- Biology Article

Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process by which phototrophs convert light energy into chemical energy, which is later used to fuel cellular activities. The chemical energy is stored in the form of sugars, which are created from water and carbon dioxide.

Table of Contents
- What is Photosynthesis?
- Site of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis definition states that the process exclusively takes place in the chloroplasts through photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene and xanthophyll. All green plants and a few other autotrophic organisms utilize photosynthesis to synthesize nutrients by using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. The by-product of the photosynthesis process is oxygen.Let us have a detailed look at the process, reaction and importance of photosynthesis.
What Is Photosynthesis in Biology?
The word “ photosynthesis ” is derived from the Greek words phōs (pronounced: “fos”) and σύνθεσις (pronounced: “synthesis “) Phōs means “light” and σύνθεσις means, “combining together.” This means “ combining together with the help of light .”
Photosynthesis also applies to other organisms besides green plants. These include several prokaryotes such as cyanobacteria, purple bacteria and green sulfur bacteria. These organisms exhibit photosynthesis just like green plants.The glucose produced during photosynthesis is then used to fuel various cellular activities. The by-product of this physio-chemical process is oxygen.
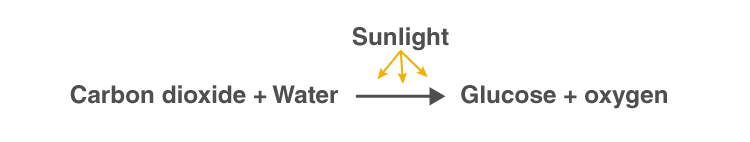
A visual representation of the photosynthesis reaction
- Photosynthesis is also used by algae to convert solar energy into chemical energy. Oxygen is liberated as a by-product and light is considered as a major factor to complete the process of photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis occurs when plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Leaves contain microscopic cellular organelles known as chloroplasts.
- Each chloroplast contains a green-coloured pigment called chlorophyll. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules whereas carbon dioxide and oxygen enter through the tiny pores of stomata located in the epidermis of leaves.
- Another by-product of photosynthesis is sugars such as glucose and fructose.
- These sugars are then sent to the roots, stems, leaves, fruits, flowers and seeds. In other words, these sugars are used by the plants as an energy source, which helps them to grow. These sugar molecules then combine with each other to form more complex carbohydrates like cellulose and starch. The cellulose is considered as the structural material that is used in plant cell walls.
Where Does This Process Occur?
Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis in plants and blue-green algae. All green parts of a plant, including the green stems, green leaves, and sepals – floral parts comprise of chloroplasts – green colour plastids. These cell organelles are present only in plant cells and are located within the mesophyll cells of leaves.
Also Read: Photosynthesis Early Experiments
Photosynthesis Equation
Photosynthesis reaction involves two reactants, carbon dioxide and water. These two reactants yield two products, namely, oxygen and glucose. Hence, the photosynthesis reaction is considered to be an endothermic reaction. Following is the photosynthesis formula:
Unlike plants, certain bacteria that perform photosynthesis do not produce oxygen as the by-product of photosynthesis. Such bacteria are called anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. The bacteria that do produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis are called oxygenic photosynthetic bacteria.
Structure Of Chlorophyll
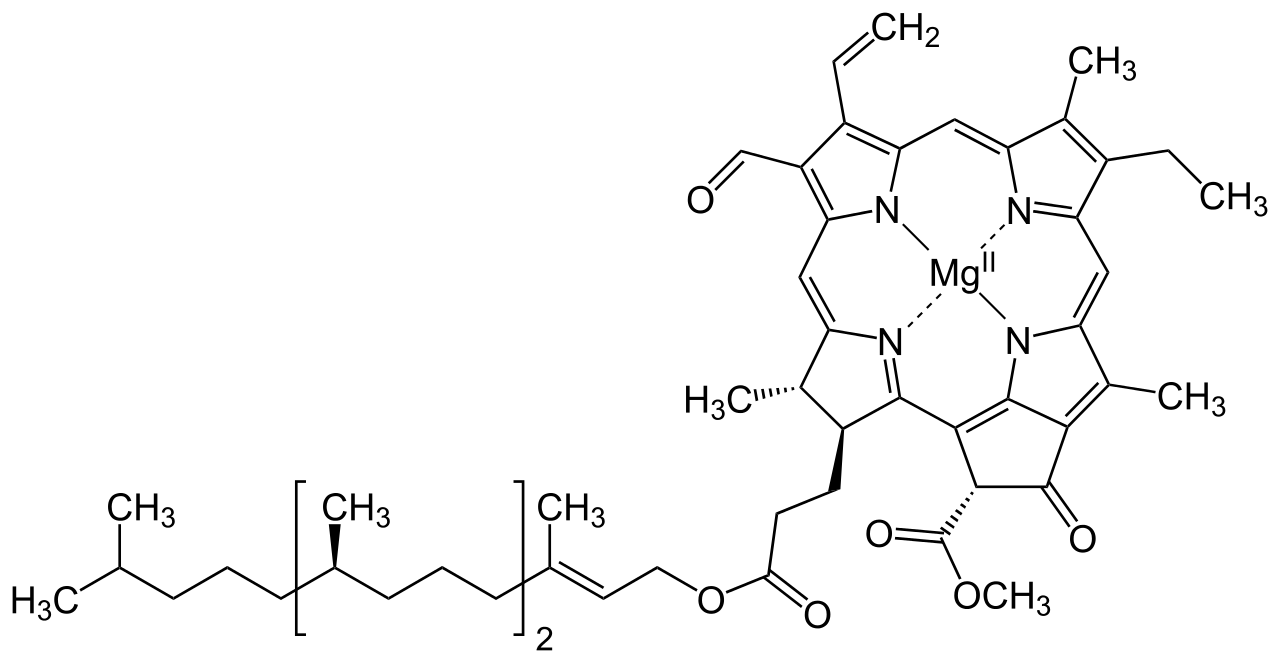
The structure of Chlorophyll consists of 4 nitrogen atoms that surround a magnesium atom. A hydrocarbon tail is also present. Pictured above is chlorophyll- f, which is more effective in near-infrared light than chlorophyll- a
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the chloroplasts of the plant cell and in the mesosomes of cyanobacteria. This green colour pigment plays a vital role in the process of photosynthesis by permitting plants to absorb energy from sunlight. Chlorophyll is a mixture of chlorophyll- a and chlorophyll- b .Besides green plants, other organisms that perform photosynthesis contain various other forms of chlorophyll such as chlorophyll- c1 , chlorophyll- c2 , chlorophyll- d and chlorophyll- f .
Also Read: Biological Pigments
Process Of Photosynthesis
At the cellular level, the photosynthesis process takes place in cell organelles called chloroplasts. These organelles contain a green-coloured pigment called chlorophyll, which is responsible for the characteristic green colouration of the leaves.
