

Designing and Conducting Case Studies
This guide examines case studies, a form of qualitative descriptive research that is used to look at individuals, a small group of participants, or a group as a whole. Researchers collect data about participants using participant and direct observations, interviews, protocols, tests, examinations of records, and collections of writing samples. Starting with a definition of the case study, the guide moves to a brief history of this research method. Using several well documented case studies, the guide then looks at applications and methods including data collection and analysis. A discussion of ways to handle validity, reliability, and generalizability follows, with special attention to case studies as they are applied to composition studies. Finally, this guide examines the strengths and weaknesses of case studies.
Definition and Overview
Case study refers to the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including the accounts of subjects themselves. A form of qualitative descriptive research, the case study looks intensely at an individual or small participant pool, drawing conclusions only about that participant or group and only in that specific context. Researchers do not focus on the discovery of a universal, generalizable truth, nor do they typically look for cause-effect relationships; instead, emphasis is placed on exploration and description.
Case studies typically examine the interplay of all variables in order to provide as complete an understanding of an event or situation as possible. This type of comprehensive understanding is arrived at through a process known as thick description, which involves an in-depth description of the entity being evaluated, the circumstances under which it is used, the characteristics of the people involved in it, and the nature of the community in which it is located. Thick description also involves interpreting the meaning of demographic and descriptive data such as cultural norms and mores, community values, ingrained attitudes, and motives.
Unlike quantitative methods of research, like the survey, which focus on the questions of who, what, where, how much, and how many, and archival analysis, which often situates the participant in some form of historical context, case studies are the preferred strategy when how or why questions are asked. Likewise, they are the preferred method when the researcher has little control over the events, and when there is a contemporary focus within a real life context. In addition, unlike more specifically directed experiments, case studies require a problem that seeks a holistic understanding of the event or situation in question using inductive logic--reasoning from specific to more general terms.
In scholarly circles, case studies are frequently discussed within the context of qualitative research and naturalistic inquiry. Case studies are often referred to interchangeably with ethnography, field study, and participant observation. The underlying philosophical assumptions in the case are similar to these types of qualitative research because each takes place in a natural setting (such as a classroom, neighborhood, or private home), and strives for a more holistic interpretation of the event or situation under study.
Unlike more statistically-based studies which search for quantifiable data, the goal of a case study is to offer new variables and questions for further research. F.H. Giddings, a sociologist in the early part of the century, compares statistical methods to the case study on the basis that the former are concerned with the distribution of a particular trait, or a small number of traits, in a population, whereas the case study is concerned with the whole variety of traits to be found in a particular instance" (Hammersley 95).
Case studies are not a new form of research; naturalistic inquiry was the primary research tool until the development of the scientific method. The fields of sociology and anthropology are credited with the primary shaping of the concept as we know it today. However, case study research has drawn from a number of other areas as well: the clinical methods of doctors; the casework technique being developed by social workers; the methods of historians and anthropologists, plus the qualitative descriptions provided by quantitative researchers like LePlay; and, in the case of Robert Park, the techniques of newspaper reporters and novelists.
Park was an ex-newspaper reporter and editor who became very influential in developing sociological case studies at the University of Chicago in the 1920s. As a newspaper professional he coined the term "scientific" or "depth" reporting: the description of local events in a way that pointed to major social trends. Park viewed the sociologist as "merely a more accurate, responsible, and scientific reporter." Park stressed the variety and value of human experience. He believed that sociology sought to arrive at natural, but fluid, laws and generalizations in regard to human nature and society. These laws weren't static laws of the kind sought by many positivists and natural law theorists, but rather, they were laws of becoming--with a constant possibility of change. Park encouraged students to get out of the library, to quit looking at papers and books, and to view the constant experiment of human experience. He writes, "Go and sit in the lounges of the luxury hotels and on the doorsteps of the flophouses; sit on the Gold Coast settees and on the slum shakedowns; sit in the Orchestra Hall and in the Star and Garter Burlesque. In short, gentlemen [sic], go get the seats of your pants dirty in real research."
But over the years, case studies have drawn their share of criticism. In fact, the method had its detractors from the start. In the 1920s, the debate between pro-qualitative and pro-quantitative became quite heated. Case studies, when compared to statistics, were considered by many to be unscientific. From the 1930's on, the rise of positivism had a growing influence on quantitative methods in sociology. People wanted static, generalizable laws in science. The sociological positivists were looking for stable laws of social phenomena. They criticized case study research because it failed to provide evidence of inter subjective agreement. Also, they condemned it because of the few number of cases studied and that the under-standardized character of their descriptions made generalization impossible. By the 1950s, quantitative methods, in the form of survey research, had become the dominant sociological approach and case study had become a minority practice.
Educational Applications
The 1950's marked the dawning of a new era in case study research, namely that of the utilization of the case study as a teaching method. "Instituted at Harvard Business School in the 1950s as a primary method of teaching, cases have since been used in classrooms and lecture halls alike, either as part of a course of study or as the main focus of the course to which other teaching material is added" (Armisted 1984). The basic purpose of instituting the case method as a teaching strategy was "to transfer much of the responsibility for learning from the teacher on to the student, whose role, as a result, shifts away from passive absorption toward active construction" (Boehrer 1990). Through careful examination and discussion of various cases, "students learn to identify actual problems, to recognize key players and their agendas, and to become aware of those aspects of the situation that contribute to the problem" (Merseth 1991). In addition, students are encouraged to "generate their own analysis of the problems under consideration, to develop their own solutions, and to practically apply their own knowledge of theory to these problems" (Boyce 1993). Along the way, students also develop "the power to analyze and to master a tangled circumstance by identifying and delineating important factors; the ability to utilize ideas, to test them against facts, and to throw them into fresh combinations" (Merseth 1991).
In addition to the practical application and testing of scholarly knowledge, case discussions can also help students prepare for real-world problems, situations and crises by providing an approximation of various professional environments (i.e. classroom, board room, courtroom, or hospital). Thus, through the examination of specific cases, students are given the opportunity to work out their own professional issues through the trials, tribulations, experiences, and research findings of others. An obvious advantage to this mode of instruction is that it allows students the exposure to settings and contexts that they might not otherwise experience. For example, a student interested in studying the effects of poverty on minority secondary student's grade point averages and S.A.T. scores could access and analyze information from schools as geographically diverse as Los Angeles, New York City, Miami, and New Mexico without ever having to leave the classroom.
The case study method also incorporates the idea that students can learn from one another "by engaging with each other and with each other's ideas, by asserting something and then having it questioned, challenged and thrown back at them so that they can reflect on what they hear, and then refine what they say" (Boehrer 1990). In summary, students can direct their own learning by formulating questions and taking responsibility for the study.
Types and Design Concerns
Researchers use multiple methods and approaches to conduct case studies.
Types of Case Studies
Under the more generalized category of case study exist several subdivisions, each of which is custom selected for use depending upon the goals and/or objectives of the investigator. These types of case study include the following:
Illustrative Case Studies These are primarily descriptive studies. They typically utilize one or two instances of an event to show what a situation is like. Illustrative case studies serve primarily to make the unfamiliar familiar and to give readers a common language about the topic in question.
Exploratory (or pilot) Case Studies These are condensed case studies performed before implementing a large scale investigation. Their basic function is to help identify questions and select types of measurement prior to the main investigation. The primary pitfall of this type of study is that initial findings may seem convincing enough to be released prematurely as conclusions.
Cumulative Case Studies These serve to aggregate information from several sites collected at different times. The idea behind these studies is the collection of past studies will allow for greater generalization without additional cost or time being expended on new, possibly repetitive studies.
Critical Instance Case Studies These examine one or more sites for either the purpose of examining a situation of unique interest with little to no interest in generalizability, or to call into question or challenge a highly generalized or universal assertion. This method is useful for answering cause and effect questions.
Identifying a Theoretical Perspective
Much of the case study's design is inherently determined for researchers, depending on the field from which they are working. In composition studies, researchers are typically working from a qualitative, descriptive standpoint. In contrast, physicists will approach their research from a more quantitative perspective. Still, in designing the study, researchers need to make explicit the questions to be explored and the theoretical perspective from which they will approach the case. The three most commonly adopted theories are listed below:
Individual Theories These focus primarily on the individual development, cognitive behavior, personality, learning and disability, and interpersonal interactions of a particular subject.
Organizational Theories These focus on bureaucracies, institutions, organizational structure and functions, or excellence in organizational performance.
Social Theories These focus on urban development, group behavior, cultural institutions, or marketplace functions.
Two examples of case studies are used consistently throughout this chapter. The first, a study produced by Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988), looks at a first year graduate student's initiation into an academic writing program. The study uses participant-observer and linguistic data collecting techniques to assess the student's knowledge of appropriate discourse conventions. Using the pseudonym Nate to refer to the subject, the study sought to illuminate the particular experience rather than to generalize about the experience of fledgling academic writers collectively.
For example, in Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman's (1988) study we are told that the researchers are interested in disciplinary communities. In the first paragraph, they ask what constitutes membership in a disciplinary community and how achieving membership might affect a writer's understanding and production of texts. In the third paragraph they state that researchers must negotiate their claims "within the context of his sub specialty's accepted knowledge and methodology." In the next paragraph they ask, "How is literacy acquired? What is the process through which novices gain community membership? And what factors either aid or hinder students learning the requisite linguistic behaviors?" This introductory section ends with a paragraph in which the study's authors claim that during the course of the study, the subject, Nate, successfully makes the transition from "skilled novice" to become an initiated member of the academic discourse community and that his texts exhibit linguistic changes which indicate this transition. In the next section the authors make explicit the sociolinguistic theoretical and methodological assumptions on which the study is based (1988). Thus the reader has a good understanding of the authors' theoretical background and purpose in conducting the study even before it is explicitly stated on the fourth page of the study. "Our purpose was to examine the effects of the educational context on one graduate student's production of texts as he wrote in different courses and for different faculty members over the academic year 1984-85." The goal of the study then, was to explore the idea that writers must be initiated into a writing community, and that this initiation will change the way one writes.
The second example is Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of a group of twelfth graders. In this study, Emig seeks to answer the question of what happens to the self as a result educational stimuli in terms of academic writing. The case study used methods such as protocol analysis, tape-recorded interviews, and discourse analysis.
In the case of Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of eight twelfth graders, four specific hypotheses were made:
- Twelfth grade writers engage in two modes of composing: reflexive and extensive.
- These differences can be ascertained and characterized through having the writers compose aloud their composition process.
- A set of implied stylistic principles governs the writing process.
- For twelfth grade writers, extensive writing occurs chiefly as a school-sponsored activity, or reflexive, as a self-sponsored activity.
In this study, the chief distinction is between the two dominant modes of composing among older, secondary school students. The distinctions are:
- The reflexive mode, which focuses on the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- The extensive mode, which focuses on conveying a message.
Emig also outlines the specific questions which guided the research in the opening pages of her Review of Literature , preceding the report.
Designing a Case Study
After considering the different sub categories of case study and identifying a theoretical perspective, researchers can begin to design their study. Research design is the string of logic that ultimately links the data to be collected and the conclusions to be drawn to the initial questions of the study. Typically, research designs deal with at least four problems:
- What questions to study
- What data are relevant
- What data to collect
- How to analyze that data
In other words, a research design is basically a blueprint for getting from the beginning to the end of a study. The beginning is an initial set of questions to be answered, and the end is some set of conclusions about those questions.
Because case studies are conducted on topics as diverse as Anglo-Saxon Literature (Thrane 1986) and AIDS prevention (Van Vugt 1994), it is virtually impossible to outline any strict or universal method or design for conducting the case study. However, Robert K. Yin (1993) does offer five basic components of a research design:
- A study's questions.
- A study's propositions (if any).
- A study's units of analysis.
- The logic that links the data to the propositions.
- The criteria for interpreting the findings.
In addition to these five basic components, Yin also stresses the importance of clearly articulating one's theoretical perspective, determining the goals of the study, selecting one's subject(s), selecting the appropriate method(s) of collecting data, and providing some considerations to the composition of the final report.
Conducting Case Studies
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of approaches and methods. These approaches, methods, and related issues are discussed in depth in this section.
Method: Single or Multi-modal?
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of methods. Some common methods include interviews , protocol analyses, field studies, and participant-observations. Emig (1971) chose to use several methods of data collection. Her sources included conversations with the students, protocol analysis, discrete observations of actual composition, writing samples from each student, and school records (Lauer and Asher 1988).
Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) collected data by observing classrooms, conducting faculty and student interviews, collecting self reports from the subject, and by looking at the subject's written work.
A study that was criticized for using a single method model was done by Flower and Hayes (1984). In this study that explores the ways in which writers use different forms of knowing to create space, the authors used only protocol analysis to gather data. The study came under heavy fire because of their decision to use only one method.
Participant Selection
Case studies can use one participant, or a small group of participants. However, it is important that the participant pool remain relatively small. The participants can represent a diverse cross section of society, but this isn't necessary.
For example, the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study looked at just one participant, Nate. By contrast, in Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composition process of twelfth graders, eight participants were selected representing a diverse cross section of the community, with volunteers from an all-white upper-middle-class suburban school, an all-black inner-city school, a racially mixed lower-middle-class school, an economically and racially mixed school, and a university school.
Often, a brief "case history" is done on the participants of the study in order to provide researchers with a clearer understanding of their participants, as well as some insight as to how their own personal histories might affect the outcome of the study. For instance, in Emig's study, the investigator had access to the school records of five of the participants, and to standardized test scores for the remaining three. Also made available to the researcher was the information that three of the eight students were selected as NCTE Achievement Award winners. These personal histories can be useful in later stages of the study when data are being analyzed and conclusions drawn.
Data Collection
There are six types of data collected in case studies:
- Archival records.
- Interviews.
- Direct observation.
- Participant observation.
In the field of composition research, these six sources might be:
- A writer's drafts.
- School records of student writers.
- Transcripts of interviews with a writer.
- Transcripts of conversations between writers (and protocols).
- Videotapes and notes from direct field observations.
- Hard copies of a writer's work on computer.
Depending on whether researchers have chosen to use a single or multi-modal approach for the case study, they may choose to collect data from one or any combination of these sources.
Protocols, that is, transcriptions of participants talking aloud about what they are doing as they do it, have been particularly common in composition case studies. For example, in Emig's (1971) study, the students were asked, in four different sessions, to give oral autobiographies of their writing experiences and to compose aloud three themes in the presence of a tape recorder and the investigator.
In some studies, only one method of data collection is conducted. For example, the Flower and Hayes (1981) report on the cognitive process theory of writing depends on protocol analysis alone. However, using multiple sources of evidence to increase the reliability and validity of the data can be advantageous.
Case studies are likely to be much more convincing and accurate if they are based on several different sources of information, following a corroborating mode. This conclusion is echoed among many composition researchers. For example, in her study of predrafting processes of high and low-apprehensive writers, Cynthia Selfe (1985) argues that because "methods of indirect observation provide only an incomplete reflection of the complex set of processes involved in composing, a combination of several such methods should be used to gather data in any one study." Thus, in this study, Selfe collected her data from protocols, observations of students role playing their writing processes, audio taped interviews with the students, and videotaped observations of the students in the process of composing.
It can be said then, that cross checking data from multiple sources can help provide a multidimensional profile of composing activities in a particular setting. Sharan Merriam (1985) suggests "checking, verifying, testing, probing, and confirming collected data as you go, arguing that this process will follow in a funnel-like design resulting in less data gathering in later phases of the study along with a congruent increase in analysis checking, verifying, and confirming."
It is important to note that in case studies, as in any qualitative descriptive research, while researchers begin their studies with one or several questions driving the inquiry (which influence the key factors the researcher will be looking for during data collection), a researcher may find new key factors emerging during data collection. These might be unexpected patterns or linguistic features which become evident only during the course of the research. While not bearing directly on the researcher's guiding questions, these variables may become the basis for new questions asked at the end of the report, thus linking to the possibility of further research.
Data Analysis
As the information is collected, researchers strive to make sense of their data. Generally, researchers interpret their data in one of two ways: holistically or through coding. Holistic analysis does not attempt to break the evidence into parts, but rather to draw conclusions based on the text as a whole. Flower and Hayes (1981), for example, make inferences from entire sections of their students' protocols, rather than searching through the transcripts to look for isolatable characteristics.
However, composition researchers commonly interpret their data by coding, that is by systematically searching data to identify and/or categorize specific observable actions or characteristics. These observable actions then become the key variables in the study. Sharan Merriam (1988) suggests seven analytic frameworks for the organization and presentation of data:
- The role of participants.
- The network analysis of formal and informal exchanges among groups.
