Looking for AI in local government? See our newest product, Madison AI.

More Like this
What is the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan.
It is not uncommon that the terms ‘strategic plan’ and ‘business plan’ get confused in the business world. While a strategic plan is a type of business plan, there are several important distinctions between the two types that are worth noting. Before beginning your strategic planning process or strategy implementation, look at the article below to learn the key difference between a business vs strategic plan and how each are important to your organization.
Definition of a business plan vs. a strategic plan
A strategic plan is essential for already established organizations looking for a way to manage and implement their strategic direction and future growth. Strategic planning is future-focused and serves as a roadmap to outline where the organization is going over the next 3-5 years (or more) and the steps it will take to get there.
Get the Free Guide for Setting OKRs that Work (with 100 examples!)
A strategic plan serves 6 functions for an organization that is striving to reach the next level of their growth:.
- Defines the purpose of the organization.
- Builds on an organization’s competitive advantages.
- Communicates the strategy to the staff.
- Prioritizes the financial needs of the organization.
- Directs the team to move from plan to action.
- Creates long-term sustainability and growth impact
Alternatively, a business plan is used by new businesses or organizations trying to get off the ground. The fundamentals of a business plan focus on setting the foundation for the business or organization. While it looks towards the future, the focus is set more on the immediate future (>1 year). Some of the functions of a business plan may overlap with a strategic plan. However, the focus and intentions diverge in a few key areas.
A business plan for new businesses, projects, or organizations serves these 5 functions:
- Simplifies or explains the objectives and goals of your organization.
- Coordinates human resource management and determines operational requirements.
- Secures funding for your organization.
- Evaluates potential business prospects.
- Creates a framework for conceptualizing ideas.
In other words, a strategic plan is utilized to direct the momentum and growth of an established company or organization. In contrast, a business plan is meant to set the foundation of a newly (or not quite) developed company by setting up its operational teams, strategizing ways to enter a new market, and obtaining funding.
A strategic plan focuses on long-term growth and the organization’s impact on the market and its customers. Meanwhile, a business plan must focus more on the short-term, day-to-day operational functions. Often, new businesses don’t have the capacity or resources to create a strategic plan, though developing a business plan with strategy elements is never a bad idea.
Business and strategic plans ultimately differ in several key areas–timeframe, target audience, focus, resource allocation, nature, and scalability.
While both a strategic and business plan is forward-facing and focused on future success, a business plan is focused on the more immediate future. A business plan normally looks ahead no further than one year. A business plan is set up to measure success within a 3- to 12-month timeframe and determines what steps a business owner needs to take now to succeed.
A strategic plan generally covers the organizational plan over 3 to 5+ years. It is set with future expansion and development in mind and sets up roadmaps for how the organization will reach its desired future state.
Pro Tip: While a vision statement could benefit a business plan, it is essential to a strategic plan.
Target Audience
A strategic plan is for established companies, businesses, organizations, and owners serious about growing their organizations. A strategic plan communicates the organization’s direction to the staff and stakeholders. The strategic plan is communicated to the essential change makers in the organization who will have a hand in making the progress happen.
A business plan could be for new businesses and entrepreneurs who are start-ups. The target audience for the business plan could also be stakeholders, partners, or investors. However, a business plan generally presents the entrepreneur’s ideas to a bank. It is meant to get the necessary people onboard to obtain the funding needed for the project.
A strategic plan provides focus, direction, and action to move the organization from where they are now to where they want to go. A strategic plan may consist of several months of studies, analyses, and other processes to gauge an organization’s current state. The strategy officers may conduct an internal and external analysis, determine competitive advantages, and create a strategy roadmap. They may take the time to redefine their mission, vision, and values statements.
Alternatively, a business plan provides a structure for ideas to define the business initially. It maps out the more tactical beginning stages of the plan.
Pro Tip: A mission statement is useful for business and strategic plans as it helps further define the enterprise’s value and purpose. If an organization never set its mission statement at the beginning stages of its business plan, it can create one for its strategic plan.
A strategic plan is critical to prioritizing resources (time, money, and people) to grow the revenue and increase the return on investment. The strategic plan may start with reallocating current financial resources already being utilized more strategically.
A business plan will focus on the resources the business still needs to obtain, such as vendors, investors, staff, and funding. A business plan is critical if new companies seek funding from banks or investors. It will add accountability and transparency for the organization and tell the funding channels how they plan to grow their business operations and ROI in the first year of the business.
The scalability of a business plan vs. strategic plan
Another way to grasp the difference is by understanding the difference in ‘scale’ between strategic and business plans. Larger organizations with multiple business units and a wide variety of products frequently start their annual planning process with a corporate-driven strategic plan. It is often followed by departmental and marketing plans that work from the Strategic Plan.
Smaller and start-up companies typically use only a business plan to develop all aspects of operations of the business on paper, obtain funding and then start the business.
Why understanding the differences between a business plan vs a strategic plan matters
It is important to know the key differences between the two terms, despite often being used interchangeably. But here’s a simple final explanation:
A business plan explains how a new business will get off the ground. A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state.
A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
10 Comments
I agree with your analysis about small companies, but they should do a strategic plan. Just check out how many of the INC 500 companies have an active strategic planning process and they started small. Its about 78%,
Strategic management is a key role of any organization even if belong to small business. it help in growth and also to steam line your values. im agree with kristin.
I agree with what you said, without strategic planning no organization can survive whether it is big or small. Without a clear strategic plan, it is like walking in the darkness.. Best Regards..
Vision, Mission in Business Plan VS Strategic Plan ?
you made a good analysis on strategic plan and Business plan the difference is quite clear now. But on the other hand, it seems that strategic plan and strategic management are similar which I think not correct. Please can you tell us the difference between these two?. Thanks
Thank you. I get points to work on it
super answer Thanking you
Hi. I went through all the discussions, comments and replies. Thanks! I got a very preliminary idea about functions and necessity of Strategic Planning in Business. But currently I am looking for a brief nice, flowery, juicy definition of “Business Strategic Planning” as a whole, which will give anyone a fun and interesting way to understand. Can anyone help me out please? Awaiting replies…… 🙂
that was easy to understand,
Developing a strategic plan either big or small company or organization mostly can’t achieve its goal. A strategic plan or formulation is the first stage of the strategic management plan, therefore, we should be encouraged to develop a strategic management plan. We can develop the best strategic plan but without a clear plan of implementation and evaluation, it will be difficult to achieve goals.
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.

- Certifications
- Associate Business Strategy Professional
- Senior Business Strategy Professional
- Examination
- Partnership
- For Academic Affiliation
- For Training Companies
- For Corporates
- Help Center
- Associate Business Strategy Professional (ABSP™)
- Senior Business Strategy Professional (SBSP™)
- Certification Process
- TSI Certification Examination
- Get your Institution TSI Affiliated
- Become a Corporate Education Partner
- Become a Strategy Educator
- Frequently Asked Questions
Business plan vs Strategic Plan - What You Must Know

Like everything else in life, the nature of business needs a plan in place to follow and measure. Crafting a strategic roadmap isn't just a suggestion—it's a necessity.
This is one of the key elements of a startup or even a business division within an organization that is expanding or diversifying. It has every resource element and needs to be mapped out for the business, including projected milestones for the future.
However, every business strategist needs to know that there are some subtle differences between what constitutes a business plan, and the several differences it has with a strategic plan. Let’s walk through the different elements that comprise each and understand the outcome each aims to achieve.
Introducing The Business Plan
A business plan is exactly what the name suggests— a plan to start and run a business or a new entity of an existing business; usually either an expansion in a newer region or a diversification into a new market. Business plans are mainly created for internal reference purposes or external funding purposes, with the latter being the common usage. They form the basis of all business strategies and decisions made at the ownership level in an organization. The most essential components of a business plan include:
Organizational Plan - This is the core of a business plan, and it includes the mission and vision statement, along with the market in which the company plans to operate. This plan also encompasses thorough market research to gauge the potential of the business, crucial for securing funding or sponsorship. It articulates the rationale behind the business's growth trajectory, outlining clear timelines for achieving milestones along the way.
Financial Plan - A robust financial plan is the bedrock of any successful business venture, where cash flow reigns supreme, and a meticulously crafted balance sheet serves as the ultimate scorecard. A financial plan includes some of the most important elements of the entire business plan and includes elements like projected cash flow statements, capital requirements, a summary of projected overheads, a projected balance sheet including assets and liabilities, and income and expense statements.
Remember to regard this as the central nervous system, for it permeates and influences almost every aspiration the enterprise hopes to attain.
Sales and Marketing Plan - We mentioned “almost” everything above for this very reason. Sales and marketing form the other significant component of the business plan. These include sales forecasts and overheads, marketing and brand management summaries, and market share projections that the business hopes to achieve within a time frame.
Business plans are indeed comprehensive and all-encompassing. They form the basis of the business's existence or the rationale for investments in it. But what about translating these plans into action? How do we ensure that the sky-high goals set forth are actually achievable?
The Actionables- A Strategic Plan
Strategic plans constitute the basis of operations and responsibilities within the business. These plans lay the paths out for each member of the organization to follow and define the functional outline and the key outcomes for every project and process within the business. A strategic plan goes on to define the operations and their outcomes within the organization, its departments, and its employees. The single thread connecting strategic planning with the business plan is the vision of the organization, and for obvious reasons— vision serves as the guiding light for strategy formation, which, in turn, directs the day-to-day operations of the business.
Why A Strategic Plan is Crucial to The Organization
In a word— synchronization. A robust and well-laid-out strategic plan establishes the much-needed sync between teams and their objectives. Not only that, it also provides a guide for daily operations alongside the focus and direction that teams often need to get the job done, on time and within budget. When all these components are integrated into a cohesive network, the true value of a strategic plan emerges—a seamless and grand orchestration of departments, teams, and individuals using the resources allocated to them to achieve the key performance indicator that they are responsible for.
Elements to Consider in a Strategic Plan
When tasked with creating a strategic plan for your business, you will need to incorporate certain components that will ensure that the stakeholders are aligned completely with the organization’s goals and objectives. These include:
Vision and Values - The vision statement is the most important component of the strategic plan and the most overarching. It propels the organization towards established goals and the values that every employee and stakeholder must incorporate.
Goals - These are short, medium, or long-term, depending on the scope of the strategic plan. They provide the much-needed context for the organization to undertake initiatives that meet the vision while maintaining the values.
Guiding Principles - Often, organizations face crossroads where they must decide which steps to take next, to reach their vision. Principles are included in strategic plans to align teams towards the vision when faced with a dilemma and form a critical part of strategic planning.
Action Plans - A sum of key initiatives, processes, and projects that are required to be performed on a pre-determined periodic basis for the goal to be accomplished. These also include the time frames for each stakeholder responsible for each option. They usually follow the DACI format for each action (Driver, Approver, Contributor, Informed)
SWOT Analysis - The quintessential component, the Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats analysis of the strategic plan lends context to all business actions vis-a-vis the external environment. This includes competitors, market forces and conditions, identification of internal and external threats, and several other factors.
Read This - SWOT Analysis: How to Strengthen Your Business Plan
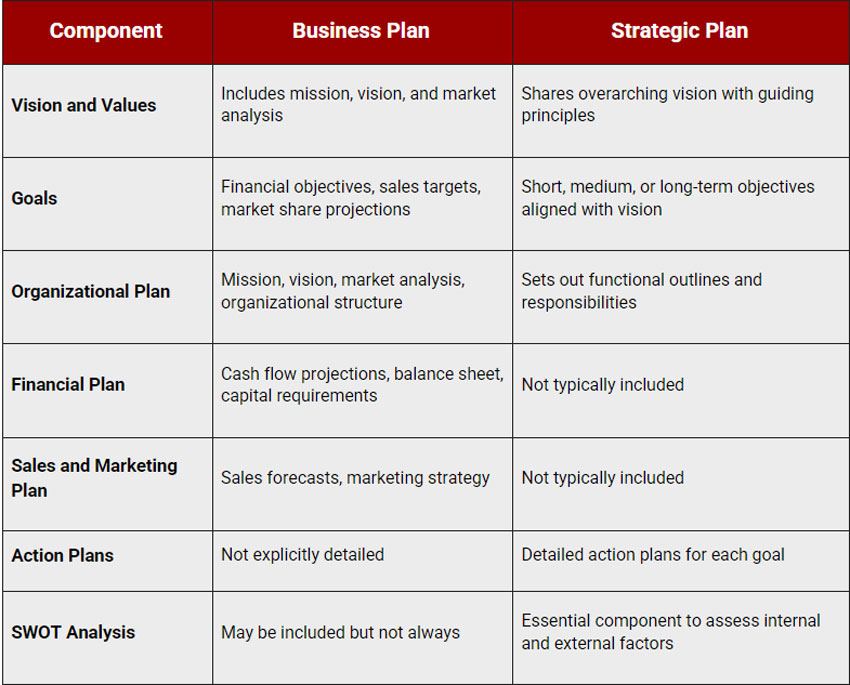
Here’s a table highlighting the main differences between a Business Plan and a Strategic Plan with a focus on the key components of each—
Learning All About Strategic Planning
In all businesses, a strategic plan serves as the foundational blueprint, akin to a meticulously drawn map for a general. It provides the essential guidance and direction needed for the entire organization to navigate toward success. It is crucial, therefore, to acquire the necessary skills and certifications for employment as a business strategist who would be entrusted with creating it. Know more about how to become a successful and sought-after business strategist today!

Recent Posts

How Data Analytics Can Revolutionize Your Business - A Strategist's Guide
Download this Strategist's Guide to empower yourself with resourceful insights:
- Roadblocks to Data Usage
- Advantages that Data Analytics offer for businesses
- Elements of a Data Analytics Strategy
- Top reasons why businesses must adopt a Data Analytics Strategy
- Case studies, Scenarios, and more

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Verify A Credential
Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TSI.
Stay Informed!
Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.
Start Your Journey with The Strategy Institute by Creating Your myTSI Account Today.
- Manage your professional profile conveniently.
- Manage your credentials anytime.
- Share your experiences and ideas with The Strategy Institute.
Account Login
- Remember Password
- Forgot Password?
Forgot Password
AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks (Coming soon...) Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan: What’s the Difference?