As already stated, photosynthesis occurs in the leaves and the specialized cell organelles responsible for this process is called the chloroplast. Structurally, a leaf comprises a petiole, epidermis and a lamina. The lamina is used for absorption of sunlight and carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
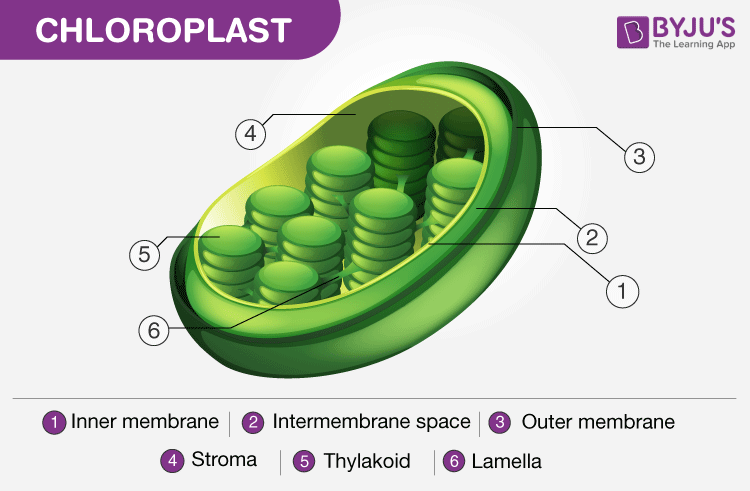
Structure of Chloroplast. Note the presence of the thylakoid
“Photosynthesis Steps:”
- During the process of photosynthesis, carbon dioxide enters through the stomata, water is absorbed by the root hairs from the soil and is carried to the leaves through the xylem vessels. Chlorophyll absorbs the light energy from the sun to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- The hydrogen from water molecules and carbon dioxide absorbed from the air are used in the production of glucose. Furthermore, oxygen is liberated out into the atmosphere through the leaves as a waste product.
- Glucose is a source of food for plants that provide energy for growth and development , while the rest is stored in the roots, leaves and fruits, for their later use.
- Pigments are other fundamental cellular components of photosynthesis. They are the molecules that impart colour and they absorb light at some specific wavelength and reflect back the unabsorbed light. All green plants mainly contain chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids which are present in the thylakoids of chloroplasts. It is primarily used to capture light energy. Chlorophyll-a is the main pigment.
The process of photosynthesis occurs in two stages:
- Light-dependent reaction or light reaction
- Light independent reaction or dark reaction
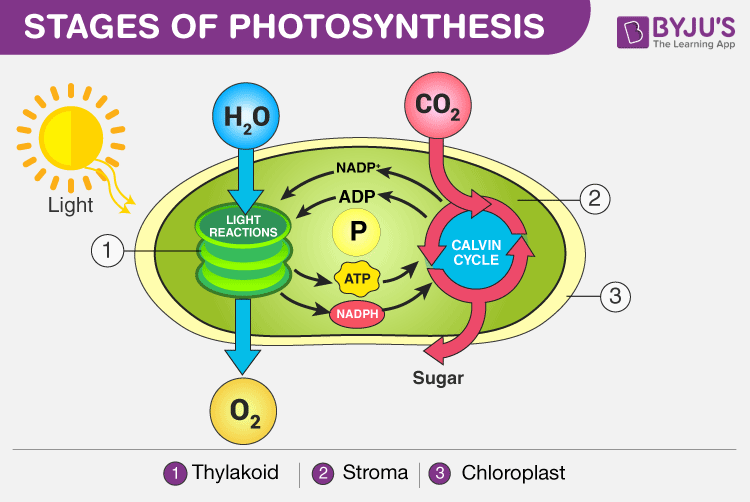
Stages of Photosynthesis in Plants depicting the two phases – Light reaction and Dark reaction
Light Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-dependent Reaction
- Photosynthesis begins with the light reaction which is carried out only during the day in the presence of sunlight. In plants, the light-dependent reaction takes place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
- The Grana, membrane-bound sacs like structures present inside the thylakoid functions by gathering light and is called photosystems.
- These photosystems have large complexes of pigment and proteins molecules present within the plant cells, which play the primary role during the process of light reactions of photosynthesis.
- There are two types of photosystems: photosystem I and photosystem II.
- Under the light-dependent reactions, the light energy is converted to ATP and NADPH, which are used in the second phase of photosynthesis.
- During the light reactions, ATP and NADPH are generated by two electron-transport chains, water is used and oxygen is produced.
The chemical equation in the light reaction of photosynthesis can be reduced to:
2H 2 O + 2NADP+ + 3ADP + 3Pi → O 2 + 2NADPH + 3ATP
Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-independent Reaction
- Dark reaction is also called carbon-fixing reaction.
- It is a light-independent process in which sugar molecules are formed from the water and carbon dioxide molecules.
- The dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast where they utilize the NADPH and ATP products of the light reaction.
- Plants capture the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through stomata and proceed to the Calvin photosynthesis cycle.
- In the Calvin cycle , the ATP and NADPH formed during light reaction drive the reaction and convert 6 molecules of carbon dioxide into one sugar molecule or glucose.
The chemical equation for the dark reaction can be reduced to:
3CO 2 + 6 NADPH + 5H 2 O + 9ATP → G3P + 2H+ + 6 NADP+ + 9 ADP + 8 Pi
* G3P – glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
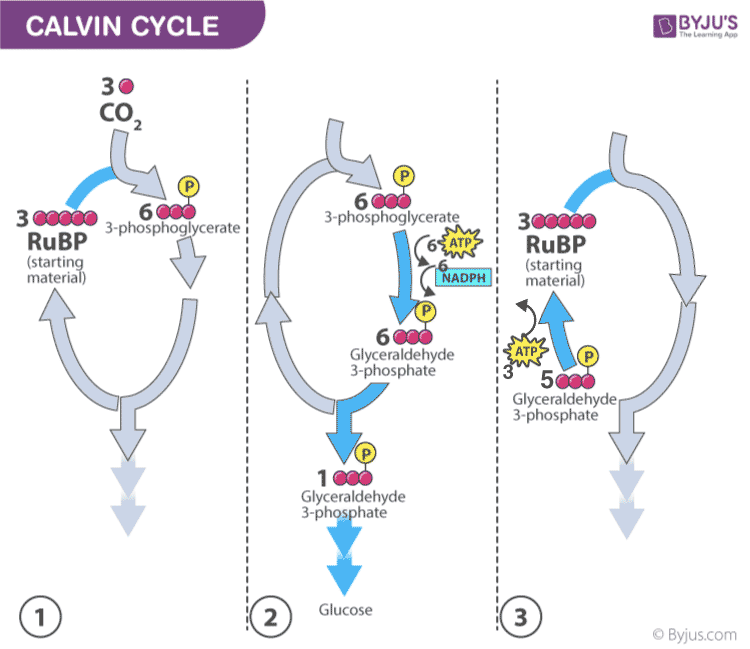
Calvin photosynthesis Cycle (Dark Reaction)
Also Read: Cyclic And Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
Importance of Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis is essential for the existence of all life on earth. It serves a crucial role in the food chain – the plants create their food using this process, thereby, forming the primary producers.
- Photosynthesis is also responsible for the production of oxygen – which is needed by most organisms for their survival.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is photosynthesis explain the process of photosynthesis., 2. what is the significance of photosynthesis, 3. list out the factors influencing photosynthesis., 4. what are the different stages of photosynthesis, 5. what is the calvin cycle, 6. write down the photosynthesis equation..

