- View Record

TRID the TRIS and ITRD database

CAPACITY-CONSTRAINED TRAFFIC ASSIGNMENT IN NETWORKS WITH RESIDUAL QUEUES
This paper proposes a capacity-constrained traffic assignment model for strategic transport planning in which the steady-state user equilibrium principle is extended for road networks with residual queues. Therefore, the road-exit capacity and the queuing effects can be incorporated into the strategic transport model for traffic forecasting. The proposed model is applicable to the congested network particularly when the traffic demands exceed the capacity of the network during the peak period. An efficient solution method is proposed for solving the steady-state traffic assignment problem with residual queues. Then a simple numerical example is employed to demonstrate the application of the proposed model and solution method, while an example of a medium-sized arterial highway network in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, is used to test the applicability of the proposed solution to real problems.
- Find a library where document is available. Order URL: http://worldcat.org/oclc/8674831
- This work was substantially supported by a grant from the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (Project No. PolyU55/95E).
American Society of Civil Engineers
- Publication Date: 2000-3
- Features: Appendices; Figures; References; Tables;
- Pagination: p. 121-128
- Journal of Transportation Engineering
- Volume: 126
- Issue Number: 2
- Publisher: American Society of Civil Engineers
- ISSN: 0733-947X
- Serial URL: https://ascelibrary.org/journal/jtepbs
Subject/Index Terms
- TRT Terms: Algorithms ; Arterial highways ; Demand ; Equilibrium (Systems) ; Highway capacity ; Mathematical models ; Peak hour traffic ; Queuing ; Steady state ; Strategic planning ; Traffic assignment ; Traffic congestion ; Traffic flow ; Traffic forecasting ; Transportation planning ; Types of roads by network
- Geographic Terms: Sioux Falls (South Dakota)
- Subject Areas: Highways; Planning and Forecasting; I72: Traffic and Transport Planning;
Filing Info
- Accession Number: 00788957
- Record Type: Publication
- Contract Numbers: PolyU55/95E
- Files: TRIS, ATRI
- Created Date: Mar 20 2000 12:00AM
A Combined Modal Split and Traffic Assignment Model With Capacity Constraints for Siting Remote Park-and-Ride Facilities
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Path-Based Dynamic User Equilibrium Model with Applications to Strategic Transportation Planning
- Published: 09 September 2019
- Volume 20 , pages 329–366, ( 2020 )
Cite this article
- Babak Javani 1 &
- Abbas Babazadeh 1
506 Accesses
Explore all metrics
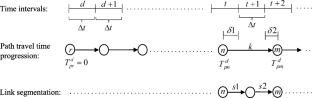
This study proposes an analytical capacity constrained dynamic traffic assignment (DTA) model along with an efficient path-based algorithm. The model can be applied to analyzing dynamic traffic demand management (TDM) strategies, but its specific feature is allowing for an evaluation of advanced traveler information systems (ATIS) within the strategic transportation planning framework. It is an extension of a former DTA model, where each link is given an infinite capacity and is assumed to be completely traversed inside any time interval it is reach by a path. Thereby, the length of time intervals should be very longer than the link travel times, and the link capacity constraints are overlooked. The paper rests on three key ideas to overcome these restrictions: (1) adding path-link fraction variables to the base model, allowing path flows to spread out over time intervals on long links; (2) uniformly dividing each link into smaller parts (segments), so that each part is more likely to be traversed inside a time interval; (3) imposing a dynamic penalty function on each link, thereby the capacity constraint can be included. The proposed DTA algorithm decomposes the augmented model in terms of origin-destination (OD) pairs and departure time intervals, and utilizes a dynamic column generation technique for generating active paths between the OD pairs. The optimal solution to a one-link network demonstrates that the model is able to approximate the dynamic flow propagation over a link with sensible accuracy. Besides, investigation of the results for a small test network reveals that the algorithm performs very well in computing temporal link flows and queuing delays. Finally, numerical experiments on a real life network indicate that the algorithm converges sufficiently fast and provides path information for each time interval. The network is further used to show the algorithm is capable of assessing a dynamic TDM strategy as well as an ATIS system.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
An excess-demand dynamic traffic assignment approach for inferring origin-destination trip matrices.
