- Scientific Methods

What is Hypothesis?
We have heard of many hypotheses which have led to great inventions in science. Assumptions that are made on the basis of some evidence are known as hypotheses. In this article, let us learn in detail about the hypothesis and the type of hypothesis with examples.
A hypothesis is an assumption that is made based on some evidence. This is the initial point of any investigation that translates the research questions into predictions. It includes components like variables, population and the relation between the variables. A research hypothesis is a hypothesis that is used to test the relationship between two or more variables.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Following are the characteristics of the hypothesis:
- The hypothesis should be clear and precise to consider it to be reliable.
- If the hypothesis is a relational hypothesis, then it should be stating the relationship between variables.
- The hypothesis must be specific and should have scope for conducting more tests.
- The way of explanation of the hypothesis must be very simple and it should also be understood that the simplicity of the hypothesis is not related to its significance.
Sources of Hypothesis
Following are the sources of hypothesis:
- The resemblance between the phenomenon.
- Observations from past studies, present-day experiences and from the competitors.
- Scientific theories.
- General patterns that influence the thinking process of people.
Types of Hypothesis
There are six forms of hypothesis and they are:
- Simple hypothesis
- Complex hypothesis
- Directional hypothesis
- Non-directional hypothesis
- Null hypothesis
- Associative and casual hypothesis
Simple Hypothesis
It shows a relationship between one dependent variable and a single independent variable. For example – If you eat more vegetables, you will lose weight faster. Here, eating more vegetables is an independent variable, while losing weight is the dependent variable.
Complex Hypothesis
It shows the relationship between two or more dependent variables and two or more independent variables. Eating more vegetables and fruits leads to weight loss, glowing skin, and reduces the risk of many diseases such as heart disease.
Directional Hypothesis
It shows how a researcher is intellectual and committed to a particular outcome. The relationship between the variables can also predict its nature. For example- children aged four years eating proper food over a five-year period are having higher IQ levels than children not having a proper meal. This shows the effect and direction of the effect.
Non-directional Hypothesis
It is used when there is no theory involved. It is a statement that a relationship exists between two variables, without predicting the exact nature (direction) of the relationship.
Null Hypothesis
It provides a statement which is contrary to the hypothesis. It’s a negative statement, and there is no relationship between independent and dependent variables. The symbol is denoted by “H O ”.
Associative and Causal Hypothesis
Associative hypothesis occurs when there is a change in one variable resulting in a change in the other variable. Whereas, the causal hypothesis proposes a cause and effect interaction between two or more variables.
Examples of Hypothesis
Following are the examples of hypotheses based on their types:
- Consumption of sugary drinks every day leads to obesity is an example of a simple hypothesis.
- All lilies have the same number of petals is an example of a null hypothesis.
- If a person gets 7 hours of sleep, then he will feel less fatigue than if he sleeps less. It is an example of a directional hypothesis.
Functions of Hypothesis
Following are the functions performed by the hypothesis:
- Hypothesis helps in making an observation and experiments possible.
- It becomes the start point for the investigation.
- Hypothesis helps in verifying the observations.
- It helps in directing the inquiries in the right direction.
How will Hypothesis help in the Scientific Method?
Researchers use hypotheses to put down their thoughts directing how the experiment would take place. Following are the steps that are involved in the scientific method:
- Formation of question
- Doing background research
- Creation of hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collection of data
- Result analysis
- Summarizing the experiment
- Communicating the results
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is hypothesis.
A hypothesis is an assumption made based on some evidence.
Give an example of simple hypothesis?
What are the types of hypothesis.
Types of hypothesis are:
- Associative and Casual hypothesis
State true or false: Hypothesis is the initial point of any investigation that translates the research questions into a prediction.
Define complex hypothesis..
A complex hypothesis shows the relationship between two or more dependent variables and two or more independent variables.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Physics related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection .
Example: Hypothesis
Daily apple consumption leads to fewer doctor’s visits.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more types of variables .
- An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls.
- A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
If there are any control variables , extraneous variables , or confounding variables , be sure to jot those down as you go to minimize the chances that research bias will affect your results.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Step 1. Ask a question
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2. Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to ensure that you’re embarking on a relevant topic . This can also help you identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalize more complex constructs.
Step 3. Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
4. Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
- H 0 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has no effect on their final exam scores.
- H 1 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has a positive effect on their final exam scores.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/hypothesis/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, operationalization | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is your plagiarism score.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
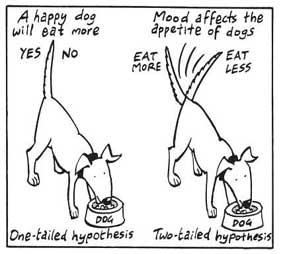
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.4: Developing a Hypothesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 16104

Learning Objectives
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis it is important to distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition. He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observation before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [1] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). A researcher begins with a set of phenomena and either constructs a theory to explain or interpret them or chooses an existing theory to work with. He or she then makes a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researcher then conducts an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, he or she reevaluates the theory in light of the new results and revises it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researcher can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 2.2 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.
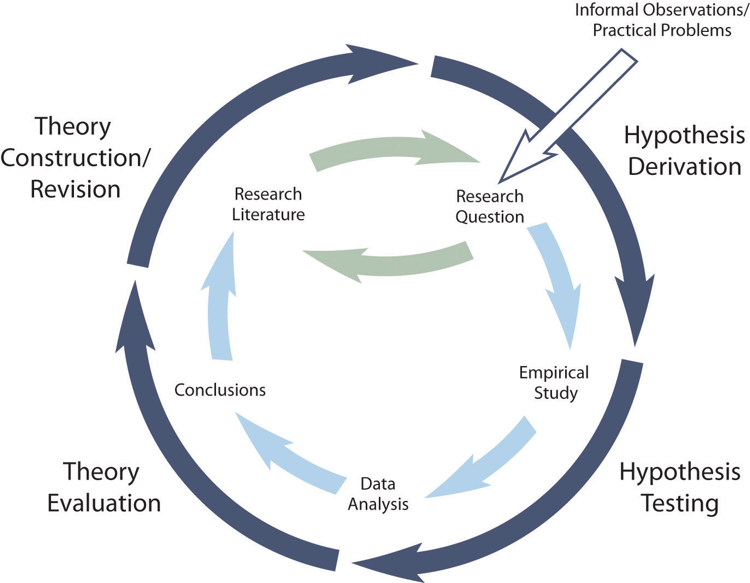
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [2] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans (Zajonc & Sales, 1966) [3] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that really it does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
Key Takeaways
- A theory is broad in nature and explains larger bodies of data. A hypothesis is more specific and makes a prediction about the outcome of a particular study.
- Working with theories is not “icing on the cake.” It is a basic ingredient of psychological research.
- Like other scientists, psychologists use the hypothetico-deductive method. They construct theories to explain or interpret phenomena (or work with existing theories), derive hypotheses from their theories, test the hypotheses, and then reevaluate the theories in light of the new results.
- Practice: Find a recent empirical research report in a professional journal. Read the introduction and highlight in different colors descriptions of theories and hypotheses.
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202.
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92.
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Developing a Hypothesis
Rajiv S. Jhangiani; I-Chant A. Chiang; Carrie Cuttler; and Dana C. Leighton
Learning Objectives
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis, it is important to distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition (1965) [1] . He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observations before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [2] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). Researchers begin with a set of phenomena and either construct a theory to explain or interpret them or choose an existing theory to work with. They then make a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researchers then conduct an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, they reevaluate the theory in light of the new results and revise it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researchers can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 2.3 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.
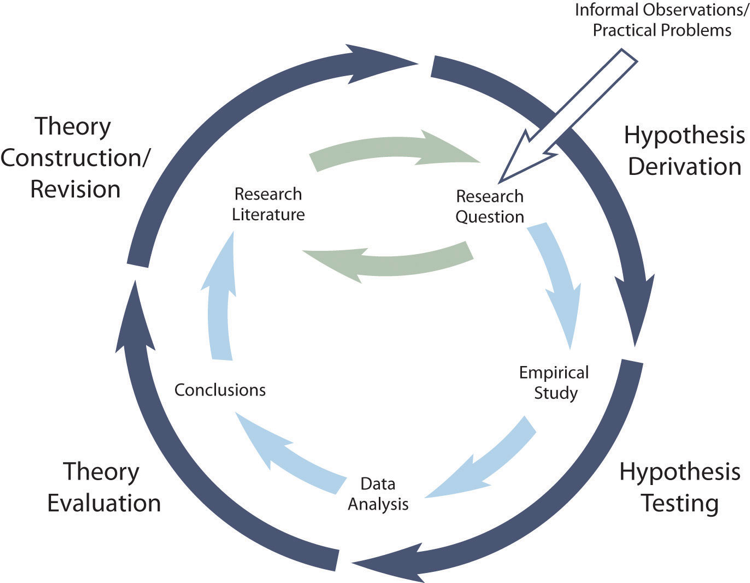
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [3] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans [Zajonc & Sales, 1966] [4] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that it really does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
- Zajonc, R. B. (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149 , 269–274 ↵
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202. ↵
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92. ↵
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168. ↵
A coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena.
A specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate.
A cyclical process of theory development, starting with an observed phenomenon, then developing or using a theory to make a specific prediction of what should happen if that theory is correct, testing that prediction, refining the theory in light of the findings, and using that refined theory to develop new hypotheses, and so on.
The ability to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and the possibility to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false.
Developing a Hypothesis Copyright © 2022 by Rajiv S. Jhangiani; I-Chant A. Chiang; Carrie Cuttler; and Dana C. Leighton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
2.4 Developing a Hypothesis
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis it is imporant to distinguish betwee a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition. He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observation before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [1] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). A researcher begins with a set of phenomena and either constructs a theory to explain or interpret them or chooses an existing theory to work with. He or she then makes a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researcher then conducts an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, he or she reevaluates the theory in light of the new results and revises it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researcher can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 2.2 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.

Figure 2.2 Hypothetico-Deductive Method Combined With the General Model of Scientific Research in Psychology Together they form a model of theoretically motivated research.
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [2] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans (Zajonc & Sales, 1966) [3] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that really it does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
Key Takeaways
- A theory is broad in nature and explains larger bodies of data. A hypothesis is more specific and makes a prediction about the outcome of a particular study.
- Working with theories is not “icing on the cake.” It is a basic ingredient of psychological research.
- Like other scientists, psychologists use the hypothetico-deductive method. They construct theories to explain or interpret phenomena (or work with existing theories), derive hypotheses from their theories, test the hypotheses, and then reevaluate the theories in light of the new results.
- Practice: Find a recent empirical research report in a professional journal. Read the introduction and highlight in different colors descriptions of theories and hypotheses.
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202. ↵
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92. ↵
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168. ↵

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size

The Best PhD and Masters Consulting Company

Characteristics Of A Good Hypothesis
What exactly is a hypothesis.
A hypothesis is a conclusion reached after considering the evidence. This is the first step in any investigation, where the research questions are translated into a prediction. Variables, population, and the relationship between the variables are all included. A research hypothesis is a hypothesis that is tested to see if two or more variables have a relationship. Now let’s have a look at the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Characteristics of
A good hypothesis has the following characteristics.
Ability To Predict
Closest to things that can be seen, testability, relevant to the issue, techniques that are applicable, new discoveries have been made as a result of this ., harmony & consistency.
- The similarity between the two phenomena.
- Observations from previous studies, current experiences, and feedback from rivals.
- Theories based on science.
- People’s thinking processes are influenced by general patterns.
- A straightforward hypothesis
- Complex Hypothesis
- Hypothesis with a certain direction
- Non-direction Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis
- Hypothesis of association and chance
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Overview of the Scientific Method
10 Developing a Hypothesis
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis, it is important to distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition (1965) [1] . He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observations before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [2] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.

Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). Researchers begin with a set of phenomena and either construct a theory to explain or interpret them or choose an existing theory to work with. They then make a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researchers then conduct an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, they reevaluate the theory in light of the new results and revise it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researchers can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 2.3 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [3] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans [Zajonc & Sales, 1966] [4] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that it really does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
- Zajonc, R. B. (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149 , 269–274 ↵
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202. ↵
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92. ↵
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168. ↵
A coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena.
A specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate.
A cyclical process of theory development, starting with an observed phenomenon, then developing or using a theory to make a specific prediction of what should happen if that theory is correct, testing that prediction, refining the theory in light of the findings, and using that refined theory to develop new hypotheses, and so on.
The ability to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and the possibility to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false.
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2019 by Rajiv S. Jhangiani, I-Chant A. Chiang, Carrie Cuttler, & Dana C. Leighton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

What is Hypothesis? Definition, Meaning, Characteristics, Sources
- Post last modified: 10 January 2022
- Reading time: 18 mins read
- Post category: Research Methodology

- What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
As an example, if we want to explore whether using a specific teaching method at school will result in better school marks (research question), the hypothesis could be that the mean school marks of students being taught with that specific teaching method will be higher than of those being taught using other methods.
In this example, we stated a hypothesis about the expected differences between groups. Other hypotheses may refer to correlations between variables.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Hypothesis?
- 2 Hypothesis Definition
- 3 Meaning of Hypothesis
- 4.1 Conceptual Clarity
- 4.2 Need of empirical referents
- 4.3 Hypothesis should be specific
- 4.4 Hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques
- 4.5 Hypothesis should be consistent with the theory
- 4.6 Hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events
- 4.7 Hypothesis should be simple
- 5.1 Observation
- 5.2 Analogies
- 5.4 State of Knowledge
- 5.5 Culture
- 5.6 Continuity of Research
- 6.1 Null Hypothesis
- 6.2 Alternative Hypothesis
Thus, to formulate a hypothesis, we need to refer to the descriptive statistics (such as the mean final marks), and specify a set of conditions about these statistics (such as a difference between the means, or in a different example, a positive or negative correlation). The hypothesis we formulate applies to the population of interest.
The null hypothesis makes a statement that no difference exists (see Pyrczak, 1995, pp. 75-84).
Hypothesis Definition
A hypothesis is ‘a guess or supposition as to the existence of some fact or law which will serve to explain a connection of facts already known to exist.’ – J. E. Creighton & H. R. Smart
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition not known to be definitely true or false, examined for the sake of determining the consequences which would follow from its truth.’ – Max Black
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition which can be put to a test to determine validity and is useful for further research.’ – W. J. Goode and P. K. Hatt
A hypothesis is a proposition, condition or principle which is assumed, perhaps without belief, in order to draw out its logical consequences and by this method to test its accord with facts which are known or may be determined. – Webster’s New International Dictionary of the English Language (1956)
Meaning of Hypothesis
From the above mentioned definitions of hypothesis, its meaning can be explained in the following ways.
- At the primary level, a hypothesis is the possible and probable explanation of the sequence of happenings or data.
- Sometimes, hypothesis may emerge from an imagination, common sense or a sudden event.
- Hypothesis can be a probable answer to the research problem undertaken for study. 4. Hypothesis may not always be true. It can get disproven. In other words, hypothesis need not always be a true proposition.
- Hypothesis, in a sense, is an attempt to present the interrelations that exist in the available data or information.
- Hypothesis is not an individual opinion or community thought. Instead, it is a philosophical means which is to be used for research purpose. Hypothesis is not to be considered as the ultimate objective; rather it is to be taken as the means of explaining scientifically the prevailing situation.
The concept of hypothesis can further be explained with the help of some examples. Lord Keynes, in his theory of national income determination, made a hypothesis about the consumption function. He stated that the consumption expenditure of an individual or an economy as a whole is dependent on the level of income and changes in a certain proportion.
Later, this proposition was proved in the statistical research carried out by Prof. Simon Kuznets. Matthus, while studying the population, formulated a hypothesis that population increases faster than the supply of food grains. Population studies of several countries revealed that this hypothesis is true.
Validation of the Malthus’ hypothesis turned it into a theory and when it was tested in many other countries it became the famous Malthus’ Law of Population. It thus emerges that when a hypothesis is tested and proven, it becomes a theory. The theory, when found true in different times and at different places, becomes the law. Having understood the concept of hypothesis, few hypotheses can be formulated in the areas of commerce and economics.
- Population growth moderates with the rise in per capita income.
- Sales growth is positively linked with the availability of credit.
- Commerce education increases the employability of the graduate students.
- High rates of direct taxes prompt people to evade taxes.
- Good working conditions improve the productivity of employees.
- Advertising is the most effecting way of promoting sales than any other scheme.
- Higher Debt-Equity Ratio increases the probability of insolvency.
- Economic reforms in India have made the public sector banks more efficient and competent.
- Foreign direct investment in India has moved in those sectors which offer higher rate of profit.
- There is no significant association between credit rating and investment of fund.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Not all the hypotheses are good and useful from the point of view of research. It is only a few hypotheses satisfying certain criteria that are good, useful and directive in the research work undertaken. The characteristics of such a useful hypothesis can be listed as below:
Conceptual Clarity
Need of empirical referents, hypothesis should be specific, hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques, hypothesis should be consistent with the theory, hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events, hypothesis should be simple.
The concepts used while framing hypothesis should be crystal clear and unambiguous. Such concepts must be clearly defined so that they become lucid and acceptable to everyone. How are the newly developed concepts interrelated and how are they linked with the old one is to be very clear so that the hypothesis framed on their basis also carries the same clarity.
A hypothesis embodying unclear and ambiguous concepts can to a great extent undermine the successful completion of the research work.
A hypothesis can be useful in the research work undertaken only when it has links with some empirical referents. Hypothesis based on moral values and ideals are useless as they cannot be tested. Similarly, hypothesis containing opinions as good and bad or expectation with respect to something are not testable and therefore useless.
For example, ‘current account deficit can be lowered if people change their attitude towards gold’ is a hypothesis encompassing expectation. In case of such a hypothesis, the attitude towards gold is something which cannot clearly be described and therefore a hypothesis which embodies such an unclean thing cannot be tested and proved or disproved. In short, the hypothesis should be linked with some testable referents.
For the successful conduction of research, it is necessary that the hypothesis is specific and presented in a precise manner. Hypothesis which is general, too ambitious and grandiose in scope is not to be made as such hypothesis cannot be easily put to test. A hypothesis is to be based on such concepts which are precise and empirical in nature. A hypothesis should give a clear idea about the indicators which are to be used.
For example, a hypothesis that economic power is increasingly getting concentrated in a few hands in India should enable us to define the concept of economic power. It should be explicated in terms of measurable indicator like income, wealth, etc. Such specificity in the formulation of a hypothesis ensures that the research is practicable and significant.
While framing the hypothesis, the researcher should be aware of the available research techniques and should see that the hypothesis framed is testable on the basis of them. In other words, a hypothesis should be researchable and for this it is important that a due thought has been given to the methods and techniques which can be used to measure the concepts and variables embodied in the hypothesis.
It does not however mean that hypotheses which are not testable with the available techniques of research are not to be made. If the problem is too significant and therefore the hypothesis framed becomes too ambitious and complex, it’s testing becomes possible with the development of new research techniques or the hypothesis itself leads to the development of new research techniques.
A hypothesis must be related to the existing theory or should have a theoretical orientation. The growth of knowledge takes place in the sequence of facts, hypothesis, theory and law or principles. It means the hypothesis should have a correspondence with the existing facts and theory.
If the hypothesis is related to some theory, the research work will enable us to support, modify or refute the existing theory. Theoretical orientation of the hypothesis ensures that it becomes scientifically useful. According to Prof. Goode and Prof. Hatt, research work can contribute to the existing knowledge only when the hypothesis is related with some theory.
This enables us to explain the observed facts and situations and also verify the framed hypothesis. In the words of Prof. Cohen and Prof. Nagel, “hypothesis must be formulated in such a manner that deduction can be made from it and that consequently a decision can be reached as to whether it does or does not explain the facts considered.”
If the research work based on a hypothesis is to be successful, it is necessary that the later is as simple and easy as possible. An ambition of finding out something new may lead the researcher to frame an unrealistic and unclear hypothesis. Such a temptation is to be avoided. Framing a simple, easy and testable hypothesis requires that the researcher is well acquainted with the related concepts.
Sources of Hypothesis
Hypotheses can be derived from various sources. Some of the sources is given below:
Observation
State of knowledge, continuity of research.
Hypotheses can be derived from observation from the observation of price behavior in a market. For example the relationship between the price and demand for an article is hypothesized.
Analogies are another source of useful hypotheses. Julian Huxley has pointed out that casual observations in nature or in the framework of another science may be a fertile source of hypotheses. For example, the hypotheses that similar human types or activities may be found in similar geophysical regions come from plant ecology.
This is one of the main sources of hypotheses. It gives direction to research by stating what is known logical deduction from theory lead to new hypotheses. For example, profit / wealth maximization is considered as the goal of private enterprises. From this assumption various hypotheses are derived’.
An important source of hypotheses is the state of knowledge in any particular science where formal theories exist hypotheses can be deduced. If the hypotheses are rejected theories are scarce hypotheses are generated from conception frameworks.
Another source of hypotheses is the culture on which the researcher was nurtured. Western culture has induced the emergence of sociology as an academic discipline over the past decade, a large part of the hypotheses on American society examined by researchers were connected with violence. This interest is related to the considerable increase in the level of violence in America.
The continuity of research in a field itself constitutes an important source of hypotheses. The rejection of some hypotheses leads to the formulation of new ones capable of explaining dependent variables in subsequent research on the same subject.
Null and Alternative Hypothesis
Null hypothesis.
The hypothesis that are proposed with the intent of receiving a rejection for them are called Null Hypothesis . This requires that we hypothesize the opposite of what is desired to be proved. For example, if we want to show that sales and advertisement expenditure are related, we formulate the null hypothesis that they are not related.
Similarly, if we want to conclude that the new sales training programme is effective, we formulate the null hypothesis that the new training programme is not effective, and if we want to prove that the average wages of skilled workers in town 1 is greater than that of town 2, we formulate the null hypotheses that there is no difference in the average wages of the skilled workers in both the towns.
Since we hypothesize that sales and advertisement are not related, new training programme is not effective and the average wages of skilled workers in both the towns are equal, we call such hypotheses null hypotheses and denote them as H 0 .
Alternative Hypothesis
Rejection of null hypotheses leads to the acceptance of alternative hypothesis . The rejection of null hypothesis indicates that the relationship between variables (e.g., sales and advertisement expenditure) or the difference between means (e.g., wages of skilled workers in town 1 and town 2) or the difference between proportions have statistical significance and the acceptance of the null hypotheses indicates that these differences are due to chance.
As already mentioned, the alternative hypotheses specify that values/relation which the researcher believes hold true. The alternative hypotheses can cover a whole range of values rather than a single point. The alternative hypotheses are denoted by H 1 .
Business Ethics
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Theories of CSR
- Arguments Against CSR
- Business Case for CSR
- Importance of CSR in India
- Drivers of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Developing a CSR Strategy
- Implement CSR Commitments
- CSR Marketplace
- CSR at Workplace
- Environmental CSR
- CSR with Communities and in Supply Chain
- Community Interventions
- CSR Monitoring
- CSR Reporting
- Voluntary Codes in CSR
- What is Corporate Ethics?
Lean Six Sigma
- What is Six Sigma?
- What is Lean Six Sigma?
- Value and Waste in Lean Six Sigma
- Six Sigma Team
- MAIC Six Sigma
- Six Sigma in Supply Chains
- What is Binomial, Poisson, Normal Distribution?
- What is Sigma Level?
- What is DMAIC in Six Sigma?
- What is DMADV in Six Sigma?
- Six Sigma Project Charter
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
- Research Methodology
- What is Research?
- Sampling Method
- Research Methods
- Data Collection in Research
Methods of Collecting Data
Application of business research.
- Levels of Measurement
- What is Sampling?
- Hypothesis Testing
Research Report
- What is Management?
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- What is Controlling?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Staffing?
- Organization Structure
- What is Departmentation?
- Span of Control
- What is Authority?
- Centralization vs Decentralization
- Organizing in Management
- Schools of Management Thought
- Classical Management Approach
- Is Management an Art or Science?
- Who is a Manager?
Operations Research
- What is Operations Research?
- Operation Research Models
- Linear Programming
- Linear Programming Graphic Solution
- Linear Programming Simplex Method
- Linear Programming Artificial Variable Technique
- Duality in Linear Programming
- Transportation Problem Initial Basic Feasible Solution
- Transportation Problem Finding Optimal Solution
- Project Network Analysis with Critical Path Method
- Project Network Analysis Methods
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
- Simulation in Operation Research
- Replacement Models in Operation Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
- What is Service?
- What is Service Operations Management?
- What is Service Design?
- Service Design Process
- Service Delivery
- What is Service Quality?
- Gap Model of Service Quality
- Juran Trilogy
- Service Performance Measurement
- Service Decoupling
- IT Service Operation
- Service Operations Management in Different Sector
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain
- What is Supply Chain Management?
- Supply Chain Planning and Measuring Strategy Performance
- What is Warehousing?
- What is Packaging?
- What is Inventory Management?
- What is Material Handling?
- What is Order Picking?
- Receiving and Dispatch, Processes
- What is Warehouse Design?
- What is Warehousing Costs?
You Might Also Like
What is research design features, components, types of hypotheses, what is scaling techniques types, classifications, techniques, what is experiments variables, types, lab, field, ethics in research, what is research problem components, identifying, formulating,, data analysis in research, what is measure of central tendency, what is questionnaire design characteristics, types, don’t, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal growth.

