- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →

Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
5 Benefits of Learning Through the Case Study Method

- 28 Nov 2023
While several factors make HBS Online unique —including a global Community and real-world outcomes —active learning through the case study method rises to the top.
In a 2023 City Square Associates survey, 74 percent of HBS Online learners who also took a course from another provider said HBS Online’s case method and real-world examples were better by comparison.
Here’s a primer on the case method, five benefits you could gain, and how to experience it for yourself.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is the Harvard Business School Case Study Method?
The case study method , or case method , is a learning technique in which you’re presented with a real-world business challenge and asked how you’d solve it. After working through it yourself and with peers, you’re told how the scenario played out.
HBS pioneered the case method in 1922. Shortly before, in 1921, the first case was written.
“How do you go into an ambiguous situation and get to the bottom of it?” says HBS Professor Jan Rivkin, former senior associate dean and chair of HBS's master of business administration (MBA) program, in a video about the case method . “That skill—the skill of figuring out a course of inquiry to choose a course of action—that skill is as relevant today as it was in 1921.”
Originally developed for the in-person MBA classroom, HBS Online adapted the case method into an engaging, interactive online learning experience in 2014.
In HBS Online courses , you learn about each case from the business professional who experienced it. After reviewing their videos, you’re prompted to take their perspective and explain how you’d handle their situation.
You then get to read peers’ responses, “star” them, and comment to further the discussion. Afterward, you learn how the professional handled it and their key takeaways.
HBS Online’s adaptation of the case method incorporates the famed HBS “cold call,” in which you’re called on at random to make a decision without time to prepare.
“Learning came to life!” said Sheneka Balogun , chief administration officer and chief of staff at LeMoyne-Owen College, of her experience taking the Credential of Readiness (CORe) program . “The videos from the professors, the interactive cold calls where you were randomly selected to participate, and the case studies that enhanced and often captured the essence of objectives and learning goals were all embedded in each module. This made learning fun, engaging, and student-friendly.”
If you’re considering taking a course that leverages the case study method, here are five benefits you could experience.
5 Benefits of Learning Through Case Studies
1. take new perspectives.
The case method prompts you to consider a scenario from another person’s perspective. To work through the situation and come up with a solution, you must consider their circumstances, limitations, risk tolerance, stakeholders, resources, and potential consequences to assess how to respond.
Taking on new perspectives not only can help you navigate your own challenges but also others’. Putting yourself in someone else’s situation to understand their motivations and needs can go a long way when collaborating with stakeholders.
2. Hone Your Decision-Making Skills
Another skill you can build is the ability to make decisions effectively . The case study method forces you to use limited information to decide how to handle a problem—just like in the real world.
Throughout your career, you’ll need to make difficult decisions with incomplete or imperfect information—and sometimes, you won’t feel qualified to do so. Learning through the case method allows you to practice this skill in a low-stakes environment. When facing a real challenge, you’ll be better prepared to think quickly, collaborate with others, and present and defend your solution.
3. Become More Open-Minded
As you collaborate with peers on responses, it becomes clear that not everyone solves problems the same way. Exposing yourself to various approaches and perspectives can help you become a more open-minded professional.
When you’re part of a diverse group of learners from around the world, your experiences, cultures, and backgrounds contribute to a range of opinions on each case.
On the HBS Online course platform, you’re prompted to view and comment on others’ responses, and discussion is encouraged. This practice of considering others’ perspectives can make you more receptive in your career.
“You’d be surprised at how much you can learn from your peers,” said Ratnaditya Jonnalagadda , a software engineer who took CORe.
In addition to interacting with peers in the course platform, Jonnalagadda was part of the HBS Online Community , where he networked with other professionals and continued discussions sparked by course content.
“You get to understand your peers better, and students share examples of businesses implementing a concept from a module you just learned,” Jonnalagadda said. “It’s a very good way to cement the concepts in one's mind.”
4. Enhance Your Curiosity
One byproduct of taking on different perspectives is that it enables you to picture yourself in various roles, industries, and business functions.
“Each case offers an opportunity for students to see what resonates with them, what excites them, what bores them, which role they could imagine inhabiting in their careers,” says former HBS Dean Nitin Nohria in the Harvard Business Review . “Cases stimulate curiosity about the range of opportunities in the world and the many ways that students can make a difference as leaders.”
Through the case method, you can “try on” roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career .
5. Build Your Self-Confidence
Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader’s perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and defend your opinions and decisions to peers, you prepare to do the same in your career.
According to a 2022 City Square Associates survey , 84 percent of HBS Online learners report feeling more confident making business decisions after taking a course.
“Self-confidence is difficult to teach or coach, but the case study method seems to instill it in people,” Nohria says in the Harvard Business Review . “There may well be other ways of learning these meta-skills, such as the repeated experience gained through practice or guidance from a gifted coach. However, under the direction of a masterful teacher, the case method can engage students and help them develop powerful meta-skills like no other form of teaching.”

How to Experience the Case Study Method
If the case method seems like a good fit for your learning style, experience it for yourself by taking an HBS Online course. Offerings span seven subject areas, including:
- Business essentials
- Leadership and management
- Entrepreneurship and innovation
- Finance and accounting
- Business in society
No matter which course or credential program you choose, you’ll examine case studies from real business professionals, work through their challenges alongside peers, and gain valuable insights to apply to your career.
Are you interested in discovering how HBS Online can help advance your career? Explore our course catalog and download our free guide —complete with interactive workbook sections—to determine if online learning is right for you and which course to take.

About the Author
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
- Nitin Nohria

Seven meta-skills that stick even if the cases fade from memory.
It’s been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment, bias recognition, judgement, collaboration, curiosity, and self-confidence.
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Jr. Professor at Harvard Business School and the former dean of HBS.
Partner Center
What is the Case Study Method?

Overview Dropdown up
Overview dropdown down, celebrating 100 years of the case method at hbs.
The 2021-2022 academic year marks the 100-year anniversary of the introduction of the case method at Harvard Business School. Today, the HBS case method is employed in the HBS MBA program, in Executive Education programs, and in dozens of other business schools around the world. As Dean Srikant Datar's says, the case method has withstood the test of time.
Case Discussion Preparation Details Expand All Collapse All
In self-reflection in self-reflection dropdown down, in a small group setting in a small group setting dropdown down, in the classroom in the classroom dropdown down, beyond the classroom beyond the classroom dropdown down, how the case method creates value dropdown up, how the case method creates value dropdown down, in self-reflection, in a small group setting, in the classroom, beyond the classroom.

How Cases Unfold In the Classroom
How cases unfold in the classroom dropdown up, how cases unfold in the classroom dropdown down, preparation guidelines expand all collapse all, read the professor's assignment or discussion questions read the professor's assignment or discussion questions dropdown down, read the first few paragraphs and then skim the case read the first few paragraphs and then skim the case dropdown down, reread the case, underline text, and make margin notes reread the case, underline text, and make margin notes dropdown down, note the key problems on a pad of paper and go through the case again note the key problems on a pad of paper and go through the case again dropdown down, how to prepare for case discussions dropdown up, how to prepare for case discussions dropdown down, read the professor's assignment or discussion questions, read the first few paragraphs and then skim the case, reread the case, underline text, and make margin notes, note the key problems on a pad of paper and go through the case again, case study best practices expand all collapse all, prepare prepare dropdown down, discuss discuss dropdown down, participate participate dropdown down, relate relate dropdown down, apply apply dropdown down, note note dropdown down, understand understand dropdown down, case study best practices dropdown up, case study best practices dropdown down, participate, what can i expect on the first day dropdown down.
Most programs begin with registration, followed by an opening session and a dinner. If your travel plans necessitate late arrival, please be sure to notify us so that alternate registration arrangements can be made for you. Please note the following about registration:
HBS campus programs – Registration takes place in the Chao Center.
India programs – Registration takes place outside the classroom.
Other off-campus programs – Registration takes place in the designated facility.
What happens in class if nobody talks? Dropdown down
Professors are here to push everyone to learn, but not to embarrass anyone. If the class is quiet, they'll often ask a participant with experience in the industry in which the case is set to speak first. This is done well in advance so that person can come to class prepared to share. Trust the process. The more open you are, the more willing you’ll be to engage, and the more alive the classroom will become.
Does everyone take part in "role-playing"? Dropdown down
Professors often encourage participants to take opposing sides and then debate the issues, often taking the perspective of the case protagonists or key decision makers in the case.
View Frequently Asked Questions
Subscribe to Our Emails

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
Case Study-Based Learning
Enhancing learning through immediate application.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

If you've ever tried to learn a new concept, you probably appreciate that "knowing" is different from "doing." When you have an opportunity to apply your knowledge, the lesson typically becomes much more real.
Adults often learn differently from children, and we have different motivations for learning. Typically, we learn new skills because we want to. We recognize the need to learn and grow, and we usually need – or want – to apply our newfound knowledge soon after we've learned it.
A popular theory of adult learning is andragogy (the art and science of leading man, or adults), as opposed to the better-known pedagogy (the art and science of leading children). Malcolm Knowles , a professor of adult education, was considered the father of andragogy, which is based on four key observations of adult learners:
- Adults learn best if they know why they're learning something.
- Adults often learn best through experience.
- Adults tend to view learning as an opportunity to solve problems.
- Adults learn best when the topic is relevant to them and immediately applicable.
This means that you'll get the best results with adults when they're fully involved in the learning experience. Give an adult an opportunity to practice and work with a new skill, and you have a solid foundation for high-quality learning that the person will likely retain over time.
So, how can you best use these adult learning principles in your training and development efforts? Case studies provide an excellent way of practicing and applying new concepts. As such, they're very useful tools in adult learning, and it's important to understand how to get the maximum value from them.
What Is a Case Study?
Case studies are a form of problem-based learning, where you present a situation that needs a resolution. A typical business case study is a detailed account, or story, of what happened in a particular company, industry, or project over a set period of time.
The learner is given details about the situation, often in a historical context. The key players are introduced. Objectives and challenges are outlined. This is followed by specific examples and data, which the learner then uses to analyze the situation, determine what happened, and make recommendations.
The depth of a case depends on the lesson being taught. A case study can be two pages, 20 pages, or more. A good case study makes the reader think critically about the information presented, and then develop a thorough assessment of the situation, leading to a well-thought-out solution or recommendation.
Why Use a Case Study?
Case studies are a great way to improve a learning experience, because they get the learner involved, and encourage immediate use of newly acquired skills.
They differ from lectures or assigned readings because they require participation and deliberate application of a broad range of skills. For example, if you study financial analysis through straightforward learning methods, you may have to calculate and understand a long list of financial ratios (don't worry if you don't know what these are). Likewise, you may be given a set of financial statements to complete a ratio analysis. But until you put the exercise into context, you may not really know why you're doing the analysis.
With a case study, however, you might explore whether a bank should provide financing to a borrower, or whether a company is about to make a good acquisition. Suddenly, the act of calculating ratios becomes secondary – it's more important to understand what the ratios tell you. This is how case studies can make the difference between knowing what to do, and knowing how, when, and why to do it.
Then, what really separates case studies from other practical forms of learning – like scenarios and simulations – is the ability to compare the learner's recommendations with what actually happened. When you know what really happened, it's much easier to evaluate the "correctness" of the answers given.
When to Use a Case Study
As you can see, case studies are powerful and effective training tools. They also work best with practical, applied training, so make sure you use them appropriately.
Remember these tips:
- Case studies tend to focus on why and how to apply a skill or concept, not on remembering facts and details. Use case studies when understanding the concept is more important than memorizing correct responses.
- Case studies are great team-building opportunities. When a team gets together to solve a case, they'll have to work through different opinions, methods, and perspectives.
- Use case studies to build problem-solving skills, particularly those that are valuable when applied, but are likely to be used infrequently. This helps people get practice with these skills that they might not otherwise get.
- Case studies can be used to evaluate past problem solving. People can be asked what they'd do in that situation, and think about what could have been done differently.
Ensuring Maximum Value From Case Studies
The first thing to remember is that you already need to have enough theoretical knowledge to handle the questions and challenges in the case study. Otherwise, it can be like trying to solve a puzzle with some of the pieces missing.
Here are some additional tips for how to approach a case study. Depending on the exact nature of the case, some tips will be more relevant than others.
- Read the case at least three times before you start any analysis. Case studies usually have lots of details, and it's easy to miss something in your first, or even second, reading.
- Once you're thoroughly familiar with the case, note the facts. Identify which are relevant to the tasks you've been assigned. In a good case study, there are often many more facts than you need for your analysis.
- If the case contains large amounts of data, analyze this data for relevant trends. For example, have sales dropped steadily, or was there an unexpected high or low point?
- If the case involves a description of a company's history, find the key events, and consider how they may have impacted the current situation.
- Consider using techniques like SWOT analysis and Porter's Five Forces Analysis to understand the organization's strategic position.
- Stay with the facts when you draw conclusions. These include facts given in the case as well as established facts about the environmental context. Don't rely on personal opinions when you put together your answers.
Writing a Case Study
You may have to write a case study yourself. These are complex documents that take a while to research and compile. The quality of the case study influences the quality of the analysis. Here are some tips if you want to write your own:
- Write your case study as a structured story. The goal is to capture an interesting situation or challenge and then bring it to life with words and information. You want the reader to feel a part of what's happening.
- Present information so that a "right" answer isn't obvious. The goal is to develop the learner's ability to analyze and assess, not necessarily to make the same decision as the people in the actual case.
- Do background research to fully understand what happened and why. You may need to talk to key stakeholders to get their perspectives as well.
- Determine the key challenge. What needs to be resolved? The case study should focus on one main question or issue.
- Define the context. Talk about significant events leading up to the situation. What organizational factors are important for understanding the problem and assessing what should be done? Include cultural factors where possible.
- Identify key decision makers and stakeholders. Describe their roles and perspectives, as well as their motivations and interests.
- Make sure that you provide the right data to allow people to reach appropriate conclusions.
- Make sure that you have permission to use any information you include.
A typical case study structure includes these elements:
- Executive summary. Define the objective, and state the key challenge.
- Opening paragraph. Capture the reader's interest.
- Scope. Describe the background, context, approach, and issues involved.
- Presentation of facts. Develop an objective picture of what's happening.
- Description of key issues. Present viewpoints, decisions, and interests of key parties.
Because case studies have proved to be such effective teaching tools, many are already written. Some excellent sources of free cases are The Times 100 , CasePlace.org , and Schroeder & Schroeder Inc . You can often search for cases by topic or industry. These cases are expertly prepared, based mostly on real situations, and used extensively in business schools to teach management concepts.
Case studies are a great way to improve learning and training. They provide learners with an opportunity to solve a problem by applying what they know.
There are no unpleasant consequences for getting it "wrong," and cases give learners a much better understanding of what they really know and what they need to practice.
Case studies can be used in many ways, as team-building tools, and for skill development. You can write your own case study, but a large number are already prepared. Given the enormous benefits of practical learning applications like this, case studies are definitely something to consider adding to your next training session.
Knowles, M. (1973). 'The Adult Learner: A Neglected Species [online].' Available here .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
How to Guides
Creating a Sales Budget
This Worked Scenario Will Help You Get to Grips With Formulating a Basic Sales Budget
The Holmes and Rahe Stress Scale
A Self-Assessment to Understand the Impact of Long-Term Stress
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

