- 1-888-SNU-GRAD
- Daytime Classes


The 8 Most Asked Questions About Dissertations

A Ph.D. represents the highest level of education in most fields. People who earn this degree earn the honorific of “doctor” and are considered experts in their field. A doctoral degree is often a prerequisite for teaching at the highest levels in academia or ascending career ladders in education, the government and the nonprofit space.
In 2020 , doctoral degree holders had median weekly earnings of $1,885 and an unemployment rate of 2.5%—lower than any other group. And yet, the dissertation is often a major barrier to completing a doctorate and realizing its many financial and personal benefits.
So what is a dissertation, and what role does it play in your educational trajectory? At SNU, we value exceptional dissertations and integrate the writing process into your coursework. Here are the most common questions we hear about writing dissertations and earning your doctorate.
1. What is a dissertation?
A dissertation is a published piece of academic research. Through your dissertation research , you become an expert in a specific academic niche. After writing your dissertation, you then defend it to a committee of experts in the field. A dissertation is integral to the process of earning a doctoral degree, contributing innovative ideas to your chosen field. Until you have written, published and defended a dissertation, you can’t graduate from a doctoral-level program.
2. Why are dissertations so important?
Dissertations are the crucial piece of research in most doctoral-level programs. The process of writing, researching and amending the dissertation serves several important goals:
- It contributes novel research to the field, supporting innovation, growth and ongoing scholarship.
- It requires students to write a substantive piece of academic research across many semesters, sharpening research skills and expertise.
- It demands that s tudents defend their research, ensuring strong communication and critical thinking skills.
- It requires deep, comprehensive research—including a literature review—improving reading comprehension and writing skills.
- It is a challenging project that serves as a test of the skills you might use as an academic professional in your chosen field.
- It helps establish new members of an academic discipline as contributors to the field.
- It fosters academic connections as you interview sources and defend your work.
3. Why do so many students struggle with the dissertation?
The dissertation process is difficult. However, this difficulty establishes the credibility of doctoral degrees, proving that the student can commit to long-term, intensive research and become a true subject-matter expert.
However, for many adult learners, the dissertation proves especially challenging thanks to work-life balance difficulties, financial constraints and lack of family or institutional support. At SNU, we know that a dissertation is critical to your growth as an academic. But we also know that institutional support can make a big difference in your ability to finish this impressive work. That’s why we integrate dissertation writing into our curriculum, rather than leaving you to do it all on your own time.
One study suggests that more than half of students never complete their dissertation. Other research indicates that academic reforms that help students with their work reduce dropout rates, ensuring more students complete their dissertation and earn the coveted title of doctor.
4. How long is a dissertation?
Most dissertations are 100 pages or longer — roughly the length of a book. The specific length of your dissertation depends on the type of research, how much research exists in the field and similar factors. The goal of dissertation writing is not to attain a specific length, but to be comprehensive and thoughtful. It anticipates and answers potential objections, gives appropriate credit to the source materials and reviews prior work in the field.
Your dissertation review committee is more interested in a comprehensive dissertation that displays your critical thinking and research skills than they are in a dissertation of a specific length. Excessive wordiness without value wastes a reader’s time.
The right length for a dissertation depends on several factors:
- How much research already exists in the field?
- What field are you publishing in?
- What type of research are you doing?
- Is your research controversial?
- How much space do you need to explain your research and address objections?
Put simply: A dissertation should be long enough to comprehensively cover the subject, but no longer.
5. How do you write a dissertation?
In general, the dissertation process follows this schedule:
- Research the field and identify potential topics.
- Meet with an advisor to choose and improve a topic.
- Perform a literature review.
- Conduct new research.
- Write the dissertation.
- Edit the dissertation.
- Defend the dissertation.
Each step involves weeks to months of work and many phases of revision, reevaluation and research. At SNU, we incorporate many phases of the writing and research process into your coursework. This ensures you are on track to graduate and addresses dissertation writing challenges before they snowball into a serious problem.
6. When should you start writing a dissertation?
The dissertation writing process should begin almost as soon as you enroll in school. That doesn’t necessarily mean you need to have content written on your first day of class. Instead, you will need to engage in substantive pre-writing that includes:
- Familiarizing yourself with relevant research in the field.
- Developing an opinion on recent research.
- Designing your research to address a clear and narrowly defined topic.
As you hone in on your topic, you can begin the writing and research portion of the project. In most cases, this starts within a semester or two of enrollment. A dissertation is not something you can leave until the last semester or shortly before graduation. SNU ensures this doesn’t happen by integrating the writing process into your coursework. You will start working on your dissertation early, preventing you from becoming overwhelmed.
7. How do you cite a dissertation?
A dissertation is a published scholarly work. Each style manual has specific instructions for citing a dissertation, so be sure to consult the style manual you’re using.
You can cite other dissertations in your dissertation. In many cases, dissertations can provide useful starting points for your research. The literature reviews they contain may also help with your literature review.
8. How do you choose a school for your dissertation?
Choosing the right school for your dissertation can mean the difference between finishing this scholarly work and languishing at the dreaded “ all-but-dissertation” (ABD) stage . SNU specializes in supporting adult learners by encouraging intensive research and protecting your work-life balance.
At SNU, your dissertation is a part of your coursework . You will get support from start to finish, including a dissertation advisor who is an expert in your chosen field. We are here for you, and we want to see you succeed.

Want to learn more about SNU's programs?
Request more information.
Have questions about SNU, our program, or how we can help you succeed. Fill out the form and an enrollment counselor will reach out to you soon!
Subscribe to the SNU blog for inspirational articles and tips to support you on your journey back to school.
Recent blog articles.

Adult Education
Supercharging Instructional Design with Artificial Intelligence
Sport Management Students Attend Fourth Professional Connections Trip

Discover Southern Nazarene University's Graduate Programs in Business

How Passion & Dedication Pave the Way for Success in Special Education
Have questions about SNU or need help determining which program is the right fit? Fill out the form and an enrollment counselor will follow-up to answer your questions!
Text With an Enrollment Counselor
Have questions, but want a faster response? Fill out the form and one of our enrollment counselors will follow-up via text shortly!

Tips for writing a PhD dissertation: FAQs answered
From how to choose a topic to writing the abstract and managing work-life balance through the years it takes to complete a doctorate, here we collect expert advice to get you through the PhD writing process
Campus team
Additional links.

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} It’s time: how to get your department off X
Deepfakes are coming for education. be prepared, campus webinar: the evolution of interdisciplinarity, emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, relieve student boredom by ‘activating’ lectures.
Embarking on a PhD is “probably the most challenging task that a young scholar attempts to do”, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith in their practical guide to dissertation and thesis writing. After years of reading and research to answer a specific question or proposition, the candidate will submit about 80,000 words that explain their methods and results and demonstrate their unique contribution to knowledge. Here are the answers to frequently asked questions about writing a doctoral thesis or dissertation.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
Whatever the genre of the doctorate, a PhD must offer an original contribution to knowledge. The terms “dissertation” and “thesis” both refer to the long-form piece of work produced at the end of a research project and are often used interchangeably. Which one is used might depend on the country, discipline or university. In the UK, “thesis” is generally used for the work done for a PhD, while a “dissertation” is written for a master’s degree. The US did the same until the 1960s, says Oxbridge Essays, when the convention switched, and references appeared to a “master’s thesis” and “doctoral dissertation”. To complicate matters further, undergraduate long essays are also sometimes referred to as a thesis or dissertation.
The Oxford English Dictionary defines “thesis” as “a dissertation, especially by a candidate for a degree” and “dissertation” as “a detailed discourse on a subject, especially one submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of a degree or diploma”.
- Ten platinum rules for PhD supervisors
- Fostering freedom in PhD students: how supervisors can shape accessible paths for doctoral research
- Lessons from students on effective research supervision
The title “doctor of philosophy”, incidentally, comes from the degree’s origins, write Dr Felix, an associate professor at Mahidol University in Thailand, and Dr Smith, retired associate professor of education at the University of Sydney , whose co-authored guide focuses on the social sciences. The PhD was first awarded in the 19th century by the philosophy departments of German universities, which at that time taught science, social science and liberal arts.
How long should a PhD thesis be?
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length ) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) – from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion.
The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social sciences and STEM all have their own conventions), location and institution. Examples and guides to structure proliferate online. The University of Salford , for example, lists: title page, declaration, acknowledgements, abstract, table of contents, lists of figures, tables and abbreviations (where needed), chapters, appendices and references.
A scientific-style thesis will likely need: introduction, literature review, materials and methods, results, discussion, bibliography and references.
As well as checking the overall criteria and expectations of your institution for your research, consult your school handbook for the required length and format (font, layout conventions and so on) for your dissertation.
A PhD takes three to four years to complete; this might extend to six to eight years for a part-time doctorate.
What are the steps for completing a PhD?
Before you get started in earnest , you’ll likely have found a potential supervisor, who will guide your PhD journey, and done a research proposal (which outlines what you plan to research and how) as part of your application, as well as a literature review of existing scholarship in the field, which may form part of your final submission.
In the UK, PhD candidates undertake original research and write the results in a thesis or dissertation, says author and vlogger Simon Clark , who posted videos to YouTube throughout his own PhD journey . Then they submit the thesis in hard copy and attend the viva voce (which is Latin for “living voice” and is also called an oral defence or doctoral defence) to convince the examiners that their work is original, understood and all their own. Afterwards, if necessary, they make changes and resubmit. If the changes are approved, the degree is awarded.
The steps are similar in Australia , although candidates are mostly assessed on their thesis only; some universities may include taught courses, and some use a viva voce. A PhD in Australia usually takes three years full time.
In the US, the PhD process begins with taught classes (similar to a taught master’s) and a comprehensive exam (called a “field exam” or “dissertation qualifying exam”) before the candidate embarks on their original research. The whole journey takes four to six years.
A PhD candidate will need three skills and attitudes to get through their doctoral studies, says Tara Brabazon , professor of cultural studies at Flinders University in Australia who has written extensively about the PhD journey :
- master the academic foundational skills (research, writing, ability to navigate different modalities)
- time-management skills and the ability to focus on reading and writing
- determined motivation to do a PhD.

How do I choose the topic for my PhD dissertation or thesis?
It’s important to find a topic that will sustain your interest for the years it will take to complete a PhD. “Finding a sustainable topic is the most important thing you [as a PhD student] would do,” says Dr Brabazon in a video for Times Higher Education . “Write down on a big piece of paper all the topics, all the ideas, all the questions that really interest you, and start to cross out all the ones that might just be a passing interest.” Also, she says, impose the “Who cares? Who gives a damn?” question to decide if the topic will be useful in a future academic career.
The availability of funding and scholarships is also often an important factor in this decision, says veteran PhD supervisor Richard Godwin, from Harper Adams University .
Define a gap in knowledge – and one that can be questioned, explored, researched and written about in the time available to you, says Gina Wisker, head of the Centre for Learning and Teaching at the University of Brighton. “Set some boundaries,” she advises. “Don’t try to ask everything related to your topic in every way.”
James Hartley, research professor in psychology at Keele University, says it can also be useful to think about topics that spark general interest. If you do pick something that taps into the zeitgeist, your findings are more likely to be noticed.
You also need to find someone else who is interested in it, too. For STEM candidates , this will probably be a case of joining a team of people working in a similar area where, ideally, scholarship funding is available. A centre for doctoral training (CDT) or doctoral training partnership (DTP) will advertise research projects. For those in the liberal arts and social sciences, it will be a matter of identifying a suitable supervisor .
Avoid topics that are too broad (hunger across a whole country, for example) or too narrow (hunger in a single street) to yield useful solutions of academic significance, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith. And ensure that you’re not repeating previous research or trying to solve a problem that has already been answered. A PhD thesis must be original.
What is a thesis proposal?
After you have read widely to refine your topic and ensure that it and your research methods are original, and discussed your project with a (potential) supervisor, you’re ready to write a thesis proposal , a document of 1,500 to 3,000 words that sets out the proposed direction of your research. In the UK, a research proposal is usually part of the application process for admission to a research degree. As with the final dissertation itself, format varies among disciplines, institutions and countries but will usually contain title page, aims, literature review, methodology, timetable and bibliography. Examples of research proposals are available online.
How to write an abstract for a dissertation or thesis
The abstract presents your thesis to the wider world – and as such may be its most important element , says the NUI Galway writing guide. It outlines the why, how, what and so what of the thesis . Unlike the introduction, which provides background but not research findings, the abstract summarises all sections of the dissertation in a concise, thorough, focused way and demonstrates how well the writer understands their material. Check word-length limits with your university – and stick to them. About 300 to 500 words is a rough guide – but it can be up to 1,000 words.
The abstract is also important for selection and indexing of your thesis, according to the University of Melbourne guide , so be sure to include searchable keywords.
It is the first thing to be read but the last element you should write. However, Pat Thomson , professor of education at the University of Nottingham , advises that it is not something to be tackled at the last minute.
How to write a stellar conclusion
As well as chapter conclusions, a thesis often has an overall conclusion to draw together the key points covered and to reflect on the unique contribution to knowledge. It can comment on future implications of the research and open up new ideas emanating from the work. It is shorter and more general than the discussion chapter , says online editing site Scribbr, and reiterates how the work answers the main question posed at the beginning of the thesis. The conclusion chapter also often discusses the limitations of the research (time, scope, word limit, access) in a constructive manner.
It can be useful to keep a collection of ideas as you go – in the online forum DoctoralWriting SIG , academic developer Claire Aitchison, of the University of South Australia , suggests using a “conclusions bank” for themes and inspirations, and using free-writing to keep this final section fresh. (Just when you feel you’ve run out of steam.) Avoid aggrandising or exaggerating the impact of your work. It should remind the reader what has been done, and why it matters.
How to format a bibliography (or where to find a reliable model)
Most universities use a preferred style of references , writes THE associate editor Ingrid Curl. Make sure you know what this is and follow it. “One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process.”
A bibliography contains not only works cited explicitly but also those that have informed or contributed to the research – and as such illustrates its scope; works are not limited to written publications but include sources such as film or visual art.
Examiners can start marking from the back of the script, writes Dr Brabazon. “Just as cooks are judged by their ingredients and implements, we judge doctoral students by the calibre of their sources,” she advises. She also says that candidates should be prepared to speak in an oral examination of the PhD about any texts included in their bibliography, especially if there is a disconnect between the thesis and the texts listed.
Can I use informal language in my PhD?
Don’t write like a stereotypical academic , say Kevin Haggerty, professor of sociology at the University of Alberta , and Aaron Doyle, associate professor in sociology at Carleton University , in their tongue-in-cheek guide to the PhD journey. “If you cannot write clearly and persuasively, everything about PhD study becomes harder.” Avoid jargon, exotic words, passive voice and long, convoluted sentences – and work on it consistently. “Writing is like playing guitar; it can improve only through consistent, concerted effort.”
Be deliberate and take care with your writing . “Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense,” advises THE ’s Ms Curl. “Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: ‘Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.’ Clarity is key.”
How often should a PhD candidate meet with their supervisor?
Since the PhD supervisor provides a range of support and advice – including on research techniques, planning and submission – regular formal supervisions are essential, as is establishing a line of contact such as email if the candidate needs help or advice outside arranged times. The frequency varies according to university, discipline and individual scholars.
Once a week is ideal, says Dr Brabazon. She also advocates a two-hour initial meeting to establish the foundations of the candidate-supervisor relationship .
The University of Edinburgh guide to writing a thesis suggests that creating a timetable of supervisor meetings right at the beginning of the research process will allow candidates to ensure that their work stays on track throughout. The meetings are also the place to get regular feedback on draft chapters.
“A clear structure and a solid framework are vital for research,” writes Dr Godwin on THE Campus . Use your supervisor to establish this and provide a realistic view of what can be achieved. “It is vital to help students identify the true scientific merit, the practical significance of their work and its value to society.”
How to proofread your dissertation (what to look for)
Proofreading is the final step before printing and submission. Give yourself time to ensure that your work is the best it can be . Don’t leave proofreading to the last minute; ideally, break it up into a few close-reading sessions. Find a quiet place without distractions. A checklist can help ensure that all aspects are covered.
Proofing is often helped by a change of format – so it can be easier to read a printout rather than working off the screen – or by reading sections out of order. Fresh eyes are better at spotting typographical errors and inconsistencies, so leave time between writing and proofreading. Check with your university’s policies before asking another person to proofread your thesis for you.
As well as close details such as spelling and grammar, check that all sections are complete, all required elements are included , and nothing is repeated or redundant. Don’t forget to check headings and subheadings. Does the text flow from one section to another? Is the structure clear? Is the work a coherent whole with a clear line throughout?
Ensure consistency in, for example, UK v US spellings, capitalisation, format, numbers (digits or words, commas, units of measurement), contractions, italics and hyphenation. Spellchecks and online plagiarism checkers are also your friend.

