Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.

How do I permanently assign an IP address with DHCP?
I am wondering if there is anything (software or hardware) out there that can do something I think I may have made up, Dynamic Static IPs. The idea is that when a new device connects to the local network this device/software acts as a DHCP server, if the device is new then it dynamically assigns it a new address that has never been used before and stores this MAC Address IP Address combination in a database, if the device's MAC is in the database the devices gets the same IP as before.
I am aware this is similar to sticky IP allocation but I don't want the IPs to stick for a while I want them to be superglued on for ever.
Bonus question: Is this possible using a Raspberry Pi running Raspbian on a network with around 100 devices? The RPi is already acting as the DHCP server and the router has this capability but it is turned off.
Many thanks in advance for any and all help offered!
- And what happens when you run out of IPs? – heavyd May 7, 2015 at 14:49
- Good point. However on the size of network I am operating the 255.255.0.0 subnet would allow this setup to operate for many years without trouble. – o.comp May 7, 2015 at 14:50
- What you're after is just a DHCP server... if you want to "permanently" provide the same device the same IP then you would need to either give it a static IP or tell the DHCP server to "reserve" that MAC address an IP... Raspberry Pi uses a Linux distro that can run a DHCP server... ronnutter.com/raspberry-pi-dhcp-server-reservation – Kinnectus May 7, 2015 at 14:53
- 1 Ideally you should update your question with a bit more information about your network... What OS is your Raspberry Pi running? Is your Raspberry Pi the DHCP server for your network? Do you have an existing router on your network that does DHCP? Do you want this to continue providing DHCP? – Kinnectus May 7, 2015 at 14:57
- Just as a remark: I have a router that has an option called static DHCP , which does exactly that (well, it drops its database when it loses power, but that's a different matter) – Slizzered May 7, 2015 at 18:16
2 Answers 2
Most DHCP servers work this way, it's just they don't permanently assign the IP to a host.
On Linux, using isc-dhcp-server , it's possible to set the lease duration to never expire .
Using Debian for your Raspberry Pi
https://wiki.debian.org/RaspberryPi
you can made a DHCP Server and assign :
https://wiki.debian.org/DHCP_Server#Assign_fixed_addresses
where are some examples to make your host with fixed address:
you can manage your dhcp leases in this path there you can set as never expires.
/var/lib/dhcpd.leases
an example:
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged networking ip dhcp ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Why configuration is so complicated
- Featured on Meta
- New Focus Styles & Updated Styling for Button Groups
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network
- Google Cloud will be Sponsoring Super User SE
Hot Network Questions
- To write letter Cyrillic letter 'Ж' in latex
- which refers to what?
- How do I find broken symbolic links in macOS?
- Is there a formalization of the butterfly effect?
- Can someone be awarded the title of doctor without having been a doctoral student?
- Can my username include a D&D monster?
- Is it possible for a humanoid to learn English within a few days, just from observing conversations?
- Book on Hilbert spaces, including non-separable
- Is this Python/Pygame that draws a maze well structured?
- What is the point of knowing symmetries, conservation quantities of a system?
- What does "in her November of life" mean in "Persuasion"?
- How do believers in hell respond to the argument "What finite crime deserves an infinite punishment?"?
- How can Diethyl Methylphosphonate be reduced into Diethyl Methylphosphonite?
- Create a snail matrix
- How can I do some sort of limited dissolve of useless vertices at the edges?
- Mathematica yields repeated solutions when only one exists
- Optimal Solution for the Four Divisors Problem on LeetCode
- How do you stay stable when landing/ Taking off on an F-35 during a VTOL landing/Takeoff?
- Embarrassment at work caused by a supervisor's reaction due to my shingles disease
- Does fixcmex work with the mlmodern fonts?
- What is "Vancian" magic in D&D?
- Different estimates of Least Squares and Maximum Likelihood Estimates under non-normality
- How practical would it be to use a handgun-knife hybrid weapon?
- Why do valence electrons not push each other away?
- Help Center

DHCP Reservations - 5 Reasons You Need to Assign a Permanent Address to Devices on Your Network
Every device on your home network has a unique IP address. When your network is small you don't really have to think about these IP addresses. Your router takes care of managing them for you, giving every new device an IP address whenever it connects. In a small network, this is usually fine, and it is the way most people's home network runs.
As your network grows, managing devices becomes more of a task. Perhaps you want to set up a port forward to access something on your network from the outside. Or maybe you are interested in home automation and want to control various devices with custom software such as Home Assistant. Maybe you are just tired of always having to look up the IP address of a security camera in order to check its feed.

Once a network becomes large it can be hard to track down which device is which. Imagine having dozens of smart switches installed in your house on your network, each of them with its own IP address, and you have no idea how your IP addresses have been assigned. The sooner you start keeping track of your devices, the better. Don't wait until you have 100 devices on your network and you don't know where any of them are (by where we mean their IP address, not their physical location.)
Using DHCP reservations in your router: lets you manage your devices from one place, fixes networking problems that you didn't even know you had, is easier than setting up static IP addresses in each device, makes your network more reliable for port forwarding, and creates permanent addresses that are needed for home automation, gaming, and VMs.
Reason #1: DHCP Reservations: Manage All Your Devices From One Place
DHCP Reservations are created in your router. When you need to manage your devices it is easiest if they can be accessed through your router. The alternative is to log in to or access each device separately. This usually involves multiple passwords and interfaces and can quickly become quite complicated.
Once you have DHCP reservations set up in your router it is easy to not only find which device is which but also to change which IP address is assigned to each device. This type of micromanagement can be useful when tackling more adventurous networking topics such as home automation and port forwarding.
What are DHCP reservations?
A DHCP reservation is an entry in your router that assigns a permanent IP address to a device on your network. Every time that device is connected to your network it is guaranteed to get the same IP address. This is different than a standard DHCP IP address, which can change every time a device is rebooted or connected to your network. DHCP reservations are managed in your router, not in your devices. This makes managing your network easier because you only have to log in to one device (your router) in order to change the IP addresses on your network.
How do DHCP reservations work?
DHCP reservations work on top of the DHCP protocol, which is implemented inside your router. When a device connects to your network it sends out a special packet called a DHCP broadcast which only your router responds to. The router's response instructs the device to use a specific IP address.
In order for a router's answer to make it to the device, it has to have a way of talking to that device (before the device even has an IP address.) This is done using a low-level unique serial number that is permanently hard-coded into each device called a MAC address.
What is a MAC address? Every device on a network has a unique serial number permanently burned into it at the factory called a MAC address . MAC, or Media Access Control, is used to communicate on an IP network even before a device has an IP address. MAC addresses do not change (except in some rare cases such as virtual machines and software access points.)
Only the device with the MAC address that sent the request will receive the router's reply and assign itself the unique IP address that the router has told it to use.
Since a router sends its reply to a MAC address, it is possible to have the router always send the same reply to the same MAC address. This is what a DHCP reservation is. It is an instruction in the router to always send the same IP address to a certain MAC address. DHCP reservations are done by MAC address.
Some routers will hide the fact that you are dealing with a MAC address by giving the device a name. If you can favor making the reservation by MAC address you should.
Reason #2: DHCP Reservations Fix Networking Problems
Especially in Windows networking, every device on your network has the possibility of having a human recognizable name. Some people like to name their computer something memorable or funny, or other times a media server will be assigned a name so that it shows up in the client app. Also, many home automation devices automatically assign themselves a name that is a mash-up of the manufacturer's name and the device model number. While these names can be convenient, they can also be problematic to use, especially in a network that is susceptible to communication hiccups such as Wi-Fi.
In a Wi-Fi network with a spotty connection, it is frequently more reliable to use the IP address of a device than the name. This is because it reduces network traffic by not requiring an additional round trip of packets to translate a given name to its assigned IP address. It can be much faster to simply access a device by its IP address in an unstable network.
Many times you can ping a device by name and notice a small delay before the first reply comes back. This is the name resolution phase and it is completely bypassed by just using the device's IP address directly.
Of course, you could skip the name resolution phase with a dynamic IP address as well, but you don't know what the device's IP address is. This is solved with a DHCP reservation which makes the IP address permanent.
Reason #3: Using DHCP Reservations Is Better Than Setting Static IP Addresses
Using DHCP reservations to assign fixed IP addresses is a great improvement over the manual method of managing static IP addresses. In the early days, home routers didn't support DHCP reservations because they did not have enough RAM to keep track of all the devices. Instead, a static IP address had to be set up on devices that needed to have the same IP address whenever they connected to the network. This required finding each device on your network, logging into that device using its username and password, and figuring out its network settings.
Furthermore, you had to keep track of which IP address you had assigned to each device manually in order to avoid an IP address conflict. It was truly tedious and cumbersome and prone to human error.
DHCP reservation vs. static IP
With DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) you cannot always be sure which IP address each device has unless you have gone through the tedious chore of logging in to each device and assigning it a static IP address.
There is a better way. With DHCP reservations, you get to control which IP address each device gets, and you do not even have to log in to that device. This allows you to take control of your network and manage which devices have a permanent IP address all from the convenience of your router's admin interface.
Using DHCP reservations consolidates device management to a single point of maintenance. You can do it all in your router instead of having to sign in to each device separately. Most routers will not allow you to accidentally create an IP address conflict, and you do not need to log in to any of your devices.
Reason #4: DHCP Reservations Make Your Network More Reliable for Port Forwarding
When you set up a port forward you are pointing a port at an IP address on your network. At the time you set up that port forward, you should know what device is using that IP address. It would be extra nice if that device's IP address never changed. If you reboot your device and it gets a new IP address then your port forward will stop working and you may not realize why.
A device that is the target of a port forward needs to have a permanent IP address. You can either log into that device and configure its network settings manually or you can set up a DHCP reservation for that device in your router. Either of these will give that device a permanent IP address and keep that port forward working through reboots.
Should I use a DHCP Reservation?
When you want your device to get the same IP address every time it connects to your network, you should create a DHCP reservation for the device. It's easier, faster, and less prone to human error than attempting to manage static IP addresses on your network.
There are no negative side effects to a DHCP reservation and many positive benefits. If you are thinking about using DHCP reservations on your network, then you should definitely get started right away.
Reason #5: DHCP Reservations Are Needed for Home Automation, Gaming and VMs
When it comes to networking, some of the more common uses for DHCP reservations are gaming, home automation, and virtual machines. The process for setting up a DHCP reservation is the same for each of these topics, and each of them has its own unique set of benefits.
Is a reserved IP good for gaming?
Many games benefit greatly from a port forward. Multiplayer games that have a lobby usually pick one of the players as the lobby host. It's usually the player with the lowest ping lag who also has a port forward. The lobby host tends to get a better response from the game engine and as a result can get a significantly better score than non-host players.
Setting up a port forward to your game can decrease your lag to the game server. It is one of the first steps you should try when you are having performance issues with online multiplayer games. See our How To Port Forward Games guide for detailed instructions on this topic.
Before you set up a port forward, the device that you are gaming on needs to have a permanent IP address. You can either set up a static IP address on the device or a DHCP reservation in your router. Of course, we prefer a DHCP reservation in your router.
Why DHCP reservations are important for home automation
For basic home automation like the popular hubs and integrated switches, a DHCP reservation is not necessary. As soon as you try to use something fancier such as Home Assistant you are going to quickly bump into some of the annoyances of dynamic IP addresses. Some of the open-source interfaces to popular home automation platforms expect a device's IP address to be unchanging.
A common symptom is when a device is discovered, it works fine, but weeks or months later it stops responding to home automation software. This very famously happened with Home Assistant and TP-Link Kasa. Since Kasa devices do not allow you to control their network settings, you are forced to use DHCP, but the open-source Kasa interface does not play well with dynamic IP addresses.
It is a simple solution to log into your router and assign a DHCP reservation to each of your smart switches, smart bulbs, and smart hubs. After doing this you will notice significantly fewer communication disruptions.
DHCP reservations and virtual machines
Virtual machines are becoming more and more popular. They are useful for running old versions of Windows, testing software before installing it, simulating old arcade cabinets, and isolating potentially dangerous programs.
All of the virtual machine platforms such as Hyper-V, Proxmox, KVM, and VirtualBox allow you to specify the MAC address of the virtual network card assigned to each of your VMs. This is super convenient because it allows you to assign an IP address to a VM before you even boot it up for the first time. This allows you to control which IP address a VM uses when pulling updates during the installation process. It also makes it much easier to connect to the VM remotely using SSH, RDP, or VNC.
How to Make a DHCP Reservation In Your Router
Remember that you are reserving the IP address that the device should have every time it connects to your network. It does not necessarily have to be the IP address that it got automatically. Feel free to come up with any sort of numbering scheme that makes sense to you. For instance, you might make all cell phones be in the .50 range and all gaming consoles in the .80 range. It's up to you how you allocate IP addresses on your network. It's best to avoid .1, .100, and .255 though because they frequently cause conflicts.
After a DHCP reservation is created for a device, you will need to reboot the device if you assigned it an IP address that is different from the one it got automatically. Depending on the device, you will need to either push the reset button on the device, cyle power to it by turning a breaker off and then on, or wait until the device times out and reboots itself before the new reservation will take effect.
Step 1: Log in to your router
DHCP reservations are created in your router so to be able to make one you need to be able to log into your router. If you are not sure how to log into your router see our Login Guides .
Step 2: Find the DHCP section
After you log in to your router, look for the DHCP section. Sometimes it is in the advanced section and sometimes it is in the networking section. You might also find it in the LAN section, but it definitely will not be in the WAN section.
Step 3: Find the device on your network
Once you find the DHCP section, you should see a list of all the devices on your network that currently have an IP address. It may list the device name, the device IP address, or the device MAC address.
Something that might make finding a device on your network easier is to know that the first half of a MAC address corresponds to the manufacturer of the network adapter in that device. For instance, if you are looking for a PlayStation, you might find that your router has labeled it Sony. Or if you are looking for an Xbox, it might show up as Microsoft. There are numerous MAC address lookup engines on the internet that can help you figure out which MAC address belongs to which device. If you are worried about privacy, you only need to include the first half of the MAC address in search. Also, when looking up MAC addresses by vendor, it might be labeled OUI instead of MAC.
On a large network with a lot of devices, it can be hard to figure out which device is which. This is why it is easier to start DHCP reservations when your network is small.
Step 4: Reserve an IP address for the device
Once you have found the device that you want to create a reservation for look for a button or a link that says either assign or make permanent. When you choose that option, your router creates an entry in its DHCP reservation table. You should be able to see the DHCP reservation table in the router's web interface. Usually, the DHCP reservation table is where you modify and delete reservations as well.
Note that if your router allows you to make a reservation by name or MAC address we recommend making reservations by MAC address.
The larger your network gets, the more you are going to wish you started making DHCP reservations years ago. If your current router doesn't support DHCP reservations then you have a great excuse to upgrade your router now.
For answers to your networking questions, visit our Networking Help Center .
More From Portforward

Mass Effect: Andromeda
Mass Effect: Andromeda issues solved. If you are having trouble joining a lobby with your friends read this.

