
How To Write A Dissertation Or Thesis
8 straightforward steps to craft an a-grade dissertation.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
Writing a dissertation or thesis is not a simple task. It takes time, energy and a lot of will power to get you across the finish line. It’s not easy – but it doesn’t necessarily need to be a painful process. If you understand the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis, your research journey will be a lot smoother.
In this post, I’m going to outline the big-picture process of how to write a high-quality dissertation or thesis, without losing your mind along the way. If you’re just starting your research, this post is perfect for you. Alternatively, if you’ve already submitted your proposal, this article which covers how to structure a dissertation might be more helpful.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps
- Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is
- Find a unique and valuable research topic
- Craft a convincing research proposal
- Write up a strong introduction chapter
- Review the existing literature and compile a literature review
- Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research
- Present the findings of your research
- Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications

Step 1: Understand exactly what a dissertation is
This probably sounds like a no-brainer, but all too often, students come to us for help with their research and the underlying issue is that they don’t fully understand what a dissertation (or thesis) actually is.
So, what is a dissertation?
At its simplest, a dissertation or thesis is a formal piece of research , reflecting the standard research process . But what is the standard research process, you ask? The research process involves 4 key steps:
- Ask a very specific, well-articulated question (s) (your research topic)
- See what other researchers have said about it (if they’ve already answered it)
- If they haven’t answered it adequately, undertake your own data collection and analysis in a scientifically rigorous fashion
- Answer your original question(s), based on your analysis findings

In short, the research process is simply about asking and answering questions in a systematic fashion . This probably sounds pretty obvious, but people often think they’ve done “research”, when in fact what they have done is:
- Started with a vague, poorly articulated question
- Not taken the time to see what research has already been done regarding the question
- Collected data and opinions that support their gut and undertaken a flimsy analysis
- Drawn a shaky conclusion, based on that analysis
If you want to see the perfect example of this in action, look out for the next Facebook post where someone claims they’ve done “research”… All too often, people consider reading a few blog posts to constitute research. Its no surprise then that what they end up with is an opinion piece, not research. Okay, okay – I’ll climb off my soapbox now.
The key takeaway here is that a dissertation (or thesis) is a formal piece of research, reflecting the research process. It’s not an opinion piece , nor a place to push your agenda or try to convince someone of your position. Writing a good dissertation involves asking a question and taking a systematic, rigorous approach to answering it.
If you understand this and are comfortable leaving your opinions or preconceived ideas at the door, you’re already off to a good start!

Step 2: Find a unique, valuable research topic
As we saw, the first step of the research process is to ask a specific, well-articulated question. In other words, you need to find a research topic that asks a specific question or set of questions (these are called research questions ). Sounds easy enough, right? All you’ve got to do is identify a question or two and you’ve got a winning research topic. Well, not quite…
A good dissertation or thesis topic has a few important attributes. Specifically, a solid research topic should be:
Let’s take a closer look at these:
Attribute #1: Clear
Your research topic needs to be crystal clear about what you’re planning to research, what you want to know, and within what context. There shouldn’t be any ambiguity or vagueness about what you’ll research.
Here’s an example of a clearly articulated research topic:
An analysis of consumer-based factors influencing organisational trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms.
As you can see in the example, its crystal clear what will be analysed (factors impacting organisational trust), amongst who (consumers) and in what context (British low-cost equity brokerage firms, based online).
Need a helping hand?
Attribute #2: Unique
Your research should be asking a question(s) that hasn’t been asked before, or that hasn’t been asked in a specific context (for example, in a specific country or industry).
For example, sticking organisational trust topic above, it’s quite likely that organisational trust factors in the UK have been investigated before, but the context (online low-cost equity brokerages) could make this research unique. Therefore, the context makes this research original.
One caveat when using context as the basis for originality – you need to have a good reason to suspect that your findings in this context might be different from the existing research – otherwise, there’s no reason to warrant researching it.
Attribute #3: Important
Simply asking a unique or original question is not enough – the question needs to create value. In other words, successfully answering your research questions should provide some value to the field of research or the industry. You can’t research something just to satisfy your curiosity. It needs to make some form of contribution either to research or industry.
For example, researching the factors influencing consumer trust would create value by enabling businesses to tailor their operations and marketing to leverage factors that promote trust. In other words, it would have a clear benefit to industry.
So, how do you go about finding a unique and valuable research topic? We explain that in detail in this video post – How To Find A Research Topic . Yeah, we’ve got you covered 😊
Step 3: Write a convincing research proposal
Once you’ve pinned down a high-quality research topic, the next step is to convince your university to let you research it. No matter how awesome you think your topic is, it still needs to get the rubber stamp before you can move forward with your research. The research proposal is the tool you’ll use for this job.
So, what’s in a research proposal?
The main “job” of a research proposal is to convince your university, advisor or committee that your research topic is worthy of approval. But convince them of what? Well, this varies from university to university, but generally, they want to see that:
- You have a clearly articulated, unique and important topic (this might sound familiar…)
- You’ve done some initial reading of the existing literature relevant to your topic (i.e. a literature review)
- You have a provisional plan in terms of how you will collect data and analyse it (i.e. a methodology)
At the proposal stage, it’s (generally) not expected that you’ve extensively reviewed the existing literature , but you will need to show that you’ve done enough reading to identify a clear gap for original (unique) research. Similarly, they generally don’t expect that you have a rock-solid research methodology mapped out, but you should have an idea of whether you’ll be undertaking qualitative or quantitative analysis , and how you’ll collect your data (we’ll discuss this in more detail later).
Long story short – don’t stress about having every detail of your research meticulously thought out at the proposal stage – this will develop as you progress through your research. However, you do need to show that you’ve “done your homework” and that your research is worthy of approval .
So, how do you go about crafting a high-quality, convincing proposal? We cover that in detail in this video post – How To Write A Top-Class Research Proposal . We’ve also got a video walkthrough of two proposal examples here .
Step 4: Craft a strong introduction chapter
Once your proposal’s been approved, its time to get writing your actual dissertation or thesis! The good news is that if you put the time into crafting a high-quality proposal, you’ve already got a head start on your first three chapters – introduction, literature review and methodology – as you can use your proposal as the basis for these.
Handy sidenote – our free dissertation & thesis template is a great way to speed up your dissertation writing journey.
What’s the introduction chapter all about?
The purpose of the introduction chapter is to set the scene for your research (dare I say, to introduce it…) so that the reader understands what you’ll be researching and why it’s important. In other words, it covers the same ground as the research proposal in that it justifies your research topic.
What goes into the introduction chapter?
This can vary slightly between universities and degrees, but generally, the introduction chapter will include the following:
- A brief background to the study, explaining the overall area of research
- A problem statement , explaining what the problem is with the current state of research (in other words, where the knowledge gap exists)
- Your research questions – in other words, the specific questions your study will seek to answer (based on the knowledge gap)
- The significance of your study – in other words, why it’s important and how its findings will be useful in the world
As you can see, this all about explaining the “what” and the “why” of your research (as opposed to the “how”). So, your introduction chapter is basically the salesman of your study, “selling” your research to the first-time reader and (hopefully) getting them interested to read more.
How do I write the introduction chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this post .

Step 5: Undertake an in-depth literature review
As I mentioned earlier, you’ll need to do some initial review of the literature in Steps 2 and 3 to find your research gap and craft a convincing research proposal – but that’s just scratching the surface. Once you reach the literature review stage of your dissertation or thesis, you need to dig a lot deeper into the existing research and write up a comprehensive literature review chapter.
What’s the literature review all about?
There are two main stages in the literature review process:
Literature Review Step 1: Reading up
The first stage is for you to deep dive into the existing literature (journal articles, textbook chapters, industry reports, etc) to gain an in-depth understanding of the current state of research regarding your topic. While you don’t need to read every single article, you do need to ensure that you cover all literature that is related to your core research questions, and create a comprehensive catalogue of that literature , which you’ll use in the next step.
Reading and digesting all the relevant literature is a time consuming and intellectually demanding process. Many students underestimate just how much work goes into this step, so make sure that you allocate a good amount of time for this when planning out your research. Thankfully, there are ways to fast track the process – be sure to check out this article covering how to read journal articles quickly .

Literature Review Step 2: Writing up
Once you’ve worked through the literature and digested it all, you’ll need to write up your literature review chapter. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is simply a summary of what other researchers have said. While this is partly true, a literature review is much more than just a summary. To pull off a good literature review chapter, you’ll need to achieve at least 3 things:
- You need to synthesise the existing research , not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how different pieces of theory fit together, what’s agreed on by researchers, what’s not.
- You need to highlight a research gap that your research is going to fill. In other words, you’ve got to outline the problem so that your research topic can provide a solution.
- You need to use the existing research to inform your methodology and approach to your own research design. For example, you might use questions or Likert scales from previous studies in your your own survey design .
As you can see, a good literature review is more than just a summary of the published research. It’s the foundation on which your own research is built, so it deserves a lot of love and attention. Take the time to craft a comprehensive literature review with a suitable structure .
But, how do I actually write the literature review chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this video post .
Step 6: Carry out your own research
Once you’ve completed your literature review and have a sound understanding of the existing research, its time to develop your own research (finally!). You’ll design this research specifically so that you can find the answers to your unique research question.
There are two steps here – designing your research strategy and executing on it:
1 – Design your research strategy
The first step is to design your research strategy and craft a methodology chapter . I won’t get into the technicalities of the methodology chapter here, but in simple terms, this chapter is about explaining the “how” of your research. If you recall, the introduction and literature review chapters discussed the “what” and the “why”, so it makes sense that the next point to cover is the “how” –that’s what the methodology chapter is all about.
In this section, you’ll need to make firm decisions about your research design. This includes things like:
- Your research philosophy (e.g. positivism or interpretivism )
- Your overall methodology (e.g. qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods)
- Your data collection strategy (e.g. interviews , focus groups, surveys)
- Your data analysis strategy (e.g. content analysis , correlation analysis, regression)
If these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these in plain language in other posts. It’s not essential that you understand the intricacies of research design (yet!). The key takeaway here is that you’ll need to make decisions about how you’ll design your own research, and you’ll need to describe (and justify) your decisions in your methodology chapter.
2 – Execute: Collect and analyse your data
Once you’ve worked out your research design, you’ll put it into action and start collecting your data. This might mean undertaking interviews, hosting an online survey or any other data collection method. Data collection can take quite a bit of time (especially if you host in-person interviews), so be sure to factor sufficient time into your project plan for this. Oftentimes, things don’t go 100% to plan (for example, you don’t get as many survey responses as you hoped for), so bake a little extra time into your budget here.
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to do some data preparation before you can sink your teeth into the analysis. For example:
- If you carry out interviews or focus groups, you’ll need to transcribe your audio data to text (i.e. a Word document).
- If you collect quantitative survey data, you’ll need to clean up your data and get it into the right format for whichever analysis software you use (for example, SPSS, R or STATA).
Once you’ve completed your data prep, you’ll undertake your analysis, using the techniques that you described in your methodology. Depending on what you find in your analysis, you might also do some additional forms of analysis that you hadn’t planned for. For example, you might see something in the data that raises new questions or that requires clarification with further analysis.
The type(s) of analysis that you’ll use depend entirely on the nature of your research and your research questions. For example:
- If your research if exploratory in nature, you’ll often use qualitative analysis techniques .
- If your research is confirmatory in nature, you’ll often use quantitative analysis techniques
- If your research involves a mix of both, you might use a mixed methods approach
Again, if these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these concepts and techniques in other posts. The key takeaway is simply that there’s no “one size fits all” for research design and methodology – it all depends on your topic, your research questions and your data. So, don’t be surprised if your study colleagues take a completely different approach to yours.

