- Skip to content
- Go to accessibility page

Undertaking a PhD in France
Are you considering doing your PhD in France? Below, discover everything you need to know. Learn more about the application criteria, project development process, and types of PhDs.
Advanced degree
In France, a PhD is the highest academic degree you can earn. Doctoral studies are a form of research-based training with the same value as professional experience. PhD students carry out research on a defined topic under the supervision of their thesis advisor(s).
PhD students are enrolled in doctoral programmes run by institutions of higher education (i.e., universities or grandes écoles ), but they are trained within research laboratories. Students carry out original scientific research either on their own or as part of collaborative projects; the results form the basis for their dissertations. Students must also go through a thesis defence in which they present their findings to a committee that judges the quality of their work. Those who succeed are awarded doctoral degrees.
Generally, earning a PhD requires 3 years of full-time research. One-year extensions may be granted under certain circumstances. In exceptional cases and for compelling reasons, a student may request a leave of absence of up to 1 year. Such requests are only granted once, upon approval by the establishment’s director. Any leave of absence is excluded when calculating thesis duration, given that the student suspends their training and research during that period.
To be eligible for doctoral studies, you must have a master’s degree. This requirement can be waived by an establishment’s director if approval is granted by the doctoral programme’s administrators. You need to show that you have an equivalent level of education or professional experience.
PhD programmes frequently have an international component. For example, doctoral students often take part in joint degree programmes or dual degree programmes, a situation that is facilitated under French law.

Status of doctoral students
In France, the status of doctoral students depends on their funding source. Anyone doing a PhD is officially recognised as a student because they must be enrolled in a doctoral programme at an institution of higher education. In addition, many are also salaried workers because they are contractual employees.
International doctoral students with foreign grants have the status of students in France.
There are different types of doctorates in France. Here are some common examples:
Traditional PhD
- 3 years of work in a single research laboratory
- Leads to a French degree
- Enrolment and thesis defence occur at a single institution
- Single thesis advisor (or co-advisors, if necessary)
Jointly supervised PhD
- Thesis jointly supervised by a set of co-advisors—one from the student’s main research laboratory (affiliated with the enrolment institution) and one from a separate institution, either in France or another country
- Enrolment and thesis defence occur at the institution affiliated with the main research laboratory
- Single degree granted by the above institution
- Thesis research might arise from a national and/or international collaboration
Dual degree PhD
- Thesis jointly supervised by a set of co-advisors, with research taking place in two laboratories
- Individual dual degree agreement ( convention individuelle de co-tutelle ) establishes a research framework
- Enrolment occurs at two institutions—one in France and one abroad
- Tuition is paid to a single institution
- Single thesis defence but two degrees (one from each institution)
Professional PhD
- Research carried out at a private company partnered with a publicly funded laboratory and its affiliated institution of higher education
- Thesis jointly supervised by a set of co-advisors—one from the company and one from the laboratory
- Work is split between the company and laboratory
- Student contractually employed by the company
- Degree is granted by the institution of enrolment
- Excellent opportunity to gain professional experience
Doctoral training
The first step in your doctoral studies is to enrol at an institution (university or grande école ) with an official PhD programme that is under the aegis of the French Ministry of Higher Education and Research. Such doctoral programmes are structured to provide a high level of personalised training and supervision during your thesis work:
- You are under the supervision of one or more thesis advisors
- You carry out your work within an affiliated research unit and take part in laboratory activities
- You can participate in courses and seminars designed to establish a solid scientific foundation and guide the development of your research
Your thesis committee will ensure your studies are advancing smoothly, notably by evaluating your training conditions and research progress. To enhance your employability, your doctoral programme and thesis advisor will
- Encourage you to attend national, European, and international conferences and publish in national, European, and international journals
- Design a training programme compatible with your PhD project
- Help you exploit your skills and training
In France, you can write and defend your thesis exclusively in English. However, your thesis summary must be translated into French.
Your PhD project
To begin your PhD, you must find a host research laboratory, a thesis topic, a thesis advisor, and funding. We recommend that you begin this process at least 1 year before your target start date. You can begin by looking at the list of thesis topics posted by doctoral programmes and institutions of higher education. You can also directly contact laboratories working in your area of interest. As a general rule, your future thesis advisor will help you with funding.
International students may be able to find other sources of funding, such as fellowships from embassies, the governments of their home countries, and/or partnership agreements between institutions.
Enrolling in a doctoral programme
Once you have resolved all of the above, you must submit your project to your doctoral programme for approval. Your thesis advisor and the laboratory director will evaluate the quality and feasibility of your proposal.
If their assessment is favourable, the director of the doctoral programme will allow you to enrol. You will be informed of the decision by the head of the doctoral programme (the university or grande école president). The French Ministry of Higher Education and Research establishes the amount of tuition paid by bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral students. Tuition levels are the same everywhere in France.
In 2023, annual tuition for doctoral students was €380. There is also a campus activities fee (CVEC) of €92. In certain cases, both may be waived.

Useful link
- Getting a PhD in France—directory of doctoral schools
Related articles
- Doctoral studies at INRAE
- Joining INRAE
- Working conditions & benefits
- Publishing results & managing data
Last update: 20 March 2024
- ENLIGHTEN THE FUTURE

Doctoral Studies
With its 21 doctoral schools, Université Paris Cité offers many doctoral students the opportunity to train through research in all major disciplinary fields. At the national level, once fully operational, Université Paris Cité will offfer 5% of all PhD degrees in France.

Université Paris Cité is committed to a doctoral policy aimed at research training and training by research. It trains future researchers and teacher-researchers as well as future high-level executives.
Astronomy and Astrophysics Ile-de-France – ED 127 Director : Mr. Thierry FOUCHET Contact : Mrs. Jacqueline PLANCY
Environmental Sciences Ile-de-France – ED 129 Director : Mrs Pascale BOURUET-AUBERTOT Contact : Mrs Laurence AMSILI-TOUCHON
Doctoral School of Computer Science, Telecommunications, Electronics of Paris (EDITE) – ED 130 Director : Mr. Carlos AGON Contact : Mrs Rose NAHAN
Language, Litterature and Imagery : civilisations and humanities – ED 131 Director : Mr. Mathieu DUPLAY Co-director : Mrs Emmanuelle ANDRE Contact : Mrs Robin CHEVALIER
Cognition, Brain, Behaviour (ED3C) – ED 158 Director : Mr Alain TREMBLEAU Deputy director UPCité :Mrs Thérèse COLLINS Contact : Mrs Hélène JOUANNE
Cognition, Behaviour, Human behaviour (3CH) – ED 261 Director : Mrs Karine DORE-MAZARS Contact : Mrs Lucie ALEX
Legal, political sciences, economics and management – ED 262 Director : Mrs Anémone CARTIER-BRESSON Contact : Mrs Josie YEYE
Mathematical science Paris Centre – ED 386 Director : M. Elisha FALBEL Co-director : M. Pierre-Henri CHAUDOUARD Contact : Mrs Amina HARITI
Physical Chemistry and Analytical chemistry – ED 388 Director : Mrs Alexa COURTY Contact : Mrs Konnavadee SOOBRAYEN
Pierre Louis Doctoral School of Public Health in Paris : Epidemiology and Biomedical Information Sciences – ED 393 Director : Mr. Pierre-Yves BOËLLE Contact : Mrs Koltoum BEN SAID
Research in Psychoanalysis – ED 450 Director : Mrs Mi-Kyung YI Co-director : Mr Thamy AYOUCH Contact : Mr Ali BRADOR
Frontiers of Innovation in Research and Education (FIRE) – ED 474 Director : Mrs Muriel MAMBRINI-DOUDET Co-directeur David TARESTE Contact : Mrs Elodie KASLIKOWSKI
Earth and Environmental Sciences and Physics of the Universe – ED 560 Director : Mr. Fabien CASSE Contacts : Mrs Alissa MARTEAU
Hematology, Oncogenesis, and Biotherapies – ED 561 Director : Mr. Raphaël ITZYKSON Contacts : Mr Maxime DA CUNHA / Mrs Aurélie BULTELLE
Bio Sorbonne Paris Cité – ED 562 Director : Mrs Caroline LE VAN KIM – Co-Director : Mrs Chantal DESDOUETS Contacts : Mr Louis DUVAL-KISTER
Drug Toxicology, Chemistry and Imaging (MTCI) – ED 563 Director : Mrs Marie-Christine LALLEMAND Contact : Mrs Elisabeth HOMBRADOS
Physics in Ile de France – ED 564 Director : Mr Frédéric CHEVY Co-director : Mr Philippe LAFARGE Contact : Mrs Monia MESTAR
Sports, Motricity and Humain mobility sciences (SSMMH) – ED 566 Director : Mrs Isabelle SIEGLER Co-director : Mr. Bernard ANDRIEU Contact : Mrs Marie-Pierre RICHOUX
Language Sciences – ED 622 Director : Mrs Caterina DONATI Contact : Mrs Chafia AIT-HELAL
Knowledge, Science, Education – ED 623 Co-Director : Mr. Fabrice VANDEBROUCK Co-Director : Mrs Anne BARRERE Contact : Mrs Agathe TRAN
Social Sciences – ED 624
Department 1 Director : Mrs Véronique PETIT Contact : Mr. Jérôme BROCHERIOU
Department 2
Director : Mr Antoine REBERIOUX Contact : Mrs Sarah RAHMANI
More information :
Doctoral School website for more information The following content is in French French higher education system chart
- How to recruit?
- Internship calendars
- Post an offer
- How to give
- Ways to give
- 2019-2024 campaign
- News and publications
- Annual Report
- Build your brand
- Work with our students
- Become a partner
- Our corporate partners

Doctoral Program Doctoral Program
Your Gateway to an International Career in Research and Higher Education.
Research Areas
Take the next step, phd block seminars.
Every year or every other year, in spring/summer we offer PhD Block Seminars for PhD students from other universities.
see all seminars
We welcome applicants from any field with a strong desire to pursue an academic career and who are curious, eager to learn and to explore new ideas.
Johan Hombert, Director of the HEC PhD program

Key Figures
students from all academic backgrounds
international students
nationalities
alumni, working in over 35 countries
Join an academic career

Finance PhD student Alyssa Rusonik’s paper on Renaissance Economic Recovery Receives Award
PhD Dissertation Defense, Yufei Shen, Information Systems & Operations Management

PhD Dissertation Defense, Jing Niu, Marketing
PhD Dissertation Defense, Daria MOROZOVA, Management & Human Resources

PhD Dissertation Defense, Maxime Bonelli, Finance
Hec phd dissertations.

- Welcome to NEOMA
- NEOMA's world
- NEOMA Foundation
- MyNEOMAgora
- twitter - X
- youtube-play
PhD in Management

- Choose your programme
- Programme overview
- Student life
- Student support
NEOMA Business School’s PhD programme provides you with personally-tailored training, courses, and instruction to obtain the knowledge and skills you need on an international, academic career in the fields of business administration and management.
Why join this programme ?
Neoma’s phd programme is especially suitable for you if you share the objectives to :.
- learn, in depth, about scientific research and about becoming a researcher yourself;
- consider an academic career (i.e. becoming an assistant professor and ultimately, a professor) in a business school or university)* ;
- be able to publish and proliferate your research ideas and results to the international scientific community (i.e., international scientific journals), as well as the general public;
- start building a network – and become a member of community – with other scholars and researchers internationally as well as in France
If you share the aforementioned four objectives with us, here is what NEOMA’s PhD programme offers you:
Intensive coaching and courses to train your research skills
- Top academic supervisors to personally train you on how to conduct and publish your research. See a list of selected supervisors
- A focused set of joint programme courses (providing basic researcher skills), complemented with individually-tailored independent learning modules at NEOMA as well as partner/network institutions (providing specialized skills needed in your own research)
- Affiliation to and collaboration with other researchers in one of NEOMA’s Areas of Excellence.
Chances to obtain job interviews – upon graduation – in high-quality business schools, in France and abroad
- Recent PhD graduates from NEOMA have obtained jobs at, among others: University of Minnesota (Minnesota, USA), National Economics University (Vietnam), University of Balamand (Lebanon), Skema Business School (France), Grenoble Ecole de Management (France), IESEG School of Management (France), EM Normandie (France), Fordham University (USA), Institut Mine-Télécom Business School (France), Universidad de Los Andes (Colombia), Duke University (UK), Coventry University (UK), NOVA IMS (Portugal), Lisbon School of Economics and Management (Portugal).
Prospects to publish your research in top-quality international journals
- In recent years, PhD graduates of NEOMA and/or NEOMA’s current faculty have published their research in e.g., the following top academic journals: Academy of Management Journal, European Journal of Operational Research, Journal of Financial Economics, Journal of Marketing, Information Systems Research, The Accounting Review (see “ Highlights ”)
Ability to network within the international scientific community
- 66% of NEOMA’s faculty and supervisors are international (i.e. not French nationals) and have an extensive international network of researchers.
- More than 90% of NEOMA’s PhD students are international (i.e. not French nationals).
*You may also apply to NEOMA’s PhD programme if you are primarily interested in a career in the corporate sector, provided you are committed to studying full-time and have funding for your studies.

HDR - Responsable du MS Analyse Financière Internationale
Finance internationale, management et éthique : 3 composantes clé du cursus.

