
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


8.5: Summary vs. Analysis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 101135

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
Summary: Using it Wisely
Knowing how to summarize something you have read, seen, or heard is a valuable skill, one you have probably used in many writing assignments. It is important, though, to recognize when you must go beyond describing, explaining, and restating texts and offer a more complex analysis. This handout will help you distinguish between summary and analysis and avoid inappropriate summary in your academic writing.
Is summary a bad thing?
Not necessarily. But it’s important that your keep your assignment and your audience in mind as you write. If your assignment requires an argument with a thesis statement and supporting evidence—as many academic writing assignments do—then you should limit the amount of summary in your paper. You might use summary to provide background, set the stage, or illustrate supporting evidence, but keep it very brief: a few sentences should do the trick. Most of your paper should focus on your argument. (Our handout on argument will help you construct a good one.)
Writing a summary of what you know about your topic before you start drafting your actual paper can sometimes be helpful. If you are unfamiliar with the material you’re analyzing, you may need to summarize what you’ve read in order to understand your reading and get your thoughts in order. Once you figure out what you know about a subject, it’s easier to decide what you want to argue.
You may also want to try some other pre-writing activities that can help you develop your own analysis. Outlining, freewriting, and mapping make it easier to get your thoughts on the page. (Check out our handout on brainstorming for some suggested techniques.)
Why is it so tempting to stick with summary and skip analysis?
Many writers rely too heavily on summary because it is what they can most easily write. If you’re stalled by a difficult writing prompt, summarizing the plot of The Great Gatsby may be more appealing than staring at the computer for three hours and wondering what to say about F. Scott Fitzgerald’s use of color symbolism. After all, the plot is usually the easiest part of a work to understand. Something similar can happen even when what you are writing about has no plot: if you don’t really understand an author’s argument, it might seem easiest to just repeat what he or she said.
To write a more analytical paper, you may need to review the text or film you are writing about, with a focus on the elements that are relevant to your thesis. If possible, carefully consider your writing assignment before reading, viewing, or listening to the material about which you’ll be writing so that your encounter with the material will be more purposeful. (We offer a handout on reading towards writing .)
How do I know if I’m summarizing?
As you read through your essay, ask yourself the following questions:
- Am I stating something that would be obvious to a reader or viewer?
- Does my essay move through the plot, history, or author’s argument in chronological order, or in the exact same order the author used?
- Am I simply describing what happens, where it happens, or to whom it happens?
A “yes” to any of these questions may be a sign that you are summarizing. If you answer yes to the questions below, though, it is a sign that your paper may have more analysis (which is usually a good thing):
- Am I making an original argument about the text?
- Have I arranged my evidence around my own points, rather than just following the author’s or plot’s order?
- Am I explaining why or how an aspect of the text is significant?
Certain phrases are warning signs of summary. Keep an eye out for these:
- “[This essay] is about…”
- “[This book] is the story of…”
- “[This author] writes about…”
- “[This movie] is set in…”
Here’s an example of an introductory paragraph containing unnecessary summary. Sentences that summarize are in italics:
- The Great Gatsby is the story of a mysterious millionaire, Jay Gatsby, who lives alone on an island in New York. F. Scott Fitzgerald wrote the book, but the narrator is Nick Carraway. Nick is Gatsby’s neighbor, and he chronicles the story of Gatsby and his circle of friends, beginning with his introduction to the strange man and ending with Gatsby’s tragic death. In the story, Nick describes his environment through various colors, including green, white, and grey. Whereas white and grey symbolize false purity and decay, respectively, the color green offers a symbol of hope.
Here’s how you might change the paragraph to make it a more effective introduction:
- In The Great Gatsby, F. Scott Fitzgerald provides readers with detailed descriptions of the area surrounding East Egg, New York. In fact, Nick Carraway’s narration describes the setting with as much detail as the characters in the book. Nick’s description of the colors in his environment presents the book’s themes, symbolizing significant aspects of the post-World War I era. Whereas white and grey symbolize the false purity and decay of the 1920s, the color green offers a symbol of hope.
This version of the paragraph mentions the book’s title, author, setting, and narrator so that the reader is reminded of the text. And that sounds a lot like summary—but the paragraph quickly moves on to the writer’s own main topic: the setting and its relationship to the main themes of the book. The paragraph then closes with the writer’s specific thesis about the symbolism of white, grey, and green.
How do I write more analytically?
Analysis requires breaking something—like a story, poem, play, theory, or argument—into parts so you can understand how those parts work together to make the whole. Ideally, you should begin to analyze a work as you read or view it instead of waiting until after you’re done—it may help you to jot down some notes as you read. Your notes can be about major themes or ideas you notice, as well as anything that intrigues, puzzles, excites, or irritates you. Remember, analytic writing goes beyond the obvious to discuss questions of how and why—so ask yourself those questions as you read.
The St. Martin’s Handbook encourages readers to take the following steps in order to analyze a text:
- Identify evidence that supports or illustrates the main point or theme as well as anything that seems to contradict it.
- Consider the relationship between the words and the visuals in the work. Are they well integrated, or are they sometimes at odds with one another? What functions do the visuals serve? To capture attention? To provide more detailed information or illustration? To appeal to readers’ emotions?
- Decide whether the sources used are trustworthy.
- Identify the work’s underlying assumptions about the subject, as well as any biases it reveals. (Lunsford 38)
Once you have written a draft, some questions you might want to ask yourself about your writing are, “What’s my point?” or, “What am I arguing in this paper?” If you can’t answer these questions, then you haven’t gone beyond summarizing. You may also want to think about how much of your writing comes from your own ideas or arguments. If you’re only reporting someone else’s ideas, you probably aren’t offering an analysis.
What strategies can help me avoid excessive summary?
- Read the assignment (the prompt) as soon as you get it. Make sure to reread it before you start writing. Go back to your assignment often while you write. (Check out our handout on reading assignments ).
- Formulate an argument (including a good thesis) and be sure that your final draft is structured around it, including aspects of the plot, story, history, background, etc. only as evidence for your argument. (You can refer to our handout on constructing thesis statements ).
- Read critically—imagine having a dialogue with the work you are discussing. What parts do you agree with? What parts do you disagree with? What questions do you have about the work? Does it remind you of other works you’ve seen?
- Make sure you have clear topic sentences that make arguments in support of your thesis statement. (Read our handout on paragraph development if you want to work on writing strong paragraphs).
- Use two different highlighters to mark your paper. With one color, highlight areas of summary or description. With the other, highlight areas of analysis. For many college papers, it’s a good idea to have lots of analysis and minimal summary/description.
- Ask yourself: What part of the essay would be obvious to a reader/viewer of the work being discussed? What parts (words, sentences, paragraphs) of the essay could be deleted without loss? In most cases, your paper should focus on points that are essential, and will be interesting to people who have already read or seen the work you are writing about.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find the latest publications on this topic. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
Barnet, Sylvan and William E. Cain. A Short Guide to Writing about Literature. 12th ed. New York: Pearson, 2011.
Corrigan, Timothy. A Short Guide to Writing About Film. 9th ed. New York: Pearson, 2014.
Lunsford, Andrea A. The St. Martin’s Handbook. 5th ed. Boston: Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2003.
Zinsser, William. On Writing Well. 6th ed. New York: Quill, 2001.
Contributors and Attributions


