Home — Essay Samples — Information Science and Technology — Internet — The Importance of Internet Privacy

The Importance of Internet Privacy
- Categories: Internet Internet Privacy
About this sample

Words: 1017 |
Published: Oct 2, 2020
Words: 1017 | Pages: 2 | 6 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, threats to personal data and privacy, legal and ethical considerations, protecting your digital sanctuary, works cited.
- Strong Passwords: Employ strong, unique passwords for online accounts and consider using a password manager to securely store and manage them.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA whenever possible to add an additional layer of security to your online accounts.
- Mindful Sharing: Be cautious about the personal information you share online, especially on social media platforms. Review and adjust privacy settings to control who can access your data.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Utilize VPNs to encrypt your internet connection, making it more difficult for third parties to monitor your online activities.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your operating system, browser, and security software up to date to protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the latest threats and best practices for online privacy. Knowledge is a powerful defense against potential threats.
- Brown, M. (2018). Facebook is watching and tracking you more than you probably realize. Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/facebook-is-tracking-you-through-apps-and-websites-2018-4
- Debatin, B., Lovejoy, J.P., Horn, A-K., & Hughes, B.N. (2009). Facebook and online privacy: Attitudes, behaviors, and unintended consequences. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 15(1), 83-108.
- National Conference of State Legislatures. (2019). Security breach notification laws. https://www.ncsl.org/research/telecommunications-and-information-technology/security-breach-notification-laws.aspx
- Online Privacy (2018). Peggy J. Parks. Greenhaven Publishing LLC.
- Pew Research Center. (2021). Internet/Broadband Fact Sheet.
- Rosenbach, M., & Stolte, J. (2018). Can you have both security and privacy in the internet age? Harvard Business Review.
- Soltani, A. (2010). Why privacy matters: Debunking the nothing-to-hide argument. The Chronicle of Higher Education, 57(3), B26.
- Statista. (2022). Number of internet users worldwide from 2005 to 2021 (in millions). https://www.statista.com/statistics/273018/number-of-internet-users-worldwide/
- Winston & Strawn. (2017). Internet Privacy: An Overview of Federal Law. Lexology.
- Zavodny, M. (2017). Why does online privacy matter? Mercatus Center at George Mason University.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Information Science and Technology Law, Crime & Punishment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1050 words
2 pages / 991 words
3 pages / 1394 words
2 pages / 1094 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Internet
In the 21st century, access to the internet has become an integral part of our daily lives. From education and employment opportunities to accessing vital information and engaging in civic participation, the internet plays a [...]
Online streaming platforms have revolutionized the way people consume media and entertainment. With the advent of digital technology, these platforms have become a dominant force in the entertainment industry, offering a wide [...]
The excessive use of the internet has become a prevalent concern in today's digital age. The internet, once a revolutionary tool for communication and information, has now transformed into an integral part of our daily lives. [...]
The question of whether students should have limited access to the internet is a complex and timely one, given the pervasive role of technology in education. While the internet offers a wealth of information and resources, [...]
The Internet could change the lives of normal people as much as did the phone in the early piece of the twentieth century and TV in the 1960s. Specialists and social commentators are debating whether the Internet is enhancing or [...]
There are many benefits of Internet of Things ( IoT) in today’s technological era, but we must also remember that with benefits there also con’s, these may involve also challenges and problems that simple can’t be left [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Battle for Digital Privacy Is Reshaping the Internet
As Apple and Google enact privacy changes, businesses are grappling with the fallout, Madison Avenue is fighting back and Facebook has cried foul.

By Brian X. Chen
Listen to This Article
SAN FRANCISCO — Apple introduced a pop-up window for iPhones in April that asks people for their permission to be tracked by different apps.
Google recently outlined plans to disable a tracking technology in its Chrome web browser.
And Facebook said last month that hundreds of its engineers were working on a new method of showing ads without relying on people’s personal data.
The developments may seem like technical tinkering, but they were connected to something bigger: an intensifying battle over the future of the internet. The struggle has entangled tech titans, upended Madison Avenue and disrupted small businesses. And it heralds a profound shift in how people’s personal information may be used online, with sweeping implications for the ways that businesses make money digitally.
At the center of the tussle is what has been the internet’s lifeblood: advertising .
More than 20 years ago, the internet drove an upheaval in the advertising industry. It eviscerated newspapers and magazines that had relied on selling classified and print ads, and threatened to dethrone television advertising as the prime way for marketers to reach large audiences.
Instead, brands splashed their ads across websites, with their promotions often tailored to people’s specific interests. Those digital ads powered the growth of Facebook, Google and Twitter, which offered their search and social networking services to people without charge. But in exchange, people were tracked from site to site by technologies such as “ cookies, ” and their personal data was used to target them with relevant marketing.
Now that system, which ballooned into a $350 billion digital ad industry, is being dismantled. Driven by online privacy fears, Apple and Google have started revamping the rules around online data collection. Apple, citing the mantra of privacy, has rolled out tools that block marketers from tracking people. Google, which depends on digital ads, is trying to have it both ways by reinventing the system so it can continue aiming ads at people without exploiting access to their personal data.

If personal information is no longer the currency that people give for online content and services, something else must take its place. Media publishers, app makers and e-commerce shops are now exploring different paths to surviving a privacy-conscious internet, in some cases overturning their business models. Many are choosing to make people pay for what they get online by levying subscription fees and other charges instead of using their personal data.
Jeff Green, the chief executive of the Trade Desk, an ad-technology company in Ventura, Calif., that works with major ad agencies, said the behind-the-scenes fight was fundamental to the nature of the web.
“The internet is answering a question that it’s been wrestling with for decades, which is: How is the internet going to pay for itself?” he said.
The fallout may hurt brands that relied on targeted ads to get people to buy their goods. It may also initially hurt tech giants like Facebook — but not for long. Instead, businesses that can no longer track people but still need to advertise are likely to spend more with the largest tech platforms, which still have the most data on consumers.
David Cohen, chief executive of the Interactive Advertising Bureau, a trade group, said the changes would continue to “drive money and attention to Google, Facebook, Twitter.”
The shifts are complicated by Google’s and Apple’s opposing views on how much ad tracking should be dialed back. Apple wants its customers, who pay a premium for its iPhones, to have the right to block tracking entirely. But Google executives have suggested that Apple has turned privacy into a privilege for those who can afford its products.
For many people, that means the internet may start looking different depending on the products they use. On Apple gadgets, ads may be only somewhat relevant to a person’s interests, compared with highly targeted promotions inside Google’s web. Website creators may eventually choose sides, so some sites that work well in Google’s browser might not even load in Apple’s browser, said Brendan Eich, a founder of Brave, the private web browser.
“It will be a tale of two internets,” he said.
Businesses that do not keep up with the changes risk getting run over. Increasingly, media publishers and even apps that show the weather are charging subscription fees, in the same way that Netflix levies a monthly fee for video streaming. Some e-commerce sites are considering raising product prices to keep their revenues up.
Consider Seven Sisters Scones, a mail-order pastry shop in Johns Creek, Ga., which relies on Facebook ads to promote its items. Nate Martin, who leads the bakery’s digital marketing, said that after Apple blocked some ad tracking, its digital marketing campaigns on Facebook became less effective. Because Facebook could no longer get as much data on which customers like baked goods, it was harder for the store to find interested buyers online.
“Everything came to a screeching halt,” Mr. Martin said. In June, the bakery’s revenue dropped to $16,000 from $40,000 in May.
Sales have since remained flat, he said. To offset the declines, Seven Sisters Scones has discussed increasing prices on sampler boxes to $36 from $29.
Apple declined to comment, but its executives have said advertisers will adapt. Google said it was working on an approach that would protect people’s data but also let advertisers continue targeting users with ads.
Since the 1990s, much of the web has been rooted in digital advertising. In that decade, a piece of code planted in web browsers — the “cookie” — began tracking people’s browsing activities from site to site. Marketers used the information to aim ads at individuals, so someone interested in makeup or bicycles saw ads about those topics and products.
After the iPhone and Android app stores were introduced in 2008, advertisers also collected data about what people did inside apps by planting invisible trackers. That information was linked with cookie data and shared with data brokers for even more specific ad targeting.