SWOT Analysis

SMART Goals
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How to stop procrastinating.
Overcoming the Habit of Delaying Important Tasks
What Is Time Management?
Working Smarter to Enhance Productivity
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Soar analysis.
Focusing on the Positives and Opening up Opportunities
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

Prepare your students to navigate business challenges by immersing them in real-world scenarios.
Transform business education
Bring excitement into your classroom with engaging case discussions and introduce students to the challenge and fun of making important decisions.
Illustrate business concepts
Help students learn by doing with over 50,000+ cases featuring real-world business scenarios spanning across multiple areas of business.
Encourage new ways of thinking
Student build confidence and critical thinking skills while learning to express their ideas and convince others, setting them up for success in the real world.
Explore Different Types of Cases
Find cases that meet your particular needs.
New! Quick Cases
Quickly immerse students in focused and engaging business dilemmas. No student prep time required.
Traditional cases from HBS and 50+ leading business schools.
Multimedia Cases
Cases that keep students engaged with video, audio, and interactive components.
Search Cases in Your Discipline
Select a discipline and start browsing available cases.
- Business & Government Relations
- Business Ethics
- Entrepreneurship
- General Management
- Human Resource Management
- Information Technology
- International Business
- Negotiation
- Operations Management
- Organizational Behavior
- Service Management
- Social Enterprise
Case Teaching Seminar
Register now for our Teaching with Cases Seminar at Harvard Business School, held June 21 - 22 . Learn how to lead case discussions like a pro and earn a certificate from Harvard Business Publishing.

Fundamentals of Case Teaching
Our new, self-paced, online course guides you through the fundamentals for leading successful case discussions at any course level.