Layout of the programme
Year 1 – learning the ropes: fundamental courses & familiarisation with your research topic, fundamental coursework.
The first year includes up to 6 intensive courses, providing you basic skills and knowledge that you need for a researcher career. The courses cover such fundamental theories and research methods that are relevant for you regardless of your own discipline/specialisation and regardless of your own research topic.
Examples of these courses include: Basics of Business Research Methods (quantitative and qualitative methods), Economics and Business Studies, Social Psychology.
The six courses are organized during six intensive seminars, each lasting from a couple of days to a week (October, December, January, February, April, May), at one of our campuses : Reims, Rouen and Paris.
Familiarisation with your own research topic
During the first year, you will also start to work with the faculty members who are assigned as your personal supervisors. This way you will start to familiarise yourself with the topic of your research project, which you will be writing your doctoral thesis on. The precise topic(s) will be decided in collaboration with your supervisors, who represent one of NEOMA’s Areas of Excellence. Towards the end of the first year, you will start preparing (in collaboration with your supervisors) a research plan for this thesis research of yours.
Research assistance tasks
During the first year of studies, you will be conducting a limited number of research assistance tasks for that Area of Excellence of NEOMA’s which your own thesis research project and topic relates to. These research assistance tasks may not, however, directly relate to your own thesis research. At any rate, the research assistance tasks will provide you with additional training in various researcher skills, such as conducting systematic literature reviews, administering surveys or experiments, cleaning and reorganising data, and analysing and visualising data.
Year 2 – Selected individual courses and start of empirical research
Selected individual courses and learning modules.
Whereas the coursework in Year 1 takes place at NEOMA, during Year 2, you may conduct a limited number (3-4) of courses or learning modules (a) either as independent learning courses, or (b) as organized by external parties (e.g., other French or international business schools or universities; doctoral education networks like EIASM.net). These studies are meant to provide you with a tailored set of specialised skills and knowledge that your own doctoral thesis research project especially calls for (e.g., special methodological skills).
Submitting/defending your own research plan
Before the beginning of the second half of Year 2, you will be required to complete, in collaboration with your supervisors, the preparation of a research plan for your own doctoral thesis research. During the first half of Year 2, you will submit it for internal review at NEOMA, and defend it in a research seminar of your own Department. The research plan shall include a general literature review about your topic, study designs and plans for the empirical studies to be conducted, and plan for the structure of the doctoral thesis (including planned outline of the contents of three articles for article-based theses).
Starting with your empirical research
In line with the aforementioned research plan, you will start gathering or compiling the first data for your thesis research. This will be done in close collaboration with your supervisors. (In the rare case that your research plan did not include empirical studies, you will be starting your non-empirical research here.) Before the beginning of Year 3, you will be required to submit your first research article to an international academic conference or peer-reviewed journal. This article can be a conceptual study or an empirical research paper that is based on your first data set.
Like during the first year, you will be conducting a limited number of research assistance tasks for an Area of Excellence of NEOMA’s during the second year as well.
Year 3 and Year 4 – Research for and writing of the doctoral thesis
Researching and writing.
The bulk of the empirical research work as well as the majority of writing work for your doctoral thesis will take place during Year 3 and Year 4. Both the conduct of research (gathering/compiling data, analysing data, modelling) and the writing work will be done with intensive support from your supervisors. At the end of Year 3, you are expected to submit another research article to an international academic conference or peer-reviewed journal.
Defending the thesis
Ultimately, when you have three research articles accepted for presentation at international academic conferences or in the review process of high-quality peer-reviewed journals, you may submit your thesis to a jury/committee at NEOMA. (If your thesis is not article-based, but instead takes the monograph/treatise format, your supervisors will determine when the thesis can be submitted to the jury). Some months later, you will defend your thesis in front of the jury/committee consisting of two external experts of your research topic (from other institutions than NEOMA) as well as two internal experts (other faculty members of NEOMA than your supervisors).
Teaching and teaching assistance tasks
During Year 3 and Year 4, most PhD candidates will be teaching a course directed at NEOMA’s MSc or BSc students, on a topic related to their expertise and research. Alternatively, you may be supporting and assisting NEOMA’s faculty members on their courses. Getting teaching experience will be highly useful for you when applying for a job after graduation.
Like during the first and second year, you may be conducting as well a limited number of research assistance tasks for an Area of Excellence during the third and fourth year.
Scholarly visit abroad
Typically during the third year of studies, you will be making a few months’ scholarly visit to a business school abroad, as recommended by your supervisor. Financial support will be available for travel costs.
Evaluation procedures
The programme is sanctioned by several levels of validation:
- continuous assessment: evaluation of each module of the programme in the form of examinations or individual files,
- the submission of a literature review, or Paper I , and of a thesis proposal at the beginning of the second year and their presentation during a seminar organized by one of the Area of Excellence,
- the submission of a doctoral research project, or Paper II , at the beginning of the third year, and the presentation in front of a committee made up of 2 internal examiners,
- the submission of a doctoral thesis at the end of the fourth year and subsequent defense: submission of a written manuscript and oral defense before a jury made up of two internal reviewers and two external reviewers.
At the end of the training and after validation of these different levels of validation, the PhD diploma is awarded to the participants.
Highlights of the programme
All phd students get affiliated with one area of excellence of neoma’s.
‘Areas of Excellence’ are the central pillar of NEOMA’s research strategy, and all admitted PhD students, from 2021 onwards, are affiliated with one of four Areas of Excellence.
The Areas of Excellence create a unique research environment wherein NEOMA’s faculty members as well as PhD students from various disciplines and departments focus on studying certain academically and practically topical research themes and phenomena.
Many of NEOMA’s faculty members (who also supervise PhD students) have a track record of publishing in top academic journals
The list below mentions selected top-tier scientific journals, in which NEOMA’s professors (who also act as supervisors to doctoral students) have published their research in recent years. Please see here for a full list of professors by department.
Please note, though, that even if one of the mentioned professors may become your supervisor as well, your supervisors will be assigned primarily based on the research theme of the open PhD position you are applying to. See the page “Admissions” for the positions).
- The Accounting Review (e.g., prof. B. Zhang )
- Contemporary Accounting Research (e.g., prof. JH. Hyun)
- American Economic Journal: Applied Economics (e.g., prof. E. Arisoy )
- American Economic Review (e.g., prof G. Cette )
- International Review of Law and Economics (e.g., prof. S. Attaoui , W. Cao , P. Six )
- Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control (e.g., prof. S. Attaoui , W. Cao )
Strategy & Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurship Theory & Practice (e.g., prof. O. Giacomin )
- Research Policy (e.g., prof. S. Lhuillery , prof. J. Jacqmin )
- Journal of World Business (e.g., prof. A. Colovic , prof HS. Du , prof B. Misganaw ).
- Industrial and Corporate Change (e.g., prof. A. Colovic )
- Journal of Financial Economics (e.g., prof. E. Arisoy )
- Journal of Banking and Finance (e.g., prof. J.H. Ahn , prof. S. Lleo )
- Management Science , (e.g., prof. S. Ain Tommar, A. Aloosh )
Management, Organisational behaviour, organisation theory
- Administrative Science Quaterly (e.g., prof. N. Bourmault )
- Human Relations (e.g., prof. A. Rouquet , prof. J.B. Suquet )
- Human Resource Management ( e.g., prof V. Pereira, prof. S. da Motta Veiga )
- Journal of Applied Psychology (e.g., prof. D. Choi, prof. S. da Motta Veiga )
- Journal of Management ( e.g., prof. F.Fonti )
- Journal of Management Studies (e.g., prof. HS. Du , prof. N. Bourmault )
- Leadership Quarterly ( e.g., prof. B. Schyns , prof D. Subramanian , prof S. Lonati )
- Organisation Studies (e.g., prof. P. Le )
- Organization Science (e.g., prof. N. Bourmault, prof. S. da Motta Veiga)
- Organization ( e.g., prof S. Dubois , E. Mandalaki , prof. M. Lenglet )
Information systems, Operations Research and Supply Chain Management
- Information Systems Research (e.g., prof. R. Wong )
- Journal of Management Information Systems (e.g., prof. R. Wong )
- Decision Support Systems (e.g., prof. A. Popovic , prof. G. Gupta , prof A. Song )
- Journal of Strategic Information Systems (e.g., prof. A. Popovic )
- European Journal of Operational Research (e.g., prof. F. Ben-Abdelaziz , prof. I. Biswas , prof. A. Ishizaka , prof. A. Llamas Vilches , prof. M. Menezes , prof. P. Six , prof. M. Bagherzadeh Niri )
- International Journal of Production Economics (e.g., prof. A. Ishizaka , prof. M. Menezes , prof. L. Trinchera, prof. H. Jalali , prof. S. Gupta , prof. G. Sbrana, prof. C. Chiappetta Jabbour )
- Information and Management (e.g., prof. A. Popovic )
- Journal of Consumer Research (e.g., prof. P. Gomez , prof. D. Vasiljevic )
- Journal of Marketing (e.g., prof. S. Borraz , prof. A. Song , prof. J. Xu , prof. Y. Kim )
Ethics and Sustainable Development Goals
- Journal of Business Ethics (e.g., prof. A. Souchaud , prof. P. Antonetti , prof. H. Gonzáles-Gómez , prof. A. Mirowska , prof. N. Spielmann , prof. A. Song , prof. E. Mandalaki , prof. V. Pereira )
- Health Economics (e.g., prof. S. Lhuillery )
- Ecological Economics (e.g., prof. N. Befort )
- Energy Journal (e.g., prof M. Russo )
Examples of universities and business schools wherein r ecent PhD graduates from NEOMA have obtained jobs are the following:
Internationally:
- University of Minnesota (Minnesota, USA)
- National Economics University (Vietnam)
- University of Balamand (Lebanon)
- Mae Fah Luang University, Chiang Rai (Thailand)
- Universidad de Los Andes (Colombia)
- Duke University (UK)
- Coventry University (UK)
- Fordham University (USA)
- NOVA IMS (Portugal)
- Lisbon School of Economics and Management (Portugal)
- Skema Business School
- Grenoble Ecole de Management
- IESEG School of Management
- EM Normandie
- Institut Mine-Télécom Business School (France)
Mae Fah Luang University; Thailand, PhD at NEOMA, 2021
“NEOMA helped me build a solid foundation for a successful academic career. The PhD program was well structured and top-notch. The supportive and collaborative environment at NEOMA made it a great place to establish strong connexions for future research and academic collaboration.”
University of Minnesota Duluth; PhD at NEOMA, 2016
“NEOMA’s PhD programme enabled me to get a job offer as an assistant professor of marketing at the University of Minnesota Duluth”
National Economics University, Hanoi, Vietnam; PhD at NEOMA, 2020
“Thanks to the PhD program at NEOMA Business School, I have been able to achieve my position as an assistant professor in marketing at National Economics University – the leading university in management, business administration and economics in Vietnam ”
Results indicators
Data soon available
Satisfaction Rating (out of 5)
Average job search time (month)
Insertion rate at 6 months
Graduation rate
2019-2020 data
Do you want to join the PhD programme?
Admission for 2024 are closed.
Information for 2025 admission will be available on our pages around December 2024.
We recommend you keep an eye on our website towards the end of the year. Thank you.
Admission types
- Admissions to funded positions of NEOMA’s Areas of Excellence :
Most of NEOMA’s new PhD students are recruited directly to one of the four Areas of Excellence . The goal is to have each new PhD student affiliated with one of the Areas, in order to closely integrate to and cooperate with research projects and faculty members working on those particular themes.
These positions, within our Areas of Excellence, are fully funded for the duration of the programme (up to 4 years). PhD students selected for these positions will receive a monthly salary, health care benefits, and support for research/study-related costs (e.g., conference travel). Further, due to your affiliation with one of the Areas of Excellence, you will benefit from supervision by and collaboration with top scholars in the Area, from the resources that the Area makes available to its members, and from joining a thriving community of researchers who are passionate about these topics.
Please see here the announcement and research themes for PhD student positions related to NEOMA four Areas of Excellence .
- Admissions to independently funded positions :
In rare cases, applicants may also be admitted to the PhD programme independently of the aforementioned salaried positions within the Areas of Excellence. If you want to apply for such an independent position, you must still provide evidence that (a) you will be a full-time student (i.e., that you will not be working elsewhere for more than 30% of your time) and that (b) you will have secured funding for the full duration of your studies (e.g., a grant from a company, foundation, government, etc). You also still need to select one of the research themes listed in the announcement for the positions within the Areas of Excellence , while also notifying on the application form, that you are applying for an independently-funded position. Please also note that in an independently-funded position, you will also be responsible for paying tuition fees, without waivers.
Admission criteria
For all types of admission, the following criteria apply.
Eligibility criteria:
- Advanced degree – e.g., Master’s degree, MSc or MBA – in business administration, management, economics, or any other relevant field for your selected research topic.* Evidence of a degree that will be completed by the start of the program (September) will also be accepted. Admission with an undergraduate degree can be considered for exceptional candidates.
- Proof of English proficiency (i.e., previous studies and degree in English language, or test certificates with a minimum score (TOEFL : 83, IELTS : 6.0 in each band, PTE : 62 or Cambridge : 175)
- Evidence of strong motivation to enrol in our PhD program and interest in a career in academia. The application form includes questions aimed at demonstrating passion for research, interest, and knowledge about the research topic you applied for, intention to study full-time for four years, and strong motivation to pursue an academic career
- Sample of academic writing (a Master’s thesis, research report, working paper, or a published article)
Ranking criteria:
- A GMAT/GRE test score (Note. You can apply even without a GMAT/GRE test score, but it is recommended to take the test. If you do not have access to the test for one reason or another, please provide evidence of high GPAs of your previous degrees)
- Short research proposal related to your selected research theme (under the Areas of Excellence)
- Two letters of recommendation
- Results of a potential interview (Short-listed candidates ranking highest with the eligibility and other ranking criteria will be invited to an interview)
* The ‘relevant other field’ can be any field relevant to the research theme of the position you are applying for. For instance, for marketing and consumer research-related themes, Master’s degrees in psychology, sociology, social anthropology, communications, information systems, computer science, statistics, systems analysis, industrial engineering, or logistics may be relevant, while for finance-related themes, Master’s degrees in econometrics, statistics, mathematics, or behavioral economics may be relevant.
Latest news
Practical information
Courses; seminars; personal coaching and mentorship by a team of instructors/supervisors; research projects; doctoral thesis
Tuition fees:
Exemption from fees for students obtaining a research grant.
Course start date:
Entry level:
Master’s degree
Degree awarded:
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Management

- Be passionate. Shape the future
- Key figures
- NEOMA Business School in the rankings
- NEOMA's World
- Our CSR policy
- Our CSR actions
- The digital transformation at NEOMA
- Innovative Pedagogy
- Become an entrepreneur
- Technology at NEOMA
- International experience at the heart of NEOMA’s DNA
- Our international partners
- Your international studies
- International Students
- Erasmus Charter
- International Advisory Board
- The Board of Directors
- Virtual campus
- Undergraduate Programmes
- Master in Management
- Masters of Science – MSc
- Part-time Specialised Masters
- Executive MBA
- Executive Education
- Doctoral School
- Executive MBA & Executive Education
- News from the Faculty
- Library & Databases
- Trading Rooms
- Experimental Lab
- Academic departments
- Language Centre
- Recruitment
- Department Research Seminars
- Chair in Bioeconomy and Sustainable Development
- Smart Products & Consumption Research Institute (SPOC)
- Centre for leadership & effective organisations
- MOBIS Research Institute
- Joint International Research Workshops
- VISTA AR – Experience the digital transformation of tourism
- Intao (Enedis) – How to support a public service organisation towards greater agility
- Greater Reims partnership and territorial attractivity
- Doctoral school
- Research Workshops
- Support to research
- Recent publications
- Innovative Teaching
- Case studies
- Events, workshops & seminars
- Wealth Management & Real Estate Chair
- Next Leader with FERRERO Chair
- Entrepreneurship & Open Innovation Chair (KPMG)
- Microsoft Learn for Educators (Microsoft)
- Harvard Business Publishing Education
- McGraw Hill
- LinkedIn Learning
- International experience
- Financing your studies
- Student Wellness
- Accommodation & insurance
- International students support
- Special offers
- Live in Reims
- Live in Rouen
- Live in Paris
- STUDENT SOCIETIES: A preview of professional life!
- Skills and Career Development
- International academic partners
- Alumni network
- Company Partnership
- Recruiting NEOMA Talents
- Apprenticeship Tax
- Corporate sponsorship with the NEOMA Foundation
- Train your collaborators
- Entrepreneurship
- Involvement in NEOMA Teaching and Research
- Chiffres-clés
October 2024
Our cookies
We use cookies for three reasons: to give you the best experience on PGS, to make sure the PGS ads you see on other sites are relevant , and to measure website usage. Some of these cookies are necessary to help the site work properly and can’t be switched off. Cookies also support us to provide our services for free, and by click on “Accept” below, you are agreeing to our use of cookies .You can manage your preferences now or at any time.
Privacy overview
We use cookies, which are small text files placed on your computer, to allow the site to work for you, improve your user experience, to provide us with information about how our site is used, and to deliver personalised ads which help fund our work and deliver our service to you for free.
The information does not usually directly identify you, but it can give you a more personalised web experience.
You can accept all, or else manage cookies individually. However, blocking some types of cookies may affect your experience of the site and the services we are able to offer.
You can change your cookies preference at any time by visiting our Cookies Notice page. Please remember to clear your browsing data and cookies when you change your cookies preferences. This will remove all cookies previously placed on your browser.
For more detailed information about the cookies we use, or how to clear your browser cookies data see our Cookies Notice
Manage consent preferences
Strictly necessary cookies
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be switched off in our systems.
They are essential for you to browse the website and use its features.
You can set your browser to block or alert you about these cookies, but some parts of the site will not then work. We can’t identify you from these cookies.
Functional cookies
These help us personalise our sites for you by remembering your preferences and settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers, whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, then these services may not function properly.
Performance cookies
These cookies allow us to count visits and see where our traffic comes from, so we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know which pages are popular and see how visitors move around the site. The cookies cannot directly identify any individual users.
If you do not allow these cookies we will not know when you have visited our site and will not be able to improve its performance for you.
Marketing cookies
These cookies may be set through our site by social media services or our advertising partners. Social media cookies enable you to share our content with your friends and networks. They can track your browser across other sites and build up a profile of your interests. If you do not allow these cookies you may not be able to see or use the content sharing tools.
Advertising cookies may be used to build a profile of your interests and show you relevant adverts on other sites. They do not store directly personal information, but work by uniquely identifying your browser and internet device. If you do not allow these cookies, you will still see ads, but they won’t be tailored to your interests.
Course type
Qualification, university name, part time phd france studies.
8 degrees at 8 universities in the UK.
Customise your search
Select the start date, qualification, and how you want to study

Related subjects:
- PhD France Studies
- PhD African Studies
- PhD Age Studies
- PhD American Studies
- PhD Americas: Studies
- PhD Anthropology
- PhD Anthrozoology
- PhD Applied Social Studies
- PhD Asian Studies
- PhD Biological Anthropology
- PhD China Studies
- PhD Classics
- PhD Combined Humanities Studies
- PhD Community Studies
- PhD Contemporary Studies
- PhD Criminology
- PhD Cultural Studies
- PhD Defence Studies
- PhD Development Politics
- PhD Diplomatic Studies
- PhD Disaster Studies
- PhD English Studies
- PhD Ethnology
- PhD Europen Politics
- PhD Gender Studies
- PhD General Humanities Studies
- PhD Germany Studies
- PhD Globalisation
- PhD Government Studies
- PhD Government and Politics
- PhD Humanities
- PhD Humanities and Social Sciences
- PhD Immigration studies
- PhD International Politics
- PhD International Relations
- PhD International Studies
- PhD Irish Studies
- PhD Islamic Studies
- PhD Italy Studies
- PhD Japan Studies
- PhD Jewish Studies
- PhD Latin America Studies
- PhD Middle East Studies
- PhD Middle Eastern Studies
- PhD Policy Studies
- PhD Political Philosophies
- PhD Politics
- PhD Politics of Specific Countries
- PhD Popular Culture
- PhD Russian Federation Studies
- PhD Social Anthropology
- PhD Social Data Analysis
- PhD Social Research
- PhD Social Research Methods
- PhD Social Sciences
- PhD Social Studies
- PhD Sociology
- PhD Sociology of Health and Sickness
- PhD Sociology of Specific Subjects
- PhD Spain Studies
- PhD Strategic Studies
- PhD UK Politics
- PhD War Studies
- PhD Women's Studies
- PhD Youth Studies

- Course title (A-Z)
- Course title (Z-A)
- Price: high - low
- Price: low - high
French and Francophone Studies PhD
Bangor university.
The School of Modern Languages offers the possibility to do a PhD/MPhil in French Studies. The School has a long tradition of excellent Read more...
- 3 years Full time degree: £4,712 per year (UK)
- 6 years Part time degree: £2,356 per year (UK)
Modern Languages and Translation Studies PhD/MPhil - French and Francophone Studies
University of leicester.
Modern Languages at Leicester offers supervision for the degrees of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - full-time and part-time Master of Read more...
- 3 years Full time degree: £4,786 per year (UK)
- 6 years Part time degree: £2,393 per year (UK)
PhD French Studies
University of exeter.
Staff in Modern Languages research a wide range of areas, including literature, linguistics, translation and film. We supervise PhD Read more...
- 4 years Full time degree: £4,900 per year (UK)
- 8 years Part time degree
University of Manchester
Programme description Our PhD French Studies programme will enable you to carry out a significant piece of in-depth research in an area of Read more...
French Studies MPhil/PhD
University of warwick.
The University of Warwick's Modern Languages and Cultures department offers an PhD in French Studies with guidance from an Read more...
- 3 years Full time degree: £11,600 per year (UK)
- 7 years Part time degree: £2,970 per year (UK)
PhD in French Studies
Queen mary university of london.
Research in Modern Languages and Cultures (MLC) contributed fully to QMUL’s strong performance in the 2014 Research Excellence Framework Read more...
MPhil/PhD French Studies
University of reading.
The Department of Languages and Cultures offers a friendly and supportive environment to research students. The collaboration between the Read more...
- 5 years Part time degree: £2,356 per year (UK)
University of Aberdeen
Investigating the rich diversity of French and Francophone cultures, histories and societies from the seventeenth century to the present Read more...
- 3 years Full time degree
- 6 years Part time degree
Course type:
- Distance learning PhD
- Full time PhD
- Part time PhD
Qualification:
Related subjects:.
Part-time PhD programme

