Flood Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on flood.
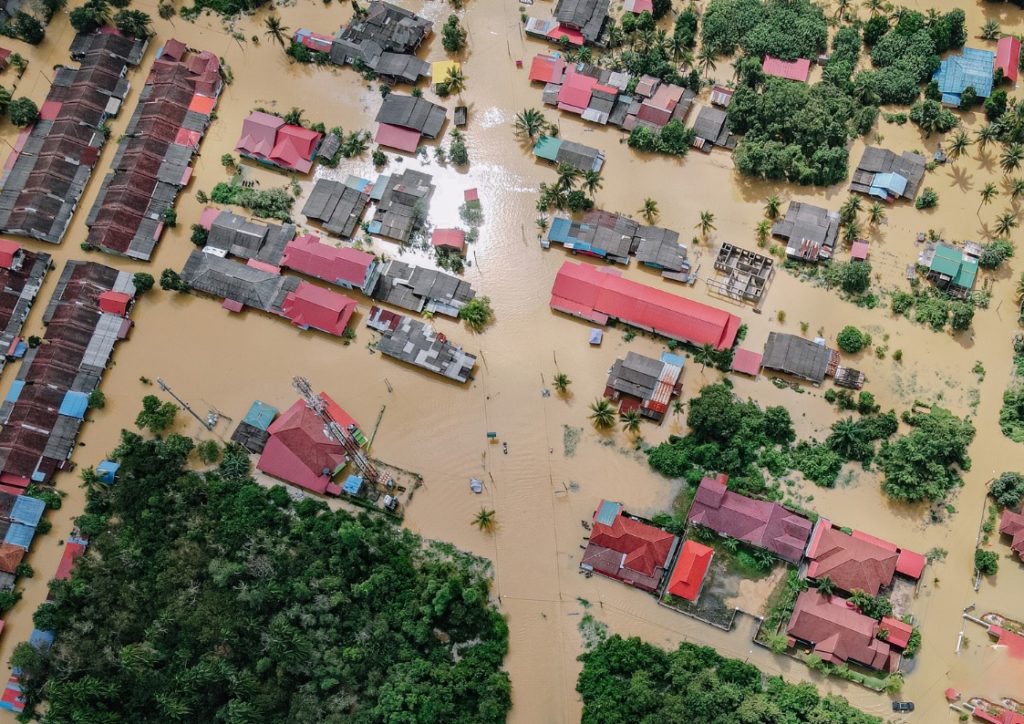
Flood is one of the most dangerous natural disasters. It happens when excessive water is collected in any area. It usually happens due to heavy rainfall. India is highly prone to flood. There are many regions in the country that face this natural disaster because of the overflowing of rivers. Moreover, it also happens because of the melting of snow. Another reason for floods is when the dam breaks down. If we look at the coastal areas, the hurricanes and tsunamis are held responsible for causing floods. In this essay on flood, we will see the prevention and after-affect of flood.

In other words, whatever the cause may be, it is equally dangerous. It has a lot of harmful consequences. Flood damages the living conditions and it takes a lot of time to recover from this disaster. Therefore, the consequences of floods must be known and steps must be taken to prevent it.

After-effects of Flood
Floods interrupt with the day to day functioning of the affected area. The severe floods sometimes cause mass destruction. A lot of people and animals lose their lives due to floods. Several others are injured. Floods also bring a rise in diseases. The stagnant water attracts mosquitoes causing malaria , dengue, and more illnesses.
Furthermore, people face power cuts due to the danger of electrocution. They also have to face expensive pricing. As the supply of food and goods gets limited, the prices naturally grow higher. This creates a big problem for the common man.
Most importantly, the whole country faces economic loss. The resources needed to rescue people and tackle this disaster demands a hefty amount. Plus, the citizens lose their houses and cars which they worked all their lives for.
Subsequently, floods also hamper the environment. It causes soil erosion and this degrades the quality of the soil. We lose out on fertile soil. Similarly, floods also damage flora and fauna. They damage crops and displace trees. Thus, the measure should be taken to avoid these grave consequences.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Ways to Prevent flood
The government and citizens must work together to formulate ways to prevent floods. Proper awareness must be spread about the steps to take when floods occur. Warning systems must be set up so people get sufficient time to save themselves. In addition, areas that are more likely to have floods must have tall buildings above the flood level.

Other than that, dams must be constructed strongly. The use of cheap materials causes dams to break. The government must ensure there is a quality building of dams to prevent floods.
In short, we cannot prevent natural causes like rain and the melting of glaciers. However, we can stop the manmade causes like breaking of dams, poor drainage system, installing warning systems and more. We should take inspiration from countries like Singapore that never experience floods despite having heavy rainfall for most time of the year.
FAQ on Flood Essay
Q.1 what are the consequences of a flood.
A.1 Floods cause immense destruction. They are responsible for the loss of human and animal lives. People lose their homes and cars in floods. They also cause soil erosion and uproot of trees.
Q.2 How can we prevent floods?
A.2 Governments must take up certain measures to prevent floods. We can install flood warning systems. Make people aware of what to do in times of flood. Moreover, we can also build a proper drainage system that will ensure no waterlogging.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

The Many Effects of Flooding
Floods can be destructive to humans and the natural environment, but they also help to drive biodiversity and are essential to the functioning of many ecosystems.
Earth Science, Climatology, Geography, Physical Geography
1931 Yangtze River Flood
In 1931, water overwhelmed the banks of the Yangtze and Huai Rivers, resulting in the Central China flood. Killing at least hundreds of thousands and potentially millions of people, it was one of the worst flooding events in recorded history. Here, people near the Yangtze River are shown.
Photograph from Adrienne Livesey, Elaine Ryder, and Irene Brien

It is hardly surprising that rivers have been an important part of human history: They provide food, freshwater, and fertile land for growing crops. While water is essential to life, it can be a destructive force too. When rivers flood, the effects can be catastrophic. Flooding is one of the most common types of natural disaster, and the results are often fatal. The Central China flood of 1931, for example, was one of the worst flooding events in recorded history. The Yangtze and Huai Rivers broke their banks, killing as many as several million people. The aftermath was devastating; deadly waterborne diseases like dysentery and cholera spread quickly, and those who survived faced the threat of starvation. The human cost of flooding can be large, but events like this have a big impact on the natural world too, and the effects are not always negative. In fact, some ecosystems rely on seasonal flooding to drive ecological processes. Floods Can Harm Wildlife Flooding can have a negative effect on wildlife, causing drowning, disease proliferation, and habitat destruction. In 2012, hundreds of animals, including many vulnerable one-horned rhinos ( Rhinoceros unicornis ), were killed in floods that swamped Kaziranga National Park in the Indian state of Assam. Unpredictable floods can be harmful even to aquatic life. For example, fish can be displaced and their nests destroyed.
Floods Cause Sedimentation and Erosion Floodwater can also alter the landscape, for instance, by eroding riverbanks and causing them to collapse. As floodwater carries material from the eroded banks, it suspends sediment in the water, which can degrade water quality and lead to harmful blooms of algae. Suspended sediment eventually settles out of the water in a process called sedimentation, which can clog riverbeds and streams, smother aquatic organisms, and destroy habitats. Erosion and sedimentation have a more negative impact on ecosystems that are already degraded or heavily modified. Floods Carry Contamination Floodwater can be contaminated with pollutants such as agricultural pesticides , industrial chemicals, debris, and sewage. If contaminated floodwater enters the ocean it can affect water quality and disrupt delicate ecosystems, such as coral reefs. In February 2019, marine biologists feared for the safety of the Great Barrier Reef off the coast of Queensland, a state in Australia, after it was inundated with polluted floodwater. Floods Spread Diseases Floods are the leading cause of weather-related infectious disease outbreaks. Flooding events increase the chance of spreading waterborne diseases, such as hepatitis A and cholera. Receding floodwater can create stagnant pools of water, which provide the perfect breeding ground for mosquitoes, which can transmit malaria and other diseases. Flood events also lead to an increase in some forms of zoonosis , such as leptospirosis. Floods Carry Nutrients While floods bring hazards, they also bring nutrients and essential components for life. Seasonal floods can renew ecosystems, providing life-giving waters in more ways than one. Floods transport vital nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic material, to the surrounding land. When the water recedes, it leaves sediment and nutrients behind on the floodplain. This rich, natural fertilizer improves soil quality and has a positive effect on plant growth, thus increasing productivity in the ecosystem. Ancient civilizations first arose along the deltas of seasonally flooded rivers, such as the Nile in Egypt, because they provided fertile soil for farmland. Floods Recharge Groundwater Floods can replenish underground water sources. Floodwater gets absorbed into the ground then percolates through layers of soil and rock, eventually reaching underground aquifers . These aquifers supply clean freshwater to springs, wells, lakes, and rivers. Ecosystems rely heavily on groundwater during dry spells when it may be the only supply of freshwater available. A good supply of groundwater has a positive impact on soil health and leads to more productive crop and pasture lands. Floods Can Trigger Breeding Events and Migrations Floods can trigger breeding events, migrations, and dispersal in some species. In 2016, thousands of water birds flocked to the Macquarie Marshes in the Australian state of New South Wales. Flooding had filled their wetland habitat for the first time in years, triggering a mass breeding event. In Cambodia, monsoon rains cause an annual flood pulse on the Mekong River that prompts migrations for some animals. The floodwaters cause the Tonle Sap river, which connects the Mekong River to Tonle Sap lake, to reverse its flow, filling the lake. When floodwater enters the lake, it triggers fish migrations, supporting one of the world’s most productive fisheries. Floods Can Boost Fish Stocks Small seasonal floods can be beneficial to native fish stocks and can help those fish outcompete invasive species that are not adapted to the river’s cycles. Sediment deposited on riverbeds during floods can provide a nursery site for small fish. Nutrients carried by floodwater can support aquatic food webs by boosting productivity. Floods Bring Life to Wetlands Wetlands are an extremely important ecosystem; approximately 40 percent of the world’s species rely on them. They filter water, mitigate flooding, and act as a carbon sink . The Okavango Delta in Botswana is a United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Site and one of the world’s largest, most important wetland habitats. The river captures rainfall from far to the north in the highlands of Angola. This causes a flood pulse that replenishes the wetlands at the height of the dry season, providing a lush oasis in the Kalahari Desert. National Geographic Explorer Steve Boyes, with a team of scientists and Explorers, has participated in a series of expeditions to trace the Okavango from source to sand to protect the waters of this unique habitat. Floods are a force of nature, and their consequences, both positive and negative, are strongly felt by affected ecosystems. Floods can be destructive to humans and the natural environment, but they also help to drive biodiversity and are essential to the functioning of many ecosystems. Whether you regard floods as good or bad, one thing is for certain: The world would be a very different place without them.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
January 22, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Climate Change
- Policy & Economics
- Biodiversity
- Conservation
Get focused newsletters especially designed to be concise and easy to digest
- ESSENTIAL BRIEFING 3 times weekly
- TOP STORY ROUNDUP Once a week
- MONTHLY OVERVIEW Once a month
- Enter your email *
What Are the Main Causes and Effects of Floods Around the World?

Floods are among the most devastating natural disasters that occur worldwide, affecting millions of people and causing significant damage to both human settlements and the environment. As our planet experiences the impacts of climate change and human activities continue to alter landscapes, understanding the main causes and effects of floods becomes increasingly crucial. In this article, we delve into the factors that contribute to flooding and explore the wide-ranging consequences it has on our ecosystems and communities.
What Are the Different Types of Floods?
Before we examine the causes and effects of floods, it’s important to note that various types of floods can occur worldwide. There are two types of floods that are most common: flash floods and river floods.
Flash floods, as the name suggests, are the rapid rise of water levels from excessive rainfall in low-lying areas. These weather events are incredibly dangerous and can often lead to fatalities due to their destructive power and incredible speed, often not giving people enough time to escape to higher grounds or adopt protective measures. Flash floods tend to be more common in areas with a dry climate and rocky terrain due to lack of soil or vegetation, which acts as a defence or barrier against torrential rains flowing overland.
River flooding on the other hand, occurs when a river overspills its banks and river waters can no longer be contained within its channel. These events are more common in areas with a wetter climate and have longer rainstorm seasons, as well as areas close to melting snow and ice.
What Are the Main Causes of Floods?
Floods can occur due to several different, and often simultaneous, factors. However, one of the biggest causes of floods, especially in cases of flash floods, is excessive and heavy rainfall. When rainfall in low-lying areas and urban environments fall faster than the ground can absorb, water height rapidly rise, resulting in floods. Extreme rainfall in river courses contribute to flooding as well, as water travels down and overflows riverbanks onto surrounding land.
Sea overflow can also cause floods, in an event also known as a storm surge. This occurs during tropical storms, cyclones and hurricanes, where these types of weather events cause sea water to overflow onto the land in coastal regions. Sea water levels have been recorded to rise as high as 20 feet during storm surges.
Rapid melting of snow and ice similarly causes a surge of sea water, while blocks of melting ice could block the flow of a river, creating a phenomenon known as ice jams.
Dam failures and breakage can also send a powerful and destructive surge of water downstream. One of the most devastating dam failures in history took place in 1889 in Johnstown, Pennsylvania . Several days of extraordinarily heavy rain placed severe pressure on the local dam, causing it to fail and releasing 20 million tons of water to the town, and more than 2,200 people died within minutes.
What Are the Biggest Effects of Floods?
More than 2 billion people worldwide were affected by floods between 1998-2017. And that number continues to climb as occurrences of major flood events become more frequent and severe.
Flooding, especially flash floods, can devastate entire cities and urban environments. Throughout history, many have lost their lives as a result of rapid floods, or events caused by severe flooding such as landslides and collapsed infrastructure.
One of the biggest consequences and effects of floods is that people lose their home and property, and essential buildings and infrastructures such as hospitals and elderly homes are left incapacitated. Loss of power and mobile communication is a common occurrence during floods, which can impact livelihoods and access to safety.
Floods can have huge economic repercussions to a region, as extreme weather events impact key industries and sectors, notably agriculture, fishing, food crops, health, labour and tourism. Studies have found that frequent flooding could shave 11% off a region’s GDP by the end of the century. Countries often take years to recover economically following the loss of resources.
People who live in regions close to rivers, in wetter climates and prone to monsoon seasons are significantly more vulnerable to floods. Many south and southeast Asian countries such as Bangladesh – a third of which was under water at one point in 2020 – and India have been particularly hit hard by flood events in recent years due to their low-lying lands and dense populations.
Consequently, there’s been high rates of mass migration and population displacement over the past few decades, causing overcrowding in urban cities and expanding the urban poor. This leads to potential long-term social inequalities and unrest.
You might also like: 86 Million People Have Been Moving Into Global Flood Zones in the Last Two Decades – Study
Climate Change is Exacerbating the Effects of Floods
Flooding has been made more likely by climate change , according to a 2021 study by climate experts. In the case of Western Europe, downpours in the region, which caused the flash floods that killed nearly 200 people, are now 3-19% heavier due to human-caused warming.
For countries that are already prone to rainy seasons, particularly in Asia, climate models predict climate change will lead to more intense flooding and prolong existing monsoon seasons . A typical monsoon season in Asia lasts from June to September. The effects of climate change could potentially result in an earlier arrival or departure of monsoons, disrupting agricultural and crop production, as well as increasing extreme precipitation over the region as more greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere.
You might also like: Climate Change Made Libya Floods Up to 50 Times More Likely, Study Finds
What Can Be Done?
One of the most salient short-term solutions is for countries, especially those in high flood risk regions, to prioritise investments in flood adaptation strategies. This means building more resilient infrastructure that are designed to withstand floods and water damage.
China, for example, has been investing heavily in ‘sponge city’ concepts , the development of which could potentially help control and mitigate flooding, and recycle rainwater resources and re-instate degraded environments at the same time. Building seawalls can be an effective form of coastal defence and protection in dealing with storm surges and flooding events associated with tropical storms.
Managed retreat, which refers to a purposeful and coordinated movement of people and infrastructure away from high risk areas, is a solution that is worth considering. With more frequent and intense flooding events, forced migration and population displacement is already a growing problem, which as discussed earlier, brings with it a wealth of complex social and economic issues. A managed retreat, which can occur over time and allow systems that account for migrants and displaced people to be in place, can be less traumatic for people and potentially less expensive in the long run.
However ultimately, the most effective way to mitigate climate change and worsening flooding events is to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions. We need to dedicate ourselves to decarbonising transportation and investing a lot more and faster into renewable energy and technologies. While many high income countries such as the US have made net zero goals by 2050 and are pushing for more electric vehicles , a majority of the countries are doing far too little and at too slow a pace to tackle the exacerbating climate crisis.
This story is funded by readers like you
Our non-profit newsroom provides climate coverage free of charge and advertising. Your one-off or monthly donations play a crucial role in supporting our operations, expanding our reach, and maintaining our editorial independence.
About EO | Mission Statement | Impact & Reach | Write for us
About the Author

15 Biggest Environmental Problems of 2024

Water Shortage: Causes and Effects

10 Deforestation Facts You Should Know About
Hand-picked stories weekly or monthly. We promise, no spam!
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Boost this article By donating us $100, $50 or subscribe to Boosting $10/month – we can get this article and others in front of tens of thousands of specially targeted readers. This targeted Boosting – helps us to reach wider audiences – aiming to convince the unconvinced, to inform the uninformed, to enlighten the dogmatic.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Advanced Cutoff
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Advanced Answer Key
- JEE Advanced Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Answer Key
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Asnwer Key 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET DU CSAS Portal 2024
- CUET Response Sheet 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET PG Counselling 2024
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Flood Essay
Floods are natural disasters that occur when a body of water, such as a river or ocean, overflows its banks and spills onto the surrounding land. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including heavy rainfall, melting snow, and storms . Here are a few sample essays on floods.
100 Words Essay on Floods
Floods are naturally occurring phenomena that are caused due to overflowing water bodies. A flood can be just a small occurrence that can cause some travel issues to highly destructive events that can cause significant damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure. In addition to physical damage, floods can also lead to loss of life and can have long-term impacts on the affected communities.

To protect against floods, people can take steps such as building floodwalls and levees and elevating homes and other structures in flood-prone areas. It is also important for individuals to be prepared for floods by having an emergency plan in place and staying informed about potential flooding in their area.
200 Words Essay On Floods
Floods are natural disasters that occur due to overflowing water sources like ponds, oceans and rivers. The reasons for the occurrence of floods can be heavy rainfall, loose soil, melting of snow, breaking of dams etc.
Impact | The impacts of floods can be far-reaching and long-lasting. In addition to physical damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure, floods can also lead to loss of life. Floodwaters can carry dangerous debris and pollutants, making them a health hazard for people and animals. Floods can also have economic impacts, as they can disrupt transportation and commerce, and can destroy crops and other sources of food.
Prevention | People living nearby water bodies take preventative measures to reduce the impact of flood damage. Building elevated homes, planting more trees to soak up an extra amount of water, having an escape plan in case of emergencies etc. It is also important for individuals to be prepared for floods by having an emergency plan in place and staying informed about potential flooding in their area. In the event of a flood, it is important to follow the advice of local authorities and evacuate if instructed.
Overall, floods are serious natural disasters that can have significant impacts on communities. By taking steps to protect against floods and being prepared for them, people can reduce the risks and impacts of this type of disaster.
500 Words Essay on Floods
Floods are a common natural disaster that occurs when excess water overflows onto land that is normally dry. This can happen for a number of reasons, including heavy rainfall, snowmelt, and coastal storms.
Types Of Floods
There are several different types of floods, each with its own characteristics and potential impacts. Flash floods, for example, are caused by sudden, intense rainfall and can happen within minutes or hours. They can be particularly dangerous because they often catch people off guard and can lead to flash flooding in urban areas.
On the other hand, river floods are caused by water flowing over the banks of rivers and streams. These floods can be more gradual, giving people time to evacuate and prepare, but they can also be very destructive.
Coastal floods, also known as storm surges, are caused by strong winds and high tides associated with coastal storms, such as hurricanes. These floods can be extremely destructive, as they can cause not only flooding but also strong winds and waves that can damage buildings and infrastructure.
Biggest Floods Recorded On Earth
One of the biggest floods in history was the 1931 China floods , also known as the Central China Floods . These floods were caused by heavy rainfall and the collapse of the Banqiao Dam. The floods affected an estimated 54 million people and resulted in the deaths of 145,000 people.
Another major flood was the 1993 Mississippi River Flood , which affected parts of the United States, including Missouri, Illinois, and Kentucky . The floods were caused by heavy rainfall and resulted in the deaths of 50 people and caused billions of dollars in damages.
In 1998, the Yangtze River Flood in China also caused widespread destruction. The floods, which were the result of heavy rainfall, affected millions of people and resulted in the deaths of over 4,000 people. The floods also caused billions of dollars in damages.
Another recent and devastating flood was the 2010 Pakistan floods, which affected the Indus River Basin in Pakistan. The floods, which were caused by heavy monsoon rains, affected an estimated 20 million people and resulted in the deaths of over 1,700 people.
Forest To Prevent Floods
Forests play a critical role in preventing floods. Trees and other vegetation in forests can act as natural barriers which absorb water. Hence, reducing the speed of flowing water and thereby reducing the risk of flooding.
When it rains, the leaves and branches of trees absorb a significant amount of water. The roots of trees also help to hold the soil in place, preventing it from eroding and being carried away by the water. This helps to reduce the amount of water that flows over the surface and into rivers and streams, lowering the risk of flooding.
In addition to absorbing water, forests also help to regulate the flow of water by releasing it slowly into rivers and streams. This helps to prevent sudden, large increases in water levels that can lead to flooding. Trees and other vegetation can help to reduce the force of the water and protect against erosion, which can help to minimise the damage caused by floods.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

ReadingJunction
Ultimate hub of educational content (Essay, Speech, Debate, Festivals, Events)
Essay on Flood for Students and Children in 1000+ Words
October 12, 2020 by ReadingJunction Leave a Comment

In this post read an Essay on Flood (Natural Disaster) for Students and Children in 1000+ Words.
Table of Contents
Essay on Flood (1000+ Words)
This essay includes what is flood?, its causes, effect, and preventive measures.
What is Flood?
A flood is a natural disaster that arises due to excessive runoff of water in the rivers due to rainfall . This causes the water of rivers to come out from the edges and flow into the plains. Floods can last from a few hours to a few days, but it can cause great harm to people, money and crops.
Causes of Flood
Among the most severe natural hazards are floods. This happens in every environment where excessive water is stored. Generally, it is heavy rainfall. In India, there is a strong probability of floods.
Due to heavy river rains, several places in the world face natural disaster . Besides, the breaking of the dam is another cause of a flood. Furthermore, this is also triggered by melting ice.
If we aim at coastal regions, floods are liable for hurricanes or tsunamis. We should look at flood avoidance and its long term side-effects throughout this essay about floods. Nevertheless, it really is equally risky, but whatever cause might be.
This has some negative effects. Floods cause harm to living conditions or recovery from this tragedy takes a very long time. The effects of flooding should therefore be understood, and steps should be taken to avoid them.
Effect of Flood
The day-to-day operation of the flood-affected region was disrupted. Extreme floods cause immense devastation often. Owing to flooding, many individuals, or animals risk their lives. Many more are being wounded. Floods raise illnesses, as well. Stagnant weather, due to malaria, dengue, and much more illnesses, attracts insects.
Moreover, due to electrical risks, individuals face power outages. They face expensive costs, too. Prices inevitably rise as the availability of food and products become reduced.
This, for the average man, is a big issue. Most significantly, economic losses are suffered by the entire world. To save lives and deal with this tragedy, a huge amount of resources are needed. At the very same time, people are losing their homes or their vehicles, which they have dedicated all their lives to.
Floods also ultimately damage the climate. This triggers soil erosion which degrades the consistency of the soil. On a fertile planet, we are destroyed.
Floods also do damage to fauna and flora in the same way. Crops are destroyed, & trees are displaced. Steps to prevent these serious effects should also be taken.
Ways to Prevent flood
To devise solutions to avoid flooding, government and people must work together. Proper knowledge of these steps can be taken and disseminated in the aftermath of a natural disaster.
In order for people to get enough time to defend themselves, an alert system must be established. Furthermore, areas more vulnerable to flooding must have elevated buildings just above the point of flooding.
In addition, an effective system for processing excessive water due to bad weather should be usable. Excess water can avoid this. Reinforcing the drainage scheme is among the most critical steps. This will eliminate water-logging, to prevent flooding.
The dams must, however, be heavily built. The use of inexpensive materials breaks dams must be applied and government should ensure that the efficiency of dams is designed to stop flooding.
We have split the causes of floods into two stages viz: organic and inorganic floods. First, natural floods would be addressed.
Natural floods
Floods are called natural floods due to natural factors.
1. Excess of rain – often at one location there is a lot of constant rainfall due to that there is water logging all over, and it comes in the form of flooding in a certain period.
2. Cloud Burst -A large volume of water that flows in the next few hours due to bursting of a cloud, because from which the water flows at a high pace as well as a flood situation occurs, the clouds mainly burst and in mountain terrain. Due to thunderstorm, the Uttarakhand region is flooded every other year in their region.
3. Melting of ice from the glacier- The glaciers are starting to melt even more snow owing to the increase in the Earth’s temperature that causes the water to fall from the mountains at a high velocity so this water has become so high. That one can easily knock out every town or village and fully submerge it.
4. When rivers are overflowing- A significant volume of drainage into the rivers is caused by excess rainfall and melting snow, allowing the water to abandon its course and flow around rather than flood its lowlands of cities and villages near the river , it goes.
5. Sea Flood – A tsunami is often considered the first flood of water. This happens when in certain areas of a sea, a cyclonic storm or even a powerful earthquake happens, due to that, high waves increase, or the seawater floods the villages and cities. This refers to areas for flooding. Because of this, many coastal communities of the sea are impacted very badly. Sea storm waves could be as higher than 10 feet, and that’s much more than the height of every building.
Unnatural floods
The work undertaken by human’s triggers unnatural floods are:
1. Dam Breakdown – Large reservoirs are designed for water storage by humans; however, the dam is not reinforced due of corruption and bad design that breaks up a dam full of thousands of liters of water in the next few years.
There is a heavy flow of water with this and the areas from around the dam were covered in water. Suddenly, the ward arrives, so citizens do not get an opportunity to regain, and there is further loss of life or property.
2. Flooding due to Global Warming – Global Warming This scenario has been produced by humans just because humans are harvesting indiscriminate trees, and also spreading a huge amount of pollution .
Since the global climate is rising while at the same time that Earth’s climate is also shifting because there is a lot of rain for certain areas, there is a lot of rain in certain areas and because of the increase in the temperature of the Earth, the ice mostly on glaciers Millions of liters of water accumulated in the form begins to melt because of the water crisis.
3. Plastic pollution – A large volume of plastic is often used in India, and this plastic is dumped in such open areas, however, this plastic is stuck in the hair created to drain the water because the water may not get in the hair when it rains as well as the flood situation occurs.
10 Lines on Flood
- The flood is an immense quantity of water that overflows covering a wide region that causes damage.
- Not only is the flood devastating a vast city, but it also takes several lives or destroys property.
- Each year, many regions of the world are hit by flooding, taking lots of lives.
- Lead to increasing rainfall or a lack of proper sewage system inside an area, flooding occurs.
- In an area that causes double harm, floods often occur like an after-effect of a horrible cyclone.
- The farmers have to be the worst impacted citizens of the flood as flood kills their fields and also their land’s productivity.
- Flood water obtained at a specific location allows individuals to have different kinds of diseases.
- When the flood situation is serious, all the stores are closed, affecting the availability of essential products.
- In order to reduce the effects of flooding, the government must develop a strong drainage system.
- Early warning implementation must be carried out, and individuals are sent to safe areas until floods occur.
In short, natural factors, such as rain or melting glaciers, could not be avoided. We may escape human-made triggers, however, like dam breakage, bad drainage systems, installation of alarm systems, and much more. We must draw inspiration in countries such as Singapore that, for much of the year, do not experience floods despite heavy rain.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Copyright Protection
All articles on this website are Copyright Protected. Copying or Using any material in any form is a serious offense.
Important Links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Flood — The Flood: Reflection and Mitigating the Impact
The Flood: Reflection and Mitigating The Impact
- Categories: Flood Natural Disasters
About this sample