Development

Principles of Research Methodology pp 31–53 Cite as
The Research Hypothesis: Role and Construction
- Phyllis G. Supino EdD 3
- First Online: 01 January 2012
5963 Accesses
A hypothesis is a logical construct, interposed between a problem and its solution, which represents a proposed answer to a research question. It gives direction to the investigator’s thinking about the problem and, therefore, facilitates a solution. There are three primary modes of inference by which hypotheses are developed: deduction (reasoning from a general propositions to specific instances), induction (reasoning from specific instances to a general proposition), and abduction (formulation/acceptance on probation of a hypothesis to explain a surprising observation).
A research hypothesis should reflect an inference about variables; be stated as a grammatically complete, declarative sentence; be expressed simply and unambiguously; provide an adequate answer to the research problem; and be testable. Hypotheses can be classified as conceptual versus operational, single versus bi- or multivariable, causal or not causal, mechanistic versus nonmechanistic, and null or alternative. Hypotheses most commonly entail statements about “variables” which, in turn, can be classified according to their level of measurement (scaling characteristics) or according to their role in the hypothesis (independent, dependent, moderator, control, or intervening).
A hypothesis is rendered operational when its broadly (conceptually) stated variables are replaced by operational definitions of those variables. Hypotheses stated in this manner are called operational hypotheses, specific hypotheses, or predictions and facilitate testing.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- Operational Definition
- Moderator Variable
- Ventricular Performance
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Group
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
Wrong hypotheses, rightly worked from, have produced more results than unguided observation
—Augustus De Morgan, 1872[ 1 ]—
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
De Morgan A, De Morgan S. A budget of paradoxes. London: Longmans Green; 1872.
Google Scholar
Leedy Paul D. Practical research. Planning and design. 2nd ed. New York: Macmillan; 1960.
Bernard C. Introduction to the study of experimental medicine. New York: Dover; 1957.
Erren TC. The quest for questions—on the logical force of science. Med Hypotheses. 2004;62:635–40.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Peirce CS. Collected papers of Charles Sanders Peirce, vol. 7. In: Hartshorne C, Weiss P, editors. Boston: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press; 1966.
Aristotle. The complete works of Aristotle: the revised Oxford Translation. In: Barnes J, editor. vol. 2. Princeton/New Jersey: Princeton University Press; 1984.
Polit D, Beck CT. Conceptualizing a study to generate evidence for nursing. In: Polit D, Beck CT, editors. Nursing research: generating and assessing evidence for nursing practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2008. Chapter 4.
Jenicek M, Hitchcock DL. Evidence-based practice. Logic and critical thinking in medicine. Chicago: AMA Press; 2005.
Bacon F. The novum organon or a true guide to the interpretation of nature. A new translation by the Rev G.W. Kitchin. Oxford: The University Press; 1855.
Popper KR. Objective knowledge: an evolutionary approach (revised edition). New York: Oxford University Press; 1979.
Morgan AJ, Parker S. Translational mini-review series on vaccines: the Edward Jenner Museum and the history of vaccination. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;147:389–94.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Pead PJ. Benjamin Jesty: new light in the dawn of vaccination. Lancet. 2003;362:2104–9.
Lee JA. The scientific endeavor: a primer on scientific principles and practice. San Francisco: Addison-Wesley Longman; 2000.
Allchin D. Lawson’s shoehorn, or should the philosophy of science be rated, ‘X’? Science and Education. 2003;12:315–29.
Article Google Scholar
Lawson AE. What is the role of induction and deduction in reasoning and scientific inquiry? J Res Sci Teach. 2005;42:716–40.
Peirce CS. Collected papers of Charles Sanders Peirce, vol. 2. In: Hartshorne C, Weiss P, editors. Boston: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press; 1965.
Bonfantini MA, Proni G. To guess or not to guess? In: Eco U, Sebeok T, editors. The sign of three: Dupin, Holmes, Peirce. Bloomington: Indiana University Press; 1983. Chapter 5.
Peirce CS. Collected papers of Charles Sanders Peirce, vol. 5. In: Hartshorne C, Weiss P, editors. Boston: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press; 1965.
Flach PA, Kakas AC. Abductive and inductive reasoning: background issues. In: Flach PA, Kakas AC, editors. Abduction and induction. Essays on their relation and integration. The Netherlands: Klewer; 2000. Chapter 1.
Murray JF. Voltaire, Walpole and Pasteur: variations on the theme of discovery. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172:423–6.
Danemark B, Ekstrom M, Jakobsen L, Karlsson JC. Methodological implications, generalization, scientific inference, models (Part II) In: explaining society. Critical realism in the social sciences. New York: Routledge; 2002.
Pasteur L. Inaugural lecture as professor and dean of the faculty of sciences. In: Peterson H, editor. A treasury of the world’s greatest speeches. Douai, France: University of Lille 7 Dec 1954.
Swineburne R. Simplicity as evidence for truth. Milwaukee: Marquette University Press; 1997.
Sakar S, editor. Logical empiricism at its peak: Schlick, Carnap and Neurath. New York: Garland; 1996.
Popper K. The logic of scientific discovery. New York: Basic Books; 1959. 1934, trans. 1959.
Caws P. The philosophy of science. Princeton: D. Van Nostrand Company; 1965.
Popper K. Conjectures and refutations. The growth of scientific knowledge. 4th ed. London: Routledge and Keegan Paul; 1972.
Feyerabend PK. Against method, outline of an anarchistic theory of knowledge. London, UK: Verso; 1978.
Smith PG. Popper: conjectures and refutations (Chapter IV). In: Theory and reality: an introduction to the philosophy of science. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2003.
Blystone RV, Blodgett K. WWW: the scientific method. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2006;5:7–11.
Kleinbaum DG, Kupper LL, Morgenstern H. Epidemiological research. Principles and quantitative methods. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold; 1982.
Fortune AE, Reid WJ. Research in social work. 3rd ed. New York: Columbia University Press; 1999.
Kerlinger FN. Foundations of behavioral research. 1st ed. New York: Hold, Reinhart and Winston; 1970.
Hoskins CN, Mariano C. Research in nursing and health. Understanding and using quantitative and qualitative methods. New York: Springer; 2004.
Tuckman BW. Conducting educational research. New York: Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich; 1972.
Wang C, Chiari PC, Weihrauch D, Krolikowski JG, Warltier DC, Kersten JR, Pratt Jr PF, Pagel PS. Gender-specificity of delayed preconditioning by isoflurane in rabbits: potential role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Anesth Analg. 2006;103:274–80.
Beyer ME, Slesak G, Nerz S, Kazmaier S, Hoffmeister HM. Effects of endothelin-1 and IRL 1620 on myocardial contractility and myocardial energy metabolism. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995;26(Suppl 3):S150–2.
PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Stone J, Sharpe M. Amnesia for childhood in patients with unexplained neurological symptoms. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;72:416–7.
Naughton BJ, Moran M, Ghaly Y, Michalakes C. Computer tomography scanning and delirium in elder patients. Acad Emerg Med. 1997;4:1107–10.
Easterbrook PJ, Berlin JA, Gopalan R, Matthews DR. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet. 1991;337:867–72.
Stern JM, Simes RJ. Publication bias: evidence of delayed publication in a cohort study of clinical research projects. BMJ. 1997;315:640–5.
Stevens SS. On the theory of scales and measurement. Science. 1946;103:677–80.
Knapp TR. Treating ordinal scales as interval scales: an attempt to resolve the controversy. Nurs Res. 1990;39:121–3.
The Cochrane Collaboration. Open Learning Material. www.cochrane-net.org/openlearning/html/mod14-3.htm . Accessed 12 Oct 2009.
MacCorquodale K, Meehl PE. On a distinction between hypothetical constructs and intervening variables. Psychol Rev. 1948;55:95–107.
Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986;51:1173–82.
Williamson GM, Schultz R. Activity restriction mediates the association between pain and depressed affect: a study of younger and older adult cancer patients. Psychol Aging. 1995;10:369–78.
Song M, Lee EO. Development of a functional capacity model for the elderly. Res Nurs Health. 1998;21:189–98.
MacKinnon DP. Introduction to statistical mediation analysis. New York: Routledge; 2008.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Medicine, College of Medicine, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, 450 Clarkson Avenue, 1199, Brooklyn, NY, 11203, USA
Phyllis G. Supino EdD
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Phyllis G. Supino EdD .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
, Cardiovascular Medicine, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Clarkson Avenue, box 1199 450, Brooklyn, 11203, USA
Phyllis G. Supino
, Cardiovascualr Medicine, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Clarkson Avenue 450, Brooklyn, 11203, USA
Jeffrey S. Borer
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Supino, P.G. (2012). The Research Hypothesis: Role and Construction. In: Supino, P., Borer, J. (eds) Principles of Research Methodology. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3360-6_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3360-6_3
Published : 18 April 2012
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-1-4614-3359-0
Online ISBN : 978-1-4614-3360-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis, operational definitions, types of hypotheses, hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
Frequently Asked Questions
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study.
One hypothesis example would be a study designed to look at the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance might have a hypothesis that states: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. It is only at this point that researchers begin to develop a testable hypothesis. Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore a number of factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk wisdom that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in a number of different ways. One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. How would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
In order to measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming other people. In this situation, the researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests that there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent variables and a dependent variable.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative sample of the population and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- Complex hypothesis: "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have scores different than students who do not receive the intervention."
- "There will be no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will perform better than students who did not receive the intervention."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when it would be impossible or difficult to conduct an experiment . These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can then be used to look at how the variables are related. This type of research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
A Word From Verywell
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Some examples of how to write a hypothesis include:
- "Staying up late will lead to worse test performance the next day."
- "People who consume one apple each day will visit the doctor fewer times each year."
- "Breaking study sessions up into three 20-minute sessions will lead to better test results than a single 60-minute study session."
The four parts of a hypothesis are:
- The research question
- The independent variable (IV)
- The dependent variable (DV)
- The proposed relationship between the IV and DV
Castillo M. The scientific method: a need for something better? . AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(9):1669-71. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3401
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