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
very useful
It’s very helpful ☺️
Please What Is Meant By 300-400 PPM
PPM stands for Parts-Per-Million. It corresponds to saying that 300 PPM of carbon dioxide indicates that if one million gas molecules are counted, 300 out of them would be carbon dioxide. The remaining nine hundred ninety-nine thousand seven hundred are other gas molecules.
Thank you very much Byju’s! I couldn’t find the answer anywhere. But luckily I hit upon this website. Awesome explanation and illustration.
byjus = Wow!
It helps me a lot thank you
Thanks in a million I love Byjus!
Super Byjus
Thanks helped a lot
Very interesting and helpful site.
Nice it is very uesful
It’s very useful 👍 Thank you Byju’s
Thank you very much Byju’s! I couldn’t find the answer anywhere. But luckily I hit upon this website. Awesome explanation and illustration.
Thank you BYJU’S for helping me in further clarifying my concepts
Excellent material easy to understand
Indeed, it’s precise and understandable. I like it.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Natural Sciences and Technology Grade 6
Published by Kristian Paul Modified over 5 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Natural Sciences and Technology Grade 6"— Presentation transcript:

Photosynthesis Write On Fourth Grade.

Plants and Photosynthesis

Oxygen Cycle chlorophyll (green color) Photosynthesis.

Chapter 3 Lessons 2 and 3 How do Materials move through plants?

Photosynthesis Leaves are green because they contain small bodies in the cells called chloroplasts. The chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll.

Plants Produce Food.

Chapter 9 Lesson1 Photosynthesis. Chapter 9 Big Question.

What do plants need to grow?

Plants People and animals need oxygen to live. Green plants make the oxygen in the air we breathe. How do plants make oxygen? Plants take in carbon dioxide.

How Do Cells Get Energy? All living things need energy

Life Support for Plants

Important Plant Processes

Photosynthesis Chapter 3.

Plant Basic Needs.
FOOD FROM THE SUN animals eat plants to get energy, other animals eat these animals, plants produce their own food from the sun.

Animation. What is photosynthesis? Leaves are green because of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from the sun. It uses that energy to convert carbon.

Plants!. Chloroplast: organelle Chlorophyll: green pigment Pigment: substance that reflects some light and absorbs the rest.
Parts of a Plant (Plant Vocabulary)

Sources of Energy All living things need energy All cells need energy to carry out their functions.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration � PowerPoint Presentation
(Harcourt Science Book, pages 206-211)
Life Science California Standards Covered:
2f. Students know plants use carbon dioxide (CO2) and energy from sunlight to build molecules of sugar and release oxygen.
2g. Students know plant and animal cells break down sugar to obtain energy, a process resulting in carbon dioxide (CO ) and water (respiration).
How Plants & Animals Get The Energy They Need
Plants make food
(glucose, a type of
sugar) through a
process called
photosynthesis
(stored energy)
is sent throughout
the plant for
its cells to use
Animals eat a
plant or another
plant-eater
in order to
obtain the energy
originally stored
This is how
both plants
and animals
energy they
need to live
Any extra sugar
not used by the
plant is stored
somewhere in the
plant (i.e: roots,
stem, leaves, etc.)
Both plants and
animals break down
this sugar into a
form they can use,
in order to release
its stored energy.
This process is called
cellular respiration
What is Photosynthesis?
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make food, using energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar.
What is the Purpose of Photosynthesis?
- To make food for the plant (food in the form of glucose, a type of sugar).
- All organisms get energy from food, but only plants can make food.
- Plants make food by a process called photosynthesis
(photo = light & synthesis = putting together)
- In photosynthesis, plants put together materials to make food with the energy of sunlight.
It is the energy of sunlight that
powers the process of photosynthesis!
The process of photosynthesis
“mostly” only happens in plants
(along with algae and some bacteria)
Photosynthesis takes place in the
chloroplast, inside the plant cells.
In most plants, this occurs in the outermost layer of the leaf (on the top part), though for a few other plants, like cactus, photosynthesis can happen in the cells that are on the stem.
Analogy: Chloroplast as a Food Factory
You can think of a chloroplast as a food factory. Carbon dioxide and water are the raw materials that go into that factory. Sunlight is the energy that changes the raw materials into the product of food, in the form of sugar (or glucose). Finally, the two by-products created in the process, oxygen and a little extra water, are released into the air as they are no longer needed by the plant.
What are the three raw materials �used in Photosynthesis?
1. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) from the air
2. Water (H 2 O) from the soil
3. Solar energy from sunlight
What are the waste products (by-products) created during Photosynthesis?
- Water - a little extra water that is no longer needed
These two are released into the air by the plant through the stomata (tiny holes in the undeside of leaves)
What Sequence of Events Takes �Place During Photosynthesis?
- Sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll in chloroplasts.
- That solar energy is then used to split apart water (H 2 O) molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Later, during a series of chemical reactions, hydrogen (H) joins with carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) to form a sugar called glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ).
- In the process of making sugars, two by-products are formed, water (H 2 O) & oxygen (O 2 ). Neither is no longer needed by the plant.
- These by-products leave the plant when they are released into the air through stomata (tiny leaf holes)
(The sugars created during this process are then sent throughout the plant, to all its cells)
What is the Chemical Formula �of Photosynthesis?
12H 2 O + 6CO 2 + Solar Energy makes > C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2 0
Carbon (energy) (sugar)
Water + Dioxide + Sunlight makes > Glucose + Oxygen + Water
Learn and Sing the Online�Photosynthesis Poem & Song
Illuminating Photosynthesis www.rrojas.com/home/rojassongs/photosynthesissong
What is Cellular Respiration?
- Cellular Respiration is the process by which cells, in plants & animals, use oxygen for breaking down sugar to release the stored energy.
What is the Purpose �of Cellular Respiration?
- To get cells the energy they need to function.
Why is Cellular Respiration �Necessary in Plants & Animals?
- The energy stored in sugar needs to be released so that it can be turned to a form useful to cells. If living things could not get the energy out of food, food would be absolutely worthless and all living thing would eventually die.
What Living Things use �Cellular Respiration?
- All living things
The process of cellular respiration
takes place in the Mitochondria of both plant and animal cells.
- Animals are able to store glucose very well.
- Yet animals are not able to store gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. This is why animals need to breathe all the time!
- With every breath, you take in the oxygen gas that you need for cellular respiration. You also breath out carbon dioxide, the waste product of the process.
What are the two raw materials �used in Cellular Respiration?
What are the waste products (by-products) created during Cellular Respiration?
- Carbon Dioxide
In animals these waste products are released into the blood. Carbon Dioxide is carried to the lungs, where it is exchanged for oxygen in the alveoli (and eventually exhaled). Water is carried to the kidneys, where it is removed in urine.
What Sequence of Events Takes �Place During Cellular Respiration?
- Oxygen helps break down sugar…
- Releasing a lot of energy, which the cell traps in a molecule called ATP.
- In addition, the two by-products of carbon dioxide and water are produced.
(ATP is like a battery for the cell. The cell easily
breaks apart ATP whenever it needs energy.)
What is the Chemical Formula �for Cellular Respiration?
Glucose + Oxygen makes > Energy + Carbon Dioxide + Water
C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 makes > ATP + 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0
Did you notice that the equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration look alike?
Glucose + Oxygen makes > Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Carbon (energy)
Dioxide + Water + Sunlight makes > Glucose + Oxygen (+ Water)
What are the similarities in their chemical formula?
C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 makes > 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + ATP
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
6CO 2 + 12H 2 0 + Solar Energy makes > C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 (+ 6H 2 0)
What is the Connection Between �Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration?
- The two processes are almost the reverse of each other. Materials made during one process are the same as those needed for the other process. In other words they form a cycle.
- Together, photosynthesis and cellular respiration form the “Carbon Dioxide-Oxygen Cycle.”
- Here’s the “cycle”: Plants take in carbon dioxide (and some oxygen) and release oxygen into the air. Animals breathe in oxygen and release carbon dioxide into the air.
- The recycling of carbon dioxide and oxygen through the environment depends on two process, photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
- This cycle provides living things with the oxygen and carbon dioxide they need.
Online Practice Quiz�for Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
www.quia.com/quiz/1646593.html
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Photosynthesis Slide Show
Subject: Biology
Age range: 12 - 18
Resource type: Unit of work
Last updated
25 October 2019
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