The result was a vast advertising ecosystem that underpinned free websites and online services. Sites and apps like BuzzFeed and TikTok flourished using this model. Even e-commerce sites rely partly on advertising to expand their businesses.
But distrust of these practices began building. In 2018, Facebook became embroiled in the Cambridge Analytica scandal, where people’s Facebook data was improperly harvested without their consent. That same year, European regulators enacted the General Data Protection Regulation , laws to safeguard people’s information. In 2019, Google and Facebook agreed to pay record fines to the Federal Trade Commission to settle allegations of privacy violations.
In Silicon Valley, Apple reconsidered its advertising approach. In 2017, Craig Federighi, Apple’s head of software engineering, announced that the Safari web browser would block cookies from following people from site to site.
“It kind of feels like you’re being tracked, and that’s because you are,” Mr. Federighi said. “No longer.”
Last year, Apple announced the pop-up window in iPhone apps that asks people if they want to be followed for marketing purposes. If the user says no, the app must stop monitoring and sharing data with third parties.
That prompted an outcry from Facebook , which was one of the apps affected. In December, the social network took out full-page newspaper ads declaring that it was “standing up to Apple” on behalf of small businesses that would get hurt once their ads could no longer find specific audiences.
“The situation is going to be challenging for them to navigate,” Mark Zuckerberg, Facebook’s chief executive, said.
Facebook is now developing ways to target people with ads using insights gathered on their devices, without allowing personal data to be shared with third parties. If people who click on ads for deodorant also buy sneakers, Facebook can share that pattern with advertisers so they can show sneaker ads to that group. That would be less intrusive than sharing personal information like email addresses with advertisers.
“We support giving people more control over how their data is used, but Apple’s far-reaching changes occurred without input from the industry and those who are most impacted,” a Facebook spokesman said.
Since Apple released the pop-up window, more than 80 percent of iPhone users have opted out of tracking worldwide, according to ad tech firms. Last month, Peter Farago, an executive at Flurry, a mobile analytics firm owned by Verizon Media, published a post on LinkedIn calling the “time of death” for ad tracking on iPhones.
At Google, Sundar Pichai, the chief executive, and his lieutenants began discussing in 2019 how to provide more privacy without killing the company’s $135 billion online ad business. In studies, Google researchers found that the cookie eroded people’s trust. Google said its Chrome and ad teams concluded that the Chrome web browser should stop supporting cookies.
But Google also said it would not disable cookies until it had a different way for marketers to keep serving people targeted ads. In March, the company tried a method that uses its data troves to place people into groups based on their interests, so marketers can aim ads at those cohorts rather than at individuals. The approach is known as Federated Learning of Cohorts, or FLOC.
Plans remain in flux. Google will not block trackers in Chrome until 2023 .
Even so, advertisers said they were alarmed.
In an article this year, Sheri Bachstein, the head of IBM Watson Advertising, warned that the privacy shifts meant that relying solely on advertising for revenue was at risk. Businesses must adapt, she said, including by charging subscription fees and using artificial intelligence to help serve ads.
“The big tech companies have put a clock on us,” she said in an interview.
Kate Conger contributed reporting.
Brian X. Chen is the lead consumer technology writer for The Times. He reviews products and writes Tech Fix , a column about the social implications of the tech we use. Before joining The Times in 2011, he reported on Apple and the wireless industry for Wired. More about Brian X. Chen
Internet Privacy - Essay Examples And Topic Ideas For Free
Internet privacy refers to the right or expectation of privacy in the digital realm, encompassing issues related to the protection of personal data, confidentiality, and anonymity online. Essays on internet privacy could delve into the risks and challenges associated with digital surveillance, data breaches, or online tracking, the impact of laws and regulations on privacy, or the ways in which individuals and organizations can protect privacy online. They might also explore the ethical, social, and political implications of privacy in the digital age, or the tensions between privacy, security, and convenience online. A substantial compilation of free essay instances related to Internet Privacy you can find at PapersOwl Website. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.
Impact of Technology on Privacy
The 21st Century is characterized by the heavy impact technology has on us as a society while it continues to develop new devices and modernize technology. Millions of individuals around the world are now connected digitally, in other words, people globally rely heavily on smartphones tablets, and/ or computers that store or save a majority of their personal information. Critical and extremely personal data is available and collected in these smart technology such as credit card details, fingerprint layout, and […]
A World Without Internet
On the street is the 21st century. Almost all people on our planet have access to the Internet. And they are actively using it. But they forget that they use it almost around the clock. From watching the weather in the morning to texting on social media in the evening. Instead of writing an essay by hand, a modern student simply downloads it. People on the Internet are already looking for work, pay for housing and communal services, participate in […]
Positive and Negative Effects of Internet
The topic of the pros and cons of the Internet is one of the most controversial topics. People often cannot give a definite answer to it. The topic of the Internet is quite versatile. Let's look at it from the positive side first. The Internet is the greatest invention of mankind, which made life easier and continues to do it for us hundreds of times. Its first plus is, of course, the available information. Now you can find out any […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Security Versus Freedom?
Welcome to the Digital Age. In today’s connected world, we are living much of our live online. As a result, companies everywhere are creating large storehouses of data on all of us. The most obvious information being collected is social media data. Everything we post publicly and some cases privately, is being stored and analysed. But it is not just social media, there is now a digital record of everything we buy, everything we watch, where we go and what […]
Internet Access Restrictions May Vary
Fantastic. In most instances, they are placed on search quarries and are most prominent at education centers. This is simply to keep minds safe from content unsuitable for most ages (Gonchar). Although this is an effective plan with good intentions, it can become more effective by being enforced on younger ages rather than those who have already been exposed to the negative side of the internet. As you enter high school you have nearly done and seen everything there […]
Securing Cyberspace: Crafting Tomorrow’s Internet Privacy Laws
In an era where digital footprints shape our daily lives, the quest to safeguard personal privacy in the vast expanse of the internet has become more critical than ever before. Transitioning from the pixels that construct our online world to the intricate policies governing its boundaries signifies a pivotal juncture in the evolution of digital governance. As we navigate through this landscape of data, the formulation of robust internet privacy legislation emerges as a beacon of protection against the perils […]
Silent Struggle: Assessing Threats to Internet Privacy and Security
In today's digital age, the internet serves as the cornerstone of modern communication, commerce, and entertainment. However, amidst the convenience and connectivity it offers, lurks a pervasive and often invisible battle for privacy and security. From data breaches to surveillance, the threats to our online well-being are manifold and ever-evolving. One of the most concerning threats is the rampant collection and misuse of personal data by corporations and governments alike. Every click, search, and purchase leaves a digital footprint, eagerly […]
Safeguarding Cyberspace: the Vital Role of AI in Preserving Online Privacy
In an era where our digital footprints grow larger with every click, the question of how to protect our online privacy becomes increasingly pertinent. Enter Artificial Intelligence, our modern-day guardians in the complex realm of cyberspace. Far beyond mere machines crunching numbers, AI has evolved into a formidable force in the fight against privacy breaches. The first and foremost duty of AI guardians is to fortify our virtual boundaries. Picture them as vigilant sentinels stationed at the gates of our […]
Preserving Digital Integrity: a Scholarly Evaluation of Internet Privacy
In the contemporary digital epoch, where the internet serves as an omnipotent conduit for global interaction, commerce, and information dissemination, the concept of cyber privacy emerges as a pivotal concern. As an academic critic, entrusted with scrutinizing the intricacies of cyber privacy, it becomes essential to unravel the diverse facets of this intricate matter, ranging from its legal and ethical dimensions to its societal and technological reverberations. Cyber privacy fundamentally entails the right of individuals to govern their personal information […]
Additional Example Essays
- Positive Effects of Social Media
- Instagram and body dysmorphia
- The Negative Effects of Social Media On Mental Health
- The Mental Health Stigma
- How the Roles of Women and Men Were Portrayed in "A Doll's House"
- Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
- Substance Abuse and Mental Illnesses
- Importance Of Accountability
- Are Electric Cars Better Than Petrol Diesel Cars?
- "A Doll's House" as a Modern Tragedy
- Poems “The Negro Speaks of Rivers” and “Still I Rise”
- The Unique Use of Literary Devices in The Tell-Tale Heart
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
How Americans View Data Privacy
1. views of data privacy risks, personal data and digital privacy laws, table of contents.
