Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2024 10:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Africa’s postdoc workforce is on the rise — but at what cost?
Career Feature 02 APR 24

Impact factors are outdated, but new research assessments still fail scientists
World View 02 APR 24

How scientists are making the most of Reddit
Career Feature 01 APR 24
Adopt universal standards for study adaptation to boost health, education and social-science research
Correspondence 02 APR 24
How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations
Allow researchers with caring responsibilities ‘promotion pauses’ to make research more equitable

Will the Gates Foundation’s preprint-centric policy help open access?
News 04 APR 24

The corpse of an exploded star and more — March’s best science images
News 28 MAR 24

How papers with doctored images can affect scientific reviews
Postdoctoral Fellow (Aging, Metabolic stress, Lipid sensing, Brain Injury)
Seeking a Postdoctoral Fellow to apply advanced knowledge & skills to generate insights into aging, metabolic stress, lipid sensing, & brain Injury.
Dallas, Texas (US)
UT Southwestern Medical Center - Douglas Laboratory
High-Level Talents at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University
For clinical medicine and basic medicine; basic research of emerging inter-disciplines and medical big data.
Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University
POSTDOCTORAL Fellow -- DEPARTMENT OF Surgery – BIDMC, Harvard Medical School
The Division of Urologic Surgery in the Department of Surgery at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School invites applicatio...
Boston, Massachusetts (US)
Director of Research
Applications are invited for the post of Director of Research at Cancer Institute (WIA), Chennai, India.
Chennai, Tamil Nadu (IN)
Cancer Institute (W.I.A)
Postdoctoral Fellow in Human Immunology (wet lab)
Join Atomic Lab in Boston as a postdoc in human immunology for universal flu vaccine project. Expertise in cytometry, cell sorting, scRNAseq.
Boston University Atomic Lab
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)..., similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and....
Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice
- Original Paper
- Open access
- Published: 14 October 2022
- Volume 16 , pages 2577–2595, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Sascha Kraus ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4886-7482 1 , 2 ,
- Matthias Breier 3 ,
- Weng Marc Lim 4 , 8 , 22 ,
- Marina Dabić 5 , 6 ,
- Satish Kumar 7 , 8 ,
- Dominik Kanbach 9 , 10 ,
- Debmalya Mukherjee 11 ,
- Vincenzo Corvello 12 ,
- Juan Piñeiro-Chousa 13 ,
- Eric Liguori 14 ,
- Daniel Palacios-Marqués 15 ,
- Francesco Schiavone 16 , 17 ,
- Alberto Ferraris 18 , 21 ,
- Cristina Fernandes 19 , 20 &
- João J. Ferreira 19
64k Accesses
261 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Review articles or literature reviews are a critical part of scientific research. While numerous guides on literature reviews exist, these are often limited to the philosophy of review procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures, triggering non-parsimonious reporting and confusion due to overlapping similarities. To address the aforementioned limitations, we adopt a pragmatic approach to demystify and shape the academic practice of conducting literature reviews. We concentrate on the types, focuses, considerations, methods, and contributions of literature reviews as independent, standalone studies. As such, our article serves as an overview that scholars can rely upon to navigate the fundamental elements of literature reviews as standalone and independent studies, without getting entangled in the complexities of review procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures.
Similar content being viewed by others

What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
Patrik Aspers & Ugo Corte