- Historical.
- Thematical.
- Ritual and symbolism.
- Critical incidents that challenge or reinforce fundamental beliefs, practices, and values.
There are two purposes of these frameworks: to look for patterns among the data and to look for patterns that give meaning to the case study.
As stated above, while most researchers begin their case studies expecting to look for particular observable characteristics, it is not unusual for key variables to emerge during data collection. Typical variables coded in case studies of writers include pauses writers make in the production of a text, the use of specific linguistic units (such as nouns or verbs), and writing processes (planning, drafting, revising, and editing). In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, researchers coded the participant's texts for use of connectives, discourse demonstratives, average sentence length, off-register words, use of the first person pronoun, and the ratio of definite articles to indefinite articles.
Since coding is inherently subjective, more than one coder is usually employed. In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, three rhetoricians were employed to code the participant's texts for off-register phrases. The researchers established the agreement among the coders before concluding that the participant used fewer off-register words as the graduate program progressed.
Composing the Case Study Report
In the many forms it can take, "a case study is generically a story; it presents the concrete narrative detail of actual, or at least realistic events, it has a plot, exposition, characters, and sometimes even dialogue" (Boehrer 1990). Generally, case study reports are extensively descriptive, with "the most problematic issue often referred to as being the determination of the right combination of description and analysis" (1990). Typically, authors address each step of the research process, and attempt to give the reader as much context as possible for the decisions made in the research design and for the conclusions drawn.
This contextualization usually includes a detailed explanation of the researchers' theoretical positions, of how those theories drove the inquiry or led to the guiding research questions, of the participants' backgrounds, of the processes of data collection, of the training and limitations of the coders, along with a strong attempt to make connections between the data and the conclusions evident.
Although the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study does not, case study reports often include the reactions of the participants to the study or to the researchers' conclusions. Because case studies tend to be exploratory, most end with implications for further study. Here researchers may identify significant variables that emerged during the research and suggest studies related to these, or the authors may suggest further general questions that their case study generated.
For example, Emig's (1971) study concludes with a section dedicated solely to the topic of implications for further research, in which she suggests several means by which this particular study could have been improved, as well as questions and ideas raised by this study which other researchers might like to address, such as: is there a correlation between a certain personality and a certain composing process profile (e.g. is there a positive correlation between ego strength and persistence in revising)?
Also included in Emig's study is a section dedicated to implications for teaching, which outlines the pedagogical ramifications of the study's findings for teachers currently involved in high school writing programs.
Sharan Merriam (1985) also offers several suggestions for alternative presentations of data:
- Prepare specialized condensations for appropriate groups.
- Replace narrative sections with a series of answers to open-ended questions.
- Present "skimmer's" summaries at beginning of each section.
- Incorporate headlines that encapsulate information from text.
- Prepare analytic summaries with supporting data appendixes.
- Present data in colorful and/or unique graphic representations.
Issues of Validity and Reliability
Once key variables have been identified, they can be analyzed. Reliability becomes a key concern at this stage, and many case study researchers go to great lengths to ensure that their interpretations of the data will be both reliable and valid. Because issues of validity and reliability are an important part of any study in the social sciences, it is important to identify some ways of dealing with results.
Multi-modal case study researchers often balance the results of their coding with data from interviews or writer's reflections upon their own work. Consequently, the researchers' conclusions become highly contextualized. For example, in a case study which looked at the time spent in different stages of the writing process, Berkenkotter concluded that her participant, Donald Murray, spent more time planning his essays than in other writing stages. The report of this case study is followed by Murray's reply, wherein he agrees with some of Berkenkotter's conclusions and disagrees with others.
As is the case with other research methodologies, issues of external validity, construct validity, and reliability need to be carefully considered.
Commentary on Case Studies
Researchers often debate the relative merits of particular methods, among them case study. In this section, we comment on two key issues. To read the commentaries, choose any of the items below:
Strengths and Weaknesses of Case Studies
Most case study advocates point out that case studies produce much more detailed information than what is available through a statistical analysis. Advocates will also hold that while statistical methods might be able to deal with situations where behavior is homogeneous and routine, case studies are needed to deal with creativity, innovation, and context. Detractors argue that case studies are difficult to generalize because of inherent subjectivity and because they are based on qualitative subjective data, generalizable only to a particular context.
Flexibility
The case study approach is a comparatively flexible method of scientific research. Because its project designs seem to emphasize exploration rather than prescription or prediction, researchers are comparatively freer to discover and address issues as they arise in their experiments. In addition, the looser format of case studies allows researchers to begin with broad questions and narrow their focus as their experiment progresses rather than attempt to predict every possible outcome before the experiment is conducted.
Emphasis on Context
By seeking to understand as much as possible about a single subject or small group of subjects, case studies specialize in "deep data," or "thick description"--information based on particular contexts that can give research results a more human face. This emphasis can help bridge the gap between abstract research and concrete practice by allowing researchers to compare their firsthand observations with the quantitative results obtained through other methods of research.
Inherent Subjectivity
"The case study has long been stereotyped as the weak sibling among social science methods," and is often criticized as being too subjective and even pseudo-scientific. Likewise, "investigators who do case studies are often regarded as having deviated from their academic disciplines, and their investigations as having insufficient precision (that is, quantification), objectivity and rigor" (Yin 1989). Opponents cite opportunities for subjectivity in the implementation, presentation, and evaluation of case study research. The approach relies on personal interpretation of data and inferences. Results may not be generalizable, are difficult to test for validity, and rarely offer a problem-solving prescription. Simply put, relying on one or a few subjects as a basis for cognitive extrapolations runs the risk of inferring too much from what might be circumstance.
High Investment
Case studies can involve learning more about the subjects being tested than most researchers would care to know--their educational background, emotional background, perceptions of themselves and their surroundings, their likes, dislikes, and so on. Because of its emphasis on "deep data," the case study is out of reach for many large-scale research projects which look at a subject pool in the tens of thousands. A budget request of $10,000 to examine 200 subjects sounds more efficient than a similar request to examine four subjects.
Ethical Considerations
Researchers conducting case studies should consider certain ethical issues. For example, many educational case studies are often financed by people who have, either directly or indirectly, power over both those being studied and those conducting the investigation (1985). This conflict of interests can hinder the credibility of the study.
The personal integrity, sensitivity, and possible prejudices and/or biases of the investigators need to be taken into consideration as well. Personal biases can creep into how the research is conducted, alternative research methods used, and the preparation of surveys and questionnaires.
A common complaint in case study research is that investigators change direction during the course of the study unaware that their original research design was inadequate for the revised investigation. Thus, the researchers leave unknown gaps and biases in the study. To avoid this, researchers should report preliminary findings so that the likelihood of bias will be reduced.
Concerns about Reliability, Validity, and Generalizability
Merriam (1985) offers several suggestions for how case study researchers might actively combat the popular attacks on the validity, reliability, and generalizability of case studies:
- Prolong the Processes of Data Gathering on Site: This will help to insure the accuracy of the findings by providing the researcher with more concrete information upon which to formulate interpretations.
- Employ the Process of "Triangulation": Use a variety of data sources as opposed to relying solely upon one avenue of observation. One example of such a data check would be what McClintock, Brannon, and Maynard (1985) refer to as a "case cluster method," that is, when a single unit within a larger case is randomly sampled, and that data treated quantitatively." For instance, in Emig's (1971) study, the case cluster method was employed, singling out the productivity of a single student named Lynn. This cluster profile included an advanced case history of the subject, specific examination and analysis of individual compositions and protocols, and extensive interview sessions. The seven remaining students were then compared with the case of Lynn, to ascertain if there are any shared, or unique dimensions to the composing process engaged in by these eight students.
- Conduct Member Checks: Initiate and maintain an active corroboration on the interpretation of data between the researcher and those who provided the data. In other words, talk to your subjects.
- Collect Referential Materials: Complement the file of materials from the actual site with additional document support. For example, Emig (1971) supports her initial propositions with historical accounts by writers such as T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, and D.H. Lawrence. Emig also cites examples of theoretical research done with regards to the creative process, as well as examples of empirical research dealing with the writing of adolescents. Specific attention is then given to the four stages description of the composing process delineated by Helmoltz, Wallas, and Cowley, as it serves as the focal point in this study.
- Engage in Peer Consultation: Prior to composing the final draft of the report, researchers should consult with colleagues in order to establish validity through pooled judgment.
Although little can be done to combat challenges concerning the generalizability of case studies, "most writers suggest that qualitative research should be judged as credible and confirmable as opposed to valid and reliable" (Merriam 1985). Likewise, it has been argued that "rather than transplanting statistical, quantitative notions of generalizability and thus finding qualitative research inadequate, it makes more sense to develop an understanding of generalization that is congruent with the basic characteristics of qualitative inquiry" (1985). After all, criticizing the case study method for being ungeneralizable is comparable to criticizing a washing machine for not being able to tell the correct time. In other words, it is unjust to criticize a method for not being able to do something which it was never originally designed to do in the first place.
Annotated Bibliography
Armisted, C. (1984). How Useful are Case Studies. Training and Development Journal, 38 (2), 75-77.
This article looks at eight types of case studies, offers pros and cons of using case studies in the classroom, and gives suggestions for successfully writing and using case studies.
Bardovi-Harlig, K. (1997). Beyond Methods: Components of Second Language Teacher Education . New York: McGraw-Hill.
A compilation of various research essays which address issues of language teacher education. Essays included are: "Non-native reading research and theory" by Lee, "The case for Psycholinguistics" by VanPatten, and "Assessment and Second Language Teaching" by Gradman and Reed.
Bartlett, L. (1989). A Question of Good Judgment; Interpretation Theory and Qualitative Enquiry Address. 70th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. San Francisco.
Bartlett selected "quasi-historical" methodology, which focuses on the "truth" found in case records, as one that will provide "good judgments" in educational inquiry. He argues that although the method is not comprehensive, it can try to connect theory with practice.
Baydere, S. et. al. (1993). Multimedia conferencing as a tool for collaborative writing: a case study in Computer Supported Collaborative Writing. New York: Springer-Verlag.
The case study by Baydere et. al. is just one of the many essays in this book found in the series "Computer Supported Cooperative Work." Denley, Witefield and May explore similar issues in their essay, "A case study in task analysis for the design of a collaborative document production system."
Berkenkotter, C., Huckin, T., N., & Ackerman J. (1988). Conventions, Conversations, and the Writer: Case Study of a Student in a Rhetoric Ph.D. Program. Research in the Teaching of English, 22, 9-44.
The authors focused on how the writing of their subject, Nate or Ackerman, changed as he became more acquainted or familiar with his field's discourse community.
Berninger, V., W., and Gans, B., M. (1986). Language Profiles in Nonspeaking Individuals of Normal Intelligence with Severe Cerebral Palsy. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 2, 45-50.
Argues that generalizations about language abilities in patients with severe cerebral palsy (CP) should be avoided. Standardized tests of different levels of processing oral language, of processing written language, and of producing written language were administered to 3 male participants (aged 9, 16, and 40 yrs).
Bockman, J., R., and Couture, B. (1984). The Case Method in Technical Communication: Theory and Models. Texas: Association of Teachers of Technical Writing.
Examines the study and teaching of technical writing, communication of technical information, and the case method in terms of those applications.
Boehrer, J. (1990). Teaching With Cases: Learning to Question. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 42 41-57.
This article discusses the origins of the case method, looks at the question of what is a case, gives ideas about learning in case teaching, the purposes it can serve in the classroom, the ground rules for the case discussion, including the role of the question, and new directions for case teaching.
Bowman, W. R. (1993). Evaluating JTPA Programs for Economically Disadvantaged Adults: A Case Study of Utah and General Findings . Washington: National Commission for Employment Policy.
"To encourage state-level evaluations of JTPA, the Commission and the State of Utah co-sponsored this report on the effectiveness of JTPA Title II programs for adults in Utah. The technique used is non-experimental and the comparison group was selected from registrants with Utah's Employment Security. In a step-by-step approach, the report documents how non-experimental techniques can be applied and several specific technical issues can be addressed."
Boyce, A. (1993) The Case Study Approach for Pedagogists. Annual Meeting of the American Alliance for Health, Physical Education, Recreation and Dance. (Address). Washington DC.
This paper addresses how case studies 1) bridge the gap between teaching theory and application, 2) enable students to analyze problems and develop solutions for situations that will be encountered in the real world of teaching, and 3) helps students to evaluate the feasibility of alternatives and to understand the ramifications of a particular course of action.
Carson, J. (1993) The Case Study: Ideal Home of WAC Quantitative and Qualitative Data. Annual Meeting of the Conference on College Composition and Communication. (Address). San Diego.
"Increasingly, one of the most pressing questions for WAC advocates is how to keep [WAC] programs going in the face of numerous difficulties. Case histories offer the best chance for fashioning rhetorical arguments to keep WAC programs going because they offer the opportunity to provide a coherent narrative that contextualizes all documents and data, including what is generally considered scientific data. A case study of the WAC program, . . . at Robert Morris College in Pittsburgh demonstrates the advantages of this research method. Such studies are ideal homes for both naturalistic and positivistic data as well as both quantitative and qualitative information."
---. (1991). A Cognitive Process Theory of Writing. College Composition and Communication. 32. 365-87.
No abstract available.
Cromer, R. (1994) A Case Study of Dissociations Between Language and Cognition. Constraints on Language Acquisition: Studies of Atypical Children . Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 141-153.
Crossley, M. (1983) Case Study in Comparative and International Education: An Approach to Bridging the Theory-Practice Gap. Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the Australian Comparative and International Education Society. Hamilton, NZ.
Case study research, as presented here, helps bridge the theory-practice gap in comparative and international research studies of education because it focuses on the practical, day-to-day context rather than on the national arena. The paper asserts that the case study method can be valuable at all levels of research, formation, and verification of theories in education.
Daillak, R., H., and Alkin, M., C. (1982). Qualitative Studies in Context: Reflections on the CSE Studies of Evaluation Use . California: EDRS
The report shows how the Center of the Study of Evaluation (CSE) applied qualitative techniques to a study of evaluation information use in local, Los Angeles schools. It critiques the effectiveness and the limitations of using case study, evaluation, field study, and user interview survey methodologies.
Davey, L. (1991). The Application of Case Study Evaluations. ERIC/TM Digest.
This article examines six types of case studies, the type of evaluation questions that can be answered, the functions served, some design features, and some pitfalls of the method.
Deutch, C. E. (1996). A course in research ethics for graduate students. College Teaching, 44, 2, 56-60.
This article describes a one-credit discussion course in research ethics for graduate students in biology. Case studies are focused on within the four parts of the course: 1) major issues, 2 )practical issues in scholarly work, 3) ownership of research results, and 4) training and personal decisions.
DeVoss, G. (1981). Ethics in Fieldwork Research. RIE 27p. (ERIC)
This article examines four of the ethical problems that can happen when conducting case study research: acquiring permission to do research, knowing when to stop digging, the pitfalls of doing collaborative research, and preserving the integrity of the participants.
Driscoll, A. (1985). Case Study of a Research Intervention: the University of Utah’s Collaborative Approach . San Francisco: Far West Library for Educational Research Development.
Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education, Denver, CO, March 1985. Offers information of in-service training, specifically case studies application.
Ellram, L. M. (1996). The Use of the Case Study Method in Logistics Research. Journal of Business Logistics, 17, 2, 93.
This article discusses the increased use of case study in business research, and the lack of understanding of when and how to use case study methodology in business.
Emig, J. (1971) The Composing Processes of Twelfth Graders . Urbana: NTCE.
This case study uses observation, tape recordings, writing samples, and school records to show that writing in reflexive and extensive situations caused different lengths of discourse and different clusterings of the components of the writing process.
Feagin, J. R. (1991). A Case For the Case Study . Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press.
This book discusses the nature, characteristics, and basic methodological issues of the case study as a research method.
Feldman, H., Holland, A., & Keefe, K. (1989) Language Abilities after Left Hemisphere Brain Injury: A Case Study of Twins. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 9, 32-47.
"Describes the language abilities of 2 twin pairs in which 1 twin (the experimental) suffered brain injury to the left cerebral hemisphere around the time of birth and1 twin (the control) did not. One pair of twins was initially assessed at age 23 mo. and the other at about 30 mo.; they were subsequently evaluated in their homes 3 times at about 6-mo intervals."
Fidel, R. (1984). The Case Study Method: A Case Study. Library and Information Science Research, 6.
The article describes the use of case study methodology to systematically develop a model of online searching behavior in which study design is flexible, subject manner determines data gathering and analyses, and procedures adapt to the study's progressive change.
Flower, L., & Hayes, J. R. (1984). Images, Plans and Prose: The Representation of Meaning in Writing. Written Communication, 1, 120-160.
Explores the ways in which writers actually use different forms of knowing to create prose.
Frey, L. R. (1992). Interpreting Communication Research: A Case Study Approach Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
The book discusses research methodologies in the Communication field. It focuses on how case studies bridge the gap between communication research, theory, and practice.
Gilbert, V. K. (1981). The Case Study as a Research Methodology: Difficulties and Advantages of Integrating the Positivistic, Phenomenological and Grounded Theory Approaches . The Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for the Study of Educational Administration. (Address) Halifax, NS, Can.
This study on an innovative secondary school in England shows how a "low-profile" participant-observer case study was crucial to the initial observation, the testing of hypotheses, the interpretive approach, and the grounded theory.
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A Case for Case Studies in Social Work Research. Social Work, 39, 4, 371-381.
This article defines case study research, presents guidelines for evaluation of case studies, and shows the relevance of case studies to social work research. It also looks at issues such as evaluation and interpretations of case studies.
Glennan, S. L., Sharp-Bittner, M. A. & Tullos, D. C. (1991). Augmentative and Alternative Communication Training with a Nonspeaking Adult: Lessons from MH. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 7, 240-7.
"A response-guided case study documented changes in a nonspeaking 36-yr-old man's ability to communicate using 3 trained augmentative communication modes. . . . Data were collected in videotaped interaction sessions between the nonspeaking adult and a series of adult speaking."