Opening Ports for Call of Duty: Black Ops Cold War using Your Router
Forwarding ports for Call of Duty: Black Ops Cold War can help improve your online multiplayer connections.

How to Forward Ports in Your Router for Madden NFL 22
You can connect with more players in Madden NFL 22 and help improve connections by forwarding some ports.

Creating a Port Forward in Your Router for Street Fighter 6
You can help improve your online connections in Street Fighter 6 by forwarding some ports in your router.

Open Ports for Roblox
If Roblox has trouble loading online games or fails to load games then you need to make sure that you have an open port.

Create a Port Forward for Mario Kart 8 Deluxe in your Router
Forwarding some ports in your router for Mario Kart 8 Deluxe can help improve your online multiplayer connections.

How to Port Forward Rocket League
Forwarding some ports for Rocket League in your router can help improve ping times and fix connection issues.

Port Forwarding for MultiVersus
You can help improve your online connections in MultiVersus by forwarding some ports for it in your router.
- Articles Automation Career Cloud Containers Kubernetes Linux Programming Security
Static and dynamic IP address configurations for DHCP
%t min read | by Damon Garn

IP address configuration is one of the most critical, if simple, settings on your network devices. Workstations, servers, routers, and other components must have properly assigned IP address settings to participate on the network.
This two-part article series covers static and dynamic IP address settings and the configuration of a DHCP server. This article (part one) defines network identities, contrasts static and dynamic configurations, and covers the commands needed to manage the settings. Part two covers the deployment of a DHCP server, DHCP scope configuration, and client-side management of dynamic IP addresses.
[ You might also enjoy: The name game: Naming network interfaces in Linux ]
Three identities
Network nodes have three identities: Hostname, logical address, and physical address. These three addresses provide different types of connectivity and are used in various ways during network communication.
The three identities are:
- Hostname - descriptive, easy to remember names for the benefit of humans
- IP address - logical address to uniquely identify a network node, primarily used by routers
- MAC address - physical address encoded on the network interface card (NIC), used mainly by switches
Hostnames are configured when the OS is installed, and MAC addresses are hard-coded on NICs. Sysadmins typically configure IP address information on servers, workstations, portable systems, and network devices.
I’ll cover the two primary ways that IP address information is provided to the nodes: Static and dynamic configurations.
Static and dynamic configurations:
- Static - manually configured by sysadmins
- Dynamic - automatically leased by clients from a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server
The standard settings are IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and nameservers.
Static configuration
NetworkManager primarily handles network configuration. NetworkManager can be used in a GUI, TUI, or CLI environment.
The nmcli process to set a static IP configuration is to create a connection profile and then set the values desired. Red Hat has documentation here .
Here is an example of creating a network connection named home-network with an IP address of 192.168.2.200/24, a default gateway of 192.168.2.1, and a name server of 8.8.8.8:
The GUI configuration can be accomplished by selecting the Manual button and then filling in the blanks with the appropriate information.

Recall that you can make no typographical errors when configuring IP addresses, and duplicate addresses will cause network connection problems.
Why static configurations?
Static IP addresses do not change unless the administrator actively reconfigures them. This is an important fact when it comes to servers because most client computers need to be able to find servers consistently.
For example, an NFS file server hosting department directories needs to keep the same IP address over time as configuration files such as a client computer’s /etc/fstab file may use the IP address for connectivity.
Other network nodes also may need an unchanging network identity. Appliance devices such as firewalls or proxies, print servers, name resolution servers, web servers, and virtually all other infrastructure devices need a consistent identity. Sysadmins will almost always configure these systems with static IP address information.
Tracking IPs
It is essential to track your statically assigned IP addresses. Depending on the size of your environment, this might be so simple as a text document or a spreadsheet, all the way up to specialized software that integrates with directory services and DHCP. I find it’s best to at least track IP address (and subnet mask), MAC address (not essential), hostname, role on the network (justifies why the devices have a static IP), and any additional notes.

Dynamic configurations
The devices that require a static IP configuration are a relatively small percentage of your network. Most network devices are end-user systems such as workstations, laptops, phones, tablets, and other transient devices. In addition, these systems do not usually host network services that need to be discoverable by other computers.
IP address configurations are unforgiving when it comes to duplicates and typos. In addition, static IP address settings are fairly time-consuming. Finally, IP address settings tend to be temporary, especially with the advent of portable devices like laptops, phones, and tablets. To save time and reduce the chances of a mistake, dynamic IP address allocation is preferable for these kinds of nodes.
Linux systems are configured as DHCP clients by using NetworkManager.
Here is an example of adding a network connection profile configured to lease an IP address from DHCP:
By not specifying an address NetworkManager assumes the DHCP client role.
Here is a screenshot of a dynamic IP address configuration from the GUI:

The dhclient command
The dhclient command is also used to manage dynamic IP address configurations. However, in RHEL 8, network configurations, including DHCP, are handled by NetworkManager. Older RHEL versions rely on dhclient , as do some other distributions.
The ip route command displays lease information.
The second article in this series goes over the dhclient command in more detail.
[ Free cheat sheet: Get a list of Linux utilities and commands for managing servers and networks . ]
IP address settings are crucial to network communications. Values such as the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and nameservers can be manually managed, but sysadmins must be very careful not to make any mistakes. Static settings don’t change unless the administrator reconfigures them, so they are essential for servers whose services are made available across the network.
Dynamic IP configurations are far more convenient for systems that don’t host network services, such as end-user devices. Furthermore, many of these devices enter and leave the network regularly, and it would be very time-consuming to set IP values each time manually. Instead, a DHCP server is used to host a pool of available addresses that client systems can lease.
Understanding the difference between static and dynamic IP addresses is straightforward but essential for administrators. As a general rule, servers and network devices utilize static, unchanging IPs, while client devices rely on dynamically allocated IP configurations.

Damon Garn owns Cogspinner Coaction, LLC, a technical writing, editing, and IT project company based in Colorado Springs, CO. Damon authored many CompTIA Official Instructor and Student Guides (Linux+, Cloud+, Cloud Essentials+, Server+) and developed a broad library of interactive, scored labs. He regularly contributes to Enable Sysadmin, SearchNetworking, and CompTIA article repositories. Damon has 20 years of experience as a technical trainer covering Linux, Windows Server, and security content. He is a former sysadmin for US Figure Skating. He lives in Colorado Springs with his family and is a writer, musician, and amateur genealogist. More about me
Try Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Download it at no charge from the red hat developer program., related content.


