TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Feb 11, 2022

90+ Must-Know Metaphor Examples to Improve Your Prose
What figure of speech is so meta that it forms the very basis of riddles? The answer: a metaphor.
As Milan Kundera wrote in The Unbearable Lightness of Being : “Metaphors are dangerous. Metaphors are not to be trifled with.” Yet, paradoxically, they are an inescapable part of our daily lives — which is why it’s all the more important to understand exactly how they function.
To help, this article has a list of 97 metaphor examples to show you what they look like in the wild. But if you have a moment to spare, let's learn a bit more about what a metaphor is.
What is a metaphor?
A metaphor is a literary device that imaginatively draws a comparison between two unlike things. It does this by stating that Thing A is Thing B. Through this method of equation, metaphors can help explain concepts and ideas by colorfully linking the unknown to the known; the abstract to the concrete; the incomprehensible to the comprehensible. It can also be a rhetorical device that specifically appeals to our sensibilities as readers.
To give you a starting point, here are some examples of common metaphors:
- “Bill is an early bird.”
- “Life is a highway.”
- “Her eyes were diamonds.”
Note that metaphors are always non-literal. As much as you might like to greet your significant other with a warhammer in hand (“love is a battlefield”) or bring 50 tanks of gasoline every time you go on a date (“love is a journey”), that’s not likely to happen in reality. Another spoiler alert: no, Katy Perry doesn't literally think that you're a firework. Rather, these are all instances of metaphors in action.
How does a metaphor differ from a simile?
Simile and metaphor are both figures of speech that draw resemblances between two things. However, the devil’s in the details. Unlike metaphors, similes use like and as to directly create the comparison. “Life is like a box of chocolates,” for instance, is a simile. But if you say, “Life is a highway,” you’re putting a metaphor in motion.
The best way to understand how a metaphor can be used is to see it in practice — luckily, we’ve got a bucket-load of metaphor examples handy for you to peruse.
The Ultimate List of 90+ Metaphor Examples
Metaphors penetrate the entire spectrum of our existence — so we turned to many mediums to dig them up, from William Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet to the Backstreet Boys’ ancient discography. Feel free to skip to your section of interest below for metaphor examples.
Literature Poetry Daily Expressions Songs Films Famous Quotations
Metaphors in literature are drops of water: as essential as they are ubiquitous. Writers use literary metaphors to evoke an emotional response or paint a vivid picture. Other times, a metaphor might explain a phenomenon. Given the amount of nuance that goes into it, a metaphor example in a text can sometimes deserve as much interpretation as the text itself.
Metaphors can make prose more muscular or imagery more vivid:
1. “Exhaustion is a thin blanket tattered with bullet holes.” ― If Then , Matthew De Abaitua
2. “But it is just two lovers, holding hands and in a hurry to reach their car, their locked hands a starfish leaping through the dark.” ― Rabbit, Run , John Updike
3. “The sun in the west was a drop of burning gold that slid near and nearer the sill of the world.” — Lord of the Flies , William Golding
4. “Bobby Holloway says my imagination is a three-hundred-ring circus. Currently I was in ring two hundred and ninety-nine, with elephants dancing and clowns cart wheeling and tigers leaping through rings of fire. The time had come to step back, leave the main tent, go buy some popcorn and a Coke, bliss out, cool down.” — Seize the Night , Dean Koontz
Writers frequently turn to metaphors to describe people in unexpected ways:
5. “But soft, what light through yonder window breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun!” — Romeo & Juliet , William Shakespeare
6. “Who had they been, all these mothers and sisters and wives? What were they now? Moons, blank and faceless, gleaming with borrowed light, each spinning loyally around a bigger sphere. ‘Invisible,’ said Faith under her breath. Women and girls were so often unseen, forgotten, afterthoughts. Faith herself had used it to good effect, hiding in plain sight and living a double life. But she had been blinded by exactly the same invisibility-of-the-mind, and was only just realizing it.” ― The Lie Tree , Frances Hardinge
7. “’I am a shark, Cassie,’ he says slowly, drawing the words out, as if he might be speaking to me for the last time. Looking into my eyes with tears in his, as if he's seeing me for the last time. "A shark who dreamed he was a man.’” ― The Last Star , Rick Yancey
8. “Her mouth was a fountain of delight.” — The Storm , Kate Chopin
9. “The parents looked upon Matilda in particular as nothing more than a scab. A scab is something you have to put up with until the time comes when you can pick it off and flick it away.” — Matilda , Roald Dahl
10. “Mr. Neck storms into class, a bull chasing thirty-three red flags." — Speak , Laurie Anderson
11. “’Well, you keep away from her, cause she’s a rattrap if I ever seen one.’” — Of Mice and Men , John Steinbeck
Which famous author do you write like?
Find out which literary luminary is your stylistic soulmate. Takes one minute!
Metaphors can help “visualize” a situation or put an event in context:
12. “But now, O Lord, You are our Father, We are the clay, and You our potter; And all of us are the work of Your hand.” —Isaiah 64:8
13. “He could hear Beatty's voice. ‘Sit down, Montag. Watch. Delicately, like the petals of a flower. Light the first page, light the second page. Each becomes a black butterfly. Beautiful, eh? Light the third page from the second and so on, chainsmoking, chapter by chapter, all the silly things the words mean, all the false promises, all the second-hand notions and time-worn philosophies.’” — Fahrenheit 451 , Ray Bradbury
To entertain and tickle the brain, metaphor examples sometimes compare two extremely unlike things:
14. “Delia was an overbearing cake with condescending frosting, and frankly, I was on a diet.” ― Lament: The Faerie Queen's Deception , Maggie Stiefvater
15. "The sun was a toddler insistently refusing to go to bed: It was past eight thirty and still light.” — Fault in Our Stars , John Green
16. “If wits were pins, the man would be a veritable hedgehog.” ― Fly by Night , Frances Hardinge
17. “What's this?" he inquired, none too pleasantly. "A circus?" "No, Julius. It's the end of the circus." "I see. And these are the clowns?" Foaly's head poked through the doorway. "Pardon me for interrupting your extended circus metaphor, but what the hell is that?” ― Artemis Fowl , Eoin Colfer
18. “Using a metaphor in front of a man as unimaginative as Ridcully was the same as putting a red flag to a bu — the same as putting something very annoying in front of someone who was annoyed by it.” ― Lords and Ladies , Terry Pratchett
Metaphors can help frame abstract concepts in ways that readers can easily grasp:
19. “My thoughts are stars I cannot fathom into constellations.” — Fault In Our Stars , John Green
20. “If you can look into the seeds of time, and say which grain will grow and which will not, speak then to me.” — Macbeth , William Shakespeare
21. “Memories are bullets. Some whiz by and only spook you. Others tear you open and leave you in pieces.” ― Kill the Dead , Richard Kadrey
22. “Wishes are thorns, he told himself sharply. They do us no good, just stick into our skin and hurt us.” ― A Face Like Glass , Frances Hardinge
23. “’Life' wrote a friend of mine, 'is a public performance on the violin, in which you must learn the instrument as you go along.” ― A Room with a View , E.M. Forster
24. “There was an invisible necklace of nows, stretching out in front of her along the crazy, twisting road, each bead a golden second.” ― Cuckoo Song , Frances Hardinge
25. “All the world’s a stage, and all the men and women merely players.” — As You Like It , William Shakespeare
Particularly prominent in the realm of poetry is the extended metaphor: a single metaphor that extends throughout all or part of a piece of work . Also known as a conceit , it is used by poets to develop an idea or concept in great detail over the length of a poem. (And we have some metaphor examples for you below.)
If you’d like to get a sense of the indispensable role that metaphors play in poetry, look no further than what Robert Frost once said: “They are having night schools now, you know, for college graduates. Why? Because they don’t know when they are being fooled by a metaphor. Education by poetry is education by metaphor.”
Poets use metaphors directly in the text to explain emotions and opinions:
26. She must make him happy. She must be his favorite place in Minneapolis. You are a souvenir shop, where he goes to remember how much people miss him when he is gone. —“ Unrequited Love Poem ,” Sierra DeMulder
27. She is all states, and all princes, I. Nothing else is. Princes do but play us; compared to this, All honour's mimic, all wealth alchemy. —“ The Sun Rising ,” John Donne
28. I watched a girl in a sundress kiss another girl on a park bench, and just as the sunlight spilled perfectly onto both of their hair, I thought to myself: How bravely beautiful it is, that sometimes, the sea wants the city, even when it has been told its entire life it was meant for the shore. —“I Watched A Girl In A Sundress,” Christopher Poindexter
Extended metaphors in particular explore and advance major themes in poems:
29. All our words are but crumbs that fall down from the feast of the mind. Thinking is always the stumbling stone to poetry. A great singer is he who sings our silences. How can you sing if your mouth be filled with food? How shall your hand be raised in blessing if it is filled with gold? They say the nightingale pierces his bosom with a thorn when he sings his love song. —“ Sand and Foam ,” Khalil Gibran
30. But a BIRD that stalks down his narrow cage / Can seldom see through his bars of rage / His wings are clipped and his feet are tied So he opens his throat to sing. —“ Caged Bird ,” Maya Angelou
31. Two roads diverged in a wood, and I— I took the one less traveled by / And that has made all the difference. —“ The Road Not Taken ,” Robert Frost
32. Marriage is not a house or even a tent it is before that, and colder: the edge of the forest, the edge of the desert the edge of the receding glacier where painfully and with wonder at having survived even this far we are learning to make fire —“ Habitation ,” Margaret Atwood
33. These poems do not live: it's a sad diagnosis. They grew their toes and fingers well enough, Their little foreheads bulged with concentration. If they missed out on walking about like people It wasn't for any lack of mother-love. —“ Stillborn ,” Sylvia Plath
34. Hope is the thing with feathers / That perches in the soul / And sings the tune without the words / And never stops at all. —“ Hope Is The Thing With Feathers ,” Emily Dickinson
Daily Expressions
Here’s some food for thought (35): you’ve probably already used a metaphor (or more) in your daily speech today without even realizing it. Metaphorical expressions pepper the English language by helping us illustrate and pinpoint exactly what we want to say. As a result, metaphors are everywhere in our common vocabulary: you may even be drowning in a sea (36) of them as we speak. But let’s cut to our list of metaphor examples before we jump the shark (37).
38. Love is a battlefield.
39. You’ve given me something to chew on.
40. He’s just blowing off steam.
41. That is music to my ears.
42. Love is a fine wine.
43. She’s a thorn in my side.
44. You are the light in my life.
45. He has the heart of a lion.
46. Am I talking to a brick wall?
47. He has ants in his pants.
48. Beauty is a fading flower.
49. She has a heart of stone.
50. Fear is a beast that feeds on attention.
51. Life is a journey.
52. He’s a late bloomer.
53. He is a lame duck now.
Which writing app is right for you?
Find out here! Takes 30 seconds
Metaphors are a must-have tool in every lyricist’s toolkit. From Elvis to Beyonce, songwriters use them to instinctively connect listeners to imagery and paint a visual for them. Most of the time, they find new ways to describe people, love — and, of course, break-ups. So if you’re thinking, “This is so sad Alexa play Titanium,” right now, you’re in the right place: here’s a look at some metaphor examples in songs.
54. You ain't nothin' but a hound dog / Cryin' all the time —“Hound Dog,” Elvis Presley
55. You're a fallen star / You're the getaway car / You're the line in the sand / When I go too far / You're the swimming pool / On an August day / And you're the perfect thing to say — “Everything,” Michael Buble
56. 'Cause baby you're a firework / Come on show 'em what your worth / Make 'em go "Oh, oh, oh!" / As you shoot across the sky-y-y — “Firework,” Katy Perry
57. I'm bulletproof nothing to lose / Fire away, fire away / Ricochet, you take your aim / Fire away, fire away / You shoot me down but I won't fall, I am titanium —“Titanium,” David Guetta
58. Life is a highway / I wanna ride it all night long / If you're going my way / I wanna drive it all night long —“Life Is A Highway,” Rascal Flatts
59. She's a Saturn with a sunroof / With her brown hair a-blowing / She's a soft place to land / And a good feeling knowing / She's a warm conversation —“She’s Everything,” Brad Paisley
60. I'm a marquise diamond / Could even make that Tiffany jealous / You say I give it to you hard / So bad, so bad / Make you never wanna leave / I won't, I won't —“Good For You,’ Selena Gomez
61. Remember those walls I built / Well, baby, they're tumbling down / And they didn't even put up a fight / They didn't even make a sound —“Halo,” Beyonce
62. Did I ever tell you you're my hero? / You're everything, everything I wish I could be / Oh, and I, I could fly higher than an eagle / For you are the wind beneath my wings / 'Cause you are the wind beneath my wings —“Wind Beneath My Wings,” Bette Midler
63. You are my fire / The one desire / Believe when I say I want it that way —“I Want It That Way,” Backstreet Boys
64. Your body is a wonderland / Your body is a wonder (I'll use my hands) / Your body is a wonderland —“Your Body Is A Wonderland,” John Mayer
65. I'm walking on sunshine (Wow!) / I'm walking on sunshine (Wow!) / I'm walking on sunshine (Wow!) / And don't it feel good —“I’m Walking On Sunshine,” Katrina and the Waves
66. If you wanna be with me / Baby there's a price to pay / I'm a genie in a bottle / You gotta rub me the right way —“Genie in a Bottle,” Christina Aguilera
67. If God is a DJ, life is a dance floor / Love is the rhythm, you are the music / If God is a DJ, life is a dance floor / You get what you're given it's all how you use it —“God Is A DJ,” P!nk
68. If this town / Is just an apple / Then let me take a bite —“Human Nature,” Michael Jackson
69. I just wanna be part of your symphony / Will you hold me tight and not let go? —“Symphony,” Clean Bandit
70. My heart's a stereo / It beats for you, so listen close / Hear my thoughts in every note —“Stereo Hearts,” Gym Class Heroes
71. I'm the sunshine in your hair / I'm the shadow on the ground / I'm the whisper in the wind / I'm your imaginary friend —“I’m Already There,” Lonestar
Films can add a different angle to the concept of a metaphor: because it’s a visual medium, certain objects on-screen will actually represent whatever the filmmaker intends it to represent. The same principle applies, of course — there’s still a direct comparison being made. It’s just that we can see the metaphor examples with our own eyes now.
Films can visually make clear comparisons between two elements on the screen:
72. “What beautiful blossoms we have this year. But look, this one’s late. I’ll bet that when it blooms it will be the most beautiful of all.” —from Mulan
73. “Love is an open door Can I say something crazy? Will you marry me? Can I say something even crazier? Yes!” —from Frozen
Metaphors are used in dialogue for characters to express themselves:
74. “You're television incarnate, Diana. Indifferent to suffering, insensitive to joy.” — Network
75. “Life's a climb. But the view is great.” — Hannah Montana: the Movie
Famous Quotations
Did you know that Plato was using metaphors to express his thoughts all the way back in 427 BC? Since then, some of our greatest minds have continued to turn to metaphors when illuminating ideas in front of the general public — a practice that’s become particularly prominent in political speeches and pithy witticisms. Here’s a sample of some of the ways that famous quotes have incorporated metaphor examples in the past.
76. “All religions, arts and sciences are branches of the same tree.” —Albert Einstein
77. “A good conscience is a continual Christmas.” —Benjamin Franklin
78. “America has tossed its cap over the wall of space.” —John F. Kennedy
79. “I don't approve of political jokes; I have seen too many of them get elected.” —Jon Stewart
80. “Conscience is a man’s compass.” —Vincent Van Gogh
81. “In the depths of winter, I finally learned that within me there lay an invincible summer.” —Albert Camus
82. “Time is the moving image of eternity.” ―Plato
83. “Every human is a school subject. This is rather a metaphorical way of saying it, to put it straight, those you love are few, and the ones you detest are many.” ―Michael Bassey Johnson
84. “Even if you're on the right track, you'll get run over if you just sit there.” —Will Rogers
85. “Life is little more than a loan shark: it exacts a very high rate of interest for the few pleasures it concedes.” —Luigi Pirandello
86. “America: in the face of our common dangers, in this winter of our hardship, let us remember these timeless words. With hope and virtue, let us brave once more the icy currents, and endure what storms may come.” —Barack Obama
87. “Bolshevism is a ghoul descending from a pile of skulls. It is not a policy; it is a disease. It is not a creed; it is a pestilence.” —Winston Churchill
88. “Books are mirrors of the soul.” —Virginia Woolf
89. “My life has a superb cast, but I can't figure out the plot.” —Ashleigh Brilliant
90. “I feel like we’re all in a super shitty Escape Room with really obvious clues like, ‘vote’ and ‘believe women’ and ‘don’t put children in cages.’” — Natasha Rothwell
91. “I travel the world, and I'm happy to say that America is still the great melting pot — maybe a chunky stew rather than a melting pot at this point, but you know what I mean.” —Philip Glass
92. “Life is a long road on a short journey.” —James Lendall Basford
93. “What therefore is truth? A mobile army of metaphors, metonymies, anthropomorphisms: in short a sum of human relations which become poetically and rhetorically intensified, metamorphosed, adorned, and after long usage seem to a nation fixed, canonic and binding.” —Nietzsche
94. “Life is a foreign language: all men mispronounce it.” —Christopher Morley
95. “Dying is a wild night and a new road.” —Emily Dickinson
96. “And your very flesh shall be a great poem.” —Walt Whitman
And as a bonus gift, here’s one last metaphor for the road, from one of our brightest philosophers. We’ll let Calvin have the last word:
Did we miss any of your favorite metaphors? Have more metaphor examples for us? Leave them in the (non-metaphorical) box below and we'll add them right in.
6 responses
James Hubbs says:
21/10/2018 – 23:44
Very useful article. Thank you. However, Fahrenheit 451 was written by Ray Bradbury, not George Orwell.
↪️ Reedsy replied:
22/10/2018 – 00:42
Great spot, James! That's now been fixed. Glad that the article was useful :)
Jonboy says:
21/05/2019 – 19:11
That Sylvia Plath quote nailed me. Ouch! Haven't read it but have to now...
21/06/2019 – 17:02
Another metaphor I love is “I’m just like them— an ordinary drone dressed in secrets and lies.” It’s from Speak by Laurie Halse Anderson
DAVID COWART says:
18/11/2019 – 01:59
life is a highway is Tom Cochrane, not Rascal Flats
↪️ Martin Cavannagh replied:
22/11/2019 – 12:54
Rascal Flatts did a cover of the song. We were deciding between the two and decided that "Rascal Flatts" sounded funnier :D
Comments are currently closed.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

Man vs Nature: The Most Compelling Conflict in Writing
What is man vs nature? Learn all about this timeless conflict with examples of man vs nature in books, television, and film.

The Redemption Arc: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
Learn what it takes to redeem a character with these examples and writing tips.

How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph?
From fiction to nonfiction works, the length of a paragraph varies depending on its purpose. Here's everything you need to know.
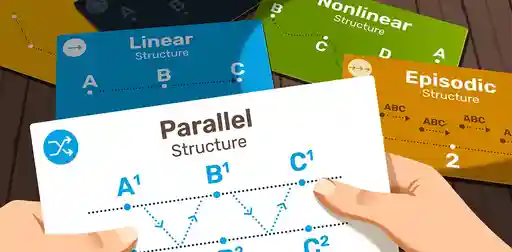
Narrative Structure: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
What's the difference between story structure and narrative structure? And how do you choose the right narrative structure for you novel?

What is the Proust Questionnaire? 22 Questions to Write Better Characters
Inspired by Marcel Proust, check out the questionnaire that will help your characters remember things past.

What is Pathos? Definition and Examples in Literature
Pathos is a literary device that uses language to evoke an emotional response, typically to connect readers with the characters in a story.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Bring your stories to life
Our free writing app lets you set writing goals and track your progress, so you can finally write that book!

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
College Nut
College Essays with Metaphors: A Guide to Crafting Powerful Personal Statements
What are college essays.
College essays are a crucial part of the application process, which can be the deciding factor in determining whether you get into your dream school. They are an opportunity for you to showcase your writing skills, creativity, and personality, all while convincing admissions officers that you are a good fit for their institution.
Why are Metaphors Important in College Essays?
Metaphors are a type of figure of speech that compares two things that may seem unrelated, but share common characteristics or traits. They add depth and meaning to your writing and allow you to express abstract or complex ideas in a more relatable and engaging way.
Using metaphors in your college essays can help you stand out from other applicants, as they demonstrate your ability to think critically, use language creatively, and connect seemingly disparate ideas. They can also make your essay more memorable and impactful, as they provide a unique perspective and show your personality and values.
An Example of a Metaphor in a College Essay
Imagine you are writing an essay about your passion for environmental activism. You could write: “I’ve always been drawn to the ocean like a moth to a flame. Its vastness and mystery have always fascinated me, but with every beach cleanup and marine life rescue, I feel like I’m slowly putting out the fire that threatens to consume it.” This metaphor compares the ocean to a flame and implies that the author is working to protect it from destruction.
How to Use Metaphors in College Essays
Using metaphors effectively in your college essays requires careful thought and planning. Here are some tips to help you incorporate metaphors into your writing:
Start with a brainstorming session: Think about the qualities, experiences, and emotions that define you and your story. Consider different objects or concepts that could represent these ideas, such as a rollercoaster, a puzzle, or a tree.
Choose a metaphor that fits your story: Once you have a list of potential metaphors, choose one that best represents your story and message. Make sure it is appropriate to the tone and topic of your essay.
Use the metaphor throughout your essay: Once you have chosen a metaphor, use it consistently throughout your essay to reinforce your message and create a cohesive narrative.
Don’t force it: While metaphors can be powerful tools, don’t force them into your essay if they don’t fit naturally. Use them sparingly and only where they add value to your writing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Metaphors in College Essays
While metaphors can add depth and meaning to your writing, they can also backfire if not used correctly. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using metaphors in your college essays:
Overusing clichés: While some metaphors are universally understood, using clichéd or overused metaphors can make your writing seem unoriginal and uninspired.
Being too abstract: While metaphors can be used to express abstract ideas, if they are too obscure or disconnected from your message, they can confuse readers and detract from your point.
Stretching the metaphor too far: While it’s important to use metaphors consistently throughout your essay, stretching them too far or using them inappropriately can undermine your credibility and make your writing seem contrived.
In conclusion, metaphors are powerful tools that can help you express complex ideas and create a more engaging and memorable college essay. By following the tips outlined above and avoiding common mistakes, you can use metaphors to showcase your unique perspective and stand out from other applicants.
Strong Personal Statements, Part 3: Extended Metaphors Add Cohesion
- August 22, 2018

We’re sharing exceptional personal statements from last year’s applicants to illustrate that a good personal statement can be on a variety of topics, but ultimately, showcases the student’s character, curiosity, and voice. These statements, written by students now enrolled at Emory University, were selected for a multitude of reasons, and we asked our admission staff to share what made each statement stand out.
This is one of a 5-part series on application writing; read Part 1 here , Part 2 here , Part 4 here , and Part 5 here .
Share an essay on any topic of your choice. It can be one you’ve already written, one that responds to a different prompt, or one of your own design.
“It’ll die.”
“No it won’t, I’ll be careful, I promise!”
“Let it go, Chul-Soo”
“But mom !”
Twelve years ago, my dad’s studies moved my family across the Pacific to a small university in the quiet New Jersey suburbs. That first night, my parents and I were exploring the campus grounds when I spotted lights sleepily blinking amidst the trees like stars. These stars I could run through, reach out and touch, gaze at up close, they were fireflies. Growing up in the hustle and bustle of the largest city in Korea, I’d never seen these luminous creatures before. Their beauty sparked curiosity and wonder in my five-year old imagination. One drifted near, and I tiptoed towards it, heart beating a little faster with giddy excitement. “Gotcha!” I breathlessly watched my cupped hands flicker. “Mom! Can I keep it?”
“Sorry honey, you can’t.”
“Please?”
I was devastated to let the lightning bug go. It had been my first companion in America, where everything and everyone was unknown to me. I’d wanted so badly for it to stay…
I hold a lightning bug in my palms again for the first time in a long while. A high school senior now, I understand the firefly’s chemical secret: bioluminescence. And yet I find the same old captivation with its beauty, its way of whispering “let there be light” into the darkness. I now comprehend why my mother had insisted I let the firefly go – to preserve its fragile beauty. To protect its gift of light, not in an empty plastic water bottle where I alone could sit entranced by it, but rather somewhere it was free to inspire the rest of the world.
I see myself in this small glowing beetle – so miniscule in a large world yet still striving to find my own light. But rather than a self-made product of reactions between oxygen, adenosine triphosphate and luciferin, my lights come from the people in my life.
I stare at a blank canvas during the entire 40 minutes of class. I’m afraid…of paint. Afraid to mess up. In moments of doubt, my high school art teacher provided me with more than instruction. She asked me questions about the things in my life that made me distinctive: how was my sports team doing? What goals did I have for the future? She reminded me that my work gained meaning not only by way of craft and composition but each weight of line and shade of color that spoke true to my individuality, my own unique light.
My fingers stiffly play through the Beethoven piano sonata once, twice… after the fifth time, I stop. I have completed my finger exercises. While I was merely reading notes, my piano teacher gently swayed my body, demonstrating how to lean into stormy moments of appassionato and recline back in delicate moments of espressivo. She gave my emotions a voice, one that transcended notes and allowed my light to illuminate the entire stage.
A long day of shy class introductions as the new kid. The phone rings- a familiar name from my old area code. Though the amount of time I spent with some were short and the distance between us now great, the friends I made in New Jersey, in Michigan, and finally in Ohio opened my eyes to the light we all have in common. I still smile at their homecoming social media posts, laugh over the phone at the new drama updates, and cry with them at their struggles with high school pressures. These lifelong friends taught me how to find happiness in the memories we still share.
Confidence, passion, love… As I encounter more people, I continue to add reactants to the secret equation for my own bioluminescence. As I share energy and curiosity with others, together we make our light stronger and the world a little bit brighter.
Feedback from Admission Staff
As we read applications, each student has a team of admission staff assigned to their file to review it and assess the student’s potential. The staff responsible for this student’s file had this to say about the personal statement:
This essay starts out as a simple encounter with a firefly and evolves into story of growth, reflection, and connection. This student writes about first noticing the beauty of the firefly, then as they get older, learning more about how and why the firefly glows. They compare themselves to the firefly and discuss the people and experiences in their life that explain how and why they shine. This essay is textured, authentic, and beautifully written.
Don’t hesitate to connect with us by posting a comment to this blog, tweeting us @emoryadmission , or emailing us at [email protected] . We look forward to hearing from you!
Related Posts

Scott is a Vice Dean of Admission here at Emory University and has been in…

As your senior year ends and graduation’s not too far in the distance, you’re probably…

Hello to all of our esteemed readers, and welcome back! My name is Javian Rojas…
This Post Has 0 Comments
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- previous post: Strong Personal Statements, Part 2: Connect Literature with your Narrative
- next post: Strong Personal Statements, Part 4: Use Accomplishments to Convey your Interests

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 177 college essay examples for 11 schools + expert analysis.
College Admissions , College Essays

The personal statement might just be the hardest part of your college application. Mostly this is because it has the least guidance and is the most open-ended. One way to understand what colleges are looking for when they ask you to write an essay is to check out the essays of students who already got in—college essays that actually worked. After all, they must be among the most successful of this weird literary genre.
In this article, I'll go through general guidelines for what makes great college essays great. I've also compiled an enormous list of 100+ actual sample college essays from 11 different schools. Finally, I'll break down two of these published college essay examples and explain why and how they work. With links to 177 full essays and essay excerpts , this article is a great resource for learning how to craft your own personal college admissions essay!
What Excellent College Essays Have in Common
Even though in many ways these sample college essays are very different from one other, they do share some traits you should try to emulate as you write your own essay.
Visible Signs of Planning
Building out from a narrow, concrete focus. You'll see a similar structure in many of the essays. The author starts with a very detailed story of an event or description of a person or place. After this sense-heavy imagery, the essay expands out to make a broader point about the author, and connects this very memorable experience to the author's present situation, state of mind, newfound understanding, or maturity level.
Knowing how to tell a story. Some of the experiences in these essays are one-of-a-kind. But most deal with the stuff of everyday life. What sets them apart is the way the author approaches the topic: analyzing it for drama and humor, for its moving qualities, for what it says about the author's world, and for how it connects to the author's emotional life.
Stellar Execution
A killer first sentence. You've heard it before, and you'll hear it again: you have to suck the reader in, and the best place to do that is the first sentence. Great first sentences are punchy. They are like cliffhangers, setting up an exciting scene or an unusual situation with an unclear conclusion, in order to make the reader want to know more. Don't take my word for it—check out these 22 first sentences from Stanford applicants and tell me you don't want to read the rest of those essays to find out what happens!
A lively, individual voice. Writing is for readers. In this case, your reader is an admissions officer who has read thousands of essays before yours and will read thousands after. Your goal? Don't bore your reader. Use interesting descriptions, stay away from clichés, include your own offbeat observations—anything that makes this essay sounds like you and not like anyone else.