- Role of social media, tech companies and government regulation
- Americans’ day-to-day experiences with online privacy
- Personal data and information
- Feelings of concern, confusion and a lack of control over one’s data
- Privacy laws and regulation
- Americans largely favor more regulation to protect personal information
- Trust in social media executives
- Children’s online privacy: Concerns and responsibility
- Law enforcement and surveillance
- AI and data collection
- Trust in companies that use AI
- How people approach privacy policies
- How people are protecting their digital privacy
- How Americans handle their passwords
- Data breaches and hacks
- Identifying the most and least knowledgeable, confident and concerned
- Knowledge and privacy choices
- Confidence and privacy choices
- Concern and privacy choices
- The case of privacy policies
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
- Appendix A: Law enforcement’s use of technology in investigations
- Appendix B: Privacy outcomes by knowledge, confidence and concern
- Appendix C: Confident and independent use of digital devices, by age and education
Online privacy is complex, encompassing debates over law enforcement’s data access, government regulation and what information companies can collect. This chapter examines Americans’ perspectives on these issues and highlights how views vary across different groups, particularly by education and age.
When managing their privacy online, most Americans say they trust themselves to make the right decisions about their personal information (78%), and a majority are skeptical that anything they do will make a difference (61%).
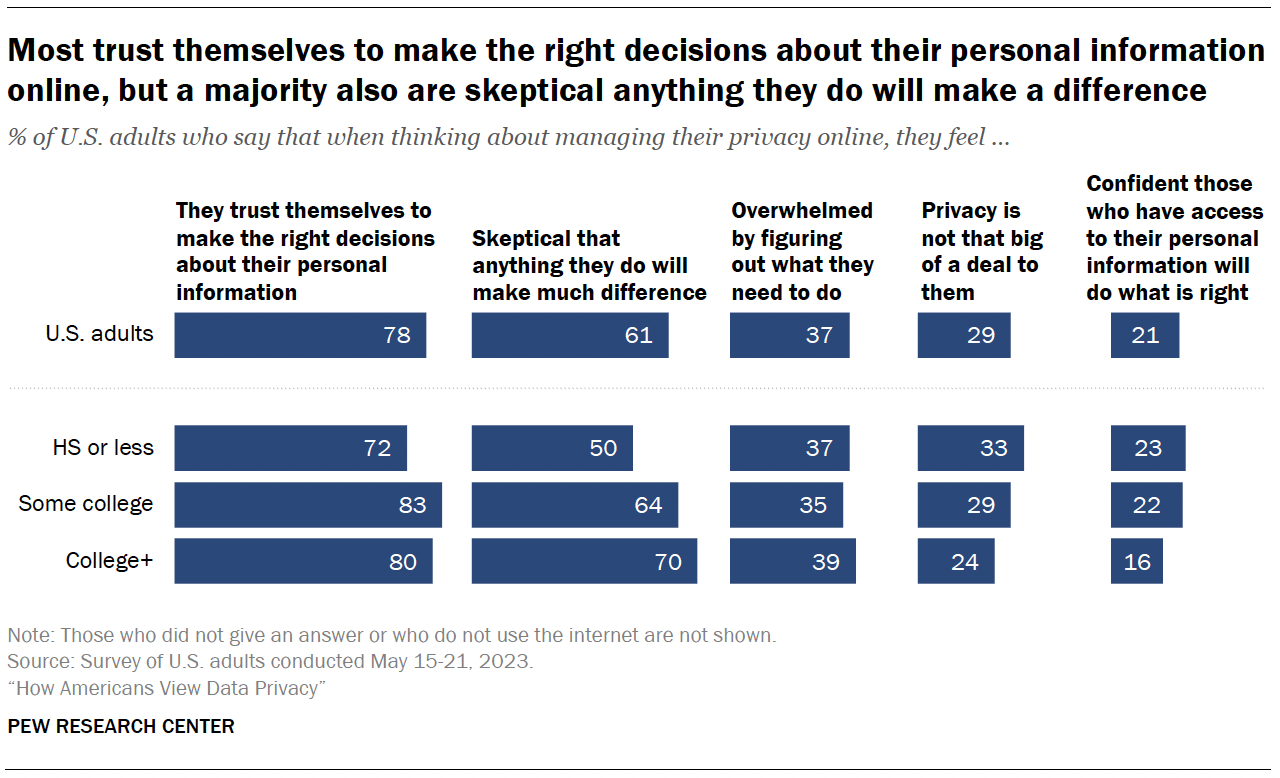
Far fewer mention being overwhelmed by figuring out what they need to do (37%) or say privacy is not that big of a deal to them (29%).
Another 21% are confident that those with access to their personal information will do what is right.
Education differences
- 81% of those with at least some college experience say they trust themselves to make the right decisions about their personal information online, compared with 72% of those with a high school diploma or less.
- 67% of those with at least some college are skeptical that anything they do to manage their online privacy will make a difference, compared with half of those with a high school diploma or less formal education.
On the other hand, those with a high school education or less are more likely than those with some college experience or more to say that privacy isn’t that big of a deal to them and that they are confident that those who have access to their personal information will do the right thing.
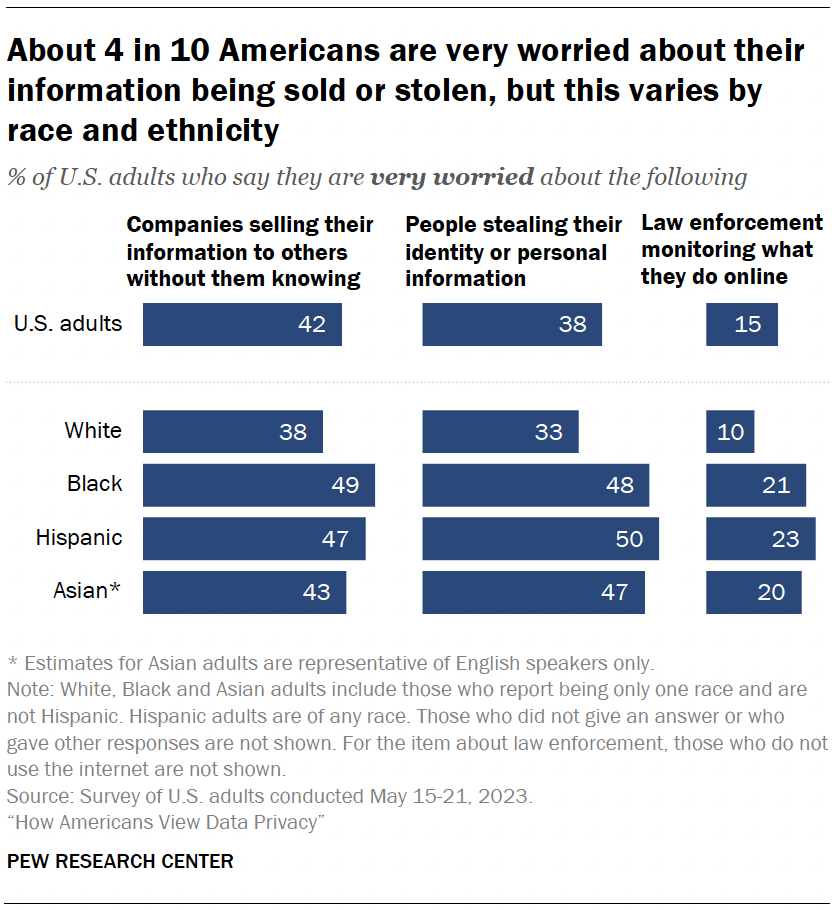
The survey also explores the concerns people have about data collection and security – specifically, how they feel about three scenarios around companies, law enforcement and identity theft.
Roughly four-in-ten Americans say they are very worried about companies selling their information to others without them knowing (42%) or people stealing their identity or personal information (38%). Fewer are apprehensive about law enforcement monitoring what they do online (15%).
Racial and ethnic differences
However, some of these shares are higher among Hispanic, Black or Asian adults: 1
- Roughly half of Hispanic, Black or Asian adults are very worried about people stealing their identity or personal information, compared with a third of White adults.
- About one-in-five of each group are very worried about law enforcement monitoring their online activity; 10% of White adults say this.