Graves, D. (1981). An Examination of the Writing Processes of Seven Year Old Children. Research in the Teaching of English, 15, 113-134.
Hamel, J. (1993). Case Study Methods . Newbury Park: Sage. .
"In a most economical fashion, Hamel provides a practical guide for producing theoretically sharp and empirically sound sociological case studies. A central idea put forth by Hamel is that case studies must "locate the global in the local" thus making the careful selection of the research site the most critical decision in the analytic process."
Karthigesu, R. (1986, July). Television as a Tool for Nation-Building in the Third World: A Post-Colonial Pattern, Using Malaysia as a Case-Study. International Television Studies Conference. (Address). London, 10-12.
"The extent to which Television Malaysia, as a national mass media organization, has been able to play a role in nation building in the post-colonial period is . . . studied in two parts: how the choice of a model of nation building determines the character of the organization; and how the character of the organization influences the output of the organization."
Kenny, R. (1984). Making the Case for the Case Study. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 16, (1), 37-51.
The article looks at how and why the case study is justified as a viable and valuable approach to educational research and program evaluation.
Knirk, F. (1991). Case Materials: Research and Practice. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 4 (1 ), 73-81.
The article addresses the effectiveness of case studies, subject areas where case studies are commonly used, recent examples of their use, and case study design considerations.
Klos, D. (1976). Students as Case Writers. Teaching of Psychology, 3.2, 63-66.
This article reviews a course in which students gather data for an original case study of another person. The task requires the students to design the study, collect the data, write the narrative, and interpret the findings.
Leftwich, A. (1981). The Politics of Case Study: Problems of Innovation in University Education. Higher Education Review, 13.2, 38-64.
The article discusses the use of case studies as a teaching method. Emphasis is on the instructional materials, interdisciplinarity, and the complex relationships within the university that help or hinder the method.
Mabrito, M. (1991, Oct.). Electronic Mail as a Vehicle for Peer Response: Conversations of High and Low Apprehensive Writers. Written Communication, 509-32.
McCarthy, S., J. (1955). The Influence of Classroom Discourse on Student Texts: The Case of Ella . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
A look at how students of color become marginalized within traditional classroom discourse. The essay follows the struggles of one black student: Ella.
Matsuhashi, A., ed. (1987). Writing in Real Time: Modeling Production Processes Norwood, NJ: Ablex Publishing Corporation.
Investigates how writers plan to produce discourse for different purposes to report, to generalize, and to persuade, as well as how writers plan for sentence level units of language. To learn about planning, an observational measure of pause time was used" (ERIC).
Merriam, S. B. (1985). The Case Study in Educational Research: A Review of Selected Literature. Journal of Educational Thought, 19.3, 204-17.
The article examines the characteristics of, philosophical assumptions underlying the case study, the mechanics of conducting a case study, and the concerns about the reliability, validity, and generalizability of the method.
---. (1988). Case Study Research in Education: A Qualitative Approach San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Merry, S. E., & Milner, N. eds. (1993). The Possibility of Popular Justice: A Case Study of Community Mediation in the United States . Ann Arbor: U of Michigan.
". . . this volume presents a case study of one experiment in popular justice, the San Francisco Community Boards. This program has made an explicit claim to create an alternative justice, or new justice, in the midst of a society ordered by state law. The contributors to this volume explore the history and experience of the program and compare it to other versions of popular justice in the United States, Europe, and the Third World."
Merseth, K. K. (1991). The Case for Cases in Teacher Education. RIE. 42p. (ERIC).
This monograph argues that the case method of instruction offers unique potential for revitalizing the field of teacher education.
Michaels, S. (1987). Text and Context: A New Approach to the Study of Classroom Writing. Discourse Processes, 10, 321-346.
"This paper argues for and illustrates an approach to the study of writing that integrates ethnographic analysis of classroom interaction with linguistic analysis of written texts and teacher/student conversational exchanges. The approach is illustrated through a case study of writing in a single sixth grade classroom during a single writing assignment."
Milburn, G. (1995). Deciphering a Code or Unraveling a Riddle: A Case Study in the Application of a Humanistic Metaphor to the Reporting of Social Studies Teaching. Theory and Research in Education, 13.
This citation serves as an example of how case studies document learning procedures in a senior-level economics course.
Milley, J. E. (1979). An Investigation of Case Study as an Approach to Program Evaluation. 19th Annual Forum of the Association for Institutional Research. (Address). San Diego.
The case study method merged a narrative report focusing on the evaluator as participant-observer with document review, interview, content analysis, attitude questionnaire survey, and sociogram analysis. Milley argues that case study program evaluation has great potential for widespread use.
Minnis, J. R. (1985, Sept.). Ethnography, Case Study, Grounded Theory, and Distance Education Research. Distance Education, 6.2.
This article describes and defines the strengths and weaknesses of ethnography, case study, and grounded theory.
Nunan, D. (1992). Collaborative language learning and teaching . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Included in this series of essays is Peter Sturman’s "Team Teaching: a case study from Japan" and David Nunan’s own "Toward a collaborative approach to curriculum development: a case study."
Nystrand, M., ed. (1982). What Writers Know: The Language, Process, and Structure of Written Discourse . New York: Academic Press.
Owenby, P. H. (1992). Making Case Studies Come Alive. Training, 29, (1), 43-46. (ERIC)
This article provides tips for writing more effective case studies.
---. (1981). Pausing and Planning: The Tempo of Writer Discourse Production. Research in the Teaching of English, 15 (2),113-34.
Perl, S. (1979). The Composing Processes of Unskilled College Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 13, 317-336.
"Summarizes a study of five unskilled college writers, focusing especially on one of the five, and discusses the findings in light of current pedagogical practice and research design."
Pilcher J. and A. Coffey. eds. (1996). Gender and Qualitative Research . Brookfield: Aldershot, Hants, England.
This book provides a series of essays which look at gender identity research, qualitative research and applications of case study to questions of gendered pedagogy.
Pirie, B. S. (1993). The Case of Morty: A Four Year Study. Gifted Education International, 9 (2), 105-109.
This case study describes a boy from kindergarten through third grade with above average intelligence but difficulty in learning to read, write, and spell.
Popkewitz, T. (1993). Changing Patterns of Power: Social Regulation and Teacher Education Reform. Albany: SUNY Press.
Popkewitz edits this series of essays that address case studies on educational change and the training of teachers. The essays vary in terms of discipline and scope. Also, several authors include case studies of educational practices in countries other than the United States.
---. (1984). The Predrafting Processes of Four High- and Four Low Apprehensive Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 18, (1), 45-64.
Rasmussen, P. (1985, March) A Case Study on the Evaluation of Research at the Technical University of Denmark. International Journal of Institutional Management in Higher Education, 9 (1).
This is an example of a case study methodology used to evaluate the chemistry and chemical engineering departments at the University of Denmark.
Roth, K. J. (1986). Curriculum Materials, Teacher Talk, and Student Learning: Case Studies in Fifth-Grade Science Teaching . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
Roth offers case studies on elementary teachers, elementary school teaching, science studies and teaching, and verbal learning.
Selfe, C. L. (1985). An Apprehensive Writer Composes. When a Writer Can't Write: Studies in Writer's Block and Other Composing-Process Problems . (pp. 83-95). Ed. Mike Rose. NMY: Guilford.
Smith-Lewis, M., R. and Ford, A. (1987). A User's Perspective on Augmentative Communication. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 3, 12-7.
"During a series of in-depth interviews, a 25-yr-old woman with cerebral palsy who utilized augmentative communication reflected on the effectiveness of the devices designed for her during her school career."
St. Pierre, R., G. (1980, April). Follow Through: A Case Study in Metaevaluation Research . 64th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. (Address).
The three approaches to metaevaluation are evaluation of primary evaluations, integrative meta-analysis with combined primary evaluation results, and re-analysis of the raw data from a primary evaluation.
Stahler, T., M. (1996, Feb.) Early Field Experiences: A Model That Worked. ERIC.
"This case study of a field and theory class examines a model designed to provide meaningful field experiences for preservice teachers while remaining consistent with the instructor's beliefs about the role of teacher education in preparing teachers for the classroom."
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
This book examines case study research in education and case study methodology.
Stiegelbauer, S. (1984) Community, Context, and Co-curriculum: Situational Factors Influencing School Improvements in a Study of High Schools. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA.
Discussion of several case studies: one looking at high school environments, another examining educational innovations.
Stolovitch, H. (1990). Case Study Method. Performance And Instruction, 29, (9), 35-37.
This article describes the case study method as a form of simulation and presents guidelines for their use in professional training situations.
Thaller, E. (1994). Bibliography for the Case Method: Using Case Studies in Teacher Education. RIE. 37 p.
This bibliography presents approximately 450 citations on the use of case studies in teacher education from 1921-1993.
Thrane, T. (1986). On Delimiting the Senses of Near-Synonyms in Historical Semantics: A Case Study of Adjectives of 'Moral Sufficiency' in the Old English Andreas. Linguistics Across Historical and Geographical Boundaries: In Honor of Jacek Fisiak on the Occasion of his Fiftieth Birthday . Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
United Nations. (1975). Food and Agriculture Organization. Report on the FAO/UNFPA Seminar on Methodology, Research and Country: Case Studies on Population, Employment and Productivity . Rome: United Nations.
This example case study shows how the methodology can be used in a demographic and psychographic evaluation. At the same time, it discusses the formation and instigation of the case study methodology itself.
Van Vugt, J. P., ed. (1994). Aids Prevention and Services: Community Based Research . Westport: Bergin and Garvey.
"This volume has been five years in the making. In the process, some of the policy applications called for have met with limited success, such as free needle exchange programs in a limited number of American cities, providing condoms to prison inmates, and advertisements that depict same-sex couples. Rather than dating our chapters that deal with such subjects, such policy applications are verifications of the type of research demonstrated here. Furthermore, they indicate the critical need to continue community based research in the various communities threatened by acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome (AIDS) . . . "
Welch, W., ed. (1981, May). Case Study Methodology in Educational Evaluation. Proceedings of the Minnesota Evaluation Conference. Minnesota. (Address).
The four papers in these proceedings provide a comprehensive picture of the rationale, methodology, strengths, and limitations of case studies.
Williams, G. (1987). The Case Method: An Approach to Teaching and Learning in Educational Administration. RIE, 31p.
This paper examines the viability of the case method as a teaching and learning strategy in instructional systems geared toward the training of personnel of the administration of various aspects of educational systems.
Yin, R. K. (1993). Advancing Rigorous Methodologies: A Review of 'Towards Rigor in Reviews of Multivocal Literatures.' Review of Educational Research, 61, (3).
"R. T. Ogawa and B. Malen's article does not meet its own recommended standards for rigorous testing and presentation of its own conclusions. Use of the exploratory case study to analyze multivocal literatures is not supported, and the claim of grounded theory to analyze multivocal literatures may be stronger."
---. (1989). Case Study Research: Design and Methods. London: Sage Publications Inc.
This book discusses in great detail, the entire design process of the case study, including entire chapters on collecting evidence, analyzing evidence, composing the case study report, and designing single and multiple case studies.
Related Links
Consider the following list of related Web sites for more information on the topic of case study research. Note: although many of the links cover the general category of qualitative research, all have sections that address issues of case studies.
- Sage Publications on Qualitative Methodology: Search here for a comprehensive list of new books being published about "Qualitative Methodology" http://www.sagepub.co.uk/
- The International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education: An on-line journal "to enhance the theory and practice of qualitative research in education." On-line submissions are welcome. http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/tf/09518398.html
- Qualitative Research Resources on the Internet: From syllabi to home pages to bibliographies. All links relate somehow to qualitative research. http://www.nova.edu/ssss/QR/qualres.html
Becker, Bronwyn, Patrick Dawson, Karen Devine, Carla Hannum, Steve Hill, Jon Leydens, Debbie Matuskevich, Carol Traver, & Mike Palmquist. (2005). Case Studies. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=60
- Open access
- Published: 16 August 2022
Developing an implementation research logic model: using a multiple case study design to establish a worked exemplar
- Louise Czosnek ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2362-6888 1 ,
- Eva M. Zopf 1 , 2 ,
- Prue Cormie 3 , 4 ,
- Simon Rosenbaum 5 , 6 ,
- Justin Richards 7 &
- Nicole M. Rankin 8 , 9
Implementation Science Communications volume 3 , Article number: 90 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
8172 Accesses
3 Citations
21 Altmetric
Metrics details
Implementation science frameworks explore, interpret, and evaluate different components of the implementation process. By using a program logic approach, implementation frameworks with different purposes can be combined to detail complex interactions. The Implementation Research Logic Model (IRLM) facilitates the development of causal pathways and mechanisms that enable implementation. Critical elements of the IRLM vary across different study designs, and its applicability to synthesizing findings across settings is also under-explored. The dual purpose of this study is to develop an IRLM from an implementation research study that used case study methodology and to demonstrate the utility of the IRLM to synthesize findings across case sites.
The method used in the exemplar project and the alignment of the IRLM to case study methodology are described. Cases were purposely selected using replication logic and represent organizations that have embedded exercise in routine care for people with cancer or mental illness. Four data sources were selected: semi-structured interviews with purposely selected staff, organizational document review, observations, and a survey using the Program Sustainability Assessment Tool (PSAT). Framework analysis was used, and an IRLM was produced at each case site. Similar elements within the individual IRLM were identified, extracted, and re-produced to synthesize findings across sites and represent the generalized, cross-case findings.
The IRLM was embedded within multiple stages of the study, including data collection, analysis, and reporting transparency. Between 33-44 determinants and 36-44 implementation strategies were identified at sites that informed individual IRLMs. An example of generalized findings describing “intervention adaptability” demonstrated similarities in determinant detail and mechanisms of implementation strategies across sites. However, different strategies were applied to address similar determinants. Dependent and bi-directional relationships operated along the causal pathway that influenced implementation outcomes.
Conclusions
Case study methods help address implementation research priorities, including developing causal pathways and mechanisms. Embedding the IRLM within the case study approach provided structure and added to the transparency and replicability of the study. Identifying the similar elements across sites helped synthesize findings and give a general explanation of the implementation process. Detailing the methods provides an example for replication that can build generalizable knowledge in implementation research.
Peer Review reports
Contributions to the literature
Logic models can help understand how and why evidence-based interventions (EBIs) work to produce intended outcomes.
The implementation research logic model (IRLM) provides a method to understand causal pathways, including determinants, implementation strategies, mechanisms, and implementation outcomes.
We describe an exemplar project using a multiple case study design that embeds the IRLM at multiple stages. The exemplar explains how the IRLM helped synthesize findings across sites by identifying the common elements within the causal pathway.
By detailing the exemplar methods, we offer insights into how this approach of using the IRLM is generalizable and can be replicated in other studies.
The practice of implementation aims to get “someone…, somewhere… to do something differently” [ 1 ]. Typically, this involves changing individual behaviors and organizational processes to improve the use of evidence-based interventions (EBIs). To understand this change, implementation science applies different theories, models, and frameworks (hereafter “frameworks”) to describe and evaluate the factors and steps in the implementation process [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. Implementation science provides much-needed theoretical frameworks and a structured approach to process evaluations. One or more frameworks are often used within a program of work to investigate the different stages and elements of implementation [ 6 ]. Researchers have acknowledged that the dynamic implementation process could benefit from using logic models [ 7 ]. Logic models offer a systematic approach to combining multiple frameworks and to building causal pathways that explain the mechanisms behind individual and organizational change.
Logic models visually represent how an EBI is intended to work [ 8 ]. They link the available resources with the activities undertaken, the immediate outputs of this work, and the intermediate outcomes and longer-term impacts [ 8 , 9 ]. Through this process, causal pathways are identified. For implementation research, the causal pathway provides the interconnection between a chosen EBI, determinants, implementation strategies, and implementation outcomes [ 10 ]. Testing causal mechanisms in the research translation pathway will likely dominate the next wave of implementation research [ 11 , 12 ]. Causal mechanisms (or mechanisms of change) are the “process or event through which an implementation strategy operates to affect desired implementation outcomes” [ 13 ]. Identifying mechanisms can improve implementation strategies’ selection, prioritization, and targeting [ 12 , 13 ]. This provides an efficient and evidence-informed approach to implementation.
Implementation researchers have proposed several methods to develop and examine causal pathways [ 14 , 15 ] and mechanisms [ 16 , 17 ]. This includes formalizing the inherent relationship between frameworks via developing the Implementation Research Logic Model (IRLM) [ 7 ]. The IRLM is a logic model designed to improve the rigor and reproducibility of implementation research. It specifies the relationship between elements of implementation (determinant, strategies, and outcomes) and the mechanisms of change. To do this, it recommends linking implementation frameworks or relevant taxonomies (e.g., determinant and evaluation frameworks and implementation strategy taxonomy). The IRLM authors suggest the tool has multiple uses, including planning, executing, and reporting on the implementation process and synthesizing implementation findings across different contexts [ 7 ]. During its development, the IRLM was tested to confirm its utility in planning, executing, and reporting; however, its utility in synthesizing findings across different contexts is ongoing. Users of the tool are encouraged to consider three principles: (1) comprehensiveness in reporting determinants, implementation strategies, and implementation outcomes; (2) specifying the conceptual relationships via diagrammatic tools such as colors and arrows; and (3) detailing important elements of the study design. Further, the authors also recognize that critical elements of IRLM will vary across different study designs.
This study describes the development of an IRLM from a multiple case study design. Case study methodology can answer “how and why” questions about implementation. They enable researchers to develop a rich, in-depth understanding of a contemporary phenomenon within its natural context [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 ]. These methods can create coherence in the dynamic context in which EBIs exist [ 22 , 23 ]. Case studies are common in implementation research [ 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ], with multiple case study designs suitable for undertaking comparisons across contexts [ 31 , 32 ]. However, they are infrequently applied to establish mechanisms [ 11 ] or combine implementation elements to synthesize findings across contexts (as possible through the IRLM). Hollick and colleagues [ 33 ] undertook a comparative case study, guided by a determinant framework, to explore how context influences successful implementation. The authors contrasted determinants across sites where implementation was successful versus sites where implementation failed. The study did not extend to identifying implementation strategies or mechanisms. By contrast, van Zelm et al. [ 31 ] undertook a theory-driven evaluation of successful implementation across ten hospitals. They used joint displays to present mechanisms of change aligned with evaluation outcomes; however, they did not identify the implementation strategies within the causal pathway. Our study seeks to build on these works and explore the utility of the IRLM in synthesizing findings across sites. The dual objectives of this paper were to:
Describe how case study methods can be applied to develop an IRLM
Demonstrate the utility of the IRLM in synthesizing implementation findings across case sites.