Business Plan Template
- May 6, 2024

Strategic and business plans are both different sides of the same coin! Some entrepreneurs use it interchangeably but they have a significant difference.
Now the question might arise, when to use which, and what is the difference, right?
Worry not—we’re here to guide you through it all. In this article, we’ll learn the differences between a business and a strategic plan, understand their meanings, and know how to use them effectively.
So, let’s kick-start this journey by exploring a business plan vs. strategic plan . Get ready to unlock everything about both!
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a written document that outlines a company’s goals, timeline, finances, and strategies for achieving them. It provides a roadmap for the future of your business.
Generally, it includes sections such as an executive summary, company description, market analysis, products & services, financial plan, and much more. Your business plan is a must-have document when it comes to securing funds for your business.
Okay! And what about the strategic plan?
What is a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan is a document that communicates an organization’s vision, mission, and core values. It focuses more on specifics about how a business will operate and generate profits.
Strategic plans are typically long-term documents, covering a period of three to five years or more, and are used to guide decision-making and resource allocation within the organization.
Key Difference Between a Business Plan and Strategic Plan
It was all about the basic definition of business and strategic plan. Now, let’s compare them side-by-side to understand their use case, and how they are distinct from each other:
Level of detail
A business plan is usually considered a granular and in-depth document. It outlines the tactics and actions necessary to achieve operational objectives. Business plans are usually 15-30 pages long .
A strategic plan typically provides a high-level overview of the organization’s goals and the strategies to achieve them without going deep into the business operations. Strategic plans are generally 10-15 pages long, but the length depends on various factors of the business.
Time horizon
A business plan focuses on a shorter time frame, often one to three years, and is more operational. It focuses on things like product development, marketing strategies, financial projections, etc.
A strategic plan answers the questions related to a longer time frame, usually five or more years. It sets the direction of the company for the future by mentioning the mission, vision, and objectives.
Audience and use
A business plan is primarily used to attract investors, bankers, or partners for securing funding or partnership.
Whereas, internal members, such as senior management or a board of directors, use a strategic plan to guide decision-making.
A business plan explains all the sections like market analysis, products & services, management team, target market, sales & marketing strategies, financial projections, and more.
While a strategic plan has a vision statement, mission statement, core values, action plans, and more. Some of the strategic planning models are SWOT analysis , PESTLE (political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental) analysis, Porter’s five forces, and more.
Entrepreneurs and startups use business plans to create a strategy to build a successful business. It is used for assessing how marketable a business idea is and also helps them gauge how they can get the funding to turn this idea into reality.
Established companies use the strategic plan to give them a clear direction for where they want the company to change or develop.
For instance, decisions like changing the products they provide or moving into a nonprofit can be made with the help of a strategic plan.
Create winning business and strategic plans with our
AI Business Plan Generator
Plans starting from $7/month

Now that we know the key differences between strategic and business planning, let us understand the common pitfalls.
Common Pitfalls in Execution
Despite the benefits of business planning as well as the strategic planning process , organizations often face many challenges in their strategy implementation. Here are some common pitfalls:
Disparity between strategy and execution: Without effective execution, even the strategic plan that is the most well-crafted may fail to give results.
Lack of alignment: Failure to align the business plan with strategic objectives often results in missed opportunities and misallocation of resources.
Inadequate marketing analysis: Insufficient analysis of external factors leads to missed opportunities or strategic blind spots that can cause more harm to a company.
To overcome these challenges, organizations need to foster a culture of communication, continuous improvement, and collaboration.
The Bottom Line
There is no one-fits-all solution when it comes to this decision! Choosing between a business and a strategic plan solely depends on the needs & objectives of your business.
Moreover, know this planning is not a one-time process! As your business evolves and external factors change, you will need to revise your plans accordingly.
A business and a strategic plan are crucial for guiding any organization to success. By using both methods effectively, businesses can navigate uncertainties, achieve steady growth, and grab opportunities in a constantly changing business world.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which comes first, strategy or business plan.
Before making a business plan, you should create a strategic plan. A business should know all its long-term growth goals before actually defining how to reach them.
So, first, create a strategic plan, then a business plan, and then edit both of them when needed according to the circumstances.
Can a business plan be used for a strategic plan?
No, both are different. While a business plan details the operational and financial aspects of a business, a strategic plan defines goals and the strategies to achieve them. Therefore, serving different purposes, a business plan can not be used to make a strategic plan.
Is there a sample business plan or strategic plan template available online?
Yes, there are many sample business plans and strategic plan templates available online. You can find such templates on:
- Upmetrics – An AI-powered business plan software
- Small Business Administration Website
- SCORE business plans
Do I need both a business and strategic plan?
Yes, both a business plan and a strategic plan are essential for a company’s growth. A business plan focuses on the initial stages of a business, aiming to get it started. In contrast, a strategic plan focuses on the business’s distant goals and strategies to achieve them.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

The Difference Between a Plan and a Strategy
Setting strategy should push your organization outside its comfort zone.
- Apple Podcasts
Planning is comforting but it’s a terrible way to make strategy, says Roger Martin , former dean of the Rotman School of Management at the University of Toronto. In contrast, setting strategy should push your organization outside its comfort zone – if you’re doing it right.
“Plans typically have to do with the resources you’re going to spend. Those are more comfortable because you control them,” Martin explains. “A strategy, on the other hand, specifies a competitive outcome that you wish to achieve, which involves customers wanting your product or service. The tricky thing about that is that you don’t control them.”
Key topics include: strategic planning, competitive strategy, risk management, innovation, and travel and tourism industry.
HBR On Strategy curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock new ways of doing business. New episodes every week.
- Watch the original HBR Quick Study episode: A Plan Is Not a Strategy (June 2022)
- Find more episodes of the HBR Quick Study series on YouTube .
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org
ANNOUNCER: HBR On Strategy .
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR On Strategy , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock new ways of doing business. Today, we bring you a conversation with one of the world’s leading thinkers on strategy – Roger Martin, former dean of the Rotman School of Management at the University of Toronto. In this episode, you’ll learn the difference between strategy and planning AND how to escape the common traps of strategic planning. Martin says starting with a plan is comforting to many of us, but it’s a terrible way to make strategy. His episode, called “A Plan is Not A Strategy,” originally aired as part of the HBR Quick Study video series in June 2022. Here it is.
ROGER MARTIN: This thing called planning has been around for a long, long time. People would plan out the activities they’re going to engage in. More recently, has been a discipline called strategy. People have put those two things together to call something strategic planning. Unfortunately, those things are not the same, strategy and planning. So, just putting them together and calling it strategic planning doesn’t help. What most strategic planning is in the world of business has nothing to do with strategy. It’s got the word, but it’s not. It’s a set of activities that the company says it’s going to do.
We’re going to improve customer experience. We’re going to open this new plant. We’re going to start a new talent development program. A whole list of them, and they all sound good, but the results of all of those are not going to make the company happy because they didn’t have a strategy. So, what’s a strategy? A strategy is an integrative set of choices that positions you on a playing field of your choice in a way that you win. So, there’s a theory. Strategy has a theory. Here’s why we should be on this playing field, not this other one, and here’s how, on that playing field, we’re going to be better than anybody else at serving the customers on that playing field. That theory has to be coherent. It has to be doable. You have to be able to translate that into actions for it to be a great strategy. Planning does not have to have any such coherence, and it typically is what people in manufacturing want– the few things they want, to build a new plant, and the marketing people want to launch a new brand, and the talent people want to hire more people– that tends to be a list that has no internal coherence to it and no specification of a way that that is going to accomplish collectively some goal for the company.
See, planning is quite comforting. Plans typically have to do with the resources you’re going to spend. So we’re going to build a plan. We’re going to hire some people. We’re going to launch a new product. Those are all things that are on the cost side of businesses. Who controls your costs? Who’s the customer of your costs? The answer is, you are. You decide how many square feet to lease, how many raw materials to buy, how many people to hire. Those are more comfortable because you control them. A strategy, on the other hand, specifies an outcome, a competitive outcome that you wish to achieve, which involves customers wanting your product or service enough that they will buy enough of it to make the profitability that you’d like to make. The tricky thing about that is that you don’t control them. You might wish you could, but you can’t. They decide, not you. That’s a harder trick. So that means putting yourself out and saying, here’s what we believe will happen. We can’t prove it in advance, we can’t guarantee it, but this is what we want to have happen and that we believe will happen. It’s much easier to say, I’ll build a factory, I will hire more people, et cetera, than I will have customers end up liking our offering more than those of competitors.
The tricky thing about planning is that while you’re planning, chances are at least one competitor is figuring out how to win. When US air carriers were busily planning what routes to fly and da-da-da, there was this little company in Texas called Southwest that had a strategy for winning. And at first, that looked largely irrelevant because it was tiny. What Southwest Airlines was aiming for was an outcome.
What they wanted to be is a substitute for Greyhound, a way more convenient way to get around at a price that wasn’t extraordinarily much greater than a Greyhound bus. Southwest said, everybody else is flying hub and spoke. They have hubs, and they fly hub and spoke. We’re going to fly point to point so that we don’t have aircraft waiting on the ground because you only make money when you’re in the air.
We’re going to only fly 737s, one kind of aircraft, so that our gates are set up for those, our systems are set up for those, our training, our simulations are set up. We’re not going to offer meals on the flights because we’re going to specialize in short flights. We’re not going to book through travel agents. We’re going to encourage people to book online because that’s less expensive for everybody and more convenient. So, their strategy ended up having a substantially lower cost than any of the major carriers so that they could offer substantially lower prices.
Because it had a way of winning, it got bigger and then bigger and then bigger and then bigger and bigger and bigger and bigger until it flies the most passenger seat miles in America. The major carriers were not trying to win against one another. They were all playing to play, as I say. They were playing to participate, maybe buy more planes, get more gates, maybe grow some, not having a theory of here’s how we could be better than our competitors.
And that was fine until somebody came along and said, here’s a way to be better than everybody else for this segment. And so that segment then goes. It’s gone. And the main playing to play players have to share a smaller pie that’s left over after Southwest takes whatever share it wants.
If you’re trying to escape this planning trap, this comfort trap of doing something that’s comfortable but not good for you, how do you start? The most important thing to recognize is that strategy will have angst associated with it. It’ll make you feel somewhat nervous because as a manager, chances are you’ve been taught you should do things that you can prove in advance.
You can’t prove in advance that your strategy will succeed. You can look at a plan and say, well, all of these things are doable. Let’s just do those because they’re within our control. But they won’t add up to much. In strategy, you have to say, if our theory is right about what we can do and how the market will react, this will position us in an excellent way.
Just accept the fact that you can’t be perfect on that, and you can’t know for sure. And that is not being a bad manager. That is being a great leader because you’re giving your organization the chance to do something great. The second thing I do is say, lay out the logic of your strategy clearly. What would have to be true about ourselves, about the industry, about competition, about customers for this strategy to work?
Why do you do that? It’s because you can then watch the world unfold. And if something that you say is in the logic that would have to be true for this to work is not working out quite the way you hoped, it’ll allow you to tweak your strategy. And strategy is a journey, what you want to have as a mechanism for tweaking it, honing it, and refining it so it gets better and better as you go along.
Another thing that helps with strategy is not letting it get overcomplicated. It’s great if you can write your strategy on a single page. Here’s where we’re choosing to play. Here’s how we’re choosing to win. Here are the capabilities we need to have in place.
Here are the management systems. And that’s why it’s going to achieve this goal, this aspiration that we have. Then you lay out the logic, what must be true for that all to work out the way we hope. Go do it, and watch and tweak as you go along.
That may feel somewhat more worry-making, angst-making than planning, but I would tell you that if you plan, that’s a way to guarantee losing. If you do strategy, it gives you the best possible chance of winning.
HANNAH BATES: That was Roger Martin — Professor Emeritus and former Dean of the Rotman School of Management at the University of Toronto. That video is part of the HBR Quick Study YouTube series – short takes on big topics in business and work. It was edited and produced by Scott LaPierre, with video and animation by Dave Di Iulio, Elie Honein, and Alex Belser. More HBR Quick Study videos can be found on YouTube or HBR.org. HBR On Strategy will be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about business strategy from the Harvard Business Review. In the meantime, we have another curated feed that you should check out: HBR On Leadership . And visit us any time at HBR.org, where you can subscribe to Harvard Business Review and explore articles, videos, case studies, books, and of course, podcasts, that will help you manage yourself, your teams, and your career. This episode of HBR On Strategy was produced by Anne Saini, and me, Hannah Bates. The show was created by Anne Saini, Ian Fox, and me. Special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Adi Ignatius, Karen Player, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener. See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about strategy.
- Strategy formulation
- Risk management
Partner Center

- Get started
Strategic Plan vs Business Plan - Which Matters More for Leaders?

In the world of business, strategic planning and business planning are two terms that are often used interchangeably. However, they are not the same thing . Strategic planning is a long-term planning process that helps a company define its vision, mission, and objectives. Business planning, on the other hand, is a short-term planning process that helps a company define its goals and strategies to achieve those goals.
Both strategic planning and business planning are important for leaders, but which one matters more? In this blog post, we will explore the differences between strategic planning and business planning and why strategic planning should be a top priority for leaders.
What is a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's vision, mission, and objectives. It is a comprehensive plan that guides a company's actions over the next three to five years. A strategic plan helps a company identify its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats ( SWOT ) and develop strategies to capitalize on its strengths and opportunities while mitigating its weaknesses and threats.
A strategic plan helps a company create a roadmap for the future. It outlines the company's goals and objectives, the strategies it will use to achieve those goals, and the metrics it will use to measure its progress. A strategic plan helps a company stay focused and aligned with its vision and mission.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a short-term plan that outlines a company's goals and strategies for the next year or two. A business plan helps a company define its products or services, target market, competition, marketing strategy, sales strategy, and financial projections. It is a tactical plan that helps a company achieve its goals in the short term.
A business plan helps a company allocate its resources effectively. It outlines the company's budget, cash flow, and profit and loss projections. A business plan helps a company make informed decisions about its operations and investments.
Strategic plan vs business plan: Which matters more for leaders?
Both strategic planning and business planning are important for leaders. However, strategic planning takes priority because it provides the long-term vision for the company. A strategic plan helps a company stay focused on its mission and vision and guides its decisions over the long term.
Business planning is important for day-to-day operations, but it is not a substitute for strategic planning. A company that only focuses on short-term goals and tactics may miss out on long-term opportunities.
If you are a leader, it is important to have a strategic plan in place to help you stay focused on your mission and vision, and guide your decisions over the long term. It will help you anticipate future trends and challenges and prepare for them. So, invest the time and resources to create a comprehensive strategic plan for your company and ensure that it is regularly updated and reviewed. By doing so, you will be able to steer your company towards success and stay ahead of the competition.
More on strategic planning
Capability-based planning vs Traditional Project Planning Approaches
How to Create an Agile Strategic Planning Process
10 Tips for Conducting a Successful Strategic Planning Session
6 Steps to Create an Effective Implementation Plan

Jibility helps business architects close the strategy-to-execution gap
When you are ready to implement your strategy, Jibility can help you formulate a proven strategic roadmap by stepping you through our unique 6-step method to create a strategic roadmap that actually works.
Related blogs

What is a business value stream?
A business value stream represents a chain of business activities that delivers stages of value outcome to the business along that chain. Every bu...

Six Steps for Developing a Strategy Roadmap
Develop a strategy roadmap with six tried-and-tested steps, covering challenges, objectives, capabilities, initiatives and more.

How to Create an Agile Strategic Planning Process
The strategic planning process of any organization needs to cope with change. Creating a sprint-based cadence is key.