Chi Xie & Jennifer Duthie
A Path-Based Solution Algorithm for Dynamic Traffic Assignment
Caixia Li, Sreenatha Gopalarao Anavatti & Tapabrata Ray
Arrival Time Reliability in Strategic User Equilibrium
Michael W. Levin, Melissa Duell & S. Travis Waller
Ban XJ, Liu HX, Ferris MC, Ran B (2008) A link-node complementarity model and solution algorithm for dynamic user equilibria with exact flow propagations. Transp Res B Methodol 42(9):823–842
Article Google Scholar
Beckmann M, McGuire CB, Winsten CB (1956) Studies in the economics of transportation. Published for the Cowles Commission for Research in Economics by Yale University Press, New Haven
Google Scholar
Ben-Akiva M, Bierlaire M, Bottom J, Koutsopoulos H, Mishalani R (1997a) Development of a route guidance generation system for real-time application. In Proceedings of the IFAC Transportation Systems 97 Conference, Chania
Ben-Akiva ME, Koutsopoulos HN, Mishalani RG, Yang Q (1997b) Simulation laboratory for evaluating dynamic traffic management systems. J Transp Eng 123(4):283–289
Ben-Akiva ME, Gao S, Wei Z, Wen Y (2012) A dynamic traffic assignment model for highly congested urban networks. Transp Res C 24:62–82
Bliemer MC, Raadsen MP, Brederode LJ, Bell MG, Wismans LJ, Smith MJ (2017) Genetics of traffic assignment models for strategic transport planning. Transp Rev 37(1):56–78
Boyce DE, Lee DH, Janson BN, Berka S (1997) Dynamic route choice model of large-scale traffic network. J Transp Eng 123(4):276–282
Carey M (1987) Optimal time-varying flows on congested networks. Oper Res 35(1):58–69
Daganzo CF (1994) The cell transmission model: a dynamic representation of highway traffic consistent with the hydrodynamic theory. Transp Res B Methodol 28(4):269–287
Daganzo CF (1995) The cell transmission model, part II: network traffic. Transp Res B Methodol 29(2):79–93
Florian M, Mahut M, Tremblay N (2008) Application of a simulation-based dynamic traffic assignment model. Eur J Oper Res 189(3):1381–1392
Friesz TL, Bernstein D, Smith TE, Tobin RL, Wie BW (1993) A variational inequality formulation of the dynamic network user equilibrium problem. Oper Res 41(1):179–191
Friesz TL, Kim T, Kwon C, Rigdon MA (2011) Approximate network loading and dual-time-scale dynamic user equilibrium. Transp Res B Methodol 45(1):176–207
Friesz TL, Han K, Neto PA, Meimand A, Yao T (2013) Dynamic user equilibrium based on a hydrodynamic model. Transp Res B Methodol 47:102–126
Gentile G (2016) Solving a dynamic user equilibrium model based on splitting rates with gradient projection algorithms. Transp Res B Methodol 92:120–147
Golden B (1976) Technical note—shortest-path algorithms: a comparison. Oper Res 24(6):1164–1168
Han L, Ukkusuri S, Doan K (2011) Complementarity formulations for the cell transmission model based dynamic user equilibrium with departure time choice, elastic demand and user heterogeneity. Transp Res B Methodol 45(10):1749–1767
Han K, Friesz TL, Yao T (2013a) A partial differential equation formulation of Vickrey’s bottleneck model, part I: methodology and theoretical analysis. Transp Res B Methodol 49:55–74
Han K, Friesz TL, Yao T (2013b) A partial differential equation formulation of Vickrey’s bottleneck model, part II: numerical analysis and computation. Transp Res B Methodol 49:75–93
Han K, Friesz TL, Yao T (2013c) Existence of simultaneous route and departure choice dynamic user equilibrium. Transp Res B Methodol 53:17–30
Han K, Piccoli B, Szeto WY (2016) Continuous-time link-based kinematic wave model: formulation, solution existence, and well-posedness. Transportmetrica B: Transp Dyn 4(3):187–222
Han K, Eve G, Friesz TL (2019) Computing dynamic user equilibria on large-scale networks with software implementation. Netw Spat Econ 19(3):869–902
Hearn DW, Ribera J (1980) Bounded flow equilibrium problems by penalty methods. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Circuits and Computers, p 162–166
