- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 04 June 2021

Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: an overview of systematic reviews
- Israel Júnior Borges do Nascimento 1 , 2 ,
- Dónal P. O’Mathúna 3 , 4 ,
- Thilo Caspar von Groote 5 ,
- Hebatullah Mohamed Abdulazeem 6 ,
- Ishanka Weerasekara 7 , 8 ,
- Ana Marusic 9 ,
- Livia Puljak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8467-6061 10 ,
- Vinicius Tassoni Civile 11 ,
- Irena Zakarija-Grkovic 9 ,
- Tina Poklepovic Pericic 9 ,
- Alvaro Nagib Atallah 11 ,
- Santino Filoso 12 ,
- Nicola Luigi Bragazzi 13 &
- Milena Soriano Marcolino 1
On behalf of the International Network of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (InterNetCOVID-19)
BMC Infectious Diseases volume 21 , Article number: 525 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
16k Accesses
28 Citations
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
Navigating the rapidly growing body of scientific literature on the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic is challenging, and ongoing critical appraisal of this output is essential. We aimed to summarize and critically appraise systematic reviews of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in humans that were available at the beginning of the pandemic.
Nine databases (Medline, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, Web of Sciences, PDQ-Evidence, WHO’s Global Research, LILACS, and Epistemonikos) were searched from December 1, 2019, to March 24, 2020. Systematic reviews analyzing primary studies of COVID-19 were included. Two authors independently undertook screening, selection, extraction (data on clinical symptoms, prevalence, pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, diagnostic test assessment, laboratory, and radiological findings), and quality assessment (AMSTAR 2). A meta-analysis was performed of the prevalence of clinical outcomes.
Eighteen systematic reviews were included; one was empty (did not identify any relevant study). Using AMSTAR 2, confidence in the results of all 18 reviews was rated as “critically low”. Identified symptoms of COVID-19 were (range values of point estimates): fever (82–95%), cough with or without sputum (58–72%), dyspnea (26–59%), myalgia or muscle fatigue (29–51%), sore throat (10–13%), headache (8–12%) and gastrointestinal complaints (5–9%). Severe symptoms were more common in men. Elevated C-reactive protein and lactate dehydrogenase, and slightly elevated aspartate and alanine aminotransferase, were commonly described. Thrombocytopenia and elevated levels of procalcitonin and cardiac troponin I were associated with severe disease. A frequent finding on chest imaging was uni- or bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacity. A single review investigated the impact of medication (chloroquine) but found no verifiable clinical data. All-cause mortality ranged from 0.3 to 13.9%.
Conclusions
In this overview of systematic reviews, we analyzed evidence from the first 18 systematic reviews that were published after the emergence of COVID-19. However, confidence in the results of all reviews was “critically low”. Thus, systematic reviews that were published early on in the pandemic were of questionable usefulness. Even during public health emergencies, studies and systematic reviews should adhere to established methodological standards.
Peer Review reports
The spread of the “Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus 2” (SARS-CoV-2), the causal agent of COVID-19, was characterized as a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) in March 2020 and has triggered an international public health emergency [ 1 ]. The numbers of confirmed cases and deaths due to COVID-19 are rapidly escalating, counting in millions [ 2 ], causing massive economic strain, and escalating healthcare and public health expenses [ 3 , 4 ].
The research community has responded by publishing an impressive number of scientific reports related to COVID-19. The world was alerted to the new disease at the beginning of 2020 [ 1 ], and by mid-March 2020, more than 2000 articles had been published on COVID-19 in scholarly journals, with 25% of them containing original data [ 5 ]. The living map of COVID-19 evidence, curated by the Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre), contained more than 40,000 records by February 2021 [ 6 ]. More than 100,000 records on PubMed were labeled as “SARS-CoV-2 literature, sequence, and clinical content” by February 2021 [ 7 ].
Due to publication speed, the research community has voiced concerns regarding the quality and reproducibility of evidence produced during the COVID-19 pandemic, warning of the potential damaging approach of “publish first, retract later” [ 8 ]. It appears that these concerns are not unfounded, as it has been reported that COVID-19 articles were overrepresented in the pool of retracted articles in 2020 [ 9 ]. These concerns about inadequate evidence are of major importance because they can lead to poor clinical practice and inappropriate policies [ 10 ].
Systematic reviews are a cornerstone of today’s evidence-informed decision-making. By synthesizing all relevant evidence regarding a particular topic, systematic reviews reflect the current scientific knowledge. Systematic reviews are considered to be at the highest level in the hierarchy of evidence and should be used to make informed decisions. However, with high numbers of systematic reviews of different scope and methodological quality being published, overviews of multiple systematic reviews that assess their methodological quality are essential [ 11 , 12 , 13 ]. An overview of systematic reviews helps identify and organize the literature and highlights areas of priority in decision-making.
In this overview of systematic reviews, we aimed to summarize and critically appraise systematic reviews of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in humans that were available at the beginning of the pandemic.
Methodology
Research question.
This overview’s primary objective was to summarize and critically appraise systematic reviews that assessed any type of primary clinical data from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. Our research question was purposefully broad because we wanted to analyze as many systematic reviews as possible that were available early following the COVID-19 outbreak.
Study design
We conducted an overview of systematic reviews. The idea for this overview originated in a protocol for a systematic review submitted to PROSPERO (CRD42020170623), which indicated a plan to conduct an overview.
Overviews of systematic reviews use explicit and systematic methods for searching and identifying multiple systematic reviews addressing related research questions in the same field to extract and analyze evidence across important outcomes. Overviews of systematic reviews are in principle similar to systematic reviews of interventions, but the unit of analysis is a systematic review [ 14 , 15 , 16 ].
We used the overview methodology instead of other evidence synthesis methods to allow us to collate and appraise multiple systematic reviews on this topic, and to extract and analyze their results across relevant topics [ 17 ]. The overview and meta-analysis of systematic reviews allowed us to investigate the methodological quality of included studies, summarize results, and identify specific areas of available or limited evidence, thereby strengthening the current understanding of this novel disease and guiding future research [ 13 ].
A reporting guideline for overviews of reviews is currently under development, i.e., Preferred Reporting Items for Overviews of Reviews (PRIOR) [ 18 ]. As the PRIOR checklist is still not published, this study was reported following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2009 statement [ 19 ]. The methodology used in this review was adapted from the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions and also followed established methodological considerations for analyzing existing systematic reviews [ 14 ].
Approval of a research ethics committee was not necessary as the study analyzed only publicly available articles.
Eligibility criteria
Systematic reviews were included if they analyzed primary data from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 as confirmed by RT-PCR or another pre-specified diagnostic technique. Eligible reviews covered all topics related to COVID-19 including, but not limited to, those that reported clinical symptoms, diagnostic methods, therapeutic interventions, laboratory findings, or radiological results. Both full manuscripts and abbreviated versions, such as letters, were eligible.
No restrictions were imposed on the design of the primary studies included within the systematic reviews, the last search date, whether the review included meta-analyses or language. Reviews related to SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses were eligible, but from those reviews, we analyzed only data related to SARS-CoV-2.
No consensus definition exists for a systematic review [ 20 ], and debates continue about the defining characteristics of a systematic review [ 21 ]. Cochrane’s guidance for overviews of reviews recommends setting pre-established criteria for making decisions around inclusion [ 14 ]. That is supported by a recent scoping review about guidance for overviews of systematic reviews [ 22 ].
Thus, for this study, we defined a systematic review as a research report which searched for primary research studies on a specific topic using an explicit search strategy, had a detailed description of the methods with explicit inclusion criteria provided, and provided a summary of the included studies either in narrative or quantitative format (such as a meta-analysis). Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews were considered eligible for inclusion, with or without meta-analysis, and regardless of the study design, language restriction and methodology of the included primary studies. To be eligible for inclusion, reviews had to be clearly analyzing data related to SARS-CoV-2 (associated or not with other viruses). We excluded narrative reviews without those characteristics as these are less likely to be replicable and are more prone to bias.
Scoping reviews and rapid reviews were eligible for inclusion in this overview if they met our pre-defined inclusion criteria noted above. We included reviews that addressed SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses if they reported separate data regarding SARS-CoV-2.
Information sources
Nine databases were searched for eligible records published between December 1, 2019, and March 24, 2020: Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews via Cochrane Library, PubMed, EMBASE, CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), Web of Sciences, LILACS (Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature), PDQ-Evidence, WHO’s Global Research on Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19), and Epistemonikos.
The comprehensive search strategy for each database is provided in Additional file 1 and was designed and conducted in collaboration with an information specialist. All retrieved records were primarily processed in EndNote, where duplicates were removed, and records were then imported into the Covidence platform [ 23 ]. In addition to database searches, we screened reference lists of reviews included after screening records retrieved via databases.
Study selection
All searches, screening of titles and abstracts, and record selection, were performed independently by two investigators using the Covidence platform [ 23 ]. Articles deemed potentially eligible were retrieved for full-text screening carried out independently by two investigators. Discrepancies at all stages were resolved by consensus. During the screening, records published in languages other than English were translated by a native/fluent speaker.
Data collection process
We custom designed a data extraction table for this study, which was piloted by two authors independently. Data extraction was performed independently by two authors. Conflicts were resolved by consensus or by consulting a third researcher.
We extracted the following data: article identification data (authors’ name and journal of publication), search period, number of databases searched, population or settings considered, main results and outcomes observed, and number of participants. From Web of Science (Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA), we extracted journal rank (quartile) and Journal Impact Factor (JIF).
We categorized the following as primary outcomes: all-cause mortality, need for and length of mechanical ventilation, length of hospitalization (in days), admission to intensive care unit (yes/no), and length of stay in the intensive care unit.
The following outcomes were categorized as exploratory: diagnostic methods used for detection of the virus, male to female ratio, clinical symptoms, pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, laboratory findings (full blood count, liver enzymes, C-reactive protein, d-dimer, albumin, lipid profile, serum electrolytes, blood vitamin levels, glucose levels, and any other important biomarkers), and radiological findings (using radiography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound).
We also collected data on reporting guidelines and requirements for the publication of systematic reviews and meta-analyses from journal websites where included reviews were published.
Quality assessment in individual reviews
Two researchers independently assessed the reviews’ quality using the “A MeaSurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews 2 (AMSTAR 2)”. We acknowledge that the AMSTAR 2 was created as “a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomized or non-randomized studies of healthcare interventions, or both” [ 24 ]. However, since AMSTAR 2 was designed for systematic reviews of intervention trials, and we included additional types of systematic reviews, we adjusted some AMSTAR 2 ratings and reported these in Additional file 2 .
Adherence to each item was rated as follows: yes, partial yes, no, or not applicable (such as when a meta-analysis was not conducted). The overall confidence in the results of the review is rated as “critically low”, “low”, “moderate” or “high”, according to the AMSTAR 2 guidance based on seven critical domains, which are items 2, 4, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15 as defined by AMSTAR 2 authors [ 24 ]. We reported our adherence ratings for transparency of our decision with accompanying explanations, for each item, in each included review.
One of the included systematic reviews was conducted by some members of this author team [ 25 ]. This review was initially assessed independently by two authors who were not co-authors of that review to prevent the risk of bias in assessing this study.
Synthesis of results
For data synthesis, we prepared a table summarizing each systematic review. Graphs illustrating the mortality rate and clinical symptoms were created. We then prepared a narrative summary of the methods, findings, study strengths, and limitations.
For analysis of the prevalence of clinical outcomes, we extracted data on the number of events and the total number of patients to perform proportional meta-analysis using RStudio© software, with the “meta” package (version 4.9–6), using the “metaprop” function for reviews that did not perform a meta-analysis, excluding case studies because of the absence of variance. For reviews that did not perform a meta-analysis, we presented pooled results of proportions with their respective confidence intervals (95%) by the inverse variance method with a random-effects model, using the DerSimonian-Laird estimator for τ 2 . We adjusted data using Freeman-Tukey double arcosen transformation. Confidence intervals were calculated using the Clopper-Pearson method for individual studies. We created forest plots using the RStudio© software, with the “metafor” package (version 2.1–0) and “forest” function.
Managing overlapping systematic reviews
Some of the included systematic reviews that address the same or similar research questions may include the same primary studies in overviews. Including such overlapping reviews may introduce bias when outcome data from the same primary study are included in the analyses of an overview multiple times. Thus, in summaries of evidence, multiple-counting of the same outcome data will give data from some primary studies too much influence [ 14 ]. In this overview, we did not exclude overlapping systematic reviews because, according to Cochrane’s guidance, it may be appropriate to include all relevant reviews’ results if the purpose of the overview is to present and describe the current body of evidence on a topic [ 14 ]. To avoid any bias in summary estimates associated with overlapping reviews, we generated forest plots showing data from individual systematic reviews, but the results were not pooled because some primary studies were included in multiple reviews.
Our search retrieved 1063 publications, of which 175 were duplicates. Most publications were excluded after the title and abstract analysis ( n = 860). Among the 28 studies selected for full-text screening, 10 were excluded for the reasons described in Additional file 3 , and 18 were included in the final analysis (Fig. 1 ) [ 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ]. Reference list screening did not retrieve any additional systematic reviews.
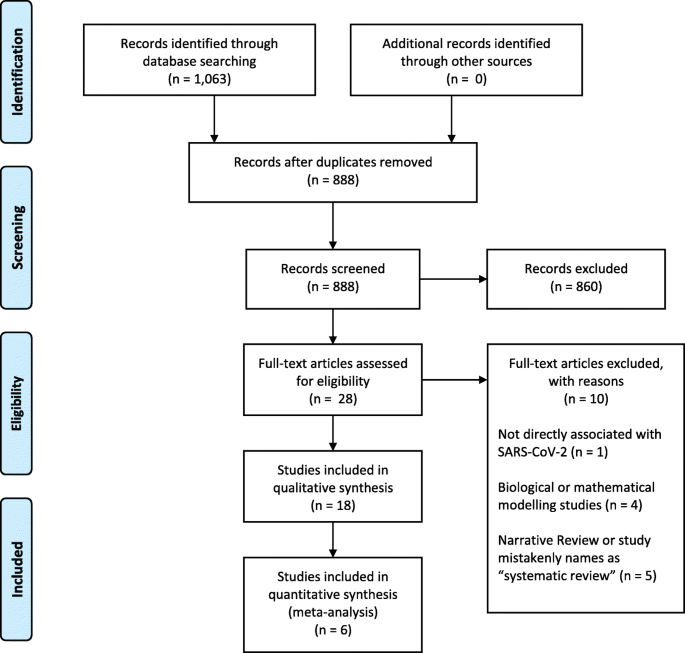
PRISMA flow diagram
Characteristics of included reviews
Summary features of 18 systematic reviews are presented in Table 1 . They were published in 14 different journals. Only four of these journals had specific requirements for systematic reviews (with or without meta-analysis): European Journal of Internal Medicine, Journal of Clinical Medicine, Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Clinical Research in Cardiology . Two journals reported that they published only invited reviews ( Journal of Medical Virology and Clinica Chimica Acta ). Three systematic reviews in our study were published as letters; one was labeled as a scoping review and another as a rapid review (Table 2 ).
All reviews were published in English, in first quartile (Q1) journals, with JIF ranging from 1.692 to 6.062. One review was empty, meaning that its search did not identify any relevant studies; i.e., no primary studies were included [ 36 ]. The remaining 17 reviews included 269 unique studies; the majority ( N = 211; 78%) were included in only a single review included in our study (range: 1 to 12). Primary studies included in the reviews were published between December 2019 and March 18, 2020, and comprised case reports, case series, cohorts, and other observational studies. We found only one review that included randomized clinical trials [ 38 ]. In the included reviews, systematic literature searches were performed from 2019 (entire year) up to March 9, 2020. Ten systematic reviews included meta-analyses. The list of primary studies found in the included systematic reviews is shown in Additional file 4 , as well as the number of reviews in which each primary study was included.
Population and study designs
Most of the reviews analyzed data from patients with COVID-19 who developed pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), or any other correlated complication. One review aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of using surgical masks on preventing transmission of the virus [ 36 ], one review was focused on pediatric patients [ 34 ], and one review investigated COVID-19 in pregnant women [ 37 ]. Most reviews assessed clinical symptoms, laboratory findings, or radiological results.
Systematic review findings
The summary of findings from individual reviews is shown in Table 2 . Overall, all-cause mortality ranged from 0.3 to 13.9% (Fig. 2 ).
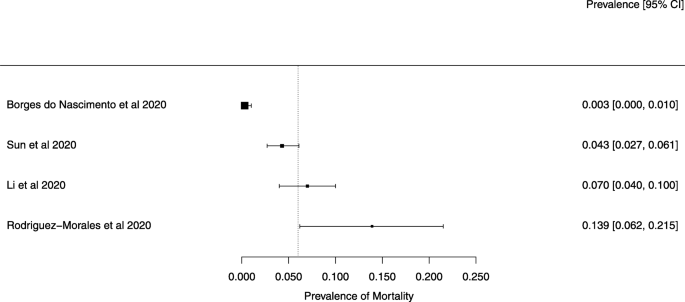
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of mortality
Clinical symptoms
Seven reviews described the main clinical manifestations of COVID-19 [ 26 , 28 , 29 , 34 , 35 , 39 , 41 ]. Three of them provided only a narrative discussion of symptoms [ 26 , 34 , 35 ]. In the reviews that performed a statistical analysis of the incidence of different clinical symptoms, symptoms in patients with COVID-19 were (range values of point estimates): fever (82–95%), cough with or without sputum (58–72%), dyspnea (26–59%), myalgia or muscle fatigue (29–51%), sore throat (10–13%), headache (8–12%), gastrointestinal disorders, such as diarrhea, nausea or vomiting (5.0–9.0%), and others (including, in one study only: dizziness 12.1%) (Figs. 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 and 9 ). Three reviews assessed cough with and without sputum together; only one review assessed sputum production itself (28.5%).
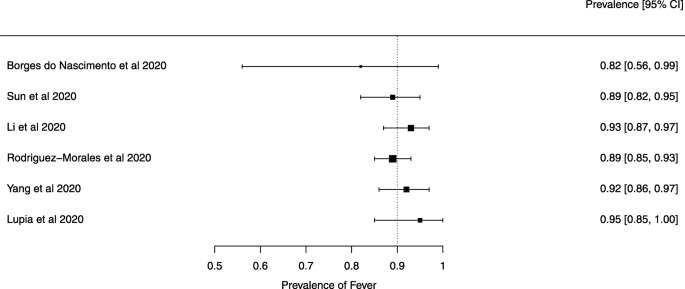
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of fever
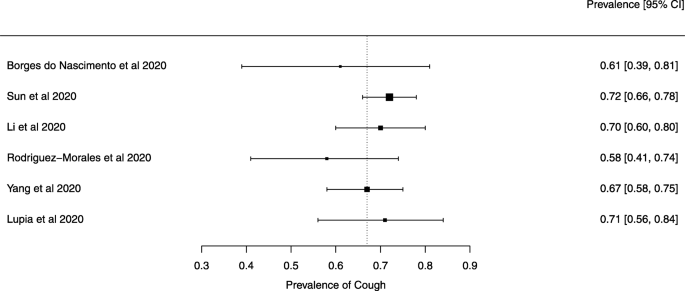
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of cough
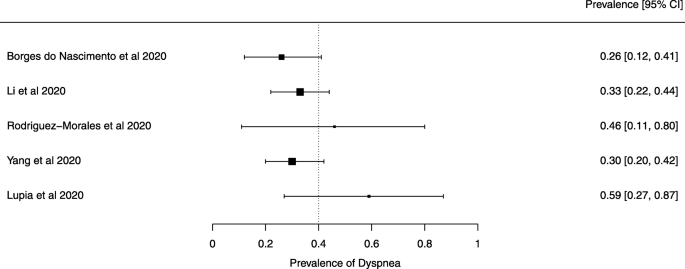
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of dyspnea
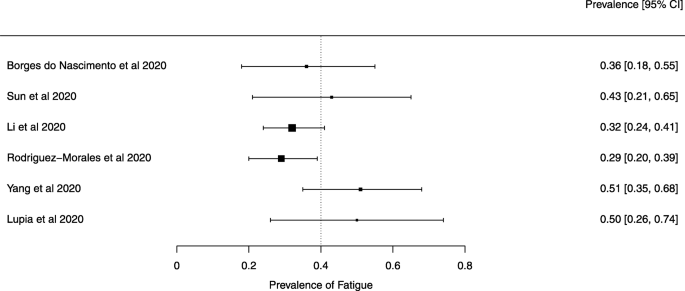
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of fatigue or myalgia
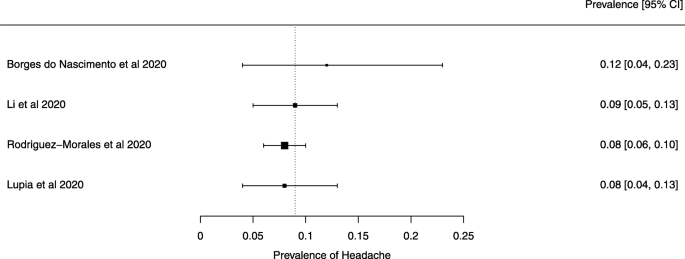
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of headache
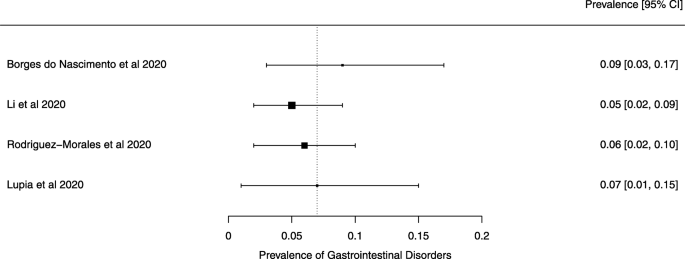
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of gastrointestinal disorders
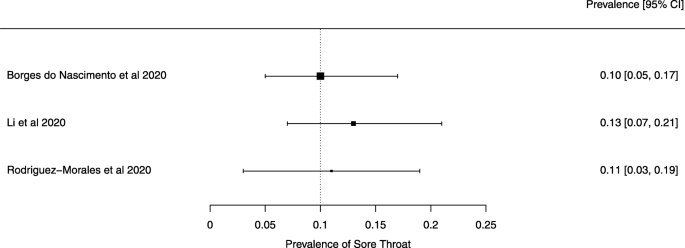
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of sore throat
Diagnostic aspects
Three reviews described methodologies, protocols, and tools used for establishing the diagnosis of COVID-19 [ 26 , 34 , 38 ]. The use of respiratory swabs (nasal or pharyngeal) or blood specimens to assess the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid using RT-PCR assays was the most commonly used diagnostic method mentioned in the included studies. These diagnostic tests have been widely used, but their precise sensitivity and specificity remain unknown. One review included a Chinese study with clinical diagnosis with no confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 infection (patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 if they presented with at least two symptoms suggestive of COVID-19, together with laboratory and chest radiography abnormalities) [ 34 ].
Therapeutic possibilities
Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions (supportive therapies) used in treating patients with COVID-19 were reported in five reviews [ 25 , 27 , 34 , 35 , 38 ]. Antivirals used empirically for COVID-19 treatment were reported in seven reviews [ 25 , 27 , 34 , 35 , 37 , 38 , 41 ]; most commonly used were protease inhibitors (lopinavir, ritonavir, darunavir), nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (tenofovir), nucleotide analogs (remdesivir, galidesivir, ganciclovir), and neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir). Umifenovir, a membrane fusion inhibitor, was investigated in two studies [ 25 , 35 ]. Possible supportive interventions analyzed were different types of oxygen supplementation and breathing support (invasive or non-invasive ventilation) [ 25 ]. The use of antibiotics, both empirically and to treat secondary pneumonia, was reported in six studies [ 25 , 26 , 27 , 34 , 35 , 38 ]. One review specifically assessed evidence on the efficacy and safety of the anti-malaria drug chloroquine [ 27 ]. It identified 23 ongoing trials investigating the potential of chloroquine as a therapeutic option for COVID-19, but no verifiable clinical outcomes data. The use of mesenchymal stem cells, antifungals, and glucocorticoids were described in four reviews [ 25 , 34 , 35 , 38 ].
Laboratory and radiological findings
Of the 18 reviews included in this overview, eight analyzed laboratory parameters in patients with COVID-19 [ 25 , 29 , 30 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 39 ]; elevated C-reactive protein levels, associated with lymphocytopenia, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, as well as slightly elevated aspartate and alanine aminotransferase (AST, ALT) were commonly described in those eight reviews. Lippi et al. assessed cardiac troponin I (cTnI) [ 25 ], procalcitonin [ 32 ], and platelet count [ 33 ] in COVID-19 patients. Elevated levels of procalcitonin [ 32 ] and cTnI [ 30 ] were more likely to be associated with a severe disease course (requiring intensive care unit admission and intubation). Furthermore, thrombocytopenia was frequently observed in patients with complicated COVID-19 infections [ 33 ].
Chest imaging (chest radiography and/or computed tomography) features were assessed in six reviews, all of which described a frequent pattern of local or bilateral multilobar ground-glass opacity [ 25 , 34 , 35 , 39 , 40 , 41 ]. Those six reviews showed that septal thickening, bronchiectasis, pleural and cardiac effusions, halo signs, and pneumothorax were observed in patients suffering from COVID-19.
Quality of evidence in individual systematic reviews
Table 3 shows the detailed results of the quality assessment of 18 systematic reviews, including the assessment of individual items and summary assessment. A detailed explanation for each decision in each review is available in Additional file 5 .
Using AMSTAR 2 criteria, confidence in the results of all 18 reviews was rated as “critically low” (Table 3 ). Common methodological drawbacks were: omission of prospective protocol submission or publication; use of inappropriate search strategy: lack of independent and dual literature screening and data-extraction (or methodology unclear); absence of an explanation for heterogeneity among the studies included; lack of reasons for study exclusion (or rationale unclear).
Risk of bias assessment, based on a reported methodological tool, and quality of evidence appraisal, in line with the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) method, were reported only in one review [ 25 ]. Five reviews presented a table summarizing bias, using various risk of bias tools [ 25 , 29 , 39 , 40 , 41 ]. One review analyzed “study quality” [ 37 ]. One review mentioned the risk of bias assessment in the methodology but did not provide any related analysis [ 28 ].
This overview of systematic reviews analyzed the first 18 systematic reviews published after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, up to March 24, 2020, with primary studies involving more than 60,000 patients. Using AMSTAR-2, we judged that our confidence in all those reviews was “critically low”. Ten reviews included meta-analyses. The reviews presented data on clinical manifestations, laboratory and radiological findings, and interventions. We found no systematic reviews on the utility of diagnostic tests.
Symptoms were reported in seven reviews; most of the patients had a fever, cough, dyspnea, myalgia or muscle fatigue, and gastrointestinal disorders such as diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting. Olfactory dysfunction (anosmia or dysosmia) has been described in patients infected with COVID-19 [ 43 ]; however, this was not reported in any of the reviews included in this overview. During the SARS outbreak in 2002, there were reports of impairment of the sense of smell associated with the disease [ 44 , 45 ].