How to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
The story of a research study begins by asking a question. Researchers all around the globe are asking curious questions and formulating research hypothesis. However, whether the research study provides an effective conclusion depends on how well one develops a good research hypothesis. Research hypothesis examples could help researchers get an idea as to how to write a good research hypothesis.
This blog will help you understand what is a research hypothesis, its characteristics and, how to formulate a research hypothesis
Table of Contents
What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is an assumption or an idea proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested. It is a precise, testable statement of what the researchers predict will be outcome of the study. Hypothesis usually involves proposing a relationship between two variables: the independent variable (what the researchers change) and the dependent variable (what the research measures).
What is a Research Hypothesis?
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It is an integral part of the scientific method that forms the basis of scientific experiments. Therefore, you need to be careful and thorough when building your research hypothesis. A minor flaw in the construction of your hypothesis could have an adverse effect on your experiment. In research, there is a convention that the hypothesis is written in two forms, the null hypothesis, and the alternative hypothesis (called the experimental hypothesis when the method of investigation is an experiment).
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
As the hypothesis is specific, there is a testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. You may consider drawing hypothesis from previously published research based on the theory.
A good research hypothesis involves more effort than just a guess. In particular, your hypothesis may begin with a question that could be further explored through background research.
To help you formulate a promising research hypothesis, you should ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the language clear and focused?
- What is the relationship between your hypothesis and your research topic?
- Is your hypothesis testable? If yes, then how?
- What are the possible explanations that you might want to explore?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate your variables without hampering the ethical standards?
- Does your research predict the relationship and outcome?
- Is your research simple and concise (avoids wordiness)?
- Is it clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Is your research observable and testable results?
- Is it relevant and specific to the research question or problem?

The questions listed above can be used as a checklist to make sure your hypothesis is based on a solid foundation. Furthermore, it can help you identify weaknesses in your hypothesis and revise it if necessary.
Source: Educational Hub
How to formulate a research hypothesis.
A testable hypothesis is not a simple statement. It is rather an intricate statement that needs to offer a clear introduction to a scientific experiment, its intentions, and the possible outcomes. However, there are some important things to consider when building a compelling hypothesis.
1. State the problem that you are trying to solve.
Make sure that the hypothesis clearly defines the topic and the focus of the experiment.
2. Try to write the hypothesis as an if-then statement.
Follow this template: If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.
3. Define the variables
Independent variables are the ones that are manipulated, controlled, or changed. Independent variables are isolated from other factors of the study.
Dependent variables , as the name suggests are dependent on other factors of the study. They are influenced by the change in independent variable.
4. Scrutinize the hypothesis
Evaluate assumptions, predictions, and evidence rigorously to refine your understanding.
Types of Research Hypothesis
The types of research hypothesis are stated below:
1. Simple Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable.
2. Complex Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables.
3. Directional Hypothesis
It specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables and is derived from theory. Furthermore, it implies the researcher’s intellectual commitment to a particular outcome.
4. Non-directional Hypothesis
It does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. The non-directional hypothesis is used when there is no theory involved or when findings contradict previous research.
5. Associative and Causal Hypothesis
The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables. A change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. On the other hand, the causal hypothesis proposes an effect on the dependent due to manipulation of the independent variable.
6. Null Hypothesis
Null hypothesis states a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. There will be no changes in the dependent variable due the manipulation of the independent variable. Furthermore, it states results are due to chance and are not significant in terms of supporting the idea being investigated.
7. Alternative Hypothesis
It states that there is a relationship between the two variables of the study and that the results are significant to the research topic. An experimental hypothesis predicts what changes will take place in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated. Also, it states that the results are not due to chance and that they are significant in terms of supporting the theory being investigated.
Research Hypothesis Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
Research Hypothesis Example 1 The greater number of coal plants in a region (independent variable) increases water pollution (dependent variable). If you change the independent variable (building more coal factories), it will change the dependent variable (amount of water pollution).
Research Hypothesis Example 2 What is the effect of diet or regular soda (independent variable) on blood sugar levels (dependent variable)? If you change the independent variable (the type of soda you consume), it will change the dependent variable (blood sugar levels)
You should not ignore the importance of the above steps. The validity of your experiment and its results rely on a robust testable hypothesis. Developing a strong testable hypothesis has few advantages, it compels us to think intensely and specifically about the outcomes of a study. Consequently, it enables us to understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved in the study. Furthermore, it helps us to make precise predictions based on prior research. Hence, forming a hypothesis would be of great value to the research. Here are some good examples of testable hypotheses.
More importantly, you need to build a robust testable research hypothesis for your scientific experiments. A testable hypothesis is a hypothesis that can be proved or disproved as a result of experimentation.
Importance of a Testable Hypothesis
To devise and perform an experiment using scientific method, you need to make sure that your hypothesis is testable. To be considered testable, some essential criteria must be met:
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is true.
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is false.
- The results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.
Without these criteria, the hypothesis and the results will be vague. As a result, the experiment will not prove or disprove anything significant.
What are your experiences with building hypotheses for scientific experiments? What challenges did you face? How did you overcome these challenges? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section.
Frequently Asked Questions
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a ‘if-then’ structure. 3. Defining the variables: Define the variables as Dependent or Independent based on their dependency to other factors. 4. Scrutinizing the hypothesis: Identify the type of your hypothesis
Hypothesis testing is a statistical tool which is used to make inferences about a population data to draw conclusions for a particular hypothesis.
Hypothesis in statistics is a formal statement about the nature of a population within a structured framework of a statistical model. It is used to test an existing hypothesis by studying a population.
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It forms the basis of scientific experiments.
The different types of hypothesis in research are: • Null hypothesis: Null hypothesis is a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. • Alternate hypothesis: Alternate hypothesis predicts the relationship between the two variables of the study. • Directional hypothesis: Directional hypothesis specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables. • Non-directional hypothesis: Non-directional hypothesis does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. • Simple hypothesis: Simple hypothesis predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable. • Complex hypothesis: Complex hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Associative and casual hypothesis: Associative and casual hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Empirical hypothesis: Empirical hypothesis can be tested via experiments and observation. • Statistical hypothesis: A statistical hypothesis utilizes statistical models to draw conclusions about broader populations.
Wow! You really simplified your explanation that even dummies would find it easy to comprehend. Thank you so much.
Thanks a lot for your valuable guidance.
I enjoy reading the post. Hypotheses are actually an intrinsic part in a study. It bridges the research question and the methodology of the study.
Useful piece!
This is awesome.Wow.
It very interesting to read the topic, can you guide me any specific example of hypothesis process establish throw the Demand and supply of the specific product in market
Nicely explained
It is really a useful for me Kindly give some examples of hypothesis
It was a well explained content ,can you please give me an example with the null and alternative hypothesis illustrated
clear and concise. thanks.
So Good so Amazing
Good to learn
Thanks a lot for explaining to my level of understanding
Explained well and in simple terms. Quick read! Thank you
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Industry News
COPE Forum Discussion Highlights Challenges and Urges Clarity in Institutional Authorship Standards
The COPE forum discussion held in December 2023 initiated with a fundamental question — is…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.34(45); 2019 Nov 25