Step 7: Present your findings
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to present your findings (finally!). In a dissertation or thesis, you’ll typically present your findings in two chapters – the results chapter and the discussion chapter .
What’s the difference between the results chapter and the discussion chapter?
While these two chapters are similar, the results chapter generally just presents the processed data neatly and clearly without interpretation, while the discussion chapter explains the story the data are telling – in other words, it provides your interpretation of the results.
For example, if you were researching the factors that influence consumer trust, you might have used a quantitative approach to identify the relationship between potential factors (e.g. perceived integrity and competence of the organisation) and consumer trust. In this case:
- Your results chapter would just present the results of the statistical tests. For example, correlation results or differences between groups. In other words, the processed numbers.
- Your discussion chapter would explain what the numbers mean in relation to your research question(s). For example, Factor 1 has a weak relationship with consumer trust, while Factor 2 has a strong relationship.
Depending on the university and degree, these two chapters (results and discussion) are sometimes merged into one , so be sure to check with your institution what their preference is. Regardless of the chapter structure, this section is about presenting the findings of your research in a clear, easy to understand fashion.
Importantly, your discussion here needs to link back to your research questions (which you outlined in the introduction or literature review chapter). In other words, it needs to answer the key questions you asked (or at least attempt to answer them).
For example, if we look at the sample research topic:
In this case, the discussion section would clearly outline which factors seem to have a noteworthy influence on organisational trust. By doing so, they are answering the overarching question and fulfilling the purpose of the research .

For more information about the results chapter , check out this post for qualitative studies and this post for quantitative studies .
Step 8: The Final Step Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications
Last but not least, you’ll need to wrap up your research with the conclusion chapter . In this chapter, you’ll bring your research full circle by highlighting the key findings of your study and explaining what the implications of these findings are.
What exactly are key findings? The key findings are those findings which directly relate to your original research questions and overall research objectives (which you discussed in your introduction chapter). The implications, on the other hand, explain what your findings mean for industry, or for research in your area.
Sticking with the consumer trust topic example, the conclusion might look something like this:
Key findings
This study set out to identify which factors influence consumer-based trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms. The results suggest that the following factors have a large impact on consumer trust:
While the following factors have a very limited impact on consumer trust:
Notably, within the 25-30 age groups, Factors E had a noticeably larger impact, which may be explained by…
Implications
The findings having noteworthy implications for British low-cost online equity brokers. Specifically:
The large impact of Factors X and Y implies that brokers need to consider….
The limited impact of Factor E implies that brokers need to…
As you can see, the conclusion chapter is basically explaining the “what” (what your study found) and the “so what?” (what the findings mean for the industry or research). This brings the study full circle and closes off the document.

Let’s recap – how to write a dissertation or thesis
You’re still with me? Impressive! I know that this post was a long one, but hopefully you’ve learnt a thing or two about how to write a dissertation or thesis, and are now better equipped to start your own research.
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows:
- Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process.
- Find a unique (original) and important research topic
- Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal
- Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
- Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review
- Undertake your own research
- Present and interpret your findings
Once you’ve wrapped up the core chapters, all that’s typically left is the abstract , reference list and appendices. As always, be sure to check with your university if they have any additional requirements in terms of structure or content.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

20 Comments
thankfull >>>this is very useful
Thank you, it was really helpful
unquestionably, this amazing simplified way of teaching. Really , I couldn’t find in the literature words that fully explicit my great thanks to you. However, I could only say thanks a-lot.
Great to hear that – thanks for the feedback. Good luck writing your dissertation/thesis.
This is the most comprehensive explanation of how to write a dissertation. Many thanks for sharing it free of charge.
Very rich presentation. Thank you
Thanks Derek Jansen|GRADCOACH, I find it very useful guide to arrange my activities and proceed to research!
Thank you so much for such a marvelous teaching .I am so convinced that am going to write a comprehensive and a distinct masters dissertation
It is an amazing comprehensive explanation
This was straightforward. Thank you!
I can say that your explanations are simple and enlightening – understanding what you have done here is easy for me. Could you write more about the different types of research methods specific to the three methodologies: quan, qual and MM. I look forward to interacting with this website more in the future.
Thanks for the feedback and suggestions 🙂
Hello, your write ups is quite educative. However, l have challenges in going about my research questions which is below; *Building the enablers of organisational growth through effective governance and purposeful leadership.*
Very educating.
Just listening to the name of the dissertation makes the student nervous. As writing a top-quality dissertation is a difficult task as it is a lengthy topic, requires a lot of research and understanding and is usually around 10,000 to 15000 words. Sometimes due to studies, unbalanced workload or lack of research and writing skill students look for dissertation submission from professional writers.
Thank you 💕😊 very much. I was confused but your comprehensive explanation has cleared my doubts of ever presenting a good thesis. Thank you.
thank you so much, that was so useful
Hi. Where is the excel spread sheet ark?
could you please help me look at your thesis paper to enable me to do the portion that has to do with the specification
my topic is “the impact of domestic revenue mobilization.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
7 tips for efficient thesis writing
Writing your thesis isn’t always a walk in the park, so here are some tips to help you out.
- Post a comment
It’s no secret that writing your master’s or doctoral thesis is no easy task. Writer’s block and procrastination haunt many graduate students. Nonetheless, Geneviève Belleville, psychology professor at Université Laval, has a few tricks that can help make things easier. Back in 2014, she compiled her advice into a book: Assieds-toi et écris ta thèse! Trucs pratiques et motivationnels (Sit Down and Write Your Thesis: Some Practical and Motivational Tips).
At the most recent Journées de la relève en recherche held by Acfas, the association of French-speaking researchers, Dr. Belleville gave a presentation on seven keys to writing a thesis efficiently and (almost) worry-free.
1. Set specific times for writing
To start off, Dr. Belleville advises that you set aside short periods of time each day to write. She encourages you to regularly re-evaluate how long these blocks of time last. Why choose shorter writing periods over longer ones? To prevent procrastination and to reduce the eventual pressure to write. While it is important to write each day, she also recommends taking complete breaks from it. “The kind of person who succeeds in graduate studies is someone who also manages to do other things in life,” she says. “It’s a bit of a paradox, but [people who are successful] are invested in their studies but are also able to do other things, for example, on evenings or weekends.”
2. Set goals
Dr. Belleville says there are different types of goals that apply to writing a thesis: long-term, specific and weekly goals, as well as time-bound or project-driven goals. “You can’t expect a master’s degree or a PhD to be easy — you have to set goals and define motivations,” she explains. She suggests taking inspiration from the concept of SMART objectives to help with this stage. This method prescribes setting objectives that are s pecific, m easurable, a chievable, r ealistic, and t ime-bound. For example, don’t take on a literature review when you have 35 minutes left at the end of a long workday!
3. Distinguish the different writing stages
There are three main stages to a thesis: planning, writing and editing. A well-thought-out plan makes it easier to start writing while reducing stress and hesitation. When it comes to writing, she recommends tackling this task without overthinking it. Writing ideas quickly without thinking about every word choice accelerates the process and prevents you from getting bogged down in one spot for too long. The editing stage is where it’s important to carefully consider the relevance of each sentence, spend more time on your structure and argumentation, correct typos and refine your style. Dr. Belleville reminds us that “We’re writing for others — not ourselves.”
4. Inspiration is a rationalization
Dr. Belleville adds that waiting for inspiration to start writing is just an excuse to procrastinate. “Writing doesn’t need inspiration, it needs structure,” she says. She believes that the best ways to get motivated are to write each day, for example, or to keep a notebook of ideas, vary your tasks, or talk about the subject with the people around you.
5. Avoid procrastination
“Scientific writing is one of the jobs most likely to be put off to the next day,” she explains. One of the reasons this happens in thesis writing is the anxiety it causes. The last stage of a PhD is also the most important, as it determines whether or not you earn your degree. More often than not, procrastination only causes more anxiety. Dr. Belleville has advice for fighting this tendency to postpone work. First, she emphasizes the importance of planning short, daily writing periods. You also need to create a pleasant, functional space that’s conducive to writing. Lastly, you need to remember that everyone procrastinates from time to time, so there’s no need to get hung up on it when you do!
6. Resist perfectionism!
Dr. Belleville argues that perfectionism and productivity are not the same thing. She says that while it’s a good thing to have high standards, having unrealistic ones is just shooting yourself in the foot. “Perfectionists are often unproductive because they are paralysed by their perfectionism.” She sees perfectionism as kind of cult “where the ideals we aim to achieve are attractive but unrealistic.” Perfection can come with certain nuances. Wanting to perform and excel is not the same issue as taking on too much, and both have very different outcomes.
7. Stay connected and talk about it with others
She concluded her presentation by stating “you have to make sure not to get lost in the thesis writing process.” Shutting yourself in, away from everyone else, is far from a good idea, and you shouldn’t hesitate to discuss any problems that come up. It’s important to remember that this kind of project will always come with setbacks.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
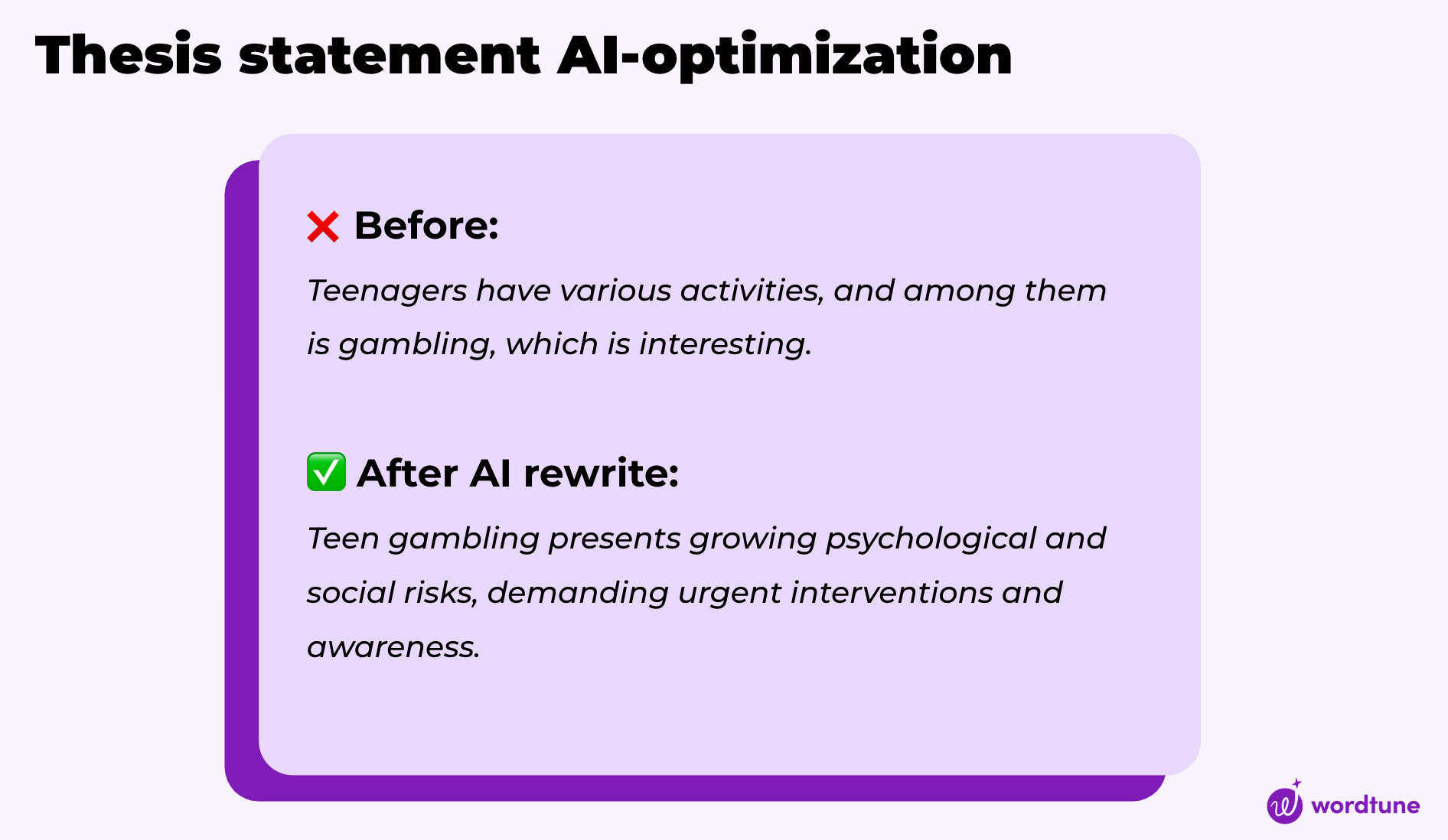
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
How to Write a Better Thesis Statement Using AI (2023 Updated)

