Essay Writing Guide
Essay Outline
Last updated on: Jun 10, 2023

A Complete Essay Outline - Guidelines and Format
By: Nova A.
13 min read
Reviewed By: Melisa C.
Published on: Jan 15, 2019

To write an effective essay, you need to create a clear and well-organized essay outline. An essay outline will shape the essay’s entire content and determine how successful the essay will be.
In this blog post, we'll be going over the basics of essay outlines and provide a template for you to follow. We will also include a few examples so that you can get an idea about how these outlines look when they are put into practice.
Essay writing is not easy, but it becomes much easier with time, practice, and a detailed essay writing guide. Once you have developed your outline, everything else will come together more smoothly.
The key to success in any area is preparation - take the time now to develop a solid outline and then write your essays!
So, let’s get started!

On this Page
What is an Essay Outline?
An essay outline is your essay plan and a roadmap to essay writing. It is the structure of an essay you are about to write. It includes all the main points you have to discuss in each section along with the thesis statement.
Like every house has a map before it is constructed, the same is the importance of an essay outline. You can write an essay without crafting an outline, but you may miss essential information, and it is more time-consuming.
Once the outline is created, there is no chance of missing any important information. Also, it will help you to:
- Organize your thoughts and ideas.
- Understand the information flow.
- Never miss any crucial information or reference.
- Finish your work faster.
These are the reasons if someone asks you why an essay outline is needed. Now there are some points that must be kept in mind before proceeding to craft an essay outline.

Easily Outline Your Essays In Seconds!
Prewriting Process of Essay Outline
Your teacher may ask you to submit your essay outline before your essay. Therefore, you must know the preliminary guidelines that are necessary before writing an essay outline.
Here are the guidelines:
- You must go through your assignments’ guidelines carefully.
- Understand the purpose of your assignment.
- Know your audience.
- Mark the important point while researching your topic data.
- Select the structure of your essay outline; whether you are going to use a decimal point bullet or a simple one.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How to Write an Essay Outline in 4 Steps
Creating an essay outline is a crucial step in crafting a well-structured and organized piece of writing. Follow these four simple steps to create an effective outline:
Step 1: Understand the Topic
To begin, thoroughly grasp the essence of your essay topic.
Break it down into its key components and identify the main ideas you want to convey. This step ensures you have a clear direction and focus for your essay.
Step 2: Brainstorm and Gather Ideas
Let your creativity flow and brainstorm ideas related to your topic.
Jot down key pieces of information, arguments, and supporting evidence that will strengthen your essay's overall message. Consider different perspectives and potential counterarguments to make your essay well-rounded.
Step 3: Organize Your Thoughts
Now it's time to give structure to your ideas.
Arrange your main points in a logical order, starting with an attention-grabbing introduction, followed by body paragraphs that present your arguments.
Finally, tie everything together with a compelling conclusion. Remember to use transitional phrases to create smooth transitions between sections.
Step 4: Add Depth with Subpoints
To add depth and clarity to your essay, incorporate subpoints under each main point.
These subpoints provide more specific details, evidence, or examples that support your main ideas. They help to further strengthen your arguments and make your essay more convincing.
By following these four steps - you'll be well on your way to creating a clear and compelling essay outline.
Essay Outline Format
It is an easy way for you to write your thoughts in an organized manner. It may seem unnecessary and unimportant, but it is not.
It is one of the most crucial steps for essay writing as it shapes your entire essay and aids the writing process.
An essay outline consists of three main parts:
1. Introduction
The introduction body of your essay should be attention-grabbing. It should be written in such a manner that it attracts the reader’s interest. It should also provide background information about the topic for the readers.
You can use a dramatic tone to grab readers’ attention, but it should connect the audience to your thesis statement.
Here are some points without which your introduction paragraph is incomplete.
To attract the reader with the first few opening lines, we use a hook statement. It helps engage the reader and motivates them to read further. There are different types of hook sentences ranging from quotes, rhetorical questions to anecdotes and statistics, and much more.
Are you struggling to come up with an interesting hook? View these hook examples to get inspired!
A thesis statement is stated at the end of your introduction. It is the most important statement of your entire essay. It summarizes the purpose of the essay in one sentence.
The thesis statement tells the readers about the main theme of the essay, and it must be strong and clear. It holds the entire crux of your essay.
Need help creating a strong thesis statement? Check out this guide on thesis statements and learn to write a statement that perfectly captures your main argument!
2. Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs of an essay are where all the details and evidence come into play. This is where you dive deep into the argument, providing explanations and supporting your ideas with solid evidence.
If you're writing a persuasive essay, these paragraphs will be the powerhouse that convinces your readers. Similarly, in an argumentative essay, your body paragraphs will work their magic to sway your audience to your side.
Each paragraph should have a topic sentence and no more than one idea. A topic sentence is the crux of the contents of your paragraph. It is essential to keep your reader interested in the essay.
The topic sentence is followed by the supporting points and opinions, which are then justified with strong evidence.
3. Conclusion
When it comes to wrapping up your essay, never underestimate the power of a strong conclusion. Just like the introduction and body paragraphs, the conclusion plays a vital role in providing a sense of closure to your topic.
To craft an impactful conclusion, it's crucial to summarize the key points discussed in the introduction and body paragraphs. You want to remind your readers of the important information you shared earlier. But keep it concise and to the point. Short, powerful sentences will leave a lasting impression.
Remember, your conclusion shouldn't drag on. Instead, restate your thesis statement and the supporting points you mentioned earlier. And here's a pro tip: go the extra mile and suggest a course of action. It leaves your readers with something to ponder or reflect on.
5 Paragraph Essay Outline Structure
An outline is an essential part of the writing as it helps the writer stay focused. A typical 5 paragraph essay outline example is shown here. This includes:
- State the topic
- Thesis statement
- Introduction
- Explanation
- A conclusion that ties to the thesis
- Summary of the essay
- Restate the thesis statement
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Essay Outline Template
The outline of the essay is the skeleton that you will fill out with the content. Both outline and relevant content are important for a good essay. The content you will add to flesh out the outline should be credible, relevant, and interesting.
The outline structure for the essay is not complex or difficult. No matter which type of essay you write, you either use an alphanumeric structure or a decimal structure for the outline.
Below is an outline sample that you can easily follow for your essay.
Essay Outline Sample
Essay Outline Examples
An essay outline template should follow when you start writing the essay. Every writer should learn how to write an outline for every type of essay and research paper.
Essay outline 4th grade
Essay outline 5th grade
Essay outline high school
Essay outline college
Given below are essay outline examples for different types of essay writing.
Argumentative Essay Outline
An argumentative essay is a type of essay that shows both sides of the topic that you are exploring. The argument that presents the basis of the essay should be created by providing evidence and supporting details.
Persuasive Essay Outline
A persuasive essay is similar to an argumentative essay. Your job is to provide facts and details to create the argument. In a persuasive essay, you convince your readers of your point of view.
Compare and Contrast Essay Outline
A compare and contrast essay explains the similarities and differences between two things. While comparing, you should focus on the differences between two seemingly similar objects. While contrasting, you should focus on the similarities between two different objects.
Narrative Essay Outline
A narrative essay is written to share a story. Normally, a narrative essay is written from a personal point of view in an essay. The basic purpose of the narrative essay is to describe something creatively.
Expository Essay Outline
An expository essay is a type of essay that explains, analyzes, and illustrates something for the readers. An expository essay should be unbiased and entirely based on facts. Be sure to use academic resources for your research and cite your sources.
Analytical Essay Outline
An analytical essay is written to analyze the topic from a critical point of view. An analytical essay breaks down the content into different parts and explains the topic bit by bit.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
A rhetorical essay is written to examine the writer or artist’s work and develop a great essay. It also includes the discussion.
Cause and Effect Essay Outline
A cause and effect essay describes why something happens and examines the consequences of an occurrence or phenomenon. It is also a type of expository essay.
Informative Essay Outline
An informative essay is written to inform the audience about different objects, concepts, people, issues, etc.
The main purpose is to respond to the question with a detailed explanation and inform the target audience about the topic.
Synthesis Essay Outline
A synthesis essay requires the writer to describe a certain unique viewpoint about the issue or topic. Create a claim about the topic and use different sources and information to prove it.
Literary Analysis Essay Outline
A literary analysis essay is written to analyze and examine a novel, book, play, or any other piece of literature. The writer analyzes the different devices such as the ideas, characters, plot, theme, tone, etc., to deliver his message.
Definition Essay Outline
A definition essay requires students to pick a particular concept, term, or idea and define it in their own words and according to their understanding.
Descriptive Essay Outline
A descriptive essay is a type of essay written to describe a person, place, object, or event. The writer must describe the topic so that the reader can visualize it using their five senses.
Evaluation Essay Outline
Problem Solution Essay Outline
In a problem-solution essay, you are given a problem as a topic and you have to suggest multiple solutions on it.
Scholarship Essay Outline
A scholarship essay is required at the time of admission when you are applying for a scholarship. Scholarship essays must be written in a way that should stand alone to help you get a scholarship.
Reflective Essay Outline
A reflective essay is written to express your own thoughts and point of view regarding a specific topic.
Getting started on your essay? Give this comprehensive essay writing guide a read to make sure you write an effective essay!
With this complete guide, now you understand how to create an outline for your essay successfully. However, if you still can’t write an effective essay, then the best option is to consult a professional academic writing service.
Essay writing is a dull and boring task for some people. So why not get some help instead of wasting your time and effort? 5StarEssays.com is here to help you. All your do my essay for me requests are managed by professional essay writers.
Place your order now, and our team of expert academic writers will help you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three types of outlines.
Here are the three types of essay outline;
- Working outline
- Speaking outline
- Full-sentence outline
All three types are different from each other and are used for different purposes.
What does a full-sentence outline look like?
A full sentence outline contains full sentences at each level of the essay’s outline. It is similar to an alphanumeric outline and it is a commonly used essay outline.
What is a traditional outline format?
A traditional essay outline begins with writing down all the important points in one place and listing them down and adding sub-topics to them. Besides, it will also include evidence and proof that you will use to back your arguments.
What is the benefit of using a traditional outline format and an informal outline format?
A traditional outline format helps the students in listing down all the important details in one palace while an informal outline will help you coming up with new ideas and highlighting important points

As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- How to Write an Essay - A Complete Guide with Examples

- The Art of Effective Writing: Thesis Statements Examples and Tips

- Writing a 500 Word Essay - Easy Guide

- What is a Topic Sentence - An Easy Guide with Writing Steps & Examples

- 220 Best Transition Words for Essays

- Essay Format: Detailed Writing Tips & Examples

- How to Write a Conclusion - Examples & Tips

- Essay Topics: 100+ Best Essay Topics for your Guidance

- How to Title an Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide for Effective Titles

- How to Write a Perfect 1000 Word Essay

- How To Make An Essay Longer - Easy Guide For Beginners

- Learn How to Start an Essay Effectively with Easy Guidelines

- Types of Sentences With Examples

- Hook Examples: How to Start Your Essay Effectively

- Essay Writing Tips - Essential Do’s and Don’ts to Craft Better Essays

- How To Write A Thesis Statement - A Step by Step Guide

- Art Topics - 200+ Brilliant Ideas to Begin With

- Writing Conventions and Tips for College Students

People Also Read
- persuasive speech topics
- process analysis essay topics
- research paper outline
- rhetorical analysis essay example
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
How to Write an Essay Outline?
28 August, 2020
8 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
Now that the school year has begun, you will start to receive many essay assignments. One way to organize your thoughts before writing is to create an essay outline. What is an essay outline? It's a tool that helps you organize your ideas and write a better essay. In this article, we will discuss why writing an outline for your essay is helpful, how it will improve your writing, and how to go about creating one.