Words: 652 |
Published: Mar 16, 2024
Words: 652 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
The impact of floods, factors contributing to floods, measures to mitigate flood effects.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Environment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 371 words
1 pages / 574 words
2 pages / 716 words
1 pages / 384 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Flood
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 'Fifth Assessment Report (AR5).' IPCC, 2014.Kwan, M. P., & Wong, M. S. 'Climate Change and Air Quality in Urban Areas: A Review.' Climatic Change, vol. 125, no. 4, 2014, pp. [...]
Climate change is an ever-present global challenge that continues to have far-reaching impacts on our planet. One of the most pressing consequences of climate change is the increase in environmental disasters, particularly [...]
The 2023 Italy floods were a catastrophic event that had devastating effects on the country's environment, economy, and society. In this essay, we will analyze the immediate and long-term impacts of the floods and evaluate the [...]
The 2022 New York flooding event has been a wake-up call for many, signaling the urgent need for climate action and resilience building in the face of extreme weather events. This essay will delve into the aftermath of the [...]
Floods are natural occurring processes that are difficult to prevent but can be managed to reduce its social and economic impacts. Flooding is a threat to life and leads to damage of property. Therefore, it is very important [...]
Flood is one of the main and most frequent natural disasters in the world (Jiang et al. , 2006). As revealed by World Meteorological Organization (WMO, 2014), storms and floods accounted for 79 percent of total number of [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Essay on Flood
Students are often asked to write an essay on Flood in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Flood
Introduction.
A flood is a natural disaster that occurs when water overflows onto dry land. This can happen due to excessive rainfall, melting snow, or dam failure.
Causes of Floods
Floods often occur due to heavy rainfall. If the ground cannot absorb all the water, it overflows into nearby areas. Melting snow can also contribute to floods.
Effects of Floods
Floods can cause severe damage. They can destroy homes, crops, and infrastructure. People may lose their possessions and, in severe cases, their lives.
Prevention and Control
We can prevent floods by building dams and levees. It’s also important to maintain a healthy environment, as deforestation can lead to floods.
Also check:
- 10 Lines on Flood
- Paragraph on Flood
- Speech on Flood
250 Words Essay on Flood
Floods represent one of the most destructive natural disasters, having catastrophic effects on human life, infrastructure, and the environment. They are typically caused by excessive rainfall, rapid snowmelt, or dam breakage and can occur in virtually any geographical location.
Causes and Types of Floods
The primary cause of floods is the excessive accumulation of water, either from heavy precipitation or from a blockage in the water flow. There are several types of floods, including river floods, coastal floods, and flash floods. River floods occur when the capacity of a river channel is exceeded, while coastal floods are caused by a storm surge or high tide. Flash floods, on the other hand, are sudden and extreme floods usually caused by heavy rainfall.
Impacts of Floods
The impacts of floods are far-reaching. They can cause loss of life, property damage, and displacement of people. Infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings can be destroyed, disrupting daily life and economic activities. Additionally, floods can lead to waterborne diseases and contaminate drinking water supplies.
Flood Management and Mitigation
Effective flood management involves a combination of structural and non-structural measures. Structural measures include constructing dams, levees, and floodwalls. Non-structural measures involve land use planning, flood forecasting, and public education.
While floods are natural phenomena, human activities often exacerbate their impacts. Therefore, understanding the causes and effects of floods and implementing effective flood management strategies is crucial for reducing their destructive potential and ensuring sustainable development.
500 Words Essay on Flood
Floods, one of the most common and destructive natural disasters, are a powerful force of nature that have shaped human civilizations and the natural environment for millennia. They are a result of excessive rainfall, rapid snowmelt, or a sudden release of water, causing a surge of water to overflow onto normally dry land.
The Causes of Floods
The primary cause of floods is excessive rainfall, particularly when it falls over saturated soil. The water table, already high due to prior precipitation, cannot absorb more water, leading to surface runoff that ultimately causes flooding. Rapid snowmelt and ice jams in rivers can also lead to floods, with the sudden influx of water overwhelming the river’s capacity.
Human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, also contribute to flooding. Deforestation reduces the land’s capacity to absorb water, increasing surface runoff. Urbanization, with its concrete landscapes, limits the soil’s ability to absorb water, enhancing the risk of flash floods.
The Impact of Floods
Floods have both destructive and constructive impacts. On the destructive side, floods can cause loss of life and property, damage infrastructure, and lead to disease outbreaks due to contaminated water supplies. They can disrupt economies, displace populations, and cause significant psychological distress.
However, floods also have a constructive side. They deposit nutrient-rich silt on floodplain areas, enhancing soil fertility and supporting agricultural productivity. They replenish wetlands, supporting biodiversity, and play a crucial role in the ecological functioning of river corridors.
Flood Management
Effective flood management requires a combination of structural and non-structural measures. Structural measures include the construction of levees, reservoirs, and floodways to control floodwaters. Non-structural measures involve land use planning, flood forecasting and warning systems, and public education about flood risks and responses.
Recently, there has been a shift towards more sustainable and integrated flood management approaches. These approaches emphasize the importance of living with floods and harnessing their benefits, rather than solely focusing on flood prevention and control.
Floods are a testament to the power of nature and our vulnerability to it. Understanding the causes and impacts of floods, and implementing effective flood management strategies, is crucial for reducing flood risks and harnessing the benefits of floods. As climate change is likely to increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, including floods, it is more important than ever to build our resilience to floods.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Railway Station
- Essay on An Hour at Railway Station
- Essay on A Scene at Railway Station
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Flood Essay

Essay on Flood
Students who are looking for a good essay to study on the topic of flood should not be worried anymore. That is because Vedantu has come up with a sample essay on the flood that students of any class of any educational board can refer to and study from. This essay is designed by subject experts in English who work with Vedantu to create more like these study materials on a regular basis.
These study materials are also updated and refreshed once in a while to make sure they are still relevant and up to date. Relevancy of the content is the most significant quality that these subject experts at Vedantu understand. And to help every student in this country, these study materials are made and maintained on a regular basis.
Why choose Vedantu?
If any educational board (including CBSE, ICSE, state board, etc.) makes any update in their guidelines or paper pattern, these subject experts at Vedantu quickly study the new guidelines and update these study materials at a moment's notice. All of this extra care is taken to make sure the content stays relevant because Vedantu wants to serve every student in the country with top-quality study material.
If students of any class and any educational board (including CBSE, ICSE, state board, etc.) learn from these study materials, they can get good marks and can score a high rank in any examination or even any small test. All they have to do is to read the sample essay provided by Vedantu on the topic of floods.
Students can read it online on the page or can download it so that they can access it whenever they need it. This study material is available in a pdf format for downloading. Being in a pdf format, students can access it from any device (like mobile phones, laptops, personal computers, or even tablets) To download, students should have to sign in on the page with their Gmail ID after clicking the download link provided on this website.

FAQs on Flood Essay
1. What Are the Consequences of Floods?
The damage caused by a flood is up to 90% when compared to other natural disasters. Major flooding causes loss of human and animal lives, they also cause severe damage to economic infrastructures. Floods also cause severe damage to government buildings and public properties.
2. How Do Satellites Help During Floods?
Weathering satellites play an important role in monitoring flood situations over a large region and detecting floods. At ISRO (Indian space research organization) Optical remote sensing from geostationary platforms helps in providing rapid and valuable information on cloud patterns and rainfall patterns for a particular area.
3. Is Vedantu's sample essay on floods PDF costly?
The brief and one-word answer to this question is, no. It is not costly. In fact, it is completely free of cost for students to access or even download. Almost all of the study materials students can find on Vedantu's website is completely free of cost and not for sale. It is open for everyone to access or download. Students don't need to pay any amount to access these study materials. They can just visit the website or download Vedantu's app to be able to access it.
4. Is Vedantu's sample essay on floods PDF downloadable?
To answer this question in one word, yes, this study material is downloadable. Students can click on the provided link on this page to download it. This link is in the form of a blue button with the text "Download PDF" written on it. After clicking on the provided download link, students will be asked to provide their Gmail ID to sign in on Vedantu's portal. After signing in, students can access the pdf version of the sample essay on floods from their mobile phones, laptops, personal computers, or tablets.
5. Why is it necessary to learn flood management in school?
By teaching the topics like flood management or disaster management in schools, the students will be prepared for almost any type of natural or man-made disaster. It is entirely clear that teaching students about managing these tough times and helping others is a great way to create leaders. These young minds learning leadership from such a young age can really be the most important asset to the country. That is why teaching flood management or disaster management in schools is necessary.
6. Can I use this essay on flood for my test or examination?
Yes, students can use this sample essay for academic application. These essays are designed by experts working at Vedantu. These experts are well versed in English and write essays in a manner that is most suitable for academic success. Also, these essays are completely up to date and relevant to the paper pattern followed by these educational boards. These essays are created in a way that will be helpful for students to score good marks in the examination.
7. Is floods a big problem in India?
Yes, floods are a big problem in India. In fact, it is considered one of the most common natural disasters, if not the most common natural disaster in India. The heavy rivers like Brahmaputra or others from any part of the country almost always end up flooding the nearby areas in monsoon. Amongst a few causes of floods are extreme precipitation, unplanned urban growth, degradation of the environment, frequent changes in monsoon etc. The most flood-prone areas in India are Punjab, Haryana, Gangetic plains, etc.

Russell Millner/Alamy
Defend Our Planet and Most Vulnerable Species
Your donation today will be triple-matched to power NRDC’s next great chapter in protecting our ecosystems and saving imperiled wildlife.
Flooding and Climate Change: Everything You Need to Know
More communities—both coastal and inland—are finding themselves underwater. Extreme weather, sea level rise, and other climate change impacts are increasingly to blame.
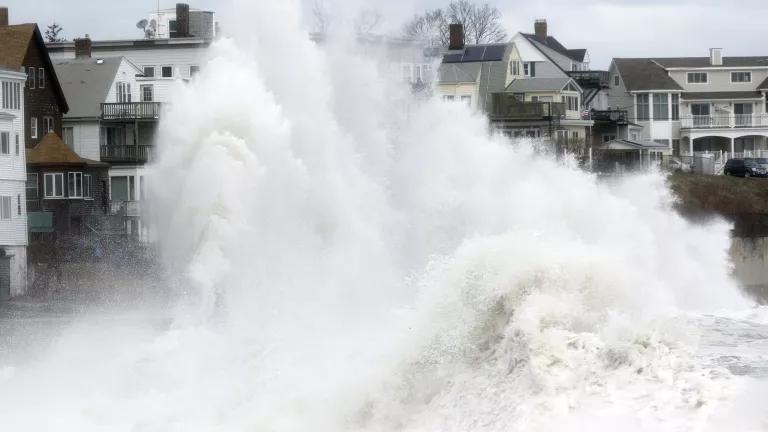

A large wave crashes into a seawall in Winthrop, Massachusetts, a day after a nor'easter in 2018.
AP Photo/Michael Dwyer
- Share this page block
Floods are already the most common and among the most deadly disasters in the United States. As global warming continues to exacerbate sea level rise and extreme weather, flood-prone areas around the country are expected to grow by nearly half in just this century. Here’s how climate change plays a role in flooding and how we can better keep our heads above water.
Flooding facts and causes
Climate change and flooding, consequences of flooding, flood preparation and prevention, what causes a flood.
A flood, put simply, is the accumulation of water over normally dry land. It’s typically caused by the overflow of coastal or inland waters (like rivers and streams) or by an unusual accumulation of water from heavy or prolonged rains, storm surges, or sudden snowmelt. Often, the ways in which we manage our waterways (via dams, levees, and reservoirs) and the alterations we make to land also play a role in flooding. Increased urbanization, for example, adds impermeable surfaces (think roads and parking lots), altering natural drainage systems. Areas can be especially prone to flooding when stormwater infrastructure isn’t maintained or homes are built in areas susceptible to flooding known as floodplains. More and more, flooding factors are also linked to climate change.
Major types of floods
River flooding This occurs when a river or stream overflows its natural banks and inundates normally dry land. Most common in early spring, river flooding can result from heavy rainfall, rapidly melting snow, or ice jams. According to the 2018 study "Estimates of Present and Future Flood Risk in the Conterminous United States," published in the journal Environmental Research Letters , more than 40 million U.S. residents are at risk from flooding along rivers and streams. And even a single episode can wreak havoc on a massive scale: For instance, in 2019, a slow-motion disaster of intense spring flooding swelled the Arkansas, Mississippi, and Missouri rivers. Hundreds of miles of levees were topped or impaired, destroying homes and supersaturating cropland. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the inland flooding caused $20 billion in damage. Some of these losses stemmed from the impact to farmers who could no longer plant or transport their crops.
Coastal flooding More than half of the U.S. population lives or works in areas susceptible to coastal flooding, which happens when winds from a coastal storm, such as a hurricane or nor’easter, push a storm surge (essentially, a wall of water) from the ocean onto land. A storm surge can produce widespread devastation, like that seen around New York and New Jersey when Hurricane Sandy arrived during high tide .
There are also increasing numbers of shallow, nondeadly floods caused by higher sea levels. These high tide floods (also known as “nuisance” or “sunny day” floods) occur when the sea washes up and over roads and into storm drains as the daily tides roll in. In places like Miami, increased nuisance flooding is raising concerns over climate gentrification , as wealthier residents looking to settle on higher ground are pricing out historically underserved BIPOC communities.
Flash floods These quick-rising floods are most often caused by heavy rains over a short period—usually six hours or less. Flash floods can happen anywhere, and low-lying areas with poor drainage are particularly vulnerable. Also caused by dam or levee breaks or the sudden overflow of water due to a debris or ice jam, flash floods combine the innate hazards of a flood with speed and unpredictability. That’s why they’re responsible for the greatest number of flood-related fatalities. In late 2022 and early 2023, California was hit by deadly flash floods during powerful wintertime atmospheric rivers, which may become more powerful as climate change increases the amount of moisture they can hold.
Urban flooding The term urban flooding refers specifically to flooding that occurs when rainfall—not an overflowing body of water—overwhelms the stormwater drainage capacity of a densely populated area. In 2021, Hurricane Ida, strengthened by warm air, shattered records across the Northeast. In New York City, the deluge made rivers of impermeable streets and subway stations. Eleven people living in basement-level apartments drowned as the floodwaters—with nowhere else to go—swiftly overwhelmed below-ground spaces.
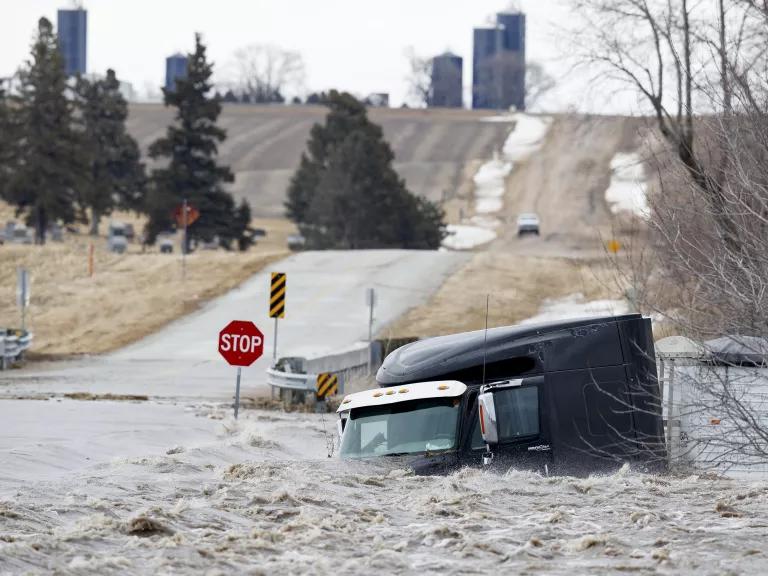

A tractor trailer is swept off the road by floodwaters in Nebraska in 2019.
Ryan Soderlin/Omaha World-Herald via AP
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has found that climate change “has detectably influenced” several of the variables that contribute to floods, such as rainfall and snowmelt. In other words, while our warming world may not be the only or most direct cause of any given flood, it exacerbates many of the factors that increase flood risk. That’s why mitigating climate change—and particularly, limiting global average temperature rise to within 1.5 degrees Celsius in this century—is an important way to avert some of the worst scenarios for sea level rise and escalating flood risks.
How does climate change lead to flooding?
These are some of the key ways that climate change increases flood risks.
Heavier precipitation A warmer atmosphere holds—and subsequently dumps—more water. As the planet has warmed by 1.9 degrees Fahrenheit since the preindustrial revolution era, the United States has also become about 4 percent wetter, according to the federal Climate Science Special Report. The same report says that heavy precipitation events are projected to increase by 50 percent to as much as three times the historical average in just this century. This includes extreme weather like atmospheric rivers, which are air currents that become heavy with water from the tropics. Meanwhile, in regions with significant seasonal snowmelt, hotter temperatures can trigger more rain-on-snow events, with warm rains inducing faster and earlier melting— a phenomenon playing out in the western United States.
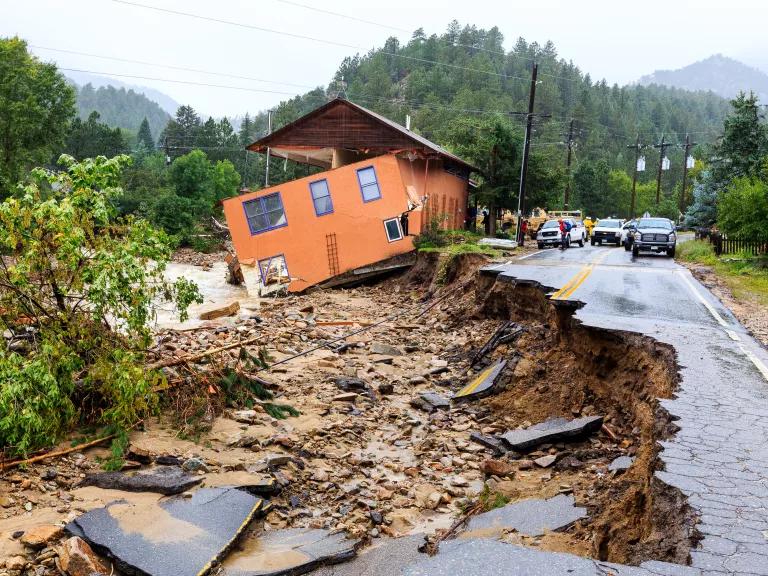

A building and road severely damaged by flooding in Jamestown, Colorado, in 2013
Steve Zumwalt/FEMA
More-frequent hurricanes Climate change is increasing the frequency of our strongest storms, which bring greater rains, including in places not known for flooding. In August 2023, Tropical Storm Hilary—the first storm of its kind to hit the West Coast in 84 years—broke rainfall records in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, and Oregon. Hurricane Harvey, which made landfall as a Category 4 storm in 2017 and soaked Houston homes and businesses with catastrophic floods, was the nation’s wettest storm in nearly 70 years. Researchers estimate that Hurricane Harvey dumped as much as 38 percent more rain than it would have without climate change. Just a month after Harvey, Hurricane Maria hit Dominica, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. The storm produced the most rainfall in the area of any weather event since 1956 and exposed the inadequacy of U.S. policies to respond to disasters.
According to the IPCC, future hurricanes are expected to be as much as 37 percent wetter near their centers and about 20 percent wetter as much as 60 miles away. In the Atlantic basin, an 80 percent increase in the frequency of Category 4 and 5 hurricanes (the most destructive) is expected over the next 80 years. And it’s not only the most severely rated storms that bring the greatest flood impacts; in fact, the rating system the government uses to categorize the severity of storms is based solely on wind speed, not rainfall—so even unrated storms can unleash lethal amounts of water.
That said, gustier winds can whip up greater storm surges, which are already higher because of sea level rise. It was Hurricane Katrina’s 28-foot storm surge that overwhelmed the levees around New Orleans in 2005. Winds can also increase the destructiveness of waves, causing storm surges to get bigger and penetrate further inland.
Higher seas As ocean temperatures rise and the glaciers and ice sheets melt, global sea levels are rising —and directly contributing to coastal flooding problems. According to the Fourth National Climate Assessment, our oceans are approximately seven to eight inches higher than they were in 1900. The IPCC predicts seas around the world will rise anywhere from just under one foot to more than three and a half feet above 2000 levels by century’s end. NOAA’s projections also show that, due to regional factors such as currents bringing water to coastlines, areas along the East Coast could experience seas rising 2 feet higher as early as 2050. By then, damaging coastal flooding is expected to occur 10 times as often as it does today.
In addition to amplifying storm surges, sea level rise increases high tide flooding, which, according to NOAA, has doubled in the United States over the past 30 years. For example, by 2045, Charleston, South Carolina, could see as many as 180 tidal floods per year , compared with just 11 in 2014.
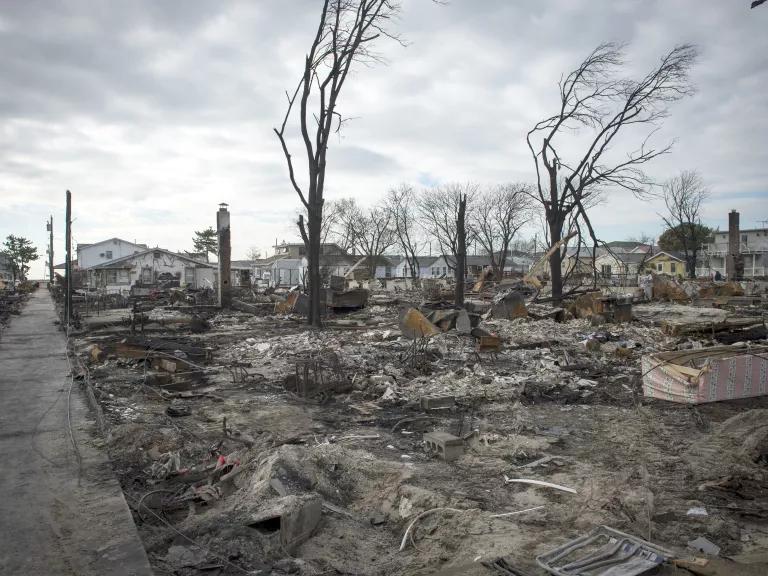

More than 100 houses burned down in Breezy Point, New York, as floodwaters isolated the community from fire and rescue workers after Hurricane Sandy.
U.S. Navy photo by Chief Mass Communication Specialist Ryan J. Courtade/Released
When flooding inundates a home or community, it upends lives. It’s important to consider flood preparation before disaster hits by doing things like signing up for alerts, packing an emergency supply kit, and researching flood insurance options.
But the impacts of flooding go far beyond our own homes. Repairing and replacing flood-damaged roads, bridges, utilities, and other public infrastructure carry enormous costs. Between 2007 and 2017, the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) paid an average of $2.9 billion per year to cover flood-related losses, with individual years often costing far more. Within two months of Hurricane Ian making landfall in Florida in 2022, the NFIP had received 44,000 flood claims from property owners. These types of estimates leave out the many people who don’t have insurance, who aren’t eligible for government disaster assistance, or who have needs above what government aid will cover.
Flooding also brings contamination and disease. Floodwaters can carry raw sewage , leaked toxic chemicals, and runoff from hazardous waste sites and factory farms. They can pollute drinking water supplies and cause eye, ear, skin, and gastrointestinal infections. When floodwaters recede, bacteria and mold may remain , and residents may suffer from mental health problems and lost business or wages.
As with many natural hazards, it is most often lower-income people, people experiencing homelessness, the elderly, and communities of color who suffer the greatest harm. These populations are least likely to have flood insurance , access to transportation during an evacuation, cash on hand, or the ability to relocate—and the structural inequities of the past and present mean they are more likely to be in harm’s way. In August 2022, flash flooding in Jackson, Mississippi, caused the city’s main water treatment plant to fail, leaving the 150,000 residents of the majority-Black city without safe water to drink, bathe in, or cook with. In the case of Jackson and many U.S. cities with similarly outdated infrastructure , flood damage was exacerbated by existing issues, including poor oversight, lack of local resources and capacity, and other unjust racial and economic disparities.
Entirely preventing floods isn’t possible. But there are steps that can be taken to lessen their devastation, like flood-proofing your home , taking personal safety precautions , and advocating the federal government to revamp its approaches to flooding, both before and after it occurs.
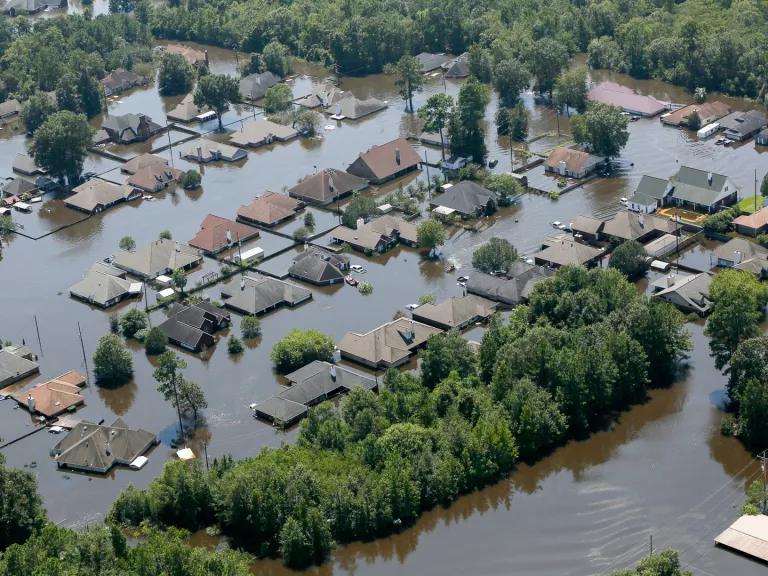