Technical correctness. No spelling mistakes, no grammar weirdness, no syntax issues, no punctuation snafus—each of these sample college essays has been formatted and proofread perfectly. If this kind of exactness is not your strong suit, you're in luck! All colleges advise applicants to have their essays looked over several times by parents, teachers, mentors, and anyone else who can spot a comma splice. Your essay must be your own work, but there is absolutely nothing wrong with getting help polishing it.
And if you need more guidance, connect with PrepScholar's expert admissions consultants . These expert writers know exactly what college admissions committees look for in an admissions essay and chan help you craft an essay that boosts your chances of getting into your dream school.
Check out PrepScholar's Essay Editing and Coaching progra m for more details!
Links to Full College Essay Examples
Some colleges publish a selection of their favorite accepted college essays that worked, and I've put together a selection of over 100 of these.
Common App Essay Samples
Please note that some of these college essay examples may be responding to prompts that are no longer in use. The current Common App prompts are as follows:
1. Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story. 2. The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure. How did it affect you, and what did you learn from the experience? 3. Reflect on a time when you questioned or challenged a belief or idea. What prompted your thinking? What was the outcome? 4. Reflect on something that someone has done for you that has made you happy or thankful in a surprising way. How has this gratitude affected or motivated you? 5. Discuss an accomplishment, event, or realization that sparked a period of personal growth and a new understanding of yourself or others. 6. Describe a topic, idea, or concept you find so engaging that it makes you lose all track of time. Why does it captivate you? What or who do you turn to when you want to learn more?
7. Share an essay on any topic of your choice. It can be one you've already written, one that responds to a different prompt, or one of your own design.
Now, let's get to the good stuff: the list of 177 college essay examples responding to current and past Common App essay prompts.
Connecticut college.
- 12 Common Application essays from the classes of 2022-2025
Hamilton College
- 7 Common Application essays from the class of 2026
- 7 Common Application essays from the class of 2022
- 7 Common Application essays from the class of 2018
- 8 Common Application essays from the class of 2012
- 8 Common Application essays from the class of 2007
Johns Hopkins
These essays are answers to past prompts from either the Common Application or the Coalition Application (which Johns Hopkins used to accept).
- 1 Common Application or Coalition Application essay from the class of 2026
- 6 Common Application or Coalition Application essays from the class of 2025
- 6 Common Application or Universal Application essays from the class of 2024
- 6 Common Application or Universal Application essays from the class of 2023
- 7 Common Application of Universal Application essays from the class of 2022
- 5 Common Application or Universal Application essays from the class of 2021
- 7 Common Application or Universal Application essays from the class of 2020
Essay Examples Published by Other Websites
- 2 Common Application essays ( 1st essay , 2nd essay ) from applicants admitted to Columbia
Other Sample College Essays
Here is a collection of essays that are college-specific.
Babson College
- 4 essays (and 1 video response) on "Why Babson" from the class of 2020
Emory University
- 5 essay examples ( 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ) from the class of 2020 along with analysis from Emory admissions staff on why the essays were exceptional
- 5 more recent essay examples ( 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ) along with analysis from Emory admissions staff on what made these essays stand out
University of Georgia
- 1 “strong essay” sample from 2019
- 1 “strong essay” sample from 2018
- 10 Harvard essays from 2023
- 10 Harvard essays from 2022
- 10 Harvard essays from 2021
- 10 Harvard essays from 2020
- 10 Harvard essays from 2019
- 10 Harvard essays from 2018
- 6 essays from admitted MIT students
Smith College
- 6 "best gift" essays from the class of 2018

Books of College Essays
If you're looking for even more sample college essays, consider purchasing a college essay book. The best of these include dozens of essays that worked and feedback from real admissions officers.
College Essays That Made a Difference —This detailed guide from Princeton Review includes not only successful essays, but also interviews with admissions officers and full student profiles.
50 Successful Harvard Application Essays by the Staff of the Harvard Crimson—A must for anyone aspiring to Harvard .
50 Successful Ivy League Application Essays and 50 Successful Stanford Application Essays by Gen and Kelly Tanabe—For essays from other top schools, check out this venerated series, which is regularly updated with new essays.
Heavenly Essays by Janine W. Robinson—This collection from the popular blogger behind Essay Hell includes a wider range of schools, as well as helpful tips on honing your own essay.

Analyzing Great Common App Essays That Worked
I've picked two essays from the examples collected above to examine in more depth so that you can see exactly what makes a successful college essay work. Full credit for these essays goes to the original authors and the schools that published them.
Example 1: "Breaking Into Cars," by Stephen, Johns Hopkins Class of '19 (Common App Essay, 636 words long)
I had never broken into a car before.
We were in Laredo, having just finished our first day at a Habitat for Humanity work site. The Hotchkiss volunteers had already left, off to enjoy some Texas BBQ, leaving me behind with the college kids to clean up. Not until we were stranded did we realize we were locked out of the van.
Someone picked a coat hanger out of the dumpster, handed it to me, and took a few steps back.
"Can you do that thing with a coat hanger to unlock it?"
"Why me?" I thought.
More out of amusement than optimism, I gave it a try. I slid the hanger into the window's seal like I'd seen on crime shows, and spent a few minutes jiggling the apparatus around the inside of the frame. Suddenly, two things simultaneously clicked. One was the lock on the door. (I actually succeeded in springing it.) The other was the realization that I'd been in this type of situation before. In fact, I'd been born into this type of situation.
My upbringing has numbed me to unpredictability and chaos. With a family of seven, my home was loud, messy, and spottily supervised. My siblings arguing, the dog barking, the phone ringing—all meant my house was functioning normally. My Dad, a retired Navy pilot, was away half the time. When he was home, he had a parenting style something like a drill sergeant. At the age of nine, I learned how to clear burning oil from the surface of water. My Dad considered this a critical life skill—you know, in case my aircraft carrier should ever get torpedoed. "The water's on fire! Clear a hole!" he shouted, tossing me in the lake without warning. While I'm still unconvinced about that particular lesson's practicality, my Dad's overarching message is unequivocally true: much of life is unexpected, and you have to deal with the twists and turns.
Living in my family, days rarely unfolded as planned. A bit overlooked, a little pushed around, I learned to roll with reality, negotiate a quick deal, and give the improbable a try. I don't sweat the small stuff, and I definitely don't expect perfect fairness. So what if our dining room table only has six chairs for seven people? Someone learns the importance of punctuality every night.
But more than punctuality and a special affinity for musical chairs, my family life has taught me to thrive in situations over which I have no power. Growing up, I never controlled my older siblings, but I learned how to thwart their attempts to control me. I forged alliances, and realigned them as necessary. Sometimes, I was the poor, defenseless little brother; sometimes I was the omniscient elder. Different things to different people, as the situation demanded. I learned to adapt.
Back then, these techniques were merely reactions undertaken to ensure my survival. But one day this fall, Dr. Hicks, our Head of School, asked me a question that he hoped all seniors would reflect on throughout the year: "How can I participate in a thing I do not govern, in the company of people I did not choose?"
The question caught me off guard, much like the question posed to me in Laredo. Then, I realized I knew the answer. I knew why the coat hanger had been handed to me.
Growing up as the middle child in my family, I was a vital participant in a thing I did not govern, in the company of people I did not choose. It's family. It's society. And often, it's chaos. You participate by letting go of the small stuff, not expecting order and perfection, and facing the unexpected with confidence, optimism, and preparedness. My family experience taught me to face a serendipitous world with confidence.
What Makes This Essay Tick?
It's very helpful to take writing apart in order to see just how it accomplishes its objectives. Stephen's essay is very effective. Let's find out why!
An Opening Line That Draws You In
In just eight words, we get: scene-setting (he is standing next to a car about to break in), the idea of crossing a boundary (he is maybe about to do an illegal thing for the first time), and a cliffhanger (we are thinking: is he going to get caught? Is he headed for a life of crime? Is he about to be scared straight?).
Great, Detailed Opening Story
More out of amusement than optimism, I gave it a try. I slid the hanger into the window's seal like I'd seen on crime shows, and spent a few minutes jiggling the apparatus around the inside of the frame.
It's the details that really make this small experience come alive. Notice how whenever he can, Stephen uses a more specific, descriptive word in place of a more generic one. The volunteers aren't going to get food or dinner; they're going for "Texas BBQ." The coat hanger comes from "a dumpster." Stephen doesn't just move the coat hanger—he "jiggles" it.
Details also help us visualize the emotions of the people in the scene. The person who hands Stephen the coat hanger isn't just uncomfortable or nervous; he "takes a few steps back"—a description of movement that conveys feelings. Finally, the detail of actual speech makes the scene pop. Instead of writing that the other guy asked him to unlock the van, Stephen has the guy actually say his own words in a way that sounds like a teenager talking.

Turning a Specific Incident Into a Deeper Insight
Suddenly, two things simultaneously clicked. One was the lock on the door. (I actually succeeded in springing it.) The other was the realization that I'd been in this type of situation before. In fact, I'd been born into this type of situation.
Stephen makes the locked car experience a meaningful illustration of how he has learned to be resourceful and ready for anything, and he also makes this turn from the specific to the broad through an elegant play on the two meanings of the word "click."
Using Concrete Examples When Making Abstract Claims
My upbringing has numbed me to unpredictability and chaos. With a family of seven, my home was loud, messy, and spottily supervised. My siblings arguing, the dog barking, the phone ringing—all meant my house was functioning normally.
"Unpredictability and chaos" are very abstract, not easily visualized concepts. They could also mean any number of things—violence, abandonment, poverty, mental instability. By instantly following up with highly finite and unambiguous illustrations like "family of seven" and "siblings arguing, the dog barking, the phone ringing," Stephen grounds the abstraction in something that is easy to picture: a large, noisy family.
Using Small Bits of Humor and Casual Word Choice
My Dad, a retired Navy pilot, was away half the time. When he was home, he had a parenting style something like a drill sergeant. At the age of nine, I learned how to clear burning oil from the surface of water. My Dad considered this a critical life skill—you know, in case my aircraft carrier should ever get torpedoed.
Obviously, knowing how to clean burning oil is not high on the list of things every 9-year-old needs to know. To emphasize this, Stephen uses sarcasm by bringing up a situation that is clearly over-the-top: "in case my aircraft carrier should ever get torpedoed."
The humor also feels relaxed. Part of this is because he introduces it with the colloquial phrase "you know," so it sounds like he is talking to us in person. This approach also diffuses the potential discomfort of the reader with his father's strictness—since he is making jokes about it, clearly he is OK. Notice, though, that this doesn't occur very much in the essay. This helps keep the tone meaningful and serious rather than flippant.

An Ending That Stretches the Insight Into the Future
But one day this fall, Dr. Hicks, our Head of School, asked me a question that he hoped all seniors would reflect on throughout the year: "How can I participate in a thing I do not govern, in the company of people I did not choose?"
The ending of the essay reveals that Stephen's life has been one long preparation for the future. He has emerged from chaos and his dad's approach to parenting as a person who can thrive in a world that he can't control.
This connection of past experience to current maturity and self-knowledge is a key element in all successful personal essays. Colleges are very much looking for mature, self-aware applicants. These are the qualities of successful college students, who will be able to navigate the independence college classes require and the responsibility and quasi-adulthood of college life.
What Could This Essay Do Even Better?
Even the best essays aren't perfect, and even the world's greatest writers will tell you that writing is never "finished"—just "due." So what would we tweak in this essay if we could?
Replace some of the clichéd language. Stephen uses handy phrases like "twists and turns" and "don't sweat the small stuff" as a kind of shorthand for explaining his relationship to chaos and unpredictability. But using too many of these ready-made expressions runs the risk of clouding out your own voice and replacing it with something expected and boring.
Use another example from recent life. Stephen's first example (breaking into the van in Laredo) is a great illustration of being resourceful in an unexpected situation. But his essay also emphasizes that he "learned to adapt" by being "different things to different people." It would be great to see how this plays out outside his family, either in the situation in Laredo or another context.
Example 2: By Renner Kwittken, Tufts Class of '23 (Common App Essay, 645 words long)
My first dream job was to be a pickle truck driver. I saw it in my favorite book, Richard Scarry's "Cars and Trucks and Things That Go," and for some reason, I was absolutely obsessed with the idea of driving a giant pickle. Much to the discontent of my younger sister, I insisted that my parents read us that book as many nights as possible so we could find goldbug, a small little golden bug, on every page. I would imagine the wonderful life I would have: being a pig driving a giant pickle truck across the country, chasing and finding goldbug. I then moved on to wanting to be a Lego Master. Then an architect. Then a surgeon.
Then I discovered a real goldbug: gold nanoparticles that can reprogram macrophages to assist in killing tumors, produce clear images of them without sacrificing the subject, and heat them to obliteration.
Suddenly the destination of my pickle was clear.
I quickly became enveloped by the world of nanomedicine; I scoured articles about liposomes, polymeric micelles, dendrimers, targeting ligands, and self-assembling nanoparticles, all conquering cancer in some exotic way. Completely absorbed, I set out to find a mentor to dive even deeper into these topics. After several rejections, I was immensely grateful to receive an invitation to work alongside Dr. Sangeeta Ray at Johns Hopkins.
In the lab, Dr. Ray encouraged a great amount of autonomy to design and implement my own procedures. I chose to attack a problem that affects the entire field of nanomedicine: nanoparticles consistently fail to translate from animal studies into clinical trials. Jumping off recent literature, I set out to see if a pre-dose of a common chemotherapeutic could enhance nanoparticle delivery in aggressive prostate cancer, creating three novel constructs based on three different linear polymers, each using fluorescent dye (although no gold, sorry goldbug!). Though using radioactive isotopes like Gallium and Yttrium would have been incredible, as a 17-year-old, I unfortunately wasn't allowed in the same room as these radioactive materials (even though I took a Geiger counter to a pair of shoes and found them to be slightly dangerous).
I hadn't expected my hypothesis to work, as the research project would have ideally been led across two full years. Yet while there are still many optimizations and revisions to be done, I was thrilled to find -- with completely new nanoparticles that may one day mean future trials will use particles with the initials "RK-1" -- thatcyclophosphamide did indeed increase nanoparticle delivery to the tumor in a statistically significant way.
A secondary, unexpected research project was living alone in Baltimore, a new city to me, surrounded by people much older than I. Even with moving frequently between hotels, AirBnB's, and students' apartments, I strangely reveled in the freedom I had to enjoy my surroundings and form new friendships with graduate school students from the lab. We explored The Inner Harbor at night, attended a concert together one weekend, and even got to watch the Orioles lose (to nobody's surprise). Ironically, it's through these new friendships I discovered something unexpected: what I truly love is sharing research. Whether in a presentation or in a casual conversation, making others interested in science is perhaps more exciting to me than the research itself. This solidified a new pursuit to angle my love for writing towards illuminating science in ways people can understand, adding value to a society that can certainly benefit from more scientific literacy.
It seems fitting that my goals are still transforming: in Scarry's book, there is not just one goldbug, there is one on every page. With each new experience, I'm learning that it isn't the goldbug itself, but rather the act of searching for the goldbugs that will encourage, shape, and refine my ever-evolving passions. Regardless of the goldbug I seek -- I know my pickle truck has just begun its journey.
Renner takes a somewhat different approach than Stephen, but their essay is just as detailed and engaging. Let's go through some of the strengths of this essay.
One Clear Governing Metaphor
This essay is ultimately about two things: Renner’s dreams and future career goals, and Renner’s philosophy on goal-setting and achieving one’s dreams.
But instead of listing off all the amazing things they’ve done to pursue their dream of working in nanomedicine, Renner tells a powerful, unique story instead. To set up the narrative, Renner opens the essay by connecting their experiences with goal-setting and dream-chasing all the way back to a memorable childhood experience:
This lighthearted–but relevant!--story about the moment when Renner first developed a passion for a specific career (“finding the goldbug”) provides an anchor point for the rest of the essay. As Renner pivots to describing their current dreams and goals–working in nanomedicine–the metaphor of “finding the goldbug” is reflected in Renner’s experiments, rejections, and new discoveries.
Though Renner tells multiple stories about their quest to “find the goldbug,” or, in other words, pursue their passion, each story is connected by a unifying theme; namely, that as we search and grow over time, our goals will transform…and that’s okay! By the end of the essay, Renner uses the metaphor of “finding the goldbug” to reiterate the relevance of the opening story:
While the earlier parts of the essay convey Renner’s core message by showing, the final, concluding paragraph sums up Renner’s insights by telling. By briefly and clearly stating the relevance of the goldbug metaphor to their own philosophy on goals and dreams, Renner demonstrates their creativity, insight, and eagerness to grow and evolve as the journey continues into college.

An Engaging, Individual Voice
This essay uses many techniques that make Renner sound genuine and make the reader feel like we already know them.
Technique #1: humor. Notice Renner's gentle and relaxed humor that lightly mocks their younger self's grand ambitions (this is different from the more sarcastic kind of humor used by Stephen in the first essay—you could never mistake one writer for the other).
My first dream job was to be a pickle truck driver.
I would imagine the wonderful life I would have: being a pig driving a giant pickle truck across the country, chasing and finding goldbug. I then moved on to wanting to be a Lego Master. Then an architect. Then a surgeon.
Renner gives a great example of how to use humor to your advantage in college essays. You don’t want to come off as too self-deprecating or sarcastic, but telling a lightheartedly humorous story about your younger self that also showcases how you’ve grown and changed over time can set the right tone for your entire essay.
Technique #2: intentional, eye-catching structure. The second technique is the way Renner uses a unique structure to bolster the tone and themes of their essay . The structure of your essay can have a major impact on how your ideas come across…so it’s important to give it just as much thought as the content of your essay!
For instance, Renner does a great job of using one-line paragraphs to create dramatic emphasis and to make clear transitions from one phase of the story to the next:
Suddenly the destination of my pickle car was clear.
Not only does the one-liner above signal that Renner is moving into a new phase of the narrative (their nanoparticle research experiences), it also tells the reader that this is a big moment in Renner’s story. It’s clear that Renner made a major discovery that changed the course of their goal pursuit and dream-chasing. Through structure, Renner conveys excitement and entices the reader to keep pushing forward to the next part of the story.
Technique #3: playing with syntax. The third technique is to use sentences of varying length, syntax, and structure. Most of the essay's written in standard English and uses grammatically correct sentences. However, at key moments, Renner emphasizes that the reader needs to sit up and pay attention by switching to short, colloquial, differently punctuated, and sometimes fragmented sentences.
Even with moving frequently between hotels, AirBnB's, and students' apartments, I strangely reveled in the freedom I had to enjoy my surroundings and form new friendships with graduate school students from the lab. We explored The Inner Harbor at night, attended a concert together one weekend, and even got to watch the Orioles lose (to nobody's surprise). Ironically, it's through these new friendships I discovered something unexpected: what I truly love is sharing research.
In the examples above, Renner switches adeptly between long, flowing sentences and quippy, telegraphic ones. At the same time, Renner uses these different sentence lengths intentionally. As they describe their experiences in new places, they use longer sentences to immerse the reader in the sights, smells, and sounds of those experiences. And when it’s time to get a big, key idea across, Renner switches to a short, punchy sentence to stop the reader in their tracks.
The varying syntax and sentence lengths pull the reader into the narrative and set up crucial “aha” moments when it’s most important…which is a surefire way to make any college essay stand out.

Renner's essay is very strong, but there are still a few little things that could be improved.
Connecting the research experiences to the theme of “finding the goldbug.” The essay begins and ends with Renner’s connection to the idea of “finding the goldbug.” And while this metaphor is deftly tied into the essay’s intro and conclusion, it isn’t entirely clear what Renner’s big findings were during the research experiences that are described in the middle of the essay. It would be great to add a sentence or two stating what Renner’s big takeaways (or “goldbugs”) were from these experiences, which add more cohesion to the essay as a whole.
Give more details about discovering the world of nanomedicine. It makes sense that Renner wants to get into the details of their big research experiences as quickly as possible. After all, these are the details that show Renner’s dedication to nanomedicine! But a smoother transition from the opening pickle car/goldbug story to Renner’s “real goldbug” of nanoparticles would help the reader understand why nanoparticles became Renner’s goldbug. Finding out why Renner is so motivated to study nanomedicine–and perhaps what put them on to this field of study–would help readers fully understand why Renner chose this path in the first place.
4 Essential Tips for Writing Your Own Essay
How can you use this discussion to better your own college essay? Here are some suggestions for ways to use this resource effectively.
#1: Get Help From the Experts
Getting your college applications together takes a lot of work and can be pretty intimidatin g. Essays are even more important than ever now that admissions processes are changing and schools are going test-optional and removing diversity standards thanks to new Supreme Court rulings . If you want certified expert help that really makes a difference, get started with PrepScholar’s Essay Editing and Coaching program. Our program can help you put together an incredible essay from idea to completion so that your application stands out from the crowd. We've helped students get into the best colleges in the United States, including Harvard, Stanford, and Yale. If you're ready to take the next step and boost your odds of getting into your dream school, connect with our experts today .
#2: Read Other Essays to Get Ideas for Your Own
As you go through the essays we've compiled for you above, ask yourself the following questions:
- Can you explain to yourself (or someone else!) why the opening sentence works well?
- Look for the essay's detailed personal anecdote. What senses is the author describing? Can you easily picture the scene in your mind's eye?
- Find the place where this anecdote bridges into a larger insight about the author. How does the essay connect the two? How does the anecdote work as an example of the author's characteristic, trait, or skill?
- Check out the essay's tone. If it's funny, can you find the places where the humor comes from? If it's sad and moving, can you find the imagery and description of feelings that make you moved? If it's serious, can you see how word choice adds to this tone?
Make a note whenever you find an essay or part of an essay that you think was particularly well-written, and think about what you like about it . Is it funny? Does it help you really get to know the writer? Does it show what makes the writer unique? Once you have your list, keep it next to you while writing your essay to remind yourself to try and use those same techniques in your own essay.

#3: Find Your "A-Ha!" Moment
All of these essays rely on connecting with the reader through a heartfelt, highly descriptive scene from the author's life. It can either be very dramatic (did you survive a plane crash?) or it can be completely mundane (did you finally beat your dad at Scrabble?). Either way, it should be personal and revealing about you, your personality, and the way you are now that you are entering the adult world.
Check out essays by authors like John Jeremiah Sullivan , Leslie Jamison , Hanif Abdurraqib , and Esmé Weijun Wang to get more examples of how to craft a compelling personal narrative.
#4: Start Early, Revise Often
Let me level with you: the best writing isn't writing at all. It's rewriting. And in order to have time to rewrite, you have to start way before the application deadline. My advice is to write your first draft at least two months before your applications are due.
Let it sit for a few days untouched. Then come back to it with fresh eyes and think critically about what you've written. What's extra? What's missing? What is in the wrong place? What doesn't make sense? Don't be afraid to take it apart and rearrange sections. Do this several times over, and your essay will be much better for it!
For more editing tips, check out a style guide like Dreyer's English or Eats, Shoots & Leaves .

What's Next?
Still not sure which colleges you want to apply to? Our experts will show you how to make a college list that will help you choose a college that's right for you.
Interested in learning more about college essays? Check out our detailed breakdown of exactly how personal statements work in an application , some suggestions on what to avoid when writing your essay , and our guide to writing about your extracurricular activities .
Working on the rest of your application? Read what admissions officers wish applicants knew before applying .