How do you manage your time to complete a PhD dissertation?
Treat your PhD like a full-time job, that is, with an eight-hour working day. Within that, you’ll need to plan your time in a way that gives a sense of progress . Setbacks and periods where it feels as if you are treading water are all but inevitable, so keeping track of small wins is important, writes A Happy PhD blogger Luis P. Prieto.
Be specific with your goals – use the SMART acronym (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and timely).
And it’s never too soon to start writing – even if early drafts are overwritten and discarded.
“ Write little and write often . Many of us make the mistake of taking to writing as one would take to a sprint, in other words, with relatively short bursts of intense activity. Whilst this can prove productive, generally speaking it is not sustainable…In addition to sustaining your activity, writing little bits on a frequent basis ensures that you progress with your thinking. The comfort of remaining in abstract thought is common; writing forces us to concretise our thinking,” says Christian Gilliam, AHSS researcher developer at the University of Cambridge ’s Centre for Teaching and Learning.
Make time to write. “If you are more alert early in the day, find times that suit you in the morning; if you are a ‘night person’, block out some writing sessions in the evenings,” advises NUI Galway’s Dermot Burns, a lecturer in English and creative arts. Set targets, keep daily notes of experiment details that you will need in your thesis, don’t confuse writing with editing or revising – and always back up your work.
What work-life balance tips should I follow to complete my dissertation?
During your PhD programme, you may have opportunities to take part in professional development activities, such as teaching, attending academic conferences and publishing your work. Your research may include residencies, field trips or archive visits. This will require time-management skills as well as prioritising where you devote your energy and factoring in rest and relaxation. Organise your routine to suit your needs , and plan for steady and regular progress.
How to deal with setbacks while writing a thesis or dissertation
Have a contingency plan for delays or roadblocks such as unexpected results.
Accept that writing is messy, first drafts are imperfect, and writer’s block is inevitable, says Dr Burns. His tips for breaking it include relaxation to free your mind from clutter, writing a plan and drawing a mind map of key points for clarity. He also advises feedback, reflection and revision: “Progressing from a rough version of your thoughts to a superior and workable text takes time, effort, different perspectives and some expertise.”
“Academia can be a relentlessly brutal merry-go-round of rejection, rebuttal and failure,” writes Lorraine Hope , professor of applied cognitive psychology at the University of Portsmouth, on THE Campus. Resilience is important. Ensure that you and your supervisor have a relationship that supports open, frank, judgement-free communication.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
Authoring a PhD Thesis: How to Plan, Draft, Write and Finish a Doctoral Dissertation (2003), by Patrick Dunleavy
Writing Your Dissertation in Fifteen Minutes a Day: A Guide to Starting, Revising, and Finishing Your Doctoral Thesis (1998), by Joan Balker
Challenges in Writing Your Dissertation: Coping with the Emotional, Interpersonal, and Spiritual Struggles (2015), by Noelle Sterne
It’s time: how to get your department off X
Using data skills to turn students’ passion for sports into rewarding careers, a diy guide to starting your own journal, the zone of proximal development in four stages, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, ‘it just isn’t safe to disclose’.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion | Checklist and Examples
Published on 9 September 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on 10 October 2022.
The conclusion is the very last part of your thesis or dissertation . It should be concise and engaging, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your main findings, as well as the answer to your research question .
In it, you should:
- Clearly state the answer to your main research question
- Summarise and reflect on your research process
- Make recommendations for future work on your topic
- Show what new knowledge you have contributed to your field
- Wrap up your thesis or dissertation
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Discussion vs. conclusion, how long should your conclusion be, step 1: answer your research question, step 2: summarise and reflect on your research, step 3: make future recommendations, step 4: emphasise your contributions to your field, step 5: wrap up your thesis or dissertation, full conclusion example, conclusion checklist, frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.
While your conclusion contains similar elements to your discussion section , they are not the same thing.
Your conclusion should be shorter and more general than your discussion. Instead of repeating literature from your literature review , discussing specific research results , or interpreting your data in detail, concentrate on making broad statements that sum up the most important insights of your research.
As a rule of thumb, your conclusion should not introduce new data, interpretations, or arguments.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Depending on whether you are writing a thesis or dissertation, your length will vary. Generally, a conclusion should make up around 5–7% of your overall word count.
An empirical scientific study will often have a short conclusion, concisely stating the main findings and recommendations for future research. A humanities topic or systematic review , on the other hand, might require more space to conclude its analysis, tying all the previous sections together in an overall argument.
Your conclusion should begin with the main question that your thesis or dissertation aimed to address. This is your final chance to show that you’ve done what you set out to do, so make sure to formulate a clear, concise answer.
- Don’t repeat a list of all the results that you already discussed
- Do synthesise them into a final takeaway that the reader will remember.
An empirical thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
A case study –based thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
In the second example, the research aim is not directly restated, but rather added implicitly to the statement. To avoid repeating yourself, it is helpful to reformulate your aims and questions into an overall statement of what you did and how you did it.
Your conclusion is an opportunity to remind your reader why you took the approach you did, what you expected to find, and how well the results matched your expectations.
To avoid repetition , consider writing more reflectively here, rather than just writing a summary of each preceding section. Consider mentioning the effectiveness of your methodology , or perhaps any new questions or unexpected insights that arose in the process.
You can also mention any limitations of your research, but only if you haven’t already included these in the discussion. Don’t dwell on them at length, though – focus on the positives of your work.
- While x limits the generalisability of the results, this approach provides new insight into y .
- This research clearly illustrates x , but it also raises the question of y .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
You may already have made a few recommendations for future research in your discussion section, but the conclusion is a good place to elaborate and look ahead, considering the implications of your findings in both theoretical and practical terms.
- Based on these conclusions, practitioners should consider …
- To better understand the implications of these results, future studies could address …
- Further research is needed to determine the causes of/effects of/relationship between …
When making recommendations for further research, be sure not to undermine your own work. Relatedly, while future studies might confirm, build on, or enrich your conclusions, they shouldn’t be required for your argument to feel complete. Your work should stand alone on its own merits.
Just as you should avoid too much self-criticism, you should also avoid exaggerating the applicability of your research. If you’re making recommendations for policy, business, or other practical implementations, it’s generally best to frame them as ‘shoulds’ rather than ‘musts’. All in all, the purpose of academic research is to inform, explain, and explore – not to demand.
Make sure your reader is left with a strong impression of what your research has contributed to the state of your field.
Some strategies to achieve this include:
- Returning to your problem statement to explain how your research helps solve the problem
- Referring back to the literature review and showing how you have addressed a gap in knowledge
- Discussing how your findings confirm or challenge an existing theory or assumption
Again, avoid simply repeating what you’ve already covered in the discussion in your conclusion. Instead, pick out the most important points and sum them up succinctly, situating your project in a broader context.
The end is near! Once you’ve finished writing your conclusion, it’s time to wrap up your thesis or dissertation with a few final steps:
- It’s a good idea to write your abstract next, while the research is still fresh in your mind.
- Next, make sure your reference list is complete and correctly formatted. To speed up the process, you can use our free APA citation generator .
- Once you’ve added any appendices , you can create a table of contents and title page .
- Finally, read through the whole document again to make sure your thesis is clearly written and free from language errors. You can proofread it yourself , ask a friend, or consider Scribbr’s proofreading and editing service .
Here is an example of how you can write your conclusion section. Notice how it includes everything mentioned above:
V. Conclusion
The current research aimed to identify acoustic speech characteristics which mark the beginning of an exacerbation in COPD patients.
The central questions for this research were as follows: 1. Which acoustic measures extracted from read speech differ between COPD speakers in stable condition and healthy speakers? 2. In what ways does the speech of COPD patients during an exacerbation differ from speech of COPD patients during stable periods?
All recordings were aligned using a script. Subsequently, they were manually annotated to indicate respiratory actions such as inhaling and exhaling. The recordings of 9 stable COPD patients reading aloud were then compared with the recordings of 5 healthy control subjects reading aloud. The results showed a significant effect of condition on the number of in- and exhalations per syllable, the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable, and the ratio of voiced and silence intervals. The number of in- and exhalations per syllable and the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable were higher for COPD patients than for healthy controls, which confirmed both hypotheses.
However, the higher ratio of voiced and silence intervals for COPD patients compared to healthy controls was not in line with the hypotheses. This unpredicted result might have been caused by the different reading materials or recording procedures for both groups, or by a difference in reading skills. Moreover, there was a trend regarding the effect of condition on the number of syllables per breath group. The number of syllables per breath group was higher for healthy controls than for COPD patients, which was in line with the hypothesis. There was no effect of condition on pitch, intensity, center of gravity, pitch variability, speaking rate, or articulation rate.
This research has shown that the speech of COPD patients in exacerbation differs from the speech of COPD patients in stable condition. This might have potential for the detection of exacerbations. However, sustained vowels rarely occur in spontaneous speech. Therefore, the last two outcome measures might have greater potential for the detection of beginning exacerbations, but further research on the different outcome measures and their potential for the detection of exacerbations is needed due to the limitations of the current study.
Checklist: Conclusion
I have clearly and concisely answered the main research question .
I have summarized my overall argument or key takeaways.
I have mentioned any important limitations of the research.
I have given relevant recommendations .
I have clearly explained what my research has contributed to my field.
I have not introduced any new data or arguments.
You've written a great conclusion! Use the other checklists to further improve your dissertation.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5-7% of your overall word count.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion | Checklist and Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 30 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/conclusion/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write an abstract | steps & examples.
- Search All Scholarships
- Exclusive Scholarships
- Easy Scholarships to Apply For
- No Essay Scholarships
- Scholarships for HS Juniors
- Scholarships for HS Seniors
- Scholarships for College Students
- Scholarships for Grad Students
- Scholarships for Women
- Scholarships for Black Students
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- College Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship Winners
- Scholarship Providers
Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here .
What is a Dissertation? Everything You Need to Know

Cait Williams is a Content Writer at Scholarships360. Cait recently graduated from Ohio University with a degree in Journalism and Strategic Communications. During her time at OU, was active in the outdoor recreation community.
Learn about our editorial policies

Cari Schultz is an Educational Review Board Advisor at Scholarships360, where she reviews content featured on the site. For over 20 years, Cari has worked in college admissions (Baldwin Wallace University, The Ohio State University, University of Kentucky) and as a college counselor (Columbus School for Girls).

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.