- Documentation Home
- Palo Alto Networks
- Live Community
- Knowledge Base
- DHCP Addressing
DHCP Address Allocation Methods
Next-generation firewall docs.
- Cloud Management of NGFWs
- PAN-OS 10.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 11.0
- PAN-OS 11.1
- Cloud Management and AIOps for NGFW
- PAN-OS 8.1 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.0 (EoL)
- Automatic allocation —The DHCP server assigns a permanent IP address to a client from its IP Pools . On the firewall, a Lease specified as Unlimited means the allocation is permanent.
- Dynamic allocation —The DHCP server assigns a reusable IP address from IP Pools of addresses to a client for a maximum period of time, known as a lease . This method of address allocation is useful when the customer has a limited number of IP addresses; they can be assigned to clients who need only temporary access to the network. See the DHCP Leases section.
- It is an address from the IP Pools . You may configure multiple reserved addresses.
- If you configure no Reserved Address , the clients of the server will receive new DHCP assignments from the pool when their leases expire or if they reboot, etc. (unless you specified that a Lease is Unlimited ).
- If you allocate all of the addresses in the IP Pools as a Reserved Address , there are no dynamic addresses free to assign to the next DHCP client requesting an address.
- You may configure a Reserved Address without configuring a MAC Address . In this case, the DHCP server will not assign the Reserved Address to any device. You might reserve a few addresses from the pool and statically assign them to a fax and printer, for example, without using DHCP.
Recommended For You
© 2024 Palo Alto Networks, Inc. All rights reserved.
How-To Geek
What is dhcp (dynamic host configuration protocol).
Ever wonder how your devices get an IP automatically?
Quick Links
Dhcp can handle ip assignments, dhcp controls the range of ip addresses, dynamically assigned addresses are temporary, static ip addresses are necessary for some devices, key takeaways.
- DHCP automates the process of assigning IP addresses to devices connecting to a network, making it easier to connect multiple devices.
- DHCP allows you to control the range of IP addresses available for use, ensuring you can limit the number of devices connected to your network.
- While DHCP assigns IP addresses temporarily, static IP addresses are necessary for certain devices (e.g. servers) to maintain consistent connectivity and configuration.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is integral to networks and controls what IP addresses devices receive so they can communicate with the internet. Usually, IP assignment is automated, but if you need static IPs, familiarity with DHCP is essential.
Every device that connects to a network needs an IP address . In the early days of networking, users manually assigned themselves an IP address, but that's a cumbersome task, especially for places with many devices, such as a corporate office. DHCP, in part, automates this process, which makes connecting devices to the network far easier. DHCP servers or routers handle this process based on a set of defined rules. Most routers are set to use a 192.168.0.x range, for instance, so you'll commonly see IP addresses like this in home networks.
The process is pretty straight forward. When a client (a computer, IOT device , tablet, cell phone, etc.) connects to the network, it sends out a signal (called DHCPDISCOVER) to the DHCP server (or router). The server responds with all the rules and settings for the network and an IP address for use (a DHCPOFFER). The client acknowledges the information and asks permission to use the assigned address (a DHCPREQUEST message). Finally, the DHCP server acknowledges the request, and the client is free to connect to the network.
You can configure DHCP to control the range of IP addresses available for use. If you state that range as starting at 192.168.0.1 and the end as 192.168.0.100, then all available addresses will fall somewhere within that range. You'll never see a device assigned to 192.168.0.101. Also, bear in mind that the start IP (192.168.0.1 in this example) is reserved for the router. Some routers only list a starting address and then include an option for a maximum number of users (which determines the end address).
The upside to this is you can control how many devices connect to your network simultaneously (no more than 100 in this example). But the downside is if you set the range too small you can unintentionally prevent connection of new devices. To allow for a lower range of IP addresses, DHCP servers only lease out IP addresses to devices.
When a DHCP server assigns an IP Address, it does so under a lease system. The machine retains this IP address for a set number of days, after which it can try to renew the IP address. If no renewal signal is sent (such as a decommissioned machine), then the DHCP server reclaims the IP address to assign to another device. When the renewal signal is detected, the device retains its IP address for another set of days. This is why your IP address may appear to change from time to time if you use the ipconfig option often.
It's possible for two devices to end up with the same IP, such as a virtual machine (VM) that spends most of its time offline. The VM won't be able to send the renew signal, so its IP address will be handed out to another machine. When the VM is brought back up, it still has a record of the old IP address (especially if restored from a snapshot), but it won't be able to use that IP address since it is taken. Without that permission, it can't connect to the network until a new IP is assigned. But using dynamic IP addresses should prevent this type of scenario.
If you have a network connected printer or media server (such as a NAS unit Plex Server, or game server), it would be inconvenient for them to have their IP addresses changed. Sometimes hosted services require special configuration to function correctly. For example, a Minecraft server requires that port 25565 is forwarded , and you may have software pointing to your NAS's local IP. If the local IP of the device changes, then any rules (like port forwards) applied to it won't work anymore.
While renewal of the lease can prevent this, it's still possible for the IP address to change. If your router is restarted, due to a power outage or because you're trying to solve a pesky problem , then all Dynamically generated IP addresses may be reassigned. For those scenarios, manually assigning a Static IP address will solve the problem.
The exact process for this varies, especially as router web interfaces can change from device to device even when made by the same manufacturer. On some routers, like the Eero Mesh Router kit , this may be referred to by another term, such as IP reservation. But a static IP address still needs to conform to any range rules, if they exist. Using a current IP address as the basis for a static IP is usually the easiest thing to do. Depending on the device and its Operating System, it may be possible to set a static IP at the device end instead of through the router or DHCP server. This may be necessary if the router itself doesn't support Static IP.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Think PowerShell
PowerShell for IT Pros
Configuring Windows DHCP, Part 3: Creating DHCP Reservations
Aaron Rothstein · August 22, 2017 · 2 Comments
Need to mix the convenience of DHCP with the consistency of a static IP? Use a DHCP reservation, and create them with PowerShell.
DHCP reservations explained
DHCP empowers us to automatically assign IP addresses to clients while adhering to standardized rules (address space, lease duration, DNS servers, etc). For most clients, we typically don’t care what IP address the client ends up with on any given day, but for other devices consistently connected to the network, there are benefits to having the device get the same IP every time. A prime example that everyone can relate to is a printer. If you have the printer shared through a print server, the print server needs to be able to consistently talk to the printer on a known IP address.
“A DHCP reservation is a permanent IP address assignment. It is a specific IP address within a DHCP scope that is permanently reserved for leased use to a specific DHCP client” ( tech-faq.com ).
In the previous post we created DHCP scopes. Let’s see how we can use PowerShell to create a DHCP reservation within one of those scopes.
Creating a DHCP reservation using PowerShell
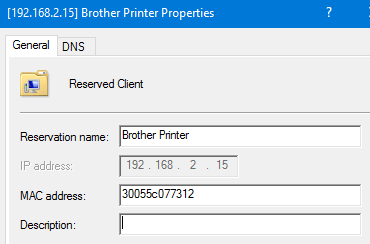
For this demo, we will reference a Brother HL-2270DW printer as the device for which we want to create a DHCP reservation. In order to create the reservation, we need the MAC address of the printer. Note that a device may have more than one MAC address, you will want to identify the MAC address for the interface you are connecting (wired or wireless).
The MAC address for my printer’s wired ethernet interface is 30055c077312. Given this information, I can use the PowerShell cmdlet Add-DhcpServerv4Reservation :
You can see that the reservation was successfully created using Get-DhcpServerv4Reservation or by using the MMC snap-in.
Copy DHCP reservations from an existing Windows DHCP Server
If you are already using a Windows DHCP server in your environment but are migrating to a new DHCP server, you can use PowerShell to copy the configured DHCP reservations from your old server to your new server. This will eliminate a lot of manual reservation creation or per-reservation scripting. The following example assumes you a have already created matching scopes on the New DHCP server from the old DHCP server:
Next Steps: Use PowerShell DSC resources xDHCPServer
Up to this point, we have used interactive PowerShell cmdlets to install and configure our DHCP server. While this is certainly a legitimate approach, in my next post we will configure the same server using a DSC configuration.
Reader Interactions
October 13, 2020 at 9:15 am
We have 3 DHCP Servers, how do I specify which server to make the Reservation on? I need to do it on all 3 servers.
December 20, 2020 at 12:28 am
I think the best approach would be to create a CimSession for the DHCP server you want to run your commands against, then specify the session object using the -CimSession parameter.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
IP Addressing: DHCP Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE 17 (Cisco ASR 920 Series)
Bias-free language.
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
DHCP Overview
- Configuring the Cisco IOS XE DHCP Server
- Configuring the Cisco IOS XE DHCP Client
- Implementing DHCP for IPv6
- IPv6 Access Services: DHCPv6 Relay Agent
- IPv6 Access Services: DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
- Configuring DHCP Features
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- IP Source Guard for an Interface
Chapter: DHCP Overview
Benefits of using dhcp, dhcp server relay agent and client operation, dhcp database, dhcp attribute inheritance, dhcp options and suboptions, dhcp server on-demand address pool management overview, additional references for dhcp overview, technical assistance.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is based on the Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP), which provides the framework for passing configuration information to hosts on a TCP/IP network. DHCP adds the capability to automatically allocate reusable network addresses and configuration options to Internet hosts. DHCP consists of two components: a protocol for delivering host-specific configuration parameters from a DHCP server to a host and a mechanism for allocating network addresses to hosts. DHCP is built on a client/server model, where designated DHCP server hosts allocate network addresses and deliver configuration parameters to dynamically configured hosts.
This module describes the concepts needed to understand Cisco IOS XE DHCP.
Information About DHCP
Cisco routers running Cisco IOS XE software include Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server and relay agent software. The Cisco IOS XE DHCP server is a full DHCP server implementation that assigns and manages IP addresses from specified address pools within the router to DHCP clients. These address pools can also be configured to supply additional information to the requesting client such as the IP address of the DNS server, the default router, and other configuration parameters. If the Cisco IOS XE DHCP server cannot satisfy a DHCP request from its own database, it can forward the request to one or more secondary DHCP servers defined by the network administrator.
DHCP supports three mechanisms for IP address allocation:
Automatic allocation—DHCP assigns a permanent IP address to a client.
Dynamic allocation—DHCP assigns an IP address to a client for a limited period of time, which is called a lease (or until the client explicitly relinquishes the address). DHCP also supports on-demand address pools (ODAPs), which is a feature in which pools of IP addresses can be dynamically increased or reduced in size depending on the address utilization level. ODAPs support address assignment for customers using private addresses.
Manual allocation—The network administrator assigns an IP address to a client and DHCP is used simply to convey the assigned address to the client.
The format of DHCP messages is based on the format of BOOTP messages, which ensures support for BOOTP relay agent functionality and interoperability between BOOTP clients and DHCP servers. BOOTP relay agents eliminate the need for deploying a DHCP server on each physical network segment. BOOTP is explained in RFC 951, Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) , and RFC 1542, Clarifications and Extensions for the Bootstrap Protocol .
The main advantage of DHCP compared to BOOTP is that DHCP does not require that the DHCP server be configured with all MAC addresses of all clients. DHCP defines a process by which the DHCP server knows the IP subnet in which the DHCP client resides, and it can assign an IP address from a pool of valid IP addresses in that subnet. Most of the other information that DHCP might supply, such as the default router IP address, is the same for all hosts in the subnet so DHCP servers can usually configure information per subnet rather than per host. This functionality reduces network administration tasks compared to BOOTP.
The DHCP implementation offers the following benefits:
Reduced Internet access costs
Using automatic IP address assignment at each remote site substantially reduces Internet access costs. Static IP addresses are considerably more expensive to purchase than are automatically allocated IP addresses.
Reduced server configuration tasks and costs
Because DHCP is easy to configure, it minimizes operational overhead and costs associated with device configuration tasks and eases deployment by nontechnical users.
Centralized management
Because the DHCP server maintains configurations for several subnets, an administrator only needs to update a single, central server when configuration parameters change.
Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) provides a framework for passing configuration information dynamically to hosts on a TCP/IP network. A DHCP client is a host that uses DHCP to obtain configuration parameters such as an IP address.
A DHCP relay agent is any host that forwards DHCP packets between clients and servers. Relay agents are used to forward requests and replies between clients and servers when they are not on the same physical subnet. Relay agent forwarding is distinct from the normal forwarding of an IP router, where IP datagrams are switched between networks somewhat transparently. By contrast, relay agents receive DHCP messages and then generate a new DHCP message to send on another interface.
The figure below shows the basic steps that occur when a DHCP client requests an IP address from a DHCP server. The client, Host A, sends a DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message to locate a DHCP server. A relay agent forwards the packets between the DHCP client and server. A DHCP server offers configuration parameters (such as an IP address, a MAC address, a domain name, and a lease for the IP address) to the client in a DHCPOFFER unicast message.
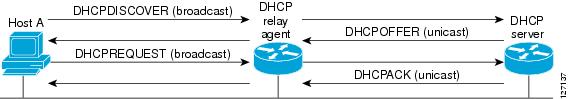
A DHCP client may receive offers from multiple DHCP servers and can accept any one of the offers; however, the client usually accepts the first offer it receives. Additionally, the offer from the DHCP server is not a guarantee that the IP address will be allocated to the client; however, the server usually reserves the address until the client has had a chance to formally request the address.
The client returns a formal request for the offered IP address to the DHCP server in a DHCPREQUEST broadcast message. The DHCP server confirms that the IP address has been allocated to the client by returning a DHCPACK unicast message to the client.
The formal request for the offered IP address (the DHCPREQUEST message) that is sent by the client is broadcast so that all other DHCP servers that received the DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message from the client can reclaim the IP addresses that they offered to the client.
If the configuration parameters sent to the client in the DHCPOFFER unicast message by the DHCP server are invalid (a misconfiguration error exists), the client returns a DHCPDECLINE broadcast message to the DHCP server.
The DHCP server will send to the client a DHCPNAK denial broadcast message, which means the offered configuration parameters have not been assigned, if an error has occurred during the negotiation of the parameters or the client has been slow in responding to the DHCPOFFER message (the DHCP server assigned the parameters to another client) of the DHCP server.
DHCP address pools are stored in non-volatile RAM (NVRAM). There is no limit on the number of address pools. An address binding is the mapping between the client’s IP and hardware addresses. The client’s IP address can be configured by the administrator (manual address allocation) or assigned from a pool by the DHCP server.
Manual bindings are stored in NVRAM. Manual bindings are just special address pools configured by a network administrator. There is no limit on the number of manual bindings.
Automatic bindings are IP addresses that have been automatically mapped to the MAC addresses of hosts that are found in the DHCP database. Automatic bindings are stored on a remote host called the database agent. A DHCP database agent is any host--for example, an FTP, TFTP, or RCP server--that stores the DHCP bindings database.The bindings are saved as text records for easy maintenance.
You can configure multiple DHCP database agents and you can configure the interval between database updates and transfers for each agent.
The DHCP server database is organized as a tree. The root of the tree is the address pool for natural networks, branches are subnetwork address pools, and leaves are manual bindings to clients. Subnetworks inherit network parameters and clients inherit subnetwork parameters. Therefore, common parameters (for example, the domain name) should be configured at the highest (network or subnetwork) level of the tree.
Inherited parameters can be overridden. For example, if a parameter is defined in both the natural network and a subnetwork, the definition of the subnetwork is used.
Address leases are not inherited. If a lease is not specified for an IP address, by default, the DHCP server assigns a one-day lease for the address.
Configuration parameters and other control information are carried in tagged data items that are stored in the options field of the DHCP message. Options provide a method of appending additional information. Vendors that want to provide additional information to their client not designed into the protocol can use options.
The Cisco IOS XE DHCP implementation also allows most DHCP server options to be customized. For example, the TFTP server, which stores the Cisco IOS XE image, can be customized with option 150 to support intelligent IP phones.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) allow the possibility that two pools in separate networks can have the same address space, with private network addresses, served by the same DHCP server. Cisco IOS XE software supports VPN-related options and suboptions such as the relay agent information option and VPN identification suboption. A relay agent can recognize these VPN-related options and suboptions and forward the client-originated DHCP packets to a DHCP server. The DHCP server can use this information to assign IP addresses and other parameters, distinguished by a VPN identifier, to help select the VPN to which the client belongs.
For more information on DHCP options and suboptions, see the “DHCP Options Reference” appendix in the Network Registrar User’s Guide , Release 6.3.
During lease negotiation, the DHCP server sends the options shown in the table below to the client.
The Cisco IOS DHCP server on-demand address pool (ODAP) manager is used to centralize the management of large pools of addresses and simplify the configuration of large networks. ODAP provides a central management point for the allocation and assignment of IP addresses. When a router is configured as an ODAP manager, pools of IP addresses are dynamically increased or reduced in size depending on the address utilization level.
ODAPs support address assignment using DHCP for customers using private addresses. Each ODAP is configured and associated with a particular Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN. Cisco IOS software also provides ODAP support for non-MPLS VPN address pools by adding pool name support to the peer default ip address dhcp-pool pool name command.
DHCP server subnet allocation is a way of offering entire subnets (ranges of addresses) to relay agents so that remote access devices can provision IP addresses to DHCP clients. This functionality can occur along with or instead of managing individual client addresses. Subnet allocation can improve IP address provisioning, aggregation, characterization, and distribution by relying on the DHCP infrastructure to dynamically manage subnets.
This capability allows the DHCP server to be configured with a pool of subnets for lease to ODAP clients. Subnet pools can be configured for global ODAP clients or MPLS VPN ODAP clients on a per-client basis. The DHCP subnet allocation server creates bindings for the subnet leases and stores these leases in the DHCP database.
Related Documents
Standards and rfcs.
address binding —A mapping between the client’s IP and hardware (MAC) addresses. The client’s IP address may be configured by the administrator (manual address allocation) or assigned from a pool by the DHCP server (automatic address allocation). The binding also contains a lease expiration date. The default for the lease expiration date is one day.
address conflict —A duplication of use of the same IP address by two hosts. During address assignment, DHCP checks for conflicts using ping and gratuitous (ARP). If a conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool. The address will not be assigned until the administrator resolves the conflict.
address pool —The range of IP addresses assigned by the DHCP server. Address pools are indexed by subnet number.
automatic address allocation --An address assignment method where a network administrator obtains an IP address for a client for a finite period of time or until the client explicitly relinquishes the address. Automatic allocation is particularly useful for assigning an address to a client that will be connected to the network only temporarily or for sharing a limited pool of IP addresses among a group of clients that do not need permanent IP addresses. Automatic allocation may also be a good choice for assigning an IP address to a new client being permanently connected to a network where IP addresses are sufficiently scarce that it is important to reclaim them when old clients are retired.
BOOTP —Bootstrap Protocol. A protocol that provides a method for a booting computer to find out its IP address and the location of the boot file with the rest of its parameters.
client —Any host requesting configuration parameters.
database —A collection of address pools and bindings.
database agent —Any host storing the DHCP bindings database, for example, a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server.
DHCP —Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A protocol that provides a mechanism for allocating IP addresses dynamically so that addresses can be reused when hosts no longer need them.
DNS —Domain Name System. A system used in the Internet for translating names of network nodes into addresses.
manual address allocation —An address assignment method that allocates an administratively assigned IP address to a host. Manual allocation allows DHCP to be used to eliminate the error-prone process of manually configuring hosts with IP addresses.
PWLAN —Public Wireless Local Area Network. A type of wireless LAN, often referred to as a hotspot, that anyone having a properly configured computer device can access.
relay agent —A device that forwards DHCP and BOOTP messages between a server and a client on different subnets.
server —Any host providing configuration parameters.
SSG —Service Selection Gateway. The feature set that provides on-demand service enforcement within the Cisco network.
Was this Document Helpful?