Get Started
Take the first step and invest in your future.

Online Programs
Offering flexibility & convenience in 51 online degrees & programs.

Prairie Stars
Featuring 15 intercollegiate NCAA Div II athletic teams.

Find your Fit
UIS has over 85 student and 10 greek life organizations, and many volunteer opportunities.

Arts & Culture
Celebrating the arts to create rich cultural experiences on campus.

Give Like a Star
Your generosity helps fuel fundraising for scholarships, programs and new initiatives.

Bragging Rights
UIS was listed No. 1 in Illinois and No. 3 in the Midwest in 2023 rankings.
- Quick links Applicants & Students Important Apps & Links Alumni Faculty and Staff Community Admissions How to Apply Cost & Aid Tuition Calculator Registrar Orientation Visit Campus Academics Register for Class Programs of Study Online Degrees & Programs Graduate Education International Student Services Study Away Student Support Bookstore UIS Life Dining Diversity & Inclusion Get Involved Health & Wellness COVID-19 United in Safety Residence Life Student Life Programs UIS Connection Important Apps UIS Mobile App Advise U Canvas myUIS i-card Balance Pay My Bill - UIS Bursar Self-Service Email Resources Bookstore Box Information Technology Services Library Orbit Policies Webtools Get Connected Area Information Calendar Campus Recreation Departments & Programs (A-Z) Parking UIS Newsroom Connect & Get Involved Update your Info Alumni Events Alumni Networks & Groups Volunteer Opportunities Alumni Board News & Publications Featured Alumni Alumni News UIS Alumni Magazine Resources Order your Transcripts Give Back Alumni Programs Career Development Services & Support Accessibility Services Campus Services Campus Police Facilities & Services Registrar Faculty & Staff Resources Website Project Request Web Services Training & Tools Academic Impressions Career Connect CSA Reporting Cybersecurity Training Faculty Research FERPA Training Website Login Campus Resources Newsroom Campus Calendar Campus Maps i-Card Human Resources Public Relations Webtools Arts & Events UIS Performing Arts Center Visual Arts Gallery Event Calendar Sangamon Experience Center for Lincoln Studies ECCE Speaker Series Community Engagement Center for State Policy and Leadership Illinois Innocence Project Innovate Springfield Central IL Nonprofit Resource Center NPR Illinois Community Resources Child Protection Training Academy Office of Electronic Media University Archives/IRAD Institute for Illinois Public Finance
Request Info