By using this website, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. View our Privacy Policy for more information.
How to Write a Business Plan: Your Step-by-Step Guide

So, you’ve got an idea and you want to start a business —great! Before you do anything else, like seek funding or build out a team, you'll need to know how to write a business plan. This plan will serve as the foundation of your company while also giving investors and future employees a clear idea of your purpose.
Below, Lauren Cobello, Founder and CEO of Leverage with Media PR , gives her best advice on how to make a business plan for your company.
Build your dream business with the help of a high-paying job—browse open jobs on The Muse »
What is a business plan, and when do you need one?
According to Cobello, a business plan is a document that contains the mission of the business and a brief overview of it, as well as the objectives, strategies, and financial plans of the founder. A business plan comes into play very early on in the process of starting a company—more or less before you do anything else.
“You should start a company with a business plan in mind—especially if you plan to get funding for the company,” Cobello says. “You’re going to need it.”
Whether that funding comes from a loan, an investor, or crowdsourcing, a business plan is imperative to secure the capital, says the U.S. Small Business Administration . Anyone who’s considering giving you money is going to want to review your business plan before doing so. That means before you head into any meeting, make sure you have physical copies of your business plan to share.
Different types of business plans
The four main types of business plans are:
Startup Business Plans
Internal business plans, strategic business plans, one-page business plans.
Let's break down each one:
If you're wondering how to write a business plan for a startup, Cobello has advice for you. Startup business plans are the most common type, she says, and they are a critical tool for new business ventures that want funding. A startup is defined as a company that’s in its first stages of operations, founded by an entrepreneur who has a product or service idea.
Most startups begin with very little money, so they need a strong business plan to convince family, friends, banks, and/or venture capitalists to invest in the new company.
Internal business plans “are for internal use only,” says Cobello. This kind of document is not public-facing, only company-facing, and it contains an outline of the company’s business strategy, financial goals and budgets, and performance data.
Internal business plans aren’t used to secure funding, but rather to set goals and get everyone working there tracking towards them.
As the name implies, strategic business plans are geared more towards strategy and they include an assessment of the current business landscape, notes Jérôme Côté, a Business Advisor at BDC Advisory Services .
Unlike a traditional business plan, Cobello adds, strategic plans include a SWOT analysis (which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) and an in-depth action plan for the next six to 12 months. Strategic plans are action-based and take into account the state of the company and the industry in which it exists.
Although a typical business plan falls between 15 to 30 pages, some companies opt for the much shorter One-Page Business Plan. A one-page business plan is a simplified version of the larger business plan, and it focuses on the problem your product or service is solving, the solution (your product), and your business model (how you’ll make money).
A one-page plan is hyper-direct and easy to read, making it an effective tool for businesses of all sizes, at any stage.
How to create a business plan in 7 steps
Every business plan is different, and the steps you take to complete yours will depend on what type and format you choose. That said, if you need a place to start and appreciate a roadmap, here’s what Cobello recommends:
1. Conduct your research
Before writing your business plan, you’ll want to do a thorough investigation of what’s out there. Who will be the competitors for your product or service? Who is included in the target market? What industry trends are you capitalizing on, or rebuking? You want to figure out where you sit in the market and what your company’s value propositions are. What makes you different—and better?
2. Define your purpose for the business plan
The purpose of your business plan will determine which kind of plan you choose to create. Are you trying to drum up funding, or get the company employees focused on specific goals? (For the former, you’d want a startup business plan, while an internal plan would satisfy the latter.) Also, consider your audience. An investment firm that sees hundreds of potential business plans a day may prefer to see a one-pager upfront and, if they’re interested, a longer plan later.
3. Write your company description
Every business plan needs a company description—aka a summary of the company’s purpose, what they do/offer, and what makes it unique. Company descriptions should be clear and concise, avoiding the use of jargon, Cobello says. Ideally, descriptions should be a few paragraphs at most.
4. Explain and show how the company will make money
A business plan should be centered around the company’s goals, and it should clearly explain how the company will generate revenue. To do this, Cobello recommends using actual numbers and details, as opposed to just projections.
For instance, if the company is already making money, show how much and at what cost (e.g. what was the net profit). If it hasn’t generated revenue yet, outline the plan for how it will—including what the product/service will cost to produce and how much it will cost the consumer.
5. Outline your marketing strategy
How will you promote the business? Through what channels will you be promoting it? How are you going to reach and appeal to your target market? The more specific and thorough you can be with your plans here, the better, Cobello says.
6. Explain how you’ll spend your funding
What will you do with the money you raise? What are the first steps you plan to take? As a founder, you want to instill confidence in your investors and show them that the instant you receive their money, you’ll be taking smart actions that grow the company.
7. Include supporting documents
Creating a business plan is in some ways akin to building a legal case, but for your business. “You want to tell a story, and to be as thorough as possible, while keeping your plan succinct, clear, interesting, and visually appealing,” Cobello says. “Supporting documents could include financial projects, a competitive analysis of the market you’re entering into, and even any licenses, patents, or permits you’ve secured.”
A business plan is an individualized document—it’s ultimately up to you what information to include and what story you tell. But above all, Cobello says, your business plan should have a clear focus and goal in mind, because everything else will build off this cornerstone.
“Many people don’t realize how important business plans are for the health of their company,” she says. “Set aside time to make this a priority for your business, and make sure to keep it updated as you grow.”
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained

Noah Parsons
5 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023
Many business owners know and understand the value of a business plan. The business plan is a key component of the startup and fundraising process and serves as a foundation for your organization. However, it only tells part of the story. To get the whole picture and have a framework on which to build your business you also need a strategic plan and an operational plan.
- What is a business plan?
In its simplest format, a business plan describes the “who” and the “what” of your business. It lays out who is running the business and what the business does. It describes the products and services that your business sells and who the customers are.
- What is a strategic plan?
A strategic plan looks beyond the basics of a business plan to explain the “how”. It explains the long-term goals of the business and how it expects to achieve those goals over the long term. A strategic plan explores future products and services that your business might offer and target markets that you might expand into. The plan explains your strategy for long-term growth and expansion.
- What is an operational plan?
An operation plan zooms into the details of your business to explain how you are going to achieve your short-term goals . It is the “when” and “where” of your planning process. The operational plan covers the details of marketing campaigns, short-term product development, and more immediate goals and projects that will happen within the next year.
- What is the difference between a strategic plan and a business plan?
First, let’s look at the difference between a business and a strategic plan. For review:
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of the business. The strategic plan gives us long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there, providing a long-term view.
In broader terms, the business plan tells us who by showing us:
- Who is running the business? What makes them qualified? What do they bring to the table that adds value?
- Who is the competition? What do they offer and what makes you different?
- Who is your customer? How big is the market? Where are they? What do they want and how will you give it to them? Also, how will you connect with your market?
The business plan answers the “what” by telling us:
- What the business provides and how it’s provided.
- Product, services, and operations are all explained so that readers understand how customer needs are met.
The strategic plan, on the other hand, outlines long term goals and the “how”, focusing on the following:
- Where will the business be in 3, 5, or even 10 years?
- How will you expand to offer different products and services over time?
- Will your market and industry change over time and how will your business react to those changes?
- How will you grow your market and reach new customers?
- What needs to happen so you can achieve your goals? What resources do you need to get there?
- How will you measure success? What metrics matter and how will you track them?
So, your business plan explains what you are doing right now. Your strategic plan explains long-term aspirations and how you plan to transition your business from where it is today to where you want it to be in the future. The strategic plan helps you look more deeply into the future and explains the key moves you have to make to achieve your vision.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What is the difference between strategic planning and operational planning?
While strategic planning looks at the long term and explains your broad strategies for growth, an operational plan looks at the short term. It explains the details of what your business is going to do and when it’s going to do it over the next twelve months or so. An operational plan covers details like:
- What activities need to happen to achieve your business goals?
- When will each activity take place, who will do it, and when do you need to reach specific milestones?
- How will your business operate? What suppliers will you work with? When do you need to have them in place?
- What marketing campaigns will you run and what will they cost?
- What investments will you make in your products and services this year?
The bottom line, your operational plan is the short-term action plan for your business. It’s the tasks, milestones, and steps needed to drive your business forward. Typically an operational plan provides details for a 1-year period, while a strategic plan looks at a 3-5 year timeline , and sometimes even longer. The operational plan is essentially the roadmap for how you will execute your strategic plan.
- How to use your business plan for strategic development and operations
A great business plan can encompass both the basic plans for the business, the long-term strategic plan, and the near-term operational plan. Using a lean planning method, you can tackle all three phases of planning and make the process easy to review and revise as your business grows, changes, and adapts.
Start with a simple plan
The lean planning methodology starts with a simple, 30-minute business plan that outlines the fundamentals of your business: who you are, what you are doing, and who your customers are. It’s a great way to provide a brief overview of your business.
Expand your plan
From there, you can expand your plan to include your longer-term strategy. Adding greater detail to elements of the plan to explain long-term goals, milestones, and how your products and services will change and expand over time to meet changing market conditions.
Finally, your lean plan will cover financial forecasts that include monthly details about the short-term revenue and expenses, as well as longer-term annual summaries of your financial goals, including profitability and potential future loans and investments.
- Use your business plan to manage your business
Regardless of the type of plan, you are working on, you need a team of players on hand to help you plan, develop, and execute both the operational and strategic plans. Remember, your business needs both to give it a clear foundation and a sense of direction. As well as to assist you with identifying the detailed work that has to happen to help you reach your long-term goals.
Learn how LivePlan can help you develop a business plan that defines your business, outlines strategic steps, and tracks ongoing operations. You can easily share it with your team and all of the right stakeholders, explore scenarios and update your plan based on real-world results. Everything you need to turn your business plan into a tool for growth.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
5 Fundamental Principles of Business Planning

10 Min. Read
When Should You Write a Business Plan?

2 Min. Read
How Long Should a Business Plan Be?

7 Min. Read
8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- What Is TAB
- Advisory Boards
- Business Coaching
- StratPro Leadership Transformation Program
- Strategic Leadership Tools
- Our Members
- Case Studies
- White Papers
- Business Diagnostic

The Alternative Board Blog
The difference between a strategic plan and a business plan.

Every business needs a strategic plan. Every business needs a business plan. It’s knowing precisely what each plan entails and when that plan can be of most use that makes the difference between these two essential documents.
Let’s start by defining the purpose behind each type of plan. This can help both budding entrepreneurs and veteran CEOs avoid the mistake of pursuing the wrong kind of plan at the wrong time in the growth cycle of their companies.
The Strategic Plan
As we have noted before, a strategic plan “is a written document that points the way forward for your business.” The focus of a strategic plan can include (but isn’t limited to):
- Expanding business operations
- Reaching into new market segments
- Solving organizational problems
- Potential restructuring a business
By staying focused on your original purpose, goals, and objectives, strategic planning reintroduces you to “the big picture.” It’s the basis for business owners to achieve their vision, which they communicate to stakeholders in a strategic business plan and program.
A strategic plan serves as a roadmap for determining what will likely lie ahead for your business in the next 3-5 years, while also including a series of actions or activities that can turn strategy into operational reality.
Want additional insight? Read 4 Step Guide to Strategic Planning now to learn more

The Business Plan
Generally speaking, a business plan is needed when a company is in its earliest phase of growth. This plan offers a description of how your business will operate, its objectives for growth and financial success, and how it aims to get there. Essentially, it articulates the why behind a business. Key elements include:
- Executive summary and mission statement
- Projected staffing and equipment needs
- Short- and long-term marketing strategy
- Financial statement, including anticipated startup expenses and capitalization
- Outline of management structure and operational processes
A business plan “is a broader, more preliminary document that sets your course when your company may still be nothing more than a twinkle in your eye,” notes BDC of Canada. This plan “not only accurately summarizes what your business is all about, but why it’s a viable proposition.”
Strategic Business Planning
Strategic planning is the systematic process for developing an organization’s direction. This includes pinpointing objectives and actions required to achieve that future vision, and metrics to measure success.
A business plan, as described by the Center for Simplified Strategic Planning, Inc., aims to define “the initial goals and objectives of the company, its structure and processes, products and services, financial resources [and] all of the basics that go into forming a company ” and getting it up and running.
TAB offers its members a different kind of approach— strategic business planning . It’s the basis for business owners to achieve their vision, which they will then communicate to stakeholders in a strategic business plan and program.
Action steps embodied in a strategic business plan include:
- Understanding your business. Assess where your business is today. Review core business information and revisit your vision, mission statement, and core values.
- Analyzing your strengths, weaknesses, and threats. Conduct a SWOT analysis to evaluate where your business is operating at peak efficiency and where organizational weaknesses (and threats from competitors) might stunt future growth.
- Defining objectives and set goals. Drill down into specific objectives that will help you achieve your vision—everything from developing new marketing strategies and launching a new product to re-allocating key financial resources.
- Putting the plan in action . Take action steps to translate the plan from paper to reality. Break tasks down into small steps, assign a responsible party to be accountable for each task, and establish a schedule for reviewing your overall plan on a regular basis.
As we enter into a new year, strategic business planning is more urgently needed than ever before. Want to learn more? Register for our free TAB white paper, “4 Step Guide to Strategic Planning.”

Read our 19 Reasons You Need a Business Owner Advisory Board

Written by The Alternative Board
Related posts, unlearning conformity: how to overhaul old business paradigms, top 3 strategic musts for the coming year, 5 “must-have” elements of a strategic plan, what does the future of remote work look like, tips on future-proofing your business, what can predictive analytics do for your business, subscribe to our blog.
- Sales and marketing (140)
- Strategic Planning (135)
- Business operations (128)
- People management (69)
- Time Management (52)
- tabboards (39)
- Technology (38)
- Customer Service (37)
- Entrepreneurship (35)
- company culture (27)
- Business Coaching and Peer Boards (24)
- Money management (24)
- businessleadership (24)
- employee retention (23)
- Work life balance (22)
- Family business (17)
- business strategy (15)
- leadership (15)
- communication (13)
- human resources (12)
- employee engagement (11)
- employment (11)
- strategy (9)
- innovation (8)
- businesscoaching (7)
- productivity (7)
- remote teams (7)
- adaptability (6)
- cybersecurity (6)
- professional development (6)
- salesstrategy (6)
- strategic planning (6)
- businessethics (5)
- leadership styles (5)
- marketing (5)
- networking (5)
- peeradvisoryboards (5)
- socialmedia (5)
- branding (4)
- employeedevelopment (4)
- hiring practices (4)
- supplychain (4)
- Mentorship (3)
- business vision (3)
- collaboration (3)
- culture (3)
- environment (3)
- future proof (3)
- newnormal (3)
- remote work (3)
- sustainability (3)
- work from home (3)
- worklifebalance (3)
- workplacewellness (3)
- Planning (2)
- ecofriendly (2)
- globalization (2)
- recession management (2)
- salescycle (2)
- salesprocess (2)
- #contentisking (1)
- #customerloyalty (1)
- accountability partners (1)
- artificial intelligence (1)
- blindspots (1)
- building trust (1)
- business owner (1)
- businesstrends (1)
- customer appreciation (1)
- customerengagement (1)
- data analysis (1)
- digitalpersona (1)
- financials (1)
- globaleconomy (1)
- greenmarketing (1)
- greenwashing (1)
- onlinepresence (1)
- post-covid (1)
- risk management (1)
- riskassessment (1)
- seasonality (1)
- social media (1)
- talent optimization (1)
- team building (1)
- transparency (1)

Do you want additional insight?
Download our 19 Reasons Why You Need a Business Advisory Board Now!

TAB helps forward-thinking business owners grow their businesses, increase profitability and improve their lives by leveraging local business advisory boards, private business coaching and proprietary strategic services.
Quick Links
- Find a Local Board
- My TAB Login
keep in touch
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Business Strategy & Why Is It Important?

- 20 Oct 2022
Every business leader wants their organization to succeed. Turning a profit and satisfying stakeholders are worthy objectives but aren’t feasible without an effective business strategy.
To attain success, leaders must hone their skills and set clear business goals by crafting a strategy that creates value for the firm, customers, suppliers, and employees. Here's an overview of business strategy and why it's essential to your company’s success.
Access your free e-book today.
What’s a Business Strategy?
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered.
According to Harvard Business School Online's Business Strategy course, an effective strategy is built around three key questions:
- How can my business create value for customers?
- How can my business create value for employees?
- How can my business create value by collaborating with suppliers?
Many promising business initiatives don’t come to fruition because the company failed to build its strategy around value creation. Creativity is important in business , but a company won't last without prioritizing value.
The Importance of Business Strategy
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including:
- Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials
- Suppliers: Whether to source materials sustainably and from which suppliers
- Employee recruitment: How to attract and maintain talent
- Resource allocation: How to allocate resources effectively
Without a clear business strategy, a company can't create value and is unlikely to succeed.
Creating Value
To craft a successful business strategy, it's necessary to obtain a thorough understanding of value creation. In the online course Business Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee explains that, at its core, value represents a difference. For example, the difference between a customer's willingness to pay for a good or service and its price represents the value the business has created for the customer. This difference can be visualized with a tool known as the value stick.
The value stick has four components, representing the value a strategy can bring different stakeholders.