Table of contents

Meredith Sell
With the exceptions of poetry and fiction, every piece of writing needs a thesis statement.
- Opinion pieces for the local newspaper? Yes.
- An essay for a college class? You betcha.
- A book about China’s Ming Dynasty? Absolutely.
All of these pieces of writing need a thesis statement that sums up what they’re about and tells the reader what to expect, whether you’re making an argument, describing something in detail, or exploring ideas.
But how do you write a thesis statement? How do you even come up with one?
This step-by-step guide will show you exactly how — and help you make sure every thesis statement you write has all the parts needed to be clear, coherent, and complete.
Let’s start by making sure we understand what a thesis is (and what it’s not).
What Is a Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a one or two sentence long statement that concisely describes your paper’s subject, angle or position — and offers a preview of the evidence or argument your essay will present.
A thesis is not:
- An exclamation
- A simple fact
Think of your thesis as the road map for your essay. It briefly charts where you’ll start (subject), what you’ll cover (evidence/argument), and where you’ll land (position, angle).
Writing a thesis early in your essay writing process can help you keep your writing focused, so you won’t get off-track describing something that has nothing to do with your central point. Your central point is your thesis, and the rest of your essay fleshes it out.
Get help writing your thesis statement with this FREE AI tool > Get help writing your thesis statement with this FREE AI tool >
Different Kinds of Papers Need Different Kinds of Theses
How you compose your thesis will depend on the type of essay you’re writing. For academic writing, there are three main kinds of essays:
- Persuasive, aka argumentative
- Expository, aka explanatory
A persuasive essay requires a thesis that clearly states the central stance of the paper , what the rest of the paper will argue in support of.
Paper books are superior to ebooks when it comes to form, function, and overall reader experience.
An expository essay’s thesis sets up the paper’s focus and angle — the paper’s unique take, what in particular it will be describing and why . The why element gives the reader a reason to read; it tells the reader why the topic matters.
Understanding the functional design of physical books can help ebook designers create digital reading experiences that usher readers into literary worlds without technological difficulties.
A narrative essay is similar to that of an expository essay, but it may be less focused on tangible realities and more on intangibles of, for example, the human experience.
The books I’ve read over the years have shaped me, opening me up to worlds and ideas and ways of being that I would otherwise know nothing about.
As you prepare to craft your thesis, think through the goal of your paper. Are you making an argument? Describing the chemical properties of hydrogen? Exploring your relationship with the outdoors? What do you want the reader to take away from reading your piece?
Make note of your paper’s goal and then walk through our thesis-writing process.
Now that you practically have a PhD in theses, let’s learn how to write one:
How to Write (and Develop) a Strong Thesis
If developing a thesis is stressing you out, take heart — basically no one has a strong thesis right away. Developing a thesis is a multi-step process that takes time, thought, and perhaps most important of all: research .
Tackle these steps one by one and you’ll soon have a thesis that’s rock-solid.
1. Identify your essay topic.
Are you writing about gardening? Sword etiquette? King Louis XIV?
With your assignment requirements in mind, pick out a topic (or two) and do some preliminary research . Read up on the basic facts of your topic. Identify a particular angle or focus that’s interesting to you. If you’re writing a persuasive essay, look for an aspect that people have contentious opinions on (and read our piece on persuasive essays to craft a compelling argument).
If your professor assigned a particular topic, you’ll still want to do some reading to make sure you know enough about the topic to pick your specific angle.
For those writing narrative essays involving personal experiences, you may need to do a combination of research and freewriting to explore the topic before honing in on what’s most compelling to you.
Once you have a clear idea of the topic and what interests you, go on to the next step.
2. Ask a research question.
You know what you’re going to write about, at least broadly. Now you just have to narrow in on an angle or focus appropriate to the length of your assignment. To do this, start by asking a question that probes deeper into your topic.
This question may explore connections between causes and effects, the accuracy of an assumption you have, or a value judgment you’d like to investigate, among others.
For example, if you want to write about gardening for a persuasive essay and you’re interested in raised garden beds, your question could be:
What are the unique benefits of gardening in raised beds versus on the ground? Is one better than the other?
Or if you’re writing about sword etiquette for an expository essay , you could ask:
How did sword etiquette in Europe compare to samurai sword etiquette in Japan?
How does medieval sword etiquette influence modern fencing?
Kickstart your curiosity and come up with a handful of intriguing questions. Then pick the two most compelling to initially research (you’ll discard one later).
3. Answer the question tentatively.
You probably have an initial thought of what the answer to your research question is. Write that down in as specific terms as possible. This is your working thesis .
Gardening in raised beds is preferable because you won’t accidentally awaken dormant weed seeds — and you can provide more fertile soil and protection from invasive species.
Medieval sword-fighting rituals are echoed in modern fencing etiquette.
Why is a working thesis helpful?
Both your research question and your working thesis will guide your research. It’s easy to start reading anything and everything related to your broad topic — but for a 4-, 10-, or even 20-page paper, you don’t need to know everything. You just need the relevant facts and enough context to accurately and clearly communicate to your reader.
Your working thesis will not be identical to your final thesis, because you don’t know that much just yet.
This brings us to our next step:
4. Research the question (and working thesis).
What do you need to find out in order to evaluate the strength of your thesis? What do you need to investigate to answer your research question more fully?
Comb through authoritative, trustworthy sources to find that information. And keep detailed notes.
As you research, evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of your thesis — and see what other opposing or more nuanced theses exist.
If you’re writing a persuasive essay, it may be helpful to organize information according to what does or does not support your thesis — or simply gather the information and see if it’s changing your mind. What new opinion do you have now that you’ve learned more about your topic and question? What discoveries have you made that discredit or support your initial thesis?
Raised garden beds prevent full maturity in certain plants — and are more prone to cold, heat, and drought.
If you’re writing an expository essay, use this research process to see if your initial idea holds up to the facts. And be on the lookout for other angles that would be more appropriate or interesting for your assignment.
Modern fencing doesn’t share many rituals with medieval swordplay.
With all this research under your belt, you can answer your research question in-depth — and you’ll have a clearer idea of whether or not your working thesis is anywhere near being accurate or arguable. What’s next?
5. Refine your thesis.
If you found that your working thesis was totally off-base, you’ll probably have to write a new one from scratch.
For a persuasive essay , maybe you found a different opinion far more compelling than your initial take. For an expository essay , maybe your initial assumption was completely wrong — could you flip your thesis around and inform your readers of what you learned?
Use what you’ve learned to rewrite or revise your thesis to be more accurate, specific, and compelling.
Raised garden beds appeal to many gardeners for the semblance of control they offer over what will and will not grow, but they are also more prone to changes in weather and air temperature and may prevent certain plants from reaching full maturity. All of this makes raised beds the worse option for ambitious gardeners.
While swordplay can be traced back through millennia, modern fencing has little in common with medieval combat where swordsmen fought to the death.
If you’ve been researching two separate questions and theses, now’s the time to evaluate which one is most interesting, compelling, or appropriate for your assignment. Did one thesis completely fall apart when faced with the facts? Did one fail to turn up any legitimate sources or studies? Choose the stronger question or the more interesting (revised) thesis, and discard the other.
6. Get help from AI
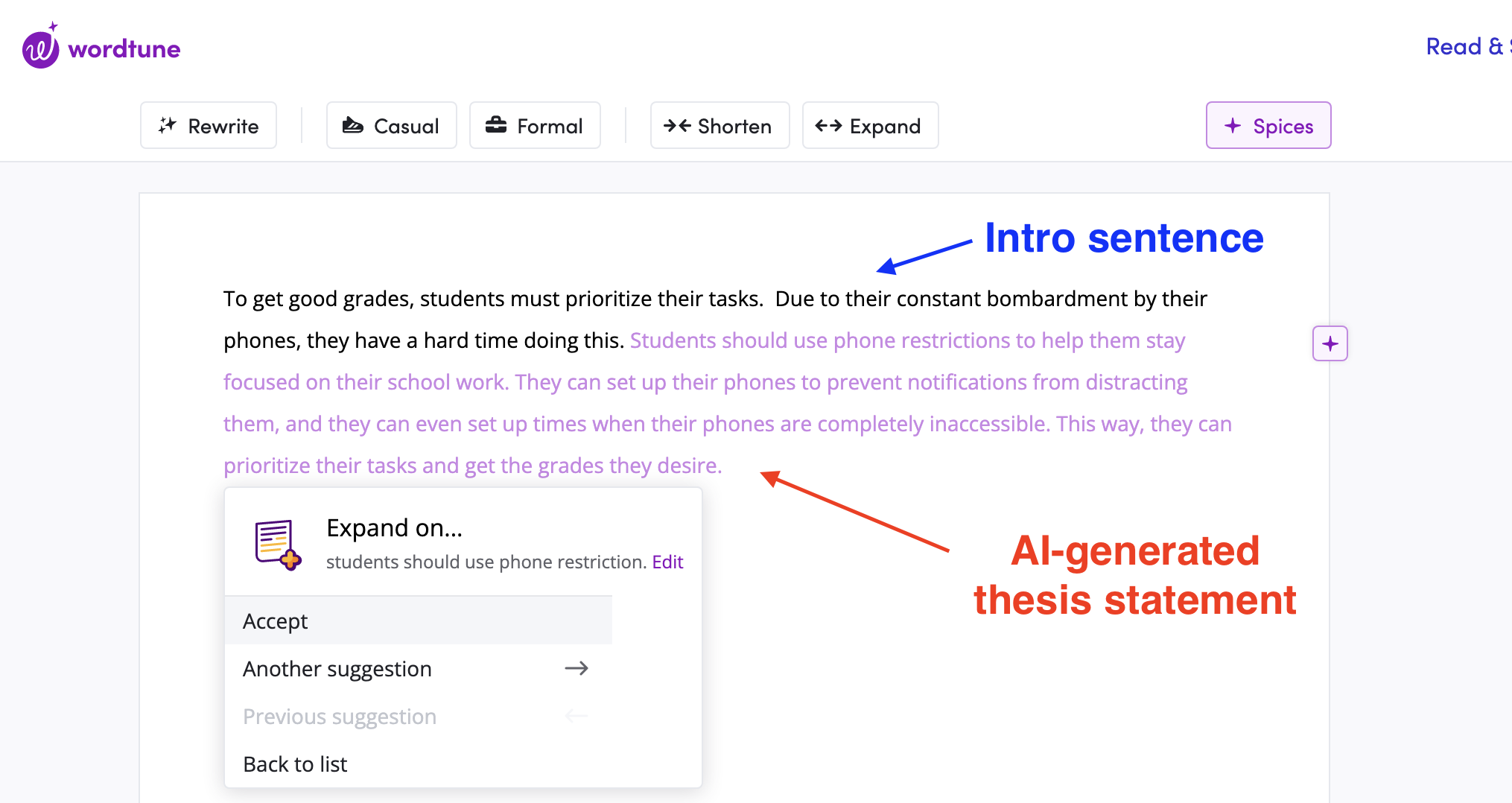
To make the process even easier, you can take advantage of Wordtune's generative AI capabilities to craft an effective thesis statement. You can take your current thesis statement and try the paraphrase tool to get suggestions for better ways of articulating it. WordTune will generate a set of related phrases, which you can select to help you refine your statement. You can also use Wordtune's suggestions to craft the thesis statement. Write your initial introduction sentence, then click '+' and select the explain suggestion. Browse through the suggestions until you have a statement that captures your idea perfectly.