summary vs analysis

- Request Info Request info for.... Undergraduate/Graduate Online Study Away Continuing & Professional Education International Student Services General Inquiries
In academic writing, writers are often expected to use a combination of summary and analysis in their papers. However, the two processes are often confused especially by beginning writers. This handout aims to help you better identify the differences between summary and analysis.
- The purpose of a summary is to reduce information already known down to its essential parts.
- The information stated usually consists of the main points and key supporting points.
- Summaries can use direct quotes or paraphrasing to convey the main or key points. However, more often, a paraphrase is used.
- Summaries do not evaluate, judge, or interpret the information. They present the facts as the original writer or speaker intended.
- When writing a summary, writers should avoid adding their personal reactions, biases, opinions, and beliefs.
- Summaries are typically substantially shorter than their source texts, as they contain only the key points presented in an abbreviated form.
- The purpose of an analysis is to interpret or find meanings or patterns in information.
- Analyzing statements will take a step beyond summary and describe the writer’s personal findings and interpretations of the source material.
- An analysis usually is presented after a statement of evidence, which can have direct quotes or summary. After the evidence is presented, the analysis of that evidence should not summarize or describe the information. Rather, an analysis will uncover something new about the evidence.
- Analysis can provide readers a more thorough understanding of the facts presented, but writers should avoid adding their personal reactions, biases, opinions, and beliefs.
- Although an analysis may be influenced by personal beliefs, an analysis tends to be based more in facts and patterns than thoughts and emotions.
Below, we have provided an example of a summary paragraph and an analysis paragraph to help you identify the differences between them.
Prompt : You will choose a short film, and determine what the short film is communicating to its audience through the marriage of narrative and technique. Your job is to construct an analysis around a thesis statement arguing what the message is that is being communicated within this short piece. This message isn’t the plot; rather, you need to find out what the main theme of the story is, and then tell us how the short film conveys that through the use of various techniques.
Summary Paragraph Example
In “Mr. Foley,” a short film directed by D.A.D.D.Y., the sound effects are the star. In film production, a Foley artist is the person who generates sound effects artificially to play over footage. This important job is exaggerated into absurdity in this short film, where a man named Mr. Foley wakes up in a hospital and suddenly all the sounds he makes and hears is produced by a team sitting in his room. The first thing we hear as an audience is white noise, almost like a record player’s static. Next, as Mr. Foley’s bandages are removed we hear music start to swell. We also catch glimpses of hands manipulating cloth and ripping tape off a surface as well. Sounds are exaggerated to the extreme: as the nurse clicks her pen one of the men across the room clicks a giant pen.
- The preceding papragraph is a great example of a summary. It merely describes what is happening in this short film, without analyzing any meaning or providing any argument about the different sounds and shots it mentions.
- However, this would not be appropriate for the prompt given above. It clearly asks for an analysis of the short film’s use of technique, so some revision of the paragraph above is needed to make it appropriate for the assignment. Below is a paragraph with more analysis added.
Analysis Paragraph Example
In “Mr. Foley,” a short film directed by D.A.D.D.Y., the sound effects are the star. In film production, a Foley artist is the person who generates sound effects artificially to play over footage. This important job is exaggerated into absurdity in this short film, where a man named Mr. Foley wakes up in a hospital and suddenly all the sounds he makes and hears is produced by a team sitting in his room. Through the exaggeration of sound effects, “Mr. Foley” emphasizes the artificiality of sound production in Hollywood, and questions its efficacy and representation of reality. For example, the very first sound we hear as an audience is white noise, almost like a record player’s static. This ambient sound represents blank, neutral noise in absence of other sounds, but is quite obviously artificial. Thus, the message of the film begins to take shape within even the first few seconds of the story. As Mr. Foley’s bandages begin to be removed, music swells and the camera cuts to close up shots of hands manipulating cloth and ripping tape off of a surface. When the camera cuts back to Mr. Foley’s face (with surprise spreading across it), we understand that these sounds represent the gauze rubbing against itself and tearing away from his skin. In the next shots, we see both occurring in the same frame as the nurse clicks her pen and one of the men making the sounds clicks a giant pen to create an extreme exaggerated version of that sound. However, by visually pointing out the artificial production of the sounds, the film highlights their fake, false nature, calling into question Hollywood’s overproduction of sounds.
- This version more appropriately responds to the above prompt, because it not only points out and describes details from the short film, but also follows through on them to connect them to the meaning presented in the thesis statement (italicized). The bolded portions indicate the analysis injected into this paragraph.
Module 3: Critical Reading
Summary vs. analysis, learning objectives.
- List strategies and techniques for summarizing a text
- Recognize the difference between summary and analysis
What is a Summary?
When you summarize, you use your own words to condense a text in a way that preserves its original meaning. The trick is to strategically select which details to include or exclude according to your purpose.
For example, in the first chapter of his 1854 book, Walden; or, Life in the Woods , Henry David Thoreau wrote the following:
Most men, even in this comparatively free country, through mere ignorance and mistake, are so occupied with the factitious cares and superfluously coarse labors of life that its finer fruits cannot be plucked by them. Their fingers, from excessive toil, are too clumsy and tremble too much for that. Actually, the laboring man has not leisure for a true integrity day by day; he cannot afford to sustain the manliest relations to men; his labor would be depreciated in the market. He has no time to be anything but a machine. How can he remember well his ignorance—which his growth requires—who has so often to use his knowledge? We should feed and clothe him gratuitously sometimes, and recruit him with our cordials, before we judge of him. The finest qualities of our nature, like the bloom on fruits, can be preserved only by the most delicate handling. Yet we do not treat ourselves nor one another thus tenderly. (4)
What is the main idea in the passage above? The following is one way the passage might be summarized.
In his 1854 text, Walden; or, Life in the Woods , Henry David Thoreau suggests that the human fixation on work and labor desensitizes man to the world around him, to the needs of his own intellectual growth, and to the complexity and frailty of his fellow humans. (4)
This summary accomplishes two goals:
- It contextualizes the information (who said it, when, and where).
- It lists the main ideas of the passage without using extensive quotations or citing specific supporting points of the passage.
- It digests a complex and difficult passage and helps the reader understand it.
Summaries can be long or short. They can be filled with concrete details or more focused on the abstract ideas communicated by a text. But they must be tailored to your purpose: the reason you’re writing or the topic you’re addressing. With this in mind, here are some general guidelines for writing effective summaries:
- Avoid “point by point” summaries. You can often spot these summaries because they use transitions like First, Second, Third, etc. to describe what happens in a text in sequential order. While they offer detail, point-by-point summaries often fail to focus on the question or topic you are writing about and risk confusing your reader.
- Stay true to the information and ideas in the original text. To do this, you need to have a strong understanding of what the author was trying to communicate, how, and why. With the example text above, for instance, it may take several readings—and maybe even the help of secondary works—to understand what Thoreau was trying to say.
- Avoid mixing your summary with your analysis. You should also use signal phrases (“Austen writes”, “I argue”) to avoid confusing your reader. It’s important they know whose ideas are whose.
- Use short quotes sparingly. Summarizing allows you to retain the continuity of the essay as it unravels in your voice. Cite all quotes to avoid plagiarism.
What is Analysis?
Etymologically, “analyze” and “analysis” come from the Greek analusis , from ana – ‘up’ + lyein ‘loosen.’ In a sense, the job of analysis is to “loosen up” the text, taking it apart to figure out how it works. Analysis is the process of methodically breaking something down to gain a better understanding of it. Analysis also includes the ability to connect pieces of information as the basis for generalization or explanation.
Analysis can be applied to content but can also cover form, function, and context. For example, an analysis assignment in an art appreciation class might ask you to analyze the subject and symbolism of a painting, but also expect you to analyze the use of shape, space, color, and texture (form), as well as the artist’s intended purpose (function) and the culture or time period in which the work was created (context).
While each academic discipline characterizes the analytic process to suit its needs, the essential skills of analysis are the following:
- Breaking down information or artifacts into component parts
- Uncovering relationships among those parts
- Determining motives, causes, and underlying assumptions
- Making inferences and finding evidence to support generalizations
It’s important to be aware of whether you are writing summary or analysis of a text. As the chart below suggests, the two ways of approaching a text are quite different. Often, the assignment will determine whether a summary or analysis is in order.
In many cases, your writing will involve a combination of summary and analysis.
Active Reading Strategies for Summary
When you’re marking up a text to summarize, it can be helpful to write keywords in the margin to help map the overall flow of the piece. To keep track of the main points for summary, put marks next to thesis and topic sentences. It can also be useful to label lists: When an author writes something like “The arctic faces three major threats…”, first mark the statement announcing the list (“…three major threats…”), then look for the three points in the paragraphs that follow. Label each one with the appropriate number. This can give you a quick overview of the structure of the argument.
Active Reading Strategies for Analysis
Reading for analysis is somewhat different than reading for summary. Rather than just trying to understand and outline the structure of the argument, you’re now looking for clues to help you sort out how the text works. You may find yourself focusing on internal tensions in the argument or cracks in its logic, or you may notice connections to other texts (intertextuality) or rhetorical patterns within the text. One of the most effective ways to mark up a text for analysis is to write questions in the margin. These can help visualize the conversation taking place between the reader and the text, and offer jumping-off points for your own argument about the text.
“Analysis.” Online Etymology Dictionary . https://www.etymonline.com/word/analysis
Thoreau, Henry. Walden . United States, Beacon Press, 2004.
- Thoreau Summary. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/research/drafting-and-integrating/drafting-and-integrating-summarizing/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Analysis. Authored by : Karen Forgette. Provided by : University of Mississippi. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/englishcomp1/chapter/what-is-analysis/ . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Forest. Authored by : Bergadder. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/trees-forest-fog-foggy-haze-mist-975091/ . License : Other . License Terms : Pixabay license


Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.

Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Cybersecurity in Higher Education: Safeguarding Students and Faculty Data

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Beyond Google Scholar: Why SciSpace is the best alternative

Graduate Writing Center
Analysis versus summary - graduate writing center.
- Citations / Avoiding Plagiarism
- Analysis versus Summary
- Argument and Analysis
- So What? On Significance
- Discipline-Specific Resources
- Generative AI
- iThenticate FAQ
- Organization and Structure
- Punctuation
- Style: Clarity and Concision
- Writing Process
- Writing a Thesis
- Quick Clips & Tips
- Presentations and Graphics
Analysis versus Summary
When asked to analyze a document, we don't always know what to do. Faced with an assignment that calls for analysis of a topic—say, how the Civil War ended slavery—one might be tempted to simply restate facts. That is summarizing.
Analysis, on the other hand, requires more than simply paraphrasing what a source says or reciting some data: it means examining the facts and reaching your own conclusions regarding the subject. What is the writer trying to say? What does it mean? Is it convincing ? Analysis is breaking down the parts to see how they fit and presenting your own synthesis.
Readers especially love seeing analysis in thesis statements and topic sentences because analysis equals your own ideas.
A good test for whether you are analyzing or summarizing is to ask whether anyone (other than a conspiracy theorist) could argue with your statement:
- The 1964 Civil Rights Act legally ended employment discrimination. (Summary: a matter of historical record.)
- Though the 1964 Civil Rights Act legally ended employment discrimination, the battle for equal employment opportunity in the United States remains incomplete almost 60 years later. (Analysis: it calls for additional explanation and evidence.)
There is a difference between quantitative and qualitative analysis, but, in both, you express how the facts or data and your ideas interact.
Analysis and Summary Links
- " Summary: Using It Wisely ," UNC Chapel Hill Writing Center
- " Writing an Analytical Research Paper ," University of Richmond Writing Center
- " What Is Analysis? " (2:25), The Seahorse Project
- " Analyzing Qualitative Data " (15:14), Center for Innovation in Research and Teaching
- " What Is Secondary Analysis of Qualitative Data? " (18:18), Libby Bishop
Writing Topics A–Z
This index makes findings topics easy and links to the most relevant page for each item. Please email us at [email protected] if we're missing something!
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Thesis Helpers
Find the best tips and advice to improve your writing. Or, have a top expert write your paper.
Thesis Summary: A Detailed Academic Writing Guide

A thesis summary is a highly condensed version of the longer paper. It highlights the main points that have been covered in the paper while concisely describing the content of the thesis. In most cases, the summary of a thesis and the abstract serve the same purpose. They provide an overview of all the major points of a thesis. Thus, a reader can quickly see the main content of your thesis when they read the summary. This enables them to determine whether they are interested in your work or not.
What is Included in a Thesis Summary?
When asked to summarize something, you’re simply required to condense the text to the main points. As such, a good summary of thesis research should include important elements only. It should capture the main idea in the paper and the supporting points that may be interwoven with content that is of lesser importance.
Many learners confuse a thesis statement summary with an analysis. An analysis is a discussion of the techniques, ideas, and meaning in the text. On the other hand, a summary does not entail responding or critiquing the ideas in the text. Analyzing a paper entails summarizing its content to establish the ideas that you will be analyzing. A summary does not substitute for analysis.
Here are some of the things that a Ph.D. or master thesis summary should include: A title that is similar to that of your thesis The main purpose of your thesis The main topic of your thesis The research methods used to gather the information The sub-sections of your thesis Recommendations, results, and conclusions
Essentially, a summary should present the points of the author in a straightforward structure. Therefore, read the thesis carefully to determine the major and minor components or points of the argument and summarize them in an organized manner.
A point that the author makes at the beginning and another one at the end should concisely be included in a summary of thesis to convey the main argument of the author. Thus, you should read, understand, and reconstruct the thesis into a more concise, shorter form.
How to Write an Executive Summary for Thesis
Perhaps, you have written a short thesis that is not longer than ten pages. In that case, follow these steps to write a summary thesis:
- Summarize every paragraph in one sentence
- Summarize the entire text in a single sentence
- Write a single paragraph that starts with a sentence that summarizes the entire text followed by a paragraph of summary sentences
- Rewrite and rearrange your paragraph to ensure that it’s concise and clear.
- Eliminate relatively minor and repetitive points and include transitions.
Make sure that the final summary is complete, coherent, and unified.
How to Write Summary of Ph.D. Thesis and Longer Texts
A longer text like a Ph.D. requires time to summarize. That’s because you have to read and understand the document before you summarize it. Here’s how to write a summary thesis for longer papers.
- Outline the thesis by breaking it down into different major sections. To do this, group the paragraphs that focus on a similar topic and then list down the supporting points for different sections.
- Write a sentence or two that summarizes every section.
- Create a single sentence that summarizes the entire text. Look for the topic sentence in the thesis to guide you.
- Write one paragraph or several to start the overall summary sentence. Follow it with sentences that summarize different sections.
- Rearrange and rewrite the paragraphs to make the text concise and clear while eliminating repetitious and relatively minor points. Also, include transitions in your summary.
The final summary should include the main supporting points of every idea. Make the final version coherent, unified, and complete.
When is the Summary of Findings in Thesis Necessary?
The summary and conclusion thesis serves the purpose of providing an overview of the paper. As such, students are required to write a summary in many instances. In some cases, an educator can assign learners to write a page or two after reading a paper or article. They can also be asked to come up with a summary of their text as part of their critique or response after reading a paper.
Students can also write article summaries as a part of their planning or note-taking process when writing a research paper. These summaries or their parts can be included in the final papers. When writing a research paper, an author can depend on the summary as their reference to source materials. A summary enables a writer to condense broad information so that they can explain and present the relevance of the sources that deal with a similar subject.
A paper can also be summarized in the introduction to present a precise and concise overview of the main ideas to be discussed in the rest of the text. The length of a summary should depend on the complexity and length of the paper. Additionally, the purpose of a summary should determine whether it will be a few sentences, a shorter paragraph, or even several paragraphs. You can even come across a thesis summary sample that looks like an entire paper.
Qualities of a Good Summary Thesis Sample
When learning how to write summary and conclusion in thesis, many students use samples as their guides. But, how do you know that you’re using a good thesis summary example? Here are the qualities to look for:
- Comprehensiveness : A good summary should be comprehensive. All important points should be isolated from the original passage and noted down in a brief list. These are the ideas that should form the summary because they are indispensable to the development of the thesis.
- Conciseness : An ideal summary should be free of repetitions. Do not repeat the same points even if they have been restated in the main document. The summary should be shorter while providing a brief overview of the paper. Therefore, avoid repetition of the main point and supporting ideas.
- Coherence : A good summary makes sense. It’s not a piece that looks like it’s been taken from the main document. It should also not sound like a collection of disjointed sentences from the main document that is being summarized.
- Independence : When writing a summary, your work is not to imitate the main text’s author. Instead, you are expected to showcase your style and voice in the summary. Thus, you should not just quote the main text’s author. Instead, express how you understand the document in your words. A summary should be based on your understanding and interpretation of the main ideas or points of the writer. Nevertheless, a good summary does not create distortion or misrepresentation through the introduction of criticisms or comments.
It’s also crucial to note that a good summary thesis example uses a structure that features an introduction, the body, and a conclusion. It presents the goal or purpose, results, and conclusion or recommendations. What’s more, it features logical connections of the included information without adding new information.
To write a great summary, work on this part after completing your thesis. Make sure that you’re guided by the main points of your thesis. What’s more, use a good executive summary for thesis sample to guide you. The length of your summary should depend on its purpose and the length of the main document. Once you have written the summary, read it carefully, and eliminate all errors when proofreading and editing it. Alternatively, ask our thesis editors to proofread the summary for you.