- Willingness to pay (WTP) : The maximum amount a customer is willing to pay for a company's goods or services
- Price : The actual price of the goods or services
- Cost : The cost of the raw materials required to produce the goods or services
- Willingness to sell (WTS) : The lowest amount suppliers are willing to receive for raw materials, or the minimum employees are willing to earn for their work
The difference between each component represents the value created for each stakeholder. A business strategy seeks to widen these gaps, increasing the value created by the firm’s endeavors.
Increasing Customer Delight
The difference between a customer's WTP and the price is known as customer delight . An effective business strategy creates value for customers by raising their WTP or decreasing the price of the company’s goods or services. The larger the difference between the two, the more value is created for customers.
A company might focus on increasing WTP with its marketing strategy. Effective market research can help a company set its pricing strategy by determining target customers' WTP and finding ways to increase it. For example, a business might differentiate itself and increase customer loyalty by incorporating sustainability into its business strategy. By aligning its values with its target audiences', an organization can effectively raise consumers' WTP.
Increasing Firm Margin
The value created for the firm is the difference between the price of an item and its cost to produce. This difference is known as the firm’s margin and represents the strategy's financial success. One metric used to quantify this margin is return on invested capital (ROIC) . This metric compares a business's operating income with the capital necessary to generate it. The formula for ROIC is:
Return on Invested Capital = Net Operating Cost After Tax (NOCAT) / Invested Capital (IC)
ROIC tells investors how successful a company is at turning its investments into profit. By raising WTP, a company can risk increasing prices, thereby increasing firm margin. Business leaders can also increase this metric by decreasing their costs. For example, sustainability initiatives—in addition to raising WTP—can lower production costs by using fewer or more sustainable resources. By focusing on the triple bottom line , a firm can simultaneously increase customer delight and margin.
Increasing Supplier Surplus & Employee Satisfaction
By decreasing suppliers' WTS, or increasing costs, a company can create value for suppliers—or supplier surplus . Since increasing costs isn't sustainable, an effective business strategy seeks to create value for suppliers by decreasing WTS. How a company accomplishes this varies. For example, a brick-and-mortar company might partner with vendors to showcase its products in exchange for a discount. Suppliers may also be willing to offer a discount in exchange for a long-term contract.
In addition to supplier WTS, companies are also responsible for creating value for another key stakeholder: its employees. The difference between employee compensation and the minimum they're willing to receive is employee satisfaction . There are several ways companies can increase this difference, including:
- Increasing compensation: While most companies hesitate to raise salaries, some have found success in doing so. For example, Dan Price, CEO of Gravity Payments, increased his company's minimum wage to $80,000 per year and enjoyed substantial growth and publicity as a result.
- Increasing benefits: Companies can also decrease WTS by making working conditions more desirable to prospective employees. Some offer remote or hybrid working opportunities to give employees more flexibility. Several have also started offering four-day work weeks , often experiencing increased productivity as a result.
There are several ways to increase supplier surplus and employee satisfaction without hurting the company's bottom line. Unfortunately, most managers only devote seven percent of their time to developing employees and engaging stakeholders. Yet, a successful strategy creates value for every stakeholder—both internal and external.

Strategy Implementation
Crafting a business strategy is just the first step in the process. Implementation takes a strategy from formulation to execution . Successful implementation includes the following steps :
- Establish clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Set expectations and ensure employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities
- Delegate work and allocate resources effectively
- Put the plan into action and continuously monitor its progress
- Adjust your plan as necessary
- Ensure your team has what they need to succeed and agrees on the desired outcome
- Evaluate the results of the plan
Throughout the process, it's important to remember to adjust your plan throughout its execution but to avoid second-guessing your decisions. Striking this balance is challenging, but crucial to a business strategy's success.

Learn More About Creating a Successful Business Strategy
Business strategy constantly evolves with changing consumer expectations and market conditions. For this reason, business leaders should continuously educate themselves on creating and executing an effective strategy.
One of the best ways to stay up-to-date on best practices is to take an online course, such as HBS Online's Business Strategy program. The course will provide guidance on creating a value-driven strategy for your business.
Do you want to learn how to craft an effective business strategy and create value for your company's stakeholders? Explore our online course Business Strategy , or other strategy courses , to develop your strategic planning skills. To determine which strategy course is right for you, download our free flowchart .

About the Author
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![business strategy vs business plan [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources

How Asana streamlines strategic planning with work management

How to create a CRM strategy: 6 steps (with examples)
What is management by objectives (MBO)?

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

Excellence in early learning
Small & Medium Business
Be released from the day-to-day
Start-Ups & Software
Find fit & grow your team
Board meetings
Run board meetings with ease.
Plans & roadmaps
Build organization or team plans.
Strategic alignment
Align leaders and teams.
Performance intelligence
AI powered performance intelligence.
Operating efficiency
Simplify, focus, and automate.
Business transformation
Run business improvement programs.
People development
Data driven people development.
Write plans, procedures, notes, or policies.
Use AI to build smart goals & OKRs.
Your vision masterplan.
Run projects, oragnize tasks across teams.
Align the operating rhythm, run effective meetings.
Diagnostics
Find growth gaps across the business.
Build scorecards, visualize performance.
Why partner?
Easier advisory with a demonstrable ROI
Become a partner
Become a fractal Chief of Staff.
ROI Calculator
See the ROI in our program.
GET CERTIFIED
Advisor Certifications
Be recognized as a strategic leader.
Platform specialist
Implement agile leadership practices.
CX Consultant
Lead sales, marketing, & service strategy.
EX Consultant
Lead people & culture strategy.
Business consultant
Lead business planning & strategy.
Leadership coach
Lead executive coaching.
Certified advisor
Fractal Chief of Staff, COO, or Strategic Advisor.
Help centre
Help and knowledge articles.

Waymaker Academy
Grow your skills.
Leadership articles.
Events & webinars
Join a masterclass.
Download resources.
Listen, learn, connect.
Product overview
3 Ways to build a better business.
Diagnose gaps, roadmap, goals & more
Watch a demo
Watch a detailed overview of Waymaker.io
For start ups & small business
Every essential step to grow
For scaling & enterprise business
Release your team to scale your business
For coaches & consultants
Become a high value advisor as a Waymaker partner
Playbooks for growth
On demand playbooks in Waymaker Academy
License types, prices and start a free trial
START MY FREE TRIAL
Lead and deliver
Get certified + free courses & playbooks
Waymaker's Leadership Curve
The framework overview
News & articles
Listen to leaders
eBooks & Webinars
Learn with our eBooks & Webinars
Get started, learn & find help
WATCH A DEMO
Build a better business with Waymaker partnership
How to partner
3 steps to a better coaching & consulting business
Get Certified
Become a Waymaker Certified Advisor
High Growth Advisor Program
Scale your advisory
Grow your partner business
Access free & paid services to grow your business
Model your partner ROI
Use our ROI calculator
SPEAK WITH OUR TEAM
About Waymaker
Join our team?
APPLY FOR A ROLE

Build a scaleable business & leadership advisory business.
Discover Waymaker partnership.
Become a Waymaker Partner
Scale your coaching & consulting.
Free courses and playbooks for Waymaker partners.
Be recognized for leadership.
Platform Specialist
For agile & business coaches.
For sales and marketing consultants.
For HR consultants and coaches.
Business Consultant
For strategic business coaches & consultants.
Leadership Coach
For executive and leadership coaches.
Certified Advisor
For recognized experts in leadership and strategy.

Bite sized brilliance to grow your business.
Leadership Blog
Podcast | leadership torque.
Helping you make business improvement, business as usual.
Learn with our downloadable eBooks.
Merch & Resources to help you achieve more by doing less.
Free courses and playbooks.
Leadership software
What is leadership software?
Waymaker Leadership Curve
A framework overview.
Get started, learn & find the help you need.

Platform features
Waymaker's intelligent platform includes goals (OKRs), roadmaps, meetings, tasks, and dashboards.
Diagnose growth gaps.
Create goals and OKRs.
Create roadmaps of goals.
Tasks, task automation, and task templates.
Automate meetings and minutes.
Build scorecards, view goal and task dashboards.
Professional services
Increase profits, reduce chaos.
Property & Development
Streamline & reduce risk.
Software & Technology
Align everyone, outperform growth
Small business
Work on your business, not in it.
WAYMAKER LEADERSHIP BLOG
- Effective Strategic Plans and Business Plans: Understanding the Difference Between
by Waymaker | Jul 25, 2023
Defining Strategic Plans and Business Plans
What is a strategic plan, what is a business plan, key components of strategic plans and business plans, elements of a strategic plan, elements of a business plan, the purpose and goals of the strategic plan and the business plan, the purpose of a strategic plan, the purpose of a business plan, the planning process: strategic plans vs. business plans, developing a strategic plan, developing a business plan, the role of stakeholders in each plan, stakeholder involvement in strategic plans, stakeholder involvement in business plans.
- You may also like...
Get started
In the world of business, the terms strategic plans and business plans are often used interchangeably. However, there are significant differences between these two types of plans that are important for entrepreneurs and business leaders to understand.

Before delving into the differences between strategic plans and business plans, it’s important to define each term.
A strategic plan is a long-term plan that outlines an organization’s goals and objectives and the actions needed to achieve them. It typically covers a three to five-year time period and focuses on broad, high-level initiatives that will position the organization for success in the future.
Strategic planning is a crucial process for any organization that wants to succeed in today’s competitive business environment. It allows organizations to identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and to develop a plan of action that will help them achieve their long-term goals.
During the strategic planning process, organizations typically conduct a thorough analysis of their internal and external environments. This includes an assessment of their current strengths and weaknesses, as well as an analysis of the market, competition, and other external factors that could impact their success.
Based on this analysis, organizations develop a set of strategic objectives and initiatives that will help them achieve their long-term goals. These initiatives may include expanding into new markets, developing new products or services, or investing in new technologies.
A business plan , on the other hand, is a detailed plan that outlines the steps a company will take to achieve its short-term goals and to operate on a daily basis. It typically covers a one to three-year time period and includes detailed financial projections, marketing plans, and operational strategies.
A business plan is a critical tool for any entrepreneur or small business owner who wants to succeed. It allows them to identify their target market, develop a marketing strategy, and create a roadmap for achieving their financial goals.
When developing a business plan, entrepreneurs typically begin by conducting market research to identify their target market and assess the competition. They then develop a marketing strategy that will help them reach their target market and differentiate themselves from the competition.
In addition to marketing, a business plan also includes detailed financial projections that outline the company’s revenue and expenses over the next one to three years. This allows entrepreneurs to identify potential financial challenges and develop strategies to overcome them.
Finally, a business plan includes operational strategies that outline how the company will operate on a day-to-day basis. This includes everything from hiring and training employees to managing inventory and fulfilling orders.
In conclusion, while both strategic plans and business plans are important tools for organizations and entrepreneurs, they serve different purposes. Strategic plans focus on long-term goals and broad initiatives, while business plans focus on short-term goals and daily operations.
Strategic plans and business plans are essential tools for any organization looking to achieve long-term success. While both plans share some common elements, they differ in their focus and level of detail.
A strategic plan is a comprehensive document that outlines an organization’s long-term goals and objectives. Key components of a strategic plan include:
- Mission Statement: This statement defines the organization’s purpose and values, and provides a framework for decision-making.
- Vision Statement: This statement describes the organization’s long-term aspirations and what it hopes to achieve in the future.
- Objectives: These are specific, measurable goals that the organization aims to achieve within a set timeframe.
- Strategies: These are the broad approaches that the organization will take to achieve its objectives.
- Tactics: These are the specific actions that the organization will take to implement its strategies.
By outlining these key components, a strategic plan provides a roadmap for the organization to follow as it works towards its long-term goals.
A business plan is a detailed document that outlines how a company will achieve its short-term and long-term goals. While it shares some elements with a strategic plan, a business plan is more focused on the day-to-day operations of the business. Key components of a business plan include:
- Executive Summary: This is a brief overview of the entire business plan, highlighting the key points and goals.
- Market Analysis: This section provides an in-depth look at the industry and market in which the company operates.
- Marketing and Sales Strategies: These are the specific tactics that the company will use to promote and sell its products or services.
- Operational Plans: This section outlines the day-to-day operations of the business, including staffing, production, and logistics.
- Financial Projections: This section provides detailed financial projections, including revenue, expenses, and profit margins.
- Funding Requirements: This section outlines the company’s funding needs and how it plans to secure financing.
By including these key components, a business plan provides a detailed roadmap for the company to follow as it seeks to achieve its goals and grow its operations.
Overall, both strategic plans and business plans are essential tools for any organization looking to achieve long-term success. By outlining clear goals and strategies, these plans provide a framework for decision-making and help ensure that the organization stays focused on its long-term objectives.
Strategic plans and business plans are both essential tools for any organization. They provide a clear roadmap for achieving goals and ensuring long-term success. While the two plans are similar in some ways, they serve different purposes and have different goals.
A strategic plan is a high-level document that outlines an organization’s long-term goals and objectives. It provides a roadmap for achieving those goals and helps to align the entire organization around a shared vision. The purpose of a strategic plan is to provide a framework for making strategic decisions that will move the organization closer to its desired future state.
Developing a strategic plan requires careful consideration of an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It involves analyzing market trends, assessing the competition, and identifying potential risks and challenges. The end result is a comprehensive plan that outlines the steps necessary to achieve the organization’s long-term goals.
One of the key benefits of a strategic plan is that it helps to ensure that everyone in the organization is working towards the same goals. By creating a shared vision and providing a clear roadmap for achieving it, a strategic plan can help to align the efforts of all employees, departments, and stakeholders.
A business plan is a detailed document that outlines an organization’s short-term goals and objectives. It provides a roadmap for achieving those goals and helps to define the company’s market niche, outline its marketing and sales strategies, and determine the funding needed to cover startup costs and ongoing expenses.
The purpose of a business plan is to provide a clear and comprehensive plan for achieving the organization’s short-term goals. This includes identifying potential customers, outlining marketing and sales strategies, and determining the resources needed to launch and maintain the business.
Developing a business plan requires careful research and analysis. This includes assessing the market demand for the product or service, analyzing the competition, and identifying potential risks and challenges. The end result is a detailed plan that outlines the steps necessary to launch and grow the business.
One of the key benefits of a business plan is that it helps to ensure that the organization is well-prepared for the challenges of starting and growing a business. By providing a clear roadmap for achieving short-term goals, a business plan can help to minimize risks and increase the chances of success.
Strategic plans and business plans are both essential tools for any organization. While they serve different purposes and have different goals, they both provide a clear roadmap for achieving success. By developing a comprehensive strategic plan and a detailed business plan, organizations can ensure that they are well-prepared for both short-term and long-term success.
Planning is an essential part of any successful business, but the planning process can differ significantly depending on the type of plan being developed. Strategic plans and business plans have different goals, and therefore require different approaches to planning.
Use Waymaker Academy to learn how to build your business plan.

A strategic plan is a long-term plan that outlines an organization’s goals and objectives, and the strategies it will use to achieve them. Developing a strategic plan typically involves a lengthy planning process that includes input from a wide range of stakeholders, such as executives, employees, customers, and shareholders. The planning process may involve conducting research and analysis to identify opportunities and threats in the market, as well as the organization’s strengths and weaknesses.
The strategic plan should be reviewed and updated annually to ensure it remains relevant and aligned with the organization’s goals. This process may involve revisiting the organization’s mission and vision statements, as well as assessing the progress made towards achieving the goals outlined in the plan.
One of the key benefits of a strategic plan is that it provides a clear direction for the organization, helping to align everyone around a common set of goals and objectives. It also helps to ensure that resources are being allocated in the most effective way possible, and that the organization is able to adapt to changes in the market.
A business plan, on the other hand, is a shorter-term plan that outlines the company’s goals and objectives for the next one to three years. The process of developing a business plan typically involves a smaller team of stakeholders focused on executing the company’s short-term goals.
The business plan may also include input from investors, lenders, and other external stakeholders who have a vested interest in the company’s success. This may involve presenting financial projections, market analysis, and other data to demonstrate the viability of the business.
One of the key benefits of a business plan is that it provides a roadmap for the company’s short-term goals, helping to ensure that everyone is working towards the same objectives. It also helps to identify potential risks and challenges, and provides a framework for measuring progress and making adjustments as needed.
Overall, both strategic plans and business plans are important tools for any organization. By taking the time to develop a clear plan, companies can ensure that they are working towards their goals in the most effective way possible.
Stakeholder involvement plays a key role in both strategic plans and business plans, although the level and type of involvement can vary depending on the plan.
Stakeholder involvement is critical in the development of a strategic plan, as it ensures that all parties have a voice in shaping the organization’s future. This involvement also helps to build consensus around the organization’s goals and the strategies needed to achieve them.
Stakeholder involvement in a business plan may be more limited, as the focus is on executing short-term goals rather than shaping the organization’s long-term future. However, investors and lenders may play a significant role in the development of a business plan, as they provide funding and have a vested interest in the success of the company.
While strategic plans and business plans share some common elements, they serve very different purposes and are designed to achieve different goals. By understanding the differences between these two plans, entrepreneurs and business leaders can better plan for the future, execute their short-term goals, and position their organizations for long-term success.
You may also like…

Streamline Your Workflow with New Folder Functionality in Waymaker.io
We're excited to introduce folders, a new feature that will transform the way you organize your content across...