Thesis Check: Look for These Three Elements
At this point, you should have a thesis that will set up an original, compelling essay, but before you set out to write that essay, make sure your thesis contains these three elements:
- Topic: Your thesis should clearly state the topic of your essay, whether swashbuckling pirates, raised garden beds, or methods of snow removal.
- Position or angle: Your thesis should zoom into the specific aspect of your topic that your essay will focus on, and briefly but boldly state your position or describe your angle.
- Summary of evidence and/or argument: In a concise phrase or two, your thesis should summarize the evidence and/or argument your essay will present, setting up your readers for what’s coming without giving everything away.
The challenge for you is communicating each of these elements in a sentence or two. But remember: Your thesis will come at the end of your intro, which will already have done some work to establish your topic and focus. Those aspects don’t need to be over explained in your thesis — just clearly mentioned and tied to your position and evidence.
Let’s look at our examples from earlier to see how they accomplish this:
Notice how:
- The topic is mentioned by name.
- The position or angle is clearly stated.
- The evidence or argument is set up, as well as the assumptions or opposing view that the essay will debunk.
Both theses prepare the reader for what’s coming in the rest of the essay:
- An argument to show that raised beds are actually a poor option for gardeners who want to grow thriving, healthy, resilient plants.
- An exposition of modern fencing in comparison with medieval sword fighting that shows how different they are.
Examine your refined thesis. Are all three elements present? If any are missing, make any additions or clarifications needed to correct it.
It’s Essay-Writing Time!
Now that your thesis is ready to go, you have the rest of your essay to think about. With the work you’ve already done to develop your thesis, you should have an idea of what comes next — but if you need help forming your persuasive essay’s argument, we’ve got a blog for that.
Share This Article:

7 Practical Solutions to Make AI Sound More Human: A Writer’s Guide

What’s a Semicolon? + When to Use It (With Examples)

The 12 Longest Words in English Defined and Explained
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
- Share on twitter
- Share on facebook
10 tips for writing a PhD thesis
Ingrid curl shares simple rules for keeping your work clear and jargon-free.
- Share on linkedin
- Share on mail

Writing up a PhD can often take place in a frenzy of activity in the last few months of your degree study, after years of hard work. But there are some steps that you can take to increase your chances of success.
- Do not be daunted by the task of “writing up”. Work on the text as your PhD takes shape, remember that all writers need editing, and help yourself by using these basic tips to make life easier. Read what great writers say about how to write before you start, and take their advice to heart. There is no dark art to clear, concise work; it is mostly a result of editing, and editing again. Above all, keep Elmore Leonard’s advice in mind: “If it reads like writing…rewrite it.”
- Plan the structure of your thesis carefully with your supervisor. Create rough drafts as you go so that you can refine them as you become more focused on the write-up. Much of writing comprises rewriting so be prepared to rework each chapter many times. Even Ernest Hemingway said: “The first draft of everything is shit.”
- Academic writing does not have to be dry. Inject some flair into your work. Read advice on writing and remember George Orwell’s words in Why I Write : “Never use the passive where you can use the active”; and Mark Twain’s on adjectives: “When you catch an adjective, kill it.” If you prefer, Stephen King said: “The road to hell is paved with adverbs.”
- Do not write up in chronological order. Work on each chapter while it is fresh in your mind or pertinent to what you are doing at that moment, but come back to it all later and work it up into a consistent, coherent piece, restructuring sections where necessary.
- Think carefully about your writing. Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense. Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: “Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.” Clarity is key.
- Most universities use a preferred style of references. Make sure you know what this is and stick to it. One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process. Helpful software includes EndNote or Paperpile. Managing your bibliography from day one may seem obsessive but it will save you a great deal of time and stress by the end of the PhD process.
- Use a house style. Professional publications such as Times Higher Education use a house style guide to ensure consistency in spelling. For example, do not use both -ise spellings and -ize spellings, stick to British spelling and be consistent when referring to organisations or bodies. Because dictionaries vary in their use of hyphenation, use one dictionary and stick to it throughout the writing process. If you consult the New Oxford Dictionary for Writers and Editors , you will note the extraordinary number of words with alternative spellings. It can also be a very useful guide to preferred spellings, use of italicisation and foreign phrases.
- Take care when quoting from other sources. Ensure you note whether the italic emphasis is in the original and take careful notes when you are collecting quotes for your thesis. Transcribe them accurately to save work later and keep original spellings (even if they differ from your chosen style) to ensure fidelity to your source.
- Think about plagiarism. If you are quoting from works, quote from them accurately and paraphrase where necessary for your argument. This is where careful note-taking and use of references is invaluable and will help you to avoid even inadvertently plagiarising another work.
- Remember that your thesis is your chance to present your work in the best possible light. Consider your opening paragraphs, entice your reader with your writing and above all be clear about your hypothesis and your conclusion. Append material where it adds value but not where it merely bulks out your work. Consider your reader at all times. This is your chance to showcase your work.
If you stick to these simple rules, your writing will be clear and jargon-free. Above all, take to heart Orwell’s advice: “Never use a foreign phrase, a scientific word, or a jargon word if you can think of an everyday English equivalent.”
Ingrid Curl is associate editor of Times Higher Education , and a former PhD student.
Register to continue
Why register?
- Registration is free and only takes a moment
- Once registered, you can read 3 articles a month
- Sign up for our newsletter
Or subscribe for unlimited access to:
- Unlimited access to news, views, insights & reviews
- Digital editions
- Digital access to THE’s university and college rankings analysis
Already registered or a current subscriber? Login
Related articles