The recommendations in this post are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Anna scored in the 99th percentile on her SATs in high school, and went on to major in English at Princeton and to get her doctorate in English Literature at Columbia. She is passionate about improving student access to higher education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
Using Metaphors in Academic Writing

Have you ever wanted to translate formidable, and sometimes tedious, academic content into one that is easily comprehensible and captivating? Academics are often told that the language of science is formal, precise and descriptive with no space for the abstract. However, using metaphors in your academic writing could be helpful if used to explain complex scientific concepts. Just remember not to be cautious and exercise restraint when using different types of metaphors or it could make your academic writing seem unprofessional.
What is a metaphor?
A metaphor is defined as a figure of speech in which a word or phrase denoting one kind of object or idea is used in place of another to suggest a likeness or analogy between them. (Merriam-Webster, 2022). Derived from the Greek word ‘metapherein,’ which means ‘to transfer,’ metaphors transfer the meaning of one word to another to encourage a feeling. For example, by writing ‘ All the world’s a stage,’ Shakespeare creates a powerful imagery of ideas through transference. By bringing life to words, metaphors add value to writing and are a great addition to a writer’s toolkit.
Difference between similes and metaphors and analogies
When you’re writing in English, you should know the difference between similes and metaphors and analogies. While these are similar in terms of purpose, i.e., comparing two things, they are different in how they are used. A simile is explicit about the comparison, while a metaphor simply points to the similarities between two things, and an analogy seeks to use comparisons to explain a concept.
This could be confusing, however, there are simple ways to detect the differences between similes and metaphors and analogies. You can identify a simile by looking for the use of words ‘like’ , ‘as’, for example, ‘Life is like a box of chocolates.’ On the other hand, metaphors are more rhetorical and not so literal, for example, ‘The news was music to her ears.’ An analogy is more complex and seeks to point out the similarity in two things to explain a point, for example, ‘Finding the right dress is like finding a needle in a haystack.’
Types of metaphors
There are several different types of metaphors in the English language, here are some of the most common variations.
- Standard metaphor: A standard metaphor directly compares two unrelated items. For instance, by drawing a link between things and feelings, we’ve been able to convey the importance of laughter in this example of a metaphor: Laughter is the best medicine.
- Implied metaphor: This type of metaphor implies comparison without mentioning one of the things being compared. Take this example, where the coach’s voice is implied to be as loud as thunder: “Don’t give up!” thundered the coach from the side lines.
- Visual metaphor: This type of metaphor compares abstract objects or ideas that are difficult to imagine to a visual image that is easily identifiable; providing the former with a pictorial identity. This type of metaphor is most widely used in advertisements. For example, for the phrase ‘ The Earth is melting’ , the visual metaphor used to signal global warming is a melting ice cream.
- Extended metaphor: This type of metaphor extends the comparison throughout an article, document, or stanza. For example, when poet Emily Dickinson wrote “Hope” is the thing with feathers, she used feathers as a metaphor to compare hope to a bird with wings.
- Grammatical metaphors : Also known as nominalization, this type of metaphor rewrites verbs or adjectives as nouns. It’s most commonly used in academic and scientific texts as a way to separate spoken and written language, remove personal pronouns, and write in a concise manner. For instance, ‘ Millions of men, women and children starved to death in the 1943 Bengal Famine as a direct result of Churchill’s policies.’ This can be rephrased as ‘British policies led to the 1943 Bengal Famine, impacting the country’s people and politics for decades.’

Using metaphors in academic writing
Scholars pride themselves on creating research papers that are factually correct and precise, and metaphors may be perceived to detract from this. However, using metaphors may be a great way to explain scientific and technical concepts to readers, who may not know as much about the subject. While metaphors can add to formal academic writing and make it more engaging, it’s important to find a balance. Here are some tips to keep in mind when using metaphors in academic writing:
- Don’t use metaphors as the foundation of your academic content, use them instead to support your argument and drive home a point.
- Choose your metaphors carefully taking into account your primary audience; using figures of speech specific to any one region can introduce confusion instead of clarity.
- Use metaphors wisely and only when needed so not to distract the reader. They should flow naturally and enhance the content rather than detract from the point.
Metaphors are a nifty way to create engaging content even for academic writers. Greek philosopher Aristotle once wrote, “The greatest thing by far is to be a master of metaphor; it is the one thing that cannot be learnt from others.” So get ready to wield that pen and reach for the stars!
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Quotation Marks: When and How to Use Quotations in Academic Writing
- Week vs. Weak: Bringing Out the Distinction
- Center vs. Centre: How to Differentiate Between The Two Words
Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
How and when to use active or passive voice in research papers, transition phrases in academic writing, you may also like, how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to paraphrase research papers effectively, 4 types of transition words for research papers , sentence length: how to improve your research paper..., navigating language precision: complementary vs. complimentary, climatic vs. climactic: difference and examples, language and grammar rules for academic writing.
Metaphors and Analogies: How to Use Them in Your Academic Life

Certain Experiences in life can't be captured in simple words. Especially if you are a writer trying to connect with your audience, you will need special threads to evoke exact feelings.
There are many literary devices to spark the readers' imagination, and analogies and metaphors are one of that magical arsenal. They enrich your text and give it the exact depth it will need to increase your readers' heartbeat.
Taking a particular characteristic and associating it with the other not only enriches your text's linguistic quality but gives the reader a correct pathway to deeper layers of a writer's psyche.
In this article, we are going to take a good look at the difference between analogy and metaphor and how to use them in your academic writing, and you will find some of the most powerful examples for each. Learn more about this and other vital linguistic tools on our essay writer service website.
What are Metaphors: Understanding the Concept
Let's discuss the metaphors definition. Metaphors are a figure of speech that compares two unrelated concepts or ideas to create a deeper and more profound meaning. They are a powerful tool in academic writing to express abstract concepts using different analogies, which can improve the reader's understanding of complex topics. Metaphors enable writers to paint vivid pictures in the reader's mind by comparing something familiar with an abstract concept that is harder to grasp.
The following are some of the most famous metaphors and their meanings:
- The world is your oyster - the world is full of opportunities just waiting for you to grab them
- Time is money - time is a valuable commodity that must be spent wisely
- A heart of stone - someone who is emotionally cold and unfeeling
Analogies Meaning: Mastering the Essence
Analogies, on the other hand, are a comparison of two concepts or ideas that have some similarity in their features. They are used to clarify complex ideas or to make a new concept more relatable by comparing it to something that is already familiar.
Analogies are often followed by an explanation of how the two concepts are similar, which helps the reader to understand and make connections between seemingly disparate ideas. For example, in academic writing, if you were explaining the function of a cell membrane, you might use an analogy, such as comparing it to a security gate that regulates what enters and exits a building.
Check out these famous analogies examples:
- Knowledge is like a garden: if it is not cultivated, it cannot be harvested.
- Teaching a child without education is like building a house without a foundation.
- A good friend is like a four-leaf clover; hard to find and lucky to have.
Benefits of Metaphors and Analogies in Writing
Chances are you are wondering why we use analogies and metaphors in academic writing anyway?

The reason why metaphors are beneficial to writers, especially in the academic field, is that they offer an effective approach to clarifying intricate concepts and enriching comprehension by linking them to more familiar ideas. Through the use of relatable frames of reference, these figures of speech help authors communicate complicated notions in an appealing and comprehensible way.
Additionally, analogies and metaphors are a way of artistic expression. They bring creativity and imagination to your writing, making it engaging and memorable for your readers. Beautiful words connect with readers on a deeper emotional level, allowing them to better retain and appreciate the information being presented. Such linguistic devices allow readers to open doors for imagination and create visual images in their minds, creating a more individualized experience.
However, one must be mindful not to plagiarize famous analogies and always use original ideas or appropriately cite sources when necessary. Overall, metaphors and analogies add depth and beauty to write-ups, making them memorable for years to come.
Understanding the Difference Between Analogy and Metaphor
While metaphors and analogies serve the similar purpose of clarifying otherwise complex ideas, they are not quite the same. Follow the article and learn how they differ from each other.
One way to differentiate between analogies and metaphors is through the use of 'as' and 'like.' Analogies make an explicit comparison using these words, while metaphors imply a comparison without any overt indication.
There is an obvious difference between their structure. An analogy has two parts; the primary subject, which is unfamiliar, and a secondary subject which is familiar to the reader. For example, 'Life is like a box of chocolates.' The two subjects are compared, highlighting their similarities in order to explain an entire concept.
On the other hand, a metaphor describes an object or idea by referring to something else that is not literally applicable but shares some common features. For example, 'He drowned in a sea of grief.'
The structural difference also defines the difference in their usage. Analogies are often used in academic writing where hard concepts need to be aligned with an easier and more familiar concept. This assists the reader in comprehending complex ideas more effortlessly. Metaphors, on the other hand, are more often used in creative writing or literature. They bring depth and nuance to language, allowing for abstract ideas to be communicated in a more engaging and imaginative way.
Keep reading and discover examples of metaphors and analogies in both academic and creative writing. While you are at it, our expert writers are ready to provide custom essays and papers which incorporate these literary devices in a seamless and effective way.
Using Famous Analogies Can Raise Plagiarism Concerns!
To avoid the trouble, use our online plagiarism checker and be sure that your work is original before submitting it.
Analogies and Metaphors Examples
There were a few analogies and metaphors examples mentioned along the way, but let's explore a few more to truly understand their power. Below you will find the list of metaphors and analogies, and you will never mistake one for the other again.
- Love is like a rose, beautiful but with thorns.
- The human body is like a machine, with many intricate parts working together in harmony.
- The structure of an atom is similar to a miniature solar system, with electrons orbiting around the nucleus.
- A computer's motherboard is like a city's central system, coordinating and communicating all functions.
- The brain is like a muscle that needs constant exercise to function at its best.
- Studying for exams is like training for a marathon; it requires endurance and preparation.
- Explaining a complex scientific concept is like explaining a foreign language to someone who doesn't speak it.
- A successful team is like a well-oiled machine, with each member playing a crucial role.
- Learning a new skill is like planting a seed; it requires nurturing and patience to see growth.
- Navigating through life is like sailing a ship with unpredictable currents and changing winds.
- Life is a journey with many twists and turns along the way
- The world's a stage, and we are all mere players.
- Her eyes were pools of sorrow, reflecting the pain she felt.
- Time is a thief, stealing away moments we can never recapture.
- Love is a flame, burning brightly but at risk of being extinguished.
- His words were daggers piercing through my heart.
- She had a heart of stone, unable to feel empathy or compassion.
- The city was a jungle, teeming with life and activity.
- Hope is a beacon, guiding us through the darkest of times.
- His anger was a volcano, ready to erupt at any moment.
How to Use Metaphors and Analogies in Writing: Helpful Tips
If you want your readers to have a memorable and engaging experience, you should give them some level of autonomy within your own text. Metaphors and analogies are powerful tools to let your audience do their personal interpretation and logical conclusion while still guiding them in the right direction.

First, learn about your audience and their level of familiarity with the topic you're writing about. Incorporate metaphors and analogies with familiar references. Remember, literary devices should cleverly explain complex concepts. To achieve the goal, remain coherent with the theme of the paper. But be careful not to overuse metaphors or analogies, as too much of a good thing can make your writing feel overloaded.
Use figurative language to evoke visual imagery and breathe life into your paper. Multiple metaphors can turn your paper into a movie. Visualizing ideas will help readers better understand and retain the information.
In conclusion, anytime is a great time to extend your text's impact by adding a well-chosen metaphor or analogy. But perfection is on the border of good and bad, so keep in mind to remain coherent with the theme and not overuse any literary device.
Metaphors: Unveiling Their Cultural Significance
Metaphors are not limited to just academic writing but can also be found in various forms of culture, such as art, music, film, and television. Metaphors have been a popular element in creative expression for centuries and continue to play a significant role in modern-day culture. For instance, metaphors can help artists convey complex emotions through their music or paintings.
Metaphors are often like time capsules, reflecting the cultural and societal values of a particular era. They shelter the prevailing beliefs, ideals, and philosophies of their time - from the pharaohs of ancient Egypt to modern-day pop culture.
Metaphors often frame our perception of the world and can shape our understanding of our surroundings. Certain words can take on new meanings when used metaphorically in certain cultural contexts and can assimilate to the phenomenon it is often compared to.
Here you can find a list of literature and poems with metaphors:
- William Shakespeare loved using metaphors, and here's one from his infamous Macbeth: 'It is a tale told by an idiot, full of sound and fury, signifying nothing.'
- Victor Hugo offers a timeless metaphor in Les Misérables: 'She is a rose, delicate and beautiful, but with thorns to protect her.'
- Robert Frost reminds us of his genius in the poem The Road Not Traveled: 'The road less traveled.'
Movies also contain a wide range of English metaphors:
- A famous metaphor from Toy Story: 'There's a snake in my boot!'
- A metaphor from the famous movie Silver Lining Playbook: 'Life is a game, and true love is a trophy.'
- An all-encompassing and iconic metaphor from the movie Star Wars: 'Fear is the path to the dark side.'
Don't forget about famous songs with beautiful metaphors!
- Bob Dylan's Blowin' in the Wind uses a powerful metaphor when he asks: 'How many roads must a man walk down?'
- A metaphor from Johnny Cash's song Ring of Fire: 'Love is a burning thing, and it makes a fiery ring.'
- Bonnie Tyler's famous lyrics from Total Eclipse of the Heart make a great metaphor: 'Love is a mystery, everyone must stand alone.'
Keep reading the article to find out how to write an essay with the effective use of metaphors in academic writing.
Exploring Types of Metaphors
There is a wide variety of metaphors used in academic writing, literature, music, and film. Different types of metaphors can be used to convey different meanings and create a specific impact or evoke a vivid image.
Some common types of metaphors include similes / simple metaphors, implicit metaphors, explicit metaphors, extended metaphors, mixed metaphors, and dead metaphors. Let's take a closer look at some of these types.
Simple metaphors or similes highlight the similarity between two things using 'like' or 'as.' For example, 'Her eyes were as bright as the stars.'
Implicit metaphors do not make a direct comparison. Instead, they imply the similarity between the two concepts. An example of an implicit metaphor is 'Her words cut deep,' where the similarity between words and a knife is implied. Good metaphors are often implicit since they require the reader to use their own understanding and imagination to understand the comparison being made.
Explicit metaphors are straightforward, making a clear comparison between two things. For instance, 'He is a shining star.'
An extended metaphor, on the other hand, stretches the comparison throughout an entire literary work or section of a text. This type of metaphor allows the writer to create a more complex and elaborate comparison, enhancing the reader's understanding of the subject.
Mixed metaphors combine two or more unrelated metaphors, often leading to confusion and lack of clarity. If you are not an expert on the subject, try to avoid using confusing literary devices.
Dead metaphors are another danger. These are metaphors that have been overused to the extent that they have lost their original impact, becoming clichés and not being able to evoke original visual images.
In academic writing, metaphors create a powerful impact on the reader, adding color and depth to everyday language. However, they need to be well-placed and intentional. Using an inappropriate or irrelevant metaphor may confuse readers and distract them from the main message. If you want to avoid trouble, pay for essay writing service that can help you use metaphors effectively in your academic writing.
Exploring Types of Analogies
Like metaphors, analogies are divided into several categories. Some of the common types include literal analogies, figurative analogies, descriptive analogies, causal analogies, and false/dubious analogies. In academic writing, analogies are useful for explaining complex ideas or phenomena in a way that is easy to understand.
Literal analogies are direct comparisons of two things with similar characteristics or features. For instance, 'The brain is like a computer.'
Figurative analogies, on the other hand, compare two unrelated things to highlight a particular characteristic. For example, 'The mind is a garden that needs to be tended.'
Descriptive analogies focus on the detailed similarities between two things, even if they are not immediately apparent. For example, 'The relationship between a supervisor and an employee is like that of a coach and a player, where the coach guides the player to perform at their best.'
Causal analogies are used to explain the relationship between a cause and an effect. For instance, 'The increase in global temperatures is like a fever caused by environmental pollution.'
Finally, false/dubious analogies are comparisons that suggest a similarity between two things that actually have little in common. For example, 'Getting a college degree is like winning the lottery.'
If you are trying to explain a foreign concept to an audience that may not be familiar with it, analogies can help create a bridge and make the concept more relatable. However, coming up with a perfect analogy takes a lot of time. If you are looking for ways on how to write an essay fast , explore our blog and learn even more.
If you want your academic papers to stand out and be engaging for the reader, using metaphors and analogies can be a powerful tool. Now that you know the difference between analogy and metaphor, you can use them wisely to create a bridge between complex ideas and your audience.
Explore our blog for more information on different writing techniques, and check out our essay writing service for more help on crafting the perfect papers.
Need to Be on Top of Your Academic Game?
We'll elevate your academic writing to the next level with papers tailored to your specific requirements!
Related Articles
.webp)
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Using Metaphors in Creative Writing

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.

What is a metaphor?
The term metaphor meant in Greek "carry something across" or "transfer," which suggests many of the more elaborate definitions below:
Related terms
Why use metaphors.
People get so accustomed to using the same words and phrases over and over, and always in the same ways, that they no longer know what they mean. Creative writers have the power to make the ordinary strange and the strange ordinary, making life interesting again.
When readers or listeners encounter a phrase or word that cannot be interpreted literally, they have to think—or rather, they are given the pleasure of interpretation. If you write "I am frustrated" or "The air was cold" you give your readers nothing to do—they say "so what?" On the other hand, if you say, "My ambition was Hiroshima, after the bombing," your readers can think about and choose from many possible meanings.
By writing "my dorm is a prison," you suggest to your readers that you feel as though you were placed in solitary, you are fed lousy food, you are deprived of all of life's great pleasures, your room is poorly lit and cramped—and a hundred other things, that, if you tried to say them all, would probably take several pages.
There are many gaps in language. When a child looks at the sky and sees a star but does not know the word "star," she is forced to say, "Mommy, look at the lamp in the sky!" Similarly, when computer software developers created boxes on the screen as a user interface, they needed a new language; the result was windows. In your poems, you will often be trying to write about subjects, feelings, etc., so complex that you have no choice but to use metaphors.
Or so says Aristotle in Poetics: "[T]he greatest thing by far is to be a master of metaphor." It is "a sign of genius, since a good metaphor implies an intuitive perception of the similarity in dissimilars."
Creative ways to use metaphors
Most books give rather boring examples of metaphors such as my father is a bear or the librarian was a beast. However, in your poetry (and fiction for that matter) you can do much more than say X is Y, like an algebraic formula. Definitely play with extended metaphors (see above) and experiment with some of the following, using metaphors...