Case Companion: Build Students’ Confidence in Case Analysis
Case Companion is an engaging and interactive introduction to case study analysis that is ideal for undergraduates or any student new to learning with cases.
Discover Trending Cases
Stay up to date on cases from leading business schools.
Discover new ideas for your courses
Course Explorer lets you browse learning materials by topic, curated by our editors, partners, and faculty from leading business schools.
Teach with Cases
Explore resources designed to help you bring the case method into your classroom.
Inspiring Minds Articles on Case Teaching
Insights from leading educators about teaching with the case method.
Book: Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide
A book featuring practical advice for instructors on managing class discussion to maximize learning.
Webinar: How ChatGPT and Other AI Tools Can Maximize the Learning Potential of Your Case-Based Classes
Register now.
Supplements: Inside the Case
Teaching tips and insights from case authors.
Guide: Teaching Cases Online
A guide for experienced educators who are new to online case teaching.
Educator Training: Selecting Cases to Use in Your Classes
Find the right materials to achieve your learning goals.
Educator Training: Teaching with Cases
Key strategies and practical advice for engaging students using the case method.
Frequently Asked Questions
What support can I offer my students around analyzing cases and preparing for discussion?
Case discussions can be a big departure from the norm for students who are used to lecture-based classes. The Case Analysis Coach is an interactive tutorial on reading and analyzing a case study. The Case Study Handbook covers key skills students need to read, understand, discuss and write about cases. The Case Study Handbook is also available as individual chapters to help your students focus on specific skills.
How can I transfer my in-person case teaching plan to an online environment?
The case method can be used in an online environment without sacrificing its benefits. We have compiled a few resources to help you create transformative online learning experiences with the case method. Learn how HBS brought the case method online in this podcast , gather some quick guidance from the article " How to Teach Any Case Online ", review the Teaching Cases Online Guide for a deep dive, and check out our Teaching Online Resources Page for more insights and inspiration.
After 35 years as an academic, I have come to the conclusion that there is a magic in the way Harvard cases are written. Cases go from specific to general, to show students that business situations are amenable to hard headed analysis that then generalize to larger theoretical insights. The students love it! Akshay Rao Professor, General Mills Chair in Marketing at the University of Minnesota
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Columbia University in the City of New York
- Office of Teaching, Learning, and Innovation
- University Policies
- Columbia Online
- Academic Calendar
- Resources and Technology
- Resources and Guides
Case Method Teaching and Learning
What is the case method? How can the case method be used to engage learners? What are some strategies for getting started? This guide helps instructors answer these questions by providing an overview of the case method while highlighting learner-centered and digitally-enhanced approaches to teaching with the case method. The guide also offers tips to instructors as they get started with the case method and additional references and resources.
On this page:
What is case method teaching.
- Case Method at Columbia
Why use the Case Method?
Case method teaching approaches, how do i get started.
- Additional Resources
The CTL is here to help!
For support with implementing a case method approach in your course, email [email protected] to schedule your 1-1 consultation .
Cite this resource: Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (2019). Case Method Teaching and Learning. Columbia University. Retrieved from [today’s date] from https://ctl.columbia.edu/resources-and-technology/resources/case-method/
Case method 1 teaching is an active form of instruction that focuses on a case and involves students learning by doing 2 3 . Cases are real or invented stories 4 that include “an educational message” or recount events, problems, dilemmas, theoretical or conceptual issue that requires analysis and/or decision-making.
Case-based teaching simulates real world situations and asks students to actively grapple with complex problems 5 6 This method of instruction is used across disciplines to promote learning, and is common in law, business, medicine, among other fields. See Table 1 below for a few types of cases and the learning they promote.
Table 1: Types of cases and the learning they promote.
For a more complete list, see Case Types & Teaching Methods: A Classification Scheme from the National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science.
Back to Top
Case Method Teaching and Learning at Columbia
The case method is actively used in classrooms across Columbia, at the Morningside campus in the School of International and Public Affairs (SIPA), the School of Business, Arts and Sciences, among others, and at Columbia University Irving Medical campus.
Faculty Spotlight:
Professor Mary Ann Price on Using Case Study Method to Place Pre-Med Students in Real-Life Scenarios
Read more
Professor De Pinho on Using the Case Method in the Mailman Core
Case method teaching has been found to improve student learning, to increase students’ perception of learning gains, and to meet learning objectives 8 9 . Faculty have noted the instructional benefits of cases including greater student engagement in their learning 10 , deeper student understanding of concepts, stronger critical thinking skills, and an ability to make connections across content areas and view an issue from multiple perspectives 11 .
Through case-based learning, students are the ones asking questions about the case, doing the problem-solving, interacting with and learning from their peers, “unpacking” the case, analyzing the case, and summarizing the case. They learn how to work with limited information and ambiguity, think in professional or disciplinary ways, and ask themselves “what would I do if I were in this specific situation?”
The case method bridges theory to practice, and promotes the development of skills including: communication, active listening, critical thinking, decision-making, and metacognitive skills 12 , as students apply course content knowledge, reflect on what they know and their approach to analyzing, and make sense of a case.
Though the case method has historical roots as an instructor-centered approach that uses the Socratic dialogue and cold-calling, it is possible to take a more learner-centered approach in which students take on roles and tasks traditionally left to the instructor.
Cases are often used as “vehicles for classroom discussion” 13 . Students should be encouraged to take ownership of their learning from a case. Discussion-based approaches engage students in thinking and communicating about a case. Instructors can set up a case activity in which students are the ones doing the work of “asking questions, summarizing content, generating hypotheses, proposing theories, or offering critical analyses” 14 .
The role of the instructor is to share a case or ask students to share or create a case to use in class, set expectations, provide instructions, and assign students roles in the discussion. Student roles in a case discussion can include:
- discussion “starters” get the conversation started with a question or posing the questions that their peers came up with;
- facilitators listen actively, validate the contributions of peers, ask follow-up questions, draw connections, refocus the conversation as needed;
- recorders take-notes of the main points of the discussion, record on the board, upload to CourseWorks, or type and project on the screen; and
- discussion “wrappers” lead a summary of the main points of the discussion.
Prior to the case discussion, instructors can model case analysis and the types of questions students should ask, co-create discussion guidelines with students, and ask for students to submit discussion questions. During the discussion, the instructor can keep time, intervene as necessary (however the students should be doing the talking), and pause the discussion for a debrief and to ask students to reflect on what and how they learned from the case activity.
Note: case discussions can be enhanced using technology. Live discussions can occur via video-conferencing (e.g., using Zoom ) or asynchronous discussions can occur using the Discussions tool in CourseWorks (Canvas) .
Table 2 includes a few interactive case method approaches. Regardless of the approach selected, it is important to create a learning environment in which students feel comfortable participating in a case activity and learning from one another. See below for tips on supporting student in how to learn from a case in the “getting started” section and how to create a supportive learning environment in the Guide for Inclusive Teaching at Columbia .
Table 2. Strategies for Engaging Students in Case-Based Learning
Approaches to case teaching should be informed by course learning objectives, and can be adapted for small, large, hybrid, and online classes. Instructional technology can be used in various ways to deliver, facilitate, and assess the case method. For instance, an online module can be created in CourseWorks (Canvas) to structure the delivery of the case, allow students to work at their own pace, engage all learners, even those reluctant to speak up in class, and assess understanding of a case and student learning. Modules can include text, embedded media (e.g., using Panopto or Mediathread ) curated by the instructor, online discussion, and assessments. Students can be asked to read a case and/or watch a short video, respond to quiz questions and receive immediate feedback, post questions to a discussion, and share resources.
For more information about options for incorporating educational technology to your course, please contact your Learning Designer .
To ensure that students are learning from the case approach, ask them to pause and reflect on what and how they learned from the case. Time to reflect builds your students’ metacognition, and when these reflections are collected they provides you with insights about the effectiveness of your approach in promoting student learning.
Well designed case-based learning experiences: 1) motivate student involvement, 2) have students doing the work, 3) help students develop knowledge and skills, and 4) have students learning from each other.
Designing a case-based learning experience should center around the learning objectives for a course. The following points focus on intentional design.
Identify learning objectives, determine scope, and anticipate challenges.
- Why use the case method in your course? How will it promote student learning differently than other approaches?
- What are the learning objectives that need to be met by the case method? What knowledge should students apply and skills should they practice?
- What is the scope of the case? (a brief activity in a single class session to a semester-long case-based course; if new to case method, start small with a single case).
- What challenges do you anticipate (e.g., student preparation and prior experiences with case learning, discomfort with discussion, peer-to-peer learning, managing discussion) and how will you plan for these in your design?
- If you are asking students to use transferable skills for the case method (e.g., teamwork, digital literacy) make them explicit.
Determine how you will know if the learning objectives were met and develop a plan for evaluating the effectiveness of the case method to inform future case teaching.
- What assessments and criteria will you use to evaluate student work or participation in case discussion?
- How will you evaluate the effectiveness of the case method? What feedback will you collect from students?
- How might you leverage technology for assessment purposes? For example, could you quiz students about the case online before class, accept assignment submissions online, use audience response systems (e.g., PollEverywhere) for formative assessment during class?
Select an existing case, create your own, or encourage students to bring course-relevant cases, and prepare for its delivery
- Where will the case method fit into the course learning sequence?
- Is the case at the appropriate level of complexity? Is it inclusive, culturally relevant, and relatable to students?
- What materials and preparation will be needed to present the case to students? (e.g., readings, audiovisual materials, set up a module in CourseWorks).
Plan for the case discussion and an active role for students
- What will your role be in facilitating case-based learning? How will you model case analysis for your students? (e.g., present a short case and demo your approach and the process of case learning) (Davis, 2009).
- What discussion guidelines will you use that include your students’ input?
- How will you encourage students to ask and answer questions, summarize their work, take notes, and debrief the case?
- If students will be working in groups, how will groups form? What size will the groups be? What instructions will they be given? How will you ensure that everyone participates? What will they need to submit? Can technology be leveraged for any of these areas?
- Have you considered students of varied cognitive and physical abilities and how they might participate in the activities/discussions, including those that involve technology?
Student preparation and expectations
- How will you communicate about the case method approach to your students? When will you articulate the purpose of case-based learning and expectations of student engagement? What information about case-based learning and expectations will be included in the syllabus?
- What preparation and/or assignment(s) will students complete in order to learn from the case? (e.g., read the case prior to class, watch a case video prior to class, post to a CourseWorks discussion, submit a brief memo, complete a short writing assignment to check students’ understanding of a case, take on a specific role, prepare to present a critique during in-class discussion).
Andersen, E. and Schiano, B. (2014). Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide . Harvard Business Press.
Bonney, K. M. (2015). Case Study Teaching Method Improves Student Performance and Perceptions of Learning Gains†. Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education , 16 (1), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v16i1.846
Davis, B.G. (2009). Chapter 24: Case Studies. In Tools for Teaching. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass.
Garvin, D.A. (2003). Making the Case: Professional Education for the world of practice. Harvard Magazine. September-October 2003, Volume 106, Number 1, 56-107.
Golich, V.L. (2000). The ABCs of Case Teaching. International Studies Perspectives. 1, 11-29.
Golich, V.L.; Boyer, M; Franko, P.; and Lamy, S. (2000). The ABCs of Case Teaching. Pew Case Studies in International Affairs. Institute for the Study of Diplomacy.
Heath, J. (2015). Teaching & Writing Cases: A Practical Guide. The Case Center, UK.
Herreid, C.F. (2011). Case Study Teaching. New Directions for Teaching and Learning. No. 128, Winder 2011, 31 – 40.
Herreid, C.F. (2007). Start with a Story: The Case Study Method of Teaching College Science . National Science Teachers Association. Available as an ebook through Columbia Libraries.
Herreid, C.F. (2006). “Clicker” Cases: Introducing Case Study Teaching Into Large Classrooms. Journal of College Science Teaching. Oct 2006, 36(2). https://search.proquest.com/docview/200323718?pq-origsite=gscholar
Krain, M. (2016). Putting the Learning in Case Learning? The Effects of Case-Based Approaches on Student Knowledge, Attitudes, and Engagement. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching. 27(2), 131-153.
Lundberg, K.O. (Ed.). (2011). Our Digital Future: Boardrooms and Newsrooms. Knight Case Studies Initiative.
Popil, I. (2011). Promotion of critical thinking by using case studies as teaching method. Nurse Education Today, 31(2), 204–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2010.06.002
Schiano, B. and Andersen, E. (2017). Teaching with Cases Online . Harvard Business Publishing.
Thistlethwaite, JE; Davies, D.; Ekeocha, S.; Kidd, J.M.; MacDougall, C.; Matthews, P.; Purkis, J.; Clay D. (2012). The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education: A BEME systematic review . Medical Teacher. 2012; 34(6): e421-44.
Yadav, A.; Lundeberg, M.; DeSchryver, M.; Dirkin, K.; Schiller, N.A.; Maier, K. and Herreid, C.F. (2007). Teaching Science with Case Studies: A National Survey of Faculty Perceptions of the Benefits and Challenges of Using Cases. Journal of College Science Teaching; Sept/Oct 2007; 37(1).
Weimer, M. (2013). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass.
Additional resources
Teaching with Cases , Harvard Kennedy School of Government.
Features “what is a teaching case?” video that defines a teaching case, and provides documents to help students prepare for case learning, Common case teaching challenges and solutions, tips for teaching with cases.
Promoting excellence and innovation in case method teaching: Teaching by the Case Method , Christensen Center for Teaching & Learning. Harvard Business School.
National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science . University of Buffalo.
A collection of peer-reviewed STEM cases to teach scientific concepts and content, promote process skills and critical thinking. The Center welcomes case submissions. Case classification scheme of case types and teaching methods:
- Different types of cases: analysis case, dilemma/decision case, directed case, interrupted case, clicker case, a flipped case, a laboratory case.
- Different types of teaching methods: problem-based learning, discussion, debate, intimate debate, public hearing, trial, jigsaw, role-play.
Columbia Resources
Resources available to support your use of case method: The University hosts a number of case collections including: the Case Consortium (a collection of free cases in the fields of journalism, public policy, public health, and other disciplines that include teaching and learning resources; SIPA’s Picker Case Collection (audiovisual case studies on public sector innovation, filmed around the world and involving SIPA student teams in producing the cases); and Columbia Business School CaseWorks , which develops teaching cases and materials for use in Columbia Business School classrooms.
Center for Teaching and Learning
The Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL) offers a variety of programs and services for instructors at Columbia. The CTL can provide customized support as you plan to use the case method approach through implementation. Schedule a one-on-one consultation.
Office of the Provost
The Hybrid Learning Course Redesign grant program from the Office of the Provost provides support for faculty who are developing innovative and technology-enhanced pedagogy and learning strategies in the classroom. In addition to funding, faculty awardees receive support from CTL staff as they redesign, deliver, and evaluate their hybrid courses.
The Start Small! Mini-Grant provides support to faculty who are interested in experimenting with one new pedagogical strategy or tool. Faculty awardees receive funds and CTL support for a one-semester period.
Explore our teaching resources.
- Blended Learning
- Contemplative Pedagogy
- Inclusive Teaching Guide
- FAQ for Teaching Assistants
- Metacognition
CTL resources and technology for you.
- Overview of all CTL Resources and Technology
- The origins of this method can be traced to Harvard University where in 1870 the Law School began using cases to teach students how to think like lawyers using real court decisions. This was followed by the Business School in 1920 (Garvin, 2003). These professional schools recognized that lecture mode of instruction was insufficient to teach critical professional skills, and that active learning would better prepare learners for their professional lives. ↩
- Golich, V.L. (2000). The ABCs of Case Teaching. International Studies Perspectives. 1, 11-29. ↩
- Herreid, C.F. (2007). Start with a Story: The Case Study Method of Teaching College Science . National Science Teachers Association. Available as an ebook through Columbia Libraries. ↩
- Davis, B.G. (2009). Chapter 24: Case Studies. In Tools for Teaching. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass. ↩
- Andersen, E. and Schiano, B. (2014). Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide . Harvard Business Press. ↩
- Lundberg, K.O. (Ed.). (2011). Our Digital Future: Boardrooms and Newsrooms. Knight Case Studies Initiative. ↩
- Heath, J. (2015). Teaching & Writing Cases: A Practical Guide. The Case Center, UK. ↩
- Bonney, K. M. (2015). Case Study Teaching Method Improves Student Performance and Perceptions of Learning Gains†. Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education , 16 (1), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v16i1.846 ↩
- Krain, M. (2016). Putting the Learning in Case Learning? The Effects of Case-Based Approaches on Student Knowledge, Attitudes, and Engagement. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching. 27(2), 131-153. ↩
- Thistlethwaite, JE; Davies, D.; Ekeocha, S.; Kidd, J.M.; MacDougall, C.; Matthews, P.; Purkis, J.; Clay D. (2012). The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education: A BEME systematic review . Medical Teacher. 2012; 34(6): e421-44. ↩
- Yadav, A.; Lundeberg, M.; DeSchryver, M.; Dirkin, K.; Schiller, N.A.; Maier, K. and Herreid, C.F. (2007). Teaching Science with Case Studies: A National Survey of Faculty Perceptions of the Benefits and Challenges of Using Cases. Journal of College Science Teaching; Sept/Oct 2007; 37(1). ↩
- Popil, I. (2011). Promotion of critical thinking by using case studies as teaching method. Nurse Education Today, 31(2), 204–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2010.06.002 ↩
- Weimer, M. (2013). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass. ↩
- Herreid, C.F. (2006). “Clicker” Cases: Introducing Case Study Teaching Into Large Classrooms. Journal of College Science Teaching. Oct 2006, 36(2). https://search.proquest.com/docview/200323718?pq-origsite=gscholar ↩
This website uses cookies to identify users, improve the user experience and requires cookies to work. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University's use of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved April 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics

We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Case Study
How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
By Danesh Ramuthi , Sep 07, 2023

Okay, let’s get real: case studies can be kinda snooze-worthy. But guess what? They don’t have to be!
In this article, I will cover every element that transforms a mere report into a compelling case study, from selecting the right metrics to using persuasive narrative techniques.
And if you’re feeling a little lost, don’t worry! There are cool tools like Venngage’s Case Study Creator to help you whip up something awesome, even if you’re short on time. Plus, the pre-designed case study templates are like instant polish because let’s be honest, everyone loves a shortcut.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a case study presentation?
What is the purpose of presenting a case study, how to structure a case study presentation, how long should a case study presentation be, 5 case study presentation examples with templates, 6 tips for delivering an effective case study presentation, 5 common mistakes to avoid in a case study presentation, how to present a case study faqs.
A case study presentation involves a comprehensive examination of a specific subject, which could range from an individual, group, location, event, organization or phenomenon.
They’re like puzzles you get to solve with the audience, all while making you think outside the box.
Unlike a basic report or whitepaper, the purpose of a case study presentation is to stimulate critical thinking among the viewers.
The primary objective of a case study is to provide an extensive and profound comprehension of the chosen topic. You don’t just throw numbers at your audience. You use examples and real-life cases to make you think and see things from different angles.