Make PhD experience your own
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6 Summary vs. Analysis
Dr. Sandi Van Lieu
In your classes, you may be asked to analyze text. Analysis is not simply summary—summary gives the reader a shortened overview of the topic.
A summary would be telling the reader what happened in the story. Take for example, summaries about the short story “The Lottery” by Shirley Jackson:
Example 1 Summary:
“The Lottery” is about a town that comes together every year for a tradition. The town’s people draw a name, and the person’s whose name is drawn is killed by everyone else.
Example 2 Summary:
The black box in “The Lottery” is used to hold slips of paper with the names of the townspeople. It is old and splintered, and every year the townspeople talk about replacing the box, but no one wants to break tradition.
The examples above tell us what the story is about. They present facts, but they are not arguments.
In your courses, you’ll be asked do higher-level thinking . Summary, which gives a brief overview of the main points, is a lower level of thinking. Using analysis and evaluation are higher levels of thinking. Analysis is when you break down something (in this case, breaking down the story) into parts in order to see how they relate.
Evaluation is to make a judgment about something based on evidence. Analysis and evaluation go above and beyond summary to explain, examine, and tell us what you think or what you believe about the text or topic. They give arguments . Take, for example, the same above summaries about “The Lottery,” but revised to show analytical thinking:
“The Lottery,” a fiction story by Shirley Jackson, was written to portray the point that tradition often overtakes reason, and humans sometimes stick to traditions that are outdated or irrelevant simply because they don’t want to make changes.
The above examples don’t just give facts; they make arguments about the text. The second example breaks down the symbol of the black box and makes arguments about what it represents.
Using Analysis for Arguments and Support
Each body paragraph of an essay should include analysis. When you’re revising your essay, look at each individual body paragraph and ask yourself: Am I simply re-telling the story/text and giving facts, or am I making an argument about the story?
In addition to having analysis in each body paragraph, you should also include support. You can tell me that “The Lottery” is an argument for breaking traditions, but I need to “see” that—you have to prove it to me. This is where using the text and outside sources as quotes, paraphrases, and summaries will come in.
Find a passage of something you have read for a college course—an article, a story, a textbook pages, etc. Then do the following:
1. Read the passage. Then without looking at it, write a summary of it.
2. Now, make an argument in the form of analysis or evaluation of the passage.
Additional Resources:
- A professor’s explanation and examples of an analysis essay.
- OWL’s basic information on what is a literary analysis, with a presentation.
- OWL’s information on writing a thesis for a literary analysis.
- A college handout that breaks down writing an analysis essay in an easy format.
- This is a professor’s assignment and helps break the analysis down.
- A college document with great advice about how to write an analysis (and specific examples of such).
Attribution
- “Summary vs. Analysis,” created by Dr. Sandi Van Lieu and licensed under CC BY NC SA 3.0 .
The RoughWriter's Guide Copyright © 2020 by Dr. Sandi Van Lieu is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Summary and Conclusion