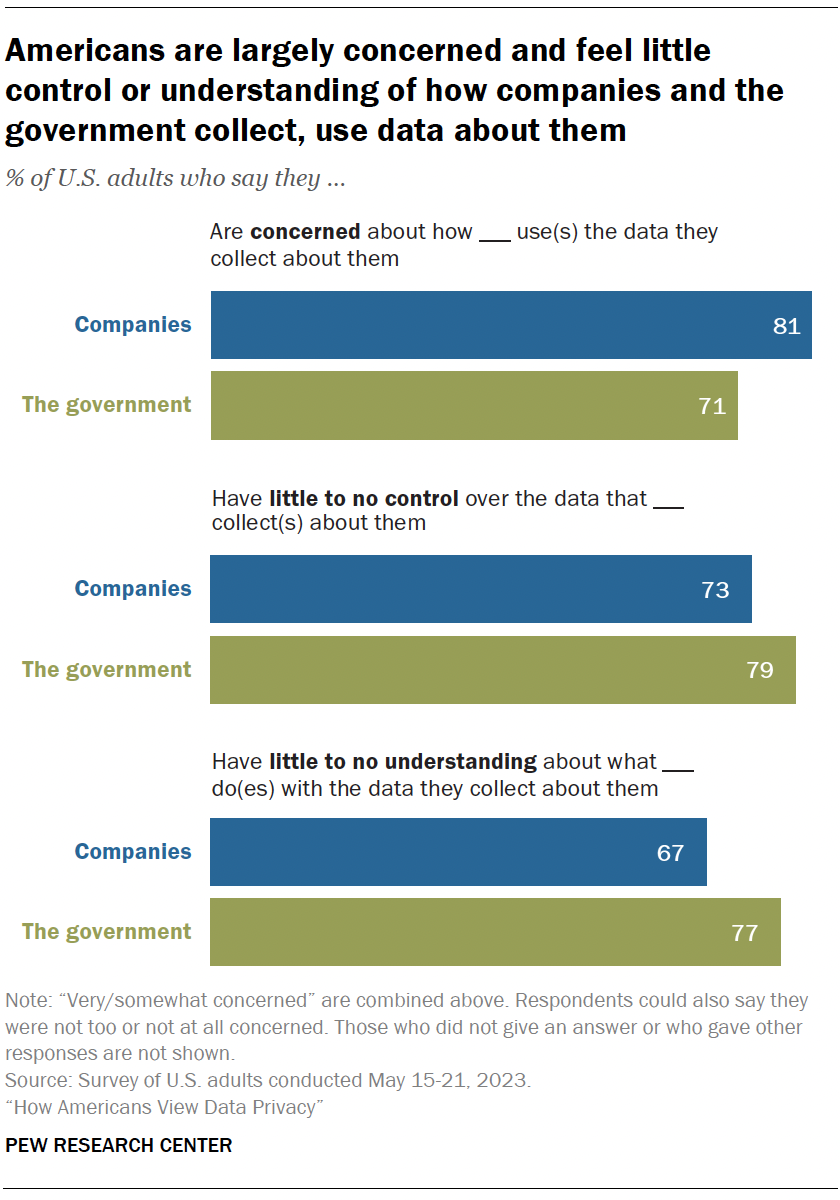
A majority of Americans say they are concerned, lack control and have a limited understanding about how the data collected about them is used. This is true whether it’s the government or companies using their data. Similar sentiments were expressed in 2019, when we last asked about this .
Concern is high: 81% say they feel very or somewhat concerned with how companies use the data they collect about them. Fully 71% say the same regarding the government’s use of data.
People don’t feel in control: Roughly three-quarters or more feel they have very little or no control over the data collected about them by companies (73%) or the government (79%).
Understanding is low: Americans also say they don’t understand what these actors are doing with the data collected about them. Majorities say they have very little or no understanding of this, whether by the government (77%) or companies (67%).
Americans are now less knowledgeable than before about how companies are using their personal data. The share who say they don’t understand this has risen from 59% in 2019 to 67% in 2023.
They have also grown more concerned about how the government uses the data it collects about them, with the share expressing concern up from 64% to 71% over this same period.
While these sentiments have not changed significantly since 2019 among Democrats and those who lean toward the Democratic Party, Republicans and GOP leaners have grown more wary of government data collection. Today, 77% of Republicans say they are concerned about how the government uses data it collects about them, up from 63% four years earlier.
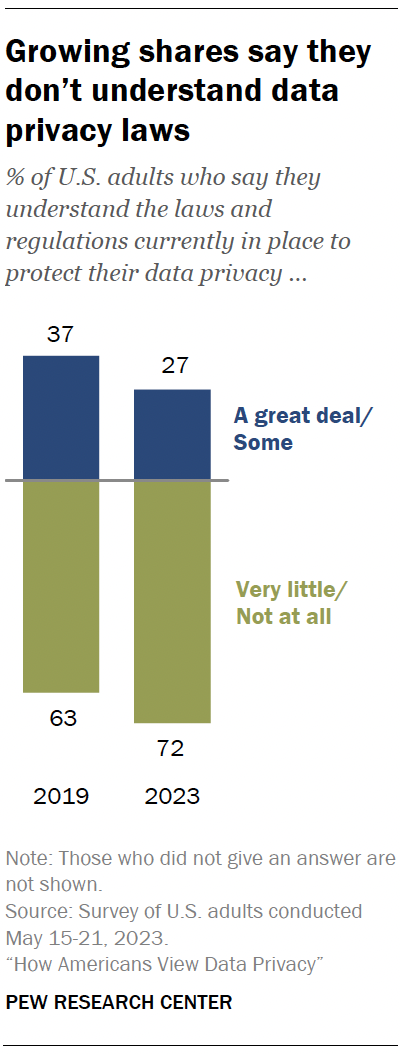
Americans are less knowledgeable about data privacy laws today than in the past.
Today, 72% of Americans say they have little to no understanding about the laws and regulations that are currently in place to protect their data privacy. This is up from 63% in 2019.
By comparison, the shares who say they understand some or a great deal about these laws decreased from 37% in 2019 to 27% in 2023.
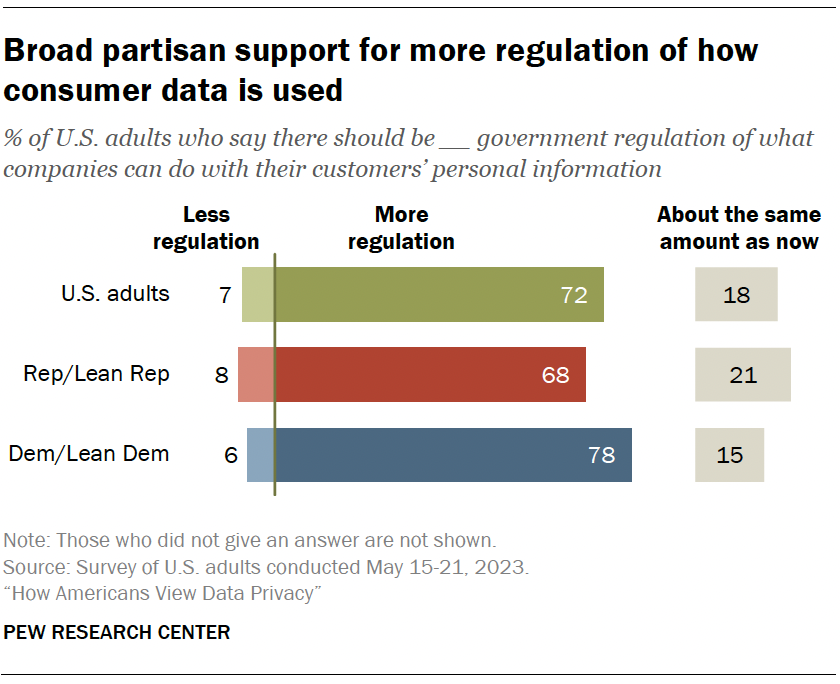
Overall, 72% say there should be more government regulation of what companies can do with their customers’ personal information. Just 7% say there should be less regulation. Another 18% say it should stay about the same.
Views by political affiliation
There is broad partisan support for greater involvement by the government in regulating consumer data.
A majority of Democrats and Republicans say there should be more government regulation for how companies treat users’ personal information (78% vs. 68%).
These findings are largely on par with a 2019 Center survey that showed strong support for increased regulations across parties.