The primary purpose of presenting a case study is to offer a comprehensive, evidence-based argument that informs, persuades and engages your audience.
Here’s the juicy part: presenting that case study can be your secret weapon. Whether you’re pitching a groundbreaking idea to a room full of suits or trying to impress your professor with your A-game, a well-crafted case study can be the magic dust that sprinkles brilliance over your words.
Think of it like digging into a puzzle you can’t quite crack . A case study lets you explore every piece, turn it over and see how it fits together. This close-up look helps you understand the whole picture, not just a blurry snapshot.
It’s also your chance to showcase how you analyze things, step by step, until you reach a conclusion. It’s all about being open and honest about how you got there.
Besides, presenting a case study gives you an opportunity to connect data and real-world scenarios in a compelling narrative. It helps to make your argument more relatable and accessible, increasing its impact on your audience.
One of the contexts where case studies can be very helpful is during the job interview. In some job interviews, you as candidates may be asked to present a case study as part of the selection process.
Having a case study presentation prepared allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to understand complex issues, formulate strategies and communicate their ideas effectively.
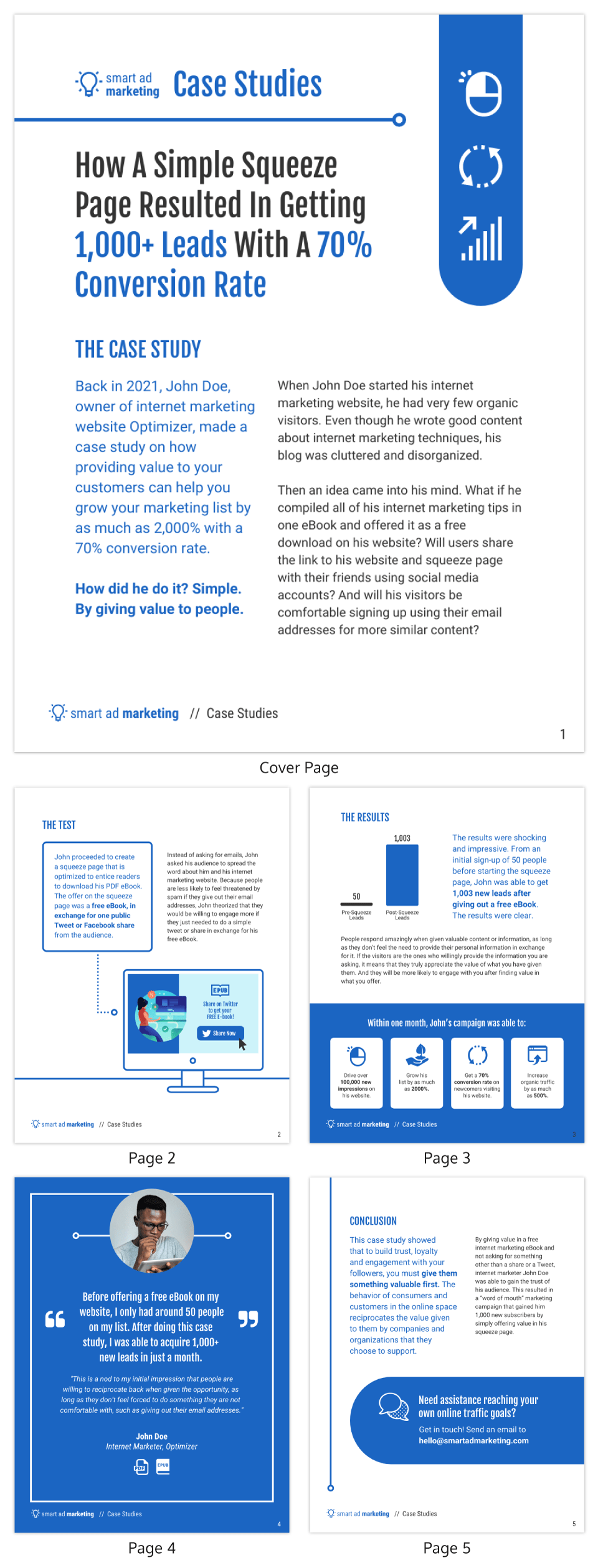
The way you present a case study can make all the difference in how it’s received. A well-structured presentation not only holds the attention of your audience but also ensures that your key points are communicated clearly and effectively.
In this section, let’s go through the key steps that’ll help you structure your case study presentation for maximum impact.
Let’s get into it.
Open with an introductory overview
Start by introducing the subject of your case study and its relevance. Explain why this case study is important and who would benefit from the insights gained. This is your opportunity to grab your audience’s attention.

Explain the problem in question
Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.

Detail the solutions to solve the problem
After outlining the problem, describe the steps taken to find a solution. This could include the methodology, any experiments or tests performed and the options that were considered. Make sure to elaborate on why the final solution was chosen over the others.

Key stakeholders Involved
Talk about the individuals, groups or organizations that were directly impacted by or involved in the problem and its solution.
Stakeholders may experience a range of outcomes—some may benefit, while others could face setbacks.
For example, in a business transformation case study, employees could face job relocations or changes in work culture, while shareholders might be looking at potential gains or losses.
Discuss the key results & outcomes
Discuss the results of implementing the solution. Use data and metrics to back up your statements. Did the solution meet its objectives? What impact did it have on the stakeholders? Be honest about any setbacks or areas for improvement as well.
Include visuals to support your analysis
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping your audience grasp complex issues. Utilize charts, graphs, images or video clips to supplement your points. Make sure to explain each visual and how it contributes to your overall argument.
Pie charts illustrate the proportion of different components within a whole, useful for visualizing market share, budget allocation or user demographics.
This is particularly useful especially if you’re displaying survey results in your case study presentation.
Stacked charts on the other hand are perfect for visualizing composition and trends. This is great for analyzing things like customer demographics, product breakdowns or budget allocation in your case study.
Consider this example of a stacked bar chart template. It provides a straightforward summary of the top-selling cake flavors across various locations, offering a quick and comprehensive view of the data.
Not the chart you’re looking for? Browse Venngage’s gallery of chart templates to find the perfect one that’ll captivate your audience and level up your data storytelling.
Recommendations and next steps
Wrap up by providing recommendations based on the case study findings. Outline the next steps that stakeholders should take to either expand on the success of the project or address any remaining challenges.
Acknowledgments and references
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis.
Feedback & Q&A session
Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may not have been considered previously.
Closing remarks
Conclude the presentation by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the takeaways. Thank your audience for their time and participation and express your willingness to engage in further discussions or collaborations on the subject.

Well, the length of a case study presentation can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the needs of your audience. However, a typical business or academic presentation often lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
This time frame usually allows for a thorough explanation of the case while maintaining audience engagement. However, always consider leaving a few minutes at the end for a Q&A session to address any questions or clarify points made during the presentation.
When it comes to presenting a compelling case study, having a well-structured template can be a game-changer.
It helps you organize your thoughts, data and findings in a coherent and visually pleasing manner.
Not all case studies are created equal and different scenarios require distinct approaches for maximum impact.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences.
Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly.
1 . Lab report case study template
Ever feel like your research gets lost in a world of endless numbers and jargon? Lab case studies are your way out!
Think of it as building a bridge between your cool experiment and everyone else. It’s more than just reporting results – it’s explaining the “why” and “how” in a way that grabs attention and makes sense.
This lap report template acts as a blueprint for your report, guiding you through each essential section (introduction, methods, results, etc.) in a logical order.

Want to present your research like a pro? Browse our research presentation template gallery for creative inspiration!
2. Product case study template
It’s time you ditch those boring slideshows and bullet points because I’ve got a better way to win over clients: product case study templates.
Instead of just listing features and benefits, you get to create a clear and concise story that shows potential clients exactly what your product can do for them. It’s like painting a picture they can easily visualize, helping them understand the value your product brings to the table.
Grab the template below, fill in the details, and watch as your product’s impact comes to life!

3. Content marketing case study template
In digital marketing, showcasing your accomplishments is as vital as achieving them.
A well-crafted case study not only acts as a testament to your successes but can also serve as an instructional tool for others.
With this coral content marketing case study template—a perfect blend of vibrant design and structured documentation, you can narrate your marketing triumphs effectively.

4. Case study psychology template
Understanding how people tick is one of psychology’s biggest quests and case studies are like magnifying glasses for the mind. They offer in-depth looks at real-life behaviors, emotions and thought processes, revealing fascinating insights into what makes us human.
Writing a top-notch case study, though, can be a challenge. It requires careful organization, clear presentation and meticulous attention to detail. That’s where a good case study psychology template comes in handy.
Think of it as a helpful guide, taking care of formatting and structure while you focus on the juicy content. No more wrestling with layouts or margins – just pour your research magic into crafting a compelling narrative.
5. Lead generation case study template
Lead generation can be a real head-scratcher. But here’s a little help: a lead generation case study.
Think of it like a friendly handshake and a confident resume all rolled into one. It’s your chance to showcase your expertise, share real-world successes and offer valuable insights. Potential clients get to see your track record, understand your approach and decide if you’re the right fit.
No need to start from scratch, though. This lead generation case study template guides you step-by-step through crafting a clear, compelling narrative that highlights your wins and offers actionable tips for others. Fill in the gaps with your specific data and strategies, and voilà! You’ve got a powerful tool to attract new customers.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
So, you’ve spent hours crafting the perfect case study and are now tasked with presenting it. Crafting the case study is only half the battle; delivering it effectively is equally important.
Whether you’re facing a room of executives, academics or potential clients, how you present your findings can make a significant difference in how your work is received.
Forget boring reports and snooze-inducing presentations! Let’s make your case study sing. Here are some key pointers to turn information into an engaging and persuasive performance:
- Know your audience : Tailor your presentation to the knowledge level and interests of your audience. Remember to use language and examples that resonate with them.
- Rehearse : Rehearsing your case study presentation is the key to a smooth delivery and for ensuring that you stay within the allotted time. Practice helps you fine-tune your pacing, hone your speaking skills with good word pronunciations and become comfortable with the material, leading to a more confident, conversational and effective presentation.
- Start strong : Open with a compelling introduction that grabs your audience’s attention. You might want to use an interesting statistic, a provocative question or a brief story that sets the stage for your case study.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Get to the point quickly and stay focused on your objectives.
- Use visual aids : Incorporate slides with graphics, charts or videos to supplement your verbal presentation. Make sure they are easy to read and understand.
- Tell a story : Use storytelling techniques to make the case study more engaging. A well-told narrative can help you make complex data more relatable and easier to digest.

Ditching the dry reports and slide decks? Venngage’s case study templates let you wow customers with your solutions and gain insights to improve your business plan. Pre-built templates, visual magic and customer captivation – all just a click away. Go tell your story and watch them say “wow!”
Nailed your case study, but want to make your presentation even stronger? Avoid these common mistakes to ensure your audience gets the most out of it:
Overloading with information
A case study is not an encyclopedia. Overloading your presentation with excessive data, text or jargon can make it cumbersome and difficult for the audience to digest the key points. Stick to what’s essential and impactful. Need help making your data clear and impactful? Our data presentation templates can help! Find clear and engaging visuals to showcase your findings.

