search that were relevant”) when searching a single resource to identify randomized controlled trials and controlled clinical trials, as opposed to searching multiple resources. The studies included in their review frequently compared a MEDLINE only search with the search involving a combination of other resources. The review found low median recall estimates (median values between 24% and 92%) and very low median precisions (median values between 0% and 49%) for most of the electronic databases when searched singularly. 19 A between‐database comparison, based on the type of search strategy used, showed better recall and precision for complex and Cochrane Highly Sensitive search strategies (CHSSS). In conclusion, the authors emphasize that literature searches for trials in SRs must include multiple sources. 19
In an SR comparing handsearching and electronic database searching, Hopewell et al. 20 found that handsearching retrieved more relevant RCTs (retrieval rate of 92%−100%) than searching in a single electronic database (retrieval rates of 67% for PsycINFO/PsycLIT, 55% for MEDLINE, and 49% for Embase). The retrieval rates varied depending on the quality of handsearching, type of electronic search strategy used (e.g., simple, complex or CHSSS), and type of trial reports searched (e.g., full reports, conference abstracts, etc.). The authors concluded that handsearching was particularly important in identifying full trials published in nonindexed journals and in languages other than English, as well as those published as abstracts and letters. 20
The effectiveness of checking reference lists to retrieve additional relevant studies for an SR was investigated by Horsley et al. 22 The review reported that checking reference lists yielded 2.5%–40% more studies depending on the quality and comprehensiveness of the electronic search used. The authors conclude that there is some evidence, although from poor quality studies, to support use of checking reference lists to supplement database searching. 22
3.3.3. Methods for selecting studies
Three approaches relevant to reviewer characteristics, including number, experience, and blinding of reviewers involved in the screening process were highlighted in an SR by Robson et al. 14 Based on the retrieved evidence, the authors recommended that two independent, experienced, and unblinded reviewers be involved in study selection. 14 A modified approach has also been suggested by the review authors, where one reviewer screens and the other reviewer verifies the list of excluded studies, when the resources are limited. It should be noted however this suggestion is likely based on the authors’ opinion, as there was no evidence related to this from the studies included in the review.
Robson et al. 14 also reported two methods describing the use of technology for screening studies: use of Google Translate for translating languages (for example, German language articles to English) to facilitate screening was considered a viable method, while using two computer monitors for screening did not increase the screening efficiency in SR. Title‐first screening was found to be more efficient than simultaneous screening of titles and abstracts, although the gain in time with the former method was lesser than the latter. Therefore, considering that the search results are routinely exported as titles and abstracts, Robson et al. 14 recommend screening titles and abstracts simultaneously. However, the authors note that these conclusions were based on very limited number (in most instances one study per method) of low‐quality studies. 14
3.3.4. Methods for data extraction
Robson et al. 14 examined three approaches for data extraction relevant to reviewer characteristics, including number, experience, and blinding of reviewers (similar to the study selection step). Although based on limited evidence from a small number of studies, the authors recommended use of two experienced and unblinded reviewers for data extraction. The experience of the reviewers was suggested to be especially important when extracting continuous outcomes (or quantitative) data. However, when the resources are limited, data extraction by one reviewer and a verification of the outcomes data by a second reviewer was recommended.
As for the methods involving use of technology, Robson et al. 14 identified limited evidence on the use of two monitors to improve the data extraction efficiency and computer‐assisted programs for graphical data extraction. However, use of Google Translate for data extraction in non‐English articles was not considered to be viable. 14 In the same review, Robson et al. 14 identified evidence supporting contacting authors for obtaining additional relevant data.
3.3.5. Methods for RoB assessment
Two SRs examined the impact of blinding of reviewers for RoB assessments. 14 , 23 Morissette et al. 23 investigated the mean differences between the blinded and unblinded RoB assessment scores and found inconsistent differences among the included studies providing no definitive conclusions. Similar conclusions were drawn in a more recent review by Robson et al., 14 which included four studies on reviewer blinding for RoB assessment that completely overlapped with Morissette et al. 23
Use of experienced reviewers and provision of additional guidance for RoB assessment were examined by Robson et al. 14 The review concluded that providing intensive training and guidance on assessing studies reporting insufficient data to the reviewers improves RoB assessments. 14 Obtaining additional data related to quality assessment by contacting study authors was also found to help the RoB assessments, although based on limited evidence. When assessing the qualitative or mixed method reviews, Robson et al. 14 recommends the use of a structured RoB tool as opposed to an unstructured tool. No SRs were identified on data synthesis and CoE assessment and reporting steps.
4. DISCUSSION
4.1. summary of findings.
Nine SRs examining 24 unique methods used across five steps in the SR process were identified in this overview. The collective evidence supports some current traditional and modified SR practices, while challenging other approaches. However, the quality of the included reviews was assessed to be moderate at best and in the majority of the included SRs, evidence related to the evaluated methods was obtained from very limited numbers of primary studies. As such, the interpretations from these SRs should be made cautiously.
The evidence gathered from the included SRs corroborate a few current SR approaches. 5 For example, it is important to search multiple resources for identifying relevant trials (RCTs and/or CCTs). The resources must include a combination of electronic database searching, handsearching, and reference lists of retrieved articles. 5 However, no SRs have been identified that evaluated the impact of the number of electronic databases searched. A recent study by Halladay et al. 27 found that articles on therapeutic intervention, retrieved by searching databases other than PubMed (including Embase), contributed only a small amount of information to the MA and also had a minimal impact on the MA results. The authors concluded that when the resources are limited and when large number of studies are expected to be retrieved for the SR or MA, PubMed‐only search can yield reliable results. 27
Findings from the included SRs also reiterate some methodological modifications currently employed to “expedite” the SR process. 10 , 11 For example, excluding non‐English language trials and gray/unpublished trials from MA have been shown to have minimal or no impact on the results of MA. 24 , 26 However, the efficiency of these SR methods, in terms of time and the resources used, have not been evaluated in the included SRs. 24 , 26 Of the SRs included, only two have focused on the aspect of efficiency 14 , 25 ; O'Mara‐Eves et al. 25 report some evidence to support the use of text‐mining approaches for title and abstract screening in order to increase the rate of screening. Moreover, only one included SR 14 considered primary studies that evaluated reliability (inter‐ or intra‐reviewer consistency) and accuracy (validity when compared against a “gold standard” method) of the SR methods. This can be attributed to the limited number of primary studies that evaluated these outcomes when evaluating the SR methods. 14 Lack of outcome measures related to reliability, accuracy, and efficiency precludes making definitive recommendations on the use of these methods/modifications. Future research studies must focus on these outcomes.
Some evaluated methods may be relevant to multiple steps; for example, exclusions based on publication status (gray/unpublished literature) and language of publication (non‐English language studies) can be outlined in the a priori eligibility criteria or can be incorporated as search limits in the search strategy. SRs included in this overview focused on the effect of study exclusions on pooled treatment effect estimates or MA conclusions. Excluding studies from the search results, after conducting a comprehensive search, based on different eligibility criteria may yield different results when compared to the results obtained when limiting the search itself. 28 Further studies are required to examine this aspect.
Although we acknowledge the lack of standardized quality assessment tools for methodological study designs, we adhered to the Cochrane criteria for identifying SRs in this overview. This was done to ensure consistency in the quality of the included evidence. As a result, we excluded three reviews that did not provide any form of discussion on the quality of the included studies. The methods investigated in these reviews concern supplementary search, 29 data extraction, 12 and screening. 13 However, methods reported in two of these three reviews, by Mathes et al. 12 and Waffenschmidt et al., 13 have also been examined in the SR by Robson et al., 14 which was included in this overview; in most instances (with the exception of one study included in Mathes et al. 12 and Waffenschmidt et al. 13 each), the studies examined in these excluded reviews overlapped with those in the SR by Robson et al. 14
One of the key gaps in the knowledge observed in this overview was the dearth of SRs on the methods used in the data synthesis component of SR. Narrative and quantitative syntheses are the two most commonly used approaches for synthesizing data in evidence synthesis. 5 There are some published studies on the proposed indications and implications of these two approaches. 30 , 31 These studies found that both data synthesis methods produced comparable results and have their own advantages, suggesting that the choice of the method must be based on the purpose of the review. 31 With increasing number of “expedited” SR approaches (so called “rapid reviews”) avoiding MA, 10 , 11 further research studies are warranted in this area to determine the impact of the type of data synthesis on the results of the SR.
4.2. Implications for future research
The findings of this overview highlight several areas of paucity in primary research and evidence synthesis on SR methods. First, no SRs were identified on methods used in two important components of the SR process, including data synthesis and CoE and reporting. As for the included SRs, a limited number of evaluation studies have been identified for several methods. This indicates that further research is required to corroborate many of the methods recommended in current SR guidelines. 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 Second, some SRs evaluated the impact of methods on the results of quantitative synthesis and MA conclusions. Future research studies must also focus on the interpretations of SR results. 28 , 32 Finally, most of the included SRs were conducted on specific topics related to the field of health care, limiting the generalizability of the findings to other areas. It is important that future research studies evaluating evidence syntheses broaden the objectives and include studies on different topics within the field of health care.
4.3. Strengths and limitations
To our knowledge, this is the first overview summarizing current evidence from SRs and MA on different methodological approaches used in several fundamental steps in SR conduct. The overview methodology followed well established guidelines and strict criteria defined for the inclusion of SRs.
There are several limitations related to the nature of the included reviews. Evidence for most of the methods investigated in the included reviews was derived from a limited number of primary studies. Also, the majority of the included SRs may be considered outdated as they were published (or last updated) more than 5 years ago 33 ; only three of the nine SRs have been published in the last 5 years. 14 , 25 , 26 Therefore, important and recent evidence related to these topics may not have been included. Substantial numbers of included SRs were conducted in the field of health, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Some method evaluations in the included SRs focused on quantitative analyses components and MA conclusions only. As such, the applicability of these findings to SR more broadly is still unclear. 28 Considering the methodological nature of our overview, limiting the inclusion of SRs according to the Cochrane criteria might have resulted in missing some relevant evidence from those reviews without a quality assessment component. 12 , 13 , 29 Although the included SRs performed some form of quality appraisal of the included studies, most of them did not use a standardized RoB tool, which may impact the confidence in their conclusions. Due to the type of outcome measures used for the method evaluations in the primary studies and the included SRs, some of the identified methods have not been validated against a reference standard.
Some limitations in the overview process must be noted. While our literature search was exhaustive covering five bibliographic databases and supplementary search of reference lists, no gray sources or other evidence resources were searched. Also, the search was primarily conducted in health databases, which might have resulted in missing SRs published in other fields. Moreover, only English language SRs were included for feasibility. As the literature search retrieved large number of citations (i.e., 41,556), the title and abstract screening was performed by a single reviewer, calibrated for consistency in the screening process by another reviewer, owing to time and resource limitations. These might have potentially resulted in some errors when retrieving and selecting relevant SRs. The SR methods were grouped based on key elements of each recommended SR step, as agreed by the authors. This categorization pertains to the identified set of methods and should be considered subjective.
5. CONCLUSIONS
This overview identified limited SR‐level evidence on various methodological approaches currently employed during five of the seven fundamental steps in the SR process. Limited evidence was also identified on some methodological modifications currently used to expedite the SR process. Overall, findings highlight the dearth of SRs on SR methodologies, warranting further work to confirm several current recommendations on conventional and expedited SR processes.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supporting information
APPENDIX A: Detailed search strategies
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The first author is supported by a La Trobe University Full Fee Research Scholarship and a Graduate Research Scholarship.
Open Access Funding provided by La Trobe University.
Veginadu P, Calache H, Gussy M, Pandian A, Masood M. An overview of methodological approaches in systematic reviews . J Evid Based Med . 2022; 15 :39–54. 10.1111/jebm.12468 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support

What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
A bibliometrics review of the journal mindfulness : science mapping the literature from 2012 to 2022.

- Department of Education and Learning Technology, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
This study conducts a bibliometric analysis using the Web of Science database on 1,950 articles published in the journal Mindfulness from 2012 to 2022. By constructing a knowledge graph, the research delineates the evolution, stages of development, and emerging trends in the field of mindfulness. Significant growth in the annual publication volume has been observed since 2012, with the research progression segmented into three distinct phases. The United States has emerged as a pivotal contributor to the field, dominating in terms of publication volume, researcher involvement, and institutional contributions. Through the application of keyword co-occurrence and reference co-citation analysis, five principal clusters were identified, focusing on mindfulness, meditation, depression, stress, and self-compassion, underscoring these as focal research areas. Furthermore, the exploration of mindfulness within the educational sphere in Taiwan is still nascent, signaling a critical need for bolstered research support in diverse thematic domains.
Introduction
Mental health, a cornerstone of contemporary society, substantially influences national productivity and interpersonal relationships. Recent advances in mindfulness research suggest that cultivating mindfulness fosters positive and resilient attitudes towards evolving social contexts. Kabat-Zinn’s pioneering work in 1979 integrated Buddhist mindfulness meditation into the medical realm, inaugurating Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) clinics—a milestone in healthcare applications of mindfulness ( Wen, 2016 ).
As research into mindfulness has deepened, its applications have broadened from medicine to fields such as psychology, education, business, and even commercialization ( Wilson, 2014 ). Empirical studies indicate that mindfulness enhances self-acceptance, care, and courage, which in turn uplifts the quality of life ( Dobkin and Zhao, 2011 ). Additionally, it mitigates symptoms of stress, depression, and anxiety, bolsters positive emotions, and improves psychological health ( Keng et al., 2011 ; Lakhan and Schofield, 2013 ; Penman and Burch, 2013 ). It also positively impacts attention and emotional regulation ( Wen, 2013 ), and strengthens interpersonal relationships ( Grossman et al., 2004 ; Davis and Hayes, 2011 ). As a holistic approach to psychological and physical well-being, mindfulness education encourages students to deepen their reflective thinking, enhance awareness, and apply mindfulness practices, thus continually advancing their academic and health outcomes. For instance, Napoli et al. (2005) observed that mindfulness improves children’s selective attention, mental health, and cognitive functions, enhancing overall well-being. Mindfulness interventions have also been shown to mitigate depressive symptoms in adolescents ( Raes et al., 2014 ; Kallapiran et al., 2015 ) and to enhance cognition, academic performance, behavior, and socio-emotional qualities among primary and secondary students ( Maynard et al., 2017 ). Hsieh (2018) advocates for the integration of mindfulness into school education and management, aiming to foster a comprehensive understanding of life’s significance, the pursuit of meaningful values, and the promotion of care and social responsibility.
In Taiwan, mindfulness research, albeit more recent, focuses on enhancing attention, body and mind awareness, emotional processing, and stress regulation through mindfulness practices, or explores its benefits in physical and mental health, professional development, and patient care ( Chen et al., 2019 ). Thus, it is necessary for Taiwan to further expand the application domains of mindfulness research and to support its development through government policies, as well as to strengthen interdisciplinary collaborations to deepen the understanding of mindfulness effects across various groups. For example, Jin and Liu (2017) implemented targeted mindfulness interventions for special student groups, providing insightful experiences applicable to broader student populations; Jiang et al. (2022) integrated insights from psychology, education, and sociology to explore how mindfulness parenting positively affects parent–child relationships and alleviates behavioral issues in children, contributing significantly to societal welfare.
The advent of Knowledge Graph technology has revolutionized the exploration of disciplines, academic communities, and intellectual traditions through the analysis of journal articles. Unlike traditional reviews and meta-analyses, bibliometric analysis offers a detailed summary of a field’s literature metrics and knowledge structure by examining the structural relationships among authors, countries, institutions, and themes, employing statistical methods such as article counts, reference co-citation analysis, and impact factors ( Donthu et al., 2021 ). This approach provides a more nuanced understanding of the dynamics across various scientific fields, enhancing the scope and depth of academic exploration.
To date, the systematic construction of knowledge graphs in the realm of mindfulness research remains limited. The journal Mindfulness serves as a critical resource for advancing the assessment, prevention, treatment, counseling, training, and collaboration of mindfulness theories and interdisciplinary studies. Given this backdrop, a comprehensive analysis of the mindfulness research literature is essential. This analysis will facilitate a macroscopic understanding of the developmental trajectory, knowledge base, research hotspots, and future research directions in this field. Moreover, it will inform recommendations and enhancements for education in Taiwan.
This paper employs VOSviewer (v.1.6.18) to analyze mindfulness-related research from 2012 to 2022, exploring thematic developments and presenting the findings via a knowledge graph, providing a foundational reference for future studies. This study addresses the following research questions:
1. What is the publication count and growth trajectory of mindfulness literature?
2. Which authors and countries have the most significant influence on mindfulness research?
3. What are the primary research hotspots within the field of mindfulness?
4. What implications does mindfulness research hold for the educational in Taiwan?
Literature review
“Mindfulness,” often associated with terms such as contemplation, introspection, and concentration, originates from the Buddhist term “sammā-sati,” which translates to “Right Mindfulness” or simply “Mindfulness.” This term encapsulates the concepts of awareness, attention, and remembering, essential for alleviating physical and mental stress ( Lv, 2014 ). Buddha, who lived approximately 2,500 years ago, emphasized that mindfulness is crucial for overcoming ‘attachment, aversion, and delusion.’
The theoretical foundation of mindfulness research was laid by Ellen Langer, a social psychologist at Harvard University. In her 1989 work, she proposed that many negative life outcomes, such as unhappiness, accidents, and poor health, could result from a lack of mindfulness ( Langer, 1989 ). Thus, she viewed mindfulness as both a method of mental training and a way of life, helping individuals to observe changes within their bodies and minds and to maintain an open, accepting, and clear presence in the moment ( Lin, 2013 ).
Mindfulness, deeply rooted in religious traditions, has evolved significantly under their influence. Wen (2013) emphasized that mindfulness focuses on present awareness and mental states, which profoundly impact human physical and mental health. The process involves causal interactions that construct what is termed “experience,” generated through the senses (eye, ear, nose, tongue, body, mind) and integrated conceptually. Mindfulness categorizes the six senses into five aggregates: form (material), sensation, perception (identification and evaluation), volitional formations (responses and actions), and consciousness. The practice asserts that identification with “self,” “mine,” or “myself” is illusory, and true awareness is based on this realization. Buddha taught that mental changes are constant and recognizing this allows for greater flexibility and acceptance in responding to life’s changes ( Ronald et al., 2009 ).
Mindfulness has been extensively researched within medicine, modern psychology, and social psychology, influenced initially by psychologist Kabat-Zinn. In 1979, he introduced the Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) technique, applying mindfulness to clinical psychology with a focus on emotional regulation, stress management, mind–body interaction, and meditation practices. Numerous studies have confirmed mindfulness’s effectiveness in alleviating physical and psychological distress ( Kabat-Zinn, 2003 ). Recent research indicates positive effects of mindfulness interventions on individuals with amphetamine-type substance use disorders (SUDs), highlighting improved mindful awareness and certain electroencephalographic functional connectivity ( Zhang et al., 2019 ). Additionally, a meta-analysis of 40 randomized controlled trials on mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) for SUDs, excluding tobacco use disorders, suggests these interventions might slightly reduce substance use days compared to standard care, cognitive-behavioral therapy, or pharmacotherapy, though further research is needed to confirm their overall effectiveness ( Goldberg et al., 2021 ). MBIs have also been successfully applied to a range of addictions, from smoking to alcohol, and behavioral addictions like gambling disorders, reducing dependency, cravings, and improving emotional states. Common MBI methods include Mindfulness-Based Relapse Prevention, Mindfulness Training for Smokers, and Mindfulness-Oriented Recovery Enhancement, with the integration of MBIs with treatment as usual (TAU) or other active treatments proving most effective ( Sancho et al., 2018 ). MBSR courses have not only benefitted the fields of medicine, psychology, and education but have also been widely promoted within the corporate sector, significantly improving physical and mental health, emotions, and quality of life ( Hsieh, 2019 ). Research by Valentine and Sweet (1999) showed that mindfulness meditators exhibit better psychological health than those practicing focused meditation. Various studies have explored the attention mechanisms of mindfulness meditation, correlating it with mental health improvements through attention regulation, body awareness, emotional regulation, and changing self-perceptions. Evidence suggests mindfulness meditation training enhances attention-related behavioral responses, cognitive abilities, reduces stress, and increases well-being ( Jha et al., 2007 ; Chiesa et al., 2011 ; Hölzel et al., 2011 ; Eberth and Sedlmeier, 2012 ; Jensen et al., 2012 ).
Research on self-compassion, particularly prevalent in Western studies, highlights its components—self-love, reduced self-judgment, decreased feelings of isolation, mindfulness, and lessened over-identification. Self-compassion interventions foster self-care, kindness, and tolerance, aiding individuals, especially the youth, in developing positive internal processing systems and reducing mental health issues. Its core aspects include treating oneself kindly, recognizing common humanity, and maintaining mindfulness ( Neff, 2003a ; MacBeth and Gumley, 2012 ; Körner et al., 2015 ; Costa et al., 2016 ; Muris et al., 2016 ; Neff et al., 2017 , 2019 ). Additionally, mindfulness regulates emotions, enhances attention, reduces stress, and positively impacts interpersonal communication and creativity ( Grossman et al., 2004 ; Corcoran et al., 2010 ; Farb et al., 2010 ; Davis and Hayes, 2011 ; Keng et al., 2011 ; Lakhan and Schofield, 2013 ; Lawlor, 2014 ; Penman and Burch, 2013 ; Wall, 2014 ; Willis and Dinehart, 2014 ; Laukkonen et al., 2020 ).
Compared to Western studies, mindfulness research in Taiwan shows distinct traits. In quantitative studies, there is a strong focus on developing mindfulness scales, therapeutic interventions, and curriculum implementation. For example, Huang et al. (2015) conducted reliability and validity analyses of the “Taiwanese Version of the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire”; Liu and Rau (2015) investigated how mindfulness meditation enhances attention; Yang (2016) integrated mindfulness practices into curricula and assessed impacts through pre- and post-tests using the “Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire,” “Stress Perception,” and “Mindfulness Attention Awareness Scale.” In qualitative research, studies often focus on specific benefits or challenges encountered during mindfulness practices. For instance, Zheng et al. (2013) examined the effects of adult mindfulness courses on depression, anxiety, and mindfulness awareness, finding no significant differences; Shin and Jin (2010) discussed how “Zen Mindfulness Groups” influence intern counselors’ self-focus and professional practices. These studies provide insights into the effects of mindfulness on specific target groups and contribute to a deeper understanding of factors influencing mindfulness practices.
The ongoing deepening of mindfulness practice enables scholars to gain profound insights into their behavioral and cognitive patterns, reflecting on and adjusting their values and beliefs. This integration of awareness and action not only advances research in mindfulness but also demonstrates its significant applicative value across various fields such as medicine, psychology, and education, effectively enhancing individual well-being and broader societal impact.
In recent years, bibliometric analysis has emerged as a fundamental method in scientific research, providing quantitative and statistical evaluation of scholarly outputs such as journal articles, citation counts, and impact factors ( Donthu et al., 2021 ). First introduced by Pritchard in 1969, the concept of bibliometrics pertains to the systematic analysis of scholarly literature to understand the evolution and structural dynamics of academic disciplines ( Pritchard, 1969 ). This review applies bibliometric techniques to scrutinize significant literature and themes within the field of mindfulness research, aiming to delineate the current state of the discipline and project future research directions.
The analysis utilizes VOSviewer (version 1.6.18) as the principal tool, capitalizing on its ability to create knowledge maps that visualize relationships between various bibliometric elements. These include descriptive analysis, examination of authorship and geographical distribution, keyword co-occurrence, and reference co-citation analyses. VOSviewer is renowned for its effectiveness in graphically representing scientific landscapes, thereby facilitating the exploration of connections across diverse research areas ( Van Eck and Waltman, 2010 ; Zupic and Čater, 2015 ).
Keyword co-occurrence analysis is particularly valuable for detecting research development trends and assessing the status of domains ( Zhang, 2013 ; Yang, 2015 ). In this analysis, keywords with higher co-occurrence frequencies are indicative of prevailing research hotspots, highlighting the central themes within the field. This method employs visual representations of co-occurrence networks, where nodes represent keywords, encapsulating the cumulative knowledge of a domain, and links illustrate the relationships between word pairs, denoting their co-occurrence ( Radhakrishnan et al., 2017 ).
Reference co-citation analysis is employed to measure the similarity between documents or topics based on the frequency of their co-citations ( Small, 1973 ). The density of connection lines in the co-citation network graphically represents the strength of relationships between documents, providing insights into the interconnectedness of research themes. This type of analysis is crucial for identifying topics that have gained traction in the short term and may also indicate emerging research frontiers ( Zhang, 2013 )
Data source, procedure, and analytic software
This study employs data sourced from the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection, which includes the Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI), Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-Expanded), and Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI). These databases are recognized for their extensive reach and integration across multiple disciplinary areas, holding significant academic influence ( Zyoud et al., 2017 ). WoS is particularly noted for its comprehensive coverage, with approximately 99.11% of its indexed journals also featured in the Scopus database, underscoring its broad applicability and prominence in global research landscapes ( Singh et al., 2021 ). The journal Mindfulness , indexed in the SSCI and ranking highly within the Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology categories, consistently achieves Q1 and Q2 status, indicative of its high-quality scholarly output. Thus, the selection of research papers from these sources ensures a reliable representation of the mindfulness research quality, supporting the validity of the study’s findings.
Bibliometric analysis serves as a crucial tool for elucidating the accumulated scientific knowledge and developmental nuances of established fields through the systematic examination of large volumes of unstructured data ( Donthu et al., 2021 ). This study adopts the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) framework ( Figure 1 ), guiding the systematic literature review process to ensure transparency and standardization in the bibliometric methodology. This approach aids in the precise selection of relevant outcomes ( Moher et al., 2009 ). This study specifically focuses on articles from the Mindfulness journal indexed in the WoS database, covering the period from 2012 to 2022. The selected articles encompass a wide array of types, including academic papers, conference proceedings, editorial materials, book reviews, and chapters. These documents collectively address diverse aspects of mindfulness, including therapy and intervention measures tailored to different populations, and explore various research directions such as the application of mindfulness in different therapeutic contexts and intervention strategies. After removing duplicates and irrelevant entries, a search conducted in December 2022 resulted in a corpus of 1,950 documents ( Figure 1 ), forming the basis for subsequent bibliometric analyses.
Figure 1 . Flow diagram of study selection process.
The extracted data includes authors, paper titles, and keywords, which were inputted into the VOSviewer software for visual mapping. This software supports the comparison of normalized cluster networks, coverage visualization, and density visualization ( Van Eck and Waltman, 2010 ), allowing for comprehensive bibliometric analysis through appropriately set threshold values.
Results and discussion
Yearly quantitative distribution of literature.
As shown in Figure 2 , the journal Mindfulness has published a total of 1,950 articles in the WoS database as of December 2022. Since its inception in 2012, the annual publication volume has exhibited a consistent upward trajectory, delineated into three distinct stages: the “Emergence Stage” (2012–2014), where fewer than 100 articles were published each year; the “Exploration Stage” (2015–2018), characterized by a gradual increase in publication numbers, with 2015 marking the first year the journal exceeded 150 articles; and the “Growth Stage” (2019–2022), noted for a robust and stable trend of publishing over 200 articles annually starting in 2019. This latter stage underscores a burgeoning interest in mindfulness research. Nonetheless, there was a notable decline in publication numbers in 2021 and 2022, a trend likely influenced by the global disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
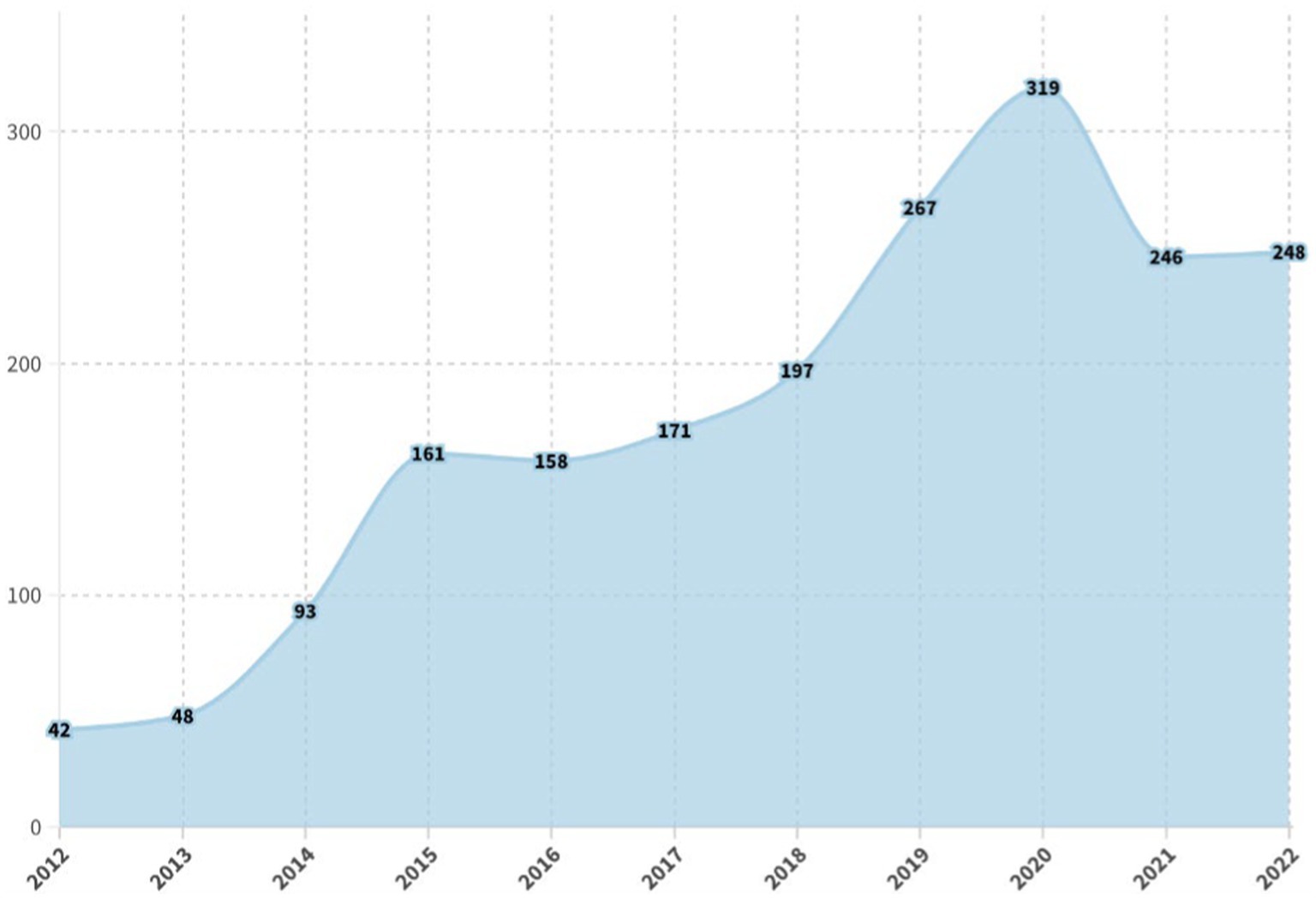
Figure 2 . Yearly quantitative distribution of literature.
Significant publications in different development stages
Table 1 categorizes key literature from the journal Mindfulness into three developmental stages, highlighting the impact of these works through the lens of “the top three most-cited articles” in the WoS database. This method underscores the relevance and significance of these articles within their respective research domains.