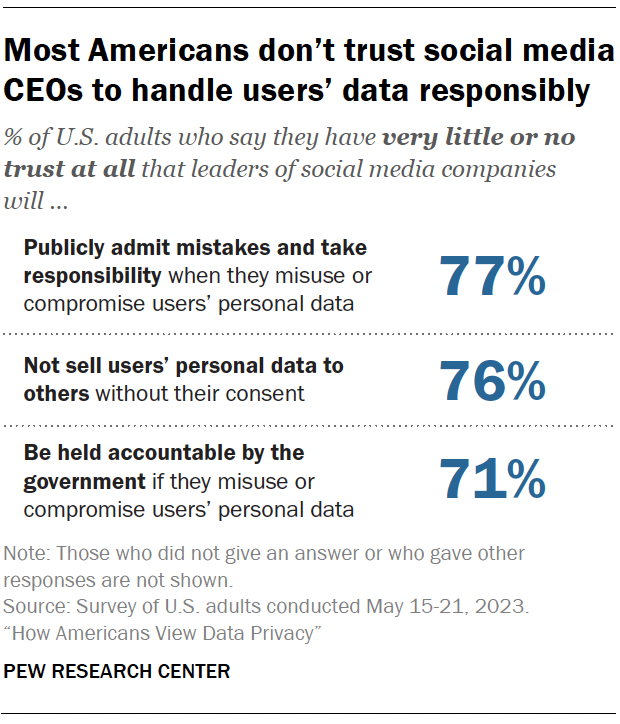
Majorities of Americans say they have little to no trust that leaders of social media companies will publicly admit mistakes regarding consumer data being misused or compromised (77%), that these leaders will not sell users’ personal data to others without their consent (76%), and that leaders would be held accountable by the government if they were to misuse or compromise users’ personal data (71%).
This includes notable shares who have no trust at all in those who are running social media sites. For example, 46% say they have no trust at all in executives of social media companies to not sell users’ data without their consent.
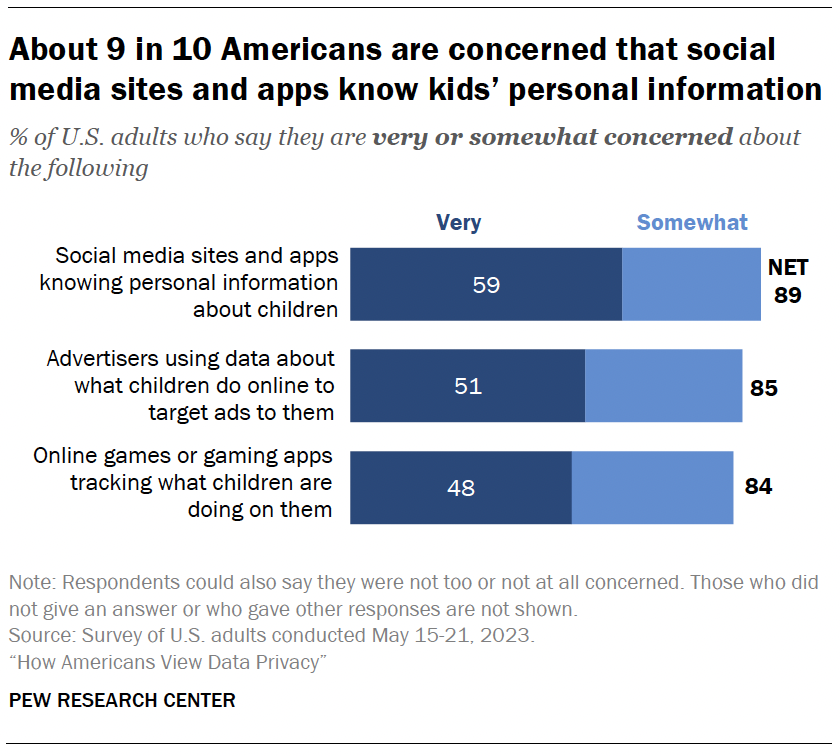
Most Americans say they are concerned about social media sites knowing personal information about children (89%), advertisers using data about what children do online to target ads to them (85%) and online games tracking what children are doing on them (84%).
Concern is widespread, with no statistically significant differences between those with and without children.
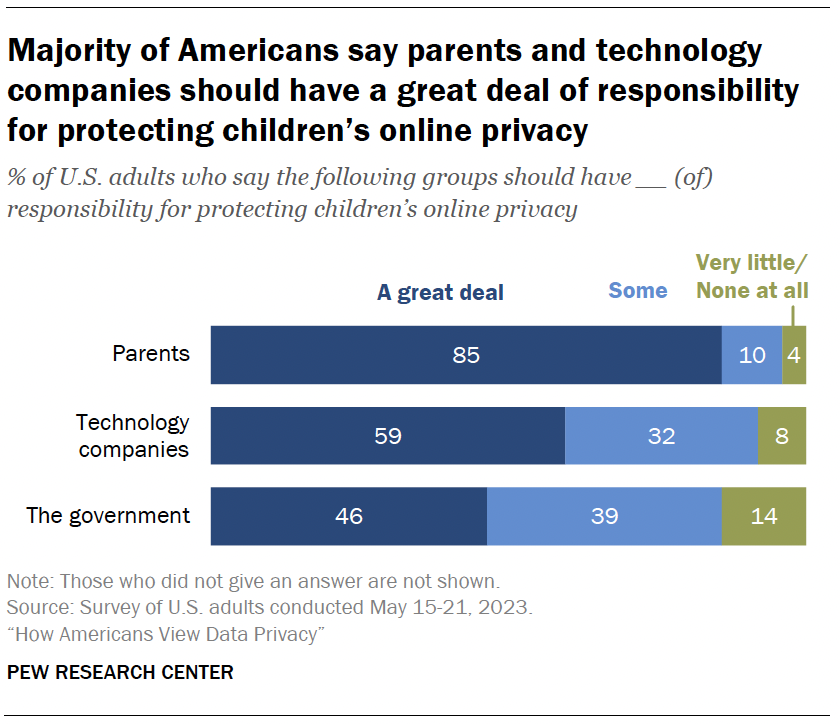
Another key question is who should be responsible for the actual protection of kids’ online privacy.
Fully 85% say parents bear a great deal of responsibility for protecting children’s online privacy. Roughly six-in-ten say the same about technology companies, and an even smaller share believe the government should have a great deal of responsibility.
The survey also measured how acceptable Americans think it is for law enforcement to use surveillance tools during criminal investigations.
