Confusion to Clarity: Definition of Terms in a Research Paper
Explore the definition of terms in research paper to enhance your understanding of crucial scientific terminology and grow your knowledge.
Have you ever come across a research paper and found yourself scratching your head over complex synonyms and unfamiliar terms? It’s a hassle as you have to fetch a dictionary and then ruffle through it to find the meaning of the terms.
To avoid that, an exclusive section called ‘ Definition of Terms in a Research Paper ’ is introduced which contains the definitions of terms used in the paper. Let us learn more about it in this article.

What Is The “Definition Of Terms” In A Research Paper?
The definition of terms section in a research paper provides a clear and concise explanation of key concepts, variables, and terminology used throughout the study.
In the definition of terms section, researchers typically provide precise definitions for specific technical terms, acronyms, jargon, and any other domain-specific vocabulary used in their work. This section enhances the overall quality and rigor of the research by establishing a solid foundation for communication and understanding.
Purpose Of Definition Of Terms In A Research Paper
This section aims to ensure that readers have a common understanding of the terminology employed in the research, eliminating confusion and promoting clarity. The definitions provided serve as a reference point for readers, enabling them to comprehend the context and scope of the study. It serves several important purposes:
- Enhancing clarity
- Establishing a shared language
- Providing a reference point
- Setting the scope and context
- Ensuring consistency
Benefits Of Having A Definition Of Terms In A Research Paper
Having a definition of terms section in a research paper offers several benefits that contribute to the overall quality and effectiveness of the study. These benefits include:
Clarity And Comprehension
Clear definitions enable readers to understand the specific meanings of key terms, concepts, and variables used in the research. This promotes clarity and enhances comprehension, ensuring that readers can follow the study’s arguments, methods, and findings more easily.
Consistency And Precision
Definitions provide a consistent framework for the use of terminology throughout the research paper. By clearly defining terms, researchers establish a standard vocabulary, reducing ambiguity and potential misunderstandings. This precision enhances the accuracy and reliability of the study’s findings.
Common Understanding
The definition of terms section helps establish a shared understanding among readers, including those from different disciplines or with varying levels of familiarity with the subject matter. It ensures that readers approach the research with a common knowledge base, facilitating effective communication and interpretation of the results.
Avoiding Misinterpretation
Without clear definitions, readers may interpret terms and concepts differently, leading to misinterpretation of the research findings. By providing explicit definitions, researchers minimize the risk of misunderstandings and ensure that readers grasp the intended meaning of the terminology used in the study.
Accessibility For Diverse Audiences
Research papers are often read by a wide range of individuals, including researchers, students, policymakers, and professionals. Having a definition of terms in a research paper helps the diverse audience understand the concepts better and make appropriate decisions.
Types Of Definitions
There are several types of definitions that researchers can employ in a research paper, depending on the context and nature of the study. Here are some common types of definitions:
Lexical Definitions
Lexical definitions provide the dictionary or commonly accepted meaning of a term. They offer a concise and widely recognized explanation of a word or concept. Lexical definitions are useful for establishing a baseline understanding of a term, especially when dealing with everyday language or non-technical terms.
Operational Definitions
Operational definitions define a term or concept about how it is measured or observed in the study. These definitions specify the procedures, instruments, or criteria used to operationalize an abstract or theoretical concept. Operational definitions help ensure clarity and consistency in data collection and measurement.
Conceptual Definitions
Conceptual definitions provide an abstract or theoretical understanding of a term or concept within a specific research context. They often involve a more detailed and nuanced explanation, exploring the underlying principles, theories, or models that inform the concept. Conceptual definitions are useful for establishing a theoretical framework and promoting deeper understanding.
Descriptive Definitions
Descriptive definitions describe a term or concept by providing characteristics, features, or attributes associated with it. These definitions focus on outlining the essential qualities or elements that define the term. Descriptive definitions help readers grasp the nature and scope of a concept by painting a detailed picture.
Theoretical Definitions
Theoretical definitions explain a term or concept based on established theories or conceptual frameworks. They situate the concept within a broader theoretical context, connecting it to relevant literature and existing knowledge. Theoretical definitions help researchers establish the theoretical underpinnings of their study and provide a foundation for further analysis.
Also read: Understanding What is Theoretical Framework
Types Of Terms
In research papers, various types of terms can be identified based on their nature and usage. Here are some common types of terms:
A key term is a term that holds significant importance or plays a crucial role within the context of a research paper. It is a term that encapsulates a core concept, idea, or variable that is central to the study. Key terms are often essential for understanding the research objectives, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
Technical Term
Technical terms refer to specialized vocabulary or terminology used within a specific field of study. These terms are often precise and have specific meanings within their respective disciplines. Examples include “allele,” “hypothesis testing,” or “algorithm.”
Legal Terms
Legal terms are specific vocabulary used within the legal field to describe concepts, principles, and regulations. These terms have particular meanings within the legal context. Examples include “defendant,” “plaintiff,” “due process,” or “jurisdiction.”
Definitional Term
A definitional term refers to a word or phrase that requires an explicit definition to ensure clarity and understanding within a particular context. These terms may be technical, abstract, or have multiple interpretations.
Career Privacy Term
Career privacy term refers to a concept or idea related to the privacy of individuals in the context of their professional or occupational activities. It encompasses the protection of personal information, and confidential data, and the right to control the disclosure of sensitive career-related details.
A broad term is a term that encompasses a wide range of related concepts, ideas, or objects. It has a broader scope and may encompass multiple subcategories or specific examples.
Also read: Keywords In A Research Paper: The Importance Of The Right Choice
Steps To Writing Definitions Of Terms
When writing the definition of terms section for a research paper, you can follow these steps to ensure clarity and accuracy:
Step 1: Identify Key Terms
Review your research paper and identify the key terms that require definition. These terms are typically central to your study, specific to your field or topic, or may have different interpretations.
Step 2: Conduct Research
Conduct thorough research on each key term to understand its commonly accepted definition, usage, and any variations or nuances within your specific research context. Consult authoritative sources such as academic journals, books, or reputable online resources.
Step 3: Craft Concise Definitions
Based on your research, craft concise definitions for each key term. Aim for clarity, precision, and relevance. Define the term in a manner that reflects its significance within your research and ensures reader comprehension.
Step 4: Use Your Own Words
Paraphrase the definitions in your own words to avoid plagiarism and maintain academic integrity. While you can draw inspiration from existing definitions, rephrase them to reflect your understanding and writing style. Avoid directly copying from sources.
Step 5: Provide Examples Or Explanations
Consider providing examples, explanations, or context for the defined terms to enhance reader understanding. This can help illustrate how the term is applied within your research or clarify its practical implications.
Step 6: Order And Format
Decide on the order in which you present the definitions. You can follow alphabetical order or arrange them based on their importance or relevance to your research. Use consistent formatting, such as bold or italics, to distinguish the defined terms from the rest of the text.
Step 7: Revise And Refine
Review the definitions for clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Ensure that they align with your research objectives and are tailored to your specific study. Seek feedback from peers, mentors, or experts in your field to further refine and improve the definitions.
Step 8: Include Proper Citations
If you have drawn ideas or information from external sources, remember to provide proper citations for those sources. This demonstrates academic integrity and acknowledges the original authors.
Step 9: Incorporate The Section Into Your Paper
Integrate the definition of terms section into your research paper, typically as an early section following the introduction. Make sure it flows smoothly with the rest of the paper and provides a solid foundation for understanding the subsequent content.
By following these steps, you can create a well-crafted and informative definition of terms section that enhances the clarity and comprehension of your research paper.
In conclusion, the definition of terms in a research paper plays a critical role by providing clarity, establishing a common understanding, and enhancing communication among readers. The definition of terms section is an essential component that contributes to the overall quality, rigor, and effectiveness of a research paper.
Also read: Beyond The Main Text: The Value Of A Research Paper Appendix
Join Our Fast-Growing Community Of Users To Revolutionize Scientific Communication!
Every individual needs a community to learn, grow, and nurture their hobbies, passions, and skills. But when you are a scientist , it becomes difficult to identify the right community that aligns with your goals, has like-minded professionals, and understands mutual collaboration.
If you are a scientist, looking for a great community, Mind the Graph is here. Join our fast-growing community of users to revolutionize scientific communication and build a healthy collaboration. Sign up for free.

Related Articles

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
About Sowjanya Pedada
Sowjanya is a passionate writer and an avid reader. She holds MBA in Agribusiness Management and now is working as a content writer. She loves to play with words and hopes to make a difference in the world through her writings. Apart from writing, she is interested in reading fiction novels and doing craftwork. She also loves to travel and explore different cuisines and spend time with her family and friends.
Content tags
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
Glossary of research terms.
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
This glossary is intended to assist you in understanding commonly used terms and concepts when reading, interpreting, and evaluating scholarly research. Also included are common words and phrases defined within the context of how they apply to research in the social and behavioral sciences.
- Acculturation -- refers to the process of adapting to another culture, particularly in reference to blending in with the majority population [e.g., an immigrant adopting American customs]. However, acculturation also implies that both cultures add something to one another, but still remain distinct groups unto themselves.
- Accuracy -- a term used in survey research to refer to the match between the target population and the sample.
- Affective Measures -- procedures or devices used to obtain quantified descriptions of an individual's feelings, emotional states, or dispositions.
- Aggregate -- a total created from smaller units. For instance, the population of a county is an aggregate of the populations of the cities, rural areas, etc. that comprise the county. As a verb, it refers to total data from smaller units into a large unit.
- Anonymity -- a research condition in which no one, including the researcher, knows the identities of research participants.
- Baseline -- a control measurement carried out before an experimental treatment.
- Behaviorism -- school of psychological thought concerned with the observable, tangible, objective facts of behavior, rather than with subjective phenomena such as thoughts, emotions, or impulses. Contemporary behaviorism also emphasizes the study of mental states such as feelings and fantasies to the extent that they can be directly observed and measured.
- Beliefs -- ideas, doctrines, tenets, etc. that are accepted as true on grounds which are not immediately susceptible to rigorous proof.
- Benchmarking -- systematically measuring and comparing the operations and outcomes of organizations, systems, processes, etc., against agreed upon "best-in-class" frames of reference.
- Bias -- a loss of balance and accuracy in the use of research methods. It can appear in research via the sampling frame, random sampling, or non-response. It can also occur at other stages in research, such as while interviewing, in the design of questions, or in the way data are analyzed and presented. Bias means that the research findings will not be representative of, or generalizable to, a wider population.
- Case Study -- the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including data derived from the subjects themselves.
- Causal Hypothesis -- a statement hypothesizing that the independent variable affects the dependent variable in some way.
- Causal Relationship -- the relationship established that shows that an independent variable, and nothing else, causes a change in a dependent variable. It also establishes how much of a change is shown in the dependent variable.
- Causality -- the relation between cause and effect.
- Central Tendency -- any way of describing or characterizing typical, average, or common values in some distribution.
- Chi-square Analysis -- a common non-parametric statistical test which compares an expected proportion or ratio to an actual proportion or ratio.
- Claim -- a statement, similar to a hypothesis, which is made in response to the research question and that is affirmed with evidence based on research.
- Classification -- ordering of related phenomena into categories, groups, or systems according to characteristics or attributes.
- Cluster Analysis -- a method of statistical analysis where data that share a common trait are grouped together. The data is collected in a way that allows the data collector to group data according to certain characteristics.
- Cohort Analysis -- group by group analytic treatment of individuals having a statistical factor in common to each group. Group members share a particular characteristic [e.g., born in a given year] or a common experience [e.g., entering a college at a given time].
- Confidentiality -- a research condition in which no one except the researcher(s) knows the identities of the participants in a study. It refers to the treatment of information that a participant has disclosed to the researcher in a relationship of trust and with the expectation that it will not be revealed to others in ways that violate the original consent agreement, unless permission is granted by the participant.
- Confirmability Objectivity -- the findings of the study could be confirmed by another person conducting the same study.
- Construct -- refers to any of the following: something that exists theoretically but is not directly observable; a concept developed [constructed] for describing relations among phenomena or for other research purposes; or, a theoretical definition in which concepts are defined in terms of other concepts. For example, intelligence cannot be directly observed or measured; it is a construct.
- Construct Validity -- seeks an agreement between a theoretical concept and a specific measuring device, such as observation.
- Constructivism -- the idea that reality is socially constructed. It is the view that reality cannot be understood outside of the way humans interact and that the idea that knowledge is constructed, not discovered. Constructivists believe that learning is more active and self-directed than either behaviorism or cognitive theory would postulate.
- Content Analysis -- the systematic, objective, and quantitative description of the manifest or latent content of print or nonprint communications.
- Context Sensitivity -- awareness by a qualitative researcher of factors such as values and beliefs that influence cultural behaviors.
- Control Group -- the group in an experimental design that receives either no treatment or a different treatment from the experimental group. This group can thus be compared to the experimental group.
- Controlled Experiment -- an experimental design with two or more randomly selected groups [an experimental group and control group] in which the researcher controls or introduces the independent variable and measures the dependent variable at least two times [pre- and post-test measurements].
- Correlation -- a common statistical analysis, usually abbreviated as r, that measures the degree of relationship between pairs of interval variables in a sample. The range of correlation is from -1.00 to zero to +1.00. Also, a non-cause and effect relationship between two variables.
- Covariate -- a product of the correlation of two related variables times their standard deviations. Used in true experiments to measure the difference of treatment between them.
- Credibility -- a researcher's ability to demonstrate that the object of a study is accurately identified and described based on the way in which the study was conducted.
- Critical Theory -- an evaluative approach to social science research, associated with Germany's neo-Marxist “Frankfurt School,” that aims to criticize as well as analyze society, opposing the political orthodoxy of modern communism. Its goal is to promote human emancipatory forces and to expose ideas and systems that impede them.
- Data -- factual information [as measurements or statistics] used as a basis for reasoning, discussion, or calculation.
- Data Mining -- the process of analyzing data from different perspectives and summarizing it into useful information, often to discover patterns and/or systematic relationships among variables.
- Data Quality -- this is the degree to which the collected data [results of measurement or observation] meet the standards of quality to be considered valid [trustworthy] and reliable [dependable].
- Deductive -- a form of reasoning in which conclusions are formulated about particulars from general or universal premises.
