Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
According to MLA style, you must have a Works Cited page at the end of your research paper. All entries in the Works Cited page must correspond to the works cited in your main text.
Basic rules
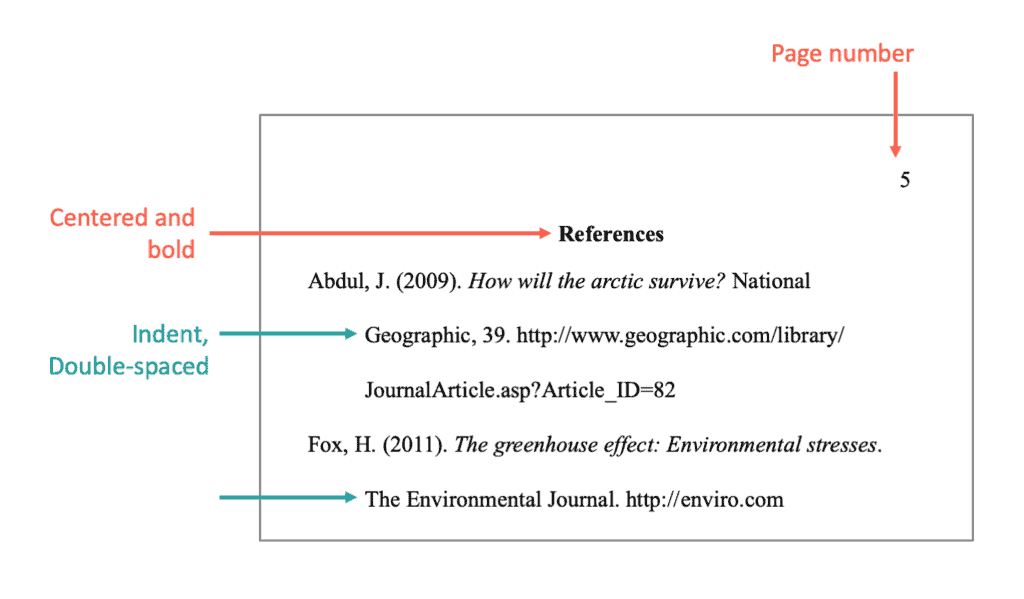
- Begin your Works Cited page on a separate page at the end of your research paper. It should have the same one-inch margins and last name, page number header as the rest of your paper.
- Only the title should be centered. The citation entries themselves should be aligned with the left margin.
- Double space all citations, but do not skip spaces between entries.
- Indent the second and subsequent lines of citations by 0.5 inches to create a hanging indent.
- List page numbers of sources efficiently, when needed. If you refer to a journal article that appeared on pages 225 through 250, list the page numbers on your Works Cited page as pp. 225-50 (Note: MLA style dictates that you should omit the first sets of repeated digits. In our example, the digit in the hundreds place is repeated between 2 25 and 2 50, so you omit the 2 from 250 in the citation: pp. 225-50). If the excerpt spans multiple pages, use “pp.” Note that MLA style uses a hyphen in a span of pages.
- If only one page of a print source is used, mark it with the abbreviation “p.” before the page number (e.g., p. 157). If a span of pages is used, mark it with the abbreviation “pp.” before the page number (e.g., pp. 157-68).
- If you're citing an article or a publication that was originally issued in print form but that you retrieved from an online database, you should type the online database name in italics. You do not need to provide subscription information in addition to the database name.
- For online sources, you should include a location to show readers where you found the source. Many scholarly databases use a DOI (digital object identifier). Use a DOI in your citation if you can; otherwise use a URL. Delete “http://” from URLs. The DOI or URL is usually the last element in a citation and should be followed by a period.
- All works cited entries end with a period.
Additional basic rules new to MLA 2021
New to MLA 2021:
- Apps and databases should be cited only when they are containers of the particular works you are citing, such as when they are the platforms of publication of the works in their entirety, and not an intermediary that redirects your access to a source published somewhere else, such as another platform. For example, the Philosophy Books app should be cited as a container when you use one of its many works, since the app contains them in their entirety. However, a PDF article saved to the Dropbox app is published somewhere else, and so the app should not be cited as a container.
- If it is important that your readers know an author’s/person’s pseudonym, stage-name, or various other names, then you should generally cite the better-known form of author’s/person’s name. For example, since the author of Alice's Adventures in Wonderland is better-known by his pseudonym, cite Lewis Carroll opposed to Charles Dodgson (real name).
- For annotated bibliographies , annotations should be appended at the end of a source/entry with one-inch indentations from where the entry begins. Annotations may be written as concise phrases or complete sentences, generally not exceeding one paragraph in length.
Capitalization and punctuation
- Capitalize each word in the titles of articles, books, etc, but do not capitalize articles (the, an), prepositions, or conjunctions unless one is the first word of the title or subtitle: Gone with the Wind, The Art of War, There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
- Use italics (instead of underlining) for titles of larger works (books, magazines) and quotation marks for titles of shorter works (poems, articles)
Listing author names
Entries are listed alphabetically by the author's last name (or, for entire edited collections, editor names). Author names are written with the last name first, then the first name, and then the middle name or middle initial when needed:
Do not list titles (Dr., Sir, Saint, etc.) or degrees (PhD, MA, DDS, etc.) with names. A book listing an author named "John Bigbrain, PhD" appears simply as "Bigbrain, John." Do, however, include suffixes like "Jr." or "II." Putting it all together, a work by Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. would be cited as "King, Martin Luther, Jr." Here the suffix following the first or middle name and a comma.
More than one work by an author
If you have cited more than one work by a particular author, order the entries alphabetically by title, and use three hyphens in place of the author's name for every entry after the first:
Burke, Kenneth. A Grammar of Motives . [...]
---. A Rhetoric of Motives . [...]
When an author or collection editor appears both as the sole author of a text and as the first author of a group, list solo-author entries first:
Heller, Steven, ed. The Education of an E-Designer .
Heller, Steven, and Karen Pomeroy. Design Literacy: Understanding Graphic Design.
Work with no known author
Alphabetize works with no known author by their title; use a shortened version of the title in the parenthetical citations in your paper. In this case, Boring Postcards USA has no known author:
Baudrillard, Jean. Simulacra and Simulations. [...]
Boring Postcards USA [...]
Burke, Kenneth. A Rhetoric of Motives . [...]
Work by an author using a pseudonym or stage-name
New to MLA 9th edition, there are now steps to take for citing works by an author or authors using a pseudonym, stage-name, or different name.
If the person you wish to cite is well-known, cite the better-known form of the name of the author. For example, since Lewis Carroll is not only a pseudonym of Charles Dodgson , but also the better-known form of the author’s name, cite the former name opposed to the latter.
If the real name of the author is less well-known than their pseudonym, cite the author’s pseudonym in square brackets following the citation of their real name: “Christie, Agatha [Mary Westmacott].”
Authors who published various works under many names may be cited under a single form of the author’s name. When the form of the name you wish to cite differs from that which appears on the author’s work, include the latter in square brackets following an italicized published as : “Irving, Washington [ published as Knickerbocker, Diedrich].”.
Another acceptable option, in cases where there are only two forms of the author’s name, is to cite both forms of the author’s names as separate entries along with cross-references in square brackets: “Eliot, George [ see also Evans, Mary Anne].”.
Creating an MLA Works cited page
General formatting information for your works cited section.
Beginning on a new page at the end of your paper, list alphabetically by author every work you have cited, using the basic forms illustrated below. Title the page Works Cited (not Bibliography), and list only those sources you actually cited in your paper. Continue the page numbering from the body of your paper and make sure that you still have 1–inch margins at the top, bottom, and sides of your page. Double-space the entire list. Indent entries as shown in the models below with what’s called a “hanging indent”: that means the first line of an entry begins at the left margin, and the second and subsequent lines should be indented half an inch from the left margin. Most word-processing programs will format hanging indents easily (look under the paragraph formatting options).
Introduction to the 8th Edition
In 2016, MLA substantially changed the way it approaches works cited entries. Each media type used to have its own citation guidelines. Writers would follow the specific instructions for how to cite a book, a translated poem in an anthology, a newspaper article located through a database, a YouTube clip embedded in an online journal, etc. However, as media options and publication formats continued to expand, MLA saw the need to revise this approach. Since a book chapter can appear on a blog or a blog post can appear in a book, how can writers account for these different formats?
MLA’s solution to this problem has been to create a more universal approach to works cited entries. No matter the medium, citations include the specifically ordered and punctuated elements outlined in the following table.
Elements of a Works Cited Entry
- Last name, First name
- Italicized If Independent ; “Put in Quotations Marks if Not.”
- Often Italicized,
- Name preceded by role title (for example: edited by, translated by, etc),
- i.e. 2nd ed., revised ed., director’s cut, etc.,
- vol. #, no. #,
- Name of Entity Responsible for Producing Source,
- i.e. 14 Feb. 2014; May-June 2016; 2017,
- i.e. pp. 53-79; Chazen Museum of Art; https://www.wiscience.wisc.edu/ (If possible, use a DOI (digital object identifier) instead of a url.)
- Optionally included when citing a web source.
If the source doesn’t include one of these elements, just skip over that one and move to the next. Include a single space after a comma or period.