A neighborhood in Port Arthur, Texas, flooded by Hurricane Harvey in 2017
Staff Sgt. Daniel J. Martinez/U.S. Air National Guard
Updating FEMA's flood maps
Mitigating potential loss from future floods requires knowing where floods are most likely to occur. In the United States, this information is provided by FEMA, which produces maps of the nation’s flood zones. Its NFIP relies on these maps to assess flood risk, determine insurance rates, and establish floodplain management standards.
FEMA flood maps depict the high-, moderate-, and low-risk flood zones of communities nationwide and can be found at FEMA’s Flood Map Service Center . High-risk areas, often referred to as floodplains, are regions with a 1 percent (1 in 100) chance of being inundated by river or stream floodwaters of a certain magnitude in any given year. (The term 100-year flood refers to this, and does not mean a flood that’s expected to occur just once every 100 years.) But even a 1 in 100 chance of flooding each year equates to about a one in five chance that a home will flood at some point over the life of a 30-year mortgage. And FEMA’s moderate- to low-risk areas aren’t entirely safe from flooding, either: Properties in these areas still account for more than 20 percent of NFIP claims.
Flood risks change as land use and other factors change. That’s why keeping flood maps up-to-date is critical. But despite a requirement that FEMA reassess its maps every five years, nearly 60 percent are out of date—some, by decades. When Hurricane Sandy hit in 2012, for example, the flooding covered an area that was 65 percent larger than the flood-vulnerable area identified by FEMA maps.
FEMA’s maps also typically fail to take into account the effects of global warming, such as sea level rise . Instead, they rely on historical data to determine future flood hazard projections. This can cause officials to designate areas as being “safe” for development today, even when they are at risk of serious floods tomorrow. In 2021, NRDC and the Association of State Floodplain Managers jointly petitioned FEMA to update its standards to reflect the new climate reality. After all, FEMA is required under law to use the best available science in its maps and standards. Among the petition’s requests: all new or substantially improved structures must be elevated higher than the level of a 100-year flood; all new and revised NFIP floodplain maps must depict how the floodplain will change over time, especially concerning sea level rise; homeowners seeking to retrofit their homes for the new climate reality should have easier access to NFIP funding.
Among other things, FEMA’s floodplains determine how and where homes and other structures will be built, as well as who is required to purchase flood insurance. (Coverage is mandatory if you live in a floodplain and have a federally backed mortgage.) The problem is, once again, that many of FEMA’s mapped floodplains are inaccurate . For instance, during Hurricane Harvey, nearly three-quarters of Houston’s flood-damaged buildings sat outside of FEMA’s identified high-risk area. According to one NOAA analysis: Greater rainfall has made what used to be a 100-year flood event in Houston, by FEMA’s standards, more like a 25-year event.
Understanding your home's flood risk
Flooding is a factor in hundreds of billions of dollars of disaster-related property damage in the United States, with many homes being repeatedly damaged . Just one inch of flooding could cost the average homeowner $25,000 in damage . But typical homeowners’ and renters’ insurance fails to cover flooding and less than 4 percent of homeowners have flood coverage. That means the vast majority of Americans must take out loans or pay out of pocket to repair or replace damaged items.
Finding out if a property is flood-prone can also be difficult . Many states have no legal requirements that a seller disclose a property’s history of flood damage to a buyer or that a landlord tell a prospective renter. While potential homebuyers should look at FEMA’s flood history maps, there’s a more low-tech option: Introduce yourself to your prospective neighbors and ask them about flooding in the area.

This Highlands, New Jersey, home was elevated prior to Hurricane Sandy and received only minor damage.
Rosanna Arias/FEMA
For residents of repeatedly flooded homes, relocation may be the best option. But a wide array of measures exist to prevent or reduce flood damage when that’s not possible. These include keeping gutters and drains free of debris; installing a sump pump for crawl spaces and basements; adding check valves in sewer lines to keep floodwater from backing up into the drains of your home; and safeguarding equipment by elevating furnaces, water heaters, electrical systems, generators, and air-conditioning units above flood levels. More drastic retrofits might be needed in areas with regular flooding, including raising the entire structure of a house.
Boosting local resilience
Flood resiliency can come from water-smart improvements to buildings and green infrastructure , restored wetlands and other natural barriers, updated FEMA maps that reflect new climate realities, and an overhaul of the NFIP to help more homeowners relocate to higher ground. One promising update is President Biden’s executive action to reinstate the Federal Flood Risk Management Standard , which includes commonsense measures such as requiring FEMA to rebuild flood-damaged public infrastructure like police stations, schools, and hospitals to be safer. (President Trump had scrapped the standard in 2017.)
According to a Pew poll, nearly 75 percent of U.S. voters support these measures. For one thing, they can save enormous amounts of money: For every $1 invested in riverine flood mitigation, taxpayers and the federal government save $7 in recovery costs. Moreover, such measures increase the odds that millions more people will stay safe—and dry.
In addition to securing your home, you can help secure your community. Checking in on your neighbors, sharing information, and determining how you might be able to help each other in an emergency are important components of disaster preparedness.
This story was originally published on April 19, 2019, and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.

Related Stories

Mapping Urban Heat Islands Is Helping These Neighborhoods Adapt

What Are the Solutions to Climate Change?

What Is Climate Gentrification?
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding
🏆 best flood topic ideas & essay examples, 📌 simple & easy flood essay titles, 👍 good essay topics on flood, ❓ research questions on flooding.
- Natural Disasters: Earthquakes, Floods and Volcanic Eruption This is due to the relationship between an eruption and the geology of the area. It was observed that the mountain swelled and increased in size due to the upward force of magma.
- Flood Damage by Hurricane Maxine in Charleston The role of the mayor and his dignitaries is to determine the duration and level of use of resources by the city.
- The Strategies of Flood Management However, it would be the most beneficial to implement these methods while planning the use of the land; for this reason, management is important.
- Sri Lanka Flood Disaster Preparedness From these findings, it is evident that floods are the major concerns for the disaster management center, with the recent damages being witnessed towards the end of 2012 and the beginning of the year 2013.
- Floods in Los Angeles and Disaster Response The Los Angeles local government is set to respond and control the effects of floods. Therefore, the local government and citizens have set aside adequate resources to respond to the disaster.
- A Climate Economics Issue: Increased Flood Risks There is a number of flood management plans in the United Kingdom for rivers where risks are known, such as the Anglian River basin.
- The Louisville Flood Photo by Margaret Bourke-White The peculiarity of this photo is that it shows the contrast between the black people standing in line and the white ones painted on the placard.
- The Devastating Flood of 1993: Lessons Learned In order to understand the causes and consequences of the flood that occurred in the summer of 1993, it is necessary to define the meaning of the concept of flood.
- Ethical News Coverage: Indian Floods 2020 As part of the assessment of the consequences of reporting these events, it should be noted that the materials presented can attract public attention to help people in the affected areas, which is important for […]
- Addressing the Threat of Flash Flood to Birmingham, Alabama The purpose of the work is to identify the key stages of threat addressing, including mitigation steps, preparedness and communication mechanisms, and response and recovery measures to address the outcomes of such disasters.
- The Flood Stories in Different Cultures The scientific community recognizes that the oldest flood myth known to humanity is the Epic of Gilgamesh, which tells the story of Utnapishtim, who attained immortality by escaping from the flood on a ship.
- Nova Killer Floods Documentary Review Flood is a phase of the water regime of the river, which is repeated every year at the same time of year, is characterized by the highest water content, increased and prolonged rise and fall […]
- Floods in the City of Austin, Texas on October 30th, 2013 The catastrophic consequences of the devastation in Central Texas and, in particular, in the city of Austin, were caused by flooding.
- Disaster Management in the Flood Scenario In such a case, the authorities and residents should adopt disaster prevention and preparedness strategies to minimize impact and adequately brace for the expected flood magnitude.
- Hydrology Methods: Flood Risk Management Digital spatial information modelling and the integration of the data and information used in the decision-support system illustrate the technical basis of the paper.
- A Flood Insurance Program in Canada: The Way to Protect Lives and Homes Floods are the major source of property loss: according to the analysis made by Munich, insurance companies do not want to take all the bills they get and ignore the majority of them.
- Flood Effects That Occurred in July 2007 at Sheffield The report, therefore, entails in detail the immediate as well as the significant risks and losses caused by the flood, the factors contributing to the occurrence of floods, identification of all the agencies which were […]
- Environmental Management: Floods Management Systems Considering the significance of environmental protection in the case of floods, the present report provides a detailed overview of such natural disasters in terms of contributory causes, impact, risks, and the role of environmental management […]
- Minimizing Flood Fatalities in Canada The main goal of this study is to compile more details in regarding flood fatalities in Canada which may be useful in avoiding and preparing for flood related disasters.
- City of Jeddah’s Flood: Cause and Disastrous Effects Jeddah is a city in Saudi Arabia found in the western region.and the it is a flat, low- lying ground next to the Red Sea.
- Great Flood in Mississippi River Basin: Major Factors Mississippi River, the longest river in the United States and, with its extensive offshoots, is one of the most important river systems of the world.
- Floods: Structural vs. Non-Structural Solutions The occurrence of hazards disorients the lives and experiences of many people. The selected community can mitigate this hazard through the use of non-structural and structural solutions.
- The Ancient Near East: Civilization of Mesopotamia and Great Flood The Great Flood in Genesis and the Epic of Gilgamesh both depict the flood, the boat, the God of gods, and persons responsible for preserving humanity.
- Floods, Technology and Price Ceiling in the Market From the graph, assuming that the equilibrium price in the fruits and vegetable market was EQ0, the floods destroy the products in the fields and this causes a shift of the supply curve to the […]
- Flood Disaster Recovery Plan and Stakeholders The scope of this document: responsibilities, major hardware and software procedures, disaster response, testing of the recovery plan. The purpose of this disaster recovery plan is to provide detailed guidelines to all the stakeholders when […]
- Gavin Flood’s Comparative Religion Studies In essence there is need to carry out more research in this field in order to be able to establish the role and the importance of religion in the life of human beings.
- Flood Mitigation Measures in the United States The mitigation measures for floods include the following; “control over rivers, establishing policies and legislation on the use of land such as terracing and assess to flood-prone areas”.
- Climate Change: Floods in Queensland Australia Over the recent past, the issue of climatic change has raised major concern about the well being of the recent as well as the future generation. The rail lines were also destroyed the fact that […]
- Great Barrier Reef: Flood Alleviation Solutions In the first presentation, solutions to protect the Great Barrier Reef, which is endangered from rising acidity levels due to methane extraction, were given while the second, third and fourth presentations focused on the measures […]
- The Flood of San Antonio in 1921: Re-Evaluating the Effects, a Catastrophe Viewed Through a Different Lens However, the reconstruction of the city takes less time than the reconstruction of the environment destroyed by the flood, which is why the effects of the San Antonio flood on the environment must be reassessed.
- Year of the Flood While the Geneva Convention on Human Rights has banned the use and development of biological agents as a means of warfare, thus sparing humanity the possibility of dying due to a virulent disease, the fact […]
- The Midwest Flood of April to October 1993 The Midwest flood of April to October 1993 is arguably the greatest flood to have hit the United States in terms of coverage and duration.
- The Similarities of The Epic of Gilgamesh and Noah & The Flood
- The Story of the Flood- the Epic of Gilgamesh
- The Flood Has Changed History Forever
- Red River Flood of 1997 & The Breakdown of Collaborate Management
- Viability of Green Roofs as a Flood Mitigation Element in the Central Region of Chile
- Rising Tide: The Great Mississippi Flood Of 1927 And How It Changed America, By John M. Barry
- Regional Flood Frequency Analysis in Tunisia: Identification of Regional Distributions
- The Economics During And After Kerala’s Flood Disaster
- Sustainability-Based Flood Hazard Mapping of the Swannanoa River Watershed
- The Demand for Index‐Based Flood Insurance in a High‐Income Country
- Understanding Flood Risk Decisionmaking: Implications for Flood Risk Communication Program Design
- Who Should Pay for Climate Adaptation? Public Attitudes and the Financing of Flood Protection in Florida
- Sea-Level Rise and Land Subsidence: Impacts on Flood Projections for the Mekong Delta’s Largest City
- The Flood Of Media Attention On Brain Injuries
- Spatial Variation in Flood Risk Perception: A Spatial Econometric Approach
- The Debate Over the Idea of the Genesis Flood in Genesis vs. Geology, an Essay by Steven Jay Gould
- The Affordability Goal and Prices in the National Flood Insurance Program
- The Fallibility of Flood Warning Chains: Can Europe’s Flood Warnings Be Effective
- Special Flood Hazard Effects on Coastal and Interior Home Values: One Size Does Not Fit All
- Land Use Scenario Modeling for Flood Risk Mitigation
- The Effects Of Flood Damage On Everyday Life
- The Bible According to Mark Twain: Writings on Heaven, Eden, and the Flood
- The Story Of The Flood, How Utnapishtim Tells His Story To Gilgamesh
- The City Of Vanport And Its Struggle With Racism Before And After The Flood Of Vanport
- The Importance of a Flood Free and Clean Living Community
- The Significant Key Elements on Climate Change in Before the Flood, a Documentary by Fisher Stevens
- Smoothing Income against Crop Flood Losses in Amazonia: Rain Forest or Rivers as a Safety Net
- Technological Advancements and Flood of Immigrants in the Turn of the Century in Ragtime, a Novel by John Pierpont Morgan
- The Different Versions of Flood Stories in Many Different Culture
- The Flood Story in Genesis, the Epic of Gilgamesh, and the Flood Story in the Holy Quran
- The Truth Behind Noah And The Great Flood
- Why the National Flood Insurance Program Is Not Financial Viable
- Risk Management Solutions For Flood And Earthquake Catastrophes In Romania
- Urban Growth and Flood Disasters in the Coastal River Basin of South-Central Chile (1943–2011)
- Regional Flood Frequency Analysis Using L-Moments for the West Mediterranean Region of Turkey
- The Intricacy of Adapting to Climate Change: Flood Protection as a Local Public Goods Game
- The Flood Accounts In The Epic Of Gilgamesh And The Genesis
- The Theme of Ancient Flood in Genesis of the Torah and the Epic of Gilgamesh
- The Differences In Gilgamesh, Atrahasis & The Deucalion & Pyrrah In Ovid Flood Myths
- The Factors that Influence the Flood Hydrograph
- The Godly Perspective of the Corruption of the World in the Story of Noah and the Flood
- The Devastation Left by the Flood in Downtown Davenport
- How Can You Survive a Flood?
- How to Promote Resistance to Flooding During Rice Germination?
- What Are the Different Techniques of Flood Forecasting?
- What Are the Consequences of Floods in Vietnam?
- Is Climate Change Leading To Extreme Floods?
- Where Is the Biggest Flood in the World?
- Are You Willing to Pay to Reduce Environmental Risks From Sewage Flooding?
- How Do Floods Affect Food Security in South Asia?
- Has Community Awareness of Flooding Improved in Boulder County, Colorado?
- What Are the Physical and Human Causes of Floods?
- When Was the Biggest Flood in Sri Lanka?
- What Could Be the Causes of a Dam Breach Leading To Flooding?
- What Are the Strategies and Practices for Urban Flood Protection?
- Does Your Insurance Cover Flooding?
- What Organisations Assist People and the Community During a Flooding Event?
- What Is the Estimated Economic Cost of Coastal Flooding?
- What Are the Steps Taken by the Government to Manage Disasters?
- Does Keeping Gutters and Drains Clear Help Against Flooding?
- How Do Drought and Flooding Affect the Development of Grain Yield?
- What Are the Types of Measures of Flood Management?
- Is Flood Insurance in the Netherlands Different From Other Countries?
- What Is the Impact of Land Use Change on Flooding Areas?
- How Pakistan Floods Linked to Climate Change?
- What Is the Interaction Between Floods and Economic Growth?
- How High Is Urban Flood Vulnerability in Guyana?
- What Are Some Tips to Prevent Basement Flooding?
- How Should We Interpret the Genesis Flood Account?
- Are Flood Risks More Physical Than Human?
- Does Water Quality Deteriorate as a Result of Severe Flooding?
- What Is the Effect of Flooding Along the Mississippi River on the Gulf of Mexico?
- Plate Tectonics Essay Titles
- Glaciers Topics
- Climate Change Titles
- Evacuation Essay Topics
- Famine Essay Titles
- Tornado Topics
- Climate Research Ideas
- Deforestation Research Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 25). 106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/
"106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding." IvyPanda , 25 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding'. 25 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/.
- Essay Topic Generator
- Summary Generator
- Thesis Maker Academic
- Sentence Rephraser
- Read My Paper
- Hypothesis Generator
- Cover Page Generator
- Text Compactor
- Essay Scrambler
- Essay Plagiarism Checker
- Hook Generator
- AI Writing Checker
- Notes Maker
- Overnight Essay Writing
- Topic Ideas
- Writing Tips
- Essay Writing (by Genre)
- Essay Writing (by Topic)
Natural Disaster Essay: How to Write, Topics, & Examples

What would you do if someone told you that a tsunami would wipe out your house tomorrow afternoon? You won’t believe them. It always seems that natural disasters happen in someone else’s life. But every year, millions of people worldwide suffer from various natural calamities. This article attempts to systemize the chaos of nature for you to write an impressive natural disaster essay. You will get acquainted with the seven types of disasters, get a long list of topics and examples of natural disaster essay in 200 words and 300 words.
- 🌪️ Natural Disaster: The Basics
- 💡 114 Essay Topics
- 📑 Outlining Your Essay
- 🌊 Essay Sample (200 Words)
- 🏜️ Essay Sample (300 Words)
🌪️ Natural Disaster Essay: What Is It About?
A natural disaster is a large-scale meteorological or geological event that can to cause loss of life or massive damage to people’s property. Floods and severe storms are the most reported acts of nature in the US, but other incidents also happen from time to time. That is why you can dedicate your essay on natural disasters to earthquakes, droughts, wildfires, floods, tsunamis, hurricanes, or tornadoes.