What is an Essay Outline?
An outline is a tool that you can use for organizing your ideas and structuring your essay in a proper manner. It should summarize your essay and help you organize your content in a logical order. An outline can guide you throughout the writing process and remind you of what you should be writing about. Most commonly, an essay is written following a 5-paragraph structure, addressing the key points that you have laid out in the outline. Below, you will find more about the proper structure of your essay outline and what these 5 paragraphs should include.
Why Do You Need It?
Sitting down to write an essay can be overwhelming. Writing an outline helps alleviate some of that frustration. Furthermore, it will help you organize thoughts, present ideas logically and with a natural flow, as well as clarify your thesis and conclusion.
Find out the basic essay information with this article: What is an Essay?
Overall, an outline will help you communicate your point in a clear and organized format. The structure of your essay will rely on the outline you compose.
Preparing Your Outline
Before you begin writing an outline for the essay, make sure you understand the assignment. Namely, what exactly is the instructor looking for? Our essay writer recommends you to follow these simple steps:
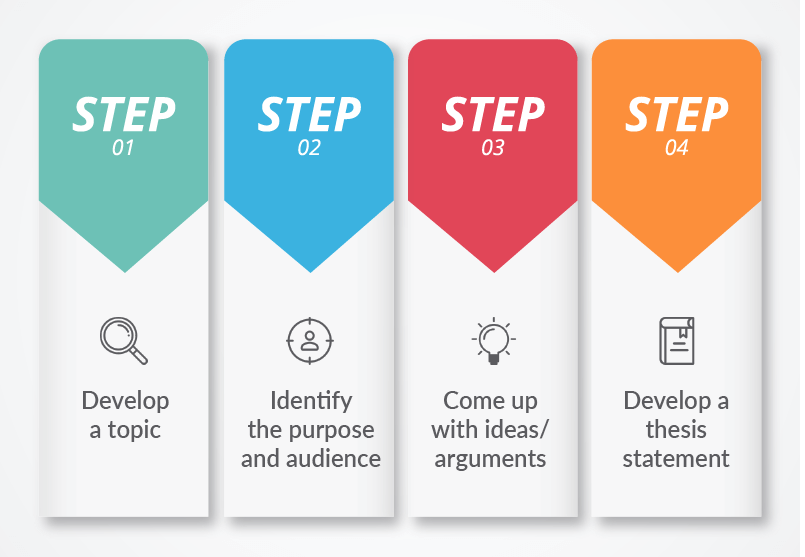
1. Develop a Topic
The first step in your outline is to identify your topic. Once you have a clear understanding of the instructor’s expectations, begin brainstorming topics that fit within the assignment. Make a list of ideas and pick the ones that are of your interest. If you are stuck between a few ideas, begin free writing. Give yourself 5 minutes for each idea and just write everything that first comes to mind without editing or stopping. The idea that inspires you the most may just be the perfect essay topic for this assignment. In fact, essays are easier to write and read if the author is passionate about what he/she is writing.
Related Posts: Argumentative essay topics | Compare&Contrast essay topics
2. Identify the purpose, audience, and argument/ideas
Once you have developed a topic, you will need to define the purpose (or the reason) for writing this essay as well as who you are writing for. By having a clear understanding of the purpose, the audience, and the necessary arguments/ideas that need to be addressed, you will be better prepared to write an influential essay.
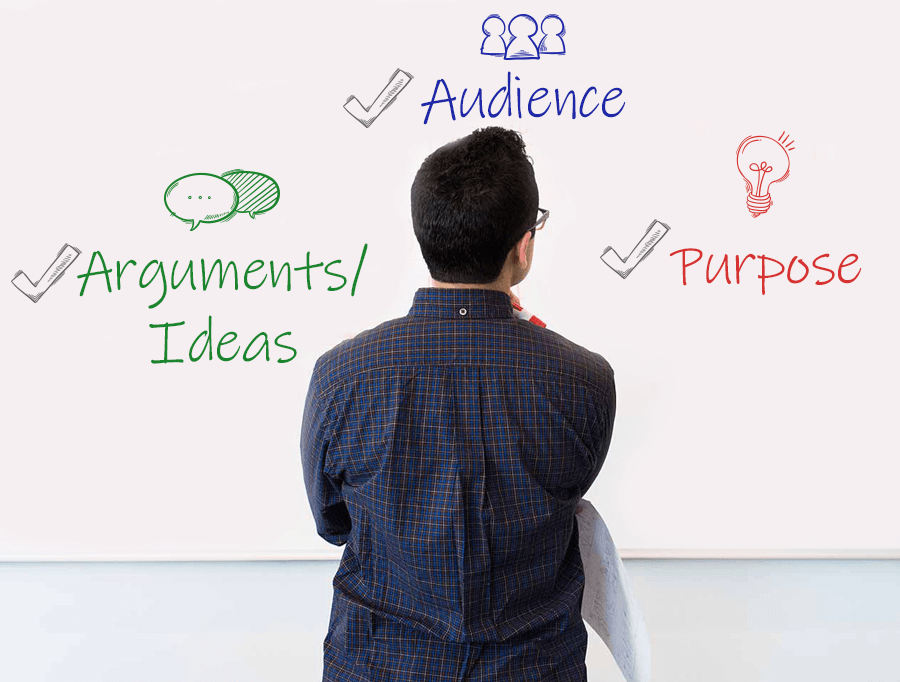
Take a second to look back over the instructions for the assignment and ask yourself the following questions.
- What are the objectives of the assignment?
- Are there keywords that stand out in the instructions?
- Are you being asked to persuade, entertain, enlighten, or educate your audience?
- Who is your audience? Is it the teacher, the other students, or someone else?
- What arguments or counter ideas might the audience have for your topic/idea?
- What emotions might these ideas bring up and how can you counterbalance them with facts?
3. Develop a thesis statement
Now that you know your topic, purpose, audience and have developed your main arguments/ideas – it is time to write your thesis statement . A thesis is only one to two sentences long and highlights the question your essay will be answering. It does not state your opinion or list facts though, but rather identifies what you will be arguing for or against within the body of your essay. Keep in mind that thesis statements must be accurate, clear, and relevant to the topic.
Structuring Your Outline
Now that you have read the above information, the question is: how to write an essay outline?
First, decide on what structure to use. There are two main essay outline formats to choose from: alphanumeric and decimal .
The alphanumeric format uses Roman numerals (I, II, III, IV, etc), capital letters (A, B, C, D, etc.), Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.), and lowercase letters (a, b, c, d, etc.). This one is more common than the other.
On the contrary, the decimal format only uses numbers. It begins with 1.0. Subsections add a decimal. The most important points under 1.0 would be 1.1, 1.2, etc. The subsections beneath 1.1 would be 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3, etc. For a visual example of an essay outline scroll to the bottom of this article.
For the visual examples of the stated outline formats, scroll down to the bottom of this article.
Apply sub-section structure. The more detailed content of your essay will be found within the sub-sections, while the main sections are your fundamental ideas and arguments. Therefore, the sub-sections are the facts that support main sections. Think of the section title as the topic sentence for your paragraph and the sub-section as the tiny details that explain the idea of the topic. Notably, your sub-sections need to flow naturally from one to another.
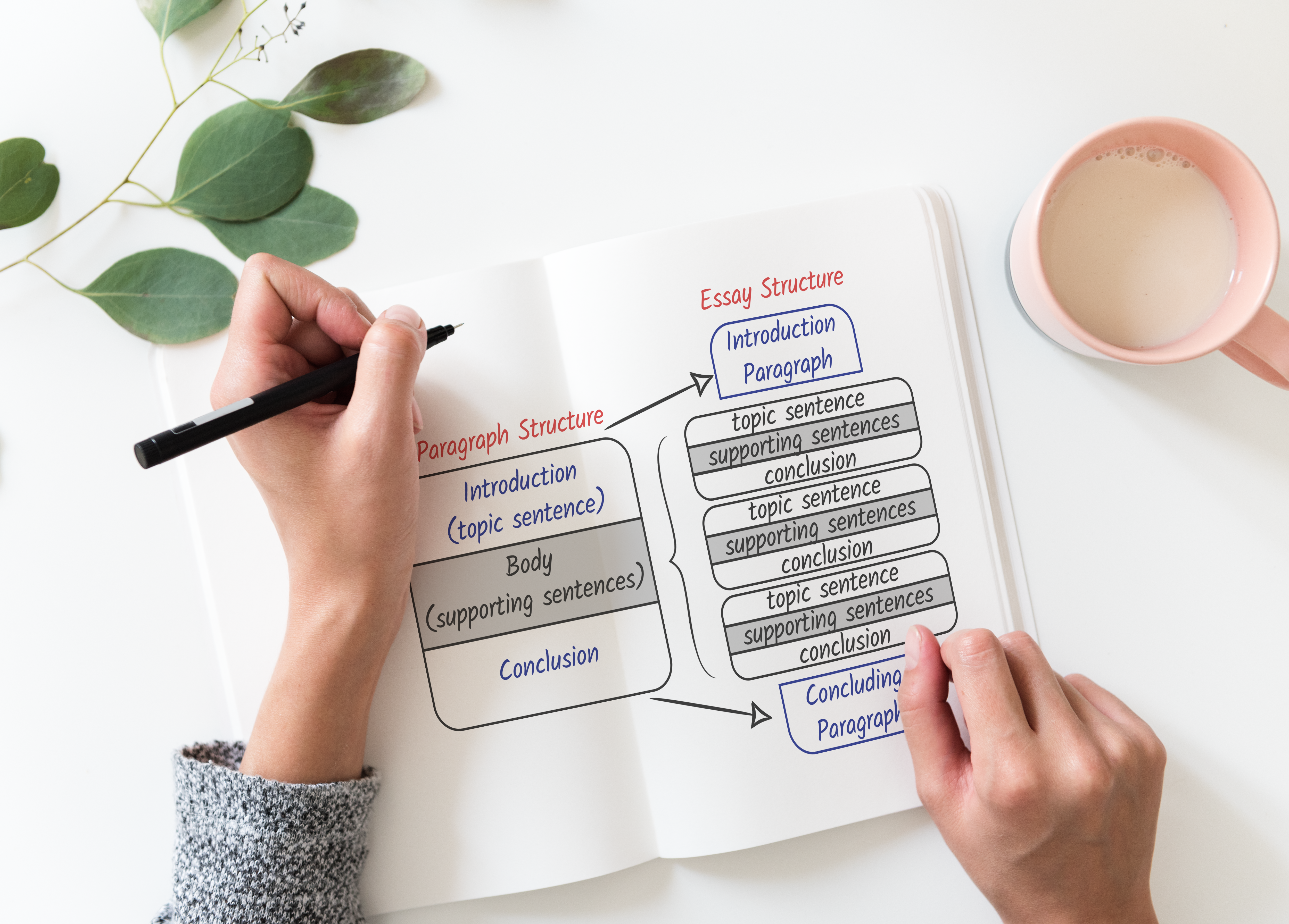
Integrate paragraphs into your outline. Start fleshing out your section and subsection notes. Your introduction will need to include your topic and thesis statement. For a short essay, this only needs to be one paragraph long. Then, refer to your assignment instructions to clarify the length. Next is the body part – a ‘skeleton’ on which the entire essay is based. This section will consist of several paragraphs, each playing a supportive role in the filling of your thesis. The final section of your outline is the conclusion. This is a summary of everything you have stated in your essay. In this part, paraphrase your thesis statement and highlight the arguments made within the essay to support it. Remember that presenting new ideas and concepts in the concluding sentences is a big academic mistake. Rather, your final words should only emphasize the points you’ve indicated earlier and focus on the already-highlighted ideas.
Essay Outline Examples
Now, it’s time to showcase the most common essay outline types. For you to get the right idea of what an outline actually is, we have transformed the content of the article you are currently reading into an outline.
Alphanumeric format essay outline sample:

Decimal format essay outline sample:

Drawing the Line
Now that you know how to use an essay outline, you are well on your way to writing clear, persuasive essays. This tool will help you improve your writing and earn a higher grade for your essay. Now it’s time for you to get started and make use of this tool.
In case you have any questions, you are free to skim through our essay writing guide where you can find helpful information on how to plan, structure and write different types of essays.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Parts of a Paper / How to Write an Essay Outline
How to Write an Essay Outline
It’s 11 p.m., your paper is due tomorrow, and you’re only about halfway done. You’re typing along and when you realize that, wait…you’re actually not a huge fan of your argument or the supporting examples you’re using. Your options are to haphazardly keep writing or to backtrack and rehash what you’ve already done. Ugh. Unsurprisingly, both options aren’t great.
This scenario is scary, but totally avoidable! Though it’s tempting to just start writing, one of the best steps you can take before you type a single word is to create an outline for your paper. By taking the time to write a paper outline, you can prevent the scenario above and make your writing process a cinch!
Guide Overview
What is a paper outline, why it’s worth writing an outline.
- Step 1: gather your relevant materials
- Step 2: create your thesis
- Step 3: find examples
- Step 4: analyze your examples
- Step 5: arrange your examples
A paper outline is a skeletal version of your paper. Another way to think about an outline is to view it as a roadmap. An outline helps you organize and streamline your thoughts ahead of time. By front loading this work, you allow the eventual writing process to be much easier: instead of having to backtrack and see if your paper makes sense, you can refer to your outline and be rest assured that you’re on the right track.
It’s understandable if you think it’s not worth the time to write an outline. After all, writing a paper in itself is a lot of work – why add an extra step?
Here’s the secret: creating an outline and then writing your paper takes about the same amount of time as jumping straight into writing your paper. Why? By immediately writing, you run the risk of having to go back and see if the flow of your paper makes sense. Backtracking takes up a lot of time: having to go back and revise your paper because you missed a point can be a pain.
Taking the time to outline your paper gives you the space to see what arguments work, which examples to include, and more. Doing this prep work ahead of time prevents you from having to do it while in the middle of your paper. Your completed outline serves as a solid reference as you write your assignment. In an ideal world, your outline should be so thorough that the writing process is essentially just you converting your bullet points into sentences that flow together!
How to outline a paper
Step 1: gather your relevant materials.
The first step to take when outlining a paper is to gather all your relevant materials. If you’re writing a paper about a book you’re reading in class, start thinking about which passages from the book are relevant to your prompt. If you’re writing a paper about a broader topic, identify what sources you’ll need to construct your argument.
Pro tip: Avoid plagiarism and keep track of the sources you’re using at EasyBib.com! Easily create an APA or MLA format citation , try out our Chicago citation generator , and find help for other citation styles.
Step 2: Create your thesis
After you’ve compiled your materials, start thinking about your thesis statement. Revisit your assignment prompt, peruse your materials, and determine what your viewpoint is regarding the prompt.
Step 3: Find examples
Once you have your thesis, come up with ways to support it. Identify the quotes you need or the arguments you want to utilize in order to bolster your thesis.
Step 4: Analyze Your Examples
Write 3-4 bullet points connecting your examples to your thesis. The analysis part of your paper is the meat of your paper, so feel free to take as much time as you want during this step.
Step 5: Arrange Your Examples
Now that you have your examples and analysis, arrange them in a logical way that helps you develop and support your thesis. This is the step in which you can start copying and pasting your notes into an outline that mimics the flow of your paper. By the end of this step, you should have a solid outline!
Here’s a template for a five paragraph essay you can use for your papers moving forward:

Before you jump into writing your paper, it might pay to take a quick look at our EasyBib grammar guides . Discover what an abstract noun is, read a determiner definition , see the difference between regular and irregular verbs , and get familiar with other parts of speech.
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Essay Outline: An Ultimate Guide
Table of contents
- 1 Understanding the Importance of Proper Essay Outline
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.3 Conclusion
- 3.1 Alphanumeric structure style
- 3.2 Decimal structure style
- 4 Steps to Creating an Outline for an Essay
- 5 Tips for a Successful Essay Outline
- 6.1 Template for a Narrative Essay Outline
- 6.2 Template of Argumentative Essay Outline
- 6.3 Template of Compare and Contrast Essay Outline
- 6.4 Template of Admission Essay Outline
- 7 Benefits of the Essay Outline in the Writing Process
- 8 Elevate Your Essay Writing with Outline
Have you ever felt like your thoughts are all over the place when you write an essay, or do you just want to make the essay writing a breeze? Well, you have hit the right spot!
In this article, we will break down how to write an outline for an essay into simple, easy-to-follow steps. No more staring at a blank page, wondering what an essay outline is or how to go about writing an essay outline.
With a well-structured essay outline and a clear thesis statement, you will have a roadmap to navigate your essay, keeping your writing process on point.
Here is a sneak peek of what we will cover in this article:
- After reading this article, you will understand the importance of essay outline;
- You will learn about the effective essay outline parts;
- Understanding various types of essay outlines is crucial for creating a well-structured essay.
Whether you are an experienced essay writer looking to level up your game or a newbie trying to score big on your first big assignment, this essay writing guide has got you covered.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Essay Outline
Essay outlines are undoubtedly the unsung heroes of the writing world. They are not there just for show but play a crucial role in making your essay shine. Now, you must wonder how a basic essay outline and a good thesis statement that sums up the main points in the essay can do such a marvelous job.
Picture reading a book with pages all out of order. It will be vast chaos, right? Similarly, a simple outline for an essay ensures your essay ideas are in the correct order, making it easy for readers to follow your train of thought.
Moreover, it also helps boost your writing speed. Having a comprehensive essay outline ready in hand will give you a clear path to follow. Therefore, you will no longer waste time wondering what comes next. It is like having a GPS for your essay writing journey.
In general, an essay outline is your secret weapon for crafting clear, well-organized, and efficient essays. They are for perfectionists and anyone who wants their essays to grab the highest grade. So, don’t skip the outline next time you write an essay outline. Remember, it is your ticket to smoother and more coherent writing!
Essential Parts of Essay Outline
Crafting an effective outline for essay writing can be like trying to bake a cake without a recipe. You know you want a delicious result, but things can get messy without understanding the key components, such as a thesis statement, introduction, and the order to mix them.
Similarly, many people struggle while creating an outline because they do not fully grasp the significance of each part and how to handle it effectively. Here is a template for a basic essay outline :

It is like having all the cake ingredients but not knowing the proportions or the order to combine them for that perfect cake. Do you fall into a similar category? Stress no more. Below, you will find all the information you need about the practical essay outline parts:
Introduction
The introduction is like the opening act in your standard essay outline structure. While many might think it requires a concise summary, it differs from how you should write your essay’s introduction. Firstly, the conclusion should have the hook statement of the thesis.
The introduction of a stellar essay should start with an engaging hook to grab your reader’s attention, provide some background information to set the stage, and end with a crisp and concise thesis statement that tells your reader what to expect in the main body of your essay.
An introduction is the writer’s chance to make a solid first impression and set the tone for the rest of the writing. Following this approach will leave your readers wanting to read more!
In the structure of an essay outline, the body parts of an essay are like the heart of your writing. Instead of filling it with meaningless information, you should focus on delving into your thesis statement, providing examples, supporting points, and evidence to support your arguments.
To clarify further, the main points are the big ideas you want to explore in your body paragraphs. They will act as topic sentences – the guiding stars—keeping your writing on track and your reader engaged.
In the context of a five-paragraph essay , your body paragraphs play a crucial role. Each body paragraph should focus on a main idea introduced in the opening or topic sentence. Afterward, you should include supporting points such as facts, quotes, anecdotes, or explanations to provide depth and context to your main idea.
Ultimately, you can incorporate real-life instances and credible data to strengthen your arguments further, adding credibility and persuasiveness to your essay and the main body paragraph.
By following this approach, your essay will be meaningful and convincing!
The last part of your academic expository essay outline is the conclusion – it is like the grand finale of a fireworks show. It is your chance to bring your main point back into focus.
However, instead of repeating it word by word, it is better to restate your thesis with a new perspective or a broader understanding, giving your readers a sense of closure.
Once you have restated your thesis, it is time to give your readers a quick recap. Summarize all the main points, reminding your readers of their incredible journey through your essay.
Finally, you have to add your personal touch by sharing your final thoughts on the topic or a call to action if it is relevant. Also, you can add a few sensory aspects to evoke deep thoughts in the reader.
In your detailed essay outline format, the final paragraph of your paper is where you tie everything together. You revisit your thesis, summarize your main ideas, and leave your readers with food for thought.
Common Types
While it is all up to you to decide how to organize an outline, we advise you to ensure your essay outline adheres to the requirements provided along with the essay topic. You can choose the most convenient if there’s no required system for formatting the outline. Some are widely accepted. What are those types?
Alphanumeric structure style
The alphanumeric structure is the most frequent one. It features and follows these characters in the order of Roman numerals, Capital letters, Arabic numerals, and Lowercase letters.
Every subdivision is described as Roman numbers, and then you go with capital letters, Arabic numerals, and lowercase letters, accordingly.
- Roman numerals (I, II, III, etc.) to identify major sections of the outline. Usually, you will have five of them, each for every paragraph of the paper.
- Capital letters (A, B, C, etc.) appear to show points in the sections.
- Arabic numbers (1,2,3, etc.) are used for further important details.
- Lowercase letters (a,b,c, etc.) indicate if more details are needed.