Janson BN (1991a) Dynamic traffic assignment for urban road networks. Transp Res B Methodol 25(2):143–161
Janson BN (1991b) Convergent algorithm for dynamic traffic assignment. Transp Res Rec (1328):69–80
Janson BN, Robles J (1995) Quasi-continuous dynamic traffic assignment model. Transp Res Rec (1493):199–206
Javani B, Babazadeh A (2017) Origin-destination-based truncated quadratic programming algorithm for traffic assignment problem. Transportation Letters 9(3):166–176
Javani B, Babazadeh A, Ceder A (2019) Path-based capacity-restrained dynamic traffic assignment algorithm. Transportmetrica B: Transp Dyn 7(1):741-764
Jayakrishnan R, Mahmassani HS, Hu TY (1994) An evaluation tool for advanced traffic information and management systems in urban networks. Transp Res C 2(3):129–147
Jin WL (2015) Point queue models: a unified approach. Transp Res B Methodol 77:1–16
Kachroo P, Shlayan N (2013) Dynamic traffic assignment: a survey of mathematical models and techniques. In: Advances in dynamic network modeling in complex transportation systems. Springer, New York, pp 1–25
Larsson T, Patriksson M (1995) An augmented Lagrangean dual algorithm for link capacity side constrained traffic assignment problems. Transp Res B Methodol 29(6):433–455
Lo HK, Szeto WY (2002a) A cell-based variational inequality formulation of the dynamic user optimal assignment problem. Transp Res B Methodol 36(5):421–443
Lo HK, Szeto WY (2002b) A cell-based dynamic traffic assignment model: formulation and properties. Math Comput Model 35(7):849–865
Mahut M, Florian M (2010) Traffic simulation with dynameq. In: Fundamentals of traffic simulation. Springer, New York, pp 323–361
Chapter Google Scholar
Mahut M, Florian M, Tremblay N, Campbell M, Patman D, McDaniel Z (2004) Calibration and application of a simulation-based dynamic traffic assignment model. Transp Res Rec 1876:101–111
Merchant DK, Nemhauser GL (1978a) A model and an algorithm for the dynamic traffic assignment problems. Transp Sci 12(3):183–199
Merchant DK, Nemhauser GL (1978b) Optimality conditions for a dynamic traffic assignment model. Transp Sci 12(3):200–207
Mun JS (2007) Traffic performance models for dynamic traffic assignment: an assessment of existing models. Transp Rev 27(2):231–249
Nie YM (2011) A cell-based Merchant–Nemhauser model for the system optimum dynamic traffic assignment problem. Transp Res B Methodol 45(2):329–342
Nie X, Zhang HM (2005a) A comparative study of some macroscopic link models used in dynamic traffic assignment. Netw Spat Econ 5(1):89–115
Nie X, Zhang HM (2005b) Delay-function-based link models: their properties and computational issues. Transp Res B Methodol 39(8):729–751
Nie YM, Zhang HM (2010) Solving the dynamic user optimal assignment problem considering queue spillback. Netw Spat Econ 10(1):49–71
Nie Y, Zhang HM, Lee DH (2004) Models and algorithms for the traffic assignment problem with link capacity constraints. Transp Res B Methodol 38(4):285–312
Nie YM, Ma J, Zhang HM (2008) A polymorphic dynamic network loading model. Comput Aided Civ Inf Eng 23(2):86–103
Papageorgiou M, Ben-Akiva M, Bottom J, Bovy PH, Hoogendoorn SP, Hounsell NB, Kotsialos A, McDonald M (2007) ITS and traffic management. Handbooks in operations research and management science, 14, p 715–774
Peeta S, Mahmassani HS (1995) System optimal and user equilibrium time-dependent traffic assignment in congested networks. Ann Oper Res 60(1):81–113
Ran B, Boyce DE, LeBlanc LJ (1993) A new class of instantaneous dynamic user-optimal traffic assignment models. Oper Res 41(1):192–202
Shahbandi MG, Babazadeh A (2019) Analysis of a joint entry-and distance-based cordon pricing scheme: a dynamic modeling approach. J Mod Transp 27(1):25–38
Shahpar AH, Aashtiani HZ, Babazadeh A (2008) Dynamic penalty function method for the side constrained traffic assignment problem. Appl Math Comput 206(1):332–345
Sheffi Y (1985) Urban transportation networks. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J