You will receive a PPT and PDF version of the slide show.
This 17 slide PPT covers
- Autotrophic organisms.
- Where it takes place.
- The overall reaction (products and reactants).
- What the molecule is.
- Where the molecule comes from.
- Where it entered the plant.
- What the function is.
- Detailed description of the light dependent reaction and the Calvin cycle with diagram.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 12%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Bundle
You will receive the following in PDF format (161 slides/pages altogether). PPT versions of the 2 slide shows are included for easier classroom viewing: * Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration comparison activity with an answer key * Photosynthesis slide show with 17 slides * Cellular Respiration slide show with 16 slides * 32 vocabulary cards with definitions * Worksheet packet * 4 weeks of Bellringers * Test and answer key * Review questions and answer key **Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration comparison activity with an answer key** This activity can work with individuals, in a group, or teacher-led. You will receive an activity where students will compare photosynthesis and cellular respiration by looking at the equations, products, and reactants of each process. Answer key included! *Students will*: * Write the equation of both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. * State which are products and reactants. * Explain where the reactants come from. * Explain what happens to the products. **Photosynthesis slide show with 17 slides** *This 17 slide PPT covers* * Autotrophic organisms. * Photosynthesis * Where it takes place. * The overall reaction (products and reactants). * Breaks down each molecule of the equation into easy to read tables with the following topics: * What the molecule is. * Where the molecule comes from. * Where it entered the plant. * What the function is. * Detailed description of the light dependent reaction and the Calvin cycle with diagram. **Cellular Respiration slide show with 16 slides** *This 16 slide PPT covers* * Cellular Respiration * ATP description * Where the steps to cellular respiration take place. * The overall reaction (products and reactants). * Breaks down each molecule of the equation into easy to read tables with the following information in the table: * What the molecule is. * Where the molecule comes from. * What the function is. * Detailed description of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. **32 vocabulary cards with definitions** You will receive 32 vocabulary cards with definitions covering terms about photosynthesis and cellular respiration. *Word List*: Acetyl-CoA, ADP, Alcohol fermentation, Anaerobic, ATP, ATP synthase, Autotrophic, Calvin cycle, Cellular respiration, Chlorophyll, Chloroplasts, Citric acid cycle, Cuticle, Electron transport chain, Epidermis, Fermentation, Glycolysis, Grana, Guard Cells, Heterotrophs, Lactic acid fermentation, Light Reactions, Mesophyll, Mitochondrion, NADPH, Oxidative phosphorylation, Photosynthesis, Pigment, Pyruvate, Stomata, Stroma, Thylakoids **Worksheet Packet with Answer Keys** You will receive a PDF of 11 unique worksheets (Some worksheets have multiple versions for classroom differentiation giving you a total of 23 worksheets). * Photosynthesis * Cellular respiration * Photosynthesis and cellular respiration comparison * Writing out the equations * Crossword puzzle * Word search Worksheets have multiple variations for differentiation in your classroom **You will receive 20 days of bellringers/warm ups** Week 1: Word of the Week: Photosynthesis Read and Respond: Light Dependent Reactions Compare and Contrast: Autotroph and Heterotroph Problem Solving: Products and Reactants Anything Goes: Photosynthesis Equation Week 2: Word of the Week: Glucose Read and Respond: Calvin Cycle Compare and Contrast: Chloroplast and Mitochondria Problem Solving: Products and Reactants Anything Goes: Autotrophic Organisms Week 3: Word of the Week: Cellular Respiration Read and Respond: Glycolysis Compare and Contrast: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Problem Solving: Products and Reactants Anything Goes: Cellular Respiration Equation Week 4: Word of the Week: Adenosine Triphosphate Read and Respond: Krebs Cycle Waste Products Compare and Contrast: Alcohol and Lactic Acid Fermentation Problem Solving: Products and Reactants Anything Goes: Plants and Cellular Respiration **Test and answer key/Review questions and answer key** *The test is multiple choice, matching, and short answer. There are 26 questions.* The following are the review questions that are covered on the test. These are not exact test questions, just topics that cover the material: 1. What is photosynthesis? 2. What happens during the first stage of photosynthesis? 3. What is the second stage called? What happens during the second stage? 4. What is cellular respiration? 5. What is broken down during glycolysis? 6. What are the wastes for photosynthesis? Cellular respiration? 7. Water can be broken into what molecules? 8. What is the chemical formula for glucose? 9. Where does carbon dioxide enter a plant? 10. What stage is the majority of ATP produced during cellular respiration? 11. What stage is water produced during cellular respiration? 12. What does oxygen do during the electron transport chain? 13. What are the products of photosynthesis? What are the reactants? 14. What are the products of cellular respiration? What are the reactants? 15. What is the formula for photosynthesis? Cellular respiration? 16. Where do the following take place: a. Glycolysis b. Krebs Cycle c. Electron Transport Chain. 17. Define the following a. ATP b. Autotroph c. Chemoautotroph d. Chlorophyll e. Chloroplast f. Photoautotroph g. Pyruvate
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

Lesson Plan Gr. 6 Natural Sciences and Technology T1 W1 & W2
Grade 6 Lesson Plan on Life and Living & Processing with focus on the CAPS Topics: Photosynthesis, addressing the Concepts: Plants and food & Plants and air. To guide and assist Teachers, Learners and Parents.
Do you have an educational app, video, ebook, course or eResource?
Contribute to the Western Cape Education Department's ePortal to make a difference.