The reported mortality rates ranged from 0.3 to 14% in the included reviews. Mortality estimates are influenced by the transmissibility rate (basic reproduction number), availability of diagnostic tools, notification policies, asymptomatic presentations of the disease, resources for disease prevention and control, and treatment facilities; variability in the mortality rate fits the pattern of emerging infectious diseases [ 46 ]. Furthermore, the reported cases did not consider asymptomatic cases, mild cases where individuals have not sought medical treatment, and the fact that many countries had limited access to diagnostic tests or have implemented testing policies later than the others. Considering the lack of reviews assessing diagnostic testing (sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of RT-PCT or immunoglobulin tests), and the preponderance of studies that assessed only symptomatic individuals, considerable imprecision around the calculated mortality rates existed in the early stage of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Few reviews included treatment data. Those reviews described studies considered to be at a very low level of evidence: usually small, retrospective studies with very heterogeneous populations. Seven reviews analyzed laboratory parameters; those reviews could have been useful for clinicians who attend patients suspected of COVID-19 in emergency services worldwide, such as assessing which patients need to be reassessed more frequently.
All systematic reviews scored poorly on the AMSTAR 2 critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews. Most of the original studies included in the reviews were case series and case reports, impacting the quality of evidence. Such evidence has major implications for clinical practice and the use of these reviews in evidence-based practice and policy. Clinicians, patients, and policymakers can only have the highest confidence in systematic review findings if high-quality systematic review methodologies are employed. The urgent need for information during a pandemic does not justify poor quality reporting.
We acknowledge that there are numerous challenges associated with analyzing COVID-19 data during a pandemic [ 47 ]. High-quality evidence syntheses are needed for decision-making, but each type of evidence syntheses is associated with its inherent challenges.
The creation of classic systematic reviews requires considerable time and effort; with massive research output, they quickly become outdated, and preparing updated versions also requires considerable time. A recent study showed that updates of non-Cochrane systematic reviews are published a median of 5 years after the publication of the previous version [ 48 ].
Authors may register a review and then abandon it [ 49 ], but the existence of a public record that is not updated may lead other authors to believe that the review is still ongoing. A quarter of Cochrane review protocols remains unpublished as completed systematic reviews 8 years after protocol publication [ 50 ].
Rapid reviews can be used to summarize the evidence, but they involve methodological sacrifices and simplifications to produce information promptly, with inconsistent methodological approaches [ 51 ]. However, rapid reviews are justified in times of public health emergencies, and even Cochrane has resorted to publishing rapid reviews in response to the COVID-19 crisis [ 52 ]. Rapid reviews were eligible for inclusion in this overview, but only one of the 18 reviews included in this study was labeled as a rapid review.
Ideally, COVID-19 evidence would be continually summarized in a series of high-quality living systematic reviews, types of evidence synthesis defined as “ a systematic review which is continually updated, incorporating relevant new evidence as it becomes available ” [ 53 ]. However, conducting living systematic reviews requires considerable resources, calling into question the sustainability of such evidence synthesis over long periods [ 54 ].
Research reports about COVID-19 will contribute to research waste if they are poorly designed, poorly reported, or simply not necessary. In principle, systematic reviews should help reduce research waste as they usually provide recommendations for further research that is needed or may advise that sufficient evidence exists on a particular topic [ 55 ]. However, systematic reviews can also contribute to growing research waste when they are not needed, or poorly conducted and reported. Our present study clearly shows that most of the systematic reviews that were published early on in the COVID-19 pandemic could be categorized as research waste, as our confidence in their results is critically low.
Our study has some limitations. One is that for AMSTAR 2 assessment we relied on information available in publications; we did not attempt to contact study authors for clarifications or additional data. In three reviews, the methodological quality appraisal was challenging because they were published as letters, or labeled as rapid communications. As a result, various details about their review process were not included, leading to AMSTAR 2 questions being answered as “not reported”, resulting in low confidence scores. Full manuscripts might have provided additional information that could have led to higher confidence in the results. In other words, low scores could reflect incomplete reporting, not necessarily low-quality review methods. To make their review available more rapidly and more concisely, the authors may have omitted methodological details. A general issue during a crisis is that speed and completeness must be balanced. However, maintaining high standards requires proper resourcing and commitment to ensure that the users of systematic reviews can have high confidence in the results.
Furthermore, we used adjusted AMSTAR 2 scoring, as the tool was designed for critical appraisal of reviews of interventions. Some reviews may have received lower scores than actually warranted in spite of these adjustments.
Another limitation of our study may be the inclusion of multiple overlapping reviews, as some included reviews included the same primary studies. According to the Cochrane Handbook, including overlapping reviews may be appropriate when the review’s aim is “ to present and describe the current body of systematic review evidence on a topic ” [ 12 ], which was our aim. To avoid bias with summarizing evidence from overlapping reviews, we presented the forest plots without summary estimates. The forest plots serve to inform readers about the effect sizes for outcomes that were reported in each review.
Several authors from this study have contributed to one of the reviews identified [ 25 ]. To reduce the risk of any bias, two authors who did not co-author the review in question initially assessed its quality and limitations.
Finally, we note that the systematic reviews included in our overview may have had issues that our analysis did not identify because we did not analyze their primary studies to verify the accuracy of the data and information they presented. We give two examples to substantiate this possibility. Lovato et al. wrote a commentary on the review of Sun et al. [ 41 ], in which they criticized the authors’ conclusion that sore throat is rare in COVID-19 patients [ 56 ]. Lovato et al. highlighted that multiple studies included in Sun et al. did not accurately describe participants’ clinical presentations, warning that only three studies clearly reported data on sore throat [ 56 ].
In another example, Leung [ 57 ] warned about the review of Li, L.Q. et al. [ 29 ]: “ it is possible that this statistic was computed using overlapped samples, therefore some patients were double counted ”. Li et al. responded to Leung that it is uncertain whether the data overlapped, as they used data from published articles and did not have access to the original data; they also reported that they requested original data and that they plan to re-do their analyses once they receive them; they also urged readers to treat the data with caution [ 58 ]. This points to the evolving nature of evidence during a crisis.
Our study’s strength is that this overview adds to the current knowledge by providing a comprehensive summary of all the evidence synthesis about COVID-19 available early after the onset of the pandemic. This overview followed strict methodological criteria, including a comprehensive and sensitive search strategy and a standard tool for methodological appraisal of systematic reviews.
In conclusion, in this overview of systematic reviews, we analyzed evidence from the first 18 systematic reviews that were published after the emergence of COVID-19. However, confidence in the results of all the reviews was “critically low”. Thus, systematic reviews that were published early on in the pandemic could be categorized as research waste. Even during public health emergencies, studies and systematic reviews should adhere to established methodological standards to provide patients, clinicians, and decision-makers trustworthy evidence.
Availability of data and materials
All data collected and analyzed within this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
World Health Organization. Timeline - COVID-19: Available at: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline . Accessed 1 June 2021.
COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). Available at: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Anzai A, Kobayashi T, Linton NM, Kinoshita R, Hayashi K, Suzuki A, et al. Assessing the Impact of Reduced Travel on Exportation Dynamics of Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19). J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):601.
Chinazzi M, Davis JT, Ajelli M, Gioannini C, Litvinova M, Merler S, et al. The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Science. 2020;368(6489):395–400. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba9757 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Fidahic M, Nujic D, Runjic R, Civljak M, Markotic F, Lovric Makaric Z, et al. Research methodology and characteristics of journal articles with original data, preprint articles and registered clinical trial protocols about COVID-19. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20(1):161. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-020-01047-2 .
EPPI Centre . COVID-19: a living systematic map of the evidence. Available at: http://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Projects/DepartmentofHealthandSocialCare/Publishedreviews/COVID-19Livingsystematicmapoftheevidence/tabid/3765/Default.aspx . Accessed 1 June 2021.
NCBI SARS-CoV-2 Resources. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sars-cov-2/ . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Gustot T. Quality and reproducibility during the COVID-19 pandemic. JHEP Rep. 2020;2(4):100141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100141 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kodvanj, I., et al., Publishing of COVID-19 Preprints in Peer-reviewed Journals, Preprinting Trends, Public Discussion and Quality Issues. Preprint article. bioRxiv 2020.11.23.394577; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.23.394577 .
Dobler CC. Poor quality research and clinical practice during COVID-19. Breathe (Sheff). 2020;16(2):200112. https://doi.org/10.1183/20734735.0112-2020 .
Article Google Scholar
Bastian H, Glasziou P, Chalmers I. Seventy-five trials and eleven systematic reviews a day: how will we ever keep up? PLoS Med. 2010;7(9):e1000326. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000326 .
Lunny C, Brennan SE, McDonald S, McKenzie JE. Toward a comprehensive evidence map of overview of systematic review methods: paper 1-purpose, eligibility, search and data extraction. Syst Rev. 2017;6(1):231. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0617-1 .
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Becker LA, Pieper D, Hartling L. Chapter V: Overviews of Reviews. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). Cochrane. 2020. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). Cochrane. 2020; Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Newton AS, Scott SD, Hartling L. The impact of different inclusion decisions on the comprehensiveness and complexity of overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-018-0914-3 .
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Newton AS, Scott SD, Hartling L. A decision tool to help researchers make decisions about including systematic reviews in overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-018-0768-8 .
Hunt H, Pollock A, Campbell P, Estcourt L, Brunton G. An introduction to overviews of reviews: planning a relevant research question and objective for an overview. Syst Rev. 2018;7(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-018-0695-8 .
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Pieper D, Tricco AC, Gates M, Gates A, et al. Preferred reporting items for overviews of reviews (PRIOR): a protocol for development of a reporting guideline for overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):335. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-019-1252-9 .
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Open Med. 2009;3(3):e123–30.
Krnic Martinic M, Pieper D, Glatt A, Puljak L. Definition of a systematic review used in overviews of systematic reviews, meta-epidemiological studies and textbooks. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):203. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-019-0855-0 .
Puljak L. If there is only one author or only one database was searched, a study should not be called a systematic review. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;91:4–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.08.002 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gates M, Gates A, Guitard S, Pollock M, Hartling L. Guidance for overviews of reviews continues to accumulate, but important challenges remain: a scoping review. Syst Rev. 2020;9(1):254. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-020-01509-0 .
Covidence - systematic review software. Available at: https://www.covidence.org/ . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017;358:j4008.
Borges do Nascimento IJ, et al. Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19) in Humans: A Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med. 2020;9(4):941.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Adhikari SP, Meng S, Wu YJ, Mao YP, Ye RX, Wang QZ, et al. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-020-00646-x .
Cortegiani A, Ingoglia G, Ippolito M, Giarratano A, Einav S. A systematic review on the efficacy and safety of chloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19. J Crit Care. 2020;57:279–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.03.005 .
Li B, Yang J, Zhao F, Zhi L, Wang X, Liu L, et al. Prevalence and impact of cardiovascular metabolic diseases on COVID-19 in China. Clin Res Cardiol. 2020;109(5):531–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-020-01626-9 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Li LQ, Huang T, Wang YQ, Wang ZP, Liang Y, Huang TB, et al. COVID-19 patients’ clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92(6):577–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25757 .
Lippi G, Lavie CJ, Sanchis-Gomar F. Cardiac troponin I in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): evidence from a meta-analysis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63(3):390–1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2020.03.001 .
Lippi G, Henry BM. Active smoking is not associated with severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Eur J Intern Med. 2020;75:107–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2020.03.014 .
Lippi G, Plebani M. Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;505:190–1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.004 .
Lippi G, Plebani M, Henry BM. Thrombocytopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: a meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;506:145–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.022 .
Ludvigsson JF. Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults. Acta Paediatr. 2020;109(6):1088–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.15270 .
Lupia T, Scabini S, Mornese Pinna S, di Perri G, de Rosa FG, Corcione S. 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak: a new challenge. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020;21:22–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2020.02.021 .
Marasinghe, K.M., A systematic review investigating the effectiveness of face mask use in limiting the spread of COVID-19 among medically not diagnosed individuals: shedding light on current recommendations provided to individuals not medically diagnosed with COVID-19. Research Square. Preprint article. doi : https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-16701/v1 . 2020 .
Mullins E, Evans D, Viner RM, O’Brien P, Morris E. Coronavirus in pregnancy and delivery: rapid review. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2020;55(5):586–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.22014 .
Pang J, Wang MX, Ang IYH, Tan SHX, Lewis RF, Chen JIP, et al. Potential Rapid Diagnostics, Vaccine and Therapeutics for 2019 Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV): a systematic review. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):623.
Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Cardona-Ospina JA, Gutiérrez-Ocampo E, Villamizar-Peña R, Holguin-Rivera Y, Escalera-Antezana JP, et al. Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020;34:101623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101623 .
Salehi S, Abedi A, Balakrishnan S, Gholamrezanezhad A. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review of imaging findings in 919 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;215(1):87–93. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.23034 .
Sun P, Qie S, Liu Z, Ren J, Li K, Xi J. Clinical characteristics of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a single arm meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92(6):612–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25735 .
Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, Pu K, Chen Z, Guo Q, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;94:91–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017 .
Bassetti M, Vena A, Giacobbe DR. The novel Chinese coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections: challenges for fighting the storm. Eur J Clin Investig. 2020;50(3):e13209. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.13209 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Hwang CS. Olfactory neuropathy in severe acute respiratory syndrome: report of a case. Acta Neurol Taiwanica. 2006;15(1):26–8.
Google Scholar
Suzuki M, Saito K, Min WP, Vladau C, Toida K, Itoh H, et al. Identification of viruses in patients with postviral olfactory dysfunction. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(2):272–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000249922.37381.1e .
Rajgor DD, Lee MH, Archuleta S, Bagdasarian N, Quek SC. The many estimates of the COVID-19 case fatality rate. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(7):776–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30244-9 .
Wolkewitz M, Puljak L. Methodological challenges of analysing COVID-19 data during the pandemic. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20(1):81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-020-00972-6 .
Rombey T, Lochner V, Puljak L, Könsgen N, Mathes T, Pieper D. Epidemiology and reporting characteristics of non-Cochrane updates of systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study. Res Synth Methods. 2020;11(3):471–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1409 .
Runjic E, Rombey T, Pieper D, Puljak L. Half of systematic reviews about pain registered in PROSPERO were not published and the majority had inaccurate status. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019;116:114–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.08.010 .
Runjic E, Behmen D, Pieper D, Mathes T, Tricco AC, Moher D, et al. Following Cochrane review protocols to completion 10 years later: a retrospective cohort study and author survey. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019;111:41–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.03.006 .
Tricco AC, Antony J, Zarin W, Strifler L, Ghassemi M, Ivory J, et al. A scoping review of rapid review methods. BMC Med. 2015;13(1):224. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-015-0465-6 .
COVID-19 Rapid Reviews: Cochrane’s response so far. Available at: https://training.cochrane.org/resource/covid-19-rapid-reviews-cochrane-response-so-far . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Cochrane. Living systematic reviews. Available at: https://community.cochrane.org/review-production/production-resources/living-systematic-reviews . Accessed 1 June 2021.
Millard T, Synnot A, Elliott J, Green S, McDonald S, Turner T. Feasibility and acceptability of living systematic reviews: results from a mixed-methods evaluation. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):325. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-019-1248-5 .
Babic A, Poklepovic Pericic T, Pieper D, Puljak L. How to decide whether a systematic review is stable and not in need of updating: analysis of Cochrane reviews. Res Synth Methods. 2020;11(6):884–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1451 .
Lovato A, Rossettini G, de Filippis C. Sore throat in COVID-19: comment on “clinical characteristics of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a single arm meta-analysis”. J Med Virol. 2020;92(7):714–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25815 .
Leung C. Comment on Li et al: COVID-19 patients’ clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92(9):1431–2. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25912 .
Li LQ, Huang T, Wang YQ, Wang ZP, Liang Y, Huang TB, et al. Response to Char’s comment: comment on Li et al: COVID-19 patients’ clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92(9):1433. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25924 .
Download references
Acknowledgments
We thank Catherine Henderson DPhil from Swanscoe Communications for pro bono medical writing and editing support. We acknowledge support from the Covidence Team, specifically Anneliese Arno. We thank the whole International Network of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (InterNetCOVID-19) for their commitment and involvement. Members of the InterNetCOVID-19 are listed in Additional file 6 . We thank Pavel Cerny and Roger Crosthwaite for guiding the team supervisor (IJBN) on human resources management.
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University Hospital and School of Medicine, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil
Israel Júnior Borges do Nascimento & Milena Soriano Marcolino
Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA
Israel Júnior Borges do Nascimento
Helene Fuld Health Trust National Institute for Evidence-based Practice in Nursing and Healthcare, College of Nursing, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
Dónal P. O’Mathúna
School of Nursing, Psychotherapy and Community Health, Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Department of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care and Pain Medicine, University of Münster, Münster, Germany
Thilo Caspar von Groote
Department of Sport and Health Science, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany
Hebatullah Mohamed Abdulazeem
School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Health and Medicine, The University of Newcastle, Callaghan, Australia
Ishanka Weerasekara
Department of Physiotherapy, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, University of Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka
Cochrane Croatia, University of Split, School of Medicine, Split, Croatia
Ana Marusic, Irena Zakarija-Grkovic & Tina Poklepovic Pericic
Center for Evidence-Based Medicine and Health Care, Catholic University of Croatia, Ilica 242, 10000, Zagreb, Croatia
Livia Puljak
Cochrane Brazil, Evidence-Based Health Program, Universidade Federal de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
Vinicius Tassoni Civile & Alvaro Nagib Atallah
Yorkville University, Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada
Santino Filoso
Laboratory for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (LIAM), Department of Mathematics and Statistics, York University, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Nicola Luigi Bragazzi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
IJBN conceived the research idea and worked as a project coordinator. DPOM, TCVG, HMA, IW, AM, LP, VTC, IZG, TPP, ANA, SF, NLB and MSM were involved in data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and initial draft writing. All authors revised the manuscript critically for the content. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Livia Puljak .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not required as data was based on published studies.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: appendix 1..
Search strategies used in the study.
Additional file 2: Appendix 2.
Adjusted scoring of AMSTAR 2 used in this study for systematic reviews of studies that did not analyze interventions.
Additional file 3: Appendix 3.
List of excluded studies, with reasons.
Additional file 4: Appendix 4.
Table of overlapping studies, containing the list of primary studies included, their visual overlap in individual systematic reviews, and the number in how many reviews each primary study was included.
Additional file 5: Appendix 5.
A detailed explanation of AMSTAR scoring for each item in each review.
Additional file 6: Appendix 6.
List of members and affiliates of International Network of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (InterNetCOVID-19).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Borges do Nascimento, I.J., O’Mathúna, D.P., von Groote, T.C. et al. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: an overview of systematic reviews. BMC Infect Dis 21 , 525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06214-4
Download citation
Received : 12 April 2020
Accepted : 19 May 2021
Published : 04 June 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06214-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Coronavirus
- Evidence-based medicine
- Infectious diseases
BMC Infectious Diseases
ISSN: 1471-2334
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Contact Tracing
- Pandemic Data Initiative
- Webcasts & Videos
- 30-Minute COVID-19 Briefing
Research Papers
Jhu has stopped collecting data as of.
After three years of around-the-clock tracking of COVID-19 data from...
The Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center has collected, verified, and published local, regional, national, and international pandemic data since it launched in March 2020. From the beginning, the information has been freely available to all — researchers, institutions, the media, the public, and policymakers. As a result, the CRC and its data have been cited in many published research papers and reports. Here we have gathered publications authored by CRC team members that focus on the CRC or its data.
July 14, 2022
Misaligned Federal and State Covid data limits demographic insights
CDC underreports cases and deaths among African American and Hispanic or Latino individuals.
February 17, 2022
Experts Call for Open Public Health Data
Johns Hopkins team highlighted the urgent need for better COVID data collection.
Unifying Epidemiologists and Economists
Researchers from disparate fields join to chart a new path for formulating policies in response to future pandemics.
Mobility Data Supported Social Distancing
Study found that physical distancing was an effective COVID mitigation strategy.
Johns Hopkins Engineers Build COVID Dashboard
Lancet Infectious Diseases published first paper detailing how the global map was built.
Researchers Identify Disparities in COVID Testing
Johns Hopkins team conducted an analysis of state-published demographic data
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on scientific research in the life sciences
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation AXES, IMT School for Advanced Studies Lucca, Lucca, Italy
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Chair of Systems Design D-MTEC, ETH Zürich, Zurich, Switzerland
- Massimo Riccaboni,
- Luca Verginer