In this section, we describe the methods used in the exemplar case study and the alignment of the IRLM to this approach. The exemplar study explored the implementation of exercise EBIs in the context of the Australian healthcare system. The exemplar study aimed to investigate the integration of exercise EBIs within routine mental illness or cancer care. The evidence base detailing the therapeutic benefits of exercise for non-communicable diseases such as cancer and mental illness are extensively documented [ 34 , 35 , 36 ] but inconsistently implemented as part of routine care [ 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 ].
Additional file 1 provides the Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR).
Case study approach
We adopted an approach to case studies based on the methods described by Yin [ 18 ]. This approach is said to have post-positivist philosophical leanings, which are typically associated with the quantitative paradigm [ 19 , 45 , 46 ]. This is evidenced by the structured, deductive approach to the methods that are described with a constant lens on objectivity, validity, and generalization [ 46 ]. Yin’s approach to case studies aligns with the IRLM for several reasons. The IRLM is designed to use established implementation frameworks. The two frameworks and one taxonomy applied in our exemplar were the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) [ 47 ], Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) [ 48 ], and Proctor et al.’s implementation outcomes framework [ 49 ]. These frameworks guided multiple aspects of our study (see Table 1 ). Commencing an implementation study with a preconceived plan based upon established frameworks is deductive [ 22 ]. Second, the IRLM has its foundation in logic modeling to develop cause and effect relationships [ 8 ]. Yin advocates using logic models to analyze case study findings [ 18 ]. They argue that developing logic models encourages researchers to iterate and consider plausible counterfactual explanations before upholding the causal pathway. Further, Yin notes that case studies are particularly valuable for explaining the transitions and context within the cause-and-effect relationship [ 18 ]. In our exemplar, the transition was the mechanism between the implementation strategy and implementation outcome. Finally, the proposed function of IRLM to synthesize findings across sites aligns with the exemplar study that used a multiple case approach. Multiple case studies aim to develop generalizable knowledge [ 18 , 50 ].
Case study selection and boundaries
A unique feature of Yin’s approach to multiple case studies is using replication logic to select cases [ 18 ]. Cases are chosen to demonstrate similarities (literal replication) or differences for anticipated reasons (theoretical replication) [ 18 ]. In the exemplar study, the cases were purposely selected using literal replication and displayed several common characteristics. First, all cases had delivered exercise EBIs within normal operations for at least 12 months. Second, each case site delivered exercise EBIs as part of routine care for a non-communicable disease (cancer or mental illness diagnosis). Finally, each site delivered the exercise EBI within the existing governance structures of the Australian healthcare system. That is, the organizations used established funding and service delivery models of the Australian healthcare system.
Using replication logic, we posited that sites would exhibit some similarities in the implementation process across contexts (literal replication). However, based on existing implementation literature [ 32 , 51 , 52 , 53 ], we expected sites to adapt the EBIs through the implementation process. The determinant analysis should explain these adaptions, which is informed by the CFIR (theoretical replication). Finally, in case study methods, clearly defining the boundaries of each case and the units of analysis, such as individual, the organization or intervention, helps focus the research. We considered each healthcare organization as a separate case. Within that, organizational-level analysis [ 18 , 54 ] and operationalizing the implementation outcomes focused inquiry (Table 1 ).
Data collection
During the study conceptualization for the exemplar, we mapped the data sources to the different elements of the IRLM (Fig. 1 ). Four primary data sources informed data collection: (1) semi-structured interviews with staff; (2) document review (such as meeting minutes, strategic plans, and consultant reports); (3) naturalistic observations; and (4) a validated survey (Program Sustainability Assessment Tool (PSAT)). A case study database was developed using Microsoft Excel to manage and organize data collection [ 18 , 54 ].
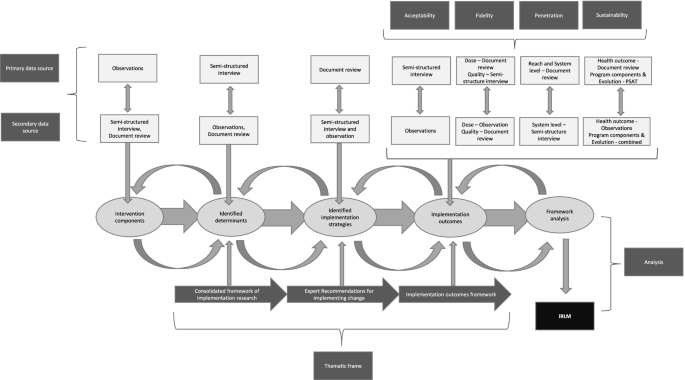
Conceptual frame for the study
Semi-structured interviews
An interview guide was developed, informed by the CFIR interview guide tool [ 55 ]. Questions were selected across the five domains of the CFIR, which aligned with the delineation of determinant domains in the IRLM. Purposeful selection was used to identify staff for the interviews [ 56 ]. Adequate sample size in qualitative studies, particularly regarding the number of interviews, is often determined when data saturation is reached [ 57 , 58 ]. Unfortunately, there is little consensus on the definition of saturation [ 59 ], how to interpret when it has occurred [ 57 ], or whether it is possible to pre-determine in qualitative studies [ 60 ]. The number of participants in this study was determined based on the staff’s differential experience with the exercise EBI and their role in the organization. This approach sought to obtain a rounded view of how the EBI operated at each site [ 23 , 61 ]. Focusing on staff experiences also aligned with the organizational lens that bounded the study. Typical roles identified for the semi-structured interviews included the health professional delivering the EBI, the program manager responsible for the EBI, an organizational executive, referral sources, and other health professionals (e.g., nurses, allied health). Between five and ten interviews were conducted at each site. Interview times ranged from 16 to 72 min, most lasting around 40 min per participant.
Document review
A checklist informed by case study literature was developed outlining the typical documents the research team was seeking [ 18 ]. The types of documents sought to review included job descriptions, strategic plans/planning documents, operating procedures and organizational policies, communications (e.g., website, media releases, email, meeting minutes), annual reports, administrative databases/files, evaluation reports, third party consultant reports, and routinely collected numerical data that measured implementation outcomes [ 27 ]. As each document was identified, it was numbered, dated, and recorded in the case study database with a short description of the content related to the research aims and the corresponding IRLM construct. Between 24 and 33 documents were accessed at each site. A total of 116 documents were reviewed across the case sites.
Naturalistic observations
The onsite observations occurred over 1 week, wherein typical organizational operations were viewed. The research team interacted with staff, asked questions, and sought clarification of what was being observed; however, they did not disrupt the usual work routines. Observations allowed us to understand how the exercise EBI operated and contrast that with documented processes and procedures. They also provided the opportunity to observe non-verbal cues and interactions between staff. While onsite, case notes were recorded directly into the case study database [ 62 , 63 ]. Between 15 and 40 h were spent on observations per site. A total of 95 h was spent across sites on direct observations.
Program sustainability assessment tool (survey)
The PSAT is a planning and evaluation tool that assesses the sustainability of an intervention across eight domains [ 64 , 65 , 66 ]: (1) environmental support, (2) funding stability, (3) partnerships, (4) organizational capacity, (5) program evaluation, (6) program adaption, (7) communication, and (8) strategic planning [ 64 , 65 ]. The PSAT was administered to a subset of at least three participants per site who completed the semi-structured interview. The results were then pooled to provide an organization-wide view of EBI sustainability. Three participants per case site are consistent with previous studies that have used the tool [ 67 , 68 ] and recommendations for appropriate use [ 65 , 69 ].
We included a validated measure of sustainability, recognizing calls to improve understanding of this aspect of implementation [ 70 , 71 , 72 ]. Noting the limited number of measurement tools for evaluating sustainability [ 73 ], the PSAT’s characteristics displayed the best alignment with the study aims. To determine “best alignment,” we deferred to a study by Lennox and colleagues that helps researchers select suitable measurement tools based on the conceptualization of sustainability in the study [ 71 ]. The PSAT provides a multi-level view of sustainability. It is a measurement tool that can be triangulated with other implementation frameworks, such as the CFIR [ 74 ], to interrogate better and understand the later stages of implementation. Further, the tool provides a contemporary account of an EBIs capacity for sustainability [ 75 ]. This is consistent with case study methods, which explore complex, contemporary, real-life phenomena.
The voluminous data collection that is possible through case studies, and is often viewed as a challenge of the method [ 19 ], was advantageous to developing the IRLM in the exemplar and identifying the causal pathways. First, it aided three types of triangulation through the study (method, theory, and data source triangulation) [ 76 ]. Method triangulation involved collecting evidence via four methods: interview, observations, document review, and survey. Theoretical triangulation involved applying two frameworks and one taxonomy to understand and interpret the findings. Data source triangulation involved selecting participants with different roles within the organization to gain multiple perspectives about the phenomena being studied. Second, data collection facilitated depth and nuance in detailing determinants and implementation strategies. For the determinant analysis, this illuminated the subtleties within context and improved confidence and accuracy for prioritizing determinants. As case studies are essentially “naturalistic” studies, they provide insight into strategies that are implementable in pragmatic settings. Finally, the design’s flexibility enabled the integration of a survey and routinely collected numerical data as evaluation measures for implementation outcomes. This allowed us to contrast “numbers” against participants’ subjective experience of implementation [ 77 ].
Data analysis
Descriptive statistics were calculated for the PSAT and combined with the three other data sources wherein framework analysis [ 78 , 79 ] was used to analyze the data. Framework analysis includes five main phases: familiarization, identifying a thematic framework, indexing, charting, and mapping and interpretation [ 78 ]. Familiarization occurred concurrently with data collection, and the thematic frame was aligned to the two frameworks and one taxonomy we applied to the IRLM. To index and chart the data, the raw data was uploaded into NVivo 12 [ 80 ]. Codes were established to guide indexing that aligned with the thematic frame. That is, determinants within the CFIR [ 47 ], implementation strategies listed in ERIC [ 48 ], and the implementation outcomes [ 49 ] of acceptability, fidelity, penetration, and sustainability were used as codes in NVivo 12. This process produced a framework matrix that summarized the information housed under each code at each case site.
The final step of framework analysis involves mapping and interpreting the data. We used the IRLM to map and interpret the data in the exemplar. First, we identified the core elements of the implemented exercise EBI. Next, we applied the CFIR valance and strength coding to prioritize the contextual determinants. Then, we identified the implementation strategies used to address the contextual determinants. Finally, we provided a rationale (a causal mechanism) for how these strategies worked to address barriers and contribute to specific implementation outcomes. The systematic approach advocated by the IRLM provided a transparent representation of the causal pathway underpinning the implementation of the exercise EBIs. This process was followed at each case site to produce an IRLM for each organization. To compare, contrast, and synthesize findings across sites, we identified the similarities and differences in the individual IRLMs and then developed an IRLM that explained a generalized process for implementation. Through the development of the causal pathway and mechanisms, we deferred to existing literature seeking to establish these relationships [ 81 , 82 , 83 ]. Aligned with case study methods, this facilitated an iterative process of constant comparison and challenging the proposed causal relationships. Smith and colleagues advise that the IRLM “might be viewed as a somewhat simplified format,” and users are encouraged to “iterate on the design of the IRLM to increase its utility” [ 7 ]. Thus, we re-designed the IRLM within a traditional logic model structure to help make sense of the data collected through the case studies. Figure 1 depicts the conceptual frame for the study and provides a graphical representation of how the IRLM pathway was produced.
The results are presented with reference to the three principles of the IRLM: comprehensiveness, indicating the key conceptual relationship and specifying critical study design . The case study method allowed for comprehensiveness through the data collection and analysis described above. The mean number of data sources informing the analysis and development of the causal pathway at each case site was 63.75 (interviews ( M = 7), observational hours ( M =23.75), PSAT ( M =4), and document review ( M = 29). This resulted in more than 30 determinants and a similar number of implementation strategies identified at each site (determinant range per site = 33–44; implementation strategy range per site = 36–44). Developing a framework matrix meant that each determinant (prioritized and other), implementation strategy, and implementation outcome were captured. The matrix provided a direct link to the data sources that informed the content within each construct. An example from each construct was collated alongside the summary to evidence the findings.
The key conceptual relationship was articulated in a traditional linear process by aligning determinant → implementation strategy → mechanism → implementation outcome, as per the IRLM. To synthesize findings across sites, we compared and contrasted the results within each of the individual IRLM and extracted similar elements to develop a generalized IRLM that represents cross-case findings. By redeveloping the IRLM within a traditional logic model structure, we added visual representations of the bi-directional and dependent relationships, illuminating the dynamism within the implementation process. To illustrate, intervention adaptability was a prioritized determinant and enabler across sites. Healthcare providers recognized that adapting and tailoring exercise EBIs increased “fit” with consumer needs. This also extended to adapting how healthcare providers referred consumers to exercise so that it was easy in the context of their other work priorities. Successful adaption was contingent upon a qualified workforce with the required skills and competencies to enact change. Different implementation strategies were used to make adaptions across sites, such as promoting adaptability and using data experts. However, despite the different strategies, successful adaptation created positive bi-directional relationships. That is, healthcare providers’ confidence and trust in the EBI grew as consumer engagement increased and clinical improvements were observed. This triggered greater engagement with the EBI (e.g., acceptability → penetration → sustainability), albeit the degree of engagement differed across sites. Figure 2 illustrates this relationship within the IRLM and provides a contrasting relationship by highlighting how a prioritized barrier across sites (available resources) was addressed.
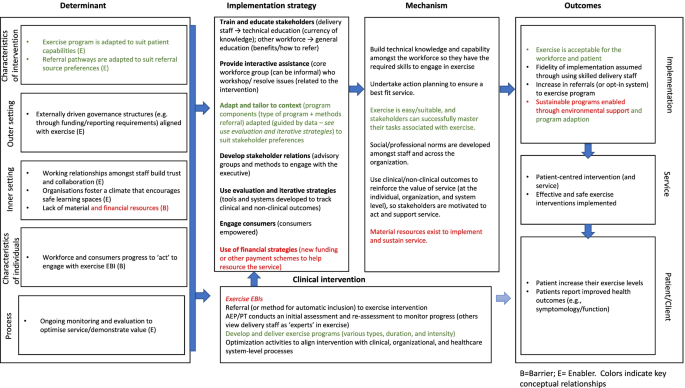
Example of intervention adaptability (E) contrasted with available resources (B) within a synthesised IRLM across case sites
The final principle is to specify critical study design , wherein we have described how case study methodology was used to develop the IRLM exemplar. Our intention was to produce an explanatory causal pathway for the implementation process. The implementation outcomes of acceptability and fidelity were measured at the level of the provider, and penetration and sustainability were measured at the organizational level [ 49 ]. Service level and clinical level outcomes were not identified for a priori measurement throughout the study. We did identify evidence of clinical outcomes that supported our overall findings via the document review. Historical evaluations on the service indicated patients increased their exercise level or demonstrated a change in symptomology/function. The implementation strategies specified in the study were those chosen by the organizations. We did not attempt to augment routine practice or change implementation outcomes by introducing new strategies. The barriers across sites were represented with a (B) symbol and enablers with an (E) symbol in the IRLM. In the individual IRLM, consistent determinants and strategies were highlighted (via bolding) to support extraction. Finally, within the generalized IRLM, the implementation strategies are grouped according to the ERIC taxonomy category. This accounts for the different strategies applied to achieve similar outcomes across case studies.
This study provides a comprehensive overview that uses case study methodology to develop an IRLM in an implementation research project. Using an exemplar that examines implementation in different healthcare settings, we illustrate how the IRLM (that documents the causal pathways and mechanisms) was developed and enabled the synthesis of findings across sites.
Case study methodologies are fraught with inconsistencies in terminology and approach. We adopted the method described by Yin. Its guiding paradigm, which is rooted in objectivity, means it can be viewed as less flexible than other approaches [ 46 , 84 ]. We found the approach offered sufficient flexibility within the frame of a defined process. We argue that the defined process adds to the rigor and reproducibility of the study, which is consistent with the principles of implementation science. That is, accessing multiple sources of evidence, applying replication logic to select cases, maintaining a case study database, and developing logic models to establish causal pathways, demonstrates the reliability and validity of the study. The method was flexible enough to embed the IRLM within multiple phases of the study design, including conceptualization, philosophical alignment, and analysis. Paparini and colleagues [ 85 ] are developing guidance that recognizes the challenges and unmet value of case study methods for implementation research. This work, supported by the UK Medical Research Council, aims to enhance the conceptualization, application, analysis, and reporting of case studies. This should encourage and support researchers to use case study methods in implementation research with increased confidence.
The IRLM produced a relatively linear depiction of the relationship between context, strategies, and outcomes in our exemplar. However, as noted by the authors of the IRLM, the implementation process is rarely linear. If the tool is applied too rigidly, it may inadvertently depict an overly simplistic view of a complex process. To address this, we redeveloped the IRLM within a traditional logic model structure, adding visual representations of the dependent and bidirectional relationships evident within the general IRLM pathway [ 86 ]. Further, developing a general IRLM of cross-case findings that synthesized results involved a more inductive approach to identifying and extracting similar elements. It required the research team to consider broader patterns in the data before offering a prospective account of the implementation process. This was in contrast to the earlier analysis phases that directly mapped determinants and strategies to the CFIR and ERIC taxonomy. We argue that extracting similar elements is analogous to approaches that have variously been described as portable elements [ 87 ], common elements [ 88 ], or generalization by mechanism [ 89 ]. While defined and approached slightly differently, these approaches aim to identify elements frequently shared across effective EBIs and thus can form the basis of future EBIs to increase their utility, efficiency, and effectiveness [ 88 ]. We identified similarities related to determinant detail and mechanism of different implementation strategies across sites. This finding supports the view that many implementation strategies could be suitable, and selecting the “right mix” is challenging [ 16 ]. Identifying common mechanisms, such as increased motivation, skill acquisition, or optimizing workflow, enabled elucidation of the important functions of strategies. This can help inform the selection of appropriate strategies in future implementation efforts.
Finally, by developing individual IRLMs and then re-producing a general IRLM, we synthesized findings across sites and offered generalized findings. The ability to generalize from case studies is debated [ 89 , 90 ], with some considering the concept a fallacy [ 91 ]. That is, the purpose of qualitative research is to develop a richness through data that is situated within a unique context. Trying to extrapolate from findings is at odds with exploring unique context. We suggest the method described herein and the application of IRLM could be best applied to a form of generalization called ‘transferability’ [ 91 , 92 ]. This suggests that findings from one study can be transferred to another setting or population group. In this approach, the new site takes the information supplied and determines those aspects that would fit with their unique environment. We argue that elucidating the implementation process across multiple sites improves the confidence with which certain “elements” could be applied to future implementation efforts. For example, our approach may also be helpful for multi-site implementation studies that use methods other than case studies. Developing a general IRLM through study conceptualization could identify consistencies in baseline implementation status across sites. Multi-site implementation projects may seek to introduce and empirically test implementation strategies, such as via a cluster randomized controlled trial [ 93 ]. Within this study design, baseline comparison between control and intervention sites might extend to a comparison of organizational type, location and size, and individual characteristics, but not the chosen implementation strategies [ 94 ]. Applying the approach described within our study could enhance our understanding of how to support effective implementation.
Limitations
After the research team conceived this study, the authors of the PSAT validated another tool for use in clinical settings (Clinical Sustainability Assessment Tool (CSAT)) [ 95 ]. This tool appears to align better with our study design due to its explicit focus on maintaining structured clinical care practices. The use of multiple data sources and consistency in some elements across the PSAT and CSAT should minimize the limitations in using the PSAT survey tool. At most case sites, limited staff were involved in developing and implementing exercise EBI. Participants who self-selected for interviews may be more invested in assuring positive outcomes for the exercise EBI. Inviting participants from various roles was intended to reduce selection bias. Finally, we recognize recent correspondence suggesting the IRLM misses a critical step in the causal pathway. That is the mechanism between determinant and selection of an appropriate implementation strategy [ 96 ]. Similarly, Lewis and colleagues note that additional elements, including pre-conditions, moderators, and mediators (distal and proximal), exist within the causal pathway [ 13 ]. Through the iterative process of developing the IRLM, decisions were made about the determinant → implementation strategy relationship; however, this is not captured in the IRLM. Secondary analysis of the case study data would allow elucidation of these relationships, as this information can be extracted through the case study database. This was outside the scope of the exemplar study.
