What is inflation?

Inflation refers to a broad rise in the prices of goods and services across the economy over time, eroding purchasing power for both consumers and businesses. In other words, your dollar (or whatever currency you use for purchases) will not go as far today as it did yesterday. To understand the effects of inflation, take a commonly consumed item and compare its price from one period with another. For example, in 1970, the average cup of coffee cost 25 cents; by 2019, it had climbed to $1.59. So for $5, you would have been able to buy about three cups of coffee in 2019, versus 20 cups in 1970. That’s inflation, and it isn’t limited to price spikes for any single item or service; it refers to increases in prices across a sector, such as retail or automotive—and, ultimately, a country’s economy.

Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on inflation.
Ondrej Burkacky is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Munich office, Axel Karlsson is a senior partner in the Stockholm office, Fernando Perez is a senior partner in the Miami office, Emily Reasor is a senior partner in the Denver office, and Daniel Swan is a senior partner in the Stamford office.
In a healthy economy, annual inflation is typically in the range of two percentage points, which is what economists consider a signal of pricing stability. And there can be positive effects of inflation when it’s within range: for instance, it can stimulate spending, and thus spur demand and productivity, when the economy is slowing down and needs a boost. Conversely, when inflation begins to surpass wage growth, it can be a warning sign of a struggling economy.
Inflation affects consumers most directly, but businesses can also feel the impact. Here’s a quick explanation of the differences in how inflation affects consumers and companies:
- Households, or consumers, lose purchasing power when the prices of items they buy, such as food, utilities, and gasoline, increase.
- Companies lose purchasing power, and risk seeing their margins decline , when prices increase for inputs used in production, such as raw materials like coal and crude oil , intermediate products such as flour and steel, and finished machinery. In response, companies typically raise the prices of their products or services to offset inflation, meaning consumers absorb these price increases. For many companies, the trick is to strike a balance between raising prices to make up for input cost increases while simultaneously ensuring that they don’t rise so much that it suppresses demand, which is touched on later in this article.
How is inflation measured?
Statistical agencies measure inflation by first determining the current value of a “basket” of various goods and services consumed by households, referred to as a price index. To calculate the rate of inflation, or percentage change, over time, agencies compare the value of the index over one period to another, such as month to month, which gives a monthly rate of inflation, or year to year, which gives an annual rate of inflation.
For example, in the United States, that country’s Bureau of Labor Statistics publishes its Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures the cost of items that urban consumers buy out of pocket. The CPI is broken down by regions and is reported for the country as a whole. The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index —published by the US government’s Bureau of Economic Analysis—takes into account a broader range of consumers’ expenditures, including healthcare. It is also weighted by data acquired through business surveys.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
What are the main causes of inflation.
There are two primary types, or causes, of inflation:
- Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services in the economy exceeds the economy’s ability to produce them. For example, when demand for new cars recovered more quickly than anticipated from its sharp dip at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, an intervening shortage in the supply of semiconductors made it hard for the automotive industry to keep up with this renewed demand. The subsequent shortage of new vehicles resulted in a spike in prices for new and used cars.
- Cost-push inflation occurs when the rising price of input goods and services increases the price of final goods and services. For example, commodity prices spiked sharply during the pandemic as a result of radical shifts in demand, buying patterns, cost to serve, and perceived value across sectors and value chains. To offset inflation and minimize impact on financial performance, industrial companies were forced to consider price increases that would be passed on to their end consumers.
Learn more about McKinsey's Pricing practice.
How does inflation today differ from historical inflation?
In January 2022, inflation in the United States accelerated to 7.5 percent, its highest level since February 1982, as a result of soaring energy costs , labor mismatches , and supply disruptions . But inflation is not a new phenomenon; countries have weathered inflation throughout history.
A common comparison to the current inflationary period is with that of the post–World War II era , when price controls, supply problems, and extraordinary demand fueled double-digit inflation gains—peaking at 20 percent in 1947—before subsiding at the end of the decade, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Consumption patterns today have been similarly distorted, and supply chains have been disrupted by the pandemic.
The period from the mid-1960s through the early 1980s, sometimes called “The Great Inflation,” saw some of the highest rates of inflation, with a peak of 14.8 percent in 1980. To combat this inflation, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates to nearly 20 percent. Some economists attribute this episode partially to monetary policy mistakes rather than to other purported causes, such as high oil prices. The Great Inflation signaled the need for public trust in the Federal Reserve’s ability to lessen inflationary pressures.
How does inflation affect pricing?
When inflation occurs, companies typically pay more for input materials . One way for companies to offset losses and maintain gross margins is by raising prices for consumers, but if price increases are not executed thoughtfully, companies can damage customer relationships, depress sales, and hurt margins. An exposure matrix that assesses which categories are exposed to market forces, and whether the market is inflating or deflating, can help companies make more informed decisions.
Done the right way, recovering the cost of inflation for a given product can strengthen relationships and overall margins. There are five steps companies can take to ADAPT (Adjust, Develop, Accelerate, Plan, and Track) to inflation:
- Adjust discounting and promotions and revisit other aspects of sales unrelated to the base price, such as lengthened production schedules or surcharges and delivery fees for rush or low-volume orders.
- Develop the art and science of price change . Don’t make across-the-board price changes; rather, tailor pricing actions to account for inflation exposure, customer willingness to pay, and product attributes.
- Accelerate decision making tenfold . Establish an “inflation council” that includes dedicated cross-functional, inflation-focused decision makers who can act nimbly and quickly on customer feedback.
- Plan options beyond pricing to reduce costs . Use “value engineering” to reimagine your portfolio and provide cost-reducing alternatives to price increases.
- Track execution relentlessly . Create a central supporting team to address revenue leakage and to manage performance rigorously.
Beyond pricing, a variety of commercial and technical levers can help companies deal with price increases in an inflationary market , but other sectors may require a more tailored response to pricing. In the chemicals industry, for instance, category managers contending with soaring prices of commodities can make the following five moves to save their companies money:
- Gain a full understanding of supply–market dynamics and outlook . Understand and track the elements that trigger price increases and rescind these increases once those drivers are no longer applicable.
- Ensure that suppliers can clearly articulate the impact that price increases in the market have on suppliers’ prices . In times of upward price pressure, sellers often overstate the share of raw materials in input costs, taking the opportunity to inflate their margins. Using cleansheet methodology to identify and challenge these situations is important.
- View unavoidable price increases as temporary surcharges, not the new future state . This mechanism, partly psychological in nature, is very effective in dealing with the stickiness of price increases because it shifts the burden of proof to the supplier.
- Prioritize cross-functional initiatives . When prices are high, the impact of yield improvements, waste reduction, or substitutions can be amplified. If any are available, now is the time to make them a priority.
- Work with sales to pass on price increases . Category managers work closely with finance and commercial teams to shed light on pure market effects and their impact on the prices of goods sold, while ensuring that the right arguments are advanced to pass market-price increases to customers.
Learn more about our Financial Services , Advanced Electronics , Operations , and Growth, Marketing & Sales practices.
What is the difference between inflation and deflation?
If inflation is one extreme of the pricing spectrum, deflation is the other. Deflation occurs when the overall level of prices in an economy declines and the purchasing power of currency increases. It can be driven by growth in productivity and the abundance of goods and services, by a decrease in aggregate demand, or by a decline in the supply of money and credit.
Generally, moderate deflation positively affects consumers’ pocketbooks, as they are able to purchase more with less money. However, deflation can be a sign of a weakening economy, leading to recessions and depressions. While inflation reduces purchasing power, it also reduces the value of debt. During a period of deflation, on the other hand, debt becomes more expensive. Additionally, consumers can protect themselves to an extent during periods of inflation. For instance, consumers who have allocated their money into investments can see their earnings grow faster than the rate of inflation. During episodes of deflation, however, investments, such as stocks, corporate bonds, and real-estate investments, become riskier.
A recent period of deflation in the United States occurred between 2007 and 2008, referred to by economists as the Great Recession. In December 2008, more than half of executives surveyed by McKinsey expected deflation in their countries, and 44 percent expected to decrease the size of their workforces.
When taken to their extremes, both inflation and deflation can significantly and negatively affect consumers, businesses, and investors.
For more in-depth exploration of these topics, see McKinsey’s Operations Insights collection. Learn more about Operations consulting , and check out operations-related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced include:
- “ How business operations can respond to price increases: A CEO guide ,” March 11, 2022, Andreas Behrendt , Axel Karlsson , Tarek Kasah, and Daniel Swan
- “ Five ways to ADAPT pricing to inflation ,” February 25, 2022, Alex Abdelnour , Eric Bykowsky, Jesse Nading, Emily Reasor , and Ankit Sood
- “ How COVID-19 is reshaping supply chains ,” November 23, 2021, Knut Alicke , Ed Barriball , and Vera Trautwein
- “ Navigating the labor mismatch in US logistics and supply chains ,” December 10, 2021, Dilip Bhattacharjee , Felipe Bustamante, Andrew Curley, and Fernando Perez
- “ Coping with the auto-semiconductor shortage: Strategies for success ,” May 27, 2021, Ondrej Burkacky , Stephanie Lingemann, and Klaus Pototzky

Want to know more about inflation?
Related articles.

What is supply chain?