Home Contact us Terms of Use Privacy Policy Western Cape Government © 2024. All rights reserved.

Main navigation
- Project Activities
- Evidence-based Interventions
- Reflections On Our Learning
- Sample Assessment Items
- Mass and Volume
- Mixtures and Pure Substances
- Evolution and Natural Selection
- Photosynthesis
- Soil profiles
- Motion Transmission and Motion Transformation Systems
- Links and Guiding Controls
- Innovative Science Teaching & Learning Activities
- Useful Links
Lesson Plan on Photosynthesis
How do plants get energy, developed by chantier 7 project team members.
Instructional goals:
Students will be able to: 1. Describe the phenomena of transpiration, photosynthesis and cellular respiration 2. Illustrate the relationship between light and photosynthesis (i.e., you need light source for plants to grow; more light more photosynthesis) 3. Illustrate the relationship between carbon dioxide and photosynthesis 4. Gather evidence of inputs and outputs of photosynthesis
Grade level: Grade 7, 8
Duration: 50-150 minutes depending on activities chosen (3-4 periods of 75 minutes)
Instructional Materials: Whiteboard (or smart board, black board) for creating public record for students’ thinking. For the materials needed for specific activities, please see below:
Activity #1: An Oxygen Factory
Plants (both aquatic and terrestrial plants) Plastic bag or plastic wrap Terrarium or 2L plastic bottle Flask 500ml or 1L beaker Water Desk Lamp
Activity #2: Light! Light! (Optional)
Any submersed aquatic plant that is in good health and appears capable of photosynthetic activity (i.e., not dried or wilted). (e.g., Canadian waterweed (Elodea canadensis) or coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum)) – you can buy waterweed from any pet store where they sell fish/aquarium supplies Glass test tubes (20 × 150 mm) Racks to hold test tubes A light source (e.g., desk lamp) Large to medium sized drinking straws Thermometer
Activity #3: More Carbon Dioxide (Optional)
Elodea, an aquatic plant available at many pet or gardening stores Bromothymol blue solution (acid-base indicator available for purchase online. Yellow pH less than 6.0, blue pH above 7.6) Lights with clamp attachment Test tubes (one for each color and two additional as controls) Plastic wrap Aluminum foil
Worksheet: Please see appendices.
QEP POLs for secondary cycle 1 relevant to the concept of photosynthesis:
Elementary school:
Students explain the essential needs of living organisms (e.g. food, respiration) and describe metabolic activity (transformation of energy, growth, maintenance of systems and body temperature). They describe the function of photosynthesis, which they distinguish from respiration.
Secondary cycle 1:
Names the inputs and outputs involved in photosynthesis. Names the inputs and outputs involved in respiration.
Children’s preconceptions relevant to the concept of photosynthesis:
There is no difference between respiration and breathing. The main component of air is oxygen. There is no oxygen in exhaled air. Lighting a candle in a sealed jar with water proves that air is 21% oxygen (the water moves up the jar because the 21 % oxygen is consumed). All essential components for plants are absorbed from the soil via rots. Roots supply plants with energy. The sun keeps plants warm, and so they grow better. Plants breath. They inhale carbon dioxide, and they exhale oxygen. Plants get energy directly from the sun.
(Adapted from: https://scienceinquirer.wikispaces.com/file/view/RespirationCorr.pdf )
Assessment Items to explore or uncover students’ preconceptions around the concept of photosynthesis:
Question 1. Which of the following is TRUE about the sugar molecules in plants? A. The sugar molecules come from the soil. B. The sugar molecules are the result of a chemical reaction. C. The sugar molecules are one of many sources of food for plants. D. The sugar molecules are made from molecules of water and minerals.
(Retrieved from AAAS Item ME095005, http://assessment.aaas.org/items/ME095005#/0 )
Question 2. Where does the food that a plant needs come from? A. The food comes in from the soil through the plant’s roots. B. The food comes in from the air through the plant’s leaves. C. The plant makes its food from carbon dioxide and water. D. The plant makes its food from minerals and water.
(Retrieved from AAAS Item ME029006, http://assessment.aaas.org/items/ME029006#/0 )
Questiom 3. What is TRUE about the inside of a plant cell? A. The inside of a plant cell is completely solid. B. The inside of a plant cell is completely filled with air. C. The inside of a plant cell is completely filled with liquid water. D. The inside of a plant cell contains liquid water and solid structures.
(Retrieved from AAAS Item CE065001, http://assessment.aaas.org/items/CE065001#/0 )
Description of the Lesson:
The goal of this lesson is for students to (1) engage in experiments that enable students to gather evidence of inputs and outputs of photosynthesis, (2) understand the relationship between light and photosynthesis, and (3) understand the relationship between carbon dioxide and photosynthesis. This lesson plan includes the following steps:
Step 1: Introduction – Engage Students in Learning : In this step, teacher introduces the driving question of this lesson: “ Plants need energy to stay alive and grow. How do you think plants get energy? ”
Step 2: Background Knowledge Probes (BKPs) : In this step, teacher use the assessments listed above to elicit students’ prior understanding and ideas of photosynthesis.
Step 3: Collecting and Making Sense of Data : In this step, teacher will conduct the Activity #1 – An Oxygen Factory . Teachers will then choose one of the option activities (i.e., Activity Option #2 – Light! Light! or Activity Option #3 – Role of Carbon Dioxide and Light ) to provide students with more evidences for the upcoming discussion at the end of the lesson. While students are engaging in these activities, teacher can ask discussion questions to track students’ understanding of the concept. Students are also invited to record their observation on the worksheet given.
Step 4: Developing Evidence-Based Explanations : Following the activities, teacher engages in this step by inviting students to share their data with other groups and the whole class. Teacher may also post summary data on a class summary chart on the board.
Step 5: Evaluation : Teacher can assess students’ learning outcomes by choosing one of the post-assessment strategies: (1) Question and Answer/Exit Cards; (2) Create a multimedia poster; (3) Using the assessment questions listed above.
Details and procedures of each step are explained as follow:
Step 1 of The Lesson: Introduction – Engage Students in Learning
In Step 1, teacher will help students to connect the idea of food-web with photosynthesis. The goal of this step is to introduce the important role of photosynthesis plays in our ecosystem.
(1) Introduction of the topic by saying: “ Hello, we are going to learn about photosynthesis today. Before starting the lesson, does there anyone know where plants get their energy from? ”
(2) Teacher can prepare a feed-web (see Figure 1.) on transparency, doc cam, computer screen, or draw the figure on the board. Teacher can than ask the following questions to guide the discussion:
- All living things need energy to survive. How do us, human get energy?
- From this food-web figure (Figure 1), how do fox and rabbits gain their energy from?
- From this food-web figure (Figure 1), how do grass and trees gain their energy from? Do grass and trees ‘eat’ any other organisms?
(3) Based on students’ response, teacher can re-voice students’ responses and write the responses on the board.
(4) After students sharing their ideas about food-web, teacher can begin the class by introducing the driving question of this lesson: “ Plants need energy to stay alive and grow. How do you think plants get energy? ”
Step 2 of The Lesson: Background Knowledge Probes (BKPs) - Eliciting Student Thinking
The goal of this step is to elicit students’ prior understanding and ideas of the topic without evaluating their response or correcting their answers at this point.
(1) Administer the instrument: To help teachers determine effective starting points for the students and to get to know students’ background knowledge, skills, attitudes, experience and motivation, before starting the lesson, you can administer the 3 assessment question provided above, in order to uncover students’ preconceptions around the concept of photosynthesis.
Teacher can use clickers to obtain students’ responses. If the school does not have clickers, teacher can ask the questions to the whole class and ask students to raise their hands for the answer. If there is no answer from students, teachers can also ask students to write their answer on a piece of paper and put them in a box. Teacher will then write some response on a board (or a chart paper) for discussion.
(2) Pressing for explanations: After administering the test, teacher can share the data with students and ask students for the explanations. You may re-voice their explanations and write their response on a board. For example, teacher can ask: “ We see that many of you choose option C as an answer. Does anybody want to share why they chose option C? What is your evidence for saying that? ”
(3) Introducing the term : Teacher can use the term “photosynthesis” to further probe students’ prior understanding. Teacher will then start the lesson by asking students what they think “photosynthesis” means and write down their responses on the board (or a chart paper).
Step 3 of the Lesson: Collecting and Making Sense of Data
The goal of this step is to help students to (1) develop their questions and/or predictions to learn more about the topic, and (2) test their predictions through hands-on inquiries, challenges, problems.