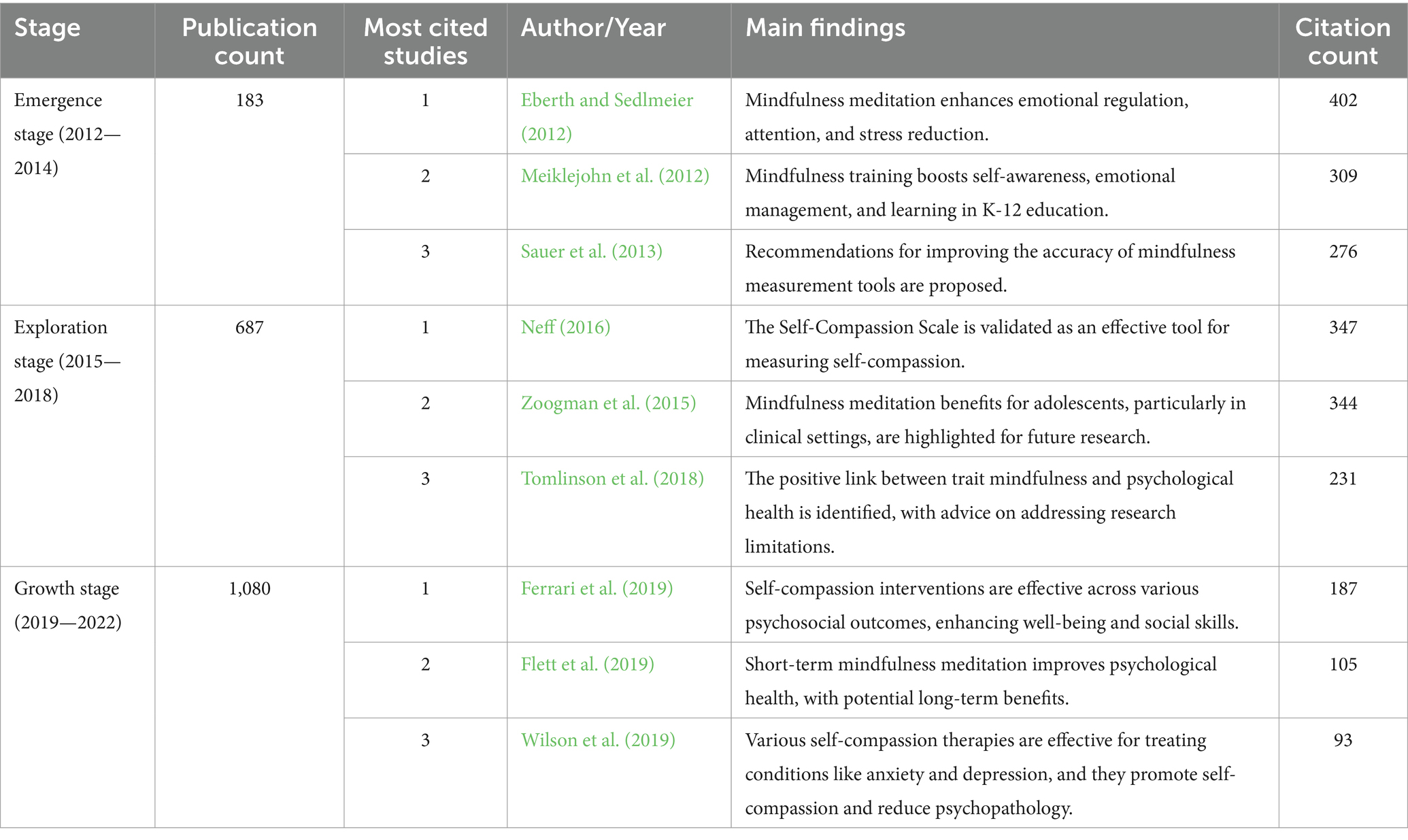
Table 1 . Significant publications in different development stages.
During the “Emergence Stage” (2012–2014), 183 articles were published. The top three most-cited articles included Eberth and Sedlmeier (2012) , Meiklejohn et al. (2012) , and Sauer et al. (2013) . Eberth and Sedlmeier (2012) offered a comprehensive review of the effects of mindfulness meditation on various psychological variables among non-clinical meditators. Meiklejohn et al. (2012) explored the integration of mindfulness training into K-12 curricula, employing a combination of direct and indirect teaching methods facilitated by teacher training. This study highlighted that continuous mindfulness practice enhances attention and emotional regulation, benefiting both teachers and students. Sauer et al. (2013) emphasized the necessity of comparing mindfulness measurement results obtained through self-assessment tools with those from other mindfulness measurement tools, providing insights for improving current methodologies.
The “Exploration Stage” (2015–2018) produced 687 articles, with Zoogman et al. (2015) , Neff (2016) , and Tomlinson et al. (2018) being the most cited. Neff (2016) introduced the Self-Compassion Scale (SCS), establishing it as an effective measure of self-compassion and highlighting the importance of the “self-criticism” factor. Zoogman et al. (2015) investigated mindfulness-based interventions for adult depression and anxiety, suggesting potential applicability to adolescents, especially in non-clinical settings. Tomlinson et al. (2018) examined the correlation between trait mindfulness and mental health, indicating positive impacts and pointing out areas for future research, including addressing conceptual and methodological challenges in the field.
From 2019 to 2022, the “Growth Stage” saw the publication of 1,080 articles, with significant contributions from Ferrari et al. (2019) , Flett et al. (2019) , and Wilson et al. (2019) . Ferrari et al. (2019) validated the effectiveness of self-compassion interventions in enhancing psychosocial outcomes. Flett et al. (2019) explored both the short-term and long-term benefits of mindfulness meditation on mental health. Wilson et al. (2019) reviewed therapies related to self-compassion, including compassion-focused therapy and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, demonstrating significant improvements in conditions like anxiety and depression, thus promoting self-compassion and reducing psychopathology among both clinical and subclinical populations.
In summary, each developmental stage of Mindfulness research progressively explores different facets, with a significant emphasis on the management and regulation of psychological processes like self-regulation, emotions, and psychological health, which are increasingly recognized as central themes in contemporary mindfulness research.
Distribution of authors
As shown in Figure 3 , this study’s analysis of author distribution provides insights into their connections with international scholars. Among the 200 authors featured on Mindfulness, notable contributors include Kabat-Zinn, Analayo, Van Gordon, Medvedev and Bögels.
Figure 3 . Distribution of authors.
In 1979, Dr. Kabat-Zinn launched the MBSR program at the University of Massachusetts Medical School, effectively helping patients handle stress, pain, and illness through mindfulness techniques. His method, practiced in over 200 medical institutions across North America, has significantly influenced healthcare, education, and other sectors for decades. Dr. Kabat-Zinn’s numerous publications, including Full Catastrophe Living and The Mindful Way Through Depression, have further popularized these approaches ( Kabat-Zinn, 2023 ).
Dr. Analayo of the Barre Center for Buddhist Studies and the Numata Centre for Buddhist Studies at The University of Hamburg focuses on early Buddhist texts and meditation practices. His work bridges ancient Buddhist techniques with modern practices, exploring mindfulness as a connection between mind and body, vital for continuous awareness in daily life ( Anālayo, 2020 ).
Dr. Van Gordon, from the University of Derby, has established credibility in studying the efficacy of Buddhist-derived meditations like Loving-Kindness Meditation (LKM) and Compassion Meditation (CM) in treating a range of mental health problems. His research emphasizes the foundational importance of Meditation Awareness Training (MAT) in enhancing psychological well-being in educational settings among other applications ( University of Derby, 2023 ).
Dr. Medvedev from the University of Waikato has refined the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire using Rasch analysis to enhance its precision and validity, supporting its application in diverse psychological and health-related fields ( The University of Waikato, 2023 ). His research covers various fields, such as assessment methods, health psychology, psychophysiology, and biostatistics.
Dr. Bögels, a professor at the University of Amsterdam, has extensively researched the interplay between cognitive-behavioral therapy and mood disorders in treating childhood social anxiety ( University of Amsterdam, 2023 ). Her findings on the effectiveness of mindful parenting as a therapeutic intervention highlight its benefits in reducing stress and improving family dynamics ( Bögels et al., 2014 ).
As shown in Table 2 , Kabat-Zinn, Analayo, and Van Gordon have predominantly focused on exploring aspects of Buddha’s teachings, the inherent purity of the meditator’s mind, and Meditation Awareness Mindfulness, among other elements. Analayo and Van Gordon bring unique perspectives to their empirical research on meditation’s role in regulating personal physical and mental states, enhancing internal awareness, insight, compassion, and peace. Kabat-Zinn, on the other hand, has been pivotal in integrating mindfulness into psychological therapy and neuropsychology, significantly advancing the therapeutic landscape by mitigating physical and mental distress and promoting overall well-being. Their collective research emphasizes the efficacy of mindfulness interventions in alleviating anxiety and stress, while also advocating for the enhancement of physical and mental health and overall happiness. Medvedev, renowned for his expertise in assessing mindfulness, excels in documenting the observable benefits and self-regulation strategies of mindfulness training through the use of questionnaires, observations, and interviews. In contrast, Bögels concentrates on the application of mindfulness counseling treatment to address stress, depressive mood, and situational trait anxiety among children and their parents, revealing significant benefits in children’s cognition, social interaction, self-care, and mental health.
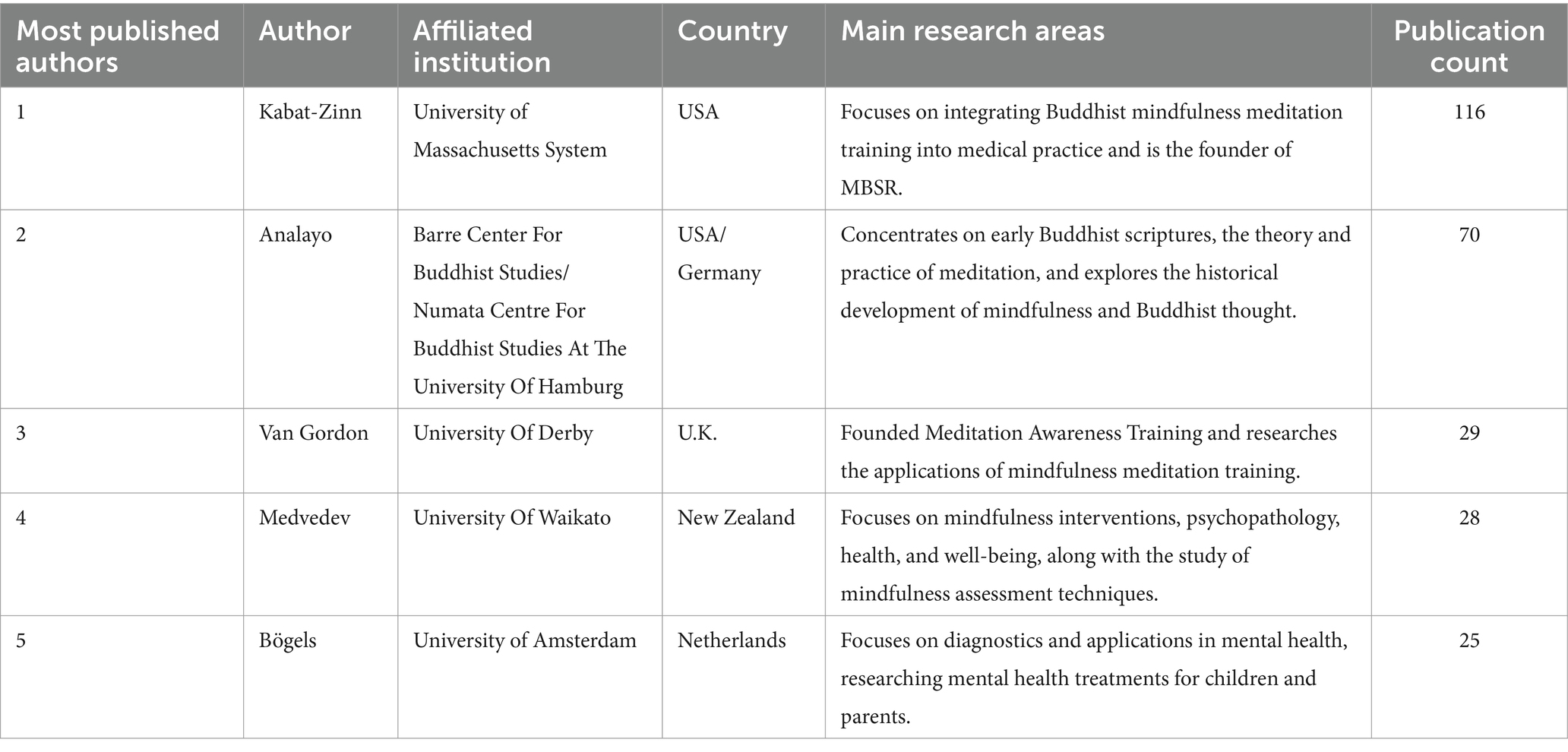
Table 2 . Distribution of authors.
Distribution of countries and institutions
As shown in Figure 4 , this study analyzes the distribution of publications and institutions to elucidate geographical knowledge networks within the field of mindfulness. An examination of publications from the Mindfulness journal indicates a wide international spread, involving researchers from 68 countries, with the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and China being the primary contributors. Among these, significant institutions include the University of Massachusetts System, University of Massachusetts Worcester, Barre Center for Buddhist Studies, University of California System, and University System of Georgia, all located in the USA, underscoring the predominant role of the United States in mindfulness research. Notably, the focus of Chinese research is primarily centered in Hong Kong, signaling its prominence in China’s mindfulness studies, while suggesting that other regions in China could enhance their contributions to this field.
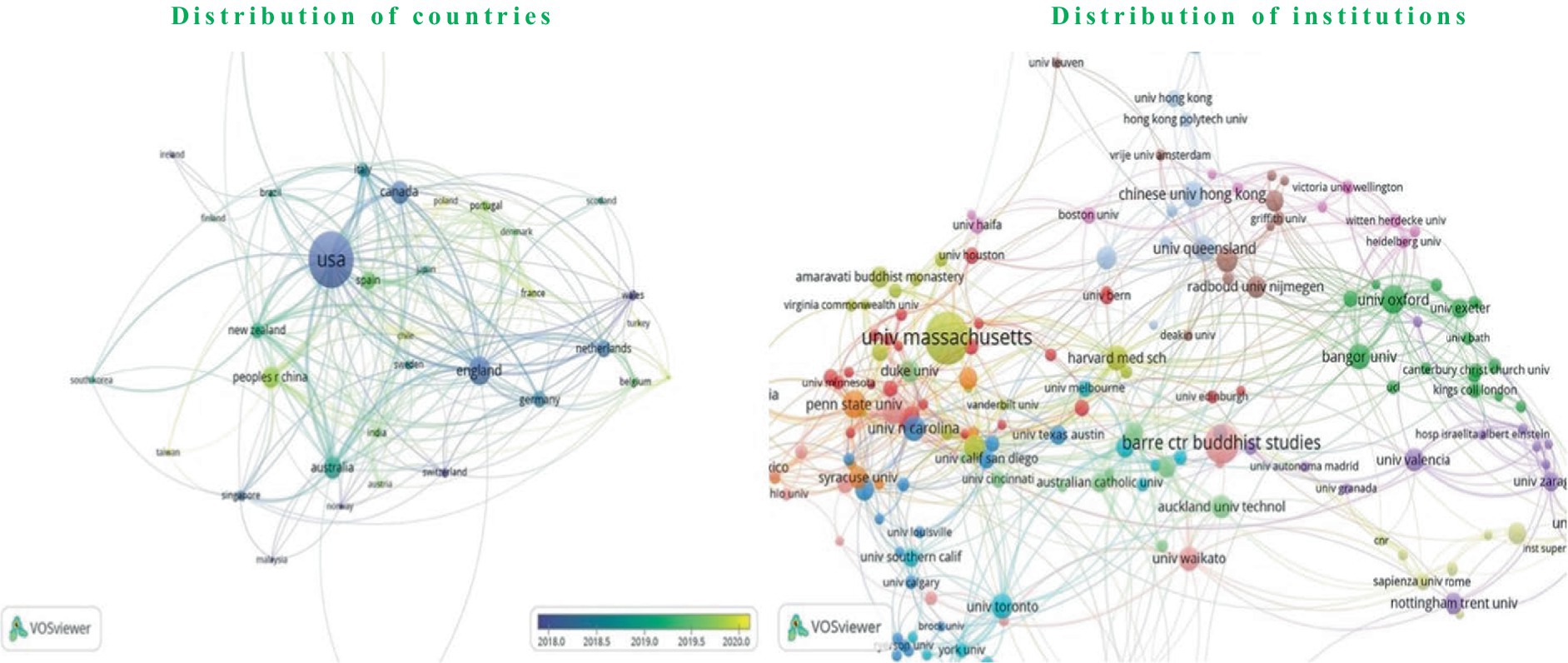
Figure 4 . Distribution of countries and institutions.
As shown in Table 3 , the United States leads in publication volume, followed by the United Kingdom, with substantial inputs from Canada and Australia, whereas China exhibits fewer publications. This distribution underscores a pronounced interest and earlier initiation of mindfulness research among scholars in the US and UK. Institutions like the University of Massachusetts System, Barre Center for Buddhist Studies, and University of Derby, which house principal authors in mindfulness research, are closely aligned with core fields such as mindfulness meditation, training, measurement, intervention, and regulation. This alignment reflects a concentrated and specialized focus in the developmental stages of mindfulness research.
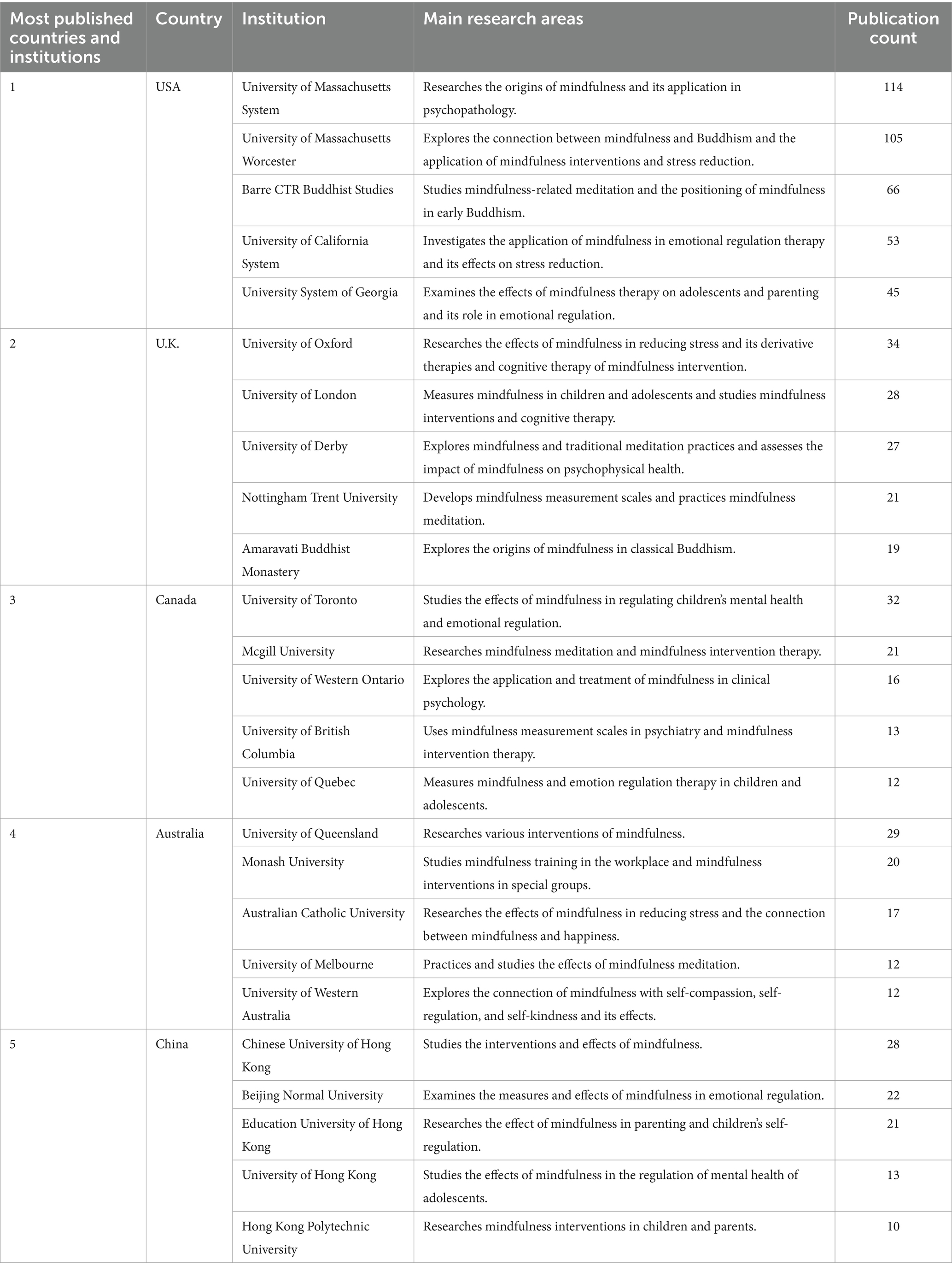
Table 3 . Distribution of countries and institutions.
Keyword co-occurrence
The analysis of keyword co-occurrence in this study is based on the size of network nodes, which represents the importance of each keyword. The larger the keyword, the closer it is to the research hotspot. As shown in Figure 5 , the high-frequency keywords in the Mindfulness journal are ‘mindfulness,’ ‘meditation,’ ‘depression,’ ‘self-compassion,’ and ‘stress,’ all of which are at the core of the clusters.
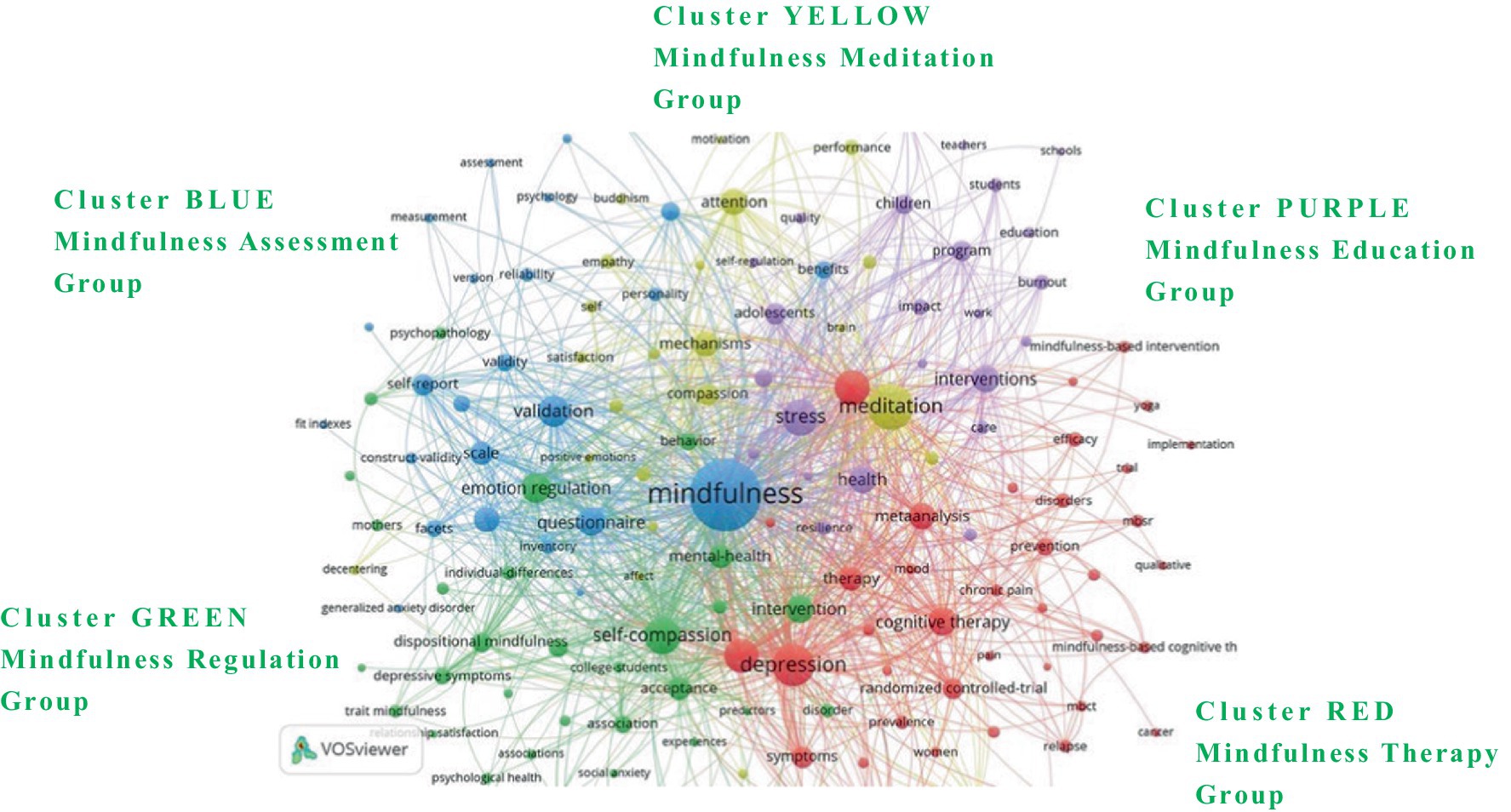
Figure 5 . Keyword co-occurrence.
As shown in Table 4 , “Mindfulness” is identified as the central term across all articles, reflecting its prevalent usage within the field. The analysis reveals other significant keywords such as “meditation,” “depression,” “self-compassion,” and “stress.” Notably, “meditation” was a dominant theme in the initial stages of research, with a marked increase in related studies between 2014 and 2018, while “self-compassion” gained prominence around 2020. This study organizes these keywords into five distinct clusters based on node size. The red cluster, focusing on “depression,” incorporates themes like anxiety, systematic analysis, cognitive therapy, and treatment, primarily concerning mindfulness treatment. The green cluster, centered around “self-compassion,” includes terms related to emotion regulation, intervention, psychological health, and acceptance, highlighting aspects of mindfulness regulation. The blue cluster, led by “mindfulness,” deals with the facets of examination, questionnaires, psychometric properties, and grading, pertinent to mindfulness assessment. The yellow cluster, under the banner of “meditation,” delves into mechanisms, attention, compassion, and empathy, enriching the discourse on mindfulness meditation. Lastly, the purple cluster, themed around “stress,” addresses issues related to health, adolescents, well-being, and education, underscoring mindfulness education. Collectively, these clusters illustrate the breadth of mindfulness research, showcasing a range of topics from treatment and regulation to assessment and educational applications, reflecting the evolving dynamics and the comprehensive scope of mindfulness as a research field.
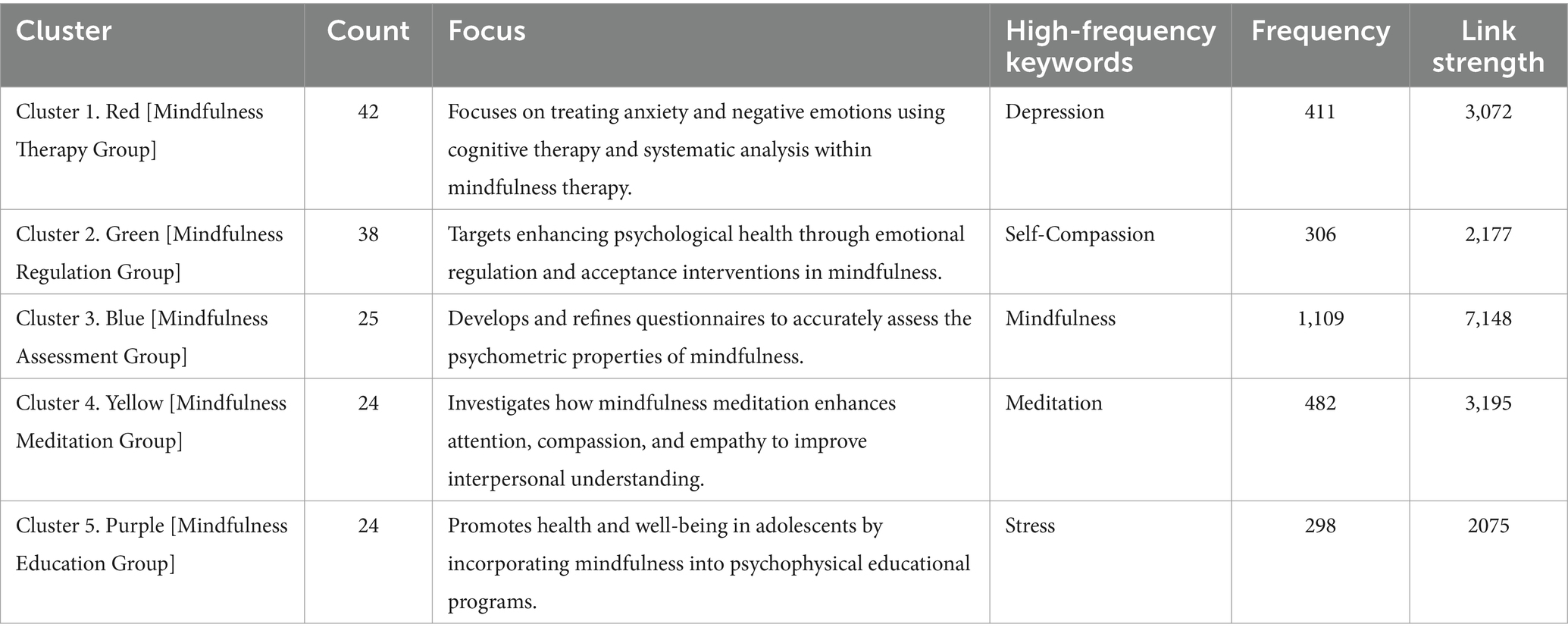
Table 4 . Keyword co-occurrence analysis.
The interconnected themes highlighted by these keywords underscore the varied research focus directions of the journal Mindfulness in recent years, reflecting the dynamic evolution of paradigms within mindfulness research. This body of work integrates several core areas, including addressing unhealthy, negative, and adverse emotions through mindfulness-based interventions, exploring strategies for mental health and emotion regulation, conducting evaluations with mindfulness-related questionnaires, investigating meditation practices to foster understanding and empathy, and developing psychophysical educational programs specifically designed for adolescents. Collectively, these focal points illustrate the journal’s commitment to advancing both the theoretical and practical aspects of mindfulness, contributing significantly to our understanding of its diverse applications across various contexts.
Reference co-citation
This study aims to explore the development and dynamic evolution of themes and their relationships within the mindfulness research field, thereby enhancing our understanding of its current state and providing valuable scientific guidance for scholars. As shown in Figure 6 , an analysis of references from the Mindfulness journal reveals that reference co-citations are divided into five clusters: the red cluster focuses on mindfulness assessment with 70 articles, primarily exploring the development and validation of related scales; the green cluster, comprising 65 articles, assesses various mindfulness therapies; the blue cluster, with 62 articles, discusses the structural aspects of mindfulness; the yellow cluster includes 43 articles on mindfulness intervention, evaluating its structural composition and clinical intervention mechanisms; and the purple cluster, consisting of 37 articles, measures the effectiveness of mindfulness across medicine, psychology, education, and other fields. Prominent researchers contributing to these clusters include Kabat-Zinn (2003) , Neff (2003a) , Bishop et al. (2004) , Baer et al. (2006) , and Kabat-Zinn (2009) , whose works significantly shape the discourse within these areas.
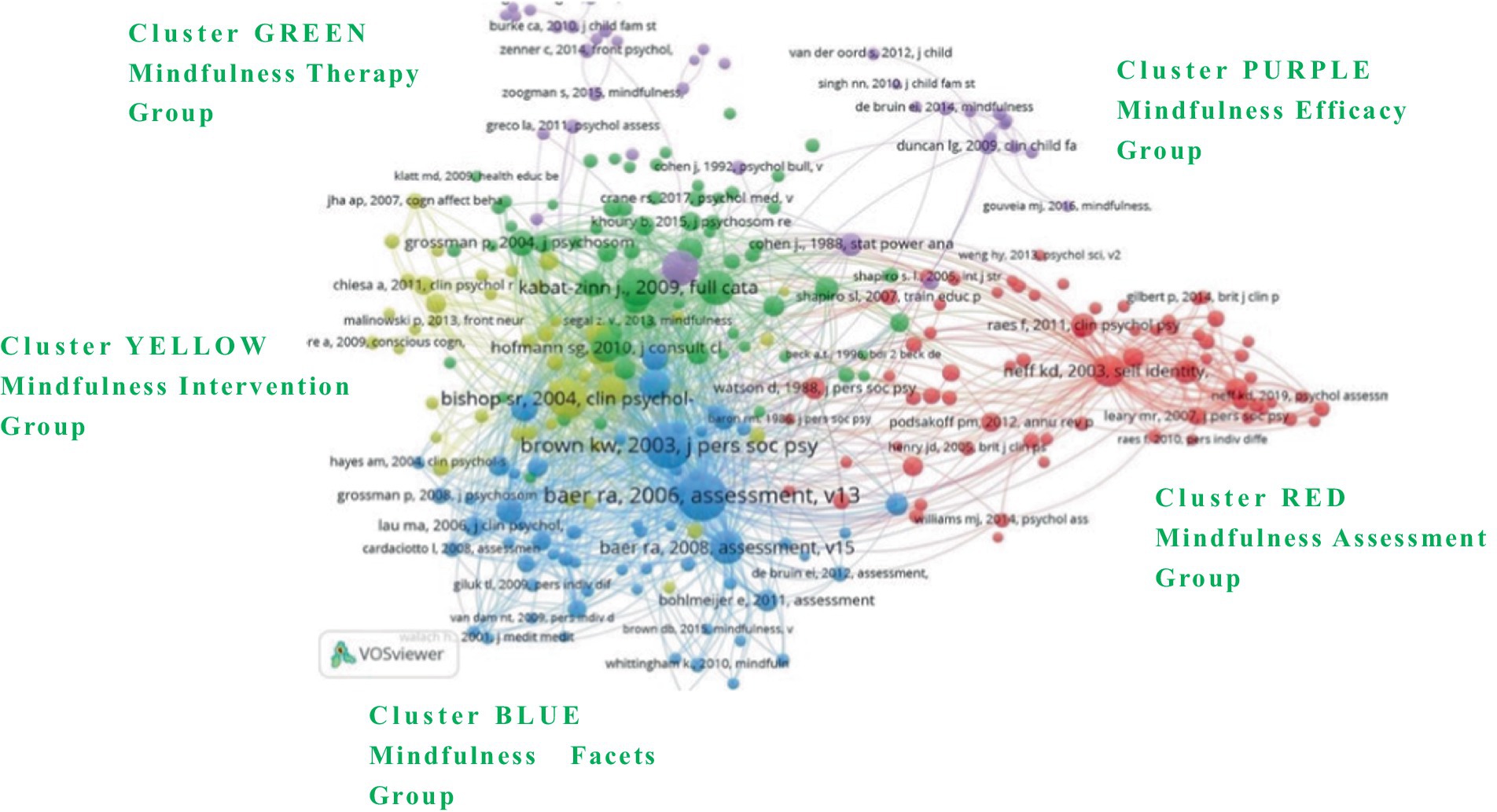
Figure 6 . Reference co-citation.
