Design a Mobile Ticketing App for a Movie Theater: User Experience Focus
Designing a user-friendly mobile app for movie theater ticketing can be tricky to get right.
By focusing on core principles of user experience (UX) design and research, you can create an intuitive and enjoyable app for seamless ticket booking.
In this guide, we'll explore practical strategies for designing an app that meets the needs of moviegoers, from visual design to personalized engagement features. Utilizing real-world examples and case studies , you'll learn actionable tips to craft an exceptional user experience .

Introduction to Mobile Ticketing App Design
Designing a user-friendly mobile ticketing app is key for movie theaters looking to provide a seamless ticket purchasing experience . As consumers increasingly rely on mobile devices, having an app that makes booking and checking in efficient and straightforward is essential.
The Significance of Mobile Ticketing in the Digital Age
Mobile apps have become the preferred platform for accessing services and information on-the-go. For movie theaters, mobile ticketing provides significant advantages:
- Convenience - Customers can quickly buy tickets anytime, anywhere instead of waiting in line at the counter
- Flexibility - Seat selection and special offers can be easily accessed
- Data - Apps provide user data to help theaters understand customer behavior
As consumers gravitate towards mobile, a well-designed app is vital for movie theaters to keep up with changing consumer expectations.
Goals and Objectives of the App
The primary goals for a movie theater mobile ticketing app are:
- Enhance user experience - Intuitive design and seamless booking process
- Increase ticket sales - Convenient access drives more purchases
- Streamline operations - Mobile ticket integration improves theater efficiency
- Build customer loyalty - Personalized offers and rewards programs
Focusing on these core objectives during the design process ensures the app provides value to both customers and movie theaters. Keeping the end-user experience front and center leads to better engagement and long-term app success.
User Research and Audience Analysis
Analyzing the needs and behaviors of potential moviegoers is crucial for designing a mobile ticketing app that delivers an excellent user experience. Here are key areas to focus on:
Identifying the Moviegoer Persona
When designing a mobile ticketing app for a movie theater , it's vital to understand your target users. Create 2-3 moviegoer personas representing your main audience segments. Include details like:
- Demographics - age, location, income level
- Goals - convenience, finding showtimes, easy checkout
- Frustrations - complicated apps, hidden fees
Aligning features with moviegoer personas ensures your app solves real user needs.
Understanding User Expectations and Requirements
Conduct user interviews and surveys to capture expectations around:
- Ease of use - intuitive navigation and flows
- Functionality - browsing movies, selecting seats, payment
- Speed - fast checkout process
- Compatibility - iOS and Android
Document these as requirements to guide the design and development . Track which are essential vs. nice-to-have.
Analyzing Pain Points and Opportunities
Look at app store reviews and support tickets to uncover pain points with existing movie apps:
- Difficulty finding showtimes
- Complicated seat selection
- Unexpected fees during checkout
Identify these user problems as opportunities to improve and exceed expectations. Fixing pain points also drives positive reviews and referrals.
Thorough user research ensures your custom mobile ticketing app delivers an intuitive, seamless moviegoer experience - leading to more sales.
Designing the User Interface (UI)
Designing an intuitive user interface (UI) is crucial for a successful mobile ticketing app. The UI should make the key tasks of browsing movies, selecting seats, and purchasing tickets as smooth as possible.
Principles of Effective UI for Ticket Booking
Here are some key principles for designing an effective UI for mobile ticket booking :
- Simplicity - Avoid clutter and only include essential elements on each screen. Use clear icons and labels so functions are obvious.
- Consistency - Maintain consistent design patterns and flows across all screens. This builds familiarity for users.
- Feedback - Provide clear feedback after each user action so they know it was successful. This builds trust.
- Prioritize Key Actions - Make primary tasks like selecting a movie, reserving seats, and paying stand out visually on each screen.
- Responsive Design - Optimize UI for mobile devices and different screen sizes. Test on target devices.
Following these principles will create an intuitive flow where users can easily complete tasks.
Creating a Cohesive Visual Language
A cohesive visual language strengthens branding and improves UX by meeting user expectations. Considerations when designing:
- Color Palette - Limit colors and reuse them consistently, especially your brand colors.
- Typography - Establish primary and secondary fonts for headings and body text.
- Iconography - Create a custom icon set that aligns to your aesthetic. Reuse them.
- Layouts - Standardize spacing, sizes, and positioning of elements across all screens.
Maintaining harmony between these aspects establishes familiarity and enhances usability.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Design
Accessible design ensures usability for people with disabilities. Some best practices:
- Add image descriptions for screen readers
- Support color contrast changes
- Design large tap targets
- Support screen magnifiers
- Allow text size adjustments
Inclusive design considers diverse user capabilities and limitations during planning. Building accessibility improves overall usability.
By focusing on user needs in the UI design, the mobile ticketing app can provide a streamlined booking experience that works for all moviegoers. This drives adoption and satisfaction.
Developing the User Experience (UX)
Prioritize must-have functionality like showtime browsing, seat selection and ticket management to fulfill core moviegoer needs.
Mapping the Ticket Ordering Flow for a Movie Theater
The key steps in the movie ticket ordering flow that the app should guide users through:
- Browse movies and showtimes
- Select movie, date, time, and number of tickets
- Select seats from an interactive theater map
- Enter ticket holder details
- Review order and payment options
- Complete payment
- Receive and store mobile tickets
The app should allow users to seamlessly navigate through these steps with clear indicators of their progress. Contextual help and tooltips can assist users if they get stuck.
Streamlining this flow to minimize taps, swipes, and data entry creates a frustration-free ticket buying experience.
Simplifying the Seat Reservation Process
The seat map interface is vital for user experience. Key UX considerations include:
- Intuitive visual representation of the theater layout
- Clear indicators of available, reserved, and selected seats
- Options to select preferred seats (aisle, middle, back rows etc.)
- Zoom and pan controls to inspect seats closely
- Real-time updates as seats are selected
- Contextual tooltip when hovering over a seat
Optimizing this interface allows moviegoers to quickly browse and reserve their desired seats.
Facilitating Easy Showtime Check-In
Hassle-free check-in is essential for app adoption. Useful features include:
- One tap check-in from the ticket dashboard
- Automatic check-in when entering geofence around theater
- Seamless ticket barcode scanning with alerts on success
- Intuitive re-scan process in case of errors
- Clear post-check-in instructions on theater entry
Prioritizing check-in convenience encourages continued app usage for future movie visits.
sbb-itb-b1b0647
Payment integration and security.
Choose secure, convenient payment options tailored to your target audience.
Implementing Diverse Payment Options
Offering a variety of payment methods in your mobile ticketing app can enhance the user experience and lead to higher conversion rates. Here are some tips:
- Integrate popular third-party payment gateways like Stripe, Braintree, or PayPal to enable credit/debit card payments. This ensures PCI compliance.
- Consider adding PayPal, Apple Pay, or Google Pay to enable mobile wallet payments. These are convenient for users.
- Allow users to store card details for faster checkout in future purchases. Enable one-click payments.
- Offer gift card payment options to allow users to redeem cinema gift cards/vouchers.
- For advanced apps, incorporate QR code or NFC payments for contactless checkout.
By supporting diverse payment methods aligned with user preferences, cinemas can drive more ticket sales.
Ensuring Transaction Security
It's crucial for cinemas to prioritize security in their mobile ticketing app to build user trust:
- Comply with industry standards like PCI DSS for securing card data.
- Encrypt sensitive user data in transit and at rest. Consider tokenization.
- Incorporate features like 2FA or biometrics for account logins to prevent fraud.
- Display trust badges and security seals prominently in the checkout flow.
- Conduct regular audits and penetration testing to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
With robust security measures in place, users will feel more assured transacting in the cinema's app.
Streamlining the Checkout Process
An optimized checkout flow is essential for minimizing cart abandonment:
- Reduce the number of checkout form fields to only necessary ones like name, email, payment details etc.
- Set default values wherever possible - registered user details, saved payment methods etc.
- Allow guest checkout options for first-time users.
- Adopt a single-page checkout to complete payment details in one go.
- Clearly display ticket details including showtime, seat numbers, concessions etc.
- Send confirmation emails/texts with QR code tickets upon successful payment.
By refining the checkout user flow, cinemas can significantly increase transaction conversion rates.
Personalization and Engagement Strategies
Increase loyalty by providing customized recommendations and promotions.
Leveraging User Data for Tailored Experiences
Collecting user data ethically allows movie theaters to better understand customer preferences and offer personalized recommendations. Some ideas:
- Allow users to rate movies and save favorites to their profile. Use this data to suggest new releases they may enjoy.
- Track purchase history and movie viewing patterns. Recommend similar titles or complementary concessions based on prior orders.
- Let customers select preferred genres, actors, etc. Notify them of relevant upcoming releases.
- Analyze seat selection tendencies. Provide customized seat recommendations based on factors like viewing angle or proximity preferences.
Incorporating Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs encourage repeat business and help cinemas foster meaningful relationships with customers. Considerations:
- Reward return visits by offering loyalty points, redeemable for concessions, tickets, or upgrades.
- Identify high-value patrons for special perks like members-only screenings or early access to blockbuster pre-sales.
- Send tailored promotions to loyalty members for personalized discounts on their favorite treats and genres.
Engaging Users with Interactive Content
Integrating interactive content into cinema apps boosts engagement:
- Allow users to view movie trailers, read reviews, and share showtimes on social media.
- Incorporate gamification by letting customers make predictions on review scores or opening weekend box office figures.
- Enable push notifications for show reminders, nearby movie deals, and updates on highly-anticipated upcoming releases.
App Analytics and Continuous Improvement
Continuously analyzing app usage data is critical for identifying issues and opportunities to improve the movie theater mobile ticketing app experience. Here are key areas to focus on:
Monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Define core KPIs to track the success of the mobile ticketing app, such as:
- Number of app downloads
- Number of tickets purchased through the app
- Conversion rate from app browse to ticket purchase
- Average time to complete a ticket purchase
Closely monitor trends for these KPIs in real-time to detect problems and identify improvement opportunities. For example, a drop in conversion rate may indicate issues with the checkout flow.
Utilizing User Feedback
Actively collect qualitative user feedback through:
- In-app surveys and ratings prompts
- App store reviews and ratings
- Social media monitoring
- Customer support interactions
Analyze user feedback to surface pain points and enhancement ideas. Prioritize addressing issues decreasing user satisfaction scores.
Benchmarking Against Competitors
Conduct a movie theater app competitive audit examining functionality, design, and performance of competing theater apps.
Key aspects to compare include:
- Core features offered
- User interface and experience
- Ratings and reviews
- KPIs like downloads and usage
This analysis identifies functionality and capabilities to emulate or avoid. Implement the best practices that could improve your app.
Continuously analyzing app data, user feedback, and the competitive landscape will highlight areas for improvement to create the best possible moviegoer mobile experience . This drives increased engagement, satisfaction, and ticket sales.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Movie theater owners face immense challenges when it comes to selling tickets and engaging audiences. Thankfully, custom mobile apps provide proven solutions, as highlighted in these real-world examples.
Analyzing a Movie Ticket Booking App Case Study
One regional cinema chain saw great success after launching a customized mobile ticketing app. The app enabled patrons to seamlessly browse showtimes, select seats, and securely pay for tickets on their phones. This led to a 15% increase in advance ticket sales in the first year.
Key factors that made this mobile ticketing app successful:
- Intuitive and attractive user interface optimized for quick ticket purchases
- Deep integration with the cinema's ticketing and concessions systems
- Targeted push notifications to drive impulse ticket buys
- Robust analytics to understand user behavior
By analyzing this case study, cinema owners can identify smart mobile app features to implement in their own theaters.
Learning from Seat Reservation App Successes
Certain movie theaters have excelled at seat reservation capabilities in their apps. For example, an art house cinema built an app allowing customers to select their favorite seats across all auditoriums. Patrons felt more engaged and bought more tickets to guarantee their preferred seats.
This app succeeded due to:
- Seat maps synced in real-time with the box office
- Seat selection workflows based on thorough user testing
- Allowing seat reservations without requiring ticket purchases
The seat reservation functionality kept patrons returning to the app and drove increased ticket sales over time.
Innovations in Showtime Check-In Apps
Streamlining the showtime check-in process via mobile apps provides a better customer experience. Apps that have successfully innovated in this area include:
- Apps that automatically check patrons in based on real-time location data. This eliminates queues and tickets altogether.
- Apps allowing patrons to preorder concessions for pick-up. This avoids missing the film's opening minutes while waiting in line.
- Apps that notify patrons when their film is about to start. This prevents late arrivals and disruptions.
These innovations illustrate how mobile technology can transform showtime logistics for the better.
By learning from these real-world examples, movie theater owners can confidently design mobile apps incorporating the most impactful features. This leads to greater ticket sales, happier customers, and sustained business growth over the long term.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for Designing a Movie Theater App
Designing an effective mobile ticketing app for a movie theater requires focusing on key principles of user-centered design to create a seamless and convenient experience for moviegoers.
Recap of User Experience Design Principles
When creating a mobile ticketing app, it's important to:
- Understand moviegoer needs and pain points through user research and testing
- Optimize the user interface for simplicity, clarity, and ease of use
- Streamline booking and payment flows for faster checkout
- Provide accurate and up-to-date showtime information
- Enable advanced features like seat selection and reservation
- Integrate with loyalty programs and offer special promotions
By focusing on these core UX principles and the overall user journey, movie theaters can drive increased ticket sales, enhance customer satisfaction, and boost engagement through their mobile apps.
Final Thoughts on the Future of Mobile Ticketing
As mobile technology continues to evolve, so too will movie theater apps with new innovations to improve convenience and personalization:
- Integration with digital wallets for frictionless payments
- Personalized film recommendations and notifications based on viewing history
- Dynamic pricing and deals based on time of day, demand, etc.
- Enhanced reality features for an immersive booking experience
- Expanded platform support across devices and operating systems
There are exciting opportunities ahead for mobile ticketing. By continually optimizing for user experience and leveraging emerging technologies, movie theaters can future-proof their apps to stay competitive, maximize sales, and deliver outstanding service to moviegoers.
Related posts
- Mobile Apps Elevate Moviegoer Experience
- Engage Moviegoers with Custom Cinema Apps
- Streamline Ticket Sales with a Custom Cinema App
- Boost Cinema Revenue with an Optimized Tickets App
Cinema Mobile App Engagement