Scientific Hypotheses: Writing, Promoting, and Predicting Implications
Armen yuri gasparyan.
1 Departments of Rheumatology and Research and Development, Dudley Group NHS Foundation Trust (Teaching Trust of the University of Birmingham, UK), Russells Hall Hospital, Dudley, West Midlands, UK.
Lilit Ayvazyan
2 Department of Medical Chemistry, Yerevan State Medical University, Yerevan, Armenia.
Ulzhan Mukanova
3 Department of Surgical Disciplines, South Kazakhstan Medical Academy, Shymkent, Kazakhstan.
Marlen Yessirkepov
4 Department of Biology and Biochemistry, South Kazakhstan Medical Academy, Shymkent, Kazakhstan.
George D. Kitas
5 Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK.
Scientific hypotheses are essential for progress in rapidly developing academic disciplines. Proposing new ideas and hypotheses require thorough analyses of evidence-based data and predictions of the implications. One of the main concerns relates to the ethical implications of the generated hypotheses. The authors may need to outline potential benefits and limitations of their suggestions and target widely visible publication outlets to ignite discussion by experts and start testing the hypotheses. Not many publication outlets are currently welcoming hypotheses and unconventional ideas that may open gates to criticism and conservative remarks. A few scholarly journals guide the authors on how to structure hypotheses. Reflecting on general and specific issues around the subject matter is often recommended for drafting a well-structured hypothesis article. An analysis of influential hypotheses, presented in this article, particularly Strachan's hygiene hypothesis with global implications in the field of immunology and allergy, points to the need for properly interpreting and testing new suggestions. Envisaging the ethical implications of the hypotheses should be considered both by authors and journal editors during the writing and publishing process.
INTRODUCTION
We live in times of digitization that radically changes scientific research, reporting, and publishing strategies. Researchers all over the world are overwhelmed with processing large volumes of information and searching through numerous online platforms, all of which make the whole process of scholarly analysis and synthesis complex and sophisticated.
Current research activities are diversifying to combine scientific observations with analysis of facts recorded by scholars from various professional backgrounds. 1 Citation analyses and networking on social media are also becoming essential for shaping research and publishing strategies globally. 2 Learning specifics of increasingly interdisciplinary research studies and acquiring information facilitation skills aid researchers in formulating innovative ideas and predicting developments in interrelated scientific fields.
Arguably, researchers are currently offered more opportunities than in the past for generating new ideas by performing their routine laboratory activities, observing individual cases and unusual developments, and critically analyzing published scientific facts. What they need at the start of their research is to formulate a scientific hypothesis that revisits conventional theories, real-world processes, and related evidence to propose new studies and test ideas in an ethical way. 3 Such a hypothesis can be of most benefit if published in an ethical journal with wide visibility and exposure to relevant online databases and promotion platforms.
Although hypotheses are crucially important for the scientific progress, only few highly skilled researchers formulate and eventually publish their innovative ideas per se . Understandably, in an increasingly competitive research environment, most authors would prefer to prioritize their ideas by discussing and conducting tests in their own laboratories or clinical departments, and publishing research reports afterwards. However, there are instances when simple observations and research studies in a single center are not capable of explaining and testing new groundbreaking ideas. Formulating hypothesis articles first and calling for multicenter and interdisciplinary research can be a solution in such instances, potentially launching influential scientific directions, if not academic disciplines.
The aim of this article is to overview the importance and implications of infrequently published scientific hypotheses that may open new avenues of thinking and research.
Despite the seemingly established views on innovative ideas and hypotheses as essential research tools, no structured definition exists to tag the term and systematically track related articles. In 1973, the Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) of the U.S. National Library of Medicine introduced “Research Design” as a structured keyword that referred to the importance of collecting data and properly testing hypotheses, and indirectly linked the term to ethics, methods and standards, among many other subheadings.
One of the experts in the field defines “hypothesis” as a well-argued analysis of available evidence to provide a realistic (scientific) explanation of existing facts, fill gaps in public understanding of sophisticated processes, and propose a new theory or a test. 4 A hypothesis can be proven wrong partially or entirely. However, even such an erroneous hypothesis may influence progress in science by initiating professional debates that help generate more realistic ideas. The main ethical requirement for hypothesis authors is to be honest about the limitations of their suggestions. 5
EXAMPLES OF INFLUENTIAL SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESES
Daily routine in a research laboratory may lead to groundbreaking discoveries provided the daily accounts are comprehensively analyzed and reproduced by peers. The discovery of penicillin by Sir Alexander Fleming (1928) can be viewed as a prime example of such discoveries that introduced therapies to treat staphylococcal and streptococcal infections and modulate blood coagulation. 6 , 7 Penicillin got worldwide recognition due to the inventor's seminal works published by highly prestigious and widely visible British journals, effective ‘real-world’ antibiotic therapy of pneumonia and wounds during World War II, and euphoric media coverage. 8 In 1945, Fleming, Florey and Chain got a much deserved Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the discovery that led to the mass production of the wonder drug in the U.S. and ‘real-world practice’ that tested the use of penicillin. What remained globally unnoticed is that Zinaida Yermolyeva, the outstanding Soviet microbiologist, created the Soviet penicillin, which turned out to be more effective than the Anglo-American penicillin and entered mass production in 1943; that year marked the turning of the tide of the Great Patriotic War. 9 One of the reasons of the widely unnoticed discovery of Zinaida Yermolyeva is that her works were published exclusively by local Russian (Soviet) journals.
The past decades have been marked by an unprecedented growth of multicenter and global research studies involving hundreds and thousands of human subjects. This trend is shaped by an increasing number of reports on clinical trials and large cohort studies that create a strong evidence base for practice recommendations. Mega-studies may help generate and test large-scale hypotheses aiming to solve health issues globally. Properly designed epidemiological studies, for example, may introduce clarity to the hygiene hypothesis that was originally proposed by David Strachan in 1989. 10 David Strachan studied the epidemiology of hay fever in a cohort of 17,414 British children and concluded that declining family size and improved personal hygiene had reduced the chances of cross infections in families, resulting in epidemics of atopic disease in post-industrial Britain. Over the past four decades, several related hypotheses have been proposed to expand the potential role of symbiotic microorganisms and parasites in the development of human physiological immune responses early in life and protection from allergic and autoimmune diseases later on. 11 , 12 Given the popularity and the scientific importance of the hygiene hypothesis, it was introduced as a MeSH term in 2012. 13
Hypotheses can be proposed based on an analysis of recorded historic events that resulted in mass migrations and spreading of certain genetic diseases. As a prime example, familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), the prototype periodic fever syndrome, is believed to spread from Mesopotamia to the Mediterranean region and all over Europe due to migrations and religious prosecutions millennia ago. 14 Genetic mutations spearing mild clinical forms of FMF are hypothesized to emerge and persist in the Mediterranean region as protective factors against more serious infectious diseases, particularly tuberculosis, historically common in that part of the world. 15 The speculations over the advantages of carrying the MEditerranean FeVer (MEFV) gene are further strengthened by recorded low mortality rates from tuberculosis among FMF patients of different nationalities living in Tunisia in the first half of the 20th century. 16
Diagnostic hypotheses shedding light on peculiarities of diseases throughout the history of mankind can be formulated using artefacts, particularly historic paintings. 17 Such paintings may reveal joint deformities and disfigurements due to rheumatic diseases in individual subjects. A series of paintings with similar signs of pathological conditions interpreted in a historic context may uncover mysteries of epidemics of certain diseases, which is the case with Ruben's paintings depicting signs of rheumatic hands and making some doctors to believe that rheumatoid arthritis was common in Europe in the 16th and 17th century. 18
WRITING SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESES
There are author instructions of a few journals that specifically guide how to structure, format, and make submissions categorized as hypotheses attractive. One of the examples is presented by Med Hypotheses , the flagship journal in its field with more than four decades of publishing and influencing hypothesis authors globally. However, such guidance is not based on widely discussed, implemented, and approved reporting standards, which are becoming mandatory for all scholarly journals.
Generating new ideas and scientific hypotheses is a sophisticated task since not all researchers and authors are skilled to plan, conduct, and interpret various research studies. Some experience with formulating focused research questions and strong working hypotheses of original research studies is definitely helpful for advancing critical appraisal skills. However, aspiring authors of scientific hypotheses may need something different, which is more related to discerning scientific facts, pooling homogenous data from primary research works, and synthesizing new information in a systematic way by analyzing similar sets of articles. To some extent, this activity is reminiscent of writing narrative and systematic reviews. As in the case of reviews, scientific hypotheses need to be formulated on the basis of comprehensive search strategies to retrieve all available studies on the topics of interest and then synthesize new information selectively referring to the most relevant items. One of the main differences between scientific hypothesis and review articles relates to the volume of supportive literature sources ( Table 1 ). In fact, hypothesis is usually formulated by referring to a few scientific facts or compelling evidence derived from a handful of literature sources. 19 By contrast, reviews require analyses of a large number of published documents retrieved from several well-organized and evidence-based databases in accordance with predefined search strategies. 20 , 21 , 22
The format of hypotheses, especially the implications part, may vary widely across disciplines. Clinicians may limit their suggestions to the clinical manifestations of diseases, outcomes, and management strategies. Basic and laboratory scientists analysing genetic, molecular, and biochemical mechanisms may need to view beyond the frames of their narrow fields and predict social and population-based implications of the proposed ideas. 23
Advanced writing skills are essential for presenting an interesting theoretical article which appeals to the global readership. Merely listing opposing facts and ideas, without proper interpretation and analysis, may distract the experienced readers. The essence of a great hypothesis is a story behind the scientific facts and evidence-based data.
ETHICAL IMPLICATIONS
The authors of hypotheses substantiate their arguments by referring to and discerning rational points from published articles that might be overlooked by others. Their arguments may contradict the established theories and practices, and pose global ethical issues, particularly when more or less efficient medical technologies and public health interventions are devalued. The ethical issues may arise primarily because of the careless references to articles with low priorities, inadequate and apparently unethical methodologies, and concealed reporting of negative results. 24 , 25
Misinterpretation and misunderstanding of the published ideas and scientific hypotheses may complicate the issue further. For example, Alexander Fleming, whose innovative ideas of penicillin use to kill susceptible bacteria saved millions of lives, warned of the consequences of uncontrolled prescription of the drug. The issue of antibiotic resistance had emerged within the first ten years of penicillin use on a global scale due to the overprescription that affected the efficacy of antibiotic therapies, with undesirable consequences for millions. 26
The misunderstanding of the hygiene hypothesis that primarily aimed to shed light on the role of the microbiome in allergic and autoimmune diseases resulted in decline of public confidence in hygiene with dire societal implications, forcing some experts to abandon the original idea. 27 , 28 Although that hypothesis is unrelated to the issue of vaccinations, the public misunderstanding has resulted in decline of vaccinations at a time of upsurge of old and new infections.
A number of ethical issues are posed by the denial of the viral (human immunodeficiency viruses; HIV) hypothesis of acquired Immune deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) by Peter Duesberg, who overviewed the links between illicit recreational drugs and antiretroviral therapies with AIDS and refuted the etiological role of HIV. 29 That controversial hypothesis was rejected by several journals, but was eventually published without external peer review at Med Hypotheses in 2010. The publication itself raised concerns of the unconventional editorial policy of the journal, causing major perturbations and more scrutinized publishing policies by journals processing hypotheses.
WHERE TO PUBLISH HYPOTHESES
Although scientific authors are currently well informed and equipped with search tools to draft evidence-based hypotheses, there are still limited quality publication outlets calling for related articles. The journal editors may be hesitant to publish articles that do not adhere to any research reporting guidelines and open gates for harsh criticism of unconventional and untested ideas. Occasionally, the editors opting for open-access publishing and upgrading their ethics regulations launch a section to selectively publish scientific hypotheses attractive to the experienced readers. 30 However, the absence of approved standards for this article type, particularly no mandate for outlining potential ethical implications, may lead to publication of potentially harmful ideas in an attractive format.
A suggestion of simultaneously publishing multiple or alternative hypotheses to balance the reader views and feedback is a potential solution for the mainstream scholarly journals. 31 However, that option alone is hardly applicable to emerging journals with unconventional quality checks and peer review, accumulating papers with multiple rejections by established journals.
A large group of experts view hypotheses with improbable and controversial ideas publishable after formal editorial (in-house) checks to preserve the authors' genuine ideas and avoid conservative amendments imposed by external peer reviewers. 32 That approach may be acceptable for established publishers with large teams of experienced editors. However, the same approach can lead to dire consequences if employed by nonselective start-up, open-access journals processing all types of articles and primarily accepting those with charged publication fees. 33 In fact, pseudoscientific ideas arguing Newton's and Einstein's seminal works or those denying climate change that are hardly testable have already found their niche in substandard electronic journals with soft or nonexistent peer review. 34
CITATIONS AND SOCIAL MEDIA ATTENTION
The available preliminary evidence points to the attractiveness of hypothesis articles for readers, particularly those from research-intensive countries who actively download related documents. 35 However, citations of such articles are disproportionately low. Only a small proportion of top-downloaded hypotheses (13%) in the highly prestigious Med Hypotheses receive on average 5 citations per article within a two-year window. 36
With the exception of a few historic papers, the vast majority of hypotheses attract relatively small number of citations in a long term. 36 Plausible explanations are that these articles often contain a single or only a few citable points and that suggested research studies to test hypotheses are rarely conducted and reported, limiting chances of citing and crediting authors of genuine research ideas.
A snapshot analysis of citation activity of hypothesis articles may reveal interest of the global scientific community towards their implications across various disciplines and countries. As a prime example, Strachan's hygiene hypothesis, published in 1989, 10 is still attracting numerous citations on Scopus, the largest bibliographic database. As of August 28, 2019, the number of the linked citations in the database is 3,201. Of the citing articles, 160 are cited at least 160 times ( h -index of this research topic = 160). The first three citations are recorded in 1992 and followed by a rapid annual increase in citation activity and a peak of 212 in 2015 ( Fig. 1 ). The top 5 sources of the citations are Clin Exp Allergy (n = 136), J Allergy Clin Immunol (n = 119), Allergy (n = 81), Pediatr Allergy Immunol (n = 69), and PLOS One (n = 44). The top 5 citing authors are leading experts in pediatrics and allergology Erika von Mutius (Munich, Germany, number of publications with the index citation = 30), Erika Isolauri (Turku, Finland, n = 27), Patrick G Holt (Subiaco, Australia, n = 25), David P. Strachan (London, UK, n = 23), and Bengt Björksten (Stockholm, Sweden, n = 22). The U.S. is the leading country in terms of citation activity with 809 related documents, followed by the UK (n = 494), Germany (n = 314), Australia (n = 211), and the Netherlands (n = 177). The largest proportion of citing documents are articles (n = 1,726, 54%), followed by reviews (n = 950, 29.7%), and book chapters (n = 213, 6.7%). The main subject areas of the citing items are medicine (n = 2,581, 51.7%), immunology and microbiology (n = 1,179, 23.6%), and biochemistry, genetics and molecular biology (n = 415, 8.3%).