Developing an IRLM via case study methods proved useful in identifying causal pathways and mechanisms. The IRLM can complement and enhance the study design by providing a consistent and structured approach. In detailing our approach, we offer an example of how multiple case study designs that embed the IRLM can aid the synthesis of findings across sites. It also provides a method that can be replicated in future studies. Such transparency adds to the quality, reliability, and validity of implementation research.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author [LC]. The data are not publicly available due to them containing information that could compromise research participant privacy.
Presseau J, McCleary N, Lorencatto F, Patey AM, Grimshaw JM, Francis JJ. Action, actor, context, target, time (AACTT): a framework for specifying behaviour. Implement Sci. 2019;14(1):102.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Damschroder LJ. Clarity out of chaos: use of theory in implementation research. Psychiatry Res. 2020;283(112461).
Bauer M, Damschroder L, Hagedorn H, Smith J, Kilbourne A. An introduction to implementation science for the non-specialist. BMC Psychol. 2015;3(1):32.
Nilsen P. Making sense of implementation theories, models and frameworks. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):53.
Lynch EA, Mudge A, Knowles S, Kitson AL, Hunter SC, Harvey G. “There is nothing so practical as a good theory”: a pragmatic guide for selecting theoretical approaches for implementation projects. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):857.
Birken SA, Powell BJ, Presseau J, Kirk MA, Lorencatto F, Gould NJ, et al. Combined use of the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) and the Theoretical Domains Framework (TDF): a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):2.
Smith JD, Li DH, Rafferty MR. The Implementation Research Logic Model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):84.
Kellogg WK. Foundation. Logic model development guide. Michigan, USA; 2004.
McLaughlin JA, Jordan GB. Logic models: a tool for telling your programs performance story. Eval Prog Plann. 1999;22(1):65–72.
Article Google Scholar
Anselmi L, Binyaruka P, Borghi J. Understanding causal pathways within health systems policy evaluation through mediation analysis: an application to payment for performance (P4P) in Tanzania. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):10.
Lewis C, Boyd M, Walsh-Bailey C, Lyon A, Beidas R, Mittman B, et al. A systematic review of empirical studies examining mechanisms of implementation in health. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):21.
Powell BJ, Fernandez ME, Williams NJ, Aarons GA, Beidas RS, Lewis CC, et al. Enhancing the impact of implementation strategies in healthcare: a research agenda. Front Public Health. 2019;7(3).
Lewis CC, Klasnja P, Powell BJ, Lyon AR, Tuzzio L, Jones S, Walsh-Bailey C and Weiner B. From classification to causality: advancing understanding of mechanisms of change in implementation science. Front Public Health. 2018;6(136).
Bartholomew L, Parcel G, Kok G. Intervention mapping: a process for developing theory and evidence-based health education programs. Health Educ Behav. 1998;25(5):545–63.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Weiner BJ, Lewis MA, Clauser SB, Stitzenberg KB. In search of synergy: strategies for combining interventions at multiple levels. JNCI Monographs. 2012;2012(44):34–41.
Powell BJ, Beidas RS, Lewis CC, Aarons GA, McMillen J, Proctor EK, et al. Methods to improve the selection and tailoring of implementation strategies. J Behav Health Serv Res. 2017;44(2):177–94.
Fernandez ME, ten Hoor GA, van Lieshout S, Rodriguez SA, Beidas RS, Parcel G, Ruiter R, Markham C and Kok G. Implementation mapping: using intervention mapping to develop implementation strategies. Frontiers. Public Health. 2019;7(158).
Yin R. Case study research and applications design and methods. 6th Edition ed. United States of America: Sage Publications; 2018.
Google Scholar
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11:100.
Stake R. The art of case study reseach. United States of America: Sage Publications; 2005.
Thomas G. How to do your case study. 2nd Edition ed. London: Sage Publications; 2016.
Ramanadhan S, Revette AC, Lee RM and Aveling E. Pragmatic approaches to analyzing qualitative data for implementation science: an introduction. Implement Sci Commun. 2021;2(70).
National Cancer Institute. Qualitative methods in implementation science United States of America: National Institutes of Health Services; 2018.
Mathers J, Taylor R, Parry J. The challenge of implementing peer-led interventions in a professionalized health service: a case study of the national health trainers service in England. Milbank Q. 2014;92(4):725–53.
Powell BJ, Proctor EK, Glisson CA, Kohl PL, Raghavan R, Brownson RC, et al. A mixed methods multiple case study of implementation as usual in children’s social service organizations: study protocol. Implement Sci. 2013;8(1):92.
van de Glind IM, Heinen MM, Evers AW, Wensing M, van Achterberg T. Factors influencing the implementation of a lifestyle counseling program in patients with venous leg ulcers: a multiple case study. Implement Sci. 2012;7(1):104.
Greenhalgh T, Macfarlane F, Barton-Sweeney C, Woodard F. “If we build it, will it stay?” A case study of the sustainability of whole-system change in London. Milbank Q. 2012;90(3):516–47.
Urquhart R, Kendell C, Geldenhuys L, Ross A, Rajaraman M, Folkes A, et al. The role of scientific evidence in decisions to adopt complex innovations in cancer care settings: a multiple case study in Nova Scotia, Canada. Implement Sci. 2019;14(1):14.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Herinckx H, Kerlinger A, Cellarius K. Statewide implementation of high-fidelity recovery-oriented ACT: A case study. Implement Res Pract. 2021;2:2633489521994938.
Young AM, Hickman I, Campbell K, Wilkinson SA. Implementation science for dietitians: The ‘what, why and how’ using multiple case studies. Nutr Diet. 2021;78(3):276–85.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
van Zelm R, Coeckelberghs E, Sermeus W, Wolthuis A, Bruyneel L, Panella M, et al. A mixed methods multiple case study to evaluate the implementation of a care pathway for colorectal cancer surgery using extended normalization process theory. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):11.
Albers B, Shlonsky A, Mildon R. Implementation Science 3.0. Switzerland: Springer; 2020.
Book Google Scholar
Hollick RJ, Black AJ, Reid DM, McKee L. Shaping innovation and coordination of healthcare delivery across boundaries and borders. J Health Organ Manag. 2019;33(7/8):849–68.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pedersen B, Saltin B. Exercise as medicine – evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25:1–72.
Firth J, Siddiqi N, Koyanagi A, Siskind D, Rosenbaum S, Galletly C, et al. The Lancet Psychiatry Commission: a blueprint for protecting physical health in people with mental illness. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019;6(8):675–712.
Campbell K, Winters-Stone K, Wisekemann J, May A, Schwartz A, Courneya K, et al. Exercise guidelines for cancer survivors: consensus statement from international multidisciplinary roundtable. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(11):2375–90.
Deenik J, Czosnek L, Teasdale SB, Stubbs B, Firth J, Schuch FB, et al. From impact factors to real impact: translating evidence on lifestyle interventions into routine mental health care. Transl Behav Med. 2020;10(4):1070–3.
Suetani S, Rosenbaum S, Scott JG, Curtis J, Ward PB. Bridging the gap: What have we done and what more can we do to reduce the burden of avoidable death in people with psychotic illness? Epidemiol Psychiatric Sci. 2016;25(3):205–10.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Stanton R, Rosenbaum S, Kalucy M, Reaburn P, Happell B. A call to action: exercise as treatment for patients with mental illness. Aust J Primary Health. 2015;21(2):120–5.
Rosenbaum S, Hobson-Powell A, Davison K, Stanton R, Craft LL, Duncan M, et al. The role of sport, exercise, and physical activity in closing the life expectancy gap for people with mental illness: an international consensus statement by Exercise and Sports Science Australia, American College of Sports Medicine, British Association of Sport and Exercise Science, and Sport and Exercise Science New Zealand. Transll J Am Coll Sports Med. 2018;3(10):72–3.
Chambers D, Vinson C, Norton W. Advancing the science of implementation across the cancer continuum. United States of America: Oxford University Press Inc; 2018.
Schmitz K, Campbell A, Stuiver M, Pinto B, Schwartz A, Morris G, et al. Exercise is medicine in oncology: engaging clinicians to help patients move through cancer. Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(6):468–84.
Santa Mina D, Alibhai S, Matthew A, Guglietti C, Steele J, Trachtenberg J, et al. Exercise in clinical cancer care: a call to action and program development description. Curr Oncol. 2012;19(3):9.
Czosnek L, Rankin N, Zopf E, Richards J, Rosenbaum S, Cormie P. Implementing exercise in healthcare settings: the potential of implementation science. Sports Med. 2020;50(1):1–14.
Harrison H, Birks M, Franklin R, Mills J. Case study research: foundations and methodological orientations. Forum: Qualitative. Soc Res. 2017;18(1).
Yazan B. Three approaches to case study methods in education: Yin, Merriam, and Stake. Qual Rep. 2015;20(2):134–52.
Damschroder L, Aaron D, Keith R, Kirsh S, Alexander J, Lowery J. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4:50.
Powell BJ, Waltz TJ, Chinman MJ, Damschroder LJ, Smith JL, Matthieu MM, et al. A refined compilation of implementation strategies: results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) project. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):21.
Proctor E, Silmere H, Raghavan R, Hovmand P, Aarons G, Bunger A, et al. Outcomes for implementation research: conceptual distinctions, measurement challenges, and research agenda. Admin Pol Ment Health. 2011;38(2):65–76.
Heale R, Twycross A. What is a case study? Evid Based Nurs. 2018;21(1):7–8.
Brownson R, Colditz G, Proctor E. Dissemination and implementation research in health: translating science to practice. Second ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2017.
Quiñones MM, Lombard-Newell J, Sharp D, Way V, Cross W. Case study of an adaptation and implementation of a Diabetes Prevention Program for individuals with serious mental illness. Transl Behav Med. 2018;8(2):195–203.
Wiltsey Stirman S, Baumann AA, Miller CJ. The FRAME: an expanded framework for reporting adaptations and modifications to evidence-based interventions. Implement Sci. 2019;14(1):58.
Baxter P, Jack S. Qualitative case study methodology: study design and implementation for novice researchers. Qual Rep. 2008;13(4):544–59.
Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research 2018. Available from: http://www.cfirguide.org/index.html . Cited 2018 14 February.
Palinkas LA, Horwitz SM, Green CA, Wisdom JP, Duan N, Hoagwood K. Purposeful sampling for qualitative data collection and analysis in mixed method implementation research. Admin Pol Ment Health. 2015;42(5):533–44.
Francis JJ, Johnston M, Robertson C, Glidewell L, Entwistle V, Eccles MP, et al. What is an adequate sample size? Operationalising data saturation for theory-based interview studies. Psychol Health. 2010;25(10):1229–45.
Teddlie C, Yu F. Mixed methods sampling: a typology with examples. J Mixed Methods Res. 2007;1(1):77–100.
Saunders B, Sim J, Kingstone T, Baker S, Waterfield J, Bartlam B, et al. Saturation in qualitative research: exploring its conceptualization and operationalization. Qual Quant. 2018;52(4):1893–907.
Braun V, Clarke V. To saturate or not to saturate? Questioning data saturation as a useful concept for thematic analysis and sample-size rationales. Qual Res Sport Exerc Health. 2021;13(2):201–16.
Burau V, Carstensen K, Fredens M, Kousgaard MB. Exploring drivers and challenges in implementation of health promotion in community mental health services: a qualitative multi-site case study using Normalization Process Theory. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):36.
Phillippi J, Lauderdale J. A guide to field notes for qualitative research: context and conversation. Qual Health Res. 2018;28(3):381–8.
Mulhall A. In the field: notes on observation in qualitative research. J Adv Nurs. 2003;41(3):306–13.
Schell SF, Luke DA, Schooley MW, Elliott MB, Herbers SH, Mueller NB, et al. Public health program capacity for sustainability: a new framework. Implement Sci. 2013;8(1):15.
Washington University. The Program Sustainability Assessment Tool St Louis: Washington University; 2018. Available from: https://sustaintool.org/ . Cited 2018 14 February.
Luke DA, Calhoun A, Robichaux CB, Elliott MB, Moreland-Russell S. The Program Sustainability Assessment Tool: a new instrument for public health programs. Prev Chronic Dis. 2014;11:E12.
Stoll S, Janevic M, Lara M, Ramos-Valencia G, Stephens TB, Persky V, et al. A mixed-method application of the Program Sustainability Assessment Tool to evaluate the sustainability of 4 pediatric asthma care coordination programs. Prev Chronic Dis. 2015;12:E214.
Kelly C, Scharff D, LaRose J, Dougherty NL, Hessel AS, Brownson RC. A tool for rating chronic disease prevention and public health interventions. Prev Chronic Dis. 2013;10:E206.
Calhoun A, Mainor A, Moreland-Russell S, Maier RC, Brossart L, Luke DA. Using the Program Sustainability Assessment Tool to assess and plan for sustainability. Prev Chronic Dis. 2014;11:E11.
Proctor E, Luke D, Calhoun A, McMillen C, Brownson R, McCrary S, et al. Sustainability of evidence-based healthcare: research agenda, methodological advances, and infrastructure support. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):88.
Lennox L, Maher L, Reed J. Navigating the sustainability landscape: a systematic review of sustainability approaches in healthcare. Implement Sci. 2018;13(1):27.
Moore JE, Mascarenhas A, Bain J, Straus SE. Developing a comprehensive definition of sustainability. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):110.
Lewis CC, Fischer S, Weiner BJ, Stanick C, Kim M, Martinez RG. Outcomes for implementation science: an enhanced systematic review of instruments using evidence-based rating criteria. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):155.
Shelton RC, Chambers DA, Glasgow RE. An extension of RE-AIM to enhance sustainability: addressing dynamic context and promoting health equity over time. Front Public Health. 2020;8(134).
Moullin JC, Sklar M, Green A, Dickson KS, Stadnick NA, Reeder K, et al. Advancing the pragmatic measurement of sustainment: a narrative review of measures. Implement Sci Commun. 2020;1(1):76.
Denzin N. The research act: A theoretical introduction to sociological methods. New Jersey: Transaction Publishers; 1970.
Grant BM, Giddings LS. Making sense of methodologies: a paradigm framework for the novice researcher. Contemp Nurse. 2002;13(1):10–28.
Gale NK, Heath G, Cameron E, Rashid S, Redwood S. Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13(1):117.
Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N. Qualitative research in health care. Analysing qualitative data. BMJ. 2000;320(7227):114–6.
QSR International. NVivo 11 Pro for Windows 2018. Available from: https://www.qsrinternational.com/nvivo-qualitative-data-analysissoftware/home .
Waltz TJ, Powell BJ, Fernández ME, Abadie B, Damschroder LJ. Choosing implementation strategies to address contextual barriers: diversity in recommendations and future directions. Implement Sci. 2019;14(1):42.
Michie S, Johnston M, Rothman AJ, de Bruin M, Kelly MP, Carey RN, et al. Developing an evidence-based online method of linking behaviour change techniques and theoretical mechanisms of action: a multiple methods study. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals. Library. 2021;9:1.
Michie S, Johnston M, Abraham C, Lawton R, Parker D, Walker A. Making psychological theory useful for implementing evidence based practice: a consensus approach. Qual Saf Health Care. 2005;14(1):26–33.
Ebneyamini S, Sadeghi Moghadam MR. Toward developing a framework for conducting case study research. Int J Qual Methods. 2018;17(1):1609406918817954.
Paparini S, Green J, Papoutsi C, Murdoch J, Petticrew M, Greenhalgh T, et al. Case study research for better evaluations of complex interventions: rationale and challenges. BMC Med. 2020;18(1):301.
Sarkies M, Long JC, Pomare C, Wu W, Clay-Williams R, Nguyen HM, et al. Avoiding unnecessary hospitalisation for patients with chronic conditions: a systematic review of implementation determinants for hospital avoidance programmes. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):91.
Koorts H, Cassar S, Salmon J, Lawrence M, Salmon P, Dorling H. Mechanisms of scaling up: combining a realist perspective and systems analysis to understand successfully scaled interventions. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2021;18(1):42.
Engell T, Kirkøen B, Hammerstrøm KT, Kornør H, Ludvigsen KH, Hagen KA. Common elements of practice, process and implementation in out-of-school-time academic interventions for at-risk children: a systematic review. Prev Sci. 2020;21(4):545–56.
Bengtsson B, Hertting N. Generalization by mechanism: thin rationality and ideal-type analysis in case study research. Philos Soc Sci. 2014;44(6):707–32.
Tsang EWK. Generalizing from research findings: the merits of case studies. Int J Manag Rev. 2014;16(4):369–83.
Polit DF, Beck CT. Generalization in quantitative and qualitative research: myths and strategies. Int J Nurs Stud. 2010;47(11):1451–8.
Adler C, Hirsch Hadorn G, Breu T, Wiesmann U, Pohl C. Conceptualizing the transfer of knowledge across cases in transdisciplinary research. Sustain Sci. 2018;13(1):179–90.
Wolfenden L, Foy R, Presseau J, Grimshaw JM, Ivers NM, Powell BJ, et al. Designing and undertaking randomised implementation trials: guide for researchers. BMJ. 2021;372:m3721.
Nathan N, Hall A, McCarthy N, Sutherland R, Wiggers J, Bauman AE, et al. Multi-strategy intervention increases school implementation and maintenance of a mandatory physical activity policy: outcomes of a cluster randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med. 2022;56(7):385–93.
Malone S, Prewitt K, Hackett R, Lin JC, McKay V, Walsh-Bailey C, et al. The Clinical Sustainability Assessment Tool: measuring organizational capacity to promote sustainability in healthcare. Implement Sci Commun. 2021;2(1):77.
Sales AE, Barnaby DP, Rentes VC. Letter to the editor on “the implementation research logic model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects” (Smith JD, Li DH, Rafferty MR. the implementation research logic model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects. Implement Sci. 2020;15 (1):84. Doi:10.1186/s13012-020-01041-8). Implement Sci. 2021;16(1):97.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the healthcare organizations and staff who supported the study.
SR is funded by an NHMRC Early Career Fellowship (APP1123336). The funding body had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, interpretation, or manuscript development.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Mary MacKillop Institute for Health Research, Australian Catholic University, Melbourne, Australia
Louise Czosnek & Eva M. Zopf
Cabrini Cancer Institute, The Szalmuk Family Department of Medical Oncology, Cabrini Health, Melbourne, Australia
Eva M. Zopf
Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, Australia
Prue Cormie
Sir Peter MacCallum Department of Oncology, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
Discipline of Psychiatry and Mental Health, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
Simon Rosenbaum
School of Health Sciences, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
Faculty of Health, Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand
Justin Richards
Faculty of Medicine and Health, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
Nicole M. Rankin
Faculty of Medicine, Dentistry and Health Sciences, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LC, EZ, SR, JR, PC, and NR contributed to the conceptualization of the study. LC undertook the data collection, and LC, EZ, SR, JR, PC, and NR supported the analysis. The first draft of the manuscript was written by LC with NR and EZ providing first review. LC, EZ, SR, JR, PC, and NR commented on previous versions of the manuscript and provided critical review. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Louise Czosnek .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study is approved by Sydney Local Health District Human Research Ethics Committee - Concord Repatriation General Hospital (2019/ETH11806). Ethical approval is also supplied by Australian Catholic University (2018-279E), Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre (19/175), North Sydney Local Health District - Macquarie Hospital (2019/STE14595), and Alfred Health (516-19).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
PC is the recipient of a Victorian Government Mid-Career Research Fellowship through the Victorian Cancer Agency. PC is the Founder and Director of EX-MED Cancer Ltd, a not-for-profit organization that provides exercise medicine services to people with cancer. PC is the Director of Exercise Oncology EDU Pty Ltd, a company that provides fee for service training courses to upskill exercise professionals in delivering exercise to people with cancer.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Czosnek, L., Zopf, E.M., Cormie, P. et al. Developing an implementation research logic model: using a multiple case study design to establish a worked exemplar. Implement Sci Commun 3 , 90 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43058-022-00337-8
Download citation
Received : 19 March 2022
Accepted : 01 August 2022
Published : 16 August 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43058-022-00337-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Logic model
- Case study methods
- Causal pathways
- Causal mechanisms
Implementation Science Communications
ISSN: 2662-2211
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Advertisement
A case study on learning basic logical competencies when utilising technologies and real-world objects
- Open access
- Published: 12 July 2020
- Volume 26 , pages 639–653, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Robert Weinhandl ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5525-6404 1 ,
- Tony Houghton 1 &
- Zsolt Lavicza 1
2123 Accesses
Explore all metrics
In our technological age, many technologies and real-world objects communicate with each other or partly merge. However, this combination of technologies and real-world objects has not yet found its way into everyday teaching practices in schools to any great extent. To investigate the possibilities of combining technologies and real-world objects in mathematics classes, we conducted an exploratory educational study with 47 students. Analysing students’ data using the principles of grounded theory demonstrated that for students in our study (A) using open tasks with multiple solutions, (B) immediate feedback and (C) novelty effects in the learning process, are essential to design mathematics learning environments with combining technologies and real-world objects when learning basic logical operations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Decolonising technological pedagogical content knowledge of first year mathematics students