Cinema Lighting Design: Techniques & Control

Cinema App Online Revenue Boosters
Pack the seats & power your theater marketing with filmgrail.
Get a free value assessment for your movie theater.
Thanks for getting in touch!
We appreciate you contacting us. A Filmgrail representative will be in touch with you shortly.
movie ticket booking app Case study

Dont copy, You can do it

Movie Booking App
A case study on improving the experience of searching, finding and booking movies in a cinema, using a User-Centered Design process.
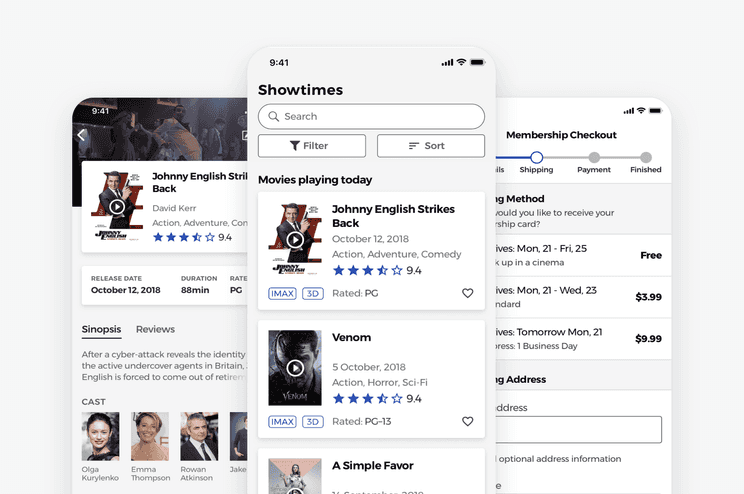
Like most people, I love seeing movies. Especially in a cinema. However, each time I used one of my local cinema’s app or website to try to buy a ticket for a movie, I found that they all had outdated and confusing designs. Furthermore, if I didn’t know which movie I’d like to see, I always had to use Google or other websites to find out more about the movie.
That’s why I decided to see how I could improve the experience of searching for a movie and then buying a ticket for it using an iOS App.
- UX Research
- Interaction Design
- Pen and paper
Deliverables
- InVision Prototype
- Moderator Guide
Project Type
- Personal Project
- User Interviews
Affinity Diagram
Problem statement.
- Paper Prototype
- High Fidelity Prototype
- 5 Act User Interview
Before I started working on this project, I had an initial assumption:
People are having trouble searching for a movie that they would like to see when they’re using my local cinema’s website or app.
To validate my assumption and design a solution, I decided to follow a User-Centered Design process with a combination of methods from Lean UX and Google Sprint.
For the first part of the discovery phase, I interviewed 4 users. This helped me better understand the pain points they were having and how they were using the products that were currently available.
But before I started doing the interviews, I made a list of the different questions I had that I needed to answer with the research.

Previous Questions
- How are people deciding which movie they would like to see?
- How are they finding out more about the movie?
- Why this many?
- With who are they seeing the movie? Alone, with a date, in a group?
- Searching for a cinema
- Searching for a movie to see
- Using the available websites to buy movie tickets
- Selecting seats
- Buying and paying for the tickets
User Interview Findings
From the user interviews I found that people:
- Think that movie tickets and snacks prices are too high.
- Would consider seeing more movies if the cinema had offers or discounts.
- Think the visual design isn’t that great.
- Use google o services such as imdb.com to learn more about each movie.
- Miss having a tool that shows them which movies are available on a particular time of day or on a specific day.
- Feel that the company just wants them to sign up so that they can send them marketing emails.
- Feel that information about the cinema is hard to find (the types of seats that are available, services, etc).
Once I had a list of all the insights from the research, I made an Affinity Diagram to help me group and identify the common paint points.