Lack of structure
Jumping haphazardly between points or topics can confuse your audience. A well-structured presentation, with a logical flow from introduction to conclusion, is crucial for effective communication.
Ignoring the audience
Different audiences have different needs and levels of understanding. Failing to adapt your presentation to your audience can result in a disconnect and a less impactful presentation.
Poor visual elements
While content is king, poor design or lack of visual elements can make your case study dull or hard to follow. Make sure you use high-quality images, graphs and other visual aids to support your narrative.
Not focusing on results
A case study aims to showcase a problem and its solution, but what most people care about are the results. Failing to highlight or adequately explain the outcomes can make your presentation fall flat.
How to start a case study presentation?
Starting a case study presentation effectively involves a few key steps:
- Grab attention : Open with a hook—an intriguing statistic, a provocative question or a compelling visual—to engage your audience from the get-go.
- Set the stage : Briefly introduce the subject, context and relevance of the case study to give your audience an idea of what to expect.
- Outline objectives : Clearly state what the case study aims to achieve. Are you solving a problem, proving a point or showcasing a success?
- Agenda : Give a quick outline of the key sections or topics you’ll cover to help the audience follow along.
- Set expectations : Let your audience know what you want them to take away from the presentation, whether it’s knowledge, inspiration or a call to action.
How to present a case study on PowerPoint and on Google Slides?
Presenting a case study on PowerPoint and Google Slides involves a structured approach for clarity and impact using presentation slides :
- Title slide : Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Introduction : Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
- Objectives : Clearly state the goals of the case study in a dedicated slide.
- Findings : Use charts, graphs and bullet points to present your findings succinctly.
- Analysis : Discuss what the findings mean, drawing on supporting data or secondary research as necessary.
- Conclusion : Summarize key takeaways and results.
- Q&A : End with a slide inviting questions from the audience.
What’s the role of analysis in a case study presentation?
The role of analysis in a case study presentation is to interpret the data and findings, providing context and meaning to them.
It helps your audience understand the implications of the case study, connects the dots between the problem and the solution and may offer recommendations for future action.
Is it important to include real data and results in the presentation?
Yes, including real data and results in a case study presentation is crucial to show experience, credibility and impact. Authentic data lends weight to your findings and conclusions, enabling the audience to trust your analysis and take your recommendations more seriously
How do I conclude a case study presentation effectively?
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner.
End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
What’s the best way to showcase data in a case study presentation ?
The best way to showcase data in a case study presentation is through visual aids like charts, graphs and infographics which make complex information easily digestible, engaging and creative.
Don’t just report results, visualize them! This template for example lets you transform your social media case study into a captivating infographic that sparks conversation.

Choose the type of visual that best represents the data you’re showing; for example, use bar charts for comparisons or pie charts for parts of a whole.
Ensure that the visuals are high-quality and clearly labeled, so the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Keep the design consistent and simple, avoiding clutter or overly complex visuals that could distract from the message.
Choose a template that perfectly suits your case study where you can utilize different visual aids for maximum impact.
Need more inspiration on how to turn numbers into impact with the help of infographics? Our ready-to-use infographic templates take the guesswork out of creating visual impact for your case studies with just a few clicks.
Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Congrats on mastering the art of compelling case study presentations! This guide has equipped you with all the essentials, from structure and nuances to avoiding common pitfalls. You’re ready to impress any audience, whether in the boardroom, the classroom or beyond.
And remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Venngage’s Case Study Creator is your trusty companion, ready to elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary. So, let your confidence shine, leverage your newly acquired skills and prepare to deliver presentations that truly resonate.
Go forth and make a lasting impact!
- Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning
- Instructional Guide
Case Studies
Case studies can be used to help students understand simple and complex issues. They typically are presented to the students as a situation or scenario which is guided by questions such as “What would you do in this situation?” or “How would you solve this problem?” Successful case studies focus on problem situations relevant to course content and which are relevant “both to the interests and experience level of learners” (Illinois Online Network, 2007).
Case studies can be simple problems where students “work out” a solution to more complex scenarios which require role playing and elaborate planning. Case studies typically involve teams although cases can be undertaken individually. Because case studies often are proposed to not have “one right answer” (Kowalski, Weaver, Henson, 1998, p. 4), some students may be challenged to think alternatively than their peers. However, when properly planned, case studies can effectively engage students in problem solving and deriving creative solutions.
The Penn State University’s Teaching and Learning with Technology unit suggests the following elements when planning case studies for use in the classroom.
Case studies actively involve students as they work on issues found in “real-life” situations and, with careful planning, can be used in all academic disciplines.
- Real-World Scenario. Cases are generally based on real world situations, although some facts may be changed to simplify the scenario or “protect the innocent.”
- Supporting Data and Documents. Effective case assignments typically provide real world situations for student to analyze. These can be simple data tables, links to URLs, quoted statements or testimony, supporting documents, images, video, audio, or any appropriate material.
- Open-Ended Problem. Most case assignments require students to answer an open-ended question or develop a solution to an open-ended problem with multiple potential solutions. Requirements can range from a one-paragraph answer to a fully developed team action plan, proposal or decision. (Penn State University, 2006, para. 2).
Most case assignments require students to answer an open-ended question or develop a solution to an open-ended problem with multiple potential solutions.
Instructor Tasks
To help you get started using case studies in the classroom, a number of tasks should be considered. Following this list are tasks to help you prepare students as they participate in the case study.
- Identify a topic that is based on real-world situations
- Develop the case that will challenge students’ current knowledge of the topic
- Link the case to one (or more) of the course goals or objectives
- Provide students with case study basic information before asking them to work on the case
- Prepare necessary data, information, that will help students come up with a solution
- Discuss how this case would relate to real life and career situations
- Place students in teams in which participants have differing views and opinions to better challenge them in discussing possible solutions to the case
- Review team dynamics with the students (prepare an outline of team rules and roles)
- Inform students that they are to find a solution to the case based on their personal experiences, the knowledge gained in class, and challenge one another to solve the problem
Student Tasks
- Determine team member roles and identify a strategic plan to solve the case
- Brainstorm and prepare questions to further explore the case
- Read and critically analyze any data provided by the instructor, discuss the facts related to the case, identify and discuss the relationship of further problems within the case
- Listen to and be open to viewpoints expressed by each member of the team
- Assess, refine, and condense solutions that are presented
- Prepare findings as required by the instructor
Case studies provide students with scenarios in which they can begin to think about their understanding and solutions to problems found in real-world situations. When carefully planned, case studies will challenge students’ critical thinking and problem solving skills in a safe and open learning environment. Case studies can help students analyze and find solutions to complex problems with foresight and confidence.
Illinois Online Network (2007). ION research: Case studies. https://www.ion.uillinois.edu/resources/casestudies/
Kowalski, T. J., Weaver, R. A., & Henson, K. T. (1998). Case studies of beginning teachers. New York, NY: Longman.
Penn State University (2006). Office of Teaching and Learning with Technology. Using cases in teaching. http://tlt.its.psu.edu/suggestions/cases/casewhat.html
Selected Resources
Study Guides and Strategies (2007). Case studies. https://www.studygs.net/casestudy.htm

Suggested citation
Northern Illinois University Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. (2012). Case studies. In Instructional guide for university faculty and teaching assistants. Retrieved from https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide
Phone: 815-753-0595 Email: [email protected]
Connect with us on
Facebook page Twitter page YouTube page Instagram page LinkedIn page

Home » Case Studies » Case Studies by Workplace Challenge
Case Studies by Workplace Challenge
The Leadership Journey™ is a customizable turnkey leadership development program for supervisors and managers:
- Short modules teach supervisors practical how-to skills.
- Supervisors apply their new skills to real workplace challenges.
- Follow-up tools hold them accountable for applying their new skills on the job.
Over 1200 organizations have used The Leadership Journey to overcome a variety of workplace challenges.
Learn how by viewing case studies relevant to the challenge your organization is facing.
Promotions Are Based on Job and Technical Skills, Not Leadership Potential
Supervisors and managers are often promoted into leadership positions based on their job and technical skills rather than leadership potential. They may lack the background and experience to be successful in their new roles. If they aren’t properly trained on how to lead and manage their teams, key performance measures like employee engagement, teamwork, and productivity can decline.
New Supervisor, Management, or Leadership Training Is Needed
Companies that understand their employees are an asset take a proactive approach. They believe in and develop their supervisors and managers, knowing they have the most direct contact with the employees who perform the work. As a result, their employees give more discretionary effort and maximize productivity for their managers and organizations.
Rapid Growth Needs to Be Managed
Whether hiring or acquiring, the employee headcount is growing exponentially for many companies. Usually, employees are promoted quickly because of their hire dates or technical competencies for the jobs they’re in—often before they are ready. Managers and employees are experiencing rapid change daily. Time is extremely valuable and a limited resource, so training must be short and relevant.
Supervisors and Managers Lack Leadership and Communication Skills
Leaders need to improve their soft skills. Managers need to refresh their management and leadership skills. Supervisors struggle with communication, conflict resolution, and accountability and have a difficult time transitioning from individual contributors to leaders. Technical workers, usually with advanced degrees, may have issues managing peers.
Frontline Leaders Are Not Prepared to Lead
Companies may have excellent leadership programs for high-level leaders, but there’s not enough room for all leaders or the content isn’t applicable for frontline leaders. They want a quick, cost-effective solution to easily develop their frontline leaders.
Existing Training Needs a Refresh
Companies often discover their old training programs no longer meet their current needs. Seminars, workshops, or classes at the community college often overwhelm supervisors with too much information. Many of these offerings are more motivational than educational. Web-based learning libraries and online PowerPoint e-learning courses don’t get used.
Employee Engagement Needs to Be Improved
Organizations understand the correlation between high-performing managers, high employee engagement, and improved productivity from employees. They know a leading factor in employee engagement is the employee’s immediate supervisor or manager.
Future Leaders Need to Be Developed (Lack of Bench Strength)
When a new leadership position opens up, new leaders need to be properly trained so they can hit the ground running in their new roles. As employees with the potential to move into leadership roles are identified, observing their performance during leadership training can help organizations gain confidence in their abilities and identify those most likely to succeed.
Many Leaders Need to Be Trained Quickly
Companies need to improve skills quickly, and often simultaneously, at many sites. Leaders may be at multiple geographically dispersed locations. Many sites are running 24/7. Others may have a primary location where some employees work onsite and others work remotely.
High Turnover
Turnover rates and their associated expenses are too high. Companies understand a leading factor in turnover is an employee’s manager. By developing leadership skills in managers, they improve employee engagement and reduce turnover.

Learnous Case Study Challenge (Season 4) Learnous
Refer & win.
MacBook, iPhone, Apple Watch, Cash and more!
Share this Competition now