- Dependability -- being able to account for changes in the design of the study and the changing conditions surrounding what was studied.
- Dependent Variable -- a variable that varies due, at least in part, to the impact of the independent variable. In other words, its value “depends” on the value of the independent variable. For example, in the variables “gender” and “academic major,” academic major is the dependent variable, meaning that your major cannot determine whether you are male or female, but your gender might indirectly lead you to favor one major over another.
- Deviation -- the distance between the mean and a particular data point in a given distribution.
- Discourse Community -- a community of scholars and researchers in a given field who respond to and communicate to each other through published articles in the community's journals and presentations at conventions. All members of the discourse community adhere to certain conventions for the presentation of their theories and research.
- Discrete Variable -- a variable that is measured solely in whole units, such as, gender and number of siblings.
- Distribution -- the range of values of a particular variable.
- Effect Size -- the amount of change in a dependent variable that can be attributed to manipulations of the independent variable. A large effect size exists when the value of the dependent variable is strongly influenced by the independent variable. It is the mean difference on a variable between experimental and control groups divided by the standard deviation on that variable of the pooled groups or of the control group alone.
- Emancipatory Research -- research is conducted on and with people from marginalized groups or communities. It is led by a researcher or research team who is either an indigenous or external insider; is interpreted within intellectual frameworks of that group; and, is conducted largely for the purpose of empowering members of that community and improving services for them. It also engages members of the community as co-constructors or validators of knowledge.
- Empirical Research -- the process of developing systematized knowledge gained from observations that are formulated to support insights and generalizations about the phenomena being researched.
- Epistemology -- concerns knowledge construction; asks what constitutes knowledge and how knowledge is validated.
- Ethnography -- method to study groups and/or cultures over a period of time. The goal of this type of research is to comprehend the particular group/culture through immersion into the culture or group. Research is completed through various methods but, since the researcher is immersed within the group for an extended period of time, more detailed information is usually collected during the research.
- Expectancy Effect -- any unconscious or conscious cues that convey to the participant in a study how the researcher wants them to respond. Expecting someone to behave in a particular way has been shown to promote the expected behavior. Expectancy effects can be minimized by using standardized interactions with subjects, automated data-gathering methods, and double blind protocols.
- External Validity -- the extent to which the results of a study are generalizable or transferable.
- Factor Analysis -- a statistical test that explores relationships among data. The test explores which variables in a data set are most related to each other. In a carefully constructed survey, for example, factor analysis can yield information on patterns of responses, not simply data on a single response. Larger tendencies may then be interpreted, indicating behavior trends rather than simply responses to specific questions.
- Field Studies -- academic or other investigative studies undertaken in a natural setting, rather than in laboratories, classrooms, or other structured environments.
- Focus Groups -- small, roundtable discussion groups charged with examining specific topics or problems, including possible options or solutions. Focus groups usually consist of 4-12 participants, guided by moderators to keep the discussion flowing and to collect and report the results.
- Framework -- the structure and support that may be used as both the launching point and the on-going guidelines for investigating a research problem.
- Generalizability -- the extent to which research findings and conclusions conducted on a specific study to groups or situations can be applied to the population at large.
- Grey Literature -- research produced by organizations outside of commercial and academic publishing that publish materials, such as, working papers, research reports, and briefing papers.
- Grounded Theory -- practice of developing other theories that emerge from observing a group. Theories are grounded in the group's observable experiences, but researchers add their own insight into why those experiences exist.
- Group Behavior -- behaviors of a group as a whole, as well as the behavior of an individual as influenced by his or her membership in a group.
- Hypothesis -- a tentative explanation based on theory to predict a causal relationship between variables.
- Independent Variable -- the conditions of an experiment that are systematically manipulated by the researcher. A variable that is not impacted by the dependent variable, and that itself impacts the dependent variable. In the earlier example of "gender" and "academic major," (see Dependent Variable) gender is the independent variable.
- Individualism -- a theory or policy having primary regard for the liberty, rights, or independent actions of individuals.
- Inductive -- a form of reasoning in which a generalized conclusion is formulated from particular instances.
- Inductive Analysis -- a form of analysis based on inductive reasoning; a researcher using inductive analysis starts with answers, but formulates questions throughout the research process.
- Insiderness -- a concept in qualitative research that refers to the degree to which a researcher has access to and an understanding of persons, places, or things within a group or community based on being a member of that group or community.
- Internal Consistency -- the extent to which all questions or items assess the same characteristic, skill, or quality.
- Internal Validity -- the rigor with which the study was conducted [e.g., the study's design, the care taken to conduct measurements, and decisions concerning what was and was not measured]. It is also the extent to which the designers of a study have taken into account alternative explanations for any causal relationships they explore. In studies that do not explore causal relationships, only the first of these definitions should be considered when assessing internal validity.
- Life History -- a record of an event/events in a respondent's life told [written down, but increasingly audio or video recorded] by the respondent from his/her own perspective in his/her own words. A life history is different from a "research story" in that it covers a longer time span, perhaps a complete life, or a significant period in a life.
- Margin of Error -- the permittable or acceptable deviation from the target or a specific value. The allowance for slight error or miscalculation or changing circumstances in a study.
- Measurement -- process of obtaining a numerical description of the extent to which persons, organizations, or things possess specified characteristics.
- Meta-Analysis -- an analysis combining the results of several studies that address a set of related hypotheses.
- Methodology -- a theory or analysis of how research does and should proceed.
- Methods -- systematic approaches to the conduct of an operation or process. It includes steps of procedure, application of techniques, systems of reasoning or analysis, and the modes of inquiry employed by a discipline.
- Mixed-Methods -- a research approach that uses two or more methods from both the quantitative and qualitative research categories. It is also referred to as blended methods, combined methods, or methodological triangulation.
- Modeling -- the creation of a physical or computer analogy to understand a particular phenomenon. Modeling helps in estimating the relative magnitude of various factors involved in a phenomenon. A successful model can be shown to account for unexpected behavior that has been observed, to predict certain behaviors, which can then be tested experimentally, and to demonstrate that a given theory cannot account for certain phenomenon.
- Models -- representations of objects, principles, processes, or ideas often used for imitation or emulation.
- Naturalistic Observation -- observation of behaviors and events in natural settings without experimental manipulation or other forms of interference.
- Norm -- the norm in statistics is the average or usual performance. For example, students usually complete their high school graduation requirements when they are 18 years old. Even though some students graduate when they are younger or older, the norm is that any given student will graduate when he or she is 18 years old.
- Null Hypothesis -- the proposition, to be tested statistically, that the experimental intervention has "no effect," meaning that the treatment and control groups will not differ as a result of the intervention. Investigators usually hope that the data will demonstrate some effect from the intervention, thus allowing the investigator to reject the null hypothesis.
- Ontology -- a discipline of philosophy that explores the science of what is, the kinds and structures of objects, properties, events, processes, and relations in every area of reality.
- Panel Study -- a longitudinal study in which a group of individuals is interviewed at intervals over a period of time.
- Participant -- individuals whose physiological and/or behavioral characteristics and responses are the object of study in a research project.
- Peer-Review -- the process in which the author of a book, article, or other type of publication submits his or her work to experts in the field for critical evaluation, usually prior to publication. This is standard procedure in publishing scholarly research.
- Phenomenology -- a qualitative research approach concerned with understanding certain group behaviors from that group's point of view.
- Philosophy -- critical examination of the grounds for fundamental beliefs and analysis of the basic concepts, doctrines, or practices that express such beliefs.
- Phonology -- the study of the ways in which speech sounds form systems and patterns in language.
- Policy -- governing principles that serve as guidelines or rules for decision making and action in a given area.
- Policy Analysis -- systematic study of the nature, rationale, cost, impact, effectiveness, implications, etc., of existing or alternative policies, using the theories and methodologies of relevant social science disciplines.
- Population -- the target group under investigation. The population is the entire set under consideration. Samples are drawn from populations.
- Position Papers -- statements of official or organizational viewpoints, often recommending a particular course of action or response to a situation.
- Positivism -- a doctrine in the philosophy of science, positivism argues that science can only deal with observable entities known directly to experience. The positivist aims to construct general laws, or theories, which express relationships between phenomena. Observation and experiment is used to show whether the phenomena fit the theory.
- Predictive Measurement -- use of tests, inventories, or other measures to determine or estimate future events, conditions, outcomes, or trends.
- Principal Investigator -- the scientist or scholar with primary responsibility for the design and conduct of a research project.
- Probability -- the chance that a phenomenon will occur randomly. As a statistical measure, it is shown as p [the "p" factor].
- Questionnaire -- structured sets of questions on specified subjects that are used to gather information, attitudes, or opinions.
- Random Sampling -- a process used in research to draw a sample of a population strictly by chance, yielding no discernible pattern beyond chance. Random sampling can be accomplished by first numbering the population, then selecting the sample according to a table of random numbers or using a random-number computer generator. The sample is said to be random because there is no regular or discernible pattern or order. Random sample selection is used under the assumption that sufficiently large samples assigned randomly will exhibit a distribution comparable to that of the population from which the sample is drawn. The random assignment of participants increases the probability that differences observed between participant groups are the result of the experimental intervention.
- Reliability -- the degree to which a measure yields consistent results. If the measuring instrument [e.g., survey] is reliable, then administering it to similar groups would yield similar results. Reliability is a prerequisite for validity. An unreliable indicator cannot produce trustworthy results.
- Representative Sample -- sample in which the participants closely match the characteristics of the population, and thus, all segments of the population are represented in the sample. A representative sample allows results to be generalized from the sample to the population.
- Rigor -- degree to which research methods are scrupulously and meticulously carried out in order to recognize important influences occurring in an experimental study.
- Sample -- the population researched in a particular study. Usually, attempts are made to select a "sample population" that is considered representative of groups of people to whom results will be generalized or transferred. In studies that use inferential statistics to analyze results or which are designed to be generalizable, sample size is critical, generally the larger the number in the sample, the higher the likelihood of a representative distribution of the population.
- Sampling Error -- the degree to which the results from the sample deviate from those that would be obtained from the entire population, because of random error in the selection of respondent and the corresponding reduction in reliability.
- Saturation -- a situation in which data analysis begins to reveal repetition and redundancy and when new data tend to confirm existing findings rather than expand upon them.
- Semantics -- the relationship between symbols and meaning in a linguistic system. Also, the cuing system that connects what is written in the text to what is stored in the reader's prior knowledge.
- Social Theories -- theories about the structure, organization, and functioning of human societies.
- Sociolinguistics -- the study of language in society and, more specifically, the study of language varieties, their functions, and their speakers.
- Standard Deviation -- a measure of variation that indicates the typical distance between the scores of a distribution and the mean; it is determined by taking the square root of the average of the squared deviations in a given distribution. It can be used to indicate the proportion of data within certain ranges of scale values when the distribution conforms closely to the normal curve.
- Statistical Analysis -- application of statistical processes and theory to the compilation, presentation, discussion, and interpretation of numerical data.
- Statistical Bias -- characteristics of an experimental or sampling design, or the mathematical treatment of data, that systematically affects the results of a study so as to produce incorrect, unjustified, or inappropriate inferences or conclusions.
- Statistical Significance -- the probability that the difference between the outcomes of the control and experimental group are great enough that it is unlikely due solely to chance. The probability that the null hypothesis can be rejected at a predetermined significance level [0.05 or 0.01].
- Statistical Tests -- researchers use statistical tests to make quantitative decisions about whether a study's data indicate a significant effect from the intervention and allow the researcher to reject the null hypothesis. That is, statistical tests show whether the differences between the outcomes of the control and experimental groups are great enough to be statistically significant. If differences are found to be statistically significant, it means that the probability [likelihood] that these differences occurred solely due to chance is relatively low. Most researchers agree that a significance value of .05 or less [i.e., there is a 95% probability that the differences are real] sufficiently determines significance.
- Subcultures -- ethnic, regional, economic, or social groups exhibiting characteristic patterns of behavior sufficient to distinguish them from the larger society to which they belong.
- Testing -- the act of gathering and processing information about individuals' ability, skill, understanding, or knowledge under controlled conditions.
- Theory -- a general explanation about a specific behavior or set of events that is based on known principles and serves to organize related events in a meaningful way. A theory is not as specific as a hypothesis.
- Treatment -- the stimulus given to a dependent variable.
- Trend Samples -- method of sampling different groups of people at different points in time from the same population.
- Triangulation -- a multi-method or pluralistic approach, using different methods in order to focus on the research topic from different viewpoints and to produce a multi-faceted set of data. Also used to check the validity of findings from any one method.
- Unit of Analysis -- the basic observable entity or phenomenon being analyzed by a study and for which data are collected in the form of variables.
- Validity -- the degree to which a study accurately reflects or assesses the specific concept that the researcher is attempting to measure. A method can be reliable, consistently measuring the same thing, but not valid.
- Variable -- any characteristic or trait that can vary from one person to another [race, gender, academic major] or for one person over time [age, political beliefs].
- Weighted Scores -- scores in which the components are modified by different multipliers to reflect their relative importance.
- White Paper -- an authoritative report that often states the position or philosophy about a social, political, or other subject, or a general explanation of an architecture, framework, or product technology written by a group of researchers. A white paper seeks to contain unbiased information and analysis regarding a business or policy problem that the researchers may be facing.
Elliot, Mark, Fairweather, Ian, Olsen, Wendy Kay, and Pampaka, Maria. A Dictionary of Social Research Methods. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2016; Free Social Science Dictionary. Socialsciencedictionary.com [2008]. Glossary. Institutional Review Board. Colorado College; Glossary of Key Terms. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Glossary A-Z. Education.com; Glossary of Research Terms. Research Mindedness Virtual Learning Resource. Centre for Human Servive Technology. University of Southampton; Miller, Robert L. and Brewer, John D. The A-Z of Social Research: A Dictionary of Key Social Science Research Concepts London: SAGE, 2003; Jupp, Victor. The SAGE Dictionary of Social and Cultural Research Methods . London: Sage, 2006.