26 Metaphors for Essays: Crafting Literary Masterpieces

Share this post:
Welcome to the realm of literary expression, where words transcend their literal meanings. In the intricate dance of language , metaphors emerge as poetic devices, breathing life into essays. This guide delves deep into the art of crafting essays with 26 metaphors, unraveling the tapestry of creativity and linguistic elegance.
26 Metaphors for Essays
- The Essay as a Journey : Navigating through the pages is like embarking on a literary expedition, each paragraph a step forward in exploration.
- Words as Building Blocks: Just as a builder meticulously selects bricks, the writer chooses words to construct the foundation of their essay.
- Essays as Time Capsules of Thought: Imagine essays as sealed capsules, preserving and encapsulating the essence of thoughts for future revelation.
- The Pen as a Sword: In the hands of a skilled writer, the pen transforms into a mighty sword, carving narratives that leave a lasting impact.
- The Canvas of Ideas: Essays are blank canvases awaiting the strokes of creativity, each idea a vibrant color adding depth to the masterpiece.
- The Musical Composition of Sentences: Sentences harmonize like musical notes, with metaphors as the chords that create a symphony of literary brilliance.
- Metaphors as Sparks of Imagination: Like sparks that ignite a fire, metaphors fuel the flames of imagination, turning the mundane into the extraordinary.
- Weaving Metaphors in the Fabric of Expression: Writers, akin to skilled weavers, interlace metaphors into the very fabric of their expression, creating textured narratives.
- The Alchemy of Creativity in Writing: Metaphors, like alchemists’ potions, possess the transformative power to turn ordinary words into literary gold.
- Essays as Gardens of Ideas: Cultivating ideas in essays is akin to tending a garden, with each thought blooming like a unique, vibrant flower.
- The Essayist as an Architect: Just as an architect plans a structure, essayists carefully design their compositions, selecting metaphors as architectural embellishments.
- Metaphors as Bridges: In the vast landscape of ideas, metaphors act as bridges, connecting the reader to the writer’s thoughts seamlessly.
- The Essayist as a Sculptor: Sculpting words, essayists chisel away the unnecessary, revealing the masterpiece within, with metaphors adding intricate details.
- The Essay as a Puzzle: Each paragraph in an essay is a puzzle piece, and metaphors are the connectors that bring coherence to the overall picture.
- Metaphors as Light in Darkness: Just as a beam of light dispels darkness, metaphors illuminate essays, revealing hidden nuances and depths.
- Essays as Culinary Delights: Crafting an essay is like preparing a culinary masterpiece, with metaphors as the seasonings that enhance the flavor.
- The Essay as a Conversation: Essays engage in a dialogue with readers, and metaphors serve as eloquent conversationalists, making the exchange more dynamic.
- Metaphors as Windows: They open windows to new perspectives, allowing readers to view familiar concepts in refreshing and insightful ways.
- The Essay as a Symphony: Like a symphony, essays require harmony, and metaphors contribute the musicality that resonates with the reader.
- Essays as Mirrors: Reflecting thoughts and ideas, essays are mirrors that reveal the depth of the writer’s insights, with metaphors as the silver lining.
- The Essayist as a Gardener of Ideas: Just as a gardener tends to plants, essayists nurture ideas, with metaphors acting as the fertilizer that promotes growth.
- Metaphors as Spice in Writing: Essays become literary dishes, and metaphors are the spices that infuse the writing with zest and vibrancy.
- Essays as Constellations: Like stars in a constellation, each idea in an essay forms a unique pattern, with metaphors connecting them into a meaningful whole.
- The Essayist as a Tour Guide: In the journey of an essay, the writer is a guide, and metaphors are the landmarks that make the experience memorable.
- Metaphors as Puzzle Pieces: Each metaphor fits into the essay like a puzzle piece, contributing to the overall coherence and completeness.
- The Essay as a Tapestry: Woven with threads of ideas, an essay is a tapestry, and metaphors add intricate patterns that make it visually and intellectually appealing.
These metaphors provide imaginative ways to conceptualize the art of essay writing.
Words as Building Blocks
In the intricate process of crafting an essay, words serve as the foundational building blocks, carefully selected to construct a robust structure that conveys the intended message. This metaphor emphasizes the importance of precision and thoughtfulness in word choice.
When to Use:
- Formal Context: In academic or professional essays where clarity and precision are paramount.
- Informal Context: When sharing personal reflections or experiences in a blog post.
Example: Formal Context: “In scholarly endeavors, each word acts as a building block, contributing to the solid foundation of academic discourse.”
Informal Context: “As I penned down my thoughts, I realized how each word became a building block, shaping the narrative of my personal journey.”
Variations:
- Colleague Interaction: “In our collaborative report, let’s ensure every word functions as a building block for a cohesive document.”
- Friend’s Feedback: “Your storytelling is fantastic! Each word feels like a building block, constructing a vivid picture in my mind .”
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Enhances clarity, strengthens the essay’s structure.
- Cons: Risk of overthinking word choice; may slow down the writing process.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that each word used aligns with the overall tone and purpose of the essay, maintaining consistency and coherence.
Definition: The metaphor “words as building blocks” underscores the foundational role of individual words in constructing a well-organized and impactful essay.
- Consider the connotation and nuance of each word.
- Use a diverse vocabulary to add richness to the essay.
Essays as Time Capsules of Thought
As we delve into the realm of essay writing, envisioning essays as time capsules offers a poignant perspective. Each essay becomes a vessel, encapsulating and preserving the essence of thoughts, ideas, and perspectives for future revelations.
- Formal Context: Reflecting on the historical significance or evolution of ideas.
- Informal Context: Sharing personal reflections on life experiences.
Example: Formal Context: “In academic writing, essays act as time capsules, capturing the intellectual evolution of concepts over the years.”
Informal Context: “As I penned my reflections on the past year, I realized my journal entries serve as time capsules, preserving my thoughts and emotions.”
- Mentor-Mentee Discussion: “Your thesis is a time capsule, showcasing the evolution of your research journey.”
- Friend’s Feedback: “Your travel essay reads like a time capsule, vividly preserving the essence of your adventures.”
- Pros: Adds depth and significance to the essay; offers a reflective element.
- Cons: May require a thoughtful selection of ideas for preservation.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure the ideas encapsulated in the essay align with the overall theme and purpose, maintaining coherence.
Definition: The metaphor “essays as time capsules” highlights the role of essays in preserving and encapsulating thoughts and ideas for future reference.
- Clearly define the time frame or context within which the ideas are encapsulated.
- Use vivid language to enhance the time-capsule imagery.
The Pen as a Sword
In the arsenal of writing metaphors, the imagery of the pen as a sword captures the transformative power wielded by skilled writers. Every stroke becomes a strategic move, carving narratives with precision and leaving a lasting impact on readers.
- Formal Context: Emphasizing the persuasive and influential nature of academic or professional writing.
- Informal Context: Crafting compelling narratives in personal essays or storytelling.
Example: Formal Context: “In legal discourse, the pen is indeed a sword, capable of shaping and reshaping the boundaries of jurisprudence.”
Informal Context: “As I penned my travel memoir, I felt the pen transform into a sword, carving tales of adventure and exploration.”
- Colleague Collaboration: “Let’s approach this proposal as if the pen is a sword, crafting a persuasive argument.”
- Friend’s Response: “Your creative writing is a sword, cutting through ordinary narratives with a unique edge.”
- Pros: Emphasizes the impact of words; encourages powerful and persuasive writing.
- Cons: Requires a nuanced approach to avoid excessive or inappropriate use.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that the metaphor aligns with the tone and objective of the writing, maintaining professionalism and impact.
Definition: The metaphor “the pen as a sword” symbolizes the influential and transformative power of words, likening them to a weapon in the hands of a skilled writer.
- Use this metaphor judiciously to highlight key points or arguments.
- Consider the ethical implications of wielding the “pen-sword.”
The Canvas of Ideas
In the realm of essay writing, viewing essays as blank canvases awaiting strokes of creativity emphasizes the unlimited potential for expression. Each idea is a vibrant color, contributing to the masterpiece being painted with words.
- Formal Context: Encouraging creativity in academic writing, particularly in subjects where innovative ideas are valued.
- Informal Context: Expressing personal thoughts, feelings, or reflections with a creative flair.
Example: Formal Context: “In scientific research, essays serve as canvases, allowing researchers to paint groundbreaking ideas that challenge existing paradigms.”
Informal Context: “My personal essay on resilience became a canvas of ideas, each paragraph a stroke depicting my journey through challenges.”
- Mentor-Mentee Discussion: “Approach your thesis as a canvas, where each idea contributes to the overall masterpiece.”
- Friend’s Feedback: “Your essay on friendship is a vibrant canvas, portraying the beauty of companionship.”
- Pros: Fosters creativity; encourages a fresh and innovative approach to writing.
- Cons: Requires a balance to prevent excessive embellishment that might dilute the message.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that the metaphor aligns with the overall purpose of the essay, maintaining coherence and relevance.
Definition: The metaphor “the canvas of ideas” illustrates the creative and expressive nature of essays, likening them to a blank canvas waiting to be adorned.
- Encourage experimentation with ideas, allowing for a diverse and colorful essay.
- Use vivid language to enhance the imagery of the canvas.
The Musical Composition of Sentences
In the symphony of essay writing, sentences harmonize like musical notes, and metaphors act as the chords that create a melodious and captivating composition. This metaphor highlights the rhythmic flow and cadence that metaphors contribute to the overall structure of an essay.
- Formal Context: Enhancing the eloquence of academic writing, particularly in literature or humanities disciplines.
- Informal Context: Infusing storytelling with a rhythmic and musical quality, making the narrative more engaging.
Example: Formal Context: “In literary analysis, consider each sentence as a musical note, and metaphors as the chords that elevate the entire composition.”
Informal Context: “As I crafted my personal essay, I aimed for a musical composition of sentences, where metaphors acted as harmonious chords guiding the reader through the narrative.”
- Colleague Collaboration: “Let’s approach the introduction like a musical composition, where each sentence sets the tone for the entire essay.”
- Friend’s Response: “Your storytelling reads like a musical composition, with metaphors serving as delightful harmonies.”
- Pros: Enhances the rhythm and flow of writing; adds a lyrical quality to the essay.
- Cons: Requires careful consideration to maintain coherence and prevent overuse.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that the musical metaphor aligns with the overall tone and theme of the essay, creating a harmonious blend.
Definition: The metaphor “the musical composition of sentences” evokes the rhythmic and harmonious quality of well-crafted sentences in essay writing.
- Pay attention to sentence structure and variety to create a musical rhythm.
- Experiment with pacing, using metaphors strategically to enhance the cadence.
Metaphors as Sparks of Imagination
Unlocking the door to creativity, metaphors serve as sparks that ignite the flames of imagination in the essay-writing process. This metaphor emphasizes the transformative power of metaphors in turning mundane concepts into vivid and imaginative expressions.
- Formal Context: Encouraging imaginative thinking in academic or technical writing, especially in fields where creativity is valued.
- Informal Context: Adding a touch of flair to personal narratives or creative non-fiction.
Example: Formal Context: “In scientific discourse, metaphors act as sparks, igniting new perspectives and fostering innovative approaches to complex problems.”
Informal Context: “As I delved into my reflective essay, I realized how metaphors served as sparks, transforming ordinary memories into vivid and imaginative stories.”
- Mentor-Mentee Discussion: “Think of metaphors as sparks in your thesis, infusing your research with imaginative and innovative thinking.”
- Friend’s Feedback: “Your metaphors are sparks of creativity, turning a simple story into a captivating adventure.”
- Pros: Stimulates creative thinking; adds a dynamic and engaging element to writing.
- Cons: Requires a balance to prevent excessive metaphorical embellishment.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that the metaphor aligns with the context and purpose of the essay, sparking imagination without veering off-topic.
Definition: The metaphor “metaphors as sparks of imagination” emphasizes the role of metaphors in sparking creative thinking and imaginative expression in essays.
- Experiment with unexpected metaphors to surprise and engage the reader.
- Use metaphors strategically to convey abstract concepts in a concrete and imaginative manner.
Weaving Metaphors in the Fabric of Expression
Imagine the act of essay writing as a textile art, where writers weave metaphors into the very fabric of their expression. This metaphor underscores the intricate and deliberate nature of incorporating metaphors seamlessly into the narrative.
- Formal Context: Emphasizing the artistry of language in academic or professional writing, particularly in literature or arts-related subjects.
- Informal Context: Conveying personal stories with a rich tapestry of metaphors, making the narrative more engaging.
Example: Formal Context: “In art history essays, consider metaphors as threads, intricately woven into the fabric of expression, adding depth and nuance to your analysis.”
Informal Context: “As I shared my life experiences in the essay, each metaphor became a thread, weaving through the fabric of expression and creating a vivid tapestry of my journey.”
- Colleague Collaboration: “Let’s approach the conclusion like skilled weavers, weaving metaphors into the fabric of expression for a memorable ending.”
- Friend’s Response: “Your metaphors are like threads, weaving through the fabric of your storytelling, creating a colorful and captivating narrative.”
- Pros: Enhances the richness of language; creates a visually appealing and immersive experience for the reader.
- Cons: Requires careful consideration to maintain coherence and prevent metaphorical overload.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that metaphors are seamlessly integrated into the overall narrative, contributing to the fabric of expression without overshadowing the main message.
Definition: The metaphor “weaving metaphors in the fabric of expression” portrays essay writing as a deliberate and artistic process where metaphors are integral to the overall composition.
- Use metaphors strategically to emphasize key points and evoke emotions.
- Ensure the metaphorical threads align with the thematic focus of the essay.
The Alchemy of Creativity in Writing
In the enchanting world of essay writing, metaphors act as alchemists’ potions, possessing the transformative power to turn ordinary words into literary gold. This metaphor emphasizes the magical and elevating quality that metaphors bring to the craft of writing.
- Formal Context: Encouraging creative thinking and expression in academic or professional essays, especially in disciplines that value originality.
- Informal Context: Elevating personal narratives or creative non-fiction with a touch of literary alchemy.
Example: Formal Context: “In philosophical discourse, metaphors act as alchemists, transmuting abstract concepts into literary gold, making complex ideas accessible and engaging.”
Informal Context: “As I explored my emotions in the essay, metaphors worked like alchemy, turning ordinary feelings into a golden tapestry of introspection.”
- Mentor-Mentee Discussion: “Think of metaphors as your writing alchemy, transforming ordinary ideas into literary treasures in your dissertation.”
- Friend’s Feedback: “Your metaphors are like alchemy, turning everyday stories into captivating narratives with a touch of magic.”
- Pros: Elevates writing to a higher level; adds a touch of magic and allure to the narrative.
- Cons: Requires careful selection to avoid overuse and maintain authenticity.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that metaphors align with the overall tone and purpose of the essay, contributing to the alchemy of creativity without becoming distracting.
Definition: The metaphor “the alchemy of creativity in writing” illustrates the transformative power of metaphors, turning ordinary words into literary gold in the process of essay crafting.
- Experiment with unconventional metaphors to infuse a sense of magic and wonder into the writing.
- Use metaphors sparingly to maintain their enchanting impact.
Essays as Gardens of Ideas
Embark with me on the metaphorical journey where essays are likened to gardens, and ideas flourish like vibrant flowers, adding color, depth, and fragrance to the narrative. This metaphor emphasizes the nurturing aspect of essay writing, where writers carefully cultivate and present a diverse array of ideas.
- Formal Context: Encouraging a comprehensive exploration of ideas in academic writing, especially in subjects that require depth and diversity of thought.
- Informal Context: Crafting personal essays that showcase a rich tapestry of thoughts and reflections.
Example: Formal Context: “In sociological essays, think of ideas as blossoming flowers, each representing a unique perspective contributing to the overall garden of knowledge.”
Informal Context: “My reflective essay on personal growth became a garden of ideas, where each paragraph bloomed like a distinct flower, revealing a different facet of my journey.”
- Colleague Collaboration: “Let’s approach this research paper like gardeners, nurturing diverse ideas that collectively enrich the overall narrative.”
- Friend’s Response: “Your essay is like a garden of ideas, with each thought blooming into a beautiful flower, creating a captivating bouquet of storytelling.”
- Pros: Encourages a holistic exploration of ideas; adds depth and diversity to the essay.
- Cons: Requires careful organization to ensure each idea contributes cohesively to the overall narrative.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that each idea is carefully cultivated and presented, contributing meaningfully to the overarching theme of the essay.
Definition: The metaphor “essays as gardens of ideas” conveys the nurturing and diverse nature of ideas in the essay-writing process, akin to tending to a garden.
- Cultivate a variety of ideas to create a rich and engaging narrative.
- Ensure a balance between depth and breadth in exploring different perspectives.
The Essayist as an Architect
Picture the essayist as an architect, meticulously planning the structure of an essay, with metaphors acting as architectural embellishments that enhance the overall design. This metaphor underscores the importance of thoughtful composition and strategic use of metaphors in crafting compelling essays.
- Formal Context: Emphasizing the strategic organization of ideas in academic or professional essays, especially in disciplines where structure is crucial.
- Informal Context: Applying a deliberate and structured approach to storytelling in personal essays.
Example: Formal Context: “In business essays, consider each section as a blueprint, and metaphors as architectural embellishments that reinforce the solidity of your argument.”
Informal Context: “As I constructed my narrative essay, I approached it like an architect, planning the structure with metaphors as decorative elements, enhancing the overall design.”
- Mentor-Mentee Discussion: “Approach your dissertation like an architect, with each chapter as a carefully planned structure, and metaphors as essential design elements.”
- Friend’s Feedback: “Your essay is like a well-designed building, with metaphors serving as architectural details that make the storytelling more compelling.”
- Pros: Enhances the organization and coherence of the essay; adds a visual and structural dimension to the writing.
- Cons: Requires careful planning to ensure metaphors align with the overall structure and theme.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that metaphors contribute to the architectural integrity of the essay, reinforcing the structure without overshadowing the core message.
Definition: The metaphor “the essayist as an architect” paints a vivid picture of the deliberate planning and structured approach to essay writing, with metaphors as integral architectural elements.
- Plan the essay structure carefully, assigning specific roles to different sections.
- Use metaphors strategically to reinforce key points and contribute to the overall coherence.
Metaphors as Bridges
Imagine the vast landscape of ideas in an essay as a series of islands, and metaphors as bridges that seamlessly connect these intellectual realms. This metaphor highlights the role of metaphors in creating smooth transitions between different concepts, ensuring a cohesive and engaging journey for the reader.
- Formal Context: Facilitating the logical progression of ideas in academic writing, especially in essays that explore diverse topics.
- Informal Context: Connecting personal anecdotes or reflections in a way that feels natural and effortless.
Example: Formal Context: “In political science essays, think of metaphors as bridges, linking theories and real-world applications to create a cohesive and insightful narrative.”
Informal Context: “As I shared my travel experiences, metaphors acted as bridges, seamlessly connecting one destination to another, creating a fluid and captivating storytelling experience.”
- Colleague Collaboration: “Let’s treat each section of our report as an island, and use metaphors as bridges to connect the ideas, ensuring a smooth transition between concepts.”
- Friend’s Response: “Your essay feels like a journey with metaphors serving as bridges, linking different aspects of your story in a way that flows naturally.”
- Pros: Enhances the flow of ideas; ensures a seamless transition between different sections.
- Cons: Requires thoughtful selection to maintain coherence and avoid abrupt shifts.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that metaphors serve as effective bridges, guiding the reader from one idea to the next without causing confusion or disconnection.
Definition: The metaphor “metaphors as bridges” emphasizes the role of metaphors in creating connections and maintaining a smooth flow of ideas in an essay.
- Use metaphors strategically at key transition points to guide the reader through the essay.
- Ensure that each metaphorical bridge enhances the overall coherence and narrative progression.
The Essayist as a Sculptor
Envision the essayist as a sculptor, shaping words and ideas with precision, and metaphors as intricate details that add depth and nuance to the crafted piece. This metaphor emphasizes the deliberate and artistic nature of essay writing, where every word contributes to the overall composition.
- Formal Context: Emphasizing the meticulous crafting of arguments and analysis in academic essays, particularly in disciplines that value precision.
- Informal Context: Adding an artistic flair to personal essays, where the narrative is shaped with care and intention.
Example: Formal Context: “In literary analysis, view metaphors as the sculptor’s chisel, carving out layers of meaning and interpretation with precision.”
Informal Context: “As I penned my reflective essay, I approached it like a sculptor, molding my experiences with metaphors as intricate details, shaping the narrative with care.”
- Mentor-Mentee Discussion: “Consider each paragraph as a piece of marble, and metaphors as the sculptor’s tools that refine and enhance the overall structure of your thesis.”
- Friend’s Feedback: “Your essay is like a sculpture, with metaphors as the detailed carvings that make the storytelling more vivid and impactful.”
- Pros: Elevates the writing to an artistic level; adds precision and depth to the overall composition.
- Cons: Requires careful consideration to avoid excessive ornamentation.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that metaphors act as sculptor’s tools, enhancing the clarity and impact of the essay without overshadowing the main message.
Definition: The metaphor “the essayist as a sculptor” conveys the intentional and artistic approach to essay writing, where metaphors serve as tools for refinement and precision.
- Approach each paragraph with the intention of sculpting a clear and impactful narrative.
- Use metaphors sparingly to maintain the overall focus and coherence of the essay.
The Essay as a Symphony
Envision the essay as a symphony, where each paragraph contributes a unique note, and metaphors act as harmonious chords that resonate throughout the composition. This metaphor underscores the rhythmic and coordinated nature of a well-structured essay, where metaphors play a vital role in creating a harmonious narrative.
- Formal Context: Emphasizing the orchestration of ideas in academic essays, particularly in subjects that require a cohesive and interconnected argument.
- Informal Context: Crafting personal essays with a rhythmic flow, where each metaphor contributes to the overall harmony of the narrative.
Example: Formal Context: “In historical essays, metaphors function as chords, weaving through each paragraph and creating a symphony of interconnected ideas that resonate with the reader.”
Informal Context: “As I shared my life story in the essay, I aimed for a symphony of emotions, where metaphors acted as chords, adding depth and resonance to my narrative.”
- Colleague Collaboration: “Let’s approach the conclusion as the grand finale of our symphony, using metaphors as chords to create a lasting impression on our readers.”
- Friend’s Response: “Your essay reads like a symphony, with metaphors serving as harmonious chords that make the storytelling captivating and memorable.”
- Pros: Enhances the overall rhythm and coherence of the essay; creates a memorable and engaging reading experience.
- Cons: Requires careful selection to maintain thematic unity and prevent discordant notes.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that metaphors contribute to the symphonic nature of the essay, creating a cohesive and well-orchestrated composition.
Definition: The metaphor “the essay as a symphony” conveys the coordinated and rhythmic nature of a well-structured essay, where metaphors function as harmonious chords.
- Use metaphors strategically to emphasize key themes and create a sense of unity.
- Consider the pacing and placement of metaphors to enhance the overall symphonic experience.
The Essayist as a Navigator
Picture the essayist as a navigator, steering through the vast sea of ideas with precision, and metaphors as navigational tools that guide readers through the intellectual journey. This metaphor emphasizes the strategic use of metaphors to ensure clarity and coherence in the exploration of complex topics.
- Formal Context: Emphasizing the logical progression and navigation of ideas in academic essays, especially in disciplines that require a clear and structured argument.
- Informal Context: Creating personal essays where metaphors act as guiding lights, making the narrative accessible and engaging.
Example: Formal Context: “In scientific essays, metaphors function as navigational tools, guiding readers through the intricate concepts and ensuring a clear understanding of the research.”
Informal Context: “As I delved into philosophical reflections, I saw myself as a navigator, using metaphors as guiding stars to lead readers through the complexities of my thoughts.”
- Mentor-Mentee Discussion: “Treat your literature review as a navigational map, and use metaphors as tools to guide your readers through the diverse scholarly perspectives.”
- Friend’s Feedback: “Your essay is like a journey with you as the navigator, and metaphors as compass points that make the exploration both insightful and enjoyable.”
- Pros: Enhances the clarity and accessibility of complex ideas; guides readers through a well-structured intellectual journey.
- Cons: Requires thoughtful selection to avoid confusion and maintain the logical flow.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that metaphors function as effective navigational tools, aiding readers in understanding the progression of ideas in the essay.
Definition: The metaphor “the essayist as a navigator” portrays the intentional and strategic role of metaphors in guiding readers through the intellectual landscape of an essay.
- Use metaphors to introduce and connect key concepts in a way that aids understanding.
- Ensure that each metaphor aligns with the overall theme and purpose of the essay.
The Essay as a Kaleidoscope
Imagine the essay as a kaleidoscope, where ideas and perspectives shift and blend, creating a vibrant and ever-changing pattern. Metaphors, in this context, serve as the colorful elements that contribute to the kaleidoscopic richness of the narrative.
- Formal Context: Emphasizing the diversity of perspectives and ideas in academic writing, particularly in subjects that encourage varied viewpoints.
- Informal Context: Crafting personal essays with a dynamic and ever-evolving exploration of experiences and reflections.
Example: Formal Context: “In cultural studies essays, metaphors function as elements in a kaleidoscope, allowing readers to see the same topic from different angles, creating a nuanced and comprehensive understanding.”
Informal Context: “As I shared my personal journey, I envisioned my essay as a kaleidoscope, with each metaphor adding a burst of color, shaping the ever-shifting pattern of my experiences.”
- Colleague Collaboration: “Let’s approach this interdisciplinary essay as a kaleidoscope, where each section contributes a unique perspective, and metaphors act as the vibrant elements that tie everything together.”
- Friend’s Response: “Your storytelling is like a kaleidoscope, with metaphors adding diverse hues to the narrative, creating a rich and captivating tapestry.”
- Pros: Adds richness and diversity to the narrative; encourages readers to appreciate multiple facets of a topic.
- Cons: Requires careful organization to prevent the essay from becoming disjointed.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that metaphors contribute to the kaleidoscopic nature of the essay, enhancing the overall vibrancy and diversity of perspectives.
Definition: The metaphor “the essay as a kaleidoscope” portrays the dynamic and ever-changing nature of ideas and perspectives, with metaphors as key elements that contribute to the kaleidoscopic richness.
- Use metaphors strategically to explore different aspects of a topic.
- Ensure a cohesive and well-structured essay, even as perspectives shift and evolve.
The Essayist as a Gardener of Thought
Visualize the essayist as a gardener, tending to the seeds of thoughts and ideas with care, and metaphors as the nutrients that enrich the intellectual soil. This metaphor emphasizes the nurturing aspect of essay writing, where metaphors play a vital role in cultivating a fertile ground for insightful discussions.
- Formal Context: Encouraging the development and growth of ideas in academic writing, particularly in essays that require in-depth exploration.
- Informal Context: Crafting personal essays with a focus on the careful cultivation of thoughts and reflections.
Example: Formal Context: “In psychological essays, metaphors serve as nutrients for the intellectual garden, fostering the growth of theories and facilitating a deeper understanding of complex concepts.”
Informal Context: “As I explored my personal beliefs, I saw myself as a gardener of thoughts, using metaphors as nutrients to cultivate a rich and flourishing landscape of ideas.”
- Mentor-Mentee Discussion: “Approach your thesis as a garden of thoughts, and let metaphors act as the nutrients that enhance the intellectual richness of your research.”
- Friend’s Feedback: “Your essay feels like a carefully tended garden, with metaphors serving as nutrients that make the ideas flourish and bloom.”
- Pros: Fosters the growth and development of ideas; contributes to a nuanced and well-explored narrative.
- Cons: Requires thoughtful selection to ensure metaphors align with the overall theme and purpose.
Grammar/Usage Rule: Ensure that metaphors act as effective nutrients, enhancing the intellectual soil and contributing to the overall richness of the essay.
Definition: The metaphor “the essayist as a gardener of thought” conveys the intentional and nurturing approach to essay writing, where metaphors play a vital role in fostering the growth of insightful ideas.
- Use metaphors strategically to enrich the intellectual landscape of the essay.
- Ensure a balanced and well-nurtured exploration of ideas, even as metaphors contribute to their growth.
How do metaphors enhance essays?
Metaphors elevate essays by adding depth and vividness, making abstract concepts relatable and engaging.
- Use metaphors when you want to evoke emotions and create a lasting impression.
- Employ metaphors in descriptive and narrative writing to paint vivid pictures for your readers.
Example: “Incorporating metaphors in your essay enhances the overall reading experience, transforming abstract concepts into tangible images that resonate with your audience.”
Tip: “Experiment with various metaphors to find the ones that best convey your intended message. Consider the emotions and images each metaphor evokes.”
Can I use metaphors in academic essays?
Absolutely! Thoughtful use of metaphors can enhance the clarity and impact of academic writing.
- Introduce metaphors sparingly in academic essays to emphasize key points.
- Ensure that the metaphor aligns with the formal tone of academic writing and enhances understanding.
Example: “While maintaining academic rigor, strategic use of metaphors can elucidate complex theories and captivate the reader’s attention in your research paper.”
Tip: “Avoid clichéd metaphors in academic writing. Instead, opt for metaphors that bring fresh perspectives to your subject matter.”
Are clichéd metaphors a red flag?
While clichés should be used sparingly, a well-placed familiar metaphor can effectively convey ideas.
How to choose the right metaphor?
Consider your message and audience; choose metaphors that resonate and enhance your intended meaning.
Can metaphors be humorous in essays?
Certainly! Humorous metaphors inject personality into your writing, making it more enjoyable for readers.
Do metaphors work in technical writing?
Yes, when used judiciously. Metaphors can simplify complex ideas, aiding understanding in technical writing.
In conclusion, the arsenal of metaphors is a potent tool for crafting essays that linger in the minds of readers. This guide has unveiled the artistry of metaphorical expression, encouraging writers to embrace creativity and wield metaphors with finesse. As you embark on your essay-writing journey, remember the transformative power of metaphors in shaping literary masterpieces.
Similar Posts

26 Metaphors for Dreams: Unlocking the Realm of Imagination
Share this post: Facebook X Pinterest Dreams, the ethereal landscapes of our subconscious, have fascinated humans for centuries. In this article, we delve into the poetic realm of…

26 Metaphors for Excitement: Spark Your Language
Excitement is like a spark igniting in our hearts, a feeling that propels us forward with unbridled energy. It’s the sensation of being on the edge of something…

26 Metaphors for Winter: Embracing the Beauty of the Season
Winter, with its frosty charm and serene landscapes, has inspired poets, writers, and artists for centuries. It’s a season of transformation, where the world is blanketed in a…

26 Metaphors for Identity: Unveiling the Layers of Self
Discovering one’s identity is a fascinating odyssey, akin to navigating through a myriad of metaphors that encapsulate the complexity of the self. In this article, we embark on…

26 Metaphors for Freedom – Unleashing the Power of Liberation
Freedom, a concept deeply ingrained in the human spirit, has been the subject of countless discussions, debates, and expressions. It is a force that transcends boundaries, ideologies, and…

26 Metaphors for the Ocean: Unveiling the Depths of Imagination
The ocean, with its vastness and mystique, has been a perennial source of inspiration for poets, writers, and dreamers throughout history. It’s a canvas upon which the human…
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
16 Strong College Essay Examples from Top Schools