Szeto WY (2013) Cell-based dynamic equilibrium models. In: Advances in dynamic network modeling in complex transportation systems. Springer, New York, pp 163–192
Szeto WY, Wong SC (2012) Dynamic traffic assignment: model classifications and recent advances in travel choice principles. Cent Eur J Eng 2(1):1–18
Ukkusuri SV, Han L, Doan K (2012) Dynamic user equilibrium with a path based cell transmission model for general traffic networks. Transp Res B Methodol 46(10):1657–1684
Wardrop J (1952) Road paper. Some theoretical aspects of road traffic research. ICE Proc: Eng Div 1(3):325–362
Zhang HM, Nie Y, Qian Z (2013) Modelling network flow with and without link interactions: the cases of point queue, spatial queue and cell transmission model. Transportmetrica B: Transp Dyn 1(1):33–51
Ziliaskopoulos AK (2000) A linear programming model for the single destination system optimum dynamic traffic assignment problem. Transp Sci 34(1):37–49
Ziliaskopoulos AK, Waller ST, Li Y, Byram M (2004) Large-scale dynamic traffic assignment: implementation issues and computational analysis. J Transp Eng 130(5):585–593
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the three anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful comments and constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran
Babak Javani & Abbas Babazadeh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Abbas Babazadeh .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Javani, B., Babazadeh, A. Path-Based Dynamic User Equilibrium Model with Applications to Strategic Transportation Planning. Netw Spat Econ 20 , 329–366 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-019-09479-0
Download citation
Published : 09 September 2019
Issue Date : June 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-019-09479-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Analytical model
- Dynamic traffic assignment
- Path-based algorithm
- Advanced traveler information systems
- Dynamic traffic demand management
- Large scale network
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

A predictive dynamic traffic assignment model in congested capacity-constrained road networks
- Author & abstract
- 27 References
- 31 Citations
- Most related
- Related works & more
Corrections
- Tong, C. O.
- Wong, S. C.
Suggested Citation
Download full text from publisher, references listed on ideas.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Models and algorithms for the traffic assignment problem with link capacity constraints

Related Papers
Transportation Research Part B-methodological
Michael Patriksson
Tomer Toledo , Joseph Prashker
Applied Mathematics and Computation
Hedayat Zokaei-Aashtiani
Optimization
Torbjörn Larsson , Michael Patriksson
2019 IEEE 58th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC)
Kshama Dwarakanath
Torbjörn Larsson
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
Takuya Maruyama
Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board
Anthony Chen
The computational performance of five algorithms for the traffic assignment problem (TAP) is compared with that of mid- to large-scale randomly generated grid networks. The applied procedures include the Frank-Wolfe, PARTAN, gradient projection, restricted simplicial decomposition, and disaggregate simplicial decomposition algorithms. A statistical analysis is performed to determine the relative importance of various properties (network size, congestion level, solution accuracy, zone-node ratio) of the traffic assignment problem for the five selected algorithms. Regression models, which measure central processing unit time and number of iterations consumed by each algorithm using various factors and their combinations, are derived to provide a quantitative evaluation. Ultimately, the findings of this research will be useful in guiding transportation professionals to choose suitable solution algorithms and to predict the resulting algorithm performance in TAPs.