- << Previous: Independent and Dependent Variables
- Next: 1. Choosing a Research Problem >>
- Last Updated: Aug 27, 2024 1:14 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
In Need of Definition: How to Select Terms to Define in your Dissertation
One section that is often required in a dissertation is the “Definitions of Terms.” This gives your readers an understanding of the concepts or factors that will be discussed throughout your study, as well as contextual information as to how you will be using those concepts in your study. The “Definitions of Terms” ensures that your readers will understand the components of your study in the way that you will be presenting them, because often your readers may have their own understanding of the terms, or not be familiar with them at all. In this section, you provide a list of terms that will be used throughout the dissertation and definitions of each of them. Seems simple enough, right? But how do you know which terms to define and which ones to leave out?
The rule of thumb is to include and define terms that are important to your study or are used frequently throughout the dissertation but are not common knowledge. You also want to include terms that have a unique meaning within the scope of your study. You do not need to include terms that most, if not all, of your readers will understand without having definitions provided. For example, something like leadership probably does not need to be included in your “Definitions of Terms,” but laissez-faire leadership would be a good choice to include. However, if your study is about leadership, then it may be beneficial to the understanding of your readers to define leadership based on how you are using it within your study. Things like success or achievement may need definition as well, if you are using them within your study, as the readers will need to know what measures or markers of success or achievement that you will focus on within your study.
For more information on “Definitions of Terms,” including what information to include within the definitions, check out our other blog: How to Write Your Definitions.
Need help with your research?
Schedule a time to speak with an expert using the calendar below.
Scientific Research and Methodology
2.2 conceptual and operational definitions.
Research studies usually include terms that must be carefully and precisely defined, so that others know exactly what has been done and there are no ambiguities. Two types of definitions can be given: conceptual definitions and operational definitions .
Loosely speaking, a conceptual definition explains what to measure or observe (what a word or a term means for your study), and an operational definitions defines exactly how to measure or observe it.
For example, in a study of stress in students during a university semester. A conceptual definition would describe what is meant by ‘stress.’ An operational definition would describe how the ‘stress’ would be measured.
Sometimes the definitions themselves aren’t important, provided a clear definition is given. Sometimes, commonly-accepted definitions exist, so should be used unless there is a good reason to use a different definition (for example, in criminal law, an ‘adult’ in Australia is someone aged 18 or over ).
Sometimes, a commonly-accepted definition does not exist, so the definition being used should be clearly articulated.
Example 2.2 (Operational and conceptual definitions) Players and fans have become more aware of concussions and head injuries in sport. A Conference on concussion in sport developed this conceptual definition ( McCrory et al. 2013 ) :
Concussion is a brain injury and is defined as a complex pathophysiological process affecting the brain, induced by biomechanical forces. Several common features that incorporate clinical, pathologic and biomechanical injury constructs that may be utilised in defining the nature of a concussive head injury include: Concussion may be caused either by a direct blow to the head, face, neck or elsewhere on the body with an “impulsive” force transmitted to the head. Concussion typically results in the rapid onset of short-lived impairment of neurological function that resolves spontaneously. However, in some cases, symptoms and signs may evolve over a number of minutes to hours. Concussion may result in neuropathological changes, but the acute clinical symptoms largely reflect a functional disturbance rather than a structural injury and, as such, no abnormality is seen on standard structural neuroimaging studies. Concussion results in a graded set of clinical symptoms that may or may not involve loss of consciousness. Resolution of the clinical and cognitive symptoms typically follows a sequential course. However, it is important to note that in some cases symptoms may be prolonged.
While this is all helpful… it does not explain how to identify a player with concussion during a game.
Rugby decided on this operational definition ( Raftery et al. 2016 ) :
… a concussion applies with any of the following: The presence, pitch side, of any Criteria Set 1 signs or symptoms (table 1)… [ Note : This table includes symptoms such as ‘convulsion,’ ‘clearly dazed,’ etc.]; An abnormal post game, same day assessment…; An abnormal 36–48 h assessment…; The presence of clinical suspicion by the treating doctor at any time…
Example 2.3 (Operational and conceptual definitions) Consider a study requiring water temperature to be measured.
An operational definition would explain how the temperature is measured: the thermometer type, how the thermometer was positioned, how long was it left in the water, and so on.

Example 2.4 (Operational definitions) Consider a study measuring stress in first-year university students.
Stress cannot be measured directly, but could be assessed using a survey (like the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) ( Cohen et al. 1983 ) ).
The operational definition of stress is the score on the ten-question PSS. Other means of measuring stress are also possible (such as heart rate or blood pressure).
Meline ( 2006 ) discusses five studies about stuttering, each using a different operational definition:
- Study 1: As diagnosed by speech-language pathologist.
- Study 2: Within-word disfluences greater than 5 per 150 words.
- Study 3: Unnatural hesitation, interjections, restarted or incomplete phrases, etc.
- Study 4: More than 3 stuttered words per minute.
- Study 5: State guidelines for fluency disorders.
A study of snacking in Australia ( Fayet-Moore et al. 2017 ) used this operational definition of ‘snacking’:
…an eating occasion that occurred between meals based on time of day. — Fayet-Moore et al. ( 2017 ) (p. 3)
A study examined the possible relationship between the ‘pace of life’ and the incidence of heart disease ( Levine 1990 ) in 36 US cities. The researchers used four different operational definitions for ‘pace of life’ (remember the article was published in 1990!):
- The walking speed of randomly chosen pedestrians.
- The speed with which bank clerks gave ‘change for two $20 bills or [gave] two $20 bills for change.’
- The talking speed of postal clerks.
- The proportion of men and women wearing a wristwatch.
None of these perfectly measure ‘pace of life,’ of course. Nonetheless, the researchers found that, compared to people on the West Coast,
… people in the Northeast walk faster, make change faster, talk faster and are more likely to wear a watch… — Levine ( 1990 ) (p. 455)
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is Research? Definition, Types, Methods, and Examples
Academic research is a methodical way of exploring new ideas or understanding things we already know. It involves gathering and studying information to answer questions or test ideas and requires careful thinking and persistence to reach meaningful conclusions. Let’s try to understand what research is.
Table of Contents
Why is research important?
Whether it’s doing experiments, analyzing data, or studying old documents, research helps us learn more about the world. Without it, we rely on guesswork and hearsay, often leading to mistakes and misconceptions. By using systematic methods, research helps us see things clearly, free from biases. (1)
What is the purpose of research?
In the real world, academic research is also a key driver of innovation. It brings many benefits, such as creating valuable opportunities and fostering partnerships between academia and industry. By turning research into products and services, science makes meaningful improvements to people’s lives and boosts the economy. (2)(3)
What are the characteristics of research?
The research process collects accurate information systematically. Logic is used to analyze the collected data and find insights. Checking the collected data thoroughly ensures accuracy. Research also leads to new questions using existing data.
Accuracy is key in research, which requires precise data collection and analysis. In scientific research, laboratories ensure accuracy by carefully calibrating instruments and controlling experiments. Every step is checked to maintain integrity, from instruments to final results. Accuracy gives reliable insights, which in turn help advance knowledge.
Types of research
The different forms of research serve distinct purposes in expanding knowledge and understanding:
- Exploratory research ventures into uncharted territories, exploring new questions or problem areas without aiming for conclusive answers. For instance, a study may delve into unexplored market segments to better understand consumer behaviour patterns.
- Descriptive research delves into current issues by collecting and analyzing data to describe the behaviour of a sample population. For instance, a survey may investigate millennials’ spending habits to gain insights into their purchasing behaviours.
- Explanatory research, also known as causal research, seeks to understand the impact of specific changes in existing procedures. An example might be a study examining how changes in drug dosage over some time improve patients’ health.
- Correlational research examines connections between two sets of data to uncover meaningful relationships. For instance, a study may analyze the relationship between advertising spending and sales revenue.
- Theoretical research deepens existing knowledge without attempting to solve specific problems. For example, a study may explore theoretical frameworks to understand the underlying principles of human behaviour.
- Applied research focuses on real-world issues and aims to provide practical solutions. An example could be a study investigating the effectiveness of a new teaching method in improving student performance in schools. (4)
Types of research methods
- Qualitative Method: Qualitative research gathers non-numerical data through interactions with participants. Methods include one-to-one interviews, focus groups, ethnographic studies, text analysis, and case studies. For example, a researcher interviews cancer patients to understand how different treatments impact their lives emotionally.
- Quantitative Method: Quantitative methods deal with numbers and measurable data to understand relationships between variables. They use systematic methods to investigate events and aim to explain or predict outcomes. For example, Researchers study how exercise affects heart health by measuring variables like heart rate and blood pressure in a large group before and after an exercise program. (5)
Basic steps involved in the research process
Here are the basic steps to help you understand the research process:
- Choose your topic: Decide the specific subject or area that you want to study and investigate. This decision is the foundation of your research journey.
- Find information: Look for information related to your research topic. You can search in journals, books, online, or ask experts for help.
- Assess your sources: Make sure the information you find is reliable and trustworthy. Check the author’s credentials and the publication date.
- Take notes: Write down important information from your sources that you can use in your research.
- Write your paper: Use your notes to write your research paper. Broadly, start with an introduction, then write the body of your paper, and finish with a conclusion.
- Cite your sources: Give credit to the sources you used by including citations in your paper.
- Proofread: Check your paper thoroughly for any errors in spelling, grammar, or punctuation before you submit it. (6)
How to ensure research accuracy?
Ensuring accuracy in research is a mix of several essential steps:
- Clarify goals: Start by defining clear objectives for your research. Identify your research question, hypothesis, and variables of interest. This clarity will help guide your data collection and analysis methods, ensuring that your research stays focused and purposeful.
- Use reliable data: Select trustworthy sources for your information, whether they are primary data collected by you or secondary data obtained from other sources. For example, if you’re studying climate change, use data from reputable scientific organizations with transparent methodologies.
- Validate data: Validate your data to ensure it meets the standards of your research project. Check for errors, outliers, and inconsistencies at different stages, such as during data collection, entry, cleaning, or analysis.
- Document processes: Documenting your data collection and analysis processes is essential for transparency and reproducibility. Record details such as data collection methods, cleaning procedures, and analysis techniques used. This documentation not only helps you keep track of your research but also enables others to understand and replicate your work.
- Review results: Finally, review and verify your research findings to confirm their accuracy and reliability. Double-check your analyses, cross-reference your data, and seek feedback from peers or supervisors. (7)
Research is crucial for better understanding our world and for social and economic growth. By following ethical guidelines and ensuring accuracy, researchers play a critical role in driving this progress, whether through exploring new topics or deepening existing knowledge.
References:
- Why is Research Important – Introductory Psychology – Washington State University
- The Role Of Scientific Research In Driving Business Innovation – Forbes
- Innovation – Royal Society
- Types of Research – Definition & Methods – Bachelor Print
- What Is Qualitative vs. Quantitative Study? – National University
- Basic Steps in the Research Process – North Hennepin Community College
- Best Practices for Ensuring Data Accuracy in Research – LinkedIn
Researcher.Life is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Researcher.Life All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 21+ years of experience in academia, Researcher.Life All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $17 a month !
Related Posts


Back to School – Lock-in All Access Pack for a Year at the Best Price

Research Paper Appendix: Format and Examples
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Research Variables: Types, Uses and Definition of Terms

The purpose of research is to describe and explain variance in the world, that is, variance that occurs naturally in the world or change that we create due to manipulation. Variables are therefore the names that are given to the variance we wish to explain and it is very critical to the research because the way the researcher uses or handles them in the research process could determine the nature and direction of the research (Nwankwo and Emunemu, 2014). Closely related to the understanding of what a variable is, is the idea of definition of terms. This chapter explores the use of variables in research, types of variables and the definition of terms, so as to help some of the students who have a problem identifying and clarifying the variables they are working on in their project work.
Related Papers
George Argyrous , Glyze Abella
This book aims to help people analyze quantitative information. Before detailing the 'hands-on' analysis we will explore in later chapters, this introductory chapter will discuss some of the background conceptual issues that are precursors to statistical analysis. The chapter begins where most research in fact begins; with research questions. A research question states the aim of a research project in terms of cases of interest and the variables upon which these cases are thought to differ. A few examples of research questions are: 'What is the age distribution of the students in my statistics class?' 'Is there a relationship between the health status of my statistics students and their sex?' 'Is any relationship between the health status and the sex of students in my statistics class affected by the age of the students?' We begin with very clear, precisely stated research questions such as these that will guide the way we conduct research and ensure that we do not end up with a jumble of information that does not create any real knowledge. We need a clear research question (or questions) in mind before undertaking statistical analysis to avoid the situation where huge amounts of data are gathered unnecessarily, and which do not lead to any meaningful results. I suspect that a great deal of the confusion associated with statistical analysis actually arises from imprecision in the research questions that are meant to guide it. It is very difficult to select the relevant type of analysis to undertake, given the many possible analyses we could employ on a given set of data, if we are uncertain of our objectives. If we don't know why we are undertaking research in the first place, then it follows we will not know what to do with research data once we have gathered them. Conversely, if we are clear about the research question(s) we are addressing the statistical techniques to apply follow almost as a matter of course. We can see that each of the research questions above identifies the entities that I wish to investigate. In each question these entities are students in my statistics class, who are thus the units of analysis – the cases of interest – to my study.
Abimbola Awotedu
International Journal of Methodology
Akaawase Mchi
This paper discusses the importance of variable conceptualisation and measurement in environmental research. The paper explains how wrong application of concepts can mislead the researcher when conducting research, and the resultant effects on each stage of the environmental research process. The paper is motivated by the problems behind many research students pursuing their masters or doctoral degree programmes face, especially with change in dissertations or theses titles and methods to match the contents of their reports. In this paper, the authors demystify the challenges encountered by unskilful researchers and students when trying to make their readers have a clear understanding of their research reports (dissertations or theses). Therefore, the paper may serve as a guide in planning and conducting environmental research by university degree students and early career researchers.
Faith Musango
Symeou, L. & Lamprianou, J.
Loizos Symeou , Iasonas Lamprianou
Santo Di Nuovo
The article deals with the use of variables in quantitative psychological research. Topics as the choice of variables, their measurement and statistical analysis, the deductions based on data, are briefly reviewed. All variables can be misleading if used in a misleading way, but the Author contends that the psychology based on the variables has not the possibility to represent selected samples of inner processes and contents. Quantitative analyses based on linear causality and probabilistic inference pose many problems, but some alternative approaches devised to cope with these problems are indicated. An hermeneutic approach aware of the constructivist ground of the scientific knowledge is proposed.