Push the boundaries of philosophical thinking to address global challenges
Ever thought of working towards a PhD alongside your fulltime job? Our parttime PhD programme offers a unique opportunity to obtain a doctorate degree to enhance your professional career. Our programme is designed to equip you with the skills necessary to research and complete a PhD project. We offer individual supervision by professors of our faculty that will be tailored to your own work commitments and according to your preferred study schedule. As a PhD candidate you will be facilitated with access to the library and IT-facilities and research seminars organised by our school.
Building on their professional experience in various fields (teaching, policy, media, societal debate), parttime PhD candidates contribute to our research ambitions, strengthen our impact and foster interdisciplinary collaboration.
How to apply Applicants are advised to write a short research proposal which fits in one of our research programmes of our school (more information about our research programmes can be found here ). Then, send your research proposal, together with a CV and motivation letter to the potential supervisor. If the potential supervisor is interested in supervising the research project, he will submit your research proposal to the admissions coordinator (Marloes Westerveld). If the Graduate Director and the Director positively advise on the project, the project will be elaborated.
When the research proposal is finished the candidate can start her or his research. The candidate will receive a hospitality agreement which will give access to the library and an ESPhil e-mail address. The candidate is required to pay a tuition fee per year:
- Year 1: € 2100;
- Year 2 and 3: € 1700;
- Year 4 onwards: € 800;
- Waivers or reduced fees for candidates who lack funding opportunities can be proposed
The programme starts in September (application deadline 31 July ) and February (application deadline 31 december ). The programme can enroll a maximum of 10 candidates.
Parttime PhD candidates will not receive a salary or scholarship, and thus must be financially independent. Only candidates with a university Master’s degree are eligible for this programme.
Participants in the program PhD’s for HBO teachers funded by NWO or on the basis of a voucher, are exempted from tuition fees because their part-time position is already funded on the basis of detailed requirements and commitments by NWO.
- Supervision by a promotor and co-promotor on the basis of a training and supervision plan;
- Mutual learning via program meetings (thrice a year) to share experiences and interact;
- Participation in ESPhil seminars and lectures;
- Enrolment in research schools (OZSW, EGSH);
- Access to research facilities (e.g. EUR library and electronic journals);
- Special skills training and, if relevant, participation in Master courses;
- Support in writing academic papers and presenting at academic meetings and conferences;
- Support in publishing your thesis;
- Formal public defence ceremony after finishing the thesis.
More information can be obtained via Ms. Marloes Westerveld ( [email protected] ), please mention ‘Parttime PhD programme’ in the subject.
General information:
- Degree: PhD
- Format: part-time
- Duration: 4-6 years
- Requirement: Master’s degree
- Start: September or February

Liesbeth Noordegraaf-Eelens
Share this page
Ms. Marloes Westerveld
Compare @count study programme
- Duration: @duration
- UFR Droit Economie Management
- UFR Médecine
- UFR Pharmacie
- UFR Sciences
- UFR Sciences du Sport
- AgroParisTech
- CentraleSupélec
- ENS Paris-Saclay
- Institut d'Optique
- Polytech Université Paris-Saclay
- Accessibility

PhD Program in Earth, Climate, Environment and Planetery Sciences - Graduate School Earth, Climate, Environment and Planetery Sciences
The Doctoral Program in Earth, Climate, Environment and Planetary sciences provide students a cutting edge training through research projects concerning the superficial envelops (hydrosphere, atmosphere) of the Earth and the other planets and their interactions with the subsurface in a context of strong societal challenges (climate change, pollution, natural resources…) using multiple approaches from field work to space missions and numerical modelling.
Geosciences / Environment / Planets / Pollution / Natural resources management / Greenhouse gases / Paleoclimate / Geochemistry / Geophysics / Geomorphology / Geodynamic / Biogeosciences / Space exploration / Climate change / Remote sensing / Climate modelling / Instrumentation.
Program content.
- Environmental Sciences in Ile-de-France (SEIF)
- Mechanical and Energy Sciences, Materials and Geosciences
- Astronomy and Astrophysics for Paris Area
Doctoral School of ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES IN ILE-DE-FRANCE (SEIF)
The doctoral school covers the multidisciplinary fields related to the understanding of the physical, chemical and biological equilibrium of the terrestrial environment such as
- study of the climate and its variations at all scales of time and space,
- dynamics and thermodynamics of the atmosphere and the ocean,
- radiative transfer,
- functioning of the continental and marine biosphere,
- biogeochemical cycles,
- physical chemistry of air, water and soil pollution,
- experimental developments and techniques related to the observation of remote sensing.
Learn more about the doctoral school SEIF
Doctoral School of MECHANICAL AND ENERGY SCIENCES, MATERIALS AND GEOSCIENCES (SMEMAG) - Geosciences division
The "Astronomy and Astrophysics of Ile-de-France" Doctoral School offers graduates from physics and mathematics studies training in and through research in the vast interdisciplinary field of astronomy and all its techniques of observation, measurement and calculation. The Doctoral School offers physicists and mathematicians training in and through research in the vast interdisciplinary field of astronomy and all its methods of observation, measurement and calculation. It covers a field whose development is considerable and unceasing: discovery of extrasolar planets, renewal of cosmology at the interface with particle physics, development of astrochemistry, in situ exploration of the solar system, space navigation, planetology at the interface with the sciences of planet Earth. Powerful observation tools are being prepared, both in space and on the ground, affirming the place of Europe, using a wide variety of advanced technologies (optics, metrology, cryogenics, automation, etc.).
Learn more about the SMEMAG doctoral school
Doctoral School of ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS OF ILE-DE-FRANCE (AAIF)
L’École Doctorale "Astronomie et Astrophysique d’Ile-de-France" offre aux diplômés issus d’études de physique et de mathématiques une formation à, et par la recherche dans le vaste domaine interdisciplinaire de l’astronomie et de toutes ses techniques d’observation, de mesure et de calcul.
L’École doctorale propose aux physiciens et mathématiciens une formation à et par la recherche dans le vaste domaine interdisciplinaire de l’astronomie et de toutes ses méthodes d’observation, de mesure et de calcul. Elle couvre un champ dont le développement est considérable et incessant : découverte des planètes extrasolaires, renouveau de la cosmologie à l’interface de la physique des particules, développement de l’astrochimie, exploration in situ du système solaire, navigation spatiale, planétologie à l’interface avec les sciences de la planète Terre. De puissants outils d’observation sont en préparation, aussi bien dans l’espace qu’au sol, affirmant la place de l’Europe, faisant appel à une grande diversité de technologies avancées (optique, métrologie, cryogénie, automatique..).
Learn more about AAIF doctoral school
- Laboratoire des Sciences du Climat et de l’Environnement (LSCE) CEA/CNRS/UVSQ
- Laboratoire Atmosphère et Observations Spatiales (LATMOS) CNRS/UVSQ/SU
- Géosciences Paris-Saclay (GEOPS) UPSaclay/CNRS
- Département Physique, Instrumentation, Environnement, Espace (DPHY) ONERA
- Département Optique et Techniques associées (DOTA) ONERA
PhD students admitted to the Phd program will have a public law doctoral contract. The duration of the contract is 3 years. The contractual Phd students are full-time employees with the sole or main mission of carrying out their doctoral project. They may also be entrusted with complementary missions of teaching, scientific mediation, valorization or expertise.
More information
Possible employers* for PhD students under contract to the program are :
- Université Paris-Saclay (Faculties of Sciences of Orsay)
- University of Versailles Saint Quentin en Yvelines
* This list remains to be completed or specified
ED ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES OF ILE-DE-FRANCE (SEIF) Students are accompanied throughout their doctoral studies. At the beginning of their thesis, they meet with the director of the ED, or one of his or her assistants, to remind them of their rights and duties. At the end of the first and second year, the PhD student presents the progress of his or her work to this committee, which advises him or her on the continuation of the thesis. A sponsor is also designated in the laboratory at the beginning of the thesis. This person can be called upon at any time by the PhD student in case of difficulties that cannot be solved or that involve the thesis director.
Doctoral days are organized each year by the ED. First year students present their thesis topics. These days are an opportunity for PhD students from the different laboratories of the ED to meet each other, to get to know each other better and to create connections.
ED ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS OF ILE-DE-FRANCE (AAIF) PhD students are welcomed at the beginning of their thesis during a meeting of newcomers (first year students) by the office and former PhD students of the doctoral school. A supervision is then organized throughout the duration of the thesis by the thesis committee. One meeting is organized per year with the participation of the director and a deputy director of the doctoral school in the second year.
The PhD students of the doctoral school organize and participate in the annual Elbereth conference, which gives them the opportunity to meet and discuss the different research themes covered by the doctoral school.
ED MECHANICAL AND ENERGY SCIENCES, MATERIALS AND GEOSCIENCES (SMEMAG) - Geosciences division
Under construction
The PhDs of the GS "Geosciences, Climate, Environment, Planets" pursue careers in academia or in the private sector in the fields of Earth observation, monitoring, protection and management of the environment, exploitation of oceans or continental surfaces. In the non-academic sector, they work in companies ranging from start-ups (The Climate data factory, LBMS Rockwinds, HD-Rain), to corporations (eLICHENS, ACRI-ST, SANOFI, KEOPSYS, EDF, SUEZ...) and organizations related to the environment and geosciences (AirParif, Bureau de Recherche Géologique et Minière, Institut de Radioprotection et de Sureté Nucléaire, Centre d'études et d'expertise sur les risques, l'environnement, la mobilité et l'aménagement, INRAE...). .
Three years after their thesis defense, on December 1, 2019, 93.3% of PhDs were employed. 6.7% were unemployed.
To help PhD students refine their professional projects, meetings with GS alumni working in the private and academic sectors are organized every year.
How to be admitted to the doctoral program in Earth, Climate, Environment and Planetary sciences ?
Find below the different steps to apply to the Geosciences, Climate, Environment, Planets doctoral program
Recruiting sectors
The recruitment of PhD students for the "Graduate School Geosciences, Climate, Environment, Planets" is open to students of the Earth Sciences, Planets, Environment major at Paris-Saclay, but also to graduates of other masters programs at the University of Paris-Saclay, in France and abroad.
The main research fields targeted are those developed in the "Geosciences, Environment, Planets" graduate school, but applications from students from other disciplines (Physics, Chemistry, Engineering Sciences, Biology, etc.) are encouraged, as they contribute to the enrichment and broadening of the multidisciplinary research themes of the Graduate School.
Evaluation criteria
- the academic level of each candidates
- the adequacy of skills and knowledge to deal with the proposed subject
- the elements of motivation for and appropriation of the subject
- contextual elements: international agreements, priority placed by a laboratory on a given subject (when and only when they are explained in the description of thesis subjects)
The jury also ensures that the students are well distributed among the various laboratories or research teams affiliated with the ED.
Discover the thesis subject offers

2021 Calendar - Candidates
- Publication of thesis topics: mid-March at the latest.
- Submission of applications: end of April (SMEMAG/AAIF) to mid-May (SEIF)
- Selection of candidates for auditions: May (early May for AA, mid-May for SMEMAG and early June for SEIF)
- Auditions: late May to mid-June (week 21-23)
- Admissions: early July (week 27) at the latest, some results being given just after the auditions.
How to apply to ED AAIF ?
Everything is clearly explained on the following page: https://ecole-doctorale.obspm.fr/spip.php?rubrique88
The jury of the competition is composed of members of the doctoral school office and external guests bringing a complementary expertise. Its composition is published each year on the doctoral school's website.
Calendar 2024 - Candidates
- Wednesday January 31, 2024 Thesis submission deadline
- Friday April 19, 2024 Closing date for submission of thesis topics on ADUM
- May 28, 29 and 30 - June 3 and 4, 2024 Audition of candidates
- Friday June 7, 2024 Announcement of results
How to apply to ED SMEMAG ?
The procedure of the competition is detailed on the ED website : https://www.universite-paris-saclay.fr/ecoles-doctorales/sciences-mecaniques-et-energetiques-materiaux-et-geosciences-smemag#edit-group-theses
The jury is composed of the members of the ED Council, except for the PhD student representatives.
Calendar 2024 - Candidates
- Thursday, February 29, 2024 Closing date for thesis submissions
- Thursday, April 25, 2024 Closing date for ADUM applications
- Wednesday May 29 to Friday May 31, 2024 Audition of candidates
- Date to be defined Announcement of results
How to apply to ED SEIF ?
Candidates contact by e-mail the thesis directors of their choice in order to present their application and to discuss the subject of the thesis Each thesis director organizes at least one interview with the candidate and sends by e-mail to the laboratory director the file he/she has selected.
The application file is described under ' Documents to be provided' here
The jury is composed of the members of the ED Council .
- Friday, February 26, 2024 Closing date for thesis submissions
- Sunday May 12, 2024 Closing date for ADUM applications
- Wednesday June 12 and Thursday June 13, 2024 Audition of candidates
- Tuesday June 18, 2024 Announcement of results
Communication tools
The employment status of graduate school earth, climate, environment and planetary phds as of december 1, 2019.

25 Best Part Time PhD Programs [2024 Guide]
Explore part time PhD programs. Compare schools and see why you should consider earning your doctorate part time.

If work or other responsibilities have been holding you back from diving headfirst into doctoral studies, consider part time PhD programs instead.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
You may enroll in an on-campus or online PhD program to earn your doctoral credentials on a schedule that fits your busy lifestyle.
Universities Offering PhD and Other Doctorate Programs Online
Methodology: The following school list is in alphabetical order. To be included, a college or university must be regionally accredited and offer degree programs online or in a hybrid format.
1. Andrews University
Andrews University is a private university in Berrien Springs, Michigan, that is affiliated with the Seventh-day Adventist Church. Founded in 1874, Andrews has a current annual enrollment of 3,366.
Students can pursue 130 undergraduate and 70 graduate majors across eight schools and colleges. Degrees at the bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral levels are available.
- PhD in Curriculum and Instruction
- PhD in Educational Leadership
- PhD in Higher Education Administration
- PhD in Leadership
Andrews University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.
2. Clemson University
Clemson University is a public research university located in Clemson, South Carolina. Founded in 1889, Clemson boasts an annual student enrollment nearing 30,000. U.S. News & World Report ranks Clemson University in 24th place among all public universities.
Students can pursue bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees across Clemson’s seven schools and colleges.
- PhD in Healthcare Genetics
- PhD in Parks, Recreation and Tourism Management
- PhD in Rhetorics, Communication and Information Design
Clemson University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
3. George Washington University
Chartered in 1821 by an act of the United States Congress, George Washington University stands today as a private research university with an annual enrollment of more than 27,000. GWU is divided into 14 colleges and schools offering bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral programs.
The Princeton Review consistently ranks George Washington University as a top college in a number of categories. In addition, GWU has been ranked as one of the Top Universities for Producing Billionaires by the Times Higher Education’s World University Rankings.
- PhD in Nursing
- PhD in Systems Engineering
GW is regionally accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.
4. Hampton University
Hampton University is a private, historically black university located in Hampton, Virginia, that was founded in 1868. The university is comprised of 10 accredited schools and colleges offering 50 bachelor’s programs, 26 master’s programs, and seven doctoral programs. The Alumni Factor has named Hampton one of the best colleges in Virginia.
- PhD in Business Administration
- PhD in Educational Management
Hampton University is accredited by the Commission on Colleges of the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools.
5. Indiana State University
Indiana State University is a public university located in Terre Haute, Indiana, with a history dating back to 1865. ISU offers more than 100 undergraduate majors and 75 graduate. Students can pursue 20 bachelor’s degrees, 22 master’s degrees, and seven doctoral degrees on campus and online through ISU’s six academic colleges.
- PhD in Educational Administration – Higher Education Leadership
- PhD in Educational Administration – School Administration
- PhD in Technology Management
Indiana State University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.
6. Keiser University
Keiser University is a private university based in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Founded in 1977, Keiser offers bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral programs available both on campus and online. Money magazine has rated Keiser University one of the top colleges for the money in Florida. Nearly 20,000 students study at Keiser.
- PhD in Criminal Justice and Criminology
- PhD in Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- PhD in Instructional Design and Technology
Keiser University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
7. Liberty University
Liberty University is a private evangelical Christian university founded in Lynchburg, Virginia, in 1971. The school consists of 17 distinct colleges offering a wide variety of bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral programs. Programs are divided between 366 on-campus options and 280 online options.
- PhD in Bible Exposition
- PhD in Communication
- PhD in Criminal Justice
- PhD in Criminal Justice – Homeland Security
- PhD in Criminal Justice – Leadership
- PhD in Education – Curriculum and Instruction
- PhD in Education – Instructional Design and Technology
- PhD in Education – Organizational Leadership
- PhD in Education – Special Education
- PhD in Higher Education Administration – Educational Leadership
- PhD in History
- PhD in Nursing – Nursing Education
- PhD in Psychology – Developmental Psychology
- PhD in Psychology – Industrial/Organizational Psychology
- PhD in Psychology – Social Psychology
- PhD in Public Policy
- PhD in Public Policy – Economic Policy
- PhD in Public Policy – Education Policy
- PhD in Public Policy – Foreign Policy
- PhD in Public Policy – National Security
- PhD in Public Policy – Social Policy
- PhD in Strategic Media
- PhD in Theology and Apologetics
Liberty University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
8. Mississippi State University
Mississippi State University is a public research university located near Starkville, Mississippi, that is classified among RI Doctoral Universities for very high research activity. MSU’s more than 22,000 enrolled students can pursue more than 180 areas of study for bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees. The school was founded in 1878.
- PhD in Community College Leadership
- PhD in Computational Engineering
- PhD in Electrical and Computer Engineering
- PhD in Engineering – Aerospace Engineering
- PhD in Engineering – Civil Engineering
- PhD in Engineering – Mechanical Engineering
- PhD in Industrial & Systems Engineering
Mississippi State University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
9. North Carolina A&T State University
North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University is a public, historically black university located in Greensboro, North Carolina. The school was founded in 1891 by the North Carolina General Assembly. It is ranked among the top historically black colleges and universities (HBCUs) by U.S. News & World Report.
A total of 54 bachelor’s, 29 master’s, and nine doctoral degrees are offered through the school’s eight colleges.
- PhD in Leadership Studies
North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
10. Texas Tech University
Established in 1923, Texas Tech University is a public research university in Lubbock, Texas, featuring 13 colleges and 60 research centers. The Princeton Review has ranked Texas Tech among the 125 best colleges in the Western United States.
Texas Tech offers 150 options for bachelor’s degrees, 110 options for master’s degrees, and 59 doctoral degree programs.
- PhD in Curriculum and Instructions – Curriculum Studies and Teacher Education
- PhD in Curriculum and Instructions – Language, Diversity & Literacy Studies
- PhD in Curriculum and Instructions – STEM
- PhD in Educational Leadership Policy
- PhD in Family and Consumer Science Education
- PhD in Special Education
Texas Tech University is accredited with the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
11. University at Buffalo
Founded in 1846, the University at Buffalo a public research university with campuses in Buffalo and Amherst, New York. Nearly 32,000 students are enrolled in what is considered to be the largest public university in New York. UB offers bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees across 13 academic schools and colleges.
- PhD in Information Science
The University at Buffalo is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.
12. University of Alabama – Huntsville
The University of Alabama in Huntsville was founded in 1950. It is one of three members of the University of Alabama System. UAH school awards 44 bachelor’s, 30 master’s and 15 doctoral degrees across nine colleges to a study body of nearly 10,000.
UAH is a space-grant university with a large focus on engineering and science programs.
- PhD in Civil Engineering
- PhD in Engineering Management
- PhD in Industrial Engineering
- PhD in Joint Nursing Science
UAH is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
13. University of Colorado – Denver
A member of the University of Colorado system, the University of Colorado Denver is a public research facility offering hundreds of degree programs for bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral studies across dozens schools and colleges.
Total annual enrollment stands at 24,910. Forbes places the University of Colorado Denver 34th on the its list of best public colleges.
University of Colorado – Denver is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.
14. University of Florida
The University of Florida is a public land-grant, sea-grant, and space-grant research university with a main campus in Gainesville, Florida. This senior member of the State University System of Florida offers bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral programs to the more than 56,000 students that enroll annually.
The list of notable UF alumni includes Erin Andrews, Emmitt Smith, Faye Dunaway, and Marc Rubio.
- PhD in Classical Civilization
- PhD in Latin and Roman Studies
The University of Florida is regionally accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools.
15. University of Kansas
The University of Kansas is a public research university based in Lawrence, Kansas. Founded in 1865, KU offers more than 345 degree programs for bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral studies. KU has an annual enrollment of more than 28,400 students.
The school’s faculty and alumni list includes four NASA astronauts, seven Pulitzer Prize winners, 27 Rhodes Scholars, and 325 Fulbright Scholars.
The University of Kansas is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.
16. University of Missouri
The University of Missouri was founded in 1839 as the flagship of the University of Missouri System. Mizzou currently offers more than 300 bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degree programs across 13 major academic divisions for its more than 30,000 enrolled students.
- PhD in Architectural Studies
The University of Missouri is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.
17. University of North Carolina – Greensboro
The University of North Carolina at Greensboro is a public research university located in Greensboro, North Carolina, that dates back to 1891. This school with an annual enrollment topping 20,000 is part of the University of North Carolina system.
More than 100 bachelor’s, 61 master’s, and 26 doctoral programs are offered at UNCG.
The University of North Carolina at Greensboro is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
18. University of North Dakota
Located in Grand Forks, the University of North Dakota offers 90 bachelor’s majors, 54 master’s programs, and 27 doctoral programs. UND was founded in 1883. Currently, UND has an annual enrollment of 13,581 students spread across its 10 academic divisions. The school’s athletic teams compete in the NCAA’s Division I.
- PhD in Aerospace Sciences
- PhD in Biomedical Engineering
- PhD in Chemical Engineering
- PhD in Electrical Engineering
- PhD in Energy Engineering
- PhD in Environmental Engineering
- PhD in Indigenous Health
- PhD in Petroleum Engineering
The University of North Dakota is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission of the North Central Association of Colleges and Schools.
19. University of South Carolina
The University of South Carolina is a public research university located in Columbia, South Carolina. The more than 35,000 students enrolled at USC today can study toward bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees from 14 degree-granting colleges and schools. The school’s history dates back to 1801.
- PhD in Computer Engineering
- PhD in Computer Science
- PhD in Mechanical Engineering
- PhD in Nuclear Engineering
University of South Carolina is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
20. University of South Dakota
The University of South Dakota is a public research university in Vermillion, South Dakota, with an enrollment of nearly 10,000 students. The university is divided between seven colleges offering hundreds of bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees. USD’s campus is home to the National Music Museum. The school was founded in 1862.
- PhD in Health Sciences
USD is accredited by the North Central Association of Colleges and Secondary Schools.
21. University of Southern Mississippi
The University of Southern Mississippi is a public research university with a main campus located in Hattiesburg, Mississippi. Southern Miss awards bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees across more than 189 programs. Founded in 1910, the school boasts an annual enrollment of more than 14,00 students.
Southern Mississippi’s academic offerings are divided across four colleges and schools.
- PhD in Nursing Leadership
The University of Southern Mississippi is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
22. University of Tennessee – Knoxville
Founded in 1794, the University of Tennessee is a public research university located in Knoxville, Tennessee. UT offers bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees across 10 undergraduate colleges and eleven graduate colleges. Annual enrollment stands at close to 29,000 students.
Established two years before Tennessee officially became a state, the University of Tennessee is one of the oldest public universities in the country.
- PhD in Industrial and Systems Engineering – Engineering Management
The University of Tennessee – Knoxville is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
23. University of the Cumberlands
The University of the Cumberlands is a private university located in Williamsburg, Kentucky, dating back to 1888. Bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral programs in a variety of specialties in the arts and sciences are offered across four colleges. Total annual enrollment is 13,476.
University of the Cumberlands is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
24. Virginia Commonwealth University
Virginia Commonwealth University is a public research university located in Richmond, Virginia, with a history dating back to 1838. VCU offers more than 217 programs for bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees across 11 schools and three colleges.
U.S. News & World Report has classified VCU as a Tier 1 University that ranks in 84th place among all public colleges and universities in the United States.
- PhD in Health Related Sciences
VCU is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
25. West Virginia University
Founded in 1875, West Virginia University is a public research university with a main campus in Morgantown, West Virginia. More than 350 academic programs for bachelor’s, master’s, doctoral, and professional degrees are offered through 14 schools and colleges for the nearly 30,000 students who enroll at WVU annually.
Designated among the R1 Research Universities for very high research activity, WVU boasts research partnerships with the Rockefeller Neurosciences Institute and the Federal Bureau of Investigation.
West Virginia University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.
Do Part Time PhD Programs Exist?