What’s Covered:
- Common App Essays
- Why This College Essays
- Why This Major Essays
- Extracurricular Essays
- Overcoming Challenges Essays
- Community Service Essays
- Diversity Essays
- Political/Global Issues Essays
- Where to Get Feedback on Your Essays
Most high school students don’t get a lot of experience with creative writing, so the college essay can be especially daunting. Reading examples of successful essays, however, can help you understand what admissions officers are looking for.
In this post, we’ll share 16 college essay examples of many different topics. Most of the essay prompts fall into 8 different archetypes, and you can approach each prompt under that archetype in a similar way. We’ve grouped these examples by archetype so you can better structure your approach to college essays.
If you’re looking for school-specific guides, check out our 2022-2023 essay breakdowns .
Looking at examples of real essays students have submitted to colleges can be very beneficial to get inspiration for your essays. You should never copy or plagiarize from these examples when writing your own essays. Colleges can tell when an essay isn’t genuine and will not view students favorably if they plagiarized.
Note: the essays are titled in this post for navigation purposes, but they were not originally titled. We also include the original prompt where possible.
The Common App essay goes to all of the schools on your list, unless those schools use a separate application platform. Because of this, it’s the most important essay in your portfolio, and likely the longest essay you’ll need to write (you get up to 650 words).
The goal of this essay is to share a glimpse into who you are, what matters to you, and what you hope to achieve. It’s a chance to share your story.
Learn more about how to write the Common App essay in our complete guide.
The Multiple Meanings of Point
Prompt: Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story. (250-650 words)
Night had robbed the academy of its daytime colors, yet there was comfort in the dim lights that cast shadows of our advances against the bare studio walls. Silhouettes of roundhouse kicks, spin crescent kicks, uppercuts and the occasional butterfly kick danced while we sparred. She approached me, eyes narrowed with the trace of a smirk challenging me. “Ready spar!” Her arm began an upward trajectory targeting my shoulder, a common first move. I sidestepped — only to almost collide with another flying fist. Pivoting my right foot, I snapped my left leg, aiming my heel at her midsection. The center judge raised one finger.
There was no time to celebrate, not in the traditional sense at least. Master Pollard gave a brief command greeted with a unanimous “Yes, sir” and the thud of 20 hands dropping-down-and-giving-him-30, while the “winners” celebrated their victory with laps as usual.
Three years ago, seven-thirty in the evening meant I was a warrior. It meant standing up straighter, pushing a little harder, “Yes, sir” and “Yes, ma’am”, celebrating birthdays by breaking boards, never pointing your toes, and familiarity. Three years later, seven-thirty in the morning meant I was nervous.
The room is uncomfortably large. The sprung floor soaks up the checkerboard of sunlight piercing through the colonial windows. The mirrored walls further illuminate the studio and I feel the light scrutinizing my sorry attempts at a pas de bourrée, while capturing the organic fluidity of the dancers around me. “Chassé en croix, grand battement, pique, pirouette.” I follow the graceful limbs of the woman in front of me, her legs floating ribbons, as she executes what seems to be a perfect ronds de jambes. Each movement remains a negotiation. With admirable patience, Ms. Tan casts me a sympathetic glance.
There is no time to wallow in the misery that is my right foot. Taekwondo calls for dorsiflexion; pointed toes are synonymous with broken toes. My thoughts drag me into a flashback of the usual response to this painful mistake: “You might as well grab a tutu and head to the ballet studio next door.” Well, here I am Master Pollard, unfortunately still following your orders to never point my toes, but no longer feeling the satisfaction that comes with being a third degree black belt with 5 years of experience quite literally under her belt. It’s like being a white belt again — just in a leotard and ballet slippers.
But the appetite for new beginnings that brought me here doesn’t falter. It is only reinforced by the classical rendition of “Dancing Queen” that floods the room and the ghost of familiarity that reassures me that this new beginning does not and will not erase the past. After years spent at the top, it’s hard to start over. But surrendering what you are only leads you to what you may become. In Taekwondo, we started each class reciting the tenets: honor, courtesy, integrity, perseverance, self-control, courage, humility, and knowledge, and I have never felt that I embodied those traits more so than when I started ballet.
The thing about change is that it eventually stops making things so different. After nine different schools, four different countries, three different continents, fluency in Tamil, Norwegian, and English, there are more blurred lines than there are clear fragments. My life has not been a tactfully executed, gold medal-worthy Taekwondo form with each movement defined, nor has it been a series of frappés performed by a prima ballerina with each extension identical and precise, but thankfully it has been like the dynamics of a spinning back kick, fluid, and like my chances of landing a pirouette, unpredictable.
The first obvious strength of this essay is the introduction—it is interesting and snappy and uses enough technical language that we want to figure out what the student is discussing. When writing introductions, students tend to walk the line between intriguing and confusing. It is important that your essay ends up on the intentionally intriguing side of that line—like this student does! We are a little confused at first, but by then introducing the idea of “sparring,” the student grounds their essay.
People often advise young writers to “show, not tell.” This student takes that advice a step further and makes the reader do a bit of work to figure out what they are telling us. Nowhere in this essay does it say “After years of Taekwondo, I made the difficult decision to switch over to ballet.” Rather, the student says “It’s like being a white belt again — just in a leotard and ballet slippers.” How powerful!
After a lot of emotional language and imagery, this student finishes off their essay with very valuable (and necessary!) reflection. They show admissions officers that they are more than just a good writer—they are a mature and self-aware individual who would be beneficial to a college campus. Self-awareness comes through with statements like “surrendering what you are only leads you to what you may become” and maturity can be seen through the student’s discussion of values: “honor, courtesy, integrity, perseverance, self-control, courage, humility, and knowledge, and I have never felt that I embodied those traits more so than when I started ballet.”
Sparking Self-Awareness
Prompt: The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure. How did it affect you, and what did you learn from the experience? (250-650 words)
Was I no longer the beloved daughter of nature, whisperer of trees? Knee-high rubber boots, camouflage, bug spray—I wore the garb and perfume of a proud wild woman, yet there I was, hunched over the pathetic pile of stubborn sticks, utterly stumped, on the verge of tears. As a child, I had considered myself a kind of rustic princess, a cradler of spiders and centipedes, who was serenaded by mourning doves and chickadees, who could glide through tick-infested meadows and emerge Lyme-free. I knew the cracks of the earth like the scars on my own rough palms. Yet here I was, ten years later, incapable of performing the most fundamental outdoor task: I could not, for the life of me, start a fire.
Furiously I rubbed the twigs together—rubbed and rubbed until shreds of skin flaked from my fingers. No smoke. The twigs were too young, too sticky-green; I tossed them away with a shower of curses, and began tearing through the underbrush in search of a more flammable collection. My efforts were fruitless. Livid, I bit a rejected twig, determined to prove that the forest had spurned me, offering only young, wet bones that would never burn. But the wood cracked like carrots between my teeth—old, brittle, and bitter. Roaring and nursing my aching palms, I retreated to the tent, where I sulked and awaited the jeers of my family.
Rattling their empty worm cans and reeking of fat fish, my brother and cousins swaggered into the campsite. Immediately, they noticed the minor stick massacre by the fire pit and called to me, their deep voices already sharp with contempt.
“Where’s the fire, Princess Clara?” they taunted. “Having some trouble?” They prodded me with the ends of the chewed branches and, with a few effortless scrapes of wood on rock, sparked a red and roaring flame. My face burned long after I left the fire pit. The camp stank of salmon and shame.
In the tent, I pondered my failure. Was I so dainty? Was I that incapable? I thought of my hands, how calloused and capable they had been, how tender and smooth they had become. It had been years since I’d kneaded mud between my fingers; instead of scaling a white pine, I’d practiced scales on my piano, my hands softening into those of a musician—fleshy and sensitive. And I’d gotten glasses, having grown horrifically nearsighted; long nights of dim lighting and thick books had done this. I couldn’t remember the last time I had lain down on a hill, barefaced, and seen the stars without having to squint. Crawling along the edge of the tent, a spider confirmed my transformation—he disgusted me, and I felt an overwhelming urge to squash him.
Yet, I realized I hadn’t really changed—I had only shifted perspective. I still eagerly explored new worlds, but through poems and prose rather than pastures and puddles. I’d grown to prefer the boom of a bass over that of a bullfrog, learned to coax a different kind of fire from wood, having developed a burn for writing rhymes and scrawling hypotheses.
That night, I stayed up late with my journal and wrote about the spider I had decided not to kill. I had tolerated him just barely, only shrieking when he jumped—it helped to watch him decorate the corners of the tent with his delicate webs, knowing that he couldn’t start fires, either. When the night grew cold and the embers died, my words still smoked—my hands burned from all that scrawling—and even when I fell asleep, the ideas kept sparking—I was on fire, always on fire.
First things first, this Common App essay is well-written. This student is definitely showing the admissions officers her ability to articulate her points beautifully and creatively. It starts with vivid images like that of the “rustic princess, a cradler of spiders and centipedes, who was serenaded by mourning doves and chickadees, who could glide through tick-infested meadows and emerge Lyme-free.” And because the prose is flowery (and beautiful!), the writer can get away with metaphors like “I knew the cracks of the earth like the scars on my own rough palms” that might sound cheesy without the clear command of the English language that the writer quickly establishes.
In addition to being well-written, this essay is thematically cohesive. It begins with the simple introduction “Fire!” and ends with the following image: “When the night grew cold and the embers died, my words still smoked—my hands burned from all that scrawling—and even when I fell asleep, the ideas kept sparking—I was on fire, always on fire.” This full-circle approach leaves readers satisfied and impressed.
While dialogue often comes off as cliche or trite, this student effectively incorporates her family members saying “Where’s the fire, Princess Clara?” This is achieved through the apt use of the verb “taunted” to characterize the questioning and through the question’s thematic connection to the earlier image of the student as a rustic princess. Similarly, rhetorical questions can feel randomly placed in essays, but this student’s inclusion of the questions “Was I so dainty?” and “Was I that incapable?” feel perfectly justified after she establishes that she was pondering her failure.
Quite simply, this essay shows how quality writing can make a simple story outstandingly compelling.
Why This College?
“Why This College?” is one of the most common essay prompts, likely because schools want to understand whether you’d be a good fit and how you’d use their resources.
This essay is one of the more straightforward ones you’ll write for college applications, but you still can and should allow your voice to shine through.
Learn more about how to write the “Why This College?” essay in our guide.
Prompt: How will you explore your intellectual and academic interests at the University of Pennsylvania? Please answer this question given the specific undergraduate school to which you are applying (650 words).
Sister Simone Roach, a theorist of nursing ethics, said, “caring is the human mode of being.” I have long been inspired by Sister Roach’s Five C’s of Caring: commitment, conscience, competence, compassion, and confidence. Penn both embraces and fosters these values through a rigorous, interdisciplinary curriculum and unmatched access to service and volunteer opportunities.
COMMITMENT. Reading through the activities that Penn Quakers devote their time to (in addition to academics!) felt like drinking from a firehose in the best possible way. As a prospective nursing student with interests outside of my major, I value this level of flexibility. I plan to leverage Penn’s liberal arts curriculum to gain an in-depth understanding of the challenges LGBT people face, especially regarding healthcare access. Through courses like “Interactional Processes with LGBT Individuals” and volunteering at the Mazzoni Center for outreach, I hope to learn how to better support the Penn LGBT community as well as my family and friends, including my cousin, who came out as trans last year.
CONSCIENCE. As one of the first people in my family to attend a four-year university, I wanted a school that promoted a sense of moral responsibility among its students. At Penn, professors challenge their students to question and recreate their own set of morals by sparking thought- provoking, open-minded discussions. I can imagine myself advocating for universal healthcare in courses such as “Health Care Reform & Future of American Health System” and debating its merits with my peers. Studying in an environment where students confidently voice their opinions – conservative or liberal – will push me to question and strengthen my value system.
COMPETENCE. Two aspects that drew my attention to Penn’s BSN program were its high-quality research opportunities and hands-on nursing projects. Through its Office of Nursing Research, Penn connects students to faculty members who share similar research interests. As I volunteered at a nursing home in high school, I hope to work with Dr. Carthon to improve the quality of care for senior citizens. Seniors, especially minorities, face serious barriers to healthcare that I want to resolve. Additionally, Penn’s unique use of simulations to bridge the gap between classroom learning and real-world application impressed me. Using computerized manikins that mimic human responses, classes in Penn’s nursing program allow students to apply their emergency medical skills in a mass casualty simulation and monitor their actions afterward through a video system. Participating in this activity will help me identify my strengths and areas for improvement regarding crisis management and medical care in a controlled yet realistic setting. Research opportunities and simulations will develop my skills even before I interact with patients.
COMPASSION. I value giving back through community service, and I have a particular interest in Penn’s Community Champions and Nursing Students For Sexual & Reproductive Health (NSRH). As a four-year volunteer health educator, I hope to continue this work as a Community Champions member. I am excited to collaborate with medical students to teach fourth and fifth graders in the city about cardiology or lead a chair dance class for the elders at the LIFE Center. Furthermore, as a feminist who firmly believes in women’s abortion rights, I’d like to join NSRH in order to advocate for women’s health on campus. At Penn, I can work with like-minded people to make a meaningful difference.
CONFIDENCE. All of the Quakers that I have met possess one defining trait: confidence. Each student summarized their experiences at Penn as challenging but fulfilling. Although I expect my coursework to push me, from my conversations with current Quakers I know it will help me to be far more effective in my career.
The Five C’s of Caring are important heuristics for nursing, but they also provide insight into how I want to approach my time in college. I am eager to engage with these principles both as a nurse and as a Penn Quaker, and I can’t wait to start.
This prompt from Penn asks students to tailor their answer to their specific field of study. One great thing that this student does is identify their undergraduate school early, by mentioning “Sister Simone Roach, a theorist of nursing ethics.” You don’t want readers confused or searching through other parts of your application to figure out your major.
With a longer essay like this, it is important to establish structure. Some students organize their essay in a narrative form, using an anecdote from their past or predicting their future at a school. This student uses Roach’s 5 C’s of Caring as a framing device that organizes their essay around values. This works well!
While this essay occasionally loses voice, there are distinct moments where the student’s personality shines through. We see this with phrases like “felt like drinking from a fire hose in the best possible way” and “All of the Quakers that I have met possess one defining trait: confidence.” It is important to show off your personality to make your essay stand out.
Finally, this student does a great job of referencing specific resources about Penn. It’s clear that they have done their research (they’ve even talked to current Quakers). They have dreams and ambitions that can only exist at Penn.
Prompt: What is it about Yale that has led you to apply? (125 words or fewer)
Coin collector and swimmer. Hungarian and Romanian. Critical and creative thinker. I was drawn to Yale because they don’t limit one’s mind with “or” but rather embrace unison with “and.”
Wandering through the Beinecke Library, I prepare for my multidisciplinary Energy Studies capstone about the correlation between hedonism and climate change, making it my goal to find implications in environmental sociology. Under the tutelage of Assistant Professor Arielle Baskin-Sommers, I explore the emotional deficits of depression, utilizing neuroimaging to scrutinize my favorite branch of psychology: human perception. At Walden Peer Counseling, I integrate my peer support and active listening skills to foster an empathetic environment for the Yale community. Combining my interests in psychological and environmental studies is why I’m proud to be a Bulldog.
This answer to the “Why This College” question is great because 1) the student shows their excitement about attending Yale 2) we learn the ways in which attending Yale will help them achieve their goals and 3) we learn their interests and identities.
In this response, you can find a prime example of the “Image of the Future” approach, as the student flashes forward and envisions their life at Yale, using present tense (“I explore,” “I integrate,” “I’m proud”). This approach is valuable if you are trying to emphasize your dedication to a specific school. Readers get the feeling that this student is constantly imagining themselves on campus—it feels like Yale really matters to them.
Starting this image with the Beinecke Library is great because the Beinecke Library only exists at Yale. It is important to tailor “Why This College” responses to each specific school. This student references a program of study, a professor, and an extracurricular that only exist at Yale. Additionally, they connect these unique resources to their interests—psychological and environmental studies.
Finally, we learn about the student (independent of academics) through this response. By the end of their 125 words, we know their hobbies, ethnicities, and social desires, in addition to their academic interests. It can be hard to tackle a 125-word response, but this student shows that it’s possible.
Why This Major?
The goal of this prompt is to understand how you came to be interested in your major and what you plan to do with it. For competitive programs like engineering, this essay helps admissions officers distinguish students who have a genuine passion and are most likely to succeed in the program. This is another more straightforward essay, but you do have a bit more freedom to include relevant anecdotes.
Learn more about how to write the “Why This Major?” essay in our guide.
Why Duke Engineering
Prompt: If you are applying to the Pratt School of Engineering as a first year applicant, please discuss why you want to study engineering and why you would like to study at Duke (250 words).
One Christmas morning, when I was nine, I opened a snap circuit set from my grandmother. Although I had always loved math and science, I didn’t realize my passion for engineering until I spent the rest of winter break creating different circuits to power various lights, alarms, and sensors. Even after I outgrew the toy, I kept the set in my bedroom at home and knew I wanted to study engineering. Later, in a high school biology class, I learned that engineering didn’t only apply to circuits, but also to medical devices that could improve people’s quality of life. Biomedical engineering allows me to pursue my academic passions and help people at the same time.
Just as biology and engineering interact in biomedical engineering, I am fascinated by interdisciplinary research in my chosen career path. Duke offers unmatched resources, such as DUhatch and The Foundry, that will enrich my engineering education and help me practice creative problem-solving skills. The emphasis on entrepreneurship within these resources will also help me to make a helpful product. Duke’s Bass Connections program also interests me; I firmly believe that the most creative and necessary problem-solving comes by bringing people together from different backgrounds. Through this program, I can use my engineering education to solve complicated societal problems such as creating sustainable surgical tools for low-income countries. Along the way, I can learn alongside experts in the field. Duke’s openness and collaborative culture span across its academic disciplines, making Duke the best place for me to grow both as an engineer and as a social advocate.
This prompt calls for a complex answer. Students must explain both why they want to study engineering and why Duke is the best place for them to study engineering.
This student begins with a nice hook—a simple anecdote about a simple present with profound consequences. They do not fluff up their anecdote with flowery images or emotionally-loaded language; it is what it is, and it is compelling and sweet. As their response continues, they express a particular interest in problem-solving. They position problem-solving as a fundamental part of their interest in engineering (and a fundamental part of their fascination with their childhood toy). This helps readers to learn about the student!
Problem-solving is also the avenue by which they introduce Duke’s resources—DUhatch, The Foundry, and Duke’s Bass Connections program. It is important to notice that the student explains how these resources can help them achieve their future goals—it is not enough to simply identify the resources!
This response is interesting and focused. It clearly answers the prompt, and it feels honest and authentic.
Why Georgia Tech CompSci
Prompt: Why do you want to study your chosen major specifically at Georgia Tech? (300 words max)
I held my breath and hit RUN. Yes! A plump white cat jumped out and began to catch the falling pizzas. Although my Fat Cat project seems simple now, it was the beginning of an enthusiastic passion for computer science. Four years and thousands of hours of programming later, that passion has grown into an intense desire to explore how computer science can serve society. Every day, surrounded by technology that can recognize my face and recommend scarily-specific ads, I’m reminded of Uncle Ben’s advice to a young Spiderman: “with great power comes great responsibility”. Likewise, the need to ensure digital equality has skyrocketed with AI’s far-reaching presence in society; and I believe that digital fairness starts with equality in education.
The unique use of threads at the College of Computing perfectly matches my interests in AI and its potential use in education; the path of combined threads on Intelligence and People gives me the rare opportunity to delve deep into both areas. I’m particularly intrigued by the rich sets of both knowledge-based and data-driven intelligence courses, as I believe AI should not only show correlation of events, but also provide insight for why they occur.
In my four years as an enthusiastic online English tutor, I’ve worked hard to help students overcome both financial and technological obstacles in hopes of bringing quality education to people from diverse backgrounds. For this reason, I’m extremely excited by the many courses in the People thread that focus on education and human-centered technology. I’d love to explore how to integrate AI technology into the teaching process to make education more available, affordable, and effective for people everywhere. And with the innumerable opportunities that Georgia Tech has to offer, I know that I will be able to go further here than anywhere else.
With a “Why This Major” essay, you want to avoid using all of your words to tell a story. That being said, stories are a great way to show your personality and make your essay stand out. This student’s story takes up only their first 21 words, but it positions the student as fun and funny and provides an endearing image of cats and pizzas—who doesn’t love cats and pizzas? There are other moments when the student’s personality shines through also, like the Spiderman reference.
While this pop culture reference adds color, it also is important for what the student is getting at: their passion. They want to go into computer science to address the issues of security and equity that are on the industry’s mind, and they acknowledge these concerns with their comments about “scarily-specific ads” and their statement that “the need to ensure digital equality has skyrocketed.” This student is self-aware and aware of the state of the industry. This aptitude will be appealing for admissions officers.
The conversation around “threads” is essential for this student’s response because the prompt asks specifically about the major at Georgia Tech and it is the only thing they reference that is specific to Georgia Tech. Threads are great, but this student would have benefitted from expanding on other opportunities specific to Georgia Tech later in the essay, instead of simply inserting “innumerable opportunities.”
Overall, this student shows personality, passion, and aptitude—precisely what admissions officers want to see!
Extracurricular Essay
You’re asked to describe your activities on the Common App, but chances are, you have at least one extracurricular that’s impacted you in a way you can’t explain in 150 characters.
This essay archetype allows you to share how your most important activity shaped you and how you might use those lessons learned in the future. You are definitely welcome to share anecdotes and use a narrative approach, but remember to include some reflection. A common mistake students make is to only describe the activity without sharing how it impacted them.
Learn more about how to write the Extracurricular Essay in our guide.
A Dedicated Musician
My fingers raced across the keys, rapidly striking one after another. My body swayed with the music as my hands raced across the piano. Crashing onto the final chord, it was over as quickly as it had begun. My shoulders relaxed and I couldn’t help but break into a satisfied grin. I had just played the Moonlight Sonata’s third movement, a longtime dream of mine.
Four short months ago, though, I had considered it impossible. The piece’s tempo was impossibly fast, its notes stretching between each end of the piano, forcing me to reach farther than I had ever dared. It was 17 pages of the most fragile and intricate melodies I had ever encountered.
But that summer, I found myself ready to take on the challenge. With the end of the school year, I was released from my commitment to practicing for band and solo performances. I was now free to determine my own musical path: either succeed in learning the piece, or let it defeat me for the third summer in a row.
Over those few months, I spent countless hours practicing the same notes until they burned a permanent place in my memory, creating a soundtrack for even my dreams. Some would say I’ve mastered the piece, but as a musician I know better. Now that I can play it, I am eager to take the next step and add in layers of musicality and expression to make the once-impossible piece even more beautiful.
In this response, the student uses their extracurricular, piano, as a way to emphasize their positive qualities. At the beginning, readers are invited on a journey with the student where we feel their struggle, their intensity, and ultimately their satisfaction. With this descriptive image, we form a valuable connection with the student.
Then, we get to learn about what makes this student special: their dedication and work ethic. The fact that this student describes their desire to be productive during the summer shows an intensity that is appealing to admissions officers. Additionally, the growth mindset that this student emphasizes in their conclusion is appealing to admissions officers.
The Extracurricular Essay can be seen as an opportunity to characterize yourself. This student clearly identified their positive qualities, then used the Extracurricular Essay as a way to articulate them.
A Complicated Relationship with the School Newspaper
My school’s newspaper and I have a typical love-hate relationship; some days I want nothing more than to pass two hours writing and formatting articles, while on others the mere thought of student journalism makes me shiver. Still, as we’re entering our fourth year together, you could consider us relatively stable. We’ve learned to accept each other’s differences; at this point I’ve become comfortable spending an entire Friday night preparing for an upcoming issue, and I hardly even notice the snail-like speed of our computers. I’ve even benefitted from the polygamous nature of our relationship—with twelve other editors, there’s a lot of cooperation involved. Perverse as it may be, from that teamwork I’ve both gained some of my closest friends and improved my organizational and time-management skills. And though leaving it in the hands of new editors next year will be difficult, I know our time together has only better prepared me for future relationships.
This response is great. It’s cute and endearing and, importantly, tells readers a lot about the student who wrote it. Framing this essay in the context of a “love-hate relationship,” then supplementing with comments like “We’ve learned to accept each other’s differences” allows this student to advertise their maturity in a unique and engaging way.
While Extracurricular Essays can be a place to show how you’ve grown within an activity, they can also be a place to show how you’ve grown through an activity. At the end of this essay, readers think that this student is mature and enjoyable, and we think that their experience with the school newspaper helped make them that way.
Participating in Democracy
Prompt: Research shows that an ability to learn from experiences outside the classroom correlates with success in college. What was your greatest learning experience over the past 4 years that took place outside of the traditional classroom? (250 words)
The cool, white halls of the Rayburn House office building contrasted with the bustling energy of interns entertaining tourists, staffers rushing to cover committee meetings, and my fellow conference attendees separating to meet with our respective congresspeople. Through civics and US history classes, I had learned about our government, but simply hearing the legislative process outlined didn’t prepare me to navigate it. It was my first political conference, and, after learning about congressional mechanics during breakout sessions, I was lobbying my representative about an upcoming vote crucial to the US-Middle East relationship. As the daughter of Iranian immigrants, my whole life had led me to the moment when I could speak on behalf of the family members who had not emigrated with my parents.
As I sat down with my congresswoman’s chief of staff, I truly felt like a participant in democracy; I was exercising my right to be heard as a young American. Through this educational conference, I developed a plan of action to raise my voice. When I returned home, I signed up to volunteer with the state chapter of the Democratic Party. I sponsored letter-writing campaigns, canvassed for local elections, and even pursued an internship with a state senate campaign. I know that I don’t need to be old enough to vote to effect change. Most importantly, I also know that I want to study government—I want to make a difference for my communities in the United States and the Middle East throughout my career.
While this prompt is about extracurricular activities, it specifically references the idea that the extracurricular should support the curricular. It is focused on experiential learning for future career success. This student wants to study government, so they chose to describe an experience of hands-on learning within their field—an apt choice!
As this student discusses their extracurricular experience, they also clue readers into their future goals—they want to help Middle Eastern communities. Admissions officers love when students mention concrete plans with a solid foundation. Here, the foundation comes from this student’s ethnicity. With lines like “my whole life had led me to the moment when I could speak on behalf of the family members who had not emigrated with my parents,” the student assures admissions officers of their emotional connection to their future field.
The strength of this essay comes from its connections. It connects the student’s extracurricular activity to their studies and connects theirs studies to their personal history.
Overcoming Challenges
You’re going to face a lot of setbacks in college, so admissions officers want to make you’re you have the resilience and resolve to overcome them. This essay is your chance to be vulnerable and connect to admissions officers on an emotional level.