Students’ Feedback into Enriching Learning Experiences for Design of Smart Devices and Applications

Designing Technology-Based Tasks for Enhancing Mathematical Understanding Through Problem Solving
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
New technologies have been having a significant impact on society in recent years. As schools and educational institutions are part of society, new technologies also have a significant impact on teaching and learning in schools, but this often happens some years later than in other fields such as business or science (Samuelsson 2006 ). Currently, we are experiencing not only the proliferation of digital technologies, but also their combination and communicating with everyday objects. Combining digital technologies, learning and real-world objects can be found slowly growing also in mathematics lessons. In their studies, Borba et al. ( 2016 ) and Pierce and Stacey ( 2011 ) summarise that using modern technologies in mathematics learning could facilitate students in mathematising real-world problems. Most combinations of digital technologies, mathematics learning and real-world objects often focus on geometry.
In our educational case study, we explored how the combination of selected technologies and real-world objects could be linked to promote mathematics learning beyond geometry. To investigate how real-world objects and technologies could be linked to enhance mathematics learning beyond geometry, we decided to use Logifaces (real-world objects) and MS Excel (technology) to learn logical operations.

2 Theoretical background
Pseudo-realistic problems are those tasks which simplify real-world phenomena for teaching and learning purposes. Carreira and Baioa ( 2018 ) summarise that pseudo-realistic problems should often trigger mathematics learning. However, pseudo-realistic problems might reduce and simplify real-world situations too much, resulting in students not using their knowledge of the real-world when learning. For this reason, Heck ( 2010 ) recommends placing real-world problems at the centre of mathematics learning. By treating real-world problems, students can learn in educational settings like real scientists. In this context, learning as real scientists is closely linked to learning by doing.
2.1 Combining basic logical competencies and technologies
In our educational case study, the real-world problem was the matching of Logifaces-stones (see Fig. 1 left). Students’ task was to determine whether or not two stones could form a pair so that their joint surface has no steps and form a smooth surface (see Fig. 1 right). To investigate whether or not two Logifaces-stones form a pair, students of our study also had to use MS Excel and develop a programme to investigate whether or not two Logifaces-stones can form a smooth surface. When developing this MS Excel program, students also had to use basic logical operations. We decided to use MS Excel because Tabach et al. ( 2006 ) showed in their study that students could achieve considerable cognitive growth in learning mathematics by using MS Excel.
Logifaces-stones and how to match them
Using technologies in our educational case study followed the well-known work of Noss and Hoyles ( 2010 ) and Noss et al. ( 1997 ) who were already able to illustrate at the end of the last Century that educational technologies facilitate turning learning environments into laboratories. Such technology-enhanced lab-like learning environments could enable students to explore mathematical content with experimentation and with their creative approaches. As educational technologies and related pedagogies have been extensively studied and significantly developed over the past 20 years and using technologies has been simplified since the late 1990s, we assume that nowadays, it is easier to develop promising technology-enhanced lab-like learning environments.
2.2 Mathematical content of our study
The mathematical content we aimed students discover in a technology-enhanced learning environment in our educational case study was basic logical operations. According to Henderson ( 2014 ), it is basic logic and conceptual problem solving that should be considered early in students’ educational careers in mathematics teaching. As logical operations and using technologies are central to the field of computing and computational thinking, and thus becoming always more relevant in our digital age, high quality teaching on logical operations is a key element for post- secondary education and professional life of today’s secondary school students. In Austria, the country where our educational case study was conducted, and in the German-speaking countries in general, this relevance of basis logic is particularly evident. Here, basic knowledge of logic and logical operations is not only crucial in mathematics, science and computing but is found in many other university curricula and vocational fields that are not per se associated with mathematics. For example, basic logic is a compulsory part of the curriculum in economics ( https://friedolin.uni-jena.de/qisserver/rds;jsessionid=D6FF041661EAC277A63205E55219A71A.worker32?state=wtree&search=1&root120192=473737%7C472876%7C472594%7C472149%7C472583&trex=step ), in digital communication and marketing ( https://online.fh-wien.ac.at/fhwienonline/wbLv.wbShowLVDetail?pStpSpNr=230291&pSpracheNr= ) or linguistics ( https://hpsg.hu-berlin.de/~stefan/Lehre/S2012/as-logik.html ). Since basic logical knowledge is part of both the curricula of mathematical related degree programmes and many curricula of other programmes, students should develop a logical knowledge framework already in secondary schools. As logical foundations are only part of the curriculum in the 9th grade (AHS) in Austria, high quality and engaging teaching on this topic should be of particular importance.
2.3 Using technologies for learning logical foundations
Considering technologies in our educational case study on learning logical foundations is supported by several educational studies which have showed that a technology-enhanced learning environment could be a fruitful setting for learning logical foundations. For example, in an educational case study, Kabaca ( 2013 ) used technologies to learn logical operations AND and OR. By combining technologies and logical operations, a holistic learning environment could be developed in which technologies made it possible to investigate whether the solutions developed are correct. Furthermore, Celedón-Pattichis et al. ( 2013 ) illustrated in their educational study that logical operations and technologies are a combination that could also inspire underrepresented groups for STEM. In our case, students with a migrant and a low socio-economic background form the group of underrepresented students.
For our educational case study, both the findings of Kabaca ( 2013 ) and Celedón-Pattichis et al. ( 2013 ) are essential as on the one hand, students in our educational experiment should be enabled to use technologies to investigate whether their considerations regarding the matching of Logifaces-stones are correct – i.e. that two Logifaces-stones form a smooth surface. On the other hand, our educational case study aims to investigate a technology-enhanced learning environment that should motivate many students to work with and learn logical operations. The fact that both mathematically interested as well as less interested students might need logical operations at a later stage in their educational careers or in their professional life justifies the focus of our educational case study on learning logical operations in a technology-enhanced learning environment using real-world objects.
Another argument for combining technologies and explorative learning is that this approach to learning could also promote students’ meta-competencies such as linguistic or social competencies. Clarkson ( 2003 ) was able to illustrate in her study that learning logic and also logical operators can also enhance students’ language skills. The fact that students should first organise internal logical thinking and then communicate through language to their classmates or teachers supports the learning of logic and logical operators. To promote this meta-competence in our educational case study, students worked in groups of two or three.
2.4 Research goal and question of our study
Since our education case study was very limited in time, we could not focus on opportunities for potential learning gains for the students or compare the design of our techno-logical learning environment with other learning environments. Instead, the goal of our education case study was to investigate how real-world objects and technologies should be linked in mathematics learning to motivate students. This focus on students’ motivation when learning basic logical competencies led us to the research question:
Which design elements of a learning environment where real-world objects and using technologies are linked are essential for students to learn basic logical competencies?
3 Our educational case study
To investigate which design elements are essential for students when learning basic logical competencies in a learning environment in which real-world objects and technologies are linked, we conducted our educational case study in a Vienna secondary school located in the city centre. In defining basic logical competencies in our study, we have used the definition of mathematical competency by Niss and Højgaard ( 2019 ) as a guideline. Consequently, we interpret basic logical competencies as the insightful readiness of a student to react appropriately to a specific type of mathematical-logical challenge in given situations.
3.1 The participants of our study
Since the distance from the school to the students’ home is a central factor in the admission of students to schools, it is assumed that the majority of our student participants live close to the city centre and have high socio-economic background as the residential area near the centre is rather expensive. The high socio-economic background of students lead to the assumption that students are familiar with working and learning with technologies in their homes, as opposed to using the technologies for leisure without learning support. The socio-economic gradient of the Pisa study (OECD 2015 ) also supported this assumption. Following the socio-economic gradient, there is a positive correlation between economic and social status on the one hand and the competence levels achieved by students in the fields of science and technologies on the other hand.
Three groups of learners with a total of 47 students participated in our educational case study. The learners attended 9th grade and were between 13 and 15 years old. Our educational case study undertook four lessons per group – two double lessons each. In the teaching units, students formed groups of two or three. Each group of two or three had a Logifaces set with 16 stones and a computer with Internet access.
3.2 The implementation of our study
A young teacher led the units, and a researcher was present in each unit. The researcher observed the learning activities of the students and took notes of the lessons, and at the same time offered help if the students had problems. In this support of the students, the researcher also conducted mini-interviews with the students to discover what was causing problems. After each double lesson, written feedback was collected from all students. When giving written feedback, students were also asked to record their satisfaction or dissatisfaction with the design elements of the lesson. Students were asked to pay particular attention to interaction with classmates and their teachers, task communication, task design and teacher expectations.
4 Methodological framework
To identify which design elements could be relevant to students when learning basic logical competencies in a technology-enhanced and real-world object based learning environment, we conducted an educational case study.
4.1 Using case study principles to reach our research goal
Since using case studies has a long tradition in mathematics education research in examining students’ solution processes and methods (e.g. Cobb 1986 ), this research method should also be appropriate for our study. Furthermore, as case studies can be used not only to investigate solution processes and methods in problem-solving but also to explore students’ emotions when solving problems in mathematics classrooms (Eynde and Hannula 2006 ), using case study principles should provide valuable results for our research aims. Our study focused on students solving a particular problem (developing an MS Excel program to solve the Logifaces problem) and our research goal was to explore which design elements could be relevant for students in technology-enhanced and real-world object based learning environments.
According to Cohen et al. ( 2007 ), case studies require a clearly defined limited system of real people in real situations experiencing a specified intervention . This limited system of real people in real situations should extend the understanding of concrete ideas and interventions beyond abstract theories. In this study, the limited system was defined as three groups of students throughout four teaching units. The situation to be investigated was defined as the students of these three groups, or more precisely students’ needs and requirements concerning a technology-enhanced learning environment based on real-world objects when learning basic logical competencies. The intervention included basic logical competencies were learned by students using Logifaces-stones and MS Excel.
According to the work of Yin ( 1984 ), our educational case study can be characterised as an explorative case study. The explorative character of our educational case study is because our study aims to develop hypotheses regarding design elements of learning environments in which real-world objects and technologies are linked. According to Cohen et al. ( 2007 ), among others, participatory observations or post-observation recordings are data collection methods that generally apply to case studies and are specifically appropriate for our case. Participatory observations were selected as the data collection instrument because a researcher was present in all teaching units and also interacted with the students when needed. The interactions of the researcher with the students also resulted in ongoing mini-interviews (Bakker and van Eerde 2015 ). The mini-interviews always lasted less than 3 min and were intended to help clarify why students encountered difficulties. The researcher made observational recordings immediately after the occurrence of any phenomena or after conducting mini-interviews. The data collected during the lessons were supplemented with final written feedback from students after each double lesson. According to Kane and Staiger ( 2012 ), collecting supplementary observation data through student feedback should lead to an increase in educational quality. Written feedback was chosen as a data collection tool to gather feedback from all students and to make it clear that their feedback could not be traced back. By making written feedback untraceable, it could be expected that the honesty of student’s feedback was possibly increased.
4.2 Using grounded theory approaches when collecting and evaluating research data
When collecting and evaluating research data, we applied techniques and principles of grounded theory approaches (GTA). In our study, we followed the constructivist interpretation of GTA (Charmaz 2006 ) and a GTA interpretation according to Strauss and Corbin (Khan 2014 ). A constructivist interpretation of GTA and a GTA interpretation according to Strauss and Corbin means, on the one hand, that the previous knowledge of researchers and the current scientific body of knowledge should be included in the development of theories and hypotheses. On the other hand, this interpretation of a GTA follows that any hypothesis or theory developed in the course of research depends on the perspectives of researchers and cases under investigation.
This constructivist interpretation of GTA was particularly relevant to our exploratory educational case study, as, on the one hand, the researchers could not be described as neutral, as they sometimes took on participating and supporting roles. On the other hand, it must be assumed that theories and hypotheses on design elements of technology-enhanced and real-world object based learning environments developed in our exploratory education case study would have been different if our study had been conducted with other classes, at a different time, or at other schools. According to Cohen et al. ( 2007 ), results or hypotheses that depend on the framework conditions of a study are a specific feature of case studies. However, if the conditions and frameworks of the study or case are described in detail, theories or hypotheses developed in a case study can be applied to similar cases, phenomena or situations.
4.3 Coding techniques of grounded theory approaches
In analysing the research data and developing theories and hypotheses, we have followed a four-part approach, namely: 1) screening of new data, 2) open coding, 3) axial coding, and 4) selective coding.
We followed Ritchie’s ( 2012 ) approach to initially view the new data. Initially viewing new data means that, in a first step, all researchers read the newly collected raw data. This repeated reading of the raw data was intended to give all researchers an overview of the current status of our educational case study and to be able to derive initial topics from the raw data. In the next step, the newly collected raw data were transcribed and then coded using a QDA software. Our approach to coding is based on the theoretical guidelines and practical applications of Breuer et al. ( 2009 ), Charmaz ( 2006 ) and Mey and Mruck ( 2011 ).
In the first phase of coding, we applied the techniques of open coding. The goal of open coding is to break up the collected data. To break up the collected data, we asked the questions what, how and why. The resulting first open codes were then grouped according to similar characteristics and definitions and provided with new keywords. This grouping of first open codes resulted in open codes of a higher degree of abstraction (see Table 1 , columns 1 and 2).
The open codes of a higher degree of abstraction were then used for axial coding. By coding open codes axially, a synthesis of the research data should be achieved again. In axial coding, open codes were grouped around a central open code (phenomenon) according to causes, activities and consequences (see Fig. 2 ). The open codes of the area of activities were then grouped and used as categories for selective coding. For selective coding, these categories were linked, and dependencies were identified. Identifying dependencies allowed us to develop the design elements relevant for students in terms of technology-enhanced and real-world object based learning environments for learning basic logical competencies core categories: (A) Using open tasks with multiple solutions, (B) Just-in-time feedback and (C) Novelty effects in the learning process.