How business operations can respond to price increases: A CEO guide

Five ways to ADAPT pricing to inflation
Home — Essay Samples — Economics — Political Economy — Inflation
Essays on Inflation
Inflation essay topics and outline examples, essay title 1: understanding inflation: causes, effects, and economic policy responses.
Thesis Statement: This essay provides a comprehensive analysis of inflation, exploring its root causes, the economic and societal effects it generates, and the various policy measures employed by governments and central banks to manage and mitigate inflationary pressures.
- Introduction
- Defining Inflation: Concept and Measurement
- Causes of Inflation: Demand-Pull, Cost-Push, and Monetary Factors
- Effects of Inflation on Individuals, Businesses, and the Economy
- Inflationary Policies: Central Bank Actions and Government Interventions
- Case Studies: Historical Inflationary Periods and Their Consequences
- Challenges in Inflation Management: Balancing Growth and Price Stability
Essay Title 2: Inflation and Its Impact on Consumer Purchasing Power: A Closer Look at the Cost of Living
Thesis Statement: This essay focuses on the effects of inflation on consumer purchasing power, analyzing how rising prices affect the cost of living, household budgets, and the strategies individuals employ to cope with inflation-induced challenges.
- Inflation's Impact on Prices: Understanding the Cost of Living Index
- Consumer Behavior and Inflation: Adjustments in Spending Patterns
- Income Inequality and Inflation: Examining Disparities in Financial Resilience
- Financial Planning Strategies: Savings, Investments, and Inflation Hedges
- Government Interventions: Indexation, Wage Controls, and Social Programs
- The Global Perspective: Inflation in Different Economies and Regions
Essay Title 3: Hyperinflation and Economic Crises: Case Studies and Lessons from History
Thesis Statement: This essay explores hyperinflation as an extreme form of inflation, examines historical case studies of hyperinflationary crises, and draws lessons on the devastating economic and social consequences that result from unchecked inflationary pressures.
- Defining Hyperinflation: Thresholds and Characteristics
- Case Study 1: Weimar Republic (Germany) and the Hyperinflation of 1923
- Case Study 2: Zimbabwe's Hyperinflationary Collapse in the Late 2000s
- Impact on Society: Currency Devaluation, Poverty, and Social Unrest
- Responses and Recovery: Stabilizing Currencies and Rebuilding Economies
- Preventative Measures: Policies to Avoid Hyperinflationary Crises
The Impact of Inflation Reduction Act on The International Economic Stage
Inflation reduction act in the frame of macroeconomic challenges, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Exploring The Implications of The Inflation Reduction Act
Report on inflation and its causes, the rise of inflation rate in the us, iflation and its causes, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Methods to Control Inflation
The grade inflation, inflation: a deceitful solution to debt, how to control inflation in pakistan, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Main Factors of Inflation in Singapore
Effects of inflation on commercial banks’ lending: a case of kenya commercial bank limited, food inflation in the republic of india, the issue of unemployment and inflation in colombia, the theory and policy of macroeconomics on inflation rate, socio-economic conditions in 'what is poverty' by jo goodwin parker, non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment (nairu), targeting zero inflation and increase of government spending as a way of curbing recession, howa spiraling inflation has impacted the venezuelan economy, how venezuela has been affected by inflation, effects of inflation on kenya commercial banks lending, exploring theories of inflation in economics, about fuel prices: factors, impacts, and solutions, analyzing the inflation reduction act, the oscillating tides of the american economy, relevant topics.
- Unemployment
- Penny Debate
- Supply and Demand
- Real Estate
- American Dream
- Minimum Wage
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Essay on Inflation
Students are often asked to write an essay on Inflation in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Inflation
Understanding inflation.
Inflation is when prices of goods and services rise over time. This means you need more money to buy the same things. It’s like a slow-motion robbery!
Causes of Inflation
Inflation is often due to increased production costs or increased demand for goods and services. When people want more of something, and it’s scarce, prices go up.
Impact of Inflation
Inflation affects everyone. If your income doesn’t increase as fast as inflation, you’ll have less buying power. But, if you’re a business owner, you might be able to raise prices and make more money.
Controlling Inflation
Governments try to control inflation by adjusting interest rates, taxes, and government spending. It’s a tricky balancing act to keep inflation low but not too low.
Also check:
- Paragraph on Inflation
250 Words Essay on Inflation
Inflation, a crucial economic concept, refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, subsequently eroding purchasing power. It’s an indicator of the economic health of a nation, with moderate inflation signifying a growing economy.
The Causes of Inflation
Inflation generally occurs due to two primary factors: demand-pull and cost-push inflation. Demand-pull inflation transpires when demand for goods and services surpasses their supply. On the other hand, cost-push inflation arises when the costs of production escalate, causing producers to increase prices to maintain profit margins.
Effects of Inflation
Inflation impacts various aspects of the economy. It erodes the purchasing power of money, causing consumers to spend more for the same goods or services. Inflation can also create uncertainty in the economy, affecting investment and saving decisions. However, moderate inflation can stimulate spending and investment, driving economic growth.
Managing Inflation
Central banks attempt to control inflation through monetary policy. By adjusting interest rates, they influence the level of spending and investment in the economy. Higher interest rates typically reduce spending, curbing inflation. Conversely, lower interest rates stimulate spending, potentially leading to inflation.
Inflation is a complex and multifaceted subject. Understanding its causes, effects, and the measures to control it is essential for both macroeconomic stability and individual financial well-being. As future leaders, it’s crucial for us as students to grasp these concepts to make informed decisions in our professional and personal lives.
500 Words Essay on Inflation
Introduction to inflation.
Inflation is a complex economic phenomenon that affects every aspect of our lives, from the cost of living to the value of money. It is defined as the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, subsequently, purchasing power is falling. Central banks attempt to limit inflation, and avoid deflation, in order to keep the economy running smoothly.
Inflation is primarily caused by an increase in the money supply that outpaces economic growth. Ever since the end of the gold standard, governments have had the ability to create money at will. If a nation’s money supply grows too rapidly compared to its production of goods and services, prices will increase, leading to inflation.
Additionally, inflation can be spurred by demand-pull conditions, where demand for goods and services exceeds their supply. Cost-push inflation, on the other hand, occurs when the costs of production increase, causing producers to raise prices to maintain their profit margins.
Impacts of Inflation
Inflation affects economies in various ways. While mild inflation is viewed as a sign of a healthy economy, hyperinflation can lead to economic instability. It erodes purchasing power as the same amount of money can buy fewer goods and services. This can lead to uncertainty and a decrease in spending and investment, which can slow economic growth.
Moreover, inflation can harm savers if the inflation rate surpasses the interest rate on their savings. It also favors borrowers, as the real value of their debt diminishes over time. This redistribution of wealth from savers to borrowers can lead to social and economic inequalities.
Central banks use monetary policy to control inflation. They adjust the money supply by setting interest rates and through open market operations. By raising interest rates, central banks can decrease the money supply, making borrowing more expensive and slowing economic activity, thereby reducing inflation.
Furthermore, governments can use fiscal policy to control inflation. This involves changing tax rates and levels of government spending to influence the level of demand in the economy. By reducing demand, governments can put downward pressure on prices and reduce inflation.
Inflation is an intricate part of our economic systems. It is a double-edged sword that can stimulate economic growth when mild, but can also lead to economic instability when it becomes too high. Understanding inflation is crucial for policymakers, investors, and consumers alike as it influences our decisions and shapes our economic reality. By effectively managing inflation, governments can promote economic stability and growth, thereby improving the standard of living for their citizens.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Indian Culture
- Essay on Importance of Education
- Essay on Immigration
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Nice Very Nice
It is helpful …thanks alot
EXCELLENT AND ALSO VERY BENIFICAL FOR US AND ALSO FOR BEGINEERS
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Economic essays on inflation
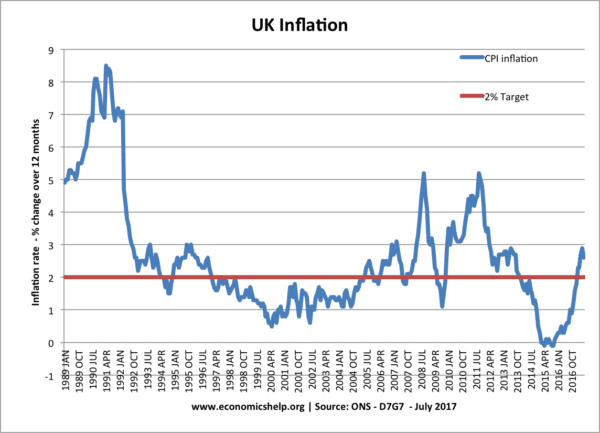
- Definition – Inflation – Inflation is a sustained rise in the cost of living and average price level.
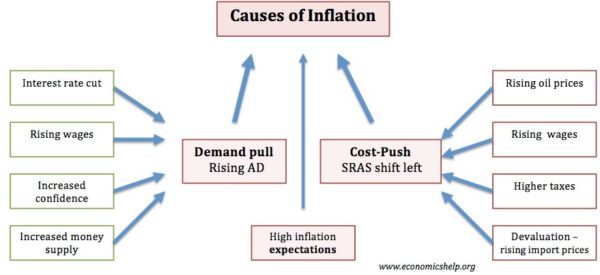
- Causes Inflation – Inflation is caused by excess demand in the economy, a rise in costs of production, rapid growth in the money supply.
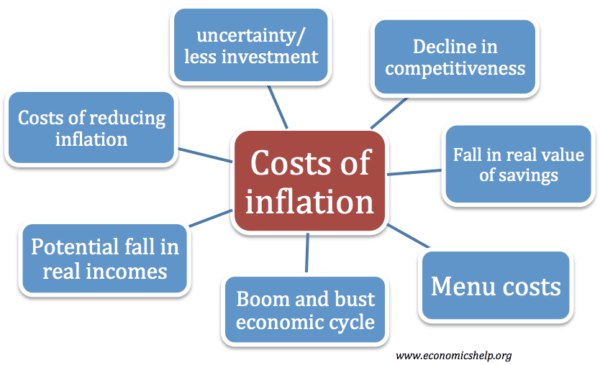
- Costs of Inflation – Inflation causes decline in value of savings, uncertainty, confusion and can lead to lower investment.
- Problems measuring inflation – why it can be hard to measure inflation with changing goods.
- Different types of inflation – cost-push inflation, demand-pull inflation, wage-price spiral,
- How to solve inflation . Policies to reduce inflation, including monetary policy, fiscal policy and supply-side policies.
- Trade off between inflation and unemployment . Is there a trade-off between the two, as Phillips Curve suggests?
- The relationship between inflation and the exchange rate – Why high inflation can lead to a depreciation in the exchange rate.
- What should the inflation target be? – Why do government typically target inflation of 2%
- Deflation – why falling prices can lead to negative economic growth.
- Monetarist Theory – Monetarist theory of inflation emphasises the role of the money supply.
- Criticisms of Monetarism – A look at whether the monetarist theory holds up to real-world scenarios.
- Money Supply – What the money supply is.
- Can we have economic growth without inflation?
- Predicting inflation
- Link between inflation and interest rates
- Should low inflation be the primary macroeconomic objective?
See also notes on Unemployment
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What Causes Inflation?
- Walter Frick