Interestingly, a recent analysis of 111 publications related to Strachan's hygiene hypothesis, stating that the lack of exposure to infections in early life increases the risk of rhinitis, revealed a selection bias of 5,551 citations on Web of Science. 37 The articles supportive of the hypothesis were cited more than nonsupportive ones (odds ratio adjusted for study design, 2.2; 95% confidence interval, 1.6–3.1). A similar conclusion pointing to a citation bias distorting bibliometrics of hypotheses was reached by an earlier analysis of a citation network linked to the idea that β-amyloid, which is involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease, is produced by skeletal muscle of patients with inclusion body myositis. 38 The results of both studies are in line with the notion that ‘positive’ citations are more frequent in the field of biomedicine than ‘negative’ ones, and that citations to articles with proven hypotheses are too common. 39
Social media channels are playing an increasingly active role in the generation and evaluation of scientific hypotheses. In fact, publicly discussing research questions on platforms of news outlets, such as Reddit, may shape hypotheses on health-related issues of global importance, such as obesity. 40 Analyzing Twitter comments, researchers may reveal both potentially valuable ideas and unfounded claims that surround groundbreaking research ideas. 41 Social media activities, however, are unevenly distributed across different research topics, journals and countries, and these are not always objective professional reflections of the breakthroughs in science. 2 , 42
Scientific hypotheses are essential for progress in science and advances in healthcare. Innovative ideas should be based on a critical overview of related scientific facts and evidence-based data, often overlooked by others. To generate realistic hypothetical theories, the authors should comprehensively analyze the literature and suggest relevant and ethically sound design for future studies. They should also consider their hypotheses in the context of research and publication ethics norms acceptable for their target journals. The journal editors aiming to diversify their portfolio by maintaining and introducing hypotheses section are in a position to upgrade guidelines for related articles by pointing to general and specific analyses of the subject, preferred study designs to test hypotheses, and ethical implications. The latter is closely related to specifics of hypotheses. For example, editorial recommendations to outline benefits and risks of a new laboratory test or therapy may result in a more balanced article and minimize associated risks afterwards.
Not all scientific hypotheses have immediate positive effects. Some, if not most, are never tested in properly designed research studies and never cited in credible and indexed publication outlets. Hypotheses in specialized scientific fields, particularly those hardly understandable for nonexperts, lose their attractiveness for increasingly interdisciplinary audience. The authors' honest analysis of the benefits and limitations of their hypotheses and concerted efforts of all stakeholders in science communication to initiate public discussion on widely visible platforms and social media may reveal rational points and caveats of the new ideas.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Gasparyan AY, Yessirkepov M, Kitas GD.
- Methodology: Gasparyan AY, Mukanova U, Ayvazyan L.
- Writing - original draft: Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Yessirkepov M.
- Writing - review & editing: Gasparyan AY, Yessirkepov M, Mukanova U, Kitas GD.
Past Papers

Characteristics Of Hypothesis: Overview
A hypothesis is a foundational element in scientific research, serving as a tentative explanation or prediction that guides the direction of study and experimentation. It’s a statement that proposes a possible reason for a phenomenon or a potential relationship between variables that can be tested through research.
The importance of hypotheses in scientific inquiry cannot be overstated—they are the starting point from which all experimental design and data collection stems.
This article delves into the essential characteristics of a well-formulated hypothesis, providing clarity and insight into what makes hypotheses both practical and foundational to scientific progress.
Table of Contents
Clear and Specific
One of the primary characteristics of a hypothesis is its clarity and specificity. A theory must be formulated to clearly state the expected relationship between variables, leaving no room for ambiguity. This specificity allows for precise testing and analysis.
For example, a clear and specific hypothesis might state, “Increasing the amount of sunlight a plant receives will directly increase its growth rate.” This hypothesis is clear and specifies the variables involved and the expected relationship between them.
The importance of avoiding vagueness cannot be understated, as it ensures that the research can be conducted with a clear focus and objective.
Testable and Falsifiable
A core principle of scientific research is that a hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. This means designing experiments or observations that prove the theory wrong should be possible.
The concept of falsifiability, introduced by philosopher Karl Popper, asserts that for a hypothesis to be scientific, it must be inherently disprovable.
For instance, the hypothesis “Plant growth rate increases with increased sunlight exposure” can be tested and potentially falsified by experimenting with different amounts of sunlight. This characteristic ensures that scientific inquiry is grounded in empirical evidence and remains objective.
Based on Theory and Observation
Compelling hypotheses often stem from a theoretical framework or prior observations. They should not be random guesses but informed propositions based on existing knowledge, theories, or empirical data.
For example, the hypothesis that “Watering plants with diluted coffee rather than water will increase their growth” might be based on observations of nitrogen’s effects on plant growth. This characteristic underscores the importance of a hypothesis being grounded in reality and informed by existing scientific understanding.
Empirical and Measurable
For a hypothesis to be actionable, it must propose an empirical and measurable relationship. This means the variables involved can be observed, quantified, and analyzed. Employing operational definitions to specify how variables are measured is crucial for making hypotheses empirically testable.
A hypothesis such as “Students’ test scores improve significantly with increased study time” is measurable because both “study time” and “test scores” can be quantified and analyzed statistically.
A well-constructed hypothesis is often predictive, indicating what the researcher expects to happen and allowing for predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations.
Predictive hypotheses guide the research process by suggesting what results might confirm or refute the proposed explanation. This predictive nature is essential for advancing scientific knowledge, as it sets the stage for experimental design and testing specific predictions.

Logical and Coherent
Logical coherence is vital in hypothesis formulation. A hypothesis should logically follow the premises or known facts and align with established scientific principles.
It should be coherent and internally consistent, not contradicting well-established theories without compelling evidence. For example, a hypothesis proposing a cause-effect relationship that violates the laws of physics would lack logical coherence.
Tentative and Subject to Revision
Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving, and a hypothesis is, by nature, tentative. It is an educated guess awaiting verification or refutation through research. As new evidence emerges, hypotheses may be revised or discarded.
This flexibility is a strength of the scientific method, allowing science to adapt and refine its understanding of the natural world. The readiness to revise hypotheses in light of new evidence is crucial for scientific progress.
Relevant to the Research Question
A hypothesis must be directly relevant to the research question it seeks to answer. It should provide a focused, direct answer or explanation related to the question, guiding the research in a meaningful direction.
For instance, if the research question involves exploring the effects of a specific educational intervention on student learning outcomes, the hypothesis should directly address the relationship between that intervention and the outcomes.
The above characteristics underscore the importance of well-formulated hypotheses in the scientific process. They ensure that research is focused, empirical, and grounded in theory, thereby enhancing the reliability and validity of scientific findings.
A reasonable hypothesis is the backbone of rigorous scientific research, paving the way for discoveries that advance our understanding of the world. As science evolves, formulating clear, testable, and meaningful hypotheses remains central to the quest for knowledge and experience.
About The Author
See author's posts
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Maths Notes Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- RD Sharma Solutions Class 12
- Maths Formulas Class 12
- Maths Previous Year Paper Class 12
- Class 12 Syllabus
- Class 12 Revision Notes
- Physics Notes Class 12
- Chemistry Notes Class 12
- Biology Notes Class 12
- Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions
- Exponential Graph
- Line Integral
- Determinant of 2x2 Matrix
- Integral of Cos x
- Algebra of Matrices
- Random Sampling
- Derivative of Sin 2x
- Integration
- Derivative of Sec Square x
- Derivative Rules
- Derivative of Sec x
- Systematic Random Sampling
- Derivative of Tan Inverse x
- Derivative of Arctan
- Zero Vector
- Triple Integrals
- Local Maxima and Minima in Calculus
Hypothesis is a testable statement that explains what is happening or observed. It proposes the relation between the various participating variables. Hypothesis is also called Theory, Thesis, Guess, Assumption, or Suggestion. Hypothesis creates a structure that guides the search for knowledge.
In this article, we will learn what is hypothesis, its characteristics, types, and examples. We will also learn how hypothesis helps in scientific research.