Teacher will first conduct the Activity #1 – An Oxygen Factory . Afterward, teachers can choose one of the option activities (i.e., Activity Option #2 – Light! Light! or Activity Option #3 – Role of Carbon Dioxide and Light ) to provide students with more evidences for the upcoming discussion at the end of the lesson. These optional activities could help teacher to engage in ongoing, formative assessments to track students’ learning (e.g., walking around class to listen to their ideas, recording and displaying their ideas, observations, worksheets, student journals, students’ work products, etc.).
Details and procedures of each activity are explained as follow:
Part 1: Preparation: Teacher will have two different demo stations (i.e., Demo Station #1– Photosynthesis of an aquatic plant and Demo Station #2– Growth factors of a plant ) prepared at least three days prior to the activity. Both teachers and students can create the demo stations.
Demo Station #1: Photosynthesis of an aquatic plant:
(1) Place a submersed aquatic plant (e.g., Canadian waterweed (Elodea canadensis) or coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum) in a flask. (2) Fill a 500mL or 1L beaker with water. (3) Place the flask (with aquatic plants) into the beaker. Make sure that the aquatic plants are submerged in water. (4) Place a light source (e.g., desk lamp) near the beaker.
Demo Station #2: Growth factors of a plant:
(1) Prepare 3 different pots of plants that are the same size (relevantly same size). (2) Prepare 3 terrariums (or 2 Liter soft drink bottles with the top cut off and saved for lid) with soil and 1 plant. (3) Terrarium 1: Add some oxygen gas, and seal the terrarium (or bottle lid). Label the terrarium. Note: If you do not have access to oxygen gas, just seal the terrarium. Make sure the plant had been in a closed system at least for 3 days. (4) Terrarium 2: Add some carbon dioxide gas, and seal the terrarium (or lid for the bottle.) Label the terrarium. Note: If you do not have access to carbon dioxide gas, place alkalizer in water, in an erlenmyer flask with a one-hole stopper, an elbow tube and glass tubing. Insert the tubing into the lid of the terrarium as the carbon dioxide is being produced). (5) Terrarium 3: The third terrarium is a control. Leave the plant in an unsealed terrarium.
Part 2: Observation: Students observe the plants at the two demo stations (i.e., Demo Station #1– Photosynthesis of an aquatic plant and Demo Station #2– Growth factors of a plant ). Teacher can ask questions to elicit students’ ideas.
For example, for the Demo Station #1 , teacher can ask the follow questions:
- What do you think is being produced in the flask?
- What is the evidence for this: Oxygen is being produced.
- The flask is foggy Inside. Why? ”
For the Demo Station #2 , teacher can ask the follow questions:
- What do you observe in the three terrariums?
- Where do you think the bubble comes from in the second terrarium?
- What gas do you think the bubbles are?
- What is happening in the third terrarium? Explain.
- What differences do you see between the first and second terrarium? ”
Part 3: Recording observation: Teacher will ask students to observe the three different terrariums and write down their observation on their worksheet (Appendix A). Note: The following Activity #2 and #3 are optional. These optional activities would allow teachers to help students collect more evidence/data for the final discussions at the end of the lesson.
Step 4 of the Lesson: Developing Evidence-Based Explanations
The goal of this step is to help students in changing their preconceptions through developing complex evidence-based explanations after their investigations in light of the data they gathered in the above activities. Teacher can ask students to share their data with other groups. Teacher may also post summary data on a class summary chart on the board.
(1) Divide students into groups. (Groups of 2-3). Ask students to answer the questions on the worksheet (Appendix B). For example:
- Where does the water that appears on the side of the terrariums (Activity 1 – An Oxygen Factory) come from?
- Which conditions are necessary for bubbles to appear in the water (Activity 2 – Light! Light!)?
- Which gas in the atmosphere encourages plant growth?
Facilitate the discussion as teacher walk around the classroom. Note: The important aspect here is that you allow students to make connection between evidence/data provided from the activities and their explanations for their answer.
(2) Once students are finished with the worksheet, facilitate a class discussion. Teacher can lead a discussion about the similarities and differences in the group analysis. Note: Teacher may go over the questions with students and have them present their answers and explanations. Or, teacher may ask students to present their data to the rest of class while teacher write down similarities and differences emerging from different groups’ data.
(3) Go back to the driving question on the board: “ Plants need energy to stay alive and grow. How do you think plants get energy? ” Ask students if their view have changed and ask why. Again, encourage students to draw their explanations from the evidence/data from the activities. Teacher can use the following strategies:
Ø Orienting students to each other’s thinking: For example, teacher can ask: Do you agree with what Student A said? and Why? Ø Pressing for explanation : For example, teacher can ask: Group A and B , both of you found results/data that are different than your previous predictions. Why do you think so?
Note: If time allows, you can show your students “photosynthesis song”: this video summarizes the process of photosynthesis, offering visual and musical sources: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C1_uez5WX1o https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C1_uez5WX1o
Step 5 of the Lesson: Evaluation
Three strategies can be used to do a post-assessment; they are:
Option #1: Question and Answer/Exit Cards : Have students to fill out the worksheet page individually (see Appendix). After students fill out most part of the worksheet, ask them to discuss in a small group (3-4 students). Teacher can facilitate the group discussion while walking around the classroom by asking questions such as: “ With regards to Input and its origin: Why do you think so? What evidence do you have from the activities we have done in class? ” After going of worksheet page. 100 together, teacher may give the assessment items tested in the beginning and/or have them write exit cards (i.e., write a short reflection on what they learned and what they still unsure about).
Option #2: Create a multimedia poster: By creating a multimedia poster on what students have learned in lessons, they can draw various ways of representing ideas (e.g., write summaries of the facts, create visual arts, add sound). This will be done as a group project. As a group, students have another opportunity to discuss about their understandings on photosynthesis with their peers in informal ways. Specific steps are describe as follow:
(1) In a group of 3-4, students will make a multi-media poster. The poster should represent their understanding of photosynthesis using multi-media of their choice (e.g., podcast, songs, YouTube, visual arts etc.). Students can draw from already existing sources (e.g., song from YouTube, pictures from encyclopedia).
(2) Ask students to connect what they observe in their daily life to the concept of photosynthesis.
(3) In their everyday life (e.g., home, school garden, or on the way to school), students can take a photo, make a collage, or draw a painting to connect the concept of photosynthesis to a moment in their daily life.
(4) With the photo/collage/drawing, students are instructed to write a short essay or record a podcast that explains how their photo/collage/drawing (e.g., photos of flowers, collages of cows eating grass, cooking meals) relates to the concept of photosynthesis.
For example, a group of students may write: “ The meals we eat are the products of photosynthesis. Vegetables grow because of photosynthesis. Meat is a product of animals eating producers or other consumers. Energy from photosynthesis is transferred to the consumer. Humans eat both vegetables and meat which are both products of photosynthesis. ”
(5) Teachers give specific guidelines and rubrics for students to follow. It is important for students to include the following key points in their short essays:
- The process of photosynthesis;
- Inputs and outputs of photosynthesis;
- Factors influencing the photosynthesis and the connection with their daily life experience.
(6) After the completion of the multimedia posters, class can have a symposium, where students will have an opportunity to present their multimedia posters to other students in the classroom.
Option #3: Assessment question : administer the same question and to see if students’ responses had been change. Teacher can use the clickers to obtain students’ responses. If the school does not have clickers, teacher can ask the questions to the whole class and ask students to raise their hands for the answer. If there is no answer from students, teachers can also ask students to write their answer on a piece of paper and put them in a box. Teacher will then write some response on a board (or a chart paper) for discussion. Note: You may re-voice their explanations and write their response on a board.
This lesson plan is inspired by the following sources: Education.com: http://www.education.com/pdf/photosynthesis-of-elodea/ Eureka!: Science and Technology, Secondary Cycle One; Student Textbook B (Activity 8: An Oxygen Factory, pp. 36-37); Worksheet (U1 38, U1 39); Teaching Resource Guide, Volume 1 (p.53). Ray, A. M., & Beardsley, P. M. (2008). Overcoming student misconceptions about photosynthesis: A model-and inquiry-based approach using aquatic plants. Science Activities: Classroom Projects and Curriculum Ideas , 45 (1), 13–22.