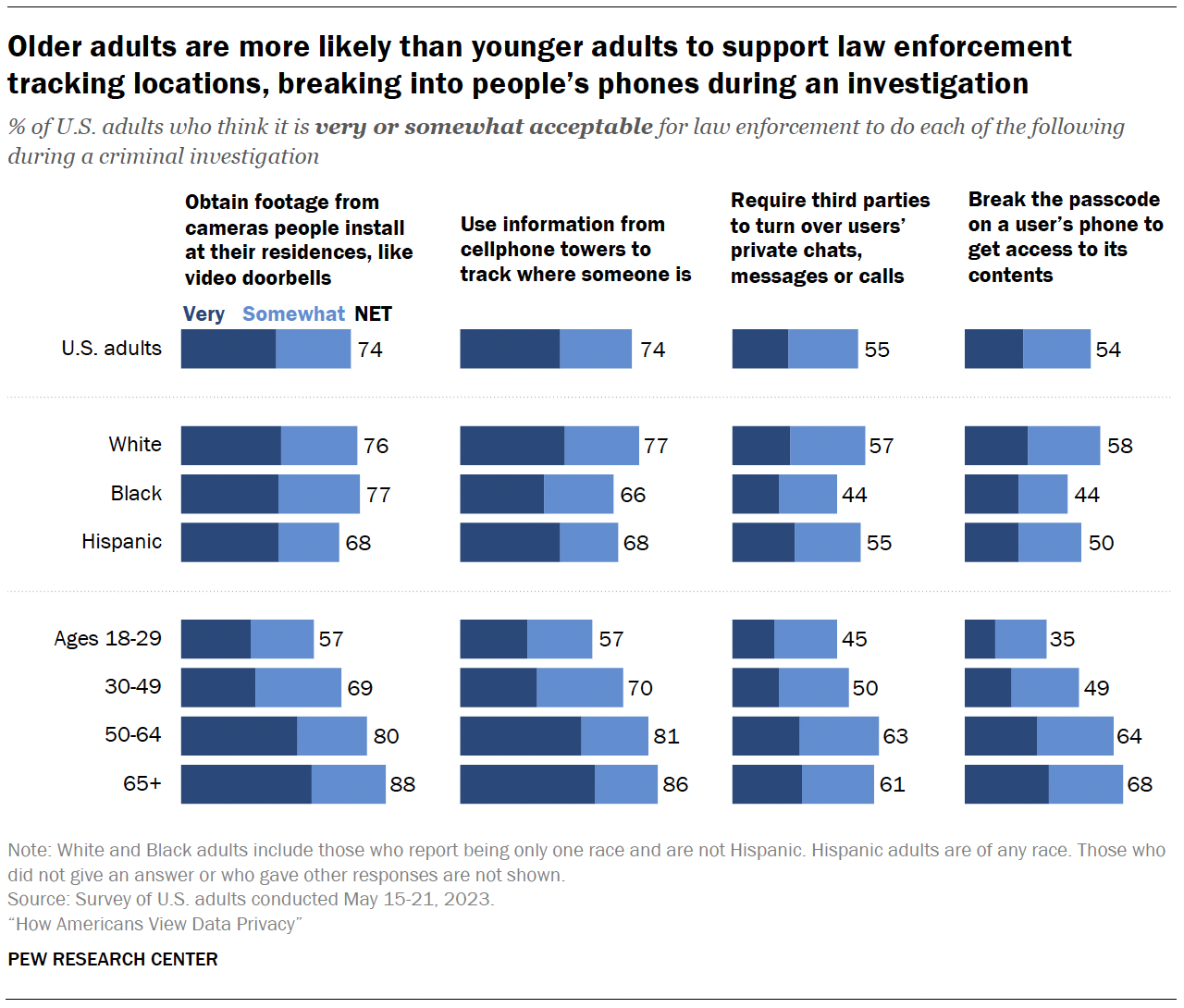
Roughly three-quarters of Americans say it’s very or somewhat acceptable for law enforcement to obtain footage from cameras people install at their residences during a criminal investigation or use information from cellphone towers to track where someone is.
By comparison, smaller shares – though still a slight majority – say it is acceptable to break the passcode on a user’s phone (54%) or require third parties to turn over users’ private chats, messages or calls (55%) during a criminal investigation. 2
About one-in-ten Americans say they aren’t sure how they feel about law enforcement doing each of these things.
Age differences
Older adults are much more likely than younger adults to say it’s at least somewhat acceptable for law enforcement to take each of these actions in criminal investigations.
For example, 88% of those 65 and older say it’s acceptable for law enforcement to obtain footage from cameras people install at their residences, compared with 57% of those ages 18 to 29.
In the case of a criminal investigation:
- White adults are more likely than Hispanic and Black adults to think it’s acceptable for law enforcement to use information from cellphone towers to track people’s locations and to break the passcode on a user’s phone to get access to its contents.
- White and Hispanic adults are more likely than Black adults to say it’s acceptable to require third parties to turn over users’ private chats, messages or calls.
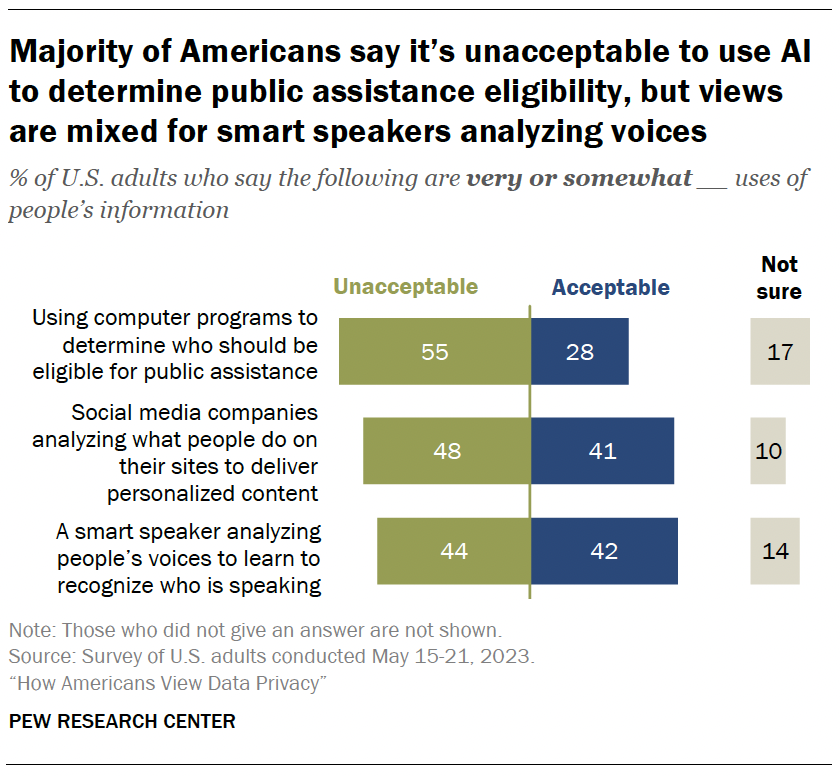
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to collect and analyze people’s personal information. Some Americans are wary of companies using AI in this way.
Fully 55% of adults say using computer programs to determine who should be eligible for public assistance is unacceptable. Roughly a quarter say it’s an acceptable use of AI.
Roughly half (48%) think it is unacceptable for social media companies to analyze what people do on their sites to deliver personalized content. Still, 41% are supportive of this.
Views are mixed when it comes to smart speakers analyzing people’s voices to learn who is speaking. Statistically equal shares say it’s unacceptable and acceptable (44% and 42%, respectively).
And some Americans – ranging from 10% to 17% – are uncertain about whether these uses are acceptable or not.
- 49% of adults 50 and older say it’s unacceptable for a smart speaker to analyze people’s voices to learn to recognize who’s speaking. This share drops to four-in-ten among adults under 50.
- Similarly, 56% of those 50 and older say social media companies analyzing what people do on their sites to deliver personalized content is unacceptable. But 41% of those under 50 say the same.
- There are no differences between those under 50 and those 50 and older over whether computer programs should be used to determine eligibility for public assistance.
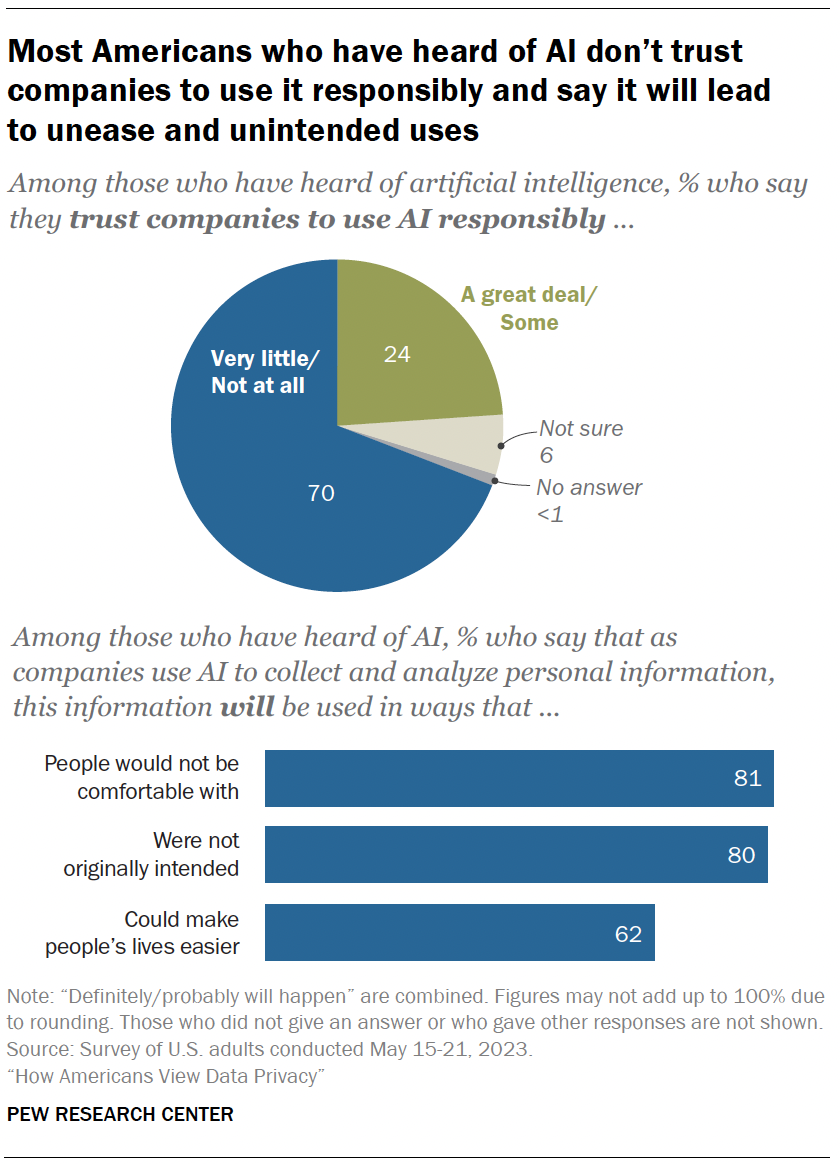
In addition to understanding people’s comfort level with certain uses of AI, the survey also measured the public’s attitudes toward companies that are utilizing AI in their products.