Yes, part time PhD programs do exist. Universities know that many people have packed schedules. To accommodate busy students, some schools give the option of part-time enrollment in PhD programs online or on-campus.
The idea is that you may work your way through one of these programs while still living at home and holding a regular job — no uprooting your life required.
Many part-time PhD programs are offered online, which can be particularly convenient. Online college allows you to attend the university of your choice without having to move away from your hometown.
You may take classes online, chat digitally with your academic advisors, and work on your dissertation from the comfort of your own home. Even still, there may be some in-person residencies or practicums required.

Finances are one of the best reasons to enroll in a part-time online program. The paycheck that you bring in each week can help you afford your grad school tuition without living on ramen noodles for five years straight.
Of course, being able to hold a full-time job while going through your doctoral program is more than just a way to make money. Particularly if your field of study is relevant to your job, you may find many opportunities to connect your classroom studies to real-world experiences.
It’s even possible that a situation at work may provide inspiration for the topic of your doctoral dissertation. If you feel that a dissertation may prevent you from finishing your PhD, then a professional doctorate may be a better choice.
For example, doctor of education programs don’t require dissertations in many cases. Instead, students may complete a final capstone project to demonstrate subject mastery.
Part-time students don’t make up the majority of doctoral candidates; even still, you certainly won’t be the only one if you choose to go this route. In the past year, approximately 44% of doctoral students were enrolled in part-time programs .
What Are the Most Popular PhD Programs?
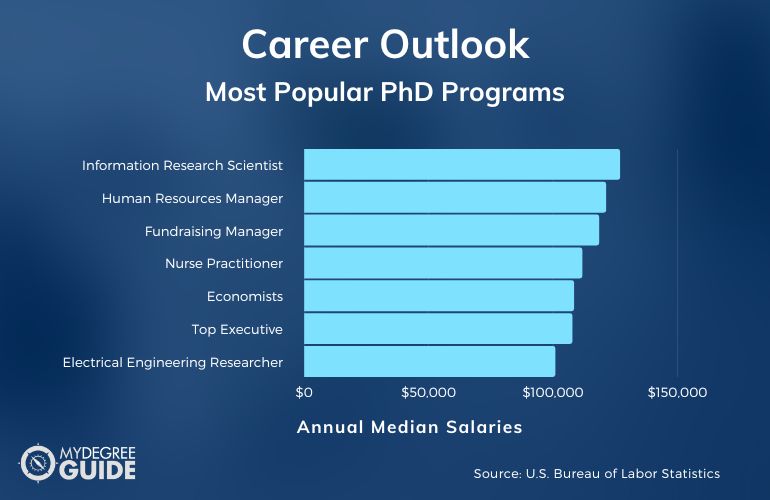
Doctorates are available in practically any field, but some are more common than others. The following table shows some of the top PhDs that you may be able to earn online.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, some related careers and their average salaries include:
Getting your doctorate may certainly increase your earning potential. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for PhDs is $110,200. That’s a large jump from $78,210, the average annual earnings for those with a master’s degree.
How Do Part Time PhD Degree Programs Work?

To graduate from a part-time doctoral program, you’ll need to do the same work that you would for a full-time course of study. You’ll simply spread the work out over a longer stretch of time.
The first portion of your program will likely be devoted to classes. If you’re enrolled on a part-time basis, you’ll probably keep your course load light instead of taking multiple classes at once.
You may be able to take the classes online, but your school may require a few in-person residencies as well.
Some classes will focus on the research methods that are essential for all doctoral candidates to know, such as analyzing data and writing scholarly reports. At this point, you may also start thinking about a topic for your upcoming research project.

Other courses will be related to your field of study. While some classes may be required of every student in your PhD department, others may be electives. That way, you may build a course of study that is tailored to your career goals and research interests.
After completing your classes, your school may require oral or written testing as a way of assessing your knowledge.
Next, you’ll turn your attention toward your dissertation or another final project. This usually requires completing original research and reporting your findings in a detailed paper.
Even for full-time students, it may take several years to complete a dissertation. On a part-time basis, you may be working on this project even longer.
Once you finish your dissertation, the school’s faculty will need to approve it. Then, you’ll answer questions during a defense of your research. If the faculty determines that you have successfully defended your dissertation, you’ll then be awarded your PhD.
How Long Does It Take to Do a PhD Part Time?

How long it takes to complete your PhD through a part-time schedule is largely up to you and how much you can commit to your studies at any point in time.
You may find that there are some seasons in which you’re able to invest a good portion of your time and other seasons when you’re only able to do the bare minimum to keep going.
As a general rule, though, you should expect your part-time studies to last for several years. Being a part-time student won’t exempt you from any of the program’s requirements.
You’ll still need to earn just as many credit hours, complete any residency or internship experiences, and do the same final projects. The work will just be spread out over a longer period of time.

You should probably plan to work on your doctoral program for six to eight years. Some students take even longer. There may be a maximum duration allowed by your program, so be sure to discuss that with your faculty advisor.
Although part-time schooling is convenient, being enrolled in the same program for years on end may start to feel tedious. It’s important to choose an area of study that you really care about.
Your passion for your studies can keep you motivated even when graduation still seems a long way off.
Admission Requirements for a PhD

No matter what type of doctoral program it is, whether it is a part time or an online accelerated doctoral program , they can be competitive and you’ll want to make sure that your application stands out to the admissions committee. The first step is making sure that you meet the requirements and include all necessary documentation.
- Application and fee: Filling out this form gives the committee basic information about you, so be sure to complete it thoroughly. The fee will be non-refundable, even if you aren’t admitted.
- College transcripts: These demonstrate whether you have the appropriate academic background. You will need to hold a bachelor’s degree, and you may need a master’s degree as well. There may be minimum GPA scores required.
- Test scores: Many schools use GRE or GMAT scores to determine whether you have what it takes to succeed in a PhD program. If you’re an international applicant, you may also need TOEFL scores to demonstrate your proficiency with the English language.
- Letters of reference: These should come from academic or professional colleagues who can attest to your commitment and character. Two or three letters may be required.
- Personal statement or research proposal: This is your chance to communicate your study goals. That way, the school can determine whether your interests align with the expertise of the faculty.
Pay close attention to application deadlines. It’s smart to submit your materials a few weeks before the cutoff since schools don’t usually take late applications.
Accreditation for PhD Programs

Accreditation is a process in which an independent organization evaluates a college’s programs and results to determine whether the school is doing a good job of educating students. If the college is up to par, then it receives approval from an accrediting body.
The primary type of accreditation to consider is regional accreditation . There are seven U.S. organizations that have the right to grant regional accreditation.
There are fairly high standards for regional accreditation. As a result, this type of accreditation is well-respected, and employers are often more inclined to select candidates whose degrees come from regionally accredited schools.
Financial Aid for PhD Students

Paying for a doctorate out of pocket can be an overwhelming prospect, but there are a number of options for funding your PhD.
- Fellowships: Based on your personal merits, your school or a private organization may give you fellowship money intended to further your research goals.
- Government grants: If your income qualifies, you may get free tuition help from the state or federal government.
- Government loans: You may have the option to take out low-interest loans from the federal government or your state.
- Private loans: To supplement your financial package, you may also need private loans. Just be aware that these can come with high interest rates.
- Scholarships: You can apply for gift money from a scholarship-granting organization, such as a professional association in your field.
- Stipends: Some schools grant PhD candidates a small stipend. There are usually stipulations to this, and the rules may differ for part-time students.
To find out more, talk to your school’s financial aid department. Be sure to fill out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) .
Also, if getting a doctorate could benefit your performance at work, you may be able to request tuition assistance from your employer.
Can You Do PhD Part Time?

Yes, you can do a PhD part time. Studying for a PhD doesn’t have to be all-or-nothing. Just as there are part time masters programs , you can likewise enroll in a doctoral program on a part-time basis.
With that approach, you may be able to go to work during the day and take classes or write papers in the evening. It may even be possible to complete the coursework online.
Is PhD Full Time or Part Time?
Both full-time and part-time PhD programs are available. Some people choose to earn their doctorates as quickly as possible by going to school full-time. Others opt to enroll part-time so that they may keep up with work or family responsibilities.
Keep in mind that not all schools give you the choice between full-time and part-time study; their traditional or online doctoral programs may be specifically designed for one or the other.
Is a PhD Worth It?

Yes, a PhD is worth it for many students. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 5.9% job growth for doctoral or professional degree holders over the next 1o years, faster than the average for all occupations.
Getting a PhD may open new doors. Earning this top degree may grant you entrance into academia as a researcher or a professor.
It may also prepare you to assume high leadership roles and earn more money in your field. Plus, there’s often a sense of personal satisfaction that comes from accomplishing a huge goal like earning a PhD.
If you’re ready to put those three letters after your name, then it’s time to think about enrolling in a doctoral program. Apply to part-time PhD programs so you may pursue your degree without putting your life on hold.

Top Streams
- Data Science Courses in USA
- Business Analytics Courses in USA
- Engineering Courses in USA
- Tax Courses in USA
- Healthcare Courses in USA
- Language Courses in USA
- Insurance Courses in USA
- Digital Marketing Courses in USA
Top Specialization
- Masters in Data Analytics in USA
- Masters in Mechanical Engineering in USA
- Masters in Supply Chain Management in USA
- Masters in Computer Science in USA
- MBA in Finance in USA
- Masters in Architecture in USA
Top Universities
- Cornell University
- Yale University
- Princeton University
- University of California Los Angeles
- University of Harvard
- Stanford University
- Arizona State University
- Northeastern University
- Project Management Courses in Australia
- Accounting Courses in Australia
- Medical Courses in Australia
- Psychology Courses in Australia
- Interior Designing Courses in Australia
- Pharmacy Courses in Australia
- Social Work Courses in Australia
- MBA in Australia
- Masters in Education in Australia
- Masters in Pharmacy in Australia
- Masters in Information Technology in Australia
- BBA in Australia
- Masters in Teaching in Australia
- Masters in Psychology in Australia
- University of Melbourne
- Deakin University
- Carnegie Mellon University
- Monash University
- University of Sydney
- University of Queensland
- RMIT University
- Macquarie University
- Data Science Courses in Canada
- Business Management Courses in Canada
- Supply Chain Management Courses in Canada
- Project Management Courses in Canada
- Business Analytics Courses in Canada
- Hotel Management Courses in Canada
- MBA in Canada
- MS in Canada
- Masters in Computer Science in Canada
- Masters in Management in Canada
- Masters in Psychology in Canada
- Masters in Education in Canada
- MBA in Finance in Canada
- Masters in Business Analytics in Canada
- University of Toronto
- University of British Columbia
- McGill University
- University of Alberta
- York University
- University of Calgary
- Algoma University
- University Canada West
- Project Management Courses in UK
- Data Science Courses in UK
- Public Health Courses in UK
- Digital Marketing Courses in UK
- Hotel Management Courses in UK
- Nursing Courses in UK
- Medicine Courses in UK
- Interior Designing Courses in UK
- Masters in Computer Science in UK
- Masters in Psychology in UK
- MBA in Finance in UK
- MBA in Healthcare Management in UK
- Masters in Education in UK
- Masters in Marketing in UK
- MBA in HR in UK
- University of Oxford
- University of Cambridge
- Coventry University
- University of East London
- University of Hertfordshire
- University of Birmingham
- Imperial College London
- University of Glasgow
Top Resources
- Universities in Germany
- Study in Germany
- Masters in Germany
- Courses in Germany
- Bachelors in Germany
- Germany Job Seeker Visa
- Cost of Living in Germany
- Best Universities in Germany
Top Courses
- Masters in Data Science in Germany
- MS in Computer Science in Germany
- Marine Engineering in Germany
- MS Courses in Germany
- Masters in Psychology in Germany
- Hotel Management Courses in Germany
- Masters in Economics in Germany
- Paramedical Courses in Germany
- Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
- University of Bonn
- University of Freiburg
- University of Hamburg
- University of Stuttgart
- Saarland University
- Mannheim University
- MBA in Ireland
- Phd in Ireland
- Masters in Computer Science Ireland
- Cyber Security in Ireland
- Masters in Data Analytics Ireland
- Ms in Data Science in Ireland
- Pharmacy courses in ireland
- Business Analytics Course in Ireland
- Universities in Ireland
- Study in Ireland
- Masters in Ireland
- Courses in Ireland
- Bachelors in Ireland
- Cost of Living in Ireland
- Ireland Student Visa
- Part Time Jobs in Ireland
- Trinity College Dublin
- University College Dublin
- Dublin City University
- University of Limerick
- Dublin Business School
- Maynooth University
- University College Cork
- National College of Ireland
Colleges & Courses
- Masters in France
- Phd in France
- Study Medicine in France
- Best Universities in Frankfurt
- Best Architecture Colleges in France
- ESIGELEC France
- Study in France for Indian Students
- Intakes in France
- SOP for France Visa
- Study in France from India
- Reasons to Study in France
- How to Settle in France
More About France
- Cost of Living in France
- France Study Visa
- Cost of Living in Frankfurt
- France Scholarship for Indian Students
- Part Time Jobs in France
- Stay Back in France After Masters
About Finland
- Universities in Finland
- Study in Finland
- Courses in Finland
- Bachelor Courses in Finland
- Masters Courses in Finland
- Cost of Living in Finland
- MS in Finland
- Average Fees in Finland Universities
- PhD in Finland
- Bachelor Degree in Medicine & Surgery
- MBBS Courses in Georgia
- MBBS Courses in Russia
- Alte University
- Caucasus University
- Georgian National University SEU
- David Tvildiani Medical University
- Caspian International School Of Medicine
- Asfendiyarov Kazakh National Medical University
- Kyrgyz State Medical Academy
- Cremeia Federal University
- Bashkir State Medical University
- Kursk State Medical University
- Andijan State Medical Institute
- IELTS Syllabus
- IELTS Prepration
- IELTS Eligibility
- IELTS Test Format
- IELTS Band Descriptors
- IELTS Speaking test
- IELTS Writing Task 1
- IELTS score validity
- IELTS Cue Card