Your dissertation, the final piece of the puzzle that stands between you and the completion of your doctoral degree . Okay, so that’s not the actual definition of the word “dissertation,” but when you’re writing one, that can feel true at times! Keep reading to learn the academic definition and take a more in depth look at what a dissertation is and how to navigate writing one. So, let’s go!
Related : Top fully funded PhD programs
Dissertation vs. thesis
While dissertation and thesis are sometimes used interchangeably, they actually refer to two different pieces of writing. A thesis is traditionally completed at the end of a master’s program . It is based on pre-existing research and showcases your ability to understand the information you have been learning about in your program.
A dissertation is much longer than a thesis and is completed at the end of a PhD or doctorate program . It is the last thing you need to complete in order to earn your doctorate in your chosen field. It will be about a topic of your choosing that is within your field of study. Instead of using all pre-existing information though, you will conduct a portion of your own research and propose new ideas.
See also : Top scholarships for graduate students
What do you write about when completing a dissertation?
What you write about will depend on what field of study you are in. A dissertation is designed to be your own. Meaning that what you write about should be a new idea, a new topic, or question that is still unanswered in your field. Something that you will need to collect new data on, potentially interview people for and explore what information is already available.
Generally, an idea will need to be approved or at least discussed with whoever is overseeing your dissertation before you begin writing. It’s important to put time and effort into choosing a topic that you will be able to find either existing research for and add to, or a topic that you will be able to establish your own methods of data collection for. Again, the goal of your dissertation is to add to your field.
How long does a dissertation need to be?
Your dissertation length will vary, but you can generally count on it to be around 2-3 times the length of your thesis. A standard thesis is roughly 80 to 100 pages. So, on the short end you’re looking at a 200 pages dissertation, while the longer end can reach as high as 400 pages.
How long does it take to write?
The page count for a dissertation is enough to scare even the best writers away, but take a breath and rest easy knowing that this is not something you complete in just one semester or even two. On the short end you will have a year to write your dissertation, while the longer end can offer as much as two years to complete your dissertation. During this time, you will work with an advisor who can watch over you and help you along the way.
The parts of a dissertation
A dissertation is not just one long paper you must write. Thankfully, it is broken down into manageable pieces that you complete over time.
Choosing a topic
The first thing you will do is come up with your topic. Again, your topic will need to be approved by whoever is overseeing your dissertation. If they think that it may not be a strong topic, they will let you know. Even if a topic is approved though, you’ll need to do research around that topic first to make sure that it has not already been covered, or if it has that you take into consideration what has been done and add to the topic in a new way.
Research can mean looking at what already exists, as well as conducting your own research to add to a proposed idea of yours. Your research can take many different forms depending on what field you are in. Research can be costly at times, so be sure to check out what funding opportunities are available for doctoral research. There are even post PhD research grants you should be familiar with if you intend to continue researching.
Chapter break down
A dissertation generally consists of five chapters. We’ve written them out below with a brief description of each and what they include.
Introduction – Just as you would expect, this is where you will introduce your topic and what you plan to discuss
Literature review – This section will address the research you have found that has already been done, or found has not been done, that pertains to your topic
Methodology – How you go about collecting information for your dissertation, whether it be conducting your own research or delving deep into what has already been done, will be discussed in the methodology section
Results – Your results will analyze the information you gathered in regard to your topic
Discussion – Finally, your discussion section will assess the meaning of your results and it is also where you will add your own ideas, rooted in research, about what those results mean in a broader context in regard to your field
There will be more parts of your dissertation that are not included in the chapters, but the bulk of your dissertation will be made up by these five chapters. Things like title pages, references, appendices, and table of contents will also be included.
Defending your dissertation
Believe it or not, it’s not enough just to write your dissertation–you also have to defend your dissertation. This is another reason why taking a thorough amount of time to choose your topic is so important. You’ll likely need to propose your initial dissertation idea, but that will be much simpler and shorter. Your final defense will be much lengthier and in depth.
During your defense, you will present your dissertation to a committee. It’s likely that you’ll be at least somewhat familiar with those on the committee; they are not just randomly picked. They will ask you questions about your research, and you will need to respond to each question. A defense generally takes around two hours. The point of a defense is not to have people try to undermine your work, but for you to exemplify your expertise in your field.
Failing your dissertation
Nobody wants to think about failing, but unfortunately, you can fail your dissertation. However, let’s talk about a few things before we just leave it at that. First, if you are afraid of failing your dissertation, this is something that you should speak to your advisor about. They can help you determine if there should be legitimate concerns or if you are getting in your own head.
Second, even if you do fail your dissertation, you are usually allowed to resubmit one time. This of course is not ideal, but it does give you a little room to breathe. Your goal is to do great from the start, but remember this is not an easy task. You’ll likely have plenty of bumps along the way!
Again, if you have concerns about failing, address them sooner rather than later and seek help. There are bound to be plenty of people and services around you, as well as additional services that you can pay for which will help review your materials and guide you along.
Key Takeaways
- Dissertations are completed as the last step of your PhD or doctorate degree
- Your dissertation will be related to a topic or question in your field of study that you choose
- Dissertations take anywhere from one to two years to complete and can be upwards of three hundred pages long
- Your dissertation is designed to showcase your expertise in your field and your addition of new ideas to the field about a particular question or area
Start your scholarship search
- Vetted scholarships custom-matched to your profile
- Access exclusive scholarships only available to Scholarships360 members
Frequently asked questions about dissertations
Do all doctorates require a dissertation, how difficult is a dissertation, who reads your dissertation, scholarships360 recommended.

10 Tips for Successful College Applications

Coalition vs. Common App: What is the difference?

College Application Deadlines 2024-2025: What You Need to Know
Trending now.

How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale

PSAT to SAT Score Conversion: Predict Your Score

What are Public Ivy League Schools?
3 reasons to join scholarships360.
- Automatic entry to our $10,000 No-Essay Scholarship
- Personalized matching to thousands of vetted scholarships
- Quick apply for scholarships exclusive to our platform
By the way...Scholarships360 is 100% free!

How Long is a Dissertation

How Long is a Dissertation? Concrete Answers
An undergraduate dissertation usually falls within the range of 8,000 to 15,000 words, while a master's dissertation typically spans from 12,000 to 50,000 words. In contrast, a PhD thesis is typically of book length, ranging from 70,000 to 100,000 words.
Let’s unravel the mystery of how long should a dissertation be. If you’ve ever wondered about this, look no further. Our comprehensive guide delves into the nitty-gritty of dissertation lengths across diverse academic realms. Whether you're a budding grad student, an academic advisor, or just curious, we've got you covered.
From Master's to PhD programs, we decode the variations in length requirements and shed light on disciplinary disparities. In general, dissertations are 150 to 300 words. But factors influence the length of these daunting scholarly requirements! But fear not as we break it down for you.
We’ll unveil the secrets behind dissertation writing, from how they reflect the depth and breadth of research to offering invaluable tips for planning and writing. So, if you're ready to demystify the daunting dissertation journey, hop on board! Let's navigate the labyrinth of academia together and empower you to conquer your scholarly aspirations.
Institutional guidelines on dissertation length
You can think of institutional guidelines as purveyors of academic excellence. Ever wondered why schools impose specific requirements like "Chapter 1: The Introduction must be at least 35 pages long and no more than 50 pages"?
It's not just about arbitrary rules! However, it's about striking the perfect balance between guidance and practicality. These guidelines serve as guardrails, steering students like you towards scholarly success without overwhelming faculty with endless pages to peruse.
Moreover, credibility is key here! A mere 8-page literature review won't cut it in the realm of academia. But fear not, for most institutions provide dissertation templates, complete with essential headings to streamline the process.
And for those seeking a helping hand, a dissertation writing service like ours stands ready to assist, ensuring your masterpiece meets the lofty standards of academic rigor. So, embrace the guidelines, weave your narrative, and let your dissertation shine with scholarly prowess.
Variations in dissertation length across academic disciplines
Dissertation length varies significantly across academic disciplines due to differences in research methods, data presentation, and writing conventions. Here's a general overview of how dissertation length can differ by discipline:
- Humanities and Social Sciences: Dissertations in these fields tend to be longer because they often involve comprehensive literature reviews, detailed theoretical analyses, and extensive qualitative data. It's not uncommon for dissertations in history, literature, or sociology to exceed 200 pages.
- Sciences and Engineering: Dissertations in the sciences and engineering might be shorter in terms of page count but are dense with technical details, data, charts, and appendices. They often range between 100 to 200 pages. However, the length can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the work and the requirements of the specific program.
- Arts and Design: In creative disciplines, the dissertation might include a practical component (like a portfolio, exhibition, or performance) alongside a written thesis. The written component might be shorter, focusing on the conceptual and contextual analysis of the creative work, usually ranging from 40 to 80 pages.
- Professional Fields (Business, Education, etc.): Dissertations in professional fields such as business or education often focus on case studies, practical applications, and policy analysis. These dissertations can vary widely in length but often fall in the range of 100 to 200 pages.
Dissertations vary in length due to many factors, which shows the diverse nature of academic research. Disciplinary differences are significant, as each field may have distinct expectations regarding the depth and scope of the study.
The type of analysis conducted, whether qualitative, quantitative, or a combination of both, also impacts the length.
For instance, qualitative studies may involve extensive textual analysis, resulting in longer manuscripts, while quantitative studies may require detailed statistical analyses. Additionally, the specific area of research within a discipline can also affect the length, as certain topics may necessitate more:
- extensive literature reviews
- data collection (e.g., fieldwork, surveys, interviews, lab work)
- discussion sections
While the average length typically falls within the range of 150-300 pages, it's essential to recognize the nuanced factors contributing to variations in dissertation length. You must remain informed about the variables shaping your document's overall size and structure to deliver exemplary results.
Factors influencing the length of doctoral dissertations
Various factors determine the length of a dissertation, such as the specific guidelines set by universities, the type of research conducted, the extent of analysis required, and the presence of supplementary materials.
Several factors come into play when determining the ideal length of a dissertation. University guidelines set the tone, with institutions offering word count ranges typically between 8,000 to 15,000 words for undergraduates and masters and 75,000 to 100,000 words for PhD.
Yet, beyond these guidelines, the nature of your research holds sway.
Disciplines vary, with humanities favoring extensive literature reviews and scientific fields emphasizing methodological intricacies. Depth of analysis matters, too; a thorough exploration demands more space.
Balancing these elements ensures a well-rounded dissertation. So, as you embark on your scholarly journey, consider these factors carefully. By understanding them, you'll craft a dissertation that not only meets academic standards but also showcases your analytical prowess and depth of intelligence.
Length, components, and scholarly dedication
Many aspiring scholars think, "How long is a doctoral dissertation?" However, the answer isn't straightforward. Yes, length varies, but let's not forget to factor in a crucial element: time. And we know because many students have instructed us to “ write my dissertation !”
Remember, a dissertation isn't penned in one sitting. Rather, it often evolves from smaller academic chapters. This gradual process allows students to explore diverse topics before committing to a book-length project they're passionate about.
Beyond the central argument lie various components that contribute to the overall length. Take the literature review, for example—an essential segment that contextualizes the research by analyzing existing scholarship. Then there's the myriad of ancillary elements like the title page, acknowledgments, abstract, and appendix, each adding to the dissertation's page count.
It’s the accumulation of these parts that determines the length. So, while the answer may not be a precise number, it's crucial to acknowledge many elements that make up a doctoral dissertation. And for those embarking on this scholarly journey, we can help you conquer this challenge.
How Long is a Dissertation Chapter? Uncover the Mystery
When it comes to dissertation length, most grad students fret over how long each chapter should be. While there's no one-size-fits-all answer, there is a golden rule–chapters should be long enough to address the research question comprehensively.
Think quality over quantity! Ask any dissertation adviser, and they’ll say aiming to fill a predetermined number of pages shouldn’t be the goal. Rather, you must thoroughly explore your topic, conduct extensive research, and present your findings effectively.
Your writing style and the unique nature of your research also play pivotal roles. So, whether your chapter spans 50 pages or 150, ensure it's packed with substantive content that advances your study. Ultimately, it's not about hitting a page count but about delivering a high-quality scholarly contribution.
Writing an Excellent PhD Dissertation: Strategies and Tips
After you’re done pondering on how many pages should a dissertation be, you can move on with production. Wondering how to write a dissertation , here are some tips:
- Start with a significant research topic that inspires you and formulate a clear research question.
- Thoroughly review existing literature to contextualize your study.
- Develop a robust methodology and collect comprehensive data.
- Analyze findings meticulously and synthesize them effectively.
- Ensure logical flow throughout your writing, striving for clarity and coherence.
- Engage with other scholars, both peers and mentors, to refine your work.
- Maintain consistency in formatting and adhere to academic standards.
Remember, with meticulous planning and dedication, you'll produce a dissertation that makes you and your mentors proud.
How long is a PhD dissertation?: The Conundrum
Do you belong to the list of students who feel bewildered about PhD dissertation length? Many wonder because of the length’s variability across disciplines and institutions. The general ballpark figure for a completed doctoral dissertation is typically between 150 to 300 pages. Yet, this can vary widely depending on factors such as:
- field of study
- research methodology used
- individual institutional requirements
- guidelines of mentors
Although there's no one-size-fits-all answer, understanding these variables can help you navigate the ambiguity surrounding dissertation length. And with proper planning, you can create an impressive output.
Frequently asked questions
How to properly plan and prepare for a long dissertation .
Thinking about how long is a dissertation for PhD stops students on their track. It can indeed be overwhelming when you think of the amount of work involved. But with proper planning, you can crush your goals. Here are some helpful tips:
- Break down your work into manageable steps.
- Define your research question clearly and set realistic milestones.
- Create an outline to help you write. `
- Have a schedule for research, writing, and revisions.
- Stay organized with notes, citations, and references.
- Seek feedback from advisors and peers throughout the process.
Remember, embrace the challenges you face as opportunities for growth!
Are supporting materials counted in the dissertation word count?
Worried about how long is a dissertation paper and if yours will make the cut? Remember, appendices, tables, and figures, while essential, aren't factored into the word count. So, you can incorporate these supplementary elements without concerns about exceeding word limits.
If you’re pressed for time, you can buy dissertation online . Just ensure to give appropriate instructions so the final output adheres to your institution's formatting guidelines. With these supporting materials appropriately included, your dissertation will be comprehensive.
Are there different types of dissertations?
When asking how long are dissertations, one of the first things to consider is the field of study. Various types of dissertations exist, often shaped by research methodology. It can be quantitative to qualitative studies or triangulation (a blend of both).
Instead of worrying about the length, determine your research approach—whether it's primary or secondary, qualitative or quantitative. This decision significantly impacts the depth and breadth of your investigation, ultimately influencing the expected length of your dissertation. By aligning your research methods with your academic goals, you'll gain clarity on the scope of your writing project.
Another aspect of the length of the entire document is the type of thesis - be it an undergraduate thesis, masters thesis, or thesis for an advanced degree, most dissertations for academic programs are lengthy. The more advanced the degree, the longer the thesis usually is.
Are dissertations just for PhDs?
How many pages in a dissertation is something most students worry about. But is a dissertation just for doctoral candidates? In some countries, dissertations are exclusive to PhDs. However, for other countries, the term “dissertation” is interchangeable with "thesis." Why so?
Because both are research projects completed for undergraduate or postgraduate degrees. Keep in mind that whether you’re pursuing a bachelor's, an MA, or a doctorate, dissertation writing demonstrates your research skills and academic proficiency.
Your doctoral degree, just like your graduate degree from a graduate school, shows you can successfully navigate the research process, theoretical framework, and dissertation defense. Sure, the scope of research was less focused while you were a graduate student with a master's thesis. Nonetheless, it shows consistent work and dedication.
How many chapters in a dissertation?
Still mulling over how long does a dissertation have to be and how many chapters you must write? Dissertations usually consist of five to seven chapters. These typically cover the following:
- introduction
- literature review
- methodology
However, the structure can vary depending on your field of study and specific institutional guidelines. Each chapter plays a vital role, leading readers through your research journey, from laying the groundwork to presenting findings and drawing conclusions.
How do I find a reputable dissertation writer to help me?
Worried about how long are PhD dissertations? No need to worry. You can opt for professional help, and there’s no shame in that! Research for online platforms that specialize in academic writing services like our Studyfy team.
You can take a peek at our positive reviews and testimonials, showing our track record of delivering high-quality work. Choose a writer who possesses expertise in your field of study and can meet your specific requirements. Prioritize the following:
- clear communication
- appropriate instructions (from word count to deadlines)
- transparency regarding pricing
- upfront about revision policies.
By vetting potential writers and choosing a reputable service, you can secure the assistance of a reliable professional to guide you through the dissertation writing process.
Academic & Employability Skills
Subscribe to academic & employability skills.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Writing your dissertation - structure and sections
Posted in: dissertations