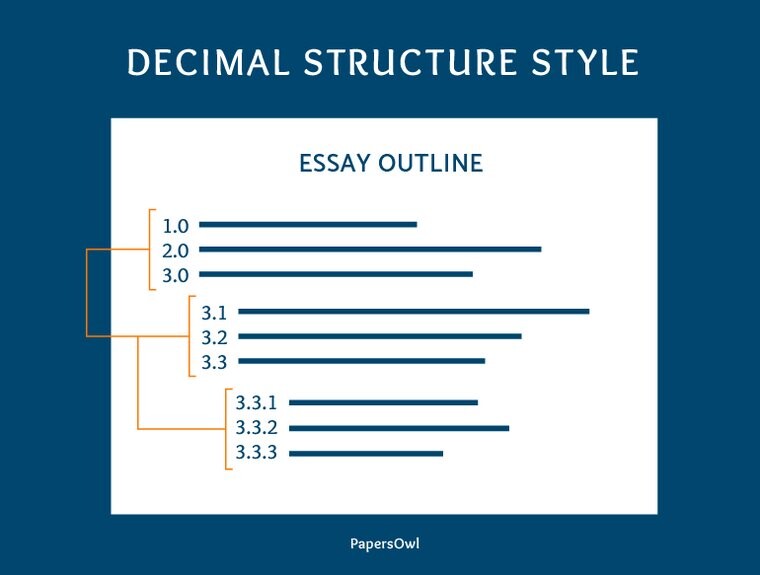
Decimal structure style
The decimal structure is similar to the alphanumeric structure but has one difference. Here we use only numerals. The added benefit of the decimal outline system relates to its decimal notation, which shows how every outline level relates to the main section.
Some people prefer this structure type because it might be easier to display the connection between each element.
- The outline begins with 1.0 and continues with 2.0, 3.0, etc. determining the beginning of every new section.
- For every new information point, we change the number after the dot. For instance, when we add information to the paragraph with the number 3.0, we name a new piece of information 3.1, 3.2, and so on.
- In case further details are needed, we add more decimals. In our case, it will look like 3.1.1, 3.2.1, etc.
Steps to Creating an Outline for an Essay
Creating a good essay outline might seem easy. However, this is not true at all. Even experienced essay writers spend a lot of time creating a clear and solid outline for their essays. Your half-work is done once you have created an effective essay outline.
It is not about following rigid rules but about crafting a flexible framework that helps you express your ideas effectively.
Do you often find yourself wondering who can “ write an essay for me ”? Following the steps mentioned below, you can create a stellar outline and, as a result, write a well-structured essay on your own:
- Understand the Essay Prompt or Choose a Topic : Consider it the starting point of your essay-writing or your writing an MLA paper journey. You either have a prompt handed to you, or you get to pick your essay topic. If you have a prompt, make sure you fully understand it. If you’re choosing a topic, pick something that genuinely interests you, making the writing process much more enjoyable.
- Conduct Preliminary Research : It’s time to gather much information and evidence for your essay. Read the books or scroll on the internet to gather some preliminary research and provide supporting evidence. It will help you understand your topic better and get a general idea of what others have said about it.
- Identify the Main Argument and Supporting Ideas: Imagine you’re building the skeleton of your essay. Identify the central point of your essay. It will be like the major bones, giving structure to your piece. Then, consider supporting ideas or arguments for the main point. These are like the smaller bones that provide strength and context.
- Arrange the Points in a Logical Order : Once you have the key points identified, it is time to put them together in an organized manner to create a coherent structure, a critical aspect of constructing effective academic works. Think about the flow of your essay. How should your primary ideas be arranged to ensure a smoother information flow? It is like assembling a puzzle—each piece should fit together seamlessly.
- Draft the Outline : In the end, you must start drafting your outline using your primary and supporting ideas. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to make it clear and organized. Your outline is your guide, so the choice is yours whether you want to make it a full-sentence outline (detailed) or a short-sentence outline (brief).
Tips for a Successful Essay Outline
Crafting an effective essay outline is like setting the stage for a well-organized and compelling essay. Whether you are working on an expository, descriptive, or literary analysis essay outline, the right approach can make all the difference. In this article, we will share valuable tips to help you create an essay outline that lays the foundation for your writing journey:
- Be Specific but Concise: Avoid unnecessary complexity and get straight to the point when outlining. The more specific you are about your key points and supporting details, the more effective the outline you will create. Take it as trimming the fat off your writing—only the lean, meaningful topic sentence remains.
- Get Rid of the Fluff: Toss all the extra words and phrases that don’t add value to your outline. Your outline should be free from unnecessary fluff. Removing it will make the essay outline simpler and more focused.
- Use Bullet Points for Clarity: Remember, bullet points are your friends in outlining. They break down your ideas into bite-sized pieces, making your outline easy to skim and understand. It is like using road signs to navigate through your outline structure.
- Maintain a Consistent Structure: Keep things tidy and consistent. If you make an alphanumeric outline with Roman numerals for the main points, stick with them throughout. The same goes for subheadings and bullet points. Consistency in your alphanumeric format makes your outline easy on the eyes and brain.
- Revise and Adjust as Necessary: An essay outline is a flexible tool, not set in stone. Therefore, feel free to revise and adjust as you go along. If a new idea pops up, incorporate it. If a section doesn’t seem to fit, reorganize. Keep refining your outline until it meets your satisfaction.
By following these tips, you can create an outline for an essay. With all the strategies mentioned above, you are well-equipped to craft a successful outline.
Examples and Templates of Various Essay Outlines
Crafting an essay can sometimes feel daunting, and sometimes you need to ask PapersOwl for help . That’s where the essay outline template comes in handy. It is like a trusty guide tailored for different essay types . Each template will serve as a roadmap, ensuring your essay is well-structured. Whether you share a personal story, build a persuasive argument, or aim for your dream school, we have covered you with these templates.
Let’s discuss each one and see how they work wonders:
Template for a Narrative Essay Outline
Imagine this as a storytelling guide. In a narrative essay, you are sharing a personal story or experience. Your outline should include sections for the introduction, plot development, characters, setting, climax, and conclusion. It is like mapping out the chapters of your own life’s story.
A narrative essay is a piece of writing that tells a story about an event on something creatively. It is similar to telling a personal story, a fiction narrative, or a literacy narrative essay. It is the least complicated kind of writing because you don’t have to perform any research. The most common topic for such an essay would be “How I spent my summer vacation.” The narrative essay has to be engaging. To do so, you have to:
- Conduct a thrilling plot.
- Include a conflict (i.e., a protagonist and an antagonist).
- Make bright characters.
- Exaggerate descriptions, but do not lie.
Using your imagination is one of the best strategies for entertaining your writing. Let it fill your essay with details and language to make your story come alive. Describe smells, emotions, feelings, and so on. However, remember that, in most cases, narrative essays are real stories.

Template of Argumentative Essay Outline
An argumentative essay outline presents a clear stance and supports it with evidence. Your outline should have sections for the introduction, thesis statement, main arguments with supporting evidence, counterarguments, and a strong conclusion.
When writing such an essay, remember to:
- Pick a topic you are interested in (the reader will always notice your disinterest).
- Provide good arguments (be concrete).
- Research as much as possible (surprise your reader with new facts).
When working on your argument, collect valuable sources such as scientific magazines, academic journals, documentaries, newspapers, etc.

Template of Compare and Contrast Essay Outline
In a compare and contrast essay , you are exploring two or more subjects. Your outline should include sections for the introduction, points of comparison, points of contrast, and a conclusion that ties it all together. It involves writing where you should highlight in which ways certain things are similar to and different from one another. This writing assignment stimulates critical thinking and forces you to conduct a compelling analysis.
Generally, comparative essays have an introduction (topic, theme, and thesis statement), body paragraphs, and a conclusion summarising the comparison. This article will describe only some of the processes of writing a comparison essay. However, I will provide you with specific tips:
- Use cue words (also, like, similar to, unlike, compared to, nevertheless, etc.)
- Be more specific in your thesis.
By the last point, write something like “BMW and Mercedes-Benz provide the same product; however, their marketing strategy differs” instead of “This essay will compare BMW and Mercedes-Benz.”
This is what your outline should look like:

Template of Admission Essay Outline
Admission essays are your chance to stand out. Your outline should cover the introduction, your personal background, achievements, challenges faced, and why you’re a perfect fit for the institution. It’s like crafting a masterpiece self-portrait in the writing world.
These templates, such as the APA outline , offer structure and direction for different essay types, making your academic journey less daunting and more organized. So, choose the one that fits your essay type, and let it be your guiding star.
Also, before creating an essay outline, you must take some time out and search for an outline example for an essay on Google. Looking through outline essay examples can provide valuable insights into structuring your academic essays.
Benefits of the Essay Outline in the Writing Process
Imagine having a powerful tool at your disposal, one that not only simplifies your writing process but also elevates the quality of your work. An outline is that very tool, often underestimated but holding the key to success in academic and creative writing. From enhancing organization to boosting your writing efficiency, it brings an overwhelming number of advantages to the table.
Also, it acts as a lifesaver when it comes to revisions. Whether you want to rearrange paragraphs, add new points, remove irrelevant details, or need to start a planning sheet for an essay , you can do so easily without losing your way. Lastly, using an essay outline enhances the final output. It ensures your essay is well-organized, coherent, and impactful.
Therefore, it would not be wrong to say that a basic outline for an essay is a secret weapon in academic writing, making drafting easier, revisions quicker, and the final result more impressive.
Elevate Your Essay Writing with Outline
As we wrap up our journey through the art of essay outlining, let’s take a moment to savor the significance of this invaluable tool. Outlining an essay is not merely a roadmap but the key to unlocking your full potential. It makes essay setup a breeze, revisions a cinch, and elevates your final output to new heights. So, the next time you face a blank page, remember the trusty outline by your side, ready to guide you through the essay layout. With this ultimate guide in your toolkit, you’re well-equipped to craft essays that captivate, persuade, and inspire.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
How to write an outline
An outline presents a picture of the main ideas and the subsidiary ideas of a subject. Some typical uses of outlining might be an essay, a term paper, a book review, or a speech. For any of these, an outline will show a basic overview and important details. It's a good idea to make an outline for yourself even if it isn't required by your professor, as the process can help put your ideas in order.
Some professors will have specific requirements, like requiring the outline to be in sentence form or have a "Discussion" section. A student’s first responsibility, of course, is to follow the requirements of the particular assignment. What follows illustrates only the basics of outlining.
Basic outline form
The main ideas take Roman numerals (I, II, ...) and should be in all-caps. Sub-points under each main idea take capital letters (A, B, ...) and are indented. Sub-points under the capital letters, if any, take Arabic numerals (1, 2, ...) and are further indented. Sub-points under the numerals, if any, take lowercase letters (a, b, ...) and are even further indented.
- Subsidiary idea or supporting idea to I
- Subsidiary idea to B
- Subsidiary idea to 2
- Subsidiary or supporting idea to II
- Subsidiary idea to II
It is up to the writer to decide on how many main ideas and supporting ideas adequately describe the subject. However, traditional form dictates that if there is a I in the outline, there has to be a II ; if there is an A , there has to be a B ; and so forth.
Outline example
Suppose you are outlining a speech about gerrymandering, and these are some of the ideas you feel should be included: voter discrimination, "majority-minority" districts, the history of the term, and several Supreme Court cases.
To put these ideas into outline form, decide first on the main encompassing ideas. These might be: I. History of the term, II. Redistricting process, III. Racial aspects, IV. Current events.
Next, decide where the rest of the important ideas fit in. Are they part of the redistricting process, or do they belong under racial aspects? The complete outline might look like this:
Gerrymandering in the U.S.
- HISTORY OF THE TERM
- Responsibility of state legislatures
- Census data
- Preclearance
- Partisan approaches
- Gomillion v. Lightfoot (1960)
- Voter discrimination
- Voting Rights Act (1965)
- Majority-minority districts
- Effects of gerrymandering in 2012 and 2016 elections
- Gill v. Whitford Supreme Court Case
It is only possible to make an outline if you have familiarity with the subject. As you do research, you may find it necessary to add, subtract or change the position of various ideas. If you change your outline, ensure that logical relationship among ideas is preserved.