Contact Cisco
- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract )
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Static IP Address assignment vs DHCP address assignment
I manage a small-ish network that consists of less than 70 nodes. The previous system administrators opted to have a dhcp server and manually set dhcp addess.
I have opted to rather use dhcp address assignment instead of static address assignment except for my domain controllers and EXS hosts. I have been critised for following this scheme, but its way easy for me to manage the address scope with out having to scan the network for available ip addresses. Am i on the right track or have i lost the plot?
7 Answers 7
Why were you criticised for doing it that way? I mean I think it's crazy not to use DHCP for workstations at least, but maybe there is something specific to the environment that changes that equation.
The only issue I can see with DHCP is ensuring that your scope is properly created and doesn't cross over with the pool of static addresses you use (even that can be got around with reservations but its more work than needed).
That aside, users should never ever need to know whether or not you use DHCP because their workstation should 'just work', except for when the DHCP server is not available (and if that's an issue, you just have more than one DHCP server online).
EDIT: Convict makes a good point about documentation, make sure you do have the IP address ranges documented, explaining what you've done, why and how to find it. I don't think people are comfortable with the idea that some tools are "self documenting" (and to an extent they might have a point, how would you easily re-create your DHCP database with all your reservations, if you couldn't restore from backup?).
- I too am seriously curious! What reasons were given for this criticism? – quux Jun 10, 2009 at 8:21
- previous network admins assignment addresses in the dhcp pool to servers, without excluding those addresses. Since 95% of the computers are infact servers offering custom applications i prefer to assign these 'servers' addresses by way of dhcp reservation – biosFF Jun 10, 2009 at 8:27
- @biosff - well the way you're doing things there certainly makes sense. I'm still boggling at the idea you'd get criticised for it, few of our users know or care about whether we use DHCP or a dartboard to assign and manage IP addresses and as long as things work they don't care either! – Rob Moir Jun 10, 2009 at 8:49
- 1 The documentation is the DHCP database, IMHO. You should back it up and test restoring it. Why keep separate documentation that will fall out of date when you can use the database / config file that drives the DHCP server as the authoritative documentation? – Evan Anderson Jun 10, 2009 at 12:03
- Evan, I'm inclined to agree but that makes people who don't understand that uncomfortable. At the very least you need to write a puff piece of documentation explaining what you've done and where to look and how to pick it all up. – Rob Moir Jun 10, 2009 at 12:31
Yes, I think you're on the right track.
I suspect that you're being criticised because ...
of the lack of documentation about your network, rather than your choice of technology to assign an IP address;
you're doing IP address assignment differently to the way it's always been done . You're challenging the status quo.
Ask more questions to find out the real reason for the criticism. You may have to teach your detractors about DHCP and its benefits to your network administration.
People will come around to your way of configuring the network once they see how much easier it is to add another workstation to the network when the IP address is allocated by DHCP. DHCP should mean the end of those pesky duplicate IP address allocation errors that have plagued your network in the past.
When you say the previous administrators "manually set DHCP address" do you mean static assignments?
If so, this is generally the easier way to manage pools of workstations on a LAN. Statically tie each machine's MAC address to a specific IP and deliver them by DHCP. You get the trade off of knowing exactly where each machine is and being able to change the assignments without visiting each discrete machine.
Adding my vote to DHCP all the way. I can't understand why someone would criticise you for suggesting this, the whole point is to make it easier to manage the address scope, and as soon as you have more than 5 or so workstations, it makes sense.
About the critics: there are still people around, that don't know DHCP with StaticIP via the MAC-Adress. They think, that DHCP = CHAOS, so you better tell em whats really in the bag.
I also can recommend different IP-ranges, something like this:
1-9 important Servers (static) 10-99 misc. Servers (static) 100-150 Sales & Marketing (DHCP with MAC) 151-200 Developers (DHCP with MAC) 200-253 Tech.Stuff (DHCP with MAC)
Another vote for DHCP is, that you can handle all IPs from one, central instance.
- 1 Tee-hee... I remember when I "cared" what host portions of their IP address were assigned to certain kinds of computers, devices, etc. I'm glad I let go of that. (Which network portion that gets assigned matters a lot, and is related to the VLAN the host lives in. As far as host portions of IP addresses, though, I couldn't care less. I have dynamic DNS, reverse lookup zones, and DHCP reservations... the host portion of the IP address is meaningless to me.) – Evan Anderson Jun 10, 2009 at 12:05
DHCP is by far the best choice as soon as you have more than a few stations.
Static entries should be for servers and communication devices.
I use IP range: Static .1 - .50 for servers, printers, routers, etc. DHCP .51 - .150 for workstations
- 1 "Static" and "DHCP" are not exclusive. It is very common to use DHCP to deliver static addresses (see mh's reply). – bortzmeyer Jun 10, 2009 at 19:58
One possible disadvantage to this is that it introduces a startup order dependancy: things which DHCP need to wait for the DHCP server to come up.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged networking ip dhcp ip-address ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Why configuration is so complicated
- Featured on Meta
- New Focus Styles & Updated Styling for Button Groups
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network
Hot Network Questions
- Do I need permissions to list companies using my library?
- A C header-only log-structured database
- Does Casting Enlarge/Reduce on a College-of-Creation-Bard's Dancing Item Cause that Item to be Inanimate?
- How to decode this Notam?
- Is there an infinite number of logic systems?
- Were people allowed to smoke on TV in the past?
- What is "Vancian" magic in D&D?
- Companies carrying out private investigations and prosecutions
- Comprehensive tutorial for CASTEP without Material Studio Visualizer
- What does "in her November of life" mean in "Persuasion"?
- Is it possible for magical Universities to become powerful political entities, and is my structure for the same sensible?
- Is this dialogue Got or get?
- How do you stay stable when landing/ Taking off on an F-35 during a VTOL landing/Takeoff?
- How do you iterate through raster bands using model designer in QGIS?
- What is the point of knowing symmetries, conservation quantities of a system?
- Why do valence electrons not push each other away?
- Double parenthesis in academic writing
- Looking for the specific font in the screen shot
- What is the difference between "more like X than Y" and "more like X than like Y"?
- Does "unique mere existence" imply "existence"?
- Can my username include a D&D monster?
- Mathematica yields repeated solutions when only one exists
- How can I regenerate the randomized MAC address on Android?
- Risk of not capping old hose spigot
Configure IP Reservation on DHCP – Windows Server 2022
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server dynamically assigns an IP address and other network configuration parameters to each device on a network. DHCP reservation is a permanent IP address assignment. It is a specific IP address within the DHCP scope that is permanently reserved for a specific DHCP client.
This step-by-step tutorial covers how to Configure IP Reservation on Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). In order to Configure DHCP Reservation in Windows Server 2022, you will need the MAC address information of the client device.
Server demo environment
- Computer Name: server1.test.com
- Operating System: Windows Server 2022 Datacenter
- IP Address: 192.168.3.3
- DHCP Scope: 192.168.3.150 to 192.168.3.200
Prerequisite Required
- Install and configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- Create DHCP Scope
Related tutorial
- Install and configure DHCP on Windows Server 2022
Backup DHCP Server
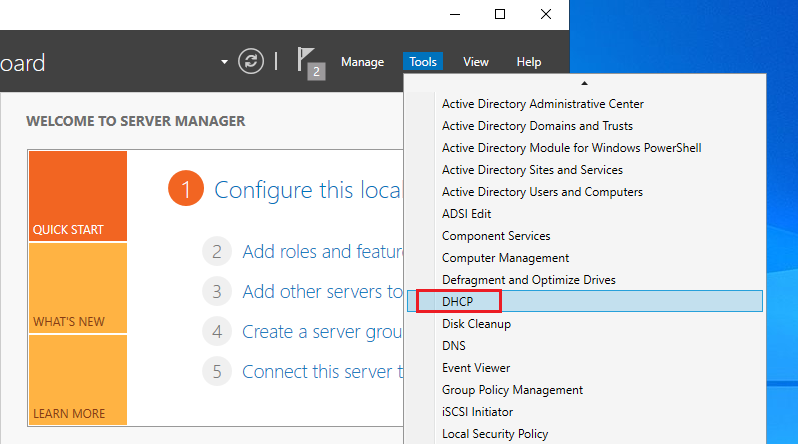
1. Open the Server Manager dashboard, click Tools , and select DHCP .
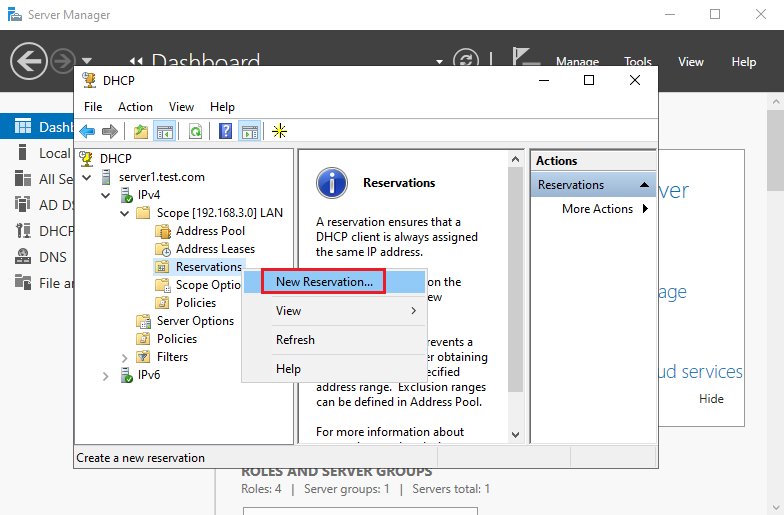
2. Open Scope right-click on Reservations and select New Reservation .
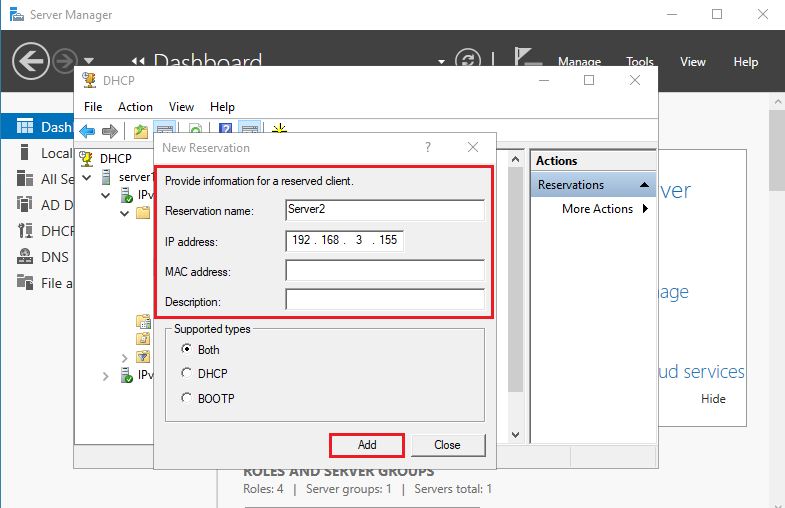
3. Enter Reservation name (specify the network name of the device), Enter IP address (specify the IP address from your DHCP scope that you want to assign to the device), Enter MAC address (MAC address of the client machine) and click Add .
- The MAC address of the Windows device can be found using the ‘ Ipconfig /all ’ command.
DHCP Reservation has been configured, restart the client device for which we have created a reservation.
Windows devices command prompt commands
- ‘ ipconfig /release ’: Release the existing IP address
- ‘ ipconfig /renew ’: Renew an IP address
Client Demo environment
- Computer Name: server2.test.com
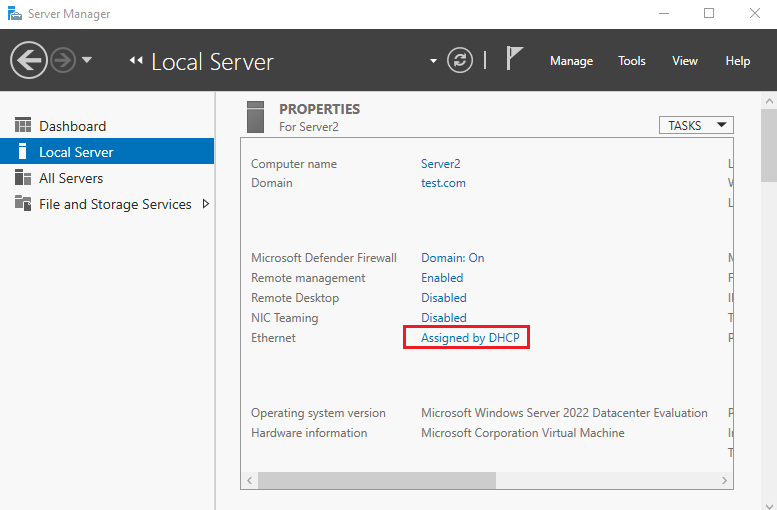
The IP address is assigned by DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) by default. Make sure the client and the server are on the same network.
4. Open Server Manager Select the local server, and Click Assigned by DHCP .
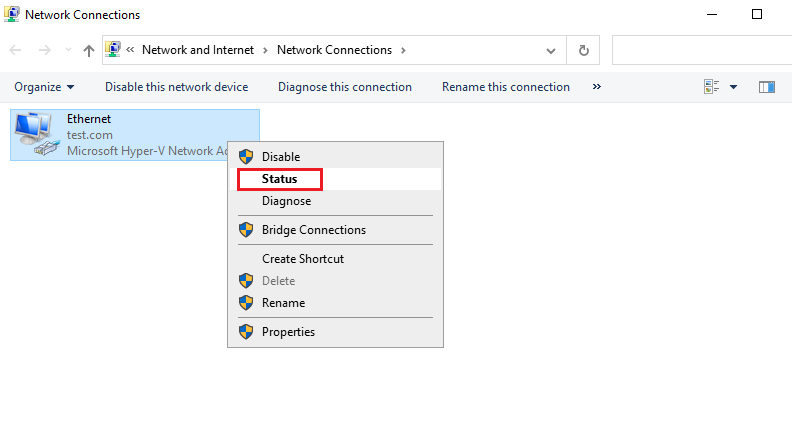
5. Right-click on the Ethernet adapter and click Status .
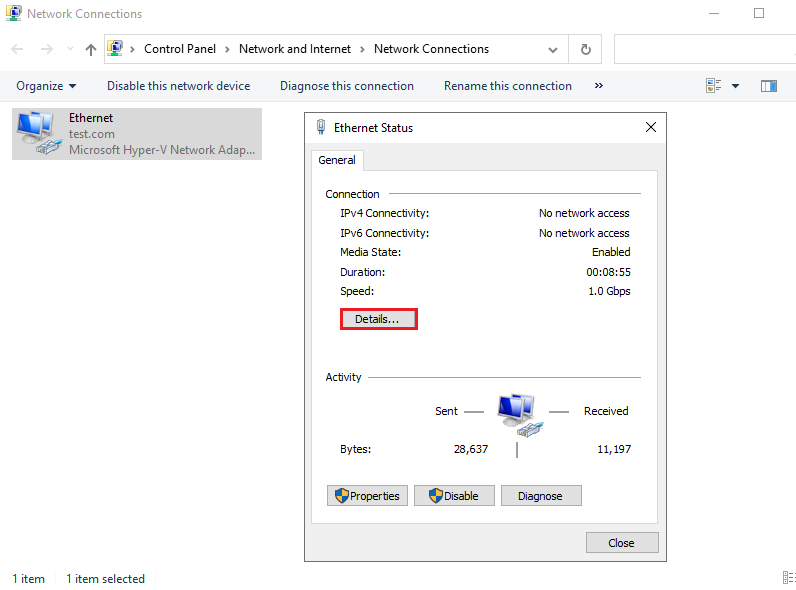
6. Click Details for Network Connection Details.
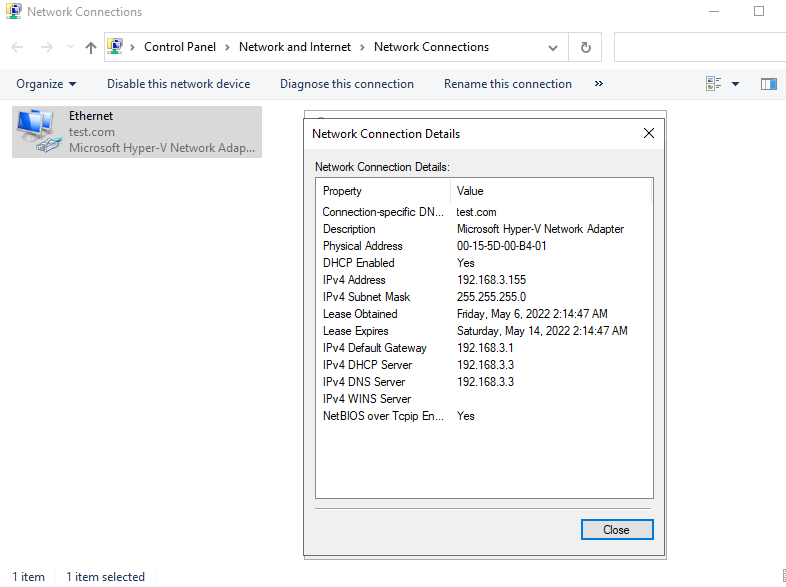
7. Verify the IP address and click Close .
Related Tutorials