So I decided to start working on the following pain points:
- People need a way to help them decide which movie to see
- People are having issues with the checkout flow
- People feel that prices are too high
Problem Statements
The next step was to identify the problem statements. Then I used the How Might We technique to help me find solutions for each one.
People are having difficulties deciding which movie they would like to see.
How Might We:
Improve our app so that we can help people decide which movie they would like to see faster?
People are frustrated when they have to create an account before they can make a purchase.
Improve the checkout process so that people can make purchases without any frustration?
Movie enthusiasts feel that ticket prices are too high, which is preventing them from being able to see as many movies as they would like to.
Reduce the cost of seeing a movie in a cinema for repeat customers?
Based on these problem statements and the research findings, I created 2 user personas. I used them to help me design the features of the app, which were based on their pain points, and on the outcomes they were trying to achieve.
He is trying to find a movie that he and his date would like to watch tonight. They are not movie experts and want to watch a movie. To decide which one, they read movie reviews, watch movie trailers and compare several ones before making a decision.
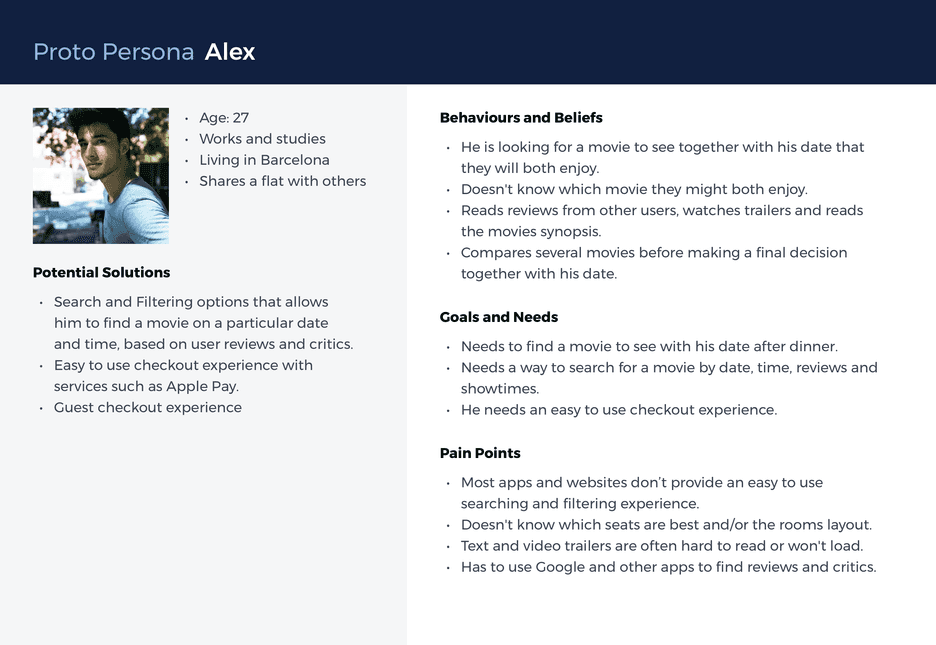
She is a movie enthusiast that likes to watch several movies each month, but she feels that current prices are too high and that cinemas are not valuing their most loyal customers.
Feature Prioritization
To decide which features to include in the initial MVP, I decided to use a Prioritisation Matrix which is based on the value it would provide to the end-user and by how difficult it would be to create.

MOSCOW Method
Then I used the MOSCOW method to find which are the most important features to be included in the MVP.

My MVP would include these 3 main features:
- Ability to search, filter and sort movies
- Optimized guest checkout experience
Membership plan with offers and discounts
Feature hypothesis statements.
Next I used the Lean UX Feature Hypothesis Statements to identify the features that will serve each persona and help them achieve their individual outcome.
Searching, filtering and sorting feature
We will create an advanced search, filter and sort feature for Alex in order to help him decide which movie he would like to see faster .
Guest checkout experience
We will create an optimized guest checkout experience for Alex in order to help him buy his movie tickets without any frustration .
We will create a membership plan for Ana in order to reduce the cost of seeing several movies a month for movie enthusiasts .
To help me ideate quick solutions to each of the features, I used the Crazy 8’s method since it’s a great way to keep you in a constant creative thinking mode and generate many different ways to design a particular feature.
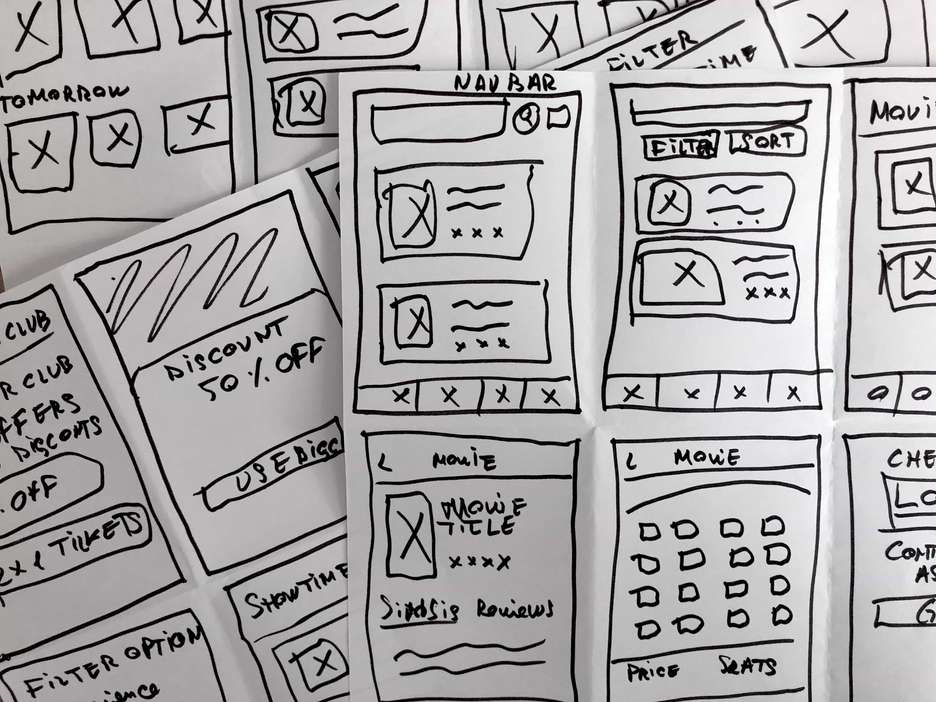