Why your money is worth less than it used to be.
What causes inflation? There is no one answer, but like so much of macroeconomics it comes down to a mix of output, money, and expectations. Supply shocks can lower an economy’s potential output, driving up prices. An increase in the money supply can stoke demand, driving up prices. And the expectation of inflation can become a self-fulfilling cycle as workers and companies demand higher wages and set higher prices.
Since the financial crisis of 2008 and the Great Recession, investors and executives have grown accustomed to a world of low interest rates and low inflation. No longer. In 2021, inflation began rising sharply in many parts of the world, and in 2022 the U.S. saw its worst inflation in decades.
- Walter Frick is a contributing editor at Harvard Business Review , where he was formerly a senior editor and deputy editor of HBR.org. He is the founder of Nonrival , a newsletter where readers make crowdsourced predictions about economics and business. He has been an executive editor at Quartz as well as a Knight Visiting Fellow at Harvard’s Nieman Foundation for Journalism and an Assembly Fellow at Harvard’s Berkman Klein Center for Internet & Society. He has also written for The Atlantic , MIT Technology Review , The Boston Globe , and the BBC, among other publications.
Partner Center
Inflation: What It Is, How It Can Be Controlled, and Extreme Examples
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Inflation?
Understanding inflation, types of price indexes.
- Pros and Cons
Controlling Inflation
Hedging against inflation, the bottom line.
What you need to know about the purchasing power of money and how it changes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/jason_mugshot__jason_fernando-5bfc261946e0fb00260a1cea.jpg)
Pete Rathburn is a copy editor and fact-checker with expertise in economics and personal finance and over twenty years of experience in the classroom.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/E7F37E3D-4C78-4BDA-9393-6F3C581602EB-2c2c94499d514e079e915307db536454.jpeg)
Inflation is a rise in prices, which can be translated as the decline of purchasing power over time. The rate at which purchasing power drops can be reflected in the average price increase of a basket of selected goods and services over some time. The rise in prices, which is often expressed as a percentage, means that a unit of currency effectively buys less than it did in prior periods. Inflation can be contrasted with deflation, which occurs when prices decline and purchasing power increases.
Key Takeaways
- Inflation is the rate at which prices for goods and services rise.
- Inflation is sometimes classified into three types: demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation.
- The most commonly used inflation indexes are the Consumer Price Index and the Wholesale Price Index.
- Inflation can be viewed positively or negatively depending on the individual viewpoint and rate of change.
- Those with tangible assets, like property or stocked commodities, may like to see some inflation as that raises the value of their assets.
While it is easy to measure the price changes of individual products over time, human needs extend beyond just one or two products. Individuals need a big and diversified set of products as well as a host of services for living a comfortable life. They include commodities like food grains, metal, fuel, utilities like electricity and transportation, and services like healthcare , entertainment, and labor.
Inflation aims to measure the overall impact of price changes for a diversified set of products and services. It allows for a single value representation of the increase in the price level of goods and services in an economy over a specified time.
Prices rise, which means that one unit of money buys fewer goods and services. This loss of purchasing power impacts the cost of living for the common public which ultimately leads to a deceleration in economic growth. The consensus view among economists is that sustained inflation occurs when a nation's money supply growth outpaces economic growth.
Investopedia / Ellen Lindner
The increase in the Consumer Price Index For All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) over the 12 months ending February 2024. Prices rose 0.4% on a seasonally adjusted basis in February from the previous month.
To combat this, the monetary authority (in most cases, the central bank ) takes the necessary steps to manage the money supply and credit to keep inflation within permissible limits and keep the economy running smoothly.
Theoretically, monetarism is a popular theory that explains the relationship between inflation and the money supply of an economy. For example, following the Spanish conquest of the Aztec and Inca empires, massive amounts of gold and silver flowed into the Spanish and other European economies. Since the money supply rapidly increased, the value of money fell, contributing to rapidly rising prices.
Inflation is measured in a variety of ways depending on the types of goods and services. It is the opposite of deflation , which indicates a general decline in prices when the inflation rate falls below 0%. Keep in mind that deflation shouldn't be confused with disinflation , which is a related term referring to a slowing down in the (positive) rate of inflation.
Investopedia / Julie Bang
Causes of Inflation
An increase in the supply of money is the root of inflation, though this can play out through different mechanisms in the economy. A country's money supply can be increased by the monetary authorities by:
- Printing and giving away more money to citizens
- Legally devaluing (reducing the value of) the legal tender currency
- Loaning new money into existence as reserve account credits through the banking system by purchasing government bonds from banks on the secondary market (the most common method)
In all of these cases, the money ends up losing its purchasing power. The mechanisms of how this drives inflation can be classified into three types: demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation.
Demand-Pull Effect
Demand-pull inflation occurs when an increase in the supply of money and credit stimulates the overall demand for goods and services to increase more rapidly than the economy's production capacity. This increases demand and leads to price rises.
When people have more money, it leads to positive consumer sentiment. This, in turn, leads to higher spending, which pulls prices higher. It creates a demand-supply gap with higher demand and less flexible supply, which results in higher prices.
Melissa Ling {Copyright} Investopedia, 2019
Cost-Push Effect
Cost-push inflation is a result of the increase in prices working through the production process inputs. When additions to the supply of money and credit are channeled into a commodity or other asset markets, costs for all kinds of intermediate goods rise. This is especially evident when there's a negative economic shock to the supply of key commodities.
These developments lead to higher costs for the finished product or service and work their way into rising consumer prices. For instance, when the money supply is expanded, it creates a speculative boom in oil prices . This means that the cost of energy can rise and contribute to rising consumer prices, which is reflected in various measures of inflation.
Built-in Inflation
Built-in inflation is related to adaptive expectations or the idea that people expect current inflation rates to continue in the future. As the price of goods and services rises, people may expect a continuous rise in the future at a similar rate.
As such, workers may demand more costs or wages to maintain their standard of living. Their increased wages result in a higher cost of goods and services, and this wage-price spiral continues as one factor induces the other and vice-versa.
Depending upon the selected set of goods and services used, multiple types of baskets of goods are calculated and tracked as price indexes. The most commonly used price indexes are the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) .
The Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The CPI is a measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of goods and services that are of primary consumer needs. They include transportation, food, and medical care.
CPI is calculated by taking price changes for each item in the predetermined basket of goods and averaging them based on their relative weight in the whole basket. The prices in consideration are the retail prices of each item, as available for purchase by the individual citizens.
Changes in the CPI are used to assess price changes associated with the cost of living , making it one of the most frequently used statistics for identifying periods of inflation or deflation. In the U.S., the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports the CPI on a monthly basis and has calculated it as far back as 1913.
The CPI-U, which was introduced in 1978, represents the buying habits of approximately 88% of the non-institutional population of the United States.
The Wholesale Price Index (WPI)
The WPI is another popular measure of inflation. It measures and tracks the changes in the price of goods in the stages before the retail level.
While WPI items vary from one country to another, they mostly include items at the producer or wholesale level. For example, it includes cotton prices for raw cotton, cotton yarn, cotton gray goods, and cotton clothing.
Although many countries and organizations use WPI, many other countries, including the U.S., use a similar variant called the producer price index (PPI) .