- Published: February 9, 2022
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263001
- Reader Comments
The COVID-19 outbreak has posed an unprecedented challenge to humanity and science. On the one side, public and private incentives have been put in place to promptly allocate resources toward research areas strictly related to the COVID-19 emergency. However, research in many fields not directly related to the pandemic has been displaced. In this paper, we assess the impact of COVID-19 on world scientific production in the life sciences and find indications that the usage of medical subject headings (MeSH) has changed following the outbreak. We estimate through a difference-in-differences approach the impact of the start of the COVID-19 pandemic on scientific production using the PubMed database (3.6 Million research papers). We find that COVID-19-related MeSH terms have experienced a 6.5 fold increase in output on average, while publications on unrelated MeSH terms dropped by 10 to 12%. The publication weighted impact has an even more pronounced negative effect (-16% to -19%). Moreover, COVID-19 has displaced clinical trial publications (-24%) and diverted grants from research areas not closely related to COVID-19. Note that since COVID-19 publications may have been fast-tracked, the sudden surge in COVID-19 publications might be driven by editorial policy.
Citation: Riccaboni M, Verginer L (2022) The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on scientific research in the life sciences. PLoS ONE 17(2): e0263001. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263001
Editor: Florian Naudet, University of Rennes 1, FRANCE
Received: April 28, 2021; Accepted: January 10, 2022; Published: February 9, 2022
Copyright: © 2022 Riccaboni, Verginer. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: The processed data, instructions on how to process the raw PubMed dataset as well as all code are available via Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5121216 .
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has mobilized the world scientific community in 2020, especially in the life sciences [ 1 , 2 ]. In the first three months after the pandemic, the number of scientific papers about COVID-19 was fivefold the number of articles on H1N1 swine influenza [ 3 ]. Similarly, the number of clinical trials related to COVID-19 prophylaxis and treatments skyrocketed [ 4 ]. Thanks to the rapid mobilization of the world scientific community, COVID-19 vaccines have been developed in record time. Despite this undeniable success, there is a rising concern about the negative consequences of COVID-19 on clinical trial research, with many projects being postponed [ 5 – 7 ]. According to Evaluate Pharma, clinical trials were one of the pandemic’s first casualties, with a record number of 160 studies suspended for reasons related to COVID-19 in April 2020 [ 8 , 9 ] reporting a total of 1,200 trials suspended as of July 2020. As a consequence, clinical researchers have been impaired by reduced access to healthcare research infrastructures. Particularly, the COVID-19 outbreak took a tall on women and early-career scientists [ 10 – 13 ]. On a different ground, Shan and colleagues found that non-COVID-19-related articles decreased as COVID-19-related articles increased in top clinical research journals [ 14 ]. Fraser and coworker found that COVID-19 preprints received more attention and citations than non-COVID-19 preprints [ 1 ]. More recently, Hook and Porter have found some early evidence of ‘covidisation’ of academic research, with research grants and output diverted to COVID-19 research in 2020 [ 15 ]. How much should scientists switch their efforts toward SARS-CoV-2 prevention, treatment, or mitigation? There is a growing consensus that the current level of ‘covidisation’ of research can be wasteful [ 4 , 5 , 16 ].
Against this background, in this paper, we investigate if the COVID-19 pandemic has induced a shift in biomedical publications toward COVID-19-related scientific production. The objective of the study is to show that scientific articles listing covid-related Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) when compared against covid-unrelated MeSH have been partially displaced. Specifically, we look at several indicators of scientific production in the life sciences before and after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic: (1) number of papers published, (2) impact factor weighted number of papers, (3) opens access, (4) number of publications related to clinical trials, (5) number of papers listing grants, (6) number of papers listing grants existing before the pandemic. Through a natural experiment approach, we analyze the impact of the pandemic on scientific production in the life sciences. We consider COVID-19 an unexpected and unprecedented exogenous source of variation with heterogeneous effects across biomedical research fields (i.e., MeSH terms).
Based on the difference in difference results, we document the displacement effect that the pandemic has had on several aspects of scientific publishing. The overall picture that emerges from this analysis is that there has been a profound realignment of priorities and research efforts. This shift has displaced biomedical research in fields not related to COVID-19.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. First, we describe the data and our measure of relatedness to COVID-19. Next, we illustrate the difference-in-differences specification we rely on to identify the impact of the pandemic on scientific output. In the results section, we present the results of the difference-in-differences and network analyses. We document the sudden shift in publications, grants and trials towards COVID-19-related MeSH terms. Finally, we discuss the findings and highlight several policy implications.
Materials and methods
The present analysis is based primarily on PubMed and the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terminology. This data is used to estimate the effect of the start of the COVID 19 pandemic via a difference in difference approach. This section is structured as follows. We first introduce the data and then the econometric methodology. This analysis is not based on a pre-registered protocol.
Selection of biomedical publications.
We rely on PubMed, a repository with more than 34 million biomedical citations, for the analysis. Specifically, we analyze the daily updated files up to 31/06/2021, extracting all publications of type ‘Journal Article’. For the principal analysis, we consider 3,638,584 papers published from January 2019 to December 2020. We also analyze 11,122,017 papers published from 2010 onwards to identify the earliest usage of a grant and infer if it was new in 2020. We use the SCImago journal ranking statistics to compute the impact factor weighted number (IFWN) of papers in a given field of research. To assign the publication date, we use the ‘electronically published’ dates and, if missing, the ‘print published’ dates.
Medical subject headings.
We rely on the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terminology to approximate narrowly defined biomedical research fields. This terminology is a curated medical vocabulary, which is manually added to papers in the PubMed corpus. The fact that MeSH terms are manually annotated makes this terminology ideal for classification purposes. However, there is a delay between publication and annotation, on the order of several months. To address this delay and have the most recent classification, we search for all 28 425 MeSH terms using PubMed’s ESearch utility and classify paper by the results. The specific API endpoint is https://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/esearch.fcgi , the relevant scripts are available with the code. For example, we assign the term ‘Ageusia’ (MeSH ID D000370) to all papers listed in the results of the ESearch API. We apply this method to the whole period (January 2019—December 2020) and obtain a mapping from papers to the MeSH terms. For every MeSH term, we keep track of the year they have been established. For instance, COVID-19 terms were established in 2020 (see Table 1 ): in January 2020, the WHO recommended 2019-nCoV and 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease as provisional names for the virus and disease. The WHO issued the official terms COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 at the beginning of February 2020. By manually annotating publications, all publications referring to COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 since January 2020 have been labelled with the related MeSH terms. Other MeSH terms related to COVID-19, such as coronavirus, for instance, have been established years before the pandemic (see Table 2 ). We proxy MeSH term usage via search terms using the PubMed EUtilities API; this means that we are not using the hand-labelled MeSH terms but rather the PubMed search results. This means that the accuracy of the MeSH term we assign to a given paper is not perfect. In practice, this means that we have assigned more MeSH terms to a given term than a human annotator would have.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263001.t001
The list contains only terms with at least 100 publications in 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263001.t002
Clinical trials and publication types.
We classify publications using PubMed’s ‘PublicationType’ field in the XML baseline files (There are 187 publication types, see https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/pubtypes.html ). We consider a publication to be related to a clinical trial if it lists any of the following descriptors:
- D016430: Clinical Trial
- D017426: Clinical Trial, Phase I
- D017427: Clinical Trial, Phase II
- D017428: Clinical Trial, Phase III
- D017429: Clinical Trial, Phase IV
- D018848: Controlled Clinical Trial
- D065007: Pragmatic Clinical Trial
- D000076362: Adaptive Clinical Trial
- D000077522: Clinical Trial, Veterinary
In our analysis of the impact of COVID-19 on publications related to clinical trials, we only consider MeSH terms that are associated at least once with a clinical trial publication over the two years. We apply this restriction to filter out MeSH terms that are very unlikely to be relevant for clinical trial types of research.
Open access.
We proxy the availability of a journal article to the public, i.e., open access, if it is available from PubMed Central. PubMed Central archives full-text journal articles and provides free access to the public. Note that the copyright license may vary across participating publishers. However, the text of the paper is for all effects and purposes freely available without requiring subscriptions or special affiliation.
We infer if a publication has been funded by checking if it lists any grants. We classify grants as either ‘old’, i.e. existed before 2019, or ‘new’, i.e. first observed afterwards. To do so, we collect all grant IDs for 11,122,017 papers from 2010 on-wards and record their first appearance. This procedure is an indirect inference of the year the grant has been granted. The basic assumption is that if a grant number has not been listed in any publication since 2010, it is very likely a new grant. Specifically, an old grant is a grant listed since 2019 observed at least once from 2010 to 2018.
Note that this procedure is only approximate and has a few shortcomings. Mistyped grant numbers (e.g. ‘1234-M JPN’ and ‘1234-M-JPN’) could appear as new grants, even though they existed before, or new grants might be classified as old grants if they have a common ID (e.g. ‘Grant 1’). Unfortunately, there is no central repository of grant numbers and the associated metadata; however, there are plans to assign DOI numbers to grants to alleviate this problem (See https://gitlab.com/crossref/open_funder_registry for the project).
Impact factor weighted publication numbers (IFWN).
In our analysis, we consider two measures of scientific output. First, we simply count the number of publications by MeSH term. However, since journals vary considerably in terms of impact factor, we also weigh the number of publications by the impact factor of the venue (e.g., journal) where it was published. Specifically, we use the SCImago journal ranking statistics to weigh a paper by the impact factor of the journal it appears in. We use the ‘citation per document in the past two years’ for 45,230 ISSNs. Note that a journal may and often has more than one ISSN, i.e., one for the printed edition and one for the online edition. SCImago applies the same score for a venue across linked ISSNs.
For the impact factor weighted number (IFWN) of publication per MeSH terms, this means that all publications are replaced by the impact score of the journal they appear in and summed up.
COVID-19-relatedness.
To measure how closely related to COVID-19 is a MeSH term, we introduce an index of relatedness to COVID-19. First, we identify the focal COVID-19 terms, which appeared in the literature in 2020 (see Table 1 ). Next, for all other pre-existing MeSH terms, we measure how closely related to COVID-19 they end up being.
Our aim is to show that MeSH terms that existed before and are related have experienced a sudden increase in the number of (impact factor weighted) papers.
Intuitively we can read this measure as: what is the probability in 2020 that a COVID-19 MeSH term is present given that we chose a paper with MeSH term i ? For example, given that in 2020 we choose a paper dealing with “Ageusia” (i.e., Complete or severe loss of the subjective sense of taste), there is a 96% probability that this paper also lists COVID-19, see Table 1 .
Note that a paper listing a related MeSH term does not imply that that paper is doing COVID-19 research, but it implies that one of the MeSH terms listed is often used in COVID-19 research.
In sum, in our analysis, we use the following variables:
- Papers: Number of papers by MeSH term;
- Impact: Impact factor weighted number of papers by MeSH term;
- PMC: Papers listed in PubMed central by MeSH term, as a measure of Open Access publications;
- Trials: number of publications of type “Clinical Trial” by MeSH term;
- Grants: number of papers with at least one grant by MeSH term;
- Old Grants: number of papers listing a grant that has been observed between 2010 and 2018, by MeSH term;
Difference-in-differences
The difference-in-differences (DiD) method is an econometric technique to imitate an experimental research design from observation data, sometimes referred to as a quasi-experimental setup. In a randomized controlled trial, subjects are randomly assigned either to the treated or the control group. Analogously, in this natural experiment, we assume that medical subject headings (MeSH) have been randomly assigned to be either treated (related) or not treated (unrelated) by the pandemic crisis.
Before the COVID, for a future health crisis, the set of potentially impacted medical knowledge was not predictable since it depended on the specifics of the emergency. For instance, ageusia (loss of taste), a medical concept existing since 1991, became known to be a specific symptom of COVID-19 only after the pandemic.
Specifically, we exploit the COVID-19 as an unpredictable and exogenous shock that has deeply affected the publication priorities for biomedical scientific production, as compared to the situation before the pandemic. In this setting, COVID-19 is the treatment, and the identification of this new human coronavirus is the event. We claim that treated MeSH terms, i.e., MeSH terms related to COVID-19, have experienced a sudden increase in terms of scientific production and attention. In contrast, research on untreated MeSH terms, i.e., MeSH terms not related to COVID-19, has been displaced by COVID-19. Our analysis compares the scientific output of COVID-19 related and unrelated MeSH terms before and after January 2020.
In our case, some of the terms turn out to be related to COVID-19 in 2020, whereas most of the MeSH terms are not closely related to COVID-19.
Thus β 1 identifies the overall effect on the control group after the event, β 2 the difference across treated and control groups before the event (i.e. the first difference in DiD) and finally the effect on the treated group after the event, net of the first difference, β 3 . This last parameter identifies the treatment effect on the treated group netting out the pre-treatment difference.
For the DiD to have a causal interpretation, it must be noted that pre-event, the trends of the two groups should be parallel, i.e., the common trend assumption (CTA) must be satisfied. We will show that the CTA holds in the results section.
To specify the DiD model, we need to define a period before and after the event and assign a treatment status or level of exposure to each term.
Before and after.
The pre-treatment period is defined as January 2019 to December 2019. The post-treatment period is defined as the months from January 2020 to December 2020. We argue that the state of biomedical research was similar in those two years, apart from the effect of the pandemic.
Treatment status and exposure.
The treatment is determined by the COVID-19 relatedness index σ i introduced earlier. Specifically, this number indicates the likelihood that COVID-19 will be a listed MeSH term, given that we observe the focal MeSH term i . To show that the effect becomes even stronger the closer related the subject is, and for ease of interpretation, we also discretize the relatedness value into three levels of treatment. Namely, we group MeSH terms with a σ between, 0% to 20%, 20% to 80% and 80% to 100%. The choice of alternative grouping strategies does not significantly affect our results. Results for alternative thresholds of relatedness can be computed using the available source code. We complement the dichotomized analysis by using the treatment intensity (relatedness measure σ ) to show that the result persists.
Panel regression.
In this work, we estimate a random effects panel regression where the units of analysis are 28 318 biomedical research fields (i.e. MeSH terms) observed over time before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. The time resolution is at the monthly level, meaning that for each MeSH term, we have 24 observations from January 2019 to December 2020.
The outcome variable Y it identifies the outcome at time t (i.e., month), for MeSH term i . As before, P t identifies the period with P t = 0 if the month is before January 2020 and P t = 1 if it is on or after this date. In (3) , the treatment level is measure by the relatedness to COVID-19 ( σ i ), where again the γ 1 identifies pre-trend (constant) differences and δ 1 the overall effect.
In total, we estimate six coefficients. As before, the δ l coefficient identifies the DiD effect.