As shown in Table 5 , the article “Using Self-Report Assessment Methods to Explore Facets of Mindfulness” by Baer et al. (2006) stands out as the most strongly linked article, published by the American Psychological Association, Society for Clinical Psychology (Division 12), Section IX (Assessment). This pivotal article investigates various methods and approaches for self-assessing mindfulness. Following closely is “The Benefits of Being Present: Mindfulness and Its Role in Psychological Well-Being” by Brown and Ryan (2003) , which utilized the Mindful Attention Awareness Scale (MAAS) to analyze mindfulness’s predictive and regulatory role in psychological health, published in Personality and Social Psychology. The reference co-citations related to these articles are organized into five clusters that reflect their influence and connections within the field. The red cluster, focusing on mindfulness assessment, is highlighted by Baer et al. (2006) , who discuss the multifaceted nature of mindfulness and its assessment techniques. This cluster emphasizes articles that delve into the development and validation of scales designed to measure mindfulness attributes accurately. The green cluster centers around mindfulness therapy, featuring Hofmann et al. (2010) who confirm the effectiveness of mindfulness therapies in treating clinical issues like anxiety and depression. This cluster collectively examines the therapeutic applications and outcomes of mindfulness-based interventions. In the blue cluster, which addresses the structural aspects of mindfulness, Brown and Ryan (2003) explore the role of mindfulness in enhancing psychological well-being, showcasing its regulatory impact on mental health through empirical studies. The yellow cluster, dedicated to mindfulness interventions, includes Kabat-Zinn (2009) , whose work discusses practical mindfulness applications in dealing with stress, pain, and illness, emphasizing the operational mechanisms and clinical efficacy of mindfulness. Finally, the purple cluster, focusing on the effectiveness of mindfulness, features Neff (2003a) who develops and validates the Self-Compassion Scale, exploring the beneficial effects of self-compassion as part of a mindfulness approach. This cluster explores how mindfulness practices contribute to overall health and education, highlighting their potential in fostering enhanced well-being across various populations. These clusters demonstrate the journal Mindfulness ’s comprehensive coverage of research that spans theoretical explorations to practical applications, reflecting the dynamic and evolving landscape of mindfulness research.
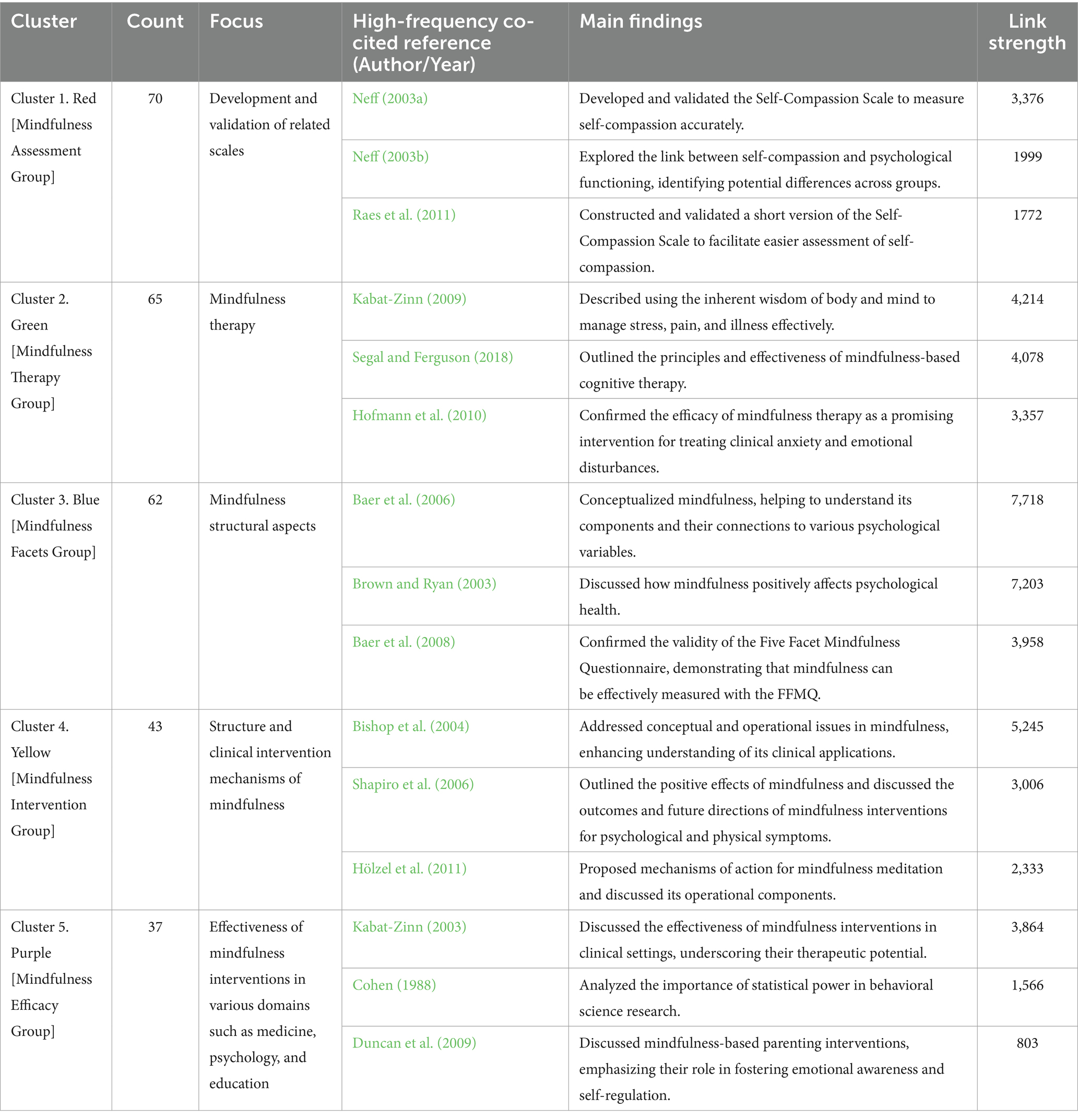
Table 5 . Reference co-citation analysis.
Conclusion and implications
This study employs bibliometric analysis to conduct a visual analysis of research published in the Mindfulness journal, aiming to provide scholars with a relatively objective perspective to grasp the dynamics and future directions of international mindfulness research. The findings indicate that over the past decade, the journal has published 1,950 articles, with publication numbers increasing over time. Among the many contributors, Kabat-Zinn, Analayo, Van Gordon, Medvedev, and Bögels stand out as key figures, with mindfulness research predominantly concentrated in Western countries, particularly the United States and the United Kingdom, which have had the most significant impact on the field. The research primarily focuses on themes such as mindfulness, meditation, depression, stress, and self-compassion. Moreover, the studies are extensively centered around specific aspects of mindfulness, including “intervention,” “therapy,” “regulation,” “assessment,” and “education.” In Taiwan, mindfulness research is relatively underdeveloped; the analysis of this data not only helps identify current research hotspots and gaps but also provides valuable references for researchers in Taiwan, further facilitating the extensive application and in-depth development of mindfulness studies.
We conducted a systematic analysis of various dimensions within mindfulness research, including institutions, nations, individual researchers, and trending topics, thus uncovering key interconnections among these elements. The distribution of these relationships not only maps the trajectory of mindfulness research but also highlights the global imbalance in research capabilities. Particularly, the cultural drivers and relationships between research hotspots, regions, institutions, and individual researchers are crucial as they facilitate collaboration across geographical, disciplinary, and cultural boundaries, which is vital for the global application and dissemination of mindfulness. For instance, Hofmann et al. (2010) have confirmed through their comprehensive analysis that mindfulness therapy positively impacts symptoms of anxiety and depression, a finding that is consistently underscored by frequent references to “depression” and “therapy.” The high-frequency keywords and reference co-citations exhibit a robust linkage pattern, illustrating interrelated connections among these themes. Not only do these connections enrich the existing literature, but they also provide invaluable references for the further development of mindfulness research, highlighting its significance across various psychological and educational settings. Although Asian countries have lesser participation in mindfulness research, their rich history of traditional meditation practices offers substantial untapped potential for future studies. Strengthening collaborations with Western countries can enhance the exchange of knowledge and technologies, bringing fresh perspectives that are essential for advancing the globalization of mindfulness research.
Implications for mindfulness research and education in Taiwan
In Taiwan, mindfulness research is still in its nascent stages, with a notable absence of publications in the international journal Mindfulness , indicative of a lack of systematic research. Scholars in Taiwan are thus encouraged to align with international research trends in mindfulness, enhancing their analytical approaches. There is a strong recommendation for scholars to focus more on demographic groups that could benefit from improved mental health. This involves intensifying global dialogue and exchange between domestic scholars and their international counterparts, which is vital for understanding the structural and developmental nuances of mindfulness research. This approach will facilitate international comparative studies, promote scientific collaboration globally, and provide robust support for individuals in high-pressure work environments. To improve Taiwan’s education directions and aid Taiwanese researchers in thoroughly exploring the development status and trends of the international mindfulness research fields, this study proposes several strategies to accelerate the internationalization of domestic research and discipline construction. These include integrating mindfulness education into curricula at all educational levels to provide students with systematic training in mindfulness practices like meditation, emotion regulation, and concentration; developing mindfulness teacher training programs to enhance educators’ emotional management skills; promoting mindfulness-friendly campuses to foster a respectful, caring, and harmonious learning environment; integrating mindfulness into special education as an auxiliary therapy for students with conditions such as autism and ADHD to enhance their emotion regulation and self-control; and conducting thorough research and assessments of mindfulness education to gauge its impact on students’ learning outcomes, psychological health, and interpersonal relationships, thereby generating empirical evidence to support the expansion of mindfulness education.
Limitations, and suggestions for future research
While this study presents notable findings, it is not without its limitations. The analysis relies exclusively on literature data from the Journal of Mindfulness in the WoS database, lacking empirical field investigations and experimental validation. This focus restricts the breadth of mindfulness-related literature reviewed, as it does not consider contributions from other journals. Future research could benefit from employing a variety of research methods and data sources, integrating themes such as “intervention, therapy, regulation, assessment, education” to expand the exploration of mindfulness applications across diverse domains and populations. Additionally, by prioritizing key terms within the co-occurrence patterns, new research avenues can be identified, which will drive the development of mindfulness research and offer valuable guidance for practical applications and policy formulation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
C-CH: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. SL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Anālayo, B. (2020). Somatics of early Buddhist mindfulness and how to face anxiety. Mindfulness 11, 1520–1526. doi: 10.1007/s12671-020-01382-x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Hopkins, J., Krietemeyer, J., and Toney, L. (2006). Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment 13, 27–45. doi: 10.1177/1073191105283504
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Lykins, E., Button, D., Krietemeyer, J., Sauer, S., et al. (2008). Construct validity of the five-facet mindfulness questionnaire in meditating and nonmeditating samples. Assessment 15, 329–342. doi: 10.1177/1073191107313003
Bishop, S. R., Lau, M., Shapiro, S., Carlson, L., Anderson, N. D., Carmody, J., et al. (2004). Mindfulness: a proposed operational definition. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 11, 230–241. doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bph077
Bögels, S. M., Hellemans, J., van Deursen, S., Römer, M., and van der Meulen, R. (2014). Mindful parenting in mental health care: effects on parental and child psychopathology, parental stress, parenting, coparenting, and marital functioning. Mindfulness 5, 536–551. doi: 10.1007/s12671-013-0209-7
Brown, K. W., and Ryan, R. M. (2003). The benefits of being present: mindfulness and its role in psychological wellbeing. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 84, 822–848. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.84.4.822
Chen, S. J., Peng, T. W., and Wu, Y. H. (2019). Review of the effectiveness of mindfulness interventions in Taiwan: reflections on evidence and practice. Appl. Psychol. Res. 70, 77–121.
Google Scholar
Chiesa, A., Calati, R., and Serretti, A. (2011). Does mindfulness training improve cognitive abilities? A systematic review of neuropsychological findings. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 31, 449–464. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2010.11.003
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power analysis for the behavioral sciences . 2nd Edn. New York: Routledge.
Corcoran, K. M., Farb, N., Anderson, A., and Segal, Z. V. (2010). “Mindfulness and emotion regulation: outcomes and possible mediating mechanisms” in Emotion regulation and psychopathology: a trans diagnostic approach to etiology and treatment . eds. A. M. Kring and D. M. Sloan (New York: Guilford Press), 339–355.
Costa, J. A., Marôco, J., Pinto-Gouveia, J., Ferreira, C., and Castilho, P. (2016). Validation of the psychometric properties of the self-compassion scale. Testing the factorial validity and factorial invariance of the measure among borderline personality disorder, anxiety disorder, eating disorder and general populations. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 23 5, 460–468. doi: 10.1002/cpp.1974
Davis, D. M., and Hayes, J. A. (2011). What are the benefits of mindfulness? A practice review of psychotherapy-related research. Psychotherapy 48, 198–208. doi: 10.1037/a0022062
Dobkin, P. L., and Zhao, Q. (2011). Increased mindfulness-the active component of the mindfulness-based stress reduction program? Complement. Therap. Clin. Pract. 17, 22–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2010.03.002
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., and Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 133, 285–296. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Duncan, L. G., Coatsworth, J. D., and Greenberg, M. T. (2009). A model of mindful parenting: implications for parent-child relationships and prevention research. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 12, 255–270. doi: 10.1007/s10567-009-0046-3
Eberth, J., and Sedlmeier, P. (2012). The effects of mindfulness meditation: a meta-analysis. Mindfulness 3, 174–189. doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0101-x
Farb, N. A. S., Anderson, A. K., Mayberg, H., Bean, J., McKeon, D., and Segal, Z. V. (2010). Minding one’s emotions: mindfulness training alters the neural expression of sadness. Emotion 10, 25–33. doi: 10.1037/a0017151
Ferrari, M., Hunt, C., Harrysunker, A., Abbott, M. J., Beath, A. P., and Einstein, D. A. (2019). Self-compassion interventions and psychosocial outcomes: a meta-analysis of RCTs. Mindfulness 10, 1455–1473. doi: 10.1007/s12671-019-01134-6
Flett, J. A., Hayne, H., Riordan, B. C., Thompson, L. M., and Conner, T. S. (2019). Mobile mindfulness meditation: a randomized controlled trial of the effect of two popular apps on mental health. Mindfulness 10, 863–876. doi: 10.1007/s12671-018-1050-9
Goldberg, S. B., Pace, B., Griskaitis, M., Willutzki, R., Skoetz, N., Zgierska, A. E., et al. (2021). Mindfulness-based interventions for substance use disorders. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 10:CD011723. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011723.pub2
Grossman, P., Niemann, L., Schmidt, S., and Walach, H. (2004). Mindfulness-based stress reduction and health benefits. A meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 57, 35–43. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00573-7
Hofmann, S. G., Sawyer, A. T., Witt, A. A., and Oh, D. (2010). The effect of mindfulness-based therapy on anxiety and depression: a meta-analytic review. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 78, 169–183. doi: 10.1037/a0018555
Hölzel, B. K., Lazar, S. W., Gard, T., Schuman-Olivier, Z., Vago, D. R., and Ott, U. (2011). How does mindfulness meditation work? Proposing mechanisms of action from a conceptual and neural perspective. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 6, 537–559. doi: 10.1177/1745691611419671
Hsieh, C. C. (2018). Developing meaningful schools: an exploration of mindful leadership by principals. Educ. Res. Monthly 292, 69–86. doi: 10.3966/168063602018080292005
Hsieh, C. C. (2019). Practice and development of mindfulness education in Taiwan. Second. Educ. 70, 6–18. doi: 10.6249/SE.201912_70(4).0032
Huang, F. Y., Wu, C. W., Bhikshu, H. M., Bhikshu, G. H., Chao, Y. P., and Dai, C. T. (2015). Validation of the Taiwanese version of the five facet mindfulness questionnaire (T-FFMQ). Psychol. Testing 62, 231–260.
Jensen, C. G., Vangkilde, S. A., Frokjaer, V. G., and Hasselbalch, S. G. (2012). Mindfulness training affects attention--or is it attentional effort? J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 141, 106–123. doi: 10.1037/a0024931
Jha, A. P., Krompinger, J. W., and Baime, M. J. (2007). Mindfulness training modifies subsystems of attention. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 7, 109–119. doi: 10.3758/CABN.7.2.109
Jiang, Y., Wang, Y. Z., and Luo, F. (2022). The current status and prospects of mindfulness parenting. Chin. J. Health Psychol. 5:30.
Jin, J. S., and Liu, X. H. (2017). Mindfulness education for children and adolescents: exploring mindfulness as a new method of mental health education. J. Capital Norm. Univ. 2:11.
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2003). Mindfulness-based intervention in context: past, present, and future. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 10, 144–156. doi: 10.1093/clipsy/bpg016
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2009). Full catastrophe living: using the wisdom of your body and mind to face stress, pain, and illness . New York: Random House Publishing Group.
Kabat-Zinn, Jon . (2023). Wikipedia. Available at: https://zh.wikipedia.org/zhtw/%E5%96%AC%C2%B7%E5%8D%A1%E5%B7%B4%E9%87%91#cite_note-5
Kallapiran, K., Koo, S., Kirubakaran, R., and Hancock, K. M. (2015). Review: effectiveness of mindfulness in improving mental health symptoms of children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. Child Adolesc. Mental Health 20, 182–194. doi: 10.1111/camh.12113
Keng, S., Smoski, M. J., and Robins, C. J. (2011). Effects of mindfulness on psychological health: a review of empirical studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 31, 1041–1056. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.04.006
Körner, A., Coroiu, A., Copeland, L., Gomez-Garibello, C., Albani, C., Zenger, M., et al. (2015). The role of self-compassion in buffering symptoms of depression in the general population. PLoS One 10:e0136598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136598
Lakhan, S. E., and Schofield, K. L. (2013). Mindfulness-based therapies in the treatment of somatization disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 8:e71834. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071834
Langer, E. J. (1989). Mindfulness . Boston: Addison-Wesley.
Laukkonen, R., Leggett, J. M. I., Gallagher, R., Biddell, H., Mrazek, A., Slagter, H. A., et al. (2020). The science of mindfulness-based interventions and learning: a review for educators . Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Lawlor, M. S. (2014). Mindfulness in practice: considerations for implementation of mindfulness-based programming for adolescents in school contexts. New Dir. Youth Dev. 2014, 83–95. doi: 10.1002/yd.20098
Lin, Y. J. (2013). An integrated framework for exploring the process of mindfulness-based psychotherapy. Chin. J. Mental Health 26, 395–442.
Liu, C. C., and Rau, J. W. (2015). A study on the influence of mindfulness meditation on elementary school children’s capability of sustained attention. Buddhism Sci. 16, 81–98.
Lv, K. W. (2014). The practice and theory of mindfulness therapy: 33 mindfulness exercises . Taiwan: Taiwan Mindfulness Association.
MacBeth, A., and Gumley, A. I. (2012). Exploring compassion: a meta-analysis of the association between self-compassion and psychopathology. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 32, 545–552. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2012.06.003
Maynard, B. R., Solis, M., Miller, V. L., and Brendel, K. E. (2017). Mindfulness-based interventions for improving cognition, academic achievement, behavior, and socioemotional functioning of primary and secondary school students. Campbell Syst. Rev. 13, 1–32. doi: 10.1002/CL2.177
Meiklejohn, J. M., Phillips, C. L., Freedman, M. L., Griffin, M., Biegel, G. M., Roach, A. T., et al. (2012). Integrating mindfulness training into K-12 education: fostering the resilience of teachers and students. Mindfulness 3, 291–307. doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0094-5
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., and Altman, D. G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 151, 264–269. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
Muris, P., Otgaar, H., and Petrocchi, N. (2016). Protection as the Mirror image of psychopathology: further critical notes on the self-compassion scale. Mindfulness 7, 787–790. doi: 10.1007/s12671-016-0509-9
Napoli, M., Krech, P. R., and Holley, L. C. (2005). Mindfulness training for elementary school students: the attention academy. J. Appl. Sch. Psychol. 21, 99–125. doi: 10.1300/J370v21n01_05
Neff, K. D. (2003a). The development and validation of a scale to measure self-compassion. Self Identity 2, 223–250. doi: 10.1080/15298860309027
Neff, K. D. (2003b). Self-compassion: an alternative conceptualization of a healthy attitude toward oneself. Self Identity 2, 85–101. doi: 10.1080/15298860309032
Neff, K. D. (2016). The self-compassion scale is a valid and theoretically coherent measure of self-compassion. Mindfulness 7, 264–274. doi: 10.1007/s12671-015-0479-3
Neff, K. D., Tóth-Király, I., Yarnell, L. M., Arimitsu, K., Castilho, P., Ghorbani, N., et al. (2019). Examining the factor structure of the self-compassion scale in 20 diverse samples: support for use of a Total score and six subscale scores. Psychol. Assess. 31, 27–45. doi: 10.1037/pas0000629
Neff, K. D., Whittaker, T. A., and Karl, A. (2017). Examining the factor structure of the self-compassion scale in four distinct populations: is the use of a Total scale score justified? J. Pers. Assess. 99, 596–607. doi: 10.1080/00223891.2016.1269334
Penman, D., and Burch, V. (2013). Mindfulness for health: A practical guide to relieving pain, reducing stress and restoring wellbeing . London: Paitkus.
Pritchard, A. (1969). Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics? J. Doc. 25, 344–349. doi: 10.1108/eb026482
Radhakrishnan, S., Erbis, S., Isaacs, J. A., and Kamarthi, S. (2017). Novel keyword co-occurrence network-based methods to foster systematic reviews of scientific literature. PLoS One 12, 1–16. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172778
Raes, F., Griffith, J. W., Gucht, K. V., and Williams, J. M. (2014). School-based prevention and reduction of depression in adolescents: a cluster-randomized controlled trial of a mindfulness group program. Mindfulness 5, 477–486. doi: 10.1007/s12671-013-0202-1
Raes, F., Pommier, E., Neff, K. D., and Van Gucht, D. (2011). Construction and factorial validation of a short form of the self-compassion scale. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 18, 250–255. doi: 10.1002/cpp.702
Ronald, D. S., Germer, C. K., and Olendzki, A. (2009). “Mindfulness: what is it? Where did it come from?” in Clinical handbook of mindfulness . ed. D. Fabrizio (New York: Springer), 17–35.
Sancho, M., De Gracia, M., Rodriguez, R. C., Mallorquí-Bagué, N., Sánchez-González, J., Trujols, J., et al. (2018). Mindfulness-based interventions for the treatment of substance and behavioral addictions: a systematic review. Front. Psych. 9:353853. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00095
Sauer, S., Walach, H., Schmidt, S., Hinterberger, T., Lynch, S., Büssing, A., et al. (2013). Assessment of mindfulness: review on state of the art. Mindfulness 4, 3–17. doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0122-5
Segal, Z. V., and Ferguson, A. M. (2018). “Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy: treatment development from a common cognitive therapy core” in Science and practice in cognitive therapy: foundations, mechanisms, and applications . ed. R. L. Leahy (New York: Guilford Press), 159–174.
Shapiro, S. L., Carlson, L. E., Astin, J. A., and Freedman, B. (2006). Mechanisms of mindfulness. J. Clin. Psychol. 62, 373–386. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20237
Shin, T. B., and Jin, S. R. (2010). The qualitative study of “mindfulness group” toward t he self-care and counseling practice of counselor interns. Bull. Educ. Psychol. 42, 163–184. doi: 10.6251/BEP.20100423
Singh, V. K., Singh, P., Karmakar, M., Leta, J., and Mayr, P. (2021). The journal of web of science, Scopus and dimensions: a comparative analysis. Scientometrics 126, 5113–5142. doi: 10.1007/s11192-021-03948-5
Small, H. G. (1973). Co-citation in the scientific literature: a new measure of the relationship between two documents. J. Am. Soc. Inform. 24, 265–269. doi: 10.1002/asi.4630240406
The University of Waikato . (2023). Available at: https://www.waikato.ac.nz/staff-profiles/people/omedvede
Tomlinson, E. R., Yousaf, O., Vittersø, A. D., and Jones, L. (2018). Dispositional mindfulness and psychological health: a systematic review. Mindfulness 9, 23–43. doi: 10.1007/s12671-017-0762-6
University of Amsterdam . (2023). Available at: https://www.uva.nl/en/profile/b/o/s.m.bogels/s.m.bogels.html#Publications
University of Derby . (2023). Available at: https://www.derby.ac.uk/staff/william-van-gordon/
Valentine, E. R., and Sweet, P. L. (1999). Meditation and attention: a comparison of the effects of concentrative and mindfulness meditation on sustained attention. Mental Health Religion Cult. 2, 59–70. doi: 10.1080/13674679908406332
Van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOS viewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scient Metrics 84, 523–538. doi: 10.1007/S11192-009-0146-3
Wall, J. M. (2014). Finding an inner voice through silence: mindfulness goes to college. J. Coll. Charact. 15, 133–140. doi: 10.1515/jcc-2014-0017
Wen, T. K. (2013). An overview of Western mindfulness education: moving towards integrating mindfulness training in Taiwan. J. Life Educ. Res. 5, 145–180.
Wen, T. K. (2016). An exploration of western mindfulness teacher training and certification. Fu Jen J. Religious Stud. 32, 71–101.
Wen, T. K. (2013). The Origins and Mechanisms of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction: From a Perspective of Buddhist Studies. New Century Religious Studies 12, 27–48. Available at: https://www.airitilibrary.com/Article/Detail?DocID=16843738-201312-201401160022-201401160022-27-48 .
Willis, E., and Dinehart, L. (2014). Contemplative practices in early childhood: implications for self-regulation skills and school readiness. Early Child Dev. Care 184, 487–499. doi: 10.1080/03004430.2013.804069
Wilson, J. (2014). Mindful America: The mutual transformation of buddhist meditation and American culture . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Wilson, A. C., Mackintosh, K., Power, K., and Chan, S. W. (2019). Effectiveness of self-compassion related therapies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mindfulness 10, 979–995. doi: 10.1007/s12671-018-1037-6
Yang, Y. W. (2015). Research hotspots and evolution on cultivating reserve talents of competitive sports in China based on knowledge maps. J. Shanghai Univ. Sport 39, 73–79.
Yang, J. Y. (2016). Teaching reflection of integrating mindfulness in general education courses of military school: the example of army academy R.O.C. J. NDU General Educ. 6, 91–109.
Zhang, J. J. (2013). Evolution of research hotspots, themes, and methods in the field of tourism management in China. Econ. Geogr. 23, 173–179.
Zhang, L. M. (2013). Research on the integration of ice and snow tourism and culture from the perspective of tourism culture industry. Academic Exchange 2013, 106–109.
Zhang, J. T., Zhang, J. Y., Du, Z. Y., Li, J., Lü, C. H., and Du, J. (2019). Effect of mindfulness-based intervention on functional connectivity of resting state electroencephalogram of amphetamine-type stimulants use patients. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 39, 1416–1421.
Zheng, Y. C., Fang, S. Y., and Huang, S. L. (2013). Exploring mindfulness therapy and experiences: qualitative study results. Taiwan J. Clin. Psychol. 7, 48–49.
Zoogman, S., Goldberg, S. B., Hoyt, W. T., and Miller, L. (2015). Mindfulness interventions with youth: a meta-analysis. Mindfulness 6, 290–302. doi: 10.1007/s12671-013-0260-4
Zupic, I., and Čater, T. (2015). Bibliometric methods in management and organization. Organ. Res. Methods 18, 429–472. doi: 10.1177/1094428114562629
Zyoud, S. H., Waring, W. S., Al-Jabi, S. W., and Sweileh, W. M. (2017). Global cocaine intoxication research trends during 1975-2015: a bibliometric analysis of web of science publications. Subst. Abuse Treat. Prev. Policy 12, 1–16. doi: 10.1186/s13011-017-0090-9
Keywords: mindfulness, science mapping, bibliometric analysis, knowledge graph, visualization analysis
Citation: Hsieh C-C and Li S (2024) A bibliometrics review of the journal mindfulness : science mapping the literature from 2012 to 2022. Front. Psychol . 15:1378143. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1378143
Received: 29 January 2024; Accepted: 01 May 2024; Published: 17 May 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Hsieh and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shun Li, [email protected]
† These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 12 May 2024
Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Mingxuan Du 1 ,
- Chengjia Zhao 2 ,
- Haiyan Hu 1 ,
- Ningning Ding 1 ,
- Jiankang He 1 ,
- Wenwen Tian 1 ,
- Wenqian Zhao 1 ,
- Xiujian Lin 1 ,
- Gaoyang Liu 1 ,
- Wendan Chen 1 ,
- ShuangLiu Wang 1 ,
- Pengcheng Wang 3 ,
- Dongwu Xu 1 ,
- Xinhua Shen 4 &
- Guohua Zhang 1
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 263 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
186 Accesses
Metrics details
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU levels and anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out. 209 studies with a total of 172 articles were included in the meta-analysis, involving 252,337 participants from 28 countries. The results showed a moderately positive association between PSNU and generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO) respectively (GA: r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]; SA: r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]), and there were different regulatory factors between PSNU and different anxiety subtypes. This study provides the first comprehensive estimate of the association of PSNU with multiple anxiety subtypes, which vary by time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tool.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Social network refers to online platforms that allow users to create, share, and exchange information, encompassing text, images, audio, and video [ 1 ]. The use of social network, a term encompassing various activities on these platforms, has been measured from angles such as frequency, duration, intensity, and addictive behavior, all indicative of the extent of social networking usage [ 2 ]. As of April 2023, there are 4.8 billion social network users globally, representing 59.9% of the world’s population [ 3 ]. The usage of social network is considered a normal behavior and a part of everyday life [ 4 , 5 ]. Although social network offers convenience in daily life, excessive use can lead to PSNU [ 6 , 7 ], posing potential threats to mental health, particularly anxiety symptoms (Rasmussen et al., 2020). Empirical research has shown that anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO), are closely related to PSNU [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. While some empirical studies have explored the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, their conclusions are not consistent. Some studies have found a significant positive correlation [ 13 , 14 , 15 ], while others have found no significant correlation [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Furthermore, the degree of correlation varies widely in existing research, with reported r-values ranging from 0.12 to 0.80 [ 20 , 21 ]. Therefore, a systematic meta-analysis is necessary to clarify the impact of PSNU on individual anxiety symptoms.
Previous research lacks a unified concept of PSNU, primarily due to differing theoretical interpretations by various authors, and the use of varied standards and diagnostic tools. Currently, this phenomenon is referred to by several terms, including compulsive social networking use, problematic social networking use, excessive social networking use, social networking dependency, and social networking addiction [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. These conceptual differences hinder the development of a cohesive and systematic research framework, as it remains unclear whether these definitions and tools capture the same underlying construct [ 27 ]. To address this lack of uniformity, this paper will use the term “problematic use” to encompass all the aforementioned nomenclatures (i.e., compulsive, excessive, dependent, and addictive use).
Regarding the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, two main perspectives exist: the first suggests a positive correlation, while the second proposes a U-shaped relationship. The former perspective, advocating a positive correlation, aligns with the social cognitive theory of mass communication. It posits that PSNU can reinforce certain cognitions, emotions, attitudes, and behaviors [ 28 , 29 ], potentially elevating individuals’ anxiety levels [ 30 ]. Additionally, the cognitive-behavioral model of pathological use, a primary framework for explaining factors related to internet-based addictions, indicates that psychiatric symptoms like depression or anxiety may precede internet addiction, implying that individuals experiencing anxiety may turn to social networking platforms as a coping mechanism [ 31 ]. Empirical research also suggests that highly anxious individuals prefer computer-mediated communication due to the control and social liberation it offers and are more likely to have maladaptive emotional regulation, potentially leading to problematic social network service use [ 32 ]. Turning to the alternate perspective, it proposes a U-shaped relationship as per the digital Goldilocks hypothesis. In this view, moderate social networking usage is considered beneficial for psychosocial adaptation, providing individuals with opportunities for social connection and support. Conversely, both excessive use and abstinence can negatively impact psychosocial adaptation [ 33 ]. In summary, both perspectives offer plausible explanations.