The third category—”container”—refers to the larger entity that contains the source. This might be a journal, a website, a television series, etc. Sometimes a source can also appear nested in more than one container. A poem, for example, might appear in an edited collection that has been uploaded to a database. A television episode fits in a larger series which may be contained by Netflix. When a source is in a larger container, provide information about the smaller one (i.e. the edited collection or the TV series), then provide information for elements 3–10 for the larger container. For example, the works cited entry detailed below is for a chapter from an economics textbook, entitled Econometrics, that is contained on UW–Madison’s Social Science Computing Cooperative website.
Example of a Works Cited Entry
Hansen, Bruce E. “The Algebra of Least Squares.” Econometrics, University of Wisconsin Department of Economics, 2017, pp. 59-87. Social Science Computing Cooperative, UW–Madison, http://www.ssc.wisc.edu/~bhansen/econometrics/Econometrics.pdf.
Here is the breakdown of these elements:
- Hansen, Bruce E.
- “The Algebra of Least Squares.”
- Econometrics,
- Other Contributors,
- University of Wisconsin Department of Economics
- Title of source.
- Social Science Computing Cooperative,
- Other contributors,
- UW-Madison,
- Publication date,
- http://www.ssc.wisc.edu/~bhansen/econometrics/Econometrics.pdf.
- (This could be included, but this site is fairly stable, so the access date wasn’t deemed to be important.)
One of the benefits of this system is that it can be applied to any source. Whether you’re citing a book, a journal article, a tweet, or an online comic, this system will guide you through how to construct your citation.
A Few Notes
- Books are considered to be self-contained, so if you’re citing an entire book, items 2 and 3 get joined. After the author’s name, italicize the title, then include a period and move on items 4–9.
- No matter what your last item of information is for a given citation, end the citation with a period.
- Also, if it is appropriate to include an access date for an online source, put a period after the full url in addition to one after the access date information.
- It is particularly important to include access dates for online sources when citing a source that is subject to change (like a homepage). If the source you are working with is more stable (like a database), it’s not as critical to let your readers know when you accessed that material.
For more information about any of this, be sure to consult the 2016 MLA Handbook itself.
Works Cited page entry: Article
Article from a scholarly journal, with page numbers, read online from the journal’s website.
Shih, Shu-Mei. “Comparative Racialization: An Introduction.” PMLA , vol. 123, no. 5, 2008, pp. 1347-62. Modern Language Association , doi:10.1632/pmla.2008.123.5.1347.
Author last name, First name. “Article title.” Journal name , vol. number, issue number, year of publication, pp. numbers. Publisher , doi
PMLA provides DOI numbers, so this is used in this citation preceded by “doi:” instead of the url address. Also, given the enduring stability of PMLA’s page, no access date has been included, but it could be if the writer preferred.
Article from a scholarly journal, with multiple authors, without page numbers, read online from the journal’s website
Bravo, Juan I., Gabriel L. Lozano, and Jo Handelsman. “Draft Genome Sequence of Flavobacterium johnsoniae CI04, an Isolate from the Soybean Rhizosphere.” Genome Announcements , vol. 5, no. 4, 2017, doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01535-16.
First author last name, First name, Middle initial., Second author first name Middle initial. Last name, and Third author First name Last name. “Article title.” Journal name , vol. number, issue number, year of publication, doi
Article from a scholarly journal, no page numbers, read through an online database
Mieszkowski, Jan. “Derrida, Hegel, and the Language of Finitude.” Postmodern Culture , vol. 15, no. 3, 2005. Project MUSE, https://muse.jhu.edu/article/186557.
Author Last name, First name. “Article title.” Journal name , vol. number, issue number, year of publication. Database , url.
Article from a scholarly journal, with page numbers, read through an online database
Sherrard-Johnson, Cherene. “‘A Plea for Color’: Nella Larsen’s Iconography of the Mulatta.” American Literature , vol. 76, no. 4, 2004, pp. 833-69. Project MUSE , https://muse.jhu.edu/article/176820.
Author Last name, First name. “Article title.” Journal name , vol. number, issue number, year of publication, pp. numbers. Database , url.
Valenza, Robin. “How Literature Becomes Knowledge: A Case Study.” ELH , vol. 76, no. 1, 2009, pp. 215-45. Project MUSE . https://muse.jhu.edu/article/260309.
Author Last name, First name. “Article title.” Journal name , vol. number, issue number, year of publication, pp. numbers. Database , url.
Article from a scholarly journal, by three or more authors, print version
Doggart, Julia, et al. “Minding the Gap: Realizing Our Ideal Community Writing Assistance Program.” The Community Literacy Journal , vol. 2, no. 1, 2007, pp. 71-80.
First author Last name, First name, et al. “Article title.” Journal name , vol. number, issue number, year of publication, pp. numbers.
Raval, Amish N., et al. “Cellular Therapies for Heart Disease: Unveiling the Ethical and Public Policy Challenges.” Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology , vol. 45, no. 4, 2008, pp. 593–601.
[The Latin abbreviation “et al.” stands for “and others,” and MLA says that you should use it when citing a source with three or more authors.]
Article from a webtext, published in a web-only scholarly journal
Butler, Janine. “Where Access Meets Multimodality: The Case of ASL Music Videos.” Kairos: A Journal of Rhetoric, Technology, and Pedagogy , vol. 21, no. 1, 2016, http://kairos.technorhetoric.net/21.1/topoi/butler/index.html. Accessed 7 June 2017.
Author Last name, First name. “Article title.” Journal name , vol. number, issue number, year of publication, url. Date of access.
Balthazor, Ron, and Elizabeth Davis. “Infrastructure and Pedagogy: An Ecological Portfolio.” Kairos: A Journal of Rhetoric, Technology, and Pedagogy , vol. 20, no. 1, 2015, http://kairos.technorhetoric.net/20.1/coverweb/balthazor-davis/index.html. Accessed 7 June 2017.
First author Last name, First name and Second author First name Last name. “Article title.” Journal name , vol. number, issue number, date of publication, url. Date of access.
Article from a magazine, print version
Oaklander, Mandy. “Bounce Back.” Time , vol. 185, no. 20, 1 June 2015, pp. 36-42.
Author Last name, First name. “Article title.” Magazine name , vol. number, issue number, month and year of publication, pp. numbers.
Article from a magazine, read through an online database
Rowen, Ben. “A Resort for the Apocalypse.” The Atlantic , vol. 319, no. 2, Mar. 2017, pp. 30-31. EBSCOhost, search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,uid&db =aph&AN=120967144&site=ehost-live&scope=site.
Author Last name, First name. “Article title.” Magazine name , vol. number, issue number, month and year of publication, pp. numbers. Database name , url.
Article from a newspaper, read through an online database
Walsh, Nora. “For Frank Lloyd Wright’s 150th, Tours, Exhibitions and Tattoos.” New York Times , 27 May 2017, international ed. ProQuest , https://search-proquest-com.ezproxy.library.wisc.edu/docview/1903523834/fulltext/71B144CD12054C76PQ/2?accountid=465.
Author Last name, First name. “Article title.” Newspaper name , day month and year of publication, edition. Database name , url.
Works Cited page entry: Short Story
Short story in an edited anthology.
Hawthorne, Nathaniel. “The Minister’s Black Veil.” Nathaniel Hawthorne’s Tales , edited by James McIntosh, Norton, 1987, pp. 97–107.
Author Last name, First name. “Short story title.” Anthology title , edited by Editor name, Publisher, year of publication, pp. numbers.
Works Cited page entry: Book
Book, written by one author, print version.
Bordwell, David. Figures Traced in Light: On Cinematic Staging . U California P, 2005.
Britland, Karen. Drama at the Courts of Queen Maria Henrietta . Cambridge UP, 2006.
Card, Claudia. The Atrocity Paradigm : A Theory of Evil . Oxford UP, 2005.
Cronon, William. Nature’s Metropolis . Norton, 1991.
Mallon, Florencia E. Courage Tastes of Blood: The Mapuche Community of Nicholás Ailío and the Chilean State , 1906–2001. Duke UP, 2005.
Author Last name, First name. Book title . Publisher, year of publication.
Book, written by more than one author, print version
Bartlett, Lesley, and Frances Vavrus. Rethinking Case Study Research: A Comparative Approach . Taylor & Francis, 2016.
First author Last name, First name, and Second author First name Last name. Book title . Publisher, year of publication.
Flanigan, William H., et al. Political Behavior of the American Electorate . CQ Press, 2015.
First author last name, First name Middle initial., et al. Book title . Publisher, year of publication.
Book, an edited anthology, print version
Olaniyan, Tejumola, and Ato Quayson, editors. African Literature: An Anthology of Criticism and Theory . Blackwell, 2007.
First editor Last name, First name, and Second editor first name Last name, editors. Anthology title . Publisher, year of publication.
Book, edited, revised edition, print version