Learn more about how to write the Overcoming Challenges Essay in our guide.
The Student Becomes the Master
”Advanced females ages 13 to 14 please proceed to staging with your coaches at this time.” Skittering around the room, eyes wide and pleading, I frantically explained my situation to nearby coaches. The seconds ticked away in my head; every polite refusal increased my desperation.
Despair weighed me down. I sank to my knees as a stream of competitors, coaches, and officials flowed around me. My dojang had no coach, and the tournament rules prohibited me from competing without one.
Although I wanted to remain strong, doubts began to cloud my mind. I could not help wondering: what was the point of perfecting my skills if I would never even compete? The other members of my team, who had found coaches minutes earlier, attempted to comfort me, but I barely heard their words. They couldn’t understand my despair at being left on the outside, and I never wanted them to understand.
Since my first lesson 12 years ago, the members of my dojang have become family. I have watched them grow up, finding my own happiness in theirs. Together, we have honed our kicks, blocks, and strikes. We have pushed one another to aim higher and become better martial artists. Although my dojang had searched for a reliable coach for years, we had not found one. When we attended competitions in the past, my teammates and I had always gotten lucky and found a sympathetic coach. Now, I knew this practice was unsustainable. It would devastate me to see the other members of my dojang in my situation, unable to compete and losing hope as a result. My dojang needed a coach, and I decided it was up to me to find one.
I first approached the adults in the dojang – both instructors and members’ parents. However, these attempts only reacquainted me with polite refusals. Everyone I asked told me they couldn’t devote multiple weekends per year to competitions. I soon realized that I would have become the coach myself.
At first, the inner workings of tournaments were a mystery to me. To prepare myself for success as a coach, I spent the next year as an official and took coaching classes on the side. I learned everything from motivational strategies to technical, behind-the-scenes components of Taekwondo competitions. Though I emerged with new knowledge and confidence in my capabilities, others did not share this faith.
Parents threw me disbelieving looks when they learned that their children’s coach was only a child herself. My self-confidence was my armor, deflecting their surly glances. Every armor is penetrable, however, and as the relentless barrage of doubts pounded my resilience, it began to wear down. I grew unsure of my own abilities.
Despite the attack, I refused to give up. When I saw the shining eyes of the youngest students preparing for their first competition, I knew I couldn’t let them down. To quit would be to set them up to be barred from competing like I was. The knowledge that I could solve my dojang’s longtime problem motivated me to overcome my apprehension.
Now that my dojang flourishes at competitions, the attacks on me have weakened, but not ended. I may never win the approval of every parent; at times, I am still tormented by doubts, but I find solace in the fact that members of my dojang now only worry about competing to the best of their abilities.
Now, as I arrive at a tournament with my students, I close my eyes and remember the past. I visualize the frantic search for a coach and the chaos amongst my teammates as we competed with one another to find coaches before the staging calls for our respective divisions. I open my eyes to the exact opposite scene. Lacking a coach hurt my ability to compete, but I am proud to know that no member of my dojang will have to face that problem again.
This essay is great because it has a strong introduction and conclusion. The introduction is notably suspenseful and draws readers into the story. Because we know it is a college essay, we can assume that the student is one of the competitors, but at the same time, this introduction feels intentionally ambiguous as if the writer could be a competitor, a coach, a sibling of a competitor, or anyone else in the situation.
As we continue reading the essay, we learn that the writer is, in fact, the competitor. Readers also learn a lot about the student’s values as we hear their thoughts: “I knew I couldn’t let them down. To quit would be to set them up to be barred from competing like I was.” Ultimately, the conflict and inner and outer turmoil is resolved through the “Same, but Different” ending technique as the student places themself in the same environment that we saw in the intro, but experiencing it differently due to their actions throughout the narrative. This is a very compelling strategy!
Growing Sensitivity to Struggles
Prompt: The lessons we take from failure can be fundamental to later success. Recount an incident or time when you experienced failure. How did it affect you, and what did you learn from the experience? (650 words)
“You ruined my life!” After months of quiet anger, my brother finally confronted me. To my shame, I had been appallingly ignorant of his pain.
Despite being twins, Max and I are profoundly different. Having intellectual interests from a young age that, well, interested very few of my peers, I often felt out of step in comparison with my highly-social brother. Everything appeared to come effortlessly for Max and, while we share an extremely tight bond, his frequent time away with friends left me feeling more and more alone as we grew older.
When my parents learned about The Green Academy, we hoped it would be an opportunity for me to find not only an academically challenging environment, but also – perhaps more importantly – a community. This meant transferring the family from Drumfield to Kingston. And while there was concern about Max, we all believed that given his sociable nature, moving would be far less impactful on him than staying put might be on me.
As it turned out, Green Academy was everything I’d hoped for. I was ecstatic to discover a group of students with whom I shared interests and could truly engage. Preoccupied with new friends and a rigorous course load, I failed to notice that the tables had turned. Max, lost in the fray and grappling with how to make connections in his enormous new high school, had become withdrawn and lonely. It took me until Christmas time – and a massive argument – to recognize how difficult the transition had been for my brother, let alone that he blamed me for it.
Through my own journey of searching for academic peers, in addition to coming out as gay when I was 12, I had developed deep empathy for those who had trouble fitting in. It was a pain I knew well and could easily relate to. Yet after Max’s outburst, my first response was to protest that our parents – not I – had chosen to move us here. In my heart, though, I knew that regardless of who had made the decision, we ended up in Kingston for my benefit. I was ashamed that, while I saw myself as genuinely compassionate, I had been oblivious to the heartache of the person closest to me. I could no longer ignore it – and I didn’t want to.
We stayed up half the night talking, and the conversation took an unexpected turn. Max opened up and shared that it wasn’t just about the move. He told me how challenging school had always been for him, due to his dyslexia, and that the ever-present comparison to me had only deepened his pain.
We had been in parallel battles the whole time and, yet, I only saw that Max was in distress once he experienced problems with which I directly identified. I’d long thought Max had it so easy – all because he had friends. The truth was, he didn’t need to experience my personal brand of sorrow in order for me to relate – he had felt plenty of his own.
My failure to recognize Max’s suffering brought home for me the profound universality and diversity of personal struggle; everyone has insecurities, everyone has woes, and everyone – most certainly – has pain. I am acutely grateful for the conversations he and I shared around all of this, because I believe our relationship has been fundamentally strengthened by a deeper understanding of one another. Further, this experience has reinforced the value of constantly striving for deeper sensitivity to the hidden struggles of those around me. I won’t make the mistake again of assuming that the surface of someone’s life reflects their underlying story.
Here you can find a prime example that you don’t have to have fabulous imagery or flowery prose to write a successful essay. You just have to be clear and say something that matters. This essay is simple and beautiful. It almost feels like having a conversation with a friend and learning that they are an even better person than you already thought they were.
Through this narrative, readers learn a lot about the writer—where they’re from, what their family life is like, what their challenges were as a kid, and even their sexuality. We also learn a lot about their values—notably, the value they place on awareness, improvement, and consideration of others. Though they never explicitly state it (which is great because it is still crystal clear!), this student’s ending of “I won’t make the mistake again of assuming that the surface of someone’s life reflects their underlying story” shows that they are constantly striving for improvement and finding lessons anywhere they can get them in life.
Community Service/Impact on the Community
Colleges want students who will positively impact the campus community and go on to make change in the world after they graduate. This essay is similar to the Extracurricular Essay, but you need to focus on a situation where you impacted others.
Learn more about how to write the Community Service Essay in our guide.
Academic Signing Day
Prompt: What have you done to make your school or your community a better place?
The scent of eucalyptus caressed my nose in a gentle breeze. Spring had arrived. Senior class activities were here. As a sophomore, I noticed a difference between athletic and academic seniors at my high school; one received recognition while the other received silence. I wanted to create an event celebrating students academically-committed to four-years, community colleges, trades schools, and military programs. This event was Academic Signing Day.
The leadership label, “Events Coordinator,” felt heavy on my introverted mind. I usually was setting up for rallies and spirit weeks, being overlooked around the exuberant nature of my peers.
I knew a change of mind was needed; I designed flyers, painted posters, presented powerpoints, created student-led committees, and practiced countless hours for my introductory speech. Each committee would play a vital role on event day: one dedicated to refreshments, another to technology, and one for decorations. The fourth-month planning was a laborious joy, but I was still fearful of being in the spotlight. Being acknowledged by hundreds of people was new to me.
The day was here. Parents filled the stands of the multi-purpose room. The atmosphere was tense; I could feel the angst building in my throat, worried about the impression I would leave. Applause followed each of the 400 students as they walked to their college table, indicating my time to speak.
I walked up to the stand, hands clammy, expression tranquil, my words echoing to the audience. I thought my speech would be met by the sounds of crickets; instead, smiles lit up the stands, realizing my voice shone through my actions. I was finally coming out of my shell. The floor was met by confetti as I was met by the sincerity of staff, students, and parents, solidifying the event for years to come.
Academic students were no longer overshadowed. Their accomplishments were equally recognized to their athletic counterparts. The school culture of athletics over academics was no longer imbalanced. Now, every time I smell eucalyptus, it is a friendly reminder that on Academic Signing Day, not only were academic students in the spotlight but so was my voice.
This essay answers the prompt nicely because the student describes a contribution with a lasting legacy. Academic Signing Day will affect this high school in the future and it affected this student’s self-development—an idea summed up nicely with their last phrase “not only were academic students in the spotlight but so was my voice.”
With Community Service essays, students sometimes take small contributions and stretch them. And, oftentimes, the stretch is very obvious. Here, the student shows us that Academic Signing Day actually mattered by mentioning four months of planning and hundreds of students and parents. They also make their involvement in Academic Signing Day clear—it was their idea and they were in charge, and that’s why they gave the introductory speech.
Use this response as an example of the type of focused contribution that makes for a convincing Community Service Essay.
Climate Change Rally
Prompt: What would you say is your greatest talent or skill? How have you developed and demonstrated that talent over time? (technically not community service, but the response works)
Let’s fast-forward time. Strides were made toward racial equality. Healthcare is accessible to all; however, one issue remains. Our aquatic ecosystems are parched with dead coral from ocean acidification. Climate change has prevailed.
Rewind to the present day.
My activism skills are how I express my concerns for the environment. Whether I play on sandy beaches or rest under forest treetops, nature offers me an escape from the haste of the world. When my body is met by trash in the ocean or my nose is met by harmful pollutants, Earth’s pain becomes my own.
Substituting coffee grinds as fertilizer, using bamboo straws, starting my sustainable garden, my individual actions needed to reach a larger scale. I often found performative activism to be ineffective when communicating climate concerns. My days of reposting awareness graphics on social media never filled the ambition I had left to put my activism skills to greater use. I decided to share my ecocentric worldview with a coalition of environmentalists and host a climate change rally outside my high school.
Meetings were scheduled where I informed students about the unseen impact they have on the oceans and local habitual communities. My fingers were cramped from all the constant typing and investigating of micro causes of the Pacific Waste Patch, creating reusable flyers, displaying steps people could take from home in reducing their carbon footprint. I aided my fellow environmentalists in translating these flyers into other languages, repeating this process hourly, for five days, up until rally day.
It was 7:00 AM. The faces of 100 students were shouting, “The climate is changing, why can’t we?” I proudly walked on the dewy grass, grabbing the microphone, repeating those same words. The rally not only taught me efficient methods of communication but it echoed my environmental activism to the masses. The City of Corona would be the first of many cities to see my activism, as more rallies were planned for various parts of SoCal. My once unfulfilled ambition was fueled by my tangible activism, understanding that it takes more than one person to make an environmental impact.
Like with the last example, this student describes a focused event with a lasting legacy. That’s a perfect place to start! By the end of this essay, we have an image of the cause of this student’s passion and the effect of this student’s passion. There are no unanswered questions.
This student supplements their focused topic with engaging and exciting writing to make for an easy-to-read and enjoyable essay. One of the largest strengths of this response is its pace. From the very beginning, we are invited to “fast-forward” and “rewind” with the writer. Then, after we center ourselves in real-time, this writer keeps their quick pace with sentences like “Substituting coffee grounds as fertilizer, using bamboo straws, starting my sustainable garden, my individual actions needed to reach a larger scale.” Community Service essays run the risk of turning boring, but this unique pacing keeps things interesting.
Having a diverse class provides a richness of different perspectives and encourages open-mindedness among the student body. The Diversity Essay is also somewhat similar to the Extracurricular and Community Service Essays, but it focuses more on what you might bring to the campus community because of your unique experiences or identities.
Learn more about how to write the Diversity Essay in our guide.
A Story of a Young Skater
“Everyone follow me!” I smiled at five wide-eyed skaters before pushing off into a spiral. I glanced behind me hopefully, only to see my students standing frozen like statues, the fear in their eyes as clear as the ice they swayed on. “Come on!” I said encouragingly, but the only response I elicited was the slow shake of their heads. My first day as a Learn-to-Skate coach was not going as planned.
But amid my frustration, I was struck by how much my students reminded me of myself as a young skater. At seven, I had been fascinated by Olympic performers who executed thrilling high jumps and dizzying spins with apparent ease, and I dreamed to one day do the same. My first few months on skates, however, sent these hopes crashing down: my attempts at slaloms and toe-loops were shadowed by a stubborn fear of falling, which even the helmet, elbow pads, and two pairs of mittens I had armed myself with couldn’t mitigate. Nonetheless, my coach remained unfailingly optimistic, motivating me through my worst spills and teaching me to find opportunities in failures. With his encouragement, I learned to push aside my fears and attack each jump with calm and confidence; it’s the hope that I can help others do the same that now inspires me to coach.
I remember the day a frustrated staff member directed Oliver, a particularly hesitant young skater, toward me, hoping that my patience and steady encouragement might help him improve. Having stood in Oliver’s skates not much earlier myself, I completely empathized with his worries but also saw within him the potential to overcome his fears and succeed.
To alleviate his anxiety, I held Oliver’s hand as we inched around the rink, cheering him on at every turn. I soon found though, that this only increased his fear of gliding on his own, so I changed my approach, making lessons as exciting as possible in hopes that he would catch the skating bug and take off. In the weeks that followed, we held relay races, played “freeze-skate” and “ice-potato”, and raced through obstacle courses; gradually, with each slip and subsequent success, his fear began to abate. I watched Oliver’s eyes widen in excitement with every skill he learned, and not long after, he earned his first skating badge. Together we celebrated this milestone, his ecstasy fueling my excitement and his pride mirroring my own. At that moment, I was both teacher and student, his progress instilling in me the importance of patience and a positive attitude.
It’s been more than ten years since I bundled up and stepped onto the ice for the first time. Since then, my tolerance for the cold has remained stubbornly low, but the rest of me has certainly changed. In sharing my passion for skating, I have found a wonderful community of eager athletes, loving parents, and dedicated coaches from whom I have learned invaluable lessons and wisdom. My fellow staffers have been with me, both as friends and colleagues, and the relationships I’ve formed have given me far more poise, confidence, and appreciation for others. Likewise, my relationships with parents have given me an even greater gratitude for the role they play: no one goes to the rink without a parent behind the wheel!
Since that first lesson, I have mentored dozens of children, and over the years, witnessed tentative steps transform into powerful glides and tears give way to delighted grins. What I have shared with my students has been among the greatest joys of my life, something I will cherish forever. It’s funny: when I began skating, what pushed me through the early morning practices was the prospect of winning an Olympic medal. Now, what excites me is the chance to work with my students, to help them grow, and to give back to the sport that has brought me so much happiness.
This response is a great example of how Diversity doesn’t have to mean race, gender, sexuality, ethnicity, age, or ability. Diversity can mean whatever you want it to mean—whatever unique experience(s) you have to bring to the table!
A major strength of this essay comes in its narrative organization. When reading this first paragraph, we feel for the young skaters and understand their fear—skating sounds scary! Then, because the writer sets us up to feel this empathy, the transition to the second paragraph where the student describes their empathy for the young skaters is particularly powerful. It’s like we are all in it together! The student’s empathy for the young skaters also serves as an outstanding, seamless transition to the applicant discussing their personal journey with skating: “I was struck by how much my students reminded me of myself as a young skater.”
This essay positions the applicant as a grounded and caring individual. They are caring towards the young skaters—changing their teaching style to try to help the young skaters and feeling the young skaters’ emotions with them—but they are also appreciative to those who helped them as they reference their fellow staffers and parents. This shows great maturity—a favorable quality in the eyes of an admissions officer.
At the end of the essay, we know a lot about this student and are convinced that they would be a good addition to a college campus!
Finding Community in the Rainforest
Prompt: Duke University seeks a talented, engaged student body that embodies the wide range of human experience; we believe that the diversity of our students makes our community stronger. If you’d like to share a perspective you bring or experiences you’ve had to help us understand you better—perhaps related to a community you belong to, your sexual orientation or gender identity, or your family or cultural background—we encourage you to do so. Real people are reading your application, and we want to do our best to understand and appreciate the real people applying to Duke (250 words).
I never understood the power of community until I left home to join seven strangers in the Ecuadorian rainforest. Although we flew in from distant corners of the U.S., we shared a common purpose: immersing ourselves in our passion for protecting the natural world.
Back home in my predominantly conservative suburb, my neighbors had brushed off environmental concerns. My classmates debated the feasibility of Trump’s wall, not the deteriorating state of our planet. Contrastingly, these seven strangers delighted in bird-watching, brightened at the mention of medicinal tree sap, and understood why I once ran across a four-lane highway to retrieve discarded beer cans. Their histories barely resembled mine, yet our values aligned intimately. We did not hesitate to joke about bullet ants, gush about the versatility of tree bark, or discuss the destructive consequences of materialism. Together, we let our inner tree huggers run free.
In the short life of our little community, we did what we thought was impossible. By feeding on each other’s infectious tenacity, we cultivated an atmosphere that deepened our commitment to our values and empowered us to speak out on behalf of the environment. After a week of stimulating conversations and introspective revelations about engaging people from our hometowns in environmental advocacy, we developed a shared determination to devote our lives to this cause.
As we shared a goodbye hug, my new friend whispered, “The world needs saving. Someone’s gotta do it.” For the first time, I believed that someone could be me.
This response is so wholesome and relatable. We all have things that we just need to geek out over and this student expresses the joy that came when they found a community where they could geek out about the environment. Passion is fundamental to university life and should find its way into successful applications.
Like the last response, this essay finds strength in the fact that readers feel for the student. We get a little bit of backstory about where they come from and how they felt silenced—“Back home in my predominantly conservative suburb, my neighbors had brushed off environmental concerns”—, so it’s easy to feel joy for them when they get set free.
This student displays clear values: community, ecoconsciousness, dedication, and compassion. An admissions officer who reads Diversity essays is looking for students with strong values and a desire to contribute to a university community—sounds like this student!
Political/Global Issues
Colleges want to build engaged citizens, and the Political/Global Issues Essay allows them to better understand what you care about and whether your values align with theirs. In this essay, you’re most commonly asked to describe an issue, why you care about it, and what you’ve done or hope to do to address it.
Learn more about how to write the Political/Global Issues Essay in our guide.
Note: this prompt is not a typical political/global issues essay, but the essay itself would be a strong response to a political/global issues prompt.
Fighting Violence Against Women
Prompt: Using a favorite quotation from an essay or book you have read in the last three years as a starting point, tell us about an event or experience that helped you define one of your values or changed how you approach the world. Please write the quotation, title and author at the beginning of your essay. (250-650 words)
“One of the great challenges of our time is that the disparities we face today have more complex causes and point less straightforwardly to solutions.”
– Omar Wasow, assistant professor of politics, Princeton University. This quote is taken from Professor Wasow’s January 2014 speech at the Martin Luther King Day celebration at Princeton University.
The air is crisp and cool, nipping at my ears as I walk under a curtain of darkness that drapes over the sky, starless. It is a Friday night in downtown Corpus Christi, a rare moment of peace in my home city filled with the laughter of strangers and colorful lights of street vendors. But I cannot focus.
My feet stride quickly down the sidewalk, my hand grasps on to the pepper spray my parents gifted me for my sixteenth birthday. My eyes ignore the surrounding city life, focusing instead on a pair of tall figures walking in my direction. I mentally ask myself if they turned with me on the last street corner. I do not remember, so I pick up the pace again. All the while, my mind runs over stories of young women being assaulted, kidnapped, and raped on the street. I remember my mother’s voice reminding me to keep my chin up, back straight, eyes and ears alert.
At a young age, I learned that harassment is a part of daily life for women. I fell victim to period-shaming when I was thirteen, received my first catcall when I was fourteen, and was nonconsensually grabbed by a man soliciting on the street when I was fifteen. For women, assault does not just happen to us— its gory details leave an imprint in our lives, infecting the way we perceive the world. And while movements such as the Women’s March and #MeToo have given victims of sexual violence a voice, harassment still manifests itself in the lives of millions of women across the nation. Symbolic gestures are important in spreading awareness but, upon learning that a surprising number of men are oblivious to the frequent harassment that women experience, I now realize that addressing this complex issue requires a deeper level of activism within our local communities.
Frustrated with incessant cases of harassment against women, I understood at sixteen years old that change necessitates action. During my junior year, I became an intern with a judge whose campaign for office focused on a need for domestic violence reform. This experience enabled me to engage in constructive dialogue with middle and high school students on how to prevent domestic violence. As I listened to young men uneasily admit their ignorance and young women bravely share their experiences in an effort to spread awareness, I learned that breaking down systems of inequity requires changing an entire culture. I once believed that the problem of harassment would dissipate after politicians and celebrities denounce inappropriate behavior to their global audience. But today, I see that effecting large-scale change comes from the “small” lessons we teach at home and in schools. Concerning women’s empowerment, the effects of Hollywood activism do not trickle down enough. Activism must also trickle up and it depends on our willingness to fight complacency.
Finding the solution to the long-lasting problem of violence against women is a work-in-progress, but it is a process that is persistently moving. In my life, for every uncomfortable conversation that I bridge, I make the world a bit more sensitive to the unspoken struggle that it is to be a woman. I am no longer passively waiting for others to let me live in a world where I can stand alone under the expanse of darkness on a city street, utterly alone and at peace. I, too, deserve the night sky.
As this student addresses an important social issue, she makes the reasons for her passion clear—personal experiences. Because she begins with an extended anecdote, readers are able to feel connected to the student and become invested in what she has to say.
Additionally, through her powerful ending—“I, too, deserve the night sky”—which connects back to her beginning— “as I walk under a curtain of darkness that drapes over the sky”—this student illustrates a mastery of language. Her engagement with other writing techniques that further her argument, like the emphasis on time—“gifted to me for my sixteenth birthday,” “when I was thirteen,” “when I was fourteen,” etc.—also illustrates her mastery of language.
While this student proves herself a good writer, she also positions herself as motivated and ambitious. She turns her passions into action and fights for them. That is just what admissions officers want to see in a Political/Global issues essay!
Where to Get Feedback on Your College Essays
Once you’ve written your college essays, you’ll want to get feedback on them. Since these essays are important to your chances of acceptance, you should prepare to go through several rounds of edits.
Not sure who to ask for feedback? That’s why we created our free Peer Essay Review resource. You can get comments from another student going through the process and also edit other students’ essays to improve your own writing.
If you want a college admissions expert to review your essay, advisors on CollegeVine have helped students refine their writing and submit successful applications to top schools. Find the right advisor for you to improve your chances of getting into your dream school!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Ten Ways To Think About Writing: Metaphoric Musings for College Writing Students
E. Shelley Reid
1. A Thousand Rules and Three Principles
Writing is hard.
I’m a writer and a writing professor, the daughter and granddaughter of writers and writing professors, and I still sit down at my keyboard every week and think, writing is hard.
I also think, though, that writing is made harder than it has to be when we try to follow too many rules for writing. Which rules have you heard? Here are some I was taught:
Always have a thesis. I before E except after C . No one-sentence paragraphs. Use concrete nouns. A semi-colon joins two complete sentences. A conclusion restates the thesis and the topic sentences. Don’t use “I,” check your spelling, make three main points, and don’t repeat yourself. Don’t use contractions. Cite at least three sources, capitalize proper nouns, and don’t use “you.” Don’t start a sentence with “And” or “But,” don’t end a sentence with a preposition, give two examples in every paragraph, and use transition words. Don’t use transition words too much.
When we write to the rules, writing seems more like a chore than a living process that connects people and moves the world forward. I find it particularly hard to cope with all those “Don’ts.” It’s no wonder we get writer’s block, hands poised above the keyboard, worried about all the ways we could go wrong, suddenly wondering if we have new messages or whether there’s another soda in the fridge.
We can start to unblock the live, negotiated process of writing for real people by cutting the thousand rules down to three broader principles:
- Write about what you know about, are curious about, are passionate about (or what you can find a way to be curious about or interested in).
- Show, don’t just tell.
- Adapt to the audience and purpose you’re writing for.
When we write this way, we write rhetorically : that is, we pay attention to the needs of the author and the needs of the reader rather than the needs of the teacher —or the rules in the textbook.
Everything that matters from the preceding list of rules can be connected to one of those three rhetorical principles, and the principles address lots of aspects of writing that aren’t on the list but that are central to why humans struggle to express themselves through written language. Write about what you know about so that you can show not just tell in order to adapt to your audience’s needs and accomplish your goals. (Unless you do a good job showing what you mean, your audience will not understand your message. You will not meet their expectations or accomplish your goals.) Make clear points early so that your audience can spot your expertise or passion right from the start. Write multi-sentence paragraphs in which you show key ideas in enough detail that your audience doesn’t have to guess what you mean. Use a semi-colon correctly in order to show how your carefully thought out ideas relate to one another—and to win your reader’s confidence.
Writing will still be hard because these are some of the hardest principles in college; they may be some of the hardest principles in the galaxy. But if you write from those three principles, and use some of the strategies listed below, your writing will finally have a fighting chance of being real , not just rules . And that’s when writing gets interesting and rewarding enough that we do it even though it’s hard.
2. Show & Telepaths
What does that “show, don’t just tell” idea really mean? Let’s try some time travel to get a better idea. Can you remember being in kindergarten on show-and-tell day? Imagine that a student gets up in front of you and your fellow five-year-olds, empty-handed, and says, “I have a baseball signed by Hank Aaron that’s in perfect condition, but I can’t bring it to school.” You’re only five years old, but you know that she’s got two problems, right? Not only can you not see the ball to know exactly what “perfect condition” looks like, to eyeball the signature and smell the leather and count the stitches, but you have no reason to believe this kid even if she describes it perfectly. If you tell without showing, your reader might not only be confused but might entirely disbelieve you. So you’re two strikes down.