- Rounds & Timeline
- Dates & Deadlines
- FAQs & Discussions
Learnous Case Study Challenge (Season 4): Stages and Timelines
Learnous case study challenge: season 4.
Participants will solve the business strategy case and submit a PPT. The number of slides is limited to 10 excluding the intro and title slides. Submissions will be evaluated based on your understanding of the problem, innovativeness and feasibility of the proposed solution, and clarity of thought. Case statement can be downloaded from the attachment section at the end of the page. Submit your solutions at [email protected] . The round is completely online and will be judged based on the solutions submitted.
All that you need to know about Learnous Case Study Challenge (Season 4)
Learnous is proud to launch the flagship event “ Learnous Case Study Challenge ” an intra- BSchool business challenge which gives you an opportunity to solve a live business problem.
With Learnous Case Study Challenge: Season 1, 2 & 3 a big hit, we are back again this season. Learnous is hosting its fourth national level case competition, we have received an overwhelming response with more than 5000+ participants overall in these 3 seasons. We are looking forward to enrich minds and bring out some excellent ideas.
The theme is Startups and evolving business models. Participants will need to conceptualize, brainstorm, and work out a strategy to steer their ideas to execution to sustain their business model.
- The opportunity is open to all.
- Anyone can participate (Incoming b-school students can also participate).
- A team can have a minimum of 1 and a maximum of 2 members
- Cross-college team formation is allowed
- The registration fee is Rs.100 per team
- The solution is to be submitted in the format of PPT/ PDF with a maximum of 10 slides
- Submit your solutions at [email protected] .
Case Release Date: 5th May 2023 (Can be downloaded now, from the attachment section at the end of the page)
Submission Deadline: 18 th June 2023
- Cash prizes worth INR 5000 to the top winner
- The top 30 winners will be provided with a certificate of excellence along with respective ranks in it.
- Live-project opportunities will be provided to the top 15 winners
- A certificate of participation will be given to all participants
Important: Please note that this event is also open to students joining b-schools this year.
Winners of Learnous Case Study Challenge: Season 3
- Winner - Team batman and Robin - Goa Institute of Management
- Runner-Up - Team Jaihind - Nikhil Kodela _ IIFT
- Second Runner-Up - Team IIMA Case Group_Utkarsh Chandra - IIM Ahmedabad
- 4th Position - Team Conquerors_Shaurya Prasad_IIFT
- 5th Position - Team Powerplay97_ yash sharma - IIM Kozhikode
- Team Go getters_Kiruthika R_ SDA Bocconi
- Team Agni_babiya - Tech Mahindra
- Team phoenix - jashraj choulkar_NMIMS
- Team phoenix - Jesus and Mary College, Delhi University
- Team untitled - Garima_XLRI Jamshedpur
- Team Achilles - Naval Mittal_IIM Shillong
- Team Atlantis - Ashish Jain, Great Lakes Institute Of Management
- Team build to last - P Sivdayadarsini_IIM Kozhikode
- Team trailblazers - Shashank Pandey_SIMSREE
- Team mindbenders Aakash doshi_SDA bocconi & Team sanchit and chinmay- IIM Calcutta
Note: All the registered participants will receive the previous year's winners' case solutions for reference. You can email your request to " [email protected] ".
Feel free to contact us at [email protected] , in case of any queries.
Happy casing :)
What are the important dates & deadlines?
- Registration Deadline 29 May 23, 06:29 PM CUT
Download attachments
- Learnous Case Statement file_download
Contact us Form
Rewards and Prizes
Top performers will be awarded with exciting cash prizes, top 30 performers will be provided with a certificate of excellence, opportunity of internship, cool goodies and much more.
National Winner
Live-project opportunity!

First Runner Up
Second runner up, rank 4 - rank 15, rank 16 - rank 30.
Certificate Of Excellence
Featured Opportunities

Similar Opportunities
Related opportunities, voice your opinion by leaving a feedback & your rating, frequently asked questions (faqs) and discussions..

GLOBAL. VIRTUAL. CONSCIOUS. SUSTAINABLE.
Global work competency laboratory
We are a female-led virtual team driving a future-oriented movement of global, conscious, and sustainable thinkers and leaders. We prepare students and young professionals for future careers. We help educators and learning professionals upskill for the digital world. We consult and train HEIs on internationalization, virtual exchange, and sustainability.
Our Mission
Bringing together a Global, Conscious and Sustainable Community to co-create better learning spaces, better workspaces, and a better society.
Key new work competencies
Diversity competency.
Understanding, communicating with, and effectively interacting with others. Mutually adapting to each other to create inclusive shared spaces to leverage uniqueness and harness synergies.
Digital Communication Competency
Understanding and making use of digital tools and technologies to communicate information digitally and communicate and interact effectively with others in a global virtual environment.
Sustainability Competency
Thinking, planning, and acting with empathy, responsibility, and care for our planet and global society. Embodying sustainability values, embracing the complexity in sustainability, envisioning sustainable futures, and acting for sustainability.
Virtual collaboration
Universities, meet our team.
#virtualspacehero
#consciousleadership
Anna is passionate about sustainability and the large number of business models that can be developed to add value to humanity.
#sustainability

GCSC expert program
“Virtual Learning Designer and Facilitator”
A transformational three-month (mid. September – mid. December) Experiential Professional Development (EPD) program helping facilitators/ trainers/ educators optimize and transform their online courses for international learners. Facilitators develop crucial competences necessary for designing and running highly effective online courses based on the formula: Knowledge, Attitudes, Skills, Tools. The certificate program is embedded in the ongoing Global Case Study Challenge project, where a certification cohort has a unique chance to apply theory to real-life scenarios, observing 400+ international students and professors from 14 countries.

LET’S MEET IN THE VIRTUAL SPACE Say Hello!
Are you interested in joining the GCSC Student Challenge or signing up for our Expert Programs, or maybe you want to partner up with us? We are open to all forms of cooperation as we believe in quality education that is available for everyone!
Email Address
Organization
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Case Challenge
Competition structure
Registration and eligibility.
Google’s Case Challenge is an initiative for business schools in India, designed to attract and engage budding early talent to creatively respond to live and realistic business challenges. This competition will give students an opportunity to stretch their imagination and come up with innovative solutions to the day to day challenges faced by teams across Google. Finalists will also get a chance to work closely with assigned Google mentors and understand Google’s ecosystem better, along with cash prizes for the winning teams.
Case Challenge is open to the participating institutes:
- Indian Institute of Management, Ahmedabad
- Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore
- Indian Institute of Management, Calcutta
- Indian Institute of Management, Indore
- Indian Institute of Management, Lucknow
- Indian Institute of Management, Kozhikode
- Indian Institute of Management, Shillong
- Faculty of Management Studies, Delhi
- Indian Institute of Foreign Trade
- Institute of Management Technology, Ghaziabad
- Management Development Institute, Gurgaon
- Indian School of Business
- XLRI - Xavier School of Management
- Mudra Institute of Communications, Ahmedabad
- Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, Mumbai
- Shailesh J. Mehta School of Management, Mumbai
- National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Mumbai
- Symbiosis Centre for Management and Human Resource development
- Tata Institute of Social Sciences
- SP Jain Institute of Management & Research, Mumbai
1 year executive programs of the above campuses are also eligible to register as Participating institutes.
Wild Card Entrants
With the endeavour to expand Case Challenge to students across India, we have introduced wild card entrants this year. In this, students from business schools across India can register and participate in the first round (Online Challenge) subject to the rules and requirements of the Competition. Further details will be discussed in the subsequent sections.
The competition will be conducted across four rounds:
- Online Challenge
- Case Study Round
- Cohort Round
- National Finale The language of the Competition will be entirely in English and will be conducted virtually.
Judging of all Rounds will be performed by a panel of judge(s) selected by Google. Please note that any entry is subject to and evaluated based on the following broad parameters:
- Structured thinking and strategy
- Originality & Innovation
- Feasibility & Scalability
- Market Intelligence/Data Insights/Consumer Insights
- Presentation Skills
- Q&A Session
Teams are prohibited from communicating with any outside party and cannot solicit assistance from anyone (including staff, faculty advisor, other students) during the time they are participants of the Competition, unless permitted by Google. Google's and/or any judge’s decision is final and binding and no correspondence will be entered in relation to such decision.
Round 1 (Online Challenge) Registration
- Digital marketing
- Sales & marketing
- Human resources
- Teams cannot change their choice of case study post registration.
- Round 1 registrations are open to students of all business schools in India.
- First 5000 registered teams will be invited to the Online Challenge round.
The Online Challenge
- The first 5000 registered teams will receive details about the Online Challenge through their registered email address.
- This 30 minute Online Challenge will assess the team’s critical thinking and logical reasoning and will be conducted on Sep. 18, 2021 .
- Atmost Top 5 Teams per campus from the participating institutes will be announced as campus winners, and will move to Round 2 .
- Top 20 teams from the wild card entrants will proceed to Round 2.
- The announcement of shortlisted Teams qualifying for the 2nd Round will be made via an email to the campus and the respective Teams.
Round 2 (Case Study Round) Making a Submission
- All the shortlisted Teams will be administered the case study on their chosen topics at the time of registration.
- The Teams will have to submit a one pager solution and a five minutes video pitching their proposed solution.
- The submission entries should consist of both the solution submission and video pitch, else the team stands disqualified.
- Only one submission per Team will be taken into consideration.
- Teams cannot change their choice of case study.
Submission Guidelines
- The format of the submission will have to be a one-page Google slide converted to a pdf document. No other formats (including zip files) will be accepted.
- Deadline for submission will be communicated to the teams.
- There are no restrictions on font size, style etc. but it should not result in a submission that is difficult to read by the judges.
- The maximum size of the PDF file to be uploaded should not exceed 10MB.
- The naming convention to be followed for the Submission is: CampusName_Team name_CaseStudyChosen. For the 'CaseStudyChosen', mention the type (Analytics, Digital marketing, Sales & marketing, Human Resources).
- We urge the Teams not to wait till the last moment to make their Submission entries. Google or its affiliates’ shall not be responsible for any technical snags that may occur due to high volume.
- No Team may revise, substitute, add, delete, or in any other manner alter their original Submission after it has been submitted.
What we expect from the Submission:
- Originality, clarity and uniqueness of the idea.
- Innovative approach to the given problem.
- Solution must be relevant to the given problem and should have a clear plan of action.
- Solution should be succinct yet self-explanatory.
- Feasibility of implementation, sustainability, scalability and fitment with Google’s vision.
- Tables, diagrams, and charts are permitted on the one-pager, but are not necessary (attachment of an appendix slide is not allowed).
- Relevant assumptions backed by proper rationale.
- References/sources to be quoted where required (as footnotes).
What the Submission should not have:
- It must not be derogatory, offensive, threatening, defamatory, disparaging, libelous or contain any content that is inappropriate, indecent, sexual, profane, tortuous, slanderous, discriminatory in any way, or that promotes hatred or harm against any group or person, or otherwise does not comply with the theme and spirit of the Competition.
- It must not contain content, material or any element that is unlawful, or otherwise in violation of or contrary to any applicable laws.
- It must not contain any content, material or element that displays any third party advertising, slogan, logo, trademark or otherwise indicates a sponsorship or endorsement by a third party, commercial entity or that is not within the spirit of the Competition.
- It must be original, unpublished work that does not contain, incorporate or otherwise use any content, material or element that is owned by a third party or entity.
- The judging panel as chosen by Google will evaluate all Submissions and shortlist Teams for Round 3 based on the judging criteria.
- Top 5 teams per case study (Analytics, Digital marketing, Sales & marketing, and Human Resources) will proceed to the next round.
Round 3 (Cohort Round) Presentation
- The shortlisted Teams will submit a presentation deepening their ideas as submitted in Round 2 and present its business solution (virtually) to a panel of judges.
- Deadline for submission will be communicated to the Teams.
- Teams will be given 12 minutes to present followed by an 8 minutes “Question and Answer” session by the judging panel.
- The Cohort Rounds will be held virtually via Google Hangouts between Oct. 22, 2021 and Oct. 28, 2021 .
Presentation Guidelines
- The presentation should not exceed ten slides.
- Case Study chosen during registrations cannot be changed.
- The format of the presentation will have to be Google slides and no other formats (including zip files) will be accepted.
- Additionally, qualifying teams will also have to submit a PDF version of their submission for our reference.
- You are free to select font type, size etc. but it should not result in a submission that is difficult to read by our panel, during the presentation.
- The maximum size of the file to be uploaded cannot exceed 100MB each (slide and PDF).
- The naming convention to be followed is: CampusName_Teamname_CaseStudyChosen. In the CaseStudyChosen, mention the type (Analytics, Digital marketing, Sales & marketing).
- Deadlines will not be extended. If the qualifying Team does not submit the presentation by the deadline, then such Team will be disqualified.
- It will be the responsibility of the Team Leader to ensure that if not all Team members at least 2 members of the Team are present for the presentations on the scheduled day. In the event of at least 2 members are present at the start of the presentation, the Team will be disqualified.
- The top two teams from each cohort round will qualify for the National Finale of the Competition.
- 8 teams in total will qualify for the National Finale.
Round 4 (National Finale) Mentoring
- Shortlisted Teams will be assigned a mentor to guide them for their pitch/presentation.
- Teams will be allowed to make changes to the presentation submitted during the Cohort Round, however the Teams cannot change the chosen case study.
- The shortlisted Teams will only be allowed to refine the solution and make cosmetic changes under the guidance of the mentor, with their permission. Major changes at this stage to the solution, approach, etc. will not be allowed.
Presentation
- The National Finale will be held virtually via Google Hangouts.
- The Finale date will be communicated to the Teams.
- Shortlisted Teams will present the revised presentation to a judging panel, and will get 12 minutes for presenting their idea, and 8 minutes for Q&A.
- At least 2 members will have to be present for the presentation on the given date of the National Finale Round.
- The judging panel as indicated by Google will review the presentation.
- The top three teams will be selected as national winners.
Student prizes
The top three teams at the National Finale will receive the following:
- Cash prize of INR 5,00,000/- to the entire team.
- Pre-placement interview offers for internship or final hiring.
Second prize:
- Cash prize of INR 3,00,000/- to the entire team.
Third prize:
- Cash prize of INR 2,00,000/- to the entire Team
Each member of the winning Teams is solely responsible for all taxes, levies and other statutory payments associated with his or her receipt and use of a cash prize received by such member. No substitution, assignment or transfer of prize is permitted. Google will withhold and/or report taxes as required by the applicable law. All prizes may be revoked if a Team is found to have violated any of the rules or instructions of Google or is disqualified. The business and location related to the pre-placement interview offers for internship and final hiring will be at the discretion of Google.
Competition period
The competition will be conducted across 4 rounds:
- National Finale
The language of the competition will be entirely in English and all the rounds will be conducted virtually.
Eligibility Criteria
- A student must be a first or second year student irrespective of their specialisation but enrolled in a full-time management program of a business school in India.
- Students must be Indian nationals. Foreign national students are not allowed to participate in this Competition.
- Every student must have an official user account provided by the business school at which the student is enrolled.
Participation as a Team
- Participation will be through teams of eligible students comprising a minimum of 2 or a maximum of 3 students and enrolled at a business school in India (a “Team”). First year students cannot form teams with 2nd year students and vice versa. A Team can only have team members from the same batch of the same institute.
- All Team members must independently meet the eligibility requirements of the Competition.
- A student cannot be a member of more than 1 Team.
- Students going on an exchange program can participate as long as there are at least 2 students in the Team that are not attending an exchange program and are available to attend the Competition.
- Modification to a Team’s composition or details after registration/communicating acceptance to participate is not allowed.
- Team members who compete at the beginning of the Competition must participate throughout the Competition Period, where the team is shortlisted for the next round.
- Any deviation from the above will result in immediate disqualification of the entire team.
How to enter
The Team must register before it can participate in the Competition.
- To enter the Competition, the Team Leader must complete the registration form and provide required information about the members of the Team.
- The Team may opt for the email address of the Team Leader as a point of contact for instructions on the Competition. The designated email address is necessary as specific communications/instructions regarding the Competition will be communicated to the Team through this address. You are required to keep yourself updated on all emails issued to you.
- The registration starts from Sept. 7, 2021 and will close on or before 22:00 hours IST on Sept. 10, 2021 .
- Only one registration per Team will be taken into consideration.
- Any questions or inquiries regarding the Competition should be directed to [email protected] .
Team Leader and Team Name
Each Team must nominate one member as the Team leader, who may not be changed during the Competition Period (the “Team Leader”).
- The Team Leader is the primary point of contact for the team during the competition.
- Each Team must decide on a name for their team. Your team name must be neutral and brief, without the use of offensive or vulgar language or violate the intellectual property rights of others. Google reserves the right to request for a change of the Team name in its sole discretion.
Verifying Eligibility
- Google reserves the right to verify your eligibility. You agree to provide Google with any proof of eligibility requested by Google and your refusal or failure to timely provide such proof may result in the Team’s disqualification from the Competition.
How can we route our queries to Google regarding the case challenge?
Please email us at [email protected] for any questions regarding the competition.
How many individuals can be on a team?
One team can have a minimum of two and maximum of three members. An individual can not be part of more than one team.
Who can participate in the competition?
Case Challenge is open to first or second year students (irrespective of their specialisation) enrolled in a full-time, management program of a business school in India.
Is the Case Challenge a continuation of Google Online Challenge (which was conducted recently for the first year students)?
No, Case Challenge and Google's Online Challenge are different programs.
I could not participate in Google Online Challenge. Can I still register for this competition?
Yes, these two are completely different initiatives.
All my team members have already appeared for Google’s Online Challenge. Do we still need to appear for the round 1 Online Challenge, post registration?
Yes. All teams who register to participate in Case Challenge will have to appear for Round 1, which is an Online Challenge. Google Online Challenge and Case Challenge are separate initiatives.
Can entries be modified after submission?
No, once submitted, entries cannot be modified.
I filled in the wrong details for one of my team members, how can I fix this?
Entries can not be modified once submitted. Please be sure to double check all details before submitting.
Do I need to register through my college email ID or can I use my personal email ID as well?
Only college email ID should be used for registration for all team members. Please don’t use your personal email ID.
What if my submission exceeds the file size limit?
The entry will be disqualified. Please ensure the files submitted are within the size limitation shared. For the first round, file size for the submission shouldn’t exceed 10MB.
Will any exceptions be made for late entries due to technical difficulties at the time of submission?
No, late entries will not be considered.
Can one person be a part of two different teams?
No, an individual cannot be part of more than one team.
Do we need to submit our resumes?
No, resumes are not required.
Will all registered teams qualify for round one?
Only the first 5000 registered teams will qualify for round one, which is the Online Challenge.
While registering, I can only see the cohort names (analytics, digital marketing and sales & marketing and human resources), but the case studies are not present?
The case studies will be available post round one. While registering, please choose the cohort of your interest. In case you qualify round one, you will be administered the case study on the cohort you have chosen.
Do all the team members have to appear for the Online Challenge or can the team leader appear for the challenge as a team representative?
Online Challenge is a team based challenge designed to assess a team’s critical thinking and decision making. Only the team leader will receive the challenge id and passkey details to login to the challenge. The team will be given 30 minutes to solve the challenge. It is the responsibility of the team leader to submit the answers on the team’s behalf. More than one submission per team will lead to the team’s disqualification.
For the video submission in Round two, do all the team members have to be present in the video?
Yes, all team members have to be a part of the video, else the team stands disqualified.
My campus is not included in the list of participating institutes. Can I still take part in the competition?
With the endeavour to expand Case Challenge to students across India, we have introduced wild card entrants. In this, student from business schools across India can register and participate in the first round (Online challenge) subject to the rules and requirements of the competition.
You might also like
Google Summer of Code
Google Summer of Code is a global, online program pairing new open source contributors with mentors from an open source organization that welcome them into their community and guide them through a 12+ week coding project.
Google's Online Challenge
Google’s Online Challenge (GOC) is a platform that presents a fair, unbiased opportunity for candidates to engage in Google's hiring or developmental program. It provides a scalable solution for candidate screening and development.
Cloud Technical Residency (CTR)
Google Cloud is on a mission to change the world of enterprise computing, and Cloud Technical Residents have a front row seat to the action. During the 12-month rotational program, Residents help shape and execute strategies to help customers “go Google.”