Rahul Pilani
Environmental Policy Convergence in Europe
Stephan Heichel
International Journal of Religion
José Mario Ochoa-Pachas , Luis Pajuelo , JOSE MARIO OCHOA PACHAS
It is common to use Bloom's taxonomy to write research objectives; however, it is often forgotten that this Bloomian classification corresponds to the teaching-learning process. Likewise, is not usual to include the levels or scope of research since so many classifications have been proposed, suggesting that science can be fragmented and that qualitative studies have nothing to do with quantitative studies and vice versa. Regardless of the coincidences and discrepancies that may exist, researchers require a guideline that is based on the principles of science to be able to organize and structure their studies and that allows for growth and development, removing biases and partialities from analysis. It is necessary to remember that a taxonomy is valid if it adheres to the criteria that scientific knowledge itself indicates. This research is an exploratory and observational study whose purpose is to identify its objectives according to its levels with their respective study variables.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Journal of Consumer Psychology
Alice Tybout
zubair arians
Research about research, as a psychologist views it.
Elisabeta Rosca
Ridwan Osman
Wafae Barkani
Racidon Bernarte
Thabologo Motsamai
MD Ashikur Rahman
The Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods
Emmanuel Achor
Naveen Kumar
Saeed Anwar
khadidja Hammoudi
Bakhtawer Zain
Dr. J. M. Ashfaque (MInstP)
Dr. IBRAHIM YUSUF
Alexis Hernandez
caroline tobing
mark vince agacite
Durga Prasad
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Glossary of Key Research Terms
This glossary provides definitions of many of the terms used in the guides to conducting qualitative and quantitative research. The definitions were developed by members of the research methods seminar (E600) taught by Mike Palmquist in the 1990s and 2000s.
Citation Information
Members of the Research Methods Seminar (E600) taught by Mike Palmquist in the 1990s and 2000s. (1994-2024). Glossary of Key Terms. The WAC Clearinghouse. Colorado State University. Available at https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/writing/guides/.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1994-2024 Colorado State University and/or this site's authors, developers, and contributors . Some material displayed on this site is used with permission.
Definition of Terms
- First Online: 19 August 2022
Cite this chapter

- Mohammad Sadegh Montazeri 2
554 Accesses
The term has categories such as ambiguous or unambiguous, clear or unclear, vague or exact.
If we can give a precise definition, many ambiguities in the client’s mind remove. Then, clients can think more clearly. For example, terms such as failure, success, and happiness are vague in the client’s thoughts.
I will introduce methods for defining terms in this chapter. We try definition to be coextensive. In Socratic dialogue, we can use violation examples to delineate terms. Using violation examples helps to have a neither limited nor extended definition.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
We apply the word mode in schema therapy.
In this case, if I analyze the client logically, I will corrupt the rapport. However, since we had many dialogues about modes and the client was aware of her schema modes, my interpretation helped empathize with the client. She found out that I had realized her mental status.
I do not validate aggressive behavior, but I verify the feelings of the client.
Microbes have some subclasses, such as bacteria and viruses. However, it is not required to explain this classification to the client.
Hurley, P. J., & Watson, L. (2016). A concise introduction to logic (13th ed.). Cengage Learning.
Google Scholar
Kreeft, P. (2010). Socratic logic: A logic text using Socratic method, Platonic questions & Aristotelian principles . St Augustine’s Press.
Overholser, J. C. (2018). The Socratic method of psychotherapy . Columbia University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Plato. (380 BC). Laches or courage . Retrieved from https://www.sacred-texts.com/cla/plato/laches.htm
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Golestan University, Gorgan, Iran
Mohammad Sadegh Montazeri
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Montazeri, M.S. (2022). Definition of Terms. In: Psychotherapist's Guide to Socratic Dialogue. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07972-6_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07972-6_4
Published : 19 August 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-07971-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-07972-6
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Academic Phrasebank
Defining terms.
- GENERAL LANGUAGE FUNCTIONS
- Being cautious
- Being critical
- Classifying and listing
- Compare and contrast
- Describing trends
- Describing quantities
- Explaining causality
- Giving examples
- Signalling transition
- Writing about the past
In academic work students are often expected to give definitions of key words and phrases in order to demonstrate to their tutors that they understand these terms clearly. More generally, however, academic writers define terms so that their readers understand exactly what is meant when certain key terms are used. When important words are not clearly understood misinterpretation may result. In fact, many disagreements (academic, legal, diplomatic, personal) arise as a result of different interpretations of the same term. In academic writing, teachers and their students often have to explore these differing interpretations before moving on to study a topic.
Introductory phrases
The term ‘X’ was first used by … The term ‘X’ can be traced back to … Previous studies mostly defined X as … The term ‘X’ was introduced by Smith in her … Historically, the term ‘X’ has been used to describe … It is necessary here to clarify exactly what is meant by … This shows a need to be explicit about exactly what is meant by the word ‘X’.
Simple three-part definitions
| A university is | an institution | where knowledge is produced and passed on to others |
| Social Economics may be defined as | the branch of economics | [which is] concerned with the measurement, causes, and consequences of social problems. |
| Research may be defined as | a systematic process | which consists of three elements or components: (1) a question, problem, or hypothesis, (2) data, and (3) analysis and interpretation of data. |
| Braille is | a system | of touch reading and writing for blind people in which raised dots on paper represent the letters of the alphabet. |
General meanings or application of meanings
X can broadly be defined as … X can be loosely described as … X can be defined as … It encompasses … In the literature, the term tends to be used to refer to … In broad terms, X can be defined as any stimulus that is … Whereas X refers to the operations of …, Y refers to the … The broad use of the term ‘X’ is sometimes equated with … The term ‘disease’ refers to a biological event characterised by … Defined as …, X is now considered a worldwide problem and is associated with …
| The term ‘X’ | refers to … encompasses A), B), and C). has come to be used to refer to … is generally understood to mean … has been used to refer to situations in which … carries certain connotations in some types of … is a relatively new name for a Y, commonly referred to as … |
Indicating varying definitions
The definition of X has evolved. There are multiple definitions of X. Several definitions of X have been proposed. In the field of X, various definitions of X are found. The term ‘X’ embodies a multitude of concepts which … This term has two overlapping, even slightly confusing meanings. Widely varying definitions of X have emerged (Smith and Jones, 1999). Despite its common usage, X is used in different disciplines to mean different things. Since the definition of X varies among researchers, it is important to clarify how the term is …
| The meaning of this term | has evolved. has varied over time. has been extended to refer to … has been broadened in recent years. has not been consistent throughout … has changed somewhat from its original definition … |
Indicating difficulties in defining a term
X is a contested term. X is a rather nebulous term … X is challenging to define because … A precise definition of X has proved elusive. A generally accepted definition of X is lacking. Unfortunately, X remains a poorly defined term. There is no agreed definition on what constitutes … There is little consensus about what X actually means. There is a degree of uncertainty around the terminology in … These terms are often used interchangeably and without precision. Numerous terms are used to describe X, the most common of which are …. The definition of X varies in the literature and there is terminological confusion. Smith (2001) identified four abilities that might be subsumed under the term ‘X’: a) … ‘X’ is a term frequently used in the literature, but to date there is no consensus about … X is a commonly-used notion in psychology and yet it is a concept difficult to define precisely. Although differences of opinion still exist, there appears to be some agreement that X refers to …
| The meaning of this term | has been disputed. has been debated ever since … has proved to be notoriously hard to define. has been an object of major disagreement in … has been a matter of ongoing discussion among … |
Specifying terms that are used in an essay or thesis
The term ‘X’ is used here to refer to … In the present study, X is defined as … The term ‘X’ will be used solely when referring to … In this essay, the term ‘X’ will be used in its broadest sense to refer to all … In this paper, the term that will be used to describe this phenomenon is ‘X’. In this dissertation, the terms ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are used interchangeably to mean … Throughout this thesis, the term ‘X’ is used to refer to informal systems as well as … While a variety of definitions of the term ‘X’ have been suggested, this paper will use the definition first suggested by Smith (1968) who saw it as …
Referring to people’s definitions: author prominent
For Smith (2001), X means … Smith (2001) uses the term ‘X’ to refer to … Smith (1954) was apparently the first to use the term … In 1987, psychologist John Smith popularized the term ‘X’ to describe … According to a definition provided by Smith (2001:23), X is ‘the maximally … This definition is close to those of Smith (2012) and Jones (2013) who define X as … Smith, has shown that, as late as 1920, Jones was using the term ‘X’ to refer to particular … One of the first people to define nursing was Florence Nightingale (1860), who wrote: ‘… …’ Chomsky writes that a grammar is a ‘device of some sort for producing the ….’ (1957, p.11). Aristotle defines the imagination as ‘the movement which results upon an actual sensation.’ Smith et al . (2002) have provided a new definition of health: ‘health is a state of being with …
Referring to people’s definitions: author non-prominent
X is defined by Smith (2003: 119) as ‘… …’ The term ‘X’ is used by Smith (2001) to refer to … X is, for Smith (2012), the situation which occurs when … A further definition of X is given by Smith (1982) who describes … The term ‘X’ is used by Aristotle in four overlapping senses. First, it is the underlying … X is the degree to which an assessment process or device measures … (Smith et al ., 1986).
Commenting on a definition
| This definition | includes … allows for … highlights the … helps distinguish … takes into account … poses a problem for … will continue to evolve. can vary depending on … was agreed upon after … has been broadened to include … |
| The following definition is | intended to … modelled on … too simplistic: useful because … problematic as … inadequate since … in need of revision since … important for what it excludes. the most precise produced so far. |
+44 (0) 161 306 6000
The University of Manchester Oxford Rd Manchester M13 9PL UK
Connect With Us
The University of Manchester
Lesson 21: Definition of Terms
A word or phrase used to describe a thing or to express concept, especially In a particular kind of language or branch of study.
Guidelines in defining terms:
1. Definition of terms works like a glossary but have a different twist. It is placed on the beginning of the research paper to tell the meaning of the terms used in the said paper.
2. Only terms, words, or phrases which have special or unique meanings in the study are defined.
3. There are two types of definition of terms. Conceptual and Operational Terms.
Theoretical Definition are based be taken from encyclopedias, books, magazines and newspaper article, dictionaries, and other publications but the researcher must acknowledge his/her sources.
Conceptual Definition are based on how the researcher may develop his own definition from the characteristics of the term define.
4. The term should be arranged alphabetically .
5. When the definition are taken from encyclopedias, books, magazine and newspaper articles, dictionaries and other publications, the researcher must acknowledge his sources .
Definition of terms
Theoretical Definition
Knowledge - the fact or condition of knowing something with familiarity gained through experience or association.
Conceptual Definition
Knowledge - it is a condition of being aware to a certain problem-cyberbullying.

Getting Started: Library Research Strategy
- Choosing Your Topic
- Gathering Background Information
- Defining Key Terms
- Crafting a Research Question
- Gathering Relevant Information
- Evaluating Sources This link opens in a new window
- Formulating a Thesis Statement
- Avoiding Plagiarism This link opens in a new window
- Citation Styles This link opens in a new window
If you have chosen a topic, you may break the topic down into a few main concepts and then list and/or define key terms related to that concept. If you have performed some background searching, you can include some of the words that were used to describe your topic.
For example, if your topic deals with the relationship between teenage smoking and advertising in the United States, the following key terms may apply:
smoking -- tobacco -- nicotine -- cigarettes
teenage -- adolescents -- children -- teens -- youth
advertising -- marketing -- media -- commercials -- TV -- billboards
When listing the key terms or concepts of your topic, be sure to consider synonyms for these terms as well. Since research is an iterative process, you will also find additional key terms to utilize through the resources you encounter throughout your research process.
- << Previous: Gathering Background Information
- Next: Crafting a Research Question >>
- Last Updated: Jul 16, 2024 9:31 AM
- URL: https://libguides.chapman.edu/strategy
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
What Is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
Published on May 24, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
A glossary is a collection of words pertaining to a specific topic. In your thesis or dissertation , it’s a list of all terms you used that may not immediately be obvious to your reader.
Your glossary only needs to include terms that your reader may not be familiar with, and it’s intended to enhance their understanding of your work. Glossaries are not mandatory, but if you use a lot of technical or field-specific terms, it may improve readability to add one.
If you do choose to include a glossary, it should go at the beginning of your document, just after the table of contents and (if applicable) list of tables and figures or list of abbreviations . It’s helpful to place your glossary at the beginning, so your readers can familiarize themselves with key terms relevant to your thesis or dissertation topic prior to reading your work. Remember that glossaries are always in alphabetical order.
To help you get started, download our glossary template in the format of your choice below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

- Table of contents
Example of a glossary
Citing sources for your glossary, additional lists to include in your dissertation, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about glossaries.