💡 114 Natural Disasters Essay Topics
What could you write in a natural disaster essay? You can invent your own topic about various types of natural disasters, their causes, and aftermath, or their impact on human life and the economy. Depending on the discipline, you can also describe historic calamities that changed the direction of human civilization. Alternatively, choose one from our comprehensive list below.
- Why are the Great Plains of the central US ideal for tornado formation?
- Global Warming and Climate Change Legislation.
- Research the atmospheric parameters inside a tornado.
- Energy, Technology and Climate Change.
- Why are the boundaries of Tornado Alley in the US so debatable?
- The global climate change as a manmade disaster.
- Which actions should you never do when a tornado is nearby?
- Volunteers’ Role During Disasters.
- Suggest your opinion on the best action strategy in a hurricane.
- The Columbia Disaster and safety violations.
- What were the causes and effects of a flood?
- Analysis on Climate Change and Global Impact.
- Describe the most devastating wildfires in the US and find their common features.
- Earthquake Engineering Considerations and Methods.
- Brainstorm ideas to prevent wildfires.
- Global warming and the greenhouse effect.
- How can building dams cause earthquakes?
- Climate Change and Its Impact on Freshwater.
- Analyze the impact of droughts on tourism.
- Climate Change Effect on Coral Reef Communities.
- Describe the most extended droughts in human history.
- Marine and Coastal Climate Change in Australia.
- Write an essay on natural disasters and earthquakes in particular.
- Air pollution and mortality rates
- What are the distinctive features of droughts in third-world countries?
- Global Warming, Climate Change, and Society’s Impact on the Environment.
- Study the relationship between global warming and droughts.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder After a Hurricane.
- Evaluate the damage caused by Hurricane Maria in 2017.
- Social Media’s Role in Disaster Response.
- Classify the effects of natural disasters in an essay.
- Sustainability and Climate Change.
- Describe the 1815 volcanic eruption of Mt. Tambora, Indonesia.
- Hurricane Katrina: Overview, Impact, Response.
- Each new leap of civilization causes new responses of nature.
- Animal Exploitation. Animal Agriculture and Climate Change.
- Think of any positive effects a volcanic eruption may have.
- In Arizona, Collaboration Averts Water Disaster.
- Children are the poorest victims of any disaster.
- A Solution to Remedy Climate Change.
- Which ways of disaster risk reduction do you know?
- An Emergency Operations Center During Hurricane Harvey.
- Research the current problems in disaster management.
- Disaster Recovery Plan for Information Technology Organizations.
- Analyze ineffective disaster management in an essay about hurricane Katrina.
- Nurse Competencies and Scope of Practice in Disaster.
- What should a household have at home in the case of a disaster?
- Hurricane Katrina: The Powerful Natural Disaster.
- Describe the humanitarian disaster during the drought in Somalia.
- Technology in Disaster Preparedness.
- Can man-made disasters entail natural calamities?
- Disaster Management in Philadelphia.
- Review the criteria for disaster classification.
- Jeddah Floods and Adaptation Strategies in the City of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- Search for real examples of hybrid disasters.
- Natural Disasters Prevention: A Tabletop Exercise.
- Who is responsible for casualties after a natural disaster?
- The Sand Storms: Remote Sensing and Meteorological Variables.
- List the lessons we could learn from our past disaster experience.
- Fire Development, Growth, and Spreads.
- The ice storm and silver thaw: A gentle disaster.
- Fire Crisis Management in the UAE.
- Rockslides: A pressing issue for rural areas.
- 1d – 2d Flood Modeling Using PCSWMM.
- What are the psychological benefits of disaster preparedness?
- Structural Control and Origin of Volcanism in the Taupo Volcanic Zone.
- When does a blizzard become a disaster?
- Extreme Weather Events + Geographies of Globalization.
- Research the causes of dust storms and name the affected areas.
- Strategies for Sustainable Integrated Oil Disaster Management in West Africa.
- Why did the San Francisco earthquake (1906) cause devastating fires?
- Causes of Climate Change.
- What could be done to help people who lost their homes in an earthquake?
- Book Review: Energy and Global Climate Change.
- Analyze the role of World Vision in humanitarian aid after disasters.
- Tangshan earthquake of 1976 showed that high population density is disastrous.
- The Role of Carbon Dioxide in Climate Change.
- Rock avalanche: Why water is the most powerful geological agent.
- Aspects of Climate Change.
- When do extreme weather conditions turn into a disaster?
- Climate Change: Reasons, Kyoto Protocol.
- Write an article on shelter-providing organizations for disaster victims.
- Establishing an IT Disaster Recovery Plan.
- Describe earthquake cycles in Haiti.
- Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture and Food.
- How can nature damage ecology in natural disasters?
- Climate Change. Problems. Effects.
- Disaster management should include psychological help to the survivors.
- Climate Change Causes: Position and Strategies.
- Suggest ways to prevent damage caused by debris flow.
- HAT 4: Disaster in Franklin Country.
- How did the lack of evacuation after the Bhola cyclone (1970) result in the massive death toll?
- The Effects of Climate Change.
- The most significant Yellow River flood: 2 million deaths in 1887.
- Resilience Building Against Natural Disasters in the Caribbean Islands.
- Sinkholes: A natural disaster or attraction for cavers and water-divers?
- Global Climate Change and Health.
- Describe the dynamics of landslides in California.
- Which early-warning systems to detect avalanches do you know?
- Los Angeles Regional Collaborative for Climate Action.
- Pyroclastic flow: The deadliest volcanic hazard.
- Communication During Disaster Response.
- Describe the volcano eruption of Vesuvius that destroyed the Herculaneum and Pompeii.
- Disaster Planning for Families.
- Disaster prevention measures: Investments that save millions of lives.
- Natural Disaster Management and Historical Prospective Study in the UAE.
- Research the PTSD in survivors of natural disasters.
- Are the latest disasters the nature’s fightback to humanity?
- Estimate the human impact on natural disasters.
- List the countries with the largest number of disasters and find their standard features.
- Everyday Communication on Climate Change.
- Insurance coverage against disasters: Our inevitable future.
- Emergency Planning Before and After Hurricane Katrina.
- One natural disaster could bring the world to its end.
Haven’t found a suitable topic in the list above? Use our essay topic generator to get more ideas.
📑 Natural Disaster Essay Outline
Outlines differ, depending on the assigned length and essay type. It is a reference sample. Feel free to modify it, extending some points and narrowing the others. Still, the overall structure should remain the same. We have chosen the “Causes of Earthquakes” essay topic for demonstrative purposes.
- Hook . There are millions of possible ways to start your essay, from a rhetorical question to any imaginable scenario. The point is to grab the reader’s attention, showing them that your writing is unique and creative. For example: We are always concerned with the consequences of a natural disaster. But what brought us into such a calamity in the first place?
- Concepts. Natural disasters can be studied in the framework of various disciplines. But in all cases, they are linked with geology, biology, chemistry, geography, and some other subjects with broad and complicated terminology. Explain the terms that could be elusive for your readers here. For example: For the purposes of this essay, an earthquake is a sudden displacement of the land surface.
- Background. How did you come to think of this problem? Why is it topical? The causes of earthquakes are numerous and often unrelated. To understand them as a system, we need a strict classification.
- Thesis statement . Clearly state the aim of your essay. This essay attempts to group the causes of earthquakes to determine which factors can be tackled by human forces.
- Transition sentence. It comes in the previous sentence (for paragraphs 2 and 3) and ensures smooth reading. E.g.: Tectonic movements are the most powerful causes of earthquakes, and we cannot influence them. But still, there is something we could do.
- Topic sentence . What will you explain in this paragraph? Human interference with nature can also cause earthquakes.
- Evidence. How can you confirm the topic sentence? Heavy clubbing of dam water can disturbance the crustal balance. Nuclear bombing causes shockwaves that penetrate the surface, changing the tectonic plates and their natural alignment. Mining can also cause earthquakes by removing extensive volumes of stone from under the ground.
- Warrant. Why does the reader need this information, and how does it relate to the thesis statement? Knowing these facts can help us change the old-fashioned approaches and lessen the ecological damage to our planet.
- Summary. Collect and summarize all your arguments here. Tectonic movements, volcano eruptions, and geological faults cause a significant part of earthquakes worldwide. But various man-made causes bring us to the same result.
- Rephrased thesis. We cannot stop the tectonic movements or hinder volcanic eruptions, but we can use natural resources with more care.
🌊 Natural Disaster Essay 200 Words
Below you will find a short natural disaster essay for 200 words. It explores the causes and effects of the tsunami in Japan in 2011.
Tsunami in Japan: Causes and Effects The proximity of the deadliest disasters is often unpredictable. As a result, the consequences of a tsunami can exceed any possible expectations. This essay looks for the decisive factors that caused the tsunami in Japan in 2011 and its results for the local population and other countries. The causes were out of human control and could not be predicted. The Pacific plate moved in the horizontal and vertical plane, advancing beneath the Eurasian Plate. It displaced the seawater above and entailed several destructive waves. The disaster had enormous consequences for the Japanese people and their economy. It killed almost 16,000 people, although the country had a sophisticated alarming system. Besides, the earthquake caused fires and explosions at oil factories. The cooling system of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant went out of service. Two people were lost, and many were injured. Nissan, like many other large corporations, had to suspend the operation of its four factories. The economic losses due to the catastrophe amounted to 300 billion dollars. But the disaster moved to other places. On 24 March 2011, the earthquake in the east of Myanmar claimed the lives of 60 people and destroyed 300 buildings. As we can see, everything is linked on our planet. Movements of the earth’ crust in any part of the world bring about earthquakes and tsunami in other countries. The series of waves in Japan was caused by the underwater earthquake and had horrible consequences.
🏜️ Natural Disaster Essay 300 Words
If your assignment is longer, you will have to provide your opinion in the essay. Or, you can make your argumentation more detailed. Below you can check our 300-word sample of a disaster essay.
The Economic Effects of the Dust Bowl Drought When someone says “a natural disaster,” we usually imagine an earthquake or a tsunami. Buildings are destroyed, and property is lost. But imagine a scenario of a devastating drought, which happened in the US in the 1930s. Its effect is less visible because it lies in the domain of the national economy. This essay reveals the economic consequences of the Dust Bowl drought. During the third decade of the XX century, strong winds raised choking dust in the southern states, from Texas to Nebraska. People and animals died as the crops failed in the area for several years in a row. The Dust Bowl lasted for almost a decade and was also called “the Dirty Thirties.” This drought intensified the impact of the Great Depression. Local farmers had to migrate to urban areas in search of better conditions and other sources of living. About 2.5 million people moved West from the worst-hit states, namely New Mexico, Texas, Nebraska, Oklahoma, and Kansas. But they found only discrimination, meager salaries, and inhuman working conditions. Many had to live in tents near irrigation ditches. They were called “Okies,” a disdainful name for migrants of any state. Regular rains returned to the southern states by the end of 1939, closing the drought. However, the economic aftermath persisted. The counties that suffered the most failed to recover the agricultural value of their land till the 1950s. Thus, the local population kept decreasing for twenty years. Although a drought does not ruin property, it can tangibly lower human life levels. The Dust Bowl threw people into a lose-lose situation. Their farms were unfit for gaining any profit, and the new places of living gave them no better opportunities. It took two decades to restore public wellbeing in the Southern States.
Researching the worst acts of nature can teach you to value what you have. We hope that this article has made your creative writing more manageable and pleasurable. You can write an essay of any length by simply following our outline. All you will need to do after that is make a cover page for it.
Please share your natural disaster essay ideas in the comments below.
❓ Natural Disaster Essay FAQ
How to write an essay about natural disaster.
Your approach should depend on the discipline. But in any case, you can discuss the types of disasters, their consequences, characteristics, and preconditions. The excellent idea is to select a past disastrous event and analyze it from the economic, social, or individual point of view.
What Is a Disaster Essay?
A disaster essay explores the stages of a natural or man-made calamity and seeks the possible ways to prevent similar emergencies in the future. An article on disaster management studies the correct and efficient activities to lower the casualties and property loss after a disaster.
What Is Disaster Preparedness Essay?
This type of writing analyzes the level of readiness of a region or municipality to an unexpected natural disaster. You can highlight the vulnerable groups of the population that will suffer the most. Or, you may invent measures that could reduce the disaster response and coping time. Such assignments teach you strategic thinking and a systematic approach to problem-solving.
How to Describe a Natural Disaster for an Essay?
You should specify that the event was unexpected and led to many deaths and property loss. The most critical things include the causes of the disaster, its progress and duration, and the negative consequences for the locals. You can also specify the negative effect on the economy and humanitarian condition of the area.
🔗 References
- Natural Disasters and Severe Weather | CDC
- Types of Disasters | SAMHSA
- Natural Disaster – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- Natural Disasters – National Geographic
- What Is Disaster Management: Prevention and Mitigation
Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Natural Hazards - Impacts, Adjustments and Resilience
Flood Disaster Hazards; Causes, Impacts and Management: A State-of-the-Art Review
Submitted: 21 June 2020 Reviewed: 17 November 2020 Published: 30 June 2021
DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.95048
Cite this chapter
There are two ways to cite this chapter:
From the Edited Volume
Natural Hazards - Impacts, Adjustments and Resilience
Edited by Ehsan Noroozinejad Farsangi
To purchase hard copies of this book, please contact the representative in India: CBS Publishers & Distributors Pvt. Ltd. www.cbspd.com | [email protected]
Chapter metrics overview
2,766 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this chapter
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Views on intechopen.com
Floods are among disasters that cause widespread destruction to human lives, properties and the environment every year and occur at different places with varied scales across the globe. Flood disasters are caused by natural phenomena, but their occurrences and impacts have been intensified through human actions and inactions. The practice of flood disaster management have evolved over the years from traditional approaches of ad-hoc response measures to integrated approaches involving technologically advanced tools in flood disaster awareness, preparedness and response measures. This chapter proffers understanding into flood disaster awareness, preparedness and management, mitigation and adaptation strategies. Most importantly, the chapter presents a review on the relevance of modern technological tools namely Geographic Information System, Remote Sensing, Internet of Things and Big Data, that are available to flood managers, in the creation of efficient early warnings and Flood decision support systems that elevates the resilience of societies to flood disasters.
- flood disaster
- disaster risk awareness
- disaster risk preparedness
- disaster management
- early warning system
Author Information
Frank jerome glago *.
- Akatsi College for Education, Akatsi, Ghana
*Address all correspondence to: [email protected]
1. Introduction
Disasters can result from forces of nature which may be aided by human actions. Some disasters build up slowly while others may happen suddenly and unexpectedly. Flood disasters can be classified among the quick and sudden disaster types, but are among few in this category that can be well predicted, anticipated and controlled to a great extent.
Floods, like other disasters, do not qualify to be labelled ‘disasters’ by the mere virtue of their happenstances. They do become disasters when they cause damage or adverse effects to human lives, livelihoods and/or properties. Floods are probably the widest spread among the various disaster events that occurs in most countries and causes the most deaths [ 1 ]. Floods, like other disasters, have the ability to cause widespread disturbances in communities, and alter the way of life of people in the affected areas.
The word flood originated from the old English word ‘flod’ akin to the German word ‘flut’ and the Dutch word ‘vloed’ seen as inflow and float of water [ 2 , 3 ]. The Oxford Reference Dictionary (ORD) defines flood as an overflowing or influx of water beyond its normal confines. Floods usually happen when the volume of water within a water body, say, a river or a lake, exceeds its total carrying capacity and as a result, some of the water flow outside the normal perimeter of the water body. Floods occur in almost every part of the world with different intensities and effects. Some of the most notable floods that have occurred include the 1981, 1991 and 2002 floods along the Chiang Jiang (Yangtze) river in China, the Mozambican floods in 2000, the 1983 and 1993 floods on the Mississippi river [ 2 ].
In the summer of 2005, the remarkable flooding brought by Hurricane Katrina which caused more than $ 108 billion in damages, constitute the costliest natural disaster in U.S. history [ 4 , 5 ]. Identified different types of floods namely riverine floods, localized and urban floods, normal flood (e.g. 1-year flood), medium flood (e.g. 5-year flood), severe floods, and catastrophic floods. It is indicated that floods can also be distinguished by their style of occurrence [ 2 ]. Flash floods occur when water quickly sweeps over an area which is difficult to deal with and it is not easy to predict the amount of rain expected within the spatial area over a short period of time [ 2 ].
Regional floods occur when rain falls over a large area for days or weeks causing river levels to rise quickly and fall slowly usually inundating large areas and causing widespread economic losses [ 6 ]. Flash floods are also referred to as upstream floods and regional floods, downstream floods [ 7 ].
There are varied effects of floods. The primary effects of flooding include physical damage to buildings and weakening of structures [ 2 ]. There are instances of loss of human lives and livestock, and the outbreak of disease epidemics. Other effects include instant losses of entire harvest as in the Mozambique flood in 2000 and northern Ghana floods of 2007. Whilst the effects of floods have come to be highly perceived in the negative, it is also true that floods are not entirely of damaging impact on human beings. Flooding can be beneficial such as making the soil more fertile and providing nutrients. Periodic flooding was essential to the development of some of the ancient civilizations especially those along the Tigris-Euphrates rivers, the Nile river, Indus river among others [ 2 ].
2. Causes and impacts of flood disasters
2.1 cause of floods.
Floods happen when soil and vegetation cannot absorb water from downpours. Floods also occur when a river outbursts its banks and the water spills onto the floodplain. Natural processes such as hurricanes, weather systems and snowmelt can cause floods. Other floods following tsunamis and coastal surges have natural causes like earthquakes in the seabed and high tides attributed to the pull of the moon [ 2 ]. There are many human-induced causes of flooding.
Urbanization has also become a major cause of flooding in cities [ 8 ], such that, a river is more likely to flood when its drainage basin is in an urban area. Inadequate drainage in some urban areas is a major cause of flooding [ 3 ], while in others, it is the lack of proper management of the drainage systems. Unplanned urban living has been identified as a significant contributor to flooding events in many developing countries. In a study into causes of flooding in Asamankese in the Eastern region of Ghana by [ 9 ] for instance, a resident succinctly summarises the problems as below;
[T]he main problem in Old Zongo and Abaase areas is the gutters. The gutters are not enough to carry the water when it rains heavily, and secondly, they pour so much rubbish in the gutters, so some of the gutters are also full of rubbish. So, when it rains heavily, where will the water go, it must flood the area. ….the way we build in this area too is a problem. I even think government is not hard on people so we just build anyhow in the waterways. We in this area also experience floods but it is not serious like in Old Zongo areas, that is why we are always trying to tell people here not to build in the waterway, because of what is going on in Old Zongo and Abaase.
This summarises the major contributions of improper managed urbanisation to flooding, a phenomena which characterises many developing countries. In Ghana, for example, perhaps the most devastating flood in the history of the country occurred in its capital, Accra, on 3rd June, 2015 where 159 people lost their lives and several people rendered homeless [ 10 ]. NADMO [ 11 ], suggests that although Ghana is vulnerable to certain disasters, flooding has become the major disaster the country has suffered in recent years especially in its urban areas due to improper management of these spaces [ 12 ].
Figure 1 shows the nature of some gutters in the urban areas of Ghana. Figure 1 shows a partially completed drainage in the flood prone zone of Asamankese, in the Eastern region of Ghana. Most of the gutters in the community, like Figure 1 , are left open and easily gets silted by inflow of sand and other waste materials. The situation of improper management of urban spaces is worse in the major Central Business Districts in many developing countries. Plastic wastes and other debris have been left to clog urban drainage which results in flood disaster when heavy rains are experienced.

Showing a partially completed drain in the Asamankese community, Eastern region of Ghana. Source: Author.
2.2 Impacts of flood disasters
What flood events share in common, is their ability to cause widespread community disruption, displacement, economic loss, property damage, deaths, injury as well as profound emotional suffering. Infrastructure and property, agricultural endeavours as well as historical and cultural sites may also be affected in flood disasters.
According to the United Nations Regional Coordinator in Dakar (October 2007) the worst flooding in 30 years that battered West Africa from July 2007 caused more than 210 death and affected more than 785,000 people [ 12 ].
The aftermaths of flood disasters in Ghana are the large-scale destruction of infrastructure, displacement of people from their dwellings, the loss of human lives, outbreak of diseases and water-borne infections, chemical exposure due to toxic pollutants being released into flood waters, huge loss of investments among other things.
Africa, which is one of the poorest continents in the world (in terms of GDP growth and income) has seen an increase in flood disasters in recent times [ 9 ]. For instance, torrential rains and flooding affected 600,000 people in 16 West African nations in September 2009 [ 13 ]. Countries with most devastating impacts were Burkina Faso, Senegal, and Niger. Another instance include the 2007 floods that displaced more than a million people in Uganda, Ethiopia, Sudan, Burkina Faso, Togo, Mali, and Nigeria, which claimed over 500 lives, and the 2008 floods in Mozambique which killed seven people and displaced tens of thousands residence [ 14 ]. Heavy seasonal rainfall starting in December 2014 also caused flooding in southern Africa [ 15 ]. As of January 2015, 135,000 people were affected by flood hazard in Malawi, Mozambique, Madagascar and Zimbabwe [ 15 ].
The impact of flooding varies both spatially and temporally. It could also be direct or indirect. Rahman [ 16 ] indicated that the direct impacts of floods are closely related to the depth of inundation of floods water. The extent of a flood has a direct relationship for the recovery time of crops, pastures and the social and economic dislocation impact to populations. The impact of floods is considered far reaching with the aftermath effects such as flood-induced disease epidemics. Disease outbreak is common, especially in less developed countries. Malaria, Typhoid and Cholera outbreaks after floods in tropical countries are also common [ 17 ]. [ 9 ] further stated that physical damage to property is one of the major causes for tangible loss in floods. This includes the cost of damage to goods and possessions, loss of income or services in the floods aftermath and clean-up costs. Some impacts of floods, on the other hand, are intangible and are hard to place a monetary figure on. Intangible losses also include increased levels of physical, emotional and psychological health problems suffered by flood-affected people.
According to [ 15 ] the cumulative number of people affected by rains and floods in 2007 in Southern Africa was more than 194,103 persons. This included 60,995 in Malawi (Mostly damage to property and crops), 94,760 people in Mozambique (all were evacuated into resettlement camps); more than 16,680 in Zambia (1890 persons had temporary accommodation, the rest were taken in by host families); and 15,168 in Zimbabwe. An estimated additional 4000 people had been affected in Lesotho and another 2500 persons in Swaziland.
Extreme events affect both the formal and informal economies, making it difficult to assess impacts which include direct and indirect ones. Depending on how well they are constructed and the severity of the event, buildings may be partially or totally destroyed by flooding. A look at Figure 2 will explain the partial damage that often happens to buildings as a result of flooding.

Depicting the impact of flood events o residents’ household in Asamankese, Eastern region of Ghana. Source: Author.
Flood destructions also hit roads and cause delays to infrastructure development initiatives and political processes [ 18 , 19 ] observed that the economic impact of natural disasters shows a marked upward trend over the last decades. The hazards tend to hit communities in developing and least developed countries more. Flood disasters have led to the loss of human life, destruction of social and economic infrastructure and degradation of already fragile ecosystems [ 20 ]. It follows therefore that social impacts include changes in people’s ways of life, their culture, community, political systems, environment, health and wellbeing, their personal and property rights and their fears and aspirations.
Rahman [ 21 ], established that social impacts of floods cause significant problems for the long term functioning of specific types of households and businesses in affected communities. The type of construction influenced the extent of flood damaged (e.g. thatched homes versus concrete high rise buildings will experience different degrees of impact). It follows that vulnerability is a key element in assessing the impact of floods. Different population segments are exposed to varied relative risks because of their socioeconomic conditions of vulnerability. Because of this, disaster reduction has become increasingly associated with practices that define efforts to achieve sustainable development. The links between flood disaster and economic systems, have become another pillar of consideration for sustainable development. Floods, however, cannot be totally prevented but their devastating impacts can surely be significantly minimized if advance warning of the event is available.
3. Flood disaster risk awareness
Disaster risk awareness is the extent of common knowledge of a person or group of persons about disaster risks, the factors that lead to disasters and the actions that can be taken individually or collectively to reduce vulnerabilities to hazards. It also includes the need to build and increase the knowledge and understanding of the many issues about disaster risk reduction, to build the capacity of the people who learn and teach others about the disaster [ 9 ]. Changes in patterns of human behaviour and decision-making at all levels of government and society could, therefore, lead to a substantial reduction in disaster risk [ 22 ]. In this respect, recent experience has shown that public awareness of natural hazards and disaster risk reduction education constitutes a foundation and pre-requisite for effective catastrophic risk management strategies at country and regional levels. More importantly, by influencing human actions and perceptions through societal behaviour and behavioural adaptation, information and education can increase flood risk awareness and play a more effective role in reducing the costs of catastrophes associated with natural perils [ 22 ].
To proffer an understanding on the flood risk awareness of residents in the Asamankese Municipality of Ghana, [ 9 ] surveyed some residents and sought to know how likely the area was susceptible to flood through the major rainy season from March to July. Figure 3 , which summarises the respondents result, pointed out that an overwhelming proportion of respondents (70.0% and 77.5% within the flood prone and Non-flood prone zones respectfully) indicated that flooding has become a regular phenomenon, and the community was likely to be flooded every time it rained.