Introducing the People module: AI powered role descriptions, automated org charts, and powerful performance alignment.
The Waymaker People module makes it easy to plan roles, align performance metrics and build world class role...

Understanding the role of a company director as a small business leader
As a small business owner who also serves as a company director and an employee of your company, you hold a unique...
Performance intelligence software for holding plans, people, and performance accountable. Achieve up to 77% better goal performance with Waymaker.io
Our content is reader-supported. Things you buy through links on our site may earn us a commission
Join our newsletter
Never miss out on well-researched articles in your field of interest with our weekly newsletter.
- Project Management
- Starting a business
Get the latest Business News
Business plans vs. strategic plans.

What sets a business plan apart is its singular focus on market and operational feasibility. In contrast, a strategic plan clarifies the long term direction of the organization; most business plans look at a shorter period of time, typically 2-3 years, and drills down thoroughly how the work will get done and dollars will be earned.
Business plans typically take more resources, both internal and often external (in the form of consulting assistance) to develop the kinds of operational and financial analysis necessary to fully test the feasibility of business venture or an organization as a whole.
It gets down to specifics about who the customers will be, what they will pay (with research backing that up), what marketing will be needed to reach them, who the competition will be, and how the finances will work out, in detail.
The feasibility part of the business plans means that it’s entirely possible that the idea you seek to develop is not feasible, at least not with your current set of assumptions.
While strategic plans in theory have that escape clause also, rarely is it used. Finally, a credible business plan has to include who (the skilled managers) who will carry it out. It’s not a business plan if it doesn’t include the people who will implement it.
The above is a graphic from our colleagues at Social Impact Architects laying out some of these differences for the social sector.
- Copyright © 2014 Rolfe Larson Associates
- Social Impact App , find social enterprises nearby and online
- Venture Forth! endorsed by Paul Newman of Newman’s Own

Rolfe Larson

Resources for Starting a Business
Legal Structures of Organizations Legal Forms and Traditional Structures of Organizations Market Research — Inbound Marketing Planning Your Research Market Research Find and Feed the Feeling Strategizing Understanding Strategy and Strategic Thinking Competitor Analysis Porter’s Five Competitive Forces (Part I) Porter’s Five Competitive Forces (Part 2) Competitive Intelligence Product Planning Product Management E-Commerce Sales and …

Ultimate Business Planning Guide with Updated Resources
Complete Business Planning Guide with Extensive Resources Copyright Carter McNamara, MBA, PhD. NOTE: Your business plan should be highly customized to your current organizational situation. Thus, using a generic business plan template could completely misrepresent the needed focus of your business plan. (This step-by-step manual is a complement to the topic How to Start Your …

Learn Strategic Thinking from Napoleon
Biographers of Napoleon Bonaparte talk about his ability to size up a situation with a single coup d’oeil,(pronounced koo-DOY), meaning “a stroke of the eye” or “glance.” Napoleon was so knowledgeable about his strategic situation—the landscape, the enemy, available technology, similar situations from the past—that he could understand and respond quickly to ever- changing circumstances. …

Strategic Planning Facilitator: Guiding the Planning Process
Strategic Planning: The Crucial Role of a Facilitator The goal of strategic planning should be to produce a Plan that is 1) relevant, realistic, and flexible; 2) with a very high likelihood of being implemented; 3) in order to achieve the purpose of the planning, e.g., a purpose to evolve to the next stage of …

Mistakes Made by Strategic Planning Facilitators
Here’s a list of the biggest mistakes that I have seen made by strategic planning facilitators over the years: 1. Not getting sufficiently trained on how to do facilitating, e.g., planning the meeting, goals, ground rules, which techniques to cultivate complete participation, doing interventions, managing conflict 2. Not learning a variety of strategic planning models, …

Strategic Thinking in the Age of LinkedIn
LinkedIn founder and triple billionaire Reid Hoffman has two endearing mannerisms that reveal the way he sees–and reasons with–the strategic environment. First, he peppers his statements with the word so. Almost a verbal tic that would grate on a speaking coach like the overuse of the dreaded uh … but he uses it more like …
Avoid the Silicon Valley Syndrome!
Guest blog from my colleague, Adam Brock, Director of Social Enterprise at Joining Vision and Action (formerly JVA Consulting): How can a well-meaning startup avoid “Silicon Valley Syndrome” and actually use a social startup to create real value for society? Every era has an industry that epitomizes its values. At the turn of the 20th …

Develop Your Strategic Intuition
The best decision-makers in chaotic “fog of war” conditions seem able to call on intuition – knowing what to do without knowing why or how they know.

Free Online Program to Learn Strategic Planning Facilitation

Moneyball: The Role of the Chief Strategy Officer
Paul DePodesta – role of the Chief Strategy Officer for the Cleveland BrownsPaul DePodesta was recently named the Chief Strategy Officer by the Cleveland Browns of the National Football League. This is significant because, as any fan of Moneyball knows, Mr. DePodesta has spent his career in the sport of baseball, not football. This matters …

50 Tips and Tools for Effective Strategic Thinking Skills
To engage in strategic thought, you must think and reflect on the big picture—on the diverse players and forces in your competitive environment. Anticipate the future. Use your right brain for intuition and wisdom, and your left for planning. As Isaac Newton said, “Truth is the offspring of silence and meditation.” Here are 50 tips …

To Learn Strategy, Know History
When you are faced with the most important and strategic decision of your life, where can you go for wisdom? Can you find insight in a book of history? Facing a world in crisis, John F. Kennedy did just that. Generally, we learn skills by trying something, failing, and trying again until we get it …

Execution Trumps Strategy
The results are in – Execution trumps strategy. Your business plan may have great strategies, but it will be a great failure if executed poorly. So just hire the right people, right? Turns out the answer is not what you think. At least according to a recent Harvard Business Review Article. Five Myths About Effective …

Is Balance Possible?
Now here’s a frank perspective: Balance doesn’t work. So don’t even try. Accept the fact that the only way to really make something happen is to go “full out” at it, with everything you have.

B Corp As A Competitive Edge?
Last week, I attended a celebration for B corps in Colorado. These are for-profit companies certified by a nonprofit called B Lab for achieving social and environmental goals along with business ones. What I noticed differently from other discussions among B Corps in the past, was a stronger focus not only on this vibrant community …
Privacy Overview
- Economy & Markets
- Digital Life

Business Plan vs. Business Strategy

Business plans are an essential facet of any business venture; they provide a clear operational structure. On the other hand, a business strategy offers a framework under which new ideas and decisions improve company performance.
The management outlines business strategies for every department to achieve a common goal. Firms need to review their business strategies to align their operations with the prevailing market trends. In extreme circumstances, managers fire staff to hire the right personnel. The move is deemed fit to incorporate relevant skills that can help a company achieve its objectives. A concerted effort between various departments in the organization is critical to attaining the set business strategies.
This article spotlights a few aspects of why firms need a business plan and clear business strategies to help achieve long-term and short-term goals.

Business Plan
A business plan is a drafted framework that guides the operations of a company. A company's business plan draws a clear road map for the effective execution of business goals. The future of a company relies on the initial business plan and its development.
Essential elements of a business plan include market analysis, competitive analysis, financial projections, management plan, marketing strategy, and budging. This provides the proper framework under which the business is going to operate.
Every business requires a business plan to help strategize and actualize the stakeholders' business ideas. Therefore, it is easier to achieve long-term and short-term business objectives by drafting a clear business plan.
Business Strategy
Contrary to a business plan, which is drafted from the onset of a business venture, the management can roll out a business strategy to transform its operations at any time. Customer satisfaction and product differentiation are among the elements managers focus on during restructuring.
New product features, lowering prices, selling on credit, and offering a discount to prospects are some of the strategies most organizations roll out to woo their clients. Notably, a business strategy focuses on injecting new ideas and concepts in a bid to improve performance.
To ensure success in business, a clear organizational structure, creativity, innovation, and market analysis play a critical role in achieving success. Most of the actions and ideas rolled out under this context aim to help a company have the upper hand against immediate competitors.
Characteristics of an Effective Business Plan
An effective business plan focuses on helping an organization to realize short term and long term objectives.
An effective business plan should have specific objectives. Rather than a general approach, specific business objectives are targeted to help bridge existing gaps and address immediate needs. Some companies tend to come up with several business objectives and lose the original goal set initially. If not handled with care, a company is likely to lose direction. Pair down objectives if the business plan has too many.
Align with Business Needs
The driving force behind a successful organization relies on setting objectives aligned with the business needs. Concepts rolled out without factoring in the needs of a company tend to fall short of the target. Eventually, achieving a return on investment becomes challenging due to the lack of an effective business framework.
A realistic business plan is easy to execute and implement. Setting up unrealistic targets and objectives in the initial business plan makes it difficult to measure results, identify gaps, and develop proper ideas to spar growth. Unrealistic expectations are difficult to achieve and may be a recipe for chaos within the organization.

Characteristics of an Effective Business Strategy
Effective business strategies support the company's business plan.
Includes a Business Plan
Though most organizations rely on initial business plans during operations, the business strategy depends on objectives spelled out in the business plan. A good business strategy relies on a business plan to fully accomplish the set goals by leading managers in the proper direction. The effective decision-making process requires the involvement of every party in a business venture.
Though the strategic business plan may be changed to suit the prevailing market demands, the intentions should be clear to help the workforce understand how to align their operations with existing concepts.
A tactical approach to an organization's strategic goals can be realized through a concerted approach by all the organization departments. It is necessary to roll out realistic concepts that can easily be implemented.
Unrealistic strategies may be difficult to actualize, leading to loss of company focus and possibly collapse. The bottom line in achieving exceptional results through any new business strategy requires a collective approach to avoid misleading the entire organization.
A business plan serves an essential purpose of offering direction in running an organization, any business strategy rolled out should be in line with the business plan. The two elements work hand in hand to achieve a common goal. The critical disparity between these two documents is apparent. A business strategy focuses on initiating an idea to change a company's current focus. A business plan is a solid framework that guides the general operation of the entire organization.
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.
Keir Starmer: Britain's Methodical New Leader

No Holiday For Biden As Debate Crisis Cleanup Continues

Beryl Foreshadows Future Hurricanes, Says UN Weather Agency

India's World Cup Winners Return To PM Modi Praise, Victory Parade

US Faces Lowest Home Affordability Since 2007

Air Pollution Drives 7% Of Deaths In Big Indian Cities: Study

Biden's Childhood Hometown 'Embarrassed' By Debate Meltdown

US Trade Deficit Expands Less Than Expected In May: Govt

Colombian Dens Of Iniquity Recycled To Serve Victims

Chad Rangers Battle To Protect Park From Poachers, Local Farmers
The magazine of Glion Institute of Higher Education
- Strategic planning vs business planning: how they’re both key to success

Any thriving hospitality business needs thorough planning to make sure it succeeds. If you’ve heard the terms business planning and strategic planning, you might think they’re interchangeable, but they’re actually two distinct things companies need at different times for continued success.
The biggest difference is that business plans are mostly used when you are starting to build a business so you can quickly and smoothly create your vision. Strategic planning is what existing companies use to grow and improve their businesses.
If you’re looking for a career in hospitality management, it’s important to know the difference between the two and how to use them to best effect. In this article, we’ll go over what strategic planning and business planning are and how they are important to running a successful hospitality business.
We’ll also look at how you can learn to harness different planning methods and get the skills needed to develop your career.
Business planning
A business plan is one of the first things a fledgling business will draft. Alternatively, it can be used to set business goals when launching a new product or service.
The business plan will usually look at short-term details and focus on how things should run for around a year or less. This will include looking at concepts such as:
- What the business idea is
- Short-term goals
- Who your customers are
- What your customers need
- What investment or financing you will need to start your business
- How you make revenue
- What profitability to expect
- How you can appeal to potential shareholders
- What the short-term operational needs of the business are
- What the company’s values are
- What the budget is for different parts of the business
This means market analysis and research are vital when you are making a business plan.
What are the objectives of business planning?
The primary objective of a business plan is to have all the main details of your business worked out before you start. This will give you a roadmap to use when you launch your business or when you start offering a different product or service.
For example, if you wanted to become an event planner and open your own event planning business, your plan might include how to get funds to rent an office and pay staff.
Strategic planning

A strategic plan is where you set out the company’s goals and define the steps you will need to take to reach those goals.
A strategic plan would include:
- What current capabilities the company has
- Making measurable goals
- A full strategy for business growth
- How the company’s values, mission and vision tie in with the services and products the company intends to offer
- Who in the organization will handle certain roles
- What the timeline is for reaching certain goals
- A SWOT analysis, looking at the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats in the company
- Examining the external environment for factors that will affect your company using a PEST (political, economic, social and technological) analysis
A strategic plan can be a long-term blueprint. You might find you use basically the same strategic plan for several years.
What is the objective and strategy of planning?
The aim of a strategic plan is to provide a tool that allows you to improve your business, grow the company, streamline processes or make other changes for the health of your business. Strategy implementation and meeting strategic objectives should generally lead to growth.
What is the difference between business planning and strategic planning?
There are a few major differences between strategic planning and business planning, which are outlined below.
Scope and time frame
A strategic plan is usually long-term, typically covering at least two to five years. By contrast, a business plan usually covers a year or less, since this is roughly how long it usually takes for a business to become established.
A business plan focuses on starting a business in its early stages. A strategic plan is used to guide the company through later stages. Put simply, the business plan is about direction and vision, while the strategic plan focuses on operations and specific tactics for business growth.
Stakeholders
A strategic plan will be presented to stakeholders and employees to make sure everyone knows what is going on in the company. This will help reassure everyone with a stake or role in the business.
By comparison, a business plan will often be shown to investors or lenders to help show the business idea is worth funding.
Flexibility and adaptability
A strategic plan typically has more flexibility. This is because it is meant to be in place for a longer period of time and the company should already be established. There is more leeway for refining strategy evolution, while your business plan should remain stable.
Similarities between business planning and strategic planning
Both of these activities will require some of the same analytical components, such as market analysis, financial projections and setting objectives you can track. Of course, both also require you to be highly organized and focused to ensure your business model or strategy development is appropriate for your business.
When to use strategic planning vs business planning

As we’ve already mentioned, you’ll generally use a business plan when you’re setting up a business or moving in a new direction. This will dictate much of the day-to-day running of a business. You would use strategic planning when you want to work on growth and drive innovation.
Can a business plan be used for strategic planning?
No, a business plan and a strategic plan are two different concepts with specific goals. While a business plan outlines short or mid-term goals and steps to achieve them, a strategic plan focuses on a company’s mid to long-term mission and how to accomplish this.
If you want to prepare for success, you need to make sure you are using the right type of plan.
Integrating strategic planning and business planning
While the two plans are different, you may end up using them together to ensure optimal success. As with any type of management role, such as hotel management , strategic and business plan management requires effective communication between different departments.
This includes different strategy managers as well as strategic and operational teams. You also need to make sure that, when you are using either plan, you find the right balance between flexibility and strict adherence to the plan. With strategic planning, this means constant strategy evaluation to assess your tactics and success.
Can strategic planning and business planning be used simultaneously?
In many hospitality careers , you’ll want to juggle growth and new directions, so you could end up using both planning types. However, it’s most common for the two to be distinct. This is because you’ll generally be using a business plan only when you are starting a new venture.
What are the career prospects in strategic and business planning?
There are plenty of options for what you can do if you have skills in strategic planning and business planning. Almost every management role will require these planning skills, including how to write strategic planning documents and measure success.
If you want to work in the hospitality sector, you could look into hotel planning and other careers with a business management degree . These will enable you to grow and nurture a business, but there is also a lot of scope to start your own business. Great planning skills can give you a real competitive advantage.
World-class degrees for making your mark in business
If you want the skills and insider knowledge to guide a business from inception to expansion, our courses provide expert teaching and real-world experience.