Department and University Information
Science education project- chantier 7.
- Faculty of Education
- Department of Integrated Studies in Education
- WOW Lab Blueprints
- Dr. Anila Asghar, Principal Investigator
- Dr. Kenneth Elliott, Researcher
- Ying-Syuan (Elaine) Huang, Graduate research assistant
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

26 templates

6 templates

first day of school
69 templates

environmental science
37 templates
49 templates
12 templates
Plants: nutrition, photosynthesis and respiration
It seems that you like this template, plants: nutrition, photosynthesis and respiration presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Download the "Plants: nutrition, photosynthesis and respiration" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and prepare to receive useful information. Even though teachers are responsible for disseminating knowledge to their students, they also embarked on a learning journey since the day they decided to dedicate themselves to education. You might find this Google Slides and PowerPoint presentation useful, as it's already completed with actual content provided by educators. It could also be interesting for parents of school-age children or teenagers.
Features of this template
- Designed for Elementary
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
- Available in different languages
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Available in, related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Register for free and start editing online
Photosynthesis
Powerpoint lecture notes: photosynthesis.

Science Presentation for Class 6
Chapter 1: food where it does come from, chapter 2: components of food, chapter 3: fibre to fabric, chapter 4: sorting materials in to groups, chapter 5: separation of substances, chapter 6: changes around us, chapter 7: getting to know plants, chapter 8: body movements, chapter 9: living organism and their surroundings, chapter 10: motion and measurement of distance, chapter 11: light shadow and reflection, chapter 12: electricity and circuit, chapter 13: fun with magnets, chapter 14: water, chapter 15: air around us, chapter 16: garbage in - garbage out.
Disclaimer: All contents are collected from various sources and updated at this platform to help teachers and students. If content owner (Original Creator) have any objection, Please mail us to [email protected] with ID Proof, content will be removed. Thanks and Regards
Notes Station: To Read Click on Title
कक्षा 6 पाठ योजना संस्कृत पाठ 1 class 6 sanskrit lesson plan chapter 1, split up of syllabus class 6 sanskrit, split up of syllabus class 6 hindi, book cart: to purchase click on title.