IELTS Reading Answers Sample
- Animal Camouflage
- Types Of Societies
- Australia Convict Colonies
- A Spark A Flint
- Emigration To The Us
- The History Of Salt
- Zoo Conservation Programmes
- The Robots Are Coming
- The Development Of Plastic
IELTS Speaking Cue Card Sample
- Describe A Puzzle You Have Played
- Describe A Long Walk You Ever Had
- Describe Your Favourite Movie
- Describe A Difficult Thing You did
- Describe A Businessman You Admire
- Memorable Day in My Life
- Describe Your Dream House
- Describe A Bag You Want to Own
- Describe a Famous Athlete You Know
- Aquatic Animal
IELTS Essay Sample Sample
- Best Education System
- IELTS Opinion Essay
- Agree or Disagree Essay
- Problem Solution Essays
- Essay on Space Exploration
- Essay On Historical Places
- Essay Writing Samples
- Tourism Essay
- Global Warming Essay
- GRE Exam Fees
- GRE Exam Syllabus
- GRE Exam Eligibility
- Sections in GRE Exam
- GRE Exam Benefits
- GRE Exam Results
- GRE Cutoff for US Universities
- GRE Preparation
- Send GRE scores to Universities
GRE Exam Study Material
- GRE Verbal Preparation
- GRE Study Material
- GRE AWA Essays
- GRE Sample Issue Essays
- Stanford University GRE Cutoff
- Harvard University GRE Cutoff
- GRE Quantitative Reasoning
- GRE Verbal Reasoning
- GRE Reading Comprehension
- Prepare for GRE in 2 months
Other Resources
- Documents Required For Gre Exam
- GRE Exam Duration
- GRE at Home
- GRE vs GMAT
- Improve GRE Verbal Scores
Free GRE Ebooks
- GRE Preparation Guide (Free PDF)
- GRE Syllabus (Free PDF)
- GMAT Eligibility
- GMAT Syllabus
- GMAT Exam Dates
- GMAT Registration
- GMAT Exam Fees
- GMAT Sections
- GMAT Purpose
GMAT Exam Study Material
- How to prepare for GMAT?
- GMAT Score Validity
- GMAT Preparation Books
- GMAT Preparation
- GMAT Exam Duration
- GMAT Score for Harvard
- GMAT Reading Comprehension
- GMAT Retake Strategy
Free GMAT Ebooks
- GMAT Guide PDF
- Download GMAT Syllabus PDF
- TOEFL Exam Registration
- TOEFL Exam Eligibility
- TOEFL Exam Pattern
- TOEFL Exam Preparation
- TOEFL Exam Tips
- TOEFL Exam Dates
- Documents for TOEFL Exam
- TOEFL Exam Fee
TOEFL Exam Study Material
- TOEFL Preparation Books
- TOEFL Speaking Section
- TOEFL Score and Results
- TOEFL Writing Section
- TOEFL Reading Section
- TOEFL Listening Section
- TOEFL Vocabulary
- Types of Essays in TOEFL
Free TOEFL Ebooks
- TOEFL Exam Guide (Free PDF)
- PTE Exam Dates
- PTE Exam Syllabus
- PTE Exam Eligibility Criteria
- PTE Test Centers in India
- PTE Exam Pattern
- PTE Exam Fees
- PTE Exam Duration
- PTE Exam Registration
PTE Exam Study Material
- PTE Exam Preparation
- PTE Speaking Test
- PTE Reading Test
- PTE Listening Test
- PTE Writing Test
- PTE Essay Writing
- PTE exam for Australia
Free PTE Ebooks
- PTE Syllabus (Free PDF)
- Duolingo Exam
- Duolingo Test Eligibility
- Duolingo Exam Pattern
- Duolingo Exam Fees
- Duolingo Test Validity
- Duolingo Syllabus
- Duolingo Preparation
Duolingo Exam Study Material
- Duolingo Exam Dates
- Duolingo Test Score
- Duolingo Test Results
- Duolingo Test Booking
Free Duolingo Ebooks
- Duolingo Guide (Free PDF)
- Duolingo Test Pattern (Free PDF)
NEET & MCAT Exam
- NEET Study Material
- NEET Preparation
- MCAT Eligibility
- MCAT Preparation
SAT & ACT Exam
- ACT Eligibility
- ACT Exam Dates
- SAT Syllabus
- SAT Exam Pattern
- SAT Exam Eligibility
USMLE & OET Exam
- USMLE Syllabus
- USMLE Preparation
- USMLE Step 1
- OET Syllabus
- OET Eligibility
- OET Prepration
PLAB & LSAT Exam
- PLAB Exam Syllabus
- PLAB Exam Fees
- LSAT Eligibility
- LSAT Registration
- TOEIC Result
- Study Guide
Application Process
- LOR for Masters
- SOP Samples for MS
- LOR for Phd
- SOP for Internship
- SOP for Phd
- Check Visa Status
- Motivation Letter Format
- Motivation Letter for Internship
- F1 Visa Documents Checklist
Career Prospects
- Popular Courses after Bcom in Abroad
- Part Time Jobs in Australia
- Part Time Jobs in USA
- Salary after MS in Germany
- Salary after MBA in Canada
- Average Salary in Singapore
- Higher Studies after MBA in Abroad
- Study in Canada after 12th
Trending Topics
- Best Education System in World
- Best Flying Schools in World
- Top Free Education Countries
- Best Countries to Migrate from India
- 1 Year PG Diploma Courses in Canada
- Canada Vs India
- Germany Post Study Work Visa
- Post Study Visa in USA
- Data Science Vs Data Analytics
- Public Vs Private Universities in Germany
- Universities Vs Colleges
- Difference Between GPA and CGPA
- Undergraduate Vs Graduate
- MBA in UK Vs MBA in USA
- Degree Vs Diploma in Canada
- IELTS vs TOEFL
- Duolingo English Test vs. IELTS
- Why Study in Canada
- Cost of Living in Canada
- Education System in Canada
- SOP for Canada
- Summer Intake in Canada
- Spring Intake in Canada
- Winter Intake in Canada
- Accommodation in Canada for Students
- Average Salary in Canada
- Fully Funded Scholarships in Canada
- Why Study in USA
- Cost of Studying in USA
- Spring Intake in USA
- Winter Intake in USA
- Summer Intake in USA
- STEM Courses in USA
- Scholarships for MS in USA
- Acceptable Study Gap in USA
- Interesting Facts about USA
- Free USA course
- Why Study in UK
- Cost of Living in UK
- Cost of Studying in UK
- Education System in UK
- Summer Intake in UK
- Spring Intake in UK
- Student Visa for UK
- Accommodation in UK for Students
- Scholarships in UK
- Why Study in Germany
- Cost of Studying in Germany
- Education System in Germany
- SOP for Germany
- Summer Intake in Germany
- Winter Intake in Germany
- Study Visa for Germany
- Accommodation in Germany for Students
- Free Education in Germany
Country Guides
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in USA
- Study in Australia
- SOP Samples for Canada Student Visa
- US F1 Visa Guide for Aspirants
Exams Guides
- Duolingo Test Pattern
Recommended Reads
- Fully Funded Masters Guide
- SOP Samples For Australia
- Scholarships for Canada
- Data Science Guide
- SOP for MS in Computer Science
- Study Abroad Exams
- Alumni Connect
- Booster Program
- Scholarship
GPA CALCULATOR Convert percentage marks to GPA effortlessly with our calculator!
Expense calculator plan your study abroad expenses with our comprehensive calculator, ielts band calculator estimate your ielts band score with our accurate calculator, education loan calculator discover your eligible loan amount limit with our education calculator, university partner explore growth and opportunities with our university partnership, accommodation discover your perfect study abroad accommodation here, experience-center discover our offline centers for a personalized experience, our offices visit us for expert study abroad counseling..
- 18002102030
- Study Abroad
PhD in France – Universities, Fees, Eligibility & Jobs
- Study in Switzerland
- Benefits of Studying in Norway
- Student Visa for Netherlands
- Why Study in France
- Study in Spain
- Study in Denmark
- Study in Poland
- Study in Italy
- Study in Sweden
- Study in Paris
- Best European Country to Study
- Why Study in Europe
Updated on 26 March, 2024

Gauri Agrawal
Sr. content writer.
France is known for its excellent higher education system and globally reputed universities. The French universities are known for nurturing greats in science, economics, technology, arts, philosophy, and fashion. Moreover, the country is culturally rich and has spectacular architecture, music, cuisine, and dance, among other things.
Thousands of aspiring international students come to France to learn from its rich culture and dive into the wide range of employment opportunities. It has an exceptional research environment; therefore, a Ph.D. in France for Indian students or any other international student is a great opportunity.
Table of Contents
1. affordable tuition fees, 2. degrees taught in english, 3. chance to improve your french, ph.d. specializations offered in france, top universities to study ph.d. in france, application process and timelines, cost of phd in france for indian students, career opportunities for france phd holders, eligibility to pursue ph.d. in france for indian students, career options, why study phd in france.
There are many reasons a graduate can choose to do a Ph.D. in France, and some are listed below:
Candidates enrolling for Ph.D. in France are not required to pay substantial tuition fees. The average cost is €380 per academic year. It applies to all Ph.D. programs offered in France.
Public, and private institutions in France offer English-taught study programs to attract more international students.
Remember that candidates who can communicate in at least two foreign languages have a better chance of earning well and being hired by top global organizations and institutions. Therefore, studying Ph.D. in France and gaining proficiency in French improves your portfolio.
Study and Settle in France : Get Free Consultation
Some of the famous Ph.D. specializations offered in France are in the following streams:
- Social Sciences and Economics
- Ecology, Biodiversity, Agronomy
- Mathematics
- Health Sciences
- Energy and processes
- Earth and space sciences
- Information technology
A ‘doctorate’ or Ph.D. in France is comprised of six semesters for a standard 3-year Ph.D., resulting in two teachings (or research) semesters per year:
- Autumn semester, which starts in late September- January with a holiday around Christmas and New Year
- The spring semester starts in early February- June, with some institutions having a spring break at Easter.
Institutions generally have exams at the end of each semester and a three-month summer holiday from July-September.
Tuition fees for Ph.D. programs in France are currently the same for all students regardless of nationality. However, the fee structure differs depending upon whether you take admission in a private or public institution. Below is the average fee you are supposed to pay based on the institution:
- Public institution- Student fees are €380 annually.
- Private institutions- The fees in private institutes are relatively high and can range between €3,000 and €10,000 annually. Additionally, the universities hold the ultimate right to charge administrative costs, which are affordable.
Apart from the tuition fees, other expenses like the cost of living would add to the total cost of studying Ph.D. in France .
The living price in France includes accommodation, transportation, health insurance, and personal expenses, among others. The range varies between 600- 800 EUR/month, but if you’re studying in the top cities, the living costs will increase, and it would range between 650- 1800 EUR/month.
There are multiple career opportunities after a PhD in France, largely based on the specialization you have chosen. In addition, your practical knowledge matters a lot. With it, you can work as a professor in any reputed university, not only in France but across the world.
You can also become a part of an education and research organization that welcomes fresher PhD graduates to add value to the ongoing programs. PhD qualified candidates are also eligible to appear for jobs in public sectors and even some private organizations that are highly competitive in terms of hiring employees.
To apply for a Ph.D. in France, you must submit a research proposal. Apart from that, every French institution is free to create its standards and conduct independent enrollment assessments. However, here are the standard eligibility requirements are:
- To enroll as a Ph.D. student, you will typically need a Master’s degree (or equivalent) in the relevant subject.
- You are also eligible to apply if you are pursuing your Master’s degree and have completed it before starting the doctorate program.
- You must attain the cut-off marks of several university entrance exams and preparatory classes.
- Language requirements, too, are set by institutions individually.
International students must submit all supporting documents to complete your Ph.D. in France requirements. Ensure the below is checked:
- Degree certificates
- CV (Resume)
- All educational transcripts
- Personal statement
- GMAT/GRE score
- Thesis chosen + Thesis supervisor selected
- English language proficiency test results
- Two online references
- Passport photo and ID proof
- Research material
- Application Fee payment ( 50 EUR- 60 EUR)
Get Free Counselling to Study in France
After completing your graduation from Ph.D. universities in France, there is a wide range of job profiles available like Assistant Professor, Senior Data Scientist and others. On average, Ph.D. graduates in France earn up to 46,000 € annually.
It can be concluded that PhD in France for Indian students is beneficial and capable of generating good career opportunities. All you need is a decent command of the language (French/ English/ Or both) and meet the eligibility requirement of the university you wish to be a part of.
Is a Ph.D. in France free?
Fees for Ph.D. in France are currently the same for all students regardless of nationality. However, the fee structure differs depending upon whether you are admission to a private or public institution.
Is it worth doing a Ph.D. in France?
Yes, pursuing a Ph.D. course in France is worth the time and effort as this country is home to the best universities worldwide, education system, and others
Study in France
Gauri Agrawal is a passionate, professional and proactive content marketer who wants to grow in the field of content creation. She carries a rich experience of working in the Digital News sector with renowned names like Times Now Digital, and News X as a Copy Editor.
Exams to Study Abroad
Top study abroad destinations, important resources to read, interested in studying abroad, similar articles.

Studying in France is a fascinating thought for anyone planning to study abroad. However, students moving to France face a setback in gearing up with their expenses as the cost of living in France is 200% higher than in India.
So, what do you do as an international student to fulfill your dream of studying there? Look out for part-time jobs and have your best shot at studying in France economically!
Understanding the tuition and living expenses involved in studying in France can get overwhelming, let alone finding the right university. However, booking a 15-minute consultation call with our Yocket experts can help you smooth the entire application process to your dream French or any abroad university!
To simplify, international students have many part-time job opportunities in France. This way, studying and exploring the country can get easier. In this blog, we will list the benefits, eligibility/rules to be fulfilled, locations and divisions to work in, and the wages that international students get while working part-time in France. So, begin reading!
Get In Touch With Yocket Counselors Today!
3 Benefits of Part Time Jobs in France
If you are interested in studying in France , what could be your main concern? Perhaps French part-time jobs are even worth your time? To evaluate that, consider some of the additional financial advantages that come with your part-time student jobs in France:
As an international student, working in Paris, particularly part-time work, opens up a world of opportunities for you. In this glitzy metropolis, you learn a great deal about business, finance, culture, and more.
You get to meet a lot of people and have the chance to socialize as a working student. By doing this, you are establishing connections that can come in handy later on.
Skill development
It's common knowledge that taking on part-time work entails working and upgrading your skills. This will guarantee that during your time in France, you will acquire a few new skills.
Also see: Job Opportunities in France for International Students
Having known the advantages, you might now be quizzed about whether you are eligible to work in France. Let’s find out in the next section!
Eligibility to Work Part Time in France for an International Student
There are several fundamental eligibility conditions that you must fulfill to work part-time in France. For example:
- Part-time employment is permitted in France for any student enrolled in any French university.
- Possess a current residency permit.
- Your part-time work in France must be approved by the university where you are enrolled.
You are free to start working in France if these conditions are satisfied. However, there are certain strict rules that international students must follow when working part-time in France. We will discuss them in the next bit.
Note: To work in France, students no longer require Autorisation Provisoire de Travail (APT, or Temporary Work Permit). There is a built-in provision for this in the residency permit.
Suggested: Post Study Work Permit in France for International Students
Part Time Job Regulations to Work in France
International students studying outside of the EU are permitted to work up to 964 hours a year as long as the following requirements are met:
- With a student visa, students in France are permitted to work 20 hours a week , or 964 hours of part-time work annually .
- You are permitted to work 472 work hours if you are enrolled in a 6-month program.
- Your work schedule should not conflict with your academic schedule or the university's curriculum.
- For overseas students working part-time in France, the minimum hourly pay is around EUR 7.61 (INR 680) . As a result, part-time employment can help them earn up to EUR 7,900 (INR 7,10,380) annually.
- In addition, a student attending a French university may find work. International students are often offered a one-year contract by universities, which runs from September 1 to August 31.
- Students may work up to 670 hours between September 1 and June 30. Contrarily, 300 hours might be worked full-time between July 1 and August 31.
Remember that programs, including internships, do not permit part-time employment. Therefore, prepare ahead for your study-related costs in France if you are expected to accept an internship.
What are the Types of Jobs International Students can take in France?
Now, the most pondering question. What jobs are available for international students working part-time? Well, there are several major divisions and locations that you can work part-time from in France. Let us discuss them in detail.
University Part-Time Jobs for International Students in France
To gain extra earnings, most French universities offer on-campus part-time jobs to students. These can help you network, build leadership skills, and flourish at your university. Some of the locations and jobs you can take up are:
- Library and Bookstore Assistant
- Administrative Office Worker
- Dining and Cafeteria
- Campus Guide
- Tech Supporter
Off-campus Part-Time Jobs for International Students in France
Apart from on-campus jobs, you also have several opportunities to tackle your expenses off-campus. Many simple jobs that don’t require a lot of mental work are available, such as:
- Server/ Bartender at restaurants
- Retail outlets
- Customer service
- Personal Tutor
Assistantships
In France, plenty of professors hire bright, motivated students on a part-time basis to serve as their assistants. Similarly, Indian students in Paris have access to several such part-time occupations. By doing this, you will get additional money for a rainy day, alongside learning from a reputable instructor.
How Much do Part Time Jobs Pay in France?
Another troubling question is regarding the wage that you earn as a part-time worker, no? Well, as mentioned earlier, international students are paid a minimum wage of EUR 7.61 (INR 680) , but this varies job-wise. This way, you can earn a minimum of EUR 7,900 (INR 7,10,380) a year by working part-time.
Some of the jobs and average salaries of French part-time jobs are tabulated below:
How to Get Part-Time Jobs in France?
What are the ways to find part-time jobs? To find part-time opportunities in France, you can use any of the following methods that work for you:
- Consult the university you are studying in and check what positions are available.
- Keep a check on bulletin boards and newspapers.
- Take guidance from seniors and professors.
- Look out for opportunities online on various job portals.
Also see: Cost of Living in France
As an international working part-time, you'll get more than simply the additional money you're hoping for. It will also facilitate your market entry, increasing your chances of landing a job in the same location and company in the long run.
Thus, it might be advantageous for your development to try to work part-time in your field of study. By choosing student loans in France , you will also be able to control your expenses!
From the Desk of Yocket
Well, that is everything about studying and working part-time in France. The advantages alone are sufficient to motivate you to take up a job while studying there. However, always be mindful of the eligibility criteria, rules, and regulations aligned with working abroad. Violating them could lead to serious repercussions. Hopefully, this blog resolved all your queries regarding the wages, locations, and types of part-time jobs available in France for international students.
If not, unveil the several Yocket Premium services by getting in touch with our Yocket experts . From finding the right university and course based on your profile to debriefing you on the costs involved and the scope of finding part-time jobs, we are here to help. Become A Premium Yocketer Now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Are part-time jobs available while studying in France?
Even if you are in your first year of study or taking a language course, all students can work part-time in France. You can, however, only work 964 hours yearly or 20 hours per week. If you are enrolled in a 6-month program, you are allowed 472 hours of work.
Can I cover all my expenses through part-time jobs in France?
No, as a student, your options for part-time employment are limited, and no single available position will provide you with sufficient income to cover all your studying and living costs.
How much can a student earn part-time in France?
The minimum hourly pay for students is around EUR 7.61 (INR 680), therefore a student can earn up to EUR 7,900 (INR 7,10,380), yearly.