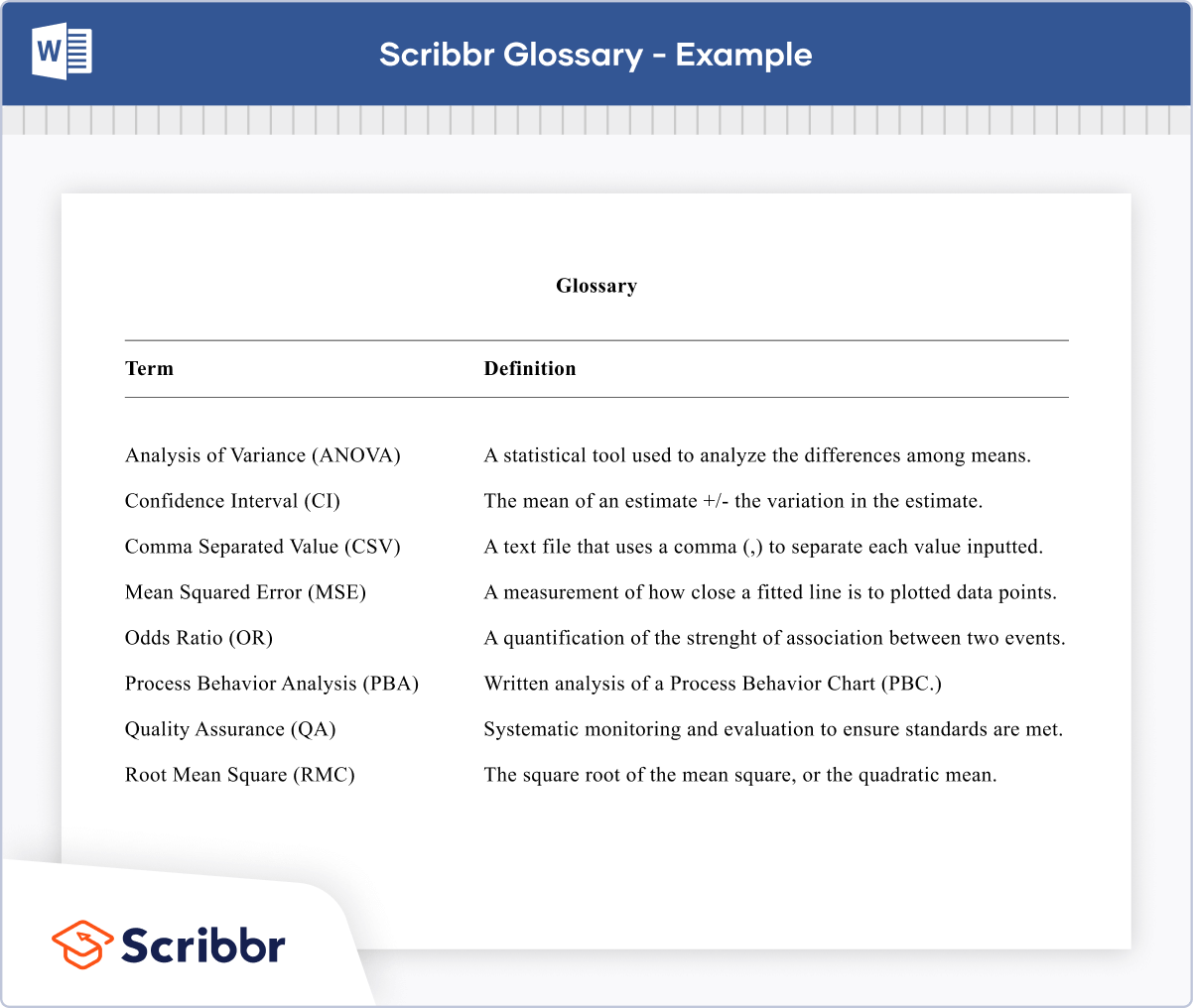
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Glossaries and definitions often fall into the category of common knowledge , meaning that they don’t necessarily have to be cited.
However, it’s always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to citing your sources , in order to avoid accidental plagiarism .
If you’d prefer to cite just in case, you can follow guidance for citing dictionary entries in MLA or APA Style for citations in your glossary. Remember that direct quotes should always be accompanied by a citation.
In addition to the glossary, you can also include a list of tables and figures and a list of abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation if you choose.
Include your lists in the following order:
- List of figures and tables
- List of abbreviations
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
A glossary is a collection of words pertaining to a specific topic. In your thesis or dissertation, it’s a list of all terms you used that may not immediately be obvious to your reader. In contrast, dictionaries are more general collections of words.
A glossary or “glossary of terms” is a collection of words pertaining to a specific topic. In your thesis or dissertation, it’s a list of all terms you used that may not immediately be obvious to your reader. Your glossary only needs to include terms that your reader may not be familiar with, and is intended to enhance their understanding of your work.
Glossaries are not mandatory, but if you use a lot of technical or field-specific terms, it may improve readability to add one to your thesis or dissertation. Your educational institution may also require them, so be sure to check their specific guidelines.
A glossary is a collection of words pertaining to a specific topic. In your thesis or dissertation, it’s a list of all terms you used that may not immediately be obvious to your reader. In contrast, an index is a list of the contents of your work organized by page number.
Definitional terms often fall into the category of common knowledge , meaning that they don’t necessarily have to be cited. This guidance can apply to your thesis or dissertation glossary as well.
However, if you’d prefer to cite your sources , you can follow guidance for citing dictionary entries in MLA or APA style for your glossary.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). What Is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/glossary-of-a-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, figure and table lists | word instructions, template & examples, list of abbreviations | example, template & best practices, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Child Care and Early Education Research Connections
Research glossary.
The research glossary defines terms used in conducting social science and policy research, for example those describing methods, measurements, statistical procedures, and other aspects of research; the child care glossary defines terms used to describe aspects of child care and early education practice and policy.
- Education Home
- Medical Education Technology Support
- Graduate Medical Education
- Medical Scientist Training Program
- Public Health Sciences Program
- Continuing Medical Education
- Clinical Performance Education Center
- Center for Excellence in Education
- Research Home
- Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics
- Biomedical Engineering
- Cell Biology
- Genome Sciences
- Microbiology, Immunology, & Cancer Biology (MIC)
- Molecular Physiology & Biological Physics
- Neuroscience
- Pharmacology
- Public Health Sciences
- Office for Research
- Clinical Research
- Clinical Trials Office
- Funding Opportunities
- Grants & Contracts
- Research Faculty Directory
- Cancer Center
- Cardiovascular Research Center
- Carter Immunology Center
- Center for Behavioral Health & Technology
- Center for Brain Immunology & Glia
- Center for Diabetes Technology
- Center for Immunity, Inflammation & Regenerative Medicine
- Center for Membrane & Cell Physiology
- Center for Research in Reproduction
- Myles H. Thaler Center for AIDS & Human Retrovirus Research
- Child Health Research Center (Pediatrics)
- Division of Perceptual Studies
- Research News: The Making of Medicine
- Core Facilities
- Virginia Research Resources Consortium
- Center for Advanced Vision Science
- Charles O. Strickler Transplant Center
- Keck Center for Cellular Imaging
- Institute of Law, Psychiatry & Public Policy
- Translational Health Research Institute of Virginia
- Clinical Home
- Anesthesiology
- Dermatology
- Emergency Medicine
- Family Medicine
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics & Gynecology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic Surgery
- Otolaryngology
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
- Plastic Surgery, Maxillofacial, & Oral Health
- Psychiatry & Neurobehavioral Sciences
- Radiation Oncology
- Radiology & Medical Imaging
- UVA Health: Patient Care
- Diversity Home
- Diversity Overview
- Student Resources
- GME Trainee Resources
- Faculty Resources
- Community Resources
- Glossary of Research Terms
General Research Glossary
A-110 . “Uniform Administrative Requirements for Grants and Agreements with Institutions of Higher Education, Hospitals, and Other Non-Profit Organizations,” an OMB circular covering the award of grants and contracts, post-award requirements, and property standards.
A-133 . “Audits of States, Local Governments, and Non-Profit Organizations,” an OMB circular setting standards for obtaining consistency and uniformity among federal agencies for the audit of recipients of federal awards.
A-21 . “Cost Principles for Educational Institutions,” an OMB circular describing financial management procedures relevant to federal agreements with academic institutions and represent the “Cost Accounting Standards” for federal awards.
AAALAC . American Association for the Accreditation of Lab Animal Care : an organization that accredits research animal facilities.
Advance spending . Authorization to expend funds on a project prior to receipt of the sponsor’s notice of award, e.g., to hire staff and purchase materials required to perform the scope of work.
Agency . Synonym for “sponsor.”
Allowable costs . Costs that may be charged to a grant, such as salaries and equipment, that meet the requirements of being reasonable, allocable to the project, and treated consistently at the institution, and not excluded by Circular A-21.
Audit . A formal examination of an organization’s or individual’s accounts, financial situation, or compliance with applicable terms, laws, and regulations.
Authorized signature . Signature of the person authorized to commit funds and facilities on grants and contracts.
AUTM . Association of University Technology Managers . Its mission is “to promote, support and improve academic technology transfer worldwide and demonstrate its benefits globally through education, advocacy, networking and communication.”
Award . Funds provided by a sponsor to support a particular project.
Bequest . An award given with few or no conditions specified, for instance to establish an endowment or to provide direct support for existing programs.
Broad Agency Announcement (BAA) . An announcement describing a federal agency’s general research interest, soliciting proposals, and specifying the criteria for selecting proposals.
Budget . The detailed estimate of the expenditures to be made under a project’s scope of work.
Budget category . A section of the budget that includes a defined type of expenditure (e.g., salaries, fringe benefits, travel, patient costs).
Budget justification . A description of the individual cost elements that together comprise the budget and the estimation methods used in costing the project.
Budget period . The interval of time into which the project period is divided for budgetary and funding purposes: generally one year.
CAS . See Cost Accounting Standards
CDC . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (DHHS)
CFDA . Catalog of Federal Domestic Assistance , a listing of all programs available to state and local governments, organizations, individuals, etc.
CFR . Code of Federal Regulations: general and permanent rules established by the Executive branch of the Federal Government.
Change order . A written order signed by the contracting officer, modifying contract clauses or scope of work without the consent of the contractor.
Classified research . Research sponsored by the federal government involving restrictions on the distribution or publication of the research findings or results following completion.
Close-out . Completion of internal procedures and sponsor requirements to terminate or complete a research project.
Cognizant audit agency . The federal office that is designated to perform audits for sponsored projects at a university (at UVA, the Department of Health and Human Services [DHHS]).
COGR . Council on Governmental Relations , an association of colleges and universities that advise the government on the impact of its regulations on their business practices.
Competing proposal . A proposal (1) submitted for the first time, (2) that was unfunded but is being re-submitted, or (3) for an ongoing project after the term of the original award expired.
Compliances and certifications . Federal and state rules and requirements concerning the responsible handling of research involving human subjects, vertebrate animal care, and hazardous substances, as well as other legal issues (such as conflict of interest, drug-free workplace, etc.). Administrative officers of an institution must regularly certify, by their signature, compliance with these rules and regulations; individual investigators must comply with institutional requirements and must sign to that effect on the proposal cover sheet.
Confidentiality agreement . A legal agreement preventing one or both party from disclosing confidential information belonging to the other party. Also called a nondisclosure agreement.
Conflict of commitment . Any situation in which non-university activities are sufficiently demanding of time and attention that they interfere with assigned duties or with responsibilities to students or the university.
Conflict of interest . Situations in which employees use their positions for purposes that are, or give the appearance of being, motivated by a desire for private gain for themselves or others, such as those with whom they have family, business or other ties.
Consideration . Anything of value that changes hands between the parties of contract.
Consortium agreement . A document formalizing the terms and conditions under which a group of collaborative investigators (i.e., a consortium) at different institutions collaborate on a project.
Consultant . An individual whose expertise is required by the PI to perform the research project. Consultant may be a paid or unpaid.
Continuation project (non-competing) . A subsequent award on a project after the previous budget period has expired, on multi-year projects. These do not compete with other proposals: rather, satisfactory progress is assessed in determining whether to provide the next period’s funding.
Contract . Agreement to provide services that primarily benefit the sponsor. For an award to be considered a contract, it normally must contain all of the following: detailed financial and legal requirements; specific statement of work to be performed; deliverables and/or reports required by the sponsor; accounting procedures to be followed; legally binding contract clauses.
Contract/grant officer . A sponsor’s designee who is responsible for the business management aspects of an award. In general, this individual works with the project (scientific) officer.
Cooperative Agreement . An award involving greater agency involvement than a grant, during proposal preparation or in carrying out the scope of work.
Co-Principal Investigator (Co-PI) . An investigator sharing responsibility for the direction of a research program. PHS/NIH does not recognize the concept of co-principal investigator, but does recognize multiple-PI projects.
Copyright . A government grant of exclusivity in reproduction and sale of creative (e.g., literary, artistic, computer programs) inventions.
Cost Accounting Standards (CAS) . Federally mandated accounting standards intended to ensure uniformity in budgeting and spending funds.
Cost-reimbursement contract/grant. A contract or grant for which the sponsor reimburses the actual allowable costs incurred during the conduct of the work.
Cost-sharing. University and nonfederal sponsor resources provided in support of sponsored programs; includes contributed effort and matching funds. Cost-sharing contributions must meet the following criteria: verifiability in University records; contributions are allowable, allocable, reasonable, and necessary to accomplish the scope of work; shared costs are not also used for other projects; and shared costs are identifiable in the proposal budget or justification.
Cover sheet . The first page of a proposal, often in a format supplied by an agency, showing summary data on the proposal and PI, plus all required compliance check-offs
CRADA or CRDA. Cooperative Research and Development Agreement. A document allowing government investigators to collaborate with non-government scientists on common research projects.
CSR. Center for Scientific Review (National Institutes of Health).
DARPA. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency , the central R&D arm of the Department of Defense.
Data. Recorded information, regardless of form or characteristic, describing the design or resulting from a scientific project.
Defense Acquisition Regulations (DAR) . The regulations governing research projects sponsored by the Department of Defense.
Deficit. Expenditures exceeding available funds.
Deliverable . Items to be delivered to the sponsor, generally as required by contracts. These might include technical reports, reagents, computer programs, etc.
DFARS. Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement
DHHS. Department of Health and Human Services
Direct costs. Costs that are identified specifically with a sponsored project, such as salaries/fringe benefits, supplies, equipment, etc.
DOD. Department of Defense (includes Air Force, Army, ARPA, and Navy)
Donation. Transfer of equipment, money, goods, services, and property, much like a gift except often with more specific intent than the latter.
DRG . Division of Research Grants (National Institutes of Health)
EDISON . Interagency Extramural Invention Information Management System (for reporting of inventions created under federal funding)
Effort . The amount of time (usually a percent of total professional effort) that individual expends on a project.
Effort report . Periodic report of the time (as a percent of total) expended by an employee on sponsored projects and other professional activities. The employee must sign the effort report, as required by law.
Effort, contributed . Effort expended on a sponsored project that the sponsor does not compensate for; a form of cost sharing.
Encumbrance. Funds set aside for a projected expense prior to their actual expenditure.
Endowment. An income-generating fund usually provided as a gift in order to generate long-term support for faculty positions or research activities.
Equipment . Property having a useful life of more than one year and an acquisition cost of more than $5,000 per unit on federal grants (exclusive of taxes and shipping).
Equipment, general purpose . Equipment that can be utilized for activities other than the specific scope of work supported by a grant or contract (e.g., office equipment and furniture, computers, and photocopiers).
Equipment, government-furnished , Equipment provided to the university by the federal government or a government contractor; title may or may not remain with the government.
Equipment, special purpose . Equipment that can be utilized only for research, medical, scientific, or technical activities.