Golden Mathematics Class - 6

Maths 6- NTSE/ KVPY/OLYMPIAD

Class 6 - Geography and History

Mathematics by R.S. Aggarwal

Oswaal Worksheets Sanskrit

Honeysuckle & A Pact With The Sun

Mathematics 6 by R.D. Sharma

Our Pasts - History - So. Science

Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya (JNV) Class 6 Guide

Sainik School Class 6 Guide

Macmillan Footprints, Our Past

Oswaal Pullout Worksheets

Olympiad - IMO, NSO, IEO. NCO

Rashtriya Military School Class 6 Guide

Social and Political Life - So. Sc. - 6
Hey, my name is Ankita Prasad
i love this wesite it is so useful when you quickly have to study for your examinations you can improve the stability of this

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which have an outer membrane and an inner membrane. Stacks of thylakoids called grana form a third membrane layer. . Photosynthesis occurs in two parts: 1) Light-dependent reactions 2) Light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle) Sketch this in your notes. Pay attention to what goes in and what comes out.
Light Reaction or Light Dependent Reaction -. Produces energy from solar power (photons) in the form of ATP and NADPH. *. SUN. Two Parts of Photosynthesis. 2. Calvin Cycle or Light Independent Reaction ("Dark Reactions") Also called Carbon Fixation or C3 Fixation. Uses energy (ATP and NADPH) from light reaction to make sugar (glucose).
DEFINITION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS • Is the process by which autotrophic organisms use light energy to make sugar and oxygen gas from carbon dioxide and water. • Occurs in plants, algae and some prokaryotes • Anabolic (small molecules combined) • Endergonic (stores energy) • Stored as carbohydrate in their bodies. 4.
This Photosynthesis PowerPoint & Google Slides for 6th-8th Grade is a visually engaging presentation for middle school students. With clear explanations and captivating visuals, it introduces the process of photosynthesis, covering its requirements, steps, influencing factors, real-world examples, and importance in human life. Show more.
Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a process by which phototrophs convert light energy into chemical energy, which is later used to fuel cellular activities. The chemical energy is stored in the form of sugars, which are created from water and carbon dioxide. 3,12,343.
Gr 6 Natural Sciences and Technology - Term 1, Topic 1. 9 Water All living things contain water. Plants absorb water and nutrients from the soil through their veins. Photosynthesis can only take place in a water solution. Water helps to move the sugar from the leaves to where it is stored by the plant (e.g. roots or leaves or fruits).
Photosynthesis is the process in which plants. 1) use energy (sunlight) 2) to convert water and carbon dioxide 3) into glucose and oxygen. . O 2. Glucose. The Photosynthesis Equation. 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2. carbon dioxide + water → sugar + oxygen. .
Materials made during one process are the same as those needed for the other process. In other words they form a cycle. Together, photosynthesis and cellular respiration form the "Carbon Dioxide-Oxygen Cycle.". Here's the "cycle": Plants take in carbon dioxide (and some oxygen) and release oxygen into the air.
Photosynthesis - Download as a PDF or view online for free. 4. WHAT IS PHOTOSYNTHESIS? Photosynthesis is the process by which organisms convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of reducing power (as NADPH or NADH) and ATP, and use these chemicals to drive carbon dioxide fixation and reduction to produce sugars. 2 + 2 2 → 2 + 2 + 2 It is estimated that photosynthesis annually ...
Oxygen is released into air Hydrogen remains in chloroplast attached to NADPH "THE LIGHT REACTION" Steps of Photosynthesis The DARK Reactions= Calvin Cycle CO2 from atmosphere is joined to H from water molecules (NADPH) to form glucose Glucose can be converted into other molecules with yummy flavors! In most plants, photosynthesis occurs ...
The complementary process, during which plants, thanks to sunlight, absorb carbon dioxide, produce organic matter and expel oxygen to the atmosphere, is called photosynthesis. The perfect lesson for kids! They'll love nature, as well as your class, if you use this template, which has all kinds of illustrations and examples of explanations about ...
PPT versions of the 2 slide shows are included for easier classroom viewing: * Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration comparison activity with an answer key * Photosynthesis slide show with 17 slides * Cellular Respiration slide show with 16 slides * 32 vocabulary cards with definitions * Worksheet packet * 4 weeks of Bellringers * Test and ...
CBSE Class 6 Science - Learn more about plants and process of photosynthesis. Science Video tutorial for CBSE/NCERT 6th Class students.Enjoy the benefits of ...
Lesson Plan Gr. 6 Natural Sciences and Technology T1 W1 & W2. Free. Download. Type: pdf. Size: 0.74MB. Share this content. Grade 6 Lesson Plan on Life and Living & Processing with focus on the CAPS Topics: Photosynthesis, addressing the Concepts: Plants and food & Plants and air.
The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to produce high-energy sugars. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to produce high-energy sugars. The process of photosynthesis includes the light-dependent reactions as well as the Calvin cycle. Chapter 6 - Photosynthesis - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
2. photosynthesis —the process by which the chlorophyll in the leaves of plants capture light energy which they then use to change carbon dioxide and water into food. This plant food is called glucose. —and in most plants all this takes place in its leaves. 3. These are the things a plant needs for photosynthesis-- the process by which a ...
Demo Station #1: Photosynthesis of an aquatic plant: (1) Place a submersed aquatic plant (e.g., Canadian waterweed (Elodea canadensis) or coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum) in a flask. (2) Fill a 500mL or 1L beaker with water. (3) Place the flask (with aquatic plants) into the beaker.
Download the "Plants: nutrition, photosynthesis and respiration" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and prepare to receive useful information. Even though teachers are responsible for disseminating knowledge to their students, they also embarked on a learning journey since the day they decided to dedicate themselves to education. You ...
Search for: Powerpoint Lecture Notes: Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis Updated from Lumen Learning
This wonderful Photosynthesis Experiment allows your Year 6 pupils to investigate if light is needed for photosynthesis. The experiment challenges children to conduct their own experiment using safety, accuracy and independence. This downloadable resource includes everything you need to conduct a Photosynthesis Experiment. Well, except the materials! But don't worry, there are instructions ...
Book Cart: To Purchase Click on Title. Science Presentation for Class 6 Science Chapter 1: Food Where it Does Come From Click Here Click Here Click Here Click Here Click Here Chapter 2: Components of Food Click Here Click Here Click Here Chapter 3: Fibre to Fabric Click Here Click Here Chapter 4: Sorting Materials in to Groups Click Here Click ...
1 of 22. Download now. Download to read offline. powerpoint presentation on topic photosynthesis. 1. 2. All life needs a constant input of energy Autotrophs: Get their energy from "sunlight" Build organic molecules (food) from CO2 Make energy & synthesize sugars through photosynthesis Heterotrophs Get their energy from "eating others ...
The synthesis of food which occurs in the presence of sunlight is called Plant prepare their own food by a process called photosynthesis photosynthesis. During this process oxygen is released. SEE-MA SINGH Class-7 (Science) 7/4/2020 Photosynthesis fppt.com. SYNTHESIS TAKES PLACE? The process of photosynthesis takes place in the leaves of the plant.
12:30-3:30 pm -- DH Research Fellows' Showcase. 12:30 - 1:50 PM : The Meaning and Measurement of Place. with presentations from: Matt Randolph (PhD Candidate in History): "Bringing AI to Archibald Grimké's Archive: A Case Study of Artificial Intelligence for Histories of Race and Slavery". This digital project builds upon two years of research ...