Qualitative Research: Ethical Considerations

How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
Clara Busse & Ella August
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
A literature review – or a review article – is “a study that analyzes and synthesizes an existing body of literature by identifying, challenging, and advancing the building blocks of a theory through an examination of a body (or several bodies) of prior work (Post et al. 2020 , p. 352). Literature reviews as standalone pieces of work may allow researchers to enhance their understanding of prior work in their field, enabling them to more easily identify gaps in the body of literature and potential avenues for future research. More importantly, review articles may challenge established assumptions and norms of a given field or topic, recognize critical problems and factual errors, and stimulate future scientific conversations around that topic. Literature reviews Footnote 1 come in many different formats and purposes:
Some review articles conduct a critical evaluation of the literature, whereas others elect to adopt a more exploratory and descriptive approach.
Some reviews examine data, methodologies, and findings, whereas others look at constructs, themes, and theories.
Some reviews provide summaries by holistically synthesizing the existing research on a topic, whereas others adopt an integrative approach by assessing related and interdisciplinary work.
The number of review articles published as independent or standalone studies has been increasing over time. According to Scopus (i.e., search database ), reviews (i.e., document type ) were first published in journals (i.e., source type ) as independent studies in 1945, and they subsequently appeared in three digits yearly from the late 1980s to the late 1990s, four digits yearly from the early 2000s to the late 2010s, and five digits in the year 2021 (Fig. 1 ). This increase is indicative that reviewers and editors in business and management research alike see value and purpose in review articles to such a level that they are now commonly accepted as independent, standalone studies. This development is also reflected in the fact that some academic journals exclusively publish review articles (e.g., the Academy of Management Annals , or the International Journal of Management Reviews ), and journals publishing in various fields often have special issues dedicated to literature reviews on certain topic areas (e.g., the Journal of Management and the Journal of International Business Studies ).
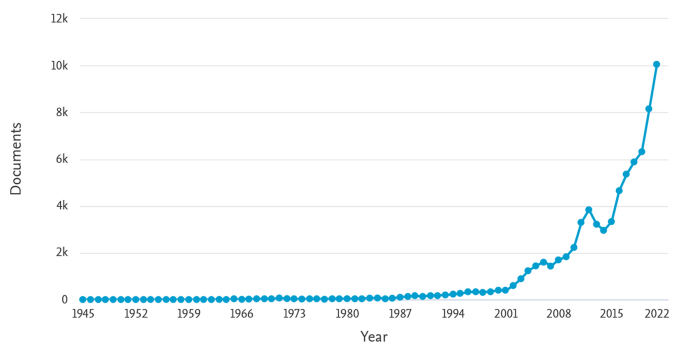
Full-year publication trend of review articles on Scopus (1945–2021)
One of the most important prerequisites of a high-quality review article is that the work follows an established methodology, systematically selects and analyzes articles, and periodically covers the field to identify latest developments (Snyder 2019 ). Additionally, it needs to be reproducible, well-evidenced, and transparent, resulting in a sample inclusive of all relevant and appropriate studies (Gusenbauer and Haddaway 2020; Hansen et al. 2021 ). This observation is in line with Palmatier et al. ( 2018 ), who state that review articles provide an important synthesis of findings and perspectives in a given body of knowledge. Snyder ( 2019 ) also reaffirmed this rationale, pointing out that review articles have the power to answer research questions beyond that which can be achieved in a single study. Ultimately, readers of review articles stand to gain a one-stop, state-of-the-art synthesis (Lim et al. 2022a ; Popli et al. 2022) that encapsulates critical insights through the process of re-interpreting, re-organizing, and re-connecting a body knowledge (Fan et al. 2022 ).
There are many reasons to conduct review articles. Kraus et al. ( 2020 ) explicitly mention the benefits of conducting systematic reviews by declaring that they often represent the first step in the context of larger research projects, such as doctoral dissertations. When carrying out work of this kind, it is important that a holistic overview of the current state of literature is achieved and embedded into a proper synthesis. This allows researchers to pinpoint relevant research gaps and adequately fit future conceptual or empirical studies into the state of the academic discussion (Kraus et al., 2021 ). A review article as an independent or standalone study is a viable option for any academic – especially young scholars, such as doctoral candidates – who wishes to delve into a specific topic for which a (recent) review article is not available.
The process of conducting a review article can be challenging, especially for novice scholars (Boell and Cecez-Kecmanovic 2015 ). Therefore, it is not surprising that numerous guides have been written in an attempt to improve the quality of review studies and support emerging scholars in their endeavors to have their work published. These guides for conducting review articles span a variety of academic fields, such as engineering education (Borrego et al. 2014 ), health sciences (Cajal et al. 2020 ), psychology (Laher and Hassem 2020 ), supply chain management (Durach et al. 2017 ), or business and entrepreneurship (Kraus et al. 2020 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ) – the latter were among the first scholars to recognize the need to educate business/management scholars on the roles of review studies in assembling, ascertaining, and assessing the intellectual territory of a specific knowledge domain. Furthermore, they shed light on the stages (i.e., planning the review, conducting the review, reporting, and dissemination) and phases (i.e., identifying the need for a review, preparation of a proposal for a review, development of a review protocol, identification of research, selection of studies, study quality assessment, data extraction and monitoring progress, data synthesis, the report and recommendations, and getting evidence into practice) of conducting a systematic review. Other scholars have either adapted and/or developed new procedures (Kraus et al. 2020 ; Snyder 2019 ) or established review protocols such as the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram (Moher et al. 2015 ). The latter provides a checklist that improves transparency and reproducibility, thus reducing questionable research practices. The declarative and procedural knowledge of a checklist allows users to derive value from (and, in some cases, produce) methodological literature reviews.
Two distinct and critical gaps or issues provide impetus for our article. First, while the endeavors of the named scholars are undoubtedly valuable contributions, they often encourage other scholars to explain the methodology of their review studies in a non-parsimonious way ( 1st issue ). This can become problematic if this information distracts and deprives scholars from providing richer review findings, particularly in instances in which publication outlets impose a strict page and/or word limit. More often than not, the early parts (i.e., stages/phases, such as needs, aims, and scope) of these procedures or protocols are explained in the introduction, but they tend to be reiterated in the methodology section due to the prescription of these procedures or protocols. Other parts of these procedures or protocols could also be reported more parsimoniously, for example, by filtering out documents, given that scientific databases (such as Scopus or Web of Science ) have since been upgraded to allow scholars to select and implement filtering criteria when conducting a search (i.e., criterion-by-criterion filtering may no longer be necessary). More often than not, the procedures or protocols of review studies can be signposted (e.g., bracket labeling) and disclosed in a sharp and succinct manner while maintaining transparency and replicability.
Other guides have been written to introduce review nomenclatures (i.e., names/naming) and their equivalent philosophical underpinnings. Palmatier et al. ( 2018 ) introduced three clearly but broadly defined nomenclatures of literature reviews as independent studies: domain-based reviews, theory-based reviews, and method-based reviews. However, such review nomenclatures can be confusing due to their overlapping similarities ( 2nd issue ). For example, Lim et al. ( 2022a ) highlighted their observation that the review nomenclatures associated with domain-based reviews could also be used for theory-based and method-based reviews.
The two aforementioned issues – i.e., the lack of a parsimonious understanding and the reporting of the review methodology , and the confusion emerging from review nomenclatures – are inarguably the unintended outcomes of diving into an advanced (i.e., higher level) understanding of literature review procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures from a philosophical perspective (i.e., underpinnings) without a foundational (i.e., basic level) understanding of the fundamental (i.e., core) elements of literature reviews from a pragmatic perspective. Our article aims to shed light on these issues and hopes to provide clarity for future scholarly endeavors.
Having a foundational understanding of literature reviews as independent studies is (i) necessary when addressing the aforementioned issues; (ii) important in reconciling and scaffolding our understanding, and (iii) relevant and timely due to the proliferation of literature reviews as independent studies. To contribute a solution toward addressing this gap , we aim to demystify review articles as independent studies from a pragmatic standpoint (i.e., practicality). To do so, we deliberately (i) move away from review procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures, and (ii) invest our attention in developing a parsimonious, scaffolded understanding of the fundamental elements (i.e., types, focuses, considerations, methods, and contributions) of review articles as independent studies.
Three contributions distinguish our article. It is worth noting that pragmatic guides (i.e., foundational knowledge), such as the present one, are not at odds with extant philosophical guides (i.e., advanced knowledge), but rather they complement them. Having a foundational knowledge of the fundamental elements of literature reviews as independent studies is valuable , as it can help scholars to (i) gain a good grasp of the fundamental elements of literature reviews as independent studies ( 1st contribution ), and (ii) mindfully adopt or adapt existing review procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures to better suit the circumstances of their reviews (e.g., choosing and developing a well-defined review nomenclature, and choosing and reporting on review considerations and steps more parsimoniously) ( 2nd contribution ). Therefore, this pragmatic guide serves as (iii) a foundational article (i.e., preparatory understanding) for literature reviews as independent studies ( 3rd contribution ). Following this, extant guides using a philosophical approach (i.e., advanced understanding) could be relied upon to make informed review decisions (e.g., adoption, adaptation) in response to the conventions of extant review procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures (Fig. 2 ).
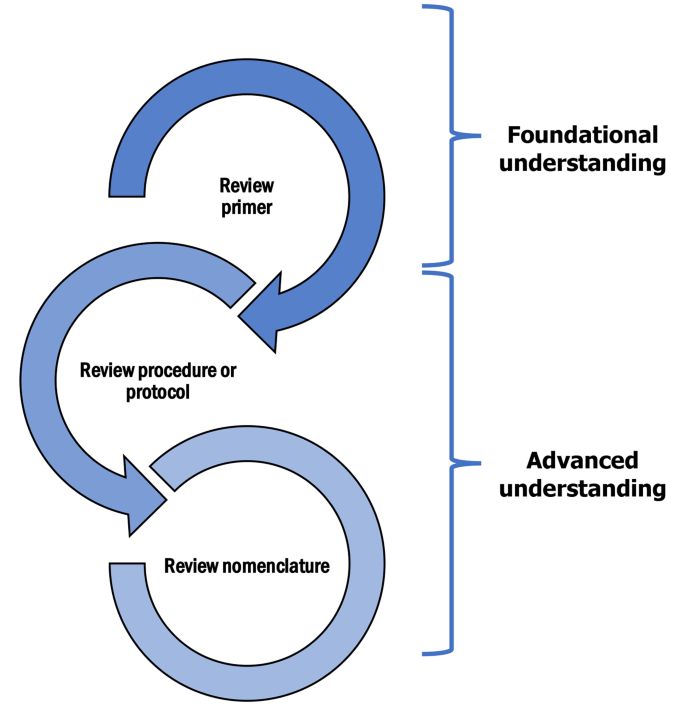
Foundational and advanced understanding of literature reviews as independent studies
2 Fundamental elements of literature reviews as independent studies
A foundational understanding of literature reviews as independent studies can be acquired through the appreciation of five fundamental elements – i.e., types, focuses, considerations, methods, and contributions – which are illustrated in Fig. 3 and summarized in the following sections.
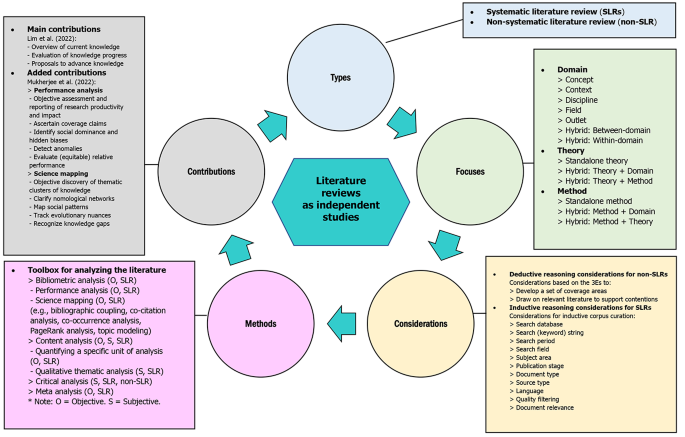
Fundamental elements of literature reviews as independent studies
There are two types of literature reviews as independent studies: systematic literature reviews ( SLRs ) and non-systematic literature reviews ( non-SLRs ). It is important to recognize that SLRs and non-SLRs are not review nomenclatures (i.e., names/naming) but rather review types (i.e., classifications).
In particular, SLRs are reviews carried out in a systematic way using an adopted or adapted procedure or protocol to guide data curation and analysis, thus enabling transparent disclosure and replicability (Lim et al. 2022a ; Kraus et al. 2020 ). Therefore, any review nomenclature guided by a systematic methodology is essentially an SLR. The origin of this type of literature review can be traced back to the evidence-based medicine movement in the early 1990s, with the objective being to overcome the issue of inconclusive findings in studies for medical treatments (Boell and Cecez-Kecmanovic 2015 ).
In contrast, non-SLRs are reviews conducted without any systematic procedure or protocol; instead, they weave together relevant literature based on the critical evaluations and (subjective) choices of the author(s) through a process of discovery and critique (e.g., pointing out contradictions and questioning assertions or beliefs); they are shaped by the exposure, expertise, and experience (i.e., the “3Es” in judgement calls) of the author(s). Therefore, non-SLRs are essentially critical reviews of the literature (Lim and Weissmann 2021 ).
2.2 Focuses
Unlike Palmatier et al. ( 2018 ) who considered domain-based reviews, theory-based reviews, and method-based reviews as review nomenclatures, we consider domain , theory , and method as three substantive focuses that can take center stage in literature reviews as independent studies. This is in line with our attempt to move away from review nomenclatures when providing a foundational understanding of literature reviews as independent studies.
A review that is domain-focused can examine: (i) a concept (e.g., customer engagement; Lim et al. 2022b ; digital transformation; Kraus et al. 2021 ; home sharing; Lim et al. 2021 ; sharing economy; Lim 2020 ), (ii) a context (e.g., India; Mukherjee et al. 2022a ), (iii) a discipline (e.g., entrepreneurship; Ferreira et al. 2015 ; international business; Ghauri et al. 2021 ), (iv) a field (e.g., family business; Lahiri et al. 2020 ; Rovelli et al. 2021 ; female entrepreneurship; Ojong et al. 2021 ), or (v) an outlet (e.g., Journal of Business Research ; Donthu et al. 2020 ; Management International Review ; Mukherjee et al. 2021 ; Review of Managerial Science ; Mas-Tur et al. 2020 ), which typically offer broad, overarching insights.
Domain-focused hybrids , such as the between-domain hybrid (e.g., concept-discipline hybrid, such as digital transformation in business and management; Kraus et al. 2022 ; religion in business and entrepreneurship; Kumar et al. 2022a ; personality traits in entrepreneurship; Salmony and Kanbach 2022 ; and policy implications in HR and OB research; Aguinis et al., 2022 ) and the within-domain hybrid (e.g., the concept-concept hybrid, such as customer engagement and social media; Lim and Rasul 2022 ; and global business and organizational excellence; Lim 2022 ; and the discipline-discipline hybrid, such as neuromarketing; Lim 2018 ) are also common as they can provide finer-grained insights.
A review that is theory-focused can explore a standalone theory (e.g., theory of planned behavior; Duan and Jiang 2008 ), as well as a theory in conjunction with a domain , such as the concept-theory hybrid (e.g., behavioral control and theory of planned behavior; Lim and Weissmann 2021 ) and the theory-discipline hybrid (e.g., theory of planned behavior in hospitality, leisure, and tourism; Ulker-Demirel and Ciftci 2020 ), or a theory in conjunction with a method (e.g., theory of planned behavior and structural equation modeling).
A review that is method-focused can investigate a standalone method (e.g., structural equation modeling; Deng et al. 2018 ) or a method in conjunction with a domain , such as the method-discipline hybrid (e.g., fsQCA in business and management; Kumar et al. 2022b ).
2.3 Planning the review, critical considerations, and data collection
The considerations required for literature reviews as independent studies depend on their type: SLRs or non-SLRs.
For non-SLRs, scholars often rely on the 3Es (i.e., exposure, expertise, and experience) to provide a critical review of the literature. Scholars who embark on non-SLRs should be well versed with the literature they are dealing with. They should know the state of the literature (e.g., debatable, underexplored, and well-established knowledge areas) and how it needs to be deciphered (e.g., tenets and issues) and approached (e.g., reconciliation proposals and new pathways) to advance theory and practice. In this regard, non-SLRs follow a deductive reasoning approach, whereby scholars initially develop a set of coverage areas for reviewing a domain, theory, or method and subsequently draw on relevant literature to shed light and support scholarly contentions in each area.
For SLRs, scholars often rely on a set of criteria to provide a well-scoped (i.e., breadth and depth), structured (i.e., organized aspects), integrated (i.e., synthesized evidence) and interpreted/narrated (i.e., describing what has happened, how and why) systematic review of the literature. Footnote 2 In this regard, SLRs follow an inductive reasoning approach, whereby a set of criteria is established and implemented to develop a corpus of scholarly documents that scholars can review. They can then deliver a state-of-the-art overview, as well as a future agenda for a domain, theory, or method. Such criteria are often listed in philosophical guides on SLR procedures (e.g., Kraus et al. 2020 ; Snyder 2019 ) and protocols (e.g., PRISMA), and they may be adopted/adapted with justifications Footnote 3 . Based on their commonalities they can be summarized as follows:
Search database (e.g., “Scopus” and/or “Web of Science”) can be defined based on justified evidence (e.g., by the two being the largest scientific databases of scholarly articles that can provide on-demand bibliographic data or records; Pranckutė 2021 ). To avoid biased outcomes due to the scope covered by the selected database, researchers could utilize two or more different databases (Dabić et al. 2021 ).
Search keywords may be developed by reading scholarly documents and subsequently brainstorming with experts. The expanding number of databases, journals, periodicals, automated approaches, and semi-automated procedures that use text mining and machine learning can offer researchers the ability to source new, relevant research and forecast the citations of influential studies. This enables them to determine further relevant articles.
Boolean operators (e.g., AND, OR) should be strategically used in developing the string of search keywords (e.g., “engagement” AND “customer” OR “consumer” OR “business”). Furthermore, the correct and precise application of quotation marks is important but is very frequently sidestepped, resulting in incorrect selection processes and differentiated results.
Search period (e.g., between a specified period [e.g., 2000 to 2020] or up to the latest full year at the time or writing [e.g., up to 2021]) can be defined based on the justified scope of study (e.g., contemporary evolution versus historical trajectory).
Search field (e.g., “article title, abstract, keywords”) can be defined based on justified assumptions (e.g., it is assumed that the focus of relevant documents will be mentioned in the article title, abstract, and/or keywords).
Subject area (e.g., “business, management, and accounting”) can be defined based on justified principles (e.g., the focus of the review is on the marketing discipline, which is located under the “business, management, and accounting” subject area in Scopus).
Publication stage (e.g., “final”) can be defined based on justified grounds (e.g., enabling greater accuracy in replication).
Document type (e.g., “article” and/or “review”), which reflects the type of scientific/practical contributions (e.g., empirical, synthesis, thought), can be defined based on justified rationales (e.g., articles selected because they are peer-reviewed; editorials not selected because they are not peer-reviewed).
Source type (e.g., “journal”) can be defined based on justified reasons (e.g., journals selected because they publish finalized work; conference proceedings not selected because they are work in progress, and in business/management, they are usually not being considered as full-fledged “publications”).
Language (e.g., “English”) can be determined based on justified limitations (e.g., nowadays, there are not many reasons to use another language besides the academic lingua franca English). Different spellings should also be considered, as the literature may contain both American and British spelling variants (e.g., organization and organisation). Truncation and wildcards in searches are recommended to capture both sets of spellings. It is important to note that each database varies in its symbology.
Quality filtering (e.g., “A*” and “A” or “4*”, “4”, and “3”) can be defined based on justified motivations (e.g., the goal is to unpack the most originally and rigorously produced knowledge, which is the hallmark of premier journals, such as those ranked “A*” and “A” by the Australian Business Deans Council [ABDC] Journal Quality List [JQL] and rated “4*”, “4”, and “3” by the Chartered Association of Business Schools [CABS] Academic Journal Guide [AJG]).
Document relevance (i.e., within the focus of the review) can be defined based on justified judgement (e.g., for a review focusing on customer engagement, articles that mention customer engagement as a passing remark without actually investigating it would be excluded).
Others: Screening process should be accomplished by beginning with the deduction of duplicate results from other databases, tracked using abstract screening to exclude unfitting studies, and ending with the full-text screening of the remaining documents.
Others: Exclusion-inclusion criteria interpretation of the abstracts/articles is obligatory when deciding whether or not the articles dealt with the matter. This step could involve removing a huge percentage of initially recognized articles.
Others: Codebook building pertains to the development of a codebook of the main descriptors within a specific field. An inductive approach can be followed and, in this case, descriptors are not established beforehand. Instead, they are established through the analysis of the articles’ content. This procedure is made up of several stages: (i) the extraction of important content from titles, abstracts, and keywords; (ii) the classification of this content to form a reduced list of the core descriptors; and (iii) revising the codebook in iterations and combining similar categories, thus developing a short list of descriptors (López-Duarte et al. 2016 , p. 512; Dabić et al. 2015 ; Vlacic et al. 2021 ).
2.4 Methods
Various methods are used to analyze the pertinent literature. Often, scholars choose a method for corpus analysis before corpus curation. Knowing the analytical technique beforehand is useful, as it allows researchers to acquire and prepare the right data in the right format. This typically occurs when scholars have decided upon and justified pursuing a specific review nomenclature upfront (e.g., bibliometric reviews) based on the problem at hand (e.g., broad domain [outlet] with a large corpus [thousands of articles], such as a premier journal that has been publishing for decades) (Donthu et al. 2021 ). However, this may not be applicable in instances where (i) scholars do not curate a corpus of articles (non-SLRs), and (ii) scholars only know the size of the corpus of articles once that corpus is curated (SLRs). Therefore, scholars may wish to decide on a method of analyzing the literature depending on (i) whether they rely on a corpus of articles (i.e., yes or no), and (ii) the size of the corpus of articles that they rely on to review the literature (i.e., n = 0 to ∞).
When analytical techniques (e.g., bibliometric analysis, critical analysis, meta-analysis) are decoupled from review nomenclatures (e.g., bibliometric reviews, critical reviews, meta-analytical reviews), we uncover a toolbox of the following methods for use when analyzing the literature:
Bibliometric analysis measures the literature and processes data by using algorithm, arithmetic, and statistics to analyze, explore, organize, and investigate large amounts of data. This enables scholars to identify and recognize potential “hidden patterns” that could help them during the literature review process. Bibliometrics allows scholars to objectively analyze a large corpus of articles (e.g., high hundreds or more) using quantitative techniques (Donthu et al. 2021 ). There are two overarching categories for bibliometric analysis: performance analysis and science mapping. Performance analysis enables scholars to assess the productivity (publication) and impact (citation) of the literature relating to a domain, method, or theory using various quantitative metrics (e.g., average citations per publication or year, h -index, g -index, i -index). Science mapping grants scholars the ability to map the literature in that domain, method, or theory based on bibliographic data (e.g., bibliographic coupling generates thematic clusters based on similarities in shared bibliographic data [e.g., references] among citing articles; co-citation analysis generates thematic clusters based on commonly cited articles; co-occurrence analysis generates thematic clusters based on bibliographic data [e.g., keywords] that commonly appear together; PageRank analysis generates thematic clusters based on articles that are commonly cited in highly cited articles; and topic modeling generates thematic clusters based on the natural language processing of bibliographic data [e.g., article title, abstract, and keywords]). Footnote 4 Given the advancement in algorithms and technology, reviews using bibliometric analysis are considered to be smart (Kraus et al. 2021 ) and technologically-empowered (Kumar et al. 2022b ) SLRs, in which a review has harnessed the benefits of (i) the machine learning of the bibliographic data of scholarly research from technologically-empowered scientific databases, and (ii) big data analytics involving various science mapping techniques (Kumar et al. 2022c ).