In this post, we look at the structural elements of a typical dissertation. Your department may wish you to include additional sections but the following covers all core elements you will need to work on when designing and developing your final assignment.
The table below illustrates a classic dissertation layout with approximate lengths for each section.

Hopkins, D. and Reid, T., 2018. The Academic Skills Handbook: Your Guid e to Success in Writing, Thinking and Communicating at University . Sage.
Your title should be clear, succinct and tell the reader exactly what your dissertation is about. If it is too vague or confusing, then it is likely your dissertation will be too vague and confusing. It is important therefore to spend time on this to ensure you get it right, and be ready to adapt to fit any changes of direction in your research or focus.
In the following examples, across a variety of subjects, you can see how the students have clearly identified the focus of their dissertation, and in some cases target a problem that they will address:
An econometric analysis of the demand for road transport within the united Kingdom from 1965 to 2000
To what extent does payment card fraud affect UK bank profitability and bank stakeholders? Does this justify fraud prevention?
A meta-analysis of implant materials for intervertebral disc replacement and regeneration.
The role of ethnic institutions in social development; the case of Mombasa, Kenya.
Why haven’t biomass crops been adopted more widely as a source of renewable energy in the United Kingdom?
Mapping the criminal mind: Profiling and its limitation.
The Relative Effectiveness of Interferon Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C
Under what conditions did the European Union exhibit leadership in international climate change negotiations from 1992-1997, 1997-2005 and 2005-Copenhagen respectively?
The first thing your reader will read (after the title) is your abstract. However, you need to write this last. Your abstract is a summary of the whole project, and will include aims and objectives, methods, results and conclusions. You cannot write this until you have completed your write-up.
Introduction
Your introduction should include the same elements found in most academic essay or report assignments, with the possible inclusion of research questions. The aim of the introduction is to set the scene, contextualise your research, introduce your focus topic and research questions, and tell the reader what you will be covering. It should move from the general and work towards the specific. You should include the following:
- Attention-grabbing statement (a controversy, a topical issue, a contentious view, a recent problem etc)
- Background and context
- Introduce the topic, key theories, concepts, terms of reference, practices, (advocates and critic)
- Introduce the problem and focus of your research
- Set out your research question(s) (this could be set out in a separate section)
- Your approach to answering your research questions.
Literature review
Your literature review is the section of your report where you show what is already known about the area under investigation and demonstrate the need for your particular study. This is a significant section in your dissertation (30%) and you should allow plenty of time to carry out a thorough exploration of your focus topic and use it to help you identify a specific problem and formulate your research questions.
You should approach the literature review with the critical analysis dial turned up to full volume. This is not simply a description, list, or summary of everything you have read. Instead, it is a synthesis of your reading, and should include analysis and evaluation of readings, evidence, studies and data, cases, real world applications and views/opinions expressed. Your supervisor is looking for this detailed critical approach in your literature review, where you unpack sources, identify strengths and weaknesses and find gaps in the research.
In other words, your literature review is your opportunity to show the reader why your paper is important and your research is significant, as it addresses the gap or on-going issue you have uncovered.
You need to tell the reader what was done. This means describing the research methods and explaining your choice. This will include information on the following:
- Are your methods qualitative or quantitative... or both? And if so, why?
- Who (if any) are the participants?
- Are you analysing any documents, systems, organisations? If so what are they and why are you analysing them?
- What did you do first, second, etc?
- What ethical considerations are there?
It is a common style convention to write what was done rather than what you did, and write it so that someone else would be able to replicate your study.
Here you describe what you have found out. You need to identify the most significant patterns in your data, and use tables and figures to support your description. Your tables and figures are a visual representation of your findings, but remember to describe what they show in your writing. There should be no critical analysis in this part (unless you have combined results and discussion sections).
Here you show the significance of your results or findings. You critically analyse what they mean, and what the implications may be. Talk about any limitations to your study, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of your own research, and make suggestions for further studies to build on your findings. In this section, your supervisor will expect you to dig deep into your findings and critically evaluate what they mean in relation to previous studies, theories, views and opinions.
This is a summary of your project, reminding the reader of the background to your study, your objectives, and showing how you met them. Do not include any new information that you have not discussed before.
This is the list of all the sources you have cited in your dissertation. Ensure you are consistent and follow the conventions for the particular referencing system you are using. (Note: you shouldn't include books you've read but do not appear in your dissertation).
Include any extra information that your reader may like to read. It should not be essential for your reader to read them in order to understand your dissertation. Your appendices should be labelled (e.g. Appendix A, Appendix B, etc). Examples of material for the appendices include detailed data tables (summarised in your results section), the complete version of a document you have used an extract from, etc.
Share this:
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Click here to cancel reply.
- Email * (we won't publish this)
Write a response
I am finding this helpful. Thank You.
It is very useful.
Glad you found it useful Adil!
I was a useful post i would like to thank you
Glad you found it useful! 🙂
Navigating the dissertation process: my tips for final years
Imagine for a moment... After months of hard work and research on a topic you're passionate about, the time has finally come to click the 'Submit' button on your dissertation. You've just completed your longest project to date as part...

8 ways to beat procrastination
Whether you’re writing an assignment or revising for exams, getting started can be hard. Fortunately, there’s lots you can do to turn procrastination into action.

My takeaways on how to write a scientific report
If you’re in your dissertation writing stage or your course includes writing a lot of scientific reports, but you don’t quite know where and how to start, the Skills Centre can help you get started. I recently attended their ‘How...

- Formatting Your Dissertation
- Introduction
Harvard Griffin GSAS strives to provide students with timely, accurate, and clear information. If you need help understanding a specific policy, please contact the office that administers that policy.
- Application for Degree
- Credit for Completed Graduate Work
- Ad Hoc Degree Programs
- Acknowledging the Work of Others
- Dissertation Advisory Committee
- Publishing Options
- Subject, Invention, and Patents
- Submitting Your Dissertation
- English Language Proficiency
- PhD Program Requirements
- Secondary Fields
- Year of Graduate Study (G-Year)
- Master's Degrees
- Grade and Examination Requirements
- Conduct and Safety
- Financial Aid
- Non-Resident Students
- Registration
- Residence Halls
- Student Groups
When preparing the dissertation for submission, students must meet the following minimum formatting requirements. The Registrar’s Office will review the dissertation for compliance and these formatting elements and will contact the student to confirm acceptance or to request revision. The Harvard Griffin GSAS resource on dissertation formatting best practices expands on many of the elements below.
Please carefully review your dissertation before submitting it to ProQuestETD. The Registrar’s Office will email you through ProQuest if they have identified major formatting errors that need correction. Students will be provided with a brief extended deadline to make only the requested formatting updates.
- Embedded Fonts : If fonts are not embedded, non-English characters may not appear as intended. It is the student’s responsibility to make sure that fonts are embedded properly prior to submission. Instructions for embedding fonts can be found on the Dissertation Formatting Guidance resource .
- Thesis Acceptance Certificate: A copy of the Thesis Acceptance Certificate (TAC) should appear as the first page. This page should not be counted or numbered. The TAC will appear in the online version of the published dissertation. The author name and date on the TAC and title page should be the same.
- Title Page: The dissertation begins with the title page; the title should be as concise as possible and should provide an accurate description of the dissertation. The author name and date on the TAC and title page should be the same. Do not print a page number on the title page. It is understood to be page i for counting purposes only.
- Abstract : An abstract, numbered as page iii , should immediately follow the copyright page and should state the problem, describe the methods and procedures used, and give the main results or conclusions of the research. The abstract will appear in the online version of the dissertation and will be made available by ProQuest and DASH. There is no maximum word count for the abstract.
- Preliminary pages (abstract, table of contents, list of tables, graphs, illustrations, and preface) should use small Roman numerals (i, ii, iii, iv, v, etc.).
- All pages must contain text or images.
- Count the title page as page i and the copyright page as page ii, but do not print page numbers on either page.
- For the body of text, use Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.) starting with page 1 on the first page of text.
- Page numbers must be centered throughout the manuscript at the top or bottom.
- Every numbered page must be consecutively ordered, including tables, graphs, illustrations, and bibliography/index (if included); letter suffixes (such as 10a, 10b, etc.) are not allowed.
- It is customary not to have a page number on the page containing a chapter heading. Check pagination carefully. Account for all pages.
- Copyright Statement: A copyright notice should appear on a separate page immediately following the title page and include the copyright symbol ©, the year of first publication of the work, and the name of the author: © [ year ] [ Author’s Name ]. All rights reserved. Alternatively, students may choose to license their work openly under a Creative Commons license. The author remains the copyright holder while at the same time granting upfront permission to others to read, share, and—depending on the license—adapt the work so long as proper attribution is given. (If a student chooses a Creative Commons license, the copyright statement must not include the “all rights reserved” disclaimer and should instead indicate the specific Creative Commons license.) Please note: The copyright statement applies only to the student’s own work; the copyright status of third-party material incorporated into the dissertation will not change. Do not print a page number on the copyright page. It is understood to be page ii for counting purposes only.
- Abstract
- Table of Contents
- Front Matter
- Body of Text
- Back Matter
Students can refer to the resource on Dissertation Formatting Best Practice Resource for information on best practices for front and back matter
Individual academic programs may require additional formatting elements to meet the standards of a specific field or discipline. Students are responsible to ensure that their Dissertation Advisory Committee is in support of the final formatting as signified by the sign off on the Thesis Acceptance Certificate. Any deviation from these requirements may lead to rejection of the dissertation and delay in the conferral of the degree.
CONTACT INFO
Katie riggs, academic programs, explore events.
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How long does it take to write a dissertation, published by steve tippins on july 11, 2019 july 11, 2019.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 05:00 am
How long does it take to write a dissertation? The most accurate (and least helpful) answer is, it depends. Since that’s probably not the answer you’re looking for, I’ll use the rest of the article to address the realities of how long it takes to write a dissertation.
How Long Does It Take to Write a Dissertation?
Based on my experience, writing your dissertation should take somewhere between 13-20 months. These are average numbers based upon the scores of doctoral students that I have worked with over the years, and they generally hold true.
I have seen people take less time and more time, but I believe that with concerted effort, the 13-20 month timeframe is reasonable.
“Based on my experience, writing your dissertation should take somewhere between 13-20 months.”
University Requirements
Once you hit the dissertation stage, some schools require a minimum number of hours in the dissertation area before you can graduate. Many schools require the equivalent of one year of dissertation credits to graduate.
So, even if you can finish your dissertation in three months, you will still have to pay for nine more months of dissertation credits before you can graduate. However, unless research and writing is your superpower, I wouldn’t worry about having to pay extra tuition.
But this requirement does offer some insight into how long it takes to write a dissertation. Based on this requirement, it’s reasonable to expect that writing your dissertation will take a year of more. This is consistent with my experience.