Incorporating findings from previous meta-analyses, we identified seven systematic reviews and two meta-analyses that investigated the association between PSNU and anxiety. The results of these meta-analyses indicated a significant positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety (ranging from 0.33 to 0.38). However, it is evident that these previous meta-analyses had certain limitations. Firstly, they focused only on specific subtypes of anxiety; secondly, they were limited to adolescents and emerging adults in terms of age. In summary, this systematic review aims to ascertain which theoretical perspective more effectively explains the relationship between PSNU and anxiety, addressing the gaps in previous meta-analyses. Additionally, the association between PSNU and anxiety could be moderated by various factors. Drawing from a broad research perspective, any individual study is influenced by researcher-specific designs and associated sample estimates. These may lead to bias compared to the broader population. Considering the selection criteria for moderating variables in empirical studies and meta-analyses [ 34 , 35 ], the heterogeneity of findings on problematic social network usage and anxiety symptoms could be driven by divergence in sample characteristics (e.g., gender, age, region) and research characteristics (measurement instrument of study variables). Since the 2019 coronavirus pandemic, heightened public anxiety may be attributed to the fear of the virus or heightened real life stress. The increased use of electronic devices, particularly smartphones during the pandemic, also instigates the prevalence of problematic social networking. Thus, our analysis focuses on three moderators: sample characteristics (participants’ gender, age, region), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms) and the time of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19).
The present study was conducted in accordance with the 2020 statement on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [ 36 ]. To facilitate transparency and to avoid unnecessary duplication of research, this study was registered on PROSPERO, and the number is CRD42022350902.
Literature search
Studies on the relationship between the PSNU and anxiety symptoms from 2000 to 2023 were retrieved from seven databases. These databases included China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Data, Chongqing VIP Information Co. Ltd. (VIP), Web of Science, ScienceDirect, PubMed, and PsycARTICLES. The search strings consisted of (a) anxiety symptoms, (b) social network, and (c) Problematic use. As shown in Table 1 , the keywords for anxiety are as follows: anxiety, generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, fear of missing out, and FoMO. The keywords for social network are as follows: social network, social media, social networking site, Instagram, and Facebook. The keywords for addiction are as follows: addiction, dependence, problem/problematic use, excessive use. The search deadline was March 19, 2023. A total of 2078 studies were initially retrieved and all were identified ultimately.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Retrieved studies were eligible for the present meta-analysis if they met the following inclusion criteria: (a) the study provided Pearson correlation coefficients used to measure the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms; (b) the study reported the sample size and the measurement instruments for the variables; (c) the study was written in English and Chinese; (d) the study provided sufficient statistics to calculate the effect sizes; (e) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, they were coded by the first measurement. In addition, studies were excluded if they: (a) examined non-problematic social network use; (b) had an abnormal sample population; (c) the results of the same sample were included in another study and (d) were case reports or review articles. Two evaluators with master’s degrees independently assessed the eligibility of the articles. A third evaluator with a PhD examined the results and resolved dissenting views.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two evaluators independently coded the selected articles according to the following characteristics: literature information, time of measurement (before the COVID-19 vs. during the COVID-19), sample source (developed country vs. developing country), sample size, proportion of males, mean age, type of anxiety, and measurement instruments for PSNU and anxiety symptoms. The following principles needed to be adhered to in the coding process: (a) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, it was coded by the first measurement; (b) if multiple studies used the same data, the one with the most complete information was selected; (c) If studies reported t or F values rather than r , the following formula \( r=\sqrt{\frac{{t}^{2}}{{t}^{2}+df}}\) ; \( r=\sqrt{\frac{F}{F+d{f}_{e}}}\) was used to convert them into r values [ 37 , 38 ]. Additionally, if some studies only reported the correlation matrix between each dimension of PSNU and anxiety symptoms, the following formula \( {r}_{xy}=\frac{\sum {r}_{xi}{r}_{yj}}{\sqrt{n+n(n-1){r}_{xixj}}\sqrt{m+m(m-1){r}_{yiyj}}}\) was used to synthesize the r values [ 39 ], where n or m is the number of dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively, and \( {r}_{xixj} \) or \( {r}_{yiyj}\) represents the mean of the correlation coefficients between the dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively.
Literature quality was determined according to the meta-analysis quality evaluation scale developed [ 40 ]. The quality of the post-screening studies was assessed by five dimensions: sampling method, efficiency of sample collection, level of publication, and reliability of PSNU and anxiety symptom measurement instruments. The total score of the scale ranged from 0 to 10; higher scores indicated better quality of the literature.
Data analysis
All data were performed using Comprehensive Meta Analysis 3.3 (CMA 3.3). Pearson’s product-moment coefficient r was selected as the effect size index in this meta-analysis. Firstly, \( {\text{F}\text{i}\text{s}\text{h}\text{e}\text{r}}^{{\prime }}\text{s} Z=\frac{1}{2}\times \text{ln}\left(\frac{1+r}{1-r}\right)\) was used to convert the correlation coefficient to Fisher Z . Then the formula \( SE=\sqrt{\frac{1}{n-3}}\) was used to calculate the standard error ( SE ). Finally, the summary of r was obtained from the formula \( r=\frac{{e}^{2z}-1}{{e}^{2z}+1}\) for a comprehensive measure of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms [ 37 , 41 ].
Although the effect sizes estimated by the included studies may be similar, considering the actual differences between studies (e.g., region and gender), the random effects model was a better choice for data analysis for the current meta-analysis. The heterogeneity of the included study effect sizes was measured for significance by Cochran’s Q test and estimated quantitatively by the I 2 statistic [ 42 ]. If the results indicate there is a significant heterogeneity (the Q test: p -value < 0.05, I 2 > 75) and the results of different studies are significantly different from the overall effect size. Conversely, it indicates there are no differences between the studies and the overall effect size. And significant heterogeneity tends to indicate the possible presence of potential moderating variables. Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis were used to examine the moderating effect of categorical and continuous variables, respectively.
Funnel plots, fail-safe number (Nfs) and Egger linear regression were utilized to evaluate the publication bias [ 43 , 44 , 45 ]. The likelihood of publication bias was considered low if the intercept obtained from Egger linear regression was not significant. A larger Nfs indicated a lower risk of publication bias, and if Nfs < 5k + 10 (k representing the original number of studies), publication bias should be a concern [ 46 ]. When Egger’s linear regression was significant, the Duval and Tweedie’s trim-and-fill was performed to correct the effect size. If there was no significant change in the effect size, it was assumed that there was no serious publication bias [ 47 ].
A significance level of P < 0.05 was deemed applicable in this study.
Sample characteristics
The PRISMA search process is depicted in Fig. 1 . The database search yielded 2078 records. After removing duplicate records and screening the title and abstract, the full text was subject to further evaluation. Ultimately, 172 records fit the inclusion criteria, including 209 independent effect sizes. The present meta-analysis included 68 studies on generalized anxiety, 44 on social anxiety, 22 on attachment anxiety, and 75 on fear of missing out. The characteristics of the selected studies are summarized in Table 2 . The majority of the sample group were adults. Quality scores for selected studies ranged from 0 to 10, with only 34 effect sizes below the theoretical mean, indicating high quality for the included studies. The literature included utilized BSMAS as the primary tool to measure PSNU, DASS-21-A to measure GA, IAS to measure SA, ECR to measure AA, and FoMOS to measure FoMO.
Flow chart of the search and selection strategy
Overall analysis, homogeneity tests and publication bias
As shown in Table 3 , there was significant heterogeneity between PSNU and all four anxiety symptoms (GA: Q = 1623.090, I 2 = 95.872%; SA: Q = 1396.828, I 2 = 96.922%; AA: Q = 264.899, I 2 = 92.072%; FoMO: Q = 1847.110, I 2 = 95.994%), so a random effects model was chosen. The results of the random effects model indicate a moderate positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (GA: r = 0.350, 95% CI [0.323, 0.378]; SA: r = 0.390, 95% CI [0.347, 0.431]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]).
Figure 2 shows the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. No significant symmetry was seen in the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and GA and between PSNU and SA. And the Egger’s regression results also indicated that there might be publication bias ( t = 3.775, p < 0.001; t = 2.309, p < 0.05). Therefore, it was necessary to use fail-safe number (Nfs) and the trim and fill method for further examination and correction. The Nfs for PSNU and GA as well as PSNU and SA are 4591 and 7568, respectively. Both Nfs were much larger than the standard 5 k + 10. After performing the trim and fill method, 14 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .a), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and GA changed to ( r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]); 10 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .b), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and SA changed to ( r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]). The correlation coefficients did not change significantly, indicating that there was no significant publication bias associated with the relationship between PSNU and these two anxiety symptoms (GA and SA).
Funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. Note: Black dots indicated additional studies after using trim and fill method; ( a ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and GA; ( b ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and SA; ( c ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and AA; ( d ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and FoMO
Sensitivity analyses
Initially, the findings obtained through the one-study-removed approach indicated that the heterogeneities in the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms were not attributed to any individual study. Nevertheless, it is important to note that sensitivity analysis should be performed based on literature quality [ 223 ] since low-quality literature could potentially impact result stability. In the relationship between PSNU and GA, the 10 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.402, 95% CI [0.375, 0.428]); In the relationship between PSNU and SA, the 8 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.431, 95% CI [0.387, 0.472]); In the relationship between PSNU and AA, the 5 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.367, 95% CI [0.298, 0.433]); In the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the 11 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.508, 95% CI [0.470, 0.544]). The revised estimates indicate that meta-analysis results were stable.
Moderator analysis
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between psnu and ga.
The results of subgroup analysis and meta-regression are shown in Table 4 , the time of measurement significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and GA ( Q between = 19.268, df = 2, p < 0.001). The relation between the two variables was significantly higher during the COVID-19 ( r = 0.392, 95% CI [0.357, 0.425]) than before the COVID-19 ( r = 0.270, 95% CI [0.227, 0.313]) or measurement time uncertain ( r = 0.352, 95% CI [0.285, 0.415]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). The relation was significantly higher when PSNU was measured with the BSMAS ( r = 0.373, 95% CI [0.341, 0.404]) compared to others ( r = 0.301, 95% CI [0.256, 0.344]).
The moderating effect of the GA measurement was significant ( Q between = 60.061, df = 5, p < 0.001). Specifically, when GA measured by the GAD ( r = 0.398, 95% CI [0.356, 0.438]) and the DASS-21-A ( r = 0.433, 95% CI [0.389, 0.475]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the STAI ( r = 0.232, 95% CI [0.187, 0.276]).
For the relation between PSNU and GA, the moderating effect of region, gender and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and SA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and SA were shown in Table 5 . The results revealed a gender-moderated variances between the two variables (b = 0.601, 95% CI [ 0.041, 1.161], Q model (1, k = 41) = 4.705, p = 0.036).
For the relation between PSNU and SA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU and SA, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and AA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and AA were shown in Table 6 , region significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and AA ( Q between = 6.410, df = 2, p = 0.041). The correlation between the two variables was significantly higher in developing country ( r = 0.378, 95% CI [0.304, 0.448]) than in developed country ( r = 0.242, 95% CI [0.162, 0.319]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). Specifically, when AA was measured by the GPIUS-2 ( r = 0.484, 95% CI [0.200, 0.692]) and the PMSMUAQ ( r = 0.443, 95% CI [0.381, 0.501]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the BSMAS ( r = 0.248, 95% CI [0.161, 0.331]) and others ( r = 0.313, 95% CI [0.250, 0.372]).
The moderating effect of the AA measurement was significant ( Q between = 17.283, df = 2, p < 0.001). The correlation was significantly higher when measured using the ECR ( r = 0.386, 95% CI [0.338, 0.432]) compared to the RQ ( r = 0.200, 95% CI [0.123, 0.275]).
For the relation between PSNU and AA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, gender, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and FoMO
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and FoMO were shown in Table 7 , the moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 8.170, df = 2, p = 0.017). Among the sub-dimensions, the others was excluded because there was only one sample. Specifically, when measured using the FoMOS-MSME ( r = 0.630, 95% CI [0.513, 0.725]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the FoMOS ( r = 0.472, 95% CI [0.432, 0.509]) and the T-S FoMOS ( r = 0.557, 95% CI [0.463, 0.639]).
For the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU, gender and age were not significant.
Through systematic review and meta-analysis, this study established a positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out), confirming a linear relationship and partially supporting the Social Cognitive Theory of Mass Communication [ 28 ] and the Cognitive Behavioral Model of Pathological Use [ 31 ]. Specifically, a significant positive correlation between PSNU and GA was observed, implying that GA sufferers might resort to social network for validation or as an escape from reality, potentially alleviating their anxiety. Similarly, the meta-analysis demonstrated a strong positive correlation between PSNU and SA, suggesting a preference for computer-mediated communication among those with high social anxiety due to perceived control and liberation offered by social network. This preference is often accompanied by maladaptive emotional regulation, predisposing them to problematic use. In AA, a robust positive correlation was found with PSNU, indicating a higher propensity for such use among individuals with attachment anxiety. Notably, the study identified the strongest correlation in the context of FoMO. FoMO’s significant association with PSNU is multifaceted, stemming from the real-time nature of social networks that engenders a continuous concern about missing crucial updates or events. This drives frequent engagement with social network, thereby establishing a direct link to problematic usage patterns. Additionally, social network’s feedback loops amplify this effect, intensifying FoMO. The culture of social comparison on these platforms further exacerbates FoMO, as users frequently compare their lives with others’ selectively curated portrayals, enhancing both their social networking usage frequency and the pursuit for social validation. Furthermore, the integral role of social network in modern life broadens FoMO’s scope, encompassing anxieties about staying informed and connected.
The notable correlation between FoMO and PSNU can be comprehensively understood through various perspectives. FoMO is inherently linked to the real-time nature of social networks, which cultivates an ongoing concern about missing significant updates or events in one’s social circle [ 221 ]. This anxiety prompts frequent engagement with social network, leading to patterns of problematic use. Moreover, the feedback loops in social network algorithms, designed to enhance user engagement, further intensify this fear [ 224 ]. Additionally, social comparison, a common phenomenon on these platforms, exacerbates FoMO as users continuously compare their lives with the idealized representations of others, amplifying feelings of missing out on key social experiences [ 225 ]. This behavior not only increases social networking usage but also is closely linked to the quest for social validation and identity construction on these platforms. The extensive role of social network in modern life further amplifies FoMO, as these platforms are crucial for information exchange and maintaining social ties. FoMO thus encompasses more than social concerns, extending to anxieties about staying informed with trends and dynamics within social networks [ 226 ]. The multifaceted nature of FoMO in relation to social network underscores its pronounced correlation with problematic social networking usage. In essence, the combination of social network’s intrinsic characteristics, psychological drivers of user behavior, the culture of social comparison, and the pervasiveness of social network in everyday life collectively make FoMO the most pronouncedly correlated anxiety type with PSNU.
Additionally, we conducted subgroup analyses on the timing of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms), sample characteristics (participants’ region), and performed a meta-regression analysis on gender and age in the context of PSNU and anxiety symptoms. It was found that the timing of measurement, tools used for assessing PSNU and anxiety, region, and gender had a moderating effect, whereas age did not show a significant moderating impact.
Firstly, the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms was significantly higher during the COVID-19 period than before, especially between PSNU and GA. However, the moderating effect of measurement timing was not significant in the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety. This could be attributed to the increased uncertainty and stress during the pandemic, leading to heightened levels of general anxiety [ 227 ]. The overuse of social network for information seeking and anxiety alleviation might have paradoxically exacerbated anxiety symptoms, particularly among individuals with broad future-related worries [ 228 ]. While the COVID-19 pandemic altered the relationship between PSNU and GA, its impact on other types of anxiety (such as SA and AA) may not have been significant, likely due to these anxiety types being more influenced by other factors like social skills and attachment styles, which were minimally impacted by the epidemic.
Secondly, the observed variance in the relationship between PSNU and AA across different economic contexts, notably between developing and developed countries, underscores the multifaceted influence of socio-economic, cultural, and technological factors on this dynamic. The amplified connection in developing countries may be attributed to greater socio-economic challenges, distinct cultural norms regarding social support and interaction, rising social network penetration, especially among younger demographics, and technological disparities influencing accessibility and user experience [ 229 , 230 ]. Moreover, the role of social network as a coping mechanism for emotional distress, potentially fostering insecure attachment patterns, is more pronounced in these settings [ 231 ]. These findings highlight the necessity of considering contextual variations in assessing the psychological impacts of social network, advocating for a nuanced understanding of how socio-economic and cultural backgrounds mediate the relationship between PSNU and mental health outcomes [ 232 ]. Additionally, the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety (such as GA and SA) presents uniform characteristics across different economic contexts.
Thirdly, the significant moderating effects of measurement tools in the context of PSNU and its correlation with various forms of anxiety, including GA, and AA, are crucial in interpreting the research findings. Specifically, the study reveals that the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) demonstrates a stronger correlation between PSNU and GA, compared to other tools. Similarly, for AA, the Griffiths’ Problematic Internet Use Scale 2 (GPIUS2) and the Problematic Media Social Media Use Assessment Questionnaire (PMSMUAQ) show a more pronounced correlation with AA than the BSMAS or other instruments, but for SA and FoMO, the PSNU instrument doesn’t significantly moderate the correlation. The PSNU measurement tool typically contains an emotional change dimension. SA and FoMO, due to their specific conditional stimuli triggers and correlation with social networks [ 233 , 234 ], are likely to yield more consistent scores in this dimension, while GA and AA may be less reliable due to their lesser sensitivity to specific conditional stimuli. Consequently, the adjustment effects of PSNU measurements vary across anxiety symptoms. Regarding the measurement tools for anxiety, different scales exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity in detecting the relationship with PSNU. The Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD) and the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales 21 (DASS-21) are more effective in illustrating a strong relationship between GA and PSNU than the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). In the case of AA, the Experiences in Close Relationships-21 (ECR-21) provides a more substantial correlation than the Relationship Questionnaire (RQ). Furthermore, for FoMO, the Fear of Missing Out Scale - Multi-Social Media Environment (FoMOS-MSME) is more indicative of a strong relationship with PSNU compared to the standard FoMOS or the T-S FoMOS. These findings underscore the importance of the selection of appropriate measurement tools in research. Different tools, due to their unique design, focus, and sensitivity, can reveal varying degrees of correlation between PSNU and anxiety disorders. This highlights the need for careful consideration of tool characteristics and their potential impact on research outcomes. It also cautions against drawing direct comparisons between studies without acknowledging the possible variances introduced by the use of different measurement instruments.
Fourthly, the significant moderating role of gender in the relationship between PSNU and SA, particularly pronounced in samples with a higher proportion of females. Women tend to engage more actively and emotionally with social network, potentially leading to an increased dependency on these platforms when confronting social anxiety [ 235 ]. This intensified use might amplify the association between PSNU and SA. Societal and cultural pressures, especially those related to appearance and social status, are known to disproportionately affect women, possibly exacerbating their experience of social anxiety and prompting a greater reliance on social network for validation and support [ 236 ]. Furthermore, women’s propensity to seek emotional support and express themselves on social network platforms [ 237 ] could strengthen this link, particularly in the context of managing social anxiety. Consequently, the observed gender differences in the relationship between PSNU and SA underscore the importance of considering gender-specific dynamics and cultural influences in psychological research related to social network use. In addition, gender consistency was observed in the association between PSNU and other types of anxiety, indicating no significant gender disparities.
Fifthly, the absence of a significant moderating effect of age on the relationship between PSNU and various forms of anxiety suggests a pervasive influence of social network across different age groups. This finding indicates that the impact of PSNU on anxiety is relatively consistent, irrespective of age, highlighting the universal nature of social network’s psychological implications [ 238 ]. Furthermore, this uniformity suggests that other factors, such as individual psychological traits or socio-cultural influences, might play a more crucial role in the development of anxiety related to social networking usage than age [ 239 ]. The non-significant role of age also points towards a potential generational overlap in social networking usage patterns and their psychological effects, challenging the notion that younger individuals are uniquely susceptible to the adverse effects of social network on mental health [ 240 ]. Therefore, this insight necessitates a broader perspective in understanding the dynamics of social network and mental health, one that transcends age-based assumptions.
Limitations
There are some limitations in this research. First, most of the studies were cross-sectional surveys, resulting in difficulties in inferring causality of variables, longitudinal study data will be needed to evaluate causal interactions in the future. Second, considerable heterogeneity was found in the estimated results, although heterogeneity can be partially explained by differences in study design (e.g., Time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tools), but this can introduce some uncertainty in the aggregation and generalization of the estimated results. Third, most studies were based on Asian samples, which limits the generality of the results. Fourth, to minimize potential sources of heterogeneity, some less frequently used measurement tools were not included in the classification of measurement tools, which may have some impact on the results of heterogeneity interpretation. Finally, since most of the included studies used self-reported scales, it is possible to get results that deviate from the actual situation to some extent.
This meta-analysis aims to quantifies the correlations between PSNU and four specific types of anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out). The results revealed a significant moderate positive association between PSNU and each of these anxiety symptoms. Furthermore, Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis indicated that gender, region, time of measurement, and instrument of measurement significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and specific anxiety symptoms. Specifically, the measurement time and GA measurement tools significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and GA. Gender significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and SA. Region, PSNU measurement tools, and AA measurement tools all significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and AA. The FoMO measurement tool significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and FoMO. Regarding these findings, prevention interventions for PSNU and anxiety symptoms are important.
Data availability
The datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Problematic social networking use
- Generalized anxiety
- Social anxiety
- Attachment anxiety
Fear of miss out
Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale
Facebook Addiction Scale
Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire
Generalized Problematic Internet Use Scale 2
Problematic Mobile Social Media Usage Assessment Questionnaire
Social Network Addiction Tendency Scale
Brief Symptom Inventory
The anxiety subscale of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
The anxiety subscale of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
State-Trait Anxiety Inventory
Interaction Anxiousness Scale
Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale
Social Anxiety Scale for Social Media Users
Social Anxiety for Adolescents
Social Anxiety Subscale of the Self-Consciousness Scale
Social Interaction Anxiety Scale
Experiences in Close Relationship Scale
Relationship questionnaire
Fear of Missing Out Scale
FoMO Measurement Scale in the Mobile Social Media Environment
Trait-State Fear of missing Out Scale
Rozgonjuk D, Sindermann C, Elhai JD, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and social media’s impact on daily-life and productivity at work: do WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat Use disorders mediate that association? Addict Behav. 2020;110:106487.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mieczkowski H, Lee AY, Hancock JT. Priming effects of social media use scales on well-being outcomes: the influence of intensity and addiction scales on self-reported depression. Social Media + Soc. 2020;6(4):2056305120961784.
Article Google Scholar
Global digital population as of April. 2023 [ https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-population-worldwide/ ].
Marengo D, Settanni M, Fabris MA, Longobardi C. Alone, together: fear of missing out mediates the link between peer exclusion in WhatsApp classmate groups and psychological adjustment in early-adolescent teens. J Social Personal Relationships. 2021;38(4):1371–9.
Marengo D, Fabris MA, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Smartphone and social media use contributed to individual tendencies towards social media addiction in Italian adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic. Addict Behav. 2022;126:107204.
Müller SM, Wegmann E, Stolze D, Brand M. Maximizing social outcomes? Social zapping and fear of missing out mediate the effects of maximization and procrastination on problematic social networks use. Comput Hum Behav. 2020;107:106296.
Sun Y, Zhang Y. A review of theories and models applied in studies of social media addiction and implications for future research. Addict Behav. 2021;114:106699.
Boustead R, Flack M. Moderated-mediation analysis of problematic social networking use: the role of anxious attachment orientation, fear of missing out and satisfaction with life. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Hussain Z, Griffiths MD. The associations between problematic social networking Site Use and Sleep Quality, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, Depression, anxiety and stress. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(3):686–700.
Gori A, Topino E, Griffiths MD. The associations between attachment, self-esteem, fear of missing out, daily time expenditure, and problematic social media use: a path analysis model. Addict Behav. 2023;141:107633.
Marino C, Manari T, Vieno A, Imperato C, Spada MM, Franceschini C, Musetti A. Problematic social networking sites use and online social anxiety: the role of attachment, emotion dysregulation and motives. Addict Behav. 2023;138:107572.
Tobin SJ, Graham S. Feedback sensitivity as a mediator of the relationship between attachment anxiety and problematic Facebook Use. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2020;23(8):562–6.
Brailovskaia J, Rohmann E, Bierhoff H-W, Margraf J. The anxious addictive narcissist: the relationship between grandiose and vulnerable narcissism, anxiety symptoms and Facebook Addiction. PLoS ONE 2020, 15(11).
Kim S-S, Bae S-M. Social Anxiety and Social Networking Service Addiction Proneness in University students: the Mediating effects of Experiential Avoidance and interpersonal problems. Psychiatry Invest. 2022;19(8):702–702.
Zhao J, Ye B, Yu L, Xia F. Effects of Stressors of COVID-19 on Chinese College Students’ Problematic Social Media Use: A Mediated Moderation Model. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Astolfi Cury GS, Takannune DM, Prates Herrerias GS, Rivera-Sequeiros A, de Barros JR, Baima JP, Saad-Hossne R, Sassaki LY. Clinical and Psychological Factors Associated with Addiction and Compensatory Use of Facebook among patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a cross-sectional study. Int J Gen Med. 2022;15:1447–57.
Balta S, Emirtekin E, Kircaburun K, Griffiths MD. Neuroticism, trait fear of missing out, and Phubbing: the mediating role of state fear of missing out and problematic Instagram Use. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2020;18(3):628–39.
Boursier V, Gioia F, Griffiths MD. Do selfie-expectancies and social appearance anxiety predict adolescents’ problematic social media use? Comput Hum Behav. 2020;110:106395.
Worsley JD, McIntyre JC, Bentall RP, Corcoran R. Childhood maltreatment and problematic social media use: the role of attachment and depression. Psychiatry Res. 2018;267:88–93.
de Bérail P, Guillon M, Bungener C. The relations between YouTube addiction, social anxiety and parasocial relationships with YouTubers: a moderated-mediation model based on a cognitive-behavioral framework. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;99:190–204.
Naidu S, Chand A, Pandaram A, Patel A. Problematic internet and social network site use in young adults: the role of emotional intelligence and fear of negative evaluation. Pers Indiv Differ. 2023;200:111915.
Apaolaza V, Hartmann P, D’Souza C, Gilsanz A. Mindfulness, compulsive Mobile Social Media Use, and derived stress: the mediating roles of self-esteem and social anxiety. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2019;22(6):388–96.
Demircioglu ZI, Goncu-Kose A. Antecedents of problematic social media use and cyberbullying among adolescents: attachment, the dark triad and rejection sensitivity. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Gao Q, Li Y, Zhu Z, Fu E, Bu X, Peng S, Xiang Y. What links to psychological needs satisfaction and excessive WeChat use? The mediating role of anxiety, depression and WeChat use intensity. BMC Psychol. 2021;9(1):105–105.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malak MZ, Shuhaiber AH, Al-amer RM, Abuadas MH, Aburoomi RJ. Correlation between psychological factors, academic performance and social media addiction: model-based testing. Behav Inform Technol. 2022;41(8):1583–95.
Song C. The effect of the need to belong on mobile phone social media dependence of middle school students: Chain mediating roles of fear of missing out and maladaptive cognition. Sichuan Normal University; 2022.
Tokunaga RS, Rains SA. A review and meta-analysis examining conceptual and operational definitions of problematic internet use. Hum Commun Res. 2016;42(2):165–99.
Bandura A. Social cognitive theory of mass communication. Media effects. edn.: Routledge; 2009. pp. 110–40.
Valkenburg PM, Peter J, Walther JB. Media effects: theory and research. Ann Rev Psychol. 2016;67:315–38.
Slater MD. Reinforcing spirals: the mutual influence of media selectivity and media effects and their impact on individual behavior and social identity. Communication Theory. 2007;17(3):281–303.
Ahmed E, Vaghefi I. Social media addiction: A systematic review through cognitive-behavior model of pathological use. 2021.
She R, han Mo PK, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, fai Lau JT. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Przybylski AK, Weinstein N. A large-scale test of the goldilocks hypothesis: quantifying the relations between digital-screen use and the mental well-being of adolescents. Psychol Sci. 2017;28(2):204–15.
Ran G, Li J, Zhang Q, Niu X. The association between social anxiety and mobile phone addiction: a three-level meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2022;130:107198.
Fioravanti G, Casale S, Benucci SB, Prostamo A, Falone A, Ricca V, Rotella F. Fear of missing out and social networking sites use and abuse: a meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;122:106839.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group* P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–9.
Card NA. Applied meta-analysis for social science research. Guilford; 2015.
Peterson RA, Brown SP. On the use of beta coefficients in meta-analysis. J Appl Psychol. 2005;90(1):175.
Hunter JE, Schmidt FL. Methods of meta-analysis: correcting error and bias in research findings. Sage; 2004.
Zhang Y, Li S, Yu G. The relationship between self-esteem and social anxiety: a meta-analysis with Chinese students. Adv Psychol Sci. 2019;27(6):1005–18.
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley; 2021.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.
Light RJ, Pillemer DB. Summing up: the science of reviewing research. Harvard University Press; 1984.
Rosenthal R. Meta-Analytic Procedures for Social Science Research Sage Publications: Beverly Hills, 1984, 148 pp. Educational Researcher 1986;15(8):18–20.
Rothstein HR, Sutton AJ, Borenstein M. Publication bias in meta-analysis. Publication bias meta‐analysis: Prev Assess Adjustments 2005:1–7.
Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta‐analysis. Biometrics. 2000;56(2):455–63.
Al-Mamun F, Hosen I, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. Facebook use and its predictive factors among students: evidence from a lower- and middle-income country, Bangladesh. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Schou Andreassen C, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behaviors: J Soc Psychologists Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252–62.
Arikan G, Acar IH, Ustundag-Budak AM. A two-generation study: The transmission of attachment and young adults’ depression, anxiety, and social media addiction. Addict Behav 2022, 124.
Arpaci I, Karatas K, Kiran F, Kusci I, Topcu A. Mediating role of positivity in the relationship between state anxiety and problematic social media use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Death Stud. 2022;46(10):2287–97.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Facebook Addiction Disorder (FAD) among German students-A longitudinal approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12(12).
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. The relationship between burden caused by coronavirus (Covid-19), addictive social media use, sense of control and anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;119:106720–106720.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Addictive social media use during Covid-19 outbreak: validation of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) and investigation of protective factors in nine countries. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Brailovskaia J, Krasavtseva Y, Kochetkov Y, Tour P, Margraf J. Social media use, mental health, and suicide-related outcomes in Russian women: a cross-sectional comparison between two age groups. Women’s Health (London England). 2022;18:17455057221141292–17455057221141292.
PubMed Google Scholar
Chang C-W, Huang R-Y, Strong C, Lin Y-C, Tsai M-C, Chen IH, Lin C-Y, Pakpour AHH, Griffiths MDD. Reciprocal relationships between Problematic Social Media Use, problematic gaming, and psychological distress among University students: a 9-Month Longitudinal Study. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Charzynska E, Sussman S, Atroszko PA. Profiles of potential behavioral addictions’ severity and their associations with gender, personality, and well-being: A person-centered approach. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y, Griffiths MD. Internet-related behaviors and psychological distress among Schoolchildren during the COVID-19 School Hiatus. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(10):654–63.
Da Veiga GF, Sotero L, Pontes HM, Cunha D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Emerging adults and Facebook Use: the validation of the Bergen Facebook Addiction Scale (BFAS). Int J Mental Health Addict. 2019;17(2):279–94.
Dadiotis A, Bacopoulou F, Kokka I, Vlachakis D, Chrousos GP, Darviri C, Roussos P. Validation of the Greek version of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale in Undergraduate Students. EMBnetjournal 2021, 26.
Fekih-Romdhane F, Jahrami H, Away R, Trabelsi K, Pandi-Perumal SR, Seeman MV, Hallit S, Cheour M. The relationship between technology addictions and schizotypal traits: mediating roles of depression, anxiety, and stress. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23(1).
Flynn S, Noone C, Sarma KM. An exploration of the link between adult attachment and problematic Facebook use. BMC Psychol. 2018;6(1):34–34.
Fung XCC, Siu AMH, Potenza MN, O’Brien KS, Latner JD, Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Lin C-Y. Problematic use of internet-related activities and Perceived Weight Stigma in Schoolchildren: a longitudinal study across different epidemic periods of COVID-19 in China. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gonzalez-Nuevo C, Cuesta M, Muniz J, Postigo A, Menendez-Aller A, Kuss DJ. Problematic Use of Social Networks during the First Lockdown: User Profiles and the Protective Effect of Resilience and Optimism. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(24).
Hou X-L, Wang H-Z, Hu T-Q, Gentile DA, Gaskin J, Wang J-L. The relationship between perceived stress and problematic social networking site use among Chinese college students. J Behav Addictions. 2019;8(2):306–17.