Expanded authorities . A policy of some federal granting agencies, which delegate prior approval authorities to awardees.
Expiration date. The end of the performance period for a sponsored award.
Extension. A delay of the expiration date by the sponsor to the awardee in order to complete the scope of work. These generally are no-cost (no additional funds provided by the sponsor).
Facilities and Administrative (F&A) costs . Also referred to as indirect costs, overhead, or administrative costs. These are incurred to conduct normal business activities of the organization receiving support that cannot be readily identified or directly charged to a particular project or activity (e.g., library, depreciation of facilities, heat).
Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR) . The policies and procedures for acquisition by federal executive agencies.
FDA . Food and Drug Administration
FDP . A cooperative effort among several 10 federal agencies to reduce the administrative burdens associated with research grants and contracts.
Federal Commons . An on-line grants management system offering grants processing to awardees. Includes funding opportunities, proposal submission, and award management modules.
Fellowship . An award directly to an individual rather than an institution.
FIC . Fogarty International Center (NIH)
Final report. The technical or financial report required by the sponsor to complete a research project.
Fiscal Year (FY) . The period for which annual accounts are kept (UVA: July 1 through June 30; federal government: October 1 through September 30).
Fixed-price contract/grant. A contract or grant for which payment is based on a predetermined price, regardless of actual costs.
FOIA . Freedom of Information Act
Fringe benefits . Employee benefits paid by the employer. (e.g., FICA, workers’ compensation, medical insurance). UVA has a negotiated fringe benefits rate with the federal government.
Funding cycle . Periodic deadlines and review and award dates, which may occur either cyclically or throughout the year.
GCP . Good Clinical Practices.
Gift . Awards given with no restrictions specified. Gifts allow the recipient can manage their use, are not associated with deliverables, and are not overseen by the donor.
GLP . Good Laboratory Practices.
GMP . Good Manufacturing Practices.
Goldenrod . UVA’s internal proposal routing form documenting PI assurances and institutional approval.
Governing law . UVA, as a Virginia state agency, cannot accept a contract governed by the laws of another state or other jurisdiction: contracts must be governed by the laws of the Commonwealth of Virginia or silent on the governing law.
Grant . A type of financial assistance awarded to an organization for the conduct of research or other program as specified in an approved proposal. A grant, as opposed to a cooperative agreement, is used whenever the agency anticipates no substantial programmatic involvement during the performance of the activities.
Grant/Contract Officer. A sponsor’s designee who is responsible for the business management aspects of an award. In general, this individual works with the project (scientific) officer.
Grantee . The recipient of a grant.
GSA . General Services Administration
IACUC (Animal Care and Use Committee) . An institutional committee that reviews and approves the use of animal subjects in all research projects. It also oversees institutional animal facilities.
IBC . Institutional Biosafety Committee
IDC. Indirect Costs (= F&A costs)
Incremental funding. A method of funding contracts that by the agency provides specific spending limits below the total estimated cost of the project. These interim limits may be exceeded at the contractor’s own risk.
Indemnification . An agreement to hold harmless the other party in a contract, from legal actions or claims for damages. State agencies such as UVA cannot indemnify other parties, but can offer insurance clauses.
Indirect cost rate . The rate established by negotiation with the cognizant federal agency (DHHS for UVA) on the basis of the institution’s projected costs for the year and distributed as prescribed in OMB Circular A-21. Various rates exist for sponsored research, service, other projects, and on- vs. off-site activities.
Indirect costs . Also referred to as facilities and administrative costs, overhead, or administrative costs. These are incurred to conduct normal business activities of the organization receiving support that cannot be readily identified or directly charged to a particular project or activity (e.g., library, depreciation of facilities, heating).
In-kind . Contributions other than money, such as equipment, materials, or services of recognized value.
Institutional Authorized Official . An individuals authorized by the Board of Regents to sign grants, contracts, and agreements on behalf of The University of Virginia.
Intellectual property (IP) . Creations of the mind that include inventions, know-how, copyrightable works, or creative or artistic works. Intellectual property may be protected legally via patents, copyrights, and so on, or protected as trade secrets.
Invention . A process, machine, manufacture, composition of matter, or design, or any new or useful improvement thereof, and any variety of plant which is or may be patentable under the laws of the United States or any other country.
Investigator-initiated proposal. A submitted proposal that is not in response to an RFP or RFA.
Intergovernmental Personnel Agreement (IPA) . A mechanism by which state employees may be assigned to work for a federal agency, or vice-versa, while remaining on the payroll of the “home” agency. Often used for a temporary assignment of a faculty member to a federal agency, with the faculty retaining his/her university benefits.
IRB . Institutional Review Board (charged with ethical review and oversight of human subjects research).
Key personnel. The personnel considered to be of primary importance to the successful conduct of a research project. The term usually refers to doctoral-level contributors, but may also include other individuals with specialized expertise. In contracts, replacement of key personnel may require approval of the funding agency.
Letter of intent . A document advising a funding agency that an application will be submitted in response to a specific solicitation. These letters often are used to guide the creation of a peer review committee.
Limitation of cost (LOC) . A mandatory clause for cost-reimbursement type contracts stating that the sponsor is not obligated to reimburse the contractor for costs in excess of the stated amount. Similarly, the contractor is not obligated to continue performance once expenses reach the stated amount.
Line item budget . A budget that lists the cost of individual project personnel and itemizes the costs for all other budgeted categories such as travel, supplies, equipment, etc. Also known as a detailed budget.
Lobbying certification . An assurance that no federal funds have been used to influence federal officials in the award of a grant or contract.
Matching funds . Funds obligated by the institution that are required by the granting or contracting agency.
Matching grant. A grant requiring that a portion of the cost be obtained from other sources.
Materials transfer agreement . A legally binding document in which one party releases a proprietary reagent, organism, or other item to another party for the purposes of research. It defines the field of use by the recipient and describes the intellectual property rights of sending and receiving parties.
Misconduct in science. Fabrication, plagiarism, or other practices that seriously deviate from those that are commonly accepted within the scientific community for proposing, conducting, or reporting research. It does not include honest error or honest differences in interpretations or judgments of data.
Modification . A document changing an existing award, such as approvals to carry over funds among project periods, changes in funding levels or in key personnel, etc.
Modified Total Direct Costs (MTDC) . For federal awards, these are a subset of direct costs, normally excluding equipment, patient care, space rental, alterations and renovations, and subcontract costs in excess of the first $25,000. These are the base on which F&A (indirect) costs are calculated.
NACUBO . National Association of College and University Business Officers
NASA . National Aeronautics and Space Administration
NCI . National Cancer Institute (NIH)
NCRR . National Center for Research Resources (NIH)
NCURA . National Council of University Research Administrators
NEI . National Eye Institute (NIH)
New award . A grant, cooperative agreement, or contract that had not previously been awarded.
New proposal . Proposals that are submitted to a particular sponsor for the first time.
NHGRI . National Human Genome Research Institute (NIH)
NHLBI . National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NIH)
NIA . National Institute on Aging (NIH)
NIAAA . National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIH)
NIAID . National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIH)
NIAMS . National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIH)
NICHD . National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NIH)
NIDA . National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIH)
NIDCD . National Institute on Deafness and other Communication Disorders (NIH)
NIDDK . National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIH)
NIDR . National Institute of Dental Research (NIH)
NIEHS . National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIH)
NIGMS . National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIH)
NIH . National Institutes of Health
NIMH . National Institute of Mental Health (NIH)
NINDS . National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NIH)
NINR . National Institute for Nursing Research (NIH)
NLM . National Library of Medicine
No-cost extension . An extension of the period of performance beyond the expiration data to accomplish the scope of work. By definition, no additional costs are provided.
Non-competing continuation . A report on project progress that requests continuation funding for the next portion of the project period.
Non-compliance . Failure to adhere to applicable regulations, policies, procedures or special conditions related to the conduct of research. These might include unapproved changes in project work scope, use of animals without IACUC approval, and breaches of clinical protocol methodology.
Nondisclosure agreement . A legal agreement preventing one or both party from disclosing confidential information belonging to the other party. Also called a confidentiality agreement.
Notice of grant award . Also called “Notice of award.” The legally binding document that serves as a notification to the recipient that a grant or cooperative agreement has been made. The document lists or references the terms of the award and obligates sponsor funds.
NSF . National Science Foundation
Off-campus . Sponsored activities, less than 50% of which are conducted on university property or which charge rent to the project as a direct cost.
OHRP . Office for Human Research Protections (DHHS). This unit oversees DHHS Regulations for the Protection of Human Subjects (45 CFR 46), and offers guidance on ethical issues in biomedical and behavioral research.
OMB . Office of Management and Budget. OMB establishes government grants management policies and guidelines through circulars and common rules.
OMB circulars . See A-21, A-110, and A-133 above.
On-campus (also on-site) . Sponsored activities conducted on university property. In general, when over 50% of such activity takes place within the University, the on-campus F&A rate will be applied to the project.
ONR . Office of Naval Research
ORI . Office of Research Integrity (in DHHS). This office promotes research integrity in projects supported by the PHS, monitors institutional investigations of research misconduct, and facilitates the responsible conduct of research (RCR) through educational, preventive, and regulatory activities.
Patent . A government grant of the right to stop others from making, using, offering for sale, or selling an invention.
Patent infringement . Violation of the rights covered by a patent.
Patent prosecution . Filing of a patent application and the subsequent actions required in order to obtain a granted patent and the maintenance thereof after the award.
Peer review . A process by which committees of researchers from several institutions review and recommend applications to the funding agency.
Per diem . A daily allowance paid to personnel working on a sponsored project to cover meals and lodging while traveling.
PHS . Public Health Service
PHS 2590 . Application for Continuation of a PHS Grant (National Institutes of Health )
PHS 398 . Application Form for a PHS Grant (NIH, in the process of being replaced by the SF 424).
PRDA . Program Research and Development Announcement: a competitive solicitation for research, development, and related projects in a specified area of interest.
Pre-proposal . A preliminary proposal of a research project and its estimated budget. Successful PIs are asked by the sponsor to submit full proposals.
Principal Investigator (PI) . The individual responsible for the conduct of research or other activity described in a proposal for an award. The PI has primary responsibility for technical compliance, completion of programmatic work, and fiscal stewardship of sponsor funds.
Prior approval . The requirement for written sponsor permission for changes in the scope of work, key personnel, use of funds for a project, etc., beyond the original proposal/approval.
Priority score . A numerical value representing the rating given a proposal by a review committee. Grants are ordered on the basis of their priority scores in order for funding decisions to be made.
Program Announcement. Notification of a research opportunity that will be available for several years. Renewed in 3 years at NIH.
Program income . Gross income earned by the recipient for activities supported by an award.
Program/Project Officer. A sponsor’s technical officially overseeing an award. This person works with the Principal Investigator of the awardee and with the sponsor’s grant/contract officer in overseeing the project.
Progress report. A periodic summary of research progress required by the sponsor.
Project period . The total time for which support of a project has been approved by the sponsor.
Proposal. An application for funding including the technical description of the project, personnel, available resources, and funds requested.
Proprietary research . Sponsored research involving restrictions placed by the sponsor on the distribution or publication of the research findings.
Rebudget . The movement of funds from one budget category to another. May require approval of the sponsor’s grant/contract officer.
Regulations . The contractual rules and procedures governing sponsored research projects.
Renewal . A competitively reviewed grant and cooperative agreement proposal requesting additional funds extending the scope of work and project period.
Representations and certifications (Reps & Certs) . Statements of policies, practices, and commitments (e.g., conflict of interest, misconduct in science, debarment/suspension, delinquent federal debt, drug-free workplace, assurances on lobbying) which must be signed as part of some proposals, and especially for federal contract proposals.
Request for Applications (RFA) . Focused programmatic announcement of a grant opportunity, for a topic of specific interest to a sponsor. Usually a one-time solicitation, as opposed to a program announcement.
Request for Proposal (RFP) . Announcement of a contract opportunity that specifies the anticipated area of research, methods to be used, deliverables, and characteristics of allowable applicants (e.g., small business concerns).
Research . Systematic investigation aimed at the discovery, interpretation, or revision of facts or accepted theories or to make practical applications with the help of such knowledge.
Research, applied . The systemic, intensive study directed toward producing results that are applicable to a particular problem.
Research, basic . A systemic, intensive study designed to increase the body of knowledge in a particular field, rather than to develop specific, practical applications.
Responsible conduct of research . As described by the DHHS Office of Research Integrity, this is comprised of the following components: honest in conveying information and keeping commitments; accuracy and precision in reporting findings; using resources wisely; avoiding improper bias.
Revised proposal . A modified request for funding for a project that previously was not funded by the sponsor.
SBIR . Small Business Innovative Research
Scope of work . The description of the work to be performed on a research project.
SF 424 . Standard Form 424 (R&R).
Site visit . An agency-initiated review of a proposed project conducted at the applicant’s institution.
Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) . A program under which a federal agency provides funds to small businesses.
Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) . A federal program providing funds to small businesses that are “teamed” with research institutions.
Sole source acquisition . A procurement that does not provide full and open competition, but rather because one source is available.
Sponsor . The organization or agency funding research project.
Sponsored project . A research, training, or service activity supported by an external agency by means of a grant or contract.
Sponsored research . Research supported by outside sources that is conducted by University employees using any University space or facilities.
SRA . Society of Research Administrators
Stipend . A payment made to an individual under a fellowship or training grant in accordance with pre-established levels to provide for the individual’s living expenses during the period of training. Such individuals are not University employees but are covered by University policies and regulations.
Subcontract, subgrant, or subagreement . A contract issued under a prime contract, agreement, purchase order, or grant for the procurement of services or program-related tasks over $10,000. Subcontracts must be consistent with the terms and conditions of the master award, transferring a portion of the research or substantive effort of the prime award to another institution or organization.
Supplemental proposal . A request to the sponsor for additional funds for an existing project: may result, for example, from increased costs or changes in project design.
Task order . A contractual document authorizing work and appropriating funds in a supplement to an existing contract or master agreement.
Teaming agreement . An agreement between two or more parties to participate in a research teaching activity.
Terms of award . Requirements imposed by the sponsor on the recipient by policy, statute, or regulations.
Total Direct Costs (TDC) . The total of all direct costs of a project.