What skills do I need for a career in planning?
If you want to work in planning and management, you should work on various skills, such as:
- Decision-making
- Analytical skills
- Risk assessment knowledge
- Market analysis and forecasting
- Team management
- Communication, both written and verbal
- Organization
What qualifications can help with a career in strategic planning or business planning?
If you want to work in hotel planning and management, the most common route is to get a hospitality degree from a well-respected hospitality school in Switzerland . This will help you get the skills and knowledge you need to properly plan businesses as well as handle the execution of these plans.
Business degrees also teach you many transferable skills, such as good communication with your strategy team or data analysis, that you can use in almost any role in hospitality. They can also reduce the need to work your way up through the hospitality industry.
How can hospitality school help with planning careers?
Attending hospitality school can help you learn skills dedicated to hospitality as well as more general management, business and planning skills. This includes everything from how to handle a team to specifics such as hotel revenue management strategies .
If you find a hospitality school offering professional hospitality internships , you’ll also get experience in managing hotels and hospitality venues, helping you leap ahead in your career.
Hospitality degrees to kickstart your career
Our international business course combines leading industry expertise with essential internships to provide an exceptional foundation for a thriving career in the hospitality industry.

Both strategic and business planning are vital to build and grow a business. While business planning focuses on setting up the business and handling investment, vision and overall goals, strategic planning concentrates on growing the business and processing operational efficiency and resource allocation on a longer-term basis.
If you want to learn how to develop a hotel business plan or manage a hospitality venue, one of the best ways to get started is to study for a hospitality degree. This will give you hands-on experience of the strategic planning process or business management as well as the skills you need to succeed.
Photo credits Main image: Westend61/Westend61via Getty Images

BUSINESS OF LUXURY

GLION SPIRIT

Hospitality internships

LISTENING TO LEADERS
LIVING WELL

HOSPITALITY UNCOVERED

WELCOME TO GLION.
This site uses cookies. Some are used for statistical purposes and others are set up by third party services. By clicking ‘Accept all’, you accept the use of cookies
Privacy Overview
Strategy Explained
- Business Strategy
- Creating a Successful Strategy
- Corporate Strategy
- The Role of Leaders
- Related Topics
All strategy is based on understanding competition. Michael Porter’s frameworks help explain how organizations can achieve superior performance in the face of competition. Strategy defines the company’s distinctive approach to competing and the competitive advantages on which it will be based. A good competitive strategy is one that creates unique value for a particular set of customers.
Key Concepts
Making trade-offs, fit across the value chain, thinking strategically, competing to be the best vs. competing to be unique.

Strategy starts with thinking the right way about competition. Many managers compete to be “the best”—but this is a dangerous mindset that leads to a destructive, zero-sum competition that no one can win. Competing to be unique, on the other hand, is the basis of a sound business strategy that leads to a positive-sum competition with multiple winners.
Setting the Right Financial Goals
Managers should also think about setting proper financial goals for the company. Pleasing today’s shareholders is not the right goal. The fundamental goal of a company is superior long-term return on invested capital (ROIC) . Only if you achieve strong ROIC are you creating true economic value, which says that you can produce a product f or a price that’s greater than the cost of making it (including the cost of capital employed). Revenue growth is good only if superiority in ROIC is achieved and sustained.
Levels of Strategy
There are two fundamental levels of strategy: corporate level strategy and business unit strategy . Cor p orate strategy defines what set of businesses to compete in, while business unit strategy describes how to compete in each distinct business or industry.
While both are essential, business units typically account for 90% or more of economic performance—and therefore it is the focus of Michael Porter’s strategy work. The business unit, and not the company overall, is the core level of strategy.
Business strategy
Competitive advantage is won or lost at the business unit level. To achieve competitive advantage, companies must position themselves strategically within their industries.
Corporate strategy
In diversified companies, corporate leaders can enhance competitive advantage by capturing synergies across business units within the corporate portfolio.
The Five Forces
The Five Forces is a framework for assessing competition in any industry by analyzing the industry’s structure and profitability. Five Forces analysis is the first step in thinking about strategy, about how to shift the forces in your favor, and where to establish a unique positioning.
Terminology
The terms “business unit strategy,” “business strategy” and “competitive strategy” are often used interchangeably in Porter's work.

Business Plan Development
Masterplans experts will help you create business plans for investor funding, bank/SBA lending and strategic direction
Investor Materials
A professionally designed pitch deck, lean plan, and cash burn overview will assist you in securing Pre-Seed and Seed Round funding
Immigration Business Plans
A USCIS-compliant business plan serves as the foundation for your E-2, L-1A, EB-5 or E-2 visa application
Customized consulting tailored to your startup's unique challenges and goals
Our team-based approach supports your project with personal communication and technical expertise.
Pricing that is competitive and scalable for early-stage business services regardless of industry or stage.
Client testimonials from just a few of the 18,000+ entrepreneurs we've worked with over the last 20 years
Free tools, research, and templates to help with business plans & pitch decks
Understanding The Distinction Between a Business Plan & Business Planning
In the dynamic world of entrepreneurship, our choice of words matters. Our vocabulary can often become a veritable alphabet soup of jargon, acronyms, and those buzzwords (I'm looking at you, "disrupt").
And let's not get started on business cliches – "circle back," "synergy," “deep-dive,” etc.
Yet sometimes, it's worth pausing to consider the words we casually sprinkle around in our business conversations. In a previous article, we explored the differences between strategic and tactical business planning , two related but distinct approaches to guiding a business. Now, we're going to delve into another pair of terms that often get used interchangeably but have unique implications: "business plan" (the noun) and "business planning" (the verb).
The business plan, a noun, is a tactical document. It's typically created for a specific purpose, such as securing a Small Business Administration (SBA) loan . Think of it as a road map – it outlines the route and the destination (in this case, the coveted bank loan). But once you've reached your tactical goal (in this case, getting the loan), it often gets shoved in the glove compartment, forgotten as part of the organization's action plan until the next road trip (i.e., additional funding ).
Business planning is not a static concept, but rather a dynamic verb. It's an ongoing process that necessitates continual adjustments. It's about creating a holistic, interconnected value-creating strategic plan that benefits all stakeholders. This includes attracting top-tier employees, ensuring a return on lending or investment, and making a positive impact on the community, whether online or in real life.
That being said, the customer remains at the heart of this process. Without customers, there are no sales, no revenue, and no value. Everything else is contingent on this key element.
If we were to compare the business plan to a map, then business planning would be the journey. It's a continuous process of making strategic decisions, adapting to new paths, and steering the business towards its goals. Sometimes, it even involves redefining objectives midway.
So, let's do a "deep-dive" (I couldn't resist) into these two terms, examining their application in the real world. Along the way, we'll uncover some tools that can aid us in the ever-evolving process of strategic business planning and the more finite task of crafting a winning business plan.
The Business Plan is a Document
Alright, let's take a closer look at a phrase we've all tossed around: the business plan. Imagine it as the detailed blueprint of your organization's goals, strategies, and tactics. It's like the North Star for your entrepreneurial ship, shedding light on the key questions: what, why, how, and when (speaking of questions, here are some FAQs about the business plan ).
Writing a solid business plan isn't easy , especially if you're just dipping your toes into the world of business planning. But don’t worry; we'll get to that (eventually).
So, let's break it down. What does a business plan document consist of, exactly?
- Executive Summary: Just as it sounds, this is a quick overview of the nitty-gritty that's in the rest of your business plan. It's the introduction to your organization, highlighting your mission statement and serving up the essential details like ownership, location, and structure.
- Company Overview: This is where you will detail your products and/or services, their pricing, and the operational plan. If you're opening a restaurant, this section is where you present your menu, and it's also where you talk about your ingredient sourcing, the type of service you'll provide, and the ambiance you're aiming for.
- Market Analysis Summary: This section demands a comprehensive analysis of your industry, target market, competitors, and your unique selling proposition. Without access to top-notch (and often not free) research tools, it can be challenging to find current industry data. Check out our guide on the best market research tools to get started.
- Strategy and Implementation Summary: Here, you'll lay out your short-term and long-term objectives along with the strategies you'll implement to attract and retain customers. This is where you’ll talk about all the different marketing and sales strategies you'll use to charm your future customers.
- Management Summary: This is your chance to spotlight your company's key personnel. Detail the profiles of your key leaders, their roles, and why they're perfect for it. Don't shy away from acknowledging talent gaps that need to be filled, and do share how you plan to fill them!
- Pro Forma Financials: This is where you get down to the dollars and cents with a detailed five-year revenue forecast along with crucial financial statements like the balance sheet and the profit & loss statement.
A business plan is an essential instrument, not just for securing funding, but also for communicating long-term goals and objectives to key stakeholders. But, while a business plan is essential for many circumstances, it's important to understand its scope and limitations. It's a tactical tool, an important one, but it's not the be-all and end-all of business strategy. Which brings us to our next point of discussion: business planning.
Business Planning is a Process
If we view the business plan as a blueprint, then business planning is the architect. But let's be clear: we're not building just any old house here. We're building the Winchester Mystery House of business. Just as the infamous Winchester House was constantly under construction , with new rooms being added and old ones revamped, so too is your business in a state of perpetual evolution. It's a dynamic, ongoing process, not a one-and-done event.
In the realm of business planning, we're always adding 'rooms' and 'corridors' – new products, services, and market strategies – to our 'house'. And just as Sarah Winchester reputedly consulted spirits in her Séance Room to guide her construction decisions, we consult our customers, market data, and strategic insights to guide our strategy. We're in a constant state of assessing, evolving, executing, and improving.
Business planning touches all corners of your venture. It includes areas such as product development, market research, and strategic management. It's not about predicting the future with absolute certainty – we’re planners, not fortune tellers. It's about setting a course and making calculated decisions, preparing to pivot when circumstances demand it (think global pandemics).
Business planning is not a 'set it and forget it' endeavor. It's akin to being your company's personal fitness coach, nudging it to continually strive for better. Much like physical fitness, if you stop the maintenance, you risk losing your hard-earned progress.
Business Planning Case Study: Solo Stove
Now that summer is here, my Solo Stove stands as a tangible testament to effective business planning.
For those unfamiliar, Solo Stove started with a simple yet innovative product – a smoke-limiting outdoor fire pit that garnered over $1.1 million on Kickstarter in 2016, far exceeding its original objective. Since then, it has expanded its portfolio with products tailored to outdoor enthusiasts. From flame screens and fire tools to color-changing flame additives, each product is designed to fit seamlessly into modern outdoor spaces, exuding a rugged elegance that resonates with their target audience.
This strategic product development, a cornerstone of business planning, has allowed Solo Stove to evolve from a product to a lifestyle brand. By continually listening to their customers, probing their desires and needs, and innovating to meet those needs, they've built a brand that extends beyond the products they sell.
Their strategy also includes a primary "Direct To Consumer" (DTC) revenue model, executed via their e-commerce website. This model, while challenging due to increased customer acquisition costs, offers significant benefits, including higher margins since revenue isn’t split with a retailer or distributor, and direct interaction with the customer.
Through its primary business model, Solo Stove has amassed an email database of over 3.4 million customers . This competitive advantage allows for ongoing evaluation of customer needs, driving product innovation and improvement, and enabling effective marketing that strengthens their mission. The success of this approach is evident in the company's growth: from 2018 to 2020, Solo Stove’s revenue grew from $16 million to $130 million , a 185% CAGR.
While 85% of their revenue comes from online DTC channels, Solo Stove has also enhanced their strategic objectives by partnering with select retailers that align with their reputation, demographic, and commitment to showcasing Solo Brands’ product portfolio and providing superior customer service.
Solo Stove's success underscores how comprehensive business planning fosters regular assessment, constant evolution, and continual improvement. It's more than setting goals – it's about ceaselessly uncovering ways to deliver value to your customers and grow your business.
However, even successful businesses like Solo Stove can explore additional strategic initiatives for growth and diversification, aligning with their strategic direction and operational planning. For instance, a subscription model could provide regular deliveries of products or a service warranty, creating a consistent revenue stream and increasing customer loyalty. Alternatively, a B2B model could involve partnerships with adventure tourism operators, who could purchase Solo Stove products in bulk.
These complementary business models, when integrated into the operational plan, could support the primary DTC model by driving customer acquisition, providing ongoing revenue streams and expanding the customer base. This strategic direction ensures that Solo Stove continues to thrive in a competitive market.
The Interplay between the Business Plan (Noun) and Business Planning (Verb)
In the realm of business strategy, there's an intriguing chicken-and-egg conundrum: which comes first, the business plan or business planning? The answer is both straightforward and complex: they're two sides of the same coin, each indispensable in its own right and yet inextricably linked.
The process of business planning informs and modifies the business plan, just as the business plan provides a strategic foundation for the planning process. This interplay embodies the concept of Model-Based Planning™, where the business model serves as a guide, yet remains flexible to the insights and adaptations borne out of proactive business planning.
Let's revisit the Solo Stove story to elucidate this concept. Their business model, primarily direct-to-consumer, laid the groundwork for their strategy. Yet, it was through continuous business planning – the assessment of customer feedback, market trends, and sales performance – that they were able to refine their model, expand their product portfolio, and enhance their growth objectives. Their business plan wasn't a static document but a living entity, evolving through the insights gleaned from ongoing business planning.
So, how can you harness the power of both the tactical business plan and strategic business planning in your organization? Here are a few guiding principles:
- Embrace Model-Based Planning™: Start with a robust business model that outlines your strategic plan. But remember, this isn't set in stone—it's a guiding framework that will evolve over time as you gain insights from your strategic planning process.
- Make business planning a routine: Regularly review and update your business plan based on your findings from market research, customer feedback, and internal assessments. Use it as a living document that grows and adapts with your business.
- Foster open communication: Keep all stakeholders informed about updates to your business plan and the insights that informed these changes. This promotes alignment and ensures everyone is working towards the same goals.
- Be agile and adaptable: A key part of business planning is being ready to pivot when necessary . Whether it's a global pandemic or a shift in consumer preferences, your ability to respond swiftly and strategically to changing circumstances is crucial for long-term success.
Fanning the Flames: From Planning to Plan
The sparks truly ignite when you understand the symbiotic relationship between tactical business plans, strategic business planning, and the achievement of strategic goals. Crafting a tactical business plan (the noun) requires initial planning (the verb), but then you need to embark on continuous strategic planning (the verb) to review, refine, and realign your strategic business plan (the noun). It's a rhythm of planning, execution, review, and adjustment, all guided by key performance indicators.
Business planning, therefore, isn't a one-off event, but rather an active, ongoing process. A business plan needs constant nurturing and adjustment to stay relevant and guide your organization's path to success. This understanding frames your business plan not as a static document, but as a living, breathing entity, evolving with each step your business takes and each shift in the business landscape. It's a strategic roadmap, continually updated to reflect your organization's objectives and the ever-changing business environment.

How to Write a Management Summary for Your Business Plan
Entrepreneurs are often celebrated for their uncanny ability to understand others – their customers, the market, and the ever-evolving global...

Understanding Venture Debt vs Venture Capital
Despite growth in sectors like artificial intelligence, venture capital funding has seen better days. After peaking at $347.5 billion in 2021, there...

Going Beyond Writing: The Multifaceted Role of Business Plan Consultants
Most people think of a professional business plan company primarily as a "business plan writer." However, here at Masterplans, we choose to approach...
UK election: What has Labour promised to do if elected?
- Medium Text

HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE
Immigration, climate and energy, constitutional reforms.
Sign up here.
Reporting by Kylie MacLellan; Editing by Alistair Smout and Toby Chopra
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron
Biden is now deporting more people than Trump
Both President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump have pledged to return more migrants to their home countries, with differing approaches as immigration has emerged as a top issue in the coming U.S. election rematch.