How to submit a PhD thesis
The final few months of a PhD can often be the hardest, so here are a few tips from a doctoral candidate who recently submitted her thesis

NIH raises postdoctoral salaries, but below target
Top US funding agency manages record increase in key programme for younger scientists, and sees gains in overall equity, while absorbing net cut in its annual budget


How to win the citation game without becoming a cynic
Boosting your publication metrics need not come at the expense of your integrity if you bear in mind these 10 tips, says Adrian Furnham

Black vice-chancellor eyes new generation of minority researchers
David Mba creates fully funded PhD studentships after taking reins at Birmingham City University

Renaming postdocs and PhD students would boost respect, pay, progression
What other industry would deem those with so much prior training to still be mere trainees? Let’s call them what they are – researchers, says Michele Nardin
Featured jobs
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Degrees
- Doctoral Studies
- Theses and Dissertations
How to Write a Master's Thesis
Last Updated: June 1, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 609,648 times.
Students learning how to write a Master's Thesis will first learn that a central thesis question must be presented and subsequently answered. A Master's Thesis will be the most prominent piece of your graduate work up to this point, and a pertinent thesis question that forms the spine of this work elevates it from the prosaic to the significant.
Choosing a Topic

- To get a degree - topic should be difficult enough, but manageable too.
- To enjoy the work - topic that you are truly interested in, something that you will not grow bored of after a short period of time.
- To get a job afterward - if you know what specifically you want to do after your studies and/or for which company, it might be useful to choose a topic, that will help with this goal.
- To be useful - thesis might actually be useful to help to make the world a little better place.
- Try thinking about your favorite subject of study - it may be a particular author, theory, time period, etc. Imagine how you might further the study of that subject.
- You might consider skimming through papers you wrote for your graduate courses and see if there is any apparent topic that you tend to gravitate towards.
- Consult with faculty members, favorite professors. They might have some good suggestions to write about. Generally, you'll be required to meet with your thesis advisor at least once before you start working.
- Consider consulting with industry partners. Your favorite company might have some work to do which might be done as a master's thesis. This might also help you get a job within the company afterward and maybe even some money for the thesis.
- If you want to help the world to be a better place, you might want to consult with your local non-profits and charities or check the Internet for possible thesis topics to write about.
- 3 Choose the right topic. From the possible topics generated in the previous step, find the one which best fits the objectives from the first step, especially the objectives most important to you. Make sure that you have a clear, specific, and organized plan on how to write a master's thesis which you will be able to then defend.

- Make sure that your question and the answers provided will provide original content to the body of research in existence. A judicious question will also keep research focused, organized, and interesting.
- Once you've formulated your topic and direction of inquiry, try formulating 5-10 different questions around your intended research. This forces you to think flexibly about your topic and visualize how small changes in wording can change the trajectory of your research.

- Usually, your committee chair will be in place before you formally start your thesis. They can help guide you and provide input into your project, so the earlier you can get their commitment, the better.
- Nothing is more frustrating than your thesis progress being held up by a professor who has too many obligations to make time to meet with you.
Selecting Your Texts

- For example, a novel written by Ernest Hemingway or a scientific journal article in which new results are documented for the first time would both be considered primary sources.

- For example, a book written about Ernest Hemingway's novel or a scientific journal article examining the findings of someone else's experiment would both be considered secondary sources.

- Use the in-text citation format appropriate to your discipline. [3] X Research source The most common formats are MLA, APA, and Chicago.
- Create a coordinating works cited or reference entry for each source you cite in the text of your document or in a footnote.
- Consider using a citation management software such as EndNote, Mendeley, or Zotero. These will enable you to insert and move citations within your word processor program and will automatically populate a works cited or reference page for you.
Planning an Outline

- Qualitative. This type of thesis involves completing a project that is exploratory, analytical, or creative in some way. Usually, students in the humanities will complete this kind of thesis.
- Quantitative. This type of thesis involves conducting experiments, measuring data, and recording results. Students in the sciences usually complete this kind of thesis.

- Signature page (with the completed signatures of your advising committee - usually attained at the defense, or after the project is deemed complete )
- Abstract - this is a short (one paragraph or so) description/summary of the work completed in your thesis
- Table of Contents (with page numbers)
- Introduction
- Body of paper
- Works Cited or Bibliography
- Any necessary appendices or endnotes
Moving through the Writing Process

- If you do not already have a review of literature written, it’s time to do your research! The review of literature is essentially a summary of all of the existing scholarship about your topic with plenty of direct quotations from the primary and secondary sources that you’re referencing.

Finalizing Your Thesis

- Many departments or programs provide a document template for theses and dissertations. If you have one of these, it may be easiest to use such a template from the beginning of your work (rather than copying and pasting your writing into it).

- Alternatively, ask a trusted colleague or friend to read over your thesis to help you catch any minor grammar/spelling/punctuation errors and typos.

- Some institutions require you to submit your thesis for a formatting check prior to uploading the document to ProQuest. Be sure to check with your department’s Director of Graduate Studies for specific instructions.
- Be aware of thesis submission deadlines, which are often well in advance of your graduation date. Late submission of your thesis may force you to push back your graduation date, which may affect your employment or continuing graduate studies.
Masters Thesis Outline

Expert Q&A

- Remember why you are writing a Master's thesis and who will want to read and use the material. You write a Master's thesis for members of your community, so keep in mind that they will have extensive knowledge and experience before reading your work. Don't bore them with unnecessary material. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Choosing the perfect question before starting research will prevent frustration and save time. Rigorous effort on finding the perfect question is probably the most important task when learning how to write a Master's thesis. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Consult other people who have completed a Master's thesis and obtained a Master's degree. It can be a long, grueling process, and having the support and advice of someone who has already done it can be very valuable. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://umb.libguides.com/PrimarySources/secondary
- ↑ https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/in-text-citation-styles/
- ↑ https://www.unk.edu/academics/gradstudies/admissions/grad-files/Grad%20Files/ThesisGdlnsFinal08.pdf
- ↑ https://u.osu.edu/hackingthethesis/managing-stuff/your-content/outline/
- ↑ http://www.imm.dtu.dk/~janba/MastersThesisAdvice.pdf
About This Article

To write a master's thesis, make it a goal to write 500 words every day, which will help you meet your deadline without having to rush at the last minute. It's also helpful if you work in 25-minute increments and take a 5-minute break in between, which will make your work sessions less overwhelming. Also, figure out a writing time that works best for you, whether it's in the morning or at night, and stick with it so you're more productive. For more help writing your master's thesis, like how to make an outline, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Abdijabaar S.
Did this article help you?
Joseph Pertey
Aug 24, 2018
Jackson Kwakwa
Nov 21, 2017
Genc Zhushi
Apr 18, 2016
İsmail Binmasudi
Jul 20, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
How to Write a Research Paper Fast
Updated: December 8, 2023
Published: January 27, 2020

As a student, you knew it was inevitable. The day has come where you have to write a research paper, but you’ve put it off until the last minute. Now the pressure is sinking in to get it done quickly and you want to know how to write a research paper fast.
The good news is that it’s doable. The better news is that there are ways to avoid waiting until the last minute. We will tackle those after we give you everything you need to know to get it done.