Total project costs . Also known as total costs. The allowable direct and indirect costs to carry out an approved project.
Unallowable costs . Specific expenditures that cannot be charged, directly or indirectly, to federally sponsored agreements.
Unrestricted funds . Monies with no requirements as to their use or disposition. Gifts represent such funds.
Unsolicited proposal . Proposals submitted to a sponsor that are not in response to an RFP or RFA. (See also Investigator-Initiated Proposal.
- Post-award Administration
- Contracts and Clinical Trials Agreements
- Getting Started in Clinical Research
- Intellectual Property (IP) and Entrepreneurial Activities
- Material Transfer Agreements
- Medical Student Research Programs at UVA
- Medical Student Research Symposium
- MSSRP On-Line Preceptor Form
- MSSRP On-Line Student Match Form
- On-line Systems
- Other Medical Student Research Opportunities
- Research: Financial Interest of Faculty
- Review of Proposed Consulting Agreements
- Transfers of NIH/Public Health Service awards
- Unmatched MSSRP projects – 2024
- Research Centers and Programs
- Roles and responsibilities in research administration
- Other Offices Supporting Research
- SBIR and STTR Awards
- Information for students and postdoctoral trainees
- For Research Administrators
- For New Research Faculty
- Funding Programs for Junior Faculty
- NIH for new faculty
- School of Medicine surplus equipment site
- Forms and Documents
- FAQs – SOM offices supporting research
- 2024 Faculty Research Retreat
- Anderson Lecture and Symposia
- Office of Clinical Trials
- Office of Research Integrity
- Office of Sponsored Programs
- International Gaming Institute
- National Supercomputing Institute
- Cannabis Policy Institute
- Policies & Forms
- Faculty Awards
- Councils & Committees
- Faculty/Staff Directory
- Directories
Quick Links
- Directories Home
- Colleges, Schools, and Departments
- Administrative Units
- Research Centers and Institutes
- Resources and Services
- Employee Directory
- Contact UNLV
- Social Media Directory
- UNLV Mobile Apps
- Research Home
- Division Units
Definition of Terms
- Info for Researchers
- Information for Research Subjects
- Institutional Review Boards
- Policies and Regulation
- Additional Resources
- Human Subjects Home
- Information For:
- Researchers
- Research Subjects
- Report a Concern/Provide Input
Any untoward occurrence in a research participant. The occurrence need not have a clear causal relationship with the individual’s participation in the research; an AE can be any unfavorable and unintended sign, symptom, event, or occurrence affecting a participant’s physical, mental, social, financial, legal, or psychological well-being. An unanticipated AE should be reported to the committee as soon as possible after it is identified.
Agreement by an individual not competent to give legally valid informed consent (e.g., a child or cognitively impaired person) to participate in research. An assent is typically paired with permission from a parent or guardian, and together they comprise the informed consent to participate.
An officer of an institution with the authority to speak for and legally commit the institution to adherence to the requirements of the federal regulations regarding the involvement of human subjects in biomedical and behavioral research.
A statement of basic ethical principles governing research involving human subjects issued by the National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects in 1979. View a summary of the Belmont Report . The Belmont Report principles permeate human subjects research to this day.
An ethical principle discussed in the Belmont Report that entails an obligation to protect persons from harm. The principle of beneficence can be expressed in two general rules: 1) do not harm; and 2) protect from harm by maximizing possible benefits and minimizing possible risks of harm.
A valued or desired outcome associated with a research project. Anticipated benefits may express the probability that subjects and society may benefit from the research procedures. Research may benefit the individual or society as a whole. If research will not benefit individuals, it is required to provide a reasonable likelihood of resulting in benefits to society. UNLV’s human research application requests information about the direct benefits accruing to the research participants and to society. Compensation and incentives given to participants are not considered benefit.
This is a certificate issued by the National Institutes of Health that protects identifiable research information of a sensitive nature from forced disclosure. It is typically requested when the researcher believes his/her research objectives could not be met without this form of protection.
Persons who have not attained the legal age for consent to treatment or procedures involved in the research, as determined under the applicable law of the jurisdiction in which the research will be conducted [45 CFR 46 46.401(a)]. In Nevada, individuals younger than 18 years of age are considered children for most research situations, and informed consent then consists of the child’s assent and the parent’s permission.(See “Assent.”)
The act of forcing or compelling one to take action against one’s will. Coercion can be overt or perceived, and it can occur when the researcher is in a position of authority or power over the subject (for example, teachers over students or physicians over patients). It can also occur when incentives become so great that the participant will only participate to attain the incentive.
Having either a psychiatric disorder (e.g., psychosis, neurosis, personality or behavior disorders, or dementia) or a developmental disorder (e.g., mental retardation) that affects cognitive or emotional functions to the extent that capacity for judgment and reasoning is significantly diminished. Others, including persons under the influence of or dependent on drugs or alcohol, those suffering from degenerative diseases affecting the brain, terminally ill patients, and persons with severely disabling physical handicaps, may also be compromised in their ability to make decisions in their best interests.
Human subjects research projects conducted by more than one institution. Each institution is responsible for safeguarding the rights and welfare of human subjects. Arrangements for joint review, relying upon one qualified IRB, or similar arrangements are acceptable. (Please contact the ORI-HS staff if this situation occurs; they can assist with the arrangements.)
Payment for participation in research. Compensation should be appropriate for the amount of effort involved, and not excessive and thereby coercive. Compensation is NOT considered a benefit.
Technically, a legal term, used to denote capacity to act on one’s own behalf; the ability to understand information presented, to appreciate the consequences of acting (or not acting) on that information, and to make a choice. (See also: Incompetence, Incapacity)
Pertains to the treatment of information that an individual has disclosed in a relationship of trust and with the expectation that it will not be divulged to others without permission in ways that are inconsistent with the understanding of the original disclosure.
Defined as a set of conditions in which an investigator’s judgment concerning a primary interest (e.g., subject welfare, integrity of research) could be biased by a secondary interest (e.g., personal or financial gain). See information regarding UNLV’s Conflict of Interest/Compensated Outside Services Policy .
See “Informed Consent.”
Subject(s) used for comparison who are not given the treatment under study or who do not have a given condition, background, or risk factor that is the object of study. Control conditions may be concurrent (occurring more or less simultaneously with the condition under study) or historical (preceding the condition under study). When the present condition of subjects is compared with their own condition on a prior regimen or treatment, the study is considered historically controlled.
The other primary scholar or researcher involved in conducting the research. Co-PIs must also meet the UNLV PI eligibility requirements.
Giving subjects previously undisclosed information about the research project following completion of their participation in research.
A code of ethics for clinical research approved by the World Medical Association in 1964 and widely adopted by medical associations in various countries. It was revised most recently in 2008.
Any study that is not truly experimental (e.g., quasi-experimental studies, correlational studies, record reviews, case histories, and observational studies).
A legal status conferred upon persons who have not yet attained the age of legal competency as defined by state law (for such purposes as consenting to medical care), but who are entitled to treatment as if they had by virtue of assuming adult responsibilities such as marriage, procreation, or being self-supporting and not living at home. (See also “Mature Minor.”)
Fair or just; used in the context of selection of subjects to indicate that the benefits and burdens of research are fairly distributed.
The code of federal regulations (45 CFR 46.101(b)) identifies several categories of minimal risk research as exempt from the Federal Policy for the Protection of Research Subjects. This determination must not be made by the PI, but by the IRB or someone appointed by the IRB. For more information, see the U.S. Health and Human Services website, “ Exempt Research and Research That May Undergo Expedited Review .”
The code of federal regulations (45 CFR 46.110 and 21 CFR 56.110) identifies several categories of minimal risk research that may be reviewed through an expedited review process. For more information, see the U.S. Health and Human Services website on “ Guidance on Expedited Review Procedures .”
This act defines the rights of students and parents concerning reviewing, amending, and disclosing educational records and requires written permission to disclose personally identifiable information from a student’s education record, except under certain circumstances such as an order of subpoena. 1
The federal policy that provides regulations for the involvement of human subjects in research. The policy applies to all research involving human subjects conducted, supported, or otherwise subject to regulation by any federal department or agency that takes appropriate administrative action to make the policy applicable to such research. Currently, 16 federal agencies have adopted this policy, commonly referred to as “The Federal Policy,” but also known as the “Common Rule.”
A formal written, binding commitment that is submitted to the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) Office of Human Research Protections (OHRP) in which an institution agrees to comply with applicable regulations governing research with human subjects and stipulates the procedures through which compliance will be achieved. UNLV’s assurance number is FWA00002305.
Review of proposed research at a convened meeting at which a majority of the membership of the IRB are present, including at least one member whose primary concerns are in nonscientific areas. For the research to be approved, it must receive the approval of a majority of those members present at the meeting. Generally, studies that undergo full board review are studies involving greater than minimal risk, risky, or novel procedures or vulnerable populations.
An individual who is authorized under applicable state or local law to give permission on behalf of a child for general medical care. In Nevada, under NRS 159.0805, guardians may not give permission for a child to enter into a research study unless a court order has been obtained.
The rule which protects the privacy of individually identifiable health information. The privacy rule provides federal protections for personal health information held by covered entities and gives patients specific rights with respect to that information.
Individuals whose physiological or behavioral characteristics and responses are the object of study in a research project. Under the federal regulations, human subjects are defined as living individual(s) about whom an investigator conducting research obtains: (1) data through intervention or interaction with the individual; or (2) identifiable private information.
Federal regulations define identifiable to mean that the identity of the individual subject is or may readily be ascertained by the investigator or may be associated with the information.
This refers to a person’s mental status and means inability to understand information presented, to appreciate the consequences of acting (or not acting) on that information, and to make a choice. The term is often used as a synonym for incompetence.
A legal term meaning inability to manage one’s own affairs, and often used as a synonym for incapacity.
A person’s voluntary agreement, based upon adequate knowledge and understanding of relevant information, to participate in research or to undergo a diagnostic, therapeutic, or preventive procedure. In giving informed consent, subjects may not waive or appear to waive any of their legal rights, or release or appear to release the investigator, the sponsor, the institution, or agents thereof from liability for negligence.
Institutional research (also called internal research) is the gathering of data from or about UNLV students, faculty, and staff by university offices or organizations, with the sole intent of using the data for internal informational purposes or for required data-collection purposes. This data would not be made generalizable. Examples include surveys to improve university services or procedures; ascertain the opinions, experiences, or preferences of the university community; or to provide necessary information to characterize the university community. This kind of data gathering does not require IRB review unless respondents are queried about sensitive aspects of their own behavior. For debatable projects, investigators should submit an exclusion review form to the ORI-HS.
A specially constituted, federally mandated review body established or designated by an entity to protect the welfare of human subjects recruited to participate in biomedical or behavioral research. UNLV has two IRBs – Social/Behavioral and Biomedical.
The federal regulations define interaction as “communication or interpersonal contact between investigator and subject.”
The federal regulations define intervention as both physical procedures by which data are gathered (for example, venipuncture) and manipulations of the subject or the subject’s environment that are performed for research purposes.
This refers to a researcher conducting the project. Investigators can be principal investigators or co-principal investigators. Students are always listed as student investigators.
A formal agreement between UNLV and another FWA-holding institution that allows the one IRB to serve as the “IRB of Record” for protocols involving collaborative research between UNLV and the other institution.
A term utilized when an institution assumes the IRB responsibilities for a human subject research protocol conducted at another institution. An IRB authorization agreement signed by institutional officials at both institutions is required.
An ethical principle discussed in the Belmont Report requiring fairness in distribution of burdens and benefits; those that bear the burdens of research should also receive the benefits. There must be fair and equitable selection of subjects.
A person authorized either by statute or by court appointment to make decisions on behalf of another person. In human subjects research, an individual or judicial or other body authorized under applicable law to consent on behalf of a prospective subject to the subject’s participation in the procedure(s) involved in the research.
Someone who has not reached adulthood (as defined by state law) but who may be treated as an adult for certain purposes (e.g., consenting to medical care). Note that a mature minor is not necessarily an emancipated minor. (See also “Emancipated Minor.”)
A risk is minimal when the probability and magnitude of harm or discomfort anticipated in the proposed research are not greater, in and of themselves, than those ordinarily encountered in daily life or during the performance of routine physical or psychological examinations or tests. For example, the risk of drawing a small amount of blood from a healthy individual for research purposes is no greater than the risk of doing so as part of routine physical examination. Note: The definition of minimal risk for research involving prisoners differs somewhat from that given for non-institutionalized adults.
Any change to an IRB-approved study protocol, regardless of the level of review it receives initially.
A federally mandated member of an Institutional Review Board who has no ties to the parent institution, its staff, or faculty. This individual is usually from the local community (e.g., business person, attorney, or teacher).
A code of research ethics developed during the trials of Nazi war criminals following World War II and widely adopted as a standard during the 1950s and 1960s for protecting human subjects.
The office within the Department of Health and Human Services that is responsible for implementing DHHS regulations (45CFR46) governing research involving human subjects.
The UNLV office, formerly known as the Office for the Protection of Research Subjects (OPRS), that serves as an administrative hub for the UNLV IRB’s oversight of human subjects research.
The agreement of parent(s) to the participation of their child in research.
The scientist or scholar with primary responsibility for the design and conduct of a research project. See UNLV’s PI Eligibility Policy for those who are eligible for automatic PI status and how to apply for PI status.
An individual involuntarily confined in a penal institution, including persons: 1) sentenced under a criminal or civil statue; 2) detained pending arraignment, trial, or sentencing; and 3) detained in other facilities (e.g., for drug detoxification or treatment of alcoholism) under statutes or commitment procedures providing such alternatives to criminal prosecution or incarceration in a penal institution. Note that this includes adjudicated youth.
Control over the extent, timing, and circumstances of disclosing personal information (physical, behavioral, or intellectual) with others.
Defined by the federal regulations to include information about behavior that occurs in a context in which an individual can reasonably expect that no observation or recording is taking place. It also includes information that has been provided for specific purposes by an individual and which the individual can reasonably expect will not be made public (e.g., a medical record). Private information must be individually identifiable (i.e., the identity of the subject is or may readily be ascertained by the investigator or associated with the information) in order for the acquisition of the information to constitute research involving human subjects.