Content analysis allows scholars to analyze a small to medium corpus of articles (i.e., tens to low hundreds) using quantitative and qualitative techniques. From a quantitative perspective , scholars can objectively carry out a content analysis by quantifying a specific unit of analysis . A useful method of doing so involves adopting, adapting, or developing an organizing framework . For example, Lim et al. ( 2021 ) employed an organizing (ADO-TCM) framework to quantify content in academic literature based on: (i) the categories of knowledge; (ii) the relationships between antecedents, decisions, and outcomes; and (iii) the theories, contexts, and methods used to develop the understanding for (i) and (ii). The rapid evolution of software for content analysis allows scholars to carry out complex elaborations on the corpus of analyzed articles, so much so that the most recent software enables the semi-automatic development of an organizing framework (Ammirato et al. 2022 ). From a qualitative perspective , scholars can conduct a content analysis or, more specifically, a thematic analysis , by subjectively organizing the content into themes. For example, Creevey et al. ( 2022 ) reviewed the literature on social media and luxury, providing insights on five core themes (i.e., luxury brand strategy, luxury brand social media communications, luxury consumer attitudes and perceptions, engagement, and the influence of social media on brand performance-related outcomes) generated through a content (thematic) analysis. Systematic approaches for inductive concept development through qualitative research are similarly applied in literature reviews in an attempt to reduce the subjectivity of derived themes. Following the principles of the approach by Gioia et al. ( 2012 ), Korherr and Kanbach ( 2021 ) develop a taxonomy of human-related capabilities in big data analytics. Building on a sample of 75 studies for the literature review, 33 first-order concepts are identified. These are categorized into 15 second-order themes and are finally merged into five aggregate dimensions. Using the same procedure, Leemann and Kanbach ( 2022 ) identify 240 idiosyncratic dynamic capabilities in a sample of 34 studies for their literature review. They then categorize these into 19 dynamic sub-capabilities. The advancement of technology also makes it possible to conduct content analysis using computer assisted qualitative data analysis (CAQDA) software (e.g., ATLAS.ti, Nvivo, Quirkos) (Lim et al. 2022a ).
Critical analysis allows scholars to subjectively use their 3Es (i.e., exposure, expertise, and experience) to provide a critical evaluation of academic literature. This analysis is typically used in non-SLRs, and can be deployed in tandem with other analyses, such as bibliometric analysis and content analysis in SLRs, which are used to discuss consensual, contradictory, and underexplored areas of the literature. For SLRs, scholars are encouraged to engage in critical evaluations of the literature so that they can truly contribute to advancing theory and practice (Baker et al. 2022 ; Lim et al. 2022a ; Mukherjee et al. 2022b ).
Meta-analysis allows scholars to objectively establish a quantitative estimate of commonly studied relationships in the literature (Grewal et al. 2018 ). This analysis is typically employed in SLRs intending to reconcile a myriad of relationships (Lim et al. 2022a ). The relationships established are often made up of conflicting evidence (e.g., a positive or significant effect in one study, but a negative or non-significant effect in another study). However, through meta-analysis, scholars are able to identify potential factors (e.g., contexts or sociodemographic information) that may have led to the conflict.
Others: Multiple correspondence analysis helps to map the field, assessing the associations between qualitative content within a matrix of variables and cases. Homogeneity Analysis by Means of Alternating Least Squares ( HOMALS ) is also considered useful in allowing researchers to map out the intellectual structure of a variety of research fields (Gonzalez-Loureiro et al. 2015 ; Gonzalez-Louriero 2021; Obradović et al. 2021 ). HOMALS can be performed in R or used along with a matrix through SPSS software. In summary, the overall objective of this analysis is to discover a low dimensional representation of the original high dimensional space (i.e., the matrix of descriptors and articles). To measure the goodness of fit, a loss function is used. This function is used minimally, and the HOMALS algorithm is applied to the least squares loss functions in SPSS. This analysis provides a proximity map, in which articles and descriptors are shown in low-dimensional spaces (typically on two axes). Keywords are paired and each couple that appears together in a large number of articles is shown to be closer on the map and vice-versa.
When conducting a literature review, software solutions allow researchers to cover a broad range of variables, from built-in functions of statistical software packages to software orientated towards meta-analyses, and from commercial to open-source solutions. Personal preference plays a huge role, but the decision as to which software will be the most useful is entirely dependent on how complex the methods and the dataset are. Of all the commercial software providers, we have found the built-in functions of (i) R and VOSviewer most useful in performing bibliometric analysis (Aria and Cuccurullo 2017 ; R Core Team 2021 ; Van Eck and Waltman 2014 ) and (ii) Stata most useful in performing meta-analytical tasks.
Many different analytical tools have been used. These include simple document counting, citation analysis, word frequency analysis, cluster analysis, co-word analysis, and cooperation analysis (Daim et al. 2006 ). Software has also been produced for bibliometric analysis, such as the Thomson Data Analyzer (TDA), which Thomson Reuters created, and CiteSpace developed by Chen ( 2013 ). VOSviewer helps us to construct and visualize bibliometric networks, which can include articles, journals, authors, countries, and institutions, among others (Van Eck and Waltman 2014 ). These can be organized based on citations, co-citations, bibliographic coupling, or co-authorship relations. In addition, VOSviewer provides text mining functions, which can be used to facilitate a better understanding of co-occurrence networks with regards to the key terms taken from a body of scientific literature (Donthu et al. 2021 ; Wong 2018 ). Other frequently used tools include for bibliometric analysis include Bibliometrix/Biblioshiny in R, CitNetExplorer, and Gephi, among others.
2.5 Contributions
Well-conducted literature reviews may make multiple contributions to the literature as standalone, independent studies.
Generally, there are three primary contributions of literature reviews as independent studies: (i) to provide an overview of current knowledge in the domain, method, or theory, (ii) to provide an evaluation of knowledge progression in the domain, method, or theory, including the establishment of key knowledge, conflicting or inconclusive findings, and emerging and underexplored areas, and (iii) to provide a proposal for potential pathways for advancing knowledge in the domain, method, or theory (Lim et al. 2022a , p. 487). Developing theory through literature reviews can take many forms, including organizing and categorizing the literature, problematizing the literature, identifying and exposing contradictions, developing analogies and metaphors, and setting out new narratives and conceptualizations (Breslin and Gatrell 2020 ). Taken collectively, these contributions offer crystalized, evidence-based insights that both ‘mine’ and ‘prospect’ the literature, highlighting extant gaps and how they can be resolved (e.g., flags paradoxes or theoretical tensions, explaining why something has not been done, what the challenges are, and how these challenges can be overcome). These contributions can be derived through successful bibliometric analysis, content analysis, critical analysis, and meta-analysis.
Additionally, the deployment of specific methods can bring in further added value. For example, a performance analysis in a bibliometric analysis can contribute to: (i) objectively assessing and reporting research productivity and impact ; (ii) ascertaining reach for coverage claims ; (iii) identifying social dominance and hidden biases ; (iv) detecting anomalies ; and (v) evaluating ( equitable ) relative performance ; whereas science mapping in bibliometric analysis can contribute to: (i) objectively discovering thematic clusters of knowledge ; (ii) clarifying nomological networks ; (iii) mapping social patterns ; (iv) tracking evolutionary nuances ; and (v) recognizing knowledge gaps (Mukherjee et al. 2022b , p. 105).
3 Conclusion
Independent literature reviews will continue to be written as a result of their necessity, importance, relevance, and urgency when it comes to advancing knowledge (Lim et al. 2022a ; Mukherjee et al. 2022b ), and this can be seen in the increasing number of reviews being published over the last several years. Literature reviews advance academic discussion. Journal publications on various topics and subject areas are becoming more frequent sites for publication. This trend will only heighten the need for literature reviews. This article offers directions and control points that address the needs of three different stakeholder groups: producers (i.e., potential authors), evaluators (i.e., journal editors and reviewers), and users (i.e., new researchers looking to learn more about a particular methodological issue, and those teaching the next generation of scholars). Future producers will derive value from this article’s teachings on the different fundamental elements and methodological nuances of literature reviews. Procedural knowledge (i.e., using control points to assist in decision-making during the manuscript preparation phase) will also be of use. Evaluators will be able to make use of the procedural and declarative knowledge evident in control points as well. As previously outlined, the need to cultivate novelty within research on business and management practices is vital. Scholars must also be supported to choose not only safe mining approaches; they should also be encouraged to attempt more challenging and risky ventures. It is important to note that abstracts often seem to offer a lot of potential, stating that authors intend to make large conceptual contributions, broadening the horizons of the field.
Our article offers important insights also for practitioners. Noteworthily, our framework can support corporate managers in decomposing and better understanding literature reviews as ad-hoc and independent studies about specific topics that matter for their organization. For instance, practitioners can understand more easily what are the emerging trends within their domain of interest and make corporate decisions in line with such trends.
This article arises from an intentional decoupling from philosophy, in favor of adopting a more pragmatic approach. This approach can assist us in clarifying the fundamental elements of literature reviews as independent studies. Five fundamental elements must be considered: types, focuses, considerations, methods, and contributions. These elements offer a useful frame for scholars starting to work on a literature review. Overview articles (guides) such as ours are thus invaluable, as they equip scholars with a solid foundational understanding of the integral elements of a literature review. Scholars can then put these teachings into practice, armed with a better understanding of the philosophy that underpins the procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures of literature reviews as independent studies.
Data availability
Our manuscript has no associate data.
Our focus here is on standalone literature reviews in contrast with literature reviews that form the theoretical foundation for a research article.
Scoping reviews, structured reviews, integrative reviews, and interpretive/narrative reviews are commonly found in review nomenclature. However, the philosophy of these review nomenclatures essentially reflects what constitutes a good SLR. That is to say, a good SLR should be well scoped, structured, integrated, and interpreted/narrated. This observation reaffirms our position and the value of moving away from review nomenclatures to gain a foundational understanding of literature reviews as independent studies.
Given that many of these considerations can be implemented simultaneously in contemporary versions of scientific databases, scholars may choose to consolidate them into a single (or a few) step(s), where appropriate, so that they can be reported more parsimoniously. For a parsimonious but transparent and replicable exemplar, see Lim ( 2022 ).
Where keywords are present (e.g., author keywords or keywords derived from machine learning [e.g., natural language processing]), it is assumed that each keyword represents a specific meaning (e.g., topic [concept, context], method), and that a collection of keywords grouped under the same cluster represents a specific theme.
Aguinis H, Jensen SH, Kraus S (2022) Policy implications of organizational behavior and human resource management research. Acad Manage Perspect 36(3):1–22
Article Google Scholar
Ammirato S, Felicetti AM, Rogano D, Linzalone R, Corvello V (2022) Digitalising the systematic literature review process: The My SLR platform. Knowl Manage Res Pract. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/14778238.2022.2041375
Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetrics 11(4):959–975
Baker WE, Mukherjee D, Perin MG (2022) Learning orientation and competitive advantage: A critical synthesis and future directions. J Bus Res 144:863–873
Boell SK, Cecez-Kecmanovic D (2015) On being ‘systematic’ in literature reviews. J Inform Technol 30:161–173
Borrego M, Foster MJ, Froyd JE (2014) Systematic literature reviews in engineering education and other developing interdisciplinary fields. J Eng Educ 103(1):45–76
Breslin D, Gatrell C (2020) Theorizing through literature reviews: The miner-prospector continuum. Organizational Res Methods. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428120943288 (in press)
Cajal B, Jiménez R, Gervilla E, Montaño JJ (2020) Doing a systematic review in health sciences. Clínica y Salud 31(2):77–83
Chen C (2013) Mapping scientific frontiers: The quest for knowledge visualization. Springer Science & Business Media
Creevey D, Coughlan J, O’Connor C (2022) Social media and luxury: A systematic literature review. Int J Manage Reviews 24(1):99–129
Dabić M, González-Loureiro M, Harvey M (2015) Evolving research on expatriates: what is ‘known’after four decades (1970–2012). Int J Hum Resource Manage 26(3):316–337
Dabić M, Vlačić B, Kiessling T, Caputo A, Pellegrini M(2021) Serial entrepreneurs: A review of literature and guidance for future research.Journal of Small Business Management,1–36
Daim TU, Rueda G, Martin H, Gerdsri P (2006) Forecasting emerging technologies: Use of bibliometrics and patent analysis. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 73(8):981–1012
Deng L, Yang M, Marcoulides KM (2018) Structural equation modeling with many variables: A systematic review of issues and developments. Front Psychol 9:580
Donthu N, Kumar S, Pattnaik D (2020) Forty-five years of Journal of Business Research: A bibliometric analysis. J Bus Res 109:1–14
Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Pandey N, Lim WM (2021) How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 133:285–296
Duan W, Jiang G (2008) A review of the theory of planned behavior. Adv Psychol Sci 16(2):315–320
Google Scholar
Durach CF, Kembro J, Wieland A (2017) A new paradigm for systematic literature reviews in supply chain management. J Supply Chain Manage 53(4):67–85
Fan D, Breslin D, Callahan JL, Szatt-White M (2022) Advancing literature review methodology through rigour, generativity, scope and transparency. Int J Manage Reviews 24(2):171–180
Ferreira MP, Reis NR, Miranda R (2015) Thirty years of entrepreneurship research published in top journals: Analysis of citations, co-citations and themes. J Global Entrepreneurship Res 5(1):1–22
Ghauri P, Strange R, Cooke FL (2021) Research on international business: The new realities. Int Bus Rev 30(2):101794
Gioia DA, Corley KG, Hamilton AL (2012) Seeking qualitative rigor in inductive research: Notes on the gioia methodology. Organizational Res Methods 16(1):15–31
Gonzalez-Loureiro M, Dabić M, Kiessling T (2015) Supply chain management as the key to a firm’s strategy in the global marketplace: Trends and research agenda. Int J Phys Distribution Logistics Manage 45(1/2):159–181. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPDLM-05-2013-0124
Grewal D, Puccinelli N, Monroe KB (2018) Meta-analysis: Integrating accumulated knowledge. J Acad Mark Sci 46(1):9–30
Hansen C, Steinmetz H, Block J(2021) How to conduct a meta-analysis in eight steps: a practical guide.Management Review Quarterly,1–19
Korherr P, Kanbach DK (2021) Human-related capabilities in big data analytics: A taxonomy of human factors with impact on firm performance. RMS. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-021-00506-4 (in press)
Kraus S, Breier M, Dasí-Rodríguez S (2020) The art of crafting a systematic literature review in entrepreneurship research. Int Entrepreneurship Manage J 16(3):1023–1042
Kraus S, Durst S, Ferreira J, Veiga P, Kailer N, Weinmann A (2022) Digital transformation in business and management research: An overview of the current status quo. Int J Inf Manag 63:102466
Kraus S, Jones P, Kailer N, Weinmann A, Chaparro-Banegas N, Roig-Tierno N (2021) Digital transformation: An overview of the current state of the art of research. Sage Open 11(3):1–15
Kraus S, Mahto RV, Walsh ST (2021) The importance of literature reviews in small business and entrepreneurship research. J Small Bus Manage. https://doi.org/10.1080/00472778.2021.1955128 (in press)
Kumar S, Sahoo S, Lim WM, Dana LP (2022a) Religion as a social shaping force in entrepreneurship and business: Insights from a technology-empowered systematic literature review. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 175:121393
Kumar S, Sahoo S, Lim WM, Kraus S, Bamel U (2022b) Fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) in business and management research: A contemporary overview. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 178:121599
Kumar S, Sharma D, Rao S, Lim WM, Mangla SK (2022c) Past, present, and future of sustainable finance: Insights from big data analytics through machine learning of scholarly research. Ann Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04410-8 (in press)
Laher S, Hassem T (2020) Doing systematic reviews in psychology. South Afr J Psychol 50(4):450–468
Leemann N, Kanbach DK (2022) Toward a taxonomy of dynamic capabilities – a systematic literature review. Manage Res Rev 45(4):486–501
Lahiri S, Mukherjee D, Peng MW (2020) Behind the internationalization of family SMEs: A strategy tripod synthesis. Glob Strategy J 10(4):813–838
Lim WM (2018) Demystifying neuromarketing. J Bus Res 91:205–220
Lim WM (2020) The sharing economy: A marketing perspective. Australasian Mark J 28(3):4–13
Lim WM (2022) Ushering a new era of Global Business and Organizational Excellence: Taking a leaf out of recent trends in the new normal. Global Bus Organizational Excellence 41(5):5–13
Lim WM, Rasul T (2022) Customer engagement and social media: Revisiting the past to inform the future. J Bus Res 148:325–342
Lim WM, Weissmann MA (2021) Toward a theory of behavioral control. J Strategic Mark. https://doi.org/10.1080/0965254X.2021.1890190 (in press)
Lim WM, Kumar S, Ali F (2022a) Advancing knowledge through literature reviews: ‘What’, ‘why’, and ‘how to contribute’. Serv Ind J 42(7–8):481–513
Lim WM, Rasul T, Kumar S, Ala M (2022b) Past, present, and future of customer engagement. J Bus Res 140:439–458
Lim WM, Yap SF, Makkar M (2021) Home sharing in marketing and tourism at a tipping point: What do we know, how do we know, and where should we be heading? J Bus Res 122:534–566
López-Duarte C, González-Loureiro M, Vidal-Suárez MM, González-Díaz B (2016) International strategic alliances and national culture: Mapping the field and developing a research agenda. J World Bus 51(4):511–524
Mas-Tur A, Kraus S, Brandtner M, Ewert R, Kürsten W (2020) Advances in management research: A bibliometric overview of the Review of Managerial Science. RMS 14(5):933–958
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Reviews 4(1):1–9
Mukherjee D, Kumar S, Donthu N, Pandey N (2021) Research published in Management International Review from 2006 to 2020: A bibliometric analysis and future directions. Manage Int Rev 61:599–642
Mukherjee D, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Goyal K (2022a) Mapping five decades of international business and management research on India: A bibliometric analysis and future directions. J Bus Res 145:864–891
Mukherjee D, Lim WM, Kumar S, Donthu N (2022b) Guidelines for advancing theory and practice through bibliometric research. J Bus Res 148:101–115
Obradović T, Vlačić B, Dabić M (2021) Open innovation in the manufacturing industry: A review and research agenda. Technovation 102:102221
Ojong N, Simba A, Dana LP (2021) Female entrepreneurship in Africa: A review, trends, and future research directions. J Bus Res 132:233–248
Palmatier RW, Houston MB, Hulland J (2018) Review articles: Purpose, process, and structure. J Acad Mark Sci 46(1):1–5
Post C, Sarala R, Gatrell C, Prescott JE (2020) Advancing theory with review articles. J Manage Stud 57(2):351–376
Pranckutė R (2021) Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The titans of bibliographic information in today’s academic world. Publications 9(1):12
R Core Team (2021) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/ Accessed 20th July 2022
Rovelli P, Ferasso M, De Massis A, Kraus S(2021) Thirty years of research in family business journals: Status quo and future directions.Journal of Family Business Strategy,100422
Salmony FU, Kanbach DK (2022) Personality trait differences across types of entrepreneurs: a systematic literature review. RMS 16:713–749
Snyder H (2019) Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 104:333–339
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14(3):207–222
Ulker-Demirel E, Ciftci G (2020) A systematic literature review of the theory of planned behavior in tourism, leisure and hospitality management research. J Hospitality Tourism Manage 43:209–219
Van Eck NJ, Waltma L (2014) CitNetExplorer: A new software tool for analyzing and visualizing citation networks. J Informetrics 8(4):802–823
Vlačić B, Corbo L, Silva e, Dabić M (2021) The evolving role of artificial intelligence in marketing: A review and research agenda. J Bus Res 128:187–203
Wong D (2018) VOSviewer. Tech Serv Q 35(2):219–220. https://doi.org/10.1080/07317131.2018.1425352
Download references
Open access funding provided by Libera Università di Bolzano within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Economics & Management, Free University of Bozen-Bolzano, Bolzano, Italy
Sascha Kraus
Department of Business Management, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
School of Business, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland
Matthias Breier
Sunway University Business School, Sunway University, Sunway City, Malaysia
Weng Marc Lim
Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia
Marina Dabić
School of Economics and Business, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia
Department of Management Studies, Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur, Jaipur, India
Satish Kumar
Faculty of Business, Design and Arts, Swinburne University of Technology, Kuching, Malaysia
Weng Marc Lim & Satish Kumar
Chair of Strategic Management and Digital Entrepreneurship, HHL Leipzig Graduate School of Management, Leipzig, Germany
Dominik Kanbach
School of Business, Woxsen University, Hyderabad, India
College of Business, The University of Akron, Akron, USA
Debmalya Mukherjee
Department of Engineering, University of Messina, Messina, Italy
Vincenzo Corvello
Department of Finance, Santiago de Compostela University, Santiago de Compostela, Spain
Juan Piñeiro-Chousa
Rowan University, Rohrer College of Business, Glassboro, NJ, USA
Eric Liguori
School of Engineering Design, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Valencia, Spain
Daniel Palacios-Marqués
Department of Management and Quantitative Studies, Parthenope University, Naples, Italy
Francesco Schiavone
Paris School of Business, Paris, France
Department of Management, University of Turin, Turin, Italy
Alberto Ferraris
Department of Management and Economics & NECE Research Unit in Business Sciences, University of Beira Interior, Covilha, Portugal
Cristina Fernandes & João J. Ferreira
Centre for Corporate Entrepreneurship and Innovation, Loughborough University, Loughborough, UK
Cristina Fernandes
Laboratory for International and Regional Economics, Graduate School of Economics and Management, Ural Federal University, Yekaterinburg, Russia
School of Business, Law and Entrepreneurship, Swinburne University of Technology, Hawthorn, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sascha Kraus .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kraus, S., Breier, M., Lim, W.M. et al. Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice. Rev Manag Sci 16 , 2577–2595 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-022-00588-8
Download citation
Received : 15 August 2022
Accepted : 07 September 2022
Published : 14 October 2022
Issue Date : November 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-022-00588-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Literature reviews
- Bibliometrics
- Meta Analysis
- Contributions
JEL classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Loading metrics
Open Access