Configure permissions on a shared folder – Windows Server 2022

Schedule Automatic Shutdown in Windows Server 2022

Install and Configure Windows Admin Center on Windows Server 2022

Install SQL Server 2022 on Windows Server 2022
What Is Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)?
- Get Free Cybersecurity Training

Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Meaning
What is DHCP? Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is used to dynamically assign Internet Protocol (IP) addresses to each host on your organization's network. In this DHCP meaning, a host can refer to any device that enables access to a network. Some examples include desktop computers and laptops, thin clients, and personal devices, among others. DHCP ensures all of these devices get assigned an IP address .
In the context of this DHCP definition, DHCP also assigns Domain Name System (DNS) addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways. All of these enable devices to communicate with the internet and each other within the confines of your network.
How Does the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Work?
DHCP protocols send messages to devices that connect to your network, providing them with what they need to interface with essential network functions. Imagine if you have a small home network that allows your laptop, your tablet, and your phone to connect to it. If you have to assign an IP address to each one, that may not be too difficult, especially because there are only three devices.
On the other hand, assigning IP addresses, as well as subnet masks, DNS addresses, and other essential data would take far too much work and time if you have to do so for a few hundred devices. DHCP automatically provides this information to all of the devices that connect to your network.
DHCP Components
The primary DHCP components include a DHCP server, client, and relay.
DHCP Server
A DHCP server is what the system uses to automatically provide IP addresses and additional network parameters to the devices that connect to your network. It is able to provide temporary or dynamic IP addresses taken from a pool of available addresses.
In addition, a DHCP server gives permanent IP addresses and DHCP configuration parameters, including those pertaining to subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS servers.
DHCP Client
A DHCP client is a device that acts as a host, and it receives the information sent from the DHCP server. This includes any device that can connect to the network and needs data from the DHCP server to interact with the network.
A DHCP relay refers to any transmission control protocol/IP (TCP/IP) host that forwards DHCP messages between servers and clients. A DHCP relay plays an essential role, for instance, when a network consists of several subnetworks. In this case, a DHCP relay enables one DHCP server to provide the necessary information to all of the clients on both the primary network and subnet.
Security Considerations for Using DHCP
To ensure your DHCP servers do not present significant risk, there are a few DHCP security-related issues to keep in mind:
1. A DHCP server can only provide a limited number of IP addresses. This means an attacker may be able to launch a denial-of-service (DoS) attack by requesting so many IP addresses, rendering essential devices unable to connect.
2. It is also possible for an attacker to use a false DHCP server to provide fraudulent IP addresses to the clients on your network.
3. Users that get an IP address also get the DNS address—meaning, it is possible they can obtain more data than they should from those servers. It is best to limit the access that people have to your network, as well as use firewalls and secure connection tunnels via virtual private networks (VPNs) .
Protection Against DHCP Starvation Attack
A DHCP starvation attack involves a malicious actor inundating a DHCP server with requests for IP addresses until it cannot provide any more. This puts the hacker in a position to deny requests from authorized network users, as well as set up an alternative DHCP connection that can pave the way for a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack .
Best Practices for DHCP Deployment
To enable a smooth, effective DHCP deployment, there are a few best practices that you can follow including:
1. Avoid Putting DHCP on Your Domain Controller
Your domain controller should only be responsible for performing core functions, particularly managing your DNS. If you avoid putting DHCP on your domain controller, you can avoid overwhelming it with additional work.
This enhances network security because it prevents those connecting to your guest Wi-Fi from having access to your domain controller. By preventing this interaction, you keep your attack surface small, especially because you deny a hacker that signs in to your guest Wi-Fi access to your domain controller. If they are able to access this sensitive system, they could hack your DNS.
2. Use DHCP Failover
Like other kinds of failover , DHCP failover helps ensure you always have a DHCP server to share the essential information needed by hosts in your network. In the event the primary DHCP server goes down, the additional server will provide the DHCP information clients need.
3. Avoid Using Static IP Addresses When Possible
Deciding between DHCP vs static IP can be a challenging puzzle. What does DHCP stand for? Well, the “dynamic” element of the acronym is important when it comes to maintaining seamless network operations, particularly because it enables the system to change DHCP data as needed. A static IP address is one that does not change. Even though this may seem like a logical decision for devices you feel will always be connected to your network, it can cause problems.
Suppose, for example, you have to replace that device with an identical but new one. This may require your IT team to manually assign an IP address to the device so it can connect with others in your network, which could take time. Of course, for some devices, such as routers and switches, you need a fixed IP address, primarily because they serve as “connection hubs,” and if their IP address continually changes, the network will not function smoothly.
‘Learn More about Static vs Dynamic IP ’

Reasons Why Enterprises Must Automate DHCP
It is important for enterprises to automate their DHCP system because it helps eliminate time-consuming manual work that could otherwise consume a lot of your IT team’s energy.
For example, there are a lot of problems, such as printers not connecting with the network or subnets not interfacing with the main network, that can result from DHCP-related issues. By automating your DHCP functions, the system can automatically prevent many of these issues.
Automated DHCP also makes it easier to scale your operations. Instead of having to bring in more people to manually handle what an automated system could manage, you can invest your human resources in other growth-related tasks.
How Can Fortinet Help
Even though DHCP can ease the burden of network administrators, there is still a lot on their plates, especially when it comes to gaining visibility into what is happening within the organization’s system. By using FortiGate Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) , network admins can gain better visibility into the nature of the traffic entering and exiting the network. Further, because FortiGate inspects individual data packets for threats, administrators can provide all users with a more secure online experience.
What is DHCP and why is it used?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a networking protocol for dynamically assigning IP addresses to each host on your organization's network. DHCP also assigns Domain Name System (DNS) addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways.
What are best practices for DHCP servers?
Some best practices for DHCP servers are to avoid putting DHCP on your domain controller, use DHCP failover, and avoid using static IP addresses when possible.
Quick Links

Free Product Demo
Explore key features and capabilities, and experience user interfaces.
Resource Center
Download from a wide range of educational material and documents.