Best Retirement Plans for Employees
Best retirement plans for self-employed individuals.
- Best Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Other Retirement Savings Options
- Why You Should Trust Us
Best Retirement Plans for 2024: Choosing the Right Path for Your Future
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us and terms apply to offers listed (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate products and services to help you make smart decisions with your money.
Why Start Saving for Retirement Now?
Financial experts all agree: The sooner you start saving, the better. Retirement savings accounts offer long-term wealth-building features like compounding, tax advantages, and retirement-focused investment strategies.
Compound interest allows you to earn interest on your interest. The longer your money grows, the faster it accumulates and the closer you are to achieving a financially secure retirement. Contributing a little here and there is better than not contributing at all.
Moreover, retirement plans like IRAs and 401(k)s offer tax benefits. You can contribute pre-tax money to lower your taxable income today. Or you can contribute after-tax money for tax-free growth and withdrawals.
Here are Business Insider's editors' top picks for the best retirement plans in 2024.
401(k) Plans
401(k)s are popular retirement savings plans offered by for-profit companies. Employees can open a traditional 401(k) or a Roth 401(k). Traditional 401(k)s grow with pre-tax dollars, but Roth 401(k)s rely on after-tax contributions, just like with IRAs.
Employees can contribute up to $23,000 in 2024, and individuals age 50 and older can contribute additional "catch-up" contributions of $7,500.
Many 401(k)s offer employer-matching contributions. Your employer matches up to a certain limit for every dollar you put into your account. This is generally considered "free money" toward your retirement. For instance, if you make $50,000 annually, and your company matches 50% of your 401(k) contributions up to 5% of your salary, you would need to contribute $2,500 into your account to receive the full match amount. Your employer would then contribute an additional $1,250 a year.
403(b) Plans
403(b)s, or tax-sheltered annuities, are retirement plans for public school employees, tax-exempt organizations, churches, and other nonprofit companies. Similar to a 401(k), 403(b)s may offer the benefit of an employer match. You can contribute pre-tax or after-tax money.
If you're under 50, you can contribute up to $23,000 in 2024. Employees 50 and up can contribute an additional $7,500. In addition to pre-tax and after-tax contributions, you can contribute to your 403(b) by allowing your employer to withhold money from your paycheck to deposit into the account.
Thrift Savings Plans
Thrift savings plans (TSPs) are retirement accounts for federal and uniformed services employees. Like 401(k)s, these plans let you contribute pre- or after-tax dollars. But, unlike many 401(k) employer matches, most TSPs offer a full 5% contribution match. Your employer will match your contributions up to 5% of your salary.
The annual contribution limit for 2024 is $23,000. The catch-up contribution limit is $7,500.
457(b) plans are retirement savings accounts offered by certain state and local governments and tax-exempt organizations. Like 403(b)s, you can contribute to your 457(b) plan by asking your employer to withhold a portion of your paycheck and deposit it in your retirement plan. Some employers allow you to make Roth contributions.
The annual contribution limit for 2024 is $23,000. The catch-up contribution limit is $7,500. Folks 50 and older can contribute up to the annual additions limit, currently $69,000.
Pension Plans
Pension plans are retirement plans fully funded by your employer, who are required to make regular contributions toward your retirement. However, depending on the plan's terms, you may not have control over how the money is invested.
There are two main types of pension plans: the defined contribution plan and the defined benefit plan. 401(k)s are technically considered defined-contribution pension plans, and your employer is not responsible if your investments perform poorly.
Traditional pension plans are defined benefit plans (plans with fixed, pre-established benefits). Employers are liable to provide retirement funds for a certain dollar amount, calculated based on employee earnings and employment years.
Solo 401(k)
Solo 401(k)s are an option for business owners who work for themselves and have no employees. They can contribute as both an employer and employee (and spouses of business owners may be able to contribute as well), meaning they can contribute twice as much. You can make pre- or post-tax (Roth) contributions to your account.
As an employee, you can defer up to $23,000 of your self-employed income in 2024. If you're 50 or older, you can make an additional $7,500 catch-up contribution. As an employer, you can contribute up to $23,000, plus the catch-up contribution if you're 50 or older. The total contribution limit is $76,500.
Simplified employee pension (SEP) IRAs are retirement vehicles managed by small businesses or self-employed individuals. According to the IRS, employees (including self-employed individuals) are eligible if they are 21 years old, have worked for the employer for at least three of the last five years, and have made a minimum of $750.
SEP IRAs also require that all contributions to the plan are 100% vested. This means that each employee holds immediate and complete ownership over all contributions to their account, including any employer match. You can contribute up to $69,000 or 25% of your employee's compensation 2024.
Vesting protects employees against financial loss. For instance, according to the IRS, an employer can forfeit amounts of an employee's account balance that isn't fully vested if that employee hasn't worked more than 500 hours in a year for five years.
SIMPLE IRAs are for self-employed individuals or small businesses with 100 employees or less. According to the IRS, these retirement plans require employers to match each employee's contributions on a dollar-for-dollar basis up to 3% of the employee's salary.
To qualify, employees (and self-employed individuals) must have made at least $5,000 in the last two years and expect to receive that amount during the current year. But once you meet this requirement, you'll be 100% vested in all your SIMPLE IRA's earnings, meaning you have immediate ownership over your and your employer's contributions.
Employees can contribute up to $16,000 in 2024. You can also add a catch-up contribution of $3,500 if you're 50 or older.
Payroll Deduction IRAs
Small businesses and self-employed people can set up employee IRAs even simpler. With payroll deduction IRAs, businesses delegate most of the hard work to banks, insurance companies, and other financial institutions.
After determining which institutions their employer has partnered with, employees can set up payroll deductions with those institutions to fund their IRAs. These accounts are generally best for employees who don't have access to other employer-sponsored retirement plans like 401(k)s and 457(b)s.
For 2024, you can contribute up to $7,000 in annual contributions and up to $1,000 in annual catch-up contributions for employees aged 50 or older.
Best Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs)
One of the most appealing components of independent retirement plans like IRAs is that you can open one as long as you've got taxable (earned) income. And even if you have an employer-sponsored retirement account, you can usually set up a traditional IRA, Roth IRA, and other independent retirement accounts.
Traditional IRA
Traditional IRAs let you save with pre-tax contributions toward your retirement savings. You'll pay tax when you withdraw during retirement. Traditional IRAs are recommended for higher-income workers who prefer to receive a tax deduction benefit now rather than later.
The 2024 contribution limit is $7,000, with up to $1,000 in catch-up contributions.
Roth IRAs are funded by after-tax dollars, meaning you pay taxes on your contributions now and make tax-free withdrawals later. As long as you're eligible, experts recommend Roth IRAs for early-career workers who expect to be in a higher tax bracket when they withdraw. Traditional and Roth IRAs share the same contribution limits: $7,000 in 2024, with up to $1,000 in catch-up contributions.
If you want to open one of the best Roth IRAs , single filers can only contribute the maximum amount in 2024 if their modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is less than $146,000. Married couples must earn less than $230,000 annually to contribute the full amount in 2024. You can still contribute less if you earn a little more, though.
You can find your MAGI by calculating your gross (before tax) income and subtracting any tax deductions from that amount to get your adjusted gross income (AGI), then adding back certain allowable deductions.
Spousal IRAs
There's also an option for married couples where one spouse doesn't earn taxable income. Spousal IRAs allow both spouses to contribute to a separate IRA as long as one spouse is employed and earns taxable income. This account allows the nonworking spouse to fund their own IRA.
In 2024, each can contribute $7,000 (or $8,000 if they are 50 or older) for up to $16,000 annually.
Rollover IRAs
The best rollover IRAs let you convert your existing employer-sponsored retirement plan into an IRA, something experts generally recommend doing when you leave a job for a few reasons: primarily because you have more control over the investment options in an IRA than in a 401(k), and also because it's easier to consolidate your accounts for record-keeping.
Many online brokerages and financial institutions offer rollover IRAs; some will even pay you to transfer your employer-sponsored plan to an IRA.
Self-Directed IRAs (SDIRAs)
You can fund a self-directed IRA using traditional or Roth contributions ($7,000 and contribution limits in 2024, plus another $1,000 for catch-up contributions). But the difference between these accounts is mainly one of account custody and investment choices.
Unlike traditional and Roth IRAs, the IRS requires that all SDIRAs have a certified custodian or trustee who manages the account. These third parties handle the setup process and administrative duties of the IRA (e.g., executing transactions and assisting with account maintenance).
SDIRAs also give investors access to a wider range of investment options. With traditional and Roth IRAs, you're limited to mutual funds, ETFs, stocks, and other traditional investments. But, SDIRAs allow you to invest in alternative assets like real estate, precious metals, and cryptocurrencies .
Nondeductible IRAs
Nondeductible IRAs are for people who earn too much to get the full tax benefits of an IRA. Contributions for these accounts aren't tax deductible, meaning you'll fund your IRA with post-tax dollars like a Roth IRA. The difference is that you'll still have to pay taxes on any earnings or interest from the account once you withdraw at age 59 1/2.
Annuities are investment vehicles purchased from insurance companies at a premium. You'll receive periodic payouts during retirement once you purchase an annuity using pre-tax or after-tax dollars. Annuities offer a reliable income stream for retirees and reassurance they won't outlive their savings.
The funds in an annuity can also be invested. Before you start receiving payouts, the investment gains grow tax-free, but you'll still be liable to pay income tax. Plus, annuities have limited liquidity and high fees that may diminish potential gains.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are savings accounts designed to cover medical expenses but can double as retirement savings. Once you're 65, you can withdraw the funds from your HSA penalty-free for non-medical expenses.
While an HSA isn't a great main retirement savings vehicle, it can be a great addition to a different long-term savings account. In addition to penalty-free withdrawals on qualifying expenses, HSAs are funded with pre-tax dollars and grow-tax-free. But you'll still be subject to income tax.
In 2024, you can contribute up to $4,150 for self-coverage and $8,300 for family coverage. Folks 55 and older can contribute an additional $1,000 catch-up contribution.
Choosing the Best Retirement Plan for You
If you're not a small-business owner or self-employed, the best retirement plan for you usually depends on your type of employer, marital status, and short- and long-term savings goals.
However, for most employer-sponsored retirement accounts, you can decide whether to make pre-tax or post-tax (Roth) contributions to your account. Roth contributions are best for those who expect to pay more in taxes as they age, but you should consider pre-tax contributions if you don't mind paying taxes when you withdraw money from your account in retirement.
You can boost your retirement savings even more by opening a separate IRA in addition to your employer-sponsored plan (you can still save toward retirement with an IRA if you're unemployed).
FAQs About Retirement Plans
Your best retirement option depends on your income, employer, financial situation, time horizon, and goals. If you can access a retirement savings account through your employer, especially a pension or 401(k) plan, that is likely your best option. If not, a traditional or Roth IRA offers tax advantages, compounding power, and flexible investment options.
A traditional or Roth IRA may be a better retirement saving account than a 401(k) due to the low fees and flexibility. Although 401(k)s come with great benefits like an employer match, they have high fees that can eat away at gains. An IRA may be a better option if your employer is not covering those fees.
A Roth IRA may be the better option, depending on your situation. In most cases, a 401(k) is the stronger retirement account due to the convenience of automatic payroll deduction and the additional benefit of an employer match. However, Roth IRAs can double as emergency funds. A Roth IRA may be better if you're looking for increased flexibility and Roth tax benefits.
Why You Should Trust Us: Our Expert Panel For The Best Retirement Plans
We interviewed the following investing experts to see what they had to say about retirement savings plans.
- Sandra Cho , RIA, wealth manager, and CEO of Pointwealth Capital Management
- Tessa Campbell , Investment and retirement reporter at Personal Finance Insider
What are the advantages/disadvantages of investing in a retirement plan?
Sandra Cho:
"The main advantage is the tax implications of the account. Depending on the account, taxes will either be deferred or not included at all. For employer-sponsored retirement plans like 401(k)s, contributions to the plan are made with pre-tax funds, and the account grows tax-deferred. Taxes are then owed upon withdrawal.
"Roth IRAs, on the other hand, are contributed to with post-tax funds but grow tax-free. Both should be included in an investor's portfolio. Another advantage is that 401(k)s often have an employer matching component. That is, an employer will match your contributions up to a certain point (usually around 3% of your salary).
"The disadvantage is that retirement accounts have a max contribution limit. Another disadvantage is that these funds cannot be used until age 59 1/2. For younger investors, that can be a long time wait."
Tessa Campbell:
"Tax benefits and compound interest are two of the major advantages of contribution to a retirement savings plan like a 401(k) or individual IRA. Depending on the kind of plan you open (traditional or Roth), you can benefit from contributions after- or post-tax dollars. In addition, some 401(k) plans are eligible for employer-sponsored matches, which are essentially free money.
"The disadvantage of a retirement plan is that you won't be able to access the funds in your account penalty-free until you're at least 59 1/2 years old. Unless there are no other options, early withdraws from a retirement savings plan isn't advised."
Who should consider opening a retirement plan?
"Every individual should be investing through a retirement plan if they have the financial capability to. At the minimum, investors should try to contribute up to the matching amount for their 401(k) and the maximum amount for their Roth IRA. The growth in these funds compounds over time, helping to enhance the long-term return."
Tessa Campbell:
"I can't think of a single person that wouldn't benefit from a retirement savings plan, other than maybe someone that is already well into retirement. Although some younger individuals don't feel the need to start contributing quite yet, it's actually better to open an account as soon as possible and take advantage of compound interest growth capabilities."
Is there any advice you'd offer someone who's considering opening a retirement plan?
"I would advise them to work with a financial advisor or trusted professional. This will give them insight into where they should be investing their money, whether that be a 401(k), Roth IRA, or another vehicle. There are plenty of people and sources out there who provide important information and can help you create a strong financial future."
"Don't contribute huge portions of your salary if it doesn't make sense with your budget. While contributing to a retirement savings plan is important, you must still afford your monthly expenses and pay down an existing debt. If you're having trouble establishing a reasonable budget, consult a financial advisor or planner for professional help."
- Credit cards
- Investing apps
- Retirement savings
- Cryptocurrency
- The stock market
- Retail investing
- Main content
The Daily Show Fan Page

Explore the latest interviews, correspondent coverage, best-of moments and more from The Daily Show.
The Daily Show
S29 E68 • July 8, 2024
Host Jon Stewart returns to his place behind the desk for an unvarnished look at the 2024 election, with expert analysis from the Daily Show news team.
Extended Interviews

The Daily Show Tickets
Attend a Live Taping
Find out how you can see The Daily Show live and in-person as a member of the studio audience.
Best of Jon Stewart

The Weekly Show with Jon Stewart
New Episodes Thursdays
Jon Stewart and special guests tackle complex issues.
Powerful Politicos

The Daily Show Shop
Great Things Are in Store
Become the proud owner of exclusive gear, including clothing, drinkware and must-have accessories.
About The Daily Show
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Biden’s Slipping Support
Donald j. trump leads the presidential race by six percentage points among likely voters in a new national survey..

Hosted by Michael Barbaro
Featuring Shane Goldmacher
Produced by Rob Szypko , Carlos Prieto and Nina Feldman
Edited by Devon Taylor
Original music by Marion Lozano , Diane Wong and Daniel Powell
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
A major Times poll has found that voters’ doubts about President Biden deepened after his poor performance in the first debate, with Donald J. Trump taking by far his biggest lead of the campaign.
Shane Goldmacher, a national political correspondent for The Times, explains what those results could mean for Mr. Biden’s future.
On today’s episode

Shane Goldmacher , a national political correspondent for The New York Times.