Douglass, Frederick. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . Edited by William L. Andrews and William S. McFeely, revised ed., Norton, 1996.
Author Last name, First name. Book title . Edited by first editor First name Middle initial. Last name and Second editor First name Middle initial. Last name, edition., publisher, year of publication.
A play in an edited collection, print version
Shakespeare, William. The Comedy of Errors: A New Variorum Edition of Shakespeare . Edited by Standish Henning, The Modern Language Association of America, 2011, pp. 1–254.
Author Last name, First name. Play title . Edited by editor First name Last name, publisher, year of publication, pp. numbers.
[Page numbers are included in this entry to draw attention to the play itself since this edition includes an additional 400 pages of scholarly essays and historical information.]
Bordwell, David. Foreword. Awake in the Dark: Forty Years of Reviews, Essays, and Interviews , by Roger Ebert, U of Chicago P, 2006, pp. xiii–xviii.
Foreward author Last name, First name. Title of work in which foreward appears , by author of work, publisher, year of publication, pp. numbers.
Chapter in an edited anthology, print version
Amodia, David, and Patricia G. Devine. “Changing Prejudice: The Effects of Persuasion on Implicit and Explicit Forms of Race Bias.” Persuasion: Psychological Insights and Perspectives , edited by T.C. Brock and C. Greens, 2nd ed., SAGE Publications, 2005, pp. 249–80.
Chapter first author Last name, First name, and Second author First name Middle initial. Last name. “Chapter title.” Anthology title , edited by first editor First initial. Middle initial. Last name and Second editor first initial. Last name, edition number, publisher, year of publication, pp. numbers.
Hawhee, Debra, and Christa Olson. “Pan–Historiography: The Challenges of Writing History across Time and Space.” Theorizing Histories of Rhetoric , edited by Michelle Ballif, Southern Illinois University Press, 2013, pp. 90–105.
Chapter first author Last name, First name, and Second author First name Last name. “Chapter title.” Anthology title, edited by editor First name Last name, publisher, date of publication, page #s.
Shimabukuro, Mira Chieko. “Relocating Authority: Coauthor(iz)ing a Japanese American Ethos of Resistance under Mass Incarceration.” Representations: Doing Asian American Rhetoric , edited by LuMing Mao and Morris Young, Utah State UP, 2008, pp. 127–52.
Author Last name, First name Middle name. “Chapter title.” Anthology title , edited by first editor First name Last name and second editor First name Last name, Publisher, year of publication, pp. numbers.
Works Cited page entry: Electronic source
Since MLA’s 8th edition does not substantially differentiate between a source that is read in print as opposed to online, see our information about citing articles for examples about citing electronic sources from periodicals.
Non-periodical web publication, with no author and no date of publication
“New Media @ the Center.” The Writing Center at the University of Wisconsin-Madison . U of Wisconsin-Madison Writing Center, 2012, http://www.writing.wisc.edu/[email protected]. Accessed 8 March 2017.
“Title of publication.” Title of the containing website . Publisher of the site, year of publication. Url. Accessed date.
The syntax for a non-periodical web publication is: author (if no author, start with the title); title of the section or page, in quotation marks; title of the containing Web site as a whole, italicized; version or edition used (if none is specified, omit); publisher or sponsor of the site (if none is mentioned, then just skip this); date of publication (if none is listed, just skip this); use a comma between the publisher or sponsor and the date; the source’s url address; date of access.
Non–periodical scholarly web publication, no date of publication
Stahmer, Carl, editor. “The Shelley Chronology.” Romantic Circles . University of Maryland, https://www.rc.umd.edu/reference/chronologies/shelcron. Accessed 26 March 2017.
Editor Last name, First name, editor. “Title of publication.” Title of the containing website . Publisher, Url. Accessed date.
Non–periodical web publication, web publication, corporate author
Rhetoric Society of America. “Welcome to the website of the Rhetoric Society of America and Greetings from Gregory Clark, President of RSA!” RSA , Rhetoric Society of America, 2017, http://www.rhetoricsociety.org/aws/RSA/pt/sp/home_page. Accessed 27 March 2017.
Name of Corporate Author. “Title of publication.” Title of the containing website , Publisher of the website, year of publication, url. Accessed date
The syntax for this entry is: corporate author; title, in quotation marks; title of the overall Web site, in italics; publisher or sponsor of the site; date of publication; the source’s url address; date of access.
Since the material on homepages is subject to change, it is particularly important to include an access date for this source.
E-mail message
Blank, Rebecca. “Re: A request and an invitation for Department Chairs and Unit Leaders.” Received by Brad Hughes, 30 August 2016.
Sender Last name, First name. “Email subject line.” Received by recipient First name Last name, day month and year email was sent and received.
@UW-Madison. “Scientists at @UWCIMSS used a supercomputer to recreate the EF-5 El Reno tornado that swept through Oklahoma 6 years ago today. #okwx.” Twitter, 24 May 2017, 2:23 p.m., https://twitter.com/UWMadison/status/867461007 362359296.
@Twitter Handle. “Entire tweet word-for-word.” Twitter, day month year of tweet, time of tweet, url.
When including tweets in the works cited page, alphabetize them according to what comes after the “@” symbol.
Include the full tweet in quotation marks as the title.
Works Cited page entry: Government publication, encyclopedia entry
Government publication.
National Endowment for the Humanities. What We Do . NEH, March 2017, https://www.neh.gov/files/whatwedo.pdf.
Name of Government entity. Title of publication . Publisher, date of publication, url.
This is treated as a source written by a corporate author.
Signed encyclopedia entry
Neander, Karen. “Teleological Theories of Mental Content.” The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , edited by Edward N. Zalta, spring ed., 2012, https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/spr2012/entries/content-teleological/.
Author Last name, First name. “Entry title.” Title of encyclopedia , edited by editor First name Middle initial. Last name, ed., year of publication, url.
Works Cited page entry: Personal interview, film, tv program, and others
An interview you conducted.
Brandt, Deborah. Personal Interview. 28 May 2008.
Interviewee Last name, First name. Personal Interview. Day month year of interview.
A published interview, read through an online database
García, Cristina. Interview by Ylce Irizarry. Contemporary Literature , vol. 48, no. 2, 2007, pp. 174-94. EBSCOhost. http://web.b.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.library.wisc.edu/ehost/pdfviewer /pdfviewer?vid=5&sid=f95943f6-5364-49e7-8b83-7341edc4b434%40sessionmgr104. Accessed 26 March 2017.
Interviewee Last name, First name. Interview by interviewer First name Last name. Journal title , vol. number, issue number, year of publication, pp. numbers. Database name. Url. Accessed day month and year.
Film or DVD
Sense and Sensibility . Directed by Ang Lee, performances by Emma Thompson, Alan Rickman, and Kate Winslet, Sony, 1999.
Title of film . Directed by director First name Last name, performances by first actor First name Last name, second actor First name Last name, and third actor First name Last name, Production company, year of release.
You only need to include performers’ names if that information is relevant to your work. If your paper focuses on the director, begin this entry with the director, i.e., Lee, Ang, director. Sense and Sensibility . . . . If your primary interest is an actor, begin the entry with the actor’s name, i.e., Thompson, Emma, perf. Sense and Sensibility . . . .
Television broadcast
“Arctic Ghost Ship.” NOVA . PBS, WPT, Madison, 10 May 2017.
“Title of episode.” Television series name . Broadcasting network, Broadcasting station, City, day month year of broadcast.
PBS is the network that broadcast this show; WPT is the Wisconsin PBS affiliate in Madison on which you watched this show.
Media accessed through streaming network
“Self Help.” The Walking Dead , season 5, episode 5, AMC, 9 Nov. 2014. Netflix , https://www.netflix.com/watch/80010531?trackId=14170286&tctx=1%2C4%2C04bba31e-60a0-4889-b36e-b708006e5d05-911831.
“Title of episode.” Title of television series , season number, episode number, Broadcasting channel, date month year of release. Name of streaming service used to access episode , url.
Gleizes, Albert. The Schoolboy . 1924, gouache or glue tempera on canvas. U of Wisconsin Chazen Museum of Art, Madison, WI.
Artist Last name, First name. Title of piece. Year of composition, medium. Name of institution housing art piece, City, State initials.
Address, lecture, reading, or conference presentation
Desmond, Matthew. “Evicted: Poverty and Profit in the American City.” 1 Nov. 2016, Memorial Union Theater, Madison, WI.
Lecturer Last name, First name. “Title of lecture.” Day month year lecture is given, Location of lecture, City, State initials.