Free Trials
Test our products and solutions.
Contact Sales
Have a question? We're here to help.
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Step-by-Step: Configure DHCP Using Policy-based Assignment
Updated: May 27, 2016
Applies To: Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server role in Windows Server 2012 introduced a new policy based IP address assignment feature. Policy based assignment (PBA) allows an administrator to group DHCP clients by specific attributes based on fields contained in the DHCP client request packet. This feature allows for targeted administration and greater control of configuration parameters delivered to network devices.
In this guide
This guide provides step-by-step instructions for deploying DHCP policy based assignment in a test lab using one server computer and two client computers. Software and hardware requirements are provided, as well as an overview of DHCP policy based assignment.
The following instructions are for configuring a test lab using the minimum number of computers. Individual computers are needed to separate the services provided on the network and to clearly show the desired functionality. This configuration is neither designed to reflect best practices nor does it reflect a desired or recommended configuration for a production network. The configuration, including IP addresses and all other configuration parameters, is designed only to work on a separate test lab network.
DHCP policy based assignment overview
With a DHCP server running Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2, administrators can define an address assignment policy at the server level or scope level. A policy contains a set of conditions to evaluate when processing client requests. Policy based assignment enables flexibility for some common scenarios, including:
Multiple device types : A network includes many different DHCP client devices, such as printers, IP phones, and desktops. Administrators need the ability to classify these devices using different IP address ranges. This enables router policies and quality of service (QoS) based on IP address range policies to control network access or traffic. For example, you can add a vendor class of “Hewlett-Packard JetDirect” or Cisco Systems, Inc. IP Phone CP-7940G and configure printer and IP-phone policies to assign a specific IP address range to these devices.
Multiple roles : A network includes different types of computers, such as laptops, desktops, and servers in the same subnet. Depending on the type of client, the administrator might wish to provide different lease duration settings. All the wireless clients that connect via a specific relay agent can be assigned a four-hour lease duration. DNS dynamic update protocol can be disabled for clients matching this policy. Similarly, a server policy can be created using a list of server MAC addresses. Servers can be assigned a 12-day lease duration
Virtualization : A data center network employs virtualization for different workloads and applications. Virtual machines are added and removed dynamically depending upon load requirements at a given time. An administrator wishing to route traffic on the network differently for VMs can create a policy based on MAC address prefix to assign a short lease duration, specific IP address range, and different default gateway.
The following fields in the DHCP client request are available when defining policies.
Vendor Class
MAC address
Client Identifier
Relay Agent Information
Policy settings and evaluation
Policy settings can be of three types.
IP address range : The IP address range within a scope from which to assign an IP address to a client. A server level policy cannot have a setting for an IP address range.
Standard DHCP options : One or more standard DHCP options to send to a client in the response based on the options requested by the client in the parameter request list.
Vendor specific DHCP options : One or more vendor specific DHCP options to send to the client based on the vendor class field in the client request.
The DHCP server evaluates policies sequentially according to an assigned processing order. The DHCP administrator assigns the processing order to the policies. If policies exist at the server and scope levels, the server applies both sets of policies and evaluates the scope policies before the server policies. The processing order for a scope level policy defines the order of evaluation within the scope. If there are no policies defined at the scope level, the policies at the server level apply to the scope.
Address assignment
The DHCP server determines the scope to which a DHCP client belongs based on the gateway IP address of the relay agent or the interface of the DHCP server on which it receives the DHCP client packet. Once the server determines the client scope, the server evaluates the DHCP packet against the policies applicable for the scope in the processing order specified. The policies applicable at a scope are those configured at the scope and those inherited from the server. A single client request can match multiple policies.
If a client request matches the conditions of a policy for which a specific IP address range is associated, the server will assign the first free IP address from the range as determined by the rule. If a policy is associated with multiple address ranges, the server will assign IP addresses by first attempting to assign an IP from the lowest address range. If no IP addresses are available to use from the lower address range, the server will then look for a free IP address from the higher address ranges. If no IP addresses are free from any of the address ranges associated with the policy, the server will process the next matched policy as defined by the processing order.
If none of the matched policies has a free IP address, the server will drop the client packet and log an event. If a DHCP client packet does not match any of the policies applicable for the scope, or none of the matched policies for a client packet is associated with an IP address range, the server will lease the client an IP address from the IP address range configured for the scope exclusive of any policy-specific IP address ranges.
Option assignment
A DHCP client uses the parameter request list field in a DHCP packet to request a list of standard options from the server. The option assignment processing for a client is similar to that of IP address assignment. The DHCP server evaluates the fields in the client request against each policy applicable for the scope in the processing order specified. If the client request matches the conditions of any of the policies applicable for the scope, and its settings include specific options, the server returns these options to the client. If multiple policies match the client request, the server returns the sum of the options specified for each of the matched policies. The DHCP server sends vendor class options to the client based on the vendor class contained in the DHCP client request.
Scenario overview
This test lab demonstrates new DHCP functionality in Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2. One server computer and two client computers are used. See the following figure.
.jpeg)
Hardware and software requirements
One server computer and two client computers are required to complete the test lab.
The following are required components of the test lab:
The product disc or other installation media for Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2.
One computer that meets the minimum hardware requirements for Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2.
At least one DHCP client computer is required.
The lab uses two computers running Windows® 8. If only one client computer is available, or clients are not running Windows 8, you must alter some of the procedures in the test lab accordingly.
Steps for configuring the test lab
The following procedures are used to configure computers for the demonstration portion of the test lab:
Configure DHCP1 : DHCP1 is a domain controller, DNS server, and DHCP server for the contoso.com Active Directory domain.
Configure Client1 : Client1 is a DHCP client computer.
Configure Client2 : Client2 is a DHCP client computer.
Configure DHCP1
DHCP1 is a computer running Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2, providing the following services:
A domain controller for the contoso.com Active Directory domain.
An authoritative DNS server for the contoso.com DNS zone.
A DHCP server.
Initial configuration of DHCP1 consists of the following steps:
Install the operating system and configure TCP/IP on DHCP1
Install ad ds, dns server, and dhcp server, create a domain administrator account, create a dhcp scope on dhcp1, to install the operating system and configure tcp/ip on dhcp1.
Start your computer using the Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2 product disc or other digital media.
When prompted, enter a product key, accept license terms, configure clock, language, and regional settings, and provide a password for the local Administrator account.
Press Ctrl+Alt+Delete and sign-in using the local Administrator account.
If you are prompted to enable Windows Error Reporting, click Accept .
Click Start , type ncpa.cpl , and then press ENTER . The Network Connections control panel will open.
The previous step demonstrates the functionality in Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2 that enables you to search and run applications, settings, and files by clicking Start and then typing a search term. You can also open the Network Connections control panel by clicking next to Ethernet in Server Manager using the Local Server view. For more information, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012 ( https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/p/?LinkId=242147 ).
In Network Connections , right-click Ethernet and then click Properties .
Double-click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) .
On the General tab, choose Use the following IP address .
Next to IP address type 10.0.0.1 and next to Subnet mask type 255.255.255.0 . It is not necessary to provide an entry next to Default gateway .
Next to Preferred DNS server , type 10.0.0.1 .
Click OK twice, and then close the Network Connections control panel.
DHCP1 will serve as a domain controller, DNS server, and DHCP server for the contoso.com Active Directory domain.
To configure DHCP1 as a domain controller, DNS server, and DHCP server
The Server Manager Dashboard is displayed by default. In the navigation pane, click Configure this local server .
Under PROPERTIES , click the name next to Computer name . The System Properties dialog box will open.
On the Computer Name tab, click Change and then type DHCP1 under Computer name .
Click OK twice, and then click Close .
When you are prompted to restart the computer, click Restart Now .
After restarting the computer, sign-in using the local Administrator account.
In Server Manager, under Configure this local server , click Add Roles and Features .
In the Add Roles and Features Wizard , click Next three times, and then on the Select server roles page select the Active Directory Domain Services checkbox.
When you are prompted to add required features, click Add Features .
Select the DHCP Server checkbox.
Select the DNS Server checkbox.
Click Next five times, and then click Install .
Wait for the installation process to complete, verify on the Installation progress page that Configuration required. Installation succeeded on DHCP1 is displayed, and then click Close .
Click the Notification flag and then click Promote this server to a domain controller . See the following example.
.jpeg)
In the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard , on the Deployment Configuration page, choose Add a new forest and then next to Root domain name , type contoso.com .
Click Next , and then on the Domain Controller Options page, under Type the Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) password , type a password next to Password and Confirm password . Confirm that Domain Name System (DNS) server and Global Catalog (GC) are selected, and then click Next .
Click Next four times, verify that All prerequisite checks passed successfully is displayed, and then click Install .
The computer will restart automatically to complete the installation process.
Sign in using the local Administrator account.
A domain administrator account is required to configure settings in the test lab.
You can use the CONTOSO\Administrator account in this test lab and skip creation of a domain administrator account if desired. This account has domain administrator privileges, and other privileges. However, it is a best practice to disable or rename this account. For more information, see Active Directory Best Practices ( https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/p/?LinkID=243071 ).
To create a domain administrator account
On the Server Manager menu bar, click Tools , and then click Active Directory Users and Computers .
In the Active Directory Users and Computers console tree, double-click contoso.com , right-click Users , point to New , and then click User .
In the New Object – User dialog box, type user1 under User logon name and next to Full name , then click Next .
Next to Password and Confirm password , type a password for the user1 account.
Clear the checkbox next to User must change password at next logon , select the Password never expires checkbox, click Next , and then click Finish .
Click the Users folder, and then double-click user1 and then click the Member Of tab.
Click Add , type domain admins under Enter the object names to select , click OK twice, and then close the Active Directory Users and Computers console.
Click Start , click Administrator , and then click Sign out .
Sign in to the computer using the user1 credentials. Click Other user and then type the user1 name and password.
Next, create a DHCP scope on DHCP1.
To create a DHCP scope on DHCP1
On the Server Manager menu bar, click Tools and then click DHCP . The DHCP console opens.
In the DHCP console tree, navigate to IPv4 . Right-click IPv4 and then click New Scope . The New Scope Wizard opens.
Click Next and then type a name for the new scope next to Name (ex: Contoso-scope1).
Click Next and then in IP Address Range , type 10.0.0.1 next to Start IP address , type 10.0.0.254 next to End IP address , and type 24 next to Length . The value of Subnet mask will change automatically to 255.255.255.0 .
Click Next , and then in Add Exclusions and Delay type 10.0.0.1 under Start IP address , type 10.0.0.10 under End IP address , and then click Add . This allows the first ten IP addresses in the 10.0.0.0/24 subnet to be used for static addressing of servers on the network.
Click Next and then in Lease Duration under Limited to enter 0 Days , 0 Hours , and 2 Minutes . This very short lease duration will simplify the DHCP demonstration.
Click Next three times, and then in Domain Name and DNS Servers , verify that the Parent domain is contoso.com and 10.0.0.1 is listed as the only DNS server.
Click Next twice, and then in Activate Scope select Yes, I want to activate this scope now .
Click Next , and then click Finish .
In the DHCP console tree, right-click dhcp1.contoso.com , and then click Authorize .
Refresh the view in the DHCP console and verify that DHCP1 is authorized and that the Contoso-scope1 is active.
Note: To review scopes on the current server using Windows PowerShell, right-click Windows PowerShell , click Run as Administrator , click Yes in the User Account Control alert that appears, and then type the following command at the Windows PowerShell prompt, and then press ENTER.
Configure Client1
Client1 is a computer running Windows® 8 that is acting as a DHCP client.
Configuration of Client1 consists of the following steps:
Install the operating system on Client1
Pin windows powershell to the taskbar.
During the demonstration portion of the test lab, Client1 will be used as a DHCP client.
To install the operating system on Client1
Start your computer using the Windows 8 product disc or other digital media.
When prompted, enter a product key and accept license terms.
When prompted to enter a computer name, type Client1 and click Next .
Click Use express settings .
On the Sign in to your PC page, click Don’t want to sign in with a Microsoft account and then click Local account .
Next to User name , type user1 , enter a password and password hint, and then click Finish .
The DHCP failover demonstration on Client1 makes use of Windows PowerShell to verify DHCP lease information. To make Windows PowerShell more easily accessible, it will be pinned to the taskbar.
To pin Windows PowerShell to the taskbar
The Start menu is displayed by default. If Start is not displayed, move the mouse cursor to the lower left corner of the screen until Start is displayed, and then click Start .
Type powershell and then under Results for “powershell” right-click Windows PowerShell and then click Pin to taskbar .Confirm that Windows PowerShell is pinned to the taskbar.
Client1 can also be joined to the contoso.com domain; however this is not required to complete the test lab.
Configure Client2
Client2 is a computer running Windows 8 that is acting as a DHCP client.
Configuration of Client2 is nearly identical to Client1. To configure Client2, repeat the identical procedures used to configure Client1, except when you enter a computer name, type Client2 instead of Client1.
DHCP policy based assignment demonstration
For the DHCP policy based assignment demonstration portion of the test lab, a MAC address based policy will be configured to assign unique DHCP options and IP address ranges to Client1 and Client2.
A demonstration of DHCP policy based assignment on Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2 consists of the following procedures:
Determine MAC addresses
Create policies, demonstrate policies.
Unique MAC addresses on Client1 and Client2 will be used to match different DHCP policies.
To determine MAC addresses
On DHCP1, open the DHCP console and navigate to IPv4\Scope [10.0.0.0] Contoso-scope1\Address Leases .
Click Address Leases and then in the details pane write down the MAC addresses listed for Client1 and Client2 under Unique ID .
.jpeg)
The DHCP Policy Configuration Wizard will be used to create a unique policy for Client1 and another policy for Client2. A policy configured for an individual computer is not typical and is only configured for demonstration purposes. On a corporate network, you can use wildcards and other conditions to match multiple DHCP client devices.
To create policies
In the DHCP console, under Scope , right-click Policies and then click New Policy .
Ensure that you select the Policy folder under the Scope folder. This is the scope-level folder. The other Policies folder is for server-level policies and if you create a policy there you will not be able to create the IP address range policy for this exercise.
Next to Policy Name , type Client1 Policy , and then click Next .
On the Configure Conditions for the policy page, click Add .
In the Add/Edit Condition dialog box, choose MAC Address next to Criteria , type the MAC address for Client1 next to Value (001DB7A63D in this example), and then click Add , then click OK .
.jpeg)
Click Next , and then in Configure settings for the policy , type 10.0.0.100 next to Start IP address and type 10.0.0.199 next to End IP address .
.jpeg)
Click Next , and then under Available Options , select 003 Router , type 10.0.0.7 under IP address , and click Add .
Repeat the previous steps for Client2 using the following conditions, IP address ranges, and options:
Policy Name : Client2 Policy
Condition : MAC Address equals (in this example) 00155DB7A63E.
Start IP address : 10.0.0.200
End IP address : 10.0.0.254
003 Router : 10.0.0.8
Next, review the effect that these policies have on the IP address configuration of Client1 and Client2.
To demonstrate policies
In the details pane, under Policy Name , right-click one of the two policies you just created.
Note that you can move the policy up or down in the processing order, delete the policy, or disable the policy.
Click Properties .
Review the available parameters that you can edit on the General , Conditions , IP Address Range , Options , and DNS tabs.
Click OK , and then on Client1 type ipconfig /all at the Windows PowerShell prompt.
.jpeg)
Client1 has been assigned the first IP address in the 10.0.0.100 – 10.0.0.199 range, and a default gateway of 10.0.0.7, as determined by the policy based assignment.
If the IP address hasn't changed yet, you can type ipconfig /release and then ipconfig /renew to get a new lease.
Repeat the previous step on Client2.
.jpeg)
Client2 has been assigned the first IP address in the 10.0.0.200 – 10.0.0.254 range, and a default gateway of 10.0.0.8.
Policy based assignment in Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2 DHCP allows you to create simple yet powerful rules to administer DHCP on your network.
Additional resources
- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
- How to Read a Traceroute?
- How to Fix the SSL/TLS Handshake Failed Error?
- What is DSLAM?
- How to Calculate Number of Host in a Subnet?
- What is a Web Application Firewall?
- What is Anonymous FTP (File Transfer Protocol)?
- FTP Server Working and its Benefits
- What is a Switch Port?
- What is Frame Check Sequence?
- Why Does the OSI Reference Model Matter?
- What is BPDU Guard and How to Configure BPDU Guard?
- What are Web Shells?
- How to Set Up a LAN Network?
- What is Pilot Channel?
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol
- What Is Poison Reverse in Networking?
- How Many IP Addresses a Computer Can Have?
- What is a Loopback Address?
- How to Find the Proper MTU Size For a Network?
Setting IP Address Using DHCP Server
Every computer on the network has to have an IP address for communication purposes. An IP address is an identifier for a computer or device on a network. The IP address can be assigned in two ways i.e. Static IP or Dynamic IP.
Static IP : A static IP is where a user assigns an IP address manually. It has certain drawbacks for example you have 100 computers or devices in your network and you want to assign IP addresses to each one statically, so keep in mind that the IP address must be unique because if you assign the same IP address twice it would cause an IP conflict and it would not have access to a network.
Dynamic IP: A dynamic IP is where a computer gets an IP address from a DHCP server. A DHCP server automatically assigns a computer an IP address along with a subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server.
DHCP Server: A Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is an application layer protocol that is used to provide dynamic IP addresses to computers and devices. DHCP is a service that runs on a server, such as a Microsoft server or a Linux server. It’s also a service that runs on routers.
Why set the IP address using the DHCP server?
When a computer obtains an IP address from a DHCP server the server assigns the IP address on lease. The computer doesn’t own the IP address its lease and lease is the amount of time an IP address is assigned to a computer. For example, the lease could be for one day.
Another reason for lease is to make sure that the DHCP server does not run out of IP addresses. A DHCP server has its scope, let’s just say that this DHCP scope has only a range of three IP addresses so it can give only three IP addresses. Now obviously this is not so realistic as no network administrator is going to create a scope with such a small range. But for now, as an example let use this example let’s go ahead and add three computers to a network once they get added, a DHCP server is going to assign them IP addresses so in this example let’s just say that the IP address given to computers is not on lease so the DHCP has reached out its limit on giving IP address all these three IP addresses are currently being used.
What if one of the computers gets removed from the network. If a computer is removed it takes the IP address that it has been given with it. Let’s say another computer gets added to the network but the problem is the computer won’t be able to access the network because the DHCP server has run out of IP addresses. Even though that third computer has been removed it still occupies an IP address that could be used for another computer.
This is why the IP address leased and are not given permanently because if IP addresses are leased then this would tell the DHCP server which IP address is still being used and which ones are not being used so in this example the IP address are leased, after a certain period during lease a computer must send a signal to the server asking to the server to renew its list of the IP addresses. In another word, we can say informing the DHCP server that it is still present on the network and its IP address is still being used.
If a computer is removed from the network that computer not going to ask the DHCP server for renewal and if it doesn’t ask for renewal then the list will expire and then the IP address will go back to their IP address pool of servers. Now the IP address can be used for another computer and this is why the IP address is leased.
How to set the IP address using the DHCP server?
Lets us see practically how to assign an IP address using DHCP to your windows 10/8/7 computer step by step :
Step 1: Go to the control panel.
Step 2: Select the Networking and sharing option.
Step 3: Select change adapter setting.
Step 4: Select and open your internet, ethernet , or wi-fi connection to which you want to set the IP address using the DHCP server.
Step 5: Once you have done with Step 4 a pop-up of wi-fi status (in my case connected with wi-fi) will appear on your screen, now click on properties.