Verifying the Common Trend Assumption (CTA).
We show that the CTA holds for this model by comparing the pre-event trends of the control group to the treated groups (COVID-19 related MeSH terms). Namely, we show that the pre-event trends of the control group are the same as the pre-event trends of the treated group.
Co-occurrence analysis
To investigate if the pandemic has caused a reconfiguration of research priorities, we look at the MeSH term co-occurrence network. Precisely, we extract the co-occurrence network of all 28,318 MeSH terms as they appear in the 3.3 million papers. We considered the co-occurrence networks of 2018, 2019 and 2020. Each node represents a MeSH term in these networks, and a link between them indicates that they have been observed at least once together. The weight of the edge between the MeSH terms is given by the number of times those terms have been jointly observed in the same publications.
Medical language is hugely complicated, and this simple representation does not capture the intricacies, subtle nuances and, in fact, meaning of the terms. Therefore, we do not claim that we can identify how the actual usage of MeSH terms has changed from this object, but rather that it has. Nevertheless, the co-occurrence graph captures rudimentary relations between concepts. We argue that absent a shock to the system, their basic usage patterns, change in importance (within the network) would essentially be the same from year to year. However, if we find that the importance of terms changes more than expected in 2020, it stands to reason that there have been some significant changes.
To show that that MeSH usage has been affected, we compute for each term in the years 2018, 2019 and 2020 their PageRank centrality [ 17 ]. The PageRank centrality tells us how likely a random walker traversing a network would be found at a given node if she follows the weights of the empirical edges (i.e., co-usage probability). Specifically, for the case of the MeSH co-occurrence network, this number represents how often an annotator at the National Library of Medicine would assign that MeSH term following the observed general usage patterns. It is a simplistic measure to capture the complexities of biomedical research. Nevertheless, it captures far-reaching interdependence across MeSH terms as the measure uses the whole network to determine the centrality of every MeSH term. A sudden change in the rankings and thus the position of MeSH terms in this network suggests that a given research subject has risen as it is used more often with other important MeSH terms (or vice versa).
We then compare the growth for each MeSH i term in g i (2019), i.e. before the the COVID-19 pandemic, with the growth after the event ( g i (2020)).
Publication growth
Changes in output and COVID-19 relatedness
Before we show the regression results, we provide descriptive evidence that publications from 2019 to 2020 have drastically increased. By showing that this growth correlates strongly with a MeSH term’s COVID-19 relatedness ( σ ), we demonstrate that (1) σ captures an essential aspect of the growth dynamics and (2) highlight the meteoric rise of highly related terms.
We look at the year over year growth in the number of the impact weighted number of publications per MeSH term from 2018 to 2019 and 2019 to 2020 as defined in the methods section.
Fig 1 shows the yearly growth of the impact weighted number of publications per MeSH term. By comparing the growth of the number of publications from the years 2018, 2019 and 2020, we find that the impact factor weighted number of publications has increased by up to a factor of 100 compared to the previous year for Betacoronavirus, one of the most closely related to COVID-19 MeSH term.
Each dot represents, a MeSH term. The y axis (growth) is in symmetric log scale. The x axis shows the COVID-19 relatedness, σ . Note that the position of the dots on the x-axis is the same in the two plots. Below: MeSH term importance gain (PageRank) and their COVID-19 relatedness.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263001.g001
Fig 1 , first row, reveals how strongly correlated the growth in the IFWN of publication is to the term’s COVID-19 relatedness. For instance, we see that the term ‘Betacoronavirus’ skyrocketed from 2019 to 2020, which is expected given that SARS-CoV-2 is a species of the genus. Conversely, the term ‘Alphacoronavirus’ has not experienced any growth given that it is twin a genus of the Coronaviridae family, but SARS-CoV-2 is not one of its species. Note also the fast growth in the number of publications dealing with ‘Quarantine’. Moreover, MeSH terms that grew significantly from 2018 to 2019 and were not closely related to COVID-19, like ‘Vaping’, slowed down in 2020. From the graph, the picture emerges that publication growth is correlated with COVID-19 relatedness σ and that the growth for less related terms slowed down.
To show that the usage pattern of MeSH terms has changed following the pandemic, we compute the PageRank centrality using graph-tool [ 18 ] as discussed in the Methods section.
Fig 1 , second row, shows the change in the PageRank centrality of the MeSH terms after the pandemic (2019 to 2020, right plot) and before (2018 to 2019, left plot). If there were no change in the general usage pattern, we would expect the variance in PageRank changes to be narrow across the two periods, see (left plot). However, PageRank scores changed significantly more from 2019 to 2020 than from 2018 to 2019, suggesting that there has been a reconfiguration of the network.
To further support this argument, we carry out a DiD regression analysis.
Common trends assumption
As discussed in the Methods section, we need to show that the CTA assumption holds for the DiD to be defined appropriately. We do this by estimating for each month the number of publications and comparing it across treatment groups. This exercise also serves the purpose of a placebo test. By assuming that each month could have potentially been the event’s timing (i.e., the outbreak), we show that January 2020 is the most likely timing of the event. The regression table, as noted earlier, contains over 70 estimated coefficients, hence for ease of reading, we will only show the predicted outcome per month by group (see Fig 2 ). The full regression table with all coefficients is available in the S1 Table .
The y axis is in log scale. The dashed vertical line identifies January 2020. The dashed horizontal line shows the publications in January 2019 for the 0–20% group before the event. This line highlights that the drop happens after the event. The bands around the lines indicate the 95% confidence interval of the predicted values. The results are the output of the Stata margins command.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263001.g002
Fig 2 shows the predicted number per outcome variable obtained from the panel regression model. These predictions correspond to the predicted value per relatedness group using the regression parameters estimated via the linear panel regression. The bands around the curves are the 95% confidence intervals.
All outcome measures depict a similar trend per month. Before the event (i.e., January 2020), there is a common trend across all groups. In contrast, after the event, we observe a sudden rise for the outcomes of the COVID-19 related treated groups (green and red lines) and a decline in the outcomes for the unrelated group (blue line). Therefore, we can conclude that the CTA assumption holds.
Regression results
Table 3 shows the DiD regression results (see Eq (3) ) for the selected outcome measures: number of publications (Papers), impact factor weighted number of publications (Impact), open access (OA) publications, clinical trial related publications, and publications with existing grants.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263001.t003
Table 3 shows results for the discrete treatment level version of the DiD model (see Eq (4) ).
Note that the outcome variable is in natural log scale; hence to get the effect of the independent variable, we need to exponentiate the coefficient. For values close to 0, the effect is well approximated by the percentage change of that magnitude.
In both specifications we see that the least related group, drops in the number of publications between 10% and 13%, respectively (first row of Tables 3 and 4 , exp(−0.102) ≈ 0.87). In line with our expectations, the increase in the number of papers published by MeSH term is positively affected by the relatedness to COVID-19. In the discrete model (row 2), we note that the number of documents with MeSH terms with a COVID-19 relatedness between 20 and 80% grows by 18% and highly related terms by a factor of approximately 6.6 (exp(1.88)). The same general pattern can be observed for the impact weighted publication number, i.e., Model (2). Note, however, that the drop in the impact factor weighted output is more significant, reaching -19% for COVID-19 unrelated publications, and related publications growing by a factor of 8.7. This difference suggests that there might be a bias to publish papers on COVID-19 related subjects in high impact factor journals.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263001.t004
By looking at the number of open access publications (PMC), we note that the least related group has not been affected negatively by the pandemic. However, the number of COVID-19 related publications has drastically increased for the most COVID-19 related group by a factor of 6.2. Note that the substantial increase in the number of papers available through open access is in large part due to journal and editorial policies to make preferentially COVID research immediately available to the public.
Regarding the number of clinical trial publications, we note that the least related group has been affected negatively, with the number of publications on clinical trials dropping by a staggering 24%. At the same time, publications on clinical trials for COVID-19-related MeSH have increased by a factor of 2.1. Note, however, that the effect on clinical trials is not significant in the continuous regression. The discrepancy across Tables 3 and 4 highlights that, especially for trials, the effect is not linear, where only the publications on clinical trials closely related to COVID-19 experiencing a boost.
It has been reported [ 19 ] that while the number of clinical trials registered to treat or prevent COVID-19 has surged with 179 new registrations in the second week of April 2020 alone. Only a few of these have led to publishable results in the 12 months since [ 20 ]. On the other hand, we find that clinical trial publications, considering related MeSH (but not COVID-19 directly), have had significant growth from the beginning of the pandemic. These results are not contradictory. Indeed counting the number of clinical trial publications listing the exact COVID-19 MeSH term (D000086382), we find 212 publications. While this might seem like a small number, consider that in 2020 only 8,485 publications were classified as clinical trials; thus, targeted trials still made up 2.5% of all clinical trials in 2020 . So while one might doubt the effectiveness of these research efforts, it is still the case that by sheer number, they represent a significant proportion of all publications on clinical trials in 2020. Moreover, COVID-19 specific Clinical trial publications in 2020, being a delayed signal of the actual trials, are a lower bound estimate on the true number of such clinical trials being conducted. This is because COVID-19 studies could only have commenced in 2020, whereas other studies had a head start. Thus our reported estimates are conservative, meaning that the true effect on actual clinical trials is likely larger, not smaller.
Research funding, as proxied by the number of publications with grants, follows a similar pattern, but notably, COVID-19-related MeSH terms list the same proportion of grants established before 2019 as other unrelated MeSH terms, suggesting that grants which were not designated for COVID-19 research have been used to support COVID-19 related research. Overall, the number of publications listing a grant has dropped. Note that this should be because the number of publications overall in the unrelated group has dropped. However, we note that the drop in publications is 10% while the decline in publications with at least one grant is 15%. This difference suggests that publications listing grants, which should have more funding, are disproportionately COVID-19 related papers. To further investigate this aspect, we look at whether the grant was old (pre-2019) or appeared for the first time in or after 2019. It stands to reason that an old grant (pre-2019) would not have been granted for a project dealing with the pandemic. Hence we would expect that COVID-19 related MeSH terms to have a lower proportion of old grants than the unrelated group. In models (6) in Table 4 we show that the number of old grants for the unrelated group drops by 13%. At the same time, the number of papers listing old grants (i.e., pre-2019) among the most related group increased by a factor of 3.1. Overall, these results suggest that COVID-19 related research has been funded largely by pre-existing grants, even though a specific mandate tied to the grants for this use is unlikely.
The scientific community has swiftly reallocated research efforts to cope with the COVID-19 pandemic, mobilizing knowledge across disciplines to find innovative solutions in record time. We document this both in terms of changing trends in the biomedical scientific output and the usage of MeSH terms by the scientific community. The flip side of this sudden and energetic prioritization of effort to fight COVID-19 has been a sudden contraction of scientific production in other relevant research areas. All in all, we find strong support to the hypotheses that the COVID-19 crisis has induced a sudden increase of research output in COVID-19 related areas of biomedical research. Conversely, research in areas not related to COVID-19 has experienced a significant drop in overall publishing rates and funding.
Our paper contributes to the literature on the impact of COVID-19 on scientific research: we corroborate previous findings about the surge of COVID-19 related publications [ 1 – 3 ], partially displacing research in COVID-19 unrelated fields of research [ 4 , 14 ], particularly research related to clinical trials [ 5 – 7 ]. The drop in trial research might have severe consequences for patients affected by life-threatening diseases since it will delay access to new and better treatments. We also confirm the impact of COVID-19 on open access publication output [ 1 ]; also, this is milder than traditional outlets. On top of this, we provide more robust evidence on the impact weighted effect of COVID-19 and grant financed research, highlighting the strong displacement effect of COVID-19 on the allocation of financial resources [ 15 ]. We document a substantial change in the usage patterns of MeSH terms, suggesting that there has been a reconfiguration in the way research terms are being combined. MeSH terms highly related to COVID-19 were peripheral in the MeSH usage networks before the pandemic but have become central since 2020. We conclude that the usage patterns have changed, with COVID-19 related MeSH terms occupying a much more prominent role in 2020 than they did in the previous years.
We also contribute to the literature by estimating the effect of COVID-19 on biomedical research in a natural experiment framework, isolating the specific effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the biomedical scientific landscape. This is crucial to identify areas of public intervention to sustain areas of biomedical research which have been neglected during the COVID-19 crisis. Moreover, the exploratory analysis on the changes in usage patterns of MeSH terms, points to an increase in the importance of covid-related topics in the broader biomedical research landscape.
Our results provide compelling evidence that research related to COVID-19 has indeed displaced scientific production in other biomedical fields of research not related to COVID-19, with a significant drop in (impact weighted) scientific output related to non-COVID-19 and a marked reduction of financial support for publications not related to COVID-19 [ 4 , 5 , 16 ]. The displacement effect is persistent to the end of 2020. As vaccination progresses, we highlight the urgent need for science policy to re-balance support for research activity that was put on pause because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
We find that COVID-19 dramatically impacted clinical research. Reactivation of clinical trials activities that have been postponed or suspended for reasons related to COVID-19 is a priority that should be considered in the national vaccination plans. Moreover, since grants have been diverted and financial incentives have been targeted to sustain COVID-19 research leading to an excessive entry in COVID-19-related clinical trials and the ‘covidisation’ of research, there is a need to reorient incentives to basic research and otherwise neglected or temporally abandoned areas of biomedical research. Without dedicated support in the recovery plans for neglected research of the COVID-19 era, there is a risk that more medical needs will be unmet in the future, possibly exacerbating the shortage of scientific research for orphan and neglected diseases, which do not belong to COVID-19-related research areas.
Limitations
Our empirical approach has some limits. First, we proxy MeSH term usage via search terms using the PubMed EUtilities API. This means that the accuracy of the MeSH term we assign to a given paper is not fully validated. More time is needed for the completion of manually annotated MeSH terms. Second, the timing of publication is not the moment the research has been carried out. There is a lead time between inception, analysis, write-up, review, revision, and final publication. This delay varies across disciplines. Nevertheless, given that the surge in publications happens around the alleged event date, January 2020, we are confident that the publication date is a reasonable yet imperfect estimate of the timing of the research. Third, several journals have publicly declared to fast-track COVID-19 research. This discrepancy in the speed of publication of COVID-19 related research and other research could affect our results. Specifically, a surge or displacement could be overestimated due to a lag in the publication of COVID-19 unrelated research. We alleviate this bias by estimating the effect considering a considerable time after the event (January 2020 to December 2020). Forth, on the one hand, clinical Trials may lead to multiple publications. Therefore we might overestimate the impact of COVID-19 on the number of clinical trials. On the other hand, COVID-19 publications on clinical trials lag behind, so the number of papers related COVID-19 trials is likely underestimated. Therefore, we note that the focus of this paper is scientific publications on clinical trials rather than on actual clinical trials. Fifth, regarding grants, unfortunately, there is no unique centralized repository mapping grant numbers to years, so we have to proxy old grants with grants that appeared in publications from 2010 to 2018. Besides, grant numbers are free-form entries, meaning that PubMed has no validation step to disambiguate or verify that the grant number has been entered correctly. This has the effect of classifying a grant as new even though it has appeared under a different name. We mitigate this problem by using a long period to collect grant numbers and catch many spellings of the same grant, thereby reducing the likelihood of miss-identifying a grant as new when it existed before. Still, unless unique identifiers are widely used, there is no way to verify this.
So far, there is no conclusive evidence on whether entry into COVID-19 has been excessive. However, there is a growing consensus that COVID-19 has displaced, at least temporally, scientific research in COVID-19 unrelated biomedical research areas. Even though it is certainly expected that more attention will be devoted to the emergency during a pandemic, the displacement of biomedical research in other fields is concerning. Future research is needed to investigate the long-run structural consequences of the COVID-19 crisis on biomedical research.
Supporting information
S1 table. common trend assumption (cta) regression table..
Full regression table with all controls and interactions.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263001.s001
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- PubMed/NCBI
- 8. Brown A, Edwin E, Fagg J. Evaluate Pharma 2021 Preview; 2020. https://www.evaluate.com/thought-leadership/vantage/evaluate-vantage-2021-preview .
- 15. Hook D, Porter S. The COVID Brain Drain; 2020. https://www.natureindex.com/news-blog/covid-brain-drain-scientific-research .
- 17. Page L, Brin S, Motwani R, Winograd T. The PageRank citation ranking: Bringing order to the web. Stanford InfoLab; 1999.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A literature review
Affiliations.
- 1 Medical Research Unit, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia; Tropical Disease Centre, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia; Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 2 Division of Infectious Diseases, AichiCancer Center Hospital, Chikusa-ku Nagoya, Japan. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 3 Department of Family Medicine, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 4 Department of Pulmonology and Respiratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 5 School of Medicine, The University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 6 Siem Reap Provincial Health Department, Ministry of Health, Siem Reap, Cambodia. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 7 Department of Microbiology and Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Warmadewa University, Denpasar, Indonesia; Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, University of California, Davis, CA, USA. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 8 Medical Research Unit, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia; Tropical Disease Centre, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia; Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia; Department of Clinical Microbiology, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 9 Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, MI 48109, USA. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 10 Medical Research Unit, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia; Tropical Disease Centre, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia; Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia. Electronic address: [email protected].
- PMID: 32340833
- PMCID: PMC7142680
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.03.019
In early December 2019, an outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by a novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), occurred in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China. On January 30, 2020 the World Health Organization declared the outbreak as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. As of February 14, 2020, 49,053 laboratory-confirmed and 1,381 deaths have been reported globally. Perceived risk of acquiring disease has led many governments to institute a variety of control measures. We conducted a literature review of publicly available information to summarize knowledge about the pathogen and the current epidemic. In this literature review, the causative agent, pathogenesis and immune responses, epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment and management of the disease, control and preventions strategies are all reviewed.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; COVID-19; Novel coronavirus; Outbreak; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Publication types
- Betacoronavirus
- Clinical Trials as Topic
- Coronavirus Infections* / epidemiology
- Coronavirus Infections* / immunology
- Coronavirus Infections* / therapy
- Coronavirus Infections* / virology
- Disease Outbreaks* / prevention & control
- Pneumonia, Viral* / epidemiology
- Pneumonia, Viral* / immunology
- Pneumonia, Viral* / therapy
- Pneumonia, Viral* / virology