Case Studies
Learn how challenge success has worked with schools since 2003..
720+ SCHOOLS AND COUNTING
Research shows our approach works in all types of schools.
Over the last 20 years, our partner schools have learned to apply our research in school settings to improve student well-being, belonging, and engagement with learning. Through our co-design model we have partnered with all types of schools: public, private/independent, religiously-affiliated, charter, magnet, single-gender, boarding, and more. Students and educators who have engaged with Challenge Success show improvement in a number of ways. A few examples of our direct impact include:

CASE STUDIES

School District Case Study
After working with Challenge Success, this district had measurable results. A few examples of our direct impact include:
- More students at a participating high school have a trusted faculty / staff member they can talk to.
- Over 86% of high school students and over 82% of middle school students reported having a peer they could go to with a personal problem.
- High school students are getting more sleep.
- Homework load is reduced during the week and also on weekends for middle and high school students.
“Every person from Challenge Success that we’ve interacted with – those hosting the professional development seminars, the survey administration and debriefs, our coaching, the conference people – has been excellent. They provide expertise and resources in the areas we’re focusing on improving. We didn’t know Challenge Success would be the weighty influence that they are, but everyone on campus is quoting or referring to Challenge Success now.” SCHOOL LEADER

Dover-Sherborn High School

Kent Denver School

Tustin Unified School District

Interested in bringing Challenge Success to your school? We’d love to hear from you! Tell us more about your school, the challenges you’re facing, and the goals you’re trying to achieve.
Explore resources
Bring us to your school
Explore more highlights from our partner schools..

Confirmed: Schools Can Effectively Reduce Student Stress
Learn more about how one school decreased stress and increased engagement with the help of the Challenge Success School Partnership.

How many students have an adult to go to for support at school?
Hear from a public school district and an

School Story: Morris County School of Technology
Learn how one school used student input and survey data to inform their changes and educate their community.
- Joseph F. Rice School of Law
- Location Location
- Contact Contact
- Colleges and Schools
- About School of Law
US Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit holds hearing at USC Joseph F. Rice School of Law
The Karen J. Williams Courtroom was standing room only on Thursday morning, March 28 for oral arguments heard by Chief Judge Albert Diaz, Judge A. Marvin Quattlebaum, Jr. ‘89, and Judge William B. Traxler, Jr. ‘73 of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit.
The three cases dealt with issues of social security, criminal charges, and insurance. On the docket were Donna Ard v. Martin O'Malley; United States of America v. Herbert Diaz; and Koppers Performance Chemicals, Inc. v. Argonaut Midwest Insurance Company.
University of South Carolina Joseph F. Rice School of Law students were given the opportunity to attend arguments and after the hearings could ask the judges questions. Students were interested in the judges' opinions on presentation style, how they approach their decisions, and how to succeed in the legal profession.
Traxler reminded future lawyers to spend adequate time preparing their cases so they can confidently and directly answer any questions.
“Look for experiences to get on your feet. Some of those things are hard to come by,” Quattlebaum said. “When you get to a firm look for opportunities, like pro bono work, to improve your craft and develop your skills.”
Diaz concluded the session by thanking Dean William Hubbard for hosting the hearing and acknowledging the appropriateness of the venue given its namesake, the Honorable Karen J. Williams ‘80.
“It’s fitting that we heard arguments in the courtroom named for our colleague,” Diaz said, referring to Williams, who was the first woman to sit on the 4th Circuit, as well as their first woman Chief Judge. “She left an indelible mark on the legal profession and we’re grateful to be here today.”
Challenge the conventional. Create the exceptional. No Limits.
Student Apathy Is a Big Classroom Challenge, Teachers Say. Cellphones Aren’t Helping

- Share article
The stakes are high: Students have a lot of academic ground to make up following the pandemic. Yet they’re not fully engaged in the classroom, teachers report in a new national survey .
Nearly half of teachers—and 58 percent of high school teachers—say that their students showing little to no interest in learning is a major problem in their classroom. And 72 percent of high school teachers and a third of middle school teachers say that students being distracted by cellphones is a major problem.
Those results are from a new survey by the Pew Research Center of more than 2,500 public school teachers, which was conducted from Oct. 17 to Nov. 14. (The teachers surveyed are members of the RAND Corp.'s nationally representative American Teacher Panel.) The survey covers a wide breadth of topics, including teachers’ job satisfaction, workload, and challenges in the classroom.
About half of the teachers who responded to the survey gave low marks to both the academic performance and behavior of students at their school. Teachers from high-poverty schools are much more likely to hold these negative views than their peers at low-poverty schools.
When teachers were asked about the problems affecting students at their schools, poverty, chronic absenteeism (generally defined as missing 10 percent or more of school days for any reason), and anxiety and depression topped the list. More than a third of middle school teachers also cited bullying.
And inside the classroom, distractions reign.
Natoria Kennell-Foster, a 7th grade English/language arts teacher in Mississippi, said she’s still seeing the lingering effects of school shutdowns and remote learning in her classroom this year.
Some of her students are “really hungry to learn,” she said. “They want all the things I have to give.”
Others, however, are still not used to the structure of the school day and have been reluctant to engage in class, she said: “Pulling them in can be difficult.”
Kennell-Foster said she’s found some success by pairing her eager students with the disengaged ones. And she’s optimistic that some of these problems will dissipate in the next few years.
“The further we’ve been removed from quarantine, each year has gotten a little closer to being normal,” Kennell-Foster said.
Cellphones are an ‘addiction,’ teachers say
While 71 percent of high school teachers say their school or district has policies regarding students’ use of cellphones in the classroom, 60 percent said those policies were difficult to enforce.
Tamika Kimble, an 8th and 9th grade science teacher at Sylvan Hill Junior High School in Sherwood, Arkansas, has a sign posted in her classroom that cellphones are not allowed. Even so, she frequently has to confiscate phones.
“Sometimes I’ll be teaching, and I notice their heads are down—I know they’re on their phones,” Kimble said. “If I’m paid to teach you to learn something, that’s what I need you to do. I’m not going to allow you to play games on your phone. You are there to learn.”
Yet keeping students engaged in instruction and off their phones is a constant battle for many teachers.
“It’s like an addiction,” said Kelly Chevalier, a science teacher at Crown Point High School in northwest Indiana. “They can’t put them away for any amount of time.”
Her students are constantly messaging their friends, scrolling social media, Googling information, listening to music, watching shows, and playing games on their phones.
And when students were told to turn their phones off and put them away for the duration of a standardized exam, they panicked: “The idea of being without their phone for three hours—it literally causes some of them physiological anxiety,” Chevalier said.
Chevalier said she sees phones akin to cars. Parents would never give their children the car keys and tell them to drive without any preparation, she said. Students need to learn how to use phones—and the unfettered access to a world of both information and mis- and disinformation—responsibly, too.