Step 6: Once you click on the properties option a new pop-up of wi-fi properties will appear on your screen. Now, select Internet Protocol version 4(TCP/IPv4) in some cases it may have IPv6. Once you select this option properties option will enable and once it is enabled click on that.

Step 7: After clicking on the properties option of the recent screen a new screen of Internet Protocol Version will appear where you have to go inside the general tab which by default opens and click on the option of obtain an IP address automatically along with this option click on obtain DNS server address automatically.

When we choose this option computer will broadcast a request for an IP address on the network then the DHCP server will assign an IP address from its pool and deliver it to the computer. once it is done you can verify that the DHCP server has given address to your computer or not by opening a command prompt on your system and typing a command ipconfig /all and you can see there is DHCP enable or not along with IPv4 or IPV6 address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
All of these settings are given by the DHCP server. Dynamic IP addressing is the best choice because it automatically manages the network and makes the process a lot easier.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- Computer Subject

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
What is DHCP? It assigns addresses dynamically
Servers and clients use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol to automatically assign IP addresses within a network.
The answer to “What is DHCP?” is that it’s the standard mechanism to dynamically assign IP addresses within a network. It stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
IP, or Internet Protocol, addressing is a logical means of assigning addresses to devices on a network. Each device connected to a network requires a unique IP address.
At home, dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) assigns IP addresses to your smartphones, laptops, tablets, and devices like doorbell cameras. When you use wifi on your home network, typically your router is a DHCP server.
In a large enterprise setting, a DHCP server is usually a dedicated computer. By simplifying IP address management, it saves money, is more secure, and doesn’t eat up valuable admin time.
In this glossary entry, we’ll explore the fundamentals of how DHCP works. Then, we’ll take a deeper look at two aspects: dynamic addressing and the communications protocol.
How does DHCP work?
DHCP is a network management protocol. A client device (or DHCP client), such as a laptop, joins a network and requests an IP address. The request is made to a DHCP server.
These servers are often configured with redundancy—often called DHCP failover —or clustering among other network servers. Servers can run on both IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
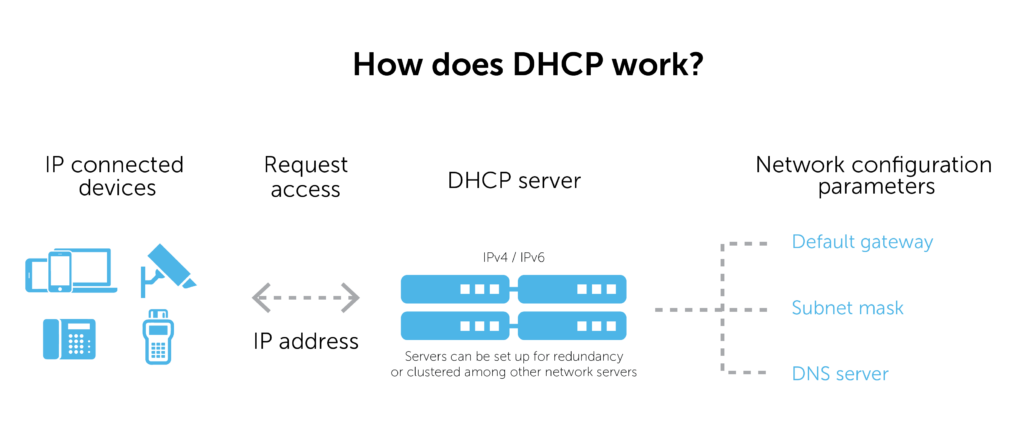
The server will quickly and automatically assign an IP address and some related network configuration parameters. Once the device has accepted the assignment, it can communicate with both the internal network and the public internet.
Relevant parameters
In addition to assigning IP addresses, these servers also provide relevant parameters, known as DHCP options. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), the global coordinator of IP addresses, defines available DHCP parameters .
Options number in the hundreds. Key among them is how long the IP address can be used—known as the lease time. They also include the default gateway, its subnet mask, and its DNS server.
Some additional definitions
To clarify, let’s quickly define some of these terms we just mentioned:
- A default gateway transfers data back and forth between the local network and the internet, or between local subnets.
- IP networking uses a subnet mask to separate the host address and the network address portions of an IP address.
- A DNS server resolves names to IP addresses, translating domain names that we easily remember, like bluecatnetworks.com, into IP addresses like 104.239.197.100.
Dynamic IP addressing with DHCP
The assignment of IP addresses happens dynamically within a given address range. As a result, a device connected to the network doesn’t have a forever address. The IP address can periodically change as its lease time expires unless the lease is successfully renewed.
For services that always need to be on, a static IP address is often a better option. Corporate enterprises commonly use static IP addresses for hardware like mail servers. Certainly, a DHCP server should have a static IP address.
However, there are drawbacks to dedicating a specific IP address to a device or service. A network administrator must manually assign, configure, and track the IP address. It’s a time-consuming task. Oftentimes, it requires the admin to physically be with the device.
Meanwhile, dynamic IP addresses are usually the preferred choice because they:
- Cost less to manage than static IP addresses;
- May offer more privacy and security with a constantly changing IP address; and
- Don’t require manual administration when a device roams from one subnet to another.
DHCP communications protocol
Communications to fulfill a DHCP request involves both the server and client. Furthermore, a relay agent or IP helper often facilitates communication between the two. Relay agents receive broadcast DHCP messages from clients and then re-send those messages with configuration information to servers.
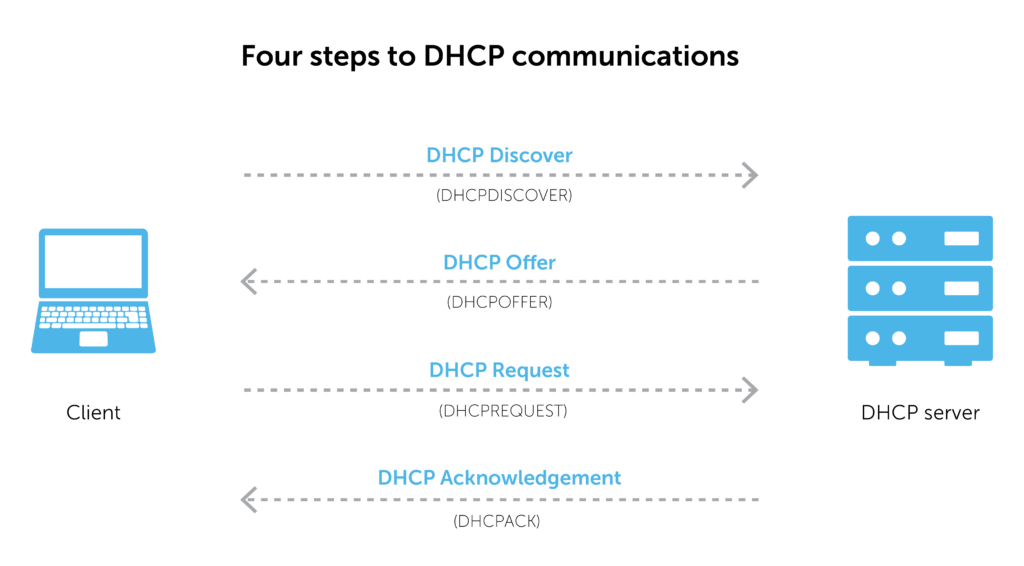
Communication happens via small units of data, called packets, that are routed through a network. Networking protocols like IP govern all its rules.
Most of the time, communication occurs in four steps. Briefly, they are:
- A discover packet is sent from the client to the server.
- The server replies to the client with a DHCP offer packet containing an IP address.
- The client receives and validates the offer, then sends a request packet back to the server to accept the address.
- The server sends an acknowledgement packet back to the client to confirm the chosen IP address.
With this in mind, one final point: DHCP alongside DNS and IP address management ( IPAM ) are together known as DDI. Want to know how to define DDI or how it works to form a complete management solution? The BlueCat platform is the place to start.
Related content

Automating DHCP reservations at a U.S. government agency
BlueCat worked with a large U.S. government agency to bring automation to a task they perform over and over, all day long: DHCP reservations.

eBook: Network Rising
The gap between what the network team can deliver and what end-users need continues to widen. You need back-end DNS that supports all of your initiatives.
Technical Know-How: Deploying DDNS with BlueCat
Dynamic DNS automatically updates DNS records when an IP address changes. Learn how to deploy DDNS on the BlueCat Address Manager and DNS/DHCP server.

eBook: The Cost of Free
This eBook outlines the journey from the functional to the inevitable, when you realize your free DNS is anything but. See how both tactical and strategic…
We’re using cookies on this site to improve your experience. Cookies help us learn how you interact with our website, and remember you when you come back so we can tailor it to your interests.
You can find out more about cookies and usage on our privacy policy page.
This site uses cookies
Some of these cookies are essential, while others help us to improve your experience by providing insights into how the site is being used.
For more detailed information on the cookies we use, please check our privacy policy
Necessary Cookies
Necessary cookies enable core functionality. The website cannot function properly without these cookies, and can only be disabled by changing your browser preferences.
Analytical Cookies
Analytical cookies help us to improve our website by collecting and reporting information on its usage.
Personalization Cookies
Personalization cookies help us to pre-fill forms you’ve already filled out before.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Assigning a Permanent, Static IP Address
I'm having difficulty assigning a permanent, static IP address to the default eth0 interface on a system running Ubuntu 14.04.5 with the system ultimately resorting to no IP address.
As a precursor to the following, the target system is an embedded system and we cannot allow any network interface changes during the operation of the system.
My set up is as follows:
network-manager has been disabled.
/etc/network/interfaces has been configured as follows:
There has been an issue during boot whereby the NTP server daemon can cause the system to hang for a good 5 minutes. Doing some Googling has indicated that a package called ntpdate goes a bit rogue - so this has been removed (we have our own method for setting the date/time of the system).
The avahi-autoip service has been disable to prevent an automatic private IP being assigned.
Fundamentally though, something is happening at some point later which is removing the static IP address bound to eth0 - whether it is a lingering DHCP service (surely the iface eth0 inet static should prevent this) or something else running which I'm unaware of.
One thing I have noticed is that at some point in time, a PING is done to the DNS server on the internal network (IP 192.168.0.5, this DNS server is not accessible due to a differing subnet) which instigates some kind of package update check which fails - after the failure, a constant stream of RTNETLINK answers: Network is unavailable messages appear with no viable way of getting rid of them.
For reference, here are some outputs:
ifconfig after PING (note, no IP address)
Ok, so what it seems was happening is that initially, when the system was configured, it was connected to a network with a DHCP server visible. The IP address of the lease obtained from the DHCP server is stored in a /var/lib/dhcp/dhclient.leases file.
The static IP address that was given to eth0 via the /etc/network/interfaces file gets withdrawn when the dhclient (and related services like avahi-autoip ) subsequently gets withdrawn after about 5 minutes when the DHCP client times out.
The system attempts to allocate the address from the previous lease however, because it cannot negotiate with a DHCP server, this address is also withdrawn and the adapter eth0 ends up with an auto private IP address. This APIPA address is allocated by the avahi-autoip service - which, if stopped, prevents a private address from being assigned.
There are a couple of temporary solutions to this:
- Delete the /var/lib/dhcp/dhclient.leases file
- Stop the dhclient service altogether using pkill
- Remove the dhclient package altogether
In our case, option 3 was the best method.
Also, whatever is causing the PING to execute and ultimately fail with the RTNETLINK answers: Network is unavailable still continues to occur. Although it clogs up the debug terminal output, its not too much of a problem.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged networking dhcp static-ip ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Why configuration is so complicated
- Featured on Meta
- New Focus Styles & Updated Styling for Button Groups
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network
- AI-generated content is not permitted on Ask Ubuntu
- Let's organize some chat workshops
Hot Network Questions
- How can five sticks with coinciding ends be arranged in space such that they are at their maximum angles to each other?
- Is it possible for magical Universities to become powerful political entities, and is my structure for the same sensible?
- Is it possible for a humanoid to learn English within a few days, just from observing conversations?
- How do I find broken symbolic links in macOS?
- How do you iterate through raster bands using model designer in QGIS?
- I forgot an item on board an airplane on a regular flight. Who should I contact to get it back?
- Is this dialogue Got or get?
- How do scholars reconcile Acts 4:12 with Mtt 1:23?
- Can hotel booking companies make up any "original price" they want, or does the claimed original price have to be somehow grounded in reality?
- Double parenthesis in academic writing
- Optimal Solution for the Four Divisors Problem on LeetCode
- What is a quick way to draw a regular pyramid?
- How can I regenerate the randomized MAC address on Android?
- Avoiding throw because we are not sure the exceptions will always be caught
- Risk of not capping old hose spigot
- Is this Python/Pygame that draws a maze well structured?
- Speed up Manipulate when including several static 3d plots in Show
- Is it safe to provide CVV number by property message in booking.com
- To write letter Cyrillic letter 'Ж' in latex
- Who is the target audience for the $60+ academic books?
- Success of Aggressive Rebuttal Strategy
- How to politely say that I am not doing extra work after back to the office policies?
- which refers to what?
- What is the difference between "more like X than Y" and "more like X than like Y"?