Helpful resources
To gain an initial familiarity with your topic, look it up in Gale Virtual Reference Library (a.k.a. "Academic Wikipedia"), a collection of entries from specialized encyclopedias. GVRL provides topic overviews, many of which are organized with an outline themselves.
Further reading
Tardiff, E., and Brizee, A. (2013). Developing an outline . In Purdue OWL . Look at all three sections. The third includes an example.
Lester, J.D., and Lester, Jr., J.D. (2010). Writing research papers: A complete guide (13th ed.). New York: Longman. Includes several models, including for a general-purpose academic paper. Check it out from the Stacks LB2369 .L4 2010.
Turabian, K.L. (2013). A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Request John Jay's copy from the Reference Desk (call number LB2369 .T8 2013).
Created by J. Dunham, 2003. Revised by R. Davis, Oct. 2017.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an Outline in APA Format
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amanda Tust is a fact-checker, researcher, and writer with a Master of Science in Journalism from Northwestern University's Medill School of Journalism.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Amanda-Tust-1000-ffe096be0137462fbfba1f0759e07eb9.jpg)
- Before Starting Your Outline
- How to Create an Outline
Writing a psychology paper can feel like an overwhelming task. From picking a topic to finding sources to cite, each step in the process comes with its own challenges. Luckily, there are strategies to make writing your paper easier—one of which is creating an outline using APA format .
Here we share what APA format entails and the basics of this writing style. Then we get into how to create a research paper outline using APA guidelines, giving you a strong foundation to start crafting your content.
At a Glance
APA format is the standard writing style used for psychology research papers. Creating an outline using APA format can help you develop and organize your paper's structure, also keeping you on task as you sit down to write the content.
APA Format Basics
Formatting dictates how papers are styled, which includes their organizational structure, page layout, and how information is presented. APA format is the official style of the American Psychological Association (APA).
Learning the basics of APA format is necessary for writing effective psychology papers, whether for your school courses or if you're working in the field and want your research published in a professional journal. Here are some general APA rules to keep in mind when creating both your outline and the paper itself.
Font and Spacing
According to APA style, research papers are to be written in a legible and widely available font. Traditionally, Times New Roman is used with a 12-point font size. However, other serif and sans serif fonts like Arial or Georgia in 11-point font sizes are also acceptable.
APA format also dictates that the research paper be double-spaced. Each page has 1-inch margins on all sides (top, bottom, left, and right), and the page number is to be placed in the upper right corner of each page.
Both your psychology research paper and outline should include three key sections:
- Introduction : Highlights the main points and presents your hypothesis
- Body : Details the ideas and research that support your hypothesis
- Conclusion : Briefly reiterates your main points and clarifies support for your position
Headings and Subheadings
APA format provides specific guidelines for using headings and subheadings. They are:
- Main headings : Use Roman numerals (I, II, III, IV)
- Subheadings: Use capital letters (A, B, C, D)
If you need further subheadings within the initial subheadings, start with Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3), then lowercase letters (a, b, c), then Arabic numerals inside parentheses [(1), (2), (3)]
Before Starting Your APA Format Outline
While APA format does not provide specific rules for creating an outline, you can still develop a strong roadmap for your paper using general APA style guidance. Prior to drafting your psychology research paper outline using APA writing style, taking a few important steps can help set you up for greater success.
Review Your Instructor's Requirements
Look over the instructions for your research paper. Your instructor may have provided some type of guidance or stated what they want. They may have even provided specific requirements for what to include in your outline or how it needs to be structured and formatted.
Some instructors require research paper outlines to use decimal format. This structure uses Arabic decimals instead of Roman numerals or letters. In this case, the main headings in an outline would be 1.0, 1.2, and 1.3, while the subheadings would be 1.2.1, 1.2.2, 1.2.3, and so on.
Consider Your Preferences
After reviewing your instructor's requirements, consider your own preferences for organizing your outline. Think about what makes the most sense for you, as well as what type of outline would be most helpful when you begin writing your research paper.
For example, you could choose to format your headings and subheadings as full sentences, or you might decide that you prefer shorter headings that summarize the content. You can also use different approaches to organizing the lettering and numbering in your outline's subheadings.
Whether you are creating your outline according to your instructor's guidelines or following your own organizational preferences, the most important thing is that you are consistent.
Formatting Tips
When getting ready to start your research paper outline using APA format, it's also helpful to consider how you will format it. Here are a few tips to help:
- Your outline should begin on a new page.
- Before you start writing the outline, check that your word processor does not automatically insert unwanted text or notations (such as letters, numbers, or bullet points) as you type. If it does, turn off auto-formatting.
- If your instructor requires you to specify your hypothesis in your outline, review your assignment instructions to find out where this should be placed. They may want it presented at the top of your outline, for example, or included as a subheading.
How to Create a Research Paper Outline Using APA
Understanding APA format basics can make writing psychology research papers much easier. While APA format does not provide specific rules for creating an outline, you can still develop a strong roadmap for your paper using general APA style guidance, your instructor's requirements, and your own personal organizational preferences.
Typically you won't need to turn your outline in with your final paper. But that doesn't mean you should skip creating one. A strong paper starts with a solid outline. Developing this outline can help you organize your writing and ensure that you effectively communicate your paper's main points and arguments. Here's how to create a research outline using APA format.
Start Your Research
While it may seem like you should create an outline before starting your research, the opposite is actually true. The information you find when researching your psychology research topic will start to reveal the information you'll want to include in your paper—and in your outline.
As you research, consider the main arguments you intend to make in your paper. Look for facts that support your hypothesis, keeping track of where you find these facts so you can cite them when writing your paper. The more organized you are when creating your outline, the easier it becomes to draft the paper itself.
If you are required to turn in your outline before you begin working on your paper, keep in mind that you may need to include a list of references that you plan to use.
Draft Your Outline Using APA Format
Once you have your initial research complete, you have enough information to create an outline. Start with the main headings (which are noted using Roman numerals I, II, III, etc.). Here's an example of the main headings you may use if you were writing an APA format outline for a research paper in support of using cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for anxiety :
- Introduction
- What CBT Is
- How CBT Helps Ease Anxiety
- Research Supporting CBT for Anxiety
- Potential Drawbacks of CBT for Anxiety and How to Overcome Them
Under each main heading, list your main points or key ideas using subheadings (as noted with A, B, C, etc.). Sticking with the same example, subheadings under "What CBT Is" may include:
- Basic CBT Principles
- How CBT Works
- Conditions CBT Has Been Found to Help Treat
You may also decide to include additional subheadings under your initial subheadings to add more information or clarify important points relevant to your hypothesis. Examples of additional subheadings (which are noted with 1, 2, 3, etc.) that could be included under "Basic CBT Principles" include:
- Is Goal-Oriented
- Focuses on Problem-Solving
- Includes Self-Monitoring
Begin Writing Your Research Paper
The reason this step is included when drafting your research paper outline using APA format is that you'll often find that your outline changes as you begin to dive deeper into your proposed topic. New ideas may emerge or you may decide to narrow your topic further, even sometimes changing your hypothesis altogether.
All of these factors can impact what you write about, ultimately changing your outline. When writing your paper, there are a few important points to keep in mind:
- Follow the structure that your instructor specifies.
- Present your strongest points first.
- Support your arguments with research and examples.
- Organize your ideas logically and in order of strength.
- Keep track of your sources.
- Present and debate possible counterarguments, and provide evidence that counters opposing arguments.
Update Your Final Outline
The final version of your outline should reflect your completed draft. Not only does updating your outline at this point help ensure that you've covered the topics you want in your paper, but it also gives you another opportunity to verify that your paper follows a logical sequence.
When reading through your APA-formatted outline, consider whether it flows naturally from one topic to the next. You wouldn't talk about how CBT works before discussing what CBT is, for example. Taking this final step can give you a more solid outline, and a more solid research paper.
American Psychological Association. About APA Style .
Purdue University Online Writing Lab. Types of outlines and samples .
Mississippi College. Writing Center: Outlines .
American Psychological Association. APA style: Style and Grammar Guidelines .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Writing Techniques
- Planning Your Writing
How to Write an Outline
Last Updated: March 27, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,953,819 times.
An outline is a great way to organize ideas and information for a speech, an essay, a novel, or a study guide based on your class notes. At first, writing an outline might seem complicated, but learning how to do it will give you an essential organizational skill! Start by planning your outline and choosing a structure for it. Then, you can organize your ideas into an easy to understand outline.
Quick Outline Slideshow
Sample outlines.

Planning Your Outline

- Some people process their ideas better when they write them down. Additionally, you can easily draw diagrams or examples, which might help you conceptualize the subject. However, it might take longer to write out your outline, and it won't be as neat.
- Typing your outline might be easier if your notes are already typed on the computer, as you can just copy and paste them into your outline. Copying and pasting also allows you to easily rearrange your sections, if necessary. Also, it will be easier to copy and paste information from your outline into your paper if you type your outline. On the other hand, it's harder to jot down notes in the margins or draw out organizational diagrams.

- If you’re working on a creative project, such as a novel, identify your concept, genre, or premise. Then, allow the outlining process to help you structure your work.
- It’s okay if your topic is somewhat broad when you first start, but you should have a direction. For example, your history paper topic could be French life during the German occupation of France in World War II. As you write your outline, you might narrow this down to the resistance fighters called maquisards .

- For a school assignment, review the assignment sheet or talk to your instructor. If the outline is for work, use an existing outline as a model for yours.
- If you are the only person who will see the outline, you can choose formatting that works for you. For example, you might write your outline in shorthand.

- Paraphrased ideas
- Historical facts

- Freewrite as ideas come to you.
- Create a mind map .
- Write your thoughts on index cards.

- For example, you may be writing a paper about policy change. Your thesis might read, “Policy makers should take an incremental approach when making policy changes to reduce conflict, allow adjustments, and foster compromise.” Each of the 3 reasons listed in your thesis will become its own main point in your outline.
Structuring Your Outline

- Roman Numerals - I, II, III, IV, V
- Capitalized Letters - A, B, C
- Arabic Numerals - 1, 2, 3
- Lowercase Letters - a, b, c
- Arabic Numerals in Parentheses - (1), (2), (3)

- 1.1.1 - Each side presents a case before the vote
- 1.1.2 - Citizens voice their opinion
- 1.2 - Neither side gets everything they want

- You might use short phrases to quickly organize your ideas, to outline a speech, or to create an outline that’s just for you.
- You might use full sentences to make it easier to write a final paper, to make a good study guide, or to fulfill the requirements of an assignment.
Organizing Your Ideas

- If you jotted down your ideas or made a mind map, use different colored highlighters to identify ideas that belong in the same group.
- Sort your index cards, if you used them to brainstorm. Put cards with related ideas together. For example, you can put them in stacks, or you can line your cards out in rows to make them easier to read.

- For example, your main point might be that Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein champions emotion over reason. Your subpoints might be that Victor Frankenstein is restored by nature and that his scientific efforts create a monster. As supporting details, you might include quotes from the book.
- If you're writing a story or presenting a historical argument, a chronological order makes sense. For an essay or speech, pick the subtopic with the most supporting materials, and lead with this argument. From there, order your major subtopics so each one naturally flows into the next.
- Your broad ideas should connect back to your thesis or controlling idea. If they don’t, rewrite your thesis to reflect the main ideas you’re putting into your outline.

- Hook to grab the audience
- 1-2 general statements about your topic

- Phrase outline: II. Frankenstein champions emotion over reason
- Full sentence outline: II. In Frankenstein , Mary Shelley champions the use of emotion over reason.

- Depending on the purpose of your outline, you might have more subpoints. For example, a novel may have many subpoints. Similarly, a study guide will likely have several subpoints, as well.

- In an essay, this is often where you “prove” your argument.
- For a creative work, you might include essential details you must include in that scene, such as an internal conflict in your main character.
- Similar to subpoints, you may have more supporting details, depending on your purpose. A novel or study guide will likely have more supporting details.

- Roman Numeral
- Capital Letter
- Arabic Numeral
- Lowercase Letter
- Arabic Numeral in Parentheses

- Restate your thesis.
- 1-2 summarizing sentences.
- Write a concluding statement.
Finalizing Your Outline

- This also gives you a chance to look for missing parts or ideas that aren’t fully fleshed. If you see areas that leave questions unanswered, it’s best to fill in those gaps in information.

- If you are making an outline for yourself, you might not worry about this.

- It’s a good idea to have someone else check it for errors, as it’s often hard to recognize errors in your own work.
- While you edit your outline, refer back to your assignment sheet or rubric to make sure you've completely fulfilled the assignment. If not, go back and correct the areas that are lacking.