COVID-19 Research Articles Downloadable Database
March 19, 2020
Updated January 12, 2024
COVID-19 Research Guide Home
- Research Articles Downloadable Database
- COVID-19 Science Updates
- Databases and Journals
- Secondary Data and Statistics
Important announcement:
The CDC Database of COVID-19 Research Articles became a collaboration with the WHO to create the WHO COVID-19 database during the pandemic to make it easier for results to be searched, downloaded, and used by researchers worldwide.
The last version of the CDC COVID-19 database was archived and remain available on this website. Please note that it has stopped updating as of October 9, 2020 and all new articles were integrated into the WHO COVID-19 database . The WHO Covid-19 Research Database was a resource created in response to the Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). Its content remains searchable and spans the time period March 2020 to June 2023. Since June 2023, manual updates to the database have been discontinued.
If you have any questions, concerns, or problems accessing the WHO COVID-19 Database please email the CDC Library for assistance.
Materials listed in these guides are selected to provide awareness of quality public health literature and resources. A material’s inclusion does not necessarily represent the views of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Public Health Service (PHS), or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nor does it imply endorsement of the material’s methods or findings.
Below are options to download the archive of COVID-19 research articles. You can search the database of citations by author, keyword (in title, author, abstract, subject headings fields), journal, or abstract when available. DOI, PMID, and URL links are included when available.
This database was last updated on October 9, 2020 .
- The CDC Database of COVID-19 Research Articles is now a part of the WHO COVID-19 database . Our new search results are now being sent to the WHO COVID-19 Database to make it easier for them to be searched, downloaded, and used by researchers worldwide. The WHO Covid-19 Research Database was a resource created in response to the Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). Its content remains searchable and spans the time period March 2020 to June 2023. Since June 2023, manual updates to the database have been discontinued.
- To help inform CDC’s COVID-19 Response, as well as to help CDC staff stay up to date on the latest COVID-19 research, the Response’s Office of the Chief Medical Officer has collaborated with the CDC Office of Library Science to create a series called COVID-19 Science Update . This series, the first of its kind for a CDC emergency response, provides brief summaries of new COVID-19-related studies on many topics, including epidemiology, clinical treatment and management, laboratory science, and modeling. As of December 18, 2021, CDC has stopped production of the weekly COVID-19 Science Update.
Excel download:
- Articles from August until October 9 2020 [XLS – 29 MB]
- Articles from December 2019 through July 2020 [XLS – 45 MB]
- The CDC Database of COVID-19 Research Articles is now a part of the WHO COVID-19 database . Our new search results are now being sent to the WHO COVID-19 Database to make it easier for them to be searched, downloaded, and used by researchers worldwide.
- October 8 in Excel [XLS – 1 MB]
- October 7 in Excel [XLS – 1 MB]
- October 6 in Excel [XLS – 1 MB]
- Note the main Excel file can also be sorted by date added.
Citation Management Software (EndNote, Mendeley, Zotero, Refman, etc.) download:
- Part 1 [ZIP – 38 MB]
- Part 2 [ZIP – 43 MB]
- October 8 in citation management software format [RIS – 2 MB]
- October 7 in citation management software format [RIS – 2 MB]
- October 6 in citation management software format [RIS – 2 MB]
- Note the main RIS file can also be sorted by date added.
The COVID-19 pandemic is a rapidly changing situation. Some of the research included above is preliminary. Materials listed in this database are selected to provide awareness of quality public health literature and resources. A material’s inclusion does not necessarily represent the views of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Public Health Service (PHS), or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nor does it imply endorsement of the material’s methods or findings.
To access the full text, click on the DOI, PMID, or URL links. While most publishers are making their COVID-19 content Open Access, some articles are accessible only to those with a CDC user id and password. Find a library near you that may be able to help you get access to articles by clicking the following links: https://www.worldcat.org/libraries OR https://www.usa.gov/libraries .
CDC users can use EndNote’s Find Full Text feature to attach the full text PDFs within their EndNote Library. CDC users, please email Martha Knuth for an EndNote file of all citations. Once you have your EndNote file downloaded, to get the full-text of journal articles listed in the search results you can do the following steps:
- First, try using EndNote’s “Find Full-Text” feature to attach full-text articles to your EndNote Library.
- Next, check for full-text availability, via the E-Journals list, at: http://sfxhosted.exlibrisgroup.com/cdc/az .
- If you can’t find full-text online, you can request articles via DocExpress, at: https://docexpress.cdc.gov/illiad/
The following databases were searched from Dec. 2019-Oct. 9 2020 for articles related to COVID-19: Medline (Ovid and PubMed), PubMed Central, Embase, CAB Abstracts, Global Health, PsycInfo, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Academic Search Complete, Africa Wide Information, CINAHL, ProQuest Central, SciFinder, the Virtual Health Library, and LitCovid. Selected grey literature sources were searched as well, including the WHO COVID-19 website, CDC COVID-19 website, Eurosurveillance, China CDC Weekly, Homeland Security Digital Library, ClinicalTrials.gov, bioRxiv (preprints), medRxiv (preprints), chemRxiv (preprints), and SSRN (preprints).
Detailed search strings with synonyms used for COVID-19 are below.
Detailed search strategy for gathering COVID-19 articles, updated October 9, 2020 [PDF – 135 KB]
Note on preprints: Preprints have not been peer-reviewed. They should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or be reported in news media as established information.
Materials listed in these guides are selected to provide awareness of quality public health literature and resources. A material’s inclusion does not necessarily represent the views of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Public Health Service (PHS), or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nor does it imply endorsement of the material’s methods or findings. HHS, PHS, and CDC assume no responsibility for the factual accuracy of the items presented. The selection, omission, or content of items does not imply any endorsement or other position taken by HHS, PHS, and CDC. Opinion, findings, and conclusions expressed by the original authors of items included in these materials, or persons quoted therein, are strictly their own and are in no way meant to represent the opinion or views of HHS, PHS, or CDC. References to publications, news sources, and non-CDC Websites are provided solely for informational purposes and do not imply endorsement by HHS, PHS, or CDC.
To receive the COVID-19 Science Update, please enter your email address to subscribe today.
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Indian Publications on SARS-CoV-2: A bibliometric study of WHO COVID-19 database
Vasantha raju n.
a Government First Grade College, Talakadu, Karnataka, India
b Department of Library & Information Science, Shivaji University, Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India
Background & aims
Nowadays, the whole World is under threat of Coronavirus disease (COVID-19). The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in many fatalities and forced scientific communities to foster their Research and Development (R&D) activities. As a result, there is an enormous growth of scholarly literature on the subject. We here in this study have assessed the Indian publications contributions on COVID-19.
WHO is curating global scientific literature on coronavirus since it declared COVID-19 a global pandemic through Global Research Database on COVID-19. The present study analyzed Indian publications on SARS-CoV-2 as found in WHO COVID-19 database. The research data was restricted for the period of March 2, 2020 to May 12, 2020.
The study found that there is a considerable and constant growth of Indian publications on COVID-19 from mid-April. It is interesting to note that, the most prolific authors belong to either AIIMS or ICMR institutes. Delhi state contributed highest number of publications on COVID-19. The AIIMS, New Delhi was the most productive institution in terms of publications. The Indian Journal of Medical Research has emerged as the productive journal contributing highest number of the publications. In terms of research area, the majority of the publications were related to Epidemiology.
Conclusions
The highly cited publications were of evidenced based studies. It is observed that the studies pertaining to virology, diagnosis and treatment, clinical features etc. have received highest citations than general studies on epidemiology or pandemic.
- • This review provides a detailed analysis of Research Publications on COVID-19 from India.
- • We also analyzed strengths and visibility of research done from various institutions and as published in various journals.
- • This study shows that evidence based research articles attracts more citations than mere general publications on COVID-19.
1. Introduction
Coronavirus or novel coronavirus which is taxonomically termed as SARS-CoV-2 and named by World Health organization (WHO) as COVID-19 which emerged from Wuhan city, Hubei Province of China by the end of 2019 has caused unprecedented panic across the world. The rapid transmission of this virus from human to human made the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare this as the public health emergency of international concern and called it as global pandemic [ 1 ]. As on May 14, 2020, globally 4248389 COVID-19 cases have been reported and caused 292046 deaths. Highest human casualty reported from USA with 109121 deaths [ 2 ].
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on January 30, 2020. As on May 17, 2020, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India has reported 90927 confirmed cases from 33 states with 2872 deaths [ 3 ]. Though India is in complete lockdown since March 24, over the weekend there is a rapid increase in COVID-19 cases in some states in India notably from Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh and few other states. The rapid increase over the weekend in the month of May has created some kind of panic in India. The government and other civil bodies are making efforts to mitigate the spread of this virus.
Scientific literature on this pandemic is important in order to combat this novel coronavirus. Researchers across the world have been involved in identifying the cause, clinical features and developing possible vaccines for COVID-19. As a result there has been a rapid growth in publishing scholarly literature on the subject. Many academic institutions of international repute and also publication houses involving in scientific publishing industry have made their literature on COVID-19 or novel coronavirus freely available to the scientific community in particular for diagnosis, treatment and preventive strategies against the virus and public in general to create awareness of the infectious virus.
The Bibliometric studies which helps in quantifying the research publication pattern in a particular domain have also been done to assess the research productivity of scientific literature on COVID-19. Bibliometric studies help in identifying the emerging area of research, provide evidence of impact of research through citations, helps in identifying right scholarly literature to consult for study and also for carrying research forward, and it also helpful for policy makers to strategize the potential research areas and funding. There were few bibliometric studies on COVID-19 publications pattern worldwide [ [4] , [5] , [6] ] . . However, there is hardly any studies on country specific. In this regard, here an attempt has been made to look into the Indian contributions to COVID-19 research publications.
2. Data source & methods
The study used World Health organization (WHO) COVID-19 database made available through WHO official website under global research on coronavirus disease (COVID-19) global research database as a data source for identifying the relevant literature on COVID-19. WHO COVID-19 [ 7 ] database is curating global literature publishing on coronavirus since it declared COVID-19 a global pandemic. WHO says that the database represents a comprehensive multilingual source of current literature on the topic. This database extract information from various bibliographic databases, hand searching, and the addition of other expert-referred scientific articles and updates daily.
WHO has made its COVID-19 database searchable freely and data can be exported to. CSV or RIS format. The search terms used for retrieving the data were “COVID-19” and “India”. The “title, abstract and subject” option available on the database website was used to retrieve the documents. The search results retrieved 107 results for the search term. The database was search on May 12, 2020. The data was exported from. CSV format to excel sheet for further refinement of data and analysis. After thoroughly reviewing the data, it was found that there were few repeatable titles and titles not associated with Indian author or authors and articles other than English language were excluded from the study. Only articles written in English were included in the study. In all 89 articles were considered for the final analysis.
The study analyzed the date-wise Indian publication pattern on COVID-19, most prolific authors, institutions with highest publications, states with highest publication based corresponding authors state affiliation, top journals in which Indians have published their publications frequently and document types and research areas, author keywords tree map analysis and highly cited COVID-19 documents of Indian authors. For retrieving the citation data for identifying the top cited documents, Google Scholar citation database was used. In order to determine the research focus or areas of Indian publications on COVID-19, the author used the similar subject categories of earlier study done by Lou et al. [ 8 ] on coronavirus. For identifying journal impact factor, the Scopus CiteScore and SCImago Journal Ranking & Country Ranking was consulted.
3. Results of the study
3.1. date-wise publications pattern.
Fig. 1 indicates the date-wise daily publication pattern of Indian authors on COVID-19. All the publications that have been included in the study were curated from March 03, 2020 to May 08, 2020 in WHO COVID-19 database. As it can be seen from Table- 1 that after mid-April there is a considerable and constant increase in number of publications published from Indian authors on the subject. Given the gravity of the problem and the virus infectivity scale, it is obvious that medical researchers have been looking for potential treatment or vaccines for this virus and this has increased the output of research in India and in other parts of the globe as well. Clinical trials for identifying vaccine or potential drug for COVID-19 is in full swing. The clinicaltrials.gov database has listed 1510 studies on COVID-19. This indicates the increasing interest and rapidity in which research studies have been carried out on this virus.