Modern Language Association Documentation
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
MLA Table of Contents
Orientation to MLA
Creating an MLA works cited page
Using MLA in–text citations
Abbreviating references to your sources

Citation Manuals
- APA Citations
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Chapters and Parts of Books
- Unpublished Manuscripts/Informal Publications (i.e. course packets and dissertations)
- MLA Citations
- MLA Works Cited Page
- Chicago Citations
- Chicago Bibliography
- Installation
- How to Gather Citations
- Word Processing with Zotero
- Basic Formatting - Microsoft Word
- Basic Formatting - Google Docs
Works Cited Basic Rules
A works-cited list should be included at the end of your research paper after any endnotes. All entries in the works-cited list must correspond to the works cited in your main text.
- Begin your Works Cited page on a separate page at the end of your research paper. The heading, Works Cited, should be centered one inch from the top of the page. If there is only one work in the list, call it Work Cited.
- Double-space between the heading and the first entry.
- Each entry should be flush against the left margin.
- For entries that run longer than a sentence, indent the second and subsequent lines of citations by 0.5 inches to create a hanging indent.
- Double-space the entire list.

Image source: MLA Sample Works Cited Page, Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL)
One Author:
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Publication Date.
Two Authors:
Last Name, First Name, and First Name Last Name. Title of Work. Publisher, Publication Date.
More than Two Authors:
Last Name, First Name, et al. Title of Work . Publisher, Publication Date.
Unknown Author:
Title of Work. Publisher, Publication Date.
Short Stories
Short Story from Edited Collection:
Last name, First name. “Story Title.” Book Title , edited by Editor first name Last name, vol, Publisher, Year, pp.
Short Story from Author's Collection:
Last name, First name. “Story Title.” Book Title , Publisher, Year, pp.
Journal Articles
Journal Article in a Database with DOI
Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article." Title of Periodical, vol. no, year, pp. Source, DOI.
Journal Article in a Database with a Permalink
Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article." Title of Periodical, vol. no, year, pp. Source, Permalink .
- The MLA Style Center, Works Cited: A Quick Guide.
- MLA Citations by Format
- Purdue Online Writing Lab sample MLA Works Cited
MLA Handbook, Ninth Edition . Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
- << Previous: MLA Citations
- Next: Chicago Citations >>
- Last Updated: Oct 23, 2023 1:26 PM
- URL: https://libguides.thomasu.edu/citations