- You can use more layers if you want to include more information.
- You might also include additional layers for a long creative work or a detailed study guide.
Expert Q&A

- Be concise and straightforward in your outline. This doesn't have to be perfectly polished writing; it just has to get your point across. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Don't be afraid to eliminate irrelevant information as you conduct more research about your topic and narrow your focus. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- You can use outlines as a memorization tool . Choose concise words to trigger a concept. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Generally, you should avoid only having one point or sub-point on any outline level. If there is an A, either come up with a B or fold A's idea into the next level up. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 2
- Your outline should not be your essay in a different form. Only write down the major assertions, not every single detail. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/writingprocess/outlining
- ↑ https://www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~cinichol/271/OutlinesHowTo.htm
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/544/02/
- ↑ https://www.writersdigest.com/write-better-fiction/7-steps-to-creating-a-flexible-outline-for-any-story
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/544/03/
- ↑ https://writing2.richmond.edu/writing/wweb/outline.html
About This Article

The easiest way to write an outline is to gather all of your supporting materials, like quotes, statistics, or ideas, before getting started. Next, go over your materials and take notes, grouping similar ideas together. Then, organize your ideas into subtopics and use your materials to provide at least two supporting points per subtopic. Be sure to keep your outline concise and clear, since you’ll have to refer to it later! For more help on how to plan and organize your outline, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Apr 22, 2018
Did this article help you?
Kember Miller
Jan 14, 2018
Oct 25, 2017
Sep 26, 2016
Apr 26, 2022

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

Basic essay structure

Improve your writing
Organise your essays to demonstrate your knowledge, show your research and support your arguments
Essays are usually written in continuous, flowing, paragraphed text and don’t use section headings. This may seem unstructured at first, but good essays are carefully structured.
How your assignment content is structured is your choice. Use the basic pattern below to get started.
Essay structure
An essay consists of three basic parts:, introduction.
The essay itself usually has no section headings. Only the title page, author declaration and reference list are written as headings, along with, for example, appendices. Check any task instructions, and your course or unit handbook, for further details.
Content in assignment introductions can vary widely. In some disciplines you may need to provide a full background and context, whereas other essays may need only a little context, and others may need none.
An introduction to an essay usually has three primary purposes:
- To set the scene
- To tell readers what is important, and why
- To tell the reader what the essay is going to do (signposting)
A standard introduction includes the following five elements:
- A statement that sets out the topic and engages the reader.
- The background and context of the topic.
- Any important definitions, integrated into your text as appropriate.
- An outline of the key points, topic, issues, evidence, ideas, arguments, models, theories, or other information, as appropriate. This may include distinctions or contrasts between different ideas or evidence.
- A final sentence or two which tells the reader your focal points and aims.
You should aim to restrict your introduction to information needed for the topic and only include background and contextual information which helps the reader understand it, or sets the scene for your chosen focal points.
In most essays you will have a considerable range of options for your focus. You will be expected to demonstrate your ability to select the most relevant content to address your focal points.
There are some exceptions. For example, if an assignment brief specifically directs the essay focus or requires you to write broadly about a topic. These are relatively rare or are discipline-specific so you should check your task instructions and discipline and subject area conventions.
Below are examples of an opening statement, a summary of the selected content, and a statement at the end of the introduction which tells the reader what the essay will focus on and how it will be addressed. We've use a fictional essay.
The title of our essay is: 'Cats are better than dogs. Discuss.'
To submit this essay you also would need to add citations as appropriate.
Example of opening statements:
People have shared their lives with cats and dogs for millenia. Which is better depends partly on each animal’s characteristics and partly on the owner’s preferences.
Here is a summary of five specific topics selected for the essay, which would be covered in a little more detail in the introduction:
- In ancient Egypt, cats were treated as sacred and were pampered companions.
- Dogs have for centuries been used for hunting and to guard property. There are many types of working dog, and both dogs and cats are now kept purely as pets.
- They are very different animals, with different care needs, traits and abilities.
- It is a common perception that people are either “cat-lovers” or “dog-lovers”.
- It is a common perception that people tend to have preferences for one, and negative beliefs about and attitudes towards, the other.
Example of closing statements at the end of the introduction:
This essay will examine both cats’ and dogs’ behaviour and abilities, the benefits of keeping them as pets, and whether people’s perceptions of their nature matches current knowledge and understanding.
Main body: paragraphs
The body of the essay should be organised into paragraphs. Each paragraph should deal with a different aspect of the issue, but they should also link in some way to those that precede and follow it. This is not an easy thing to get right, even for experienced writers, partly because there are many ways to successfully structure and use paragraphs. There is no perfect paragraph template.
The theme or topic statement
The first sentence, or sometimes two, tells the reader what the paragraph is going to cover. It may either:
- Begin a new point or topic, or
- Follow on from the previous paragraph, but with a different focus or go into more-specific detail. If this is the case, it should clearly link to the previous paragraph.
The last sentence
It should be clear if the point has come to an end, or if it continues in the next paragraph.
Here is a brief example of flow between two summarised paragraphs which cover the historical perspective:
It is known from hieroglyphs that the Ancient Egyptians believed that cats were sacred. They were also held in high regard, as suggested by their being found mummified and entombed with their owners (Smith, 1969). In addition, cats are portrayed aiding hunters. Therefore, they were both treated as sacred, and were used as intelligent working companions. However, today they are almost entirely owned as pets.
In contrast, dogs have not been regarded as sacred, but they have for centuries been widely used for hunting in Europe. This developed over time and eventually they became domesticated and accepted as pets. Today, they are seen as loyal, loving and protective members of the family, and are widely used as working dogs.
There is never any new information in a conclusion.
The conclusion usually does three things:
- Reminds your readers of what the essay was meant to do.
- Provides an answer, where possible, to the title.
- Reminds your reader how you reached that answer.
The conclusion should usually occupy just one paragraph. It draws together all the key elements of your essay, so you do not need to repeat the fine detail unless you are highlighting something.
A conclusion to our essay about cats and dogs is given below:
Both cats and dogs have been highly-valued for millenia, are affectionate and beneficial to their owners’ wellbeing. However, they are very different animals and each is 'better' than the other regarding care needs and natural traits. Dogs need regular training and exercise but many owners do not train or exercise them enough, resulting in bad behaviour. They also need to be 'boarded' if the owner is away and to have frequent baths to prevent bad odours. In contrast, cats do not need this level of effort and care. Dogs are seen as more intelligent, loyal and attuned to human beings, whereas cats are perceived as aloof and solitary, and as only seeking affection when they want to be fed. However, recent studies have shown that cats are affectionate and loyal and more intelligent than dogs, but it is less obvious and useful. There are, for example, no 'police' or 'assistance' cats, in part because they do not have the kinds of natural instincts which make dogs easy to train. Therefore, which animal is better depends upon personal preference and whether they are required to work. Therefore, although dogs are better as working animals, cats are easier, better pets.
Download our basic essay structure revision sheet
Download this page as a PDF for your essay structure revision notes
Better Essays: Signposting

Paragraphs main body of an assessment


What does a "good" outline look like? What does a full-sentence outline look like? How do I create one?
An outline is a tool used to organize written ideas about a topic or thesis into a logical order. Outlines arrange major topics, subtopics, and supporting details. Writers use outlines when writing their papers in order to know which topic to cover in what order. Outlines for papers can be very general or very detailed. Check with your instructor to know which is expected of you. Here are some examples of different outlines. You can also learn more by watching the short video below .
The most common type of outline is an alphanumeric outline , or an outline that uses letters and numbers in the following order:
I. Roman Numerals
A. I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, etc.
B. Represent main ideas to be covered in the paper in the order they will be presented
II. Uppercase Letters
A. A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, etc.
B. Represent subtopics within each main idea
III. Arabic Numbers
A. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, etc.
B. Represent details or subdivisions within subtopics
IV. Lowercase Letters
A. a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, l, m, etc.
B. Represent details within subdivisions
Outline with main ideas, subtopics, subdivisions and details :
Thesis: Drugs should be legalized.
I. Legalization of drugs would reduce crime rates
A. Prohibition
1. Before Prohibition, crime rate related to alcohol were low-to-medium
2. During Prohibition, crime rates related to alcohol were high
a. Arrests for drunkenness and disorderly conduct increase 41%
b. Federal prison population increased 366%
3. After Prohibition, crime rates related to alcohol were very low
B. Amsterdam/Netherlands
1. Before Amsterdam had legalized marijuana, drug-related crime rates were high
2. After Amsterdam had legalized marijuana, drug-related crime rates dropped
II. Legalization of drugs would benefit the economy
1. Local taxes
2. State taxes
3. Federal taxes
B. Business Owners
1. Drug production
2. Drug quality testing
3. Drug sales
III. Legalization of drugs would benefit public health
A. Quality of drugs would increase
1. Fake/dangerous drugs eliminated
2. Fake/placebo drugs eliminated
3. Amount of active ingredient standardized and stabilized
B. Drug users with addiction issues would get more help
1. Hospitals
3. Public health clinics
C. Your people would be less likely to start drugs
F ull-sentence outline :
- Each roman numeral (I, II, III, IV…) indicates the start of a new paragraph. So I. is the first sentence of the introduction, II. is the first sentence of the first paragraph of the body, III. is the first sentence of the second paragraph of the body, and so on.
- Each capital letter (A, B, C, D…) indicates a main point within the structure of the paragraph. So in our introduction, A. is the attention getter, B. is another attention getter, C. describes a point that makes the topic personal, and D. is the thesis statement.
- Each Arabic numeral (1, 2, 3, 4…) indicates a sentence or piece of supporting evidence for each main point. So in the first body paragraph (II.), point A. is a general statement that needs some additional support, so 1. provides a supporting statement of fact and the citation of where that information came from. 2. provides another sentence with supporting evidence, as does 3.
Example of a full-sentence outline:
Warming Our World and Chilling Our Future
Thesis Statement: Today I want to share what I have learned about global warming and its causes.
I. Global warming is alive and well and thriving in Antarctica.
A. In winter 1995, an iceberg the size of Rhode Island broke off.
B. In October 1998, an iceberg the size of Delaware broke off.
C. All of us have a lot at stake.
1. Now, I am what you call a “country mouse.”
2. I love the outdoors.
3. You can be a “city mouse,” and like clean air, good water, and not having to worry about sun.
D. Today I want to share what I have learned about global warming and its causes.
II. Global warming is a gradual warming of the Earth from human activities (citation).
A. It is characterized by a high concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
1. Each year five tons of CO2 are pumped into the atmosphere (citation).
2. The carbon dioxide traps heat.
3. 1998 set temperature records (citation).
B. Carbon pollutants also eat a hole in the ozone layer (citation).
1. In 1998 this hole set a size record.
2. This allows more ultraviolet radiation to reach Earth.
C. If this problem is not corrected; we may see disastrous results (citation).
1. There could be dramatic climate changes.
a. There could be drought in the middle of continents.
b. There could be many severe storms.
c. There could be rising sea levels that would destroy coastal areas.
2. There could be serious health problems.
a. There could be an increase in skin cancer.
b. There could be an increase in cataracts.
c. There could be damaged immune systems.
D. Now that you understand what global warming is and why it is important, let’s examine its major causes.
III. The loss of woodlands adds to global warming (citation). …..
IV. Industrial emissions accelerate global warming (citation). …..
V. Personal energy consumption magnifies global warming (citation). …..
VI. In conclusion, if you want to know why we have global warming, listen for the falling trees, watch the industrial smokestacks darkening the sky, and smell the exhaust fumes we are pumping into the air.
A. Gore told a story on how global warming can sneak up on us.
B. Addressing the National Academy of Sciences, the vice president said, “If dropped into a pot of boiling water….”
C. The more we know about global warming, the more likely we are to jump and the less likely we are to be cooked.
Links & Files
- Outline Template
- Reading and Writing
- Weekly Written Assignments
- Research Papers
- Last Updated Jul 27, 2022
- Views 702512
- Answered By Kerry Louvier
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (41)
- This is very helpful. Thanks a lot! by krystal on Apr 01, 2015
- Very nice and very helpful. I mean my parents are making me do a outline about a state. by Zelda on Apr 09, 2015
- Very helpful, it cleared things up a lot for me, so thanks! by Roxy on Oct 05, 2015
- Very helpful! Thank You! (Thumbs up!!) by Mavis on Oct 14, 2015
- Were very helpful Thanks! by annette on Oct 18, 2015
- Thank you guys this helped me out big time! It's actually saving my English grade from dropping. ;) And I really didn't know how a 'good' outline was suppose to look like soo Thank you Thank you Thank you!!!!! by Tiffanie on Nov 16, 2015
- Thanks so much! This is perfect, especially the way you've explained what each area should contain. It's something writers need to know but so often get wrong. by Tammy on Oct 28, 2016
- Thank you!! This was very helpful, as I am a watch and do type of person! by Alisa on Mar 23, 2017
- The hardest part in writing a paper is the outlining. this is real good and helpful. thanks very much. by Archie on Jul 25, 2017
- You made outlining easy for me Am forever grateful by joana jewel on Oct 02, 2017
- This is a great video, very helpful and easy to follow. by cvelez on Apr 25, 2018
- This was VERY helpful. Thank you! by Donna on May 18, 2018
- Exactly what I needed. Thank you. by Sharon on Aug 12, 2018
- i totally had no idea about the outline, thank you so much. by ngare irene on Aug 16, 2018
- THIS!! Thank-you for taking the time to do this, I found it very helpful. by Lauren B. on Sep 22, 2018
- After 45 minutes of surfing the web, this is the first helpful article I have come across in my attempt to find an outline example. Thank you. by Kate Metcalfe on Oct 10, 2018
- Thank you so much. This was very helpful. The video and explanation was very easy to follow. by Linda Armstrong on Feb 18, 2019
- Thankyou for putting the outline in full detail it helped me out alot. by Rosio on Mar 19, 2019
- Thank you very much! Very helpful! by Loretha M on Apr 09, 2019
- Exactly what I need. This is so helpful. Thank you!!! by My Le on May 15, 2019
- thank you so much. it's such a big help. God Bless by flor timbal on Jun 21, 2019
- This was extremely helpful towards my assignment that I am required to do in order to receive a grade. by Rhelle on Jul 27, 2019
- Very, very helpful!!!!!!!! :D by Miranda S. on Aug 23, 2019
- I found this video most useful. Thank you! by Ibironke on Sep 14, 2019
- very helpful, its been a long time since I had to d this. This was by far the easiest to understand. Thanks, by Ms P on Apr 15, 2020
- interesting thank you so much by Fausat Wellington on Apr 25, 2020
- Many thanks! Very helpful, simple and effective. by Oliver on May 25, 2020
- Great video...... Thanks by Belle on Jun 17, 2020
- This is a great tutorial! Thanks by Jeff on Jun 22, 2020
- This is good to explain. regards Devansh Chaurasiya by Devansh Chaurasiya on Jun 26, 2020
- Thank you. This is very helpful. More power!!! by Gina Fatawil on Aug 11, 2020
- This was super effective for my English class thanks!! by Jackie B on Sep 11, 2020
- Overall, its very interesting by Yban Meradores on Sep 11, 2020
- excellent explanations. by very helpful . Thanks on Sep 23, 2020
- Very helpful, it makes me complete university assignment with ease by Manje on Nov 14, 2020
- thank you ,my history teacher was making my class do outlines and i didn't know what to put in one thxs,thxs,and thxs by Maggie on Feb 17, 2021
- Thanks just what I needed by Royce Castellanos on Apr 05, 2021
- Thank you very much. This was really, really helpful. I had no idea how to do an outline and the other sites only says what it should be there, no examples. This was something that guided me and I could finish my outline fine. by Maria on Jun 25, 2021
- This is wonderful, real. I have always been wondering, given a research title where do one get all the subtitles from but now I perfectly understand...Thank you. by Karen Mwangangi on Aug 09, 2021
- Great video indeed, very helpful and understandable. by Linah on Sep 27, 2021
- Very concise with with well thought-out examples. Thanks. by Definite on Mar 16, 2022
Hello! We're here to help! Please log in to ask your question.
Need an answer now? Search our FAQs !
How can I find my course textbook?
You can expect a prompt response, Monday through Friday, 8:00 AM-4:00 PM Central Time (by the next business day on weekends and holidays).
Questions may be answered by a Librarian, Learning Services Coordinator, Instructor, or Tutor.
Writing Get your essay and assignment written from scratch by PhD expert
Rewriting: Paraphrase or rewrite your friend's essay with similar meaning at reduced cost
Editing: Proofread your work by experts and improve grade at Lowest cost
Enter phone no. to receive critical updates and urgent messages !
Error goes here
Please upload all relevant files for quick & complete assistance.
New User? Start here.
The Role of Essay Outlines in Writing