Photo by Russ Ward
The process.
A research paper is what it sounds like — a paper that requires a thesis (or argument) along with the research to back it up. Research papers involve citing a variety of sources, analyzing arguments, and pulling different academic pieces together to prove a point.
1. Understand the Assignment:
The first thing you have to make sure you do before you get to outlining and writing is to understand the assignment. You will need to organize different pieces of information, from books, essays, interviews, articles and more.
2. Choose a Topic:
Depending on the assignment provided, you will either have a topic in front of you or you will have to decide on one yourself. If your professor did not provide you with a topic, here are some helpful ways to choose one that will work for your needs:
- Choose something you understand enough so that you will be able to interpret the research about it
- Before you get started, check that there is a lot of content about that topic by performing a simple online search to see what turns up
- Write out your topic as a research question that you plan to answer
- Research more about your topic and find evidence to back up what you want to answer
- Make a list of keywords that you continue to see pop up about the topic
- Create your thesis
3. Perform Research:
While performing research is as easy as conducting an online search for sources, the more important element is evaluating the validity of a source. Don’t use Wikipedia as a source, because it is crowdsourced and can be edited by anyone. Instead, rely on digital encyclopedias, scholarly databases, trustworthy publications like TIME magazine and the New York Times, and the like. Since you’re writing this research paper at the last minute, the library may not be a possible option. However, for the next time you write a research paper and plan in advance, definitely utilize books from the library.
4. Write Your Thesis:
A thesis statement is the gist of your entire paper. It is what you will spend your writing proving; therefore, it has to be strong and to the point. A thesis statement appears in the introduction of your research paper, following the strong hook statement that draws your readers in. There is a formulaic way to write a strong thesis statement, and it looks something like this:
“By examining (argument 1), (argument 2), and (argument 3), it is clear that (statement you will prove).”
A thesis statement is typically one sentence and it is clearly written so that the reader knows exactly what they will read about in your paper.
To check that you’ve written a strong thesis statement, ask yourself if it achieves the following:
- Is it in the introduction?
- Does it answer the question from the prompt?
- Can others argue against my thesis?
- Is it going to prove a single claim?
- Does it answer something meaningful?
5. Outline Your Paper:
Now that you have the main ingredients for your research paper, namely your thesis and supporting research, you can start outlining. Everyone has their own way they like to create an outline for papers. Here’s one good example of how it can be done — this is called a flat outline:
- List the topics you will discuss
- Under each topic, write your sources
- If you are lacking sources, revisit and research more to give more meat to your paper
- Move your topics and their information onto your paper in an organized flow
- Write your thesis at the top so you can ensure that you are answering/proving your thesis throughout the paper’s argument
6. The Body/Intro and Conclusion:
So, do you start with your introduction and conclusion and then fill in the body? Or, do you do it the other way around? Really, there is no right or wrong way. It ultimately depends on your preference. Some people like to write their introduction and use it to serve as an outline of their paper and then flow from there. Others like to write their points in the body of their paper and then extrapolate the introduction and conclusion from what they wrote.
Regardless of how you perform your work, there is a structure that the paper must follow, which looks like this:
- Introduction – includes a hook sentence (grabs the reader), your thesis and a menu sentence (a list of what you will discuss).
- Body paragraphs – each body paragraph comes from what you mentioned in your introduction’s menu sentence. Each body paragraph has a topic sentence, or a first sentence that clearly states what it will be about. Each body paragraph includes support and sources that prove the topic sentence or argument.
- Conclusion – here, you restate your introduction and thesis in different words. You want to end with a strong and memorable sentence. Just like your introduction began with a hook statement, your conclusion should end with something that will be remembered.
7. Cite Sources:
One of the major differences between a research paper and any other academic paper is that you must cite your sources. The end of your paper will have a list of sources, or a bibliography. Depending on your professor’s preferences, they will either be listed in APA format , MLA , Chicago , etc. This is an imperative step because your entire research paper’s evidence is based on and backed up by these sources, so you must give them credit where credit is due.
While this is not in the cards for all paper writing, it is very important for a last minute research paper. You’ve likely spent hours crunching the information and regurgitating it in your own words to fill up the once blank pages. As such, it’s a good idea to step away from your paper, get some sleep, and then revisit it with fresh eyes in the morning.
9. Proofread Revise and Editing:
As with any paper, you want to make sure you read it over to catch any mistakes. Not only should you use the Word processing tool that checks spelling and grammar for you, but you must also read it out loud to find any mistakes.
10. Find and Remove Plagiarism:
Once you are done with the entire proofreading and checking phase, the last thing that you have to do is find and remove plagiarism in your research paper. Plagiarism has a lot of consequences, and you have to make sure that your research paper is completely free of it. To do this, you first have to use a plagiarism checker to find all the plagiarized parts. Once found, you can either remove them or give the required accreditations.
If there is time to ask a friend or peer to read over your paper one time, that will be a good idea, too.

Photo by Dan Dimmock on Unsplash
How to write a research paper in a day.
Granted, all the steps above can help you write a research paper fast. Here’s a brief look at how you can do this in a day:
1. Brainstorm Quickly
- Use the prompt
- Outline possible options
- Perform a simple Google search and find what has the most information
- Choose your topic
- Create an outline
2. Research
- Find research to support each point in your outline
3. Write Quickly
- Put it all on paper as you think of it
- Take time to edit, condense, and rewrite

Photo by Nick Morrison on Unsplash
Find a good writing environment.
Before sitting down to get started on your last-minute task, make sure you set up an environment that is conducive to getting your work done. Things you want to consider:
1. Distraction-free:
Choose somewhere quiet and distraction-free. You will have to stay focused for a few hours, so you’ll want to choose a comfortable setting.
2. Good lighting:
Along with comfort, make sure you have adequate lighting to read and write.
3. Go somewhere studious:
Perhaps, if time permits, you can choose to work in somewhere like a library or a study lounge.
4. Bring just your supplies needed:
Even if you work at home, make sure you set up a table with only the supplies you need, as to limit distractions. This could include: a computer, tablet, pen, paper, highlighter, books, and sticky notes. Plus, don’t forget water!
Tips to Avoid Procrastination
Writing a last-minute paper, especially that involves research, is stressful and less than optimal . Instead of finding yourself in this position, you can follow this advice to avoid such a situation.
1. Start early:
Once you’re given the prompt, start thinking about what you want to write about. You can write down ideas on paper and look into the research that supports each point.
2. Outline first and take breaks:
Begin outlining your paper so that when you sit to write, you already have the bulk of it prepared. If you start early, you will have the advantage and ability to take breaks. This helps to revisit your argument with a clear head and potentially see things that you may have otherwise missed.
3. Ask for help if you need it:
Starting early means that you are not crunched for time. So, you have the added benefit of asking for help. You can solicit advice from friends, peers, family, your professors, teacher assistants, the online community, and more. Plus, when you finish writing your paper, you have time to ask for help from someone other than you to read it over and edit it.
The Bottom Line
While knowing how to write a paper fast is useful and at times necessary, it is not the optimal way to approach assignments. However, sometimes being in a bind is out of your control. Therefore, the best way to write a research paper fast is to follow the aforementioned steps and remember to stay calm.
While a research paper involves a lot of work, from creating a strong thesis to finding supporting research, it can be made into an enjoyable activity when you choose to write about something you are interested in. It gives you a chance to digest other people’s findings and make your own inferences about what they mean.
By following the typical structure of a research paper, creating an outline and finding good sources, you can get your research paper done in a night. Good luck!
Related Articles

10 Tips For Fast Thesis Writing
THESIS WRITING 10 tips for writing a fast thesis Decide when to start Decide when to stop Set chapter deadlines Easy targets each day Set a date when you will start writing once research is complete. Set your own thesis completion deadline (ideally 3 months after your start date). You should already have a rough idea of what your content will be in terms of chapter titles etc. Aim to do 500 words each day. This might seem pretty easy, but this way you achieve and beat your target every time. Setting a finish date for your research will help you focus and therefore add more value to your thesis. f you don't think it's possible to write a thesis in that time, write down every reason why not, and ask yourself if it's impossible, or just difficult. Set tight deadlines for completion of each chapter (say 2 weeks per chapter) otherwise you'll be always be able to "start tomorrow". It takes the pressure off, and gives you time to write the right 500 words, saving a huge amount of time in the long run. You will never complete everything on your to-do list, but this is liberating if you accept it as true. Created a relaxed environment Use your time wisely 2 hours then break 25 minutes at a time Ideally, work at a computer with no internet connection, but if this isn't possible, switch off all automatic email Only turn on the computer when you know exactly what you're going to work Check your email and social media notifications only after you've completed at least 2 hours work. Use a timer, work intensively for 25 minutes on one thing, then take a 5 minute break. on. notifications and chat Otherwise, you're likely to open up to a world of distractions, and waste precious writing time. Even then it's not really necessary because you're likely to get distracted, but if you really feel the need then go ahead. During those five minutes, get away from the computer, make a cup of tea, stretch your legs, whatever you want to do. programs. Put your monitor at eye level, otherwise you'll suffer back and neck pain. Visual by... Challenge yourself Look after yourself Walter Newbury Ltd Get away from your computer when you aren't working. Many find this a challenge but try not to create a binary state, you're either working or not. Be nice to yourself; eat well, sleep well, and socialise. This is far easier if you follow the tips above, because you'll have the time to spare for things you actually enjoy doing. Thesis Printing & Binding www.walternewbury.co.uk Source: http://jameshaytonphd.com/top-10-tips-for-fast-thesis-writing/
You may also like...