Movie Searching and Filtering
The first feature I started working on was on the ability to search, filter and sort movies.
I designed this feature to help users find a movie faster, using different filtering options, while also being able to sort the results based on several category-specific criteria.
Most users had difficulties deciding which movie they would like to see, so the feature is meant to help them find a movie based on its genre, showtime, user reviews or duration. This way they didn’t have to use other products or services to learn more about the movie.
Before I started sketching the app’s nav bar, I decided to see which patterns were being used by other apps or websites that also needed a similar feature.
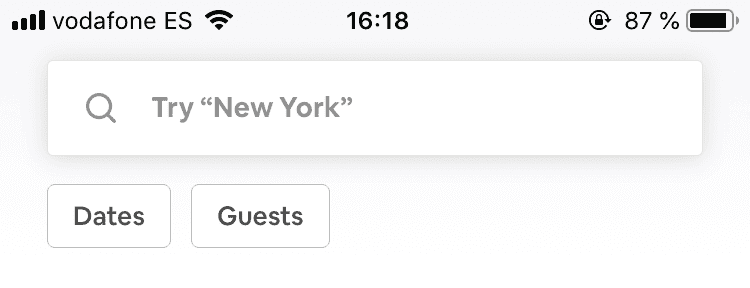
The first product I compared was Airbnb’s iOS app. One of the reasons for which I started with their app was because the design pattern they were using, allowed them to show their buttons for “Dates” and “Guests”, always visible below the search bar. This way, their users can always see them and know where to go if they need to filter the search results they are seeing.
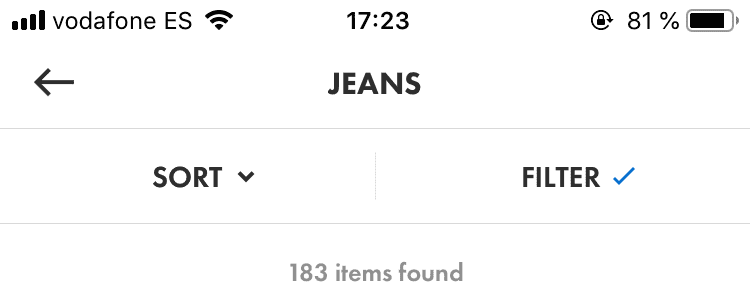
The next app I compared was Asos’s iOS app. Their sort and filter buttons have more visual weight that Airbnb’s ones, but they didn’t include a search bar since it was on a different screen.
One of the benefits of the way Asos.com implements their sorting and filtering options is that it allows them to show which sorting or filtering options are applied. This way they can remind the user that the search results are being affected by the filters applied.
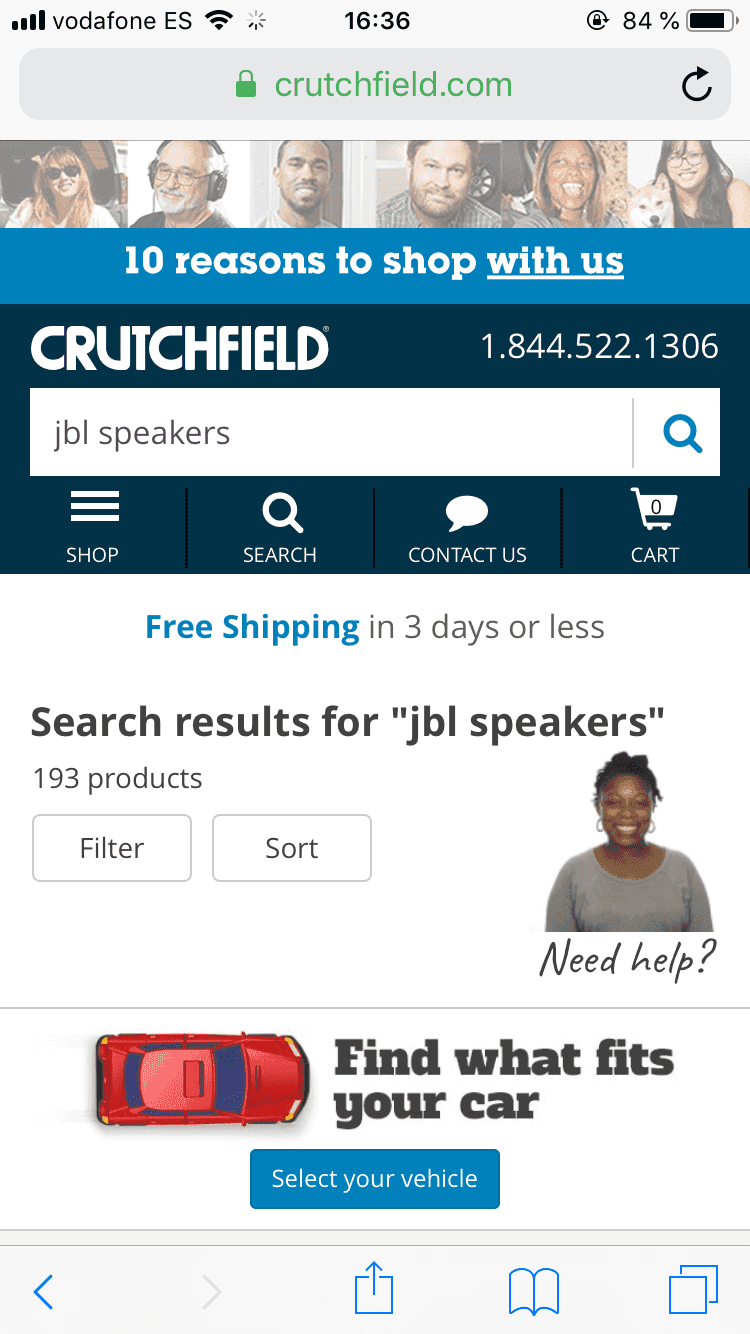
Crutchfield.com’s website has the search bar and sorting and filtering options at the same time. However, their sort and filter buttons are more separated from the search bar and don’t have the same visual weight as the Asos.com example. This could mean that their users might overlook the options because they don’t stand out as much.
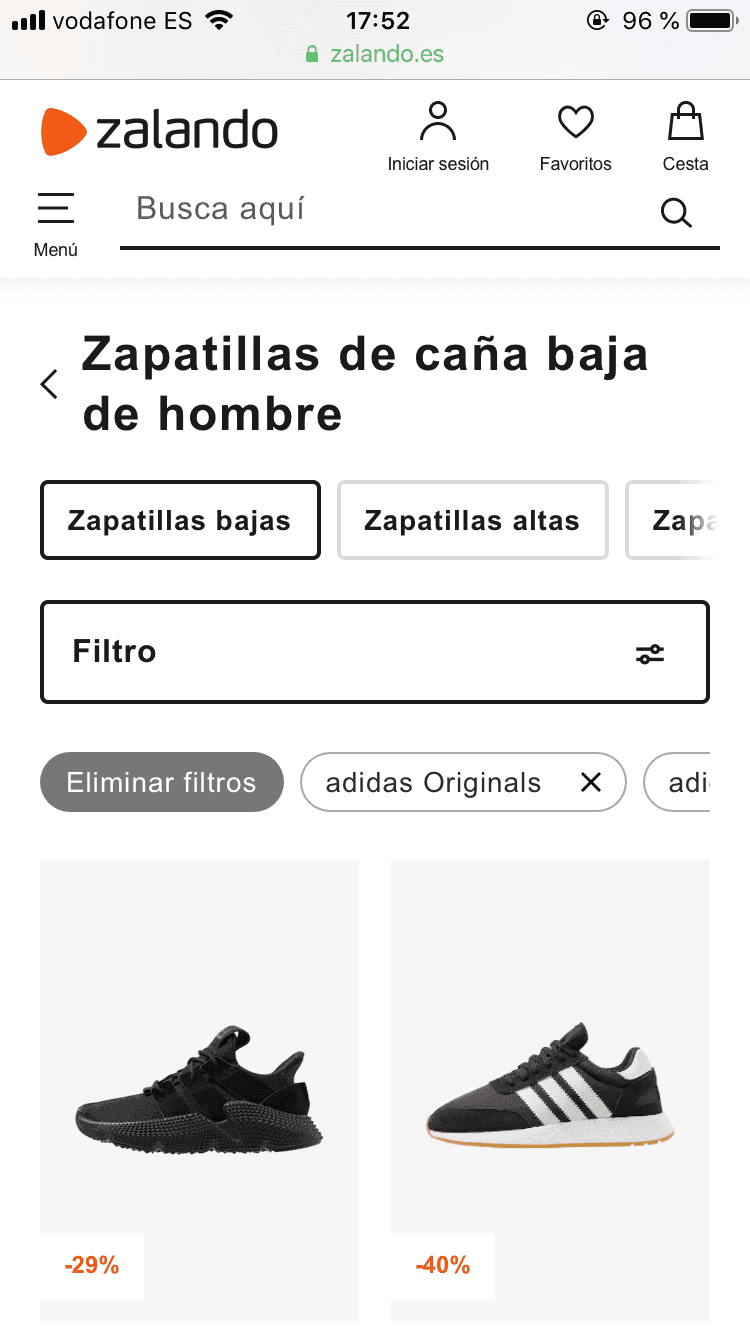
zalando.es had one of the most complete searching and filtering experience for their users. Besides always showing the filtering button, they also indicate which filtering options are active. Furthermore, their users can remove individual filters without having to open the filters menu.
A “clear all filters” button is also used to allow their users to remove all the applied filters if they want to start over with a new search.
Final Version of the Movie Searching and Filtering Feature
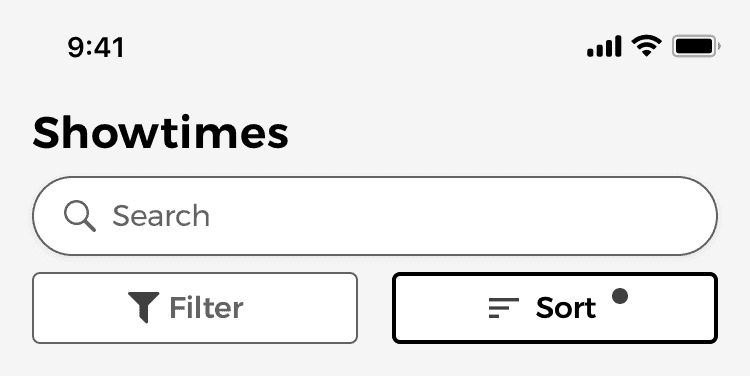
For the final version of the feature, I decided to use a combination of the different design patterns mentioned above. This allowed me to include a full-width search bar without having to hide the filter and sort buttons. This way I could also show if any filters or sorting options are active.
Another benefit is that users could also remove any of filters, either one by one, or all of them at once, by using the clear filters button.
The filtering options are also designed in a way that users can combine them to improve their search, without having mutually exclusive options, following the recommendations from the article on E-Commerce UX made by the Baymard Institute, where they found that up to 45% of the users tested, tried to apply several filters at some point during their search.
Movie Searching and Filtering Wireflow Diagram
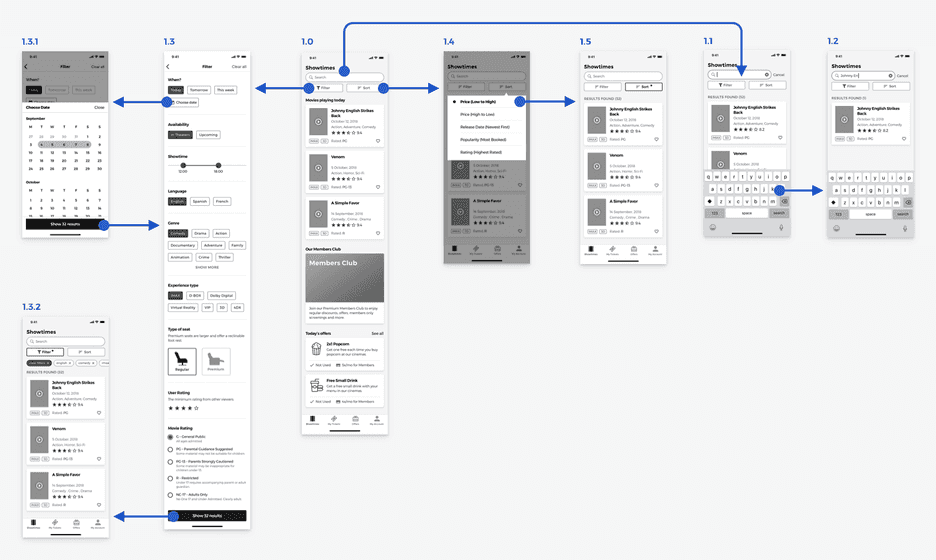
Movie Searching and Filtering High-Fidelity Prototypes
Movie searching.
Your browser does not support HTML5 video.
This website works best with JavaScript enabled.
Movie Filtering