However, this timeframe is based on several assumptions. First, I am assuming that you are continually working towards finishing your dissertation. This means that no family emergencies, funding conundrums, or work issues get in the way of completing. Second, there are no major changes in your dissertation committee. Third, you will have access to the data that you need.
Assuming these assumptions hold true, this article should give you a general idea of how long it might take to write your dissertation.
How Long Does it Take to Write A Dissertation? Stage-By-Stage
Let’s break down each stage of the dissertation writing process and how long it takes.
Prospectus
This is the hardest one to judge, as this is where you lay the groundwork for the rest of your dissertation and get buy-in from committee members. Normally this takes from 3-6 months. Not all of this is writing time, though–much of it is spent refining your topic and your approach.
Why does this stage take so long? For many people, starting to express themselves using an academic voice can take time. This can hold up the review process as your committee members ask for writing-related revisions before they even get to evaluating the content. Don’t worry, once you learn the academic language things will start to flow more easily.
One common mistake students make is lack of specificity, both in their writing in general and in their topic focus.
Proposal (Chapters 1-3)

Chapter 1 is often an expansion of your Prospectus. However, you’ll be expected to develop your ideas more and have even more specificity on things like your research question and methodology, so don’t underestimate how long this chapter will take.
Chapter 2 can take some time as you will be digging deep into the literature but I think this can be done in 3-4 months. One caution, some people, and committees, like to start with Chapter 2 so that you are immersed in the literature before completing Chapters 1 and 3. Regardless of where you start, 3-4 months is a good estimate.
Chapter 3 requires an in-depth explanation of your methodology. I suggest working closely with your Chair on this one to avoid multiple submissions and revisions. Get clear on your methodology and make sure you and your chair are on the same page before you write, and continue to check in with your chair, if possible, throughout the process.
IRB Approval
While this step can be full of details and require several iterations it seems that allowing 2 months is sufficient. Most schools have an IRB form that must be submitted. To save time you can usually start filling out the form while your committee is reviewing your Proposal.

Collecting Data
This step varies a great deal. If you are using readily available secondary data this can take a week but if you are interviewing hard to get individuals or have trouble finding a sufficient number of people for your sample this can take 4 months or more. I think 1-4 months should be appropriate
Chapters 4 and 5
These two chapters are the easiest to write as in Chapter 4 you are reporting your results and in Chapter 5 you explain what the results mean. I believe that these two chapters can be written in 2 months.

Defense and Completion
You will need to defend your dissertation and then go through all of the university requirements to finalize the completion of your dissertation. I would allow 2 months for this process.
Variables That Affect How Long It Takes to Write A Dissertation
When students say something like, “I’m going to finish my dissertation in three months,” they likely aren’t considering all of the variables besides the actual writing. Even if you’re a fast writer, you’ll have to wait on your committee’s comments,
Timing Issues
Many schools have response times for committee members. This is important when looking at how long it takes to finish a dissertation. For example, it you have two committee members and they each get up to 2 weeks for a review, it can take up to a month to get a document reviewed, each time you submit. So, plan for these periods of time when thinking about how long that it will take you.
Addressing Comments
How long it takes to write your dissertation also depends on your ability to address your committee’s comments thoroughly. It’s not uncommon for a committee member to send a draft back several times, even if their comments were addressed adequately, because they notice new issues each time they read it. Save yourself considerable time by making sure you address their comments fully, thus avoiding unnecessary time waiting to hear the same feedback.

This is the biggest variable in the dissertation model. How dedicated are you to the process? How much actual time do you have? How many outside interests/requirements do you have? Are you easily distracted? How clean does your workspace need to be? (This may seem like a strange thing to discuss, but many people need to work in a clean space and can get very interested in cleaning if they have to write). Are you in a full-time program or in a part time program? Are you holding down a job? Do you have children?
All of these things will affect how much time you have to put into writing–or rather, how disciplined you need to be about making time to write.
One of the things that can influence how long it takes to write your dissertation is your committee. Choose your committee wisely. If you work under the assumption that the only good dissertation is a done dissertation, then you want a committee that will be helpful and not trying to prove themselves on your back. When you find a Chair that you can work with ask her/him which of their colleagues they work well with (it’s also worth finding out who they don’t work well with).
Find out how they like to receive material to review. Some members like to see pieces of chapters and some like to see completed documents. Once you know their preferences, you can efficiently submit what they want when they want it.
How Long Does it Take to Write a Dissertation? Summary
Barring unforeseen events, the normal time range for finishing a dissertation seems to be 13-19 months, which can be rounded to one to one and a half years. If you are proactive and efficient, you can usually be at the shorter end of the time range.

That means using downtime to do things like changing the tense of your approved Proposal from future tense to past tense and completing things like you Abstract and Acknowledgement sections before final approval.
I hope that you can be efficient in this process and finish as quickly as possible. Remember, “the only good dissertation is a done dissertation.”
On that note, I offer coaching services to help students through the dissertation writing process, as well as editing services for those who need help with their writing.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
Dissertation memes.
Sometimes you can’t dissertate anymore and you just need to meme. Don’t worry, I’ve got you. Here are some of my favorite dissertation memes that I’ve seen lately. My Favorite Dissertation Memes For when you Read more…

Surviving Post Dissertation Stress Disorder
The process of earning a doctorate can be long and stressful – and for some people, it can even be traumatic. This may be hard for those who haven’t been through a doctoral program to Read more…

PhD by Publication
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…
- FindAMasters
- Researching and Writing a Masters Dissertation
Written by Mark Bennett
All Masters programmes include some form of extended individual project. Research-focussed programmes, such as an MRes , may include multiple independent research components. Taught courses usually culminate with a substantial research task, referred to as the Masters dissertation or thesis.
This article talks about how long a Masters dissertation is and the structure it follows.Before you get started on your dissertation, you'll usually need to write a proposal. Read our full guide to Masters dissertation proposals for more information on what this should include!
| Length | 15,000 - 20,000 words |
| Structure | Abstract (300 words) Introduction (1,000 words) Literature review (1,000 words) Research methodology (1,500 words) Results Discussion (12,000 words) Conclusion (1,500 words) References/Bibliography Appendices |
| Supervision | Yes, you’ll be paired with an academic from your own university |
| Assessment | External examiner along with additional members of faculty. There is not usually a viva at Masters level. |
On this page
What’s the difference between a masters dissertation and an undergraduate dissertation.
The Masters thesis is a bridge between undergraduate study and higher level postgraduate degrees such as the PhD .
A postgraduate dissertation may not look that different to its undergraduate equivalent. You’ll likely have to produce a longer piece of work but the foundations remain the same.
After all, one of the purposes of an undergraduate dissertation or final year project is to prepare you for more in-depth research work as a postgraduate. That said, there are some important differences between the two levels.
So, how long is a Masters dissertation? A Masters dissertation will be longer than the undergraduate equivalent – usually it’ll be somewhere between 15,000 and 20,000 words, but this can vary widely between courses, institutions and countries.
To answer your overall research question comprehensively, you’ll be expected to identify and examine specific areas of your topic. This can be like producing a series of shorter pieces of work, similar to those required by individual modules. However, there’s the additional requirement that they collectively support a broader set of conclusions.
This more involved Masters dissertation structure will:
- Give you the scope to investigate your subject in greater detail than is possible at undergraduate level
- Challenge you to be effective at organising your work so that its individual components function as stages in a coherent and persuasive overall argument
- Allow you to develop and hone a suitable research methodology (for example, choosing between qualitative and quantitative methods)
If the individual topics within your overall project require you to access separate sources or datasets, this may also have an impact on your research process.
As a postgraduate, you’ll be expected to establish and assert your own critical voice as a member of the academic community associated with your field .
During your Masters thesis you’ll need to show that you are not just capable of analysing and critiquing original data or primary source material. You should also demonstrate awareness of the existing body of scholarship relating to your topic .
So, if you’ll excuse the pun, a ‘Masters’ degree really is about achieving ‘mastery’ of your particular specialism and the dissertation is where you’ll demonstrate this: showing off the scholarly expertise and research skills that you’ve developed across your programme.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
A dissertation is a long piece of (usually) written work on the same topic. A thesis is a little more specific: it usually means something that presents an original argument based on the interpretation of data, statistics or content.
So, a thesis is almost always presented as a dissertation, but not all dissertations present a thesis.
Masters dissertation structure
As you can probably imagine, no two dissertations follow the exact same structure, especially given the differences found between Masters programmes from university to university and country to country .
That said, there are several key components that make up the structure of a typical Masters dissertation
How long is a Masters dissertation?
Most dissertations will typically be between 15,000 and 20,000 words long, although this can vary significantly depending on the nature of the programme.
You should also check with your university exactly which sections of the dissertation count towards the final word count (the abstract, bibliography and appendices won’t usually be included in the total).
Usually around 300 words long, the abstract is meant to be a concise summary of your dissertation. It should briefly cover the question(s) you aim to answer, your primary argument and your conclusion.
Introduction
The purpose of the introduction is to provide context for the rest of the dissertation, setting out your aims and the scope of what you want to achieve with your research. The introduction should give a clear overview of the dissertation’s chapters and will usually be around 1,000 words long.
Literature review
This part of the dissertation should examine the scholarship that has already been published in your field, presenting various arguments and counter-arguments while situating your own research within this wider body of work.
You should analyse and evaluate other publications and explain how your dissertation will contribute to the existing literature in your subject area. The literature review sometimes forms part of the introduction or follows immediately on from it. Most literature reviews are up to 1,000 words long.
Research methodology
Not all dissertations will require a section covering research methodology (Arts and Humanities dissertations won’t normally undertake the kind of research that involves a set methodology). However, if you are using a particular method to collect information for your dissertation, you should make sure to explain the rationale behind your choice of methodology. The word count for this part of the dissertation is usually around the 1,500 mark.
Those in the Arts and Humanities will usually outline their theoretical perspectives and approaches as part of the introduction, rather than requiring a detailed explanation of the methodology for their data collection and analysis.
Results / findings
If your research involves some form of survey or experiment, this is where you’ll present the results of your work. Depending on the nature of the study, this might be in the form of graphs, tables or charts – or even just a written description of what the research entailed and what the findings were.
This section forms the bulk of your dissertation and should be carefully structured using a series of related chapters (and sub-chapters). There should be a logical progression from one chapter to the next, with each part building on the arguments of its predecessor.
It can be helpful to think of your Masters dissertation as a series of closely interlinked essays, rather than one overwhelming paper. The size of this section will depend on the overall word count for your dissertation. However, to give you a rough idea for a 15,000-word dissertation, the discussion part will generally be about 12,000 words long.
Here you should draw together the threads of the previous discussion chapters and make your final concluding statements, drawing on evidence and arguments that you’ve already explored over the course of the dissertation. Explain the significance of your findings and point towards directions that future research could follow. This section of the Masters thesis will be around 1,500 words long.
References / bibliography
While planning and writing your dissertation, you should keep an extensive, organised record of any papers, sources or books you’ve quoted (or referred to). This will be a lot easier than leaving all of it until the end and struggling to work out where a particular quotation is from!
Appendices won’t be necessary in many dissertations, but you may need to include supplementary material to support your argument. This could be interview transcripts or questionnaires. If including such content within the body of the dissertation won’t be feasible – i.e. there wouldn’t be enough space or it would break the flow of your writing – you should consult with your supervisor and consider attaching it in an appendix.
It’s worth bearing in mind that these sections won’t always be discretely labelled in every dissertation. For example, everything up to ‘discussion’ might be covered in introductory chapter (rather than as distinct sections). If you’re unsure about the structure of your Masters dissertation, your supervisor will be able to help you map it out.
How does supervision work for a Masters dissertation?
As a Masters student at the dissertation stage you’ll usually be matched with an academic within your institution who will be tasked with guiding your work. This might be someone who has already taught you, or it may be another scholar whose research interests and expertise align well with what you want to do. You may be able to request a particular supervisor, but taught postgraduates are more likely to be assigned them by their department.
Specific arrangements with your supervisor will vary depending on your institution and subject area. They will usually meet with you at the beginning of the dissertation period to discuss your project and agree a suitable schedule for its undertaking. This timetable will probably set dates for:
- Subsequent discussions and progress checks
- The submission of draft chapters or sections
- Feedback appointments
Though your supervisor is there to help and advise you, it is important to remember that your dissertation is a personal research project with associated expectations of you as an independent scholar.
As a rule of thumb, you can expect your supervisor to read each part of your dissertation once at the draft stage and to offer feedback. Most will not have time to look at lots of subsequent revisions, but may respond favourably to polite requests for exceptions (provided their own workload permits it).
Inundating your supervisor with emails or multiple iterations of draft material is best avoided; they will have their own research to manage (as well as other supervision assignments) and will be able to offer better quality feedback if you stick to an agreed schedule.
How is a Masters dissertation assessed and examined?
On most courses your dissertation will be assessed by an external examiner (as well as additional members of faculty within your university who haven’t been responsible for supervising you), but these will read and critique the work you submit without personally questioning and testing you on it.
Though this examination process is not as challenging as the oral defence or ‘ viva voce ’ required for a PhD thesis, the grading of your Masters dissertation is still a fundamental component of your degree.
On some programmes the result awarded to a student’s dissertation may determine the upper grade-band that can be awarded to their degree.
Search for a Masters
Ready to start looking for your ideal postgraduate opportunity? Browse and compare Masters degrees on FindAMasters.com.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

Applying for a Masters can feel a bit daunting. Here is a checklist of all the things you need to do to make sure you have everything covered in your Masters application.

Postgraduate study is often very flexible, with the option to study a Masters degree or other qualification part-time, online or through blended learning.

How do Bachelors and Masters courses differ? We’ve covered the main differences you’ll encounter when making the transition from undergrad to postgrad study.

Our guide explains how online Masters degree work, what the benefits of online learning are and how to choose what to study online.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a Masters in Italy.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a Masters in the USA.
FindAMasters. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about Masters study?
Select your nearest city
- Aberystwyth
- Beaconsfield
- Bishop Burton
- Bournemouth
- Bridlington
- Chatham Maritime
- Cirencester
- East Malling
- Hemel Hempstead
- High Wycombe
- Huddersfield
- Isle of Man
- Jordanstown
- London Central
- London East
- London South
- London West
- Londonderry
- Loughborough
- Middlesbrough
- Milton Keynes
- Musselburgh
- Northampton
- Potters Bar
- Saffron Waldon
- Scarborough
- Southampton
- St Leonards on Sea
- Stoke on Trent
- Wolverhampton
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAMasters, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, application tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAMasters account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest Masters news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite courses, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your Masters courses? Log in here .