Studies designed to observe outcomes or events that occur subsequent to the identification of the group of subjects to be studied. Prospective studies need not involve manipulation or intervention but may be purely observational or involve only the collection of data.
Applies to survey research conducted in schools and states that parents have the right to inspect surveys and questionnaires distributed within schools. This amendment also specifies that parental permission must be obtained to have minors participate in surveys that disclose certain types of sensitive information. 1
The formal design or plan of an experiment or research study; specifically, the plan submitted to an IRB for review and to an agency for research support. The protocol includes a description of the research design or methodology to be employed, the eligibility requirements for prospective subjects and controls, the treatment regimen(s), and the proposed methods of analysis that will be performed on the collected data.
A systematic investigation (i.e., the gathering and analysis of information) designed to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.
An ethical principle discussed in the Belmont Report requiring that individual autonomy be respected and persons with diminished autonomy be protected.
Research conducted by reviewing records from the past (e.g., birth and death certificates, medical records, school records, or employment records) or by obtaining information about past events elicited through interviews or surveys. Case control studies are an example of this type of research. This requires IRB review, as long as it involves private information about humans.
The probability of harm or injury (physical, psychological, social, or economic) occurring as a result of participation in a research study. Both the probability and magnitude of possible harm may vary from minimal to significant. Risks include immediate risks of study participation as well as risks of long-term effects.
This involves two types of data: 1) data collected by someone other than the principal investigator for a research or non-research purpose, or 2) data that was collected by the principal investigator, but when collected was not intended to be used for human subjects research. For data to be considered secondary data, the data must exist prior to the initiation of the current research study or be “on the shelf” at the time of study initiation. Principal investigators must submit and receive approval for use of secondary human subjects data prior to initiation of the project.
A visit by agency officials, representatives, or consultants to the location of a research activity to assess the adequacy of IRB protection of human subjects or the capability of personnel to conduct the research.
“Participant” is the preferred term since it more correctly portrays the participatory aspects of research. Sometimes “subject” more accurately describes the role.
Free of coercion, duress, or undue inducement or influence. Used in the research context to refer to a subject’s decision to participate (or to continue to participate) in a research activity.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals
You are here
- Volume 83, Issue 9
- ASAS consensus definition of early axial spondyloarthritis
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4527-852X Victoria Navarro-Compán 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9119-5330 Diego Benavent 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9336-0416 Dafne Capelusnik 3 , 4 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5781-158X Désirée van der Heijde 5 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0577-6620 Robert BM Landewé 6 , 7 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4537-6015 Denis Poddubnyy 8 , 9 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8477-0683 Astrid van Tubergen 10 , 11 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9475-9362 Xenofon Baraliakos 12 , 13 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3561-5932 Filip E Van den Bosch 14 , 15 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8448-7407 Floris A van Gaalen 5 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6314-5336 Lianne Gensler 16 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2309-5837 Clementina López-Medina 17 , 18 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9683-3407 Helena Marzo-Ortega 19 , 20 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2246-1986 Anna Molto 21 , 22 ,
- Rodolfo Pérez-Alamino 23 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5445-548X Martin Rudwaleit 24 ,
- Marleen van de Sande 25 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9720-0396 Raj Sengupta 26 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6701-670X Ulrich Weber 27 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8899-9087 Sofia Ramiro 5 , 7
- 1 Rheumatology , La Paz University Hospital , Madrid , Spain
- 2 IdiPAZ , Madrid , Spain
- 3 Universiteit Maastricht Care and Public Health Research Institute , Maastricht , The Netherlands
- 4 Rheumatology , Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center , Tel Aviv , Israel
- 5 Rheumatology , Leiden University Medical Center , Leiden , The Netherlands
- 6 Department of Rheumatology & Clinical Immunology , Amsterdam University Medical Centres , Duivendrecht , The Netherlands
- 7 Rheumatology , Zuyderland Medical Centre Heerlen , Heerlen , The Netherlands
- 8 Department of Gastroenterology, Infectious Diseases and Rheumatology , Charite Universitatsmedizin Berlin , Berlin , Germany
- 9 German Rheumatism Research Center , Berlin , Germany
- 10 Maastricht University Care and Public Health Research Institute , Maastricht , The Netherlands
- 11 Rheumatology , Maastricht University Medical Centre+ , Maastricht , The Netherlands
- 12 Rheumatology , Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet , Herne , Germany
- 13 Ruhr-Universitat Bochum , Bochum , Germany
- 14 Internal Medicine and Pediatrics , VIB-UGent Center for Inflammation Research , Zwijnaarde , Belgium
- 15 Ghent University , Gent , Belgium
- 16 Medicine, Division of Rheumatology , University of California , San Francisco , California , USA
- 17 Rheumatology , Reina Sofia University Hospital , Cordoba , Spain
- 18 Maimonides Biomedical Research Institute of Cordoba , Cordoba , Spain
- 19 Rheumatology , Leeds Biomedical Research Centre , Leeds , UK
- 20 University of Leeds Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine , Leeds , UK
- 21 APHP, INSERM U-1158, Rheumatology , Hospital Cochin , Paris , France
- 22 Center of Research in Epidemiology and Statistics Sorbonne Paris Cité , Paris , France
- 23 Rheumatology , Avellaneda Hospital , Tucuman , Argentina
- 24 Internal Medicine and Rheumatology , Klinikum Bielefeld Rosenhohe , Bielefeld , Germany
- 25 Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology , University of Amsterdam , Amsterdam , The Netherlands
- 26 Rheumatology , Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases , Bath , UK
- 27 Practice Buchsbaum, Rheumatology , Schaffhausen Hospitals , Schaffhausen , Switzerland
- Correspondence to Dr Victoria Navarro-Compán; mvictoria.navarroc{at}gmail.com
Objectives To develop a consensual definition for the term ‘early axial spondyloarthritis—axSpA’—and ‘early peripheral spondyloarthritis—pSpA’.
Methods The ASAS (Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society-Spondyloarthritis EARly definition) steering committee convened an international working group (WG). Five consecutive steps were followed: (1) systematic literature review (SLR); (2) discussion of SLR results within the WG and ASAS community; (3) a three-round Delphi survey inviting all ASAS members to select the items that should be considered for the definition; (4) presentation of Delphi results to the WG and ASAS community and (5) ASAS voting and endorsement (2023 annual meeting).
Results Following the SLR, consensus was to proceed with an expert-based definition for early axSpA (81% in favour) but not for pSpA (54% against). Importantly, early axSpA should be based on symptom duration taking solely axial symptoms into account. 151–164 ASAS members participated in the Delphi surveys. Consensus was achieved for considering the following items within early axSpA definition: duration of symptoms ≤2 years; axial symptoms defined as cervical/thoracic/back/buttock pain or morning stiffness; regardless of the presence/absence of radiographic damage. The WG agreed that in patients with a diagnosis of axSpA ‘early axSpA’ should be defined as a duration of ≤2 years of axial symptoms. Axial symptoms should include spinal/buttock pain or morning stiffness and should be considered by a rheumatologist as related to axSpA. The ASAS community endorsed this proposal (88% in favour).
Conclusions Early axSpA has newly been defined, based on expert consensus. This ASAS definition should be adopted in research studies addressing early axSpA.
- Spondylitis, Ankylosing
- Outcome Assessment, Health Care
https://doi.org/10.1136/ard-2023-224232
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Handling editor Josef S Smolen
X @annamolto, @sofiaramiro82
Contributors VN-C and SR designed the study and developed the study protocol. DB and DC performed the survey and summarised the data. All authors participated actively in the project. VN-C and SR wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual contribution and approved the final version.
Funding The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) funded Diego Benavent to work on this project.
Competing interests VN-C: Speaker fees—AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma; Consultancy fees- AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, MoonLake, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma; Grants: AbbVie, Novartis. DB: Grant/research support from Novartis, and speaker fees from Janssen, Abbvie, and Galapagos. DvdH: Consulting AbbVie, Bayer, BMS, Cyxone, Eisai, Galapagos, Gilead, Glaxo-Smith-Kline, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma. Director of Imaging Rheumatology bv. RBML: Consulting AbbVie, Eli-Lilly, Janssen, Galapagos, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB. Director of Rheumatology Consultancy BVD. DP: Research grant from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Consultation AbbVie, Biocad, BMS, Eli Lilly, Gilead, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, UCB, Speaker AbbVie, BMS, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB. AvT: Speaker fees: Pfizer; Consulting fees: Novartis, Galapagos, UCB; Grants: Pfizer, UCB, Novartis XB: Abbvie, Amgen, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, UCB. FEVdB: received speaker and/or consultancy fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Moonlake, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB FAvG: Research Grants—Novartis; consultancy -MSD, AbbVie, Novartis and BMS LG: Research grants UCB, Novartis, Consulting fees AbbVie, Acelyrin, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma CL-M: Speaker fees AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Janssen, UCB Pharma. Consulting fees Eli Lilly, Novartis, UCB Pharma. HM-O: Speaker fees/consultancy: ABvie, Eli-Lilly, Janssen, Moonlake, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB. Research grants from Janssen, Novartis and UCB. AM: Consulting fees AbbVie, Biogen, BMS, Cyxone, Eisai, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma. Grants: UCB RP-A: Speaker fees Abbvie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Janssen, Pfizer. Consulting fees Abbvie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis. MR: Speaker- AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, UCB Pharma; Consultancy AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma MvdS: Speaker -Janssen, Novartis, UCB; Consultancy Abbvie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, UCB; Research Grants: Eli Lily, Novartis, UCB RS: Speaker - AbbVie, Biogen, Eli Lilly, MSD, Novartis, UCB; Consultancy—AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB. Grants: AbbVie, Novartis, UCB UW: Speaker fees NovartisS. SR: Research Grants—AbbVie, Galapagos, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB; consultancy—AbbVie, Eli Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

COMMENTS
Learn how to write a clear and concise definition of terms section in a research paper to enhance clarity, consistency, and accessibility. Find out the purpose, benefits, types, and steps of defining terms in a research paper with examples and tips.
This glossary is intended to assist you in understanding commonly used terms and concepts when reading, interpreting, and evaluating scholarly research. Also included are common words and phrases defined within the context of how they apply to research in the social and behavioral sciences.
The study is intended to describe the methods of defining terms found in the theses of the English Foreign Language (EFL) students of IAIN Palangka Raya. The method to be used is a mixed method, qualitative and quantitative. Quantitative approach was used to identify, describe the frequencies, and classify the methods of defining terms.
Learn why and how to define key terms in your dissertation, such as concepts, factors, and context. Find out which terms to include or exclude, and how to make them clear and consistent.
Learn how to choose the terms that are important, unique, or uncommon in your study and provide definitions for them in the "Definitions of Terms" section. Find out what information to include within the definitions and why this section is essential for your dissertation.
Learn how to define terms in research studies using conceptual and operational definitions. See examples of how to measure or observe concepts such as stress, concussion and temperature.
The term is used for precise definition in a particular field of knowledge" 18 (Ponomariv 2001, 72); • "a basic unit of science, special area of expertise and area of human activity denomi ...
Definition, Types, Methods, and Examples. Academic research is a methodical way of exploring new ideas or understanding things we already know. It involves gathering and studying information to answer questions or test ideas and requires careful thinking and persistence to reach meaningful conclusions. Let's try to understand what research is.
A PDF document that explains the concept of variable and its use in research, as well as the definition of terms related to research variables. It also provides examples of research questions, types of variables and related papers on research methods.
Glossary of Key Research Terms. This glossary provides definitions of many of the terms used in the guides to conducting qualitative and quantitative research. The definitions were developed by members of the research methods seminar (E600) taught by Mike Palmquist in the 1990s and 2000s.
Learn the basic concepts and terminology of research, such as purpose, hypothesis, methodology, statistics, and ethics. Find out how to conduct and review research involving human participants according to IRB guidelines and policies.
Learn how to define terms in psychotherapy using Socratic dialogue, a method of questioning and reasoning. Find out the categories, types, and methods of defining terms, and see examples and exercises.
Learn how to define key words and phrases in your academic work to demonstrate your understanding and avoid misinterpretation. Find examples of different types of definitions, introductory phrases, and commenting on definitions.
This book proposes guidelines for constructing and evaluating definitions of terms, i.e. words or phrases of general application. The guidelines extend to adoption of nomenclature. The book is ...
Learn the meanings of words and phrases used in clinical research, such as consent, placebo, IRB, and HIPAA. This guide provides definitions, examples, and links to more resources for understanding research terms.
Terms. A word or phrase used to describe a thing or to express concept, especially In a particular kind of language or branch of study. Guidelines in defining terms: 1. Definition of terms works like a glossary but have a different twist. It is placed on the beginning of the research paper to tell the meaning of the terms used in the said paper.
For videos discussing the other parts of the Research Paper, here are the links:WRITING THE RESEARCH TITLE - https://youtu.be/hkh9WIleVEMWRITING THE BACKGROU...
Defining Key Terms. If you have chosen a topic, you may break the topic down into a few main concepts and then list and/or define key terms related to that concept. If you have performed some background searching, you can include some of the words that were used to describe your topic. For example, if your topic deals with the relationship ...
Learn the legal definitions of terms related to research guidelines and human subjects protection, such as advocate, conflict of interest, informed consent and more. The web page also explains the FDA requirements for investigational device exemption and the Belmont Report principles.
A glossary is a list of terms that may not be obvious to your reader. Learn how to create a glossary for your thesis or dissertation, when to use it, and how to cite it.
Find definitions of terms used in social science and policy research, such as accuracy, action research, adjusted R-squared, and more. The glossary also covers child care and early education topics.
The technical or financial report required by the sponsor to complete a research project. The period for which annual accounts are kept (UVA: July 1 through June 30; federal government: October 1 through September 30). A contract or grant for which payment is based on a predetermined price, regardless of actual costs.
A valued or desired outcome associated with a research project. Anticipated benefits may express the probability that subjects and society may benefit from the research procedures. Research may benefit the individual or society as a whole. If research will not benefit individuals, it is required to provide a reasonable likelihood of resulting ...
Objectives To develop a consensual definition for the term 'early axial spondyloarthritis—axSpA'—and 'early peripheral spondyloarthritis—pSpA'. Methods The ASAS (Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society-Spondyloarthritis EARly definition) steering committee convened an international working group (WG). Five consecutive steps were followed: (1) systematic literature ...