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France, Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
- Marco Pautasso

Published: July 18, 2013
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
- Reader Comments
Citation: Pautasso M (2013) Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review. PLoS Comput Biol 9(7): e1003149. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
Editor: Philip E. Bourne, University of California San Diego, United States of America
Copyright: © 2013 Marco Pautasso. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149.g001
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
- 1. Rapple C (2011) The role of the critical review article in alleviating information overload. Annual Reviews White Paper. Available: http://www.annualreviews.org/userimages/ContentEditor/1300384004941/Annual_Reviews_WhitePaper_Web_2011.pdf . Accessed May 2013.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 7. Budgen D, Brereton P (2006) Performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering. Proc 28th Int Conf Software Engineering, ACM New York, NY, USA, pp. 1051–1052. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/1134285.1134500 .
- 16. Eco U (1977) Come si fa una tesi di laurea. Milan: Bompiani.
- 17. Hart C (1998) Doing a literature review: releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE.
- 21. Ridley D (2008) The literature review: a step-by-step guide for students. London: SAGE.
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview

Literature Review Guide: Examples of Literature Reviews
- What is a Literature Review?
- How to start?
- Search strategies and Databases
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- How to organise the review
- Library summary
- Emerald Infographic
All good quality journal articles will include a small Literature Review after the Introduction paragraph. It may not be called a Literature Review but gives you an idea of how one is created in miniature.
Sample Literature Reviews as part of a articles or Theses
- Sample Literature Review on Critical Thinking (Gwendolyn Reece, American University Library)
- Hackett, G and Melia, D . The hotel as the holiday/stay destination:trends and innovations. Presented at TRIC Conference, Belfast, Ireland- June 2012 and EuroCHRIE Conference
Links to sample Literature Reviews from other libraries
- Sample literature reviews from University of West Florida
Standalone Literature Reviews
- Attitudes towards the Disability in Ireland
- Martin, A., O'Connor-Fenelon, M. and Lyons, R. (2010). Non-verbal communication between nurses and people with an intellectual disability: A review of the literature. Journal of Intellectual Diabilities, 14(4), 303-314.
Irish Theses
- Phillips, Martin (2015) European airline performance: a data envelopment analysis with extrapolations based on model outputs. Master of Business Studies thesis, Dublin City University.
- The customers’ perception of servicescape’s influence on their behaviours, in the food retail industry : Dublin Business School 2015
- Coughlan, Ray (2015) What was the role of leadership in the transformation of a failing Irish Insurance business. Masters thesis, Dublin, National College of Ireland.
- << Previous: Search strategies and Databases
- Next: Tutorials >>
- Last Updated: Feb 27, 2024 4:07 PM
- URL: https://ait.libguides.com/literaturereview
Want to publish a literature review? Think of it as an empirical paper
What to consider if you want to publish a literature review paper
Tatiana Andreeva - Fri 23 Apr 2021 07:50 (updated Fri 27 Oct 2023 17:26)

[Guest post by CYGNA member Tatiana Andreeva ]
When you’ve been reading a lot on a particular topic – for example, reviewing the literature for your research project or for your PhD – at some point it looks like you have enough material and reflections to publish this piece of work as a separate paper. Recognize this? If you ever tried it, you might know that publishing a literature review paper in an academic journal is a tricky task. The literature review publications come in so many forms, and there is no single cheat-sheet or established format like for empirical papers that you could follow to ensure success in publication.
Through my own journey of trial-and-error on this path, as well as through reviewing for journals and for PhD students in my course, I came up with an idea that will help you to increase the chances of publishing a literature review: think of a literature review as simply another empirical research project. Think of it as an empirical study, in which your data comes not from your usual fieldwork but from the articles that you review.
Many literature reviews can be thought of as a qualitative empirical study, in which the papers included in the review substitute interviews or field observations that you would usually collect and code. Some literature reviews, e.g., meta-analyses, are more like a quantitative empirical paper, in which various numbers you extract from the papers in your dataset substitute your survey data.
Seeing literature review in this way has three important implications for how we think about our literature review, and how we can design it to increase its chances of being interesting to others - that is, of being published.
Start with a relevant research problem and an interesting research question
We learn early in our academic career that any empirical paper should have a clear research problem and a clear research question. We frequently hear from journal editors and reviewers that just having a gap in the literature, or the fact that something has not been researched before, are not good enough to justify doing yet another empirical study. They say: you need to have a problem that your study can address, and you need to have a question that we currently don’t have an answer to. Only then your empirical study can add value to existing research.
When we think of a literature review as of an empirical study, just with the different type of data at hand, we realize that the very same rationale applies. From this perspective the arguments that I often see in literature reviews – that there is no literature review in this particular area or that the existing literature reviews are quite dated – are not sufficient in the journal’s eyes to justify the publication of a literature review on a topic. If you aim to publish your literature review, start by thinking – what is the problem I would like to address? What would be my research question about this problem, that other readers would find interesting?
Design a methodologically-sound data collection and analysis protocol
When we think of any empirical study, we know that if we want to have reliable findings that will be accepted by our peers as trustworthy, we need to follow a transparent and well-thought data collection protocol. We also need to carefully choose and correctly apply relevant data analysis method. This goes without saying, right?
The same applies to the literature review! If we want our readers to trust our conclusions from the literature review, we need to make sure that the data we collect speaks to our research question, is of good quality, representative of the field, etc. The growing attention in business and management field to the systematic approach to literature reviews (Denyer & Tranfield, 2009; Rojon et al., 2021) reflects the rising expectations of the quality of the data used in literature review papers. Indeed, this approach offers exactly that: a clear data collection protocol, transparently communicated, so that someone else could replicate your study. For example, do the very same thing in 10 years and see how thinking on the topic has changed.

In the literature on doing literature reviews you will read that systematic literature review is only one of the types of literature reviews. Yet all recommendations on doing different types of the literature reviews share the idea that the data that you base your conclusions on has to be collected in a rigorous and transparent way (e.g., Callahan, 2014). In this post you can find more references on how to ensure that your literature review “data collection” protocol meets the quality expectations.
So now you have all the papers you have carefully selected, how do you go about analysing them, so that peer academics would recognize your conclusions as reliable and robust? This is the trickiest part, and we have limited methodological advice published on this. In this post I’ve mentioned some papers that discuss specific methods of literature analysis. For example, I found that a sophisticated coding rubric leveraged our literature analysis to a different level (Sergeeva & Andreeva, 2016), but must acknowledge that developing this rubric was one of the most challenging tasks of this review paper. In O’Higgins et al. (forthcoming) we used a combination of qualitative content analysis with Pearson’s chi-squared (χ²) goodness of fit test in order to validate some of our conclusions. The trick is - as with any empirical study - your choice of the analytical method needs to fit with your research question. In sum, the message is: choose your method for analysis of the selected literature carefully, apply it rigorously, and explain it transparently.
Think of the theoretical contribution beyond description of the findings
When we think of our usual empirical work, be it qualitative or quantitative, we are well-aware that just the description of our data wouldn’t do. We know that we need to leverage what our data shows to explain how it informs the broader theory, how it compares to previous studies, what is new that we see from this data?
Again, the same logic applies to the literature reviews. In practice though, we often find it difficult to apply this advice to our literature review papers, because the description of the field in itself seems to be novel, especially if nobody did such a review before. In my experience, this argument does not persuade editors and reviewers of the journals, and often rightfully so.

For example, think of a typical quantitative empirical paper: a descriptive statistics table must be provided, but no one would claim a contribution based on it, right? Cropanzano (2009:1306-1307) offers a good exercise that explains why reviewers often don’t buy the description of the field as a novel contribution. He suggests: imagine somebody who read all the primary articles in your dataset, would they still learn anything from your literature review? And if the answer is “no”, then it’s likely that your review paper doesn’t have yet the level of contribution that is needed to turn it into a publication.
I think this exercise can also help to stimulate your thinking of what a theoretical contribution of your literature review could be. For example, think – what it is that I see in this literature that others are not likely to see? In this blogpost you can find some papers that offer insights on how to leverage your literature review to have a theoretical contribution.
Callahan, J.L. (2014). Writing literature reviews: A reprise and update. Human Resource Development Review , 13(3), 271–275. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484314536705
Cropanzano, R. (2009). Writing nonempirical articles for Journal of Management: General thoughts and suggestions. Journal of Management , 35(6), 1304–1311. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206309344118
Denyer, D., Tranfield, D. (2009). Producing a systematic review. In Buchanan, D., Bryman, A. (Eds.), The Sage handbook of organizational research methods (pp. 671–689). London, UK: Sage.
O’Higgins, C., Andreeva, T., Aramburu, N. (forthcoming). International management challenges of professional service firms: a synthesis of the literature. Review of International Business and Strategy.
Rojon, C., Okupe, A., McDowall, A. (2021). Utilization and development of systematic reviews in management research: What do we know and where do we go from here? International Journal of Management Reviews, 1– 33. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12245
Sergeeva, A., Andreeva, T. (2016). Knowledge sharing: bringing the context back in, Journal of Management Inquiry , 25, 240-261. https://doi.org/10.1177/1056492615618271
Related blogposts
- Resources on doing a literature review
- Do you really want to publish your literature review? Advice for PhD students
- How to keep up-to-date with the literature, but avoid information overload?
- Is a literature review publication a low-cost project?
- Using Publish or Perish to do a literature review
- How to conduct a longitudinal literature review?
- New: Publish or Perish now also exports abstracts
Find the resources on my website useful?
I cover all the expenses of operating my website privately. If you enjoyed this post and want to support me in maintaining my website, consider buying a copy of one of my books (see below) or supporting the Publish or Perish software .
A story about perseverance and publication failures
Copyright © 2023 Tatiana Andreeva . All rights reserved. Page last modified on Fri 27 Oct 2023 17:26