Showing respondents awareness to flood disaster risk at Asamankese, Eastern region, Ghana. Source: Author.
Awareness is a very crucial element for a society to effectively adapt to a flood risk. As stated by [ 23 ] awareness is diminished when the provision of an appropriate information is minimal or when memories of past experiences or events are diminished. Awareness can generally be uplifted through efforts that are centred on local issues, contain the simple solution to reduce the flood risk and are repeated on a regular basis [ 24 ].
Scholars like [ 25 ] posit that worry is an important risk characteristic that serves as a normative value for awareness. Society can be aware of a flood risk, however, if it is not afraid of the risk, it will not take any action to prepare for it. A higher level of worry is more likely to result in a higher level of awareness and preparedness. There is a positive correlation between these two variables. This was reinforced by [ 26 ] with their assertion that most people become aware and prepared for disasters based on their previous personal experiences with flood disasters. Early warning information can, therefore, allow the disaster managers to be pre-informed and take steps which may significantly reduce the loss of life and damage to property.
4. Flood disaster preparedness and resilience strategies and practices
The argument now is that adequate preparation can make it possible to significantly reduce the impacts of flood disasters through a good understanding of preventive action as well as knowledge of some life-saving techniques during disasters [ 27 ]. Nowhere has the issue of floods become a developmental issue than in poor and developing countries where systemic problems and institutional constraints have increased vulnerability (social, economic and physical) to flood risk and thus, reducing resilience to flood disasters.
Disaster preparedness is defined as the state of taking measures to reduce to the minimum level possible, the loss of human lives and other damages from flood disasters through prompt and efficient actions of response and rehabilitation. That is, preparedness is to put in place the necessary measures for effective and timely response to an event. The objectives of preparedness are to ensure that appropriate mechanisms and resources are in place to assist those afflicted by the disaster and enable them to help themselves [ 9 ].
Flood disaster preparedness consists of a wide range of activities and protective measures that might be instigated from the physically or procedurally. Preparedness is very important in the disaster management process, and includes the knowledge, capacities, activities and measures carried out in advance by governments, professional response and recovery organizations, communities and individuals to effectively anticipate, respond to and recover from the impacts of imminent or current disaster situations or conditions.
The [ 26 ], conceives preparedness as a medium-term plan that involves the development and the implementation of disaster management plans. It involves the development and implementation of early warning systems, resource inventory and stockpiling of resources, coordinating of agencies and ensuring evacuation plans work. Preparedness is seen as tools for ensuring the effective coordination and enhancement of capacities to prevent, to protect, to respond to, recover from and mitigate the devastating effects of natural and man- made disasters [ 9 ].
Apart from personal experiences informing residents’ awareness and preparedness towards flood disasters, external factors such as occupation, level of education of an individual, radio programs and community meetings serve as conduits for disseminating flood information. Hence, these factors may act to increase awareness and preparedness levels to flood disasters.
Studies show that residents’ awareness of flood disaster is usually high. For instance, in [ 9 ]’s study of residents’ level of flood disaster awareness in Asamankese, in Ghana, showed that more than 65 percent of residents in both the Flood prone and Non-flood prone settlements ranked themselves to be at a high risk of flood disasters. Furthermore, the study showed that, the awareness of human factors that exacerbate their risk to flood was also high. However, preparedness of residents’ in most cases were poor, and in Asamankese, like in other developing countries, victims of flood had to usually depend on extended social networks, and government institutions for support to regain their livelihoods after being hit by flood events, a situation which results from their ill preparedness to flood disasters especially financially.
5. Strategies and technologies for improved flood disaster management
5.1 flood disaster management strategies.
Flood Disaster Management Strategies refer to a bundle of processes and activities that are aimed at reducing the overall impacts of floods on societies. Flood management needs to be considered within the overall national development planning strategy of every country and must involve strategic institutional arrangements and collaborations for a sustainable flood management.
The management of floods as problems in isolation almost necessarily results in a piecemeal, localized approach (World Meteorological Organization [ 28 ]). The flood disaster management process should also be coordinated with efforts made in closely related fields. For example, the disaster mitigation process should consider human health impacts during flooding (e.g. cholera, malaria), thereby more effectively address a health issue that arises during and after flooding [ 28 ].
The management of floods takes several approaches ranging from traditional approaches to integrated approaches. The traditional management response to a severe flood was typically an ad- hoc reaction, the quick implementation of a project that considered both the problem and its solution to be distinct and self-evident. Traditional approaches usually gives no thought to the consequences for upstream and downstream flood risks [ 28 ]. Thus, flood management practices have largely focused on reducing flooding and reducing the susceptibility to flood damage. Traditional flood management has employed structural and non-structural interventions, as well as physical and institutional interventions. These interventions have occurred before, during and after flooding, and have often overlapped.
There has been a paradigm shift in flood management. Traditionally, controlling floods has always been the main focus of flood management, with the emphasis on draining flood water as quickly as possible, or storing it temporarily, and separating the river from the population through structural measures such as dams and levees [ 28 ].
The concept of integrated flood management has led to a paradigm shift: absolute protection from floods is a myth, and focus should aim at maximizing net benefits from the use of flood plains, rather than trying to fully control floods [ 28 ].
A proactive approach towards the management of floods over a traditionally reactive approach is rapidly gaining recognition among flood managers. The proactive approach does not treat floods only as an emergency or an engineering problem, but as an issue with social, economic, environmental, legal and institutional aspects. The proactive approach is not limited to a post-event reaction but includes preparedness (including flood risk awareness) and response measures to flood management at different stakeholders’ levels [ 28 ].
Recent calls in flood management are geared at taking a transboundary approach since floods do not respect borders; neither national nor regional or institutional [ 29 ]. The great advantages of transboundary cooperation are that it broadens the knowledge/information base, enlarges the set of available strategies and enables better and more cost-effective solution. Furthermore, widening the geographical area considered by basin planning enables measures to be located where they create the optimum effect [ 29 ].
5.2 Early warning systems
The term ‘early warning’ is used in many fields to describe the provision of information on an emerging perilous circumstance where that information can enable action in advance to reduce the risks involved. The early warning system comprise the set of capacities needed to generate and disseminate timely and meaningful warning information to enable individuals, communities and organizations that are threatened by hazards to take necessary preparedness measures and act appropriately in sufficient time to reduce the possibility of harms or losses [ 30 ].
Early warning systems exist for natural geophysical and biological hazards, complex socio-political emergencies, industrial hazards, personal health risks and many other related hazards. Studies have demonstrated that disaster prevention can pay high dividends and found that for every Euro invested in risk management, broadly 2 to 4 Euros are returned in terms of avoided or reduced impacts on life, property, the economy and the environment [ 31 ]. Early warning systems can be set up to avoid or reduce the impact of flood hazards and other disasters such as, landslides, storms and forest fires and volcanic eruptions. The significance of an effective early warning system lies in the recognition of its benefits by the members of the general public.
Early warning is a major element of flood disaster risk reduction. It saves life and reduces economic and material losses from flood disasters. To be effective, community-based early warning systems need the active involvement of the community people, a strong public education on and awareness of risks, an effective communication system ensuring a constant state of preparedness [ 31 ]. Early warning systems contribute with other Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) interventions to protect and support sustainable economic development and early detection of undesirable situations. The society benefits from early warning systems if they are in place. Many governments have failed to take early warning into account while formulating their development and disaster risk reduction policies. Subsequently, it results in heavy losses to human lives and economic entities when disasters strike [ 31 ].
A people-centered early warning system necessarily comprises four key elements: (I) knowledge of the risks; (II) monitoring, analysis, and forecasting of the hazards; (III) communication or dissemination of alerts and warnings, and (IV) local capacities to respond to the warnings received. The expression “end-to-end warning system” emphasizes that early warning systems need to span all steps from hazard detection to community response. It is essential to link downstream communities and upstream communities for the effective operation of an early warning system [ 31 ]. There are several instances where early warning systems have helped to mitigate the impact of disasters. As an example, the Bangladesh cyclone preparedness program has successfully warned, evacuated and sheltered millions of people from cyclones since its inception in the early 1970s by the International Federation, the Bangladesh Red Crescent Society and the government of Bangladesh. In the Caribbean, during 2004’s hurricane season, most countries successfully alerted their populations to approaching storms and saved many lives as a result. The key to their success was putting people, not just technology, at the centre of their warning systems. As a result of early warning systems, there were no deaths reported in La Independencia, Guatemala during the hurricane season in October 2005 [ 26 ].
The importance of early warning has been underlined in various UN General Assembly resolutions as a critical element of disaster reduction. Early warning received very high attention after the 26 December 2004 tsunami, when it became clear that a tsunami warning system and associated public education could have saved thousands of lives. The UN Secretary-General in his report; In Larger Freedom: Towards development, security and human rights for all , proposed that the United Nations system should take a leadership role in developing comprehensive global capacities for systematic people-centered early warning systems, which would cover all hazards for all countries and communities. Subsequently, he requested that a global survey is undertaken, with a view to advance the development of a Global Early Warning System (GEWS) for all natural hazards [ 32 ]. Thus early warning systems are very important for disaster management and should be a priority at global, national and local levels.
5.3 Flood disaster mitigation strategies
Flood Disaster Mitigation measures tend to be potentially more efficient long term sustainable solutions to water-related problems and should be enhanced, in particular, to reduce the vulnerability of human beings and goods exposed to flood risk. Flood forecasting and warning is a prerequisite for successful mitigation of flood damage. In the field of environmental engineering, flood mitigation involves the managing and control of flood water movement, such as redirecting flood run-off through the use of floodwalls and flood gates, rather than trying to prevent floods altogether. It also involves the management of people, through measures such as evacuation and dry/wet proofing properties for example. The mitigation of flooding can be done on an individual, community and at city authority or national levels.
5.4 Flood disaster adaptation strategies
Flood disaster adaptation refers to actual adjustments made that are geared towards mitigating the severity of flood disasters. Flood disaster adaptation strategies vary from before flood adaptation, during flood adaptation, to post flood adaptation strategies. It also ranges from individual, community, to citywide adaptation strategies. Discussions on flood adaptation strategies pointed out that embankments, for instance, either concrete or sandy may be constructed to prevent water from entering residential houses [ 33 ]. Adaptation options that would be effective for flood disaster in developing nations include Environmental policy reforms, changes in urban and housing design, removal of laws that can inadvertently increase flood vulnerability [ 34 ]. Capacity building is also required to integrate climate change and its impact on urban development planning, engaging local communities, raising public awareness and education on climate change and enabling wider representation at stakeholder meetings. Planting of vegetative cover to reduce runoff speed, terracing hillsides to slow flow down hills as well as control of man-made channels to divert flood water among others, serve as adaptation strategies. Generally, adaptation strategies adopted in flood disasters range from structural to non-structural [ 35 ].
5.5 Monitoring, evaluation and mainstreaming of flood disaster management
Being able to count on institutionalized capacities to mobilize and coordinate resources when and where they are needed is crucial in all phases of the disaster cycle, sometimes with very little room for delay or errors of judgment. Coordination among agencies and stakeholder groups is important for flood mitigation, in particular, the design and execution of programmes and policies to help address underlying causes of extreme vulnerability [ 36 ]. Monitoring of activities is necessary because there is often the need to link responsibilities and budgets for programmes over time. The performance of institutions and organisations responsible for disaster management should be monitored and evaluated on a regular bases. The relevance of monitoring and evaluation as a means of reducing flood disaster events cannot be overemphasised.
The capacity to monitor and evaluate flood prevention, mitigation, relief and recovery operations and institutional arrangements would create opportunities for learning and improve the accountability of authorities [ 36 ]. Monitoring is a key element in pre-flooding, flooding and post flooding stages of flood disaster management. Evaluation goes hand in hand with monitoring to assess the impact of flooding and the effects of key interventions engaged in mitigating the impact of flooding on people, infrastructure, and the environment in general. In a study on the environmental aspects of integrated flood management, [ 28 ], noted that adaptive management requires continuous monitoring of the state of the environment and evaluation at regular intervals.
The importance of monitoring has been recognized from various perspectives [ 28 ] Pre-plan monitoring of various natural processes provides the basic input for assessment of resource, risks and development options. Monitoring at a development planning level is based on actions taken in line with selected plan and factors of environmental impacts indicated in environmental assessment at the strategic level [ 28 ]. In the context of awareness of flood hazards, monitoring encapsulates awareness of causes and how these causes change over time, knowledge of interventions and how these interventions are shaping the frequency and nature of flood events in an area. Monitoring is essential in flood management from a first-hand point of providing timely and efficient early warning information. Immediate and post-implementation monitoring is important in order to assess whether the flood management measure has succeeded [ 28 ].
Mainstreaming of disaster risk reduction into development planning, policy, and implementation should be at the heart of every sustainable Development Planning agenda. Disasters, such as floods, have an enormous impact on development. There is, therefore, the need for mainstreaming disaster planning into development planning. The importance of mainstreaming is also recognized by the Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) adopted at the World Conference for Disaster Risk Reduction (WCDRR), where integration of disaster risk reduction into the development programmes is a priority [ 5 ]. There has been increasing recognition by both governments and donors for the need to mainstream disaster risk reduction into development planning [ 37 ]. Mainstreaming disaster planning into development planning considers risks emanating from natural hazards in medium-term strategic development frameworks, in legislations and institutional structures, in sectoral strategies and policies, in budgetary processes, in the design and implementation of individual projects and in monitoring and evaluating all of the above [ 37 ].
5.6 Sustainable flood management
The concept of sustainable development is firmly rooted in all flood management. Sustainable flood management involves: ensuring quality of life by reducing flood damages but being prepared for floods, mitigating the impact of risk management measures on ecological systems at a variety of spatial and temporal scales, the wise use of resources in providing, maintaining and operating infrastructure and risk management measures, maintaining appropriate economic activity [ 38 ]. Sustainable flood management as a concept is not new, its methods have been practiced on many continents for years [ 39 ]. With increasing scrutiny of traditional engineering solutions, there is a growing realisation throughout the world that there is a huge and urgent need for pro-active and sustainable flood management solutions.
The notion of sustainability in the context of flood management is still rather ambiguous but generally embraces economic, environmental and social objectives. Sustainable flood management therefore refers to the provision of possible social and economic resilience against flooding, by protecting and working with the environment, in a way which is fair and affordable both now and in the future [ 40 ]. In practice a sustainable approach should integrate a range of flood management requirements using best practices and involving the economics of a scheme, good planning, understanding flood generation processes, protecting natural environments and working with communities [ 39 ]. Sustainable flood management is, therefore, an integrated set of procedures linked into a physical catchment.
6. Technological advancements in flood disaster management
Advanced technologies have been developed and integrated into higher institutional level decision support systems to aid the prediction, monitoring and management of flood disasters in some countries. These advanced flood decision support systems’ architecture include technologies such as Geographic Information Systems, remote sensing and photogrammetry, and hydrologic models.
The Flood Decision Support System (FDSS) refers to interactive computing environment designed for specific contexts which include interlinked models/analytical tools, databases, graphical user interfaces and other systems. The FDSSs according to [ 41 ] have the potential to improve flood disaster assessment and mitigation through improved data collection and rapid dissemination of flood information to affected areas. For an effective FDSS on the technology aspect of disaster management, analysts have to ensure effective interoperability of the technologies. This will ensure that, all aspects of the technology that singularly may be responsible for data capture, storage, manipulation, analysis, retrieval or display of information, work in a smooth interwoven network and relay information to other parts of the system without technical hindrances to ensure the overall goal is achieved.
There are three main components to the Flood Disaster Support System. These include the Database component, the Modelling component, and the Display component also known as the Graphical User Interface (GUI) component. The Database component of the FDSS comprises the data used in the modelling functions. This component uses to tools to capture and store flood related data. Some data stored include historical rainfall data, geological data, soil and ecological data, population data, boundary and administrative data. Tools used in data capture for the Database varies depending on the data to be captured. For example, Remote sensing techniques are used to capture satellite data on flood zones, flood buffer zone monitoring. Sensors are also deployed to monitor flow, volume and carrying capacities of rivers while rain gauges capture precipitation volumes. These data may be complemented with census data on population and livelihoods of residents. All these various data are kept in the Database component of the DSS.
The second component of the FDSS are functions of analytics and modelling. Various analysis are carried out and the data in the database taking through several processes of manipulation. These processes of data manipulation and analysis differ in approach and are tailored to meet various goals in the decision making process. Prominent among the tools used at this stage is Geographic Information Systems (GIS) tools. Regarding flood modelling, advanced tools available to flood managers include advanced technological tools in soft computing, for instance, evolutionary computing, as well as probabilistic predictions techniques of inundation recurrence intervals [ 41 ]. These tools afford flood managers varieties of techniques that can be applied in simulation, modelling, analysis and management of flood.
The User Interface component of the FDSS provides flood decision makers an interactive graphical interface, enabling users to query the data stored in the system. It again enable users to display and visualise the models and reports from the manipulations of the data. This component of the advanced FDSS enables users to prepare and appreciate maps and animations of the hydrologic phenomena being studied.
6.1 Remote sensing and geographic information systems in disaster management
Advances in remote sensing tools and techniques over the past few years have provided disaster managers, especially flood disaster managers with powerful tools in the acquisition of flood sense data, in forecasting and monitoring of flood occurrences and in the management of watersheds, rivers and wetland areas.
Remote sensing refers to the Science of obtaining information about objects, areas or phenomena from a distance [ 42 ]. Typically, these information are collected through sensors that are planted on aircrafts or satellites. In flood disaster management, remote sensing can be applied to monitor and map events such as changes in river volume, changes in coastline, map wetlands and flood prone zones and boundaries of inundation.
A Geographic Information System(s) (GISs) refers to a framework for gathering, managing and analysing location-based data. This framework is used to analyse and organize several distinct layers of location-based information into concise visualizations through maps and 3D scenes. Ultimately, GISs present powerful capabilities that proffer deeper insights into data, which may include revelation of patterns and relationships for smarter decision making [ 43 ].
Reliable flood maps are therefore produced using GIS techniques and remotely sensed data to manage floods. GIS tools aid in the preparations to Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) for high level hydrological modelling using sensors such as The Light Detecting and Ranging (LiDAR) sensors.
With the help of data interpretation techniques of GIS, remotely-sensed imageries are interpreted to create suitable flood risk mitigation frameworks and FDSSs. Although flood disasters have increased in scale and frequency in recent years, there has been a commensurate improvement in flood data capturing and analyses techniques, that when applied in time, can significantly mitigate the risks and impacts of floods. As summarised in Table 1 , GIS and RS are of great importance in the pre and post disaster management processes.
Showing GIS and Remote Sensing Application in flood disaster management. Source: Authors’ Construct with reference to [ 44 ].
6.2 Internet of Things (IoT) and Big Data in flood disaster management
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of devices connected over the internet to sense, track and respond to issues. Patel and Patel [ 45 ] defines the IoT as “ a type of network to connect anything with the internet based on stipulated protocols through information sensing equipment to conduct information exchange and communications in order to achieve smart recognitions, positioning, tracing, monitoring and administration.”
The network of physical objects are able collect data on a regular bases and in a structured form, perform high level analysis and predict changes, as well as initiate actions based on results from the analyses. IoT is hence a powerful technological tool that can provide a wealth of high level intelligence which is needed in planning and management.
There are three levels of IoT. The first is people to people interconnectivity, the second is people to machine interconnectivity and the third being machine to machine or things to things interconnectivity [ 45 ]. In all interconnectivity of things and people, the internet remains the main driver. This interconnectivity of Things, enables the swift transmission of meteorological, hydrological and geological data pertaining to flood events.
In flood disaster management, providing a quick feedback on the occurrence of floods can be a great step in preventing and mitigating flood disasters and their impact on livelihoods in society. Deploying IoT in flood management puts disaster managers at a position to create enhanced early warning systems that do not only measure the water levels and the speed of inundation, but early warning systems that could also send alerts to residents and flood managers through mobile phones and other personal electronic devices, and additionally, prescribe the best prevention and mitigation strategies based on data such as direction of runoff, speed of rise of water levels and the time at the disposal of residents to take necessary action.
Big Data on the other hand, refers to “ the evolution and use of technologies that provide the right user at the right time with the right information from a mass of data that has been growing exponentially for a long time in our society ” [ 46 ]. Digital data collection has not only seen growth in volume but also in variety in storage formats, hence Big Data is often described as high-volume, high-velocity and/or high variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing to enable enhanced insight, decision making and process automation [ 47 ].
Big data typically defines data that exceeds the storage, processing and computing capacity of conventional database [ 46 ]. Hence Big Data analytics typically involves automated software that assist in the collection, organisation and analysis of the data being generated to discover trends, correlations and other useful results to prompt necessary action.
Through Big data process automation, precipitation data, soil moisture data, temperature data, water content data of water bodies, data on evapotranspiration, ground water data, etc., are collected and processed in real-time without human supervision to make predictions and early warnings about flood disasters’ occurrence [ 47 ].
7. Conclusion
Flood disasters have had very devastating impacts on societies and have destroyed livelihoods and investments of staggering monetary value and importance to development. However, adequate involvement of technology are leading to the creation of people-centered early warning systems that enhances residents’ awareness and preparedness to flood events to significantly reduce the adverse impacts of these disasters on people. This chapter discussed various aspects of flood disaster management including early warning systems, flood mitigation and adaptation strategies, the relevance of monitoring, evaluation and mainstreaming flood disaster management into national level development planning. The chapter again discussed and encourage the integration of advanced technological tools into the frontier of flood disaster management, as these tools have the capacity to capture, analyse and disseminate real-time flood data to all stakeholders to safeguard lives and precious investments.
- 1. Ghapar, A. A., Yussof, S., & Bakar, A. A. (2018). Internet of Things (IoT) architecture for flood data management. International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking, 11 (1), 55-62
- 2. Adams, A.G. (2008). Perennial flooding in the Accra Metropolis: The human factor. (Unpublished Master of Science Thesis). Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi
- 3. Ahmad, K., & Moeeni, S. (2019). Recent flood risk scenario of Bihar: a preventive strategy. NDCWWC Journal (A Half Yearly Journal of New Delhi Centre of WWC), 8(2), 3-14
- 4. Blake, E. S., Landsea, C. W., & Gibney, E. J. (2011). The deadliest, costliest, and most intense United States tropical cyclones from 1851 to 2010. NOAA Technical Memorandum NWS NHC-6, NOAA National Hurricane Center. Dept. of Commerce (Available at http://www.nhc.noaa . gov/Deadliest_Costliest. shtml)
- 5. Dodman, D., Bicknell, J., & Satterthwaite, D. (2012). Unjust Waters: Climate Change, Flooding and the Urban Poor in Africa: Ian Douglas, Kurshid Alam, MaryAnne Maghenda, Yasmin McDonnell, Louise McLean and Jack Campbell. In Adapting Cities to Climate Change (pp. 216-238). Routledge
- 6. Abbott, P.L., (2006), Natural disasters, 5th Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies Inc
- 7. USGS, (2020). What are the two types of floods? Retrieved from https://www.usgs.gov/faqs/what-are-two-types-floods?qt-news_science_products=0#qt-news_science_products . Retrieved on 27 th September, 2020
- 8. Zhang, W., Villarini, G., Vecchi, G. A., & Smith, J. A. (2018). Urbanization exacerbated the rainfall and flooding caused by hurricane Harvey in Houston. Nature, 563(7731), 384-388
- 9. Glago, F. J. (2019). Household disaster awareness and preparedness: A case study of flood hazards in Asamankese in the West Akim Municipality of Ghana. Jàmbá: Journal of Disaster Risk Studies, 11(1), 1-11
- 10. Daily Graphic (2015). Ghana among the worst hit by torrential rains, Daily Graphic, 28 July 2015
- 11. NADMO, (2015). Unpublished Annual Report 2015, NADMO, Asamankese
- 12. Oppong, B. (2011). Environmental hazards in Ghanaian Cities: The incidence of annual floods along the Aboabo River in the Kumasi Metropolitan Area (KMA) of the Ashanti Region of Ghana. (Unpublished Mphil. Thesis). Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi-Ghana
- 13. Baldassare, G., Montanari A., Lins, H., Koutsoyiannis, D., Brandimarte Luigia, and Bloschl, G. (2010). Flood fatalities in Africa: From diagnosis to mitigation. Geophysical research letters, 37(22). doi:10.1029/2010GL045467, 2010
- 14. Church World Service, (2008). CWS situation report: 2008 Mozambique floods. Retrieved January 16, 2008, from http://reliefweb.int/report/mozambique/cws-situation-report-2008-mozambique-floods
- 15. OCHA, (2015). Situation report for Southern Africa floods. Retrieved January 16, 2015, from reliefweb.int/map/malawi/southern-africa-floods-and-cyclones-update-16-Jan-2015
- 16. Rahman, S. U. (2014). Impacts of flood on the lives and livelyhoods of people in Bangladesh: A case study of a village in Manikganj district (Doctoral dissertation, BRAC University)
- 17. Mwape, Y. P. (2009). An impact of floods on the socio-economic livelihoods of people: A case study of Sikaunzwe Community in Kazungula District of Zambia. University of Free State Press
- 18. Octavianti, T., & Charles, K. (2019). The evolution of Jakarta’s flood policy over the past 400 years: The lock-in of infrastructural solutions. Environment and Planning C: Politics and Space, 37(6), 1102-1125
- 19. Know Risk (2005). United Nations, Geneva, Switzerland. Available at: https://www.unisdr.org/we/inform/publications/654
- 20. Cui, Y., Cheng, D., Choi, C. E., Jin, W., Lei, Y., & Kargel, J. S. (2019). The cost of rapid and haphazard urbanization: lessons learned from the Freetown landslide disaster. Landslides, 16(6), 1167-1176
- 21. Rahman, S. U. (2014). Impacts of flood on the lives and livelyhoods of people in Bangladesh: A case study of a village in Manikganj district (Doctoral dissertation, BRAC University)
- 22. Aerts, J. C., Botzen, W. J., Clarke, K. C., Cutter, S. L., Hall, J. W., Merz, B., … & Kunreuther, H. (2018). Integrating human behaviour dynamics into flood disaster risk assessment. Nature Climate Change, 8(3), 193-199
- 23. Shen, X. (2009). Flood risk perception and communication in different cultural contexts-a comparative case study between Wuhan, China and Cologne, Germany. (Ph.D. Dissertation), University of Bonn
- 24. Poortinga,W., Bronstering, K., and Lannon, S. (2011). Awareness and perceptions of the risks of exposure to indoor radon: A population based approach to evaluate a radon awareness and testing campaign in England and Wales. Risk Anal., 31, 1800-1812
- 25. Miceli, R., Sotgiu, I., and Settanni, M. (2008). Disaster preparedness and perception of flood risk: A study in an Alpine valley in Italy. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 28, 164– 173
- 26. International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC), 2007, Disaster response and contingency planning guide, IFRC, Geneva
- 27. Ibem, E. O. (2011). Challenges of disaster vulnerability reduction in Lagos Megacity Area, Nigeria, disaster prevention and management. An International Journal, 20(1), 27-40
- 28. World Meteorological Organization (2011). .Partnerships in weather, climate and water for development: Integrated flood management. Fact sheet 11, Version 1-2011
- 29. UNECE (2009). Transboundary flood risk management: Experiences from the UNECE region. New York and Geneva: United Nation Publication
- 30. UNISDR, (2009). Global assessment report on disaster risk reduction: Risk and poverty in a changing climate, Geneva
- 31. Practical Action, (2014). Poor people’s energy outlook 2014. Available at: http://policy.practicalaction.org/policy-themes/energy/poor-peoples-energy outlook/poor-peoples-energy-outlook-2014
- 32. UN-Chronicle, (2007). Global early warning systems needed: Creating partnership to cope with natural disasters. The Magazine of the United Nations. 64(2), 2007
- 33. Terungwa, C. U. and Torkwase, C. I. (2013). Current issues in flood disaster: Challenges and implications for science and technology to enhance environmental education. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 2(6), 61-65
- 34. Kolawole, O.M, Olayemi, A.B. and Ajayi, K.T. (2011). Managing flood in Nigerian Cities: Risk analysis and adaptation options – Ilorin City as a case study. Archives of Applied Science Research, 3(1), 17-24
- 35. Sakijege, T., Sartohadi, J., Marfai, M.A., Kassenga, G.R. and Kasala, S.E., (2014). Assessment of adaptation strategies to flooding: A comparative study between informal settlements of Keko Machungwa in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania and Sangkrah in Surakarta, Indonesia’, Jàmbá. Journal of Disaster Risk Studies, 6(1), 131-141
- 36. Lebel, L., Nikitina, E., Kotov, V., Manuta, J., & Birkmann, J. (2006). Assessing institutionalized capacities and practices to reduce the risks of flood disasters (pp. 359-379). United Nations University Press, Tokyo
- 37. Miyan, A. (2014). Challenge of Mainstreaming Disaster Risk Reduction in Development Initiatives with Special Reference to Bangladesh. An input paper of the 2015 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction, UNISDR, United Nations, Geneva
- 38. Gouldby, B. and Samuels, P. (2005). Language of risk -project definitions. Floodsite report T32-04-01. Available at: http://www.unisdr.org/files/657_lwr1.pdf
- 39. Johnson, R. Watson, M. and McOuat. E. (2008). The way forward for natural flood management in Scotland, Scottish Environment link: MNV/WWF/0808/1038
- 40. FIAC, (2007). Sustainable flood management report, Scotland. Available at: http://reliefweb.int/report/mozambique/cws-situation-report-2008 Mozambique-floods
- 41. Levy, J. K., Gopalakrishnan, C., & Lin, Z. (2005). Advances in decision support systems for flood disaster management: Challenges and opportunities. Water Resources Development, 21(4), 593-612
- 42. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, (2020). What is remote sensing? National Ocean Service, U.S Department of Commerce. Retrieved from https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/remotesensing.html Retrieved on 20 th July, 2020
- 43. ESRI, (2020). What is GIS? Retrieved from https://www.esri.com/en-us/what-is-gis/overview . Retrieved on 20 th July, 2020
- 44. Faisal, A., & Khan, H. (2018). Application of GIS and Remote Sensing In Disaster Management: A Critical Review of Flood Management. In International Conference on Disaster Risk Mitigation
- 45. Patel, K. K., & Patel, S. M. (2016). Internet of things-IOT: definition, characteristics, architecture, enabling technologies, application & future challenges. International journal of engineering science and computing, 6(5)
- 46. Youssra, R., & Sara, R. (2018). Big data and big data analytics: Concepts, types and technologies. Int J Res Eng, 5(9), 524-528
- 47. Zakaria, M. M. K. N. H., & Rashid, A. (2017). Big Data Value Dimensions in Food Disaster Domain. Innovation, 11(1), 25-29
© 2020 The Author(s). Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Continue reading from the same book
Natural hazards.
Published: 30 June 2021
By Md. Shahin, Sanjida Akter, Prome Debnath and A.K.M...
651 downloads
By Diana Dimitrova
548 downloads
By Keyoor Pathak and Chittaranjan Subudhi
580 downloads