MLA Citation Guide (MLA 8th edition)
- Advertisments
- Books & e-Books
- Class Notes & Presentations
- Creative Commons Licensed Works.
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Charts, Graphs, Maps & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- When Creating Digital Assignments
- When Information Is Missing
- Works Cited in Another Source
- Quoting and Paraphrasing
- Works Cited and Sample Page
- Annotated Bibliography
Sample MLA Paper
The MLA Sample Paper Template may be used to set up your assignment. The template includes:
- A sample assignment page;
- and a Works CIted list in MLA format.
- MLA Sample Paper Template
If you are adding an appendix to your paper there are a few rules to follow that comply with MLA guidelines:
- The Appendix appears before the Works Cited list
- If you have more than one appendix you would name the first appendix Appendix A, the second Appendix B, etc.
- The appendices should appear in the order that the information is mentioned in your essay
- Each appendix begins on a new page
- MLA Sample Paper - with Appendix (Purdue OWL example) Note that while this example shows the correct way to format your Appendix, the individual MLA citations are incorrect as they are formatted according to the 7th (not 8th) edition of MLA.
- Sample Template with Appendix
- << Previous: Quoting and Paraphrasing
- Next: Annotated Bibliography >>
- Last Updated: Aug 7, 2023 3:03 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.uwm.edu/c.php?g=1017599
- Utility Menu
fa3d988da6f218669ec27d6b6019a0cd
A publication of the harvard college writing program.
Harvard Guide to Using Sources
- The Honor Code
- Works Cited Format
What is a Works Cited list?
MLA style requires you to include a list of all the works cited in your paper on a new page at the end of your paper. The entries in the list should be in alphabetical order by the author's last name or by the element that comes first in the citation. (If there is no author's name listed, you would begin with the title.) The entire list should be double-spaced.
For each of the entries in the list, every line after the first line should be indented one-half inch from the left margin. "Works Cited" should be centered at the top of the page. If you are only citing one source, the page heading should be “Work Cited” instead of “Works Cited.” You can see a sample Works Cited here .
Building your Works Cited list
MLA citations in the Works Cited list are based on what the Modern Language Association calls "core elements." The core elements appear in the order listed below, in a citation punctuated with the punctuation mark that follows the element. For some elements, the correct punctuation will be a period, and for other elements, the correct punctuation will be a comma. Since you can choose the core elements that are relevant to the source you are citing, this format should allow you to build your own citations when you are citing sources that are new or unusual.
The author you should list is the primary creator of the work—the writer, the artist, or organization that is credited with creating the source. You should list the author in this format: last name, first name. If there are two authors, you should use this format: last name, first name, and first name last name. For three or more authors, you should list the first author followed by et al. That format looks like this: last name, first name, et al.
If a source was created by an organization and no individual author is listed, you should list that organization as the author.
Title of source .
This is the book, article, or website, podcast, work of art, or any other source you are citing. If the source does not have a title, you can describe it. For example, if you are citing an email you received, you would use this format in the place of a title:
Email to the author.
Title of container ,
A container is what MLA calls the place where you found the source. It could be a book that an article appears in, a website that an image appears on, a television series from which you are citing an episode, etc. If you are citing a source that is not “contained” in another source—like a book or a film—you do not need to list a container. Some sources will be in more than one container. For example, if you are citing a television episode that aired on a streaming service, the show would be the first container and the streaming service would be the second container.
Contributor ,
Contributors include editors, translators, directors, illustrators, or anyone else that you want to credit. You generally credit other contributors when their contributions are important to the way you are using the source. You should always credit editors of editions and anthologies of a single author’s work or of a collection of works by more than one author.
If you are using a particular version of a source, such as an updated edition, you should indicate that in the citation.
If your source is one of several in a numbered series, you should indicate this. So, for example, you might be using “volume 2” of a source. You would indicate this by “vol. 2” in the citation.
Publisher ,
For books, you can identify the publisher on the title or copyright page. For web sites, you may find the publisher at the bottom of the home page or on an “About” page. You do not need to include the publisher if you are citing a periodical or a Web site with the same name as the publisher.
Publication date ,
Books and articles tend to have an easily identifiable publication date. But articles published on the web may have more than one date—one for the original publication and one for the date posted online. You should use the date that is most relevant to your work. If you consulted the online version, this is the relevant date for your Works Cited list. If you can’t find a publication date—some websites will not include this information, for example—then you should include a date of access. The date of access should appear at the end of your citation in the following format:
Accessed 14 Oct. 2022.
The location in a print source will be the page number or range of pages you consulted. This is where the text you are citing is located in the larger container. For online sources, the location is generally a DOI, permalink, or URL. This is where your readers can locate the same online source that you consulted. MLA specifies that, if possible, you should include the DOI. Television episodes would be located at a URL. A work of art could be located in the museum where you saw it or online.
Your citations can also include certain optional elements. You should include optional elements if you think those elements would provide useful information to your readers. Optional elements follow the source title if they provide information that is not about the source as a whole. Put them at the end of the entry if they provide information about the source as a whole. These elements include the following:
Date of original publication .
If you think it would be useful to a reader to know that the text you are citing was originally published in a different era, you can put this information right after the title of the source. For example, if you are citing The Federalist Papers , you would provide the publication date of the edition you consulted, but you could also provide the original publication date:
Hamilton, Alexander, et al., editors. The Federalist Papers . October 1787-May 1788. Oxford University Press, 2008.
City of publication .
You should only use this information if you are citing a book published before 1900 (when books were associated with cities of publication rather than with publishers) or a book that has been published in a different version by the publisher in another city (a British version of a novel, for example). In the first case, you would put this information in place of the publisher's name. In the second case, the city would go before the publisher.
Descriptive terms .
If you are citing a version of a work when there are multiple versions available at the same location, you should explain this by adding a term that will describe your version. For example, if you watched a video of a presidential debate that was posted to YouTube along with a transcript, and you are quoting from the transcript, you should add the word “Transcript” at the end of your citation.
Dissertations
- Citation Management Tools
- In-Text Citations
- In-Text Citation Examples
- Examples of Commonly Cited Sources
- Frequently Asked Questions about Citing Sources in MLA Format
- Sample Works Cited List
PDFs for This Section
- Citing Sources
- Online Library and Citation Tools
Research: MLA Documentation
Mla works cited, formatting the works cited section.
In MLA style, all the sources you cite throughout the text of your paper are listed together in full in the Works Cited section, which comes after the main text of your paper.
- Page numbers: Just as the rest of your paper, the top of the page should retain the right-justified header with your last name and the page number.
- Title: On the first line, the title of the page—“Works Cited”—should appear centered, and not italicized or bolded.
- Spacing: Like the rest of your paper, this page should be double-spaced and have 1-inch margins (don’t skip an extra line between citations).
- Alphabetical order: Starting on the next line after the page title, your references should be listed in alphabetical order by author. Multiple sources by the same author should be listed chronologically by year within the same group.
- Hanging indents: Each reference should be formatted with what is called a hanging indent. This means the first line of each reference should be flush with the left margin (i.e., not indented), but the rest of that reference should be indented 0.5 inches further. Any word-processing program will let you format this automatically so you don’t have to do it by hand. (In Microsoft Word, for example, you simply highlight your citations, click on the small arrow right next to the word “Paragraph” on the home tab, and in the popup box choose “hanging indent” under the “Special” section. Click OK, and you’re done.)

- MLA: The Works Cited Section. Authored by : Catherine McCarthy. Provided by : Boundless. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-writing/ . Project : Boundless Writing. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- MLA 8th Edition - What's New? sample of student works cited page. Provided by : College of DuPage Library. Located at : http://www.codlrc.org/IL/Future/MLA . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Works Cited Page
Last Updated: December 7, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 226,759 times.
If you’re writing in MLA format, the Works Cited page is the final piece to the puzzle that is your paper. [1] X Research source A Works Cited page is a complete list of the works that you cite in your paper, and it’s different than a Bibliography, which includes any works you used to write your paper, whether you cite them or not. A References page is similar to Works Cited, but is used in the APA format. Once you’re sure that Works Cited is the format you need, making sure that your Works Cited page is up to par can have a huge impact on both on the professionalism of your work as well as your final grade.
Collecting Necessary Information

- Published date
- Publisher location
- Medium (Print, web, film, DVD, etc.)
- Page numbers/Act, or section and line numbers

- Chicago Manual of Style refers to the Works Cited page as a Reference page using the author-date system.
- There is a difference between a bibliography and a Works Cited page. A bibliography includes any sources that you used while researching and preparing your paper, even if you don’t reference them in your writing. A Works Cited page only includes sources that are directly referenced.

- One-inch margins all around.
- Label the page “Works Cited”, and center it on the top line.
- All citations should be double-spaced, with no extra lines between entries.
- Indent all lines after the first of an entry by 0.5 inches (1.3 cm).

- Not all instructors in the arts follow MLA guidelines for formatting, so make sure that you know how your instructor would like the Works Cited page formatted.
Writing the Works Cited Page

- If the book has more than one author, only the first listed author goes last name first. Subsequent authors are listed as First Name Last Name.
- Periodicals : Author(s). “Article Title.” Periodical Title Day Month Year: Pages. Medium.
- MLA no longer requires URLs in Works Cited. Check with your instructor for specifics for your project.
- If no publisher is available, use the abbreviation “np”
- If no date is available, use the abbreviation “nd”
- Interview : Interviewee. Personal interview. Day Month Year.

FREE MLA online

- Type ISBN, title, or key words your book to begin MLA to search and automated citation;
- Verify the information that the ISBN id number brings up.
- Click to add a citation of a chapter title, add page numbers, etc.

Sample Works Cited Page

Community Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://openoregon.pressbooks.pub/wrd/back-matter/creating-a-works-cited-page/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_page_basic_format.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_and_style_guide.html
- ↑ https://irsc.libguides.com/mla/workscitedlist
About This Article

To write a works cited page using MLA style, list each work in alphabetical order with each entry on a new line. For a book, cite the author’s last name and first name, book’s title in italics, city of publication, publisher, year of publication, and medium. If you’re citing a periodical, provide the author, article’s title in quotes, periodical title in italics, publication date, relevant pages, and medium. Before you finalize your paper, check to see that the citations and footnotes are clearly marked and correspond correctly to your works cited page. For tips from our English reviewer on how to collect the information you need to write your works cited page, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Nov 8, 2017
Did this article help you?
Apr 19, 2017
I like wolves
Mar 17, 2022