Table of Contents
Don’t know about essay outlines? If not, you are not doing anything right. An outline is essentially the skeleton of an essay. In other words, it is a text representation of the thesis and critical supporting points of an essay.
Essays are the most common type of academic writing. Outlines serve many purposes, including assisting writers in arranging their thoughts before starting work, allowing readers to read a quick synopsis of the essay, and acting as a guide for the writer as they work on their next supporting paragraph. Writing an essay outline is not a challenging task. In this blog post, we are going to shed light on this topic. Go through it to gather valuable insights and learn about the key points that you must consider to come up with an effective essay outline.
Understanding the Essay Outline
An essay outline is an informal document that lists the essay parts to ensure the writer stays on track and doesn’t miss a single point. As it’s not formal, the outline is mostly written in incomplete sentences, just like notes.
Outlining is a crucial early stage in the writing process. This is the stage where you arrange all of your ideas and understandings into a clear and concise roadmap. Your outline can possibly help you get back on track if you get stuck while composing your essay.
In colleges and universities, students need to submit the outline of an essay before they can start writing. This is because the instructors want to make sure each student is on the right track in terms of picking an appropriate essay topic that comes with ample referencing sources. Most importantly, it helps the instructors ensure that the essay criteria are met and that the students master the task.
Components of an Effective Essay Outline
Even though every essay is unique, all follow the same fundamental essay structure , which is as follows:
- Introduction Section
The introduction is the very first section of your essay. As the name suggests, this is the part where you introduce the points you will be explaining in your essay.
Hook or Opening Statement
This comes under the introduction part. A hook or opening statement is a full sentence that you need to incorporate to draw the attention of the readers. It is more of a concise statement that the audience relates to.
Thesis Statement
Talk about your thesis in the introduction part as well. It is the definitive sentence where you make clear arguments. This allows the reader to understand your perspective when going through the paper.
Body Paragraphs Section
Your essay might feature only two paragraphs, or it may even be a five-paragraph essay. Unless your instructor allocated a specific number of paragraphs, it’s completely your call when it comes to creating categories to divide the essay.
If you want to add multiple sources to support your thesis statement, follow the universal rule of one body paragraph per source cited. However, depending on the kind of essay you are writing, you might have to stray from this rule.
Conclusion Section
Once you get to the conclusion paragraph, you are almost done! This is the part of your essay where you summarise and list the main ideas from each of your body paragraphs. This is an opportunity to share any final ideas or viewpoints you would like the reader to see before they end up consuming your essay.
Crafting Your Essay Outline
So, you are ready to craft the outline of your essay. That’s great! But how can you get started? Follow four key steps and make the rest of your work simpler and easier. Scroll down and have a look:
- Determine your goal— Consider your thesis statement. Though the exact terminology may not yet be clear to you, you should have some idea of the argument you will put forward and defend in your essay. It is easier to go over your brainstorming thoughts and create a solid outline when you have a defined purpose.
- Filter out the fluff— When you came up with ideas, you considered every angle you could explore and every piece of information you possibly wanted to include. Now, it’s time to review the brainstorming notes and select the ideas that will help you write your essay efficiently.
- Track down the points you will make in each paragraph— Determine the primary arguments that you will make in your essay with the set of concepts you wrote down.
- Use a standard template for your outline— Arrange your main ideas into an understandable, well-organised framework that you will fill in with information as you prepare your first essay draft using a template that suits the type of essay you are assigned to compose (more on that in the following section).
Tips for Creating an Effective Essay Outline
You can easily create a detailed outline for your essay if you follow a few key points as mentioned below:
Understand the purpose of your essay – Prior to outlining, figuring out your essay purpose is the key. In other words, you must keep track of:
- Grasping the paper requirements
- The essay topic
- The thesis statement of your essay
- Your audience
Pick an order – When you draft an outline, you effectively provide your future essay with structure and purpose. You will need to consider whether to arrange your essay chronologically, spatially, or importance-based.
Creating the structure for a short essay – If you are writing a short essay or a 500-word five-paragraph essay, your structure should be like the following:
- Primary idea
- Supporting idea 1
- Supporting idea 2
- Supporting idea 3
Developing an outline – Using templates is the best option for creating sentence outlines. You can select the template essay that best suits your needs and only answer each text box question with a single sentence, which will provide you with a concise, one-sentence summary. After that, you can share or export the outline with classmates or instructors for their input.
Types of Essay Outlines with Examples
Among all, the most common is the alphanumeric outline, and most people can able to recognise it. While all outlines have a similar overall structure, several significant differences must be considered when drafting one for a particular essay format . The different types of essay outlines are as follows:
- Argumentative essay outline
- Admission essay outline
- Persuasive essay outline
- Literary analysis essay outline
- Personal essay outline
- Alphanumeric outline
- Expository essay outline
Take a look at more than one common example outline for varied essay types:
1. Argumentative essays
Title: “Italian Ice is a Superior Dessert to Ice Cream”
Introduction
State the features of Italian Ice
Why is it more refreshing?
2. Admissions Essays
Title: “Arigato, Sato Sensei”
Discuss how English speakers struggle to learn Japanese language
Talk about the Japanese culture
Your experience
3. Persuasive Essays
Title: “We Need More Security Cameras in the Student Parking Deck”
Share updated student car break-in statistics
Talk about the intangible value of high-end security
State the installation cost
4. Personal Essays
Title: “The Two Best Birthdays of my Life”
Talk about your 18th birthday
Talk about your last birthday
The Importance of Essay Outlines
An outlined essay helps you stay on track and prove your argument in the best possible way. To avoid deviating from the topic, always start writing an essay after creating the outline. The main reason behind this is that essays with an outline are less confusing and easier to follow. Here’s what an essay outline brings to your paper:
- An essay with an outline has more transitions, and that too, in appropriate places— The lack of transitional words and phrases in an essay is a sign of an essay without an outline. Whether you write an essay in the field of academics or a pitch to persuade your customer, transitions allow the readers to understand your arguments with ease.
- Improved paragraph structure— Outlining can significantly improve your paragraph structure. Every paragraph should begin with a topic sentence and end with an argument, supporting points, an analysis, and a closing statement. Students who don’t outline frequently violate these rules of structure and eventually lose points.
- No distractions or misplaced paragraphs— An experienced reader or writer can easily identify an essay with no outline as it is more or less confusing. When you create an outline, you know what type of argument you are going to support. The possibility of mistakenly mixing things up doubles when you start writing without first considering the essay’s structure.
- No repetition of the writer’s arguments and ideas— Finally, experts from MyAssignmentHelp say that most essays without an outline tend to be repetitive. When you write a longer essay without any clear thought in mind, it’s easy to get carried away and lose track. For this reason, nearly all professional writing services provide an exclusive outlining feature. Though it’s not free, it’s rather affordable, so if you are not very good at outlining, getting it is quite relevant.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Essay Outlines
As we write an essay outline, we make common mistakes. After all, we are humans and we do get out of focus sometimes. Here are the mistakes students must consider, or they might have a significant impact on the quality of your essay:
Basic spelling
When reviewing your paper, the most common type of mistake you will find is the spelling mistake. Focus more on your spelling and take help from Microsoft Word and other processors to ensure your paper is error-free.
Sentence fragments
You can modify this part by reading it aloud. There are different types of sentences that just couldn’t stand on their own without an intro. If there is any type of sentence like this, simply remove it or merge it with another sentence. Make sure there are all full sentences in your essay, which is a strong criterion for securing excellent grades.
Bad spacing
If necessary, make sure your paper is double-spaced. However, it extends beyond that. The paper must look consistent and well-organised overall. If it is not, there may be an issue with your spacing. Most students lose points because of it, so keep a close eye on this.
Missing transitions
Again, reading your essay aloud will help you identify problems like, “What transitions are you missing? Is the paper clear? Do you have a thesis statement?”. Moreover, you can easily contact our expert essay writers at MyAssignmentHelp and ask them to highlight any flaws that you might have overlooked.
Once your outline is ready, proceed with the next steps in the writing process to finish the paper. If the above information falls short for you, don’t hesitate to seek expert essay help from MyAssignmentHelp. They can assist you in refining your first draft into an error-free and quality piece of writing. They can help you with any necessary edits that maintain a clear, consistent tone that precisely communicates what you are trying to convey.