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
127 Flood Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Floods are natural disasters that can have devastating effects on communities and ecosystems. They can cause widespread destruction, displacement of people, and loss of life. Writing an essay on flood-related topics can help raise awareness about the importance of preparedness and resilience in the face of such disasters. Here are 127 flood essay topic ideas and examples to inspire your writing:
- The impact of floods on agriculture and food security
- The role of climate change in increasing the frequency and intensity of floods
- How urbanization and deforestation contribute to flooding
- The social and economic costs of flood disasters
- The psychological effects of experiencing a flood
- The importance of early warning systems in flood preparedness
- How communities can build resilience to floods
- The role of government in mitigating flood risks
- The intersection of race, class, and vulnerability in flood disasters
- A comparative analysis of flood management strategies in different countries
- The ethical implications of rebuilding in flood-prone areas
- The impact of floods on wildlife and ecosystems
- The challenges of providing aid and relief after a flood
- The role of technology in predicting and monitoring floods
- The relationship between floods and water pollution
- The long-term effects of flooding on infrastructure
- The cultural significance of floods in different societies
- The role of insurance in mitigating the financial impact of floods
- The health risks associated with flooding
- The impact of floods on tourism and local economies
- The role of NGOs in disaster response and recovery after a flood
- The connection between floods and water scarcity
- The impact of floods on education and school infrastructure
- The role of community-based organizations in flood preparedness
- The impact of floods on mental health
- The effectiveness of flood protection measures such as levees and dams
- The ethical dilemmas of prioritizing resources in flood response
- The impact of floods on vulnerable populations such as the elderly and disabled
- The relationship between floods and infectious diseases
- The impact of floods on transportation and mobility
- The role of media in shaping public perceptions of floods
- The impact of floods on small businesses and entrepreneurship
- The challenges of rebuilding after a flood
- The impact of floods on water quality and sanitation
- The role of education in increasing awareness about flood risks
- The impact of floods on cultural heritage sites
- The connection between floods and climate refugees
- The impact of floods on mental health in children
- The role of community engagement in flood preparedness
- The impact of floods on gender dynamics and women's empowerment
- The relationship between floods and humanitarian crises
- The impact of floods on energy infrastructure
- The role of faith-based organizations in flood response and recovery
- The impact of floods on indigenous communities
- The effectiveness of early warning systems in reducing flood casualties
- The impact of floods on housing and homelessness
- The role of international aid in responding to flood disasters
- The impact of floods on waterborne diseases
- The relationship between floods and food insecurity
- The impact of floods on mental health in first responders
- The role of social media in disaster communication during floods
- The impact of floods on air quality and respiratory health
- The connection between floods and environmental justice
- The impact of floods on mental health in displaced populations
- The role of community-based adaptation in flood resilience
- The impact of floods on educational attainment and school performance
- The relationship between floods and conflict and violence
- The impact of floods on access to healthcare and medical services
- The role of local government in flood preparedness and response
- The impact of floods on water scarcity and drought
- The connection between floods and food waste
- The impact of floods on social cohesion and community resilience
- The role of art and storytelling in documenting flood experiences
- The impact of floods on wildlife conservation and biodiversity
- The relationship between floods and mental health stigma
- The impact of floods on infrastructure and public services
- The role of technology in connecting flood survivors with resources
- The impact of floods on cultural traditions and practices
- The connection between floods and displacement and migration
- The impact of floods on access to clean water and sanitation
- The role of youth in advocating for flood resilience and preparedness
- The impact of floods on LGBTQ+ communities and mental health
- The relationship between floods and poverty and inequality
- The impact of floods on access to education and learning opportunities
- The role of faith and spirituality in coping with flood trauma
- The impact of floods on mental health in older adults
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Flood
List of essays on flood in english, essay on flood – essay 1 (150 words), essay on flood: reasons, effects and conclusion – essay 2 (250 words), essay on flood in india – essay 3 (300 words), essay on flood: causes, consequences and prevention – essay 4 (400 words), essay on flood: types, causes and adverse effects – essay 5 (500 words), essay on flood: with causes, mitigating steps and warning system – essay 6 (600 words), essay on flood: with causes – essay 7 (750 words), essay on flood in india – essay 8 (1000 words).
Introduction:
Flood, simply put is an overflow of water from several sources. The nature of the world is to have dry land and water. When water gets on dry land in large quantity flood is said to have occurred.
Causes of Flood:
There are several events that can lead to a flood.
A few of them are highlighted below:
1. Heavy rain pours.
2. Melting ice and snow.
3. Rising sea levels and the overflowing river.
4. Bad drainage systems.
How Flood Affects our Environment:
A flood is by far a negative occurrence. Heavy flooding can have a damaging effect on our environment and the infrastructures in it. First, they can destroy houses and make them inhabitable. Also, they can remove sand from farmland making it difficult to grow crops. Aside from the above, flooding also contaminates clean water causing diseases and ailments.
Conclusion:
Governments around the world can reduce the risk of flooding by building a solid drainage system. We as individuals could also help by stopping drainage blockage.
Any dry land filled by excess water is called flood. It is a natural calamity caused due to several factors.
Reasons for Flood:
The reasons for floods can be natural and unnatural caused due to human activities. When there is excessive rainfall in river banks and coastal areas, there is an increase in water level which leads to overflow of water into the nearby dry land. Also, natural calamities like earthquakes cause Tsunami in oceans which leads to flooding of lands close to beaches. In heavily populated cities, due to congested buildings and roadways, flooding happens as there is not enough room for water to drain. In such cases clogged drainages lead to even more flooding of the area.
Global warming has resulted in the melting of glaciers which increase water levels of rivers and flooding of river banks. Deforestation also plays a major role in flooding.
Effects of Flood:
Floods cause large scale destruction to life and property. Buildings, roads and bridges are heavily damaged. Vast acres of crops are destroyed. Arable lands turn barren and clogged with salts. Countless homes and cattle get washed away. All electronic and digital communication seizes. Many lives are lost. And it does not stop there. Post flood, there is a huge risk in the spreading of water borne diseases. Scarcity of food and basic necessities arises. On the whole, floods cause multiple hardships and turn the livelihood of affected people upside-down.
Effective weather forecasting systems are to be maintained by the Government for timely intimation and evacuation of flood prone areas which will greatly help in keeping the many losses due to floods in check.
Flood is a natural disaster that involves overflowing of water over a region of land that is dry under usual conditions. It submerges the area with water. They are the most common kind of weather-related disasters and are a costly hazard. The level of flood can vary a lot – from a few inches to a level that goes up to meters high like a roof level of a house.
The causes of floods are many. They can happen during heavy rains when the drainage system is unable to handle the amount of rain fall. It can also happen even if low levels of rain occur continuously for many days. Floods can occur when the snow melts as temperature changes and it can result in bulk movement of water in the plains. Rivers can overflow sometimes and create flood in the neighboring regions. They can also be a result of breaking of dam which can flood the nearby areas.
There has been increase in the frequency of floods recently. Because of global warming, the average temperature of sea has increased significantly. This has led to higher rate of tropical storms in the Caribbean. It is also responsible for increase in sea level because of melting of ice caps and glaciers.
Floods cause large-scale loss to life and great damage to properties. Floods cause severe damage to agricultural regions of the affected area. There is loss of life of humans as well as animals. People and the government both suffer from loss in financial terms. Re-building of affected areas takes a lot of time and money.
In India, there are many regions which are affected by floods. Some of these are the Gangetic plains, coastal Andhra Pradesh and Orissa, Brahmaputra valley and South Gujarat. Within this year, more than 70 lakh people were affected by floods in India.
Flood is one of the recurring natural disasters which is an outcome of above average rainfall and accumulation of excessive water in every living area. Floods may occur due to overflow of water from the reservoirs or due to heavy down pour of rain in places where the drainage systems are not properly maintained.
Water may look so harmless and peaceful until the large quantities termed Floods harms us.
Common Causes of Flood:
Some of the common causes of Flooding are Heavy Rains, Overflowing Rains, Broken Dams, Urban Drainage Basins, Storm Surges & Tsunami’s, Channels with steep sides, lack of vegetation and melting of snow and Ice. Although the causes of floods are varied, most of the causes can be managed if not prevented.
Global Warming and Floods:
Another primary factor of Flood is increase in the atmospheric temperature i.e., Global Warming. Heating up of earth’s surface can lead to melting of ice glaciers and ice caps which leads to the rise in sea level thereby leading to overflowing floods in the coastal regions. Global Warming brings instability in the climatic condition of the earth, where one part of the world experiences floods and the other goes through drought.
Consequences of Flood:
Floods mostly disrupt the normalcy of living things on the planet. Floods are a great threat to the living things; floods also make way for mosquitoes to thrive thereby leading to all communicable diseases such as malaria, Dengue etc. Another impact of floods is loss of drinking water . Floods also lead to power cuts, damage of crops and soil erosion. Floods can also have an economic backslide, thus putting the country at risk.
Preventing Floods:
Some of the measures that can be done to prevent Floods are:
i. To ensure the meteorological departments are well equipped to provide flood warnings to the indicated zones.
ii. Flood resilient homes with efficiency to waterproof homes and moving electric sockets which moves higher as the flood rises.
iii. Protecting wetlands and planting trees systematically can help alleviate the direct floods.
iv. Stop encroaching of river beds and allowing the rivers to take its natural course can drastically bring down floods.
Floods can be scary, but it is in the hands of human beings to ensure it doesn’t impact our daily life. Water storing areas such as ponds, lakes and other water reservoirs should be maintained. Floods can be avoided by improving the soil conditions thereby allowing easy water absorption. Flood barriers can be used as a defense during Flood crisis.
Floods can either occur naturally or they can be facilitated by environmental factors that destruct the flow of water. Flood incidences have increased due to global warming. Global warming is an adverse effect of environmental pollution that causes a rise in temperatures on the earth’s surface. Global warming is associated with intense climatic changes like heavy storms, snowing and raised sea water levels. These changes in climate contribute to flooding. A flood is the spilling of water on dry land surfaces and causes it to submerge. It occurs when water overflows from the water bodies beyond its usual boundaries. Floods are destructive to the environment.
Types of Floods:
There are three main types of floods. Surge floods are floods that occur in the coast regions due to surges and tidal changes that occur in the sea or ocean. Hurricanes and storm surges on the sea or ocean can cause minor, moderate or major floods. The extent or severity of the floods are determined by the strength, size, speed and directions of the surges. Surge flood are usually severe and massively destructive.
Another type of floods is fluvial floods that occurs due to overflow of rivers. Rivers overflow due to heavy rains that increase water levels in rivers beyond its capacity therefore resulting in floods. Heavy snowing can also cause fluvial floods when the ice melts. Fluvial floods are risky when dams are involved because the increased levels of water in rivers creates immense pressure that cause increase pressure on the walls of dams and cause breakage which results in excessive flooding and environmental destruction.
The other type of floods is pluvial floods. Pluvial floods are caused by surface water as a result of heavy rainfall. Pluvial floods are destructive because they disrupt the drainage systems and cause an overflow which affects structures. Pluvial flooding occurs together with surge floods and fluvial floods. Although pluvial flooding does not involve a lot of water, it causes massive destruction of the environment and the infrastructure.
Causes of Floods:
Floods occur naturally due to some environmental factors. Heavy rains can cause an overflow of water form water bodies. Breakage of water body boundaries like riverbanks or walls of dams. Catastrophes like tsunamis and surges in storms cause heavy flooding. During heavy rains the lack of vegetation on the surface of the earth.
Adverse Effects of Floods:
Foods are destructive in nature and have negative impacts on the environment and the ecosystem. Floods cause death of living things and humans. Destruction of property and infrastructure negatively affects the economy of the region affected and economic activities are at a standstill due to disrupted livelihoods. Migrations from areas that are prone to floods is common, which results in overpopulation in urban areas. Financial constraints are experienced due to the rehabilitations from flood destructions. Prevention of floods that result from natural causes is a challenge.
In conclusion, it is evident that floods are destructive. The adverse effects of floods affects normal livelihood and the environment.
Flood is one of the natural calamities which is known to wreck a lot of havoc. There are so many different instances wherein floods are known to damage the whole area and bring massive loss of life and property as well.
Let us check further into the possible causes of flood and how we can eradicate it too.
The Causes of Flood:
Of course, there can be a lot of different cases of floods. Some of the key ones among them are as follows.
Heavy rains: owing to climate changes, many a times, it so happen that it rains torrentially. If the rain is much above normal, it can lead to flooding.
Broken dams: Dams help in keeping the water level in check. If the dams get broken sometimes, it is likely to lead to flood.
Tsunami: Natural calamities like tsunami is likely to create problems of flood and can bring massive loss of life and property.
Global warming: Owing to the increase in global temperature, the ice cap is melting and the increased level of water in the river bed is going to cause a flood.
Of course, there can be a lot of other reasons too which leads to flood and it is important to keep an eye on the water levels to issue a warning well in time.
The Mitigating Steps:
Now that we know the key causes which leads to flood, let us focus on some of the best mitigation measures which you can take to steer clear of this problem.
Flood Warning System:
This is by far the most important thing which one needs to do. It is important to have a sound flood warning system in place. When you have a dedicated system, it can help warn people who can move to higher altitude or take the right steps.
Restore Rivers to their Natural Courses:
Owing to the excessive development work which we have been carried out and harming the environment, too many rivers have diverted from their natural courses. This is another important reason for excessive flood. So, the right thing to do is to help in restoring the rivers to their natural course as it may prevent flood.
The Global Warming Remedial:
Action must be taken to cure the problem of global warming as it is definitely the cause of too many natural disasters. By choosing to cut the level of air and water pollution and minimizing the use of non bio-degradable products, we may be able to directly or indirectly help in controlling the problem of flood and its aftermath.
Modern Day Construction:
While flood is a natural calamity which may sometime come unannounced, it is important that we construct buildings in accordance with the modern technical advancements. The buildings should be so made that they are above the flood levels and they should be sturdy enough to withstand flood as well.
So, these are some of the important points which you should keep in mind. While some of them are ways by which we can prevent the implication and aftermath of flood, a few of them would help in preventing its occurrence as well.
Whenever any calamity occurs, it is important to do your bit to create awareness. The kind of destruction which can happen is whopping. By knowing about it a little ahead of time helps people be better prepared for it.
The bottom line remains the fact that we should all try and minimize the negative impact we are having on the environment. Doing this will ensure that we will be able to curtail the frequency of natural disasters like flood.
Flood is simply defined as the overflow of a very huge quantity of water that covers a very large area of land and leads to the destruction of land and properties and sometimes lives in the areas that are affected. A lot of regions in the world experience flooding every year. A flood basically occurs when there is excessive rain and there is no proper or good drainage system. The amount of flood is different from place to place and the extent of destruction also varies. For the overflow of water to be classified as flood, the area of land affected has to be mostly dry. Flooding can also happen as a result of water overflowing from bodies of water like lakes, oceans and rivers. Floods cause mass destruction. The effects and destruction caused by flood can take many years to fix and repair.
There are a lot of causes of flood; a few of them are discussed below:
1. Heavy Rains:
As discussed earlier, flood is mostly caused by an extended period of rain. This can happen if the quantity of rainfall is a lot more than the capacity of the drainage system. Flood can also be a result of high intensity rainfall in a short period of time.
2. Snow Melting:
Mountains that were covered with snow in the season of winter start to melt once temperature begins to rise. The sudden rise of the temperature causes the snow to melt and this leads to the massive movement of a lot of water to the plains and lands around. If the area receiving the water does not have a proper and good drainage system that will help in getting rid of the large quantity of water, there is going to be flooding. Flood that is caused by snow melting is also called a snowmelt flood.
3. Dam Breaking:
Dams are constructed to be able to hold the water that is flowing downwards from an area of land that is higher. The energy of the water can be used to turn and power propellers that can be used for the generation and creation of electricity. The dam can sometimes break when they can’t hold a large quantity of water and this causes the areas nearby to experience flooding. Sometimes, excessive water can be released intentionally by the dam to stop the dam from breaking which also results in flood but the flood from the intentional release of water isn’t as harsh as that from the dam breaking.
4. Water Bodies Overflowing:
Rivers and other water bodies can overflow sometimes and this leads to a situation that is flood like in the areas nearby. The areas that are low lying and are near the water body are the ones that are affected the most during the periods of water overflowing downstream.
5. Coastal Region Winds:
Hurricanes and very strong winds have the ability to carry sea water into coastal lands that are dry and this is a serious cause of flood. The coastal regions can experience severe damage and destruction. Tsunamis and hurricanes are widely known causes of serious devastation to areas of coastal lands.
Apart from all of the causes of flood discussed above, it is very important to note that the major cause of flood is global warming. The frequency and rate of flood has drastically increased recently. Researchers have said that the average temperature of the sea has wildly increased because of global warming and it has led to the increased sternness and rate of storms that are tropical in and around the Caribbean. The storms are said to have caused the countries in the region experiencing heavy rainfall. Global warming causes an increase in the atmosphere’s temperature and also causes the ice caps and glaciers to melt which in turn causes flood in a lot of regions. Global warming is believed to have a very major effect on the ice caps at the poles and it is believed that the situation is only going to get worse with time.
Overall, the climatic conditions of the earth have gone through a lot of very major changes and it is believed that global warming is the main cause of all of the change. It is believed that global warming is the reason why there is extreme drought in some places and serious flood in other places. Even though there isn’t much we can do about the glaciers melting or rain, we can do our part by building very good and reliable drainage systems that can handle water.
What is a flood? In normal terms, the excess availability of water in a region then it can usually hold is called flood. Floods are usually heard of it in news and through channels as every year, large portions of India are drastically affected by floods. It is mainly during the monsoon season with the onset of rain, we hear of different floods and the havoc they have caused to humans, animals and plant life. It is, therefore; very important to understand what floods are all about?
Types of Floods and their Causes:
Flood is not just the excess rainfall we talk about. There is a lot more to it. For instance, there are Flash Floods in which there is a sudden heavy downpour due to a cloudburst and the entire area is flooded within minutes. In India, areas in the states of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir and Uttarakhand witness occurrence of flash flood every year. Similarly, we have river floods in which the areas around a river are flooded due to the swelling of the river. Some parts in Delhi witness river flood every year due to the overflowing of the river Yamuna due to excessive rains and the excess flow of water from the Hathnikund Dam. Another type of floods is the inland flooding . In the case of inland flooding, the area witnessing a rainfall get flooded with the roads and lanes all filled with water. This happens usually when proper drainage system is not in place or is inefficient due to severe blockages which obstruct the flow of water and leading to flooding of lanes and roads in the city. Again, Delhi and Mumbai are cities which see such floods even after an hour of continuous rainfall. People living in coastal areas are prone to coastal floods . These floods are usually caused by high tides or Tsunami which bring huge volumes of water on the land thereby flooding it. Another reason for coastal floods is global warming due which the rise in sea level temperatures has led to the subsequent rise in water level in coastal areas. Coastal areas of Kerala, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Orissa witness such floods every year.
Deadliest Floods in Indian History:
India witness floods every year in different states. In fact, some regions are sure to be flooded with the onset of monsoon season. However, there have been occurrences of the flood which have caused massive destruction and hence are termed as the deadliest floods. Hence there is a need to know about them so as to understand and analyse what can be done in order to minimise such destruction in future years.
Deadly floods are a common occurrence in India after every few years. One of the deadliest floods in recent times was the flood in Gujarat in the year 1979 in the Machhu Dam-II. The Machhu Dam-II flopped on Aug. 11, 1979, discharging the full power of the Macchu River on the town of Morbi. The flood thus created in western India caused somewhere around 1,335 deaths, as per the Press Trust of India at the time.
Another of the deadliest floods in India is the one that shook Bihar in the year 1987 in the Kosi River. In any case, the Kosi River is prone to floods and is flooded almost every year. However, this year was particularly exceptional. The most decimating surge in Bihar’s history happened in 1987, when an avalanche obstructed the Bhote Kosi River, making it surge and crush more than 1.7 million homes. As per the statistics of the state, government flooding led to the death of 1,399 individuals and 5,302 animals.
The Tsunami that struck coastal India in the year 2004 was another such disaster which engulfed a number of lives. An extent 9.0 quake under the Indian Ocean on Dec. 26, 2004, set off a tidal wave that crushed southern India. As per the Government statistics 10,749 individuals died, 5,640 went missing and 2.79 million people were affected by the wave. It likewise devastated 11,827 hectares of products and demolished the occupation of 300,000 fishermen.
The Recent Kerala and Kedarnath Floods:
The most noticeably bad climate-related floods in India’s history happened in June 2013, when a few days of overwhelming precipitation activated blaze surges and avalanches in the northern territory of Uttarakhand. The downpour struck amid the bustling visitor season in Uttarakhand when a huge number of Hindu pilgrims rush to the region to visit its memorable sanctuaries. The rain happened some time before the start of rainstorm season, getting numerous off guard. An expected 4,094 individuals died and about 1 million were influenced by the catastrophe in Uttarakhand and neighbouring Himachal Pradesh, the worst affected being the region around Kedarnath. The military was brought in to evacuate around 100,000 people from rocky parts of the state, where they had turned out to be caught by the avalanches.
The recent floods in Kerala are another perfect example of how human activities have led to calling of nature’s ire in different forms such as floods. Had it there been a proper drainage system with no blockages, Kerala would not have witnessed such a massive flood.
The Need for Action:
We must not forget that older civilisations emerged around rivers and seas only and they just vanished with time due to the ever-rising water level on the earth. With the recent back to back occurrences in Kedarnath and Kerala, it is high time the Government as well all of us sit down and think what harm we have done to nature. The blooming of industrial units with no waste management in place, the inefficient drainage system and the careless attitude of both the Government and the people are all collectively responsible for these disasters. Not all disasters can be avoided, but, at least measures can be taken to minimise their impact or at least the ones caused by own carelessness can surely be avoided. It is for own good and for the benefit of future generations that we all do our bit to protect the life on earth from the backlash of nature.
Flood , Flood in India , Natural Disasters
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Essay on Success
- Essay on My School
- Essay on Noise Pollution
- Essay on Christmas
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Disaster Management
- Updated on
- May 10, 2023

Disaster Management has been essentially included in the study curriculums of secondary education. Whether it is natural or man-made, disasters can wreak havoc on our surroundings and cost human lives as well. To familiarise students with efficiently preventing and ensuring the safety of living beings and our environment from unprecedented events, the study of Disaster Management has been included as an important part of the Geography class 10 syllabus. This blog aims to focus on imparting how you can draft a well-written essay on Disaster Management.
This Blog Includes:
What is disaster management, essay on disaster management: tips & tricks, sample format for essay on disaster management in 150 words, sample essay of disaster management (150 words), sample essay on disaster management (300 words) , sample essay on disaster management (500 words), essay on disaster management for class 9 onwards, essay on disaster management in india.
To begin with your essay on Disaster Management, the most important thing is to comprehend this concept as well as what it aims to facilitate. In simple terms, Disaster Management is termed as the management and utilisation of resources as well as responsibilities to tackle different emergencies, be it man-made disasters or natural ones. It concentrates on preparing human beings for a varied range of calamities and helping them respond in a better way as well as ensure recovery thus lessening their overall impact.
Preparing for the Writing Section for Your English Exam? Then Check Out Message Writing and Letter Writing !
Before drafting your essay on Disaster Management, another thing you need to ensure is familiarising yourself with the structure of essay writing. To help you understand the do’s and don’ts, we have listed down some of the major things you need to keep in mind.

- Research thoroughly about your topic. For example, while writing an essay on Disaster Management, explore the recent happenings and mention them to provide the reader with a view into your understanding of this concept.
- Create important pointers while researching that you can further incorporate into your essay.
- Don’t mug up the definitions but comprehend them through examples.
- Use transitions between paragraphs to keep a coherent flow for the reader as a long paragraph might seem too lengthy and segregating your introduction and conclusion can provide a better structure.
- Quote important examples not only in your introduction but also in the following paragraphs where you detail the given topic.
- Revise and add finishing touches once you have completed the essay to locate any grammatical errors as well as other mistakes.
Now that you are aware of the key elements of writing an essay on Disaster Management, take a look at the format of essay writing first:
Introduction (30-40 words)
Begin with defining your topic explained in simple terms. For Disaster Management, You can make it more interesting by adding a question or a recent instance. The introduction should be understandable aiming to become more specific in the subsequent paragraphs.
Related Article: Geography for UPSC Preparation
Body of Content (80 words)
Also termed as the thesis statement , the content after the introduction should explain your given topic in detail. It should contain the maximum content out of the whole format because it needs to be detailed. For Disaster Management, you can delve deeper into its process, how it is carried out for different situations as well as prevention and protection.
Conclusion (30-40 words)
This section should mainly wrap up what you have described in the above paragraphs. For an essay on Disaster Management, you can focus on summing it up by writing its aim, types and purposes briefly.

Disaster can be simply termed as a sudden incident or happening which can be either natural or man-made and can potentially cause damage to the surroundings or loss of human life. To facilitate preparedness and better responsiveness to unforeseen events which can harm human beings and the environment, Disaster Management came into the picture.
Disaster Management aims to lessen the impact of natural and man-made calamities by designing and planning efficient ways to tackle them. It centrally comprises ensuring better control of the situation, its immediate evaluation, calling up required medical aids and transports, supplying drinking and food sources, among others and during this whole process, protecting the surroundings from more harm and keeping the lawfulness. The importance of Disaster Management has further increased in the contemporary scenario with the prevalent climate change and some of its latest examples include the unprecedented Australian wildfires.
Thus, the planet is getting bogged down by infinite technological devices, and their possible effects on the climate and the environment are inescapable. This has led to Disaster Management becoming the need of the hour as every country is aiming to become efficient and prepared to face both natural and man-made calamities.
Since the dawn of time, disasters, whether natural or man-made, have been a part of man’s evolution. Tsunamis, cyclones, earthquakes, floods, accidents, plane crashes, forest fires, chemical disasters, and other natural disasters frequently strike without notice, leading to massive loss of life and property. Disaster management refers to the strategies and actions put in place to lessen and prevent the effects of a disaster.
The word “disaster management” refers to all aspects of catastrophe mitigation, including preventive and protective measures, preparedness, and relief activities. The disaster management process can be separated into two phases: pre-disaster planning and post-disaster recovery. This encompasses measures such as prevention, mitigation, and preparedness aimed at minimising human and property losses as a result of a possible danger.
The second category is activity post-disaster recovery in which response, rehabilitation, and reconstruction are all included. Search and rescue evacuation, meeting the victims’ basic needs, and rapid medical support from regional, national, and international authorities were all part of the response phase. The immediate purpose of the recovery phase is to restore some degree of normalcy to the afflicted areas. In resource-scarce countries, ex-ante risk mitigation investment in development planning is critical for decreasing disaster damage. It would be prudent to go from a risk-blind to a risk-informed investment decision.
We cannot prevent disasters, but we can reduce their severity and arm ourselves with knowledge so that too many lives are spared.
Introduction:
The globe is plagued with disasters, some of which are terrible and others that are controllable. Natural calamities, for example, are sudden occurrences that wreak significant devastation to lives and property. Disasters can occur either naturally or are man-made. To repair the damage caused by these disasters, emergency management is required. Through a disaster management procedure, the damage is contained and the hazards of the event are controlled. The procedure is aimed at averting disasters and reducing the effects of those that are unavoidable. Floods, droughts, landslides, and earthquakes are all threats to India. The Indian government’s disaster management measures have vastly improved over time.
The Process of Disaster Management:
The disaster management process is split into four stages. The first phase is mitigation, which involves reducing the likelihood of a disaster or its negative consequences. Public education on the nature of the calamity and how people may prepare to protect themselves, as well as structural construction projects, are among the actions. These projects are intended at reducing the number of people killed and property destroyed in the event of a disaster.
Preparedness is the second phase of disaster management, and it aims to improve government-led preparedness to deal with emergencies. The majority of the preparations are aimed toward life-saving activities. Plan writing, communication system development, public education, and drills are all part of the preparation process. The disaster management team implements measures to keep people alive and limit the number of people affected in the third phase, reaction. Transport, shelter, and food are provided to the afflicted population as part of the response. Repairs are being made, and temporary solutions, such as temporary housing for the impacted population, are being sought.
Recovery is the ultimate stage of disaster management. This normally happens after the tragedy has subsided and the harm has been done. During the recovery process, the team works to restore people’s livelihoods and infrastructure. Short-term or long-term recovery is possible. The goal is to return the affected population to a normal or better way of life. During public education, the importance of health safety is highlighted. The recovery phase allows catastrophe management to move forward with long-term solutions.
Disaster Management Challenges:
The management of disasters is a difficult task, and there are certain flaws to be found. Since the individual dangers and disasters in some countries are not well understood, the government is unable to deploy disaster management in the event of an unforeseen disaster. There’s also the issue of a country’s technical and framework capabilities being insufficient. Government support is required for disaster management frameworks. Due to the generally large population, the disaster management approach includes public education, but there is no psychological counselling for individuals. People are more likely to develop post-traumatic stress disorder and psychiatric illnesses.
Conclusion:
Disaster management is a very important activity that countries should embrace to prevent disasters and lessen the negative consequences of disasters. However, disaster management has limitations that restrict the techniques’ ability to be implemented successfully.
Disasters can cause chaos, mass death of humans and animals, and a rise in crime rates. Disasters are unfavourable events that cause widespread anxiety and terror. They also make it difficult for society to respond to its causes.
Natural or man-made disasters can emerge. In both circumstances, they have the potential to cause significant loss of life and property. A combination of man-made and natural disasters can occur in severe circumstances. For example, violent conflicts and food scarcity. As a result, disaster management is required to limit or prevent massive loss and damage.
Disaster management includes disaster avoidance, disaster awareness, and disaster planning. These ideas will be discussed further down.
Prevention of Disaster:
Countries all across the world have taken precautions to prevent diseases or viruses from spreading. These initiatives include the funding of research into natural disaster aversion. Other sources of revenue include food distribution, healthcare services, and so on. In Africa and the Middle East, the latter is commonly used in economically challenged areas.
Improved scientific research has also made it feasible to predict potential natural disasters. For example, equipment to detect earthquakes and tsunamis has been developed. As a result, more people are concerned about the environment. In this sense, consciousness translates to a reduction in all forms of pollution in the environment.
Disaster Awareness :
Another strategy to minimise the excesses of widespread epidemics is to raise disaster awareness. Members of the public must be made aware of the importance of maintaining peace, de-escalating dangerous circumstances, and prioritising safety in the face of any possible tragedy.
The goal of disaster management is to reduce human death and suffering. The impact of disasters can be reduced if all of these factors are successfully managed. As a result, the necessity of disaster management cannot be emphasised.
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) is the main agency charged with establishing rules and guidelines for disaster management in order to ensure prompt and effective disaster response. There is also a separate fund for mitigation called the “national disaster management fund” (NDMF). Functions performed by this agency are:
- Administration
- Formation of policies for disaster management
- Approval of the strategies made up for disaster mitigation
- Formation of revenue or funds for disaster mitigation
- Managing multiple programmes and disseminating instructions.
The disaster has had both direct and indirect repercussions on human life, both of which have been deadly devastating and detrimental. There have been fatalities as well as stock losses. Natural disasters are unavoidable; even if we have mechanisms in place to predict or forecast them, we cannot prevent them from occurring. While preparing plans for our disaster management, the best that can be done is to prevent behaviours that are detrimental to the environment and lead to environmental deterioration. When a disaster strikes, it causes widespread devastation and loss of life. In the event of a disaster such as earthquakes, floods, or other natural disasters, a large number of people are displaced, and a large number of people die as a result of the disaster. This is when the true emergency begins by providing first aid to the injured, as well as rescue and relief efforts for the victims. To limit the risk of human life, everyone must participate actively in disaster management. When a crisis happens, the appropriate disaster management team can seize over as soon as possible.
Also Read: Career in Ecology and Environment
The 4 phases of disaster management are Mitigation, Preparedness, Response, and Recovery.
The 3 types of disasters are natural, man-made, and hybrid disasters.
On 23 December 2005, the Government of India enacted the Disaster Management Act
Hence, we hope that this blog has helped you understand the key steps to writing a scoring essay on Disaster Management. If you are at the conclusion of the 10th grade and confused about which stream to take in the next standard, reach out to our Leverage Edu expert and we’ll guide you in choosing the right stream of study as well as gain clarity about your interests and aspirations so that you take an informed step towards a rewarding career.
Sonal is a creative, enthusiastic writer and editor who has worked extensively for the Study Abroad domain. She splits her time between shooting fun insta reels and learning new tools for content marketing. If she is missing from her desk, you can find her with a group of people cracking silly jokes or petting neighbourhood dogs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.