Date-wise Indian publications on COVID-19.
3.2. Prolific Indian authors engaged in COVID-19 research
Table 1 depicts the most prolific Indian authors who have published three or more articles. Of the 89 articles, only 13 (14.60%) articles were single authored publications remaining articles were authored collaboratively. Nivedita Gupta of Division of Epidemiology & Communicable Diseases, ICMR, New Delhi, topped the list with 6 (6.74%) publications. Following her, Tarun Bhatnagar, National Institute of Epidemiology-ICMR, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, Raman R Gangakhedkar, SidharthaGiri of Division of Epidemiology & Communicable Diseases, ICMR New Delhi have contributed 4 articles each. Other authors with three or more publications can be seen in Table 1 . Anoop Misra is the only outlier in the Table. The other authors listed in the Table either have associated with Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi or National Institute of Virology, Pune which is also part of ICMR. Except Anoop Misra of Fortis CDOC Hospital, New Delhi, the rest of the prolific authors have published their articles in collaboration. Nivedita Gupta, Bhatnagar, Gangakhedkar and Giri have published together and other group consisting of Potdar, Yadav, Abraham and other authors from NIV have published together.
Table 1
Author(s) with three or more publication on COVID-19.
3.3. State-wise Publications Based on corresponding Author’s state affiliation
The state-wise publication profile was created by using corresponding author state affiliation. The geographic heat map ( Fig. 2 ) indicates state-wise publications on COVID-19. Delhi with 20 (22.47%) publications has produced highest number of publications on this subject. West Bengal with 11 (12.36%) publications ranked second in the order followed by Maharashtra with 9 (10.11%) publications. Chandigarh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu have contributed 4 publications each with 4.49% share among the total output of India. Haryana, Punjab and Rajasthan have published 3 (3.37%) papers each. In Northern part, Delhi, Punjab and smaller state like Chandigarh has performed better. BIMARU states like Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh have published only one article each, Bihar has not published even a single paper on this topic. These states are largest in terms of their population. No research publications on COVID-19 have appeared from North Eastern region. It is right time to increase the research output and have better healthcare facilities across India, instead situating in few pockets.