Articles you might like

- An unforgettable adventure
- Educational excellence in France
- Study at the heart of Europe
- Enjoy numerous benefits
- Industrial dynamism and French innovation
- The art of living à la française

- French system
- Higher education institutions
- French degrees, LMD system and equivalences
- Cost of studies
- Quality of degrees and institutions
- Online or distance programme
- Scholarships programmes
- Scholarships for French students or students living in France
- Welcoming of students and researchers in exile

- Student and Campus Life Contribution (CVEC)
- Reception services in your city
- Prepare your budget
- Bank account
Working while studying in France
- Learning French
- Finding a student sponsor
- Organising your stay as a scholarship holder
- Being a student with a disability in France

- French regions
- French language
- Getting around
- Join the France Alumni network
- Finding work in France
- How to start a company in France

- Le séjour de recherche
- The role of Campus France
- The tools of Campus France for international researchers
- Research Labs
- Mapping French research
- Outstanding French researchers
- Overview of French research by field
- Excellence of French research in videos
- Accueil des étudiants et des chercheurs en exil

- What is involved in a Doctorate in France?
- Doctoral Schools directory
- PhD subjects
- Pre-Doctorate programmes
- How to enrol in a Doctorate
- How to finance your Doctorat (PhD)
- Use the "Research" portal
- FAQ – Doing my Doctorate in France

- Study in a Post-Doctorate in France
- Join a summer school
- Come to France with the status of invited professor

- Reception programmes and doctoral student associations
- Apply for your visa / Validate your residence permit
- Prepare for your arrival in France
- Finding accommodation in France
- Social Security for doctoral students and researchers
- Living in France

- Programs with Sub-Saharan Africa countries
- Programs with Asian countries
- Programs with European countries
- Programs with Oceania countries
- Programs with American countries

- Campus France missions
- Campus France organisation
- Campus France activities by geographic area
- Events organised by Campus France
- Public procurement
- Mobile applications

- Operation and governance
- Joining the Forum
- Member benefits
- Committees and workshops
- Updating your information online

- France Alumni network
- European projects
- Choose France, La stratégie d'attractivité des étudiants internationaux
- The French+Sciences program

- Campus France expertise
- Make Our Planet Great again
- Le programme « Partenariats avec l’enseignement supérieur africain »
- Le programme de bourses IsDB-France
- Scholarships program for Syrian students in exile in France
- Pakistan: Higher Education Commission scholarships programmes
- Les bourses pour les étudiants français ou résidant en France

- L'accueil des étudiants internationaux
- Label Bienvenue en France
- Nos événements
- Le réseau des responsables de l'accueil
- L'accueil des étudiants réfugiés et en exil
- L'accueil des étudiants en situation de handicap
- Les mémos de Campus France
- Afrique du Sud
- Burkina Faso
- Congo - Brazzaville
- Côte d'Ivoire
- République Démocratique du Congo
- Corée du Sud
- Ouzbékistan
- Philippines
- Territoire de Taïwan
- Biélorussie
- République tchèque
- Royaume-Uni
- Arabie Saoudite
- Émirats arabes unis
- République dominicaine
- Resources center

You can supplement your income by working while studying in France, regardless of the level of education you are undertaking and regardless of your nationality. All students have the right to work on or off campus. A few rules to be aware of.
Every foreign student has the right to work in France
All foreign students have the right to work while studying in France. This right applies to all students in France. Students who are not European Union nationals must have a student resident permit
French law allows foreign students to work up to 964 hours per year, or the equivalent of 60% of the maximum working hours permitted . (50% for Algerian students whose status remains defined by the Franco-Algerian Agreement of December 27, 1968). The income received from such work is a bonus.
When working in France, whether a student or not , a minimum wage is guaranteed by law. This statutory minimum wage is commonly called the Smic (salaire minimum interprofessionnel de croissance or guaranteed minimum wage ) . As of January 1, 2024, this minimum wage is €11.65 . This salary is gross; mandatory social security contributions have to be deducted (around 20%) to determine actual earnings (i.e. €9.22/hour) . A student working 10 hours a week at minimum wage will earn approximately €92 net.
The autorisation provisoire de travail (APT) or provisional work permit is no longer required to work while studying , provided no more than 964 hours per year are worked (different rules apply for Algerian students).
Studying and working at university
In France, foreign students are also permitted to work at their host institution or university. These student jobs generally last twelve months, from September 1st to August 31st. Welcoming students at the start of the school year, tutoring, cultural or sporting events, support for students with disabilities, etc. These types of jobs contribute to the sense of community and enhance life at the university.
To promote academic success and the vocational integration of students, students jobs at the university are scheduled around class times and study times. For the same reason, students working at French universities are not permitted to work more than 670 hours between September 1st and June 30th and not more than 300 hours between July 1st and August 31st.
Interships while studying
Some degree programs require a student to complete an internship. French and foreign students are subject to the same rules:
- The internship requires an agreement (signed between the institution and the structure hosting the student);
- If the internship lasts more than two months, the student must be paid compensation of €650 per month (January 1, 2024).
- Internships completed as part of a degree course do not count towards the 964 hours of permitted work per year.
Apprenticeships and professional training contracts
An apprenticeship contract is an employment contract of limited or indefinite duration between an employee and an employer. An apprenticeship allows practitioners of a trade or profession (the apprentice) to gain on-the-job training under a journeyperson/employer while studying (learn more about apprenticeship contracts) .
Apprenticeships and professional training contracts , previously only accessible to international students who had completed a year of training in France , are now open to first-year students enrolled in a master's (recognized by the State) or in one of the training programs approved by the Conférence des Grandes Écoles and included in this list . All other training programs that include an apprenticeship or professional training contracts are not open to first-year students.
For countries implementing the "Etudes en France" procedure , applications for apprenticeships are made on this platform prior to the visa application.
If the number of hours provided for in the contract exceeds 964 hours per year for an international student from a non-EU country, the student's employer must, on the student's arrival in France, apply for a temporary work permit on the Ministry of the Interior website .
For Algerian students, the employer must apply for a provisional work permit (APT) regardless of the number of hours worked.
S'engager pendant ses études
Pendant vos études, vous pouvez vous engager et donner de votre temps pour effectuer des missions au sein d'organisations publiques ou associatives qui cherchent des bénévoles. La plateforme nationale jeveuxaider.gouv.fr vous permet de trouver facilement une mission partout en France.

Proposé par la plateforme publique du bénévolat JeVeuxAider.gouv.fr
Related contents

- Check out the official website of the French administration to know more (in French) https://www.service-public.fr/particuliers/vosdroits/F2713
Recommended items

Follow the main steps to come study in France
Enjoy this post? Rate it!

Here’s everything you know about part-time jobs in France for international students!
If you are an international student studying in France, you may be interested in finding a part-time job to support your living expenses or gain valuable work experience. This guide provides tips and resources for international students seeking part-time employment in France.
Table of Contents
An introduction to the part time jobs in france, understanding part-time jobs in france, financial benefits, work experience, improved language skills, networking opportunities, language barrier, limited availability of jobs, competition for jobs, legal restrictions, university job boards, online job search engines, local job agencies, time management, language skills, cultural adaptation, professionalism, key takeaways.
France has long been a popular destination for international students seeking a world-class education. However, studying in France can be expensive, with tuition fees and living costs adding up quickly. To help ease this financial burden, many international students in France look for part-time jobs to supplement their income. In this blog, we will explore the benefits of part-time jobs for international students in France, the challenges they face in finding these jobs, resources available for job hunting, and tips for succeeding in part-time jobs.
Part-time jobs are a popular option for students, especially those who are studying abroad. In France, part-time jobs are defined as any work that is less than 35 hours per week. The types of part-time jobs available in France are varied, ranging from retail and hospitality to tutoring and translation services. International students can also find opportunities to work on campus, such as in the library or as a teaching assistant.
However, it is important to note that there are legal requirements for international students looking for part-time jobs in France. Students from the European Union, European Economic Area, and Switzerland are allowed to work up to 964 hours per year, or 60% of a full-time job. Students from other countries are allowed to work up to 964 hours per year, or 20 hours per week during term time and full-time during holidays.
Benefits of part time jobs in France for international students

Part-time jobs offer several benefits for international students in France, including financial benefits, work experience, improved language skills, and networking opportunities. Let’s take a closer look at each of these benefits.
Part-time jobs can help international students in France pay for their living expenses, including accommodation, food, and transportation. This can help reduce the financial stress of studying abroad and allow students to enjoy their time in France without worrying about their finances.
Part-time jobs can provide valuable work experience that can be included in a student’s resume. This can be especially beneficial for students who are looking for a job after graduation. Work experience can also help students develop important skills such as time management, communication, and teamwork.
Working in France can also help international students improve their French language skills. This is especially true for students who are not studying in French, as it can be difficult to improve language skills through coursework alone. Working in a French-speaking environment can provide a practical opportunity to practice speaking and listening skills.
Part-time jobs can also provide international students with networking opportunities. Working alongside French colleagues can help students build professional relationships and potentially open doors to future job opportunities.
Challenges faced by international students in finding part-time jobs

While part-time jobs offer many benefits, international students in France also face several challenges in finding these jobs. These challenges include language barriers, limited availability of jobs, competition for jobs, and legal restrictions.
One of the biggest challenges for international students in France is the language barrier. Many part-time jobs require fluency in French, which can be a barrier for students who are not studying in French or who do not have advanced language skills.
Another challenge is the limited availability of part-time jobs in certain areas of France. For example, students in smaller cities or rural areas may find it difficult to find part-time jobs.
International students in France may also face competition from other students or local residents for part-time jobs. This can make it difficult to find a job, especially during peak hiring seasons.
International students in France also face legal restrictions on the number of hours they can work per week. This can limit the number of job opportunities available to students, as many employers may require full-time availability.
Resources for finding jobs
Despite these challenges, there are resources available to international students in France who are looking for part-time jobs. Some of these resources include university job boards, online job search engines, local job agencies, and networking with classmates and professionals.
Many universities in France have job boards specifically for students, where part-time job opportunities are posted. These job boards can be a great resource for international students looking for part-time jobs.
Online job search engines such as Indeed and LinkedIn are also a great resource for international students in France. These platforms allow students to search for jobs based on their location, language skills, and other criteria.
Local job agencies can also be a helpful resource for international students looking for part-time jobs in France. These agencies can connect students with job opportunities in their area and provide guidance on the application process.
Finally, networking with classmates and professionals can be a great way for international students to learn about job opportunities in France. Joining student organizations, attending job fairs, and connecting with alumni can all help students expand their network and find job opportunities.
Tips for succeeding in part-time jobs
Once international students in France have secured a part-time job, there are several tips they can follow to succeed in their role. These tips include time management, language skills, cultural adaptation, and professionalism.
International students in France need to manage their time effectively to balance their studies with their part-time job. It is important to prioritize tasks and create a schedule that allows for both work and study time.
International students in France can improve their language skills by speaking with colleagues and practicing outside of work. Students can also take language classes to improve their skills and gain confidence in their abilities.
Working in a new culture can be challenging for international students in France. It is important to adapt to the workplace culture and learn about the customs and norms of the local community.
Finally, international students in France should always maintain a professional attitude and behavior in the workplace. This includes dressing appropriately, being punctual, and following company policies and procedures.
- Part-time jobs offer many benefits for international students in France, including financial benefits, work experience, improved language skills, and networking opportunities.
- However, international students also face challenges in finding these jobs, such as language barriers and legal restrictions. By using resources such as university job boards, online job search engines, and local job agencies, students can increase their chances of finding a part-time job in France.
- Once they have secured a job, international students can succeed by managing their time effectively, improving their language skills, adapting to the local culture, and maintaining a professional attitude in the workplace.
Did you find this blog helpful? Do share your perspectives about the blog in the comments below. Please get in touch with us by clicking here for more information on Part time jobs in France for international students. We would be happy to assist you with your queries.
Liked this blog? Read more: How to write a winning SOP for Stanford University’s MS program?
Q1. Can international students in France work part-time?
Answer: Yes, international students in France are allowed to work part-time for up to 964 hours per year.
Q2: What are some resources for international students in France looking for part-time jobs?
Answer: Some resources include university job boards, online job search engines, local job agencies, and networking with classmates and professionals.
Q3. What are some tips for succeeding in part-time jobs as an international student in France?
Answer: Some tips include managing time effectively, improving language skills, adapting to the local culture, and maintaining a professional attitude in the workplace.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
People also liked

Cost of living and studying in the USA | A guide for MS and MBA students

Study in Singapore | A comprehensive guide for Indian students

Top courses in 2024 to study abroad

Student life in Germany | Highest paying part-time jobs and more

Cost of studying in the Netherlands 2024 | A guide

Entrance exams to study abroad | A complete guide
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Start your journey with iSchoolConnect
Need help with your study abroad applications? Try iSchoolConnect for free!
- Where to Study? USA | UK | Canada | Australia | Singapore | Netherlands | Ireland | Germany | New Zealand
- Tests and Preparation GRE | GMAT | IELTS | TOEFL | SAT | PTE
- Visa Process Student visa for USA | Student visa for Canada | Student visa for UK
- Programs and Universities How to choose a university? | How to choose a career? | University interview tips
- Application Process How to apply? | Letter of Recommendation (LOR) | Essay and Statement of Purpose (SOP) | Document checklist | Finance documents
- Fees and Finances Cost of studying abroad | How to apply for scholarships? | Types of scholarships | Student loan | Accommodation | Part-time jobs
- Calculators Calculate your chances of studying abroad | Calculate cost of studying abroad | Which scholarship are you eligible for?