Background reading
Mr. Trump now leads Mr. Biden 49 percent to 43 percent among likely voters nationally.
Mr. Biden has been left fighting for his political future after his faltering debate performance. Read the latest .
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson, Nina Lassam and Nick Pitman.
Shane Goldmacher is a national political correspondent, covering the 2024 campaign and the major developments, trends and forces shaping American politics. He can be reached at [email protected] . More about Shane Goldmacher
Advertisement
Politics latest: Labour begins first week in government - as Tories to discuss way forward
New PM Keir Starmer is continuing his "reset" tour of the UK, as he seeks to improve the UK government's relations with the devolved administrations. Meanwhile, the Tory party board is due to meet to discuss the upcoming leadership contest.
Monday 8 July 2024 07:16, UK
- General Election 2024
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
- Starmer to meet leaders of Wales and Northern Ireland as UK tour continues
- His administration is announcing a policy blitz as the first full week kicks off
- Chancellor will deliver first major speech later
- Tory party board to meet to discuss leadership contest - reports
- Live reporting by Ben Bloch
Election fallout
- Starmer's challenges: Tackling exhausted NHS | Looming chaos abroad | Defence to dominate early days | Small boats plan? | Rift with scientists needs healing
- Listen: Politics At Jack And Sam's - what's in Starmer's in-tray?
- Results in every constituency
After Thursday's devastating general election defeat, the board of the Conservative Party is due to meet today to discuss the way forward, it is being reported.
A leadership contest will need to take place after Rishi Sunak announced his intention to resign as party leader after losing the election.
The board of the party is due to meet to discuss the way forward - although the exact timing and manner of the leadership contest is the decision of the 1922 Committee of backbench Tory MPs.
However, the committee does not have a chair or any members after the election - something that the party will likely have to resolve before a party leadership contest can take place.
Jockeying for position is already under way, and Sky News understands Jeremy Hunt has ruled himself out of the contest.
There are a number of other contenders, and Sky News takes a look at all the runners and riders - and their chances - below:
The Labour government has made a swathe of announcements as it enters its first full week in power, including plans to liberalise planning laws, boost dentist appointments and recruit more teachers.
The Starmer administration is taking action on the economy, health and education today, while the prime minister continues his tour of the UK in Northern Ireland.
Over the weekend, the new government made announcements on Ukraine and illegal migration.
Sir Keir Starmer, meanwhile, said he plans to have a closer relationship with Europe during a visit to Scotland.
After his visit to Northern Ireland, the prime minister is then set to meet with metro mayors before heading to a NATO summit in Washington DC on Tuesday.
Later today, Chancellor Rachel Reeves is set to speak with business leaders as she aims to "deliver on the government's mandate" and declare economic growth "a national mission" in her first major speech in office.
She will also propose changes to the planning system and "announce swift changes to unblock infrastructure and private investment".
Meanwhile, Health Secretary Wes Streeting is set to meet with the British Dentist Association to discuss Labour's campaign promise to deliver 700,000 urgent appointments.
And the same time, Education Secretary Bridget Phillipson is writing to those in the education workforce to highlight their importance to the new government.
Read more here:
Good morning!
Welcome back to the Politics Hub for the first full week of the new Labour government.
Here's what's coming up today:
- Sir Keir Starmer is continuing his tour of the UK, starting in Northern Ireland, followed by Wales;
- Chancellor Rachel Reeves will be giving her first major speech since taking office, and is expected to announce swift changes to unblock infrastructure and private investment;
- The broader Starmer administration is taking action on the economy, health and education today;
- Health Secretary Wes Streeting is set to meet with the British Dentist Association to discuss Labour's campaign promise to deliver 700,000 urgent appointments;
- Education Secretary Bridget Phillipson is writing to those in the education workforce to highlight their importance to the new government;
- Meanwhile, the record number of new MPs will be flooding to Westminster to set up their offices before being sworn in tomorrow;
- The Conservative Party is working out how to proceed after the devastating election defeat, with the party's board due to meet today to discuss the impending leadership contest.
We'll be discussing all of that and more with:
- Darren Jones , chief secretary to the Treasury, at 7.15am ;
- Kevin Hollinrake , Tory MP and former minister, at 8.15am .
Follow along for the latest political news.
That's all for tonight from the Politics Hub.
We'll be back tomorrow for Labour's first full week in power.
Before you go, here were today's main stories:
Sir Keir Starmer has met with Scotland's first minister, John Swinney.
Speaking to broadcasters afterwards, both men were asked if Scottish independence had come up in the talks.
After losing the vast majority of their seats last week, the SNP are arguing the Holyrood results in 2021 still give them a mandate to work towards leaving the UK.
Sir Keir - whose party grew sizeably in Scotland - has said he is targeting the next Holyrood election in 2026 to win even more of a mandate.
On the talks today, Sir Keir said he would not go into details of what was discussed - but said that the two "can work constructively together".
He added that he has made a commitment to deliver for Scotland, and that he plans to make good on it.
Sir Keir added that he took the opportunity to "reset relations" with the first and deputy first ministers.
He conceded there were "clearly differences of opinion" between them on constitutional matters, but the meeting was still constructive.
Mr Swinney said he "very much welcomed" the engagement and was committed to improving the relationship between the Scottish and UK administrations.
He said the SNP made clear they have "different views" on the constitution - but also that the SNP is taking time "to reflect and consider" the issues posed by the election.
They lost 39 of their 48 seats on Thursday.
Mr Swinney said the party intends to focus on issues like economic growth, child poverty, public services and net zero ahead of securing independence.
By Tim Baker , political reporter
The government is to divert tens of millions of pounds from the Rwanda scheme to set up a new Border Security Command (BSC), as it announces its plans to tackle illegal migration.
Home Secretary Yvette Cooper has also announced an audit of the monies sent to Kigali as the Labour administration looks to find ways to save or recoup cash committed under the Conservatives.
Ms Cooper plans to raise the issue of illegal migration with her European colleagues at the European Political Community Summit on 18 July.
Before the general election, Sir Keir Starmer said his party wanted to send around £75m a year to their new border scheme, from the scrapped Rwanda deportation programme.
The prime minister described the Conservative-era plans to send asylum seekers to Africa as "dead and buried" earlier this weekend.
However, it is understood Labour has not reached out to Kigali to discuss the way forward, as the previous UK government promised hundreds of millions of pounds for migrants to be sent to Rwanda.
Read more below:
Defence Secretary John Healey has already met with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy, with the Labour government making a new pledge on sending arms to Ukraine.
Mr Healey also promised that the equipment Rishi Sunak announced in April will be delivered within the first 100 days of the new government.
He said: "Our commitment to stand with the Ukrainian people is absolute, as is our resolve to confront Russian aggression and pursue Putin for his war crimes.
"This government is steadfast in our commitment to continue supplying military assistance and will stand shoulder to shoulder with our Ukrainian friends for as long as it takes."
The newly promised package of aid includes:
- A quarter of a million of 50 calibre ammunition;
- 90 anti-armour Brimstone missiles;
- 50 small military boats to support river and coastal operations;
- 40 de-mining vehicles;
- 10 AS-90 artillery guns;
- 61 bulldozers to help build defensive positions;
- Support for previously gifted AS-90s.
The new home secretary has wasted little time in getting started in her role - launching the promised Border Security Command (BSC) just days after her appointment.
The BSC was one of the cornerstones of Sir Keir Starmer's manifesto - Labour's solution to the small boats crisis.
The set-up is being at least partly funded by diverting £75m from the now cancelled Rwanda scheme.
Yvette Cooper has set out the first steps for establishing the BSC, which promises to "strengthen Britain's borders security and smash the criminal smuggling gangs making millions out of small boat crossings".
The plan includes the rapid recruitment of an "exceptional leader", which begins tomorrow.
'We can't carry on like this'
The new recruit, who is expected to take up their post in the coming weeks, will report directly to the office of the home secretary.
They will be tasked with providing a "strategic direction" across agencies, including the National Crime Agency, police, immigration enforcement, and the Border Force.
Ms Cooper is also preparing early legislation which will introduce new counter-terror style powers for the BSC, and has commissioned an investigation into the routes and tactics used by smuggling gangs.
She said it would be a "major step change" in the UK's efforts to tackle organised immigration crime, working "across Europe" and co-ordinating with prosecutors on the continent.
"We can't carry on like this," she said, adding the BSC will act as a "major upgrade" on the immigration system Labour have inherited.
Sunday might be a day of rest for many of us, but for prime ministers and political journalists there's no such thing.
Sir Keir Starmer has had a busy day, kicking off a tour of the UK, and there's been plenty else keeping us busy.
Here are the main things you need to know from today:
- Sir Keir Starmer has headed to Edinburgh for the start of a UK tour, where he'll meet with First Minister John Swinney;
- Speaking to Scottish Labour supporters beforehand, he promised to "serve every single person in Scotland" no matter who they voted for;
- The PM hopes his visits to Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland will signal a "reset in relations" between Westminster and the devolved administrations;
- It comes after Labour enjoyed a revival in Scotland to become the largest party north of the border, and kept that status in Wales too.
- New government ministers are settling into their roles and were quick to rule out introducing ID cards to tackle illegal immigration this morning;
- Labour's top team distanced themselves from the suggestion made by former party leader and prime minister Sir Tony Blair ;
- The new Northern Ireland secretary, Hilary Benn, also denied there was a case for a border poll on the island of Ireland after Sinn Fein became the largest Northern Irish party at Westminster.
- Meanwhile, the Tory leadership race may well be under way after several former ministers refused to rule themselves out;
- Robert Jenrick and Suella Braverman were among those on the media round this morning who indicated they could be up for replacing Rishi Sunak;
- But our political correspondent Darren McCaffrey says there are some in the party who want them to take their time before deciding, rather than rushing towards a right-wing candidate looking to stave off the threat from Reform UK.
You can also get the lowdown on the new prime minister's first few days from our Politics At Jack And Sam's podcast below:
Sir Keir Starmer has just spoken alongside the Scottish Labour leader Anas Sarwar, who introduced the new PM to a rapturous applause of party supporters in Edinburgh.
After a long intro from his Scottish colleague, Sir Keir says it's "hugely important" for him to visit the devolved nations as soon as possible.
"That was an incredible election result, a historic result and a real mandate for change - we start here," he says.
He says there's nothing "inevitable" about an election win, adding "we won because we campaigned as changed Labour".
"We [will] govern in the same spirit… we will serve the entirety of Scotland, we will serve every single person in Scotland because that change matters to everyone."
Our political correspondent Amanda Akass says the speech was a reminder of the unique opportunity Sir Keir has to unite the UK's devolved administrations.
Scottish Labour "really rose out of the ashes of their previous defeats" in this week's general election, she says, going from one MP to 37.
The PM wants those new MPs "to be a big part of the government in Westminster to deliver for the people of Scotland as part of that mandate for change".
He'll also be meeting First Minister John Swinney, as part of what he hopes will be a "reset" in relations between Westminster and Holyrood.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Existing companies use the strategic plan to grow their business, while entrepreneurs use business plans to start a company. There is also a different timeframe for each plan. Generally, a strategic plan is conducted over several years while a business plan, with all the right components, can operate in less than a year.
What is a strategic plan? In contrast to a business plan, a strategic plan sets out a company's goals and defines the actions it takes to get there. The audience is your own team. Its key purpose is to build alignment and decision-making capacity to ready your company for the future. For example, if a company's business model is ...
The scalability of a business plan vs. strategic plan. Another way to grasp the difference is by understanding the difference in 'scale' between strategic and business plans. Larger organizations with multiple business units and a wide variety of products frequently start their annual planning process with a corporate-driven strategic plan.
Strategic plans constitute the basis of operations and responsibilities within the business. These plans lay the paths out for each member of the organization to follow and define the functional outline and the key outcomes for every project and process within the business. A strategic plan goes on to define the operations and their outcomes ...
Business plans are usually 15-30 pages long. A strategic plan typically provides a high-level overview of the organization's goals and the strategies to achieve them without going deep into the business operations. Strategic plans are generally 10-15 pages long, but the length depends on various factors of the business.
A business plan usually lays the foundations of a company's business decisions and strategies at the ownership level. A strategic plan typically establishes the foundations of responsibilities and operations within an existing business. It explains the strategy for each team member to follow and defines the functional outline and significant ...
In contrast, setting strategy should push your organization outside its comfort zone - if you're doing it right. "Plans typically have to do with the resources you're going to spend. Those ...
A business plan helps a company allocate its resources effectively. It outlines the company's budget, cash flow, and profit and loss projections. A business plan helps a company make informed decisions about its operations and investments. Strategic plan vs business plan: Which matters more for leaders? Both strategic planning and business ...
The intended audiences for both a business plan and a strategic plan also differ. Business plans are meant for both internal (business owner, shareholders, and management team) and external (lenders, investors or suppliers) audiences. On the other hand, strategic plans are usually meant for internal audiences only, such as the organisation's ...
Unlike a traditional business plan, Cobello adds, strategic plans include a SWOT analysis (which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) and an in-depth action plan for the next six to 12 months. Strategic plans are action-based and take into account the state of the company and the industry in which it exists.
It's the tasks, milestones, and steps needed to drive your business forward. Typically an operational plan provides details for a 1-year period, while a strategic plan looks at a 3-5 year timeline, and sometimes even longer. The operational plan is essentially the roadmap for how you will execute your strategic plan.
A business plan, as described by the Center for Simplified Strategic Planning, Inc., aims to define "the initial goals and objectives of the company, its structure and processes, products and services, financial resources [and] all of the basics that go into forming a company " and getting it up and running. TAB offers its members a ...
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including: Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
A strategic plan differs from a business plan in terms of time horizon (long-term vs. short-term), purpose (guiding overall growth vs. launching a new venture), focus (high-level goals and ...
A business plan is more focused than a strategic plan, it should be a detailed report on the operations of the core business activities of the business or nonprofit. These efforts should outline everything from production to sales. It should include detailed information on costs, sales figures, suppliers, customer data, etc.
A business plan is a detailed document that outlines how a company will achieve its short-term and long-term goals. While it shares some elements with a strategic plan, a business plan is more focused on the day-to-day operations of the business. Key components of a business plan include:
In contrast, a strategic plan clarifies the long term direction of the organization; most business plans look at a shorter period of time, typically 2-3 years, and drills down thoroughly how the work will get done and dollars will be earned. Business plans typically take more resources, both internal and often external (in the form of ...
A good business strategy relies on a business plan to fully accomplish the set goals by leading managers in the proper direction. The effective decision-making process requires the involvement of ...
A business plan focuses on starting a business in its early stages. A strategic plan is used to guide the company through later stages. Put simply, the business plan is about direction and vision, while the strategic plan focuses on operations and specific tactics for business growth.
Levels of Strategy. There are two fundamental levels of strategy: corporate level strategy and business unit strategy. Cor p orate strategy defines what set of businesses to compete in, while business unit strategy describes how to compete in each distinct business or industry. While both are essential, business units typically account for 90% or more of economic performance—and therefore it ...
The business plan, a noun, is a tactical document. It's typically created for a specific purpose, such as securing a Small Business Administration (SBA) loan. Think of it as a road map - it outlines the route and the destination (in this case, the coveted bank loan). But once you've reached your tactical goal (in this case, getting the loan ...
Its plan focuses on wealth creation. It has said it will be "pro-business and pro-worker" and introduce a new industrial strategy, which will end short-term economic policy.
Explore the best retirement plans to grow your nest egg and secure a comfortable retirement. Compare 401(k)s, IRAs, and other savings options.
The source for The Daily Show fans, with episodes hosted by Jon Stewart, Ronny Chieng, Jordan Klepper, Dulcé Sloan and more, plus interviews, highlights and The Weekly Show podcast.
A Novel Legal Strategy for Mass Shooting Victims' Families Biden's Slipping Support Donald J. Trump leads the presidential race by six percentage points among likely voters in a new national ...
By Tim Baker, political reporter. The government is to divert tens of millions of pounds from the Rwanda scheme to set up a new Border Security Command (BSC), as it announces its plans to tackle ...