Tatiana Andreeva's profile and contact details >>
- Open access
- Published: 23 August 2022
Prognostic risk factors for moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic literature review
- John R. Hurst 1 ,
- MeiLan K. Han 2 ,
- Barinder Singh 3 ,
- Sakshi Sharma 4 ,
- Gagandeep Kaur 3 ,
- Enrico de Nigris 5 ,
- Ulf Holmgren 6 &
- Mohd Kashif Siddiqui 3
Respiratory Research volume 23 , Article number: 213 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
6315 Accesses
20 Citations
33 Altmetric
Metrics details
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. COPD exacerbations are associated with a worsening of lung function, increased disease burden, and mortality, and, therefore, preventing their occurrence is an important goal of COPD management. This review was conducted to identify the evidence base regarding risk factors and predictors of moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with COPD.
A literature review was performed in Embase, MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL). Searches were conducted from January 2015 to July 2019. Eligible publications were peer-reviewed journal articles, published in English, that reported risk factors or predictors for the occurrence of moderate-to-severe exacerbations in adults age ≥ 40 years with a diagnosis of COPD.
The literature review identified 5112 references, of which 113 publications (reporting results for 76 studies) met the eligibility criteria and were included in the review. Among the 76 studies included, 61 were observational and 15 were randomized controlled clinical trials. Exacerbation history was the strongest predictor of future exacerbations, with 34 studies reporting a significant association between history of exacerbations and risk of future moderate or severe exacerbations. Other significant risk factors identified in multiple studies included disease severity or bronchodilator reversibility (39 studies), comorbidities (34 studies), higher symptom burden (17 studies), and higher blood eosinophil count (16 studies).
Conclusions
This systematic literature review identified several demographic and clinical characteristics that predict the future risk of COPD exacerbations. Prior exacerbation history was confirmed as the most important predictor of future exacerbations. These prognostic factors may help clinicians identify patients at high risk of exacerbations, which are a major driver of the global burden of COPD, including morbidity and mortality.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide [ 1 ]. Based upon disability-adjusted life-years, COPD ranked sixth out of 369 causes of global disease burden in 2019 [ 2 ]. COPD exacerbations are associated with a worsening of lung function, and increased disease burden and mortality (of those patients hospitalized for the first time with an exacerbation, > 20% die within 1 year of being discharged) [ 3 ]. Furthermore, patients with COPD consider exacerbations or hospitalization due to exacerbations to be the most important disease outcome, having a large impact on their lives [ 4 ]. Therefore, reducing the future risk of COPD exacerbations is a key goal of COPD management [ 5 ].
Being able to predict the level of risk for each patient allows clinicians to adapt treatment and patients to adjust their lifestyle (e.g., through a smoking cessation program) to prevent exacerbations [ 3 ]. As such, identifying high-risk patients using measurable risk factors and predictors that correlate with exacerbations is critical to reduce the burden of disease and prevent a cycle of decline encompassing irreversible lung damage, worsening quality of life (QoL), increasing disease burden, high healthcare costs, and early death.
Prior history of exacerbations is generally thought to be the best predictor of future exacerbations; however, there is a growing body of evidence suggesting other demographic and clinical characteristics, including symptom burden, airflow obstruction, comorbidities, and inflammatory biomarkers, also influence risk [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. For example, in the prospective ECLIPSE observational study, the likelihood of patients experiencing an exacerbation within 1 year of follow-up increased significantly depending upon several factors, including prior exacerbation history, forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV 1 ), St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) score, gastroesophageal reflux, and white blood cell count [ 9 ].
Many studies have assessed predictors of COPD exacerbations across a variety of countries and patient populations. This systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted to identify and compile the evidence base regarding risk factors and predictors of moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with COPD.
- Systematic literature review
A comprehensive search strategy was designed to identify English-language studies published in peer-reviewed journals providing data on risk factors or predictors of moderate or severe exacerbations in adults aged ≥ 40 years with a diagnosis of COPD (sample size ≥ 100). The protocol is summarized in Table 1 and the search strategy is listed in Additional file 1 : Table S1. Key biomedical electronic literature databases were searched from January 2015 until July 2019. Other sources were identified via bibliographic searching of relevant systematic reviews.
Study selection process
Implementation and reporting followed the recommendations and standards of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement [ 10 ]. An independent reviewer conducted the first screening based on titles and abstracts, and a second reviewer performed a quality check of the excluded evidence. A single independent reviewer also conducted the second screening based on full-text articles, with a quality check of excluded evidence performed by a second reviewer. Likewise, data tables of the included studies were generated by one reviewer, and another reviewer performed a quality check of extracted data. Where more than one publication was identified describing a single study or trial, data were compiled into a single entry in the data-extraction table to avoid double counting of patients and studies. One publication was designated as the ‘primary publication’ for the purposes of the SLR, based on the following criteria: most recently published evidence and/or the article that presented the majority of data (e.g., journal articles were preferred over conference abstracts; articles that reported results for the full population were preferred over later articles providing results of subpopulations). Other publications reporting results from the same study were designated as ‘linked publications’; any additional data in the linked publications that were not included in the primary publication were captured in the SLR. Conference abstracts were excluded from the SLR unless they were a ‘linked publication.’
Included studies
A total of 5112 references (Fig. 1 ) were identified from the database searches. In total, 76 studies from 113 publications were included in the review. Primary publications and ‘linked publications’ for each study are detailed in Additional file 1 : Table S2, and study characteristics are shown in Additional file 1 : Table S3. The studies included clinical trials, registry studies, cross-sectional studies, cohort studies, database studies, and case–control studies. All 76 included studies were published in peer-reviewed journals. Regarding study design, 61 of the studies were observational (34 retrospective observational studies, 19 prospective observational studies, four cross-sectional studies, two studies with both retrospective and prospective cohort data, one case–control study, and one with cross-sectional and longitudinal data) and 15 were randomized controlled clinical trials.
PRISMA flow diagram of studies through the systematic review process. CA conference abstract, CENTRAL Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, PRISMA Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Of the 76 studies, 16 were conducted in North America (13 studies in the USA, two in Canada, and one in Mexico); 26 were conducted in Europe (seven studies in Spain, four in the UK, three in Denmark, two studies each in Bulgaria, the Netherlands, and Switzerland, and one study each in Sweden, Serbia, Portugal, Greece, Germany, and France) and 17 were conducted in Asia (six studies in South Korea, four in China, three in Taiwan, two in Japan, and one study each in Singapore and Israel). One study each was conducted in Turkey and Australia. Fifteen studies were conducted across multiple countries.
The majority of the studies (n = 54) were conducted in a multicenter setting, while 22 studies were conducted in a single-center setting. The sample size among the included studies varied from 118 to 339,389 patients.
Patient characteristics
A total of 75 studies reported patient characteristics (Additional file 1 : Table S4). The mean age was reported in 65 studies and ranged from 58.0 to 75.2 years. The proportion of male patients ranged from 39.7 to 97.6%. The majority of included studies (85.3%) had a higher proportion of males than females.
Exacerbation history (as defined per each study) was reported in 18 of 76 included studies. The proportion of patients with no prior exacerbation was reported in ten studies (range, 0.1–79.5% of patients), one or fewer prior exacerbation in ten studies (range, 46–100%), one or more prior exacerbation in eight studies (range, 18.4–100%), and two or more prior exacerbations in 12 studies (range, 6.1–55.0%).
Prognostic factors of exacerbations
A summary of the risk factors and predictors reported across the included studies is provided in Tables 2 and 3 . The overall findings of the SLR are summarized in Figs. 2 and 3 .
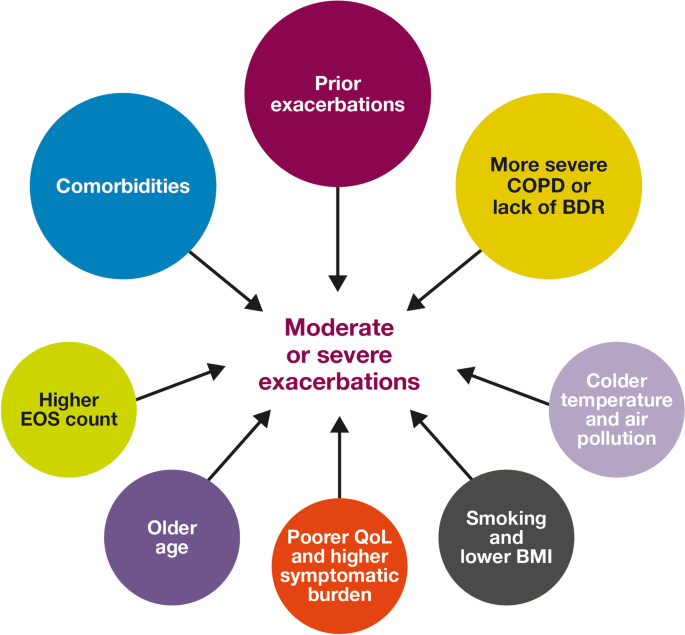
Risk factors for moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with COPD. Factors with > 30 supporting studies shown as large circles; factors with ≤ 30 supporting studies shown as small circles and should be interpreted cautiously. BDR bronchodilator reversibility, BMI body mass index, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, EOS eosinophil, QoL quality of life
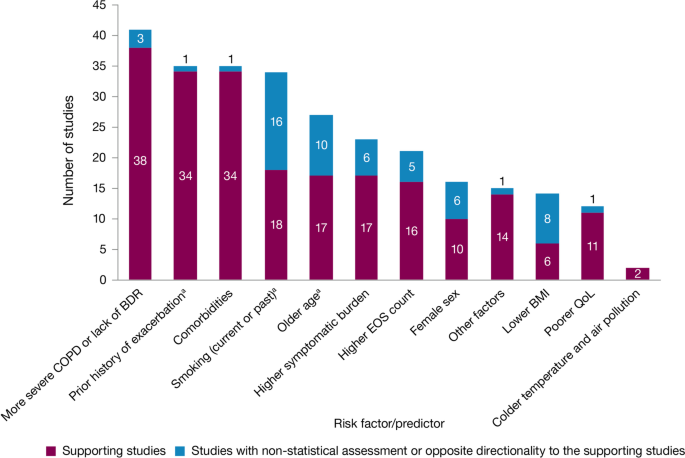
Summary of risk factors for exacerbation events. a Treatment impact studies removed. BDR bronchodilator reversibility, BMI body mass index, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, EOS eosinophil, QoL quality of life
Exacerbation history within the past 12 months was the strongest predictor of future exacerbations. Across the studies assessing this predictor, 34 out of 35 studies (97.1%) reported a significant association between history of exacerbations and risk of future moderate-to-severe exacerbations (Table 3 ). Specifically, two or more exacerbations in the previous year or at least one hospitalization for COPD in the previous year were identified as reliable predictors of future moderate or severe exacerbations. Even one moderate exacerbation increased the risk of a future exacerbation, with the risk increasing further with each subsequent exacerbation (Fig. 4 ). A severe exacerbation was also found to increase the risk of subsequent exacerbation and hospitalization (Fig. 5 ). Patients experiencing one or more severe exacerbations were more likely to experience further severe exacerbations than moderate exacerbations [ 11 , 12 ]. In contrast, patients with a history of one or more moderate exacerbations were more likely to experience further moderate exacerbations than severe exacerbations [ 11 , 12 ].
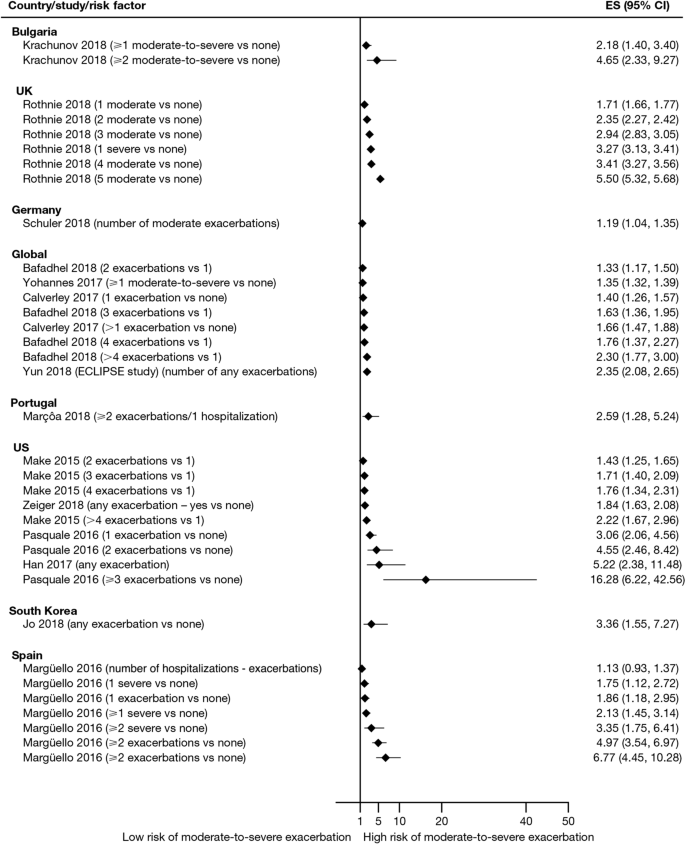
Exacerbation history as a risk factor for moderate-to-severe exacerbations. Yun 2018 included two studies; the study from which data were extracted (COPDGene or ECLIPSE) is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, ES effect size
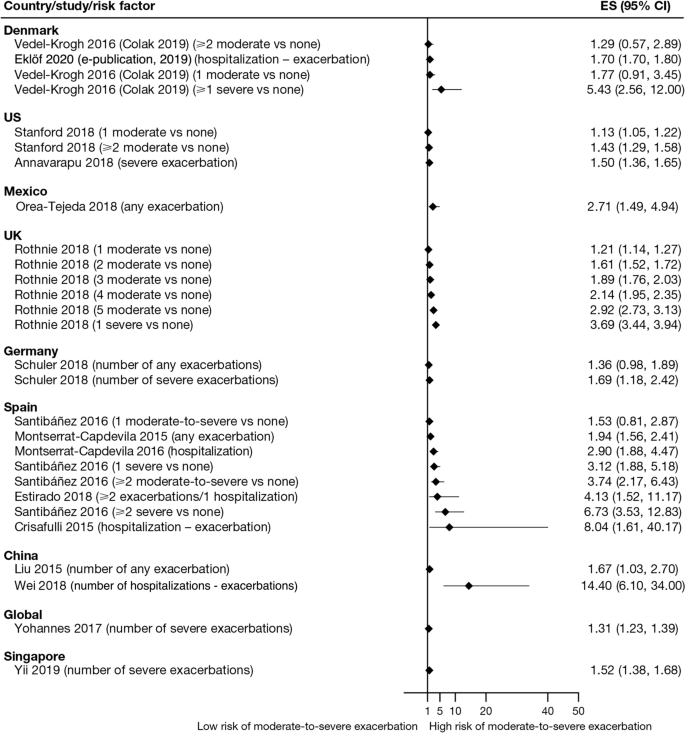
Exacerbation history as a risk factor for severe exacerbations. Where data have been extracted from a linked publication rather than the primary publication, the linked publication is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, ES , effect size
Overall, 35 studies assessed the association of comorbidities with the risk of exacerbation. All studies except one (97.1%) reported a positive association between comorbidities and the occurrence of moderate-to-severe exacerbations (Table 3 ). In addition to the presence of any comorbidity, specific comorbidities that were found to significantly increase the risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations included anxiety and depression, cardiovascular comorbidities, gastroesophageal reflux disease/dyspepsia, and respiratory comorbidities (Fig. 6 ). Comorbidities that were significant risk factors for severe exacerbations included cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, and respiratory comorbidities, diabetes, and malignancy (Fig. 7 ). Overall, the strongest association between comorbidities and COPD readmissions in the emergency department was with cardiovascular disease. The degree of risk for both moderate-to-severe and severe exacerbations also increased with the number of comorbidities. A Dutch cohort study found that 88% of patients with COPD had at least one comorbidity, with hypertension (35%) and coronary heart disease (19%) being the most prevalent. In this cohort, the comorbidities with the greatest risk of frequent exacerbations were pulmonary cancer (odds ratio [OR] 1.85) and heart failure (OR 1.72) [ 7 ].
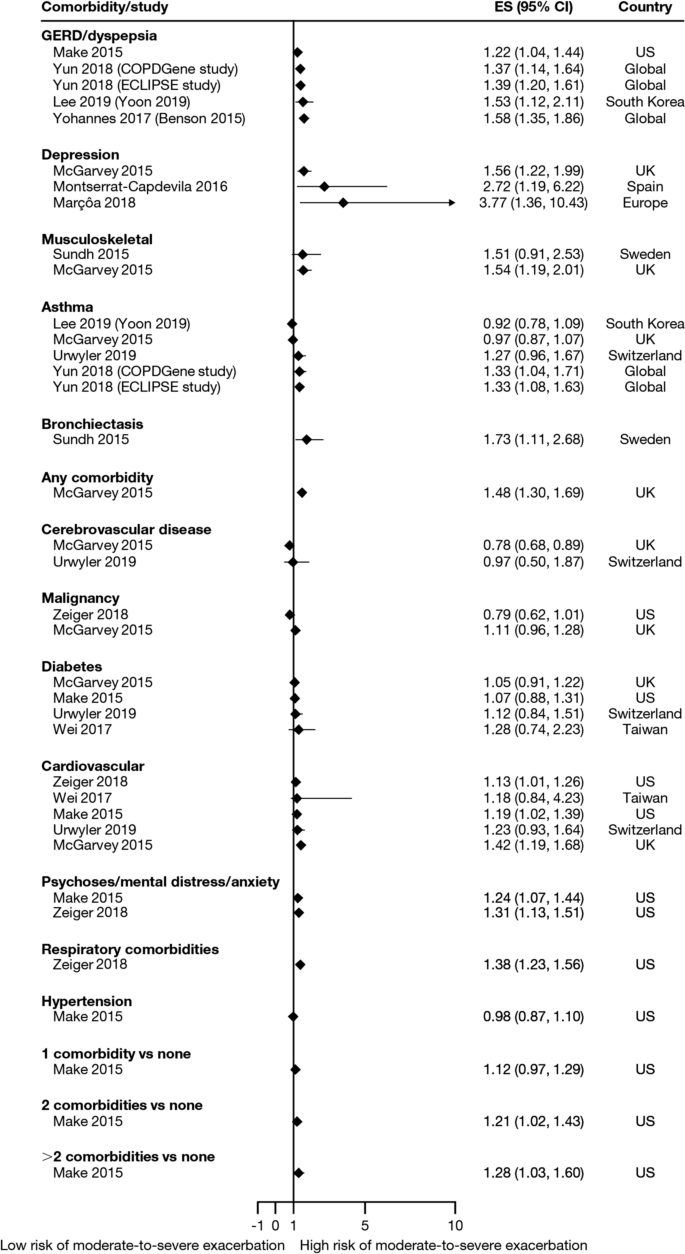
Comorbidities as risk factors for moderate-to-severe exacerbations. Yun 2018 included two studies; the study from which data were extracted (COPDGene or ECLIPSE) is listed in parentheses. Where data have been extracted from a linked publication rather than the primary publication, the linked publication is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, ES effect size, GERD gastroesophageal disease
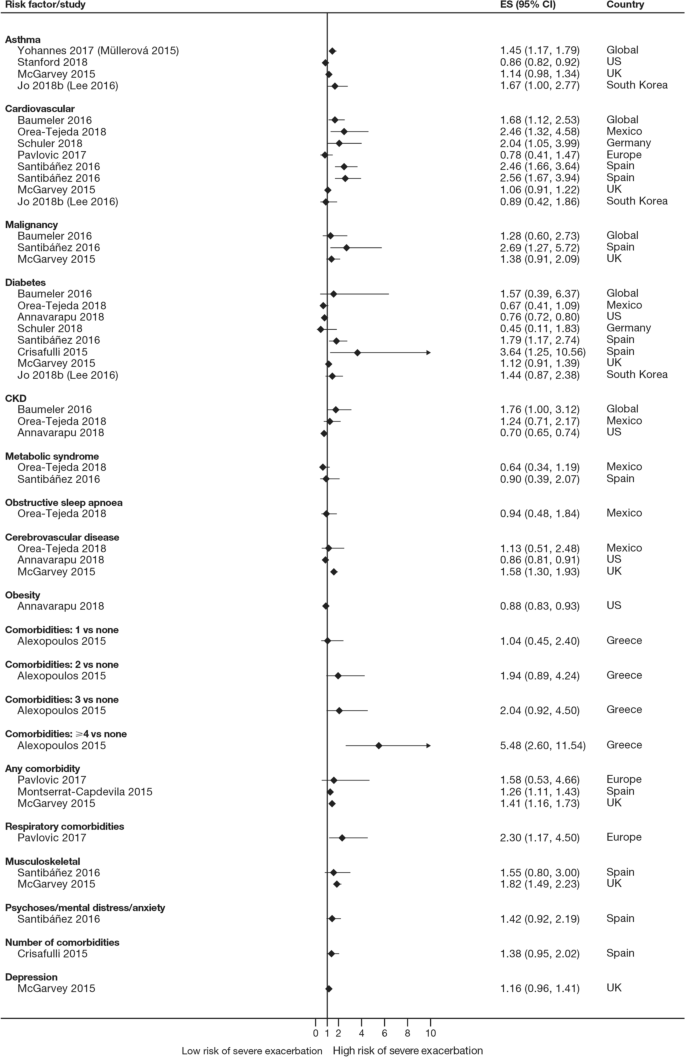
Comorbidities as risk factors for severe exacerbations. Where data have been extracted from a linked publication rather than the primary publication, the linked publication is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, CKD , chronic kidney disease, ES effect size
The majority of studies assessing disease severity or bronchodilator reversibility (39/41; 95.1%) indicated a significant positive relation between risk of future exacerbations and greater disease severity, as assessed by greater lung function impairment (in terms of lower FEV 1 , FEV 1 /forced vital capacity ratio, or forced expiratory flow [25–75]/forced vital capacity ratio) or more severe Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) class A − D, and a positive relationship between risk of future exacerbations and lack of bronchodilator reversibility (Table 3 , Figs. 8 and 9 ).
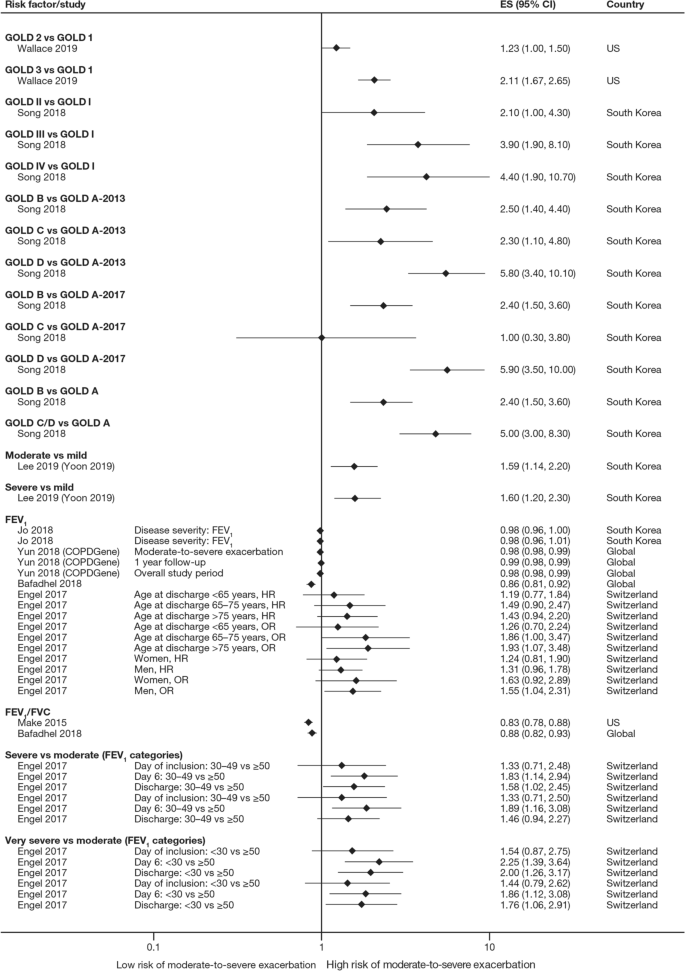
Disease severity as a risk factor for moderate-to-severe exacerbations. Yun 2018 included two studies; the study from which data were extracted (COPDGene or ECLIPSE) is listed in parentheses. Where data have been extracted from a linked publication rather than the primary publication, the linked publication is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, ES effect size, FEV 1 f orced expiratory volume in 1 s, FVC , forced vital capacity, GOLD Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease, HR hazard ratio, OR odds ratio
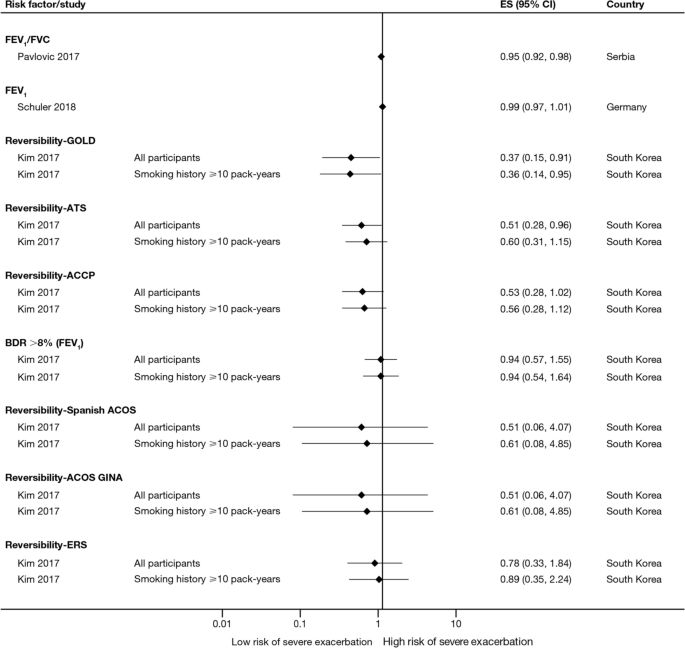
Disease severity and BDR as risk factors for severe exacerbations. ACCP American College of Chest Physicians, ACOS Asthma-COPD overlap syndrome, ATS American Thoracic Society, BDR bronchodilator reversibility, CI confidence interval, ERS European Respiratory Society, ES effect size, FEV 1 forced expiratory volume in 1 s, FVC forced vital capacity, GINA Global Initiative for Asthma, GOLD Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease
Of 21 studies assessing the relationship between blood eosinophil count and exacerbations (Table 3 ), 16 reported estimates for the risk of moderate or severe exacerbations by eosinophil count. A positive association was observed between higher eosinophil count and a higher risk of moderate or severe exacerbations, particularly in patients not treated with an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS); however, five studies reported a significant positive association irrespective of intervention effects. The risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations was observed to be positively associated with various definitions of higher eosinophil levels (absolute counts: ≥ 200, ≥ 300, ≥ 340, ≥ 400, and ≥ 500 cells/mm 3 ; % of blood eosinophil count: ≥ 2%, ≥ 3%, ≥ 4%, and ≥ 5%). Of note, one study found reduced efficacy of ICS in lowering moderate-to-severe exacerbation rates for current smokers versus former smokers at all eosinophil levels [ 13 ].