Hussain Z, Wegmann E. Problematic social networking site use and associations with anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and resilience. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100125.
Imani V, Ahorsu DK, Taghizadeh N, Parsapour Z, Nejati B, Chen H-P, Pakpour AH. The mediating roles of anxiety, Depression, Sleepiness, Insomnia, and Sleep Quality in the Association between Problematic Social Media Use and Quality of Life among patients with Cancer. Healthcare 2022, 10(9).
Islam MS, Sujan MSH, Tasnim R, Mohona RA, Ferdous MZ, Kamruzzaman S, Toma TY, Sakib MN, Pinky KN, Islam MR et al. Problematic smartphone and Social Media Use among Bangladeshi College and University students amid COVID-19: the role of Psychological Well-Being and Pandemic related factors. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Islam MS, Jahan I, Dewan MAA, Pontes HM, Koly KN, Sikder MT, Rahman M. Psychometric properties of three online-related addictive behavior instruments among Bangladeshi school-going adolescents. PLoS ONE 2022, 17(12).
Jahan I, Hosen I, Al Mamun F, Kaggwa MM, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted Internet Use behaviors and facilitated problematic internet use? A Bangladeshi study. Psychol Res Behav Manage. 2021;14:1127–38.
Jiang Y. Problematic social media usage and anxiety among University Students during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating role of Psychological Capital and the moderating role of academic burnout. Front Psychol. 2021;12:612007–612007.
Kim M-R, Oh J-W, Huh B-Y. Analysis of factors related to Social Network Service Addiction among Korean High School Students. J Addictions Nurs. 2020;31(3):203–12.
Koc M, Gulyagci S. Facebook addiction among Turkish college students: the role of psychological health, demographic, and usage characteristics. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2013;16(4):279–84.
Lin C-Y, Namdar P, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Mediated roles of generalized trust and perceived social support in the effects of problematic social media use on mental health: a cross-sectional study. Health Expect. 2021;24(1):165–73.
Lin C-Y, Imani V, Griffiths MD, Brostrom A, Nygardh A, Demetrovics Z, Pakpour AH. Temporal associations between morningness/eveningness, problematic social media use, psychological distress and daytime sleepiness: mediated roles of sleep quality and insomnia among young adults. J Sleep Res 2021, 30(1).
Lozano Blasco R, Latorre Cosculluela C, Quilez Robres A. Social Network Addiction and its impact on anxiety level among University students. Sustainability 2020, 12(13).
Marino C, Musetti A, Vieno A, Manari T, Franceschini C. Is psychological distress the key factor in the association between problematic social networking sites and poor sleep quality? Addict Behav 2022, 133.
Meshi D, Ellithorpe ME. Problematic social media use and social support received in real-life versus on social media: associations with depression, anxiety and social isolation. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Mitropoulou EM, Karagianni M, Thomadakis C. Social Media Addiction, Self-Compassion, and Psychological Well-Being: a structural equation Model. Alpha Psychiatry. 2022;23(6):298–304.
Ozimek P, Brailovskaia J, Bierhoff H-W. Active and passive behavior in social media: validating the Social Media Activity Questionnaire (SMAQ). Telematics Inf Rep. 2023;10:100048.
Phillips WJ, Wisniewski AT. Self-compassion moderates the predictive effects of social media use profiles on depression and anxiety. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100128.
Reer F, Festl R, Quandt T. Investigating problematic social media and game use in a nationally representative sample of adolescents and younger adults. Behav Inform Technol. 2021;40(8):776–89.
Satici B, Kayis AR, Griffiths MD. Exploring the Association between Social Media Addiction and relationship satisfaction: psychological distress as a Mediator. Int J Mental Health Addict 2021.
Sediri S, Zgueb Y, Ouanes S, Ouali U, Bourgou S, Jomli R, Nacef F. Women’s mental health: acute impact of COVID-19 pandemic on domestic violence. Archives Womens Mental Health. 2020;23(6):749–56.
Shabahang R, Shim H, Aruguete MS, Zsila A. Oversharing on Social Media: anxiety, Attention-Seeking, and Social Media Addiction Predict the breadth and depth of sharing. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221122861–332941221122861.
Sotero L, Ferreira Da Veiga G, Carreira D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Facebook Addiction and emerging adults: the influence of sociodemographic variables, family communication, and differentiation of self. Escritos De Psicología - Psychol Writings. 2019;12(2):81–92.
Stockdale LA, Coyne SM. Bored and online: reasons for using social media, problematic social networking site use, and behavioral outcomes across the transition from adolescence to emerging adulthood. J Adolesc. 2020;79:173–83.
Wang Z, Yang H, Elhai JD. Are there gender differences in comorbidity symptoms networks of problematic social media use, anxiety and depression symptoms? Evidence from network analysis. Pers Indiv Differ. 2022;195:111705.
White-Gosselin C-E, Poulin F. Associations Between Young Adults’ Social Media Addiction, Relationship Quality With Parents, and Internalizing Problems: A Path Analysis Model. 2022.
Wong HY, Mo HY, Potenza MN, Chan MNM, Lau WM, Chui TK, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y. Relationships between Severity of Internet Gaming Disorder, Severity of Problematic Social Media Use, Sleep Quality and Psychological Distress. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17(6).
Yam C-W, Pakpour AH, Griffiths MD, Yau W-Y, Lo C-LM, Ng JMT, Lin C-Y, Leung H. Psychometric testing of three Chinese online-related addictive Behavior instruments among Hong Kong University students. Psychiatr Q. 2019;90(1):117–28.
Yuan Y, Zhong Y. A survey on the use of social networks and mental health of college students during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Campus Life Mental Health\. 2021;19(3):209–12.
Google Scholar
Yurdagul C, Kircaburun K, Emirtekin E, Wang P, Griffiths MD. Psychopathological consequences related to problematic Instagram Use among adolescents: the mediating role of body image dissatisfaction and moderating role of gender. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(5):1385–97.
Zhang W, Pu J, He R, Yu M, Xu L, He X, Chen Z, Gan Z, Liu K, Tan Y, et al. Demographic characteristics, family environment and psychosocial factors affecting internet addiction in Chinese adolescents. J Affect Disord. 2022;315:130–8.
Zhang L, Wu Y, Jin T, Jia Y. Revision and validation of the Chinese short version of social media disorder. Mod Prev Med. 2021;48(8):1350–3.
Zhang X, Fan L. The influence of anxiety on colleges’ life satisfaction. Chin J Health Educ. 2021;37(5):469–72.
Zhao M, Wang H, Dong Y, Niu Y, Fang Y. The relationship between self-esteem and wechat addiction among undergraduate students: the multiple mediating roles of state anxiety and online interpersonal trust. J Psychol Sci. 2021;44(1):104–10.
Zhao J, Zhou Z, Sun B, Zhang X, Zhang L, Fu S. Attentional Bias is Associated with negative emotions in problematic users of Social Media as measured by a dot-probe Task. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(24).
Atroszko PA, Balcerowska JM, Bereznowski P, Biernatowska A, Pallesen S, Schou Andreassen C. Facebook addiction among Polish undergraduate students: validity of measurement and relationship with personality and well-being. Comput Hum Behav. 2018;85:329–38.
Chen Y, Li R, Zhang P, Liu X. The moderating role of state attachment anxiety and avoidance between social anxiety and social networking sites Addiction. Psychol Rep. 2020;123(3):633–47.
Chen B, Zheng X, Sun X. The relationship between problematic social media use and online social anxiety: the roles of social media cognitive overload and dispositional mindfulness. Psychol Dev Educ. 2023;39(5):743–51.
Chentsova VO, Bravo AJ, Mezquita L, Pilatti A, Hogarth L, Cross-Cultural AS. Internalizing symptoms, rumination, and problematic social networking site use: a cross national examination among young adults in seven countries. Addict Behav 2023, 136.
Chu X, Ji S, Wang X, Yu J, Chen Y, Lei L. Peer phubbing and social networking site addiction: the mediating role of social anxiety and the moderating role of Family Financial Difficulty. Front Psychol. 2021;12:670065–670065.
Dempsey AE, O’Brien KD, Tiamiyu MF, Elhai JD. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and rumination mediate relations between social anxiety and problematic Facebook use. Addict Behav Rep. 2019;9:100150–100150.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yildiz Durak H, Seferoglu SS. Modeling of variables related to problematic social media usage: Social desirability tendency example. Scand J Psychol. 2019;60(3):277–88.
Ekinci N, Akat M. The relationship between anxious-ambivalent attachment and social appearance anxiety in adolescents: the serial mediation of positive Youth Development and Instagram Addiction. Psychol Rep 2023:332941231159600–332941231159600.
Foroughi B, Griffiths MD, Iranmanesh M, Salamzadeh Y. Associations between Instagram Addiction, academic performance, social anxiety, Depression, and life satisfaction among University students. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2022;20(4):2221–42.
He L. Influence mechanism and intervention suggestions on addiction of social network addiction. Gannan Normal University; 2021.
Hu Y. The influencing mechanism of type D personality on problematic social networking sites use among adolescents and intervention research. Central China Normal University; 2020.
Jia L. A study of the relationship between neuroticism, perceived social support, social anxiety and problematic social network use in high school students. Harbin Normal University; 2022.
Lee-Won RJ, Herzog L, Park SG. Hooked on Facebook: the role of social anxiety and need for Social Assurance in Problematic Use of Facebook. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2015;18(10):567–74.
Li H. Social anxiety and internet interpersonal addiction in adolescents and countermeasures. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Lin W-S, Chen H-R, Lee TS-H, Feng JY. Role of social anxiety on high engagement and addictive behavior in the context of social networking sites. Data Technol Appl. 2019;53(2):156–70.
Liu Y. The influence of family function on social media addiction in adolescents: the chain mediation effect of social anxiety and resilience. Hunan Normal University; 2021.
Lyvers M, Salviani A, Costan S, Thorberg FA. Alexithymia, narcissism and social anxiety in relation to social media and internet addiction symptoms. Int J Psychology: J Int De Psychologie. 2022;57(5):606–12.
Majid A, Yasir M, Javed A, Ali P. From envy to social anxiety and rumination: how social media site addiction triggers task distraction amongst nurses. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2020;28(3):504–13.
Mou Q, Zhuang J, Gao Y, Zhong Y, Lu Q, Gao F, Zhao M. The relationship between social anxiety and academic engagement among Chinese college students: a serial mediation model. J Affect Disord. 2022;311:247–53.
Ruggieri S, Santoro G, Pace U, Passanisi A, Schimmenti A. Problematic Facebook use and anxiety concerning use of social media in mothers and their offspring: an actor-partner interdependence model. Addict Behav Rep. 2020;11:100256–100256.
Ruiz MJ, Saez G, Villanueva-Moya L, Exposito F. Adolescent sexting: the role of body shame, Social Physique anxiety, and social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(12):799–805.
She R, Kit Han Mo P, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, Tak Fai Lau J. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Stănculescu E. The Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale Validity in a Romanian sample using item response theory and network analysis. Int J Mental Health Addict 2022.
Teng X, Lei H, Li J, Wen Z. The influence of social anxiety on social network site addiction of college students: the moderator of intentional self-regulation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):514–7.
Tong W. Influence of boredom on the problematic mobile social networks usage in adolescents: multiple chain mediator. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):932–6.
Tu W, Jiang H, Liu Q. Peer victimization and adolescent Mobile Social Addiction: mediation of social anxiety and gender differences. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(17).
Wang S. The influence of college students self-esteem, social anxiety and fear of missing out on the problematic mobile social networks usage. Huaibei Normal University; 2021.
Wang X. The impact of peer relationship and social anxiety on secondary vocational school students’ problematic social network use and intervention study. Huaibei Normal University; 2022.
Wegmann E, Stodt B, Brand M. Addictive use of social networking sites can be explained by the interaction of internet use expectancies, internet literacy, and psychopathological symptoms. J Behav Addictions. 2015;4(3):155–62.
Yang W. The relationship between the type of internet addiction and the personality traits in college students. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2004.
Yang Z. The relationship between social variables and social networking usage among shanghai working population. East China Normal University; 2013.
Zhang C. The relationship between perceived social support and problematic social network use among junior high school students: a chain mediation model and an intervention study. Hebei University; 2022.
Zhang J, Chang F, Huang D, Wen X. The relationship between neuroticism and the problematic mobile social networks use in adolescents: the mediating role of anxiety and positive self-presentation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):598–602.
Zhang Z. College students’ loneliness and problematic social networking use: Chain mediation of social self-efficacy and social anxiety. Shanghai Normal University; 2019.
Zhu B. Discussion on mechanism of social networking addiction——Social anxiety, craving and excitability. Liaoning Normal University; 2017.
Blackwell D, Leaman C, Tramposch R, Osborne C, Liss M. Extraversion, neuroticism, attachment style and fear of missing out as predictors of social media use and addiction. Pers Indiv Differ. 2017;116:69–72.
Chen A. From attachment to addiction: the mediating role of need satisfaction on social networking sites. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;98:80–92.
Chen Y, Zhong S, Dai L, Deng Y, Liu X. Attachment anxiety and social networking sites addiction in college students: a moderated mediating model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(3):497–500.
Li J. The relations among problematic social networks usage behavior, Childhood Trauma and adult attachment in University students. Hunan Agricultural University; 2020.
Liu C, Ma J-L. Adult attachment orientations and social networking site addiction: the Mediating effects of Online Social Support and the fear of missing out. Front Psychol. 2019;10:2629–2629.
Mo S, Huang W, Xu Y, Tang Z, Nie G. The impact of medical students’ attachment anxiety on the use of problematic social networking sites during the epidemic. Psychol Monthly. 2022;17(9):1–4.
Teng X. The effect of attachment anxiety on problematic mobile social network use: the role of loneliness and self-control. Harbin Normal University; 2021.
Worsley JD, Mansfield R, Corcoran R. Attachment anxiety and problematic social media use: the Mediating Role of Well-Being. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2018;21(9):563–8.
Wu Z. The effect of adult attachment on problematic social network use: the chain mediating effect of loneliness and fear of missing out. Jilin University; 2022.
Xia N. The impact of attachment anxiety on adolescent problem social networking site use: a moderated mediation model. Shihezi University; 2022.
Young L, Kolubinski DC, Frings D. Attachment style moderates the relationship between social media use and user mental health and wellbeing. Heliyon 2020, 6(6).
Bakioglu F, Deniz M, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Adaptation and validation of the online-fear of missing out inventory into Turkish and the association with social media addiction, smartphone addiction, and life satisfaction. BMC Psychol. 2022;10(1):154–154.
Bendayan R, Blanca MJ. Spanish version of the Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire (FIQ-S). Psicothema. 2019;31(2):204–9.
Blachnio A, Przepiorka A. Facebook intrusion, fear of missing out, narcissism, and life satisfaction: a cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Res. 2018;259:514–9.
Casale S, Rugai L, Fioravanti G. Exploring the role of positive metacognitions in explaining the association between the fear of missing out and social media addiction. Addict Behav. 2018;85:83–7.
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang K. Effect of fear of’ missing out on college students negative social adaptation: Chain¬ - mediating effect of rumination and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(4):581–6.
Cheng S, Zhang X, Han Y. Relationship between fear of missing out and phubbing on college students: the chain intermediary effect of intolerance of uncertainty and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(9):1296–300.
Cui Q, Wang J, Zhang J, Li W, Li Q. The relationship between loneliness and negative emotion in college students: the chain-mediating role of fear of missing out and social network sites addiction. J Jining Med Univ. 2022;45(4):248–51.
Ding Q, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhou Z. The more gossip, the more addicted: the relationship between interpersonal curiosity and social networking sites addiction tendencies in college students. Psychol Dev Educ. 2022;38(1):118–25.
Fabris MA, Marengo D, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Investigating the links between fear of missing out, social media addiction, and emotional symptoms in adolescence: the role of stress associated with neglect and negative reactions on social media. Addict Behav. 2020;106:106364.
Fang J, Wang X, Wen Z, Zhou J. Fear of missing out and problematic social media use as mediators between emotional support from social media and phubbing behavior. Addict Behav. 2020;107:106430.
Gao Z. The study on the relationship and intervention among fear of missing out self-differentiation and problematic social media use of college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Gioia F, Fioravanti G, Casale S, Boursier V. The Effects of the Fear of Missing Out on People’s Social Networking Sites Use During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Role of Online Relational Closeness and Individuals’ Online Communication Attitude. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gu X. Study on the Inhibitory Effect of Mindfulness Training on Social Media Addiction of College Students. Wuhan University; 2020.
Gugushvili N, Taht K, Schruff-Lim EM, Ruiter RA, Verduyn P. The Association between Neuroticism and problematic social networking sites Use: the role of fear of missing out and Self-Control. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221142003–332941221142003.
Hou J. The study on FoMO and content social media addiction among young people. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Hu R, Zhang B, Yang Y, Mao H, Peng Y, Xiong S. Relationship between college students’ fear of missing and wechat addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. J Bio-education. 2022;10(5):369–73.
Hu G. The relationship between basic psychological needs satisfaction and the use of problematic social networks by college students: a moderated mediation model and online intervention studies. Jiangxi Normal University; 2020.
Jiang Y, Jin T. The relationship between adolescents’ narcissistic personality and their use of problematic mobile social networks: the effects of fear of missing out and positive self-presentation. Chin J Special Educ 2018(11):64–70.
Li J. The effect of positive self-presentation on social networking sites on problematic use of social networking sites: a moderated mediation model. Henan University; 2020.
Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang X. The impact of Freshmen Social Exclusion on problematic Social Network Use: a Moderated Mediation Model. J Heilongjiang Vocat Inst Ecol Eng. 2023;36(1):118–22.
Li M. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction among middle school students——The moderating role of self-control. Kashi University; 2022.
Li R, Dong X, Wang M, Wang R. A study on the relationship between fear of missing out and social network addiction. New Educ Era 2021(52):122–3.
Li Y. Fear of missing out or social avoidance? The influence of peer exclusion on problematic social media use among adolescents in Guangdong Province and Macao. Guangzhou University; 2020.
Ma J, Liu C. The effect of fear of missing out on social networking sites addiction among college students: the mediating roles of social networking site integration use and social support. Psychol Dev Educ. 2019;35(5):605–14.
Mao H. A follow-up study on the mechanism of the influence of university students’ Qi deficiency quality on WeChat addiction. Hunan University of Chinese Medicine; 2021.
Mao Y. The effect of dual filial piety to the college students ’internet social dependence: the mediation of maladaptive cognition and fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Moore K, Craciun G. Fear of missing out and personality as predictors of Social networking sites usage: the Instagram Case. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(4):1761–87.
Niu J. The relationship of college students’ basic psychological needs and social media dependence: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Pi L, Li X. Research on the relationship between loneliness and problematic mobile social media usage: evidence from variable-oriented and person-oriented analyses. China J Health Psychol. 2023;31(6):936–42.
Pontes HM, Taylor M, Stavropoulos V. Beyond Facebook Addiction: the role of cognitive-related factors and Psychiatric Distress in Social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2018;21(4):240–7.
Quaglieri A, Biondi S, Roma P, Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Burrai J, Lausi G, Marti-Vilar M, Gonzalez-Sala F, Di Domenico A et al. From Emotional (Dys) Regulation to Internet Addiction: A Mediation Model of Problematic Social Media Use among Italian Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(1).
Servidio R, Koronczai B, Griffiths MD, Demetrovics Z. Problematic smartphone Use and Problematic Social Media Use: the predictive role of Self-Construal and the Mediating Effect of Fear Missing Out. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Sheldon P, Antony MG, Sykes B. Predictors of problematic social media use: personality and life-position indicators. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(3):1110–33.
Sun C, Li Y, Kwok SYCL, Mu W. The relationship between intolerance of uncertainty and problematic Social Media Use during the COVID-19 pandemic: a serial mediation model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(22).
Tang Z. The relationship between loneliness and problematic social networks use among college students: the mediation of fear of missing out and the moderation of social support. Jilin University; 2022.
Tomczyk Ł, Selmanagic-Lizde E. Fear of missing out (FOMO) among youth in Bosnia and Herzegovina — Scale and selected mechanisms. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2018;88:541–9.
Unal-Aydin P, Ozkan Y, Ozturk M, Aydin O, Spada MM. The role of metacognitions in cyberbullying and cybervictimization among adolescents diagnosed with major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders: a case-control study. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy; 2023.
Uram P, Skalski S. Still logged in? The Link between Facebook Addiction, FoMO, Self-Esteem, Life satisfaction and loneliness in social media users. Psychol Rep. 2022;125(1):218–31.
Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Mari E, Giannini AM. Social Media Addiction, fear of missing out (FoMO) and online vulnerability in university students. Revista Digit De Investigación en Docencia Universitaria. 2020;14(1):e1187.
Wang H. Study on the relationship and intervention between fear of missing and social network addiction in college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Wang M, Yin Z, Xu Q, Niu G. The relationship between shyness and adolescents’ social network sites addiction: Moderated mediation model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2020;28(5):906–9.
Wegmann E, Oberst U, Stodt B, Brand M. Online-specific fear of missing out and internet-use expectancies contribute to symptoms of internet-communication disorder. Addict Behav Rep. 2017;5:33–42.
Wegmann E, Brandtner A, Brand M. Perceived strain due to COVID-19-Related restrictions mediates the Effect of Social needs and fear of missing out on the risk of a problematic use of Social Networks. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Wei Q. Negative emotions and problematic social network sites usage: the mediating role of fear of missing out and the moderating role of gender. Central China Normal University; 2018.
Xiong L. Effect of social network site use on college students’ social network site addiction: A moderated mediation model and attention bias training intervention study. Jiangxi Normal University; 2022.
Yan H. The influence of college students’ basic psychological needs on social network addiction: The intermediary role of fear of missing out. Wuhan University; 2020.
Yan H. The status and factors associated with social media addiction among young people——Evidence from WeChat. Chongqing University; 2021.
Yang L. Research on the relationship of fear of missing out, excessive use of Wechat and life satisfaction. Beijing Forestry University; 2020.
Yin Y, Cai X, Ouyang M, Li S, Li X, Wang P. FoMO and the brain: loneliness and problematic social networking site use mediate the association between the topology of the resting-state EEG brain network and fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;141:107624.
Zhang C. The parental rejection and problematic social network sites with adolescents: the chain mediating effect of basic psychological needs and fear of missing out. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Zhang J. The influence of basic psychological needs on problematic mobile social networks usage of adolescent: a moderated mediation model. Liaocheng University; 2020.
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Jin J, Yu G. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(5):1082–5.
Zhang Y, Jiang W, Ding Q, Hong M. Social comparison orientation and social network sites addiction in college students: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):928–31.
Zhou J, Fang J. Social network sites support and addiction among college students: a moderated mediation model. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2021;9(5):293–9.
Andreassen CS, Torsheim T, Brunborg GS, Pallesen S. Development of a Facebook addiction scale. Psychol Rep. 2012;110(2):501–17.
Andreassen CS, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252.
Elphinston RA, Noller P. Time to face it! Facebook intrusion and the implications for romantic jealousy and relationship satisfaction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2011;14(11):631–5.
Caplan SE. Theory and measurement of generalized problematic internet use: a two-step approach. Comput Hum Behav. 2010;26(5):1089–97.
Jiang Y. Development of problematic mobile social media usage assessment questionnaire for adolescents. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2018;6(10):613–21.
Wang X. College students’ social network addiction tendency: Questionnaire construction and correlation research. Master’s thesis Southwest University; 2016.
Derogatis LR. Brief symptom inventory 18. Johns Hopkins University Baltimore; 2001.
Lovibond PF, Lovibond SH. The structure of negative emotional states: comparison of the Depression anxiety stress scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and anxiety inventories. Behav Res Ther. 1995;33(3):335–43.
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Löwe B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(10):1092–7.
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 1983;67(6):361–70.
Spielberger CD, Gonzalez-Reigosa F, Martinez-Urrutia A, Natalicio LF, Natalicio DS. The state-trait anxiety inventory. Revista Interamericana de Psicologia/Interamerican Journal of Psychology 1971, 5(3&4).
Marteau TM, Bekker H. The development of a six-item short‐form of the state scale of the Spielberger State—trait anxiety inventory (STAI). Br J Clin Psychol. 1992;31(3):301–6.
Leary MR. Social anxiousness: the construct and its measurement. J Pers Assess. 1983;47(1):66–75.
Liebowitz MR. Social phobia. Modern problems of pharmacopsychiatry 1987.
Alkis Y, Kadirhan Z, Sat M. Development and validation of social anxiety scale for social media users. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;72:296–303.
La Greca AM, Stone WL. Social anxiety scale for children-revised: factor structure and concurrent validity. J Clin Child Psychol. 1993;22(1):17–27.
Fenigstein A, Scheier MF, Buss AH. Public and private self-consciousness: Assessment and theory. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1975;43(4):522.
Mattick RP, Clarke JC. Development and validation of measures of social phobia scrutiny fear and social interaction anxiety. Behav Res Ther. 1998;36(4):455–70.
Peters L, Sunderland M, Andrews G, Rapee RM, Mattick RP. Development of a short form Social Interaction anxiety (SIAS) and Social Phobia Scale (SPS) using nonparametric item response theory: the SIAS-6 and the SPS-6. Psychol Assess. 2012;24(1):66.
Brennan KA, Clark CL, Shaver PR. Self-report measurement of adult attachment: an integrative overview. Attachment Theory Close Relationships. 1998;46:76.
Wei M, Russell DW, Mallinckrodt B, Vogel DL. The experiences in Close Relationship Scale (ECR)-short form: reliability, validity, and factor structure. J Pers Assess. 2007;88(2):187–204.
Bartholomew K, Horowitz LM. Attachment styles among young adults: a test of a four-category model. J Personal Soc Psychol. 1991;61(2):226.
Przybylski AK, Murayama K, DeHaan CR, Gladwell V. Motivational, emotional, and behavioral correlates of fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(4):1841–8.
Xiaokang S, Yuxiang Z, Xuanhui Z. Developing a fear of missing out (FoMO) measurement scale in the mobile social media environment. Libr Inform Service. 2017;61(11):96.
Bown M, Sutton A. Quality control in systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010;40(5):669–77.
Turel O, Qahri-Saremi H. Problematic use of social networking sites: antecedents and consequence from a dual-system theory perspective. J Manage Inform Syst. 2016;33(4):1087–116.
Chou H-TG, Edge N. They are happier and having better lives than I am: the impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2012;15(2):117–21.
Beyens I, Frison E, Eggermont S. I don’t want to miss a thing: adolescents’ fear of missing out and its relationship to adolescents’ social needs, Facebook use, and Facebook related stress. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;64:1–8.
Di Blasi M, Gullo S, Mancinelli E, Freda MF, Esposito G, Gelo OCG, Lagetto G, Giordano C, Mazzeschi C, Pazzagli C. Psychological distress associated with the COVID-19 lockdown: a two-wave network analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;284:18–26.
Yang X, Hu H, Zhao C, Xu H, Tu X, Zhang G. A longitudinal study of changes in smart phone addiction and depressive symptoms and potential risk factors among Chinese college students. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):252.
Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. Social networking sites and addiction: ten lessons learned. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(3):311.
Ryan T, Chester A, Reece J, Xenos S. The uses and abuses of Facebook: a review of Facebook addiction. J Behav Addictions. 2014;3(3):133–48.
Elhai JD, Levine JC, Dvorak RD, Hall BJ. Non-social features of smartphone use are most related to depression, anxiety and problematic smartphone use. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;69:75–82.
Jackson LA, Wang J-L. Cultural differences in social networking site use: a comparative study of China and the United States. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(3):910–21.
Ahrens LM, Mühlberger A, Pauli P, Wieser MJ. Impaired visuocortical discrimination learning of socially conditioned stimuli in social anxiety. Soc Cognit Affect Neurosci. 2014;10(7):929–37.
Elhai JD, Yang H, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FOMO): overview, theoretical underpinnings, and literature review on relations with severity of negative affectivity and problematic technology use. Brazilian J Psychiatry. 2020;43:203–9.
Barker V. Older adolescents’ motivations for social network site use: the influence of gender, group identity, and collective self-esteem. Cyberpsychology Behav. 2009;12(2):209–13.
Krasnova H, Veltri NF, Eling N, Buxmann P. Why men and women continue to use social networking sites: the role of gender differences. J Strateg Inf Syst. 2017;26(4):261–84.
Palmer J. The role of gender on social network websites. Stylus Knights Write Showc 2012:35–46.
Vannucci A, Flannery KM, Ohannessian CM. Social media use and anxiety in emerging adults. J Affect Disord. 2017;207:163–6.
Primack BA, Shensa A, Sidani JE, Whaite EO, yi Lin L, Rosen D, Colditz JB, Radovic A, Miller E. Social media use and perceived social isolation among young adults in the US. Am J Prev Med. 2017;53(1):1–8.
Twenge JM, Campbell WK. Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: evidence from a population-based study. Prev Med Rep. 2018;12:271–83.
Download references
This research was supported by the Social Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 23BSH135).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Mental Health, Wenzhou Medical University, 325035, Wenzhou, China
Mingxuan Du, Haiyan Hu, Ningning Ding, Jiankang He, Wenwen Tian, Wenqian Zhao, Xiujian Lin, Gaoyang Liu, Wendan Chen, ShuangLiu Wang, Dongwu Xu & Guohua Zhang
School of Education, Renmin University of China, 100872, Beijing, China
Chengjia Zhao
School of Media and Communication, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Dongchuan Road 800, 200240, Shanghai, China
Pengcheng Wang
Department of Neurosis and Psychosomatic Diseases, Huzhou Third Municipal Hospital, 313002, Huzhou, China
Xinhua Shen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GZ, XS, XL and MD prepared the study design, writing - review and editing. MD and CZ wrote the main manuscript text. MD and HH analyzed data and edited the draft. ND, JH, WT, WZ, GL, WC, SW, PW and DX conducted resources and data curation. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Xinhua Shen or Guohua Zhang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Du, M., Zhao, C., Hu, H. et al. Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychol 12 , 263 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Download citation
Received : 25 January 2024
Accepted : 03 April 2024
Published : 12 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Fear of missing out
- Meta-analysis
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
Neighborhood based computational approaches for the prediction of lncRNA-disease associations
- Mariella Bonomo 1 &
- Simona E. Rombo 1 , 2
BMC Bioinformatics volume 25 , Article number: 187 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
106 Accesses
Metrics details
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a class of molecules involved in important biological processes. Extensive efforts have been provided to get deeper understanding of disease mechanisms at the lncRNA level, guiding towards the detection of biomarkers for disease diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and prevention. Unfortunately, due to costs and time complexity, the number of possible disease-related lncRNAs verified by traditional biological experiments is very limited. Computational approaches for the prediction of disease-lncRNA associations allow to identify the most promising candidates to be verified in laboratory, reducing costs and time consuming.
We propose novel approaches for the prediction of lncRNA-disease associations, all sharing the idea of exploring associations among lncRNAs, other intermediate molecules (e.g., miRNAs) and diseases, suitably represented by tripartite graphs. Indeed, while only a few lncRNA-disease associations are still known, plenty of interactions between lncRNAs and other molecules, as well as associations of the latters with diseases, are available. A first approach presented here, NGH, relies on neighborhood analysis performed on a tripartite graph, built upon lncRNAs, miRNAs and diseases. A second approach (CF) relies on collaborative filtering; a third approach (NGH-CF) is obtained boosting NGH by collaborative filtering. The proposed approaches have been validated on both synthetic and real data, and compared against other methods from the literature. It results that neighborhood analysis allows to outperform competitors, and when it is combined with collaborative filtering the prediction accuracy further improves, scoring a value of AUC equal to 0966.
Availability
Source code and sample datasets are available at: https://github.com/marybonomo/LDAsPredictionApproaches.git
Peer Review reports
Introduction
More than \(98\%\) of the human genome consists of non-coding regions, considered in the past as “junk” DNA. However, in the last decades evidence has been shown that non-coding genome elements often play an important role in regulating various critical biological processes [ 1 ]. An important class of non-coding molecules which have started to receive great attention in the last few years is represented by long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), that is, RNAs not translated into functional proteins, and longer than 200 nucleotides.
LncRNAs have been found to interplay with other molecules in order to perform important biological tasks, such as modulating chromatin function, regulating the assembly and function of membraneless nuclear bodies, interfering with signalling pathways [ 2 , 3 ]. Many of these functions ultimately affect gene expression in diverse biological and physiopathological contexts, such as in neuronal disorders, immune responses and cancer. Therefore, the alteration and dysregulation of lncRNAs have been associated with the occurrence and progress of many complex diseases [ 4 ].