Movie seat choosing, guest checkout flow.
The second feature of this app was the guest checkout user flow.
One of the main issues people had in the interviews was that they didn’t like the fact that they have to register before they can pay for the movie ticket. Most of them felt that they would receive a lot of spam, especially if the overall design of the website/app isn’t that up-to-date.
Even though guest checkout flows are usually designed for users which don’t have an account yet, they are also useful for users that have forgotten their password and don’t want to go through the password-reset-process at the moment.
After some initial research to see which are the design patterns and best practices used for designing a checkout flow, I started working on the prototype of the feature.
Delayed Account Creation
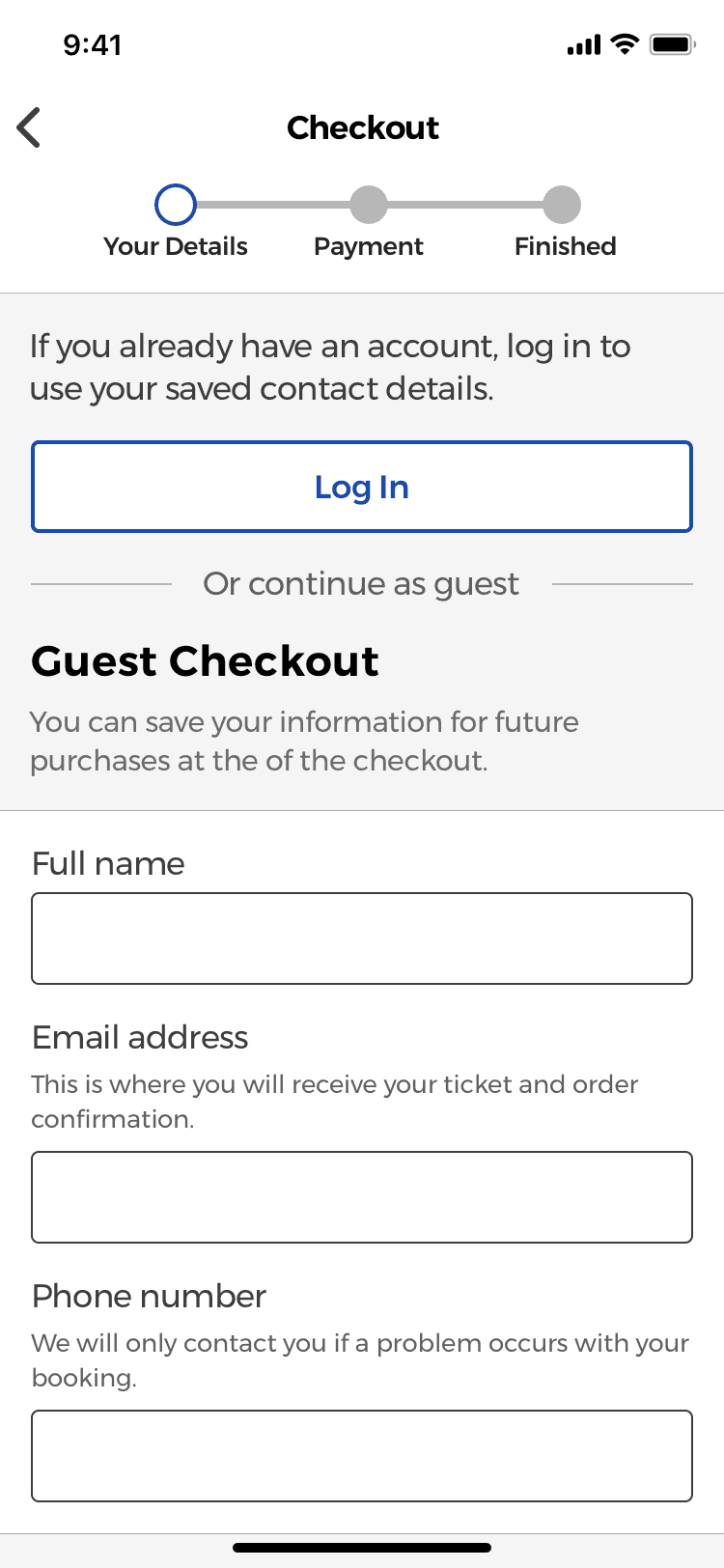
Guest checkout as an option for all users
According to the research made by the Baymard Institute, up to 37% of the users tested, would abandon the checkout if they are forced to create an account. Therefore, I decided to allow the users of the app to be able to make a payment without having to create an account first, by creating a guest checkout experience for everyone, no mather if they have an account or not.
Create an account in the checkout confirmation step
Since I wasn’t asking for every user to create an account first, I decided to let them know that they can make a purchase now, and if they would like to register to save their payment or shipping information for future purchases, they can still create an account at the end of the checkout process if they would like to.
Explain why information is needed
Furthermore —according to the same research—, if users are concerned about their privacy, the product can explain why their personal information is needed, which will help reduce their fear that it’s just for sending them marketing emails.
Guest Checkout Payment Methods
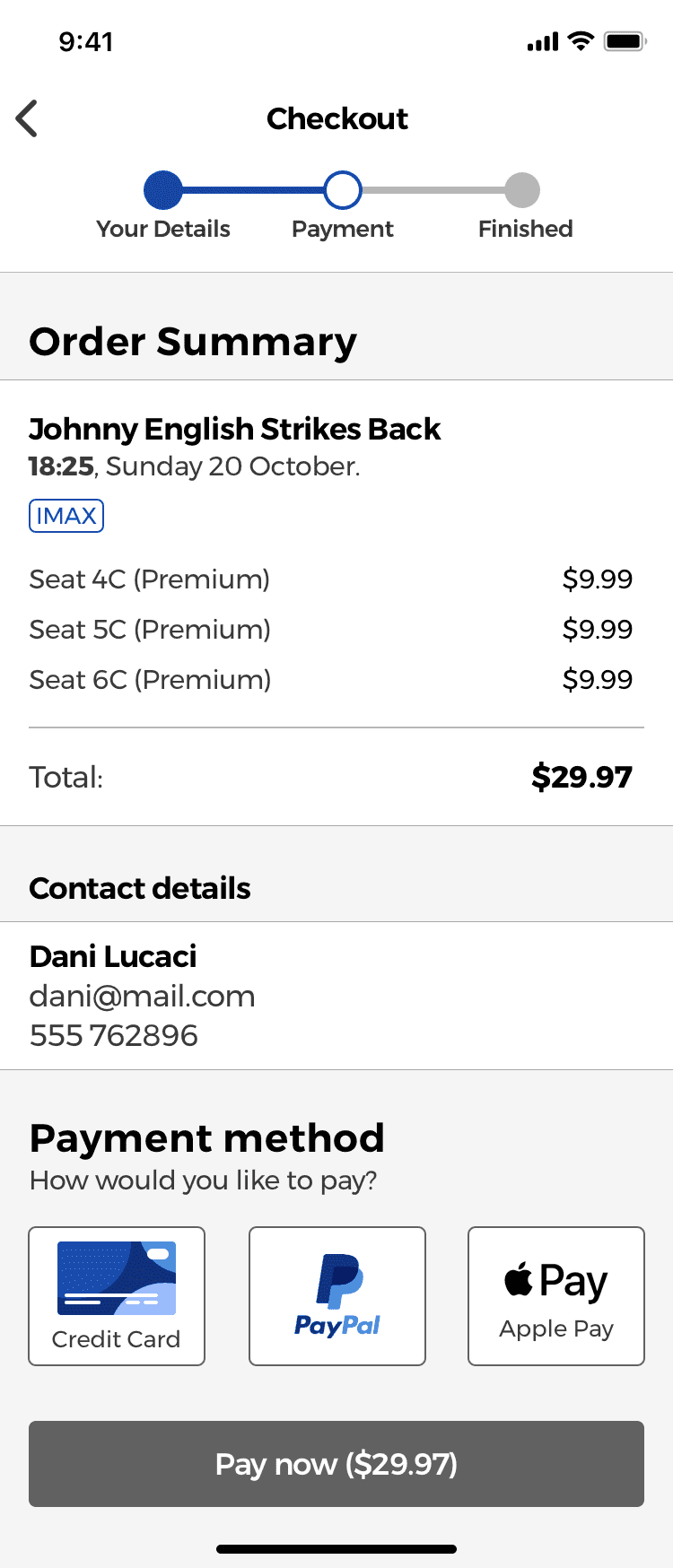
Payment methods placed in close proximity
The different payment methods that the app accepts are shown using 3 buttons placed next to each other, following the recommendations of the research made by the Baymard Institute.
According to them, payment methods should be placed together in close proximity (Gestalt principles would help here) so that users can easily compare them with a single glance and see which one is currently active.
Users should also be able to compare the different costs associated with each payment method —if they apply— such as a 2% fee when using a particular payment type.
Optimizing The Payment Form
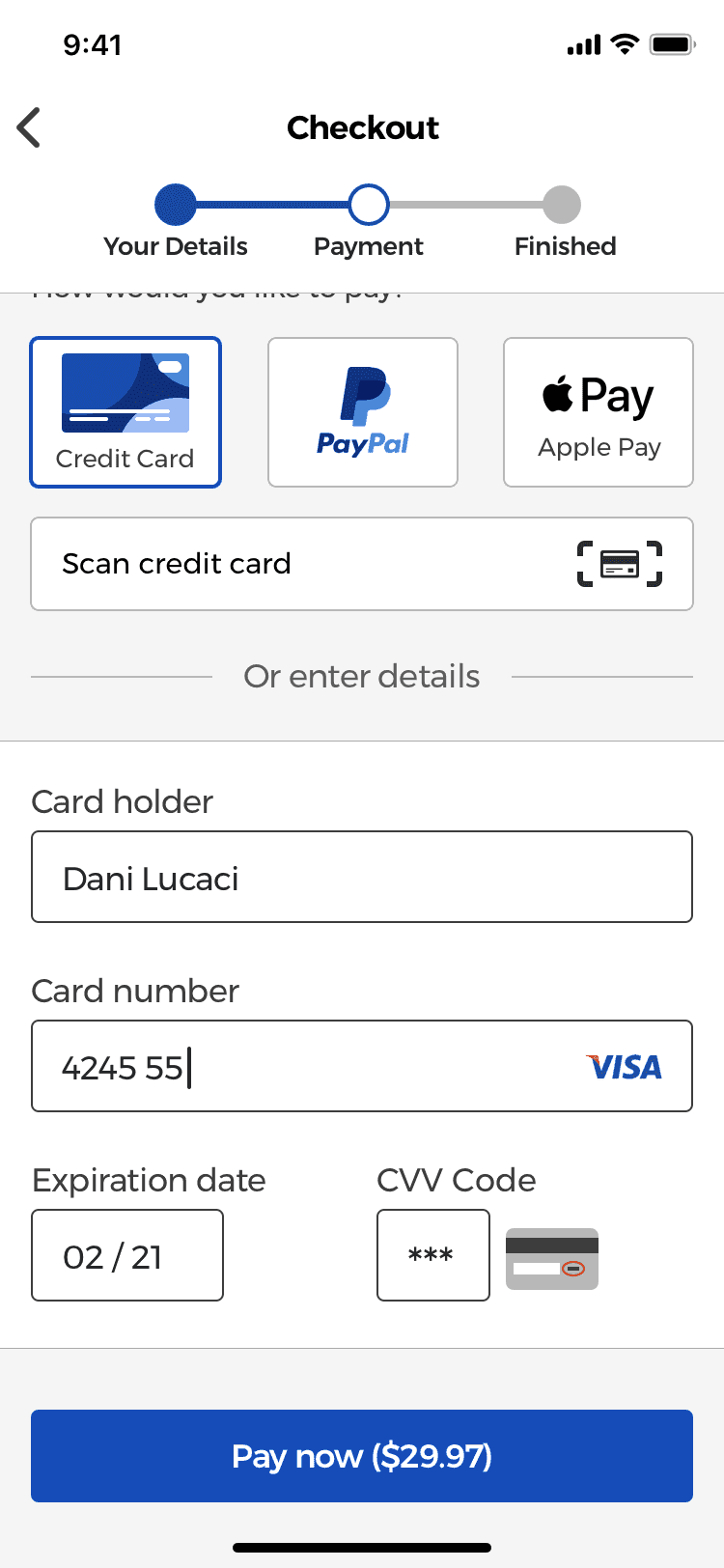
Insert spaces every 4 digits
I designed the input field for the credit card number so that it auto inserts spaces every 4 digits (in the case of Visa cards, others may differ). According to a research study, most users double check the card numbers they typed in groups of 4 digits by manually inserting spaces, which they do so that they can easily read and verify the number they typed.
Furthermore, a Luhn validation script could be used to check if the card number typed is valid.
Match the printed format of the expiration date
The expiration date input field was designed to match the physical layout and format of “MM/YY” found on most credit cards. Research has found that most users will try to follow the same format printed on the card when typing the number. Therefore, forms should be designed in a way that they respect the physical format found on credit cards.
Form fields used for credit cards should also use input masks that auto-insert a forwards slash character after the MM in the expiration date and use the appropriate keyboard type for each input field.