For hosted site:
For wordpress.com:
8 Tips to Write a Thesis in 30 Days (Bonus Tip Included)
Every student wants to know how to write a thesis in a month . Before sharing the tips that I’ve used in my writing journey, we first need to ask: is it possible to write a thesis in one month, and actually finish it? The answer to this question is yes! You absolutely can write a thesis in 30 days. And you can write your thesis, from start to finish, without the emotional distress that often comes with such a monumental task. And, before you ask, no you’re not going to pay anybody to write a thesis for you. You’re going to write your thesis by yourself.
I’ve written two Masters’ theses, a PhD dissertation and a draft of a book. Here are the 8 tips that have helped me write my thesis as quickly as possible and get to the other side.
3.1 Use Grammarly: An Online Writing Assistant
My 8 tips on how to write a thesis or dissertation in a month.
Before we start, let me say that no one is born knowing how to write a thesis. My professors were not born knowing how to write a thesis and I wasn’t born knowing how to write a thesis either.
I learned how to write a thesis. It was not easy, and I struggled a lot in writing my first thesis. That’s until I discovered what I needed to do to push through and finish writing it.
I then used those lessons and applied them to my second thesis and every writing assignments since then. Writing became fun.
In fact, I was having so much fun writing my second thesis that I took on extra writing assignments. Hence the birth of this blog.
1. Adjust Your Expectations
If you want to finish writing your thesis in a month, the first thing you need to recognize is that you don’t need to break new grounds in your thesis for your thesis to be acceptable.
If for some reason you think you need to break new grounds, then you need to quickly adjust your expectations. The point of a thesis is to demonstrate mastery of the literature and show that you’re able to competently synthesize and present those works persuasively.
That’s all you need to do.
If you’re aiming for more, then consider these two points:
- You don’t have the advanced training or the experience yet to “contribute” to the field. It’s certainly not impossible, but that’s not what’s expected of you in your M.A thesis (and even in your PhD thesis). In fact, if you can just slightly “advance” the research, that’s considered a great accomplishment!
- You need much longer than 30 days or 3 months or even 3 years to come up with something new. Why? Because you need to read literally everything on your subject. And that’s what you’re expected to do when you’ve already finished writing your thesis, and decided to pursue an academic career.
For these two reasons, I think it’s best to view your thesis as something that reflects what you’ve been trained to do, which is to write a good thesis using the skills you already have. You are enough and you probably already have what it takes to write your thesis. So don’t be too hard on yourself. Think of this: Just like you can’t run a marathon if you’ve been training for a 5k, you also can’t “contribute to the field” when you’re still in the process of being trained on how to write a thesis. Most probably, this is your first time writing a masters degree thesis, so take it easy. (More on writing a PhD dissertation below).
So, adjust your expectations accordingly.
Now, if you are trying to write your PhD thesis in a month, let me first say that it’s almost impossible. But if you have certain circumstances (say like a serious illness), then talk to your advisor about it and see what he/she suggests.
2. Don’t Be a Perfectionist
A professor once told me, if you want to write a perfect thesis, “you will never finish writing.” And he was right. I can’t begin to tell you just how much time I wasted trying to write a flawless thesis (AHHH!). In the end, it was not worth it. I ended up procrastinating and wasting time. I wish I could have that time back. Please, don’t make the same mistake I made.
After that emotionally draining experience, I changed my approach. I strove to write something good (and not perfect). I then got feedback on my ideas from my professors and went back and made them better. Eventually, they were, in my eyes, perfect. I was happy.
If you still think you need to be a perfectionist, consider this: there’s always more you can say about your topic. There are more examples you can discuss, more evidence to support your arguments with, and there is an infinite number of ways to organize your ideas, paragraphs and chapters to eventually turn your thesis into a “masterpiece.” You literally can go on forever writing and re-writing your thesis.
If you’re tight on time and you want to finish writing your thesis in 30 days, then do yourself a favor and focus on being done . Write something that’s good enough and move on knowing that you will get back to it later.
So stop fixing things day in and day out. The goal is to make linear progress every single day until you’re done.
Remember, a mediocre finished thesis is better than a perfect unfinished one.
3. Take the 80/20 Rule Seriously
Each writing assignment will take you as much time as you’re willing to give it.
So if you give yourself 10 hours to write what usually takes 2 hours, then you will spend 10 hours working on it.
And the opposite is true.
If you have an assignment that usually takes 10 hours to finish, and I give you 2 hours to work on it, you will probably finish it in 2 hours.
On this basis, if you want to write your thesis in 30 days, you have to decide that 30 days is all you have to finish writing it. Be firm about this deadline, and work with the aim of finishing.
To help speed up the writing process, you can benefit from using a powerful writing assistant like Grammarly . ( Disclosure : these are affiliate links which means I will receive a commission if you make a purchase using my referral links.) Please know that I only talk about services that I believe in and can stand behind. And this is one of those amazing products that can be of tremendous benefit to you if you are looking to get over writer’s block and avoid unnecessary slowdowns .
Okay, so quickly: what should you expect from Grammarly?
Grammarly can help save you a lot of time – especially when you are stuck looking for the right word, or the right way to phrase a sentence. Grammarly gives you a list of context-specific vocabulary suggestions/enhancements/corrections and allows you to make an informed decision about what’s best in your specific writing context. This makes your writing flow better and allow you to move forward at a faster rate.
Here are testimonies by students about how Grammarly has helped them with writing their thesis.

Just downloaded Grammarly for the first time and it has transformed my essays. I sound so smart! #Grammarly #Student — Lucy Jade ANutr (@lucyj_nutrition) March 2, 2019
#WhiteSmoke online editor combined with #Grammarly Chome extension..genius… Why didn't I discovered that earlier #Writing #Thesis #PhD — Quirina de Ruiter (@QuirinaDeRuiter) June 28, 2016
Here are some statistics on how Grammarly has helped students and writers get better results.

With Grammarly, you don’t have to worry about proofreading. It will do that for you. You don’t have to worry about manually checking for plagiarism , style, punctuation, and even wordiness. Grammarly can help you do all of that and will also offer explanations for the reasoning behind each correction.

You can also use Grammarly for better and more professional sounding emails – especially when you want to email your advisor and your committee. You can also use Grammarly across pretty much all of your social media platforms including twitter, facebook, linkedin and more.

In order to get access to all the tools that will help you write your thesis efficiently, I recommend their premium plan . The total cost comes out to 2 – 3 cups of cappuccinos… it’s worth it.
4. Don’t Reinvent the Wheel
Here’s a dose of realism.
As original as you would like to be in your thesis, someone has already written on your topic… and that’s a great thing!
Someone has read the same sources, summarized them and put them in their literature review. You can save yourself a whole lot of time by reading literature reviews. There, you will see exactly how they used those sources and how they might fit into your work. Consult the original sources briefly, but as much as necessary to get the main ideas out of them, and move on.
A literature review shouldn’t take you more than a week to complete if you plan to finish writing in 30 days, and that’s totally doable.
5. Complete a Quick First Draft
The fastest way to finish writing is to write quickly…duh.
What I mean by that is if you’re stuck and you can’t quite round up the paragraph or idea you’re working on, don’t dwell on it. Move on to other topics within your thesis and write them out.
The most helpful tip that I can share with you is to force yourself to write a quick high school draft (first draft) of the entire thesis. Go all the way through until you have a completed first draft of your thesis in your hands.
This is going to be tremendously helpful for your progress because if you can see the conclusion of your thesis, you will a have better sense of which parts of your thesis need work, and which parts need to be completely cut out.
In fact, that’s, in my opinion, the only way to know what your thesis really needs. I say this because imagine if you had spent tens of hours fixing a paragraph only to discover later on (or be told by your advisor) that you really don’t need it.
Let me tell you, it freakin sucks!
6. Journal Articles Are Your Best Friend
Journal articles are usually less than 25 pages in length and sometimes even less than 15 pages long. The best part about them: they’re succinct. You can pretty much read the abstract and you’ll know exactly what the main argument is and the strategy of the paper.
All you need to do then is to look for the evidence in the paper itself. It shouldn’t take you anything more than 3 hours to get this information out of the paper. And when you get good at this, it will take you even less than 3 hours.
Moreover, journal articles are a great way to help position your thesis within the literature on the topic, and you will have a much clearer destination when you do so.
See my post on how to read faster .
7. Write (Your Thesis) Everywhere
If you’ve been following my blog, then you know that I champion using free time effectively.
Plan to read or write everywhere : whether you’re waiting on a friend, waiting for the bus, or eating lunch. It will help you address what I’ve called elsewhere as the “familiarity deficit.” Read that post here . Don’t underestimate the value of that time. It will give you a much needed head-start when it’s time to sit down and work on the relevant chapter within your thesis.
The key to finishing your thesis in 30 days is to keep writing even when you don’t feel you’ve got much to say. It will come to you, just don’t give up too soon.
If you experience some mental roadblocks and you’re dealing with procrastination, then give this article a quick read to help you overcome procrastination and take action.
8. Bonus Tip – Join Online Writing Communities
Yes. Join online writing communities. They’re free and you will get a whole lot of support from people who are going through the same thing. Try Phinished . I’ve used it when I wrote my first thesis and it helped me a bunch.
I need to caution that it is easy to spend a lot of time on Phinished reading what others have to say. You might find yourself reading page after page about the challenges others are going through: including what they’re doing to move through the process, and how far they are in their thesis writing.
If you want to finish, then use it with the intention to finish and not to waste more time or procrastinate.
Hope this will help you finish your thesis in 30 days!
Privacy Overview
Thesis Writing Retreat – Applications Open!
Applications are now open for GRADskills’ annual intensive writing event.
The Thesis Writing Retreat is designed for doctoral students nearing completion and will take place in July 2024.
The event will run in person over the course of three days and is designed to support and motivate you in moving past writers’ block and procrastination to getting words down on the page. The ultimate aim of the retreat is to write a significant amount of first draft material.
- Applications are now open: Places are limited to ensure participants can develop a writing community and have ample access to support.
- Thesis Writing Retreat will run in person from Monday 8 July-Wednesday 10 July 2024 , 9.15am-6.30pm . Applicants must be able to commit to attending for the full three days.
- The deadline for applications is Thursday 30 May 2024 – late applications will not be accepted.
For more information on how to apply, visit the Thesis Writing Retreat webpage .
Dissertation Writing Retreat for Masters Students – Applications Open!
Applications are now open for Mskills’ annual intensive writing event.
The Dissertation Writing Retreat is designed for taught postgraduate (Masters) students nearing completion and will take place in July 2024.
The event will run in person over the course of two days and is designed to support and motivate you in moving past writers’ block and procrastination to getting words down on the page. The ultimate aim of the retreat is to write a significant amount of first draft material for your final Masters project/dissertation.
- Dissertation Writing Retreat will run in person from Monday 8 July-Tuesday 9 July 2024 , 9.15am-6.30pm . Applicants must be able to commit to attending for the full three days.
For more information on how to apply, visit the Dissertation Writing Retreat webpage .
Cookie preferences
Death of the thesis? An update on AI and writing skills
24 April 2024 In February, Gea Dreschler and Abby Gambrel led a workshop on the VU Education Day called ‘The Death of the Thesis?’. With a big group of teachers and staff from various faculties and departments, we discussed the value of writing and asked ourselves the question of whether, in this age of AI, the thesis is still the best choice for a final assessment at the end of a programme.
Login with your VU account to view the content on this page
This website uses cookies
You can accept all cookies or set your preferences per cookie category. You can always alter your choice by removing the cookies from your browser. VU Amsterdam and others use cookies to: 1) analyse website use; 2) personalise the website; 3) connect to social media networks; 4) show relevant advertisements. More information about the cookies we use
Cookie preferences
You can accept all cookies or you can set your preferences per cookie category. You can always alter your choice by removing the cookies from your browser. See more information in the cookie statement.
Personal settings:
These cookies are used to ensure that our website operates properly.
These cookies help to analyse the use of the website. These measurement data are subsequently used to improve the website.
Personalisation
These cookies are used to analyse how you use our website. This enables us to adapt our website content with information that suits your interests.
Social media
These cookies are placed by social media networks. For example, if you watch a YouTube video embedded in the website, or use the social media buttons on our website to share or like a post. This allows social media networks to track your internet behaviour and use that for their own purposes.
Advertising
These cookies are placed by advertising partners. They are used to show you relevant advertisements for Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam on other websites that you visit. They enable advertising networks to track your internet behaviour.
Advertisement
Day 3 of Trump’s Criminal Trial: Five Takeaways
A jury of 12 people was chosen, and alternate members will be picked Friday. They will help write American history.
- Share full article

By Jesse McKinley and Kate Christobek
- April 18, 2024
The third day of Donald J. Trump’s trial started with drama and ended with a jury.
After two jurors were dismissed on Thursday morning, a flurry of afternoon activity produced a full panel of 12 jurors who will decide the former president’s fate. Several alternates remain to be seated on Friday, with opening statements expected on Monday.
Their work will be a unique challenge: the first prosecution of a former American president. Mr. Trump, 77, is charged with falsifying 34 business records in an attempt to cover up a payment to a porn star, Stormy Daniels, who has said she had a brief sexual encounter with him in 2006. He has denied the charges; he could face probation or prison time if convicted.
Here are five takeaways from Mr. Trump’s third day on trial:
Things slowed down fast.
Court officials had earlier thought jury selection might take as long as two weeks. But hopes were high on Thursday that the 12 members might be seated by close of business after seven members were picked Tuesday. Justice Juan M. Merchan had suggested that, if the fast pace continued, the prosecution and defense would offer introductory remarks on Monday morning.
Then Thursday began as a slog, with both sides angling to gain any advantage, or — conversely — to get rid of any problems. For the prosecutors, that meant challenging a previously seated juror who they had discovered had credibility issues. Justice Merchan spent a long sidebar discussing the issue with lawyers from both sides and the juror. In the end, the juror was excused.
By lunchtime, the jury was shrinking, not growing.