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / APA Reference Page
How to Format an APA Reference Page
In APA, the “Works Cited” page is referred to as a “Reference List” or “Reference Page.” “Bibliography” also may be used interchangeably, even though there are some differences between the two.
If you are at the point in your article or research paper where you are looking up APA bibliography format, then congratulations! That means you’re almost done.
In this guide, you will learn how to successfully finish a paper by creating a properly formatted APA bibliography. More specifically, you will learn how to create a reference page . The guidelines presented here come from the 7 th edition of the APA’s Publication Manual .
A note on APA reference page style: In this guide, “bibliography” and “references” may be used interchangeably, even though there are some differences between the two. The most important thing is to use the label “References” when writing your paper since APA style recommends including a reference page.
Here’s a run-through of everything this page includes:
Difference between an APA bibliography and a reference page
What about annotated bibliographies, understanding apa reference page format, apa reference page formatting: alphabetizing by surname, q: what should not be on an apa reference page.
The difference between a bibliography and a reference page is a matter of scope. A bibliography usually includes all materials and sources that were used to write the paper. A reference page, on the other hand, only includes entries for works that were specifically cited in the text of the paper.
There are some cases in which a professor or journal might request an annotated bibliography . An annotated bibliography is basically a reference page that includes your comments and insights on each source.
An annotated bibliography can be a document all on its own, or part of a bigger document. That means creating an annotated bibliography by itself could be an assignment, or you may have to include one as part of your research paper, journal submission, or other project.
If you do need to add an APA annotated bibliography , it goes after the reference page on its own page, inside the appendices.
A properly formatted APA reference page begins on a new page, after the end of the text. It comes before any figures, tables, maps, or appendices. It’s double-spaced and features what’s called a hanging indent , where the first line of each reference is not indented, and the second line of each reference is indented 0.5 inches. The reference page is also labeled with a bold, center-justified, and capitalized “References.”
To summarize, the reference page should be:
- Placed on its own page, after the text but before any tables, figures, or appendices.
- In the same font as the rest of the paper.
- Double-spaced the whole way through (including individual references).
- Formatted with hanging indents (each line after the first line of every entry indented 0.5 inches).
- Labeled with a bold, center-justified, and capitalized “References.”
Note: You can use the paragraph function of your word processing program to apply the hanging indent.
Q: What font am I supposed to use for the reference page or bibliography?
The APA reference page/bibliography should be in the same font as the rest of your paper. However, APA Style does not actually call for one specific font. According to Section 2.19 of the Publication Manual , the main requirement is to choose a font that is readable and accessible to all users. Some of the recommended font options for APA style include:
- Sans serif fonts: Calibri (11pt), Arial (11pt), or Lucida (10pt).
- Serif fonts: Times New Roman (12pt), Georgia (11pt), or Normal/Computer Modern (10pt).
Q: What are the margins supposed to be for the reference page or bibliography?
Aside from the 0.5 inch hanging indent on the second line of each reference entry, you do not need to modify the margins of the reference page or bibliography. These should be the same as the rest of your paper, which according to APA is 1-inch margins on all sides of the page. This is the default margin setting for most computer word processors, so you probably won’t have to change anything.
Q: What information goes into an APA style reference page or bibliography?
An APA style reference page should include full citations for all the sources that were cited in your paper. This includes sources that were summarized, paraphrased, and directly quoted. Essentially, if you included an in-text citation in your paper, that source should also appear in your reference list. The reference list is organized in alphabetical order by author.
The formatting for reference list citations varies depending on the kind of source and the available information. But for most sources, your reference list entry will include the following:
- The last name(s) and initials of the author(s).
- The date the source was published (shown in parentheses).
- The title of the source in sentence case. The title should be in italics if the source stands on its own (like a book, webpage, or movie).
- The name of the periodical, database, or website if the source is an article from a magazine, journal, newspaper, etc. Names of periodicals are usually italicized; names of databases and websites usually are not.
- The publisher of the source and/or the URL where the source can be found.
Here are a few templates and examples for how common sources should be formatted in an APA style reference list. If your source is not found here, there is also a guide highlighting different APA citation examples .
Citing a Book
Author’s last name, Author’s first initial. Author’s middle initial. (Year of publication). Title of work . Publisher.
James, Henry. (2009). The ambassadors . Serenity Publishers.
Citing a Journal
Author’s last name, Author’s first initial. Author’s middle initial. (Year, Month Date published). Article title. Journal Name , Volume(Issue), page number(s). https://doi.org/ or URL (if available)
Jacoby, W. G. (1994). Public attitudes toward government spending. American Journal of Political Science , 38(2), 336-361. https://doi.org/10.2307/2111407
Citing a Website
Author’s last name, Author’s first initial. Author’s middle initial. (Year, Month Date published). Article title or page title . Site Name. URL
Limer, E. (2013, October 1). Heck yes! The first free wireless plan is finally here . Gizmodo. https://gizmodo.com/heck-yes-the-first-free-wireless-plan-is-finally-here
Next, let’s take a look at a real example of a properly formatted APA reference page to see how these pieces come together.
APA reference page example
Creating an APA reference page is actually a lot easier than creating a bibliography with other style guides. In fact, as long as you are aware of the formatting rules, the reference page practically writes itself as you go.
Below is an example reference page that follows the guidelines detailed above. EasyBib also has a guide featuring a complete APA style sample paper , including the reference page.
All APA citations included in the reference page should be ordered alphabetically, using the first word of the reference entry. In most cases, this is the author’s surname (or the surname of the author listed first, when dealing with citations for sources with multiple authors ). However, there are times when a reference entry might begin with a different element.
Creating an alphabetized reference page or bibliography might seem like a simple task. But when you start dealing with multiple authors and similar last names, it can actually get a little tricky. Fortunately, there are a few basic rules that can keep you on track.
The “nothing precedes something” rule
When the surnames of two or more authors begin with the same letters, the “nothing precedes something” rule is how to figure it out. Here is an example of how it works.
Imagine your reference page includes the authors Berg, M.S. and Bergman, H.D. The first four letters of each author are the same. The fifth letters are M and H respectively. Since H comes before M in the alphabet, you might assume that Bergman, H.D. should be listed first.
APA Style requires that “nothing precede something,” which means that Berg will appear before Bergman. Similarly, a James would automatically appear before a Jameson, and a Michaels before a Michaelson.
Disregard spaces and punctuation marks
If a surname has a hyphen, apostrophe, or other punctuation mark, it can be ignored for alphabetization purposes. Similarly, anything that appears inside of parentheses or brackets should be disregarded.
Ordering multiple works by the same author
It is not uncommon for a research paper to reference multiple books by the same author. If you have more than one reference entry by the same person, then the entries should be listed chronologically by year of publication.
If a reference entry has no year of publication available, then it should precede any entries that do have a date. Here’s an example of a properly alphabetized order for multiple entries from the same author:
Guzman, M.B. (n.d.).
Guzman, M.B. (2016).
Guzman, M.B. (2017).
Guzman, M.B. (2019).
Guzman, M.B. (in press).
“In press” papers do not yet have a year of publication associated with them. All “in press” sources are listed last, like the one shown above.
Ordering works with the same author and same date
If the same author has multiple entries with the same year of publication, you need to differentiate them with lowercase letters. Otherwise, the in-text citations in your paper will correspond to more than one reference page entry.
Same author and same year of publication
Here’s a look at how to use lowercase letters to differentiate between entries with the same author and same year of publication:
Guzman, M.B. (2020a).
Guzman, M.B. (2020b).
Guzman, M.B. (2020c).
These lowercase letters are assigned to make the in-text citations more specific. However, it does not change the fact that their year of publication is the same. If no month or day is available for any of the sources, then they should be ordered alphabetically using the title of the work.
When alphabetizing by title, ignore the words “A,” “An,”,and “The” if they’re the first word of the title.
Same author and same year of publication, with more specific dates
If more specific dates are provided, such as a month or day, then it becomes possible to order these entries chronologically.
Guzman, M.B. (2020b, April 2).
Guzman, M.B. (2020c, October 15).
Ordering authors with the same surname but different initials
Authors who share the same surname but have different first or middle names can be alphabetized by their first initial or second initial.
Guzman, R.L. (2015).
Ordering works with no listed author, or an anonymous author
If you have reference entries with no listed author, the first thing to double-check is whether or not there was a group author instead. Group authors can be businesses, task forces, nonprofit organizations, government agencies, etc.
If there is no individual author listed, then have another look at the source. If it is published on a government agency website, for instance, there is a good chance that the agency was the author of the work, and should be listed as such in the reference entry. You can read more about how to handle group authors in Section 9.11 of the Publication Manual .
What if the work is actually authored by “Anonymous”?
If the work you’re referencing actually has the word “Anonymous” listed as the author, then you can list it as the author and alphabetize it as if it were a real name. But this is only if the work is actually signed “Anonymous.”
What if there is no listed author and it’s definitely not a group author?
If you have confirmed that there is no individual or group author for the work, then you can use the work’s title as the author element in the reference entry. In any case where you’re using the work’s title to alphabetize, you should skip the words “A,” “An,” and “The.”
An APA reference page should not contain any of the following:
- The content of your paper (the reference page should start on its own page after the end of your paper).
- Entries for works for further reading or background information or entries for an epigraph from a famous person (the reference page should only include works that are referenced or quoted in your paper as part of your argument).
- Entries for personal communications such as emails, phone calls, text messages, etc. (since the reader would not be able to access them).
- Entries for whole websites, periodicals, etc. (If needed, the names of these can be mentioned within the body of your paper instead.)
- Entries for quotations from research participants (since they are part of your original research, they do not need to be included).
Published October 28, 2020.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
The following rules will help you identify when to use DOIs and when to use URLs in references:
- Use a DOI wherever available, be it a print version or online version.
- For a print publication that does not have a DOI, do not add a DOI or URL (even if a URL is available).
- For an online publication, if both a DOI and URL are given, include only the DOI.
- For online publications that only have a URL (and no DOI), follow the below recommendations:
- Add a URL in the reference list entry for publications from websites (other than databases). Double check that the URL will work for readers.
- For publications from most academic research databases, which are easily accessible, do not include a URL or database information in the reference. In this case, the reference will be the same as the print version.
- For publications from databases that publish limited/proprietary work that would only be available in that database, include the database name and the URL. If the URL would require a login, include the URL for the database home page or login page instead of the URL for the work.
- If a URL will not work for the reader or is no longer accessible, follow the guidance for citing works with no source.
To format your APA references list, follow these recommendations:
- Begin the references on a new page. This page should be placed at the end of the paper.
- All sides of the paper should have a 1-inch margin.
- Set the heading as “References” in bold text and center it.
- Arrange the reference entries alphabetically according to the first item within the entries (usually the author surname or title).
- Add a hanging indent of 0.5 inches (i.e., indent any line after the first line of a reference list entry).
See above for a visual example of a reference page and additional examples.
Special Cases
Multiple entries with the same author(s) are arranged by publication year. Entries with no dates first, then in chronological order. If the year published is also the same, a letter is added to the year and the entries are arranged alphabetically (after arrangement by year).
- Robin, M. T. (n.d.)
- Robin, M. T. (1987)
- Robin, M. T. (1989a)
- Robin, M. T. (1989b)
Single-author source and multi-author source that share one author. One-author entries are listed first even if the multi-author entries were published earlier.
- Dave, S. P., Jr. (2006)
- Dave, S. P., Jr., & Glyn, T. L. (2005)
For references with multiple authors that have the same first author but different subsequent authors, alphabetize the entries by the last name of the second author (or third if the first two authors are the same).
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, works cited page checklist.