Let us help you find a Masters
Never miss a course
Enter our ambassador competition
Get funding news, tips and advice
Hear about upcoming events
Sign up to our newsletter today
We've been helping students find the right postgraduate course for over a decade.
Login to your account
Enter your username below to login to your account.

How long is a PhD dissertation? [Data by field]
The final piece of the PhD journey is the PhD dissertation. It takes many years to accumulate enough original and new data to fill out a dissertation to the satisfaction of experts in your field. Interestingly, the PhD dissertation length and content vary significantly based on the field you are studying and the publishing conventions.
A PhD can be anywhere from 50 pages to over 450 pages long. This equates to between about 20,000 words to 100,000 words. Most PhD theses are between 60,000 and 80,000 words long excluding contents, citations and references.
A PhD thesis contains different sections including an introduction, methods, results and discussion, conclusions, further work, and references. Each one of these different sections will vary in length depending on the field of study and your particular topic.
Ultimately, a PhD dissertation should contain as many pages and words as it takes to communicate the results of your multi-year investigation.
It is very rewarding to see your thesis come together as you are writing day after day. When I was writing my PhD dissertation I wrote the sections separately and my heart filled with joy when I finally put them all together and compile them into a single PDF document.
Counting the pages should not be the way to determine a PhD dissertation’s value but it certainly helps when your thesis is starting to look substantial in thickness.
How many pages should a PhD dissertation be?
A PhD dissertation should contain as many pages and words as it takes to outline the current state of your field and provide adequate background information, present your results, and provide confidence in your conclusions. A PhD dissertation will also contain figures, graphs, schematics, and other large pictorial items that can easily inflate the page count.
Here is a boxplot summary of many different fields of study and the number of pages of a typical PhD dissertation in the field. It has been created by Marcus Beck from all of the dissertations at the University of Minnesota.

Typically, the mathematical sciences, economics, and biostatistics theses and dissertations tend to be shorter because they rely on mathematical formulas to provide proof of their results rather than diagrams and long explanations.
On the other end of the scale, English, communication studies, political science, history and anthropology are often the largest theses in terms of pages and word count because of the number of words it takes to provide proof and depth of their results.
At the end of the day, it is important that your thesis gets signed off by your review committee and other experts in the field. Your supervisor will be the main judge of whether or not your dissertation is capable of satisfying the requirements of a PhD in your field.
If you want to know more about how long a Masters’s thesis and PhD dissertation is you can check out my other articles:
- How Long is a Masters Thesis? [Your writing guide]
- How long is a Thesis or dissertation? [the data]
Can a PhD dissertation be too long?
A PhD thesis should contain enough evidence and discussion to report on the most significant findings of your PhD research.
A PhD dissertation should not contain everything that you have done during your PhD. It should only include the data and information required to convince your PhD examining body that wraps up and tells the full story of particular lines of investigation.
Including random results, thoughts, or superfluous explanation can result in a dissertation that is unfocused. I have heard of music PhD is being described as too verbose and physical sciences PhD dissertations as being unfocused.
Therefore, a PhD thesis can be too long if the information it contains does not form a full and cohesive story.
One of my colleagues during their PhD removed an entire chapter from the thesis after writing it as the supervisor said that it needed more experiments to be a full story. They did not want to spend the next six months gathering the data and simply removed the chapter altogether.
How short can PhD dissertation be?
The shortest PhD dissertations are typically found in mathematics.
George Bernard Danzig was an American mathematical scientist who made contributions to industrial engineering and many other mathematical-related fields. An interesting miscommunication led to 1 of the shortest PhD theses ever.
In 1939 his professor wrote two problems on the blackboard and Danzig thought they were homeless assignments. He stated that they were harder than usual but handed in solutions to the surprise of the professor.
They were, in fact, open mathematical problems in statistics.
His professor said to bind the solution to the two problems together and submit them as his thesis – the total thesis length = 14 pages.
Obviously, most PhD theses and dissertations will be so much longer than that!
My PhD dissertation was 256 pages long. It was full of schematics, diagrams, and tables to demonstrate and communicate my findings.
I would say that most people’s PhD thesis experience will be closer to mine than Prof George Bernard Danzig’s.
Why PhD dissertations are typically so long
PhD dissertations are often over 200 pages long.
One of the primary reasons they are so long is that it is a single document that summarises many years of hard work. Also, summarising the research field to date and making sure that all of your references and citations are included so you avoid plagiarism will bolster the word count of the thesis dramatically.
Here are all of the reasons PhD dissertations tend to be so long.
Many years of work
PhD theses or dissertations contain many years of research and analysis.
In many of my YouTube videos I recommend that a PhD student work towards their PhD thesis by doing at least three hours of focused work every work day.
This amount of work quickly adds up.
Of course, not every bit of work makes it into the PhD dissertation but a lot of it does. It can be difficult to work out what to include or leave out of your thesis.
As a PhD student, I perfected the art of turning one experiment into many different types of grafts and schematics to fully explore the limits of my data. The graphs can take up a lot of space in your PhD thesis and, therefore, bolster the page count significantly.
In depth literature review
One of the most substantial parts of a PhD dissertation is the literature review.
The literature review can take up a huge portion of the early part of your PhD dissertation depending on the amount of data and publications in your field.
Writing an in-depth literature review requires just as much meticulous data analysis and searching as the central part of your dissertation.
Figures and schematics
Some fields end up producing a lot of figures and schematics.
My thesis had many full-page figures of atomic force microscopy experiments with much more explanation on subsequent pages.

As they say, a picture paints a thousand words and a dissertation can really benefit from having many schematics to highlight the important aspects of your findings.
References and citations
The recommended PhD dissertation word count from an institution or university does not include citations, references, or other thesis parts such as summary of abbreviations, table of figures, et cetera.
However, these components of your dissertation can take up many pages and add to the overall thickness of your PhD dissertation.
University formatting rules
University formatting rules will also dictate how you many pages your words take up.
I often get roasted on my YouTube channel for having doublespaced lines and wide margins. Unfortunately, this layout was dictated by my university before printing.
PhD dissertations often end up going into long-term storage and therefore, need to adhere to archival and standardised formatting rules.
Deep in the depths of the University of Newcastle, there is a copy of my thesis on a shelf. The formatting and binding rules mean that my thesis looks like everyone else’s.
Universities will often have their own requirements for PhD dissertation cover colour, quality, and type of paper. Even the quality of the paper can change the thickness of the PhD dissertation significantly.
PhD by publication
It is becoming increasingly common to submit a number of peer-reviewed papers bound together with supplementary information in between instead of a PhD dissertation.
The benefits of this to the researcher and university are:
- More early career peer-reviewed journals for career advancement
- an easier review process – they have already been peer-reviewed
- an early focus on publishing means better research outcomes for the researcher, supervisor, and Department.
- No mad rush at the end to finish a thesis
- continually writing peer-reviewed papers throughout your PhD helps with timely analysis and communication of results
Even though this option has been available to PhD students for a number of years, I have only known a handful of students actually submit their PhD via publication.
Nonetheless, having this option will suit some research fields better than others and lead to a more productive PhD.
Wrapping up
This article has been through everything you need to know about the length of a PhD dissertation and the common lengths of PhD dissertations for various fields.
Ultimately, there is no predefined length of a PhD .
A PhD thesis is as long as it needs to be to convince your examiners that you have contributed significantly enough to an academic field to be awarded the title of Dr of philosophy.
Mathematical and analytical theses tend to be shorter and can be as short as 50 pages (with one of the shortest being only 14 pages long). At the other end of the spectrum, PhD students in anthropology and history tend to produce the longest dissertations.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


- How Long Is a PhD Thesis?
- Doing a PhD
It’s no secret that one of the most challenging aspects of a PhD degree is the volume of work that goes into writing your thesis . So this raises the question, exactly how long is a thesis?
Unfortunately, there’s no one size fits all answer to this question. However, from the analysis of over 100 PhD theses, the average thesis length is between 80,000 and 100,000 words. A further analysis of 1000 PhD thesis shows the average number of pages to be 204 . In reality, the actual word count for each PhD thesis will depend on the specific subject and the university it is being hosted by. This is because universities set their own word length requirements, with most found to be opting for around 100,000.
To find out more about how these word limits differ between universities, how the average word count from STEM thesis differ from non-STEM thesis and a more detailed breakdown from the analysis of over 1000 PhDs, carry on reading the below.
Word Count Differences Between Universities
For any PhD student writing a thesis, they will find that their document will be subject to a word limit set by their university. In nearly all cases, the limit only concerns the maximum number of words and doesn’t place any restrictions on the minimum word limit. The reason for this is that the student will be expected to write their thesis with the aim of clearly explaining their research, and so it is up to the student to determine what he deems appropriate.
Saying this, it is well accepted amongst PhD students and supervisors that the absence of a lower limit doesn’t suggest that a thesis can be ‘light’. Your thesis will focus on several years worth of original research and explore new ideas, theories or concepts. Besides this, your thesis will need to cover a wide range of topics such as your literature review, research methodology, results and conclusion. Therefore, your examiners will expect the length of your thesis to be proportional to convey all this information to a sufficient level.
Selecting a handful of universities at random, they state the following thesis word limits on their website:
- University of Edinburgh: 100,000
- University of Exeter: 100,000
- University of Leister: 80,000
- University of Bath: 80,000
- University of Warwick: 70,000
The above universities set upper word limits that apply across the board, however, some universities, such as the University of Birmingham and the University of Sheffield, set different word limits for different departments. For example, the University of Sheffield adopts these limits:
- Arts & Humanities: 75,000
- Medicine, Dentistry & Health: 75,000
- Science: 80,000
- Social Sciences: 75,000-100,000
Although there’s a range of limit, it’s safe to say that the majority fall within the 80,000 to 100,000 bracket.
Word Count Based on Data from past Theses
A poll of 149 postdocs.
In mid-2019, Dr Eva Lantsoght, a published author, academic blogger and Structural Engineering Professor, conducted a poll which asked postgraduate doctoral students to share the length of their final thesis. 149 PostDoc students responded to the survey, with the majority reporting a length falling within the ‘80,000 – 120,000 words’ bracket as seen below.
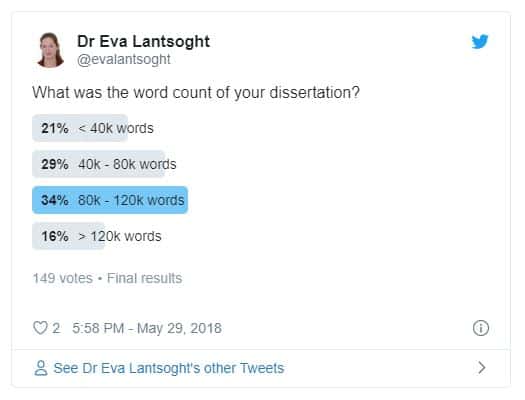
Analysis of 1000 PhD Theses
Over a three-year time period, Dr Ian Brailsford, a then Postgraduate Learning Adviser at the University of Auckland, analysed 1000 doctoral thesis submitted to his university’s library. The PhD theses which formed the basis of his analysis were produced between 2008 to 2017 and showed:
- Average number of pages = 204
- Median number of pages = 198
- Average number of chapters = 7.6
We should note that the above metrics only cover the content falling within the main body of the thesis. This includes the introduction, literature review, methods section, results chapter, discussions and conclusions. All other sections, such as the title page, abstract, table of contents, acknowledgements, bibliography and appendices were omitted from the count.
Although it’s impossible to draw the exact word count from the number of pages alone, by using the universities recommended format of 12pt Times New Roman and 1.5 lines spacing, and assuming 10% of the main body are figures and footnotes, this equates to an average main body of 52,000 words.
STEM vs Non-STEM
As part of Dr Ian Brailsford’s analysis, he also compared the length of STEM doctorate theses to non-STEM theses. He found that STEM theses tended to be shorter. In fact, he found STEM theses to have a medium page length of 159 whilst non-STEM theses had a medium of around 223 pages. This is a 40% increase in average length!
Can You Exceed the Word Count?
Whilst most universities will allow you to go over the word count if you need to, it comes with the caveat that you must have a very strong reason for needing to do so. Besides this, your supervisor will also need to support your request. This is to acknowledge that they have reviewed your situation and agree that exceeding the word limit will be absolutely necessary to avoid detriment unnecessary detriment to your work.
This means that whilst it is possible to submit a thesis over 100,000 words or more, it’s unlikely that your research project will need to.
How Does This Compare to a Masters Dissertation?
The average Masters dissertation length is approximately 20,000 words whilst a thesis is 4 to 5 times this length at approximately 80,000 – 100,000.
The key reason for this difference is because of the level of knowledge they convey. A Master’s dissertation focuses on concluding from existing knowledge whilst a PhD thesis focuses on drawing a conclusion from new knowledge. As a result, the thesis is significantly longer as the new knowledge needs to be well documented so it can be verified, disseminated and used to shape future research.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Related Reading
Unfortunately, the completion of your thesis doesn’t mark the end of your degree just yet. Once you submit your thesis, it’s time to start preparing for your viva – the all-to-fun thesis defence interview! To help you prepare for this, we’ve produced a helpful guide which you can read here: The Complete Guide to PhD Vivas.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings . In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Enjoy a completely custom, expertly-written dissertation. Choose from hundreds of writers, all of whom are career specialists in your subject.
How Long Is a Dissertation? Here’s the Average Length