Prototypical process of axial coding
Student quotes given in the section Results have been translated from German to English by us. Individual student quotes were accompanied by information whether this feedback was collected via written feedback [F] or mini-interview [I]. If feedback was collected via mini-interviews, the composition of the student group in terms of gender is also given. Here, g stands for girl and b for boy.
Examining and analysing students’ feedback to explore which design elements could be relevant when learning basic logical competencies in a learning environment where real-world objects and technologies are combined, demonstrated that A) Using open tasks with multiple solutions, B) Just-in-time feedback and C) Novelty effects in the learning process are central to students in our exploratory educational case study.
In developing the design elements of the learning environment that are central to students in our study, we did not focus on the feedback related to learning environments per se – i.e. combining technologies, using Logifaces and the intended learning of mathematics. Instead, we focused on the design elements that are central to students in such a learning environment. As the design elements central to students, we qualified those student feedbacks which could be central to students’ learning or motivation, and which could support or hinder learning processes.
5.1 Using open tasks with multiple solutions
A key design element for students in our exploratory educational case study was that students were able to take their learning paths in solving the problem, using their strategies. The students described the associated thinking and experimenting with their strategies or solutions as very motivating.
[F] It was good that you were able to work at your own pace and that you could work on your own idea and not just have to meet specifications. [I, b-b-b] The fact that you can or have to think for yourself before working is really good.
In this process of learning, students described the task as a brainteaser rather than a classical mathematics task. According to the teacher’s feedback, working on this brainteaser activated students much more during lessons than usual. In this context, the teacher mentioned that a high involvement could be observed in mathematical high-achievers as well as in mathematical low-achievers. An increase in activity and motivation of otherwise mathematically below average successful students is reflected in the following quote.
[I, b-b] It is really cool that we can learn and do brainteasers at the same time. [F] I liked the fact that we were able to do more tinkering and puzzling around in the classroom than just learning normally in class.
When working on open-tasks with multiple solutions, it was positive for students that new mathematical or technological knowledge or competencies could be associated with achieving a concrete goal. Students emphasised that it was positive that only those new concepts were learned that could be used immediately when utilising a new solution strategy.
[I, g-g] We learn exactly just the things we need to solve the problem – we would not have learned these things otherwise, would we?
A key design element for students in our exploratory educational case study was that tasks were open-ended and there were several possible solutions. Achieving these open tasks was described by students as a brainteaser rather than an everyday mathematics lesson. When processing these brainteasers, it was crucial for the students that only those new concepts were introduced that were needed in the specific case.
5.2 Just-in-time feedback
When experimenting with Logifaces stones and Excel, it was vital for students of our study that they received immediate feedback or knew that they could get feedback at any time. Students emphasised that they found it enjoyable that a teacher and another person they could ask were present in all lessons.
[F] A good thing about the lessons was that you could always ask the teacher or the other person if your concept is right and what the commands are to realise your concept.
In addition to teachers’ feedback, students also pointed out in their feedback that classmates as feedback providers were an essential element of our case study. In connection to classmates as feedback providers, it was emphasised that classmates were consulted both when problems were acute and when feedback on new strategies or ideas for solving the problem was needed.
[I, b-b] Working or learning in a group is really great. We only argue from time to time how we will implement our ideas. Do not think about it, it is quite normal for us. [F] It was good that in a first step you could immediately ask your seat neighbour if you did not understand something.
In addition to feedback on concrete strategies or ideas for solving the mathematical-logical problem of our case study, it was vital to students that the learning goal and task communication were clear and that questions concerning learning goal or task could be asked at any time.
[I, g-g-g] It was really good that you explained at the beginning exactly what we should do – and thank you that we can ask you again because we do not know all the details. [F] If the task and the images related to the task would have remained visible on the beamer for the whole lesson, that would have helped. But as we could always ask you, it was not that bad.
However, not only the teacher or classmates were described by the students as feedback instruments. Also Logifaces-stones and Excel could be used to test developed strategies for solving the mathematical-logical problem was described by the students as a means of feedback.
[I, b-b] Experimenting with the stones and the program is cool – and you can immediately check if the program is correct.
In summary, feedback for students is a key design element in our exploratory educational study. The decisive aspect for the students in our study was, on the one hand, that they could choose from a variety of feedback options. On the other hand, the feedback from the students made it evident that regardless of the type of feedback, it was important for the students that the desired feedback medium was available immediately when questions or problems arose. Thus, not only just-in-time learning but also just-in-time feedback was a central design element for the students of our exploratory educational study.
5.3 Novelty effects in the learning process
Students’ feedback made it clear that what was new or different in our exploratory educational study was a key design element for the students in our study. Students often described the new or different in our study in an undifferentiated way, merely contrasting the new or different with everyday teaching.
[I, b-b] Today it is a real change compared to normal lessons – that is exciting. [F] What I liked about working with Logifaces was that it was really creative and different learning than usual.
However, much of students’ feedback also related to concrete design elements of our study. An essential aspect for the students was combining mathematics learning as well as using Logifaces-stones and technologies. The surprise associated with this combination had a positive effect on the students’ motivation, which can be found in the teaching notes as well as in the written feedback from the students:
[F] I found working with the building blocks really interesting and I would not have thought at first that the building blocks could have anything to do with mathematics or information.
In addition to combining mathematics, Logifaces-stones and technologies, new insights into the potential uses of Excel were a design element of our study that was remarkable for students.
[I, b-b-b] These lessons reveal just how powerful Excel actually is ... I would not have thought that you can almost do coding with Excel.
The feedback revealed that learning in our case study was always exciting and therefore motivating for students when something new or unexpected occurred during the learning process. This new or unexpected could refer to the design as a whole or very specific elements of our exploratory educational case study.
6 Discussion
In our explorative educational case study, examining how real-world objects and technologies could be combined in mathematics learning, the analysis of students’ feedback indicated that key design elements in the learning process were A) using open tasks with multiple solutions, B) just-in-time feedback, and C) novelty effects .
The importance of using multi-step open tasks to improve the quality of mathematics teaching has already been identified by Carreira and Baioa ( 2018 ) and Heck ( 2010 ). Following Carreira and Baioa ( 2018 ), real-world problems, and therefore problems that are open-ended and allow multiple solutions, should lead to students using school and non-school knowledge and competencies in solving these tasks in mathematics lessons. Heck ( 2010 ) emphasises that one of the advantages of using real-world problems is that students learn like scientists when dealing with such problems. Also, treating open tasks with multiple solutions could be described as learning and researching like real scientists. Results of our study add to these findings dealing with real-world or open-ended problems with multiple solutions could improve not only the quality of mathematics teaching but also the motivation of students. Findings of Noss and Hoyles ( 2010 ) and Noss et al. ( 1997 ) suggest that learning environments could be developed into laboratories by using technologies. In such environments, mathematical content could be explored experimentally and creatively following the feedback from students in our exploratory educational study.
Furthermore, according to students’ feedback, it could be concluded that this learning environment could increase students’ motivation, which, in turn, should have a positive effect on students’ learning outcomes.
Similar to Tabach et al. ( 2006 ), students in our exploratory educational study showed considerable cognitive gains in learning logical operations according to their feedback. If students are to achieve significant cognitive gains in open and real-world problem-based learning environments, it was important for students in our study to receive continuous feedback on their problem-solving strategies and help when the learning process has stalled; feedback on solution strategies concerned using technologies and real-world objects. Using technologies and real-world objects as feedback tools means, following the feedback of the students of our study, that the developed Excel program and the Logifaces-stones were used to examine if the logical operations were used correctly. Furthermore, it was also essential for students of our study to get personal feedback. The personal feedback included feedback from the teacher as well as feedback from classmates. This high demand for personal feedback from the students in our study confirms the results of Clarkson ( 2003 ) that learning logical operators and the associated communication regarding logical operators could also improve the students’ language skills.
The importance of novelty effects in the learning process for the students in our study extends the findings of Carreira and Baioa ( 2018 ) and Heck ( 2010 ) as well as Noss and Hoyles ( 2010 ) and Noss et al. ( 1997 ). For students in our study, it was essential to be able to learn with real-world problems like a real scientist (Carreira and Baioa 2018 ; Heck 2010 ) and to expand knowledge experimentally and creatively in laboratory-like learning environments (Noss and Hoyles 2010 ; Noss et al. 1997 ). It was equally important to students that new and unexpected insights could be gained during these learning processes.
Analysing feedback from students in our exploratory educational study highlighted the importance for students of addressing real-world and open problems in class. In dealing with these real-world and open problems, students wanted to be able to use their ideas and strategies, and experiment with these ideas and strategies. In order to facilitate experimentation with their ideas, it could be fruitful to combine technological and real-world object-based learning environments. When experimenting with their ideas and using self-developed strategies, the students of our study were motivated by the fact that they not only gained insights that could have been gained in a teacher-centred classroom. Students of our study emphasised that it was central to them that new and unexpected things could be discovered while learning. In order to discover new and unexpected things, it was vital for the students of our study that they had confidence in the learning process. In order to have confidence in the learning process, it was important for the students of our exploratory educational study to be able to receive feedback when needed. This feedback could be either personal or technology based.
7 Conclusion and implications for education
To find out which design elements are essential for students to learn basic logical skills in a learning environment where real-world objects and technologies are linked, we conducted an exploratory educational study. Analysing students’ feedback demonstrated that using open tasks with multiple solutions, just-in-time feedback and novelty effects in the learning process was key for students in our study. In this context, it was interesting to note that those activities that were cognitively most challenging were most often positively mentioned by the students. It was the ‘puzzling around’ and experimenting, which was described by the students as particularly motivating elements of our study. In this puzzling around or experimenting with their solution strategies, it was also crucial for the students in our study that new or unexpected things could be discovered in these challenging processes. According to these results of our exploratory educational study, essential design elements of a productive mathematics learning environment are that students have challenging tasks to solve in the course of which new and, above all, unexpected things can be discovered. To ensure that the learning process in such environments is not overstrained, it was crucial for the students of our study that there is a rich repository of feedback possibilities. What was interesting in terms of feedback possibilities was that using technologies and the associated testing of solutions was described by the students as feedback. This possibility of using technologies could also be helpful in other mathematics learning settings and could increase students’ confidence in mathematics learning, as well as accessible to a wider and/or different skill set of teachers, for example by moving the feedback task further from teacher to technology.
Challenging and demanding tasks in combination with real-world objects and technologies as well as the provision of personal and technological feedback make it evident that the designers and implementers of such learning settings should currently be highly qualified. Designers and implementers of such learning settings are usually only one person – the teacher. To be able to use the potential of a mathematics learning environment based on real-world tasks, real-world objects and technologies in the best possible way, highly trained teachers are required.
Specific tasks and requirements for such teachers in a learning environment such as in our exploratory educational study were not investigated in this study but will be the focus of our next research step. It is the intention that this will allow us to identify teacher training requirements and also how or if certain tasks e.g. feedback, may be flexibly allocated between teacher and technology making the learning environment accessible to a wider and/or different skill set of teachers.
Data availability
Extracts from the data collected and analysed are included in the text. Please inform us if you want us to transmit the complete data set and code book.
Bakker, A., & van Eerde, D. (2015). An introduction to design-based research with an example from statistics education. In A. Bikner-Ahsbahs, C. Knipping, & N. Presmeg (Eds.), Approaches to qualitative research in mathematics education: examples of methodology and methods (pp. 429–466). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9181-6_16 .
Borba, M. C., Askar, P., Engelbrecht, J., Gadanidis, G., Llinares, S., & Aguilar, M. S. (2016). Blended learning, e-learning and mobile learning in mathematics education. ZDM, 48 (5), 589–610.
Article Google Scholar
Breuer, F., Dieris, B., & Lettau, A. (2009). Reflexive grounded theory: Eine Einführung für die Forschungspraxis (2009th ed.). Wiesbaden: VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften.
Carreira, S., & Baioa, A. M. (2018). Mathematical modelling with hands-on experimental tasks: On the student’s sense of credibility. ZDM, 50 (1), 201–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-017-0905-1 .
Celedón-Pattichis, S., LópezLeiva, C. A., Pattichis, M. S., & Llamocca, D. (2013). An interdisciplinary collaboration between computer engineering and mathematics/bilingual education to develop a curriculum for underrepresented middle school students. Cultural Studies of Science Education, 8 (4), 873–887.
Charmaz, K. (2006). Constructing grounded theory: A practical guide through qualitative analysis (1st ed.). London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
Clarkson, P. C. (2003). Language, logical thinking and communication in school mathematics: Whose responsibility. In Studies in science, mathematics and technical education (pp. 99–116).
Cobb, P. (1986). Concrete can be abstract: A case study. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 17 (1), 37–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00302377 .
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2007). Research methods in education (Sixth ed.). London: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Eynde, P. O., & Hannula, M. S. (2006). The case study of frank. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 63 (2), 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-006-9030-8 .
Heck, A. (2010). Modelling in cross-disciplinary authentic student research projects. International Journal for Technology in Mathematics Education, 17 (3), 115–120.
Google Scholar
Henderson, P. B. (2014). Pre-college computing math. ACM Inroads, 5 (3), 40–41.
Kabaca, T. (2013). Using dynamic mathematics software to teach one-variable inequalities by the view of semiotic registers. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science & Technology Education, 9 (1), 73–81.
Kane, T. J., & Staiger, D. O. (2012). Gathering feedback for teaching: Combining high-quality observations with student surveys and achievement gains. Research Paper. MET Project. Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Khan, S. N. (2014). Qualitative research method: Grounded theory. International Journal of Business and Management, 9 (11). Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijbm.v9n11p224 .
Mey, G., & Mruck, K. (2011). Grounded theory reader (2nd ed.). Wiesbaden: VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften.
Niss, M., & Højgaard, T. (2019). Mathematical competencies revisited. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 102 (1), 9–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-019-09903-9 .
Noss, R., & Hoyles, C. (2010). Modeling to address techno-mathematical literacies in work. In Modeling students’ mathematical modeling competencies (pp. 75–86). Springer.
Noss, R., Healy, L., & Hoyles, C. (1997). The construction of mathematical meanings: Connecting the visual with the symbolic. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 33 (2), 203–233.
OECD. (2015). PISA-2015-Datenbanken. https://doi.org/10.1787/888933432735 .
Pierce, R., & Stacey, K. (2011). Using dynamic geometry to bring the real world into the classroom. In L. Bu & R. Schoen (Eds.), Model-centered learning: Pathways to mathematical understanding using GeoGebra (pp. 41–55). SensePublishers. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-6091-618-2_4 .
Ritchie, S. (2012). Incubating and sustaining: How teacher networks enable and support social justice education. Journal of Teacher Education, 63 (2), 120–131. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022487111428327 .
Samuelsson, J. (2006). ICT as a change agent of mathematics teaching in Swedish secondary school. Education and Information Technologies, 11 (1), 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-005-5713-5 .
Tabach, M., Hershkowitz, R., & Schwarz, B. (2006). Constructing and consolidating of algebraic knowledge within dyadic processes: A case study. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 63 (3), 235–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-005-9012-2 .
Yin, R. K. (1984). Case study research: Design and methods . Newbury Park: Sage.
Links to the curricula
https://friedolin.uni-jena.de/qisserver/rds;jsessionid=D6FF041661EAC277A63205E55219A71A.worker32?state=wtree&search=1&root120192=473737%7C472876%7C472594%7C472149%7C472583&trex=step . 11.02.2020.
https://online.fh-wien.ac.at/fhwienonline/wbLv.wbShowLVDetail?pStpSpNr=230291&pSpracheNr= . 11.02.2020.
https://hpsg.hu-berlin.de/~stefan/Lehre/S2012/as-logik.html . 11.02.2020.
Download references
Acknowledgements
At this point we would like to thank the teachers and the management of the Akademisches Gymnasium Wien, who made our case study possible. A special thanks goes to Alexander Kandl and Katharina Krebs from the management as well as to Michael Molnar and the teaching team.
Open access funding provided by Johannes Kepler University Linz.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria
Robert Weinhandl, Tony Houghton & Zsolt Lavicza
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Robert Weinhandl .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest, code availability, additional information, publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Weinhandl, R., Houghton, T. & Lavicza, Z. A case study on learning basic logical competencies when utilising technologies and real-world objects. Educ Inf Technol 26 , 639–653 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10282-5
Download citation
Received : 23 May 2020
Accepted : 07 July 2020
Published : 12 July 2020
Issue Date : January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10282-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Basic logical operations
- Hands-on learning
- Learning logical competencies
- Technology-enhanced learning environments
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Case Study Research Design and Methods
- Robert K. Yin - COSMOS Corporation
This text provides a useful overview of how to conduct, structure and design case study research. It is a useful text for undergraduates as it also introduces ethical considerations that are, at times, overlooked in other texts. The specific boundaries that require evaluation as part of the research design process are well represented in this text.
Good view of case study research by one of the key authors on the area. Easy to read for students and very useful for those using case study method for their dissertations
This Book is the latest for Yin's case study as far as I am aware of. Well thought and structured Book which most of the students in the class liked. I will strongly recommend.
It is an essential reading for those doing a research project. Explains in detail every notion and construct. Shows what one have do in practice when approaching a research problem from a case study perspective
A must read for any researcher that intends to design and undertake case study research.
Robert K. Yin
Robert K. Yin is President of COSMOS Corporation, an applied research and social science firm. Over the years, COSMOS has successfully completed hundreds of projects for federal agencies, state and local agencies, and private foundations.
Outside of COSMOS, Dr. Yin has assisted numerous other research groups, helping to train their field teams or to design research studies. The most recent such engagements have been with The World Bank, the Division of Special Education and disAbility Research at George Mason University, the Department of Nursing Research and Quality Outcomes at the Children’s National Health System (Washington, DC), and the School of Education, Southern New Hampshire University.
Dr. Yin has authored over 100 publications, including authoring or editing 11 books (not counting the multiple editions of any given book). Earlier editions of the present book have been translated into eight languages (Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Swedish, Romanian, Italian, Polish, and Portuguese), and a second book on Qualitative Research from Start to Finish (2016) is in its 2nd edition and has been translated into four languages (Chinese, Korean, Swedish, and Portuguese). Dr. Yin received his B.A. in history from Harvard College (magna cum laude) and his Ph.D. in brain and cognitive sciences from MIT.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Logic in Computer Science
Title: cut elimination for cyclic proofs: a case study in temporal logic.
Abstract: We consider modal logic extended with the well-known temporal operator `eventually' and provide a cut-elimination procedure for a cyclic sequent calculus that captures this fragment. The work showcases an adaptation of the reductive cut-elimination method to cyclic calculi. Notably, the proposed algorithm applies to a cyclic proof and directly outputs a cyclic cut-free proof without appealing to intermediate machinery for regularising the end proof.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
SaaS Log Analytics Platform
Monitor, troubleshoot and secure your apps
Troubleshooting and Monitoring
Monitor and troubleshoot issues fast—at scale.
Cloud Infrastructure Security
Quickly consolidate and identify risks and threats in your environment.
Compliance and Audit
Prove your data is safe and compliant across all cloud and on-site setups.
Accelerate your incident investigations with enhanced visibility.
PLATFORM CAPABILITIES
- APIs and integrations
- Powered by AI/ML
- OpenTelemetry collection
- Platform security attestations
- Observability
Our approach resulted in a doubling of our log ingestion at an ingest cost increase of only 10%, saving us around $1 million.”
Iwan Eising
Team Lead of Service Reliability Architecture
BY OBSERVABILITY USE CASE
BY SECURITY USE CASE
BY INITIATIVE
BY COMPETITION
Sumo Logic ahead of the pack
Cyber attackers hit the jackpot
The SEC's new cybersecurity rules
Migrate from Splunk to Sumo
Click through interactive platform demos now.
Schedule a platform demo with a Sumo Logic expert.
Case Study | Resource Center
Browse our library of ebooks, solutions briefs, research reports, case studies, webinars and more.
Sumo Logic recognized as a Strong Performer in the 2022 Forrester Wave for Security Analytics Platforms
All resources.
18 of 112 results
Five reasons why every CIO should consider Kubernetes
New standard set for managed security services, fintech compliance made fast and secure, data is at the heart of cloud-native bank, ai platform thrives with huge data intake, unified siem dashboard automates security investigations, how security and performance redefine banking, reliability and happy customers with slos, automating insider threat monitoring, from legacy on-prem to a modern cloud siem, monitor and secure 10,000 clouds, log analysis: from days to 30 minutes, scaling a soc with cloud siem, rule every threat with cloud siem, cloud siem powers devsecops, a new soc in 35 days, tool consolidation on time and under budget, data tiering saves infor $1 million in one year, featured collections.
Best practices for successful adoption and management for AWS technologies
213 articles
Dive deep into DevOps practices
692 articles
Insights and analytics for Apache technologies
Please check your inbox
[email protected]@[email protected], start your free trial today.
No credit card required. Up and running in minutes.
Already have an account? Login