The discovery of novel lncRNA-disease associations (LDAs) may provide valuable input to the understanding of disease mechanisms at lncRNA level, as well as to the detection of disease biomarkers for disease diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and prevention. Unfortunately, verifying that a specific lncRNA may have a role in the occurrence/progress of a given disease is an expensive process, therefore the number of disease-related lncRNAs verified by traditional biological experiments is yet very limited. Computational approaches for the prediction of potential LDAs can effectively decrease the time and cost of biological experiments, allowing for the identification of the most promising lncRNA-disease pairs to be further verified in laboratory (see [ 5 ] for a comprehensive review on the topic). Such approaches often train predictive models on the basis of the known and experimentally validated lncRNA-disease pairs (e.g., [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]). In other cases, they rely on the analysis of lncRNAs related information stored in public databases, such as their interaction with other types of molecules (e.g., [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]). As an example, large amounts of lncRNA-miRNA interactions have been collected in public databases, and plenty of experimentally confirmed miRNA-disease associations are available as well. However, although non-coding RNA function and its association with human complex diseases have been widely studied in the literature (see [ 16 , 17 , 18 ]), how to provide biologists with more accurate and ready-to-use software tools for LDAs prediction is yet an open challenge, due to the specific characteristics of lncRNAs (e.g., they are much less characterized than other non-coding RNAs.)
We propose three novel computational approaches for the prediction of LDAs, relying on the use of known lncRNA-miRNA interactions (LMIs) and miRNA-disease associations (MDAs). In particular, we model the problem of LDAs prediction as a neighborhood analysis performed on tripartite graphs, where the three sets of vertices represent lncRNAs, miRNAs and diseases, respectively, and vertices are linked according to LMIs and MDAs. Based on the assumption that similar lncRNAs interact with similar diseases [ 12 ], the first approach proposed here (NGH) aims at identifying novel LDAs by analyzing the behaviour of lncRNAs which are neighbors , in terms of their intermediate relationships with miRNAs. The main idea here is that neighborhood analysis automatically guides towards the detection of similar behaviours, and without the need of using a-priory known LDAs for training. Therefore, differently than other approaches from the literature, those proposed here do not involve verified LDAs in the prediction step, thus avoiding possible biases due to the fact that the number and variety of verified LDAs is yet very limited. The second presented approach (CF) relies on collaborative filtering, applied on the basis of common miRNAs shared by different lncRNAs. We have also explored the combination of neighborhood analysis with collaborative filtering, showing that this notably improves the LDAs prediction accuracy. Indeed, the third approach we have designed (NGH-CF) boosts NGH with collaborative filtering, and it is the best performing one, although also NGH and CF have been able to reach high accuracy values across all the different considered validation tests. In particular, Fig. 1 summarizes the research flowchart explained above.
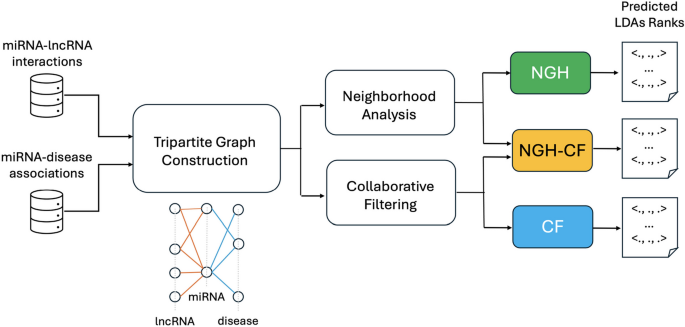
Flowchart of the research pipeline. The miRNA-lncRNA interactions and miRNA-disease associations are exploited for the construction of the tripartite graph. The tripartite graph, in its turn, is at the basis of both neighborhood analysis and collaborative filtering steps, from which the three proposed approaches are obtained: NGH from neighborhood analysis, CF from collaborative filtering, NGH-CF from the combination of the two ones. Each prediction approach returns in output a LDAs rank
The proposed approaches have been exhaustively validated on both synthetic and real datasets, and the result is that they outperform (also significantly) the other methods from the literature. The experimental analysis shows that the improvement in accuracy achieved by the methods proposed here is due to their ability in capturing specific situations neglected by competitors. Examples of that are represented by true LDAs, detected by our approaches and not by the other approaches in the literature, where the involved lncRNA does not present intermediate molecules in common with the associated disease, although its neighbor lncRNAs share a large number of miRNAs with that disease. Moreover, it is shown that our approaches are robust to noise obtained by perturbing a controlled percentage of lncRNA-miRNA interactions and miRNA-disease associations, with NGH-CF the best one also for robustness. The obtained experimental results show that the prediction methods proposed here may effectively support biologists in selecting significant associations to be further verified in laboratory.
Novel putative LDAs coming from the consensus of the three proposed methods, and not yet registered in the available databases as experimentally verified, are provided. Interestingly, the core of novel LDAs returned with highest score by all three approaches finds evidence in the recent literature, while many other high scored predicted LDAs involve less studied lncRNAs, thus providing useful insights for their better characterization.
A first group of approaches aim at using existing true validated cases to train the prediction system, in order to make it able to correctly detect novel cases.
In [ 19 ] a Laplacian Regularized Least Squares is proposed to infer candidates LDAs ( LRLSLDA ) by applying a semi-supervised learning framework. LRLSLDA assumes that similar diseases tend to correlate with functionally similar lncRNAs, and vice versa. Thus, known LDAs and lncRNA expression profiles are combined to prioritize disease-associated lncRNA candidates by LRLSLDA, which does not require negative samples (i.e., confirmed uncorrelated LDAs). In [ 20 ] the method SKF-LDA is proposed that constructs a lncRNA-disease correlation matrix, based on the known LDAs. Then, it calculates the similarity between lncRNAs and that between diseases, according to specific metrics, and integrates such data. Finally, a predicted LDA matrix is obtained by the Laplacian Regularized Least Squares method. The method ENCFLDA [ 6 ] combines matrix decomposition and collaborative filtering. It uses matrix factorization combined with elastic networks and a collaborative filtering algorithm, making the prediction model more stable and eliminating the problem of data over-fitting. HGNNLDA recently proposed in [ 21 ] is based on hypergraph neural network, where the associations are modeled as a lncRNA-drug bipartite graph to build lncRNA hypergraph and drug hypergraph. Hypergraph convolution is then used to learn correlation of higher-order neighbors from the lncRNA and drug hypergraphs. LDAI-ISPS proposed in [ 22 ] is a LDAs inference approach based on space projections of integrated networks, recostructing the disease (lncRNA) integrated similarities network via integrating multiple information, such as disease semantic similarities, lncRNA functional similarities, and known LDAs. A space projection score is finally obtained via vector projections of the weighted networks. In [ 7 ] a consensual prediction approach called HOPEXGB is presented, to identify disease-related miRNAs and lncRNAs by high-order proximity preserved embedding and extreme gradient boosting. The authors build a heterogeneous disease-miRNA-lncRNA (DML) information network by linking lncRNA, miRNA, and disease nodes based on their correlation, and generate a negative dataset based on the similarities between unknown and known associations, in order to reduce the false negative rate in the data set for model construction. The method MAGCNSE proposed in [ 23 ] builds multiple feature matrices based on semantic similarity and disease Gaussian interaction profile kernel similarity of both lncRNAs and diseases. MAGCNSE adaptively assigns weights to the different feature matrices built upon the lncRNAs and diseases similarities. Then, it uses a convolutional neural network to further extract features from multi-channel feature matrices, in order to obtain the final representations of lncRNAs and diseases that is used for the LDAs prediction task.
LDAFGAN [ 8 ] is a model designed for predicting associations between long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and diseases. This method is based on a generative and a discriminative networks, typically implemented as multilayer fully connected neural networks, which generate synthetic data based on some underlying distribution. The generative and discriminative networks are trained together in an adversarial manner. The generative network tries to generate realistic representations of lncRNA-disease associations, while the discriminative network tries to distinguish between real and fake associations. This adversarial training process helps the generative network learn to generate more realistic associations. Once the model is trained, it can predict associations between new lncRNAs and diseases without requiring associated data for those specific lncRNAs. The model captures the data distribution during training, which enables it to make predictions even for unseen lncRNAs. The approach GCNFORMER [ 9 ] is based on graph convolutional network and transformer. First, it integrates the intraclass similarity and interclass connections between miRNAs, lncRNAs and diseases, building a graph adjacency matrix. Then, the method extracts the features between various nodes, by a graph convolutional network. To obtain the global dependencies between inputs and outputs, a transformer encoder with a multiheaded attention mechanism to forecast lncRNA-disease associations is finally applied.
As for the approaches summarized above, it is worth to point out that they may suffer of the fact that the experimentally verified LDAs are still very limited, therefore the training set may be rather incomplete and not enough diversified. For this reason, when such approaches are applied for de novo LDAs prediction, their performance may drastically go down [ 12 ].
Other approaches from the literature use intermediate molecules (e.g., miRNA) to infer novel LDAs. Such approaches are the most related to those we propose here.
The author in [ 11 ] proposes HGLDA , relying on HyperGeometric distribution for LDAs inference, that integrates MDAs and LMIs information. HGLDA has been successfully applied to predict Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer and Colorectal Cancer-related lncRNAs. NcPred [ 10 ] is a resource propagation technique, using a tripartite network where the edges associate each lncRNA with a disease through its targets. The algorithm proposed in [ 10 ] is based on a multilevel resource transfer technique, which computes the weights between each lncRNA-disease pair and, at each step, considers the resource transferred from the previous step. The approach in [ 24 ], referred to as LDA-TG for short in the following, is the antecedent of the approaches proposed here. It relies on the construction of a tripartite graph, built upon MDAs and LMIs. A score is assigned to each possible LDA ( l , d ) by considering both their respective interactions with common miRNAs, and the interactions with miRNAs shared by the considered disease d and other lncRNAs in the neighborhood of l on the tripartite graph. The approaches proposed here differ from LDA-TG for two main reasons. First, the score of LDA-TG is different from the one we introduce here, that allows to reach a better accuracy. Second, a further step based on collaborative filtering is considered here, which also improves the accuracy performance. A method for LDAs prediction relying on a matrix completion technique inspired by recommender systems is presented in [ 14 ]. A two-layer multi-weighted nearest-neighbor prediction model is adopted, using a method similar to memory-based collaborative filtering. Weights are assigned to neighbors for reassigning values to the target matrix, that is an adjacency matrix consisting of lncRNAs, diseases and miRNA. SSMF-BLNP [ 25 ] is based on the combination of selective similarity matrix fusion (SSMF) and bidirectional linear neighborhood label propagation (BLNP). In SSMF, self-similarity networks of lncRNAs and diseases are obtained by selective preprocessing and nonlinear iterative fusion. In BLNP, the initial LDAs are employed in both lncRNA and disease directions as label information for linear neighborhood label propagation.
A third category includes approaches based on integrative frameworks, proposed to take into account different types of information related to lncRNAs, such as their interactions with other molecules, their involvement in disorders and diseases, their similarities. This may improve the prediction step, taking into account simultaneously independent factors.
IntNetLncSim [ 26 ] relies on the construction of an integrated network that comprises lncRNA regulatory data, miRNA-mRNA and mRNA-mRNA interactions. The method computes a similarity score for all pairs of lncRNAs in the integrated network, then analyzes the information flow based on random walk with damping. This allows to infer novel LDAs by exploring the function of lncRNAs. SIMCLDA [ 12 ] identifies LDAs by using inductive matrix completion, based on the integration of known LDAs, disease-gene interactions and gene-gene interactions. The main idea in [ 12 ] is to extract feature vectors of lncRNAs and diseases by principal component analysis, and to calculate the interaction profile for a new lncRNA by the interaction profiles. MFLDA [ 27 ] is a Matrix Factorization based LDAs prediction model that first encodes directly (or indirectly) relevant data sources related to lncRNAs or diseases in individual relational data matrices, and presets weights for these matrices. Then, it simultaneously optimizes the weights and low-rank matrix tri-factorization of each relational data matrix. RWSF-BLP , proposed in [ 28 ], applies a random walk-based multi-similarity fusion method to integrate different similarity matrices, mainly based on semantic and expression data, and bidirectional label propagation. The framework LRWRHLDA is proposed in [ 15 ] based on the construction of a global multi-layer network for LDAs prediction. First, four isomorphic networks including a lncRNA similarity network, a disease similarity network, a gene similarity network and a miRNA similarity network are constructed. Then, six heterogeneous networks involving known lncRNA-disease, lncRNA-gene, lncRNA-miRNA, disease-gene, disease-miRNA, and gene-miRNA associations are built to design the multi-layer network. In [ 29 ] the LDAP-WMPS LDA prediction model is proposed, based on weight matrix and projection score. LDAP-WMPS consists on three steps: the first one computes the disease projection score; the second step calculates the lncRNA projection score; the third step fuses the disease projection score and the lncRNA projection score proportionally, then it normalizes them to get the prediction score matrix.
For most of the approaches summarized above, the performance is evaluated using the LOOCV framework, such that each known LDA is left out in turn as a test sample, and how well this test sample is ranked relative to the candidate samples (all the LDAs without the evidence to confirm their relationships) is computed.
The main goal of the research presented here is to provide more accurate computational methods for the prediction of novel LDAs, candidate for experimental validation in laboratory. To this aim, external information on both molecular interactions (e.g., lncRNA-miRNA interactions) and genotype-phenotype associations (e.g., miRNA-disease associations) is assumed to be available. Indeed, while only a restricted number of validated LDAs is yet available, large amounts of interactions between lncRNAs and other molecules (e.g., miRNAs, genes, proteins), as well as associations between these other molecules and diseases, are known and annotated in curated databases.
A commonly recognized assumption is that lncRNAs with similar behaviour in terms of their molecular interactions with other molecules, may also reflect such a similarity for their involvement in the occurrence and progress of disorders and diseases [ 12 ]. This is even more effective if the correlation with diseases is “mediated” by the molecules they interact with. Based on this observation, we have designed three novel prediction methods that all consider the notion of lncRNA “neighbors”, intended as lncRNAs which share common mediators among the molecules they physically interact with. Here, we focus on miRNAs as mediator molecules. However, the proposed approaches are general enough to allow also the inclusion of other different molecules. Relationships among lncRNAs, mediators and diseases are modeled through tripartite graphs in all the proposed approaches (see Fig. 1 that illustrates the flowchart of the presented research pipeline).
Problem statement Let \({\mathcal {L}}=\{l_1, l_2, \ldots , l_h\}\) be a set of lncRNAs and \({\mathcal {D}}=\{d_1, d_2, \ldots , d_k\}\) be a set of diseases. The goal is to return an ordered set of triplets \({\mathcal {R}}=\{\langle l_x, d_y, s_{xy}\rangle \}\) (with \(x\in [1,h]\) , and \(y\in [1,k]\) ), ranked according to the score \(s_{xy}\) .
The top triplets in \({\mathcal {R}}\) correspond to those pairs \((l_x, d_y)\) with most chances to represent putative LDAs which may be considered for further analysis in laboratory, while the triplets in the bottom correspond to lncRNAs and diseases which are unlikely to be related each other. A key aspect for the solution of the problem defined above is the score computation, that is the main aim of the approaches introduced in the following.
NGH: neighborhood based approach
A model of tripartite graph is adopted here to take into account that lncRNAs interacting with common mediators may be involved in common diseases.
Let \(T_{LMD}=\langle I, A \rangle\) be a tripartite graph defined on the three sets of disjoint vertexes L , M and D , such that \((l,m) \in I\) are edges between vertexes \(l \in L\) and \(m \in M\) , \((m,d) \in A\) are edges between vertexes \(m \in M\) and \(d \in D\) , respectively. In particular, L is associated to a set of lncRNAs, M to a set of miRNA and D to a set of diseases. Moreover, edges of the type ( l , m ) represent molecular interactions between lncRNAs and miRNA, experimentally validated in laboratory; edges of the type ( m , d ) correspond to known miRNA-disease associations, according to the existing literature. In both cases, interactions and associations annotated and stored in public databases may be taken into account.
The following definitions hold.
Definition 1
(Neighbors) Two lncRNAs \(l_h, l_k \in L\) are neighbors in \(T_{LMD}=\langle I, A \rangle\) if there exists at least a \(m_x \in M\) such that \((l_h, m_x) \in I\) and \((l_k, m_x) \in I\) .
Definition 2
(Prediction Score) The Prediction Score for the pair \((l_i,d_j)\) such that \(l_i \in L\) and \(d_j \in D\) is defined as:
\(M_{l_i}\) is the set of annotated miRNA interacting with \(l_i\) ,
\(M_{d_j}\) is the set of miRNA found to be associated to \(d_j\) ,
\(M_{l_x}\) is the set of miRNA interacting with the neighbor \(l_x\) of \(l_i\) (for each neighbor of \(l_i\) ),
\(\alpha\) is a real value in [0, 1] used to balance the two terms of the formula.
Definition 3
(Normalized prediction score) The Normalized Prediction Score for the pair \((l_i,d_j)\) such that \(l_i \in L\) , \(d_j \in D\) and \(s_{ij}\) is the Prediction Score for \((l_i,d_j)\) , is defined as:
NGH-CF: NGH extended with collaborative filtering
We remark that the main idea here is trying to infer the behaviour of a lncRNA, from that of its neighbors. Moreover, it is worth to point out that the notion of neighbor is related to the presence of miRNAs interacting with the same lncRNAs. However, not all the miRNA-lncRNA interactions have already been discovered, and miRNA-disease associations as well. This intuitively reminds to a typical context of data incompleteness where Collaborative Filtering may be successful in supporting the prediction process [ 30 ].
In more detail, what to be encoded by the Collaborative Filter is that lncRNAs presenting similar behaviours in terms of interactions with miRNAs, should reflect such a similarity also in their involvement with the occurrence and progress of diseases, mediated by those miRNAs. To this aim, a matrix R is considered here such that each element \(r_{ij}\) represents if (or to what extent) the lncRNA i and the disease j may be considered related. We call R relationship matrix (it is also known as rating matrix in other contexts, such as for example in the prediction of user-item associations). How to obtain \(r_{ij}\) is at the basis of the two variants of the approach presented in this section.
Due to the fact that R is usually a very sparse matrix, it can be factored into other two matrices L and D such that R \(\approx\) \(L\) \(^T\) \(D\) . In particular, matrix factorization models map both lncRNAs and diseases to a joint latent factor space F of dimensionality f , such that each lncRNA i is associated with a vector \(l_i \in F\) , each disease j with a vector \(d_j \in F\) , and their relationships are modeled as inner products in that space. Indeed, for each lncRNA i , the elements of \(l_i\) measure the extent to which it possesses those latent factors, and the same holds for each disease j and the corresponding elements of \(d_j\) . The resulting dot product in the factor space captures the affinity between lncRNA i and disease j , with reference to the considered latent factors. To this aim, there are two important tasks to be solved:
Mapping lncRNAs and diseases into the corresponding latent factors vectors.
Fill the matrix R , that is, the training set.
To learn the factor vectors \(l_i\) and \(d_j\) , a possible choice is to minimize the regularized squared error on the set of known relationships:
where \(\chi\) is the set of ( i , j ) pairs for which \(r_{ij}\) is not equal to zero in the matrix R . To this aim, we apply the ALS technique [ 31 ], which rotates between fixing the \(l_i\) ’s and fixing the \(d_j\) ’s. When all \(l_i\) ’s are fixed, the system recomputes the \(d_j\) ’s by solving a least-squares problem, and vice versa.
Filling the matrix R is performed according to two different criteria, resulting in the two different variants of the approach presented in this section, namely, CF and NGH-CF, respectively. According to the first criteria (CF), \(r_{ij}\) is set equal to 1 if the lncRNA i and the disease j share at least one miRNA in common, to 0 otherwise. The second variant (NGH-CF) works instead as a booster to improve the accuracy of NGH. In this latter case, the matrix R is filled by the normalized score ( 2 ). For both variants, the considered score to rank the predicted LDAs is given by the final value returned by the ALS technique applied on the corresponding matrix R .
Validation methodologies
We remark that the proposed approaches for LDAs prediction return a rank of LDAs, sorted according to the score that is characteristic of the considered approach, such that top triplets may be assumed as the most promising putative LDAs for further analysis in laboratory. As in other contexts [ 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 ], the performance of a prediction tool may be evaluated using suitable external criteria . Here, an external criterion relies on the existence of LDAs that are known to be true from the literature or, even better, from public repositories, where associations already verified in laboratory are annotated. A gold standard is constructed, containing only such true LDAs. The putative LDAs returned by the prediction method can thus be compared against those in the gold standard. In order to work properly, this validation methodology requires the gold standard information to be independent on that considered, in its turn, from the method under evaluation during its prediction task. This is satisfied in our case, due to the fact that all three approaches introduced in the previous sections do not exploit any type of knowledge referred to known LDAs during prediction, relying instead on known miRNA-lncRNA interactions and miRNA-disease associations, which come from independent sources.
According to the above mentioned validation methodology, the proposed approaches can be validated with references to the Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) analysis [ 34 ]. In particular, each predicted LDA is associated to a label, that is true if that association is contained in the considered gold standard, and false otherwise.
By varying the threshold value, it is possible to compute the true positive rate (TPR) and the false positive rate (FPR), by refferring to the percentage of the true/false predictions whose ranking is higher/below than the considered threshold value. ROC curve can be drawn by plotting TPR versus FPR at different threshold values. The Area Under ROC Curve (ROC-AUC) is further calculated to evaluate the performance of the tested methods. ROC-AUC equal to 1 indicates perfect performance, ROC-AUC equal to 0.5 random performance.
Similarly to the ROC curve, the Precision-Recall (PR) curve can be drawn as well, combining the positive predictive value (PPV, Precision), i.e., the fraction of predicted LDAs which are true in the gold standard, and the TPR (Recall), in a single visualization, at the threshold varying. The higher on y-axis the obtained curve is, the better the prediction method performance. The Area Under PR curve (AUPR) is more sensitive than AUC to the improvements for the positive class prediction [ 35 ], that is important for the case studied here. Indeed, only true LDAs are known, therefore no negative samples are included in the gold standard.
Another important measure useful to evaluate the prediction accuracy of a method and that can be considered here is the F1-score, defined as the harmonic mean of Precision and Recall to symmetrically represent both metrics in a single one.
We have validated the proposed approaches on both syntetic and real datasets, as explained below.
Synthetic data
A synthetic dataset has been built with 15 lncRNAs, 35 miRNA and 10 diseases, such that three different sets of LDAs may be identified, as follows (see also Table 1 , where the characteristics of each LDA are summarized).
Set 1: 26 LDAs, such that each lncRNA has from 3 to 4 miRNAs shared with the same disease (strongly linked lncRNAs) .
Set 2: 16 LDAs, each lncRNA having only one miRNA shared with a disease, and from 2 to 5 neighbors that are strongly linked with that same disease (directly linked lncRNAs and strong neighborhood) .
Set 3: 12 LDAs involving lncRNAs without any miRNA in common with a certain disease, and a number between 2 and 5 neighbors that are strongly linked with that same disease (only strong neighborhood) .
Experimentally verified data downloaded from starBase [ 36 ] and from HMDD [ 37 ] have been considered for the lncRNA-miRNA interactions and for the miRNA-disease associations, respectively. In particular, the latest version of HMDD, updated at 2019, has been used. Overall, \(1,\!114\) lncRNAs, \(1,\!058\) miRNAs, 885 diseases, \(10,\!112\) lncRNA-miRNA interactions and \(16,\!904\) miRNA-disease associations have been included in the analysis.
In order to evaluate the prediction accuracy of the approaches proposed here against those from the literature, three different gold standards have been considered. A first gold standard dataset GS1 has been obtained from the LncRNA-Disease database [ 38 ], resulting in 183 known and verified LDAs. A second, more restrictive, gold standard GS2 with 157 LDAs has been built by the intersection of data from [ 38 ] and [ 39 ]. Finally, also a larger gold standard dataset GS3 has been included in the analysis, by extracting LDAs from MNDRv2.0 database [ 40 ], where associations both experimentally verified and retrieved from manual literature curation are stored, resulting in 408 known LDAs.
Comparison on real data
The approaches proposed here have been compared against other approaches from the literature, over the three different gold standards described in the previous Section. In particular, all approaches considered from the literature have been run according to the default setting of their parameters, reported on the corresponding scientific publications and/or on their manual instructions.
Our approaches have been compared at first on GS1 against those approaches taking exactly the same input than ours, that are HGLDA [ 11 ], ncPred [ 10 ] and LDA-TG [ 24 ]. In particular, we have implemented HGLDA and used the corresponding p-value score, corrected by FDR as suggested by [ 11 ], for the ROC analysis. Moreover, we have normalized also the scores returned by ncPred and LDA-TG for the predicted LDAs, according to the formula in Definition 3 . Indeed, we have observed experimentally that such a normalization improves the accuracy of both methods from the literature, resulting in a better AUC. As for the novel approaches proposed here, the Normalized Prediction Score has been considered for NGH, while the approximated rating score resulting from ALS [ 31 ] is used for both CF and NGH-CF. Figure 2 shows the AUC scored by each method on GS1, while in Fig. 3 the different ROC curves are plotted. In particular, NGH scores a value of AUC equal to 0.914, thus outperforming the other three methods previously presented in the literature, i.e., HGLDA, ncPred and LDA-TG, that reach 0.876, 0.886 and 0.866, respectively (we remark also that performance of both ncPred and LDA-TG has been slightly improved with respect to their original one, by normalizing their scores). As for the novel approaches based on collaborative filtering, they both present a better accuracy than the others, with CF having AUC equal to 0.957 and NGH-CF to 0.966, respectively. Therefore, these results confirm that taking into account the collaborative effects of lncRNAs and miRNAs is useful to improve LDAs prediction, and the most successful approach is NGH-CF, that is, the neighborhood based approach boosted by collaborative filtering.
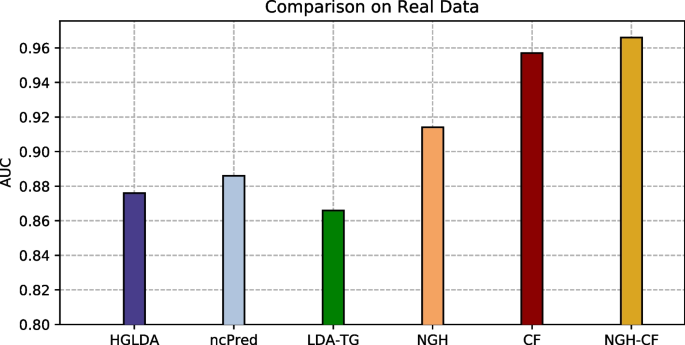
Comparison of the scored AUC on GS1
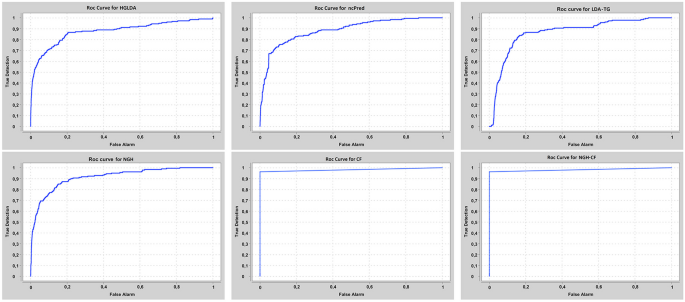
ROC curves for the compared methods on GS1
Another interesting issue is represented by the “agreement” between the different methods taking the same input, in terms of the returned best scoring LDAs. Table 2 shows the Jaccard Index computed between the proposed approaches and those receiving the same input, on the top \(5\%\) LDAs in the corresponding ranks, sorted from the best to the worst score values for each method. It emerges that results by HGLDA and ncPred have a small match with the other approaches (at most 0.23), while NGH-CF has high agreement with CF (0.74), as well as with NGH and LDA-TG (both 0.70). LDA-TG and CF present a sufficient match in their best predictions (0.59). This latter comparison based on agreement shows that approaches based on neighborhood analysis share a larger set of LDAs, in the top part of their ranks.
The proposed approaches have been compared also against other two recent methods from the literature, i.e., SIMCLDA and HGNNLDA, which receive in input different data than ours, including mRNA and drugs. For this reason, the more restrictive gold standard GS2 has been exploited for the comparison, where only lncRNAs and diseases having some correspondences with the additional input data of SIMCLDA and HGNNLDA are included. Figure 4 shows the comparison of the scored AUC on GS2, while Fig. 5 the corresponding ROC curves. In particular, the behaviour of all approaches previously tested does not change significantly on this other gold standard, moreover all the other approaches overcome SIMCLDA. On the other hand, HGNNLDA has a better performance than HGLDA, NcPred and LDA-TG, although it has a worse accuracy than NGH, CF and NGH-CF. The former confirms its superiority with regards to all considered approaches.
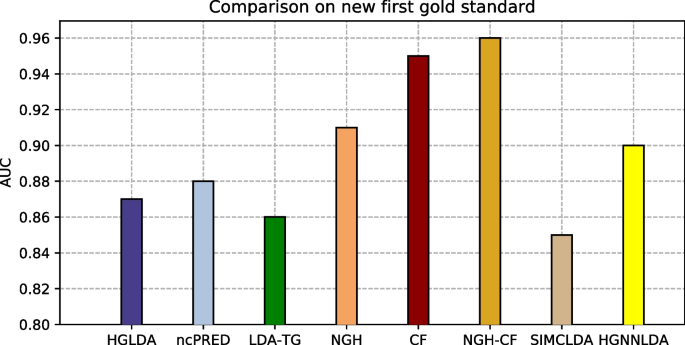
Comparison of the scored AUC on GS2
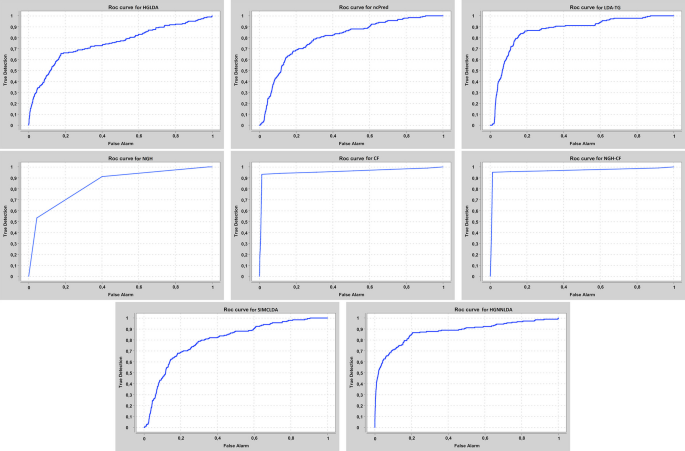
ROC curves for the compared methods on GS2
The proposed approaches have been compared also against LDAP-WMPS on GS3. Figure 6 shows the AUC values scored by all compared approaches on GS3, while Fig. 7 the corresponding ROC curves. In particular, the behaviour of all approaches previously tested does not change on this other gold standard, and LDAP-WMPS has better performance than the other approaches except for NGH, CF, NGH-CF and HGNNLDA.
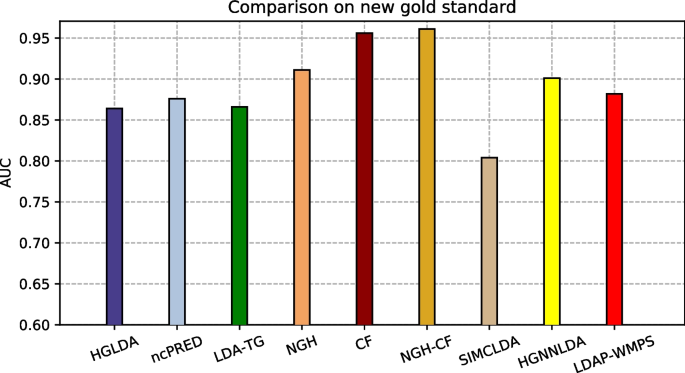
Comparison of the scored AUC on GS3
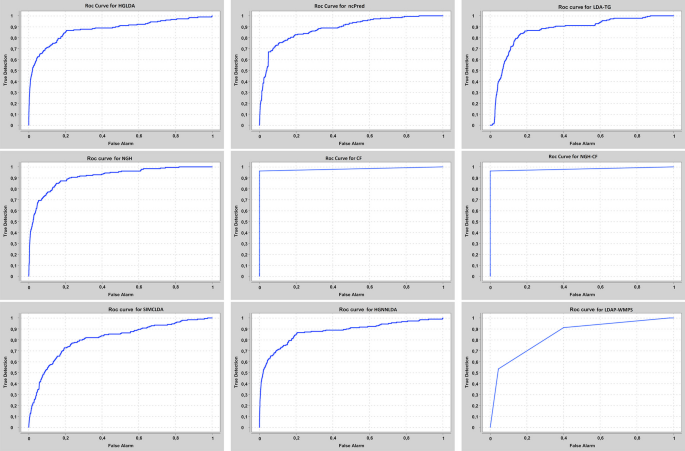
ROC curves for the compared methods on GS3
The AUPR values scored by the compared methods on GS1, GS2, and GS3 are shown in Fig. 8 , while the corresponding PR-curves are plotted in Fig. 9 . In particular, for GS1 results are analogous to the ROC analysis, with NGH-CF the best performing one, followed by CF and NGH, while HGLDA is the worst. On GS2, NGH-CF and CF keep their superiority, followed by SMCLDA and NGH, while HGLDA is yet the worst one. On GS3, NGH-CF is the first, Cf the second and both HGNNLDA and LDAP-WMPS outperform NGH, while HGLDA in this case slightly outperforms LDA-TG, ncPred and SMCLDA, which results to be the worst one.