part time phd in france
France is known for its elite universities and excellent higher education system. It isn’t surprising that France boasts the fourth highest number of Nobel laureates in the world (68) and the second highest rated student city (Paris).
Producing influential minds such as Descartes, Laplace and Monet, the French higher education system attracts the largest number of international students in mainland Europe. This is due to its well-funded institutions, affordable fees and excellent https://www.findaphd.com/phds/france/?g0g920 “>PhD research opportunities
This page covers everything you will need to know about studying in France this year, from the higher education history, to the application processes and how much it will cost you.
PhD opportunities in France – what’s on offer for 2021?
The French higher education system has a proud history and is home to one of the oldest universities in the world: The University of Paris (which has existed in some form since 1160).
France’s famous landmarks and rich culture also make it incredibly popular with tourists and international students (over 250,000 studied there in 2020).
Here are a few reasons why France could be the ideal place for you to study your PhD this year:
- Affordability – the French state covers most of students’ fees at public institutions (regardless of your nationality), resulting in significantly lower tuition costs than many other countries
- Welcoming to international students – 12% of students in France are international – not surprising given the number of scholarships offered to attract the top foreign minds for PhD study
- Unique higher education system – the French higher education system features large networks of smaller institutions, offering the benefits of highly specialised universities and a wide range of resources
- Leisure and tourism – France has repeatedly been identified as the number 1 destination in the world for international tourists, due to its rich culture and historical sites
Coronavirus updates for international students at French universities
For the latest information on the impact of coronavirus on studying a PhD in France, please read Campus France’s COVID-19 guidance page . Here you can find updates regarding teaching, exams and travel restrictions.
PhD life in France
Want to know more about life for international PhD students in France? Our detailed guide covers everything from accommodation and living costs to culture and entertainment.
French universities
The French higher education system is unique in comparison to other countries, with larger education hubs housing smaller universities that share resources.
This has resulted in several different institutions within France.
Public universities
The 140 public institutions are referred to as ‘Éstablissement public á caractére scientifique, culturel et professionnel’ (EPSCP) (Public Establishments of a Scientific, Cultural or Professional Character).
The two main varieties of public university within the EPSCP grouping are:
- Universities – France has 83 public universities, that offer comprehensive academic research and training in a wide range of subject areas. All can award PhDs.
- Major Public Establishments – The ‘Grands éstablissements publics’ are top public universities, governed under ministerial charter by the French Government. They specialise within specific disciplines and have entrance exams.
Grandes Écoles
These are the highly specialised, elite private higher education institutions, comparable in some sense to the Ivy League or Russell Group universities in the USA and UK.
Grandes Écoles are not part of the EPSCP and include more specific groups such as the elite publically-funded universities ( Écoles Normales Supérieures ) and high profiles business and engineering schools ( Grandes Écoles de Commerce and Grandes Écoles d’Ingénieurs ).
Communautés d’Universités et d’Etablissements
These are local networks of institutions, formed from the modernisation and development of the French higher education system .
The 27 Communities of Universities and Schools (COMUE) promote collaboration between public universities, Grandes Écoles and specialist research and training centres.
Students are typically enrolled at a specific university but can use the facilities and opportunities at partnering institutions.
French university rankings
The French higher education system has a rich history and boasts a brilliant reputation; therefore, it isn’t surprising that a significant number of French universities are globally ranked. With five of the institutions featuring in the top 200 in the world.
Do ranking matter for PhD study?
University rankings can help you choose a PhD project or programme, provided you know what to look at. Our guide explains how to use rankings as a prospective postgraduate.
French university cities
The French capital, Paris, is frequently named as one of the best cities for student life in the world. However, there are several other large university cities in France, offering excellent opportunities for PhD study:
- Study in Paris
- Study in Marseille
- Study in Lyon
- Study in Montpellier
- Study in Saint Etienne
PhD structure
Since the adoption of the Bologna Process in 1999, a doctorate ( doctorat ) in France is a third-cycle degree .
It is usually completed after a Masters (or similar ‘second-cycle’ qualification) and is intended for students who demonstrate the necessary aptitude to pursue substantial independent research projects.
The Bologna Process
The Bologna Process brings together a range of countries to form the European Higher Education Area (EHEA). Members of the EHEA share a common three-cycle framework that allows degrees from one country to be easily recognised within others.
PhD programmes
Although French universities do sometimes advertise specific doctoral research projects, the majority of PhDs are conducted as part of a programme within doctoral schools .
There are 266 of these. They are affiliated with universities and operate in collaboration with associated research laboratories and other centres to provide doctoral training for PhD candidates and develop early career researchers.
Programme length
A ‘doctorat’ is composed of six semesters for a standard 3-year PhD , resulting in two teaching (or research) semesters per year:
- Autumn semester – late September-January with a holiday around Christmas and New Year
- Spring semester – early February-June with some institutions having a spring break at Easter
Institutions typically have exams at the end of each semester, and a three-month summer holiday from July-September .
You will usually be studying your PhD in France for 3-4 years as a full-time student .
The French PhD process
A French PhD is slightly different to doctorates in other countries, with an emphasis on training professional researchers. Institutions will differ, but you will typically have to complete several other components alongside your thesis in order to gain your qualification.
During your doctoral training you will be required to take research courses , which include teaching sessions and seminars related to your project. These courses correspond to 150 hours over the duration of the Doctorate.
In addition, you may have to do several training sessions organised within the framework of your doctoral school.
Alongside this you will have to carry out your research to meet the aims of your project. Which will eventually result in the production of a thesis .
Many doctoral schools also encourage integration and collaborations between other institutions, as well as helping students find project related work placements.
Supervision
If you are applying directly to a project this will already have a designated supervisor; whereas if you apply to doctoral school, you may be assigned a supervisor or be required to apply to one yourself .
Once assigned a supervisor you will sign a moral contract (thesis charter) depicting the preparation of your thesis, objectives and resources.
In France a thesis may be supervised by one or two supervisors . In addition, to further the collaboration and mobility prospects of a French PhD it is also possible to have international joint supervision.
Supervisors
For more advice on supervision read our guides on working with your supervisor and what to expect from them .
Assessment and examination
Although you may be required to attend courses as a French PhD student, the primary form of assessment for you to obtain PhD status is the production of an original doctoral thesis fit for public presentation.
There are two stages to this process:
First, your thesis will first be examined by two external assessors appointed by the head of your doctoral school to determine whether it is fit for presentation.
If your intent to present your thesis is approved, a thesis jury will be appointed, consisting of 3-8 members specialised in your field of research. At least half of the members will be French and external to your institution and doctoral school, the other half will be members of the National university council ( Conseil national des universités ). After presenting your research methods and results you will debate and ‘defend’ them to the jury, this viva voce (oral examination) is public.
Prior to your presentation a description of your thesis is circulated and afterwards the full thesis is circulated within the university community.
The jury will grade your report as: honourable , very honourable and very honourable “cum laude” . The highest grade in France is reserved for students with exceptional qualities demonstrated in their thesis and presentation.
Fees and funding
French PhD fees are currently the same for every student regardless of nationality. However, the price can vary significantly depending upon whether you choose to study at a public or private institution (such as a Grandes École).
PhD fees in 2021-20
Fees are significantly lower at public institutions as the State invests on an average of €14,000 per student, per year.
You can expect to pay the following depending upon your institution:
- Public institutes – fees for doctoral students are €380 per year
- Private institutes – fees in private institutes, especially business schools, are typically high and cost between €3,000-10,000 per year
Universities may charge administrative fees (frais de dossier) which are typically low – tens of euros .
Planned changes
The French Government increased university fees for international (non-EU / EEA) students in 2019, but only at Bachelors and Masters level. The annual cost of a programme for these students is €3,770 for Masters courses at public universities. PhD fees will remain at €380, regardless of nationality.
You can check if your chosen institution receives government funding and therefore offers low fees directly on their website or on the French Ministry of Higher Education’s website .
Employment contracts
A doctoral contract ( contrat doctoral ) is a job placement within a research laboratory. These are mainly offered within public institutions (to students of any nationality).
You will receive benefits such as a PhD salary and social security, however you will also be subject to income tax.
The contract is for 3-years and is renewable for 1-year . There are two types of contract resulting in two salary levels: research only (lower pay grade) and research + professional tasks (teaching).
Scholarships
The French Foreign Ministry awards several scholarships to international students for doctoral level study. With several programmes designed by the government to attract the top international minds.
The scholarships available are:
- The Eiffel Scholarship Program of Excellence – Available for Science, Economics, Management, Law and Political Science students. Benefits include: €1,400 per month for up to 10-months , medical insurance , subsidised housing and international round-trip airfare .
- CROUS Scholarship The CROUS scholarships are means tested, if you are awarded one you will receive €750 per month to cover accommodation and living costs.
- Conventions Industrielles de Formation par la Recherche (CIFRE) – You will complete a 3-year full-time work contract leading to PhD research for a French company and French public laboratory. You will receive €23,484 per year .
- Public body funding – public organisations such as the National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), Institute for Research and Development (IRD) and the French Research Institute for Exploitation of the SEA (IFREMER) finance research
There are a number of other scholarships available for international students, such as the Horizon 2020 Scheme , Erasmus Mundus as well as scholarship from Regional Authorities for foreign students enrolled in programmes within their region.
For information on earning money, working whilst you’re studying consult our Living in France guide.
Institutes offer their own higher education scholarships to foreign students, to find out more you should contact their international relations department.
Applying for a PhD in France
The application process in France is similar to other countries such as the UK, as you will be applying for specific advertised projects , or submitting a research proposal for your own project.
You must submit an application to the doctoral school you wish to study in (or approach a specific supervisor if your university doesn’t have a doctoral school).
Entry requirements
Each institution in France is free to set its own criteria and make assessments on an individual basis. However, you will typically be required to have a Masters degree (or equivalent) in a relevant subject to be enrolled as a PhD student .
You may apply if you are working towards your Masters degree and will have graduated prior to the doctoral programme start date.
You may also be admitted based on performance in entrance exams and preparatory classes such as the ‘ Classe préparatoire aux grandes écoles ’ (CPGE) commonly used by France’s Grandes Écoles .
Language requirements
Most PhD programmes in France are delivered in French, with language requirements set individually by institutions. Some may require international students to produce a thesis abstract in French (with the rest of the thesis written in their native language) as part of their final assessment.
Candidates will generally have to sit a French proficiency test ( test de connaissance du français ) unless you have studied in a country where French is one of the official languages or you already have a proficiency certificate.
It is recommended that you learn basic levels of French, even if your PhD is delivered in English. This will allow you to communicate well (and benefit from additional extra-curricular and cultural experiences during your PhD).
French language
For PhD studies, French fluency may not be required depending upon your subject, it is therefore best to check with the institution you are applying to.
Application process
The application process is different depending upon your nationality.
For EU/EEA students there are no specific pre-application procedures to go through, you must contact your chosen doctoral school or supervisor and apply to the institution directly.
If you are applying for an advertised project , then you should simply follow the application procedure. You will typically need to provide the following materials with your application:
- Academic transcripts – Certified copies of your degree contents and qualification certificates, with original stamps. Your transcript may have to be translated into French and approved by a lawyer.
- Research proposal – If you are applying directly to a doctoral school rather than an advertised project you will have to submit a research proposal .
- References – You will usually need to provide at least two academic references , who have had experience working with you.
The national closing date for applications at public universities for all candidates is January 31st. This may be different for Grandes Ecoles and other private institutions.
If you get an offer from a doctoral school, you and your supervisor will have to sign a document called the ‘Charte des théses’ (Thesis Charter), which is a moral contract between you, your supervisor, director of the doctoral school and director of the research facility.
‘Studying in France’ initiative
For non-EU/EEA students you will need to check whether you are from one of the 41 countries implementing the ‘Studying in France’ procedure.
If you are you will need to apply directly through the Campus France centralised application facility. You may create an account allowing you to submit an application to several institutions.
Some institutions in France will require you to have an interview for admission on to PhD programmes.
For international students this is typically conducted over skype and will involve questions about yourself and the project, to determine your suitability.
What happens during a PhD interview?
Your interview for a PhD in France will follow a fairly standard format (apart from the fact in may take place online). Our guides give advice on what happens at a PhD interview and an overview of some questions you might be asked.
Student visas
Depending upon your nationality you may need a visa to study your PhD within France.
There are two types of visa available for students a short-stay for studies ( court sojourn pour études ) for 90-days and a long-stay student visa ( visa etudiant long séjour valant titre de séjour ) for over 90-days. For PhD study you will need to apply for the long-stay student visa.
Who needs a visa to study in France?
Students from any country may study in France; however, there are requirements depending upon your nationality:
- Students from the EU/EEA and Switzerland – you may study for a PhD in France without a visa , however you must have valid health insurance
- Other international students – you will need a Talent passport VLS-TS extended-stay student visa, with a residency permit
Visa information for UK students in France
UK students will no longer be EU citizens from the 2021-22 academic year onwards. This means you may be considered as an international student when studying in France. You may be subject to different visa requirements and fee rates, unless otherwise stated.
Applying for a French student visa (VLS-TS)
There are three ways to apply for you VLS-TS for PhD study in France:
- Campus France’s CEF procedure – If yours is one of the 33 countries in which the official French portal for international students and education (Campus France), maintains an office, you should apply for a visa directly through their website .
- French consulate – If Campus France doesn’t have an office in your country contact your local French consulate or embassy and apply via the Demande d’Admission Prélable (DAP) procedure.
- Government visa website – Alternatively you can apply for a long-term visa directly on the French government’s visa website .
Application requirements
You will typically need to provide the following documents for your visa application:
- Identification documents – A valid passport with 3 months validity after your departure date
- Proof of enrolment – A letter of enrolment from a recognised institution including the start/end dates and length of course
- Proof of funds – Evidence of a maintenance grant or proof of at least €650 per month
- Health insurance – valid for the entirety of your stay, from a recognised insurer
You must validate your visa and receive a residence permit upon arrival, by sending your visa to the Office Français de l’Immigration et de l’Intégration with copies of your passport and your Demande d’attestation OFII (issued with your visa).
Visa validation
There is a €60 fee for validating your visa, as this is a tax, you must obtain a ‘fiscal stamp’ from news agents or the OFII website .
Student social security
Registering for Student Social Security is mandatory in France if you are under 28 years of age , enrolled at an institute recognised by Social Security and are studying for a period longer than 3-months .
It provides you with social coverage during your stay and will be registered alongside your administrative enrolment at your institution.
Registration for social security is free .
To study in France, you must have valid health insurance . For students from the EU/EEA this is covered if you hold a valid EU/EEA European Health Insurance Card (EHIC).
Other international students will have 70% of healthcare expenses reimbursed as part of their Student Social Security. You will have the option to take out an additional healthcare plan ( Mutuelle ) for €100 per year to have 100% of healthcare costs reimbursed.
If you are in receipt of a scholarship or bursary check the conditions as you may receive healthcare coverage as part of the funding.
The combination of highly ranked education institutions and doctoral skill training programmes will result in you becoming a capable independent graduate, with skills applicable to a range of different employment opportunities. But will you be able to remain in France?
With the French government trying to improve researchers and workers in areas of skill shortages, it is easy to gain a post-study work visa if you remain in your academic field. If you want to work outside of your field it is more difficult to obtain a visa.
Can I work in France after my PhD?
The regulations for working in France after your studies is dependent upon your nationality.
Students from the EU/EEA can work in France without acquiring a work permit after you have graduated.
Other international students can apply for a non-renewable temporary residency authorisation ‘ autorisation provisoire de séjour ’ ( APS ) which is valid for 6-months after the expiry of your student’s residence permit. Your APS allows you to work in any job for 60% of the official work week.
If you obtain a job related to your academic profession with a salary equal to or above 1.5 times the national minimum wage, you may upgrade your student visa to a working visa .
Similar Posts
Tu wien architecture.
Master programme Architecture Study codeE 066 443LanguageGermanDuration of Study4 SemestersCredits120 ECTSDegreeDiplom-Ingenieur (Dipl.-Ing.) / Master of Science (MSc) Qualification profile Entry requirements, Structure of the programme Entry requirements Candidates must have successfully completed a bachelor’s programme in Architecture. Candidates with bachelor’s, master’s or equivalent degrees in related technical or creative academic subjects may be considered if…
is ucla a good engineering school
UCLA is ranked among the world’s best for engineering and technology. The Times Higher Education World University Rankings by Subject for 2020 include UCLA in the top 10 for engineering and technology. The rankings are based on an extensive analysis of the leading universities’ performance across all their core missions: teaching, research, knowledge transfer, and…
Clark University tuition
Searching for a site where you can obtain info on Clark University with success after many failed attempts then you’ve landed on the perfect website. At College learners you get access to information you need to get make learning easier! There is indeed a web site where you can obtain info on Clark University for…

diploma of paramedical science victoria
OVERVIEW Begin a rewarding career treating and transporting patients with a Diploma of Paramedical Science HLT51015 at Victoria University Polytechnic. You will gain clinical skills and theoretical knowledge to treat and transport patients. This course will prepare you to work in pre-hospital and out-of-hospital care in the health care industry. You’ll be qualified to work…
University Of Hawai’i Business Major
The University of Hawai’i Business program offers a unique opportunity to study in one of the most beautiful places in the world. UH, Mānoa is located in Honolulu, Hawaii — widely recognized as one of America’s most popular vacation destinations. Collegelearners provides information about uh mānoa Shidler double major, the uh mānoa marketing major, university…