Essay on Flood for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Essay on Flood: Flood is an overflow of huge amount of water covering large areas causing destruction at the places affected. Many regions across the globe face the problem of floods each year.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Flood occurs due to excessive downpour and lack of proper drainage system. The severity of flood may vary from region to region and the destruction caused due to the same varies accordingly.
Long and Short Essay on Flood in English
Here are essays on flood of varying lengths to help you with the topic whenever you required. You can chose any flood essay according to your need:
Flood Essay – 1 (200 words)
Floods are caused in areas where there is excessive downpour and poor drainage system. Flood is also caused because of other reasons including overflow of water from rivers and oceans, overflow of water in the plains due to dam break, excessive flow of water owing to sudden melting of glaciers. In coastal areas hurricanes and tsunamis cause flood. Floods can cause major destruction just as other natural calamities.
Several towns and cities around the world have suffered from severe floods that have cost lives of people and animals, resulted in loss of property and other valuable assets and destruction of soil and plants. Farmers are majorly impacted by floods as their crops get ruined owing to this weather condition. Water accumulated for days at a particular place also results in the outbreak of various diseases. When the condition is severe, the schools and offices are shut and it thus disturbs the normal life of people. Places that face severe floods take months to resurrect.
The irony is that there are certain regions that are hit by flood frequently and even though the government is aware about the problem, proper measures are not being taken to overcome it. The government must build good drainage system and water storage systems to control this problem.
Flood Essay – 2 (300 words)
Flood caused due water logging that is mostly a result of heavy rainfall are known to have fatal consequences. It results in loss of life, rise in diseases, price rise, economic loss and destruction of the environment among other issues. The impact the floods depend on their type and severity.
Types of Floods
Some floods can subside in a few days while others take weeks to subside and have a major impact on the lives of the people living in that area. Here is a look at the different types of floods:
- Slow On-set Floods
This type of flood is caused when the water bodies such as rivers overflow and affect the nearby areas. This flood develops slowly and may last from a few days to weeks. These spread over several kilometres and mostly impact the low lying areas. Water accumulated due to flood in such areas may cause harm to property and can also be a cause of various diseases.
- Rapid On-set Floods
These take a slightly longer to build and can last for a day or two. These are also known to be extremely destructive. However, people are mostly warned about these and have a chance to escape before the situation becomes worse. Tourists planning holiday to such places can postpone or cancel the plan when there is still time and avoid the trauma caused by this situation.
- Flash Floods
Flash floods mostly occur within a very short duration of time such as a few hours or even minutes. These are mostly caused due to heavy rainfall, melting of snow or dam break. These are known to be the most fatal among all and can result in mass destruction as these are almost sudden and people do not get any time to take caution.
Floods disrupt the day to day life in the affected regions. They cause various problems for the people living in such areas. Regions hit by severe floods take months and at times even years to rebuild.
Flood Essay – 3 (400 words)
Flood is a natural disaster that is caused due to the accumulation of excessive water in a region. This is often an outcome of heavy rainfall. Many regions also face flood due to overflow of river or ocean water, breaking of dams and melting of snow. In the coastal areas, hurricanes and tsunamis are known to bring about this condition.
Flood-Prone Regions around the World
Several regions across the globe are prone to frequent floods. The cities around the world that face severe and frequent floods include Mumbai and Kolkata in India, Guangzhou, Shenzen and Tianjin in China, Guayaquil in Ecuador, New York, NY-Newark, NJ, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, Miami and New Orleans. Floods are known to have caused mass destruction in these areas in the past.
How to Control the Problem Caused Due to Floods?
From damaging the environment to disrupting the human life – floods have several negative repercussions that are difficult to deal with. It is thus important to take measures to control the same. Here are a few ways to control this problem:
- Flood Warning Systems
It is the need of the hour to set up better flood warning systems so that people are warned about the upcoming problem right on time and they have enough time to safeguard themselves and their belongings
- Construct Buildings Above the Flood Level
Buildings in the flood prone area must be constructed above the flood level so as to avoid damage to the property as well as the people living there.
- Introduce Water Storage System
The government must invest in building water storage systems to store and reuse the rain water. This way the excessive water can be put to use instead of letting it overflow on the plains and cause flood.
- Strengthen Drainage System
One of the main causes of flood is the poor drainage system. It is essential to build good drainage systems to avoid water logging that results in flood.
- Install Flood Barriers
Flood barriers should be installed in the areas that are prone to flood. These can be removed once the water recedes.
While the occurrence of rainfall, melting of snow-mountains, overflowing of water bodies and hurricanes can be difficult to control however these can be predicted in most cases and the government can take measures to ensure that water logging, that in turn results in flood, does not happen as a result of these conditions. This can be done by employing few of the methods shared above.
Flood Essay – 4 (500 words)
Floods are caused by a number of reasons including heavy rainfall, overflow of water from water bodies such as rivers and oceans, melting of glaciers, hurricanes and strong winds along the coastlines. When there is a lack of good drainage system to suck up the excessive water it results in water logging that causes flood.
Consequences of Flood
Floods disrupt the normal functioning of the region affected. Severe floods can result in mass destruction. Here is how floods impact life on earth:
- Threat to Life
Many people and animals lose their lives because of severe flash floods. Many others get injured and are infected by various diseases. Water accumulated at places for days result in the breeding of mosquitoes and other insects that are the cause of various diseases such as malaria and dengue. Cases of dysentery, pneumonic plague and military fever are also on rise during this time.
The supply of electricity and water is disrupted during this time thereby adding to the problems of the general public. There is also a risk of catching current in places where the electricity supply is still intact.
- Economic Loss
Many people lose their houses and other assets such as automobiles that they take years to earn. It is also a costly affair for the government as it has to deploy a number of policemen, firemen and other officials to conduct the rescue operation. In case of severe floods, the affected regions take years to re-build.
The supply of goods in the flood affected areas lowers as the road transport cannot reach there. Besides, the goods stored in these areas also get spoiled due to floods. There is a shortage of supply and the demand is high and it thus results in increased prices of the commodities.
- Soil Erosion
When the downpour is too heavy, the soil cannot absorb the entire water and it often results in soil erosion which in turn has dreadful consequences. In addition to the erosion of soil, the quality of soil is also impacted, often degraded.
- Damage of the Flora
Floods are not just a threat to the human beings and animals but also destroy the flora. Heavy rains are often accompanied by thunder, lightning and strong winds. These storms are a cause of uprooting of trees. Besides, the crops are damaged and several other plants are eroded during floods.
Flood Prone Areas in India
A number of regions in India face the problem of floods year after year. The major areas affected by this natural calamity in the country are most of the Gangetic plains including North Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal, Mumbai, Maharashtra, parts of Punjab and Haryana, coastal Andhra Pradesh and Orissa, the Brahmaputra valley and South Gujarat. Floods are known to have caused severe damage to these places in the past and are still a threat here.
Floods are one of the natural disasters that are known to have caused major destruction in various regions. It is time the government of India must take this issue seriously and come up with strong measures to control this problem.
Flood Essay – 5 (600 words)
Floods occur when excessive rainfall in a particular region results in the overflow of water on the land that is mostly dry. It can also occur due to the overflow of water from water bodies like river, ocean and lake. Floods are known to cause mass destruction. In certain regions, the destruction caused is so severe that it takes years to repair the loss.
Causes of Flood
Here is a closer look at the various causes of flood:
- Heavy Rains
Flood like situation arises each time the downpour is more than the drainage system can absorb. At times, heavy rainfall occurring for a short period of time can cause flood while on other occasions light rainfall that goes on for days may result in flood like situation.
- Melting of Snow
The mountains covered with snow during the winter season begin to melt as the temperature rises. The sudden melting of the ice usually causes the temperature to rise and this results in enormous movement of water into the plains. The areas that do not have proper drainage system to get rid of the excessive water face flood. This is often referred to as snowmelt flood.
- Breaking of Dam
Dams are created to hold water that flows down from a highland. The power in the water is employed to turn propellers for the generation of electricity. At times the dams break as they are unable to hold large amount of water thereby resulting in flood in the nearby areas. At times, excessive water is deliberately released from the dam so as to stop it from breaking. This may also result in flood.
- Overflow of Water Bodies
Water bodies such as rivers may overflow at times and cause flood like situation in the nearby areas. The low-lying areas near the rivers are worst impacted during this time as the water flows downstream.
- Winds in the Coastal Region
Strong winds and hurricanes have the capacity of carrying the sea water to the dry coastal lands and this causes flood. This can cause severe damage to the coastal regions. Hurricanes and Tsunamis are known to have caused major devastation in the coastal lands.
Global Warming: The Main Cause of Flood
The frequency of floods has increased in the recent past. It is said that the average sea temperature has increased a great deal due to global warming and this has resulted in the increased rate and sternness of tropical storms in the Caribbean. These storms are a cause of heavy downpour in the countries in their path. Global warming that is causing a rise in the temperature in the atmosphere is also a cause of the melting of glaciers and ice caps that is again a cause of flood in many regions. This is said to have a major impact on the polar ice caps in the times to come and the situation is likely to worsen.
The overall climatic conditions on earth have undergone a major change and global warming is said to be a cause of this transformation. While certain areas experience extreme floods others experience drought.
Though we cannot do much about the rain or the melting of the glaciers however we can certainly build good drainage systems to deal with the water they bring along. Many countries, such as Singapore that receive heavy rainfall for most part of the year, have really good drainage system. They come out clean even after days of heavy downpour. The government of India must also build good drainage system in order to avoid the problem of flood and the damage it does to the affected regions.
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
- Paragraph Writing
- Paragraph On Flood
Paragraph on Flood - Check Samples for 100, 150, 200, 250 Words
Floods are a type of natural disaster that can cause heavy destruction to life and property. It is a condition when rainwater accumulates at a place, flooding populated areas. They can also lead to the loss of numerous lives. At times, it can be highly dangerous and can wipe off an entire village or city.
Table of Contents
Paragraph on flood in 100 words, paragraph on flood in 150 words, paragraph on flood in 200 words, paragraph on flood in 250 words, frequently asked questions on flood.
It is impossible to stop a natural disaster, but the effects of the disaster can be reduced. The government has been taking major steps to reduce the effects of such disasters and save many lives. Before you write a paragraph on floods and their effects, you can refer to the samples provided below.
A flood is a condition when an area is fully or partially submerged in water for a period of time due to man-made or natural causes. The natural reasons behind floods can be heavy and continuous rain for an extended time period. Dam bursts or breaking of dam gates can be a man-made reason for a flood to occur. Floods can be highly dangerous at times because they may lead to loss of lives and property, and at certain places, it also leads to landslides. One cannot stop floods, but they can be avoided by constructing dams. One can definitely reduce the effects of floods and can reduce the damage caused by floods. Planting more trees in flood-prone areas and constructing dams might be helpful in controlling the adverse effects of floods.
A flood is a type of natural disaster that can be caused due to heavy and continuous rainfall at a place for a long time. Heavy rain, cyclones, storms, etc., can lead to flooding in an area. The water reserves are filled due to rain, and when it rains for a long time continuously, the overflow of water in water reserves may cause flooding.
Some parts of India are prone to flooding during the monsoon, causing large-scale destruction to human lives, natural habitats, etc. But in some places, floods can occur due to man-made disasters and cause loss of property and human lives. Breaking the dam’s gates can be a major reason behind man-made disasters. Due to these floods, the flood water accumulates in the agricultural fields, damaging crops. It can lead to starvation and more deaths. Many farmers have been committing suicide due to the loss. Floods are dangerous to human lives as well as the economy of the country. Therefore, it is essential to take necessary measures to limit the effects of floods.
A flood is a condition when an area is fully or partially submerged in water for a few days leading to hazardous diseases and loss of lives and property. Floods can be dangerous to factories, buildings, cities, hospitals, etc. Deforestation has been causing many hazards to the environment, and floods are one of these disasters. The rainwater is absorbed by the trees, and they act as natural barriers preventing soil erosion and landslides. Floods occur mostly in the rainy season in flood-prone areas, and the water levels may vary in such places. Naturally, floods can occur when it rains heavily for an extended period of time, and the water reserves are filled, causing an overflow of water. The breakage of dams can also cause floods and can lead to hazardous damage to lives and the environment. Floods can cause heavy loss of life and property and can also affect the agricultural system of the country, hence leading to starvation. It brings huge losses to public and private properties, affecting the country’s economy. At times, the revival also takes a lot of time. When the effects of floods are highly severe, it might take years to recover the physical damages. Almost every year, the country goes through such natural disasters leading to great loss and damage.
One of the major reasons for floods is heavy rain. Due to heavy rain, water levels in rivers and lakes are expected to rise. As the rainwater rises over the banks of rivers, it overflows and causes floods. With the increasing global warming, it is also possible that there might be floods due to the massive melting of snow. If global warming increases, with the rise in temperature, the ice might melt faster, leading to floods in various parts of the country. Floods pose a threat to factories, buildings, cities, hospitals, etc. Deforestation has resulted in a variety of environmental risks, one of which is flooding. Rainwater was absorbed by the trees, limiting the amount of water stored at a location. Floods are most common during the monsoon season in flood-prone areas, and water levels can fluctuate. During the monsoon season, floods are widespread in several places in India. It has a large-scale impact on human life and property. Houses are submerged in water, making day-to-day life difficult. Water also floods vast swaths of agricultural areas, wreaking havoc on crops and undermining the economy. A flood is a natural occurrence that has no benefits and is always a cause of loss. It is impossible to stop a natural disaster from occurring, but we can always limit the effects of the disasters. We can always take necessary measures to reduce the damage caused by it. Floods can leave adverse effects around the world, and at times, the revival of the damages may take years.
What is meant by flood?
A flood is a type of natural disaster that can leave adverse effects on the environment. During floods, an area is fully or partially submerged in water due to heavy rain or an overflow of dams and rivers.
What can be the effects of floods?
Floods can have adverse effects on the environment. It causes loss of public and private property, loss of lives, starvation and hunger, etc.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Brief Communication
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
Assessing the myth of disaster risk reduction in the wake of catastrophic floods
- Daniel Nohrstedt 1 , 2 ,
- Elena Mondino 2 , 3 ,
- Giuliano Di Baldassarre 2 , 3 &
- Charles F. Parker 1 , 2
npj Natural Hazards volume 1 , Article number: 5 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
209 Accesses
7 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Climate-change adaptation
- Environmental studies
- Natural hazards
Whether disasters serve as focusing events leading to measures that reduce future disaster risks is contested. Here, we study flood disasters in 23 of the world’s most flood-prone countries to assess whether catastrophic floods, those milestone events with the highest fatalities, have been followed by decreasing mortality in subsequent floods. Results from a trend analysis, controlling for flood magnitude and subtypes, find that reductions in mortality rates have rarely followed the most devastating floods.
Similar content being viewed by others
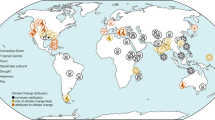
Harbingers of decades of unnatural disasters
Exposure to natural hazard events unassociated with policy change for improved disaster risk reduction
The challenge of unprecedented floods and droughts in risk management
One of the sustainable development goals (target 11.5) is to significantly reduce, by 2030, the number of deaths and people affected by disasters. Although evidence suggests that disaster-related fatalities have fallen globally since the 1970s 1 , the 2022 IPCC report 2 called for continued efforts to minimize climate risks and strengthen community resilience. Understanding what prompts countries to take measures to mitigate disaster-related fatalities is thus an urgent scientific and practical challenge.
Scientific and public discourses have increasingly focused on conditions for transformative adaptation 3 , including measures to reduce societal vulnerability. Disruptive disasters are often depicted as seminal events that provide opportunities for ambitious risk reduction actions, yet scholars debate whether disasters actually play this role. While some studies find that fatal disasters, including major floods 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , enhance risk mitigation 8 , especially if exposing flaws in pre-existing policies 9 and sparking debates about causes and consequences 10 , 11 , other studies 8 , 12 , 13 found negligible or no effects. Others yet have pointed to the risk that certain disasters may, in reality, increase vulnerability through maladaptive responses 14 .
These sometimes-contradictory insights are mainly derived from single-case studies of individual countries or events. Except for a few large-n studies, time-series and cross-sectional studies have been rare. Thus, we lack knowledge of how common it is that major disasters are followed by decreasing mortality in subsequent disasters. One central hypothesis holds that adaptation is generally most likely after large-scale catastrophic disasters. Compared to lower magnitude events, these ‘mega-disasters’ are likely to challenge dominant ideas and policies 15 . The scale of these events often comes as a surprise, introducing a sense of novelty as previously unimaginable scenarios materialize and expose neglected risks and unanticipated capacity needs. Meanwhile, past studies have only partially controlled for event magnitude or relied on various proxy measures of magnitude 16 . Whether catastrophic disasters enable adaptation actions that reduce losses from consecutive disasters remains to be explored.
In this study, we assess whether milestone flood disasters – events whose death toll exceeds historical country averages – incentivize countries to take actions that reduce future flood fatalities. The study includes riverine, coastal, ice jam, and flash floods. Floods can enable adaptation by a range of measures that reduce fatalities, typically by targeting human settlement, public awareness, flood defense, and early warning systems 17 . Decisions about these measures are often taken at the national level 18 , and much previous work on flood losses consists of country-level comparisons 8 , 17 , 19 . Our study spans the 23 countries worldwide with the greatest number of flood disasters in the period from 1970 to 2021 (Fig. 1a ). Some flood-prone countries, for instance, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands, were excluded as the number of floods reported for these countries was below the cutoff point applied in this study. Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Table 3 provide details on milestone flood events included in the study.