Of 12 studies assessing QoL scales, 11 (91.7%) studies reported a significant association between the worsening of QoL scores and the risk of future exacerbations (Table 3 ). Baseline SGRQ [ 14 , 15 ], Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (for which increased scores may indicate impaired QoL) [ 16 ], and Clinical COPD Questionnaire [ 17 , 18 ] scores were found to be associated with future risk of moderate and/or severe COPD exacerbations. For symptom scores, six out of eight studies assessing the association between moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbations with COPD Assessment Test (CAT) scores reported a significant and positive relationship. Furthermore, the risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations was found to be significantly higher in patients with higher CAT scores (≥ 10) [ 15 , 19 , 20 , 21 ], with one study demonstrating that a CAT score of 15 increased predictive ability for exacerbations compared with a score of 10 or more [ 18 ]. Among 15 studies that assessed the association of modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) scores with the risk of moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbation, 11 found that the risk of moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbations was significantly associated with higher mMRC scores (≥ 2) versus lower scores. Furthermore, morning and night symptoms (measured by Clinical COPD Questionnaire) were associated with poor health status and predicted future exacerbations [ 17 ].
Of 36 studies reporting the relationship between smoking status and moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbations, 22 studies (61.1%) reported a significant positive association (Table 3 ). Passive smoking was also significantly associated with an increased risk of severe exacerbations (OR 1.49) [ 20 ]. Of note, three studies reported a significantly lower rate of moderate-to-severe exacerbations in current smokers compared with former smokers [ 22 , 23 , 24 ].
A total of 14 studies assessed the association of body mass index (BMI) with the occurrence of frequent moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with COPD. Six out of 14 studies (42.9%) reported a significant negative association between exacerbations and BMI (Table 3 ). The risk of moderate and/or severe COPD exacerbations was highest among underweight patients compared with normal and overweight patients [ 23 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ].
In the 29 studies reporting an association between age and moderate or severe exacerbations, more than half found an association of older age with an increased risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations (58.6%; Table 3 ). Four of these studies noted a significant increase in the risk of moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbations for every 10-year increase in age [ 25 , 26 , 29 , 30 ]. However, 12 studies reported no significant association between age and moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbation risk.
Sixteen out of 33 studies investigating the impact of sex on exacerbation risk found a significant association (48.5%; Table 3 ). Among these, ten studies reported that female sex was associated with an increased risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations, while six studies showed a higher exacerbation risk in males compared with females. There was some variation in findings by geographic location and exacerbation severity (Additional file 2 : Figs. S1 and S2). Notably, when assessing the risk of severe exacerbations, more studies found an association with male sex compared with female sex (6/13 studies vs 1/13 studies, respectively).
Both studies evaluating associations between exacerbations and environmental factors reported that colder temperature and exposure to major air pollution (NO 2 , O 3 , CO, and/or particulate matter ≤ 10 μm in diameter) increased hospital admissions due to severe exacerbations and moderate-to-severe exacerbation rates [ 31 , 32 ].
Four studies assessed the association of 6-min walk distance with the occurrence of frequent moderate-to-severe exacerbations (Table 3 ). One study (25.0%) found that shorter 6-min walk distance (representing low physical activity) was significantly associated with a shortened time to severe exacerbation, but the effect size was small (hazard ratio 0.99) [ 33 ].
Five out of six studies assessing the relationship between race or ethnicity and exacerbation risk reported significant associations (Table 3 ). Additionally, one study reported an association between geographic location in the US and exacerbations, with living in the Northeast region being the strongest predictor of severe COPD exacerbations versus living in the Midwest and South regions [ 34 ].
Overall, seven studies assessed the association of biomarkers with risk of future exacerbations (Table 3 ), with the majority identifying significant associations between inflammatory biomarkers and increased exacerbation risk, including higher C-reactive protein levels [ 8 , 35 ], fibrinogen levels [ 8 , 30 ], and white blood cell count [ 8 , 15 , 16 ].
This SLR has identified several demographic and clinical characteristics that predict the future risk of COPD exacerbations. Key factors associated with an increased risk of future moderate-to-severe exacerbations included a history of prior exacerbations, worse disease severity and bronchodilator reversibility, the presence of comorbidities, a higher eosinophil count, and older age (Fig. 2 ). These prognostic factors may help clinicians identify patients at high risk of exacerbations, which are a major driver of the burden of COPD, including morbidity and mortality [ 36 ].
Findings from this review summarize the existing evidence, validating the previously published literature [ 6 , 9 , 23 ] and suggesting that the best predictor of future exacerbations is a history of exacerbations in the prior year [ 8 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 26 , 29 , 34 , 35 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ]. In addition, the effect size generally increased with the number of prior exacerbations, with a stronger effect observed with prior severe versus moderate exacerbations. This effect was observed across regions, including in Europe and North America, and in several global studies. This relationship represents a vicious circle, whereby one exacerbation predisposes a patient to experience future exacerbations and leading to an ever-increasing disease burden, and emphasizes the importance of preventing the first exacerbation event through early, proactive exacerbation prevention. The finding that prior exacerbations tended to be associated with future exacerbations of the same severity suggests that the severity of the underlying disease may influence exacerbation severity. However, the validity of the traditional classification of exacerbation severity has recently been challenged [ 61 ], and further work is required to understand relationships with objective assessments of exacerbation severity.
In addition to exacerbation history, disease severity and bronchodilator reversibility were also strong predictors for future exacerbations [ 8 , 14 , 16 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 26 , 28 , 29 , 33 , 37 , 40 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 48 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 56 , 59 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 ]. The association with disease severity was noted in studies that used GOLD disease stages 1–4 and those that used FEV 1 percent predicted and other lung function assessments as continuous variables. Again, this risk factor is self-perpetuating, as evidence shows that even a single moderate or severe exacerbation may almost double the rate of lung function decline [ 79 ]. Accordingly, disease severity and exacerbation history may be correlated. Margüello et al. concluded that the severity of COPD could be associated with a higher risk of exacerbations, but this effect was partly determined by the exacerbations suffered in the previous year [ 23 ]. It should be noted that FEV 1 is not recommended by GOLD for use as a predictor of exacerbation risk or mortality alone due to insufficient precision when used at the individual patient level [ 5 ].
Another factor that should be considered when assessing individual exacerbation risk is the presence of comorbidities [ 7 , 14 , 16 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 40 , 41 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 56 , 58 , 59 , 63 , 64 , 73 , 74 , 76 , 77 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 ]. Comorbidities are common in COPD, in part due to common risk factors (e.g., age, smoking, lifestyle factors) that also increase the risk of other chronic diseases [ 7 ]. Significant associations were observed between exacerbation risk and comorbidities, such as anxiety and depression, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory comorbidities. As with prior exacerbations, the strength of the association increased with the number of comorbidities. Some comorbidities that were found to be associated with COPD exacerbations share a common biological mechanism of systemic inflammation, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and depression [ 86 ]. Furthermore, other respiratory comorbidities, including asthma and bronchiectasis, involve inflammation of the airways [ 87 ]. In these patients, optimal management of comorbidities may reduce the risk of future COPD exacerbations (and improve QoL), although further research is needed to confirm the efficacy of this approach to exacerbation prevention. As cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension and coronary heart disease, are the most common comorbidities in people with COPD [ 7 ], reducing cardiovascular risk may be a key goal in reducing the occurrence of exacerbations. For other comorbidities, the mechanism for the association with exacerbation risk may be related to non-biological factors. For example, in depression, it has been suggested that the mechanism may relate to greater sensitivity to symptom changes or more frequent physician visits [ 88 ].
There is now a growing body of evidence reporting the relationship between blood eosinophil count and exacerbation risk [ 8 , 13 , 14 , 20 , 37 , 48 , 52 , 56 , 59 , 60 , 62 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 ]. Data from many large clinical trials (SUNSET [ 89 ], FLAME [ 96 ], WISDOM [ 98 ], IMPACT [ 13 ], TRISTAN [ 99 ], INSPIRE [ 99 ], KRONOS [ 91 ], TRIBUTE [ 48 ], TRILOGY [ 52 ], TRINITY [ 56 ]) have also shown relationships between treatment, eosinophil count, and exacerbation rates. Evidence shows that eosinophil count, along with other effect modifiers (e.g., exacerbation history), can be used to predict reductions in exacerbations with ICS treatment. Identifying patients most likely to respond to ICS should contribute to personalized medicine approaches to treat COPD. One challenge in drawing a strong conclusion from eosinophil counts is the choice of a cut-off value, with a variety of absolute and percentage values observed to be positively associated with the risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations. The use of absolute counts may be more practical, as these are not affected by variations in other immune cell numbers; however, there is a lack of consensus on this point [ 100 ].
Across the studies examined, associations between sex and the risk of moderate and/or severe exacerbations were variable [ 14 , 16 , 18 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 37 , 40 , 42 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 51 , 52 , 56 , 58 , 59 , 63 , 73 , 74 , 77 , 80 , 83 , 84 , 85 ]. A greater number of studies showed an increased risk of exacerbations in females compared with males. In contrast, some studies failed to detect a relationship, suggesting that country-specific or cultural factors may play a role. A majority of the included studies evaluated more male patients than female patients; to further elucidate the relationship between sex and exacerbations, more studies in female patients are warranted. Over half of the studies that assessed the relationship between age and exacerbation risk found an association between increasing age and increasing risk of moderate-to-severe COPD exacerbations [ 14 , 16 , 18 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 33 , 40 , 42 , 44 , 45 , 47 , 51 , 52 , 54 , 56 , 63 , 73 , 74 , 77 , 80 , 83 , 85 ].
Our findings also suggested that patients with low BMI have greater risk of moderate and/or severe exacerbations. The mechanism underlying this increased risk in underweight patients is poorly understood; however, loss of lean body mass in patients with COPD may be related to ongoing systemic inflammation that impacts skeletal muscle mass [ 101 , 102 , 103 ].
A limitation of this SLR, that may have resulted in some studies with valid results being missed, was the exclusion of non-English-language studies and the limitation by date; however, the search strategy was otherwise broad, resulting in the review of a large number of studies. The majority of studies captured in this SLR were from Europe, North America, and Asia. The findings may therefore be less generalizable to patients in other regions, such as Africa or South America. Given that one study reported an association between geographic location within different regions of the US and exacerbations [ 34 ], it is plausible that risk of exacerbations may be impacted by global location. As no formal meta-analysis was planned, the assessments are based on a qualitative synthesis of studies. A majority of the included studies looked at exposures of certain factors (e.g., history of exacerbations) at baseline; however, some of these factors change over time, calling into question whether a more sophisticated statistical analysis should have been conducted in some cases to consider time-varying covariates. Our results can only inform on associations, not causation, and there are likely bidirectional relationships between many factors and exacerbation risk (e.g., health status). Finally, while our review of the literature captured a large number of prognostic factors, other variables such as genetic factors, lung microbiome composition, and changes in therapy over time have not been widely studied to date, but might also influence exacerbation frequency [ 104 ]. Further research is needed to assess the contribution of these factors to exacerbation risk.
This SLR captured publications up to July 2019. However, further studies have since been published that further support the prognostic factors identified here. For example, recent studies have reported an increased risk of exacerbations in patients with a history of exacerbations [ 105 ], comorbidities [ 106 ], poorer lung function (GOLD stage) [ 105 ], higher symptomatic burden [ 107 ], female sex [ 105 ], and lower BMI [ 106 , 108 ].
In summary, the literature assessing risk factors for moderate-to-severe COPD exacerbations shows that there are associations between several demographic and disease characteristics with COPD exacerbations, potentially allowing clinicians to identify patients most at risk of future exacerbations. Exacerbation history, comorbidities, and disease severity or bronchodilator reversibility were the factors most strongly associated with exacerbation risk, and should be considered in future research efforts to develop prognostic tools to estimate the likelihood of exacerbation occurrence. Importantly, many prognostic factors for exacerbations, such as symptom burden, QoL, and comorbidities, are modifiable with optimal pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic treatments or lifestyle modifications. Overall, the evidence suggests that, taken together, predicting and reducing exacerbation risk is an achievable goal in COPD.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Body mass index
COPD Assessment Test
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Forced expiratory volume in 1 s
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
Inhaled corticosteroid
Modified Medical Research Council
Quality of life
St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire
World Health Organization. The top 10 causes of death. 2018. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death . Accessed 22 Jul 2020.
GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet. 2020;396:1204–22.
Article Google Scholar
Hurst JR, Skolnik N, Hansen GJ, Anzueto A, Donaldson GC, Dransfield MT, Varghese P. Understanding the impact of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations on patient health and quality of life. Eur J Intern Med. 2020;73:1–6.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Morgan RL, Alonso-Coello P, Wiercioch W, Bała MM, Jaeschke RR, Styczeń K, Pardo-Hernandez H, Selva A, Ara Begum H, et al. A systematic review of how patients value COPD outcomes. Eur Respir J. 2018;52:1800222.
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. 2022 GOLD Report. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD. 2022. https://goldcopd.org/2022-gold-reports-2/ . Accessed 02 Feb 2022.
Müllerová H, Shukla A, Hawkins A, Quint J. Risk factors for acute exacerbations of COPD in a primary care population: a retrospective observational cohort study. BMJ Open. 2014;4: e006171.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Westerik JAM, Metting EI, van Boven JFM, Tiersma W, Kocks JWH, Schermer TR. Associations between chronic comorbidity and exacerbation risk in primary care patients with COPD. Respir Res. 2017;18:31.