Transportmetrica A: Transport Science
Michael Florian
Transportation Research Record
This paper presents a mathematical programming model and solution method for the path-constrained traffic assignment problem, in which route choices simultaneously follow the Wardropian equilibrium principle and yield the distance constraint imposed on the path. This problem is motivated by the need for modeling distance-restrained electric vehicles in congested networks, but the resulting modeling and solution method can be applied to various conditions with similar path-based constraints. The equilibrium conditions of the problem reveal that any path cost in the network is the sum of corresponding link costs and a path-specific out-of-range penalty term. The suggested method, based on the classic Frank-Wolfe algorithm, incorporates an efficient constrained shortest path algorithm as its subroutine. This algorithm fully exploits the underlying network structure of the problem and is relatively easy to implement. Numerical results from the provided example problems clearly show how the equilibrium conditions are reshaped by the path constraint and how the traffic flow patterns are impacted by different constraint tightness levels.
RELATED PAPERS
Jurgen Hagmann
NICOLÒ FERRI
Ricardo Santos
Electra GONZÁLEZ
Journal of Hematopathology
Smart Learning Environments
ÖMER FARUK FATSA
Edossa Etissa , Ebisa Dufera
CoSMo | Comparative Studies in Modernism
Alessandro Casiccia
Imola Küllős
Jurnal Manajemen dan Bisnis Indonesia
Tuwanku Aria Auliandri
Mamudu Akudugu
Alain Chauvot
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
Benoit Schilter
Animal cognition
André Wunder
Cambridge Astrophysics Series
Juhan Frank
Hữu Thắng 28 Nguyễn
Analytical Chemistry
Kamil Wojciechowski
Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly
William R. Davie
Water Research
Mangroves and Salt Marshes
Jurgen Tack
Revista Brasileira de Ciências do Esporte
Ezequiel Müller
Communications Biology
Yuri K Peterson
Science of The Total Environment
Mehwish Jamil Noor
Amanda Newsom , Sarah Mohammed Hameed
Social Science Research Network
Elena Ianchovichina
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This paper proposes a capacity-constrained traffic assignment model for strategic transport planning in which the steady-state user equilibrium principle is extended for road networks with residual queues. Therefore, the road-exit capacity and the queuing effects can be incorporated into the strategic transport model for traffic forecasting.
In order to overcome problems of the implicit capacity approach in the investigation of congested transit networks, Papola et al. (2009) present the extension to scheduled services of an existing Dynamic Traffic Assignment (DTA) model based on a macroscopic representation of time-continuous flows proposed for multimodal networks. The transit ...
A model is provided to capture capacity phenomena in passenger traffic assignment to a transit network. These pertain to the interaction of passenger traffic and vehicle traffic: vehicle seat capacity drives the internal comfort, vehicle total capacity determines internal comfort and also platform waiting, passenger flows at vehicle egress and access interplay with dwell time, dwell time ...
The presence of capacity constraints, unfortunately, destroys the Cartesian product structure of the feasible set in classic TAP and results in a more complex model. The critical difficulty in solving the capacitated traffic assignment problem (CTAP) is that the subproblem becomes a multi-commodity minimum cost flow problem, whose computation ...
This paper proposes a capacity-constrained traffic assignment model for strategic transport planning in which the steady-state user equilibrium principle is extended for road networks with residual queues. Therefore, the road-exit capacity and the queuing effects can be incorporated into the strategic transport model for traffic forecasting.
For road traffic assignment problem with capacity constraints, one may refer to, e.g., Yang and Bell (1997); Tong and Wong (2000); Nie et al. (2004); Ryu et al. (2014). In order to show the ...
A combined modal split and traffic assignment model with capacity constraints is developed as a lower-level model, and a nested-logit model is adopted to manage the mode similarity. The upper-level optimization is conducted based on the generalized cost of the transportation system according to the budget and environmental limits.
@article{osti_20080362, title = {Capacity-constrained traffic assignment in networks with residual queues}, author = {Lam, W H.K. and Zhang, Y}, abstractNote = {This paper proposes a capacity-constrained traffic assignment model for strategic transport planning in which the steady-state user equilibrium principle is extended for road networks with residual queues.
A capacity-constrained traffic assignment model for strategic transport planning in which the steady-state user equilibrium principle is extended for road networks with residual queues is proposed and the road-exit capacity and the queuing effects can be incorporated into the strategic transport model for traffic forecasting. This paper proposes a capacity-constrained traffic assignment model ...