Map ( a ) shows countries ( n = 23) in the study. b shows that most countries are close to the no-change line (dotted) with close to flat trends. Some error bars in ( b ) extend beyond the plotted interval. Only Indonesia ( c ) shows a statistically significant difference in mortality rate, with a decreasing trend after the milestone event. All other countries show no significant difference, as illustrated here by Viet Nam ( d ). Data span all flood types.
This sample reduces the confounding effects of event frequency since all countries recorded a large number of flood events in the study period (ranging from 47 events in Algeria to 279 events in India). Most countries here are classified by the World Bank as lower- or upper-middle-income countries, except France and Australia (high-income) and Afghanistan and Ethiopia (low-income). Our study hereby reduces, albeit not eliminates, the influence of development factors, including, for example, income inequality and quality of institutions, which have been shown to reduce flood disaster fatalities 17 . However, since the sample is too small to control for income level fully, this remains a potential confounder.
By examining the deadliest floods affecting a country over time relative to its historical average, we are able to utilize disaster mortality trend lines as a proxy measure for adaptation action outcomes. This approach enables an assessment of adaptive potential as a reduction in fatalities from subsequent disasters can be seen as evidence of adaptation measures initiated after previous disasters 8 . Mortality rates were calculated for each milestone event, which normalized fatalities by the number of affected people (Methods). Eight countries (Brazil, Sri Lanka, Argentina, Haiti, Nigeria, Nepal, Bolivia, and Algeria) recorded one milestone flood, while the remaining 15 countries recorded two or more flood disasters during the milestone event year (Supplementary Table 1 ). There is also a temporal spread of milestone event years in the sample, with the first occurring in 1978 (India) and the most recent in 2013 (Argentina). As a result, the length of the period for calculating mortality rate trends varies across countries.
We estimated bivariate linear regression models of the difference in mortality rate before and after the milestone event year in each country, respectively (Supplementary Table 2 ). The models confirm that Indonesia (Fig. 1c ) is the only country with a statistically significant difference in mortality rate trends before and after the milestone event year (β coeff. = 0.12, p < 0.05), indicating a small decrease in fatalities in the period after the milestone event year. For Indonesia, this result includes the 2001 floods affecting the island of Nias 1400 km northwest of Jakarta, for which EM-DAT reports 257 casualties and over 3500 affected people. The fact that none of the other countries displayed a significant downward trend indicates that decreased flood mortality after milestone events is rare overall. Figure 2 shows mortality rate trends by country before and after milestone event years.
Mortality rate trends (log10) by country for all floods (riverine, coastal, ice jam, and flash floods) before and after milestone events (vertical dashed line), 1970−2021.
The results remain similar when controlling for flood frequency, intensity, and subtypes, suggesting that the trend is robust. Since we focus on the most flood-prone countries globally, the results suggest that mortality trends are unassociated with the frequency of past flood disasters. We performed separate analyses to investigate whether the results hold for riverine (Supplementary Fig. 1 ) and flash floods (Supplementary Fig. 2 ), respectively. Results for these analyses, including separate bivariate regression models by country, confirm that milestone events are not generally followed by reduced fatality trends for either one flood subtype. The lack of any statistically significant effects in these models suggests that milestone flood disasters, regardless of flood subtype, are not systematically followed by measures that reduce fatalities from subsequent disasters.
This exploratory study suggests that adaptation policy punctuations triggered by milestone flood disasters are uncommon. When mortality rates are normalized by the number of affected people, most countries are located near the no-change line with close to flat fatality trends (Fig. 1b ). This pattern indicates that historically in the most flood-affected countries around the world, milestone flood disasters have generally been unassociated with a reduction in fatalities from subsequent floods. This finding is inconsistent with the assumption that major catastrophic disasters increase the likelihood of adaptation measures that reduce disaster risk 20 .
The study corroborates results reported elsewhere that higher climate risks do not necessarily lead to fewer flood fatalities 8 . In addition, this study explores mortality rate trends after the most fatal flood disasters, which differs from previous studies assessing impacts of flood magnitude measured by, for example, precipitation anomalies and annual rainfall variability. The results of this study suggest that even the most devastating flood disasters, alongside precipitation anomalies, may not provide momentum for measures that reduce future flood fatalities. One implication is that flood disaster magnitude, in terms of high-loss/low-probability events, does not necessarily increase the probability of effective adaptation.
The finding reported elsewhere that more recent disasters (happening within roughly a decade) lead to adaptation measures that reduce fatalities could not be supported here. Studies of hurricanes 21 and floods 8 have found that more recent events matter more for reducing fatalities in subsequent events, suggesting that memories and knowledge from past shocks fade with time. In contrast to these findings, we found no difference between mortality rate trends after recent and more distant milestone events (Fig. 2 ).
Several caveats apply to the study and suggest directions for future research. Most countries in the study classify as low- and upper-middle-income countries, which generally have low institutional capacity to achieve effective adaptation in the wake of disasters 16 . Recurring disasters have been hypothesized to reinforce this effect as short-term reconstruction needs can override long-term adaptation measures 12 , 13 . Although this study finds no association between milestone flood events and mortality across income levels, this remains to be tested with a more diverse sample of countries across income levels. Other studies 17 , 22 have demonstrated that flood fatalities decrease with increasing income, but, again, these do not investigate the effects of milestone events specifically.
It is also possible that countries have initiated, yet not effectively implemented, adaptation measures after milestone events, or, alternatively, invested in measures with limited risk reduction potential 23 . Implementation gaps and maladaptation after milestone events could be studied more closely by estimating the effects of different types of adaptation measures. Studies 24 point to certain cost-effective measures that contribute to mitigating disaster fatalities (e.g., medical facilities, road infrastructure, electrification, and financial accessibility), but these should be investigated further 8 . The trend analysis here may also not capture effective risk reduction measures that take several decades to implement. For example, in the United Kingdom and Netherlands, the 1953 coastal floods led to major flood protection measures, including the Thames Barrier and the Delta Works programme, which were completed in 1982 and the 1990s, respectively 25 . Such long-term measures may not have been finalized yet in countries with more recent milestone events, such as Argentina and Nigeria.
To reduce disaster fatalities, disaster risk reduction discourse urges communities to “build back better” after disasters by adopting adaptation measures to reduce vulnerability. Our study suggests that this is generally uncommon, which is inconsistent with success stories reported in some case studies of flood adaptation 26 and comparisons of mortality after consecutive floods affecting the same region 27 . Investigating circumstances that constrain adaptation after disasters, such as blame-game politics, inertia, or exposure to repeated disasters 12 , is an essential next step in this research. More robust analyses are also required to uncover milestone events that deviate from this general pattern, as indicated by trends of decreased mortality. This can be achieved by studies controlling for different types of adaptation actions and their potential effects on mortality and taking into account that implementation of risk reduction measures may take decades to complete.
The flood mortality rates utilized for this study normalized fatalities by the total number of affected people, which indirectly accounts for flood disaster intensity. As a result, the mortality rates can capture increased flood intensity, as indicated by an increase in affected populations.
Data were retrieved from the International Disasters Database 28 (EM-DAT), which includes events with ten or more casualties, 100 or more affected people, a state of emergency declaration, and/or an appeal for international assistance. Coastal, riverine, flash floods, and ice jam floods, 1970−2021, were included. Events before 1970 were excluded from the study due to underreporting 19 . We extracted each event’s ID, country, region, continent, starting year, fatalities, affected individuals (injured, homeless, affected), and economic damage (in thousands of US$). Most countries in the study were classified (by the World Bank, as of 2021) as lower- or upper-middle-income countries, but in some cases, the classification has changed over time.
Countries were ranked in descending order according to the number of flood events. The top 30 countries (Supplementary Table 1 , Fig. 1a ) were included to ensure sufficient observations for the trend analysis. Seven countries (Bangladesh, China, Kenya, Malaysia, Philippines, Romania, USA) were excluded due to too few events ( n < 5 before and/or after the milestone event) or missing data.
To normalize the different levels of flood severity over time, mortality rates were computed by dividing fatalities by the total number of affected people. Moreover, since total fatalities are not included in the total affected in EM-DAT, we calculated the mortality rate ( R ) for each event as follows:
Mortality rates were log10-transformed for visualization and plotted over time (Fig. 2 , Figs. S 1 , S 2 ). Milestone events were defined as the first in chronological order between first, the first event belonging to the 99 th percentile in terms of fatalities, and, second, the event with the greatest number of fatalities. In cases where countries recorded several events during a milestone event year (Supplementary Table 1 ), only fatalities from the deadliest event were included.
The study fitted linear trends for all floods before and after the milestone event. We then compared the angles between the first and the second linear trend and the y-axis, referred to as α and β, respectively. Instances when α is greater than β provide evidence of decreased mortality after milestone events (Fig. 1b ). Results were corroborated by using linear regression to compare differences in mortality rates before and after milestone events. We estimated models for all floods and separate models for riverine and flash floods, respectively. No models were estimated for coastal and ice jam floods due to too few data points. None of these models returned p -values below 0.05.
A challenge of utilizing this approach is whether the number of included events is sufficient to derive trend lines. Nonetheless, our study was able to capture strong trends for analysis. Future work can enhance the number of events by adding additional hazard types and countries.
It is important to acknowledge that several caveats apply to our study. Despite being one of the most reliable and comprehensive global sources of disaster information, EM-DAT’s data are heterogeneous and sometimes subject to uncertainty due to missing information. Another issue is that it can be difficult in larger countries to trace the effects of measures to reduce disaster risk in one specific flood-affected region. Although we found consistent results independent of country size (Fig. 2 ), determining the scale of adaptation measures (local, regional, national) is potentially arbitrary. Our results were also robust for sub-samples of different flood types (Supplementary Figs. 1 , 2 ).
Data availability
Disaster event data are publicly available from the International Disaster Database (EM-DAT) ( https://www.emdat.be ). Income level data retrieved from the World Bank ( https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups ). Data and the custom code generated for preparing, analysing, and visualizing data have been deposited in the following public repository: https://www.statsvet.uu.se/research/trampoline/data-repository/ .
World Meteorological Organization. WMO Atlas of Mortality and Economic Losses from Weather, Climate and Water Extremes (1970–2019) (WMO-No. 1267) . (WMO, 2021).
Pörtner, H. et al. IPCC, 2022: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . (Cambridge University Press, 2022).
Kates, R. W., Travis, W. R. & Wilbanks, T. J. Transformational adaptation when incremental adaptations to climate change are insufficient. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109 , 7156–7161 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Penning-Rowsell, E. C., Johnson, C. & Tunstall, S. Understanding policy change in flood risk management. Water Secur. 2 , 11–18 (2017).
Article Google Scholar
Johnson, C. L., Tunstall, S. M. & Penning-Rowsell, E. C. Floods as catalysts for policy change: historical lessons from England and Wales. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 21 , 561–575 (2005).
Lumbroso, D. M., Suckall, N. R., Nicholls, R. J. & White, K. D. Enhancing resilience to coastal flooding from severe storms in the USA: international lessons. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 17 , 1357–1373 (2017).
Samuels, P., Klijn, F. & Dijkman, J. An analysis of the current practice of policies on river flood risk management in different countries. Irrig. Drain. 55 , S141–S150 (2006).
Miao, Q. Are we adapting to floods? Evidence from global flooding fatalities. Risk Anal. 39 , 1298–1313 (2019).
Neil Adger, W., Arnell, N. W. & Tompkins, E. L. Successful adaptation to climate change across scales. Glob. Environ. Chang. 15 , 77–86 (2005).
Boudet, H., Giordono, L., Zanocco, C., Satein, H. & Whitley, H. Event attribution and partisanship shape local discussion of climate change after extreme weather. Nat. Clim. Change 10 , 1–8 (2019).
Google Scholar
Onuma, H., Shin, K. J. & Managi, S. Reduction of future disaster damages by learning from disaster experiences. Nat. Hazards 87 , 1435–1452 (2017).
Nohrstedt, D., Mazzoleni, M., Parker, C. F. & Di Baldassarre, G. Exposure to natural hazard events unassociated with policy change for improved disaster risk reduction. Nat. Commun. 12 , 1–11 (2021).
Nohrstedt, D., Hileman, J., Mazzoleni, M., Di Baldassarre, G. & Parker, C. F. Exploring disaster impacts on adaptation actions in 549 cities worldwide. Nat. Commun. 13 , 1–10 (2022).
Wenger, C. Better use and management of levees: reducing flood risk in a changing climate. Environ. Rev. 23 , 240–255 (2015).
Birkmann, J. et al. Extreme events and disasters: a window of opportunity for change? Analysis of organizational, institutional and political changes, formal and informal responses after mega-disasters. Nat. Hazards 55 , 637–655 (2010).
Fankhauser, S. & McDermott, T. K. J. Understanding the adaptation deficit: why are poor countries more vulnerable to climate events than rich countries? Glob. Environ. Change 27 , 9–18 (2014).
Jongman, B. et al. Declining vulnerability to river floods and the global benefits of adaptation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112 , E2271–E2280 (2015).
Kreibich, H. et al. Adaptation to flood risk: results of international paired flood event studies. Earth’s Futur. 5 , 953–965 (2017).
Paprotny, D., Sebastian, A., Morales-Nápoles, O. & Jonkman, S. N. Trends in flood losses in Europe over the past 150 years. Nat. Commun. 9 , 1–12 (2018).
Birkland, T. Policy Process Theory and Natural Hazards. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Natural Hazard Science 1–26 (Oxford University Press, 2016).
Sadowski, N. C. & Sutter, D. Mitigation motivated by past experience: prior hurricanes and damages. Ocean Coast. Manag. 51 , 303–313 (2008).
Formetta, G. & Feyen, L. Empirical evidence of declining global vulnerability to climate-related hazards. Glob. Environ. Change 57 , 101920 (2019).
Nohrstedt, D. & Parker, C. F. Revisiting the role of disasters in climate policy-making. Clim. Policy 1–12 https://doi.org/10.1080/14693062.2024.2301781 (2024).
Parida, Y., Agarwal Goel, P., Roy Chowdhury, J., Sahoo, P. K. & Nayak, T. Do economic development and disaster adaptation measures reduce the impact of natural disasters? A district-level analysis. Odisha India Environ. Dev. Sustain. 23 , 3487–3519 (2021).
Wadey, M. P. et al. A comparison of the 31 January–1 February 1953 and 5–6 December 2013 coastal flood events around the UK. Front. Mar. Sci. 2 , 1–27 (2015).
Barbour, E. J. et al. The unequal distribution of water risks and adaptation benefits in coastal Bangladesh. Nat. Sustain. 5 , 294–302 (2022).
Kreibich, H. et al. The challenge of unprecedented floods and droughts in risk management. Nature 608 , 80–86 (2022).
Centre for research on the epidemiology of disasters (CRED). The International Disaster Database– EM-DAT. The International Disaster Database– EM-DAT https://www.emdat.be/ (2019).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Marianne and Marcus Wallenberg Foundation Grant 2022-0049, the Swedish Research Council Grant 2018-03977, and the Centre of Natural Hazards and Disaster Science (CNDS). The funders played no role in study design, data collection, analysis and interpretation of data, or the writing of this manuscript.
Open access funding provided by Uppsala University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Government, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
Daniel Nohrstedt & Charles F. Parker
Department of Earth Sciences, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
Daniel Nohrstedt, Elena Mondino, Giuliano Di Baldassarre & Charles F. Parker
Centre of Natural Hazards and Disaster Science, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
Elena Mondino & Giuliano Di Baldassarre
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
D.N, E.M., G.DB. and C.F.P. designed the study; E.M. and G.DB. collected and analyzed the data; E.M. created the figures; and D.N, E.M., G.DB. and C.F.P. interpreted the results and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Daniel Nohrstedt .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Nohrstedt, D., Mondino, E., Di Baldassarre, G. et al. Assessing the myth of disaster risk reduction in the wake of catastrophic floods. npj Nat. Hazards 1 , 5 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44304-024-00007-w
Download citation
Received : 25 September 2023
Accepted : 13 March 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s44304-024-00007-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Floods Break Dams and Submerge Highways in Southern Germany
Several towns declared states of emergency and evacuated citizens as water submerged streets and highways and derailed a high-speed train.

By Christopher F. Schuetze
Reporting from Berlin
After a weekend of heavy rains, severe floods in regions of southern Germany led several towns to declare states of emergency and to evacuate their citizens from heavily affected areas. Water submerged streets and highways, broke dams and derailed a high-speed train. Even as rain let up on Monday, emergency crews rushed to fortify dams along rivers in anticipation of further flooding.
On Monday morning, a 43-year-old woman was found dead in her basement in the Neuburg-Schrobenhausen district in Bavaria, according to the local authorities. She had been missing since Saturday night.
Several hours later, responders who were pumping water out of a basement in Schorndorf in Baden-Württemberg found the bodies of a man and a woman, according to the police. On Saturday, a firefighter died trying to save people, according to the district he served; another firefighter has been missing since Saturday.
Tens of thousands of emergency workers, both local and from other regions, are responding to the disaster, which affected Germany’s two southern states, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg. The responders, who include 800 soldiers, have rescued people stranded in their houses and cars, built emergency dams and set up crisis accommodations.

The German chancellor, Olaf Scholz, visited the small market town of Reichertshofen, roughly 35 miles north of Munich, on Monday and said that the flooding represented a new reality as the effects of climate change are being felt in Central Europe.
“What is also important to me is that we are very clear that this is not just an event that has been happening for centuries,” he told reporters, noting that he had visited four active flooding sites this year alone.
“We must not neglect the task of halting man-made climate change,” he told reporters on Monday. “This, too, is a lesson that we must learn from this event and this disaster.”
Between Friday at noon and Monday at noon, 120 to 160 liters of rain, or about 30 to 40 gallons, fell per square meter (about 11 square feet), which is more than usually falls in a month, according to Sebastian Altnau, a meteorologist with the German Weather Office.
The firefighter who became the first victim of the floods had set out with three colleagues on a boat late on Saturday to save a family stranded inside a building. Before they reached the house, the boat flipped. While three of the firefighters were able to save themselves, the body of the fourth was found early Sunday, a spokeswoman for the district confirmed.
In the small southwestern town of Ebersbach in Baden-Württemberg, the water pushed through a highway wall on Sunday night. A video published on the city’s Facebook feed shows how the water turned the road into an impassable river in seconds.
About 15 miles to the northeast, near Schwäbisch Gmünd, a sudden mudslide pushed a high-speed train off the rails and buried a car on Saturday night, according to the national rail service. Rescue workers were able to evacuate the train of its 185 passengers, and no one was hurt. After signaling with a flashlight, the driver, too, was picked up by rescue workers, he told the German newspaper Bild .
In both Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg over the weekend, several dams broke, in some cases leading to flooding of entire neighborhoods. On Saturday in Reichertshofen, where the chancellor visited Monday, two dams broke despite being fortified with sandbags, allowing the Baar River to flood neighborhoods. Around 5,000 emergency workers helped with rescue and evacuation operations.
Responders spent much of Monday safeguarding against flooding from bigger rivers, which have swelled since the downpour. In the medieval city of Regensburg in Bavaria, in the southeast, emergency workers built a dam on Monday along the Danube River as it continued to rise. On Monday afternoon, the Danube’s level measured at over six meters, or nearly 20 feet — twice as high as it was on Friday morning.
The flooding has brought up memories of the disastrous Ahr Valley floods in 2021, which killed 189 people. The heavy rains, which scientists said were driven by climate change , led the Ahr River to rise sharply, sweeping up buildings, bridges and roads. At the time, the authorities were criticized for not warning the local populations properly.
Nancy Faeser, who, as Germany’s interior minister, is responsible for disaster response, traveled with Mr. Scholz on Monday. She told local reporters that she could see “lessons had been learned” in the Ahr catastrophe. “Coordination and organization work much better,” she said.
Christopher F. Schuetze is a reporter for The Times based in Berlin, covering politics, society and culture in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. More about Christopher F. Schuetze
Explore Our Weather Coverage
Extreme Weather Maps: Track the possibility of extreme weather in the places that are important to you .
Heat Safety: Heat waves are becoming increasingly common across the world. Here is how to keep yourself and your loved ones cool, hydrated and healthy .
Tornado Alerts: A tornado warning demands instant action. Here’s what to do if one comes your way .
Flash Flooding: Fast rising water can be deadly. Here’s what to do if you’re caught off guard , and how to prepare for a future flooding event.
Evacuating Pets: When disaster strikes, household pets’ lives are among the most vulnerable. You can avoid the worst by planning ahead .
Climate Change: What’s causing global warming? How can we fix it? Our F.A.Q. tackles your climate questions big and small .

- High contrast
- OUR REPRESENTATIVE
- CHILDREN IN AFGHANISTAN
- OUR MANDATE
- WORK FOR UNICEF
- PRESS CENTRE
Search UNICEF
Flash floods in afghanistan posing urgent and persistent threat to children, unicef calls for increased investment in disaster preparedness and climate resilience as the recent floods provide a grave forewarning of potential future climate hazards..

Tens of thousands of children in Afghanistan remain affected by ongoing flash floods, especially in the northern provinces of Baghlan and Badakhshan and the western province of Ghor. The most recent floods claimed nearly 350 lives – including at least a dozen children. Over 7,800 homes were damaged or destroyed and over 5,000 families have been displaced.
UNICEF immediately trucked in safe water and distributed hygiene kits containing soap, buckets, jerry cans, toothbrushes and more, and mobilized hygiene promoters to educate communities on handwashing and safe water storage following the disaster. In addition, UNICEF mobilized mobile health and nutrition teams to treat the injured and ill, and brought warm clothing, blankets, and household items and cooking equipment for families who lost possessions. UNICEF also provided immediate cash assistance through its rapid response mechanism to help families recover and provide for their basic needs.
The recent extreme weather in Afghanistan has all the hallmarks of the intensifying climate crisis — some of the affected areas experienced drought last year. Reports suggest extreme weather events in the country are increasing in frequency and ferocity, resulting in the loss of lives and livelihoods and significant damage to infrastructure.
“The international community must redouble efforts and investments to support communities to alleviate and adapt to the impact of climate change on children. At the same time, UNICEF and the humanitarian community must prepare ourselves for a new reality of climate-related disasters,” said Dr. Tajudeen Oyewale, UNICEF Representative in Afghanistan.
“The growing number and severity of extreme weather events will require UNICEF and other humanitarian actors to step in with even more rapid and large-scale humanitarian responses. But this can only be possible with strengthened preparedness measures, such as greater pre-positioning of emergency relief supplies and enhanced coordination with partners.”
“UNICEF must simultaneously concentrate on building communities’ resilience to adapt to climate and environmental shocks in order to reduce their dependence on humanitarian aid.”
Afghanistan ranks 15th out of 163 nations on UNICEF’s 2021 Children's Climate Risk Index. This means that not only are climate and environmental shocks and stresses predominant across the country, but children here are particularly vulnerable to their effects compared with elsewhere in the world. However, although children in Afghanistan are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, their country is among the least responsible for creating the problem. In contrast, the 10 highest emitting countries of CO2 collectively account for nearly 70 per cent of global emissions.
“Heavy rainfall shouldn’t immediately spell disaster for Afghanistan’s children. We need to prioritise the unique needs of children in decision making and address these needs now to protect children from future disasters while simultaneously investing in the basic services they rely on,” said Dr. Oyewale. “UNICEF is grateful to all partners for their generous support, enabling UNICEF Afghanistan to deliver for children and their families in Afghanistan.”
Media contacts
Additional resources.

About UNICEF
UNICEF works in some of the world’s toughest places, to reach the world’s most disadvantaged children. Across 190 countries and territories, we work for every child, everywhere, to build a better world for everyone.
UNICEF has been in Afghanistan for over 70 years. For more information about UNICEF and its work for children in Afghanistan, visit https://www.unicef.org/afghanistan/ or follow us on X , Facebook , Instagram or subscribe to our YouTube channel .
Related topics
More to explore, while flood waters subside, the devastating impact lingers.
Flash floods claimed hundreds of lives and destroyed thousands of homes. UNICEF is concerned extreme weather events could become the norm.
Faces of the floods
As climate change brings more frequent extreme weather events, children in Afghanistan are among the most vulnerable with their lives and futures threatened
Statement by UNICEF Afghanistan on the devastating flash floods in northeast of Afghanistan
A safe school for Nadia
Improving learning environments with water, sanitation, and hygiene facilities

Bharatha Mallawarachi, Associated Press Bharatha Mallawarachi, Associated Press
Leave your feedback
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/world/sri-lanka-closes-schools-as-floods-and-mudslides-leave-10-dead-and-6-others-missing
Sri Lanka closes schools as floods and mudslides leave 10 dead and 6 others missing
COLOMBO, Sri Lanka (AP) — Sri Lanka closed schools on Monday as the death toll due to floods and mudslides triggered by heavy rains in many parts of the island nation, rose to 16 people, officials said.
The education ministry announced that the reopening of schools would depend on how the weather develops.
Heavy downpours have wreaked havoc in many parts of the country since Sunday, flooding homes, fields and roads, and forcing authorities to cut electricity as a precaution.
READ MORE: In Bangladesh and India, cyclone floods coastal villages, blows away thatched roofs and cuts power
Twelve people died after being washed away and drowning near the capital, Colombo, and the remote Rathnapura, Matara and Galle districts on Sunday, according to the disaster management center. Three others died when mounds of earth collapsed on their houses, and one person died when a tree fell on him.
Separately, five people were injured when mudslides struck and damaged two houses in Ratnapura, which is about 86 kilometers (53 miles) southeast of Colombo, said the center.
By Monday, over 6,000 people had been moved to evacuation centers and more than 12,000 homes had been damaged, the center said in a statement.
Navy and army troops have been deployed to rescue victims and provide food and other essentials to those affected.
Sri Lanka has been grappling with severe weather conditions since mid-May caused by heavy monsoon rains. Earlier, strong winds downed trees in many areas, killing nine people.
Support Provided By: Learn more
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ words Essay on Flood. Flood is one of the most dangerous natural disasters. It happens when excessive water is collected in any area. It usually happens due to heavy rainfall. India is highly prone to flood. There are many regions in the country that face this natural disaster because of the overflowing of rivers.
Flood Essay: Flood is one of the recurring natural disasters, which is an outcome of heavy rainfall and the accumulation of excessive water in every living area. Floods may occur due to the overflow of water from the reservoirs or due to heavy downpour of rain in places where the drainage systems are not adequately maintained.
While water is essential to life, it can be a destructive force too. When rivers flood, the effects can be catastrophic. Flooding is one of the most common types of natural disaster, and the results are often fatal. The Central China flood of 1931, for example, was one of the worst flooding events in recorded history.
However, one of the biggest causes of floods, especially in cases of flash floods, is excessive and heavy rainfall. When rainfall in low-lying areas and urban environments fall faster than the ground can absorb, water height rapidly rise, resulting in floods. Extreme rainfall in river courses contribute to flooding as well, as water travels ...
Floods are natural disasters that occur when a body of water, such as a river or ocean, overflows its banks and spills onto the surrounding land. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including heavy rainfall, melting snow, and storms.Here are a few sample essays on floods. 100 Words Essay on Floods. Floods are naturally occurring phenomena that are caused due to overflowing water bodies.
Flood Essay for Students in English. Flood is a natural phenomenon that occurs due to various geological processes. It is one of the most dangerous natural calamities that can cause lethal damage. The main reason for flooding is excessive rainfall. Rainwaters are collected usually in rivers and are prevented from flooding through dams.
A flood is a natural disaster that arises due to excessive runoff of water in the rivers due to rainfall. This causes the water of rivers to come out from the edges and flow into the plains. Floods can last from a few hours to a few days, but it can cause great harm to people, money and crops.
Floods have been a recurring natural disaster that has affected millions of people worldwide. Whether caused by heavy rainfall, snowmelt, or hurricanes, floods have the potential to cause significant damage to property, infrastructure, and the environment.In this essay, we will reflect on the impact of floods, the factors contributing to their occurrence, and the measures that can be taken to ...
500 Words Essay on Flood Introduction. Floods, one of the most common and destructive natural disasters, are a powerful force of nature that have shaped human civilizations and the natural environment for millennia. They are a result of excessive rainfall, rapid snowmelt, or a sudden release of water, causing a surge of water to overflow onto ...
FAQs on Flood Essay. The damage caused by a flood is up to 90% when compared to other natural disasters. Major flooding causes loss of human and animal lives, they also cause severe damage to economic infrastructures. Floods also cause severe damage to government buildings and public properties.
Flash floods can happen anywhere, and low-lying areas with poor drainage are particularly vulnerable. Also caused by dam or levee breaks or the sudden overflow of water due to a debris or ice jam ...
Floods in the City of Austin, Texas on October 30th, 2013. The catastrophic consequences of the devastation in Central Texas and, in particular, in the city of Austin, were caused by flooding. Disaster Management in the Flood Scenario. In such a case, the authorities and residents should adopt disaster prevention and preparedness strategies to ...
🌪️ Natural Disaster Essay: What Is It About? A natural disaster is a large-scale meteorological or geological event that can to cause loss of life or massive damage to people's property. Floods and severe storms are the most reported acts of nature in the US, but other incidents also happen from time to time.
Floods are among disasters that cause widespread destruction to human lives, properties and the environment every year and occur at different places with varied scales across the globe. Flood disasters are caused by natural phenomena, but their occurrences and impacts have been intensified through human actions and inactions. The practice of flood disaster management have evolved over the ...
the w orst flooding in 30 years that ba ttered W est Africa from July 200 7 caused more. than 21 0 death and aff ected more than 78 5,000 people [ 12]. The aftermaths of flood disasters in Ghana ...
Writing an essay on flood-related topics can help raise awareness about the importance of preparedness and resilience in the face of such disasters. Here are 127 flood essay topic ideas and examples to inspire your writing: The impact of floods on agriculture and food security. The role of climate change in increasing the frequency and ...
Coastal areas may be flooded by storm surges combining with high tides and large wave events at sea, resulting in waves over-topping flood defenses or in severe cases by tsunami or tropical cyclones. A storm surge, from either a tropical cyclone or an extratropical cyclone, falls within this category.A storm surge is "an additional rise of water generated by a storm, over and above the ...
Essay on Flood: Causes, Consequences and Prevention - Essay 4 (400 Words) Introduction: Flood is one of the recurring natural disasters which is an outcome of above average rainfall and accumulation of excessive water in every living area. Floods may occur due to overflow of water from the reservoirs or due to heavy down pour of rain in places where the drainage systems are not properly ...
Sample Essay on Disaster Management (300 Words) Since the dawn of time, disasters, whether natural or man-made, have been a part of man's evolution. Tsunamis, cyclones, earthquakes, floods, accidents, plane crashes, forest fires, chemical disasters, and other natural disasters frequently strike without notice, leading to massive loss of life ...
Flood Essay - 3 (400 words) Flood is a natural disaster that is caused due to the accumulation of excessive water in a region. This is often an outcome of heavy rainfall. Many regions also face flood due to overflow of river or ocean water, breaking of dams and melting of snow.
Paragraph on Flood in 100 Words. A flood is a condition when an area is fully or partially submerged in water for a period of time due to man-made or natural causes. The natural reasons behind floods can be heavy and continuous rain for an extended time period. Dam bursts or breaking of dam gates can be a man-made reason for a flood to occur.
Urban flooding is one of the main challenges affecting sustainable urban development worldwide, threatening the safety and well-being of communities and citizens. The aim of this study is to assess the development and trends in urban flood resilience at the city scale, as well as to improve the resilience of cities to these risks over time. The study constructs a model for assessing urban ...
Whether disasters serve as focusing events leading to measures that reduce future disaster risks is contested. Here, we study flood disasters in 23 of the world's most flood-prone countries to ...
Tens of thousands of emergency workers, both local and from other regions, are responding to the disaster, which affected Germany's two southern states, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg.
"Heavy rainfall shouldn't immediately spell disaster for Afghanistan's children. We need to prioritise the unique needs of children in decision making and address these needs now to protect children from future disasters while simultaneously investing in the basic services they rely on," said Dr. Oyewale.
COLOMBO, Sri Lanka (AP) — Sri Lanka closed schools on Monday as the death toll due to floods and mudslides triggered by heavy rains in many parts of the island nation, rose to 16 people ...