The Producer Price Index (PPI)
The PPI is a family of indexes that measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers of intermediate goods and services over time. The PPI measures price changes from the perspective of the seller and differs from the CPI which measures price changes from the perspective of the buyer.
In all variants, the rise in the price of one component (say oil) may cancel out the price decline in another (say wheat) to a certain extent. Overall, each index represents the average weighted price change for the given constituents which may apply at the overall economy, sector , or commodity level.
The Formula for Measuring Inflation
The above-mentioned variants of price indexes can be used to calculate the value of inflation between two particular months (or years). While a lot of ready-made inflation calculators are already available on various financial portals and websites, it is always better to be aware of the underlying methodology to ensure accuracy with a clear understanding of the calculations. Mathematically,
Percent Inflation Rate = (Final CPI Index Value ÷ Initial CPI Value) x 100
Say you wish to know how the purchasing power of $10,000 changed between January 1975 and January 2024. One can find price index data on various portals in a tabular form. From that table, pick up the corresponding CPI figures for the given two months. For September 1975, it was 52.1 (initial CPI value) and for January 2024, it was 308.417 (final CPI value).
Plugging in the formula yields:
Percent Inflation Rate = (308.417 ÷ 52.1) x 100 = (5.9197) x 100 = 591.97%
Since you wish to know how much $10,000 from January 1975 would worth be in January 2024, multiply the inflation rate by the amount to get the changed dollar value:
Change in Dollar Value = 5.9197 x $10,000 = $59,197
This means that $10,000 in January 1975 will be worth $59,197 today. Essentially, if you purchased a basket of goods and services (as included in the CPI definition) worth $10,000 in 1975, the same basket would cost you $59,197 in January 2024.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Inflation
Inflation can be construed as either a good or a bad thing, depending upon which side one takes, and how rapidly the change occurs.
Individuals with tangible assets (like property or stocked commodities) priced in their home currency may like to see some inflation as that raises the price of their assets, which they can sell at a higher rate.
Inflation often leads to speculation by businesses in risky projects and by individuals who invest in company stocks because they expect better returns than inflation.
An optimum level of inflation is often promoted to encourage spending to a certain extent instead of saving. If the purchasing power of money falls over time, there may be a greater incentive to spend now instead of saving and spending later. It may increase spending, which may boost economic activities in a country. A balanced approach is thought to keep the inflation value in an optimum and desirable range.
Disadvantages
Buyers of such assets may not be happy with inflation, as they will be required to shell out more money. People who hold assets valued in their home currency, such as cash or bonds, may not like inflation, as it erodes the real value of their holdings.
As such, investors looking to protect their portfolios from inflation should consider inflation-hedged asset classes, such as gold, commodities, and real estate investment trusts (REITs). Inflation-indexed bonds are another popular option for investors to profit from inflation .
High and variable rates of inflation can impose major costs on an economy. Businesses, workers, and consumers must all account for the effects of generally rising prices in their buying, selling, and planning decisions.
This introduces an additional source of uncertainty into the economy, because they may guess wrong about the rate of future inflation. Time and resources expended on researching, estimating, and adjusting economic behavior are expected to rise to the general level of prices. That's opposed to real economic fundamentals, which inevitably represent a cost to the economy as a whole.
Even a low, stable, and easily predictable rate of inflation, which some consider otherwise optimal, may lead to serious problems in the economy. That's because of how, where, and when the new money enters the economy.
Whenever new money and credit enter the economy, it is always in the hands of specific individuals or business firms. The process of price level adjustments to the new money supply proceeds as they then spend the new money and it circulates from hand to hand and account to account through the economy.
Inflation does drive up some prices first and drives up other prices later. This sequential change in purchasing power and prices (known as the Cantillon effect) means that the process of inflation not only increases the general price level over time. But it also distorts relative prices , wages, and rates of return along the way.
Economists, in general, understand that distortions of relative prices away from their economic equilibrium are not good for the economy, and Austrian economists even believe this process to be a major driver of cycles of recession in the economy.
Leads to higher resale value of assets
Optimum levels of inflation encourage spending
Buyers have to pay more for products and services
Impose higher prices on the economy
Drives some prices up first and others later
A country’s financial regulator shoulders the important responsibility of keeping inflation in check. It is done by implementing measures through monetary policy , which refers to the actions of a central bank or other committees that determine the size and rate of growth of the money supply.
In the U.S., the Fed's monetary policy goals include moderate long-term interest rates, price stability, and maximum employment. Each of these goals is intended to promote a stable financial environment. The Federal Reserve clearly communicates long-term inflation goals in order to keep a steady long-term rate of inflation , which is thought to be beneficial to the economy.
Price stability or a relatively constant level of inflation allows businesses to plan for the future since they know what to expect. The Fed believes that this will promote maximum employment, which is determined by non-monetary factors that fluctuate over time and are therefore subject to change.
For this reason, the Fed doesn't set a specific goal for maximum employment, and it is largely determined by employers' assessments. Maximum employment does not mean zero unemployment, as at any given time there is a certain level of volatility as people vacate and start new jobs.
Hyperinflation is often described as a period of inflation of 50% or more per month.
Monetary authorities also take exceptional measures in extreme conditions of the economy. For instance, following the 2008 financial crisis, the U.S. Fed kept the interest rates near zero and pursued a bond-buying program called quantitative easing (QE) .
Some critics of the program alleged it would cause a spike in inflation in the U.S. dollar, but inflation peaked in 2007 and declined steadily over the next eight years. There are many complex reasons why QE didn't lead to inflation or hyperinflation , though the simplest explanation is that the recession itself was a very prominent deflationary environment, and quantitative easing supported its effects.
Consequently, U.S. policymakers have attempted to keep inflation steady at around 2% per year. The European Central Bank (ECB) has also pursued aggressive quantitative easing to counter deflation in the eurozone, and some places have experienced negative interest rates . That's due to fears that deflation could take hold in the eurozone and lead to economic stagnation.
Moreover, countries that experience higher rates of growth can absorb higher rates of inflation. India's target is around 4% (with an upper tolerance of 6% and a lower tolerance of 2%), while Brazil aims for 3.25% (with an upper tolerance of 4.75% and a lower tolerance of 1.75%).
Stocks are considered to be the best hedge against inflation , as the rise in stock prices is inclusive of the effects of inflation. Since additions to the money supply in virtually all modern economies occur as bank credit injections through the financial system, much of the immediate effect on prices happens in financial assets that are priced in their home currency, such as stocks.
Special financial instruments exist that one can use to safeguard investments against inflation . They include Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) , low-risk treasury security that is indexed to inflation where the principal amount invested is increased by the percentage of inflation.
One can also opt for a TIPS mutual fund or TIPS-based exchange-traded fund (ETF). To get access to stocks, ETFs, and other funds that can help avoid the dangers of inflation, you'll likely need a brokerage account. Choosing a stockbroker can be a tedious process due to the variety among them.
Gold is also considered to be a hedge against inflation, although this doesn't always appear to be the case looking backward.
Examples of Inflation
Since all world currencies are fiat money , the money supply could increase rapidly for political reasons, resulting in rapid price level increases. The most famous example is the hyperinflation that struck the German Weimar Republic in the early 1920s.
The nations that were victorious in World War I demanded reparations from Germany, which could not be paid in German paper currency, as this was of suspect value due to government borrowing. Germany attempted to print paper notes, buy foreign currency with them, and use that to pay their debts.
This policy led to the rapid devaluation of the German mark along with the hyperinflation that accompanied the development. German consumers responded to the cycle by trying to spend their money as fast as possible, understanding that it would be worth less and less the longer they waited. More money flooded the economy, and its value plummeted to the point where people would paper their walls with practically worthless bills. Similar situations occurred in Peru in 1990 and in Zimbabwe between 2007 and 2008.
What Causes Inflation?
There are three main causes of inflation: demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation.
- Demand-pull inflation refers to situations where there are not enough products or services being produced to keep up with demand, causing their prices to increase.
- Cost-push inflation, on the other hand, occurs when the cost of producing products and services rises, forcing businesses to raise their prices.
- Built-in inflation (which is sometimes referred to as a wage-price spiral) occurs when workers demand higher wages to keep up with rising living costs. This in turn causes businesses to raise their prices in order to offset their rising wage costs, leading to a self-reinforcing loop of wage and price increases.
Is Inflation Good or Bad?
Too much inflation is generally considered bad for an economy, while too little inflation is also considered harmful. Many economists advocate for a middle ground of low to moderate inflation, of around 2% per year.
Generally speaking, higher inflation harms savers because it erodes the purchasing power of the money they have saved; however, it can benefit borrowers because the inflation-adjusted value of their outstanding debts shrinks over time.
What Are the Effects of Inflation?
Inflation can affect the economy in several ways. For example, if inflation causes a nation’s currency to decline, this can benefit exporters by making their goods more affordable when priced in the currency of foreign nations.
On the other hand, this could harm importers by making foreign-made goods more expensive. Higher inflation can also encourage spending, as consumers will aim to purchase goods quickly before their prices rise further. Savers, on the other hand, could see the real value of their savings erode, limiting their ability to spend or invest in the future.
Why Is Inflation So High Right Now?
In 2022, inflation rates around the world rose to their highest levels since the early 1980s. While there is no single reason for this rapid rise in global prices, a series of events worked together to boost inflation to such high levels.
The COVID-19 pandemic led to lockdowns and other restrictions that greatly disrupted global supply chains, from factory closures to bottlenecks at maritime ports. Governments also issued stimulus checks and increased unemployment benefits to counter the financial impact on individuals and small businesses. When vaccines became widespread and the economy bounced back, demand (fueled in part by stimulus money and low-interest rates) quickly outpaced supply, which still struggled to get back to pre-COVID levels.
Russia's unprovoked invasion of Ukraine in early 2022 led to economic sanctions and trade restrictions on Russia, limiting the world's supply of oil and gas since Russia is a large producer of fossil fuels. Food prices also rose as Ukraine's large grain harvests could not be exported. As fuel and food prices rose, it led to similar increases down the value chains. The Fed raised interest rates to combat the high inflation, which significantly came down in 2023, though it remains above pre-pandemic levels .
Inflation is a rise in prices, which results in the decline of purchasing power over time. Inflation is natural and the U.S. government targets an annual inflation rate of 2%; however, inflation can be dangerous when it increases too much, too fast. Inflation makes items more expensive, especially if wages do not rise by the same levels of inflation. Additionally, inflation erodes the value of some assets, especially cash. Governments and central banks seek to control inflation through monetary policy.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " CONSUMER PRICE INDEX - FEBRUARY 2024 ," Page 1.
Edo, Anthony and Melitz, Jacques. " The Primary Cause of European Inflation in 1500-1700: Precious Metals or Population? The English Evidence ." CEPII Working Paper , October 2019, pp. 13-14. Download PDF.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Consumer Price Index: Overview ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Chapter 17. The Consumer Price Index (Updated 2-14-2018) ," Page 2.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Consumer Price Index Chronology ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Producer Price Index Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) ," Select "4. How does the Producer Price Index differ from the Consumer Price Index?"
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Producer Price Index Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) ," Select "3. When did the Wholesale Price Index become the Producer Price Index?"
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Producer Price Indexes ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Consumer Price Index Historical Tables for U.S. City Average ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Historical CPI-U ," Page 3.
Adam Smith Institute. " The Cantillion Effect ."
Foundation for Economic Education. " The Current Economic Crisis and the Austrian Theory of the Business Cycle ."
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. " Review of Monetary Policy Strategy, Tools, and Communication ."
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. " What is the Lowest Level of Unemployment that the U.S. Economy Can Sustain? "
Fischer, Stanley and et al. " Modern Hyper- and High Inflations ." Journal of Economic Literature , vol. 40, no. 3, September 2002, pp. 837.
Federal Reserve History. " The Great Recession and its Aftermath ."
Federal Reserve Bank of New York. " Liberty Street Economics: Ten Years Later—Did QE Work? "
Congressional Budget Office. " How the Federal Reserve’s Quantitative Easing Affects the Federal Budget ."
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. " FAQs: Why Does the Federal Reserve Aim for Inflation of 2 Percent Over the Longer Run? "
European Central Bank. " How Quantitative Easing Works ."
Reserve Bank of India. " Monetary Policy ," Select "The Monetary Policy Framework."
Central Bank of Brazil. " Inflation Targeting Track Record ."
TreasuryDirect. " Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) ."
University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. " 1920s Hyperinflation in Germany and Bank Notes ."
Rossini, Renzo (Editors Alejandro M. Werner and Alejandro Santos). " Staying the Course of Economic Success: Chapter 2. Peru’s Recent Economic History: From Stagnation, Disarray, and Mismanagement to Growth, Stability, and Quality Policies ." International Monetary Fund, September 2015.
Kramarenko, Vitaliy and et al. " Zimbabwe: Challenges and Policy Options after Hyperinflation ." International Monetary Fund , June 2010, no. 6.
The World Bank. " Inflation, Consumer Prices (Annual %) ."
Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, FRED. " Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: All Items in U.S. City Average ."
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. " Open Market Operations ."
- Inflation: What It Is, How It Can Be Controlled, and Extreme Examples 1 of 41
- 10 Common Effects of Inflation 2 of 41
- How to Profit From Inflation 3 of 41
- When Is Inflation Good for the Economy? 4 of 41
- History of the Cost of Living 5 of 41
- Why Are P/E Ratios Higher When Inflation Is Low? 6 of 41
- What Causes Inflation? 7 of 41
- Understand the Different Types of Inflation 8 of 41
- Wage Push Inflation: Definition, Causes, and Examples 9 of 41
- Cost-Push Inflation: When It Occurs, Definition, and Causes 10 of 41
- Cost-Push Inflation vs. Demand-Pull Inflation: What's the Difference? 11 of 41
- Inflation vs. Stagflation: What's the Difference? 12 of 41
- What Is the Relationship Between Inflation and Interest Rates? 13 of 41
- Inflation's Impact on Stock Returns 14 of 41
- How Does Inflation Affect Fixed-Income Investments? 15 of 41
- How Inflation Affects Your Cost of Living 16 of 41
- How Inflation Impacts Your Savings 17 of 41
- How Inflation Impacts Your Retirement Income 18 of 41
- What Impact Does Inflation Have on a Dollar's Value Over Time? 19 of 41
- Inflation and Economic Recovery 20 of 41
- What Is Hyperinflation? Causes, Effects, Examples, and How to Prepare 21 of 41
- Why Didn't Quantitative Easing Lead to Hyperinflation? 22 of 41
- Worst Cases of Hyperinflation in History 23 of 41
- How the Great Inflation of the 1970s Happened 24 of 41
- What Is Stagflation, What Causes It, and Why Is It Bad? 25 of 41
- Understanding Purchasing Power and the Consumer Price Index 26 of 41
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): What It Is and How It's Used 27 of 41
- Why Is the Consumer Price Index Controversial? 28 of 41
- Core Inflation: What It Is and Why It's Important 29 of 41
- What Is Headline Inflation (Reported in Consumer Price Index)? 30 of 41
- What Is the GDP Price Deflator and Its Formula? 31 of 41
- Indexation Explained: Meaning and Examples 32 of 41
- Inflation Accounting: Definition, Methods, Pros & Cons 33 of 41
- Inflation-Adjusted Return: Definition, Formula, and Example 34 of 41
- What Is Inflation Targeting, and How Does It Work? 35 of 41
- Real Economic Growth Rate: Definition, Calculation, and Uses 36 of 41
- Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP): How to Calculate It, vs. Nominal 37 of 41
- Real Income, Inflation, and the Real Wages Formula 38 of 41
- Real Interest Rate: Definition, Formula, and Example 39 of 41
- Real Rate of Return: Definition, How It's Used, and Example 40 of 41
- Wage-Price Spiral: What It Is and How It’s Controlled 41 of 41
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wall_street_179681980-5bfc2b9746e0fb0083c07d29.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Introduction to Inflation
Chapter objectives.
In this chapter, you will learn about:
- Tracking Inflation
- How to Measure Changes in the Cost of Living
- How the U.S. and Other Countries Experience Inflation
- The Confusion Over Inflation
- Indexing and Its Limitations
Bring It Home
A $550 million loaf of bread.
If you were born within the last three decades in the United States, Canada, or many other countries in the developed world, you probably have no real experience with a high rate of inflation. Inflation is when most prices in an entire economy are rising. However, there is an extreme form of inflation called hyperinflation. This occurred in Germany between 1921 and 1928, and more recently in Zimbabwe between 2008 and 2009. In November 2008, Zimbabwe had an inflation rate of 79.6 billion percent. In contrast, in 2014, the United States had an average annual rate of inflation of 1.6%.
Zimbabwe’s inflation rate was so high it is difficult to comprehend, so let’s put it into context. It is equivalent to price increases of 98% per day. This means that, from one day to the next, prices essentially double. What is life like in an economy afflicted with hyperinflation? Most of you reading this will have never experienced this phenomenon. The government adjusted prices for commodities in Zimbabwean dollars several times each day . There was no desire to hold on to currency since it lost value by the minute. The people there spent a great deal of time getting rid of any cash they acquired by purchasing whatever food or other commodities they could find. At one point, a loaf of bread cost 550 million Zimbabwean dollars. Teachers' salaries were in the trillions a month; however, this was equivalent to only one U.S. dollar a day. At its height, it took 621,984,228 Zimbabwean dollars to purchase one U.S. dollar.
Government agencies had no money to pay their workers so they started printing money to pay their bills rather than raising taxes. Rising prices caused the government to enact price controls on private businesses, which led to shortages and the emergence of black markets. In 2009, the country abandoned its currency and allowed people to use foreign currencies for purchases.
How does this happen? How can both government and the economy fail to function at the most basic level? Before we consider these extreme cases of hyperinflation, let’s first look at inflation itself.
Inflation is a general and ongoing rise in the level of prices in an entire economy. Inflation does not refer to a change in relative prices. A relative price change occurs when you see that the price of tuition has risen, but the price of laptops has fallen. Inflation, on the other hand, means that there is pressure for prices to rise in most markets in the economy. In addition, price increases in the supply-and-demand model were one-time events, representing a shift from a previous equilibrium to a new one. Inflation implies an ongoing rise in prices. If inflation happened for one year and then stopped, then it would not be inflation any more.
This chapter begins by showing how to combine prices of individual goods and services to create a measure of overall inflation. It discusses the historical and recent experience of inflation, both in the United States and in other countries around the world. Other chapters have sometimes included a note under an exhibit or a parenthetical reminder in the text saying that the numbers have been adjusted for inflation. In this chapter, it is time to show how to use inflation statistics to adjust other economic variables, so that you can tell how much of, for example, we can attribute the rise in GDP over different periods of time to an actual increase in the production of goods and services and how much we should attribute to the fact that prices for most items have risen.
Inflation has consequences for people and firms throughout the economy, in their roles as lenders and borrowers, wage-earners, taxpayers, and consumers. The chapter concludes with a discussion of some imperfections and biases in the inflation statistics, and a preview of policies for fighting inflation that we will discuss in other chapters.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Steven A. Greenlaw, David Shapiro, Daniel MacDonald
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Economics 3e
- Publication date: Dec 14, 2022
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e/pages/22-introduction-to-inflation
© Jan 23, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