How long is a dissertation? This is a question that you’re likely to ask if you’ve just enrolled for a doctoral program. But, this question is not new because other students have asked it too. Perhaps, the simplest answer to this question is that a dissertation should be sufficiently long to answer the stated question satisfactorily.
How Long Is a Dissertation?
There is no single answer to the question of a doctoral dissertation length. But most dissertations are on average 100-200 pages long. Somebody can say it should be 146 pages while somebody else can say 90 pages. Another person can say it should be 200 pages. Essentially, the length of this important academic document should depend on the topic, writing style, and goals of the writer.
Universities require students to write dissertations when pursuing masters and PhD degree programs. This paper forms an invaluable part of these academic programs in reputable learning institutions. As such, most undergraduate students are worried about the length of this document because it forms an important aspect of their academic life.
There are generally practical suggestions about how long should a dissertation be. For instance, the areas that your dissertation project focuses on should influence its length. For instance, a dissertation on a history topic will most likely be longer than an average dissertation on a chemistry topic. That means your academic discipline will influence the length of your dissertation.
How Long Is a PhD Dissertation?
Most academicians say that a PhD dissertation length should not exceed 80, 000 words . Thus, your text should be near this length. This word count includes the appendices while excluding references, footnotes, and bibliography. The footnotes of a dissertation shouldn’t exceed 20% of the text.
Students are discouraged from including discursive footnotes. What’s more, they should not use footnotes to include materials that should be in their main text. Doing so would circumvent the average length of the dissertation.
The statistical tables of a dissertation are counted as around 150 words each . But, the Degree Committee can allow learners to exceed the limits after application and under exceptional situations. Therefore, students should apply for this exception early before the date they propose to submit their thesis. The Graduate Committee evaluates the application and decides whether to allow the student to alter the average dissertation length.
The committee considers the dissertation proposal, as well as, a signed statement attesting to their proposed dissertation length. If they don’t and their dissertation exceeds the average length, it will be referred back for revision before it is forwarded to the institution’s examiners.
Average Dissertation Length
Many factors should generally be considered when answering the question of how long is a PhD dissertation. However, students should limit their writing between 80,000 and 100,000 words . On average, this document should have around 204 pages. But, the average length of a PhD thesis also depends on the university and the specific subject.
Essentially, a university can set the requirements of a dissertation, including the length. Nevertheless, most institutions opt for around 100,000 words. Research has shown that STEM dissertations have a medium length of 159 pages. Non-STEM dissertations, on the other hand, have a medium length of about 223 pages. Thus, there is a significant difference in length between STEM and non-STEM dissertations.
How Long Is a Dissertation Chapter?
Another question that might be lingering in your mind is how long is a dissertation chapter? Well, this varies because each chapter is a separate section that should address something specific. If you include the right information succinctly and adequately, your final write-up should have the right length. So, how long is a doctoral dissertation in every section? Here is a rough estimate.
Introduction
This section of a dissertation should tell readers why the topic is important. It should also mention relevant facts about the topic. Essentially, the introduction should tell readers why you have chosen the topic or issue and what makes it relevant. On average, the introduction should be between 10 and 15 pages . This is a perfect size because it allows you to mention everything concisely. Focus on intriguing the audience without disclosing or revealing anything in detail. Thus, your dissertation introduction should be more of a teaser.
Literature review
This is the section where you analyze relevant sources that you have chosen for your paper. It should include only sources that can be used to write the dissertation. In this section, you analyze and point out the strengths and weaknesses of your chosen sources. The literature review should be between 20 and 25 pages long.
Methodology
The length of this part of a dissertation ranges from 10 to 15 pages . It focuses on the methods used to conduct the research. Here, you discuss the specific method and data-selection processes used. This section also includes ways of contacting the sample population, as well as, the gathered data. What’s more, the encountered challenges can be included.
This section of a dissertation should not exceed 10 pages . It features the list and clarification of the obtained findings. Research findings are mentioned alongside the hypotheses explicitly. For instance, you should state whether they were refuted or confirmed. This section should also include a conclusion for everything done as far as your investigation is concerned.
This is also called the discussion section. Its length should range between 15 and 20 pages . This is the section where you explain the implications of your research. Provide a current and bigger perspective regarding your research. What’s more, diversify the current evidence base regarding the topic. Also, provide recommendations while acknowledging limitations in this section.
So, how long is a dissertation chapter? Well, it boils down to factors of the topic, learning institution, and goals of the study. Each section varies in length based on the nature of the research conducted and gathered data.
But, exactly how long does a dissertation have to be? There is no clear answer to this question. However, psychology, history, communication, nursing, and management dissertation can be up to 300 pages long. Education, Environmental Health, and Political Science dissertations can be around 100 pages. Overall, this length is influenced by the nature of the conducted research and the data that must be included in the document.
How Long Should a Dissertation Proposal Be?
You’re no longer asking how long is a dissertation word count because this question has been answered. But, you probably want to know the length of its proposal. Well, there is no specific length for this document. However, it should be considered as a long, formal treatise.
Well, most faculties recommend between 15 and 20 pages . However, the length of a proposal should depend on factors like the problem to be pursued, reasons to address the problem, where the answers will come from, and why you will go for certain sources.
This document proposes the work to be done. The focus of this text should be on convincing the thesis committee of your faculty that you have a research question that’s worth pursuing. Thus, you must present a convincing document for your faculty to allow you to proceed with the dissertation writing project. So, how long should it be?
How Long Should a Dissertation Abstract Be?
Lastly, you may want to know how long the abstract section of your dissertation should be. This is a separate page of the entire document. It is a summary of the dissertation. It reports the outcomes and aims of the research. Essentially, readers should know what your document is all about by reading the abstract. As such, this section should be written at the end. It should state the research objectives, problem, methods, key results, and the conclusion.
The dissertation abstract length ranges between 150 and 300 words . But just like with the main sections of a dissertation, there is a strict limit on the number of words that can be included. Therefore, check with the journal or university for which you are writing the dissertation.
Dissertation Length Consulting: Expert Guidance
When it comes to the length of your dissertation, our dissertation consulting service is here to provide expert guidance. Wondering about the ideal length for your dissertation? Look no further! Our experienced team offers personalized assistance to help you navigate this aspect of your research. With our dissertation consulting services, you can ensure that your dissertation meets the required length while maintaining its academic rigor. Contact us today for valuable insights and support throughout your dissertation journey.
The Bottom Line
There is no specific number of words or pages that determine the length of any dissertation. Therefore, check with your university, faculty, or journal to know the specific requirements for your dissertation in terms of length.
after completing the dissertation. However, you should have a rough draft or use the proposal’s introduction as a template because it has most of the elements that you need.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQ
How long is a dissertation should be.
The dissertation length, on average, is between 100 to 200 pages long. Nevertheless, a dissertation can be 146 pages or 96 pages long. The length depends on the goals of the writer, topic, and writing style.
What is the average length of the dissertation?
The length of the dissertations is from 100 to 200 pages. On average the dissertation should be at least 80 000 words . However, this depends on the scope, expertise, and knowledge in the field of study. Longer dissertation papers have more words with a relatively higher number of pages.
How long does it take to write a dissertation?
Writing a dissertation will depend on several considerations. The subject of study, such as chemistry, may take longer because of the logistics involved. On the other hand, a simple sociology dissertation may take one month.
How long is a Ph.D. dissertation have to be?
Ph.D. dissertation length does not exceed more than 80 000 words . Therefore, your paper should be within these limits. Note that these words do not include references, footnotes, and bibliography.
Richard Ginger is a dissertation writer and freelance columnist with a wealth of knowledge and expertise in the writing industry. He handles every project he works on with precision while keeping attention to details and ensuring that every work he does is unique.

Succeed With A Perfect Dissertation

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

Preparing to defend your thesis from home
- Degrees and Programs
- Slides (PDF, 950KB)
- Transcript (DOC, 41KB)
This content is disabled due to your privacy settings. To re-enable, please adjust your cookie preferences.
Due to COVID-19, defending your graduate thesis or dissertation in person is likely off the table. That doesn’t mean you have to wait to defend. Many schools and programs are allowing remote defenses — meaning you could find yourself defending from your living room! In this presentation, a recent psychology doctoral student that completed a remote defense, a current dean of psychology, and APA’s Office of Graduate and Postgraduate Education and Training, share how to prepare for and complete your thesis or dissertation defense remotely.
This program does not offer CE credit.
Alvin Akibar, PhD

Hideko Sera, PsyD

Garth Fowler, PhD
An associate executive director for education, and the director of the Office for Graduate and Postgraduate Education and Training at APA. He leads the directorate’s efforts to develop resources, guidelines, and policies that promote and enhance disciplinary education and training in psychology at the graduate and postdoctoral level.
More events and training
Learn where you should focus your marketing efforts, how to evaluate the performance of various online marketing strategies, and put yourself on a pathway towards sustained improvement in regards to online marketing.
October 2018 On Demand Webinar
Gain knowledge on potential ethical issues associated with marketing to clients. Tips and advice for building a personal website.
August 2018 On Demand Webinar
Use LinkedIn to find collaborators, post research and communicate with colleagues and students
Vertiv Holdings: Future Looks Bright, Should Own This Stock For Long Term
- Vertiv Holdings' strong order growth and healthy demand environment across regions are expected to drive continued topline growth in 2024.
- The company benefits from significant exposure to the data center market, a diverse product portfolio, and capacity expansion should lead to longer-term growth.
- Margin performance has been strong historically, and should continue further leading to valuation enhancement.
- Despite a higher valuation, strong growth prospects suggest this stock is a good buy at current levels for the longer term.