Who Are Key Players in the Trump Manhattan Criminal Trial?
The first criminal trial of former President Donald J. Trump is underway. Take a closer look at central figures related to the case.
They sped up fast, too.
Justice Merchan was quick to get back on track. After 18 potential jurors were seated in the jury box, he kept them moving as they navigated a lengthy questionnaire with Mr. Trump looking on.
After lawyers on both sides had spent 30 minutes each quizzing them, Justice Merchan gave the lawyers about a half-hour to prepare challenges — both for cause, which require lawyers to give reasons, and peremptory challenges that can be made without explanation.
But with both sides having limited peremptory challenges, and Merchan unwilling to strike many jurors for cause, the panel filled up fast.
Trump was still driving people from the jury.
Ninety-six additional prospective jurors were called in on Thursday and asked whether they had a problem with being impartial. Dozens said they did and were dismissed.
That attrition speaks to the difficulties that lawyers have faced in finding people who feel they can be fair in a trial of a man who inspires strong emotions. And there were second thoughts: Several potential jurors told the judge that they would be impartial, only to later admit that they simply could not.
There were also moments of unintentional hilarity: One potential juror, who had said she could be fair, was confronted by the defense team over social media posts she’d made in the past, including one in which she called Mr. Trump a racist and a sexist.
Reading it aloud, she stopped.
“Oops,” she said. “That sounds bad.”
She was excused.
The judge is concerned about the press.
Justice Merchan, a veteran jurist, has overseen trials that attracted great public interest. But there has been nothing to compare with Mr. Trump’s trial, which has drawn scores of reporters to the courthouse. That swarm has been quick to report and post even the smallest developments, including personal details that potential jurors offered up during selection.
On Thursday, that eagerness earned a rebuke from the judge, who cited press coverage that revealed details about a juror as part of the reason she said she could not serve. He said she “probably would have been a very good juror.”
Justice Merchan seemed particularly annoyed by reporters’ firsthand observations, asking them to “refrain from writing about anything that you observe with your eyes and hear with your ears related to the jurors that’s not on the record.”
He also suggested sterner steps if those rules were broken.
“If you can’t do that, if we can’t stick to that, we will have to see what else we need to do to ensure that the jurors remain safe,” Justice Merchan said.
The jury is as diverse as New York.
The 12 members of the panel, seven men and five women, reflect the diversity of Manhattan.
Mr. Trump grew up in Queens. But he made his name in Manhattan, literally putting “Trump” on his buildings. He reveled in a brash love-him-or-hate-him reputation, an outsize figure in an outsize city. He bestrode the tabloid newspapers and craved headlines and front pages.
But then many New Yorkers turned against him after he declared he would run for president in 2015 and voiced right wing views.
In 2020, he declared himself a Florida resident.
He returned to Manhattan under duress and under indictment. His fate will now be in the hands of New Yorkers.
Jesse McKinley is a Times reporter covering upstate New York, courts and politics. More about Jesse McKinley
Kate Christobek is a reporter covering the civil and criminal cases against former president Donald J. Trump for The Times. More about Kate Christobek
Our Coverage of the Trump Hush-Money Trial
News and Analysis
Prosecutors accused Donald Trump of violating a gag order four additional times , saying that he continues to defy the judge’s directions not to attack witnesses , prosecutors and jurors in his hush-money trial.
Trump’s criminal trial in Manhattan is off to an ominous start for the former president, and it might not get any easier in the days ahead. Here’s why.
The National Enquirer was more than a friendly media outlet for Trump’s presidential campaign in 2016. It was a powerful, national political weapon that was thrust into the service of a single candidate , in violation of campaign finance law.
More on Trump’s Legal Troubles
Key Inquiries: Trump faces several investigations at both the state and the federal levels, into matters related to his business and political careers.
Case Tracker: Keep track of the developments in the criminal cases involving the former president.
What if Trump Is Convicted?: Could he go to prison ? And will any of the proceedings hinder Trump’s presidential campaign? Here is what we know , and what we don’t know .
Trump on Trial Newsletter: Sign up here to get the latest news and analysis on the cases in New York, Florida, Georgia and Washington, D.C.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Instead of inserting "work on thesis" into your calendar, insert measurable goals like "finish Figure 1" or "write two pages of Chapter 2.". 7. Write In Very Short Bursts. Writing in several short bursts is more efficient than writing in a few, long extended periods of time. If you ever tried to write for several hours in a row, you ...
For English it is closer to 5, alas I was required to write the thesis in my native tongue which is Polish. I assumed 7 characters per word and took a safe thesis length of 77k characters. That ...
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
Trucs pratiques et motivationnels (Sit Down and Write Your Thesis: Some Practical and Motivational Tips). At the most recent Journées de la relève en recherche held by Acfas, the association of French-speaking researchers, Dr. Belleville gave a presentation on seven keys to writing a thesis efficiently and (almost) worry-free. 1.
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
Look for common themes and connections that seem to pop up. Then, draft a working thesis based on the facts, themes, and evidence that you discover during your research. [4] Example: GMOs provide a high volume of delicious, long-lasting food, making them an essential service to society.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Once you have a clear idea of the topic and what interests you, go on to the next step. 2. Ask a research question. You know what you're going to write about, at least broadly. Now you just have to narrow in on an angle or focus appropriate to the length of your assignment.
Above all, keep Elmore Leonard's advice in mind: "If it reads like writing…rewrite it." Plan the structure of your thesis carefully with your supervisor. Create rough drafts as you go so that you can refine them as you become more focused on the write-up. Much of writing comprises rewriting so be prepared to rework each chapter many times.
Here are two ways that I managed to do it. Write. Even when you have zero motivation. This applies especially to those who are in the situation I was in. Since the aim is to fill your content ...
I suggest setting targets that allow you to finish writing in eight days, not 10. This gives you some padding in case life gets in the way. To be clear, there are 192 hours in eight days. Allowing for a 12-hour work day, then you need to write 15,000 words in 96 hours or about 156 words an hour. Set a target of 400 words an hour.
Help you achieve your academic goals. Whether we're proofreading and editing, checking for plagiarism or AI content, generating citations, or writing useful Knowledge Base articles, our aim is to support students on their journey to become better academic writers. We believe that every student should have the right tools for academic success.
How do you finish a Ph.D. quickly? Well, it takes a lot of dedication and ruthlessness towards how you spend your time. Follow these 5 tips and you'll be abl...
First, you need to find a topic (or "thesis question"), often with the help and/or approval of your faculty-led thesis committee. Next comes the process of research, which is often the most time-intensive. Then, you must take the time to analyze your research. Lastly, you outline and write the actual thesis. Thanks!
4. Write Your Thesis: A thesis statement is the gist of your entire paper. It is what you will spend your writing proving; therefore, it has to be strong and to the point. A thesis statement appears in the introduction of your research paper, following the strong hook statement that draws your readers in.
Transcribed. 10 Tips For Fast Thesis Writing. THESIS WRITING 10 tips for writing a fast thesis Decide when to start Decide when to stop Set chapter deadlines Easy targets each day Set a date when you will start writing once research is complete. Set your own thesis completion deadline (ideally 3 months after your start date).
5. Add Emphasis. Steps 1-4 will help you build a solid thesis, but if you want to bump it up to the next level, you can do two more steps: tell how your view contrasts with other people, and use intensifying transitions like "in reality" or "in fact." Example Format: Thesis Question.
a definition. an interesting fact. a question that will be answered in your paper. some background information on your topic. The idea is to begin broadly and gradually bring the reader closer to the main idea of the paper. At the end of the introduction, you will state your thesis statement.
Table Of Contents. My 8 tips on how to write a thesis or dissertation in a month. 1. Adjust Your Expectations. 2. Don't Be a Perfectionist. 3. Take the 80/20 Rule Seriously. 3.1 Use Grammarly: An Online Writing Assistant.
The Thesis Writing Retreat is designed for doctoral students nearing completion and will take place in July 2024. The event will run in person over the course of three days and is designed to support and motivate you in moving past writers' block and procrastination to getting words down on the page. The ultimate aim of the retreat is to ...
In February, Gea Dreschler and Abby Gambrel led a workshop on the VU Education Day called 'The Death of the Thesis?'. With a big group of teachers and staff from various faculties and departments, we discussed the value of writing and asked ourselves the question of whether, in this age of AI, the thesis is still the best choice for a final assessment at the end of a programme.
Given how fast AI tools are improving and how much better they're becoming at writing text that sounds human, many are beginning to wonder how far off we might be from a textual singularity.
A jury of 12 people was chosen, and alternate members will be picked Friday. They will help write American history. By Jesse McKinley and Kate Christobek The third day of Donald J. Trump's trial ...