Another way to explain show vs. tell is with a story. There is a very, very short science fiction story in a collection of very short science fiction stories entitled “Science Fiction for Telepaths.”
This is the entire story, just six words: “Aw, you know what I mean” (Blake 235).
“Wah-ha-ha!” go the telepaths, “what a great story! I really liked the part about the Martian with three heads trying to use the gamma blaster to get the chartreuse kitchen sink to fly out the window and land on the six-armed Venusian thief! Good one!” Since the telepaths can read the storyteller’s mind, they don’t need any other written details: they know the whole story instantly.
This story is a little like when you say to your best friend from just about forever, you know what I mean, and sometimes she even does, because she can almost read your mind. Sometimes, though, even your best buddy from way back gives you that look . You know that look: the one that says he thinks you’ve finally cracked. He can’t read your mind, and you’ve lost him.
If you can confuse your best friend in the whole world, even when he’s standing right there in front of you, think how easy it could be to confuse some stranger who’s reading your writing days or months or years from now. If we could read each other’s minds, writing wouldn’t be hard at all, because we would always know what everyone meant, and we’d never doubt each other. If you figure out how to read minds this semester, I hope you’ll tell us how it works! In the meantime, though, you have to show what you mean.
3. The Little Green Ball and Some People: Doing Details Right
Now we know: I can read my own mind, and you can read your own mind, and this self-mind-reading is even easier to do than breathing in and out on a lovely April morning. When I write something like “I have a little green ball” on the whiteboard, I read my mind as I read the board, so I understand it—and I’m positive, therefore, that you understand it. Meanwhile, you read my sentence and your own mind together and the meaning is so perfectly clear to you that it’s nearly impossible to imagine that you’re not understanding exactly what I intended.
I have a little green ball. Even a five-year-old could read this sentence and know what I mean, right?
Try something. Bring both hands up in front of your face, and use each one to show one possible size of this “little” ball. (You can try this with friends: have everyone close their eyes and show the size of a “little” ball with their hands, then open their eyes, and look around.) Hmm. Already there’s some possible disagreement, even though it seemed so clear what “little” meant.
Maybe “green” is easier: you know what “green” is, right? Of course. But now, can you think of two different versions of “green”? three versions? five? In the twenty-five minds in a classroom, say, we might have at least twenty kinds of little, and maybe a hundred kinds of green, and we haven’t even discussed what kind of “ball” we might be talking about. Those of you who are math whizzes can see the permutations that come from all those variables. If I sent you to Mega Toyland with the basic instructions, “Buy me a little green ball,” the chances are slim that you would come home with the ball I had in mind.
If I don’t care about the exact ball—I just need something ball-like and not too huge and somewhat greenish—then it doesn’t matter. I can leave it up to you to decide. (Occasionally, it’s effective to avoid details: if I were writing a pop song about my broken heart, I’d be deliberately vague so that you’d think the song was about your heart, and then you’d decide to download or even buy my song.) But the more I care that you know exactly what I’m thinking, the more the details matter to me, then the more information I need to give you.
What information would you need to write down so that someone would buy the exact little green ball that you’re thinking of while he or she is shopping at Mega Toyland?
If you’re going to show me, or each other, what you’re thinking, using only language, it will take several sentences, perhaps a whole paragraph—filled with facts and statistics, comparisons, sensory description, expert testimony, examples, personal experiences—to be sure that what’s in your mind is what’s in my mind. After my students and I finish examining my ball and choosing rich language to show it, the whiteboard often reads something like this: “I have a little green ball about an inch in diameter, small enough to hide in your hand. It’s light neon green like highlighter ink and made of smooth shiny rubber with a slightly rough line running around its equator as if two halves were joined together. When I drop it on the tile floor, it bounces back nearly as high as my hand; when I throw it down the hallway, it careens unpredictably off the walls and floor.” Now the ball in your mind matches the ball in my hand much more closely.
Showing is harder than just telling, and takes longer, and is dependent on your remembering that nobody reads your mind like you do. Can you think of other “little green ball” words or phrases that you might need to show more clearly? How do you describe a good movie or a bad meal? How would you describe your mother, your hometown, your car? Try it on a blank page or in an open document: write one “you know what I mean” sentence, then write every detail and example you can think of to make sure that a reader does know what you mean. Then you can choose the most vivid three or four, the ones that best show your readers what you want them to understand.
There’s another kind of description that requires mind reading. If I write on the board that “some people need to learn to mind their own business sometimes,” would you agree with me? (By now, you should be gaining some skepticism about being able to read my mind.) In my head, I’m filling in “some people” and “their business” and “sometimes” with very specific, one-time-only examples. It’s like I have a YouTube clip playing in my head, or a whole season’s worth of a reality TV show, and you don’t have access to it yet. (I might as well be saying “I have cookies!” but not offering to share any of them with you.)
If I give you a snapshot from that film, if I use language to provide a one-time-only example, I show you: “My ninety-year-old grandmother needs to stop calling up my younger cousin Celia like she did last night and telling her to persuade me to move back home to Laramie so my mom won’t get lonely and take up extreme snowboarding just to go meet some nice people.” Does that help you see how the onetime-only example you were thinking of, when you read my boring sentence along with your own mind, is different from what I wanted you to think? As writers, we need to watch out for the some-people example and the plural example: “Sometimes things bother me” or “Frederick Douglass had lots of tricks for learning things he needed to know.” If an idea is important, give an exact one-time snapshot with as much detail as possible.
In a writing class, you also have to learn to be greedy as a reader, to ask for the good stuff from someone else’s head if they don’t give it to you, to demand that they share their cookies: you have to be brave and say, “I can’t see what you mean.” This is one of the roles teachers take up as we read your writing. (One time during my first year teaching, one of my students snorted in exasperation upon receiving his essay back from me. “So, like, what do you do,” he asked, “just go through the essay and write ‘Why? How so? Why? How so? Why? How so?’ randomly all over the margins and then slap that ‘B–’ on there?” I grinned and said, “Yep, that’s about it.”)
It’s also your job as a peer reader to read skeptically and let your fellow writer know when he or she is assuming the presence of a mind reader—because none of us knows for sure if we’re doing that when we write, not until we encounter a reader’s “Hunh?” or “Wha-a-a-?” You can learn a lot about writing from books and essays like this one, but in order to learn how not to depend on reading your own mind, you need feedback from a real, live reader to help you gauge how your audience will respond.
4. Lost Money and Thank-you Notes: What’s in an Audience?
Writing teachers are always going on and on about audience , as if you didn’t already know all about this concept. You can do a simple thought-experiment to prove to them, and to yourself, that you already fully understand that when the audience changes, your message has to change, sometimes drastically.
Imagine that you’ve done something embarrassingly stupid or impulsive that means you no longer have any money to spend this semester. (I won’t ask you what it is, or which credit card or 888 phone number or website it involves, or who was egging you on.) You really need the money, but you can’t get it back now. If I just said, “Write a message to try to get some money from someone,” you might struggle a bit, and then come up with some vague points about your situation.
But if I say, “Ask your best friend for the money,” you should suddenly have a very clear idea of what you can say. Take a minute and consider: what do you tell this friend? Some of my students have suggested, “Remember how you owe me from that time I helped you last February?” or “I’ll pay you back, with interest” or “I’ll do your laundry for a month.” Most of my students say they’ll tell their friends the truth about what happened: would you? What else might you say to your own friend, particularly if he were giving you that skeptical look?
Suppose then that your friend is nearly as broke as you are, and you have to ask one of your parents or another family adult. Now what do you say to help loosen the parental purse strings? Do you tell the truth about what happens? (Does it matter which parent it is?) Do you say, “Hey, you owe me”? Some of my students have suggested choosing messages that foreground their impending starvation, their intense drive for a quality education, or their ability to learn a good lesson. Would your parent want you to offer to pay back the money? What else might you say?
Notice how easy it is for you to switch gears: nothing has changed but the audience, and yet you’ve quickly created a whole new message, changing both the content and the language you were using.
One more try: when your parent says there’s just no extra cash to give you, you may end up at the local bank trying to take out a loan. What will you tell the bank? Should the loan officer hear how you lost your money, or how you promise you’ll be more responsible in the future? Should you try looking hungry and wan? Probably not: by discussing collateral (your five-year-old Toyota) and repayment terms (supported by your fry-jockey job at McSkippy’s), you’re adjusting your message once again.
Sometimes writing teachers talk about a “primary” and “secondary” audience, as if that were really a complicated topic, but you know all about this idea, too. Take just a minute and think about writing a thank-you note. If it’s a thank-you note to your grandmother, then your primary audience is your grandmother, so you write to her. But if your grandmother is like mine, she may show your note to someone else, and all those people become secondary audiences. Who might see, or hear about, your note to your grandmother? Neighbors, other relatives, her yoga group or church friends? If you know your note will be stuck up on the fridge, then you can’t use it as a place to add snarky remarks about your younger brother: you write for a primary audience, but you also need to think for a minute to be sure your message is adjusted for the needs of your secondary audiences. (If you haven’t written a thank-you note recently, try to remember the last time someone forwarded your email or text message to someone else, without asking you first.)
In a writing classroom, everyone knows that, in reality, your primary audience is the teacher—just as during rehearsal or team practice the primary audience is the director or coach who decides whether you’ll be first clarinet or take your place in the starting line-up. Your classmates (or teammates) may be part of a secondary audience who also need considering. It can be tempting to take the middle-of-the-road route and forget about any other audiences. But in all these cases, you won’t be practicing forever. It helps to imagine another primary audience—sometimes called a “target audience”—outside the classroom, in order to gain experience tailoring your performance to a “real” audience. It also helps to imagine a very specific primary audience (a person or small group or publication), so that instead of staring at the screen thinking vague “some people” thoughts, you can quickly come up with just the right words and information to match that audience’s needs, and it helps to consider some exact secondary audiences so that you can include ideas that will appeal to those readers as well. (Who do you suppose are the specific primary and secondary audiences for this essay? How does the writing adapt to those audiences?)
5. Pink Houses & Choruses: Keeping Your Reader With You
Once you’ve identified a target audience, and put down all the detail you can think of to help show your ideas to those readers, you need to focus on not losing them somewhere along the way. Earlier in your writing career as you worked on writing cohesive essays, you may have watched writing teachers go totally ballistic over thesis statements and topic sentences —even though some teachers insisted that they weren’t requiring any kind of set formula. How can this be? What’s up with all this up-front information?
The concept is actually pretty simple, if we step out of the writing arena for a minute. Say you’re driving down the interstate at sixty-five miles an hour with three friends from out of town, and you suddenly say to them, “Hey, there’s that amazing Pink House!” What happens? Probably there’s a lot of whiplash-inducing head swiveling, and someone’s elbow ends up in someone else’s ribs, and maybe one of your friends gets a glimpse, but probably nobody really gets a chance to see it (and somebody might not believe you if she didn’t see it for herself!). What if you had said instead, “Hey, coming up on the right here in about two miles, there’s an amazing huge neon Pink House: watch for it”? They’d be ready, they’d know where to look and what to look for, and they’d see what you wanted them to see.
Writers need to advise their readers in a similar way. That advice doesn’t always need to be in a thesis statement or a topic sentence, but it does need to happen regularly so that readers don’t miss something crucial.
“But,” you say, “I’m not supposed to repeat things in my essay; it gets boring!” That’s true, up to a point, but there are exceptions. Have you ever noticed how the very same company will run the exact same advertisement for light beer five or six times during one football game? It’s not as if the message they are trying to get across is that complex: Drink this beer and you will be noticed by this beautiful woman, or get to own this awesome sports car, or meet these wonderful friends who will never ever let you down. The ad costs the company hundreds of thousands of dollars each time, but there it is again. Beer: sports car. Beer: sports car. Contemporary Americans have a very high tolerance for repeated messages; we even come to depend on them, like football fans relishing the instant replay. Beer: sports car.
If you’d rather think like an artist than an advertising executive, consider popular music. Pick a pop song, any song—“Jingle Bells,” for instance, or whatever song everybody’s listening to this month—and the next time you listen, count the number of times the chorus, or even the title phrase, comes up. Do we get bored by the repetition? Not usually. In fact, the chorus is crucial for audience awareness because it’s often the first (or even the only) part of the song the listener learns and can sing along with. Repeating the chorus helps bring the audience along with you from verse to verse: the audience thinks, “Aha, I know this!”
Now, what you’re trying to say in your essay is much more complex than beer: sports car or I will always love you . If you only say it once or twice—there, in the last paragraph, where you finally figured out the most important point, or maybe once at the start and once at the end—we might miss it, or only get a piece of it. Here you’ve spent hundreds of minutes working on this idea, and we zoom past it at sixty-five m.p.h. and miss it entirely! You have to bring it back to our attention throughout the essay. Of course, you don’t want to repeat just anything. You certainly don’t want to repeat the same examples or vague “some people” theories, stuffing baloney into the middle of the paper to fill it out. But the core idea—beer: sports car—needs to appear early and often, using the same key words, even, as an anchor for all the complex ideas and examples you’re connecting to it, as a place for the audience to recognize the main idea and find a way to “sing along.”
So as you’re revising, add your chorus back into some key middle parts of your essay—the beginnings and endings of paragraphs, like commercial breaks, can be places that readers expect repetition—until you start to really feel uncomfortable about your repetition . . . and then add it one more time, and it might be enough, but it shouldn’t be too much. (Since you read the essay dozens of times and you read your own mind, you’ll get antsy about repetition long before your readers will in their one trip through your essay.) If you get a good balance, your reader—the same person who keeps laughing at the beer ad or mumbling the chorus to the pop song without knowing the rest of the lyrics—won’t even notice that you’re repeating. When I work with my students, I say: “I promise to tell you—no harm, no penalty—if you’re ever too clear about your main point.” I find that very few people make it that far, but they like having the encouragement to try. You and your peer readers can make the same agreement.
6. Fruit Jell-O: Balancing Arguments & Examples
“Great,” you say, “so I’m supposed to have all these examples and to have all these Pink House reminders, but it’s hard to keep it all straight.” That’s a very smart observation—because one of the main challenges writers face, when we can’t read someone’s mind or get them to read ours, is learning how to balance the writing that states our theories and arguments with the writing that provides our evidence and example s. It turns out that it’s easier to do just one of these things at a time when writing, but having theories and arguments without evidence and examples is a recipe for confusion and misunderstanding.
I find that it helps sometimes to think about fruit Jell-O™, the kind my mom used to take to family get-togethers: lime Jell-O with mandarin orange slices in it, or berry Jell-O with cherries in it. Fruit Jell-O is a pretty good balance of foods to take to an informal family gathering: it meets the needs of the audience.
You wouldn’t want to take plain gelatin to show off to your family, after all. Think of the last time you ate plain old Jell-O, with no additional food (or beverage) added to it. Weren’t you in a hospital, or a school cafeteria, or some other unhappy place? Hospitals serve plain gelatin because it looks and behaves like food, but it has so few ingredients that it won’t irritate your mouth or upset your digestion. That same blandness means that not a lot of family members will choose it over the tortilla chips or the macaroons.
Writing just your opinions, theories, and arguments is a lot like serving plain Jell-O: it seems like you’re doing something productive, but there’s not much substance to it. Politicians often write plain Jell-O speeches with no details or examples, because that kind of talk motivates people but won’t irritate voters with tiny details about time or money. Talent-show contestants sometimes choose to sing plain Jell-O songs for the same reason.
On the other hand, if you took a bowl of cherries with you, your family might perk up a bit, but cherries are kind of hard to serve. They roll out of the bowl and off of those flimsy paper plates and end up sliding into the cheese dip or being squished into the new carpet by your two-year-old cousin. People finger all the cherries but take just a few (using tongs on cherries just seems too formal!), and it’s hard to know how to handle the pits, or to eat gooey already-pitted cherries with your hands.
Writing just your examples, reasons, and details is a lot like bringing cherries to the party: it’s interesting and lively, but readers don’t know what to make of it all. Some of your reasons or stories will roll out of readers’ heads if they aren’t firmly attached to an argument; some readers will meander through all your details and just randomly remember one or two of them rather than building a whole picture.
Good writers blend argument and evidence as they write, so that readers get both elements together all the way through. Good revisers go back and adjust the recipe, seeking a workable combination. Sometimes as you’re revising it can feel odd to be just adding cherries: it can seem like you’re packing in too many extra details when there’s already a perfectly good piece of fruit there. Other times it seems weird to be just adding Jell-O, because all those “chorus” sentences sound the same and have the same flavor, and you don’t want to repeat yourself unnecessarily. It’s hard to get the balance right, and you’ll want to have your readers help you see where to adjust the ingredients. But if you remember that the fruit/evidence is the tastiest part (so you want the most vibrant examples), and the point of Jell-O/argumentation is to provide consistency to hold everything together (you want statements that sound alike), you may start to gain additional confidence in balancing your writing.
7. Wash-and-wear Paragraphs
If you’re going to have Jell-O and cherries, a chorus and one-time-only examples, in every paragraph, that’s going to take some managing— and you’ll want to manage rhetorically rather than going by some rules you once heard about exactly how long a paragraph should be. What paragraph-length rules have you been taught? Should a paragraph be five to eight sentences? always more than two sentences? never longer than a page? Some of my students have learned rules that specify that all paragraphs have twelve sentences and each sentence has a specific job. That sounds complicated—and you know that a rule like that can’t be universally true. What if you’re writing for a newspaper? for a psychology journal? for a website? Paragraph length doesn’t follow clear rules, but once again depends upon a rhetorical negotiation between the writer’s needs and the reader’s needs.
Switch gears for a minute and try out another metaphor: what do you know about how big a load of laundry should be? Right: it depends. What’s wrong with a very small or a very large load? Paragraphs face the same kinds of boundaries: too small, and they can waste a reader’s energy, always starting and stopping; too large, and they overload a reader and nothing gets clean. But there are no definite rules in laundry or in paragraphs. Is there ever reason to do one tiny laundry load, even if it might waste money or energy? Sure: maybe you’ve got an important event to attend Friday night and you just need to wash your best black shirt quickly, or maybe you have a small washing machine. Is there ever reason to do one slightly oversized load? Absolutely: perhaps you’re low on quarters or there’s only one machine open in the dormitory laundry room, and you need to get all those t-shirts clean. The same is true for paragraphs: sometimes, you have just one important thing to say, or your readers have a short attention span, so you want a short paragraph—even a one-sentence paragraph. On the other hand, sometimes you have a complex explanation that you want your reader to work through all at once, so you stretch your paragraph a little longer than usual, and hope your reader stays with you.
You want to write paragraphs that your target audience can handle without straining their brains or leaving suds all over the floor. I bet you’re pretty good at sorting laundry into the basic loads: darks, colors, whites, like the three body paragraphs of a five-paragraph essay. But what if you’re writing an eight-page paper using three basic points? What if you have an enormous pile of whites?
You sometimes have to split up even the loads that look alike. Would you split an all-whites pile into all the long-drying socks vs. all the quick-drying shirts? the dirty stuff vs. the really gross, stinky stuff? the underwear you need tomorrow vs. the towels you could wash later? You can find lots of ways to split a too-long paragraph based on how you want your reader to think about the issue: pros and cons, first steps and next steps, familiar information and more surprising information.
Writers need to remember that paragraphs help readers focus and manage their analytical energies. It’s good to have some variance in size and shape but not to overtax your readers with too much variation; it’s useful to write each paragraph with a clear beginning and ending to direct readers’ attention; and it’s helpful if paragraphs come with a blend of information and analysis to help readers “see what you mean” about your subpoints and see how they relate to the overall point of your essay. It’s not true that paragraphs are “one size fits all,” and it’s not true that “anything goes”: you need to adjust your paragraphs to connect your ideas to your readers’ brains.
8. Hey Hey Hey and the Textbook Conspiracy: Annotating Your Reading
I know, you thought this was an essay about writing. But part of being a writer, and being a helpful companion to other writers, is being a careful reader, a reader who writes.
Besides, I want to be sure you get what you pay for: that kind of critical thinking helps all of us be better writers. Did you know that you pay for most textbooks in two ways, and most students never do the simplest thing to recoup their investment?
How do you pay? First, except for texts like the one you’re reading right now, you’ve paid some exorbitant price for your books, even if you bought them used. Why would you do that, instead of checking them out of the library or sneaking a look from a friend? Right: you can read them whenever and wherever you get around to it. (No, I don’t want to know where you read your class book!) But you may be overlooking one more benefit, which I’ll get to in a minute.
Second, you pay for the book—even a free one like this one—with your time. You pore over page after page, the minutes ticking by, instead of building houses for orphans in Botswana or coming up with a cure for insomnia or even giving that double-crossing elf what he deserves in World of Warcraft . Did you ever finish all that poring (with a “p,” not a “b,” really) and realize you had tuned out and didn’t remember a thing? Now you’ve paid dearly, and you may have to pay yet another time when you re-read it.
The simplest thing you can do to get your money’s worth and your time’s worth from your books and other reading material is this: you can write on them.
Whatever you pay for the book (minus whatever you might sell it back for), the only two benefits you get are convenient reading access, and the chance to write in the book . If you don’t write in your book, or type notes into the document, you’re being cheated, as if you’d paid for a Combo Meal but ate only the fries. (Do you think maybe you won’t be able to re-sell your book if you write in it? Check with your friends: I bet someone’s bought a used book that’s been scribbled all over. So clearly someone will buy your book back even if you write in it. Don’t let the textbook industry scare you out of getting what you pay for.)
Some of you may think you are writing on your text, but I wonder if that’s true. Smearing it with hot pink highlighter pen doesn’t count as writing. Why not? That takes another story and another metaphor. There’s a classic Far Side cartoon from back in the twentieth century that reveals what dogs are really saying when they bark all day long. According to cartoonist Gary Larson, when we finally translate their secret language, we find that they say, “Hey! Hey! Hey!” (144). You can just see a dog thinking that way, everything new and surprising, but not much complexity of analysis. Hey!
When you read something and gloss it with your highlighter pen, that’s what you’re saying: Hey! Hey! Hey! You can come back six weeks later to write an essay or study for an exam, and you have an entire book filled with Hey! It’s a good start, but as a smart writing student, you’re ready to go further to get your money’s worth.
Without having to expend much more energy, you can begin to add a wholly intelligent commentary, putting your own advanced brain down on the page, using an actual writing utensil such as a pen or pencil (or a comment function for an electronic document). For starters, let’s just vary Hey:
Ha. Heh. Hee. Hooboy! Hmm. Hmph. Huh? Whoa!
Each of those responses records some higher-brain judgment : if you go back later, you’ll know whether you were saying “Hey, this is cool!” or “Hey, this is fishy.” You can also use other abbreviations you know: LOL, OMG, WTH(eck), or :). You can underline short phrases with a solid or a squiggly underline, depending on your reaction. And of course, you can always go back to “Why? How so? Show me!” If you get really bold, you can ask questions (“will this take too much time?”), write quick summaries (“annotate so there’s no hey”) or note connections (“sounds like the mind-reading thing”). It doesn’t take very long, and it keeps your brain involved as you read. What other short annotations could you write or type on this page right now?
Every time you write on the page and talk back to the text, you get your money’s worth, because you make the text truly your own, and you get your time’s worth, because you’re staying awake and you’re more likely to remember and learn what you read. If you don’t remember, you still have an intelligent record of what you should’ve remembered, not just a pile of Hey! Bonus: being a writer when you’re a reader helps you become a better reader and a better writer.
9. Short-Time Writing: Use Your Higher Brain
So far, we’ve been thinking about writing when you have plenty of time to consider your audience, play with your paragraphs, and recalibrate your Jell-O/cherry balance. But you won’t always have that much time: sometimes you’ll get a late start or have an early deadline. In college, you might encounter essay questions on an exam. Learning how to be a good timed-exam writer can help you in lots of short-time writing situations.
What’s hard about writing an essay exam? The stress, the pressure, the clock ticking, the things you don’t know. It’s like trying to think with a jet airplane taking off overhead, or a pride of hungry lions racing your way. But wait: the coolest thing about the essay exam is that, in contrast to a multiple choice exam that shows what you don’t know, the essay exam allows you to focus on what you do know. The problem is that only your higher brain can show off that knowledge, and for most people in a stressful situation like an essay exam, the higher brain starts to lose out to the lower brain, the fight-or-flight brain, the brain that sees breathing in and breathing out as one of its most complicated tasks, and so the writing goes awry.
Essay exams—or those last-minute, started-at-1:22-a.m. essays that you may be tempted or forced to write this semester (but not for your writing teacher, of course!)—generally go wrong by failing to meet one of the three principles described at the beginning of this essay. Sometimes students fail to study well so that they can write from knowledge. (Unfortunately, I don’t know if I can help you with your midnight cram sessions.) More often, though, some very smart, well-prepared students fail to adapt to their audience’s needs, or fail to provide specific support. All that late-night study-session agony goes for nothing if your lower brain takes over while you’re writing. Your lower brain can barely remember “I before E,” and it knows nothing about complicated rhetorical strategies like ours: you have to make sure your higher brain sets the pace and marks the trail.
So the teacher hands out the questions, and the first thing you do is . . . panic? No. Start writing? Heavens, no. Never start an essay exam—or a truly last-minute essay—by starting to write the essay, even if (like me) you generally prefer to “just start writing” rather than doing a lot of restrictive planning. Freewriting is an excellent writing exercise, but only when you know you have plenty of time to revise. Instead, ignore all those keyboards clacking, all those pens scribbling: they are the signs of lower brains at work, racing off screeching wildly about lions without remembering the way writing happens. You’re smarter than that. You’re going to use your higher brain right at the start, before it gets distracted. Speed, right now, is your enemy, a trick of the lower brain
The first thing you want to do is . . . read the gosh darn question. Really, really read it. Annotate the assignment sheet or exam prompt, or write the key question out on a separate piece of paper, so you know you’re actually reading it, and not just pretending to. (If you’re in a workplace setting, write down a list of the top things you know your audience—or your boss—wants to see.) In every essay exam I’ve ever given, some body has not answered the question. When I say this in a class, everyone frowns or laughs at me just the way you are now, thinking, “What kind of idiot wouldn’t read the question? Certainly not me!” But someone always thinks she’s read the whole question, and understood it, when she hasn’t. Don’t be that writer. Circle the verbs: analyze, argue, describe, contrast. Underline the key terms: two causes, most important theme, main steps, post–Civil War . Read it again, and read it a third time: this is your only official clue about what your audience—the teacher—wants. On a piece of scratch paper, write out an answer to the question, in so many words : if it asks, “What are two competing explanations for language acquisition?” write down, “Two competing explanations for language acquisition are ___ and ___ .” In an examination setting, this may even become your opening line, since readers of essay exams rarely reward frilly introductions or cute metaphors.
But don’t start to write the whole answer yet, even though your lower brain is begging you, even though the sweat is breaking out on your brow and your muscles are tensing up with adrenaline because you know the lions and probably some rampaging T-Rexes are just around the corner. In real time, it has only taken you two minutes to read and annotate the question. Some students are still pulling out their pens, while across campus at least one student is just waking up in a panic because his alarm didn’t go off. Meanwhile, far from being hopelessly behind, you’re ahead of everyone who’s writing already, because you’re still working with your higher brain.