Among those who have heard of AI:
- 70% say they have little to no trust in companies to make responsible decisions about how they use AI in their products.
- Roughly eight-in-ten say the information will be used in ways people are not comfortable with or that were not originally intended.
- Views are more mixed regarding the potential that using AI to analyze personal details could make life easier. A majority of those who have heard of AI say this will happen (62%). Regarding differences by age, adults under 50 are more optimistic than those 50 and older (70% vs. 54%).
- 87% of those with a college degree or higher say companies will use AI to analyze personal details in ways people would not be comfortable with. Some 82% of those with some college experience and 74% with a high school diploma or less say the same.
- 88% of those with a bachelor’s degree or more say companies will use this information in ways that were not originally intended. This share drops to 80% among those with some college experience and 71% among those with a high school diploma or less.
- About three-quarters of those with a college degree or more (74%) say this information will be used in ways that could make people’s lives easier. But this share drops to 60% among those with some college experience and 52% among those with a high school diploma or less.
- This survey includes a total sample size of 364 Asian adults. The sample primarily includes English-speaking Asian adults and, therefore, it may not be representative of the overall Asian adult population. Despite this limitation, it is important to report the views of Asian adults on the topics in this study. As always, Asian adults’ responses are incorporated into the general population figures throughout this report. Asian adults are shown as a separate group when the question was asked of the full sample. Because of the relatively small sample size and a reduction in precision due to weighting, results are not shown separately for Asian adults for questions that were only asked of a random half of respondents (Form 1/Form 2). ↩
- Half of respondents were asked the questions above, and the other half received the same questions with the added context of it being a “criminal investigation where public safety is at risk.” Differences in response were largely modest. See Appendix A for these findings. ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Artificial Intelligence
- Online Privacy & Security
- Social Media
- Tech Companies
Social Media Fact Sheet
Teens and social media fact sheet, more americans are getting news on tiktok, bucking the trend seen on most other social media sites, life on social media platforms, in users’ own words, charting congress on social media in the 2016 and 2020 elections, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
Your Technology Is Tracking You. Take These Steps For Better Online Privacy

Laurel Wamsley

Before I became a reporter at NPR, I worked for a few years at tech companies.
One of the companies was in the marketing technology business — the industry that's devoted in part to tracking people and merging their information, so they can be advertised to more effectively.
That tracking happens in multiple senses: physical tracking, because we carry our phones everywhere we go. And virtual tracking, of all the places we go online.
The more I understood how my information was being collected, shared and sold, the more I wanted to protect my privacy. But it's still hard to know which of my efforts is actually effective and which is a waste of time.
So I reached out to experts in digital security and privacy to find out what they do to protect their stuff – and what they recommend most to us regular folks.
Here's what they told me.

How Are Apple, Amazon, Facebook, Google Monopolies? House Report Counts The Ways
1. to protect your accounts, practice good security hygiene..
There are some steps that make sense for almost all of us, says Eva Galperin , director of cybersecurity at the Electronic Frontier Foundation. Those include using strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and downloading the latest security updates.
She and other experts make a distinction between privacy and security when it comes to your data. Security generally refers to protecting against someone trying to access your stuff — such as stealing your credit card number or hacking your accounts. Privacy is more often used to talk about keeping your movements from being tracked for purposes of advertising or surveillance.
It turns out that the steps to protect your security are more clear-cut than those for privacy — but we'll come back to that.

TED Radio Hour
Edward snowden: why does online privacy matter.
Use strong passwords or passphrases for your accounts. Longer than a password, passphrases should be strong and unique for each site. Don't use 1234. Bring some randomness and special characters into it. And don't use the same password for different websites: You don't want all your accounts to be compromised just because one gets hacked.
Use a password manager to keep track of your passwords, Galperin says — then all you have to do is remember the passphrase for your password manager.
Turn on two-factor authentication for your important accounts. You've seen this: Usually you're asked to put in your mobile number so that you can receive a text with an additional number you input before you can log in.
That's the most common type of two-factor authentication — but it's not the strongest, Galperin says, because SMS messages can be intercepted by your Internet provider, law enforcement or the government.
If you want to go a step further, Galperin recommends using an application that sends the second factor to an app on your phone, such as Authy or Google Authenticator , as these are harder to intercept. (Full disclosure here: NPR receives funding from Google and Facebook.) You can also use a physical key you carry with you that plugs into your computer's USB port and serves as the second factor.

6 Tips For Making A Career Change, From Someone Who Has Done It
Download the latest security updates.
Those nudges you get from your computer or phone to install the latest security update? You should download those.
"Most applications, when they're compromised, are not compromised by scary zero-day bugs that nobody knows about," Galperin says. "They are compromised by problems that everybody knows exist that have been publicly reported, and that the company has fixed and they have issued a patch in their security update. But if you do not take the security update, you do not get the benefit of the work of the security engineers at that company."

How To Sign Up To Work The Polls On Election Day
2. beware of phishing..
Not all attacks on our security come through malware or hackers invisibly breaking into your account. It's common that we're tricked into handing over our passwords or personal information to bad actors.
These attempts can happen via email, text message or a phone call. And generally they're trying to get your username and password, or perhaps your Social Security number. But there are often signs that these messages aren't legit – spelling or grammar errors, links to websites other than the one it should be linking to, or the email is coming from a weird domain.
If it feels fishy, it might be phishing.

Twitter Expands Warning Labels To Slow Spread of Election Misinformation
3. protect what matters most..
Depending on your situation, you might want to take additional precautions to safeguard your privacy and security.
To figure out what steps people should take to safeguard their stuff, Galperin suggests you make a security plan. The Electronic Frontier Foundation has a guide to doing this, which starts by asking yourself these questions:
- What do I want to protect?
- Whom do I want to protect it from?
- How bad are the consequences if I don't?
- How likely is it to need protecting?
- And how much trouble am I willing to go through to try to protect it?
Resources For Securing Your Data
The Surveillance Self-Defense site from the Electronic Frontier Foundation is a good place to start. Here's its guide to making your own security plan and figuring out what you most want to protect.
From Tactical Tech, here are handy how-to kits for different scenarios, including securing your data , increasing your online privacy and making your phone less addictive .
You can use the answers to those questions to focus your efforts on securing the things that matter most to you.
4. Delete some apps from your phone. Use a browser instead.
Matt Mitchell is a tech fellow at the Ford Foundation, and the founder of CryptoHarlem , an organization that teaches people to protect their privacy, including from surveillance.
Apps can learn a lot about you due to all the different types of data they can access via your phone. Seemingly harmless apps – like say, a flashlight app — could be selling the data they gather from you.
That's why Mitchell recommends "Marie Kondo-ing" your apps: Take a look at your smartphone and delete all the apps you don't really need. For many tasks, you can use a browser on your phone instead of an app.
Privacy-wise, browsers are preferable, because they can't access as much of your information as an app can.
I mentioned to Mitchell that even though I use Facebook and Twitter, I don't have those apps on my phone — partly so that I'll use them less, and partly for privacy reasons. I wanted to know — did I accomplish anything by not having those apps on my phone?