Case Studies

Spectra Storage Solutions help CERN advance the boundaries of human knowledge

Imperial War Museums digitally preserve the history of modern war indefinitely with Spectra

Notre Dame employs hybrid cloud storage platform from Spectra Logic

The ACCRE at Vanderbilt University expands capacity with Spectra T950 and BlackPearl

AWE innovates computational programs that support the UK’s nuclear defence strategy with the help of Spectra Logic

Spectra Logic solutions help Brooks Lab at University of Michigan archive research data

CPi – CAM Productions International – selects Spectra Digital Archive to preserve media content

DiRAC Memory Intensive Service at Durham University preserves complex cosmological simulation data with Spectra Solution

EIDF enables world-leading data-driven innovation with storage solutions from Spectra Logic.

FHNW Switzerland deploys Spectra tape library in hybrid cloud infrastructure

Hormel Institute UMN preserves cancer research data and breakthrough findings with Spectra Logic Solution
Our Products
Our end-to-end solutions, on-prem glacier, spectra digital archive, spectra media archive, our industry focus, data management software, multi-cloud object management.
Unify object access across on-prem & public clouds
Active & Long-Term Archive
Automate digital preservation to disk, tape & cloud
High-Performance Data Mover
Supercharge file transfers & streamline media workflows
File & Object Storage
Hybrid cloud storage.
Get public cloud storage perks without the public cloud cost
Nearline Media Gateway
Integrate popular media management applications with object-based tape
Network-Attached Storage
Lower the cost of secondary file storage with economical scale-up NAS
Tape Storage
Tape libraries.
Affordably preserve, protect & defend enterprise data for the long term
Tape Drive Technology
Mix or match industry-leading tape drives to meet wide-ranging needs
Maintain peak media performance using Spectra-certified media

Get our latest blog in your inbox.

StorCycle Demo Program
Fill out the form below and a Spectra representative will contact you regarding our StorCycle Demo Program.
Customer Purchase Agreements
Customer Purchase Agreement, North America and regions other than EMEA and APJ (PDF)
Customer Purchase Agreement, EMEA (PDF)
Customer Purchase Agreement, APJ (PDF)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study: Logic. explore a variety of dimensions of the community and. can thereby create a multidimensional, or holistic, sense of the community rather than, let us say, a. unidimensional one ...
A multiple case study may serve a replication logic by which the findings have relevance beyond the cases under investigation. In "social construction of reality", the sampling is purposeful as well, but for different reasons. Either the case is of interest per se or the case represents a good opportunity to understand a theoretical issue.
13 Causal mechanisms are central to scientific realist epistemology, which is often invoked by case study researchers to validate their approach (George & Bennett, 2005: Chapter 7). 14. 14 A similar logic could apply to the role of plausibility probes in theory-driven idiographic studies. 15.
This article describes a one-credit discussion course in research ethics for graduate students in biology. Case studies are focused on within the four parts of the course: 1) major issues, 2 )practical issues in scholarly work, 3) ownership of research results, and 4) training and personal decisions. DeVoss, G. (1981).
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
Case study can accommodate a variety of epistemological orientations, but these will influence research design . positivist: there is a single reality, independent of any observer ... the logic linking the data to the propositions: e.g., pattern matching,explanation building, time-series analysis, logic models, cross-case synthesis 3.
Case study selection and boundaries. A unique feature of Yin's approach to multiple case studies is using replication logic to select cases [].Cases are chosen to demonstrate similarities (literal replication) or differences for anticipated reasons (theoretical replication) [].In the exemplar study, the cases were purposely selected using literal replication and displayed several common ...
Case studies can be viewed as "quasi-experimental", i.e. situations in which the experimenter cannot manipulate behavior but in which the logic of experimental design may . 4 still be applied (Yin, 1994: 9). In other words, Yin's case study methodology is based on ... Case studies, using replication logic, allow analytic generalization,
The question of how we deploy logic in developing and justifying scientific theories of any sort is an important one. In this commentary, I consider William Stiles' (2009) arguments about the logical operations that are deployed especially in theory-building case-study research in psychotherapy. My commentary contains three sections, defined by three sets of distinctions: (a) the distinction ...
The question of how we deploy logic in developing and justifying scientific theories of any sort is an important one. In this commentary, I consider William Stiles' (2009) arguments about the logical operations that are deployed especially in theory-building case-study research in psychotherapy. My commentary contains three sections, defined ...
In Austria, the country where our educational case study was conducted, and in the German-speaking countries in general, this relevance of basis logic is particularly evident. Here, basic knowledge of logic and logical operations is not only crucial in mathematics, science and computing but is found in many other university curricula and ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Getting Started: How to Know Whether and When to Use the Case Study as a Research Method. Chapter 2. Designing Case Studies: Identifying Your Case (s) and Establishing the Logic of Your Case Study. Chapter 3. Preparing to Collect Case Study Evidence: What You Need to Do before Starting to Collect Case Study Data. Chapter 4.
Building theory from case studies is a research strategy that involves using one or more cases to. create theoretical constructs, propositions and/or. midrange theory from case-based, empirical evi dence (Eisenhardt, 1989b). Case studies are rich, empirical descriptions of particular instances of a.
One of the most often-heard design and analysis approaches for case study research is "replication logic". We analyze all case studies on team and innovation (N=135) published in the period 1996-2006 in Strategic Management Journal, Academy of Management Journal, Administrative Science Quarterly, Organization Science and Management Science, and find that replication logic is underutilized ...
This work analyzes all case studies on team and innovation published in the period 1996-2020 and concludes that replication logic is the most often-heard design and analysis approach for case study research. One of the most often-heard design and analysis approaches for case study research is "replication logic". We analyze all case studies on team and innovation (N=135) published in the ...
The case study method is a research strategy that aims to gain an in-depth understanding of a specific phenomenon by collecting and analyzing specific data within its true context (Rebolj, 2013 ...
This article describes an instance where a US funder of a multi-site initiative fully engaged the funded organizations in developing the initiative logic model. The focus of the case study is ...
Case Study: Logic 1. The Case Study Defined The case study is a research strategy with special implications for theoretical analysis and data col-lection. A single case of a particular phenomenon is
A unique feature of Yin's approach to multiple case studies is using replication logic to select cases . Cases are chosen to demonstrate similarities (literal replication) or differences for anticipated reasons (theoretical replication) . In the exemplar study, the cases were purposely selected using literal replication and displayed several ...
We consider modal logic extended with the well-known temporal operator `eventually' and provide a cut-elimination procedure for a cyclic sequent calculus that captures this fragment. The work showcases an adaptation of the reductive cut-elimination method to cyclic calculi. Notably, the proposed algorithm applies to a cyclic proof and directly outputs a cyclic cut-free proof without appealing ...
Sumo Logic recognized as a Strong Performer in the 2022 Forrester Wave for Security Analytics Platforms. In the report showcasing "The 14 Providers That Matter Most And How They Stack Up", Sumo Logic was recognized as a strong performer. "Security information and event management (SIEM) capabilities alone are no longer sufficient for security ...
Case studies - Spectra Logic. Case Studies. Let our customers help you make the case for Spectra Logic becoming a key part of your data preservation & protection strategy. Spectra Storage Solutions help CERN advance the boundaries of human knowledge. Imperial War Museums digitally preserve the history of modern war indefinitely with Spectra.
Study Case Logic Study, simplified. Everyone learns in their own way, but all students need to find the right balance between schoolwork, friends, and family. ... Case Logic laptop sleeve 13.3" laptop sleeve $39.99 39.99 USD Case Logic Reflect 14" laptop sleeve $34.99 34.99 USD Case Logic Surefit 9-11" tablet folio