An economist explains: What you need to know about inflation
Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, Toronto Metropolitan University
Disclosure statement
Nicholas Li does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Toronto Metropolitan University provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation CA.
Toronto Metropolitan University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA-FR.
View all partners
- Bahasa Indonesia
Inflation is one of the most pressing political and economic issues of the moment, but there are many misconceptions about how inflation is measured, where it comes from and how it impacts the average person.
In June, inflation in Canada reached a 40-year high of 8.1 per cent . While there are signs inflation may be moderating , many Canadians have dealt with the surging cost of living by cutting back on expenses , working more to increase their income, drawing on their savings or taking on more debt .
As an economics professor who conducts research on prices and consumption, I would like to provide some insight into how inflation is measured and how it is impacting Canadians and the economy at large.
What is inflation?
Inflation refers to a general increase in prices and the resulting decline in the purchasing power of money. While most of us can sense whether inflation is high or low from everyday purchases, the inflation rate that gets reported in the press and discussed by policy-makers is a specific measure created by a small army of statisticians and data collectors.
Statistics Canada constructs the Consumer Price Index (CPI) used to track inflation through a two-step process. In the first step, Statistics Canada collects over one million price quotes on virtually anything purchasable in the country.
Prices are recorded in a variety of ways, and the frequency and geography of price collection depends on the item. For example, items with prices that change quickly like food or gasoline, or vary across locations like rent, are collected more frequently than items that are collected once a year, like university tuition or insurance rates.