Order Confirmation With Option To Sign Up
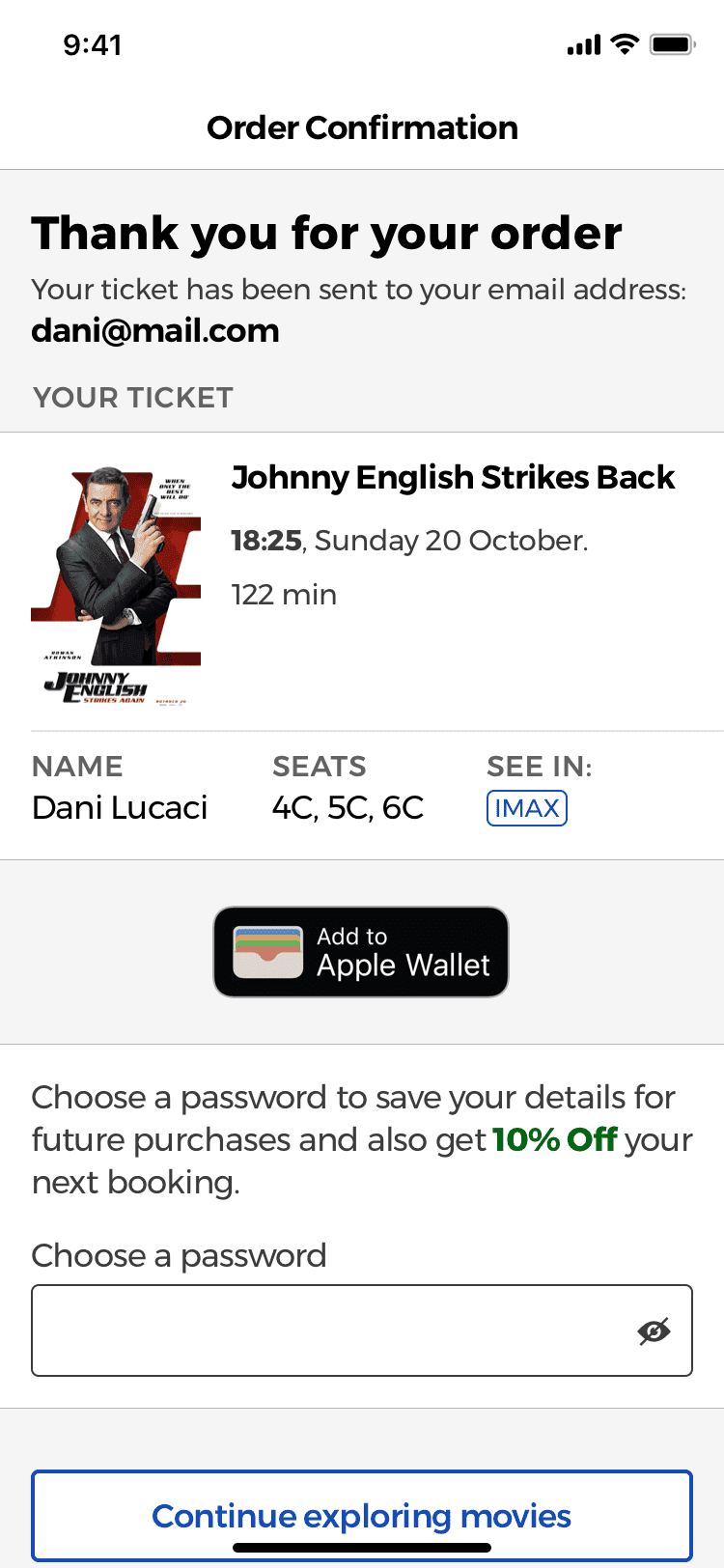
Sign up in the last step of the checkout process
The order confirmation screen was designed to allow users to save their personal details such as their email or payment information for future purchases.
Rather then being forced to create an account before they can make a purchase, the option to create an account is placed at the end of the checkout process.
This way users can still sign up and create an account with the app, but instead of being in their way of paying for the ticket, it’s a helpful feature that let’s them make future purchases faster if they use the app again.
Even though it’s still the same amount of input fields, users will not think it’s just so that you can send them marketing emails.
Guest Checkout Wireflow Diagram
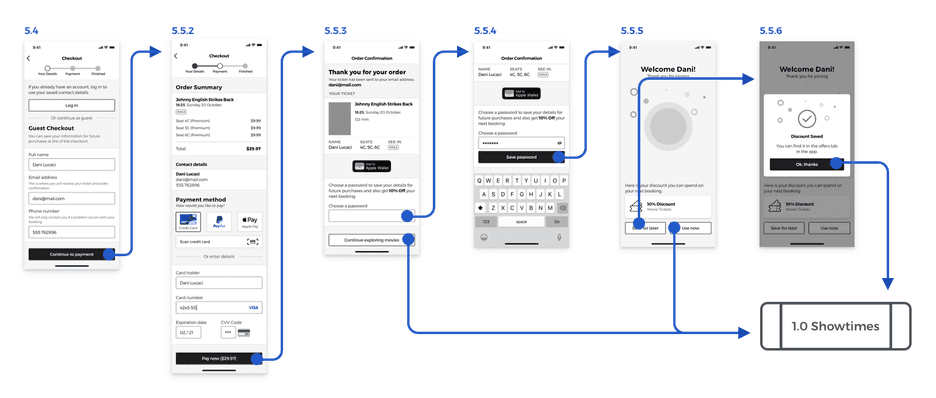
Guest Checkout High-Fidelity Prototype
Membership plan.
The third feature of the app was the membership plan with offers and discounts.
In the interviews, most users complained that even though most cinemas had membership plans, they didn’t offer any decent value.
Most of them gave you a point for each euro spent. Then, these points could be used to get a movie ticket or snacks from the bar. However, if you’d like to exchange them for a ticket, you would need about 100 points, which means you would need to spend 100 euros before you can get a free ticket, so it’s not really worth it.
This feature of the app was my attempt to see how I could improve the experience in a way that users feel that it is worth it and they would recognize the value it provides them.
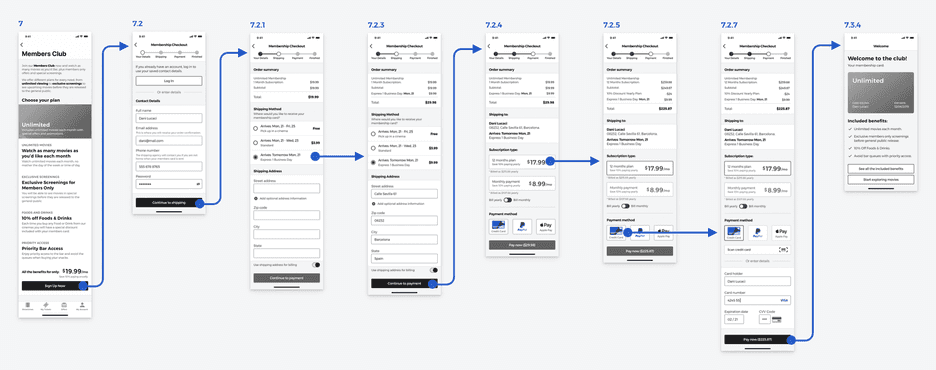
Designing The Membership Plan Sign Up Process
The sign flow for the membership plan was divided into 4 segments to avoid overwhelming the users with too many form fields at once.
The 4 segments were:
- Contact details
- Shipping information
- Payment information
- Finished (confirmation screen)
Membership Sign Up Wireflow Diagram
Shipping Information Optimizations
The shipping information step is needed so that users can receive a copy of their membership card. To design this checkout step I decided to do some previous research to see which are the UX best practices of designing a Shipping Information checkout step.
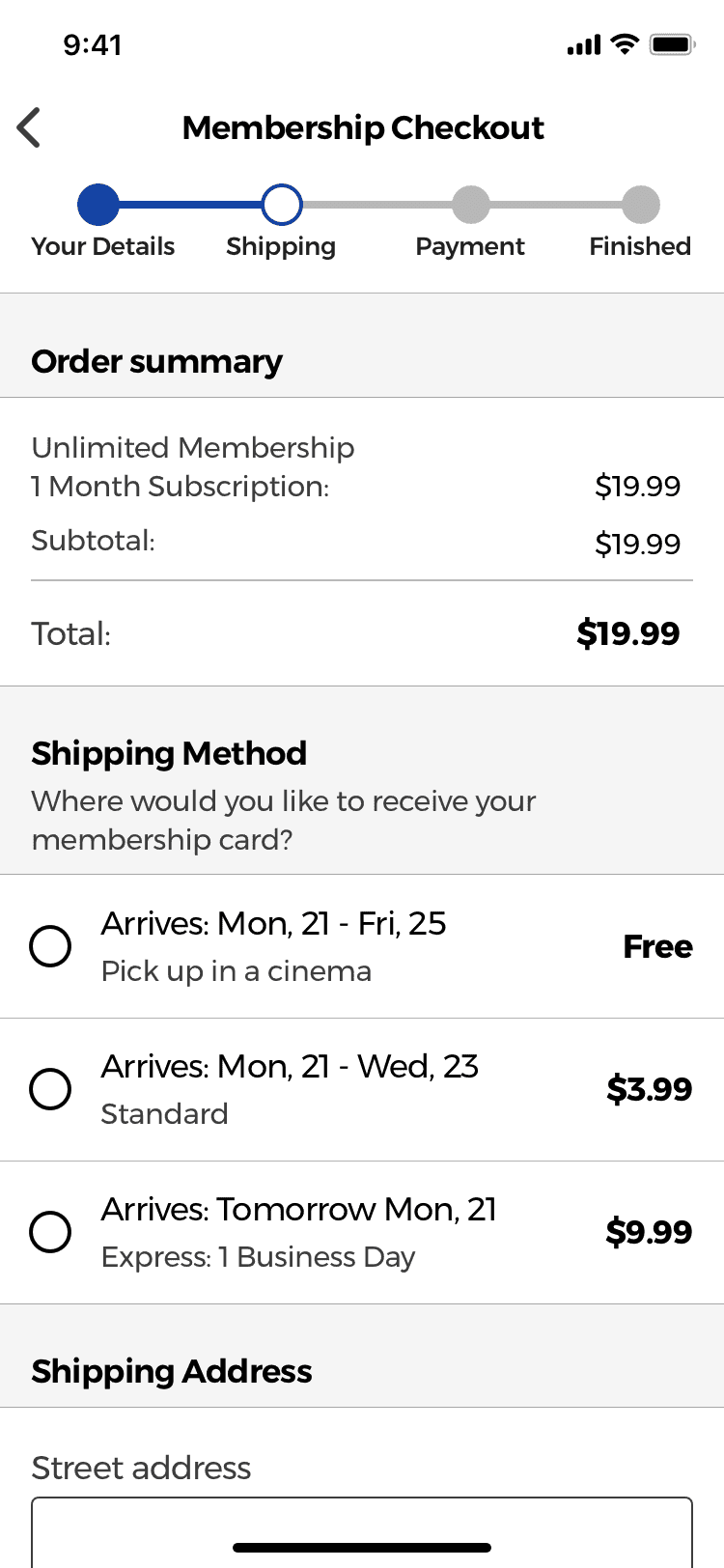
No hidden fees
Hidden charges and delivery costs are one of the main reasons why customers decide to abandon a checkout, so I decided to clearly indicate all the delivery costs the users would have to pay.
Store pick-up and delivery methods
Research has found that when the store pick-up option isn’t listed next to the other delivery methods, users will miss it and won’t be able to compare if the extra cost of paying the extra 2 or 3 euros for a faster delivery method is worth it.
The different delivery methods are also designed following the recommendations of a study which found that when using labels such as 2 Days Express or 1 Day Premium users would be confused of the exact date they would receive the product.
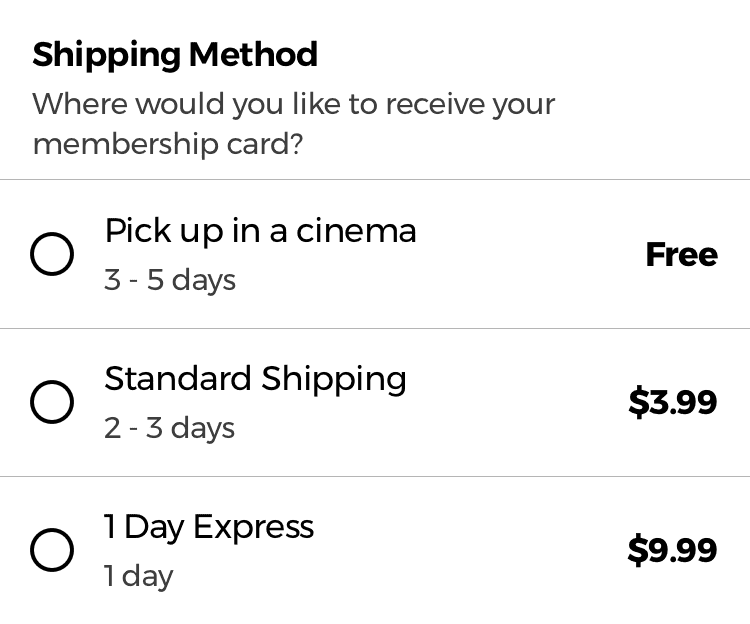
By using labels like these, users are forced to have to personally calculate the day in which the product would arrive.
A label of “3-5 days” doesn’t take into consideration the processing time each order might need, the daily cut off time (orders after 4 pm will be sent the following day), or if the user chooses a 1 Day Premium shipping option on a Friday, which would mean that the order is shipped Monday, ultimately making it a 3 day shipping method with a premium cost.