Yet parents are not always partners in teachers’ efforts to stem the use of phones in class, teachers say.
Sometimes, Chevalier will tell a student to put away their phone—and they’ll respond that they’re texting their mom, who’s asking them what they want from the store.
Kimble said she’s experienced pushback from parents when she or school leaders have taken students’ phones.
“The parents feel like, ‘This is my phone, I bought it. You have no right to take it,’” Kimble said. “But this is my classroom. I have a right to take it, and I have a right to teach.”
The Pew survey found that 79 percent of teachers say parents do too little when it comes to holding their children accountable if they misbehave in school. Sixty-three percent of all teachers—and three-fourths of high school teachers—say parents do too little to ensure their children’s attendance.
“I think one striking finding [from the survey] is that while teachers navigate through all these challenges, they just don’t feel like they’re getting the support or reinforcement they need from parents,” said Luona Lin, a research associate at Pew Research Center.
Most teachers—65 percent—do say that parents show appreciation for their efforts at least sometimes, with about a quarter saying it happens frequently.
Even so, 40 percent of teachers say that parents at least sometimes communicate with them in a disrespectful way.
Teachers are less satisfied with their jobs than other workers
Only a third of teachers say they’re “extremely” or “very” satisfied with their job overall, compared to about half of all U.S. workers. EdWeek’s The State of Teaching survey , released last month, found similar themes of low morale, an ambivalence toward recommending their profession to loved ones, and a heavy workload.

Indeed, the Pew survey found that more than 8 in 10 teachers said there’s not enough time in the day to get all their work done—mostly because they simply have too much work to do, respondents said, but also because they have other responsibilities, like hallway or lunch duty, that cut into their core work .
A strong majority of teachers said their job is often stressful (77 percent) or overwhelming (68 percent). Smaller majorities said their job is often fulfilling (56 percent) or enjoyable (53 percent).
Female teachers are more likely than male teachers to say their job is frequently stressful or overwhelming. Similarly, female teachers are more likely to say that work-life balance is difficult for them to achieve.
Lin pointed to prior Pew research that shows that female workers overall are more likely than male workers to say their job is stressful and overwhelming all or most of the time. That’s perhaps in part because research shows women in opposite-sex marriages typically take on a heavier load at home with household chores and caregiving responsibilities.
The Pew survey also found that 82 percent of teachers say that the overall state of public K-12 education has gotten worse in the last five years, with large shares pointing to the current political climate, the lasting effects of the pandemic, and changes in the availability of funding and resources.
About half of teachers expect the state of education to be worse five years from now.
Meanwhile, Pew separately surveyed about 5,000 U.S. adults in November and found that about half say the public K-12 education system is going in the wrong direction . Just 16 percent say it’s going in the right direction; the rest aren’t sure.
Large shares of people who held a negative view of the education system pointed to the following reasons: schools are not spending enough time on core academic subjects; teachers are bringing their personal political and social views into the classroom; and schools don’t have the funding and resources they need.
Lin highlighted the fact that while both teachers and the general public hold a largely negative view of education, their reasons for doing so are mostly different.
“All these issues that teachers are facing in the classroom ... they’re not known to the general public,” she said. “We definitely hope that our report sparks some discussion.”
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Advertisement
Was Today’s Earthquake Connected to the Solar Eclipse?
The tidal forces on Earth grow as the sun, moon and Earth begin to align, a configuration that can lead to a solar eclipse. But the results of several studies of the relationship between earthquakes and tides are inconclusive, a geophysicist said.
- Share full article

By Katrina Miller
- April 5, 2024
With a total solar eclipse set to pass through the United States on Monday, it is easy to imagine a linkage between unusual events in the heavens and on Earth. But geoscientists were cautious about making such a connection.
Earthquakes happen along fault lines, or cracks between two blocks of rock on Earth’s crust. Tides stretch and squish the land on Earth just as they contribute to waves in the ocean, and those tidal forces grow as the sun, moon and Earth begin to align — a configuration that sometimes creates a solar eclipse.
One theory is that this may introduce additional stress along Earth’s fault lines.
“We do know that the relative position of the Earth and the moon and the sun does exert tidal forces,” said William Frank, a geophysicist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. “And we know that changes the stress that can be on a fault that can host an earthquake.”
But the results of several studies of the relationship between earthquakes and tides are inconclusive, according to Seth Stein, a geophysicist at Northwestern University. “If there’s any effect, it would be incredibly weak,” he said.
Earthquakes are driven most often by the motion between two tectonic plates making up Earth’s crust — either when two plates slide along each other in opposite directions, or when one slides under the other.
Both types of movements introduce strain at the junction, which often gets relieved by an earthquake.
But at the moment, it’s difficult to say that plate motion was responsible for the quake that shook the Northeast Friday morning.
“It’s not quite as obvious, because there is no tectonic plate boundary that is active,” Dr. Frank said.
Still, he added, fault lines from past activity are everywhere on Earth’s crust.
“Some of these faults can still be storing stress and be closure to failure,” he said. “And it can just require a little bit more to push it over the edge.”
Katrina Miller is a science reporting fellow for The Times. She recently earned her Ph.D. in particle physics from the University of Chicago. More about Katrina Miller

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Through the case method, you can "try on" roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career. 5. Build Your Self-Confidence. Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader's perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and ...
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches. Summary. It's been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study ...
Overview. Simply put, the case method is a discussion of real-life situations that business executives have faced. On average, you'll attend three to four different classes a day, for a total of about six hours of class time (schedules vary). To prepare, you'll work through problems with your peers. Read More.
Case studies are a form of problem-based learning, where you present a situation that needs a resolution. A typical business case study is a detailed account, or story, of what happened in a particular company, industry, or project over a set period of time. The learner is given details about the situation, often in a historical context.
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
Learning by the Case Method. The case method is not only the most relevant and practical way to learn managerial skills, it's exciting and fun. But, it can also be very confusing if you don't know much about it. This brief note is designed to remove the confusion by explaining how the case method works and then to suggest how you can get ...
1 Benefits of case study learning. One of the main benefits of case study learning is that it engages you in active and experiential learning. You are not just passively listening to lectures or ...
Bring excitement into your classroom with engaging case discussions and introduce students to the challenge and fun of making important decisions. Illustrate business concepts Help students learn by doing with over 50,000+ cases featuring real-world business scenarios spanning across multiple areas of business.
Case method 1 teaching is an active form of instruction that focuses on a case and involves students learning by doing 2 3. Cases are real or invented stories 4 that include "an educational message" or recount events, problems, dilemmas, theoretical or conceptual issue that requires analysis and/or decision-making.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A USAID-led initiative to challenge partner organizations to share case studies of locally led development, both the successes and the failures, could provide invaluable recommendations for how to ...
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences. Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly. 1. Lab report case study template.
To date, "The Case Study Challenge" has resulted in over 1,000 volunteer hours, approximately 250 personal phone calls, and nearly 1,000 handwritten thank you notes. This service-learning project has also raised more than $13,000 in donations toward the Dennis Gregory Mechatronics Scholarship - a scholarship
Summary. Case studies provide students with scenarios in which they can begin to think about their understanding and solutions to problems found in real-world situations. When carefully planned, case studies will challenge students' critical thinking and problem solving skills in a safe and open learning environment.
Types of Case Studies. Case studies can vary widely, from business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) to more specific scenarios like the development of an online store or the launch of a website using an AI website maker. Some focus on the process (how a challenge was met), while others emphasize the results (the impact of a ...
Case Studies by Workplace Challenge. The Leadership Journey™ is a customizable turnkey leadership development program for supervisors and managers: Short modules teach supervisors practical how-to skills. Supervisors apply their new skills to real workplace challenges. Follow-up tools hold them accountable for applying their new skills on the ...
All that you need to know about Learnous Case Study Challenge (Season 4) Learnous is proud to launch the flagship event " Learnous Case Study Challenge " an intra- BSchool business challenge which gives you an opportunity to solve a live business problem. With Learnous Case Study Challenge: Season 1, 2 & 3 a big hit, we are back again this ...
learning model in Maijdee town, a community of 75,000 residents in Noakhali district. Linking Paragraph leading into the case: Challenge and Hope • Having grown up in Majidee, Sheikh knew the challenges of working in the community well. It was a diverse community of Muslims, Hindus and Christians.
We help educators and learning professionals upskill for the digital world. We consult and train HEIs on internationalization, virtual exchange, and sustainability. ... Attitudes, Skills, Tools. The certificate program is embedded in the ongoing Global Case Study Challenge project, where a certification cohort has a unique chance to apply ...
Overview. Google's Case Challenge is an initiative for business schools in India, designed to attract and engage budding early talent to creatively respond to live and realistic business challenges. This competition will give students an opportunity to stretch their imagination and come up with innovative solutions to the day to day ...
School District Case Study. After working with Challenge Success, this district had measurable results. A few examples of our direct impact include: More students at a participating high school have a trusted faculty / staff member they can talk to. Over 86% of high school students and over 82% of middle school students reported having a peer ...
Request PDF | Exploring the factors influencing students' experience with challenge-based learning: a case study | Challenge-Based Learning (CBL) is an active-learning pedagogy increasingly used ...
The CEC was saddened to learn of the death of USC alum, and former Dean Emeritus and Civil and Environmental Engineering Professor Emeritus Wilfred Kenneth Humphries. Learn more about Wilfred Kenneth Humphries, Ph.D.
The Karen J. Williams Courtroom was standing room only on Thursday morning, March 28 for oral arguments heard by Chief Judge Albert Diaz, Judge A. Marvin Quattlebaum, Jr. '89, and Judge William B. Traxler, Jr. '73 of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit.
The distractions of cellphones compound a general lack of interest in learning, a new national survey of teachers shows. Student Apathy Is a Big Classroom Challenge, Teachers Say. Cellphones Aren ...
Prediction of fine particulate matter with particle size less than 2.5 µm (PM2.5) is an important component of atmospheric pollution warning and control management. In this study, we propose a deep learning model, namely, a spatiotemporal weighted neural network (STWNN), to address the challenge of poor long-term PM2.5 prediction in areas with sparse and uneven stations. The model, which is ...
The tidal forces on Earth grow as the sun, moon and Earth begin to align, a configuration that can lead to a solar eclipse. But the results of several studies of the relationship between ...