In the second step, Statistics Canada aggregates these prices to generate the all-item Consumer Price Index by weighing each item’s price change by its share of total consumer spending. These weights are occasionally updated to reflect changes in consumer spending patterns .
The most recent update in 2021 reflects some pandemic-related spending changes, such as a lower weight for food (15.75 per cent) and transportation (16.16 per cent), but a higher weight for shelter (29.67 per cent).
Statistics Canada and the Bank of Canada also measure “ core inflation ” which removes items with the most volatile prices (food and energy) from the CPI to provide a better sense of slower-moving, long-term cost pressures.
What causes inflation?
Prices are determined by supply and demand . High inflation is a sign that, across the economy, demand for goods and services exceeds their supply.
Demand has been strong due to strong employment and wage growth , cheap credit , pandemic-related payments from governments and pandemic-related shifts in demand towards goods consumed at home .
Supply has been disrupted by the pandemic’s effects on Chinese factories , international supply chains , container shipping , trucking and the Russian invasion of Ukraine that led to recent spikes in food and energy prices around the world.
Inflation feels higher than it is
Many Canadians feel like prices rose by more than 8.1 per cent in the last year. Beyond specific criticism of the CPI methodology in Canada , there are at least two reasons for this.
First, consumer spending is measured through surveys that capture the diversity of spending patterns in the population, but collapse this diversity into a single set of weights that treats each dollar of spending equally. Spending patterns vary with age, income, location, household composition and taste, and your personal budget might bear little resemblance to the weights used for the CPI.
Second, we are more likely to notice price changes for items we purchase frequently , and we tend to notice price increases more than decreases . The items with the highest price increases in the last year — energy and food — have these characteristics, and we are less likely to notice the (lower) inflation rate for furniture, electronics, education and health goods that balance these out.

We also pay a lot of attention to soaring house prices and interest rates — especially in big cities — but the cost of owned accommodation in the CPI is based on historical averages of housing prices (25 years) and interest rates (five years) that reflect long-term financing costs for the average homeowner, not someone buying a house today.
How does inflation impact us?
There are winners and losers when it comes to inflation. While it can hurt businesses that end up passing cost increases onto their customers , it can benefit others by allowing them to raise their prices without customer backlash because “everyone else is doing it.”
High inflation is often, but not always, accompanied by high wage growth . Individuals who earn no or below-inflation wages are hurt, while individuals with wages indexed to inflation or who are able to negotiate better wages can benefit. Individuals like seniors on fixed incomes are often hurt by inflation, although many government benefits are indexed to inflation .
Some asset prices are better at keeping pace with inflation. Prices of housing, stocks, art and precious metals may go up, while assets with fixed dollar values like cash and bonds do not.
Inflation can make it easier to repay debts, as long as wages or other asset prices keep pace. Inflation can also benefit government finances as tax revenues rise relative to the dollar value of the debt.
While the source of our current inflation is irrelevant to consumers, it matters for economic policy. Central banks and governments must decide whether to curb demand and risk recession by raising interest rates , cutting spending or raising taxes, or wait and hope that supply-side inflation pressures ease up on their own.
We can only hope that it will not take a major recession to end this period of high inflation (unlike the last major effort by the Bank of Canada to lower inflation ) and that Canada avoids “ stagflation ,” the combination of high inflation and high unemployment that afflicted many economies in the late 1970s.
- Supply and demand
- Cost of living
- Consumer price index (CPI)
- Economic crisis
- Statistics Canada
- Consumer Price Index
- Listen to this article
- Cost of living crisis

Biocloud Project Manager - Australian Biocommons

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

School of Social Sciences – Public Policy and International Relations opportunities

Deputy Editor - Technology
Introduction to "Inflation: Causes and Effects"
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
More from NBER
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .


Introduction to Inflation

A $550 Million Loaf of Bread?
If you were born within the last three decades in the United States, Canada, or many other countries in the developed world, you probably have no real experience with a high rate of inflation. Inflation is when most prices in an entire economy are rising. However, there is an extreme form of inflation called hyperinflation. This occurred in Germany between 1921 and 1928, and more recently in Zimbabwe between 2008 and 2009. In November 2008, Zimbabwe had an inflation rate of 79.6 billion percent. In contrast, in 2014, the United States had an average annual rate of inflation of 1.6%.
Zimbabwe’s inflation rate was so high it is difficult to comprehend, so let’s put it into context. It is equivalent to price increases of 98% per day. This means that, from one day to the next, prices essentially double. What is life like in an economy afflicted with hyperinflation? Most of you reading this will have never experienced this phenomenon. The government adjusted prices for commodities in Zimbabwean dollars several times each day . There was no desire to hold on to currency since it lost value by the minute. The people there spent a great deal of time getting rid of any cash they acquired by purchasing whatever food or other commodities they could find. At one point, a loaf of bread cost 550 million Zimbabwean dollars. Teachers’ salaries were in the trillions a month; however, this was equivalent to only one U.S. dollar a day. At its height, it took 621,984,228 Zimbabwean dollars to purchase one U.S. dollar.
Government agencies had no money to pay their workers so they started printing money to pay their bills rather than raising taxes. Rising prices caused the government to enact price controls on private businesses, which led to shortages and the emergence of black markets. In 2009, the country abandoned its currency and allowed people to use foreign currencies for purchases.
How does this happen? How can both government and the economy fail to function at the most basic level? Before we consider these extreme cases of hyperinflation, let’s first look at inflation itself.
In this chapter, you will learn about:
- Tracking Inflation
- How to Measure Changes in the Cost of Living
- How the U.S. and Other Countries Experience Inflation
- The Confusion Over Inflation
- Indexing and Its Limitations
Inflation is a general and ongoing rise in the level of prices in an entire economy. Inflation does not refer to a change in relative prices. A relative price change occurs when you see that the price of tuition has risen, but the price of laptops has fallen. Inflation, on the other hand, means that there is pressure for prices to rise in most markets in the economy. In addition, price increases in the supply-and-demand model were one-time events, representing a shift from a previous equilibrium to a new one. Inflation implies an ongoing rise in prices. If inflation happened for one year and then stopped, then it would not be inflation any more.
This chapter begins by showing how to combine prices of individual goods and services to create a measure of overall inflation. It discusses the historical and recent experience of inflation, both in the United States and in other countries around the world. Other chapters have sometimes included a note under an exhibit or a parenthetical reminder in the text saying that the numbers have been adjusted for inflation. In this chapter, it is time to show how to use inflation statistics to adjust other economic variables, so that you can tell how much of, for example, we can attribute the rise in GDP over different periods of time to an actual increase in the production of goods and services and how much we should attribute to the fact that prices for most items have risen.
Inflation has consequences for people and firms throughout the economy, in their roles as lenders and borrowers, wage-earners, taxpayers, and consumers. The chapter concludes with a discussion of some imperfections and biases in the inflation statistics, and a preview of policies for fighting inflation that we will discuss in other chapters.
Principles of Economics: Scarcity and Social Provisioning (2nd Ed.) Copyright © 2020 by Rice University; Dean, Elardo, Green, Wilson, Berger is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Essay on Inflation: Meaning, Measurement and Causes
Let us make in-depth study of the meaning, measurement and causes of inflation.
Meaning of Inflation:
By inflation we mean a general rise in prices. To be more correct, inflation is a persistent rise in general price level rather than a once-for-all rise in it.
Rate of inflation is either measured by the percentage change in wholesale price index number (WPI) over a period or by percentage change in consumer price index number (CPI).
Opinion surveys conducted in India and the United States reveal that inflation is the most important concern of the people as it affects their standard of living adversely A high rate of inflation erodes the real incomes of the people. A high rate of inflation makes the life of the poor people miserable. It is therefore described as anti-poor, inflation redistributes income and wealth in favour of the rich.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Thus, it makes the rich richer and the poor poorer. Above all, a high rate inflation adversely effects output and encourages investment in unproductive channels such as purchase of gold, silver, jewellery and real estate. Therefore, it adversely affects long-run economic growth, especially in developing countries like India. Inflation has therefore been described ‘as enemy number one’.
Measurement of Rate of Inflation:
Inflation has been one of the important problems facing the economies of the world. Precisely stated, inflation is the rate of change of general price level during a period of time. And the general price level in a period is the result of inflation in the past. Through rate of inflation economists measures the cost of living in an economy. Let us explain how rate of inflation is measured. Suppose P i X represents the price level on 31st March 2006 and P represents the price level on 31st March 2007. Then the rate of inflation in year 2006-07 will be equal to
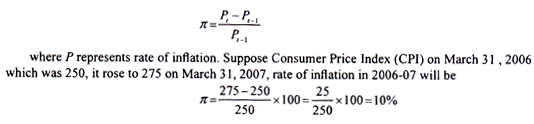
Thus, rate of inflation during 2006-07 will be 10 per cent. This is called point-to-point inflation rate. There are 52 weeks in a year, average of price indexes of 52 weeks of a year (say 2005-06) can be calculated to compare the average of price indexes of 52 weeks of year 2006-07 and find the inflation rate on the basis of average weekly price levels of a year. In both these ways rate of inflation in different years is measured and compared.
It is evident from above that price level in a period is measured by a price index. There are several commodities in an economy which are produced and consumed by the people. It is through construction of a weighted price index that economists aggregate money prices of several commodities which are assigned different weights.
In India the wholesale price Index (WPI) of all commodities with base year 1993-94 price level at the end of fiscal year is used to measure rate of inflation and is widely reported in the media. Since the wholesale price index does not truly indicate the cost of living, separate Consumer Price Index (CPI) for agricultural labourers and Consumer Price Index (CPI) for industrial workers (with base 1982 = 100) at the end of fiscal year are constructed to measure rate of inflation.
In constructing the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the price of a basket of goods which a typical consumer, industrial worker or agricultural labourer as the case may be are taken into account.
What Causes Inflation?
1. keynes’s view:.
Classical economists thought that it was the quantity of money in the economy that determined the general price level in the economy. According to them, rate of inflation depends on the growth of money supply in the economy. Keynes criticized the ‘ Quantity Theory of Money’ and showed that expansion in money supply did not always lead to inflation or rise in price level.
Keynes who before the Second World War explained that involuntary unemployment and depression were due to the deficiency of aggregate demand, during the war period when price rose very high he explained that inflation was due to excessive aggregate demand. Thus, Keynes put forward what is now called demand-pull theory of inflation.
Demand – Pull Inflation
Thus, according to Keynes, inflation is caused by a situation whereby the pressure of aggregate demand for goods and services exceeds the available supply of output (both begging counted at the prices ruling at the beginning of a period). In such a situation, rise in price level is the natural consequence.
Now, this imbalance between aggregate demand and supply may be the result of more than one force at work. As we know aggregate demand is the sum of consumers’ spending on consumer goods and services, government spending on consumer goods and services and net investment being planned by the entrepreneurs.
But excess of aggregate demand over aggregate supply does not explain persistent rise in prices, year after year. An important factor which feeds inflation is wage-price spiral. Wage-price spiral operates as follows: A rise in prices reduces the real consumption of the wage earners. They will, therefore, press for higher money wages to compensate them for the higher cost of living. Now, an increase in wages, if granted, will raise the prime cost of production and, therefore, entrepreneurs will raise the prices of their products to recover the increment in cost.
This will add fuel to the inflationary fire. A further rise in prices raises the cost of living still further and the workers ask for still higher wages. In this way, wages and prices chase each other and the process of inflationary rise in prices gathers momentum. If unchecked, this may lead to hyper-inflation which signifies a state of affairs where wages and prices chase each other at a very quick speed.
2. Monetarist View:
The Keynesian explanation of demand-pull inflation is important to note that both the original quantity theorists and the modem monetarists, prominent among whom is Milton Friedman, explain inflation in terms of excess demand for goods and services. But there is an important difference between the monetarist view of demand-pull inflation and the Keynesian view of it. Keynes explained inflation as arising out of real sector forces.
In his model of inflation excess demand comes into being as a result of autonomous increase in expenditure on investment and consumption or increase in government expenditure. That is, the increase in aggregate expenditure or demand occurs independent of any increase in the supply of money.
On the other hand, monetarists explain the emergence of excess demand and the resultant rise in prices on account of the increase in money supply in the economy. To quote Milton Friedman, a Nobel Laureate in economics. “Inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon…… and can be produced only by a more rapid increase in the quantity of money than in output.”
Friedman holds that when money supply is increased in the economy, then there emerges an excess supply of real money balances with the public over their demand for money. This disturbs the monetary equilibrium. In order to restore the equilibrium the public will reduce the money balances by increasing expenditure on goods and services.
Thus, according to Friedman and other modern quantity theorists, the excess supply of real monetary balances results in the increase in aggregate demand for goods and services. If there is no proportionate increase in output, then extra money supply leads to excess demand for goods and services. This causes inflation or rise in prices. Thus, according to monetarists let by Prof. Milton Friedman, excess creation of money supply is the main factor responsible for inflation.
Cost-Push Inflation:
Even when there is no increase in aggregate demand, prices may still rise. This may happen if the costs, particularly the wage costs, increase. Now, as the level of employment increases, the demand for workers rises progressively so that the bargaining position of the workers is enhanced. To exploit this situation, they may ask for an increase in wage rates which are not justifiable either on grounds of a prior rise in productivity or cost of living.
The employers in a situation of high demand and employment are more agreeable to concede to these wage claims because they hope to pass on these rises in costs to the consumers in the form of rise in prices. Therefore, when inflation is caused by rise in wages or hike in other input costs such as rise in prices of raw materials, rise in prices of petroleum products, it is called cost-push inflation. If this happens we have another inflationary factor at work.
Besides the increase in wages of labour without any increase in its productivity, or rise in costs of other inputs there is another factor responsible for cost-push inflation. This is the increase in the profit margins by the firms working under monopolistic or oligopolistic conditions and as a result charging higher prices from the consumers. In the former case when the cause of cost-push inflation is the rise in wages it is called wage-push inflation and in the latter case when the cause of cost-push inflation is the rise in profit margins, it is called profit-push inflation.
In addition to the rise in wage rate of labour and increase in profit margin, in the seventies the other cost-push factors (also called supply shocks) causing increase in marginal cost of production became more prominent in bringing about rise in prices. During the seventies, rise in prices of raw materials, especially energy inputs such a hike in crude oil prices made by OPEC resulted in rise in prices of petroleum products.
For example, sharp rise in world oil prices during 1973-75 and again in 1979-80 produced significant cost-push factor which caused inflation not only in Indian but all over the world. Now, in June-August 2004 again the world oil prices have greatly risen. As a result, in India prices of petrol, diesel, cooking gas were raised by petroleum companies. This is tending to raise the rate of inflation.
Related Articles:
- Essay on the Causes of Inflation (473 Words)
- Demand Pull Inflation and Cost Push Inflation | Money
- Difference between Demand Inflation and Cost Inflation
- Cost-Push Inflation and Demand-Pull or Mixed Inflation