What is Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a suggested idea or plan that has little proof, meant to lead to more study. It’s mainly a smart guess or suggested answer to a problem that can be checked through study and trial. In science work, we make guesses called hypotheses to try and figure out what will happen in tests or watching. These are not sure things but rather ideas that can be proved or disproved based on real-life proofs. A good theory is clear and can be tested and found wrong if the proof doesn’t support it.
Hypothesis Meaning
A hypothesis is a proposed statement that is testable and is given for something that happens or observed.
- It is made using what we already know and have seen, and it’s the basis for scientific research.
- A clear guess tells us what we think will happen in an experiment or study.
- It’s a testable clue that can be proven true or wrong with real-life facts and checking it out carefully.
- It usually looks like a “if-then” rule, showing the expected cause and effect relationship between what’s being studied.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some key characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable: An idea (hypothesis) should be made so it can be tested and proven true through doing experiments or watching. It should show a clear connection between things.
- Specific: It needs to be easy and on target, talking about a certain part or connection between things in a study.
- Falsifiable: A good guess should be able to show it’s wrong. This means there must be a chance for proof or seeing something that goes against the guess.
- Logical and Rational: It should be based on things we know now or have seen, giving a reasonable reason that fits with what we already know.
- Predictive: A guess often tells what to expect from an experiment or observation. It gives a guide for what someone might see if the guess is right.
- Concise: It should be short and clear, showing the suggested link or explanation simply without extra confusion.
- Grounded in Research: A guess is usually made from before studies, ideas or watching things. It comes from a deep understanding of what is already known in that area.
- Flexible: A guess helps in the research but it needs to change or fix when new information comes up.
- Relevant: It should be related to the question or problem being studied, helping to direct what the research is about.
- Empirical: Hypotheses come from observations and can be tested using methods based on real-world experiences.
Sources of Hypothesis
Hypotheses can come from different places based on what you’re studying and the kind of research. Here are some common sources from which hypotheses may originate:
- Existing Theories: Often, guesses come from well-known science ideas. These ideas may show connections between things or occurrences that scientists can look into more.
- Observation and Experience: Watching something happen or having personal experiences can lead to guesses. We notice odd things or repeat events in everyday life and experiments. This can make us think of guesses called hypotheses.
- Previous Research: Using old studies or discoveries can help come up with new ideas. Scientists might try to expand or question current findings, making guesses that further study old results.
- Literature Review: Looking at books and research in a subject can help make guesses. Noticing missing parts or mismatches in previous studies might make researchers think up guesses to deal with these spots.
- Problem Statement or Research Question: Often, ideas come from questions or problems in the study. Making clear what needs to be looked into can help create ideas that tackle certain parts of the issue.
- Analogies or Comparisons: Making comparisons between similar things or finding connections from related areas can lead to theories. Understanding from other fields could create new guesses in a different situation.
- Hunches and Speculation: Sometimes, scientists might get a gut feeling or make guesses that help create ideas to test. Though these may not have proof at first, they can be a beginning for looking deeper.
- Technology and Innovations: New technology or tools might make guesses by letting us look at things that were hard to study before.
- Personal Interest and Curiosity: People’s curiosity and personal interests in a topic can help create guesses. Scientists could make guesses based on their own likes or love for a subject.
Types of Hypothesis
Here are some common types of hypotheses:
Simple Hypothesis
Complex hypothesis, directional hypothesis.
- Non-directional Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis (H0)
Alternative hypothesis (h1 or ha), statistical hypothesis, research hypothesis, associative hypothesis, causal hypothesis.
Simple Hypothesis guesses a connection between two things. It says that there is a connection or difference between variables, but it doesn’t tell us which way the relationship goes.
Complex Hypothesis tells us what will happen when more than two things are connected. It looks at how different things interact and may be linked together.
Directional Hypothesis says how one thing is related to another. For example, it guesses that one thing will help or hurt another thing.
Non-Directional Hypothesis
Non-Directional Hypothesis are the one that don’t say how the relationship between things will be. They just say that there is a connection, without telling which way it goes.
Null hypothesis is a statement that says there’s no connection or difference between different things. It implies that any seen impacts are because of luck or random changes in the information.
Alternative Hypothesis is different from the null hypothesis and shows that there’s a big connection or gap between variables. Scientists want to say no to the null hypothesis and choose the alternative one.
Statistical Hypotheis are used in math testing and include making ideas about what groups or bits of them look like. You aim to get information or test certain things using these top-level, common words only.
Research Hypothesis comes from the research question and tells what link is expected between things or factors. It leads the study and chooses where to look more closely.
Associative Hypotheis guesses that there is a link or connection between things without really saying it caused them. It means that when one thing changes, it is connected to another thing changing.
Causal Hypothesis are different from other ideas because they say that one thing causes another. This means there’s a cause and effect relationship between variables involved in the situation. They say that when one thing changes, it directly makes another thing change.
Hypothesis Examples
Following are the examples of hypotheses based on their types:
Simple Hypothesis Example
- Studying more can help you do better on tests.
- Getting more sun makes people have higher amounts of vitamin D.
Complex Hypothesis Example
- How rich you are, how easy it is to get education and healthcare greatly affects the number of years people live.
- A new medicine’s success relies on the amount used, how old a person is who takes it and their genes.
Directional Hypothesis Example
- Drinking more sweet drinks is linked to a higher body weight score.
- Too much stress makes people less productive at work.
Non-directional Hypothesis Example
- Drinking caffeine can affect how well you sleep.
- People often like different kinds of music based on their gender.
- The average test scores of Group A and Group B are not much different.
- There is no connection between using a certain fertilizer and how much it helps crops grow.
Alternative Hypothesis (Ha)
- Patients on Diet A have much different cholesterol levels than those following Diet B.
- Exposure to a certain type of light can change how plants grow compared to normal sunlight.
- The average smarts score of kids in a certain school area is 100.
- The usual time it takes to finish a job using Method A is the same as with Method B.
- Having more kids go to early learning classes helps them do better in school when they get older.
- Using specific ways of talking affects how much customers get involved in marketing activities.
- Regular exercise helps to lower the chances of heart disease.
- Going to school more can help people make more money.
- Playing violent video games makes teens more likely to act aggressively.
- Less clean air directly impacts breathing health in city populations.
Functions of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have many important jobs in the process of scientific research. Here are the key functions of hypotheses:
- Guiding Research: Hypotheses give a clear and exact way for research. They act like guides, showing the predicted connections or results that scientists want to study.
- Formulating Research Questions: Research questions often create guesses. They assist in changing big questions into particular, checkable things. They guide what the study should be focused on.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by saying what connections between variables should be found. They set the targets that scientists try to reach with their studies.
- Testing Predictions: Theories guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By doing tests in a planned way, scientists can check if what they see matches the guesses made by their ideas.
- Providing Structure: Theories give structure to the study process by arranging thoughts and ideas. They aid scientists in thinking about connections between things and plan experiments to match.
- Focusing Investigations: Hypotheses help scientists focus on certain parts of their study question by clearly saying what they expect links or results to be. This focus makes the study work better.
- Facilitating Communication: Theories help scientists talk to each other effectively. Clearly made guesses help scientists to tell others what they plan, how they will do it and the results expected. This explains things well with colleagues in a wide range of audiences.
- Generating Testable Statements: A good guess can be checked, which means it can be looked at carefully or tested by doing experiments. This feature makes sure that guesses add to the real information used in science knowledge.
- Promoting Objectivity: Guesses give a clear reason for study that helps guide the process while reducing personal bias. They motivate scientists to use facts and data as proofs or disprovals for their proposed answers.
- Driving Scientific Progress: Making, trying out and adjusting ideas is a cycle. Even if a guess is proven right or wrong, the information learned helps to grow knowledge in one specific area.
How Hypothesis help in Scientific Research?
Researchers use hypotheses to put down their thoughts directing how the experiment would take place. Following are the steps that are involved in the scientific method:
- Initiating Investigations: Hypotheses are the beginning of science research. They come from watching, knowing what’s already known or asking questions. This makes scientists make certain explanations that need to be checked with tests.
- Formulating Research Questions: Ideas usually come from bigger questions in study. They help scientists make these questions more exact and testable, guiding the study’s main point.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by stating what we think will happen between different things. They set the goals that scientists want to reach by doing their studies.
- Designing Experiments and Studies: Assumptions help plan experiments and watchful studies. They assist scientists in knowing what factors to measure, the techniques they will use and gather data for a proposed reason.
- Testing Predictions: Ideas guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By checking these guesses carefully, scientists can see if the seen results match up with what was predicted in each hypothesis.
- Analysis and Interpretation of Data: Hypotheses give us a way to study and make sense of information. Researchers look at what they found and see if it matches the guesses made in their theories. They decide if the proof backs up or disagrees with these suggested reasons why things are happening as expected.
- Encouraging Objectivity: Hypotheses help make things fair by making sure scientists use facts and information to either agree or disagree with their suggested reasons. They lessen personal preferences by needing proof from experience.
- Iterative Process: People either agree or disagree with guesses, but they still help the ongoing process of science. Findings from testing ideas make us ask new questions, improve those ideas and do more tests. It keeps going on in the work of science to keep learning things.
People Also View:
Mathematics Maths Formulas Branches of Mathematics
Summary – Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a testable statement serving as an initial explanation for phenomena, based on observations, theories, or existing knowledge. It acts as a guiding light for scientific research, proposing potential relationships between variables that can be empirically tested through experiments and observations. The hypothesis must be specific, testable, falsifiable, and grounded in prior research or observation, laying out a predictive, if-then scenario that details a cause-and-effect relationship. It originates from various sources including existing theories, observations, previous research, and even personal curiosity, leading to different types, such as simple, complex, directional, non-directional, null, and alternative hypotheses, each serving distinct roles in research methodology. The hypothesis not only guides the research process by shaping objectives and designing experiments but also facilitates objective analysis and interpretation of data, ultimately driving scientific progress through a cycle of testing, validation, and refinement.
FAQs on Hypothesis
What is a hypothesis.
A guess is a possible explanation or forecast that can be checked by doing research and experiments.
What are Components of a Hypothesis?
The components of a Hypothesis are Independent Variable, Dependent Variable, Relationship between Variables, Directionality etc.
What makes a Good Hypothesis?
Testability, Falsifiability, Clarity and Precision, Relevance are some parameters that makes a Good Hypothesis
Can a Hypothesis be Proven True?
You cannot prove conclusively that most hypotheses are true because it’s generally impossible to examine all possible cases for exceptions that would disprove them.
How are Hypotheses Tested?
Hypothesis testing is used to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis by using sample data
Can Hypotheses change during Research?
Yes, you can change or improve your ideas based on new information discovered during the research process.
What is the Role of a Hypothesis in Scientific Research?
Hypotheses are used to support scientific research and bring about advancements in knowledge.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- Geeks Premier League 2023
- Maths-Class-12
- Geeks Premier League
- Mathematics
- School Learning
- How to Use ChatGPT with Bing for Free?
- 7 Best Movavi Video Editor Alternatives in 2024
- How to Edit Comment on Instagram
- 10 Best AI Grammar Checkers and Rewording Tools
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Research Hypothesis – Types, Examples Characteristics, and Sources
Research hypothesis.
A research hypothesis is referred to as a scientific hypothesis. This is a clear, specific, and testable statement that predicts the expected result in a scientific study. It is a prediction, reasonable guess, and logical supposition about the relationship between the variables. A research hypothesis is an integral and central part of research whether it is exploratory or explanatory, qualitative or quantitative. It creates the base of scientific experiments. So, you must be very careful while building any hypothesis.
A hypothesis can be correct or wrong. It is tested through experiments or research to determine whether it is correct or incorrect.
Functions of research hypothesis
There are major functions of research hypothesis that are as follow:
- It helps in making observations and experiments possible.
- It is the basic point for the research.
- It verifies the observations.
- It leads the inquiries in the right regulation.
- It provides the extension of knowledge.
- It helps to explore different aspects of the research.
- It introduces different research techniques.
- It ensures the precision and accuracy of the results of the research.
- It enables the researcher to be focused. Because without a hypothesis, he may focus on unnecessary aspects and wastes his resources like time, money, and effort.
Sources of hypothesis
Following are the sources of the hypothesis:
- Scientific theories
- Personal experience
- Observation
- Imagination and thinking
- Previous study
- General patterns
Characteristics of an effective research hypothesis
Following are the characteristics of an effective research hypothesis:
- It must be logical.
- It must be simple and clear.
- It needs to be precise.
- It must identify the research objectives.
- It must be empirically testable with experimentation and research.
- It must be manageable.
- It must be relevant and specific to the theme of the research.
- It must be predictable.
- It must be falsifiable.
- It must be neither specific nor general.
- It must be considered valuable even if it proves false.
Types of research hypothesis
Following are the types of research hypotheses.
- Simple hypothesis
It shows a relationship between a single dependent variable and an independent variable. For instance, if you take in more carbs and fats, you will gain obesity. Here taking more carbs and fats are an independent variable and gaining weight is the dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between two or more independent variables and dependent variables. For example, we can say that taking in more carbs and fats can cause obesity along with other problems like high blood pressure, heart disease, and so on.
- Directional hypothesis
Typically, directional hypotheses are derived from theory. This type of hypothesis shows the researcher’s intellectual commitment towards a specific outcome. The researcher predicts the existence and nature of a relationship between variables.
- Non-directional hypothesis
The non-directional hypothesis is used when there is no theory and the findings of studies are contradictory. It shows the relationship between two variables but does not set down the expected direction or nature of the relationship.
- Null hypothesis
Null hypotheses are made when there is no empirical and adequate theoretical information to show a hypothesis. The null hypothesis negates the relationship between variables. It is denoted by Ho. This hypothesis is made when the researcher wants to reject or disapprove the null hypothesis. It is contrary to what an experimenter or investigator expects. The purpose is to confirm the existence of a relationship between the variables.
The null hypothesis can be:
- Associative or causal
- Simple or complex
1. Alternative hypothesis
When a hypothesis is rejected, then another hypothesis is made to be tested and show the desired results. This is called an alternative hypothesis. It is opposite to the null hypothesis and is made to disprove that hypothesis. This hypothesis is denoted by H1.
2. Statistical hypothesis
As the name mentions, this hypothesis has the quality to be verified statistically. It is tested by using quantitative techniques. The variables in this hypothesis are quantifiable and can also transform into quantifiable indicators to verify it statistically.
- Empirical hypothesis
This hypothesis is used when a theory is tested with observation and experiment. It is just a notion or idea. This hypothesis goes through trial and error by changing independent variables. The series of trial and error helps to find the best result. The outcomes of these experiments can be proven over time.
- Associative and causal hypothesis
The associative hypothesis shows interdependency between variables. Any change in one variable causes the change in another variable. Whereas, the causal hypothesis shows a cause and effect between variables.
How to formulate a research hypothesis
There are some important points you must consider while formulating a hypothesis:
- Ask a question
The first and foremost thing for creating a research hypothesis is to generate a research question. The question should be specific, focused, and researchable within the limitations of your project.
- Do preliminary research
Now try to find the answer to your question. The initial answer must be based on previous knowledge about the topic. Concern theories and previous studies and try to form assumptions about what you will find in your research.
Create a conceptual framework about different variables you are going to study and the relationships between them.
- Formulate the hypothesis
Now you have an idea of what you are expecting to find. Make a clear and concise answer to the question.
- Refine your hypothesis
Now check whether your hypothesis is testable. There must be clear definitions of your hypothesis while phrasing. It should contain:
- The relevant variables
The particular group being studied.
The predicted result of the analysis or experiment
- Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To recognize the variables, write a prediction in (if-then) form. Like, if a particular action is taken, a certain result is expected. The first part of the phrase shows the independent variable while the second part shows the dependent variable.
- Write a null hypothesis
If the research requires statistical hypothesis testing, you must have to make a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis.
Now test your hypothesis through observations, techniques, and experiments by keeping necessary things and resources in consideration.
Related Posts:
- Correlational Research Design [Examples, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages, Characteristics]
- Which of the following is the first step in hypothesis testing?
- Which of the following is considered one of the earliest literary sources in human history?
- Sources of Islamic law (Islamic Study) MCQs
- Quantitative research Examples, Methods, Characteristics, Advantages, Disadvantages
- Hierarchical Model with examples and characteristics
You must be logged in to post a comment.
A hypothesis (plural hypothesis) is a proposed clarification for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be logical speculation. These are the logical strategy necessitate that one can test it. Researchers for the most part base logical hypothesis on past perceptions that can’t sufficiently be clarified with the accessible logical hypothesis.
Despite the fact that the word “hypothesis” is regularly in use. Equivalently, a logical hypothesis isn’t equivalent to a scientific hypothesis. A working hypothesis is a temporarily acknowledged hypothesis proposed for additional exploration, in a cycle starting with an informed estimate or thought.