By using labels such as “Arrives by“ or “Get it by”, users would take the delivery date as a promise which would increase their confidence when they have to decide if the extra cost of a premium delivery is worth it.
However, in order for the final date to be useful to the user, it should take into account all the necessary factors such as order cut of time, the current time and date or the delivery estimate of the shipping company.

This is a great example of how to design the delivery methods as seen on amazon.co.uk’s checkout flow.
Membership Sign Up High-Hidelity Prototype
Usability testing.
The final step in my process was to test the app. For the testing I used the Google Ventures 5 Act Interview, in which I interviewed 5 people and gave each of them tasks that they would have to try to complete using the app.
The questions I wanted to answer with the interviews were:
- Does the app help people decide which movie they’d like to see faster?
- Does the app help people learn more the each movie?
- Will people sign up for the membership plans?
- Can people go through the checkout process without any issues?
- Is the guest checkout flow helpful?
The results:
- 4 out of 5 users signed up for the membership plan
- 5 out 5 users used the search bar and filters to search for a movie
- 5 out of 5 users said that it’s much easier to learn more about a movie without having to leave the app
- 4 out of 5 users used the guest checkout flow and 3 of them signed up at the end
Overall, this was a great personal project for me. I learned how important it is to focus every design decision on the outcome people are trying to achieve rather than forcing them to sign up for an account. By including users in the design process early on, we can create better products that people will be more likely to use.
Even though this project started out with an initial assumption, by validating it with real users I knew that I could help them if I created a better experience.
Furthermore, the initial research also helped me learn which pain points people were having so that I could have a better understanding of what I needed to work on and which features I should design to try to solve them.
I had a lot of fun working on this project as I learned about the small details involved in designing a searching experience and a checkout flow, but sadly my local cinemas will continue to have the same user experience on their apps and websites.
I hope you enjoyed reading this case study, and if you have any questions about it feel free to get in touch.
Next project
Username or Email Address
Remember Me Forgot Password?
Get New Password