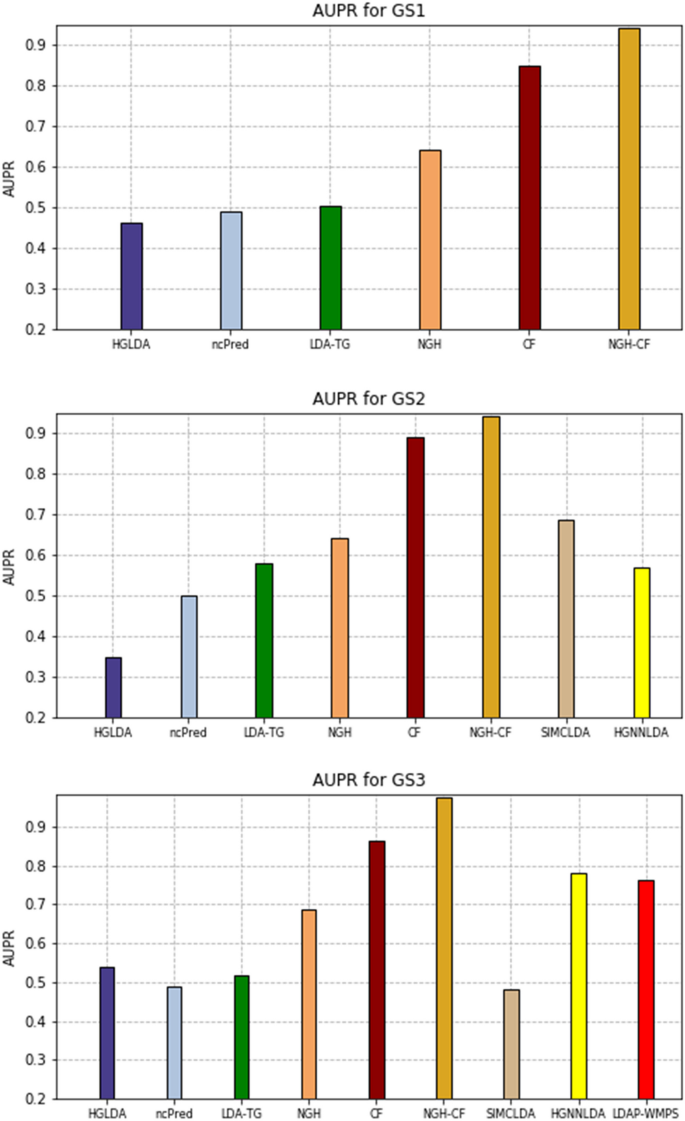
AUPR hystogram for the compared methods on GS1, GS2, GS3
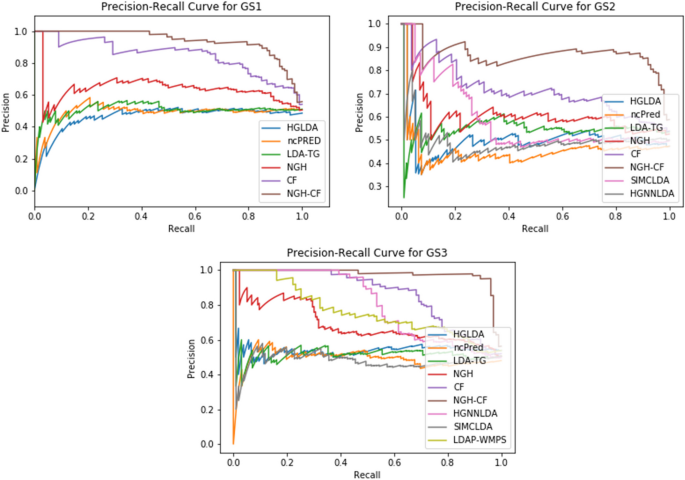
Precision-recall curves for the compared methods on GS1,GS2,GS3
Figures 10 , 11 and 12 show the F1-score values obtained, for all methods compared on GS1, GS2 and GS3, respectively, at the varying of a threshold fixed on the method score. In Tables 3 , 4 and 5 it is shown, for each gold standard, the highest value of F1-score obtained by each considered method, as well as the corresponding Precision and Recall values, and the minimum threshold value for which the highest F1-score value has been reached. On GS1 and GS2, the three best performing approaches are NGH-CF, CF and NGH, in this order. On GS3 the order is the same, and LDAP-WMPS performs equally to NGH.
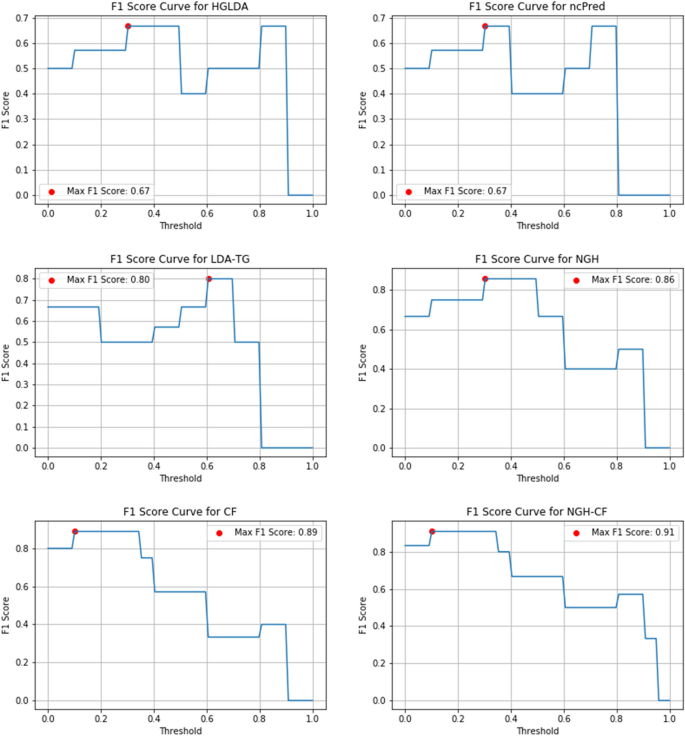
F1-score for the compared methods on GS1
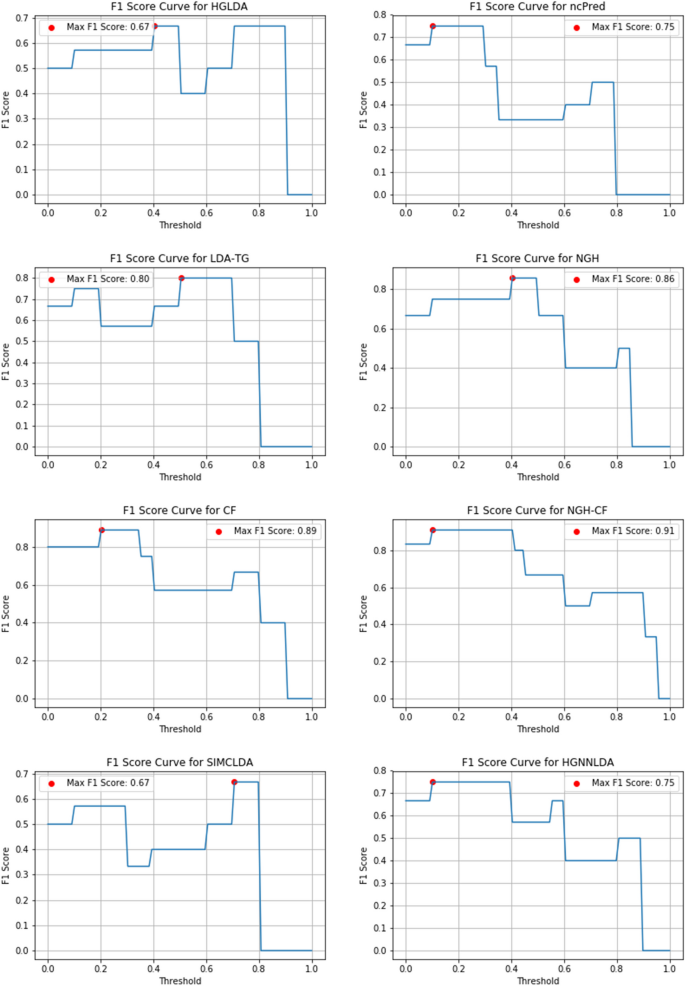
F1-Score for the compared methods on GS2
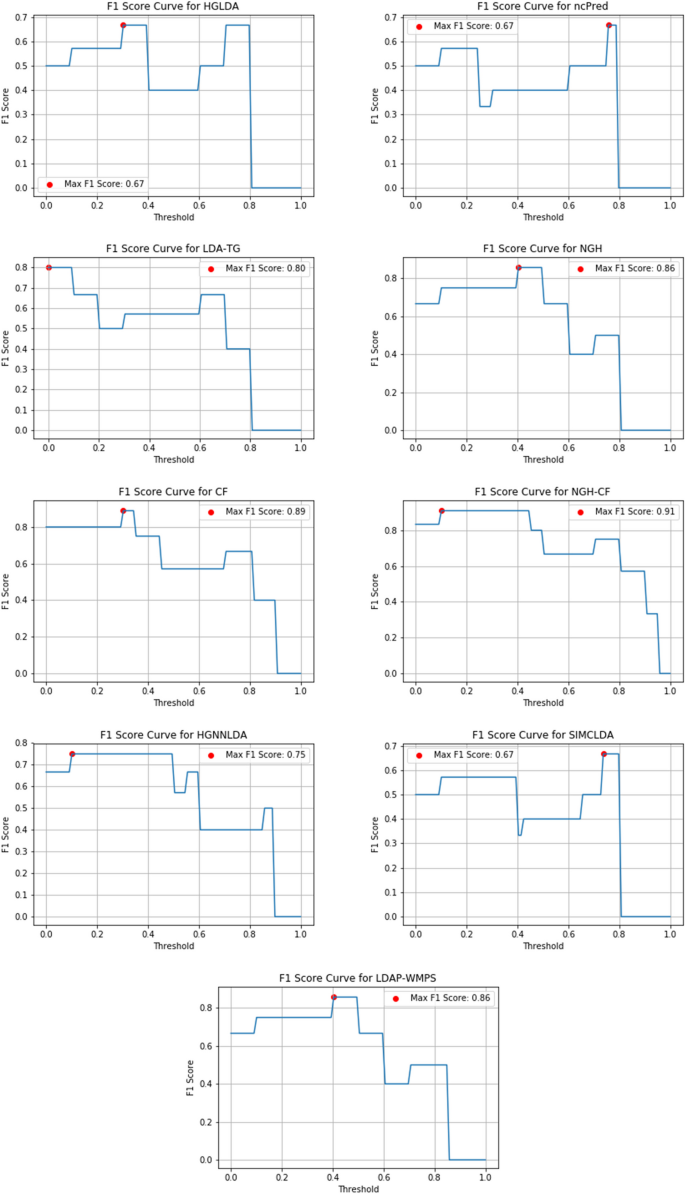
F1-Score for the compared methods on GS3
Robustness analysis
The main aim of the analysis discussed here is to measure to what extent the proposed methods are able to correctly recognize verified LDAs, even if part of the existing associations are missed, i.e., the sets of known and verified lncRNA-miRNA interactions and miRNA-disease associations are not complete. This is important to verify that the proposed approaches can provide reliable predictions also in presence of data incompleteness, that is often the case when lncRNAs are involved. Therefore, the robustness of each proposed method has been evaluated by performing progressive alterations of the input associations coming from the real datasets, according to the following three different criteria.
Progressively eliminate the \(5\%\) , \(10\%\) , \(15\%\) and \(20\%\) of lncRNA-miRNA interactions from the input data.
Progressively eliminate the \(5\%\) , \(10\%\) , \(15\%\) and \(20\%\) of miRNA-disease associations from the input data.
Progressively eliminate the \(5\%\) , \(10\%\) , \(15\%\) and \(20\%\) of both lncRNA-miRNA interactions and miRNA-disease associations (half and half), from the input data.
Tests summarized above have been performed for 20 times each. Tables 6 , 7 and 8 show the mean of the AUC values for NGH, CF and NGH-CF, respectively, over the 20 tests. In particular, all methods perform well on the three test typologies at \(5\%\) , the worst being NGH-CF, which however presents an average AUC equal to 0.84 for case 1), that is still a high value. NGH-CF is also the method that presents the best robustness on case 3), keeping the value of 0.92 also at \(20\%\) , while CF is the worst performing in case 3), indeed its average AUC decreases from 0.95 at \(5\%\) to 0.63 already at \(10\%\) , and then to 0.50 at \(20\%\) . This behaviour in case 3), where both lncRNA-miRNA interactions and miRNA-disease associations are progressively eliminated, deserves some observations. Indeed, results show that the combination of neighborhood analysis and collaborative filtering is the most robust one with regards to this perturbation, while collaborative filtering alone is the worst performing. On the other hand, CF results to be the most robust in case 1), where only lncRNA-miRNA interactions are eliminated, and this is due to the fact that CF does not take into account how many miRNAs are shared by pairs of lncRNAs. As for case 2), performance of all methods is comparable and generally good, possibly in consideration of the fact that a large number of miRNA-disease associations are available, therefore discarding small percentages of them does not affect largely the final prediction.
Comparison on specific situations
In this section further experimental tests are described, showing how well the considered methods perform in detecting specific situations, depicted through the synthetic dataset first, and then searched for in the real data. In particular, the basic observation here is that prediction approaches from the literature usually fail in detecting true LDAs, when the involved lncRNAs and diseases do not have a large number of shared miRNAs (referring to those approaches taking the same input than ours). The novel approaches we propose are particularly effective in managing the situation depicted above, through neighborhood analysis and collaborative filtering, allowing to detect similar behaviours shared by different lncRNAs, depending on the miRNAs they interact with.
For each set of LDAs defined in the synthetic data (i.e., set 1, set 2, and set 3), and for each tested method (i.e., HGLDA, NCPRED, NHG, CF, NGH-CF), Table 9 shows the percentage of LDAs in that set which is recognized at the top \(10\%\) , \(20\%\) , \(30\%\) , \(50\%\) of the rank of all LDAs, sorted by the score returned by the considered method. As an example, for HGLDA the \(32\%\) of LDAs of set 1 are located in the top \(10\%\) of its rank, where instead none LDAs in set 2 or 3 find place.
Looking at these results some interesting considerations come out. First of all, for the methods HGLDA, NCPRED, NHG and CF most associations of the set 1 are located in the top \(50\%\) of their corresponding ranks, while NGH-CF has a different behaviour. Indeed, it locates a lower number of such LDAs in the highest part of its rank than the other approaches, possibly due to the fact that it leaves room for a larger number of associations in the other two sets in the top ranked positions. As for LDAs in the set 2, all methods recognize some of them already in the top \(10\%\) , except for HGLDA, as alredy highlighted. The approaches able to recognize the larger percentages of these associations at the top \(50\%\) of their rank are NGH and NGH-CF. LDAs in the set 3 are the most difficult to recognize, due to the fact that the lncRNA and the disease do not share any miRNA in common. Indeed, the worst performing methods in this case are HGLDA, which is able to locate some of these associations only at the top \(50\%\) (according to the percentages we considered here), and NCPRED, which performs slightly better although it reaches the same percentage of located associations than HGLDA at \(50\%\) (the \(28\%\) ). As expected, approaches based on neighborhood analysis and collaborative filtering perform better, with the best one resulting to be NGH-CF.
In the previous section we have shown that all methods proposed here are able to detect specific situations, characterized by the fact that a lncRNA may have very few (or none) common miRNAs with a disease, and its neighbors share instead a large set of miRNAs with that disease. We have checked if this case occurs among the verified LDAs that our approaches find and their competitors do not. Table 10 shows, only by meaning of example, 10 experimentally verified LDAs, included in GS1, that are top ranked for the novel approaches proposed here, whereas they are in the bottom rank of the other approaches from the literature compared on GS1. Six out of such LDAs do not present any common miRNAs between the lncRNA and the disease, while four share only one miRNA. All involved lncRNAs present neighbors with a large number of miRNAs in common with the disease in that LDA, in accordance with the hypothesis that the ability in capturing this situation allows to obtain a better accuracy.
Survival analysis has been also performed by one of the TCGA Computational Tools, that is, TANRIC [ 41 ], on four of the pairs in Table 10 . In particular, those lncRNAs and diseases available in TANRIC have been chosen. Results are reported in Figures 13 , 14 , 15 and 16 , showing that the over-expression of the considered lncRNA determines a lower survival probability over the time, for all four considered cases.
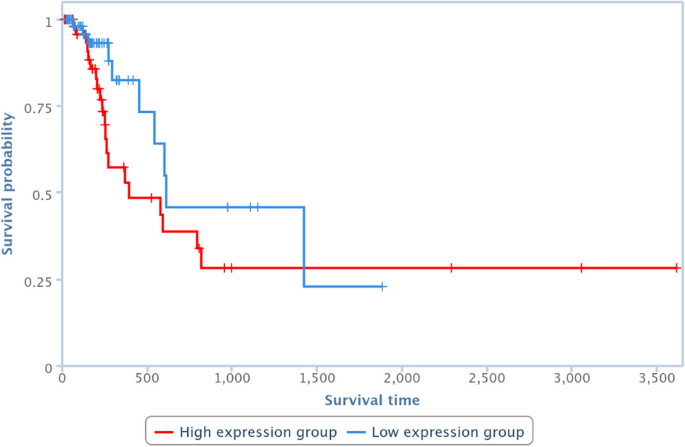
Survival analysis related to SNHG16 and bladder neoplasm
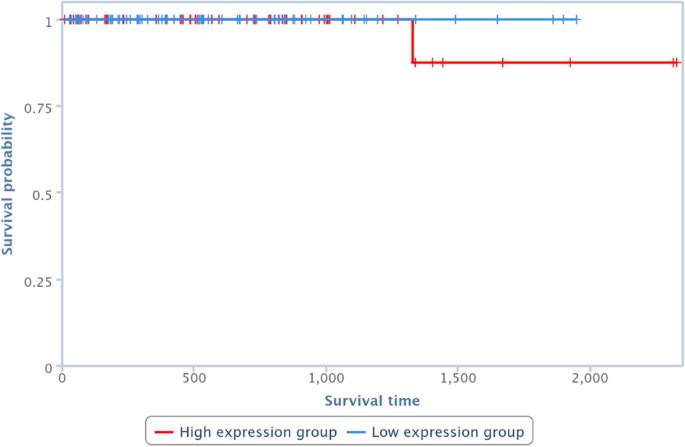
Survival analysis related to CBR3-AS1 and prostate neoplasm
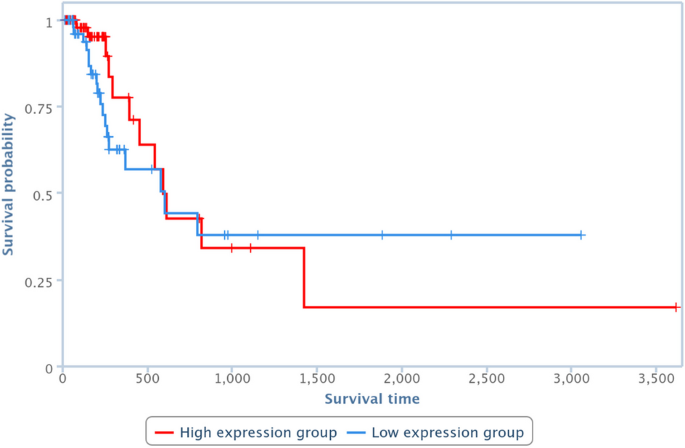
Survival analysis related to MALAT1 and bladder neoplasm
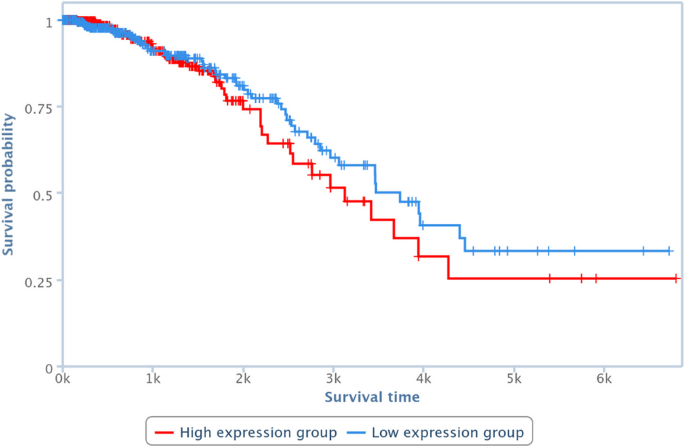
Survival analysis related to MEG3 and breast neoplasm
In the previous sections the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed approaches have been illustrated, showing that all three are able to return reliable predictions, as well as to detect specific situations which may occur in true predictions and are missed by competitors. Here we provide a discussion on some novel LDAs predicted by NGH, CF and NGH-CF.
Table 11 shows seven LDAs which are not present in the considered gold standards, and that have been returned by all three methods proposed here, with highest score. The first of these associations is between CDKN2B-AS1 and LEUKEMIA, confirmed by recent literature [ 42 , 43 ]. Indeed, CDKN2B-AS1 was found to be highly expressed in pediatric T-ALL peripheral blood mononuclear cells [ 42 ], moreover genome-wide association studies show that it is associated to Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia risk in Europeans [ 43 ]. As for the second association between DLEU2 and LEUKEMIA, DLEU2 is a long non-coding transcript with several splice variants, which has been identified by [ 44 ] through a comprehensive sequencing of a commonly deleted region in leukemia (i.e., the 13q14 region). Different investigations reported up regulation of this lncRNA in several types of cancers. The lncRNA H19 regulates GLIOMA angiogenesis [ 45 , 46 ], while MAP3K14 is one of the well-recognized biomarkers in the prognosis of renal cancer, which is reminiscent of the pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma [ 47 ]. MEG3 has been recently found to be important for the prediction of LEUKEMIA risk [ 48 ]. Multiple studies have shown that MIR155HG is highly expressed in diffuse large B-cell (DLBC) lymphoma and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, and in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. The transcription factor MYB activates MIR155HG activity, which causes the epigenetic state of MIR155HG to be dysregulated and causes an abnormal increase in MIR155 [ 49 ]. Also the last top-ranked association in Table 11 between TUG1 and NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMA has found evidence in the literature [ 50 , 51 , 52 ].
Tables 12 , 13 , and 14 show the top 100 (sorted by the scores returned by each method) novel LDA predictions that NGH and CF, NGH and NGH-CF, CF and NGH-CF have in common, respectively. Many of the lncRNAs involved in such top-ranked LDAs are not yet characterized in the literature, therefore results presented here may be considered a first attempt to provide novel knowledge about them, through their inferred association with known diseases.
We have explored the application of neighborhood analysis, combined with collaborative filtering, for the improvement of LDAs prediction accuracy. The three approaches proposed here have been evaluated and compared first against their direct competitors from the literature, i.e., the other methods which also use lncRNA-miRNA interactions and miRNA-disease associations, without exploiting a priori known LDAs. It results that all methods proposed here are able to outperform direct competitors, the best one (NGH-CF) also significantly (AUC equal to 0.966 against the 0.886 by NCPRED). In particular, it has been shown that the improvement in accuracy is due to the fact that our approaches capture specific situations neglected by competitors, relying on similar lncRNAs behaviour in terms of their interactions with the considered intermediate molecules (i.e., miRNAs). The proposed approaches have been then compared also against other recent methods, taking different inputs (e.g., integrative approaches), and the experimental evaluation shows that they are able to outperform them as well.
It is worth pointing out the importance of providing reliable data in input to the LDAs prediction approaches. As discussed in this manuscript, information on the lncRNAs relationships with other molecules, and between intermediate molecules and diseases, is provided in input to the proposed approaches. Reliable datasets have been used to perform the experimental analysis provided here. However, as the user may provide also different input datasets, it is important to point out that the reliability of the obtained predictions strictly depends on that of input information.
As neighborhood analysis has resulted to be effective in characterizing lncRNAs with regards to their association with known diseases, we plan to apply it also for predicting possible common functions among lncRNAs, for example by clustering them according to their interactions, which has shown to be successful for other types of molecules [ 53 ]. Moreover, due to the success of integrative approaches on the analysis of biological data [ 54 ], we expect that including other types of intermediate molecules, such as for example genes and proteins, in the main pipeline of the proposed approaches may further improve their accuracy.
In conclusion, the use of reliable input data and the integration of different types of information coming from molecular interactions seem to be the most promising future directions for LDAs prediction.
Availability of data and materials
The source code is available at: https://github.com/marybonomo/LDAsPredictionApproaches.git In particular, executable software for NGH, CF, and NGH-CF are provided, as well as syntetic and real input datasets used here; the three different gold standard datasets GS1, GS2, GS3; the final obtained results.
Medico-Salsench E, et al. The non-coding genome in genetic brain disorders: New targets for therapy? Essays Biochem. 2021;65(4):671–83.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Statello L, Guo CJ, Chen LL, et al. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:96–118.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Zhao H, Shi J, Zhang Y, et al. LncTarD: a manually-curated database of experimentally-supported functional lncRNA–target regulations in human diseases. Nucl Acids Res. 2019;48(D1):D118–D126. ISSN: 0305-1048.
Liao Q, et al. Large-scale prediction of long non-coding RNA functions in a coding-non-coding gene co- expression network. Nuc Acids Res. 2011;39:3864–78.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Chen X, et al. Long non-coding RNAs and complex diseases: from experimental results to computational models. Brief Bioinf. 2017;18(4):558–76.
CAS Google Scholar
Wang B, et al. lncRNA-disease association prediction based on matrix decomposition of elastic network and collaborative filtering. Sci Rep. 2022;12:7.
Google Scholar
He J, et al. HOPEXGB: a consensual model for predicting miRNA/lncRNA-disease associations using a heterogeneous disease-miRNA-lncRNA information network. J Chem Inf Model 2023
Zhong H, et al. Association filtering and generative adversarial networks for predicting lncRNA-associated disease. BMC Bioinf. 2023;24(1):234.
Dengju Y, et al. GCNFORMER: graph convolutional network and transformer for predicting lncRNA-disease associations. BMC Bioinf. 2024;25(1):5.
Article Google Scholar
Alaimo S, Giugno R, Pulvirenti A. ncPred: ncRNA-disease association prediction through Tripartite network-based inference. Front Bioeng Biot. 2014;2:71.
Chen X. Predicting lncRNA-disease associations and constructing lncRNA functional similarity network based on the information of miRNA. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13186.
Lu C, et al. Prediction of lncRNA-disease associations based on inductive matrix completion. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(19):3357–64.
Xuan Z, Li J, Yu X, Feng J, et al. A probabilistic matrix factorization method for identifying lncRNA-disease associations. Genes 2019;10(2)
Du X, et al. lncRNA-disease association prediction method based on the nearest neighbor matrix completion model. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):21653.
Wang L, et al. Prediction of lncRNA-disease association based on a Laplace normalized random walk with restart algorithm on heterogeneous networks. BMC Bioinf. 2022;23(1):1–20.
Huang L, Zhang L, Chen X. Updated review of advances in microRNAs and complex diseases: taxonomy, trends and challenges of computational models. Brief Bioinf. 2022;23(5):bbac358.
Huang L, Zhang L, Chen X. Updated review of advances in microRNAs and complex diseases: experimental results, databases, webservers and data fusion. Brief Bioinf. 2022;23(6):bbac397.
Huang L, Zhang L, Chen X. Updated review of advances in microRNAs and complex diseases: towards systematic evaluation of computational models. Brief Bioinf. 2022;23(6):bbac407.
Chen X, Yan G. Novel human lncRNA-disease association inference based on lncRNA expression profiles. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(20):2617–24.
Xie G, et al. SKF-LDA: similarity kernel fusion for predicting lncRNA-disease association. Mol Therapy-Nucleic Acids. 2019;18:45–55.
Liu D, et al. HGNNLDA: predicting lncRNA-drug sensitivity associations via a dual channel hypergraph neural network. IEEE/ACM transactions on computational biology and bioinformatics, 2023;1–11.
Zhang Y, et al. LDAI-ISPS: lncRNA-disease associations inference based on integrated space projection scores. Int J Molecular Sci. 2020;21(4):1508.
Liang Y, et al. MAGCNSE: predicting lncRNA-disease associations using multi-view attention graph convolutional network and stacking ensemble model. BMC Bioinf. 2022;23(1):189.
Bonomo M, La Placa A, Rombo SE. Prediction of lncRNA-disease associations from tripartite graphs. In: Heterogeneous data management, polystores, and analytics for healthcare - VLDB workshops, poly 2020 and DMAH 2020, virtual event, August 31 and September 4, 2020, Revised Selected Papers. Springer, Berlin, 2020;205–210. ISSN: 978-3-030-71054-5
Xie G, et al. Predicting lncRNA-disease associations based on combining selective similarity matrix fusion and bidirectional linear neighborhood label propagation. Brief Bioinform. 2023;24(1):bbac595.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Cheng L, et al. ntNetLncSim: an integrative network analysis method to infer human lncRNA functional similarity. Oncotarget. 2016;7(30):47864–74.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Guangyuan F, et al. Matrix factorization-based data fusion for the prediction of lncRNA-disease associations. Bioinformatics. 2018;34:1529–37.
Xie G, et al. RWSF-BLP: a novel lncRNA-disease association prediction model using random walk-based multi-similarity fusion and bidirectional label propagation. Mol Genet Genom. 2021;296:473–83.
Wang B, et al. lncRNA-disease association prediction based on the weight matrix and projection score. PLOS One. 2023;18(1): e0278817.
Duan R, Jiang C, Jain HK. Combining review-based collaborative filtering and matrix factorization: a solution to rating’s sparsity problem”. Decis Support Syst 2022;156:113748. ISSN: 0167–9236.
Koren Y, Bell R, Volinsky C. Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer. 2009;42(8):30–7.
Parida L, Pizzi C, Rombo SE. Irredundant tandem motifs. Theoret Comput Sci. 2014;525:89–102.
Bonomo M, et al. Topological ranks reveal functional knowledge encoded in biological networks: a comparative analysis. Brief Bioinform. 2022;23(3):bbac101.
Fawcett T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit Lett. 2006;27(8):861–74.
Saito T, Rehmsmeier M. The precision-recall plot is more informative than the ROC plot when evaluating binary classifiers on imbalanced datasets. PLOS One. 2015;10(3): e0118432.
Li J, et al. starBase v2. 0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;42:D92–7.
Li Y, et al. HMDD v2.0: a database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D1070–4.
Chen G, et al. LncRNADisease: a database for long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D983–6.
Gao Y, et al. Lnc2Cancer 3.0: an updated resource for experimentally supported lncRNA/circRNA cancer associations and web tools based on RNA-seq and scRNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D1251–8.
Cui T, et al. MNDR v2. 0: an updated resource of ncRNA-disease associations in mammals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D371–4.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Li J, et al. TANRIC: an interactive open platform to explore the function of lncRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75(18):3728–37.
Chen L, et al. lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 contributes to tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia through miR-335-3p/TRAF5 axis. In: Anti-cancer drugs, Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. (2020)
Song C, et al. CDKN2B-AS1: an indispensable long non-coding RNA in multiple diseases. Current Pharm Des. 2020;26(41):5335–46.
Ghafouri-Fard S, et al. Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2): an lncRNA with dissimilar roles in different cancers. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133: 111093.
Jia P, et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates glioma angiogenesis and the biological behavior of glioma-associated endothelial cells by inhibiting microRNA-29a. Cancer Lett. 2016;381(2):359–69.
Liu Z, et al. LncRNA H19 promotes glioma angiogenesis through miR-138/HIF-1 α /VEGFaxis. Neoplasma. 2020;67(1):111–8.
Zhou S, et al. A novel immune-related gene prognostic Index (IRGPI) in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD) and its implications in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers. 2022;14(22):5652.
Pei J, et al. Novel contribution of long non-coding RNA MEG3 genotype to prediction of childhood leukemia risk. Cancer Genom Proteom. 2022;19(1):27–34.
Peng L, et al. MIR155HG is a prognostic biomarker and associated with immune infiltration and immune checkpoint molecules expression in multiple cancers. Cancer Med. 2019;8(17):7161–73.
Zhang E, et al. P53-regulated long non-coding RNA TUG1 affects cell proliferation in human non-small cell lung cancer, partly through epigenetically regulating HOXB7 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(5):e1243–e1243.
Lin P, et al. Long noncoding RNA TUG1 is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and can regulate CELF1 on binding to PRC2. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:1–10.
Niu Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 is involved in cell growth and chemoresistance of small cell lung cancer by regulating LIMK2b via EZH2. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):1–13.
Pizzuti C, Rombo SE. An evolutionary restricted neighborhood search clustering approach for PPI networks. Neurocomputing. 2014;145:53–61.