Hi, I am Mark, a Literature writer by profession. Fueled by a lifelong passion for Literature, story, and creative expression, I went on to get a PhD in creative writing. Over all these years, my passion has helped me manage a publication of my write ups in prominent websites and e-magazines. I have also been working part-time as a writing expert for myassignmenthelp.com for 5+ years now. It’s fun to guide students on academic write ups and bag those top grades like a pro. Apart from my professional life, I am a big-time foodie and travel enthusiast in my personal life. So, when I am not working, I am probably travelling places to try regional delicacies and sharing my experiences with people through my blog.
Related Post

How to write an essay
- Essay format
Essay structure
- Essay structure guide
- Essay outline
- Essay title
- Essay introduction
- Paragraph structure
- Topic sentence
- Transition sentences
- Essay conclusion
- How to make an essay longer
- Short essay
- 150 words essay
- 200 word essay
- 250 word essay
- How many pages is 1000 words essay
- 1400 word essay
- 2000 word essay
- 5 paragraph essay
- 10 page essay
- 100 page essay
Essay topics
How to revise an essay, essay hooks.
Get original papers written according to your instructions and save time for what matters most.
What Does an Essay Look Like? Tips and Answers to Succeed
What does an essay look like? At a glance, the answer is obvious. An essay looks like a mere piece of paper (one page or several pages) with an organized text. It’s generally divided into five paragraphs, though there may be more. The essential essay structure includes:
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
- introduction;
- 2-3 body paragraphs;
- conclusion.
Yet, will this description help you write a good essay? We suppose not because this piece of paper “hides” many secrets inside!
Let our team give you more details and describe what a good essay looks like in reality. We’ll show the inside and out of this academic paper with a few tips on writing it.
📃 What Does an Essay Look Like on the Outside?
First of all, you should know that a good essay should look pretty. How can you do that? By following all the requirements set by your teacher or of a particular formatting style.
- What does an essay look like according to the teacher’s requirements? It is usually a paper with 1-inch margins on all sides typed using a 12 pt. standard font. Standard school and college essays have a five-paragraph format.
- What does an essay look like if it should be arranged according to a format? Depends on the format. MLA and APA are the most popular ones, but there are many more (Chicago, Harvard, Vancouver, etc.). Besides, each of them has different editions. Before writing an essay, ensure that you understand what format is required.
You will also have to set up 1-inch margins, use a 12 pt. font and double spacing throughout the text. However, it is better to get a specific style manual for more details. You can also check our article about MLA or APA styles.
✒️ What Does an Essay Look like on the Inside?
What we mean is how the text itself should be organized. Its content relies on the task given and the paper’s type.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
We recommend you follow the instructions and understand clearly what the tutor wants from you regarding the task. If you’re unsure, don’t hesitate to clarify before writing. Checking out some examples of academic essay writing would be helpful too.
The essay type defines the contents of your assignment, considerably affecting the main body of your text. To identify it, make sure you read the task well, and understand what the tutor asked you to do.
In other words:
Not everyone knows that what makes a good essay is how precisely you follow your essay guidelines. First, underline the keywords from your assignment that will help you in doing that. Then, complete the task.
Here is the list of the most common keywords:
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
- Agree/Disagree. Identify your position and think about a list of arguments that can support your point of view. It can help come up with an essay plan at this point because it will allow you not to deviate from your arguments.
- Analyze. Here, the college instructor or your school teacher wants to test your analytical abilities. They want to see if you can build bridges between the arguments and analyze the relationships between them.
- Compare. This keyword means that you need to demonstrate differences and similarities between problems, ideas, or concepts in your essay.
- Describe/Discuss. On a surface level, to describe is to examine an issue or an object in detail.
- Explain. Similarly, to explain is to tell why the things the way they are.
- Illustrate. Here, your teacher expects you to come up with some great examples to bring the topic alive.
- Interpret. If you find this keyword in your assignment, you should give your understanding of the matter. It should provide some interesting angles of looking at the topic.
- List/State. To write an essay with this keyword in the assignment, make a list of facts or points.
- Summarize. Your essay should focus on the main ideas and problems.
A typical essay structure is split into five paragraphs:
- Introduction: The goal of an introduction is to hook your reader. It sets a tone and prepares for what is yet to come. It is done through your thesis statement. You can start your introduction paragraph with a quote, a short joke, a question, or a historical reference. Don’t try to bring complicated terminology and wording into this part of your essay. Use clear sentences that are engaging and catchy for a high-quality essay introduction.
- Body Paragraphs: Think about this part of your essay as the essay base. Here, you are expected to prove your thesis and find an interesting approach to looking at it. You will have to restate your main idea again, provide evidence that proves it, analyze the evidence, and connect these ideas.
- Conclusion: A conclusion is the last part of your essay, which summarizes the arguments and explains the broader importance of the topic. In a way, a concluding paragraph should answer a “so what?” question. To have a clearer vision of what a conclusion for your essay may look like, you can put its text into a summary machine and see what comes out.
It is a standard structure that allows disclosing a topic properly, logically expressing all your ideas. What does an essay look like if you want to make it original? In this case, it will look like a paper with a couple of pictures, diagrams, or maps.
It is always useful to check some examples before getting down to work. Here you can check how 9th-grade essays should look like.
Thank you for reading this article. We hope you found it useful. Don’t forget to share it with your peers!
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
References:
- Essay Structure: Elizabeth Abrams, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
- General Essay Writing Tips: Essay Writing Center, International Student
- What is an Essay? How to Write a Good Essay: LibGuides at Bow Valley College
- Academic Essay Structures: Student Support Center Quick Tips, University of Minnesota
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Some students find writing literary analysis papers rather daunting. Yet, an English class cannot go without this kind of work. By the way, writing literary analysis essays is not that complicated as it seems at a glance. On the contrary, this work may be fascinating, and you have a chance...

These days, leadership and ability to work in a team are the skills that everybody should possess. It is impossible to cope with a large educational or work project alone. However, it can also be challenging to collaborate in a team. You might want to elaborate on importance and difficulties...

Racial profiling is not uncommon. It’s incredibly offensive and unfair behavior that causes most of the protests in support of people of color. It occurs when people are suspected of committing a crime based on their skin color or ethnicity. Unfortunately, most people are unaware that racial profiling is an everyday...

Without a doubt, a natural disaster essay is a tough paper to write. To begin with, when people encounter a disaster risk, it’s a tragedy. Emergency situations can affect hundreds, thousands, and millions of people. These are the crises and events that change people’s lives drastically. So, disaster and emergency...

“You are not only responsible for what you say, but also for what you do not say”Martin Luther There are a lot of other good quotations that can serve as a good beginning for your essay on responsibility and provide good ideas for writing.

Exemplification essays, which are also called illustration essays, are considered one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the easiest tasks require some experience and practice. So, if you are not experienced enough in writing exemplification essays, you will face certain challenges.

You push the snooze button once again and finally open your eyes. It is already 8:50, and your classes start at 9. “I’m going to be late again!”— you think, already in full panic mode. In a minute, you rush out the door half-dressed, swallowing your sandwich on the go. ...

An essay about Harriet Tubman is to focus on the biography and accomplishments of a famous American abolitionist and political activist of the 19th century. Harriet Tubman was born into slavery, escaped it herself, and helped others escape it. She changed many jobs throughout her lifetime, being a housekeeper, a...

What is a documented essay and what is the purpose of it? It is a type of academic writing where the author develops an opinion relying on secondary resources. A documented essay can be assigned in school or college. You should incorporate arguments and facts from outside sources into the...

What is a reflexive essay? If you have just received the assignment and think there is a typo, you’re in the right place. Long story short, no, there is no mistake. You actually need to write a reflexive essay, not a reflective one. The thing is that reflective and reflexive...

Fairies and evil spirits, noble kings and queens, beautiful princesses and brave princes, mysterious castles and abandoned huts somewhere in a thick a wood… This is all about fairy tales. Fairy tales are always associated with childhood. Fairy tales always remind us that love rules the world and the Good...

Subjective or objective essay writing is a common task students have to deal with. On the initial stage of completing the assignment, you should learn how to differentiate these two types of papers. Their goals, methods, as well as language, tone, and voice, are different. A subjective essay focuses on...
I would like an essay to be written for me about Accepting Immigrants as a Citizen
I really don’t understand the connection been a topic and a thesis.

Hey Anna, It’s our pleasure to hear from you. A lot of students have difficulties understanding the connection between a topic and a thesis statement. That’s why we’ve created a super useful guide to cover all your questions. Or, you may want to check out the best examples of thesis statements here . We hope it helps. In case of any questions, do not hesitate to contact us.
Wonder, what does an essay look like! Read the post, and you’ll find the answer to your question and many tips to use in your paper.
It is a common question among first-year students: what does an essay look like and how to write it? You answer all the questions in full! Thank you very much for this!

COMMENTS
An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate assignment before you ...
Step 4: Add Depth with Subpoints. To add depth and clarity to your essay, incorporate subpoints under each main point. These subpoints provide more specific details, evidence, or examples that support your main ideas. They help to further strengthen your arguments and make your essay more convincing.
Compare and contrast essays examine the similarities and differences between two subjects, offering a balanced view. For example, a compare and contrast essay on "Online Learning vs. Traditional Classroom" might follow this outline: I. Introduction. A. Discuss the rise of online learning platforms.
1. Develop a Topic. The first step in your outline is to identify your topic. Once you have a clear understanding of the instructor's expectations, begin brainstorming topics that fit within the assignment. Make a list of ideas and pick the ones that are of your interest.
Outlining is a tool we use in the writing process to help organize our ideas, visualize our paper's potential structure, and to further flesh out and develop points. It allows the writer to understand how he or she will connect information to support the thesis statement and the claims of the paper. An outline provides the writer with a space ...
There are no set rules for how to structure a college application essay, but you should carefully plan and outline to make sure your essay flows smoothly and logically. Typical structural choices include. a series of vignettes with a common theme. a single story that demonstrates your positive qualities. Although many structures can work, there ...
Why it's worth writing an outline. How to outline a paper. Step 1: gather your relevant materials. Step 2: create your thesis. Step 3: find examples. Step 4: analyze your examples. Step 5: arrange your examples. An example.
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Essay outlines are excellent tools for organizing your writing. A strong outline can turn a meandering essay into a focused, persuasive piece of writing.
This is what your outline should look like: Template of Admission Essay Outline. Admission essays are your chance to stand out. Your outline should cover the introduction, your personal background, achievements, challenges faced, and why you're a perfect fit for the institution. It's like crafting a masterpiece self-portrait in the writing ...
An outline presents a picture of the main ideas and the subsidiary ideas of a subject. Some typical uses of outlining might be an essay, a term paper, a book review, or a speech. For any of these, an outline will show a basic overview and important details.
Both your psychology research paper and outline should include three key sections: Introduction: Highlights the main points and presents your hypothesis. Body: Details the ideas and research that support your hypothesis. Conclusion: Briefly reiterates your main points and clarifies support for your position.
For example, if you're writing an essay about whether education institutions opening amidst a global pandemic your outline might look like this: Main idea: Schools reopen and allow in-person teaching. Supporting idea 1: Vaccine is here. Supporting idea 2: In-person learning is most effective.
If you're writing an essay, this would be the body of your essay. These ideas should be drawn directly from your thesis or controlling idea. For example, your outline heading for the main point presented above would look like this: Phrase outline: II. Frankenstein champions emotion over reason; Full sentence outline: II.
An essay consists of three basic parts: Introduction. Body. Conclusion. The essay itself usually has no section headings. Only the title page, author declaration and reference list are written as headings, along with, for example, appendices. Check any task instructions, and your course or unit handbook, for further details.
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
An outline is a tool used to organize written ideas about a topic or thesis into a logical order. Outlines arrange major topics, subtopics, and supporting details. Writers use outlines when writing their papers in order to know which topic to cover in what order. Outlines for papers can be very general or very detailed.
Creating the structure for a short essay - If you are writing a short essay or a 500-word five-paragraph essay, your structure should be like the following: Primary idea; Supporting idea 1; Supporting idea 2; ... Take a look at more than one common example outline for varied essay types: 1. Argumentative essays
At a glance, the answer is obvious. An essay looks like a mere piece of paper (one page or several pages) with an organized text. It's generally divided into five paragraphs, though there may be more. The essential essay structure includes: Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you! conclusion.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.