Did I do this right? A checklist for your Works Cited Page!
We get it: formatting can be tough, especially when you’ve been working on a paper for a while and your eyes are starting to cross and the letters are bleeding into one another. If you find yourself nearing the end, use this handy checklist to make sure your Works Cited Page follows all of the rules!
- Is your Works Cited on a new page of the paper? For instance, if your essay is four pages long, your Works Cited Page should be on page five. While you’re checking out page numbers, do a quick scan of your page layout. You should have your header in the upper right hand corner (last name page number) and the words “Works Cited” centered above your list. That’s it!
- Is your list double-spaced? Nicely done. How about those margins? Still one inch all the way around? Great!

- Scan the left side of your page. The first line of each new entry should be aligned with the margin. The rest of each citation (each line of text below the first one) should be indented. This makes it easier for readers to find the source they are seeking without wading through extra information.
- Did you add any unnecessary extras? Scan your page now and delete any bullet points or numbers. Your list is alphabetized—that’s enough organization for MLA. Also, you do not need to repeat your first page heading on this page (Name, teacher name, class, date). Just the upper right hand corner name and page number is enough.
You made it! Now your readers can use the Works Cited Page as MLA intended. Thanks for being a courteous MLA format user.

Brevity – Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence – How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow – How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity – Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style – The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing
University of Tasmania, Australia
Referencing guide: works cited - more examples.
- Systems and Styles
- Using in-text citations
- Using Turnitin
- Managing references
- AGLC This link opens in a new window
- Health & Medicine examples This link opens in a new window
- Transition from Harvard to APA
- General principles
- In-text citations
Works Cited
- Works Cited - Author
- Works Cited - Title
- Works cited - Title of Container
- Works Cited - Other Contributors
- Works Cited - Version & Number
- Works Cited - Publisher & Publication Date
- Works Cited - Location
- Works Cited - Optional Elements
- Works Cited - More Examples
- Simplified Author-date & Writing guide
Works Cited is a list of sources from which you have borrowed information or ideas. You need to acknowledge – or cite – all your sources.
Below are some examples of different types of works formatted according to the MLA style. Omit any elements that are not applicable.
Author. Title of source . Title of container , Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location.
Style Manual
If you cannot find an example for what you are looking for here, consult the MLA website , or the MLA Handbook (below)
Need more help?
Ask a librarian
Visit our webpage
- << Previous: Works Cited - Optional Elements
- Next: Chicago >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2024 11:29 AM
- URL: https://utas.libguides.com/referencing

Scribbr Citation Generator
Accurate APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard citations, verified by experts, trusted by millions
Scribbr for Chrome: Your shortcut to citations
Cite any page or article with a single click right from your browser. The extension does the hard work for you by automatically grabbing the title, author(s), publication date, and everything else needed to whip up the perfect citation.