You have one more task, though. You know that showing takes longer, and is more complicated, than telling . Given the choice, your lower brain will tell, tell, and tell again, blathering on about Jell-O generalities that don’t let readers see all the best thinking going on in your mind. Before your higher brain starts to abandon you, make it give you the cherries: write yourself a list of very specific examples that you can use in this essay, as many as you can think of. Do not just “think them over.” That’s a lower brain shortcut, a flight move, and it’s a trick, because your lower brain will forget them as soon as the lions get a bit closer. Write them down. If you don’t know all the possible transmission vectors for tuberculosis that were discussed, write down excellent examples of the ones you do know. If you can, number them in an order that makes sense, so that you leave a good breadcrumb trail for your lower brain to follow. Don’t call it an “outline” if you don’t want to; that can feel intimidating. Just call it a “trail guide.”
Now you can start writing: take a deep, calming breath and begin with your in so many words sentence , then follow the trail your higher brain has planned. About every two or three sentences, you should start out with “For example, . . .” or “Another example of this is . . . ,” to be sure that you’re not forgetting your higher brain’s advice or sliding into a vague “some people” sentence. About every three or four sentences, you should start out with “Therefore, . . .” or “In other words, . . .” and come back to a version of that very first, question-answering sentence you wrote on your paper. Bring the chorus back in; stay in tune and on the trail. Don’t try for too much variation or beauty. Knowing that your higher brain has already solved the problem, all you have to do is set it down on paper, to show what you know . Writing is hard, especially under time pressure, but when you use higher brain strategies and don’t get trapped in the rules or caught up in random flight, when you take control and anticipate your reader’s needs, you can make writing work for you in very powerful ways even without a lot of time.
10. Rules vs. Rhetoric, or, The Five Paragraph Essay vs. “Try Something!”
We started out by thinking of all the rules—all those “Don’ts”—that writers can face. Each of the metaphors here replaces a rule with an idea that helps you consider how real people communicate with each other through writing, and how writers make judgments and choices in order to have the most powerful effect on their readers. That is, we’ve been thinking rhetorically, about the audience and purpose and context of a writing situation.
Interestingly, many of those rules are just short-cut versions of really good rhetorical principles. If you were a middle-school teacher faced with a room full of thirty squirrelly teenagers who all wanted to know What’s Due On Friday? and who didn’t have patience for one more part of their chaotic lives to be in the “it just depends” category, you might be tempted to make some rules, too. You might even come up with The Five Paragraph Essay.
That is, instead of saying, “Most readers in the U.S. prefer to know exactly what they’re getting before they invest too much time,” which is a thoughtful rhetorical analysis that can help writers make good choices, you might say, “Your thesis must come in the first paragraph.” Instead of saying, “In Western cultures, many readers are comfortable with threes: three bears, three strikes, three wishes, even the Christian Trinity,” you might make a rule and say, “You must write an essay with a beginning, an end, and three middle paragraphs.” Instead of saying, “Your readers need to know how your examples connect to one another, and how each set of examples is related to your overall point,” you might say, “Every paragraph needs to start with a transition and a topic sentence and finish with a concluding sentence.” And instead of saying, “Writers in the U.S. face one of the most heterogeneous groups of readers in the world, so we need to be as careful as possible to make our meaning clear rather than assuming that all readers know what we’re talking about,” you might just say, “Each paragraph needs to include two concrete-detail sentences and two commentary sentences.”
You would intend to be helping your students by saying these things, and for many young writers, having clear rules is more useful than being told, “It depends.” But eventually the rules start to be more limiting than helpful, like a great pair of shoes that are now a size too small. Good writers need some space to grow.
As a writer in college now, and as a writer in the larger world full of real readers—whether they’re reading your Facebook page, your letter to the editor, or your business plan—you need to free yourself from the rules and learn to make rhetorical decisions. From now on, when you hear someone tell you a rule for writing, try to figure out the rhetorical challenge that lies behind it, and consider the balancing acts you may need to undertake. What do you want to say, and what will help the readers in your primary audience “see what you mean” and follow your main points?
There aren’t any easy answers: writing is still hard. But the good news is that you can use a few helpful “rules” as starting points when they seem appropriate, and set aside the rest. You can draw on some key principles or metaphors to help you imagine the needs of your readers, and when you come to an open space where there doesn’t seem to be a perfect rule or strategy to use, you can try something. In the end, that’s what writers are always doing as we write: trying this, trying that, trying something else, hoping that we’ll make a breakthrough so that our readers will say “Aha, I see what you mean!”—and they really, truly will see it. You know James Bond 007 would try something; Jane Eyre would try something; those Olympic medalists and rock stars and pioneering cardiac surgeons and Silicon Valley whiz kids are always trying something. In the same way, being a good writer is always more about trying something than about following the rules, about adapting to a new situation rather than replicating last year’s essay. So take a deep breath, push all those nay-saying rule-makers into the far corners of your brain, focus on your current audience and purpose, and write!
- Which section of this essay do you remember most clearly? Write down what you remember about it, and explain how you might use an idea in that section to help with a writing task that you’re doing this week. Why do you think this section stuck with you?
- Without looking back at the essay, what would you say is the chorus of the essay, the “beer: sports car” message that keeps getting restated? Write it down: it may be a sentence, a phrase, and/or a few key words. Now go back to a section of the essay and underline or highlight sentences or phrases where Reid repeats this chorus or key words. Does she repeat them as much as you thought she did?
- What other rules for writing have you been told to follow, either at school or outside of school in your workplace, community group, or online setting? List a couple of rules that weren’t described in this essay, and note down whether you think they’re most connected to the principle of writing from knowledge, showing enough detail, or adapting to readers’ needs. Also, if there’s another principle for writing that helps you a lot, something you always try to do, add a note about it so you can share it with your classroom peers.
- Where in this essay does Reid practice what she preaches? Go back through the essay and label a few places where she seems to be doing what she says writers should do (“here she gives a Pink House heads-up sentence at the start of a section”), and note a few places where she doesn’t. Even though Reid admits that writing is hard and depends on a specific context, her essay may make some of the strategies sound easier or more universal than they are. Which one of her suggestions seems like it would be the hardest for you to do, or seems like it would be the least effective in the kind of writing you do most often? Explain why this suggestion is trickier than it looks, and how you might cope with that challenge as a writer.
Works Cited
Blake, E. Michael. “Science Fiction for Telepaths.” 100 Great Science Fiction Short Short Stories . Ed. Isaac Asimov, Martin Greenberg, and Joseph D. Olander. New York: Avon, 1978. 235. Print
Larson, Gary. The Far Side Gallery 5. Kansas City: Andrews and McMeel, 1995. Print.
Ten Ways To Think About Writing: Metaphoric Musings for College Writing Students Copyright © 2019 by E. Shelley Reid is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
25 Metaphors for College
Metaphors are a powerful tool for understanding and communicating complex ideas.
They can help us to make sense of experiences and concepts that might otherwise seem abstract or difficult to grasp.
In this blog post, we’ll be exploring a variety of metaphors for college, each of which offers a unique perspective on the college experience.
From journeys and rollercoasters to laboratories and playgrounds, these metaphors can help us to better understand and appreciate the challenges and opportunities of college life.
Whether you’re a current college student, a recent graduate, or just starting to think about your own college journey, we hope these metaphors will give you something to think about and maybe even inspire you to come up with your own!
Metaphors for College
- “The college experience is a journey.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to traveling on a journey, implying that it is a learning experience that involves both challenges and growth.
- “College is a rollercoaster ride.” This metaphor likens the ups and downs of college life to the ups and downs of a rollercoaster, suggesting that it can be both exciting and challenging.
- “College is a marathon, not a sprint.” This metaphor compares the process of completing college to running a marathon, implying that it requires endurance and persistence.
- “College is a battlefield.” This metaphor compares the challenges and competition of college to the challenges and competition of a battlefield, suggesting that it requires a certain level of resilience and fortitude.
- “College is a melting pot.” This metaphor compares the diverse student body of a college to a melting pot, implying that it is a place where different cultures and experiences come together and merge.
- “College is a training ground.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to preparing for a sport or other activity, implying that it is a place where students can develop skills and knowledge that will serve them in the future.
- “College is a laboratory.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to conducting scientific experiments, implying that it is a place where students can explore and test ideas.
- “College is a garden.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to tending to a garden, implying that it requires cultivation and care in order to grow and flourish.
- “College is a puzzle.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to solving a puzzle, implying that it requires problem-solving skills and patience.
- “College is a stage.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to performing on a stage, implying that it is a place where students can develop and showcase their skills and talents.
- “College is a game.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to playing a game, implying that it requires strategy and competition.
- “College is a fishbowl.” This metaphor compares the experience of attending college to living in a fishbowl, implying that it is a place where students are constantly under scrutiny and observation.
- “College is a maze.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to navigating a maze, implying that it can be confusing and require careful planning and decision-making.
- “College is a tree.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to growing a tree, implying that it requires nurturing and support in order to reach its full potential.
- “College is a bridge.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to crossing a bridge, implying that it is a transitional period that leads to new opportunities.
- “College is a ladder.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to climbing a ladder, implying that it requires hard work and effort to achieve success.
- “College is a buffet.” This metaphor compares the variety of options and experiences available in college to a buffet, implying that students have the opportunity to explore a wide range of interests and activities.
- “College is a playground.” This metaphor compares the atmosphere of college to a playground, implying that it is a place for fun and exploration.
- “College is a workshop.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to working in a workshop, implying that it is a place where students can develop and hone their skills.
- “College is a sandbox.” This metaphor compares the freedom and experimentation available in college to playing in a sandbox, implying that it is a place where students can try out new ideas and approaches.
- “College is a greenhouse.” This metaphor compares the supportive environment of college to a greenhouse, implying that it is a place where students can grow and develop in a protected environment.
- “College is a laboratory of ideas.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to exploring and testing new ideas in a laboratory, implying that it is a place where students can engage in intellectual experimentation.
- “College is a museum of knowledge.” This metaphor compares the wealth of information and learning opportunities available in college to a museum, implying that it is a place where students can discover and explore new ideas.
- “College is a construction site.” This metaphor compares the process of attending college to building a structure, implying that it requires hard work and collaboration to achieve a final goal.
- “College is a tapestry.” This metaphor compares the diverse experiences and perspectives of college to a tapestry, implying that it is a place where different threads come together to create a rich and complex whole.
In conclusion, the college experience is rich and multifaceted, and it can be difficult to capture all of its complexities in words.
However, by using metaphors, we can gain a deeper understanding of the college journey and the many ways in which it can shape our lives.
Whether you see college as a journey, a rollercoaster ride, or something entirely different, the metaphor you choose can reveal something about your own perspective and experience.
Ultimately, the metaphors we use to describe college are just one way to make sense of this exciting and transformative period of life, and we hope that this blog post has given you some food for thought as you navigate your own college journey.
Related Posts
25 metaphors for poetry, 25 metaphors for kids.
Writing resource for college students
- Definition essays
- Analytical essay topics
- Essay sample about the vise president of operations
- Business ethics essay sample
- Abortion argumentative essay writing
- Advice on writing services
- Essay example on The Chrysanthemums
- Sample about animal testing
- Cause and Effect Essay Writing Help
- Strong topics for expository essays
- Java programming essay
- Good persuasive essay topic ideas
- Collecting your thoughts for an essay
- Reflective essay in a couple hours
- Atlas Shrugged essay research
- Persuasive essay in 30 minutes
- General paper essays tips
- President Obama inauguration essay sample
- Expert dissertation writers
- Definition Essays - How To Write Them
- Writing an essay outline
- Can you do my paper for me?
- Sample about Epicurism
- Essay on elementary school
- The Glass Menagerie essay sample
- Essay example on disaster management
- Pension for nurses essay example
- Essay sample on General Motors
- Essay sample on health insurance acts
- Essay sample on abnormal eating
- Narcolepsy essay sample
- Get started with your essays
- Essay writing agencies are very reliable
- Tips for writing your essays faster
- Citations and quotes in an essay
- Writing essays: most popular questions
- Custom writing prices
- Expert essay help is quite expensive
- Corporate success essay example
- A clear thesis is vital for an essay
- College narrative essay topics
- How to conclude article review
- Homework services can be helpful
- An easy way to hire a writer
- Great textual analysis essay
- Creating an elaborate article review
- Writing great argumentative essays
- Beginning academic essay writing
- MBA essay editing service
- Essay writing services in the UK
- Chicago style guide
- Writing a school essay conclusion
- Career research papers
- 15-page essay writing
- APA formatting style
- College essay cheating
- The typical cyber crimes essay sample
- Scholarship essay topics
- Movie evaluation essay writing hints
- Ordering custom-written essays
- How to write an elaborate body part
- Popular tips to avoid
- Process essay guides
- Essay sample on prisoners’ rights
- Social networks: sample
- creating a comparison essay
- Starting your college essay
- Simple essay guide
- Already written persuasive speeches
- Buying essay papers online
- Rigidity of wages essay sample
- Essay outline writing importance
- Picking up a topic for an essay
- Creating interesting for readers essays
- Metaphors in a college essay
- 5 expository topics to avoid
- Cause and effect essay structure
- Book reports examples
- Custom essays will cost a lot
- I have no time for my term paper
- Downloading an original essay
- Online essay helpers 24/7
Using Metaphors When Writing A College Essay
There are many tools that writers can use to improve their essays and to make them more intriguing and engaging for the reader. One of these tools is metaphor. Metaphor allows the writer to describe a concept as if it were something else, drawing a comparison between these two ideas to deepen the reader’s understanding of the original concept.
Difference between metaphor and simile
Metaphors and similes are similar, but there is an important distinction between them. While they may be used to draw comparisons between the same two concepts, they do so in different ways.
“Her eyes were as deep as the ocean.”
The above quote is a simile.
“Her eyes were deep oceans.”
This one is a metaphor. Note that when using a simile, terms like “like” and “as” are used, while in a metaphor, the two concepts are equated. Her eyes are not like oceans, they are oceans.
Reasons to Use Metaphors
Metaphors are primarily used for three reasons:
In the above quote, equating the woman’s eyes to oceans explains to the reader that that the narrator finds them almost unbelievably deep and mysterious; the ocean imagery does the best possible job of portraying this.
- To increase interest
Metaphors paint vivid pictures that pique the reader’s interest and heighten their sense of creativity and imagination.
Metaphors are a strong way to use imagery. Similes are somewhat softer. For this reason, many writers limit their use of metaphors so that when they do use them, they have the maximum impact.
Metaphors: Tips
When using metaphors, it’s a good idea to try and avoid being trite. Trite metaphors are those which are used too frequently, so they lose their impact. The above example, comparing eyes and oceans, could be considered trite. Instead, try to think of a concept for comparison which your reader will be surprised by, despite how applicable it is.
Also, be careful not to mix metaphors. When you compare something tangible in your story to a concept, fulfill that comparison before equating it to something else. If, for example, you are using a metaphor to equate an argument and a boxing match, do not change it to a hockey game midway through. This may or may not actually confuse the reader, but even if it doesn’t, it comes across as sloppy and ineffectual, and is best avoided.
Learn to write
Testimonials.
Jonathan (ND): This is probably the best free college resource I have found online. I needed urgent help with picking a good essay topic and found a great list here. Thank you guys!
Andy (MO): Thank you for creating such a great resource for struggling students
Erika (WV): I spend much time playing lacrosse for my college team so I am constantly stuck with my writing assignments. This blog is gift from heaven for students like me.
We recommend:
Useful essay writing guides for students.
Questions answered
Guest posts.
We love guest posts related to education, writing problems, formatting and proofreading questions, research paper topic generation, college and campus life - basically anything related to students. Please mind that we will thoroughly check each and every submission before posting it to our readers. We are partners with the most respected and well-known student networks, so writing for us will be beneficial to both you and our visitors.
Getting in touch with us is easy and convenient. If you would like to ask a question, report a bug, send an inquiry, or contact us for any other reason, simply leave an email to info [at] collegelax dot us. Since we receive hundreds of emails every day, we will need at least 3-4 business days to get back to you.
Please mind that we are not an academic writing service and we do not accept writing tasks.
© 2008-2024 - CollegeLax.us Modified: 04.18.2024
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Samples >
- Essay Types >
- College Essay Example
Metaphors College Essays Samples For Students
124 samples of this type
Over the course of studying in college, you will surely have to write a bunch of College Essays on Metaphors. Lucky you if putting words together and turning them into meaningful content comes naturally to you; if it's not the case, you can save the day by finding an already written Metaphors College Essay example and using it as a template to follow.
This is when you will definitely find WowEssays' free samples database extremely helpful as it contains numerous professionally written works on most various Metaphors College Essays topics. Ideally, you should be able to find a piece that meets your criteria and use it as a template to build your own College Essay. Alternatively, our qualified essay writers can deliver you an original Metaphors College Essay model written from scratch according to your personal instructions.
Use Of Metaphors In Science Essay
Career metaphors essay examples, career metaphors.
As an introduction, it is vital to understand that Kerr Inkson (2007) proposes metaphors as a way to view careers. The following paper compares and contrasts Inkson’s characterization of careers as inheritance and journeys. It also assesses whether this conceptualization expands my understanding of career. Also, Inkson places a reliance on metaphors to understand careers coupled with assessing this reliance in relation to the three metaphors of careers provided by Inkson; Career as actions, roles, relationships and resources. A logical argument will be provided to support the use of one of the metaphors over the other three metaphors.
Careers as inheritance and journeys
Example of essay on history and theory.
Don't waste your time searching for a sample.
Get your essay done by professional writers!
Just from $10/page
Why We Live In An Organizational World Essay Example
Example of metaphors essay, brain as metaphor essays examples, example of essay on reaction paper - sfard, example of essay on online shopping behavior, aids and its metaphors essay sample, good metaphor essay example, free essay on en 621, analysis of allusions, metaphors and their interpretation in christopher marlow’s “hero and leander”, essay on christopher marlowe "hero and leader", critique of the through other eyes initiative essays example, executive summary, pisani and sontag essay examples, "don’t go chasing waterfalls, please stick to the rivers / and the lakes that you’re used to.", the kingdom of god essay example, metaphors essay example, good essay about reading response, essay on aids denial and discourse, "don’t go chasing waterfalls, please stick to the rivers / and the lakes that you’re used to.", literary analysis of the border: double sonnet essay sample, expertly written essay on notable aspects in three werner herzog films: to follow, aguirre, stroszek and fitzcarraldo, good example of essay on the african experience, the healers, the african experience, the healers, similarities and differences between ‘i have a dream’ and ‘this is water’ speeches essay sample, rhetorical analysis essay example, example of essay on africa by maya angelou, good example of essay on a study of individualism and simplicity in robert frosts poems, analyze two speeches essay, example of essay on analyze two speeches, example of william shakespeare essay, overview and analysis of shakespeare and king lear, secretary chant written by marge piercy essay, the water and culture reader essay examples, good example of time in “sonnet 73” essay, john woo: from hong kong to hollywood essays examples, good essay about metaphysical characteristics in the poem “death.”, workplace bullying by tracy, lutgen-sandvik & alberts, j. k essays examples, a consideration of conceptual metaphor theory: free sample essay to follow, perfect model essay on martin luther king and rhetoric, alice in wonderland as an experiment with dreamscape essay example, essay on a rhetorical analysis of john f. kennedy’s inaugural speech, levin and kitty, anna and vronsky essay sample, good example of beyond fracking: rhetorical analysis essay, free literary criticism: the psychoanalytical mode order 229838249 essay sample, free environmental situation in china essay sample, introduction, free to his coy mistress essay example, example of essay on the dying of the light, a red, red rose by robert burns essay.
This poem is a love song composed by Robert burns, a Scottish poet whose poems mostly fall under the genre of love. In “red rose”, the reader is made to read about a romantic affair of two persons who are intimately in love. This essay will ventilate the poem with a view to analyzing its structure, theme, subject matter, characters, stylistic devices that the poet uses to convey his message and the traits of the characters that the poet uses in the poem.
Structure of the poem:
Good example of namedate essay, good poetry interpretation paper essay example, speaker: muhammad ali clay essay, good the dying of the light essay example, free essay on historical contextual analysis in the case of no name woman, a brief of the story, free essay on the sun rising by john donne, crossing and dwelling a theory of religion by tomas a tweed essay, “confluences: towards a theory of religion” chapter 3., a-level essay on rhetoric in health and medicine for free use, free speaking in hands and bubbling with tongues: imagery in titus andronicus essay sample, sonnet 130 and arthurian legend essays example, the women men don’t see literary analysis essays example.
Invisibility of Women - Literature analyses of “The Women Men Don’t See” by James Tiptree Jr. in compare and contrast to “Invisibility in Academe” by Adrienne Rich
Write By Example Of This Songs Of Innocence And Songs Of Experience By William Blake's Essay
Perfect model essay on comparison of poems, plays, and short stories, example of essay on critical response 6, richard iii by william shakespeare essay, act v, scene iii.
“The lights burn blue. It is now dead midnight.
Cold and fearful drops stand on my trembling flesh.
What do I fear? myself? there's none else by: Richard loves Richard; that is, I am I. Is there a murderer here? No. Yes, I am: Then fly. What, from myself? Great reason why: Lest I revenge. What, myself upon myself? Alack. I love myself. Wherefore? for any good
That I myself have done unto myself?
O, no! alas, I rather hate myself For hateful deeds committed by myself! I am a villain: yet I lie. I am not”.
“Methought the souls of all who I had murdered
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A metaphor can be a strong device to use in your college essays, but you'll need to keep a few important considerations in mind. You'll need to choose something unique to stand out, and describe it well. Use imagery and other rhetorical devices to frame your metaphor. Be descriptive. Also remember that admissions committees read many, many ...
Metaphors for Essays. "The world is a stage.". This metaphor suggests that life is a performance and we are all actors on the stage of the world. "Time is money.". This metaphor equates the value of time with the value of money, implying that time is a valuable resource that should not be wasted. "He is a snake in the grass.".
The following sections also discuss a number of studies exploring good metaphors to use in creative writing, the use of metaphors in various situations and environments outside literature, and metaphor essay examples. ... What Are The Real Benefits of College Education - A Complex Reality of 2024 by Imed Bouchrika, Phd. Education APR 17, 2024
Metaphors can make prose more muscular or imagery more vivid: 1. "Exhaustion is a thin blanket tattered with bullet holes." ―If Then, Matthew De Abaitua. 2. "But it is just two lovers, holding hands and in a hurry to reach their car, their locked hands a starfish leaping through the dark." ―Rabbit, Run, John Updike. 3.
Using metaphors effectively in your college essays requires careful thought and planning. Here are some tips to help you incorporate metaphors into your writing: Start with a brainstorming session: Think about the qualities, experiences, and emotions that define you and your story. Consider different objects or concepts that could represent ...
We're sharing exceptional personal statements from last year's applicants to illustrate that a good personal statement can be on a variety of topics, but ultimately, showcases the student's character, curiosity, and voice. ... Extended Metaphors Add Cohesion. August 22, 2018 ... This is one of a 5-part series on application writing; ...
Now, let's get to the good stuff: the list of 177 college essay examples responding to current and past Common App essay prompts. Connecticut College. ... One Clear Governing Metaphor. This essay is ultimately about two things: Renner's dreams and future career goals, ...
Grammatical metaphors: Also known as nominalization, this type of metaphor rewrites verbs or adjectives as nouns. It's most commonly used in academic and scientific texts as a way to separate spoken and written language, remove personal pronouns, and write in a concise manner. For instance, ' Millions of men, women and children starved to ...
A metaphor from Johnny Cash's song Ring of Fire: 'Love is a burning thing, and it makes a fiery ring.' Bonnie Tyler's famous lyrics from Total Eclipse of the Heart make a great metaphor: 'Love is a mystery, everyone must stand alone.' Keep reading the article to find out how to write an essay with the effective use of metaphors in academic writing.
Keep the comparison simple. Use a few other literary devices such as imagery or anecdotes to enrich your extended metaphor. Avoid making cliché comparisons. Don't exaggerate or make an unrealistic comparison. In the example below, a student uses the extended metaphor of a museum to explore the theme of identity.
Or so says Aristotle in Poetics: "[T]he greatest thing by far is to be a master of metaphor." It is "a sign of genius, since a good metaphor implies an intuitive perception of the similarity in dissimilars." Creative ways to use metaphors. Most books give rather boring examples of metaphors such as my father is a bear or the librarian was a beast.
26 Metaphors for Essays. The Essay as a Journey: Navigating through the pages is like embarking on a literary expedition, each paragraph a step forward in exploration.; Words as Building Blocks: Just as a builder meticulously selects bricks, the writer chooses words to construct the foundation of their essay. Essays as Time Capsules of Thought: Imagine essays as sealed capsules, preserving and ...
These are only a select few of the vast array of rhetorical devices that can be used to enhance an essay. Try browsing a list of devices and attempting to incorporate several into the latest draft of your personal statement. The greatest advantage of rhetorical devices is that they are incredibly effective in lending an essay a strong emotional ...
This college essay tip is by Abigail McFee, Admissions Counselor for Tufts University and Tufts '17 graduate. 2. Write like a journalist. "Don't bury the lede!" The first few sentences must capture the reader's attention, provide a gist of the story, and give a sense of where the essay is heading.
Three years ago, seven-thirty in the evening meant I was a warrior. It meant standing up straighter, pushing a little harder, "Yes, sir" and "Yes, ma'am", celebrating birthdays by breaking boards, never pointing your toes, and familiarity. Three years later, seven-thirty in the morning meant I was nervous.
Ten Ways To Think About Writing: Metaphoric Musings for College Writing Students E. Shelley Reid. 1. A Thousand Rules and Three Principles. Writing is hard. I'm a writer and a writing professor, the daughter and granddaughter of writers and writing professors, and I still sit down at my keyboard every week and think, writing is hard.
18. A Theater of the Mind. Meaning: This metaphor compares writing to a play, with words and ideas being used to create a vivid and immersive experience for the reader. In a Sentence: The writer stages a theater of the mind, where the reader becomes an active participant in the unfolding drama of the narrative. 19.
Metaphors for College. "The college experience is a journey.". This metaphor compares the process of attending college to traveling on a journey, implying that it is a learning experience that involves both challenges and growth. "College is a rollercoaster ride.". This metaphor likens the ups and downs of college life to the ups and ...
Testimonials. Jonathan (ND):This is probably the best free college resource I have found online.I needed urgent help with picking a good essay topic and found a great list here. Thank you guys! Andy (MO): Thank you for creating such a great resource for struggling students Erika (WV): I spend much time playing lacrosse for my college team so I am constantly stuck with my writing assignments.
TheHeadmasterConsult. •. Metaphors for common application essays need to come naturally. We do not recommend forcefully inserting metaphors that do not naturally flow with the essay, theme, idea, and topic. Furthermore, using common metaphors often hurts more than helps.
adviceguru25. • 3 yr. ago. It'll only be good if the metapor makes sense and you know how to write a compelling story. Just following the format won't get you anywhere. 6. Reply. platinum-peony. • 3 yr. ago. You can always give it a shot, and if you feel like it's a crappy essay don't use it!
George Herbert (1593-1633) adopted the Metaphysical style of poetry from Donne but in a simpler manner. His famous poem "Death" is an example of the poetry that uses rhetorical forms of writing like a paradox, hyperbole, and conceits. The poem constitutes two parts that have a contradicting view of death.