In the absence of conclusion, the research paper might seem incomplete. It is often contrasted with a summary, but there are subtle differences between the two. A summary is nothing but a short and clear account of the text, covering the main points, facts or elements only.
Content: Summary Vs Conclusion
Comparison chart, definition of summary.
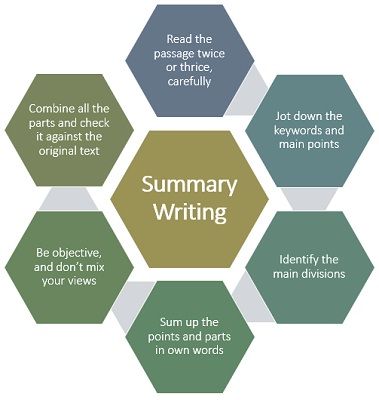
A summary is the compact account of the main text, i.e. an article, essay, drama, or some other form of literature. It gives an overview of the key points of the piece of writing. Moreover, one can also summarize anything which he/she has seen and heard, like speech, movie or lecture, etc.
It is typically about 5% to 15% of the original work, i.e. it may extend up to one to three paragraphs, which is around 100 to 300 words. It simply depends on the length of the text which is summarized. Its aim is to describe a piece of writing while including considerably less content than its original.
Ideal Summary
- An ideal summary is one that objectively highlights the entire form of literature.
- It should cover the focal point of every paragraph and the evidence supporting it.
- It should exclude all the irrelevant examples, details and information.
- It can make use of the keywords used in the original work, but should not use the same sentences and phrases, except if quotation marks are used.
- It must express the sense of the original work while using your own words and sentences.
Definition of Conclsuion
Conclusion refers to the epilogue which is given at the end of something, to deduce the findings. It forms part of the thought process, which combines all the points discussed, so as to reach a comprehensive idea or statement.
It is the final step in the process of reasoning, in which judgement, decision or opinion is formed after complete investigation and consideration. To conclude something, different types of perspectives are considered. It is only 10% of the research paper, which has two segments – summary and final thought .
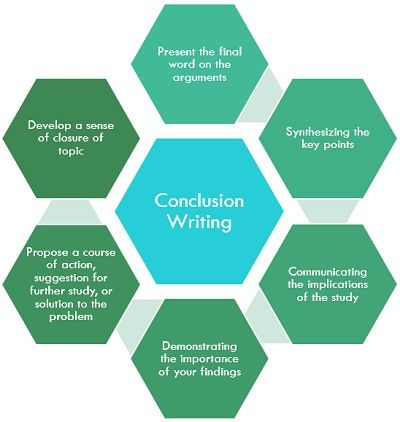
Ideal Conclusion
- The conclusion is said to be ideal when it gives an interesting insight and should end on a positive note.
- Highlights the main argument presented in the piece of writing.
- Sums up the answer to the question, often stated in the introduction.
- Refer back the questions, states the key points and findings, and wind up the discussion with the final observation.
- Reinforces the primary theme of the study.
- Makes a strong and long-lasting impression on the reader.
- It should never introduce new points.
Key Differences Between Summary and Conclusion
The points stated below discuss the differences between summary and conclusion:
- A summary is an abridgement of the work of literature, which covers the key points succinctly. On the contrary, conclusion refers to the final part of the discourse which sums up the argument and gives a statement of opinion or judgement.
- A summary is written to provide the reader with a precise and objective narrative of the central ideas and aspects of the original text. Conversely, conclusion paragraph wraps up the text and presents the reader that you have accomplished, what you have set forth in the beginning.
- While a summary restates the facts and elements, which are discussed in the original text, conclusion tends to synthesize all the points and wrap up the discussion. It helps the reader understand the importance of the research.
- Ideally, the length of the summary is 5% to 15%, whereas the conclusion constitutes only 10% of the original work.
- A summary often demonstrates the central ideas of the text clearly and concisely. In contrast, the conclusion introduces a new outlook, proposes a course of actions, provides a solution to the problem, makes suggestions for further study, and makes deductions on the basis of the argument.
- A summary only includes the ideas of the original text. One should not insert their opinion, criticism, comments or interpretations. As against, the conclusion can include the researcher’s or writer’s views, ideas and criticisms at the end.
In a nutshell, a summary condenses the material as well as it informs the reader about the vital points. Contrastingly, a conclusion gives the reader the sense of completeness of the argument or topic, with a reason or final thought. It focuses on the final outcome of the argumentation or research.
You Might Also Like:

essay ordering says
September 23, 2022 at 10:59 pm
Irresistible! Thank you a lot for this type and precise carrier.your offerings is higher than higher.
September 25, 2022 at 2:50 am
I will recommend my students to visit and read the explanation you give here. Thank you.
Endalkachew Sisay says
January 24, 2023 at 2:09 pm
I really appreciate the points you have addressed for us. Keep up the good work!!!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Summary is a brief understanding of the main point (thesis) or most important points (supporting points) of a text or source. When writing a summary, the writer should put the main idea or point in their own words. A summary is usually much shorter than the source it is summarizing, typically just a few sentences.
The Great Gatsby is the story of a mysterious millionaire, Jay Gatsby, who lives alone on an island in New York. F. Scott Fitzgerald wrote the book, but the narrator is Nick Carraway. Nick is Gatsby's neighbor, and he chronicles the story of Gatsby and his circle of friends, beginning with his introduction to the strange man and ending with ...
Summary vs. Analysis. When asked to write an analysis, it is not enough to simply summarize. You must also add your own analysis of what you've discovered about your topic. Analysis means breaking something down into its various elements and then asking critical thinking questions such as WHY and HOW in order to reach some conclusions of your ...
The Great Gatsby is the story of a mysterious millionaire, Jay Gatsby, who lives alone on an island in New York. F. Scott Fitzgerald wrote the book, but the narrator is Nick Carraway. Nick is Gatsby's neighbor, and he chronicles the story of Gatsby and his circle of friends, beginning with his introduction to the strange man and ending with ...
Ineffective thesis statement that summarizes the text Consumers who purchase coffee from farmers in the Equal Exchange network are helping farmers stay on their land. Effective thesis statement that indicates writer's judgment of the text Although the ad works successfully on an emotional level, it is less successful on a logical
Elaborate a thesis statement. The thesis statement. is the most important part. This is a sentence usually placed at the beginning of the summary and it is aimed at clarifying the main research questions of your work. The thesis statement must be clear and concise. MA theses, but also PhD dissertations, usually concern very narrow topics.
Thesis vs. thesis statement. ... An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it's should include brief descriptions of your research objectives, methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis. ...
Analysis. The purpose of an analysis is to interpret or find meanings or patterns in information. Analyzing statements will take a step beyond summary and describe the writer's personal findings and interpretations of the source material. An analysis usually is presented after a statement of evidence, which can have direct quotes or summary.
Summary vs. Analysis. It's important to be aware of whether you are writing summary or analysis of a text. As the chart below suggests, the two ways of approaching a text are quite different. ... To keep track of the main points for summary, put marks next to thesis and topic sentences. It can also be useful to label lists: When an author ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Summary, which gives a brief overview of the main points, is a lower level of thinking. Using analysis and evaluation are higher levels of thinking. Analysis is when you break down something (in this case, breaking down the story) into parts in order to see how they relate. Evaluation is to make a judgment about something based on evidence.
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper. ... Dissertation vs. Thesis. Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct ...
Analysis versus Summary. When asked to analyze a document, we don't always know what to do. Faced with an assignment that calls for analysis of a topic—say, how the Civil War ended slavery—one might be tempted to simply restate facts. That is summarizing. Analysis, on the other hand, requires more than simply paraphrasing what a source says ...
Table of contents. When to write a summary. Step 1: Read the text. Step 2: Break the text down into sections. Step 3: Identify the key points in each section. Step 4: Write the summary. Step 5: Check the summary against the article. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about summarizing.
Generally, the summary is about 200-350 words long, but you should verify this with your supervisor. Also, it generally follows an introduction-body-conclusion structure. Related reading: The basics of converting your PhD thesis into journal articles. Answered by Editage Insights on 13 Sep, 2017.
The summary is a short, to-the-point summary of the whole article, thesis, or other text. If you want to get the main idea of a topic as a reader, you should read the summary. Usually, a summary is written at the beginning of the text and in every paragraph if there are sections and subsections. ... One more difference between summary vs ...
A thesis summary is a highly condensed version of the longer paper. It highlights the main points that have been covered in the paper while concisely describing the content of the thesis. In most cases, the summary of a thesis and the abstract serve the same purpose. They provide an overview of all the major points of a thesis.
Summary, which gives a brief overview of the main points, is a lower level of thinking. Using analysis and evaluation are higher levels of thinking. Analysis is when you break down something (in this case, breaking down the story) into parts in order to see how they relate. Evaluation is to make a judgment about something based on evidence.
In lang=en terms the difference between thesis and summary is that thesis is the accented part of the measure, expressed by the downward beat; the opposite of arsis while summary is performed by cutting the procedures of a standard and fair trial. As nouns the difference between thesis and summary is that thesis is a statement supported by arguments while summary is an abstract or a condensed ...
An abstract concisely explains all the key points of an academic text such as a thesis, dissertation or journal article. It should summarize the whole text, not just introduce it. An abstract is a type of summary, but summaries are also written elsewhere in academic writing. For example, you might summarize a source in a paper, in a literature ...
A summary is an abridgement of the work of literature, which covers the key points succinctly. On the contrary, conclusion refers to the final part of the discourse which sums up the argument and gives a statement of opinion or judgement. A summary is written to provide the reader with a precise and objective narrative of the central ideas and ...
Summary is the most catch-all term of this group, and the one that shows up the most in general everyday English.. Abstract is most commonly used in the scientific context. It is typically a formal requirement for publication, as the initial section of a scientific paper. Often times if you find scientific papers online, it is just the abstract that is available.