This study proposes an analytical capacity constrained dynamic traffic assignment (DTA) model along with an efficient path-based algorithm. The model can be applied to analyzing dynamic traffic demand management (TDM) strategies, but its specific feature is allowing for an evaluation of advanced traveler information systems (ATIS) within the strategic transportation planning framework. It is ...
As shown in Bliemer et al. (2014) and Brederode et al. (2019), static capacity constraint TA models already greatly improve accuracy in congested conditions compared to capacity-restrained TA models while maintaining scalability and stability properties required for strategic applications.Approaches using a semi-dynamic capacity restrained TA model (first two rows in Table 1) lack this ...
Although capacity constraints in traffic assignment can represent many realistic features, ... A Strategic Flow Model of Traffic Assignment in Static Capacitated Networks. Operations Research, Vol. 52, No. 2, 2004, pp. 191-212. Crossref. Google Scholar. 34. Spiess H. Technical Note—Conical Volume-Delay Functions.
By extending static traffic assignment with explicit capacity constraints, quasi-dynamic traffic assignment yields more realistic results while avoiding many disadvantages of a dynamic assignment. ... "Static Traffic Assignment with Queuing: Model Properties and Applications." Transportmetrica A: Transport Science 15 : 179-214. doi: 10. ...
Downloadable (with restrictions)! In this paper, a predictive dynamic traffic assignment model in congested capacity-constrained road networks is formulated. A traffic simulator is developed to incrementally load the traffic demand onto the network, and updates the traffic conditions dynamically. A time-dependent shortest path algorithm is also given to determine the paths with minimum actual ...
A passenger traffic assignment model dealing with capacity constraints for transit networks is provided. The CapTA model constitutes a framework for introducing capacity effects, in addition to those included: in-vehicle capacity in terms of seated and standing passengers, the exchange capacity of vehicles at stations and the line capacity on vehicle flows. Traffic equilibrium is intrinsically ...
This note resolves a hitherto open question as to whether a dynamic traffic assignment model, which was developed and analyzed in earlier issues of this journal, satisfies a "constraint qualification.". It is shown that the model does in fact satisfy a constraint qualification, which establishes the validity of the optimality analysis ...
In this paper, the formulation of a predictive dynamic traffic assignment model in congested capacity-constrained road networks has been given. With a traffic simulator to load traffic flows onto the network and a time-dependent shortest path algorithm, the method of successive averages has been employed to determine the dynamic user-optimal ...
The multi-modal transportation network equilibrium approach proposed in this article takes into account the capacity constraints of different travel modes and solves the path overlapping problem in combined modes. A multi-modal urban transportation network provides travelers with diversified and convenient travel options. The study of multi-modal traffic assignment encounters great challenges ...
The presence of capacity constraints, unfortunately, destroys the Cartesian product structure of the feasible set in classic TAP and results in a more complex model. The critical difficulty in solving the capacitated traffic assignment problem (CTAP) is that the subproblem becomes a multi- commodity minimum cost flow problem, whose computation ...
DOI: 10.1016/J.SBSPRO.2012.09.794 Corpus ID: 18991912; A Passenger Traffic Assignment Model with Capacity Constraints for Transit Networks @article{Leurent2011APT, title={A Passenger Traffic Assignment Model with Capacity Constraints for Transit Networks}, author={Fabien Leurent and Ektoras Chandakas and Alexis Poulh{\`e}s}, journal={Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences}, year={2011 ...
In this paper, the formulation of a predictive dynamic traffic assignment model in congested capacity-constrained road networks has been given. With a traffic simulator to load traffic flows onto the network and a time-dependent shortest path algorithm, the method of successive averages has been employed to determine the dynamic user-optimal ...
An Augmented Lagrangean Dual Algorithm for Link Capacity Side Constrained Traffic Assignment Problems. Transportation Research Part B , Vol. 29, 1995, pp. 433-455. Crossref
In this paper, we propose a novel capacity constrained static traffic assignment model with (vertical) point queues (i.e., we do not consider spillback) that aims to describe the locations of the queues in a more realistic way using a fairly general analytical problem formulation that can be efficiently solved.