State(s) publications based on the correspondence Author’s affiliation.
3.4. Most prolific Indian institutions on COVID-19 research
The bubble chart ( Fig. 3 ) depicts the top 8 highly productive Indian institutions that have published three or more publications on COVID-19 during the reported period. In all, two hundred and forty two institutions have involved in publishing 89 papers. The All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi with 8 (3.31%) publications topped the list followed by Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh with 7 publications (2.89%) and Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi and National Institute of Virology, Pune with 6 (2.48%) publications each respectively. National Institute of Epidemiology, Tamil Nadu and Fortis CDOC Hospital for Diabetes and Allied Sciences, New Delhi have 4 (1.65%) publications each to their credit. Armed Force Medical College, Pune and Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi have published 3 (1.24%) papers each. It is noteworthy that AIIMS and ICMR are two premier medical institutions in India that have been guiding Government of India in combating the lethal infectious disease COVID-19. It is worth mentioning that, the National Institute of Virology, Pune has recently developed IgG ELISA test kit for coronavirus for speeding the antibody test, which is a first of its kind in India [ 9 ].

Most prolific institutions on COVID-19 research through bubble chart.
3.5. Most prolific journals preferred by Indian authors for publishing their works on COVID-19
The Indian authors have published their publications on novel coronavirus or COVID-19 in 51 journals. Table 2 presents the top journals in which publications were frequently appeared. The Indian Journal of Medical Research (IJMR) has emerged as the top journal with 14 (15.73%) publications followed by Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews and Science of the Total Environment with 6 (6.74%) publications each. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology has 4 (4.49%) publications to its credits and it’s in third position in the Table. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences and Virus Disease have contributed 3 (3.37%) publications each and stands at fourth position. In all, these 13 journals have published 50 research papers which accounts for 56.19% share among the total publications output. All the journals which are even under Paywall content have made their preprints available freely for the researchers working on SARS-CoV-2. This will help the researchers to speed up their works related to the development of potential vaccines or drugs for this virus.
Table 2
Top journals in which Indian COVID-19 research published frequently.
3.6. Research Area and Document Type of COVID-19 publications
Fig. 4 indicates the research area and the document type of the Indian publications. Of the 89 publications 38 (42.70%) were articles, 13 (almost 15%) were of letters to editor or correspondence, 12 (13.48%) were commentary/opinion/perspective/viewpoints kind of documents, 7 (7.87%) were reviews, 6 (6.74%) were of guidelines/protocol/report related publications, another same number of documents were news items, 5 (5.62%) were editorials and 2 (2.25%) were short communications. If one were to see the document type, all kinds of documents ranging from articles to short communications were published. In terms of research area, of the 89 publications 75 of them were related to Epidemiology, which accounts for 84.27% of the total publications, 6 (6.74%) were related to Diagnosis & Treatment, 4 (4.49%) publications were on virology and 3 (3.37%) publications were of laboratory Examinations related studies and 1 (1.12%)publication was on clinical features of COVID-19 patients. Fig. 4 clearly indicates the Indian research publication pattern with regard to research area. There were lot of studies on Epidemiology and its impact on diabetes, cardiologic patients and pandemic outbreak in India, less on clinical and laboratory examinations of COVID-19 patients and virology which are important for finding drugs or vaccine for the virus.

Research area and document type on COVID-19.
3.7. COVID-19 publications keyword frequency
The hierarchical tree map ( Fig. 5 ) indicates the frequency of author assigned keywords to the documents that they have published on COVID-19. Keywords are helpful in identifying key domains of research and its growth. The keyword corpus contained 415 words with 208 unique words, same have been used to identify the frequency of keyword occurrences on COVID-19. It is found that the keywords “covid” (34 times), “coronavirus” (23 times), “India” (14 times), “pandemic” (12 times), “sars” (8 times) etc., have the highest frequency of occurrences.