- PowerShell / CMD
- System Administration
- Windows Server
- System Administration , Operating Systems , Windows Server
How to Reserve IP Address on Windows Server DHCP?
DHCP reservation is the creation of a special entry on the DHCP server. Thanks to this, the same IP address from the DHCP scope address pool will be issued for a specific device (MAC address). In this article, we’ll look at how to create and manage reservations on a DHCP server running Windows Server 2019.
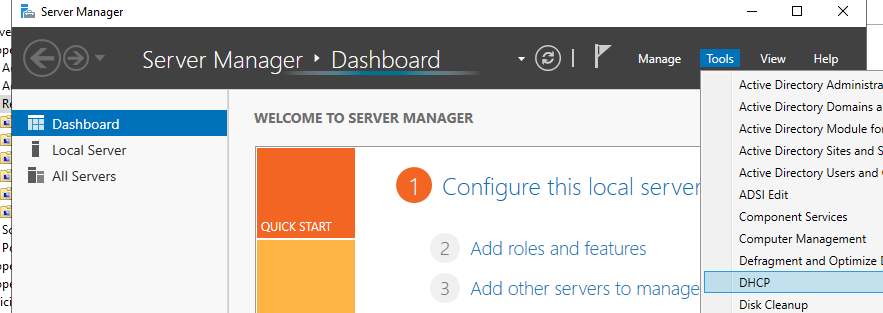
If some network devices (printers, scanners, workstations) require a permanent IP address (instead of manually setting a static IP address in the device settings), you can reserve an IP address on a DHCP server. In the DHCP server on Windows Server 2019, you can create a reservation from any leased IP address, or manually create a new entry.
Open the DHCP Management Console (System Manager > Tools > DHCP) or simply run the dhcpmgmt.msc command. Expand your DHCP server, select IPv4, then select the scope where you want to manage reservations.
If the DHCP server client already received a dynamic IP address from your DHCP server, you can reserve this address. Go to the Address Leases section, find the DHCP client you need in the list (the fact that this IP address is dynamic is indicated by the presence of a date in the Lease Expiration field), right-click on it, and select Add to Reservation .
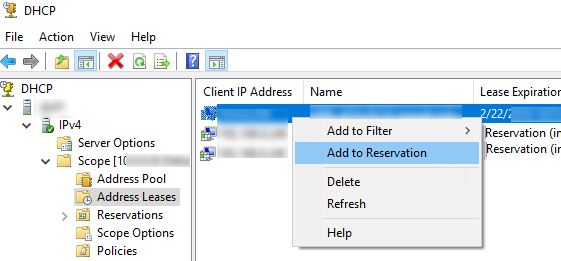
You can also create a DHCP reservation manually. To do this, you need to find out the MAC address of the device. In case you use a Windows device, you can find out the MAC address of your network adapter with the command:
In this example, the Physical Address is 08-3E-8E-AA-F3-0D, copy it.
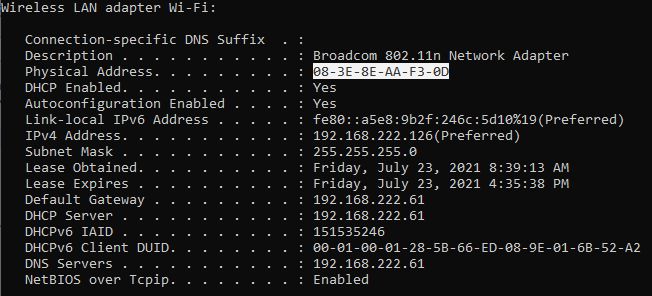
To create a new reservation, right-click the Reservations section in the DHCP console and select New Reservation .
Fill in the following fields in the New reservation window:
- Reservation name : specify the network name of the device;
- IP address : specify the IP address from your DHCP scope that you want to assign to the device;
- MAC address : use the physical device address obtained earlier;
- Descriptions : provide a description of the device (optional).
After you have filled in the fields, click the Add button.
Note . Check how to fix Active Directory domain controller could not be contacted issue.
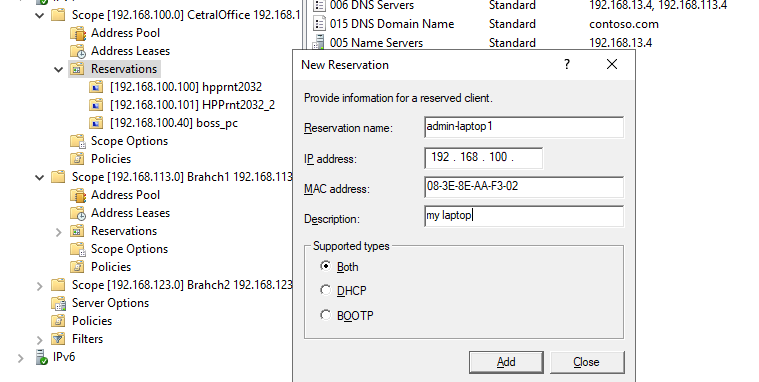
If you entered the MAC address in the wrong format, an error will appear “The Unique Identifier you have entered may not be correct. Do you want to use this Identifier anyway?”. In this case, check the MAC address.
Network clients won’t switch to reserved IP addresses automatically. The client will get a new IP address when trying to renew its current lease, on reboot, or when manually use the ipconfig command:
You can manage your reserved IP addresses in the Reservation section. Here you can delete or change the parameters of any DHCP reservation.
Alternatively, you can create a DHCP reservation from the PowerShell command line. To do this, use the Add-DhcpServerv4Reservation cmdlet.
The following command will reserve the leased IP address for a device that has already received an IP address from your DHCP server:
If you need to create a new DHCP reservation for a specific MAC address, use the command:
To create multiple DHCP reservations in bulk, create a CSV file in the following format:
ScopeId,Name,ClientId,IPAddress 192.168.1.0,computer1,08-3E-8E-AA-F3-1D,192.168.1.56 192.168.1.0,computer2,08-3E-8E-AA-F3-2D,192.168.1.57 192.168.1.0,computer3,08-3E-8E-AA-F3-3D,192.168.1.58
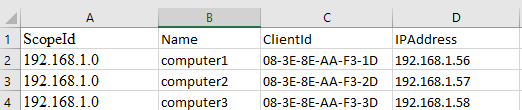
To create reservations for all devices in this file, run the command:
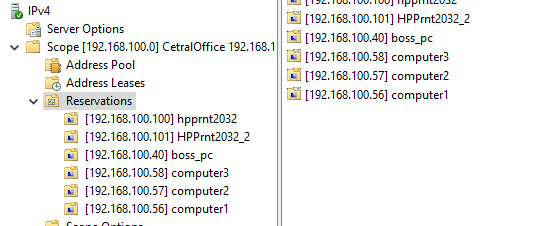
Share this post
DigitalGeekery
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts
How to do Drive Mapping in Windows – All Options Explained
Even though we store more and more data in the cloud, drive mapping is still a common practice these days.... read more

How to Convert ESD to WIM File on Windows
In this tutorial, we will show you how to convert ESD to WIM file from the Command prompt, using the... read more
Auto Shutdown cmd Script
Here's a sample batch script that you can use to automatically shutdown a computer at 11:03pm every day and display... read more
List of ms-settings URI commands to open specific settings in Windows 10
How to use the URI commands Here some different examples for using ms-setting commands: Press Win+R to open the Run dialog... read more
Deploy Scheduled Task Using GPO
You can use the Group Policy to create and deploy scheduled tasks to domain computers. For example, you can create... read more
Copy Files and Folders to User Computers via GPO
You can use Group Policies to copy specific files and folders to user computers in the Active Directory domain. You... read more
User PowerShell To Bulk Change users Password
Table of Contents If you are managing multiple user accounts, it can be tedious and time-consuming to change passwords for each... read more
How to Set Proxy Settings via Group Policy?
The article shows how to use Active Directory Group Policies (GPOs) to configure proxy server settings on domain-joined computers running... read more
How to Disable or Enable USB Drives using Group Policy
When you connect a new USB device to your computer, Windows automatically detects the device and installs the appropriate driver.... read more
How to Quickly Check if C Drive is Accessible on Multiple Machines with PowerShell
Table of Contents Introduction When managing a network of machines, it can be useful to quickly determine which machines have accessible C... read more

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The idea is that when a new device connects to the local network this device/software acts as a DHCP server, if the device is new then it dynamically assigns it a new address that has never been used before and stores this MAC Address IP Address combination in a database, if the device's MAC is in the database the devices gets the same IP as ...
Start the server in DHCP. In the router panel, name it, basing on its mac address so that the router will remember it. 4. In the server switch IP from DHCP mode to manual and assign an IP that is beyond the ones that the router would assign to other devices (eg. 192.168.1.100).
Of course, you could skip the name resolution phase with a dynamic IP address as well, but you don't know what the device's IP address is. This is solved with a DHCP reservation which makes the IP address permanent. Reason #3: Using DHCP Reservations Is Better Than Setting Static IP Addresses . Using DHCP reservations to assign fixed IP ...
This is not the same thing as a statically-assigned IP address. Static IP addresses are configured manually, directly on the client. Reserved IP addresses are leased from the DHCP server, but the given client will always receive the same IP address. The DHCP service identifies the client by MAC address, as seen below.
IP address configuration is one of the most critical, if simple, settings on your network devices. Workstations, servers, routers, and other components must have properly assigned IP address settings to participate on the network. This two-part article series covers static and dynamic IP address settings and the configuration of a DHCP server.
The client IP address may be pre-configured by the administrator (manual address allocation) or assigned from a pool by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server (automatic address allocation). address pool —The range of IP addresses assigned by the DHCP server. The pool may also store client parameters, such as default router and ...
DHCP Address Allocation Methods. There are three ways that a DHCP server either assigns or sends an IP address to a client: On the firewall, a. means the allocation is permanent. of addresses to a client for a maximum period of time, known as a lease . This method of address allocation is useful when the customer has a limited number of IP ...
The machine retains this IP address for a set number of days, after which it can try to renew the IP address. If no renewal signal is sent (such as a decommissioned machine), then the DHCP server reclaims the IP address to assign to another device. When the renewal signal is detected, the device retains its IP address for another set of days.
"A DHCP reservation is a permanent IP address assignment. It is a specific IP address within a DHCP scope that is permanently reserved for leased use to a specific DHCP client" (tech-faq.com). In the previous post we created DHCP scopes. Let's see how we can use PowerShell to create a DHCP reservation within one of those scopes.
During address assignment, DHCP checks for conflicts using ping and gratuitous (ARP). If a conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool. The address will not be assigned until the administrator resolves the conflict. address pool —The range of IP addresses assigned by the DHCP server. Address pools are indexed by subnet number.
I also can recommend different IP-ranges, something like this: 1-9 important Servers (static) 10-99 misc. Servers (static) 100-150 Sales & Marketing (DHCP with MAC) 151-200 Developers (DHCP with MAC) 200-253 Tech.Stuff (DHCP with MAC) Another vote for DHCP is, that you can handle all IPs from one, central instance.
1. Open the Server Manager dashboard, click Tools , and select DHCP. 2. Open Scope right-click on Reservations and select New Reservation. 3. Enter Reservation name (specify the network name of the device), Enter IP address (specify the IP address from your DHCP scope that you want to assign to the device), Enter MAC address (MAC address of the ...
DHCP Server. A DHCP server is what the system uses to automatically provide IP addresses and additional network parameters to the devices that connect to your network. It is able to provide temporary or dynamic IP addresses taken from a pool of available addresses. In addition, a DHCP server gives permanent IP addresses and DHCP configuration ...
IP address range: The IP address range within a scope from which to assign an IP address to a client. A server level policy cannot have a setting for an IP address range. Standard DHCP options: One or more standard DHCP options to send to a client in the response based on the options requested by the client in the parameter request list.
Dynamic IP: A dynamic IP is where a computer gets an IP address from a DHCP server. A DHCP server automatically assigns a computer an IP address along with a subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server. DHCP Server: A Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is an application layer protocol that is used to provide dynamic IP addresses to computers and devices.
DHCP is a network management protocol. A client device (or DHCP client), such as a laptop, joins a network and requests an IP address. The request is made to a DHCP server. These servers are often configured with redundancy—often called DHCP failover —or clustering among other network servers. Servers can run on both IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
DHCP server IP reservation; same DHCP server; ... On the other hand, a static IP ensures we always assign the same address. Of course, this comes with its own problems: ... However, a system reboot now would wipe our network setup and restore the IP to what DHCP provides. 3.4. Permanent Static IP via ip.
The system attempts to allocate the address from the previous lease however, because it cannot negotiate with a DHCP server, this address is also withdrawn and the adapter eth0 ends up with an auto private IP address. This APIPA address is allocated by the avahi-autoip service - which, if stopped, prevents a private address from being assigned ...
DNS SNMP NAT DHCP, One of the features of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is the capability for static allocation of an IP address based on the IP-to-MAC address mapping. True False, Which of the following terms refers to permanent IP address assignment from a DHCP server?
In the DHCP server on Windows Server 2019, you can create a reservation from any leased IP address, or manually create a new entry. Open the DHCP Management Console (System Manager > Tools > DHCP) or simply run the dhcpmgmt.msc command. Expand your DHCP server, select IPv4, then select the scope where you want to manage reservations.
False. Static IP address. Which of the answers listed below refers to a permanent assignment of an IP address? Static IP address. Private IP address. Dynamic IP address. Public IP address. DHCP. APIPA addresses are valid only for communications within a network segment that a given host is connected to.
The time a DHCP client can use an IP address dynamically assigned by the DHCP server is referred to as: Lease. Which of the terms listed below refers to permanent IP address assignment from a DHCP server? Reservation. A range of IP addresses that a DHCP server can lease out to DHCP clients is known as:
True. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A range of IP addresses that a DHCP server can lease out to DHCP clients is known as:, A DHCP server's IP exclusion configuration option allows network administrators to remove a single IP address or a range of IP addresses from the pool of addresses being assigned ...