Vedel-Krogh S, Nielsen SF, Lange P, Vestbo J, Nordestgaard BG. Blood eosinophils and exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The Copenhagen General Population Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193:965–74.
Hurst JR, Vestbo J, Anzueto A, Locantore N, Müllerová H, Tal-Singer R, Miller B, Lomas DA, Agusti A, Macnee W, et al. Susceptibility to exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1128–38.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097.
Çolak Y, Afzal S, Marott JL, Nordestgaard BG, Vestbo J, Ingebrigtsen TS, Lange P. Prognosis of COPD depends on severity of exacerbation history: a population-based analysis. Respir Med. 2019;155:141–7.
Rothnie KJ, Müllerová H, Smeeth L, Quint JK. Natural history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations in a general practice-based population with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:464–71.
Pascoe S, Barnes N, Brusselle G, Compton C, Criner GJ, Dransfield MT, Halpin DMG, Han MK, Hartley B, Lange P, et al. Blood eosinophils and treatment response with triple and dual combination therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: analysis of the IMPACT trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7:745–56.
Yun JH, Lamb A, Chase R, Singh D, Parker MM, Saferali A, Vestbo J, Tal-Singer R, Castaldi PJ, Silverman EK, et al. Blood eosinophil count thresholds and exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:2037-2047.e10.
Yoon HY, Park SY, Lee CH, Byun MK, Na JO, Lee JS, Lee WY, Yoo KH, Jung KS, Lee JH. Prediction of first acute exacerbation using COPD subtypes identified by cluster analysis. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:1389–97.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yohannes AM, Mulerova H, Lavoie K, Vestbo J, Rennard SI, Wouters E, Hanania NA. The association of depressive symptoms with rates of acute exacerbations in patients with COPD: results from a 3-year longitudinal follow-up of the ECLIPSE cohort. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;18:955-959.e6.
Tsiligianni I, Metting E, van der Molen T, Chavannes N, Kocks J. Morning and night symptoms in primary care COPD patients: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. An UNLOCK study from the IPCRG. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2016;26:16040.
Jo YS, Yoon HI, Kim DK, Yoo CG, Lee CH. Comparison of COPD Assessment Test and Clinical COPD Questionnaire to predict the risk of exacerbation. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:101–7.
Marçôa R, Rodrigues DM, Dias M, Ladeira I, Vaz AP, Lima R, Guimarães M. Classification of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) according to the new Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2017: comparison with GOLD 2011. COPD. 2018;15:21–6.
Han MK, Quibrera PM, Carretta EE, Barr RG, Bleecker ER, Bowler RP, Cooper CB, Comellas A, Couper DJ, Curtis JL, et al. Frequency of exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an analysis of the SPIROMICS cohort. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5:619–26.
Yii ACA, Loh CH, Tiew PY, Xu H, Taha AAM, Koh J, Tan J, Lapperre TS, Anzueto A, Tee AKH. A clinical prediction model for hospitalized COPD exacerbations based on “treatable traits.” Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:719–28.
McGarvey L, Lee AJ, Roberts J, Gruffydd-Jones K, McKnight E, Haughney J. Characterisation of the frequent exacerbator phenotype in COPD patients in a large UK primary care population. Respir Med. 2015;109:228–37.
Margüello MS, Garrastazu R, Ruiz-Nuñez M, Helguera JM, Arenal S, Bonnardeux C, León C, Miravitlles M, García-Rivero JL. Independent effect of prior exacerbation frequency and disease severity on the risk of future exacerbations of COPD: a retrospective cohort study. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2016;26:16046.
Engel B, Schindler C, Leuppi JD, Rutishauser J. Predictors of re-exacerbation after an index exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the REDUCE randomised clinical trial. Swiss Med Wkly. 2017;147: w14439.
PubMed Google Scholar
Benson VS, Müllerová H, Vestbo J, Wedzicha JA, Patel A, Hurst JR. Evaluation of COPD longitudinally to identify predictive surrogate endpoints (ECLIPSE) investigators. Associations between gastro-oesophageal reflux, its management and exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med. 2015;109:1147–54.
Santibáñez M, Garrastazu R, Ruiz-Nuñez M, Helguera JM, Arenal S, Bonnardeux C, León C, García-Rivero JL. Predictors of hospitalized exacerbations and mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE. 2016;11: e0158727.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Jo YS, Kim YH, Lee JY, Kim K, Jung KS, Yoo KH, Rhee CK. Impact of BMI on exacerbation and medical care expenses in subjects with mild to moderate airflow obstruction. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:2261–9.
Alexopoulos EC, Malli F, Mitsiki E, Bania EG, Varounis C, Gourgoulianis KI. Frequency and risk factors of COPD exacerbations and hospitalizations: a nationwide study in Greece (Greek Obstructive Lung Disease Epidemiology and health ecoNomics: GOLDEN study). Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:2665–74.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Liu D, Peng SH, Zhang J, Bai SH, Liu HX, Qu JM. Prediction of short term re-exacerbation in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:1265–73.
Müllerová H, Maselli DJ, Locantore N, Vestbo J, Hurst JR, Wedzicha JA, Bakke P, Agusti A, Anzueto A. Hospitalized exacerbations of COPD: risk factors and outcomes in the ECLIPSE cohort. Chest. 2015;147:999–1007.
de Miguel-Díez J, Hernández-Vázquez J, López-de-Andrés A, Álvaro-Meca A, Hernández-Barrera V, Jiménez-García R. Analysis of environmental risk factors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation: a case-crossover study (2004–2013). PLoS ONE. 2019;14: e0217143.
Krachunov II, Kyuchukov NH, Ivanova ZI, Yanev NA, Hristova PA, Borisova ED, Popova TP, Pavlov PS, Nikolova PT, Ivanov YY. Impact of air pollution and outdoor temperature on the rate of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2017;59:423–9.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Baumeler L, Papakonstantinou E, Milenkovic B, Lacoma A, Louis R, Aerts JG, Welte T, Kostikas K, Blasi F, Boersma W, et al. Therapy with proton-pump inhibitors for gastroesophageal reflux disease does not reduce the risk for severe exacerbations in COPD. Respirology. 2016;21:883–90.
Annavarapu S, Goldfarb S, Gelb M, Moretz C, Renda A, Kaila S. Development and validation of a predictive model to identify patients at risk of severe COPD exacerbations using administrative claims data. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:2121–30.
Crisafulli E, Torres A, Huerta A, Méndez R, Guerrero M, Martinez R, Liapikou A, Soler N, Sethi S, Menéndez R. C-reactive protein at discharge, diabetes mellitus and ≥1 hospitalization during previous year predict early readmission in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD. 2015;12:311–20.
Bollmeier SG, Hartmann AP. Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a review focusing on exacerbations. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2020;77:259–68.
Bafadhel M, Peterson S, De Blas MA, Calverley PM, Rennard SI, Richter K, Fagerås M. Predictors of exacerbation risk and response to budesonide in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a post-hoc analysis of three randomised trials. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6:117–26.
Calverley PM, Anzueto AR, Dusser D, Mueller A, Metzdorf N, Wise RA. Treatment of exacerbations as a predictor of subsequent outcomes in patients with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1297–308.
Calverley PM, Tetzlaff K, Dusser D, Wise RA, Mueller A, Metzdorf N, Anzueto A. Determinants of exacerbation risk in patients with COPD in the TIOSPIR study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:3391–405.
Eklöf J, Sørensen R, Ingebrigtsen TS, Sivapalan P, Achir I, Boel JB, Bangsborg J, Ostergaard C, Dessau RB, Jensen US, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and risk of death and exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an observational cohort study of 22 053 patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26:227–34.
Estirado C, Ceccato A, Guerrero M, Huerta A, Cilloniz C, Vilaró O, Gabarrús A, Gea J, Crisafulli E, Soler N, Torres A. Microorganisms resistant to conventional antimicrobials in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res. 2018;19:119.
Fuhrman C, Moutengou E, Roche N, Delmas MC. Prognostic factors after hospitalization for COPD exacerbation. Rev Mal Respir. 2017;34:1–18.
Krachunov I, Kyuchukov N, Ivanova Z, Yanev NA, Hristova PA, Pavlov P, Glogovska P, Popova T, Ivanov YY. Stability of frequent exacerbator phenotype in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2018;60:536–45.
Make BJ, Eriksson G, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Postma DS, Peterson S, Östlund O, Anzueto A. A score to predict short-term risk of COPD exacerbations (SCOPEX). Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:201–9.
Montserrat-Capdevila J, Godoy P, Marsal JR, Barbé F. Predictive model of hospital admission for COPD exacerbation. Respir Care. 2015;60:1288–94.
Montserrat-Capdevila J, Godoy P, Marsal JR, Barbé F, Galván L. Risk factors for exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a prospective study. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2016;20:389–95.
Orea-Tejeda A, Navarrete-Peñaloza AG, Verdeja-Vendrell L, Jiménez-Cepeda A, González-Islas DG, Hernández-Zenteno R, Keirns-Davis C, Sánchez-Santillán R, Velazquez-Montero A, Puentes RG. Right heart failure as a risk factor for severe exacerbation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: prospective cohort study. Clin Respir J. 2018;12:2635–41.
Papi A, Vestbo J, Fabbri L, Corradi M, Prunier H, Cohuet G, Guasconi A, Montagna I, Vezzoli S, Petruzzelli S, et al. Extrafine inhaled triple therapy versus dual bronchodilator therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (TRIBUTE): a double-blind, parallel group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391:1076–84.
Lipson DA, Barnhart F, Brealey N, Brooks J, Criner GJ, Day NC, Dransfield MT, Halpin DMG, Han MK, Jones CE, et al. Once-daily single-inhaler triple versus dual therapy in patients with COPD. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1671–80.
Pasquale MK, Xu Y, Baker CL, Zou KH, Teeter JG, Renda AM, Davis CC, Lee TC, Bobula J. COPD exacerbations associated with the modified Medical Research Council scale and COPD assessment test among Humana Medicare members. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016;11:111–21.
Schuler M, Wittmann M, Faller H, Schultz K. Including changes in dyspnea after inpatient rehabilitation improves prediction models of exacerbations in COPD. Respir Med. 2018;141:87–93.
Singh D, Papi A, Corradi M, Pavlišová I, Montagna I, Francisco C, Cohuet G, Vezzoli S, Scuri M, Vestbo J. Single inhaler triple therapy versus inhaled corticosteroid plus long-acting β 2 -agonist therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (TRILOGY): a double-blind, parallel group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:963–73.
Søgaard M, Madsen M, Løkke A, Hilberg O, Sørensen HT, Thomsen RW. Incidence and outcomes of patients hospitalized with COPD exacerbation with and without pneumonia. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016;11:455–65.
Stanford RH, Nag A, Mapel DW, Lee TA, Rosiello R, Schatz M, Vekeman F, Gauthier-Loiselle M, Merrigan JFP, Duh MS. Claims-based risk model for first severe COPD exacerbation. Am J Manag Care. 2018;24:e45–53.
Stanford RH, Lau MS, Li Y, Stemkowski S. External validation of a COPD risk measure in a commercial and medicare population: the COPD treatment ratio. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2019;25:58–69.
Vestbo J, Papi A, Corradi M, Blazhko V, Montagna I, Francisco C, Cohuet G, Vezzoli S, Scuri M, Singh D. Single inhaler extrafine triple therapy versus long-acting muscarinic antagonist therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (TRINITY): a double-blind, parallel group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:1919–29.
Wei X, Ma Z, Yu N, Ren J, Jin C, Mi J, Shi M, Tian L, Gao Y, Guo Y. Risk factors predict frequent hospitalization in patients with acute exacerbation of COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:121–9.
Whalley D, Svedsater H, Doward L, Crawford R, Leather D, Lay-Flurrie J, Bosanquet N. Follow-up interviews from The Salford Lung Study (COPD) and analyses per treatment and exacerbations. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2019;29:20.
Zeiger RS, Tran TN, Butler RK, Schatz M, Li Q, Khatry DB, Martin U, Kawatkar AA, Chen W. Relationship of blood eosinophil count to exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6:944-954.e945.
Vogelmeier CF, Kostikas K, Fang J, Tian H, Jones B, Morgan CL, Fogel R, Gutzwiller FS, Cao H. Evaluation of exacerbations and blood eosinophils in UK and US COPD populations. Respir Res. 2019;20:178.
Celli BR, Fabbri LM, Aaron SD, Agusti A, Brook R, Criner GJ, Franssen FME, Humbert M, Hurst JR, O’Donnell D, et al. An updated definition and severity classification of COPD exacerbations: the Rome proposal. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204:1251–8.
Adir Y, Hakrush O, Shteinberg M, Schneer S, Agusti A. Circulating eosinophil levels do not predict severe exacerbations in COPD: a retrospective study. ERJ Open Research. 2018;4:00022–2018.
Bartels W, Adamson S, Leung L, Sin DD, van Eeden SF. Emergency department management of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: factors predicting readmission. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1647–54.
Kim V, Zhao H, Regan E, Han MK, Make BJ, Crapo JD, Jones PW, Curtis JL, Silverman EK, Criner GJ, COPDGene Investigators. The St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire definition of chronic bronchitis may be a better predictor of COPD exacerbations compared with the classic definition. Chest. 2019;156:685–95.
Abston E, Comellas A, Reed RM, Kim V, Wise RA, Brower R, Fortis S, Beichel R, Bhatt S, Zabner J, et al. Higher BMI is associated with higher expiratory airflow normalised for lung volume (FEF25-75/FVC) in COPD. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2017;4: e000231.
Emura I, Usuda H, Satou K. Appearance of large scavenger receptor A-positive cells in peripheral blood: a potential risk factor for severe exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pathol Int. 2019;69:187–92.
Erol S, Sen E, Gizem Kilic Y, Yousif A, Akkoca Yildiz O, Acican T, Saryal S. Does the 2017 revision improve the ability of GOLD to predict risk of future moderate and severe exacerbation? Clin Respir J. 2018;12:2354–60.
Han MZ, Hsiue TR, Tsai SH, Huang TH, Liao XM, Chen CZ. Validation of the GOLD 2017 and new 16 subgroups (1A–4D) classifications in predicting exacerbation and mortality in COPD patients. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:3425–33.
Huang TH, Hsiue TR, Lin SH, Liao XM, Su PL, Chen CZ. Comparison of different staging methods for COPD in predicting outcomes. Eur Resp J. 2018;51:1700577.
Jung YH, Lee DY, Kim DW, Park SS, Heo EY, Chung HS, Kim DK. Clinical significance of laryngopharyngeal reflux in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:1343–51.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kim J, Kim WJ, Lee CH, Lee SH, Lee MG, Shin KC, Yoo KH, Lee JH, Lim SY, Na JO, et al. Which bronchodilator reversibility criteria can predict severe acute exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients? Respir Res. 2017;18:107.
Kobayashi S, Hanagama M, Ishida M, Sato H, Ono M, Yamanda S, Yamada M, Aizawa H, Yanai M. Clinical characteristics and outcomes in Japanese patients with COPD according to the 2017 GOLD classification: the Ishinomaki COPD Network Registry. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:3947–55.
Lee SH, Lee JH, Yoon HI, Park HY, Kim TH, Yoo KH, Oh YM, Jung KS, Lee SD, Lee SW. Change in inhaled corticosteroid treatment and COPD exacerbations: an analysis of real-world data from the KOLD/KOCOSS cohorts. Respir Res. 2019;20:62.
Pavlovic R, Stefanovic S, Lazic Z, Jankovic S. Factors associated with the rate of COPD exacerbations that require hospitalization. Turk J Med Sci. 2017;47:134–41.
Song JH, Lee CH, Um SJ, Park YB, Yoo KH, Jung KS, Lee SD, Oh YM, Lee JH, Kim EK, Kim DK. Clinical impacts of the classification by 2017 GOLD guideline comparing previous ones on outcomes of COPD in real-world cohorts. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:3473–84.
Sundh J, Johansson G, Larsson K, Lindén A, Löfdahl CG, Sandström T, Janson C. The phenotype of concurrent chronic bronchitis and frequent exacerbations in patients with severe COPD attending Swedish secondary care units. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:2327–34.
Urwyler P, Hussein NA, Bridevaux PO, Chhajed PN, Geiser T, Grendelmeier P, Zellweger LJ, Kohler M, Maier S, Miedinger D, et al. Predictive factors for exacerbation and reexacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an extension of the Cox model to analyze data from the Swiss COPD cohort. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2019;14:7.