Erik Isakson
As anticipated earlier in my last article, Vertiv Holdings ( NYSE: VRT ) topline continued its strong growth into the second quarter of 2024 as order growth remains strong. I am expecting this to continue further in 2024 due to a healthy demand environment across all the regions in both the industrial and commercial end markets and strong elevated backlog levels. The company is also well-positioned to benefit from a tailwind in the data center end market and its significant exposure in it, which along with its diverse product portfolio and capacity expansion initiative to deal with rising demand for cooling technologies should drive the company's sales growth in the coming years. Margins also look good with volume growth in the future, which along with continued focus on operational improvements should drive margin growth further beyond 2024. The stock is currently trading at a premium to its historical levels, but the outlook remains strong, making me stick with a buy rating at the current levels.
Last Quarter Performance
VRT exited the first half of 2024 with another strong quarter , reporting approximately 14% organic topline line growth versus the prior year's second quarter. This continued growth was primarily a result of consistent robust performance in the Americas region, which grew 17% during the last quarter as order growth remains strong followed by continued AI scaling, particularly in this region. APAC region also continued its mid-single-digit growth after a bad 2023, as it grew 6% organically during the quarter despite a slowdown in China, due to strong growth in India and the rest of Asia. Talking about the EMEA region, it delivered double-digit topline growth for the second consecutive quarter due to healthy growth in the company’s modular solutions in the region.
VRT Q2 2024 data (Company presentation)
Strong topline performance is also reflected in the company’s margin performance, as VRT’s adjusted operating margin jumped by 510 bps year-on-year to a record 19.6% during the second quarter of 2024, just 40 bps short of its long-term target. This was primarily driven by higher volume and benefits from price cost and productivity gains during the quarter. While America's margin climbed the most, by 540 bps to 25.4%, EMEA reported the highest margin at 25.9% during the quarter with the help of strong volume growth and operational benefits. The Bottom-line performance was also good, with a year-on-year increase in adjusted EPS to $0.67, beating the consensus estimates by $0.10 during the quarter.
VRT started 2024 at a slower pace, with topline growth in mid-single digits in the first quarter; however, the second quarter was strong due to a significant jump in the Americas sales during the last quarter. In my last bullish article on VRT, I expected the company to report its topline growth in the high single-digit despite strong order growth and backlog, due to tougher comparisons from the 2023 quarter. However, VRT exceeded my expectations due to robust performance, mainly in America. I remain optimistic about the company’s top line as the market activity remains healthy across all the regions in both commercial and industrial end markets. The Americas region is benefiting from continued strong momentum in the hyper-scale (large Data Centers operated by big tech companies)and co-location market (renting space in these large Data Centers to small companies), while, the EMEA region is increasing the use of modular solutions among its customers to accelerate data center capacity expansion. In my opinion, these tailwinds along with record backlog levels and increased pipeline velocity should drive the company’s sales further in 2024.
VRT is seeing a continued acceleration of infrastructure built out in hyper-scale and colo markets due to increasing demand for AI-driven technologies like high-density and liquid-cooled chips. This growth is visible in the Americas, EMEA, and Asia along with favorable signs in co-location and cloud sectors in China. Infrastructure spending is also happening across the region, indicating a healthy market environment, mainly for data centers. The good thing is that approximately 75% of VRT end market exposure consists of data centers, which should benefit the company’s business in the coming years. In addition to this, In my view, the company’s significant exposure in the data center market should act as a competitive advantage due to VRT’s complete solutions ranging from power and cool to service data centers.
While the company’s focus is mainly on the liquid cooling part of the market, it also has a comprehensive portfolio apart from cooling tech, which includes, direct-to-chip, immersion, in-row-CDUs, and in-rack CDUs. The company also has a complete portfolio of technology solutions ready for deployment with a strong network of locally available field service engineers globally, which should also benefit the company’s sales through enhanced customer experience in the longer term.
VRT service capabilities (Company presentation)
Vertiv is also significantly expanding its production capacity primarily for its modular, liquid cooling, and thermal management technologies and is on track to achieve 45x growth in the liquid cooling production capacity by the end of 2024 versus the prior year. As AI is scaling in North America, the need for liquid cooling is rising for next-generation chips and is expected to continue growing further. This aggressive expansion aligns with the company’s demand projections, which along with the capital expenditure forecast of $175 million to $200 million should help the company meet the expected rise in demand in the future, benefiting the company’s sales in the coming years.
Overall, I remain confident about the company demand outlook in 2024 as the demand environment remains healthy across all the regions, resulting in strong order growth. The longer term, on the other hand, should benefit from scaling AI and the rising need for AI infrastructure primarily in the Americas region, which along with VRT’s strong market position and a comprehensive product portfolio should drive the company’s top-line growth in the coming years.
Since my last bullish article on VRT in July, the stock is down approximately 9% and reaching $79.92, however, is still up over 70% YTD. Currently, the company's stock is trading at a Non-GAAP forward P/E ratio of 31.61 based on FY2024 EPS estimates of $2.55 . While compared with its five-year average P/E ratio of 22.9, the stock still looks at a premium, however, the recent stock correction has cooled down the stock valuation a bit, making the valuation better, considering the strong growth prospects in the coming quarters.
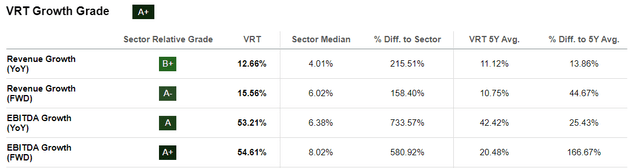
VRT Growth Grade (Seeking Alpha)
I am expecting the company's top line to continue its consistent growth further in 2024 as the order activity remains healthy and pipeline velocity increases. Backlog levels also remain strong, which should drive volume growth in the coming quarter, leading to top-line growth in 2024. The volume increase should help the company's margin, which along with the company's focus on operational execution and benefits from productivity gains should drive the company's margin in 2024.
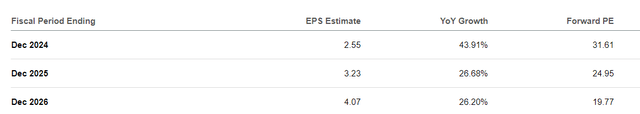
Consensus EPS estimates (Seeking Alpha)
As we can see in the VRT growth table above, its EBITDA has grown at an average of approximately 42% in the past five years, versus the average revenue growth of 10.75%. This has resulted in a significant jump in the company's margin in the last few quarters, reaching a record high of 19.6% during the last quarter from just 5.9% in the same quarter two years ago. This has helped in the valuation improvement of the company as the bottom line expanded with increased profitability. As we discussed, the company's margin should continue to grow in the future, the bottom line should also continue to grow as the market is also expecting, further leading to valuation enhancement in the quarters ahead.
Similar to my last article on VRT, the stock premium valuation is justified only if it continues to deliver strong topline and margin growth going forward to make the valuation better. However, if the company couldn't sustain its margin growth in the coming quarters, its bottom line might be impacted, potentially leading to deteriorated valuation and poor stock performance in the future.
As discussed above, the company's stock is down 9% since my last article, and currently trading higher than its historical average. VRT topline is expected to continue its strong momentum going ahead in the near term as the end market demand remains good. This should deliver strong volume growth, which along with the company's continued focus on operational improvements should drive margin growth in 2024. While the stock still appears to be at a higher valuation, promising longer-term prospects still make it a decent BUY.
This article was written by
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha's Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.
Recommended For You
About vrt stock.
| Symbol | Last Price | % Chg |
|---|
More on VRT
Related stocks.
| Symbol | Last Price | % Chg |
|---|---|---|
| VRT | - | - |
Trending Analysis
Trending news.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
Published on September 6, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 20, 2023.
The conclusion is the very last part of your thesis or dissertation . It should be concise and engaging, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your main findings, as well as the answer to your research question .
In it, you should:
- Clearly state the answer to your main research question
- Summarize and reflect on your research process
- Make recommendations for future work on your thesis or dissertation topic
- Show what new knowledge you have contributed to your field
- Wrap up your thesis or dissertation
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Discussion vs. conclusion, how long should your conclusion be, step 1: answer your research question, step 2: summarize and reflect on your research, step 3: make future recommendations, step 4: emphasize your contributions to your field, step 5: wrap up your thesis or dissertation, full conclusion example, conclusion checklist, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.
While your conclusion contains similar elements to your discussion section , they are not the same thing.
Your conclusion should be shorter and more general than your discussion. Instead of repeating literature from your literature review , discussing specific research results , or interpreting your data in detail, concentrate on making broad statements that sum up the most important insights of your research.
As a rule of thumb, your conclusion should not introduce new data, interpretations, or arguments.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Depending on whether you are writing a thesis or dissertation, your length will vary. Generally, a conclusion should make up around 5–7% of your overall word count.
An empirical scientific study will often have a short conclusion, concisely stating the main findings and recommendations for future research. A humanities dissertation topic or systematic review , on the other hand, might require more space to conclude its analysis, tying all the previous sections together in an overall argument.
Your conclusion should begin with the main question that your thesis or dissertation aimed to address. This is your final chance to show that you’ve done what you set out to do, so make sure to formulate a clear, concise answer.
- Don’t repeat a list of all the results that you already discussed
- Do synthesize them into a final takeaway that the reader will remember.
An empirical thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
A case study –based thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
In the second example, the research aim is not directly restated, but rather added implicitly to the statement. To avoid repeating yourself, it is helpful to reformulate your aims and questions into an overall statement of what you did and how you did it.
Your conclusion is an opportunity to remind your reader why you took the approach you did, what you expected to find, and how well the results matched your expectations.
To avoid repetition , consider writing more reflectively here, rather than just writing a summary of each preceding section. Consider mentioning the effectiveness of your methodology , or perhaps any new questions or unexpected insights that arose in the process.
You can also mention any limitations of your research, but only if you haven’t already included these in the discussion. Don’t dwell on them at length, though—focus on the positives of your work.
- While x limits the generalizability of the results, this approach provides new insight into y .
- This research clearly illustrates x , but it also raises the question of y .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
You may already have made a few recommendations for future research in your discussion section, but the conclusion is a good place to elaborate and look ahead, considering the implications of your findings in both theoretical and practical terms.
- Based on these conclusions, practitioners should consider …
- To better understand the implications of these results, future studies could address …
- Further research is needed to determine the causes of/effects of/relationship between …
When making recommendations for further research, be sure not to undermine your own work. Relatedly, while future studies might confirm, build on, or enrich your conclusions, they shouldn’t be required for your argument to feel complete. Your work should stand alone on its own merits.
Just as you should avoid too much self-criticism, you should also avoid exaggerating the applicability of your research. If you’re making recommendations for policy, business, or other practical implementations, it’s generally best to frame them as “shoulds” rather than “musts.” All in all, the purpose of academic research is to inform, explain, and explore—not to demand.
Make sure your reader is left with a strong impression of what your research has contributed to the state of your field.
Some strategies to achieve this include:
- Returning to your problem statement to explain how your research helps solve the problem
- Referring back to the literature review and showing how you have addressed a gap in knowledge
- Discussing how your findings confirm or challenge an existing theory or assumption
Again, avoid simply repeating what you’ve already covered in the discussion in your conclusion. Instead, pick out the most important points and sum them up succinctly, situating your project in a broader context.
The end is near! Once you’ve finished writing your conclusion, it’s time to wrap up your thesis or dissertation with a few final steps:
- It’s a good idea to write your abstract next, while the research is still fresh in your mind.
- Next, make sure your reference list is complete and correctly formatted. To speed up the process, you can use our free APA citation generator .
- Once you’ve added any appendices , you can create a table of contents and title page .
- Finally, read through the whole document again to make sure your thesis is clearly written and free from language errors. You can proofread it yourself , ask a friend, or consider Scribbr’s proofreading and editing service .
Here is an example of how you can write your conclusion section. Notice how it includes everything mentioned above:
V. Conclusion
The current research aimed to identify acoustic speech characteristics which mark the beginning of an exacerbation in COPD patients.
The central questions for this research were as follows: 1. Which acoustic measures extracted from read speech differ between COPD speakers in stable condition and healthy speakers? 2. In what ways does the speech of COPD patients during an exacerbation differ from speech of COPD patients during stable periods?
All recordings were aligned using a script. Subsequently, they were manually annotated to indicate respiratory actions such as inhaling and exhaling. The recordings of 9 stable COPD patients reading aloud were then compared with the recordings of 5 healthy control subjects reading aloud. The results showed a significant effect of condition on the number of in- and exhalations per syllable, the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable, and the ratio of voiced and silence intervals. The number of in- and exhalations per syllable and the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable were higher for COPD patients than for healthy controls, which confirmed both hypotheses.
However, the higher ratio of voiced and silence intervals for COPD patients compared to healthy controls was not in line with the hypotheses. This unpredicted result might have been caused by the different reading materials or recording procedures for both groups, or by a difference in reading skills. Moreover, there was a trend regarding the effect of condition on the number of syllables per breath group. The number of syllables per breath group was higher for healthy controls than for COPD patients, which was in line with the hypothesis. There was no effect of condition on pitch, intensity, center of gravity, pitch variability, speaking rate, or articulation rate.
This research has shown that the speech of COPD patients in exacerbation differs from the speech of COPD patients in stable condition. This might have potential for the detection of exacerbations. However, sustained vowels rarely occur in spontaneous speech. Therefore, the last two outcome measures might have greater potential for the detection of beginning exacerbations, but further research on the different outcome measures and their potential for the detection of exacerbations is needed due to the limitations of the current study.
Checklist: Conclusion
I have clearly and concisely answered the main research question .
I have summarized my overall argument or key takeaways.
I have mentioned any important limitations of the research.
I have given relevant recommendations .
I have clearly explained what my research has contributed to my field.
I have not introduced any new data or arguments.
You've written a great conclusion! Use the other checklists to further improve your dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Important evidence or analysis that wasn’t mentioned in the discussion section and results section
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion …”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g., “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion. Scribbr. Retrieved August 29, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/write-conclusion/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How long should a dissertation introduction be? The unofficial rule is 10 percent of the entire paper, so if your dissertation is 20,000 words, your introduction should be about 2,000 words. Keep in mind this is a rough estimate, as your introduction could vary. Literature review.
Learn how word counts vary across different fields, institutions, and levels of education for dissertations. Find out how to check the guidelines provided by your university and what to include in your dissertation.
Put simply: A dissertation should be long enough to comprehensively cover the subject, but no longer. 5. How do you write a dissertation? In general, the dissertation process follows this schedule: Research the field and identify potential topics. Meet with an advisor to choose and improve a topic. Perform a literature review. Conduct new research.
How long should a PhD thesis be? A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words (100 to 300 pages in length) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) - from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion.
A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the level and field of study. Learn how to choose your topic, supervisor, research method, and structure for your dissertation.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
The truth is, there is no one answer to how long a dissertation is. I can't say 146 pages is what's needed, as you may write to page 146 and stop without fully exploring your topic. 90 pages could adequately address your research question, or you could write 200 pages and still not fully answer what you set out to.
How long should your conclusion be? Depending on whether you are writing a thesis or dissertation, your length will vary. Generally, a conclusion should make up around 5-7% of your overall word count. An empirical scientific study will often have a short conclusion, concisely stating the main findings and recommendations for future research.
Learn what a dissertation is, how to choose a topic, conduct research, and write chapters. Find out how long a dissertation should be, how long it takes, and how to defend it.
Learn how to determine the ideal length of your dissertation based on institutional guidelines, academic disciplines, and research methods. Explore the factors influencing dissertation length and get tips for planning and writing.
An undergraduate thesis is likely to be about 20 to 50 pages long. A Master's thesis is likely to be between 30 and 100 pages in length and a PhD dissertation is likely to be between 50 and 450 pages long. In the table below I highlight the typical length of an undergraduate, master's, and PhD. Level of study.
The table below illustrates a classic dissertation layout with approximate lengths for each section. Hopkins, D. and Reid, T., 2018. The Academic Skills Handbook: Your Guide to Success in Writing, Thinking and Communicating at University. Sage. Title. Your title should be clear, succinct and tell the reader exactly what your dissertation is about.
Title Page: The dissertation begins with the title page; the title should be as concise as possible and should provide an accurate description of the dissertation. The author name and date on the TAC and title page should be the same. ... and—depending on the license—adapt the work so long as proper attribution is given. (If a student ...
Barring unforeseen events, the normal time range for finishing a dissertation seems to be 13-19 months, which can be rounded to one to one and a half years. If you are proactive and efficient, you can usually be at the shorter end of the time range.
It can be helpful to think of your Masters dissertation as a series of closely interlinked essays, rather than one overwhelming paper. The size of this section will depend on the overall word count for your dissertation. However, to give you a rough idea for a 15,000-word dissertation, the discussion part will generally be about 12,000 words long.
It takes many years to accumulate enough original and new data to fill out a dissertation to the satisfaction of experts in your field. Interestingly, the PhD dissertation length and content vary significantly based on the field you are studying and the publishing conventions. A PhD can be anywhere from 50 pages to over 450 pages long.
Unfortunately, there's no one size fits all answer to this question. However, from the analysis of over 100 PhD theses, the average thesis length is between 80,000 and 100,000 words. A further analysis of 1000 PhD thesis shows the average number of pages to be 204. In reality, the actual word count for each PhD thesis will depend on the ...
Dissertation research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue; Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources; ... While a thesis proposal is often only 3-7 pages long, a prospectus for your dissertation is usually much longer, with more detailed analysis. Dissertation proposals can be up to 25-30 pages in length.
Learn how to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project with this comprehensive guide. Find out the generic dissertation structure and layout, the core contents of each chapter, and the common variations across universities.
Learn how long a dissertation should be based on your academic discipline, writing style, and goals. Find out the average length of a PhD dissertation, a dissertation chapter, and a dissertation proposal.
Due to COVID-19, defending your graduate thesis or dissertation in person is likely off the table. That doesn't mean you have to wait to defend. Many schools and programs are allowing remote defenses — meaning you could find yourself defending from your living room!
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
The Thesis. As anticipated earlier in my last article, ... margin jumped by 510 bps year-on-year to a record 19.6% during the second quarter of 2024, just 40 bps short of its long-term target ...
Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.