Case Study:Movie Ticket Booking System
- October 18, 2023

In today’s digital age, movie ticket booking systems have become an essential part of the entertainment industry. The Movie Ticket Booking System presented here is a simplified text-based application created using Python. It allows users to view available seats, purchase movie tickets, and access booking statistics. This case study showcases a straightforward implementation of a movie ticket booking system.
Objectives:
- To provide an easy-to-use interface for booking movie tickets.
- To display available seats and their status (booked or available).
- To calculate and display booking statistics.
- To create a simple and functional movie ticket booking system in Python.

Implementation:
The Movie Ticket Booking System includes the following components:
- MovieTicketBookingSystem Class: This class initializes the system with the specified number of rows and seats per row, manages the seating arrangement, and calculates income.
- Display Seating: The system displays the current seating arrangement, indicating available seats with ‘S’ and booked seats with ‘E’.
- Buy Ticket: Users can select a seat by specifying the row and seat number. The system checks seat availability, calculates the ticket price, and allows users to book or cancel a seat.
- Statistics: Users can access booking statistics, including the number of purchased tickets, the percentage of booked seats, and the current and total income.
- Main Function: The main function takes user inputs to perform actions like displaying seats, buying tickets, accessing statistics, or exiting the system.
Case Study Steps:
- Launch the Movie Ticket Booking System.
- Input the number of rows and seats per row, configuring the theater.
- Select options from the menu to view available seats, purchase tickets, or check booking statistics.
- To view available seats, select option ‘1’. The system displays the current seating arrangement.
- To buy a ticket, select option ‘2’. Specify the row and seat number, and the system will calculate the ticket price. Confirm the purchase or cancel.
- To view booking statistics, select option ‘3’. The system displays the number of purchased tickets, the percentage of booked seats, and the current and total income.
- To exit the system, select option ‘0’.
Conclusion:
The Movie Ticket Booking System presented in this case study demonstrates the fundamental concepts of creating a movie ticket booking application using Python. Although this is a basic text-based implementation, it highlights the essential components of a real-world movie ticket booking system, such as seat availability, pricing, and booking statistics. Further development could include a graphical user interface (GUI) and database integration for a more user-friendly and robust system.
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
Trending now


BookMyShow - UX Case Study

Case study exploring user engagement and booking flow improvements in BookMyShow mobile app. Based in India, BookMyShow is an aggregator service Read More
Creative fields.

Interaction Design

Attribution, Non-commercial, No Derivatives

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Movie Ticket Booking App (UX/UI Case Study) 260. 10.3k. 19. Published: December 20th 2021. Abdulmuiz Raji. Follow Following Unfollow. Owner. Abdulmuiz Raji. Liverpool, United Kingdom. Follow Following Unfollow. Hire. Movie Ticket Booking App (UX/UI Case Study) ...
There are four phases in this journey map: User Journey Map. Awareness: the phase when users find our app to book the ticket. Consideration: The phase when users consider and decide what movie to watch. Registration: Users start to register in-app. Conversion: Users book the ticket and make a payment.
I conducted a usability study with 10 participants to assess the user experience of the Cinemate app. The study involved three tasks: Task 1: Sign In, Movie Selection, and Details Input. Task 2 ...
The prompt for this project is "Mobile Ticketing App for a movie theater", therefore I defined the scope of the project to serve the needs of a single movie theater. It is not an aggregator platform. I assumed a fictitious client, a local movie theater company named "Magic Movies" that wants to introduce mobile ticket booking to its ...
Category 1: Regular movie watchers (more than twice a month) who book tickets online and use the bookmyshow app 3/5 times. Category 2: Occasional movie (Once a month or less) watchers who book tickets online and use bookmyshow app 2/5 times. Interviewed both categories of users, drew empathy maps and user personas and in the end collectively ...
This case study is based on a movie booking application TicketNew. It is quite popular, it has over 50L+ downloads on Android App Store. This app provides the best and latest place to check for movies and cinemas around you. Booking tickets is now an effortless, fun and exciting experience for its user's .
MovieDom is a seat reservation app set to revolutionize users' theater experience. This app enables users to say goodbye to every difficulty they face while making seat reservations. With the user-friendly interface, you can effortlessly browse through available movies, see the latest and coming soon movies, book your ticket and refreshments ...
10. At the end of last year, we made a little project on designing a movie ticket app. This case study is something that we did in our free time just for fun, so there might be some part of this ...
This is a case study project that aims to create a user-friendly mobile app for booking movie tickets. It focuses on simplifying the process of finding, selecting seats, and purchasing tickets. This case study showcases the development of a convenient and enjoyable solution to enhance the movie theater experience.
Third, after buying a ticket online, a barcode appears on the screen that can be downloaded to a mobile phone and scanned at the entrance to the hall, so that the case of copying the ticket is not ...
Analyzing a Movie Ticket Booking App Case Study. One regional cinema chain saw great success after launching a customized mobile ticketing app. The app enabled patrons to seamlessly browse showtimes, select seats, and securely pay for tickets on their phones. This led to a 15% increase in advance ticket sales in the first year.
Background. A common problem when going to the cinema is people hate being stuck in a long queue to buy tickets. Not only waiting too long, turns out seats already full and can't find another schedule. This problem has been solved since the online ticket booking application existed. But the new problem persists, like the apps not user ...
7. A while ago, I got an opportunity to do a UX assignment on Book My Show, an event booking app based in India. Though the app covers a multitude of events — from theatre to sports to activities, my focus was primarily on movie ticket booking as the product is probably most associated with it. The following case study covers Engagement and ...
The Product. MyTix is an app designed to simplify the process of booking movie theater tickets through mobile phones. MyTix also offers the facility of ordering food and beverages along with ticket purchases. MyTix targets customers such as students and workers who don't have the time, prefer to avoid queues, or are worried about running out ...
libraries ui-kits wireframes design-templates desktop-apps-websites mobile-apps presentations resume-templates portfolio-templates design-tools accessibility editing-effects file-organization import-export prototyping-animation visual-assets fonts-typography illustrations shapes-colors stock-photography whiteboarding brainstorming diagramming ...
3. Check out process. Here's the ticket check out. After choosing the time and the cinema, user can select the seat they are preferred and the number of tickets they need. Then, they are confirming their payment. When they are successfully booking the ticket, the user will land on the ticket page.
The goal is to design an app that is simple for all users to allow them to find the nearest cinema and book a movie ticket easily. The app should provide all the movie information, ratings, and users' feedback. Log In. ... Movies Booking App UI/UX Case Study. 35. 819. 6. Published: September 2nd 2022. Haitham Said. Follow Following Unfollow ...
Movie Booking App. A case study on improving the experience of searching, finding and booking movies in a cinema, using a User-Centered Design process. Overview. Like most people, I love seeing movies. Especially in a cinema. However, each time I used one of my local cinema's app or website to try to buy a ticket for a movie, I found that ...
Introduction. This project was a part of Google UX certification program. At the beginning of the courses, I received the prompt for the project. I had to create a mobile ticketing app for a movie theatre. Going to the cinema should be a fun and relaxing activity. In reality, dealing with queues, choosing to sit, and waiting for snacks was ...
The Movie Ticket Booking System presented here is a simplified text-based application created using Python. It allows users to view available seats, purchase movie tickets, and access booking statistics. This case study showcases a straightforward implementation of a movie ticket booking system. To provide an easy-to-use interface for booking ...
A while ago, I got an opportunity to do a UX assignment on BookMyShow, an event booking app based in India. Though the app covers a multitude of events — from theatre to sports to activities, my focus was primarily on movie ticket booking as the product is probably most associated with it. The following case study explores user engagement and ...
Jul 23, 2023. --. People are more and more getting attracted to movies in today's world to take a break from their busy and monotonous lives. This case study helps in improving the experience of ...
Movie Ticket Booking App • UX Design Case Study. Cinetix is a mobile app designed to book online movie tickets with a reminder for showtime and ETA to the theater. This is my first UX Case Study, your feedback is appreciated. For full case study, click here. Press F to show love :)
B.J. Rains and KTVB sports director Jay Tust discuss a variety of Boise State topics on an ICCU Friday edition of Bronco Nation News LIVE.