Perfectly formatted references every time
Inaccurate citations can cost you points on your assignments, so our seasoned citation experts have invested countless hours in perfecting Scribbr’s citation generator algorithms. We’re proud to be recommended by teachers and universities worldwide.
Enjoy a citation generator without flashy ads
Staying focused is already difficult enough, so unlike other citation generators, Scribbr won’t slow you down with flashing banner ads and video pop-ups. That’s a promise!
Citation Generator features you'll love
Look up your source by its title, URL, ISBN, or DOI, and let Scribbr find and fill in all the relevant information automatically.
APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard
Generate flawless citations according to the official APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard style, or many other rules.
Export to Word
When your reference list is complete, export it to Word. We’ll apply the official formatting guidelines automatically.
Lists and folders
Create separate reference lists for each of your assignments to stay organized. You can also group related lists into folders.
Export to Bib(La)TeX
Are you using a LaTex editor like Overleaf? If so, you can easily export your references in Bib(La)TeX format with a single click.
Custom fonts
Change the typeface used for your reference list to match the rest of your document. Options include Times New Roman, Arial, and Calibri.
Industry-standard technology
Scribbr’s Citation Generator is built using the same citation software (CSL) as Mendeley and Zotero, but with an added layer for improved accuracy.
Annotations
Describe or evaluate your sources in annotations, and Scribbr will generate a perfectly formatted annotated bibliography .
Citation guides
Scribbr’s popular guides and videos will help you understand everything related to finding, evaluating, and citing sources.
Secure backup
Your work is saved automatically after every change and stored securely in your Scribbr account.
- Introduction
- Finding sources
Evaluating sources
- Integrating sources
Citing sources
Tools and resources, a quick guide to working with sources.
Working with sources is an important skill that you’ll need throughout your academic career.
It includes knowing how to find relevant sources, assessing their authority and credibility, and understanding how to integrate sources into your work with proper referencing.
This quick guide will help you get started!
Finding relevant sources
Sources commonly used in academic writing include academic journals, scholarly books, websites, newspapers, and encyclopedias. There are three main places to look for such sources:
- Research databases: Databases can be general or subject-specific. To get started, check out this list of databases by academic discipline . Another good starting point is Google Scholar .
- Your institution’s library: Use your library’s database to narrow down your search using keywords to find relevant articles, books, and newspapers matching your topic.
- Other online resources: Consult popular online sources like websites, blogs, or Wikipedia to find background information. Be sure to carefully evaluate the credibility of those online sources.
When using academic databases or search engines, you can use Boolean operators to refine your results.
Generate APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard citations in seconds
Get started
In academic writing, your sources should be credible, up to date, and relevant to your research topic. Useful approaches to evaluating sources include the CRAAP test and lateral reading.
CRAAP is an abbreviation that reminds you of a set of questions to ask yourself when evaluating information.
- Currency: Does the source reflect recent research?
- Relevance: Is the source related to your research topic?
- Authority: Is it a respected publication? Is the author an expert in their field?
- Accuracy: Does the source support its arguments and conclusions with evidence?
- Purpose: What is the author’s intention?
Lateral reading
Lateral reading means comparing your source to other sources. This allows you to:
- Verify evidence
- Contextualize information
- Find potential weaknesses
If a source is using methods or drawing conclusions that are incompatible with other research in its field, it may not be reliable.
Integrating sources into your work
Once you have found information that you want to include in your paper, signal phrases can help you to introduce it. Here are a few examples:
Following the signal phrase, you can choose to quote, paraphrase or summarize the source.
- Quoting : This means including the exact words of another source in your paper. The quoted text must be enclosed in quotation marks or (for longer quotes) presented as a block quote . Quote a source when the meaning is difficult to convey in different words or when you want to analyze the language itself.
- Paraphrasing : This means putting another person’s ideas into your own words. It allows you to integrate sources more smoothly into your text, maintaining a consistent voice. It also shows that you have understood the meaning of the source.
- Summarizing : This means giving an overview of the essential points of a source. Summaries should be much shorter than the original text. You should describe the key points in your own words and not quote from the original text.
Whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize a source, you must include a citation crediting the original author.
Citing your sources is important because it:
- Allows you to avoid plagiarism
- Establishes the credentials of your sources
- Backs up your arguments with evidence
- Allows your reader to verify the legitimacy of your conclusions
The most common citation styles are APA, MLA, and Chicago style. Each citation style has specific rules for formatting citations.
Generate APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard citations in seconds
Scribbr offers tons of tools and resources to make working with sources easier and faster. Take a look at our top picks:
- Citation Generator: Automatically generate accurate references and in-text citations using Scribbr’s APA Citation Generator, MLA Citation Generator , Harvard Referencing Generator , and Chicago Citation Generator .
- Plagiarism Checker : Detect plagiarism in your paper using the most accurate Turnitin-powered plagiarism software available to students.
- AI Proofreader: Upload and improve unlimited documents and earn higher grades on your assignments. Try it for free!
- Paraphrasing tool: Avoid accidental plagiarism and make your text sound better.
- Grammar checker : Eliminate pesky spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Summarizer: Read more in less time. Distill lengthy and complex texts down to their key points.
- AI detector: Find out if your text was written with ChatGPT or any other AI writing tool. ChatGPT 2 & ChatGPT 3 supported.
- Proofreading services : Have a human editor improve your writing.
- Citation checker: Check your work for citation errors and missing citations.
- Knowledge Base : Explore hundreds of articles, bite-sized videos, time-saving templates, and handy checklists that guide you through the process of research, writing, and citation.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you refer to a journal article that appeared on pages 225 through 250, list the page numbers on your Works Cited page as pp. 225-50 (Note: MLA style dictates that you should omit the first sets of repeated digits. In our example, the digit in the hundreds place is repeated between 2 25 and 2 50, so you omit the 2 from 250 in the citation: pp ...
Place the works cited page after the body of your paper or thesis. Maintain a one-inch margin on all sides. Add an MLA header (last name and page number) in the upper right corner. Double-space the entire page. Use an 11- to 13-point standard font (Times New Roman, Arial, Georgia, or Calibri).
According to MLA format guidelines, the Works Cited page(s) should look like this: Running head containing your surname and the page number. The title, Works Cited, centered and in plain text. List of sources alphabetized by the author's surname. Left-aligned. Double-spaced. 1-inch margins. Hanging indent applied to all entries.
Title the page Works Cited (not Bibliography), and list only those sources you actually cited in your paper. Continue the page numbering from the body of your paper and make sure that you still have 1-inch margins at the top, bottom, and sides of your page. Double-space the entire list. Indent entries as shown in the models below with what ...
Works Cited page. The Works Cited list is included on a separate page at the end of your paper. You list all the sources you referenced in your paper in alphabetical order. Don't include sources that weren't cited in the paper, except potentially in an MLA annotated bibliography assignment.. Place the title "Works Cited" in the center at the top of the page.
MLA Works Cited refers to t he MLA's (Modern Language Association's) guidelines for formatting a list of references at the end of a text that cites sources. The MLA Handbook, 9th Edition requires authors to provide a list of references — aka a works cited page — at the end of their texts. to acknowledge the people and ideas that have ...
See an example in the "Sample Paper & Works Cited List" box on this page. Here are eight quick rules for this list: Start a new page for your Works Cited list (e.g., if your paper is 4 pages long, start your Works Cited list on page 5). Center the title, Works Cited, at the top of the page and do not bold or underline it. Double-space the list.
Begin your Works Cited page on a separate page at the end of your research paper. The heading, Works Cited, should be centered one inch from the top of the page. If there is only one work in the list, call it Work Cited. Double-space between the heading and the first entry. Each entry should be flush against the left margin.
A sample assignment page; and a Works CIted list in MLA format. The Word document sample paper template may display incorrect margins. Please double check to ensure 1" margins on all sides. MLA Sample Paper Template. Appendix.
Center the words "Works Cited" at the top of the new page. The page should have your last name and the next page number in the header, as on all the other essay pages. Double space every line—no additional spacing required. Alphabetize entries by authors' last names. If author names are unavailable for an entry, alphabetize by the first ...
For each of the entries in the list, every line after the first line should be indented one-half inch from the left margin. "Works Cited" should be centered at the top of the page. If you are only citing one source, the page heading should be "Work Cited" instead of "Works Cited.". You can see a sample Works Cited here .
In MLA style, all the sources you cite throughout the text of your paper are listed together in full in the Works Cited section, which comes after the main text of your paper. Page numbers: Just as the rest of your paper, the top of the page should retain the right-justified header with your last name and the page number. Title: On the first ...
Quizlet is a great tool to help you study and learn different topics. In this flashcard set, you can test your knowledge of writing a works cited page, a crucial skill for academic writing. You will learn how to cite sources correctly, avoid plagiarism, and organize your references. Try it now and see how well you can master this skill.
Updated on September 22, 2022 Students. The works cited page is the part of a research paper that lists all the sources used by the author along with additional information like the publisher or URL. The works cited page is an integral part of any paper written in MLA format as it is a way to verify that the information in the paper is factual.
One-inch margins all around. Label the page "Works Cited", and center it on the top line. All citations should be double-spaced, with no extra lines between entries. Indent all lines after the first of an entry by 0.5 inches (1.3 cm). 4. Review the course syllabus, if your works cited page is for an academic course.
3.7. ( 155) In APA, the "Works Cited" page is referred to as a "Reference List" or "Reference Page." "Bibliography" also may be used interchangeably, even though there are some differences between the two. If you are at the point in your article or research paper where you are looking up APA bibliography format, then ...
For instance, if your essay is four pages long, your Works Cited Page should be on page five. While you're checking out page numbers, do a quick scan of your page layout. You should have your header in the upper right hand corner (last name page number) and the words "Works Cited" centered above your list. That's it!
Works Cited is a list of sources from which you have borrowed information or ideas. You need to acknowledge - or cite - all your sources. Below are some examples of different types of works formatted according to the MLA style. Omit any elements that are not applicable. Author. Title of source.
Learn Writing a Works Cited Page with free interactive flashcards. Choose from 500 different sets of Writing a Works Cited Page flashcards on Quizlet.
Citing a website in MLA Style. An MLA Works Cited entry for a webpage lists the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the site (in italics), the date of publication, and the URL. The in-text citation usually just lists the author's name. For a long page, you may specify a (shortened) section heading to ...
Proofreading services: Have a human editor improve your writing. Citation checker: Check your work for citation errors and missing citations. Knowledge Base: Explore hundreds of articles, bite-sized videos, time-saving templates, and handy checklists that guide you through the process of research, writing, and citation.
Check all that apply. Three more line spaces should be added before the footnote. The number 1 should be written in a superscript. There should be no punctuation after the author's name. The page numbers should be written "437/39." There needs to be a period at the end. Click the card to flip 👆. -- A.