Essay on Inflation in Pakistan for Students
by Pakiology | Mar 22, 2024 | Essay | 0 comments
In this essay on inflation in Pakistan, we will look at the causes, effects, and solutions to this issue that has been affecting the country for decades. The term ‘inflation’ refers to a sustained rise in the prices of goods and services in an economy. In Pakistan, inflation has been a major concern since the late 1990s, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reaching a peak in 2023. We will explore the various factors that have contributed to inflation in Pakistan, its economic effects, and what can be done to address the issue.
Page Contents
Essay on Inflation Outlines
Causes of inflation in pakistan, effects of inflation, solution to control inflation.
- Introduction
Inflation in Pakistan is caused by several factors, which can be divided into two main categories: domestic and external. The main domestic causes of inflation are an increase in money supply, an increase in government spending, an increase in indirect taxes, and a decrease in economic growth.
The most significant contributor to inflation in Pakistan is an increase in the money supply. When there is too much money chasing after too few goods, prices rise, creating a situation known as demand-pull inflation. An increase in the money supply can be caused by the central bank printing more money or by the government borrowing more money from the public.
In addition, higher government spending can lead to inflation. This occurs when the government prints more money to finance its expenditure or borrows from the public and transfers the cost of this additional spending to businesses and consumers. This leads to higher prices for goods and services. Indirect taxes are another major factor that contributes to inflation in Pakistan. When indirect taxes are increased, prices of goods and services also increase, leading to an overall rise in prices.
Finally, low economic growth can also cause inflation in Pakistan. A weak economy reduces people’s purchasing power, forcing them to buy less, which reduces demand and leads to lower prices. However, when economic growth stalls, businesses are unable to sell their products at the same price as before, leading to a rise in prices.
Overall, inflation in Pakistan is caused by a combination of domestic and external factors. These include an increase in money supply, higher government spending, increases in indirect taxes, and a decrease in economic growth.
The effects of inflation on the economy can be both positive and negative. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, meaning that each unit of currency is worth less than it was before. This means that, as the cost of living increases, people can purchase fewer goods and services for the same amount of money. As a result, their standard of living decreases.
Inflation also reduces the real return on investments and savings, which can have a detrimental effect on economic growth. When inflation is high, people prefer to save their money rather than invest in a business or other activities. This reduces the availability of capital and results in slower economic growth.
In addition to decreasing standards of living, inflation can lead to unemployment if companies are not able to increase wages at the same rate as prices rise. This can lead to an increase in poverty, as people struggle to afford necessities. Furthermore, when prices rise faster than wages, it puts pressure on government budgets and can increase public debt.
Inflation can also cause the value of the local currency to depreciate against foreign currencies. This has a direct impact on the cost of imports and makes domestic goods less competitive in international markets. It can also have an indirect impact on exports, as it reduces the competitiveness of local producers in foreign markets.
Inflation is a serious issue in Pakistan, and it needs to be addressed to improve the country’s economic conditions. The following are some of the measures that can be taken to control inflation in Pakistan:
1. Fiscal policy: A strong fiscal policy is necessary for controlling inflation. The government should increase its revenue by implementing taxes on the wealthy and reducing public spending. This will help reduce budget deficits, which will result in lower inflation.
2. Monetary policy: The State Bank of Pakistan should adopt a tighter monetary policy to control inflation. It should raise interest rates so that investors have an incentive to save rather than spend, thus curbing demand-pull inflation.
3. Supply-side measures: There should be an increase in the production of essential commodities and products to meet the demand of consumers. This will help reduce prices and inflation in the long run.
4. Subsidies: The government should provide subsidies to those who are suffering due to the high prices of essential items. This will help them cope with the rising cost of living and ensure that they have access to essential goods and services.
5. Stabilizing exchange rate: A stable exchange rate between foreign currencies and the rupee is necessary for controlling inflation. The State Bank of Pakistan should strive to keep the rupee’s value stable by using currency swaps and other methods.
These measures can go a long way in controlling inflation in Pakistan. By taking these measures, the government can help improve the country’s economic condition and create an environment conducive to investment and growth.
What is inflation in simple words?
Inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
What are the 4 main causes of inflation?
The 4 main causes of inflation are: Demand-pull inflation: when there is an increase in demand for goods and services that outstrip the economy’s ability to produce them. Cost-push inflation: when the cost of production increases, causing companies to raise prices to maintain their profit margins. Built-in inflation: when businesses expect prices to rise and build that expectation into their prices, causing a self-fulfilling cycle of inflation. Imported inflation: when the cost of imported goods increases, leading to higher prices for consumers.
What are the 5 main causes of inflation?
The 4 main causes of inflation are: 1. Demand-pull inflation 2. Cost-push inflation 3. Built-in inflation 4. Imported inflation 5. Monetary inflation
What is inflation introduction?
Inflation is a phenomenon that has been observed throughout history. It refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
Find more Essays on the following Topics
Ask Your Questions
You might like, democracy in pakistan essay with quotations.
Explore the evolution, challenges, and progress of democracy in Pakistan in this in-depth essay. Gain insights into...
Problems of Karachi Essay | 200 & 500 Words
Explore the multifaceted challenges faced by Karachi in this comprehensive essay. From overpopulation to traffic...
A True Muslim Essay With Quotations 2023
A true Muslim essay is about the qualities of a true Muslim and how they embody the teachings of Islam in their daily...
Health is Wealth Essay For Students
In this essay, we explore why health is wealth and why it is crucial to prioritize our physical and mental well-being...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- class-9-notes
- Friendship quotes
- Scholarships
- Science News
- Study Abroad
- Study in Australia
- SZABMU MDCAT
- UHS Past MCQs
- Universities

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What are the main causes of inflation? There are two primary types, or causes, of inflation: Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services in the economy exceeds the economy's ability to produce them. For example, when demand for new cars recovered more quickly than anticipated from its sharp dip at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, an intervening shortage in the ...
Essay on Inflation! Essay on the Meaning of Inflation: Inflation and unemployment are the two most talked-about words in the contemporary society. These two are the big problems that plague all the economies. Almost everyone is sure that he knows what inflation exactly is, but it remains a source of great deal of confusion because it is difficult to define it unambiguously. Inflation is often ...
Inflation is a general and ongoing rise in the level of prices in an entire economy. Inflation does not refer to a change in relative prices. A relative price change occurs when you see that the price of tuition has risen, but the price of laptops has fallen. Inflation, on the other hand, means that there is pressure for prices to rise in most ...
Analyzing The Inflation Reduction Act. 1 page / 497 words. Video Description This essay explores the provisions and impacts of the Inflation Reduction Act, analyzing its effects on inflation rates, economic growth, distributional outcomes, and sector-specific implications. It outlines how the act aimed to reduce inflation rates and stabilize ...
Introduction Robert E. Hall The essays in this volume are the product of the NBER'S Project on Inflation and reflect a dozen diverse views on one of the nation's central economic problems. Our emphasis here is on diagnosis of the causes of inflation and a description of the effects of inflation, not on specific policy recommendations to end ...
500 Words Essay on Inflation Introduction to Inflation. Inflation is a complex economic phenomenon that affects every aspect of our lives, from the cost of living to the value of money. It is defined as the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, subsequently, purchasing power is falling.
Introduction to U.S. Economy: Inflation https://crsreports.congress.gov. decreases the supply of oil and other petroleum products. The decrease in oil supplies increases the price of oil and petroleum products. Petroleum products are an input good for a significant portion of goods and services across the economy, and as the price of this ...
UK inflation since 1989. Definition - Inflation - Inflation is a sustained rise in the cost of living and average price level. Causes Inflation - Inflation is caused by excess demand in the economy, a rise in costs of production, rapid growth in the money supply. Costs of Inflation - Inflation causes decline in value of savings ...
What causes inflation? There is no one answer, but like so much of macroeconomics it comes down to a mix of output, money, and expectations. Supply shocks can lower an economy's potential output ...
Inflation is the rate of increase in prices over a given period of time. Inflation is typically a broad measure, such as the overall increase in prices or the increase in the cost of living in a country. But it can also be more narrowly calculated—for certain goods, such as food, or for services, such as a haircut, for example.
Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising and, consequently, the purchasing power of currency is falling. Central banks attempt to limit inflation ...
Ch. 22 Introduction to Inflation - Principles of Economics 3e | OpenStax. Highlights. Figure 22.1 Big Bucks in Zimbabwe This bill was worth 100 billion Zimbabwean dollars when issued in 2008. There were even bills issued with a face value of 100 trillion Zimbabwean dollars. The bills had $100,000,000,000,000 written on them.
Prices are determined by supply and demand. High inflation is a sign that, across the economy, demand for goods and services exceeds their supply. Demand has been strong due to strong employment ...
1. The quantity theory of money. Thesis: Inflation is determined by the money supply. As the first and oldest of the inflation theories, the quantity theory of money views inflation as primarily a "monetary" occurrence. In other words, the influence of the amount of money in the economy takes precedence over all other factors, including income levels, demand for goods, and frequency of ...
In addition to working papers, the NBER disseminates affiliates' latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter, the NBER Digest, the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability, the Bulletin on Health, and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports, video lectures, and interviews.
Inflation is a general and ongoing rise in the level of prices in an entire economy. Inflation does not refer to a change in relative prices. A relative price change occurs when you see that the price of tuition has risen, but the price of laptops has fallen. Inflation, on the other hand, means that there is pressure for prices to rise in most ...
Introduction to Inflation. Inflation is a general and ongoing rise in the level of prices in an entire economy. Inflation does not refer to a change in relative prices. A relative price change occurs when you see that the price of tuition has risen, but the price of laptops has fallen.
Sample Essays (1) Inflation is a measure of the rate at which the general price level of goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling. ... I. Introduction Inflation is an economic phenomenon in which the general price level of goods and services in an economy increases over time. It is measured as the percentage ...
1. Introduction. After long-lasting theoretical debates between the 1970s and late 1990s, the academic literature on inflation has reached a fair range of consensus (see Goodfriend and King Citation 1997).Despite some dissent regarding the specific causes and channels through which inflation is worked out into the system, it is generally accepted that inflation is caused by three primal causes ...
Thus, rate of inflation during 2006-07 will be 10 per cent. This is called point-to-point inflation rate. There are 52 weeks in a year, average of price indexes of 52 weeks of a year (say 2005-06) can be calculated to compare the average of price indexes of 52 weeks of year 2006-07 and find the inflation rate on the basis of average weekly price levels of a year.
Economics. This essay provides a detailed and concise analysis of the causes and effects of inflation. It covers the various factors that can lead to inflation, including an increase in demand, production costs, money supply, and taxes. Additionally, it explores the potential negative impacts of inflation, such as a decrease in purchasing power ...
INTRODUCTION. 1.0 Background of Study. Inflation is one of the economic issues in the world economic development. Literally, inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services are increasing and purchasing power is decreasing. So that, when price of goods and services increasing, therefore people will buy less ...
In this essay on inflation in Pakistan, we will look at the causes, effects, and solutions to this issue that has been affecting the country for decades. The term 'inflation' refers to a sustained rise in the prices of goods and services in an economy. In Pakistan, inflation has been a major concern since the late 1990s, with the Consumer ...