"You've accomplished a lot," he says. He compares it to oil companies turning crude into petrol: Your data can be turned into profit for these companies. "Every time you don't use an app, you're giving them less data, which is less money."
Mitchell says that's true even if you've been on Facebook a long time, and it feels like the company already knows everything about you. He compares it to smoking: It's never too late to cut back or quit — you'll still benefit by giving it less data to harvest.
5. To protect your chats, use an encrypted app for messaging.
If you want the contents of your messages to be secure, it's best to use an app that has end-to-end encryption, such as Signal or WhatsApp. That means you and the recipient can read the message you send — but no one in the middle.
But even though the contents of your messages are protected by encryption in apps such as Signal and WhatsApp, your metadata isn't — and someone could learn a lot about you from your metadata, Galperin warns. She compares it to what you can learn just by looking at the outside of an envelope in the mail: who sent it to whom, when and where it was sent from.
And WhatsApp is owned by Facebook — so when you share your contacts with WhatsApp, Facebook is getting that info, though it can't read the contents of your messages.
If you're on an iPhone, iMessages are encrypted when you're messaging another iOS device — but not when you're messaging an Android phone. Signal offers encrypted messaging on both Android and iPhone.
What about Facebook Messenger? Jen King , director of privacy at Stanford Law School's Center for Internet and Society, advises against using the Messenger app.
The app "has access to far more info on your phone than using Facebook through a browser," she says, recommending something such as WhatsApp or regular SMS texting instead.
And if encryption matters to you, be careful about backing up your chats to the cloud. If you back up your WhatsApp messages to iCloud or Google Drive , for example, they're no longer encrypted.
"That backup is just a database. And that database is easy for someone to open and read," Mitchell says, if they were able to access your cloud account. To keep your messages from prying eyes, turn off cloud backups and delete existing WhatsApp backups from iCloud or Google Drive.

California Rings In The New Year With A New Data Privacy Law
6. turn off ad personalization..
Whenever possible, Mitchell recommends going into your settings and turning off ad personalization, which often gives companies permission to do invasive tracking.
Opting Out Of Ad Personalization On Some Major Platforms
Google and Android
Here's a link to limit ad personalization on Google and Android.
This page shows you how to opt out of ad personalization on Apple. As of this writing, it hasn't been updated for iOS 14. If you have updated to iOS 14, go to Settings > Privacy > Apple Advertising > turn off Personalized Ads.
- On this page , you can go to the ad settings tab and toggle the settings to not allowed.
- This page has steps to disconnect your activity off Facebook that is shared with Facebook, and clear that history.
- On the Off-Facebook activity page , under What You Can Do, you can click on More Options > Manage Future Activity > and toggle it to off. ( This page has those steps.)
This page explains how to opt out of ad personalization.
He also recommends going to myactivity.google.com and deleting everything you can. On the left, there's a tab that says "Delete activity by." Select "All time." On your My Google Activity page, you can turn off Web & App Activity, Location History and YouTube History.
"It will show you every search term and everything you've ever done, every YouTube video you've ever looked at, all that stuff," he says. "It'll say, are you sure you want to delete this? 'Cause if you delete this, it might affect some stuff." Mitchell says: Delete it.
7. It's difficult to protect your privacy online if there aren't laws to protect your privacy online.
Tighter privacy settings only get you so far without laws that protect your privacy, says Ashkan Soltani , the former chief technologist for the Federal Trade Commission and one of the architects of the 2018 California Consumer Privacy Act .
Activist Aims To Strengthen California's Consumer Privacy Act
There are laws around health information and credit and financial information, he explains, and some states have Internet privacy-related laws .
But nationally, the U.S. doesn't have a universal data privacy law safeguarding everyday online privacy.
Soltani says he rarely recommends steps such as using ad blockers or VPNs for most people. They require too much attention and persistence to deliver on privacy, and even then they are limited in their effectiveness.
"The incentives are so high on the other side," Soltani says, "to uniquely identify people and track them that [users] will never have enough motivation and incentive to do it to the degree of this multibillion dollar ad tech industry."
So how do you protect your privacy? Get involved and call your congressperson, he says — tell the policymakers that you care about online privacy.
8. Start small and take it one step at a time.
Faced with this landscape, getting a tighter hold on your digital privacy and security can feel daunting. But Galperin has this sound advice: Just do a little bit at a time.
You don't need to make a list of all of your accounts to integrate into a password manager — you can just do each account as you log into it.
Even just doing the basics — strengthening your passwords, turning on two-factor authentication and watching out for scammers — can make your accounts a lot more secure. Then keep going: There are a lot of other steps you might want to take, depending on your needs.
We're going to be on the Internet for a long time. The more each of us understands how our data are collected and used — and how to keep private what we want to keep private — the better, safer and healthier our digital lives will be.
The podcast portion of this episode was produced by Audrey Nguyen. She also contributed research.
We'd love to hear from you. Leave us a voicemail at 202-216-9823, or email us at [email protected] .
For more Life Kit, subscribe to our newsletter .
- Life Kit: Life Skills
Home / Essay Samples / Social Issues / Human Rights / Internet Privacy
Internet Privacy Essay Examples
Forms of cybercrime and online fraud.
Much of our lives revolve around screens and the internet. We spend at least two hours out of our days on our phones, computers, watching television, or playing on our iPads. Cybercrime is a form of crime that takes place on the internet and it...

Staying Safe Online: Strategies for Digital Security
The purpose of this how do you keep yourself safe and secure online essay is to enlighten the reader about how to keep your information as secure as possible on the Internet. Today, when the use of technology is part of our everyday life, young...
Technology Privacy Data: Research Based Investigation
To start with, my aim for this paper concerns writing a research based argumentative essay about technology. The term technology has a diverse meaning that can be summarized as the use and application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes in the quest to make work...
Why Facebook Should Be Banned: the Issue of Privacy Policy
Facebook is a social networking organization, which makes enables people to connect with each other. Mark Zuckerberg launched Facebook in 2004. While he was studying at Harvard University. The biggest problem faced by Facebook is the privacy of users. I belive that Facebook should be...
The Future of Radio Frequency Identification Technology
As products evolve to satisfy today’s efficiency demands, it can seem to some that our world is shifting towards one that we observe in science fiction. The article, “This firm already microchips employees. Could your ailing relative be next?” from Washington Post mentions Three Square...
Techniques of Privacy Preserving Based on K-anonymity
In location based services on mobile the k anonymity tries to preserve the identity of the sender by generating k-1 same requests, so that exact user can not be identified. Bettini propose a framework based on location based quasi identifier concept related with k-anonymity. Quasi...
Ethical Hacking as a Defence Mechanism
Computer Crime is often referred to as ‘cybercrime’, “cybercrime can be thought of as crime that involves computers and computer networks. ” (Hill and Marion, 2016 [1]). Cybercrime “refers to acts that involve criminal uses of the Internet or other networked systems to cause harm...
Location Based Services for Privacy Preserving
With the rapid development of wireless communication, mobile networks and positioning technologies, location based services (LBSs) have been gaining traction among consumers in recent years. Users can download location-based applications from the App Store through smartphones, such as Twitter, Gowalla and Foursquare. With the help...
Loss of Privacy on the Internet
Nowadays, the Internet plays an important role in people’s life and work for example education and self-improvement, friendship and dating, electronic newspapers and magazines, entertainment and gaming, and it gradually becomes an indispensable part of human. How much of personal life have people shared on...
Panopticon as the Concept of a Security System in the Digital Age
The Digital Age, also known as New Media Age, Computer or Information Age, is a period that associates with the Industrial Revolution of the 18th century which led to the nowadays technological development era (in the 21st century). Digital Age is characterized by the rapid...
Trying to find an excellent essay sample but no results?
Don’t waste your time and get a professional writer to help!
You may also like
- Cyber Bullying
- Racial Discrimination
- Gender Equality
- Public Shaming
- Black Lives Matter
- Sexual Abuse
- 2Nd Amendment
- Population Growth
- Emmett Till
- Capital Punishment Essays
- Civil Rights Essays
- Malcolm X Essays
- Gender Inequality Essays
- Freedom of Speech Essays
- Censorship Essays
- Corporal Punishment Essays
- Gender Discrimination Essays
- Gender Wage Gap Essays
- Privacy Essays
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->