University of Nebraska kearney ranking
Dive in deep with all the information you need on University of Nebraska kearney from University of Nebraska System kearney ranking, University of Nebraska kearney tuition, University of Nebraska kearney acceptance rate and University of Nebraska kearney. Need all this information and have not been able to find? I bring you the latest information on…
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
The Evolving Danger of the New Bird Flu
An unusual outbreak of the disease has spread to dairy herds in multiple u.s. states..
This transcript was created using speech recognition software. While it has been reviewed by human transcribers, it may contain errors. Please review the episode audio before quoting from this transcript and email [email protected] with any questions.
From “The New York Times,” I’m Sabrina Tavernise, and this is “The Daily.”
[MUSIC PLAYING]
The outbreak of bird flu that is tearing through the nation’s poultry farms is the worst in US history. But scientists say it’s now starting to spread into places and species it’s never been before.
Today, my colleague, Emily Anthes, explains.
It’s Monday, April 22.
Emily, welcome back to the show.
Thanks for having me. Happy to be here.
So, Emily, we’ve been talking here on “The Daily” about prices of things and how they’ve gotten so high, mostly in the context of inflation episodes. And one of the items that keeps coming up is eggs. Egg prices were through the roof last year, and we learned it was related to this. Avian flu has been surging in the United States. You’ve been covering this. Tell us what’s happening.
Yes, so I have been covering this virus for the last few years. And the bird flu is absolutely tearing through poultry flocks, and that is affecting egg prices. That’s a concern for everyone, for me and for my family. But when it comes to scientists, egg prices are pretty low on their list of concerns. Because they see this bird flu virus behaving differently than previous versions have. And they’re getting nervous, in particular, about the fact that this virus is reaching places and species where it’s never been before.
OK, so bird flu, though, isn’t new. I mean I remember hearing about cases in Asia in the ‘90s. Remind us how it began.
Bird flu refers to a bunch of different viruses that are adapted to spread best in birds. Wild water birds, in particular, are known for carrying these viruses. And flu viruses are famous for also being shapeshifters. So they’re constantly swapping genes around and evolving into new strains. And as you mentioned back in the ‘90s, a new version of bird flu, a virus known as H5N1, emerged in Asia. And it has been spreading on and off around the world since then, causing periodic outbreaks.
And how are these outbreaks caused?
So wild birds are the reservoir for the virus, which means they carry it in their bodies with them around the world as they fly and travel and migrate. And most of the time, these wild birds, like ducks and geese, don’t even get very sick from this virus. But they shed it. So as they’re traveling over a poultry farm maybe, if they happen to go to the bathroom in a pond that the chickens on the farm are using or eat some of the feed that chickens on the farm are eating, they can leave the virus behind.
And the virus can get into chickens. In some cases, it causes mild illness. It’s what’s known as low pathogenic avian influenza. But sometimes the virus mutates and evolves, and it can become extremely contagious and extremely fatal in poultry.
OK, so the virus comes through wild birds, but gets into farms like this, as you’re describing. How have farms traditionally handled outbreaks, when they do happen?
Well, because this threat isn’t new, there is a pretty well-established playbook for containing outbreaks. It’s sometimes known as stamping out. And brutally, what it means is killing the birds. So the virus is so deadly in this highly pathogenic form that it’s sort of destined to kill all the birds on a farm anyway once it gets in. So the response has traditionally been to proactively depopulate or cull all the birds, so it doesn’t have a chance to spread.
So that’s pretty costly for farmers.
It is. Although the US has a program where it will reimburse farmers for their losses. And the way these reimbursements work is they will reimburse farmers only for the birds that are proactively culled, and not for those who die naturally from the virus. And the thinking behind that is it’s a way to incentivize farmers to report outbreaks early.
So, OK, lots of chickens are killed in a way to manage these outbreaks. So we know how to deal with them. But what about now? Tell me about this new strain.
So this new version of the virus, it emerged in 2020.
After the deadly outbreak of the novel coronavirus, authorities have now confirmed an outbreak of the H5N1 strain of influenza, a kind of bird flu.
And pretty quickly it became clear that a couple things set it apart.
A bald eagle found dead at Carvins Cove has tested positive for the highly contagious bird flu.
This virus, for whatever reason, seemed very good at infecting all sorts of wild birds that we don’t normally associate with bird flu.
[BIRD CRYING]
He was kind of stepping, and then falling over, and using its wing to right itself.
Things like eagles and condors and pelicans.
We just lost a parliament of owls in Minneapolis.
Yeah, a couple of high profile nests.
And also in the past, wild birds have not traditionally gotten very sick from this virus. And this version of the virus not only spread widely through the wild bird population, but it proved to be devastating.
The washing up along the East Coast of the country from Scotland down to Suffolk.
We were hearing about mass die-offs of seabirds in Europe by the hundreds and the thousands.
And the bodies of the dead dot the island wherever you look.
Wow. OK. So then as we know, this strain, like previous ones, makes its way from wild animals to farmed animals, namely to chickens. But it’s even more deadly.
Absolutely. And in fact, it has already caused the worst bird flu outbreak in US history. So more than 90 million birds in the US have died as a result of this virus.
90 million birds.
Yes, and I should be clear that represents two things. So some of those birds are birds who naturally got infected and died from the virus. But the vast majority of them are birds that were proactively culled. What it adds up to is, is 90 million farmed birds in the US have died since this virus emerged. And it’s not just a chicken problem. Another thing that has been weird about this virus is it has jumped into other kinds of farms. It is the first time we’ve seen a bird flu virus jump into US livestock.
And it’s now been reported on a number of dairy farms across eight US states. And that’s just something that’s totally unprecedented.
So it’s showing up at Dairy farms now. You’re saying that bird flu has now spread to cows. How did that happen?
So we don’t know exactly how cows were first infected, but most scientists’ best guess is that maybe an infected wild bird that was migrating shed the virus into some cattle feed or a pasture or a pond, and cattle picked it up. The good news is they don’t seem to get nearly as sick as chickens do. They are generally making full recoveries on their own in a couple of weeks.
OK, so no mass culling of cows?
No, that doesn’t seem to be necessary at this point. But the bad news is that it’s starting to look like we’re seeing this virus spread from cow to cow. We don’t know exactly how that’s happening yet. But anytime you see cow-to-cow or mammal-to-mammal transmission, that’s a big concern.
And why is that exactly?
Well, there are a bunch of reasons. First, it could allow the outbreak to get much bigger, much faster, which might increase the risk to the food supply. And we might also expect it to increase the risk to farm workers, people who might be in contact with these sick cows.
Right now, the likelihood that a farmer who gets this virus passes it on is pretty low. But any time you see mammal-to-mammal transmission, it increases the chance that the virus will adapt and possibly, maybe one day get good at spreading between humans. To be clear, that’s not something that there’s any evidence happening in cows right now. But the fact that there’s any cow-to-cow transmission happening at all is enough to have scientists a bit concerned.
And then if we think more expansively beyond what’s happening on farms, there’s another big danger lurking out there. And that’s what happens when this virus gets into wild animals, vast populations that we can’t control.
We’ll be right back.
So, Emily, you said that another threat was the threat of flu in wild animal populations. Clearly, of course, it’s already in wild birds. Where else has it gone?
Well, the reason it’s become such a threat is because of how widespread it’s become in wild birds. So they keep reintroducing it to wild animal populations pretty much anywhere they go. So we’ve seen the virus repeatedly pop up in all sorts of animals that you might figure would eat a wild bird, so foxes, bobcats, bears. We actually saw it in a polar bear, raccoons. So a lot of carnivores and scavengers.
The thinking is that these animals might stumble across a sick or dead bird, eat it, and contract the virus that way. But we’re also seeing it show up in some more surprising places, too. We’ve seen the virus in a bottle-nosed dolphin, of all places.
And most devastatingly, we’ve seen enormous outbreaks in other sorts of marine mammals, especially sea lions and seals.
So elephant seals, in particular in South America, were just devastated by this virus last fall. My colleague Apoorva Mandavilli and I were talking to some scientists in South America who described to us what they called a scene from hell, of walking out onto a beach in Argentina that is normally crowded with chaotic, living, breathing, breeding, elephant seals — and the beach just being covered by carcass, after carcass, after carcass.
Mostly carcasses of young newborn pups. The virus seemed to have a mortality rate of 95 percent in these elephant seal pups, and they estimated that it might have killed more than 17,000 of the pups that were born last year. So almost the entire new generation of this colony. These are scientists that have studied these seals for decades. And they said they’ve never seen anything like it before.
And why is it so far reaching, Emily? I mean, what explains these mass die-offs?
There are probably a few explanations. One is just how much virus is out there in the environment being shed by wild birds into water and onto beaches. These are also places that viruses like this haven’t been before. So it’s reaching elephant seals and sea lions in South America that have no prior immunity.
There’s also the fact that these particular species, these sea lions and seals, tend to breed in these huge colonies all crowded together on beaches. And so what that means is if a virus makes its way into the colony, it’s very conducive conditions for it to spread. And scientists think that that’s actually what’s happening now. That it’s not just that all these seals are picking up the virus from individual birds, but that they’re actually passing it to each other.
So basically, this virus is spreading to places it’s never been before, kind of virgin snow territory, where animals just don’t have the immunity against it. And once it gets into a population packed on a beach, say, of elephant seals, it’s just like a knife through butter.
Absolutely. And an even more extreme example of that is what we’re starting to see happen in Antarctica, where there’s never been a bird flu outbreak before until last fall, for the first time, this virus reached the Antarctic mainland. And we are now seeing the virus move through colonies of not only seabirds and seals, but penguin colonies, which have not been exposed to these viruses before.
And it’s too soon to say what the toll will be. But penguins also, of course, are known for breeding in these large colonies.
Probably. don’t have many immune defenses against this virus, and of course, are facing all these other environmental threats. And so there’s a lot of fear that you add on the stress of a bird flu virus, and it could just be a tipping point for penguins.
Emily, at this point, I’m kind of wondering why more people aren’t talking about this. I mean, I didn’t know any of this before having this conversation with you, and it feels pretty worrying.
Well, a lot of experts and scientists are talking about this with rising alarm and in terms that are quite stark. They’re talking about the virus spreading through wild animal populations so quickly and so ferociously that they’re calling it an ecological disaster.
But that’s a disaster that sometimes seems distant from us, both geographically, we’re talking about things that are happening maybe at the tip of Argentina or in Antarctica. And also from our concerns of our everyday lives, what’s happening in Penguins might not seem like it has a lot to do with the price of a carton of eggs at the grocery store. But I think that we should be paying a lot of attention to how this virus is moving through animal populations, how quickly it’s moving through animal populations, and the opportunities that it is giving the virus to evolve into something that poses a much bigger threat to human health.
So the way it’s spreading in wild animals, even in remote places like Antarctica, that’s important to watch, at least in part because there’s a real danger to people here.
So we know that the virus can infect humans, and that generally it’s not very good at spreading between humans. But the concern all along has been that if this virus has more opportunities to spread between mammals, it will get better at spreading between them. And that seems to be what is happening in seals and sea lions. Scientists are already seeing evidence that the virus is adapting as it passes from marine mammal to marine mammal. And that could turn it into a virus that’s also better at spreading between people.
And if somebody walks out onto a beach and touches a dead sea lion, if their dog starts playing with a sea lion carcass, you could imagine that this virus could make its way out of marine mammals and into the human population. And if it’s this mammalian adapted version of the virus that makes its way out, that could be a bigger threat to human health.
So the sheer number of hosts that this disease has, the more opportunity it has to mutate, and the more chance it has to mutate in a way that would actually be dangerous for people.
Yes, and in particular, the more mammalian hosts. So that gives the virus many more opportunities to become a specialist in mammals instead of a specialist in birds, which is what it is right now.
Right. I like that, a specialist in mammals. So what can we do to contain this virus?
Well, scientists are exploring new options. There’s been a lot of discussion about whether we should start vaccinating chickens in the US. The government, USDA labs, have been testing some poultry vaccines. It’s probably scientifically feasible. There are challenges there, both in terms of logistics — just how would you go about vaccinating billions of chickens every year. There are also trade questions. Traditionally, a lot of countries have not been willing to accept poultry products from countries that vaccinate their poultry.
And there’s concern about whether the virus might spread undetected in flocks that are vaccinated. So as we saw with COVID, the vaccine can sometimes stop you from getting sick, but it doesn’t necessarily stop infection. And so countries are worried they might unknowingly import products that are harboring the virus.
And what about among wild animals? I mean, how do you even begin to get your head around that?
Yeah, I mean, thinking about vaccinating wild animals maybe makes vaccinating all the chickens in the US look easy. There has been some discussion of limited vaccination campaigns, but that’s not feasible on a global scale. So unfortunately, the bottom line is there isn’t a good way to stop spread in wild animals. We can try to protect some vulnerable populations, but we’re not going to stop the circulation of this virus.
So, Emily, we started this conversation with a kind of curiosity that “The Daily” had about the price of eggs. And then you explained the bird flu to us. And then somehow we ended up learning about an ecological disaster that’s unfolding all around us, and potentially the source of the next human pandemic. That is pretty scary.
It is scary, and it’s easy to get overwhelmed by it. And I feel like I should take a step back and say none of this is inevitable. None of this is necessarily happening tomorrow. But this is why scientists are concerned and why they think it’s really important to keep a very close eye on what’s happening both on farms and off farms, as this virus spreads through all sorts of animal populations.
One thing that comes up again and again and again in my interviews with people who have been studying bird flu for decades, is how this virus never stops surprising them. And sometimes those are bad surprises, like these elephant seal die-offs, the incursions into dairy cattle. But there are some encouraging signs that have emerged recently. We’re starting to see some early evidence that some of the bird populations that survived early brushes with this virus might be developing some immunity. So that’s something that maybe could help slow the spread of this virus in animal populations.
We just don’t entirely know how this is going to play out. Flu is a very difficult, wily foe. And so that’s one reason scientists are trying to keep such a close, attentive eye on what’s happening.
Emily, thank you.
Thanks for having me.
Here’s what else you should know today.
On this vote, the yeas are 366 and the nays are 58. The bill is passed.
On Saturday, in four back-to-back votes, the House voted resoundingly to approve a long-stalled package of aid to Ukraine, Israel and other American allies, delivering a major victory to President Biden, who made aid to Ukraine one of his top priorities.
On this vote, the yeas are 385, and the no’s are 34 with one answering present. The bill is passed without objection.
The House passed the component parts of the $95 billion package, which included a bill that could result in a nationwide ban of TikTok.
On this vote, the yeas are 311 and the nays are 112. The bill is passed.
Oh, one voting present. I missed it, but thank you.
In a remarkable breach of custom, Democrats stepped in to supply the crucial votes to push the legislation past hard-line Republican opposition and bring it to the floor.
The House will be in order.
The Senate is expected to pass the legislation as early as Tuesday.
Today’s episode was produced by Rikki Novetsky, Nina Feldman, Eric Krupke, and Alex Stern. It was edited by Lisa Chow and Patricia Willens; contains original music by Marion Lozano, Dan Powell, Rowan Niemisto, and Sophia Lanman; and was engineered by Chris Wood. Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Andrew Jacobs.
That’s it for “The Daily.” I’m Sabrina Tavernise. See you tomorrow.

- April 24, 2024 • 32:18 Is $60 Billion Enough to Save Ukraine?
- April 23, 2024 • 30:30 A Salacious Conspiracy or Just 34 Pieces of Paper?
- April 22, 2024 • 24:30 The Evolving Danger of the New Bird Flu
- April 19, 2024 • 30:42 The Supreme Court Takes Up Homelessness
- April 18, 2024 • 30:07 The Opening Days of Trump’s First Criminal Trial
- April 17, 2024 • 24:52 Are ‘Forever Chemicals’ a Forever Problem?
- April 16, 2024 • 29:29 A.I.’s Original Sin
- April 15, 2024 • 24:07 Iran’s Unprecedented Attack on Israel
- April 14, 2024 • 46:17 The Sunday Read: ‘What I Saw Working at The National Enquirer During Donald Trump’s Rise’
- April 12, 2024 • 34:23 How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
- April 11, 2024 • 28:39 The Staggering Success of Trump’s Trial Delay Tactics
- April 10, 2024 • 22:49 Trump’s Abortion Dilemma
Hosted by Sabrina Tavernise
Produced by Rikki Novetsky , Nina Feldman , Eric Krupke and Alex Stern
Edited by Lisa Chow and Patricia Willens
Original music by Marion Lozano , Dan Powell , Rowan Niemisto and Sophia Lanman
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
The outbreak of bird flu currently tearing through the nation’s poultry is the worst in U.S. history. Scientists say it is now spreading beyond farms into places and species it has never been before.
Emily Anthes, a science reporter for The Times, explains.
On today’s episode

Emily Anthes , a science reporter for The New York Times.

Background reading
Scientists have faulted the federal response to bird flu outbreaks on dairy farms .
Here’s what to know about the outbreak.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
Special thanks to Andrew Jacobs .
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3 years. The Physics program from Institut Polytechnique de Paris reflects this variety by offering possibilities of PhD thesis work in theoretical or experimental fundamental physics, as well as in more applied fields based on the properties of light and matter, energy, or applications to biosciences. Ph.D. / Full-time / On Campus.
The PhD degree attests skills acquired through research in the framework of the doctoral training, which has a 3 years reference duration when the research work is carried out full-time, and a 3 to 6 years duration when the thesis is prepared part-time. The PhD degree can also be obtained by the validation of the acquired experience (VAE). The PhD degree - the highest internationnaly ...
In France, a PhD is the highest academic degree you can earn. Doctoral studies are a form of research-based training with the same value as professional experience. PhD students carry out research on a defined topic under the supervision of their thesis advisor (s). PhD students are enrolled in doctoral programmes run by institutions of higher ...
Affordability - PhD fees in France are fixed by the State, and international students pay the same amount as French students, making it one of the more affordable study destinations in Europe. Specialisations - The French higher education system is proud of its specialisations. Many institutions, like the Grandes Ecoles and Schools of Arts ...
At the national level, once fully operational, Université Paris Cité will offfer 5% of all PhD degrees in France. Université Paris Cité is committed to a doctoral policy aimed at research training and training by research. It trains future researchers and teacher-researchers as well as future high-level executives. Social Sciences - ED 624.
Now the doctoral school has to approve it so you can enrol in a Doctorate. If funding is required by the doctoral school, it must be approved before you can enrol. The annual registration fee for a Doctorate is €380 (2022/23 academic year). Even if you have a doctoral fellowship, you will have to pay the registration fee.
Alyssa Rusonik is a PhD student at the Finance department of HEC Paris. In just the second year of her PhD, she has received an award for the best article from a doctoral student at the annual conference... Nov 27, 2023. PhD Dissertation Defense, Yufei Shen, Information Systems & Operations Management.
The PhD in Management is a three-year programme that develops leading-edge research skills to help you identify, analyse and solve key managerial questions. ... it opens the doors to the part-time MSc. Global Executive MBA. Part time. 15 to 20 months. ... upon graduation - in high-quality business schools, in France and abroad. Recent PhD ...
University of Manchester. (4.1) Programme description Our PhD French Studies programme will enable you to carry out a significant piece of in-depth research in an area of Read more... 3 years Full time degree: £4,786 per year (UK) 6 years Part time degree: £2,393 per year (UK) Request info. Compare.
In France, it takes three to six years to complete a Doctorate, depending on the field, although there is no legal time limit. In the natural and technological sciences (mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, engineering, etc.), it usually takes three years and can be extended for a fourth year. In the social sciences and humanities (law ...
Yes, international students can undertake part-time job opportunities while studying PhD in France. The part-time working hours are 20hrs/week. Do PhD students pay taxes in France? No, PhD students are not required to pay any taxes, however, they do need to pay student social insurance. ...
Many holders of this degree might pursue academic careers as college professors, scholarly writers and researchers. While the most common research degree is the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree, other research doctorates are available. Some popular PhD Majors near France include: (Ed.D.)Doctor of Education (D.A.) Doctor of Arts
More information can be obtained via Ms. Marloes Westerveld ( [email protected] ), please mention 'Parttime PhD programme' in the subject. General information: Degree: PhD. Format: part-time. Duration: 4-6 years. Requirement: Master's degree. Start: September or February.
The contractual Phd students are full-time employees with the sole or main mission of carrying out their doctoral project. They may also be entrusted with complementary missions of teaching, scientific mediation, valorization or expertise. ... ED ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS OF ILE-DE-FRANCE (AAIF) PhD students are welcomed at the beginning of ...
To be included, a college or university must be regionally accredited and offer degree programs online or in a hybrid format. 1. Andrews University. Andrews University is a private university in Berrien Springs, Michigan, that is affiliated with the Seventh-day Adventist Church.
Therefore, a PhD in France for Indian students can be an enriching experience and offer excellent research opportunities. Study Abroad Programs. Masters Programs; Help +966 11 497 0009. Study Abroad; ... Canada Part Time Jobs - Top Jobs, Salary, Regulations & More. 07 Nov'23. Jobs in Ireland - Top Recruiters, Highest Paying Jobs Etc.
University of Kent, ParisParis School of Arts and Culture. This MA, taught at Kent's Paris School of Arts and Culture, provides a structured introduction to the postgraduate study of the history and philosophy of art. Read more. Video (s) On Campus Part Time Full Time. Showing results 1 to 15 of 16.
For overseas students working part-time in France, the minimum hourly pay is around EUR 7.61 (INR 680). As a result, part-time employment can help them earn up to EUR 7,900 (INR 7,10,380) annually. In addition, a student attending a French university may find work. International students are often offered a one-year contract by universities ...
All foreign students have the right to work while studying in France. This right applies to all students in France. Students who are not European Union nationals must have a student resident permit French law allows foreign students to work up to 964 hours per year, or the equivalent of 60% of the maximum working hours permitted.. (50% for Algerian students whose status remains defined by the ...
International students in France can work part-time for up to 964 hours per year. While part-time jobs offer many benefits, international students in France also face several challenges in finding these jobs. These challenges include language barriers, limited availability of jobs, competition for jobs, and legal restrictions.
28,137 USD / year. 4 years. Through the Finance MPhil/PhD programme from The University of Exeter you'll be part of a vibrant research community, with more than 150 current doctoral students. Ph. D. / Full-time, Part-time / On Campus. The University of Exeter Exeter, England, United Kingdom.
part time phd in france. By Blessing Umahi June 18, 2021 February 9, 2022. France is known for its elite universities and excellent higher education system. It isn't surprising that France boasts the fourth highest number of Nobel laureates in the world (68) and the second highest rated student city (Paris).
An unusual outbreak of the disease has spread to dairy herds in multiple U.S. states.