Hypothesis
In its antiquated utilization, hypothesis alluded to an outline of the plot of an old-style dramatization. The English word hypothesis comes from the antiquated Greek word hypothesis. Its exacting or etymological sense is “putting or setting under”. Henceforth in broad use has numerous different implications including “assumption”.
In Common Utilization
In common utilization, a hypothesis alludes to a temporary thought whose legitimacy requires assessment. For legitimate assessment, the composer of a hypothesis needs to characterize particulars in operational terms. A hypothesis requires more work by the scientist to either affirm or negate it. At the appointed time, an affirmed hypothesis may turn out to be important for a hypothesis. At times may develop to turn into a hypothesis itself.
Regularly, a logical hypothesis has the type of numerical model. Sometimes, however not generally, one can likewise plan them as existential proclamations. Expressing that some specific case of the phenomenon under assessment has some trademark and causal clarifications. This has the overall type of explanations, expressing that each case of the specific trademark.
In Innovative Science
In innovative science, a hypothesis is useful to define temporary thoughts inside a business setting. The figured hypothesis is then assessed where either the hypothesis is demonstrated to be “valid” or “bogus”. It is through an undeniable nature or falsifiability-arranged test.
Any valuable hypothesis will empower forecasts by thinking (counting deductive thinking). It may foresee the result of an analysis in a research centre setting or the perception of wonder in nature. The forecast may likewise conjure measurements and just discussion about probabilities. Karl Popper, following others, has contended that a hypothesis must be falsifiable. One can’t view a suggestion or hypothesis as logical on the off chance that it doesn’t concede the chance of being indicated bogus. Different thinkers of science have dismissed the model of falsifiability or enhanced it with other measures.
For example, undeniable nature for e.g., verificationism or soundness like affirmation comprehensive quality. The logical technique includes experimentation, to test the capacity of some hypothesis to satisfactorily address the inquiry under scrutiny. Conversely, liberated perception isn’t as liable to bring up unexplained issues or open issues in science. As it would the plan of a pivotal trial to test the hypothesis. A psychological test may likewise be utilized to test the hypothesis too.
In outlining a hypothesis, the examiner must not right now know the result of a test. It remains sensibly under proceeding with examination. Just in such cases does the analysis, test or study conceivably increment the likelihood of indicating the reality of a hypothesis.
If the specialist definitely knows the result, it considers an “outcome”. The scientist ought to have just thought about this while detailing the hypothesis. On the off chance that one can’t survey the expectations by perception or by experience. The hypothesis should be tried by others giving perceptions. For instance, another innovation or hypothesis may make the essential trials practical.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Following are the characteristics of the hypothesis:
- The theory ought to be clear and exact to believe it to be solid.
- If the hypothesis is a social theory, at that point it ought to express the connection between factors.
- The theory must be explicit and ought to have scope for leading more tests.
- The method of clarification of the theory must be basic and it should likewise be perceived that the straightforwardness of the hypothesis isn’t identified with its essentialness.
Sources of Hypothesis
Following are the sources of the hypothesis:
- The likeness between the wonder.
- Observations from past investigations, present-day encounters and from the contenders.
- Scientific hypothesis.
- General designs that impact the considering cycle individuals.
Types of Hypothesis
There are six forms of the hypothesis and they are:
- Simple hypothesis
- Complex hypothesis
- Directional hypothesis
- Non-directional hypothesis
- Null hypothesis
- Associative and casual hypothesis
Simple Hypothesis
It shows a connection between one ward variable and a solitary autonomous variable. For instance, If you eat more vegetables, you will get in shape quicker. Here, eating more vegetables is a free factor, while getting more fit is the needy variable.
Complex Hypothesis
It shows the connection between at least two ward factors and at least two autonomous factors. Eating more vegetables and natural products prompts weight reduction. May be sparkling skin, diminishes the danger of numerous infections, for example, coronary illness, hypertension and a few diseases.
Directional Hypothesis
It shows how an analyst is scholarly and focused on a specific result. The connection between the factors can likewise foresee its inclination. For instance, kids matured four years eating appropriate food over a five-year time frame are having higher IQ levels than youngsters not having a legitimate dinner. This shows the impact and course of impact.
Non-directional Hypothesis
It is utilized when there is no theory included. It is an explanation that a relationship exists between two factors, without foreseeing the specific nature (course) of the relationship.
Null Hypothesis
It gives the explanation which is in opposition to the theory. It’s a negative assertion, and there is no connection between autonomous and subordinate factors. The image is indicated by “HO”.
Associative and Causal Hypothesis
Acquainted hypothesis happens when there is an adjustment in one variable bringing about an adjustment in the other variable. Though, the causal hypothesis proposes a circumstances and logical results connection between at least two factors.
Examples of Hypothesis
Following are the examples of the hypothesis according to their types:
- Consumption of sweet beverages consistently prompts weight is a case of a straightforward theory.
- All lilies have a similar number of petals is a case of an invalid hypothesis.
- If an individual gets 7 hours of rest, at that point he will feel less weakness than if he dozens less.
FAQs about Hypothesis
Q.1. Write a short note on the term hypothesis.
Answer: A hypothesis (plural hypothesis) is a proposed clarification for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be logical speculation. The logical strategy necessitates that one can test it. Researchers for the most part base logical hypothesis on past perceptions that can’t sufficiently be clarified with the accessible logical hypotheses. Despite the fact that the words “hypothesis” and “hypothesis” are regularly utilized equivalently, a logical hypothesis isn’t equivalent to a scientific hypothesis.
Q.2. What are the functions of the Hypothesis?
Answer: Following are the functions performed by the hypothesis:
- Hypothesis helps in mentioning an objective fact and tests conceivable.
- It turns into the beginning point for the formal examination.
- Hypothesis helps in checking the perceptions.
- It helps in coordinating the requests in the correct ways.
Q.3. How will Hypothesis help in Scientific Method?
Answer: Scientists use theory to put down their considerations coordinating how the test would happen. Following are the means that are engaged with the logical strategy:
- Formation of inquiry
- Doing foundation research
- Creation of hypothesis
- Designing an investigation
- Collection of information
- Result examination
- Summarizing the trial
- Communicating the outcomes
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Statistical Physics
- Physics Diagrams
- Constants In Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Electron Spin
- Bridge Construction
- Physics Symbols
- Murphy’s Law
- Difference Between in Physics
2 responses to “Difference Between in Physics”
I want to prepare for nda
I want to prepare physics for x group exam
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Following are the characteristics of the hypothesis: The hypothesis should be clear and precise to consider it to be reliable. If the hypothesis is a relational hypothesis, then it should be stating the relationship between variables. The hypothesis must be specific and should have scope for conducting more tests.
Here are some good research hypothesis examples: "The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.". "Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.".
scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world.The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If…then" statement summarizing the idea and in the ability to be supported or refuted through observation and experimentation.
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
7. Statistical hypothesis. The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like "44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27." leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement. Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis. There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you'll recall Popper's falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm ...
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis. There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you'll recall Popper's falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm ...
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis. There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you'll recall Popper's falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm ...
A good hypothesis has the following characteristics. Ability To Predict One of the most valuable qualities of a good hypothesis is the ability to anticipate the future. It not only clarifies the current problematic scenario, but also predicts what will happen in the future. As a result of the predictive capacity, hypothesis is the finest ...
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis. There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you'll recall Popper's falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm ...
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
A hypothesis is a logical construct, interposed between a problem and its solution, which represents a proposed answer to a research question. ... As indicated earlier, one of the characteristics of a hypothesis that sets it apart from other types of statements is that it is testable. The hypotheses discussed thus far are conceptual. A ...
Simple hypothesis: This type of hypothesis suggests that there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.; Complex hypothesis: This type of hypothesis suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent variables and a dependent variable.; Null hypothesis: This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a 'if-then' structure. 3.
One of the experts in the field defines "hypothesis" as a well-argued analysis of available evidence to provide a realistic (scientific) explanation of existing facts, fill gaps in public understanding of sophisticated processes, and propose a new theory or a test.4 A hypothesis can be proven wrong partially or entirely. However, even such ...
A hypothesis is a foundational element in scientific research, serving as a tentative explanation or prediction that guides the direction of study and experimentation. It's a statement that proposes a possible reason for a phenomenon or a potential relationship between variables that can be tested through research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis. Here are some key characteristics of a hypothesis: Testable: An idea (hypothesis) should be made so it can be tested and proven true through doing experiments or watching. It should show a clear connection between things.
A research hypothesis is referred to as a scientific hypothesis. This is a clear, specific, and testable statement that predicts the expected result in a scientific study. It is a prediction, reasonable guess, and logical supposition about the relationship between the variables. A research hypothesis is an integral and central part of research ...
A researcher's hypothesis is a formal question that he intends to resolve. Some of the characteristics of the hypothesis are being: Hypothesis should be clear and precise. If the hypothesis is not clear and precise, the inferences drawn on its basis cannot be taken as reliable. Hypothesis should be capable of being tested.
Characteristics of Hypothesis. Following are the characteristics of the hypothesis: The theory ought to be clear and exact to believe it to be solid. If the hypothesis is a social theory, at that point it ought to express the connection between factors. The theory must be explicit and ought to have scope for leading more tests.
The various types of Hypothesis are-. 1. Simple Hypothesis. Simple Hypothesis defines the relation between the two variables such as independent and dependent variables. For example - If you exercise, you will lose weight faster. Here, exercising is an independent variable, while losing weight is the dependent variable. 2.
Second hypothesis: Risk and return characteristics differ among segregated periods. To empirically establish the presence of aggregation bias, equality between the means and variances of the segregated periods (1990-2000, 2001-2010, and 2011-2020) and the aggregated period is tested. This is shown in Table 14.