Rombo SE, Ursino D (2021) Integrative bioinformatics and omics data source interoperability in the next-generation sequencing era
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Anonymous Reviewers, for the constructive and useful suggestions that allowed to significantly improve the quality of this manuscript. Some of the results shown here are in part based upon data generated by the TCGA Research Network: https://www.cancer.gov/tcga .
PRIN “multicriteria data structures and algorithms: from compressed to learned indexes, and beyond”, Grant No. 2017WR7SHH, funded by MIUR (closed). “Modelling and analysis of big knowledge graphs for web and medical problem solving” (CUP: E55F22000270001), “Computational Approaches for Decision Support in Precision Medicine” (CUP:E53C22001930001), and “Knowledge graphs e altre rappresentazioni compatte della conoscenza per l’analisi di big data” (CUP: E53C23001670001), funded by INdAM GNCS 2022, 2023, 2024 projects, respectively. “Models and Algorithms relying on knowledge Graphs for sustainable Development goals monitoring and Accomplishment - MAGDA” (CUP: B77G24000050001), funded by the European Union under the PNRR program related to “Future Artificial Intelligence - FAIR”.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Kazaam Lab s.r.l., Palermo, Italy
Mariella Bonomo & Simona E. Rombo
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Simona E. Rombo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MB and SER equally contributed to the research presented in this manuscript. MB implemented and run the software, SER performed the analysis of results. Both authors wrote and reviewed the entire manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mariella Bonomo .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not Applicable
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
SER is editor of BMC Bionformatics. MB has no Conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bonomo, M., Rombo, S.E. Neighborhood based computational approaches for the prediction of lncRNA-disease associations. BMC Bioinformatics 25 , 187 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-024-05777-8
Download citation
Received : 13 December 2023
Accepted : 11 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-024-05777-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- LncRNA-disease associations
- Molecular interactions
- Bioinformatics
- Long non-coding RNA
BMC Bioinformatics
ISSN: 1471-2105
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Financial hardship among patients suffering from neglected tropical diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of global literature
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft
Affiliations Department of Pharmacotherapy, College of Pharmacy, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, United States of America, Department of Social and Administrative Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing
Affiliations Department of Pharmacotherapy, College of Pharmacy, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, United States of America, School of Pharmacy, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, South Korea
Roles Investigation, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Corvaxan Foundation, Villanova, Pennsylvania, United States of America
Roles Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Department of Global Programme for Neglected Tropical Diseases, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Roles Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations Department of Pharmacotherapy, College of Pharmacy, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, United States of America, IDEAS Center, Veterans Affairs Salt Lake City Healthcare System, Salt Lake City, Utah, United States of America
- Chanthawat Patikorn,
- Jeong-Yeon Cho,
- Joshua Higashi,
- Xiao Xian Huang,
- Nathorn Chaiyakunapruk

- Published: May 13, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086
- Peer Review
- Reader Comments
Introduction
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) mainly affect underprivileged populations, potentially resulting in catastrophic health spending (CHS) and impoverishment from out-of-pocket (OOP) costs. This systematic review aimed to summarize the financial hardship caused by NTDs.
We searched PubMed, EMBASE, EconLit, OpenGrey, and EBSCO Open Dissertations, for articles reporting financial hardship caused by NTDs from database inception to January 1, 2023. We summarized the study findings and methodological characteristics. Meta-analyses were performed to pool the prevalence of CHS. Heterogeneity was evaluated using the I 2 statistic.
Ten out of 1,768 studies were included, assessing CHS (n = 10) and impoverishment (n = 1) among 2,761 patients with six NTDs (Buruli ulcer, chikungunya, dengue, visceral leishmaniasis, leprosy, and lymphatic filariasis). CHS was defined differently across studies. Prevalence of CHS due to OOP costs was relatively low among patients with leprosy (0.0–11.0%), dengue (12.5%), and lymphatic filariasis (0.0–23.0%), and relatively high among patients with Buruli ulcers (45.6%). Prevalence of CHS varied widely among patients with chikungunya (11.9–99.3%) and visceral leishmaniasis (24.6–91.8%). Meta-analysis showed that the pooled prevalence of CHS due to OOP costs of visceral leishmaniasis was 73% (95% CI; 65–80%, n = 2, I 2 = 0.00%). Costs of visceral leishmaniasis impoverished 20–26% of the 61 households investigated, depending on the costs captured. The reported costs did not capture the financial burden hidden by the abandonment of seeking healthcare.
NTDs lead to a substantial number of households facing financial hardship. However, financial hardship caused by NTDs was not comprehensively evaluated in the literature. To develop evidence-informed strategies to minimize the financial hardship caused by NTDs, studies should evaluate the factors contributing to financial hardship across household characteristics, disease stages, and treatment-seeking behaviors.
Author summary
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) mainly affect underprivileged populations, potentially resulting in catastrophic health spending (CHS) and impoverishment from out-of-pocket (OOP) costs. This systematic review aimed to summarize the financial hardship caused by NTDs. We found that NTDs lead to a substantial number of households facing financial hardship. CHS risk due to direct OOP costs was relatively low among patients with leprosy (0.0–11.0%), dengue (12.5%), and lymphatic filariasis (0.0–23.0%), and relatively high among patients with Buruli ulcers (45.6%). CHS risk varied widely among patients with chikungunya (11.9–99.3%) and visceral leishmaniasis (24.6–91.8%). Costs of visceral leishmaniasis impoverished 20–26% of 61 households, depending on the costs captured. Nevertheless, financial hardship caused by NTDs was not comprehensively evaluated in the literature. Therefore, to develop evidence-informed strategies to minimize the financial hardship caused by NTDs, studies should evaluate the factors contributing to financial hardship across household characteristics, disease stages, and treatment-seeking behaviors.
Citation: Patikorn C, Cho J-Y, Higashi J, Huang XX, Chaiyakunapruk N (2024) Financial hardship among patients suffering from neglected tropical diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of global literature. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 18(5): e0012086. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086
Editor: Yoel Lubell, Mahidol-Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit, THAILAND
Received: November 7, 2023; Accepted: March 20, 2024; Published: May 13, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Patikorn et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: The authors confirm that all data underlying the findings are fully available without restriction. All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding: This study is funded by the Department of Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. XXH, as an employee of the World Health Organization, contributed to this study in terms of study design, data interpretation, and report writing.
Competing interests: I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests:XXH works for the World Health Organization. The author alone is responsible for the views expressed in this publication and does not necessarily represent the decisions, policies, or views of the World Health Organization.
In 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported that 1.65 billion people required treatment and care for neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) as they faced humanistic, social, and economic burdens incurred by the diseases. NTDs are a diverse group of diseases that mainly affect underprivileged communities in tropical and subtropical areas [ 1 ]. NTDs predominantly affect disadvantaged populations in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) due to the lack of timely access to affordable care. It has been reported that every low-income country is affected by at least five NTDs [ 2 ]. Even worse, impoverishment serves as a structural determinant. At the same time, it is a consequence of NTDs due to the direct and indirect costs incurred [ 3 ]. Therefore, the WHO has advocated in their recent NTDs 2021–2023 roadmap that NTDs must be overcome to attain Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and ensure Universal Health Coverage (UHC). The NTDs 2021–2030 roadmap targets that 90% of the population at risk are protected against catastrophic out-of-pocket (OOP) health spending caused by NTDs [ 1 ].
Financial hardship is usually quantified as catastrophic health spending (CHS) (as known as catastrophic health expenditure) and impoverishment. CHS is the proportion of households with OOP costs incurred by a specific disease that exceed a specific threshold of the total household income or expenditure (budget share approach) or non-subsistent household expenditure (capacity-to-pay approach). Impoverishment is when the OOP costs push households below the poverty line [ 4 – 6 ]. CHS and impoverishment are well-established indicators for the financial risk protection of the healthcare system, which was an essential dimension of the UHC as indicated under the SDG 3.8.2 indicators [ 1 , 7 ].
Financial hardship poses a greater challenge for individuals affected by NTDs, as they frequently reside in poverty before the onset of the disease. To evaluate the long-term economic risk imposed by health spending on NTDs, it is important to understand the coping strategies of this population. Literature has shown that coping strategies, such as seeking financial assistance through loans or selling their assets, could push households into or further into poverty if it impacts their productivity [ 8 ]. Thus, providing coverage to these groups effectively strengthens the financial risk protection of the health system [ 7 ]. Since some types of NTD are closely related to financial hardship, improving their financial protection may help attain UHC, especially for LMICs [ 9 ].
Financial protection is an essential indicator for NTDs and UHC; however, there was limited research on the financial hardship of NTDs. Although many studies addressed the question of the economic burden of NTDs, there is no systematic review and meta-analysis summarizing the financial hardship faced by the population affected by NTDs. Therefore, to fill this knowledge gap and build a baseline for the NTDs roadmap’s financial risk protection indicator, this study aimed to summarize the prevalence and magnitude of financial hardship among patients suffering from NTDs. Additionally, we assessed the methodologies of quantifying CHS and impoverishment incurred by NTDs.
Scope of the review
The protocol of this systematic review was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42023385627) [ 10 ]. This study was reported following the 2020 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) reporting guideline ( S1 PRISMA Checklist) [ 11 ]. Differences from the original review protocol are described with rationale ( S1 Table ).
This systematic literature review focused on 20 diseases selected as NTDs by WHO: Buruli ulcer, Chagas disease, dengue and chikungunya, dracunculiasis (Guinea-worm disease), echinococcosis, foodborne trematodiases, human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness), leishmaniasis, leprosy (Hansen’s disease), lymphatic filariasis, mycetoma, chromoblastomycosis and other deep mycoses, onchocerciasis (river blindness), rabies, scabies and other ectoparasitoses, schistosomiasis, soil-transmitted helminthiases, snakebite envenoming, taeniasis/cysticercosis, trachoma, and yaws and other endemic treponematoses [ 12 ].
Outcomes of interest of this systematic review were the prevalence and magnitude of victims who faced financial hardship caused by NTDs, including CHS, impoverishment, and coping strategies.
Search strategy and selection process
We searched three bibliographic databases, PubMed, EMBASE, and EconLit, to identify articles reporting financial hardship among patients suffering from NTDs from any country indexed from database inception to January 1, 2023. We also searched for grey literature in two databases, OpenGrey and EBSCO Open Dissertations. The search terms used were ( Disease name and its synonyms ) AND (catastroph* OR impoverish* OR coping OR economic consequence* OR out-of-pocket OR "out of pocket" OR ((household OR family OR patient AND (cost* OR spending OR expen*))), that was adapted to match the search techniques of each database. A full search strategy is shown in S2 Table . There was no language restriction applied in this systematic review. A supplemental search was performed by tracking citation and snowballing the eligible articles’ reference list.
Two reviewers (CP and JYC) independently performed the study selection. They screened the titles and abstracts of identified articles from database searches for relevance. Potentially relevant articles were sought for full-text articles. We requested the authors for full-text articles or reports of highly relevant articles without full-text articles, such as conference abstracts. The retrieved full-text articles were selected based on the eligibility criteria. Discrepancies arising during study selection were resolved by discussion with the third reviewer (NC).
Eligibility criteria
We included empirical studies reporting CHS, impoverishment, or coping strategies incurred by NTDs using primary data collection.
Data extraction
We developed a data extraction sheet by performing a pilot test of extracting five randomly selected articles and refining it until finalization. Two reviewers (CP and JYC) independently performed data extraction. Another reviewer (JH) checked the extracted data for correctness. Any discrepancies were resolved by discussion among reviewers.
Study findings and methodological characteristics extracted from the eligible articles are as follows: first author, publication year, NTDs, study setting, study design, sample characteristics, sample size, data collection period, data collection methods, time horizon, a perspective of the analysis, discount rate, costing year, reported currency, cost units, the definition of CHS and impoverishment, prevalence and magnitude of CHS and impoverishment incurred, economic consequences and coping strategies of financial hardship. Corresponding authors of the eligible articles were contacted to request individual patient-level data. However, we received no response.
The financial risk protection metric is intended to capture only the OOP costs for medical services (e.g., treatment and diagnosis costs). However, some studies considered certain types of direct non-medical costs (e.g., transportation, food, and accommodation costs) and indirect costs (e.g., productivity and income losses) when quantifying financial hardship. Some studies also included informal care costs, such as traditional medicine, as OOP costs [ 6 ]. Thus, our systematic review categorized costs extracted from the eligible studies as direct costs (OOP costs) and indirect costs. Direct costs were further categorized as direct medical costs and direct non-medical costs. The combination of direct costs and indirect costs was categorized as total costs.
Quality assessment
Two reviewers independently assessed the eligible articles’ quality (CP and JYC). Any discrepancies were resolved by consensus among the reviewers. To the best of our knowledge, there is no risk-of-bias assessment tool for economic burden studies. Hence, we assessed the quality of the eligible articles using the cost-of-illness evaluation checklist by Larg and Moss [ 13 ].
Data synthesis
A narrative synthesis was performed to summarize study findings, methodological characteristics, and the quality of the eligible studies. The identified countries were categorized based on the World Bank’s income levels and regions [ 14 ].
Statistical analysis
We performed meta-analyses to calculate the pooled prevalence of households experiencing financial hardship. However, this was possible only for studies that quantified financial hardship using the same measurement definition for a particular NTD. For example, we performed a meta-analysis to calculate the pooled prevalence of households experiencing CHS due to visceral leishmaniasis based on two studies that defined CHS as direct costs exceeding 10% of annual household income [ 8 , 15 ]. The remaining studies were not meta-analyzed due to the differences in the definitions of CHS. We estimated the pooled prevalence of CHS and 95% confidence intervals (CI) using a random-effects model under the DerSimonian and Laird approach [ 16 ]. Effect sizes were computed using each study’s Freeman–Tukey double-arcsine-transformed proportion. This variance-stabilizing transformation is particularly preferable when the proportions are close to 0 or 1 [ 17 ]. p < .05 was considered statistically significant in 2-sided tests.
Heterogeneity was evaluated by observing the forest plots and using the I 2 statistic that estimated the proportion of variability in a meta-analysis that is explained by differences between the included trials rather than by sampling error. Subgroup analyses were performed to explore possible causes of heterogeneity among study results. Publication bias was assessed using the funnel plot asymmetry test and the Egger regression asymmetry test [ 18 ]. Statistical analyses were conducted using Stata version 18.0 (Stata Corporation).
Patient and public involvement
Patients or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of our research.
Overall characteristics of the included studies
A total of 1,768 articles were identified from the search, of which 10 studies were included ( Fig 1 ) [ 8 , 15 , 19 – 26 ]. A list of excluded studies with reasons is presented in S3 Table . These studies quantified financial hardship among 2,761 patients in five LMICs (India, Nepal, Nigeria, Sudan, and Vietnam) who had been diagnosed with six out of the WHO’s 20 NTDs, including Buruli ulcer [ 20 ], chikungunya [ 21 , 26 ], dengue [ 22 ], visceral leishmaniasis [ 8 , 15 , 25 ], leprosy [ 19 , 23 ], and lymphatic filariasis [ 24 ]. Table 1 provides a summary of the study characteristics. We found no major concern in the quality of the included studies ( S4 Table )
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.g001
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.t001
Financial hardship caused by NTDs was quantified as CHS (10 studies) [ 8 , 15 , 19 – 26 ], and impoverishment (1 study) [ 8 ]. All studies were conducted in LMICs with a focus on South Asia (7 studies) [ 8 , 19 , 21 , 23 – 26 ], Sub-Saharan Africa (2 studies) [ 15 , 20 ], East Asia & Pacific (1 study) [ 22 ]. Patients were mostly identified using a hospital-based approach (7 studies) [ 8 , 15 , 19 , 20 , 22 , 23 , 25 ], with active case-finding intervention implemented in two of those studies [ 20 , 23 ]. Five studies reported that patients sought informal healthcare, such as traditional healers, ayurveda, and homeopathy [ 19 – 21 , 25 , 26 ].
Costs captured in the financial hardship were direct medical costs (10 studies, 100%) [ 8 , 15 , 19 – 26 ], direct non-medical costs (9 studies, 90%) [ 8 , 15 , 19 – 21 , 23 – 26 ], and indirect costs (7 studies, 70%) [ 8 , 15 , 19 , 21 , 23 , 25 , 26 ], as summarized in Table 2 . These costs were captured with a different timeframe, including during a disease episode [ 8 , 15 , 20 , 21 , 25 , 26 ], during hospitalization in an intensive care unit [ 22 ], monthly costs with a maximum recall period of 3 years [ 19 ], per one outpatient visit in the last 6 months [ 23 ], and per one hospitalization episode in the last year and per one outpatient visit in the last 15 days [ 24 ]. Abandonment of healthcare seeking due to financial burden was not reflected in the reported costs as the included studies captured only patients who sought healthcare.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.t002
The health insurance systems or special programs covered some of the costs. The costs for diagnosis and treatment of visceral leishmaniasis were provided free of charge to patients under the publicly financed health insurance system in Nepal [ 8 , 25 ] and Sudan [ 15 ]. In Nigeria, international development partners funded a special program that provided free diagnosis and treatment of Buruli ulcers, as well as accommodation, school funding, and basic allowance [ 20 ]. Additionally, the Indian government had a special program that provides financial assistance to families of patients affected by leprosy [ 19 ]. However, patients in India had to pay high OOP costs for medical services for leprosy [ 19 , 23 ], chikungunya [ 21 , 26 ], and lymphatic filariasis [ 24 ]. Similarly, patients in Vietnam also paid high OOP costs for the medical treatment of dengue [ 22 ]. For more details, refer to Table 3 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.t003
Financial hardship among patients suffering from NTDs
Catastrophic health spending..
CHS was variedly defined across studies in terms of types of costs (medical costs, medical and transportation costs, direct costs, indirect costs, or total costs), thresholds (5%, 10%, 15%, 25%, 30%, 40%, or 100%), timeframe (monthly, quarterly, or annual), household resources (income, consumption expenditure, national average annual household expenditure, or international poverty line) and perspective (household or individual). All studies used the budget share approach to quantify CHS. The most commonly used definitions of CHS caused by NTDs were direct costs of a disease episode exceeding 10% of annual household income (3 studies) [ 8 , 15 , 20 ] and total costs of a disease episode exceeding 10% of annual household income (3 studies) [ 8 , 15 , 25 ]. CHS that included only the direct medical costs was reported in two studies [ 8 , 22 ].
We summarized the prevalence of households experiencing CHS and the magnitude of CHS, determined as the percentage of the costs of NTDs as a share of income, in Table 4 . The prevalence and magnitude of CHS varied depending on the definitions of CHS, disease duration (episodic or chronic), and thresholds used (≤10% or >10%). Overall, the direct costs of NTDs resulted in a wide range of households experiencing CHS. CHS was generally low among patients with leprosy (0.0–11.0%) [ 19 , 23 ], dengue (12.5%) [ 22 ], and lymphatic filariasis (0.0–23.0%) [ 24 ], and relatively high among patients with Buruli ulcers (45.6%) [ 20 ]. CHS varied widely among patients with chikungunya (11.9–99.3%) [ 21 , 26 ] and visceral leishmaniasis (24.6–91.8%) [ 8 , 15 , 25 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.t004
Meta-analyses were performed to pool the prevalence of CHS in studies reporting CHS using the same measurement definition in a particular CHS. This was only possible for visceral leishmaniasis, in which CHS was quantified as direct costs of a disease episode exceeding 10% of annual household income in two studies [ 8 , 15 ], and total costs exceeding 10% of annual household income in three studies [ 8 , 15 , 25 ].
The pooled prevalence of CHS, defined as direct costs exceeding 10% of annual household income, was 73% (95% CI; 65–80%, n = 2, I 2 = 0.00%), as shown in Fig 2A . Egger’s test (P = 0.80) indicated no evidence of small-study effects. Visual inspection of the funnel plot indicated no evidence of publication bias ( S1A Fig ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.g002
The pooled prevalence of CHS, defined as total costs exceeding 10% of annual household income, was 74% (95% CI; 49–93%, n = 3, I 2 = 94.72%), as shown in S2 Fig . We explored the source of heterogeneity by visual inspection of the forest plot. We found that the source of heterogeneity was the differences in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis, where sodium stibogluconate was used in two studies [ 8 , 15 ], and miltefosine in one study [ 25 ]. Therefore, we performed a subgroup meta-analysis based on different treatments, as shown in Fig 2B . We removed one study [ 25 ] from the meta-analysis to investigate the publication bias without the presence of heterogeneity. Egger’s test (P = 0.81) indicated no evidence of small-study effects. Visual inspection of the funnel plot indicated no evidence of publication bias ( S1B Fig ).
Impoverishment.
Impoverishment was investigated in one study in patients with visceral leishmaniasis, which defined impoverishment as annual household income falling below the poverty line after paying for treatment [ 8 ]. Costs of visceral leishmaniasis impoverished 20–26% of the 61 households investigated, depending on the costs captured (20% medical costs, 21% medical and transportation costs, 26% direct costs), as shown in Table 2 .
Coping strategies
Four studies reported coping strategies used by patients to pay the costs of NTDs. These strategies included using savings (71–100% of patients), taking out loans (32–80%), selling livestock or other assets (17–32%), or borrowing money (0–23%), as shown in Table 2 . However, these studies did not distinguish between coping strategies used by patients who experienced CHS and those who did not [ 8 , 19 , 24 , 25 ].
Cost drivers and determinants of financial hardship
To understand the cost drivers of financial hardship caused by NTDs, we analyzed the percentage share of types of costs captured in the direct costs. The findings are presented in Fig 3 . Direct medical costs were the primary cost driver in nine studies [ 8 , 19 – 21 , 23 – 26 ]. However, one study identified food and transportation costs as the main cost drivers [ 15 ].
Abbreviation: ENL–erythema nodosum leprosum. Tripathy et al, 2020 [ 24 ]; Tiwari et al, 2018 [ 23 ]; Chandler et al, 2015 [ 19 ]; Uranw et al, 2013 [ 25 ], Meheus et al, 2013 [ 15 ], Adhikari et al, 2009 [ 8 ], McBride et al, 2019[ 22 ], Vijayakumar et al, 2013 [ 26 ], Gopalan et al, 2009 [ 21 ], Chukwu et al, 2017 [ 20 ] .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.g003
Determinants of CHS were assessed in one study among patients with Buruli ulcers. The study concluded that neither age, gender, rural/urban location, education, occupation, religion, nor patient income group was a determinant of CHS [ 20 ]. There was no study investigating determinants of impoverishment.
NTDs primarily impact populations with limited financial means, yet the literature addressing the financial hardship caused by NTDs is relatively scarce. Our systematic review revealed that there were only ten studies covering six NTDs. We discovered that many households are facing financial hardship as a result of NTDs, despite having access to publicly funded healthcare systems or special NTD programs. The costs related to NTDs resulted in significant financial hardship for these households, mainly due to the high OOP costs associated with medical treatment. Even in situations where drugs used to treat NTDs were provided free of charge, the costs for supportive care, medical procedures, transportation, and food were still high and could have a devastating financial impact on these households. Moreover, these financial hardship indicators might not fully reflect the financial risk of the population affected by NTDs because many live in poverty or even extreme poverty. Victims of NTDs are usually those who are socially disadvantaged. They need to make trade-offs between suffering from the disease and seeking healthcare because not all victims can afford the costs of NTDs, especially OOP costs for medical treatment and transportation, which could lead to the abandonment of healthcare [ 1 – 3 ].
The research findings have shown that merely providing funding for treatments of NTDs is insufficient for protecting those affected by NTDs from financial hardship. Therefore, it is crucial to strengthen the entire healthcare system to effectively address the challenges of NTDs and provide financial protection to the victims. Additionally, it is important to encourage and engage communities to change the behavior of those affected by NTDs so that they seek medical assistance at appropriate healthcare facilities instead of relying on traditional healers or not seeking care at all. Our research also supports the need for an economic framework to guide NTD investments [ 27 ]. The ability to prioritize investments, informed partially by economic parameters, may appeal to a broad set of stakeholders and help facilitate the process of building coalitions to achieve the WHO’s goal that 90% of the at-risk population is protected against financial hardship caused by NTDs [ 1 ].
Although there is no consensus regarding the estimation approach and thresholds in quantifying CHS, it is important to note that these differences can significantly impact the findings and consequently impact the applications and implications of the findings [ 6 , 28 ]. We found that CHS was variedly defined across studies in terms of estimation approach, types of costs, thresholds, timeframe, household resources, and perspective. Our review revealed that 90% of the included studies captured direct non-medical costs as part of the OOP costs [ 8 , 15 , 19 – 21 , 23 – 26 ]. Furthermore, Seventy percent of the included studies considered indirect costs in quantifying financial hardship [ 8 , 15 , 19 , 21 , 23 , 25 , 26 ]. This approach aligned with an indicator called “catastrophic costs” that has emerged in tuberculosis studies. Catastrophic costs occur when the total healthcare costs, including direct and indirect costs, exceed 20% of the annual household income [ 28 ]. This indicator could be a more comprehensive measure of the overall financial burden of NTDs on the household beyond just the OOP costs which will be useful when evaluating and monitoring different healthcare policies and interventions to mitigate financial hardship caused by NTDs.
The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis should be interpreted under the following limitations. The included studies in our review only focused on patients who sought healthcare, so the financial burden of those who did not seek healthcare was not captured in the reported OOP costs. This means that people who could not afford healthcare may have been excluded from these studies. Moreover, we could not perform meta-analyses of the prevalence of CHS on all identified NTDs due to differences in how CHS was quantified across studies and lack of access to individual patient-level data.
Hence, we highlighted some methodological considerations to guide future studies on financial hardship among households suffering from NTDs to gain a better understanding of the neglected public health issues and to inform the development of strategies of what to address to tackle the financial burden of NTDs. Firstly, methods to quantify financial hardship should be coherent to allow comparability across studies. For instance, CHS and impoverishment should be defined and measured in a relevant manner to the nature of the NTD, including estimation approach, thresholds, types of costs, timeframe, household resources, and perspective. Secondly, subgroup analyses should be conducted to evaluate the determinants of financial hardship across household characteristics (e.g., income, socioeconomic status) or phases of disease (e.g., disease onset, treatment seeking, diagnosis, treatment, post-treatment). Lastly, coping strategies should be assessed among those who did and did not experience financial hardship to understand the economic consequences of financial hardship across subgroups.
NTDs can be a devastating burden on households, not only in terms of physical and mental health but also financially. NTDs lead to a substantial number of households facing financial hardship. However, financial hardship caused by NTDs was not comprehensively evaluated in the literature. Furthermore, OOP costs represented only a partial picture of the financial hardship the population affected by NTDs faces. To mitigate this financial hardship, it is imperative to conduct thorough research to identify the factors contributing to it. Future research should consider various household characteristics, such as income, education level, and geographic location, as well as the different disease stages, from onset to treatment completion. Future studies should also investigate the hidden financial burden due to the abandonment of healthcare-seeking to capture the economic burden and opportunity costs of those who did not seek healthcare. By carefully examining these factors, researchers and decision-makers can gain insight into the specific challenges faced by households affected by NTDs and develop targeted interventions to alleviate financial hardships. Ultimately, these studies can help inform the development of strategies to reduce the burden of NTDs on households and improve overall health outcomes.
Supporting information
S1 prisma checklist. prisma checklist..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.s001
S1 Table. Differences from original review protocol.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.s002
S2 Table. Full search strategy.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.s003
S3 Table. Excluded studies with reasons.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.s004
S4 Table. Quality assessment using Larg, A., and Moss, J. R. (2011) Cost-of-illness studies: a guide to critical evaluation.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.s005
S1 Fig. Assessment of publication bias.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.s006
S2 Fig. Forest plot of pooled proportion of catastrophic health spending defined as total costs exceeding 10% of annual household income.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012086.s007
Acknowledgments
The authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this article and they do not necessarily represent the views, decisions or policies of the institutions with which they are affiliated.
- 1. World Health Organization. Ending the neglect to attain the Sustainable Development Goals: a road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021–2030. Geneva: World Health Organization 2020.
- 2. World Health Organization. Neglected tropical diseases, hidden successes, emerging opportunities. 2009. World Health Organization, Geneva. 2014.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 4. World Health Organization. Distribution of health payments and catastrophic expenditures methodology. World Health Organization; 2005.
- PubMed/NCBI
- 10. Chaiyakunapruk N, Patikorn C, Cho J-Y, Oh SH, Huang XX. Financial catastrophe among patients suffering from neglected tropical diseases: a systematic review of global literature. CRD42023385627: PROSPERO; 2023 [cited 2023 April 27]. Available from: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42023385627 .
- 12. World Health Organization. Neglected tropical diseases Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2023 [cited 2023 April 27]. Available from: https://www.who.int/health-topics/neglected-tropical-diseases#tab=tab_1 .
- 14. World Bank Country and Lending Groups [Internet]. 2022 [cited July 6, 2022]. Available from: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
A literature review is defined as "a critical analysis of a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles." (The Writing Center University of Winconsin-Madison 2022) A literature review is an integrated analysis, not just a summary of scholarly work on a specific topic.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations. EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic.
The general literature review is a synthesis and analysis of published research on a relevant clinical issue, and is a common format for academic theses at the bachelor's and master's levels in nursing, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, public health and other related fields. ... The data analysis methods described here are based on ...
Literature reviews allow scientists to argue that they are expanding current. expertise - improving on what already exists and filling the gaps that remain. This paper demonstrates the literatu ...
In this chapter, we have discussed ways that the literature review represents a data collection tool, a method, a mixed research study, and, most of all, a methodology. Further, because oftentimes a methodology can be an abstract process, a methodology needs some type of mechanism, or process, to bring it to fruition.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question. ... A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies. Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. ...
Introduction Researchers and practitioners rely on literature reviews to synthesize large bodies of knowledge. Many types of literature reviews have been developed, each targeting a specific purpose. However, these syntheses are hampered if the review type's paradigmatic roots, methods, and markers of rigor are only vaguely understood. One literature review type whose methodology has yet to ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources that establishes familiarity with and an understanding of current research in a particular field. It includes a critical analysis of the relationship among different works, seeking a synthesis and an explanation of gaps, while relating findings to the project at hand.
This. paper discusses literature review as a methodology for conducting research and o ffers an overview of different. types of reviews, as well as some guidelines to how to both conduct and ...
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
Elements of a Literature Review. Summarize subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with objectives of the review; Divide works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, those offering alternative theories entirely) Explain how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others
Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews. In this article, through a systematic search on the methodology of literature review, we categorize a typology of literature reviews, discuss steps in conducting a systematic literature review, and provide suggestions on how to enhance rigor in literature ...
What kinds of literature reviews are written? Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
1. INTRODUCTION. Evidence synthesis is a prerequisite for knowledge translation. 1 A well conducted systematic review (SR), often in conjunction with meta‐analyses (MA) when appropriate, is considered the "gold standard" of methods for synthesizing evidence related to a topic of interest. 2 The central strength of an SR is the transparency of the methods used to systematically search ...
sources that inform a literatur e synthesis comprising the following four major source. type s to inform research syntheses: talk, observations, drawings/photographs/videos, and. documents, and we ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
Review Manager (RevMan) is a web-based software that manages the entire literature review process and meta-analysis. The meta-analyst uploads all studies to RevMan library, where they can be managed and exanimated for inclusion. Like CMA, RevMan enables authors to conduct overall analysis and moderator analysis. 4.4.6.3 Stata
Systematic reviews define a topic and identify, summarize, and evaluate the findings of all well-designed research for that topic that is reported in the literature. This review method uses strict criteria designed to limit bias and emphasize scientific validity with the aim to produce an impartial analysis. Systematic reviews are the preferred ...
Unlike traditional reviews and meta-analyses, bibliometric analysis offers a detailed summary of a field's literature metrics and knowledge structure by examining the structural relationships among authors, countries, institutions, and themes, employing statistical methods such as article counts, reference co-citation analysis, and impact ...
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU ...
A survey and semi-structured interview forms were preferred as data collection methods. In the analysis of the survey data, AMOS was adopted to test the hypothetical model and the Hayes Process macro was employed to determine the moderating effect. ... In the literature review, it was seen that the moderating role of different variables such as ...
Storytelling is of paramount importance in tourism, contributing to the transformation of something seemingly unremarkable and insignificant into a compelling tourist destination (Ben Youssef et al., 2019; Hartman et al., 2019; Pera, 2017).It appeals to the visitors' imagination and influences visitors' expectations and attitudes, providing them with an added-value experience (Mossberg, 2008).
The proposed approaches have been validated on both synthetic and real data, and compared against other methods from the literature. It results that neighborhood analysis allows to outperform competitors, and when it is combined with collaborative filtering the prediction accuracy further improves, scoring a value of AUC equal to 0966.
Author summary Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) mainly affect underprivileged populations, potentially resulting in catastrophic health spending (CHS) and impoverishment from out-of-pocket (OOP) costs. This systematic review aimed to summarize the financial hardship caused by NTDs. We found that NTDs lead to a substantial number of households facing financial hardship.