Hierarchical tree map of frequency of keywords on COVID-19.
3.8. Top five highly cited Indian Publications on COVID-19
Eighty Nine articles have received 186 citations in all with an average citations of 2.18 per documents. The article entitled “ Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19 with or without diabetes: A systematic search and a narrative review with a special reference to India and other developing countries ” authored by Awadhesh Kumar Singh et al. and “ Prudent public health intervention strategies to control the coronavirus disease 2019 transmission in India: A mathematical model-based approach ” authored by Sandip Mandal et al., and “ Fear of COVID 2019: First suicidal case in India! ” by Kapil Goyal and others have received 28 citations each and topped the Table, followed by the article “ Full-genome sequences of the first two SARS-CoV-2 viruses from India ” authored by Pragya Yadav with 18 citations. Other highly cited articles can be seen in Table 3 .
Table 3
Top five highly cited Indian publications on COVID-19.
If one were to simply observe the highly cited documents, it can be seen that publications which are of virology related, diagnosis and treatment or clinical features and simulations or mathematical related studies have received more citation than general studies on epidemiology or pandemic. Eight out of six highly cited publications were appeared in two journals, they are: Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews and Indian Journal of Medical Research (IJMR).
4. Discussion and conclusion
The results of the study reflects the current Indian scholarly publications on COVID-19 or SARS-CoV-2. Result of this study found some significant insights. The authors who have published more number of publications have all come from either AIIMS or ICMR institutions. Most of these authors have collaborated each other in publishing research papers on COVID-19 and have come from same institutions. This emphasizes that there is need to collaborate with other medical research institutions outside the intra-institute collaborations. It is interesting to note that more than eighty five percent of the articles on coronavirus were collaborative publications. Since COVID-19 is a global pandemic, collaborative research is the need of the hour to mitigate this infectious disease. The state-wise publication pattern indicates that except smaller states like Delhi, Chandigarh, Punjab and Haryana there are no significant publications from North India’s largest states like Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Bihar. This can be attributed for lack of medical or health science education and research institutions in this part. This is high time that the Government of India establishes medical research institutes and strengthen healthcare facilities across India. The study found no publication from North Eastern Region states. This emphasizes need of robust medical infrastructure in this region.
In terms of institutional publications profile, again ICMR, PGIMER and AIIMS and National Institute of Virology, National Institute of Epidemiology and other few have three or more publications. One of the interesting fact is that it is the government medical research institutions that have published large number of publications on COVID-19. AIIMS and ICMR, New Delhi and its other institutions in other parts of India, like National Institute of Virology, Pune and National Institute of Epidemiology, Tamil Nadu have shared largest publications on COVID-19. China and USA are way ahead of India in terms of their research publications on COVID-19 compared to their GDP and publications per million populations [ 10 ]. Central and State Universities which are in large numbers in India and they should accelerate their research capabilities at this time of global health crisis. In terms of journals, it is Indian Journal of Medical Research (IJMR) which has published more number of articles than any other journals, it accounts for almost 16% of total publications. ICMR and its other associated institutions have published largely in this journal on COVID-19.
Indian research is largely done in the area of epidemiology and its impact on diabetes, cardio patients, environmental impact and pandemic outbreak, less studies on clinical prognosis, pharmaceutical interventions, and laboratory based studies or virology related studies on SARS-CoV-2. The highly cited publications were of evidence based studies, for instance “Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19 with or without diabetes: A systematic search and a narrative review with a special reference to India and other developing countries” or “Prudent public health intervention strategies to control the coronavirus disease 2019 transmission in India: A mathematical model-based approach” which have been cited by 28 times and other studies as well. As this pandemic is no way to go early, the research is shifting from basic to experimental studies across the globe [ 6 ], if we see the top highly cited documents in India also gradually studies are shifting more towards evidence based medical research for finding drugs or vaccine at the earliest for this highly infectious disease.
This bibliometric study though provides a bird-eye-view of the publications pattern of Indian authors on COVID-19, one must be a bit cautious in generalizing the results of this study. WHO COVID-19 database curated only expert-referred scientific articles and literature available through LitCOVID database of National Library of Medicine (NLM). It has not included the articles available through preprint servers or central subject repositories such as medRxiv and bioRxiv or arXiv, Research Square or SSRN preprint servers. It is suggested to take up a similar study using dimension. ai or semantic scholar’s CORD-19 dataset which includes articles deposited in preprint servers on COVID-19 to see the different publications pattern of Indian Publications on novel coronavirus or COVID-19 in a much larger scale. The dynamic nature of inclusion of literature to the WHO database on a daily basis is also be considered while generalizing this study.
The author(s) received no financial support for the study.
Author contributions
Idea and study design: Vasantha Raju N., and Patil S.B; Data collection and draft writing: Vasantha Raju N.; Revision and Finalization: Done by Both the Authors.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Research for Development Outputs
Poverty dynamics in Bangladesh
This paper looks at multiple data sources and considering COVID-19 and a high vulnerability to poverty across the country
This paper is a selective review of poverty dynamics in Bangladesh, looking at multiple data sources and considering COVID-19 and a high vulnerability to poverty across the country.
This is an output from the Data and Evidence for Tackling Extreme Poverty (DEEP) Research Programme
López-Moreno, I. Poverty dynamics in Bangladesh: Selective literature review. DEEP Working Paper 16. Data and Evidence to End Extreme Poverty Research Programme, Oxford, 2024
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Latest science news, discoveries and analysis

Could a rare mutation that causes dwarfism also slow ageing?

Bird flu in US cows: is the milk supply safe?

Future of Humanity Institute shuts: what's next for ‘deep future’ research?

Judge dismisses superconductivity physicist’s lawsuit against university
Nih pay raise for postdocs and phd students could have us ripple effect, hello puffins, goodbye belugas: changing arctic fjord hints at our climate future, china's moon atlas is the most detailed ever made, ‘shut up and calculate’: how einstein lost the battle to explain quantum reality, ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork chris mantegna.

Should the Maldives be creating new land?

Lethal AI weapons are here: how can we control them?

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias

How gliding marsupials got their ‘wings’
Audio long read: why loneliness is bad for your health, nato is boosting ai and climate research as scientific diplomacy remains on ice, rat neurons repair mouse brains — and restore sense of smell, plastic pollution: three numbers that support a crackdown.
Retractions are part of science, but misconduct isn’t — lessons from a superconductivity lab

Any plan to make smoking obsolete is the right step

Citizenship privilege harms science
European ruling linking climate change to human rights could be a game changer — here’s how charlotte e. blattner, will ai accelerate or delay the race to net-zero emissions, current issue.

The Maldives is racing to create new land. Why are so many people concerned?
Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species, stripped-envelope supernova light curves argue for central engine activity, optical clocks at sea, research analysis.

Ancient DNA traces family lines and political shifts in the Avar empire
A chemical method for selective labelling of the key amino acid tryptophan
Robust optical clocks promise stable timing in a portable package
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
Bioengineered ‘mini-colons’ shed light on cancer progression, galaxy found napping in the primordial universe, tumours form without genetic mutations, marsupial genomes reveal how a skin membrane for gliding evolved.

Scientists urged to collect royalties from the ‘magic money tree’

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists

Shrouded in secrecy: how science is harmed by the bullying and harassment rumour mill
How ground glass might save crops from drought on a caribbean island, londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs, books & culture.

How volcanoes shaped our planet — and why we need to be ready for the next big eruption

Dogwhistles, drilling and the roots of Western civilization: Books in brief

Cosmic rentals
Las borinqueñas remembers the forgotten puerto rican women who tested the first pill, dad always mows on summer saturday mornings, nature podcast.

Latest videos
Nature briefing.
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

COMMENTS
This paper attempts to shed light on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on college students. First, we describe and quantify the causal e ects of the COVID-19 outbreak on a wide set of students' out-comes/expectations. In particular, we analyze enrollment and graduation decisions, academic performance,
According to a study published in 2019, An-. Corona virus causes respiratory infection including pneumonia, cold, sneezing and coughing while in animal it causes. diarrhea and upper respiratory ...
The Impact of Covid-19 on Small Business Owners: Evidence of Early-Stage Losses from the April 2020 Current Population Survey Robert W. Fairlie NBER Working Paper No. 27309 June 2020 JEL No. J15,J16,L26 ABSTRACT Social distancing restrictions and demand shifts from COVID-19 are expected to shutter many
The spread of the "Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus 2" (SARS-CoV-2), the causal agent of COVID-19, was characterized as a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) in March 2020 and has triggered an international public health emergency [].The numbers of confirmed cases and deaths due to COVID-19 are rapidly escalating, counting in millions [], causing massive economic strain ...
The Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center has collected, verified, and published local, regional, national and international pandemic data since it launched in March 2020. From the beginning, the information has been freely available to all — researchers, institutions, the media, the public, and policymakers. As a result, the CRC and its data have been cited in many published research ...
A two-dose regimen of BNT162b2 (30 μg per dose, given 21 days apart) was found to be safe and 95% effective against Covid-19. The vaccine met both primary efficacy end points, with more than a 99 ...
Introduction. The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has resulted in over 192 million cases and 4.1 million deaths as of July 22, 2021. 1 This pandemic has brought along a massive burden in morbidity and mortality in the healthcare systems. Despite the implementation of stringent public health measures, there ...
Browse our 25 most downloaded COVID-19 articles published in 2021. ... These papers highlight valuable research into the biology of coronavirus infection, its detection, treatment as well as into ...
Vaccines are needed to prevent coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) and to protect persons who are at high risk for complications. ... Research Summary (nejmoa2035389_research-summary.pdf) Download ...
longer duration of SIP policies are the ones with higher excess deaths per 100,000 residents in. the 24 weeks following a COVID-19 death. Across countries, a one-week increase in the. duration of SIP policies is associated with a 2.7 (95% CI: 1.0 to 4.3) increase in excess deaths. per 100,000 population.
The COVID-19 shock can be interpreted as a combination of supply and demand shocks (Baqaee and Farhi, 2020; Caballero and Simsek, 2020; Guerrieri et al., 2020). The supply
The COVID-19 outbreak has posed an unprecedented challenge to humanity and science. On the one side, public and private incentives have been put in place to promptly allocate resources toward research areas strictly related to the COVID-19 emergency. However, research in many fields not directly related to the pandemic has been displaced. In this paper, we assess the impact of COVID-19 on ...
Download MP3. In the final Coronapod of 2020, we dive into the scientific literature to reflect on the COVID-19 pandemic. Researchers have discovered so much about SARS-CoV-2 - information that ...
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly contagious viral illness caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). COVID-19 has had a catastrophic effect on the world, resulting in more than 6 million deaths worldwide. After the first cases of this predominantly respiratory viral illness were reported in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, in late December 2019, SARS ...
Long COVID is an often debilitating illness that occurs in at least 10% of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections. More than 200 symptoms have been identified with ...
There have been around 96,000 reported cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-2019) and 3300 reported deaths to date (05/03/2020). The disease is transmitted by inhalation or contact with infected droplets and the incubation period ranges from 2 to 14 d. The symptoms are usually fever, cough, sore throat, breathlessness, fatigue, malaise ...
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by SARS-CoV-2, a newly emergent coronavirus, that was first recognized in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Globally, as of 19 December 2020, there have been 74.299.042 confirmed cases of COVID-19, including 1.669.982 deaths, reported to WHO. 1
Abstract. In early December 2019, an outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by a novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), occurred in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China. On January 30, 2020 the World Health Organization declared the outbreak as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.
systemic long COVID symptoms is still inconclusive. Added value of this study. There is a dearth of research on SARS-CoV-2 persistence in . diverse tissue samples collected from people who have recovered from COVID-19. Our study in patients who had recovered from mild COVID-19 includes not only blood samples
COVID-19 CFR here refer to several locations in China during the earl y stages of the outbreak, from the beginning of J anuary 2020 to 20th February 2020. 36 We see that in the earliest stages of ...
Detailed search strategy for gathering COVID-19 articles, updated October 9, 2020 [PDF - 135 KB] The CDC Database of COVID-19 Research Articles is now a part of the WHO COVID-19 database. Our new search results are now being sent to the WHO COVID-19 Database to make it easier for them to be searched, downloaded, and used by researchers ...
The WHO COVID-19 Research Database was a resource created in response to the Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). It contained citations with abstracts to scientific articles, reports, books, preprints, and clinical trials on COVID-19 and related literature. The WHO Covid-19 Research Database was maintained by the WHO ...
A study shows that this disease has an impact on the mental, physical and social well-being of health care professionals and three groups of people are prone to the complication of covid-19. Introduction The world health organization defines the Corona virus disease (covid-19) is an infectious disease which is caused by a newly discovered corona virus [1]. It was formerly known as severe acute ...
Abstract. This work was designed with the aim of analyzing research methodologies in social sciences, ethnography and case studies, and how digital tools could or could not enhance the obtaining higher quality qualitative results in these areas, given the conditions of virtualization, and which in the context of a pandemic forced the implementation of absolute virtualization in the unlikely ...
The study found that there is a considerable and constant growth of Indian publications on COVID-19 from mid-April. It is interesting to note that, the most prolific authors belong to either AIIMS or ICMR institutes. Delhi state contributed highest number of publications on COVID-19. The AIIMS, New Delhi was the most productive institution in ...
Abstract. This paper is a selective review of poverty dynamics in Bangladesh, looking at multiple data sources and considering COVID-19 and a high vulnerability to poverty across the country.
The surprising power of small language models. Microsoft Research Blog, 2023. [JCWZ17]Mandar Joshi, Eunsol Choi, Daniel S. Weld, and Luke Zettlemoyer. Triviaqa: A large scale distantly supervised challenge dataset for reading comprehension, 2017. [JLD+23]Jiaming Ji, Mickel Liu, Juntao Dai, Xuehai Pan, Chi Zhang, Ce Bian, Chi Zhang, Ruiyang
Find breaking science news and analysis from the world's leading research journal.
Search 218,031,843 papers from all fields of science. Search. Sign In Create Free Account. DOI: ... ABSTRACT The upheaval caused by the spread of COVID-19 is having a devastating effect on small businesses. ... AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at the Allen Institute for AI. Learn More.