Wallace AE, Kaila S, Bayer V, Shaikh A, Shinde MU, Willey VJ, Napier MB, Singer JR. Health care resource utilization and exacerbation rates in patients with COPD stratified by disease severity in a commercially insured population. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2019;25:205–17.
Halpin DMG, Decramer M, Celli BR, Mueller A, Metzdorf N, Tashkin DP. Effect of a single exacerbation on decline in lung function in COPD. Respir Med. 2017;128:85–91.
Bade BC, DeRycke EC, Ramsey C, Skanderson M, Crothers K, Haskell S, Bean-Mayberry B, Brandt C, Bastian LA, Akgün KM. Sex differences in veterans admitted to the hospital for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16:707–14.
Iyer AS, Bhatt SP, Dransfield M, Kinney G, Holm K, Wamboldt FS, Hanania N, Martinez C, Regan E, Foreman MG, et al. Psychological distress prospectively predicts severe exacerbations in smokers with and without airflow limitation—a longitudinal follow-up study of the COPDGene cohort [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2017.195.1_MeetingAbstracts.A4709 .
Diamond M, Zhao H, Armstrong HF, Morrison M, Bailey KL, Carretta EE, Criner GJ, Han MK, Bleeker E, Cooper CB, et al. Anxiety and depression, either alone or in combination, are associated with respiratory exacerbations in smokers with and without COPD [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:1615–31.
Google Scholar
Lau CS, Siracuse BL, Chamberlain RS. Readmission After COPD Exacerbation Scale: determining 30-day readmission risk for COPD patients. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:1891–902.
Pikoula M, Quint JK, Nissen F, Hemingway H, Smeeth L, Denaxas S. Identifying clinically important COPD sub-types using data-driven approaches in primary care population based electronic health records. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019;19:86.
Wei YF, Tsai YH, Wang CC, Kuo PH. Impact of overweight and obesity on acute exacerbations of COPD—subgroup analysis of the Taiwan Obstructive Lung Disease cohort. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:2723–9.
Barnes PJ, Celli BR. Systemic manifestations and comorbidities of COPD. Eur Resp J. 2009;33:1165–85.
Polverino E, Dimakou K, Hurst J, Martinez-Garcia MA, Miravitlles M, Paggiaro P, Shteinberg M, Aliberti S, Chalmers JD. The overlap between bronchiectasis and chronic airway diseases: state of the art and future directions. Eur Respir J. 2018;52:1800328.
Xu W, Collet JP, Shapiro S, Lin Y, Yang T, Platt RW, Wang C, Bourbeau J. Independent effect of depression and anxiety on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations and hospitalizations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:913–20.
Chapman KR, Hurst JR, Frent SM, Larbig M, Fogel R, Guerin T, Banerji D, Patalano F, Goyal P, Pfister P, et al. Long-term triple therapy de-escalation to indacaterol/glycopyrronium in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (SUNSET): a randomized, double-blind, triple-dummy clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:329–39.
Couillard S, Larivée P, Courteau J, Vanasse A. Eosinophils in COPD exacerbations are associated with increased readmissions. Chest. 2017;151:366–73.
Ferguson GT, Rabe KF, Martinez FJ, Fabbri LM, Wang C, Ichinose M, Bourne E, Ballal S, Darken P, DeAngelis K, et al. Triple therapy with budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate with co-suspension delivery technology versus dual therapies in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (KRONOS): a double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6:747–58.
Ko FWS, Chan KP, Ngai J, Ng SS, Yip WH, Ip A, Chan TO, Hui DSC. Blood eosinophil count as a predictor of hospital length of stay in COPD exacerbations. Respirology. 2019;25:259–66.
MacDonald MI, Osadnik CR, Bulfin L, Hamza K, Leong P, Wong A, King PT, Bardin PG. Low and high blood eosinophil counts as biomarkers in hospitalized acute exacerbations of COPD. Chest. 2019;156:92–100.
Müllerová H, Hahn B, Simard EP, Mu G, Hatipoğlu U. Exacerbations and health care resource use among patients with COPD in relation to blood eosinophil counts. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:683–92.
Bafadhel M, Greening NJ, Harvey-Dunstan TC, Williams JEA, Morgan MD, Brightling CE, Hussain SF, Pavord ID, Singh SJ, Steiner MC. Blood eosinophils and outcomes in severe hospitalised exacerbations of COPD. Chest. 2016;150:320–8.
Roche N, Chapman KR, Vogelmeier CF, Herth FJF, Thach C, Fogel R, Olsson P, Patalano F, Banerji D, Wedzicha JA. Blood eosinophils and response to maintenance chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treatment. Data from the FLAME trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:1189–97.
Vestbo J, Vogelmeier CF, Small M, Siddall J, Fogel R, Kostikas K. Inhaled corticosteroid use by exacerbations and eosinophils: a real-world COPD population. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:853–61.
Watz H, Tetzlaff K, Wouters EFM, Kirsten A, Magnussen H, Rodriguez-Roisin R, Vogelmeier C, Fabbri LM, Chanez P, Dahl R, et al. Blood eosinophil count and exacerbations in severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease after withdrawal of inhaled corticosteroids: a post-hoc analysis of the WISDOM trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2016;4:390–8.
Pavord ID, Lettis S, Locantore N, Pascoe S, Jones PW, Wedzicha JA, Barnes NC. Blood eosinophils and inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting beta-2 agonist efficacy in COPD. Thorax. 2016;71:118–25.
Singh D. Predicting corticosteroid response in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Blood eosinophils gain momentum. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196:1098–100.
Vestbo J, Prescott E, Almdal T, Dahl M, Nordestgaard BG, Andersen T, Sørensen TIA, Lange P. Body mass, fat-free body mass, and prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease from a random population sample: findings from the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:79–83.
Agustí AGN, Noguera A, Sauleda J, Sala E, Pons J, Busquets X. Systemic effects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2003;21:347–60.
Agustí AGN, Sauleda J, Miralles C, Gomez C, Togores B, Sala E, Batle S, Busquets X. Skeletal muscle apoptosis and weight loss in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:485–9.
Labaki WW, Martinez FJ. Time to understand the infrequency of the frequent exacerbator phenotype in COPD. Chest. 2018;153:1087–8.
Hartley BF, Barnes NC, Lettis S, Compton CH, Papi A, Jones P. Risk factors for exacerbations and pneumonia in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a pooled analysis. Respir Res. 2020;21:5.
Kim Y, Kim YJ, Kang YM, Cho WK. Exploring the impact of number and type of comorbidities on the risk of severe COPD exacerbations in Korean Population: a Nationwide Cohort Study. BMC Pulm Med. 2021;21:151.
Mackay AJ, Kostikas K, Roche N, Frent SM, Olsson P, Pfister P, Gupta P, Patalano F, Banerji D, Wedzicha JA. Impact of baseline symptoms and health status on COPD exacerbations in the FLAME study. Respir Res. 2020;21:93.
Smulders L, van der Aalst A, Neuhaus EDET, Polman S, Franssen FME, van Vliet M, de Kruif MD. Decreased risk of COPD exacerbations in obese patients. COPD. 2020;17:485–91.
Battisti WP, Wager E, Baltzer L, Bridges D, Cairns A, Carswell CI, Citrome L, Gurr JA, Mooney LA, Moore BJ, et al. Good publication practice for communicating company-sponsored medical research: GPP3. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163:461–4.
Putcha N, Barr RG, Han M, Woodruff PG, Bleecker ER, Kanner RE, Martinez FJ, Tashkin DP, Rennard SI, Breysse P, et al. Understanding the impact of passive smoke exposure on outcomes in COPD [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;191:411–20.
Wu Z, Yang D, Ge Z, Yan M, Wu N, Liu Y. Body mass index of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is associated with pulmonary function and exacerbations: a retrospective real world research. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10:5086–99.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Medical writing support, under the direction of the authors, was provided by Julia King, PhD, and Sarah Piggott, MChem, CMC Connect, McCann Health Medical Communications, funded by AstraZeneca in accordance with Good Publication Practice (GPP3) guidelines [ 109 ].
This study was supported by AstraZeneca.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
UCL Respiratory, University College London, London, WC1E 6BT, UK
John R. Hurst
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
MeiLan K. Han
Formerly of Parexel International, Mohali, India
Barinder Singh, Gagandeep Kaur & Mohd Kashif Siddiqui
Parexel International, Mohali, India
Sakshi Sharma
Formerly of AstraZeneca, Cambridge, UK
Enrico de Nigris
AstraZeneca, Gothenburg, Sweden
Ulf Holmgren
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors have made the following declaration about their contributions. JRH and MKH made substantial contributions to the interpretation of data; BS, SS, GK, and MKS made substantial contributions to the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data; EdN and UH made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work and the interpretation of data. All authors contributed to drafting or critically revising the article, have approved the submitted version, and agree to be personally accountable for their own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to John R. Hurst .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
JRH reports consulting fees from AstraZeneca; speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Chiesi, Pfizer, and Takeda; and travel support from GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca. MKH reports assistance with conduction of this research and publication from AstraZeneca; personal fees from Aerogen, Altesa Biopharma, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Cipla, DevPro, GlaxoSmithKline, Integrity, Medscape, Merck, Mylan, NACE, Novartis, Polarean, Pulmonx, Regeneron, Sanofi, Teva, Verona, United Therapeutics, and UpToDate; either in kind research support or funds paid to the institution from the American Lung Association, AstraZeneca, Biodesix, Boehringer Ingelheim, the COPD Foundation, Gala Therapeutics, the NIH, Novartis, Nuvaira, Sanofi, and Sunovion; participation in Data Safety Monitoring Boards for Novartis and Medtronic with funds paid to the institution; and stock options from Altesa Biopharma and Meissa Vaccines. BS, GK, and MKS are former employees of Parexel International. SS is an employee of Parexel International, which was funded by AstraZeneca to conduct this analysis. EdN is a former employee of AstraZeneca and previously held stock and/or stock options in the company. UH is an employee of AstraZeneca and holds stock and/or stock options in the company.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file1: table s1..
Search strategies. Table S2. List of included studies with linked publications. Table S3. Study characteristics across the 76 included studies. Table S4. Clinical characteristics of the patients assessed across the included studies.
Additional file 2: Fig. S1.
Sex (male vs female) as a risk factor for moderate-to-severe exacerbations. Fig. S2. Sex (male vs female) as a risk factor for severe exacerbations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hurst, J.R., Han, M.K., Singh, B. et al. Prognostic risk factors for moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic literature review. Respir Res 23 , 213 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-022-02123-5
Download citation
Received : 02 March 2022
Accepted : 20 July 2022
Published : 23 August 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-022-02123-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Exacerbations
- Comorbidities
- Hospitalization
Respiratory Research
ISSN: 1465-993X
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Case report
- Open access
- Published: 31 March 2024
Atypical lipoma of the right piriformis muscle: a case report and review of the literature
- Xiao Qiu 1 ,
- Xiaoyong Luo 1 &
- Renmei Wu 1
Journal of Medical Case Reports volume 18 , Article number: 189 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
149 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Piriformis muscle mass is rare, which is particular for intrapiriformis lipoma. Thus far, only 11 cases of piriformis muscle mass have been reported in the English literature. Herein, we encountered one patient with intrapiriformis lipoma who was initially misdiagnosed.
Case presentation
The patient is a 50-year-old Chinese man. He complained of osphyalgia, right buttock pain, and radiating pain from the right buttock to the back of the right leg. Both ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated a cyst-like mass in the right piriformis muscle. Ultrasonography-guided aspiration was performed on this patient first, but failed. He was then recommended to undergo mass resection and neurolysis of sciatic nerve. Surprisingly, final histology revealed the diagnosis of intrapiriformis lipoma. The patient exhibited significant relief of symptoms 3 days post-surgery.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of radicular pain are potentially challenging but necessary. Atypical lipoma is prone to be misdiagnosed, especially in rare sites. It is notable for clinicians to be aware of the presence of intrapiriformis lipoma to avoid misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment.
Peer Review reports
Piriformis syndrome (PS), also known as sciatic nerve outlet syndrome, caused by compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle, is characterized by occasional sciatic-type pain, tingling, and numbness in the buttock along the sciatic nerve pathway down to the lower thigh and the calf [ 1 ]. The causes of PS are diversified, including inflammatory, traumatic, tumoral, and malformative factors [ 2 , 3 ]. PS triggered by space-occupying lesions of the piriformis muscle is very rare. Up to date, only 11 cases of piriformis muscle mass have been reported in the English literature [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ].
Lipomas are one of the most common mesenchymal neoplasms and can occur in any region of the body that contains fat component, including the subcutaneous soft tissues, mediastinum, retroperitoneum, bones, or along the gastrointestinal tract [ 11 ]. Intrapiriformis lipoma is rare and the diagnosis might be intractable when presenting atypical. In addition, misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment, which causes unsatisfactory outcomes. Here, we present a case of a large intrapiriformis lipoma that was initially misdiagnosed, highlighting that clinicians should be aware that intrapiriformis lipoma might harbor atypical manifestations upon examination.
A 50-year-old Chinese man presented to the orthopedics department with chief complaints of osphyalgia, right buttock pain, and radiating pain from the right buttock to the back of the right leg. The right buttock pain was the most prominent symptom. The pain was accelerated by movement and relieved by lying supine, which induced abnormal walk in the patient. No previous relevant treatment or surgery was reported. Additionally, there was no significant relevant family or social history.
Lasegue’s sign and its strengthening test were positive. Physical examination also demonstrated the positive findings of right femoral nerve traction test and Faber test, and the limitation of right hip abduction was observed. Neurological examination of the lower limb did not demonstrate any loss of sensation or reduced muscle power in any of the nerve root distributions. Non-remarkable finding was revealed after the abdominal examination.
As no apparent abnormalities were indicated upon the plain radiograph imaging of his lumbar spine, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the lumbar/sacral area of the spine was then suggested, showing lumbar disc herniation (LDH), which did not account for the patient’s predominant right buttock pain. Thus, the musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSK-US) for the sciatic nerve scanning was performed, implying that the right sciatic nerve was pushed by an anechoic mass within the right piriformis muscle measuring 6 cm mediolateral, 2.3 cm anteroposterior, and 2.6 cm craniocaudal. The lobulated mass was cystic-like with regular margins and no posterior wall enhancement (Fig. 1 ). Subsequently, further MRI of the pelvis and ipsilateral hip indicated a cystic-like lesion in piriformis muscle region with low T1 signal and high T2 signal, and the maximum measurement was about 3.1 cm mediolateral and 2.2 cm anteroposterior (Fig. 2 ). Considering these results, a piriformis ganglion was suspected, and the differential diagnoses included hematoma, metastatic tumor, and so forth.
Sonographic examination showing a separate anechoic mass (white arrows) above the outlet of the right piriformis muscle pushing the right sciatic nerve (blue arrows). A Sagittal view(low- frequency probe); B Transverse view (high-frequency probe)
MRI demonstrating multiple cysts (arrows) in piriformis muscle region with long T1 ( A ) and long T2 ( B ) signals
Aiming to achieve the final diagnosis, the ultrasonography-guided aspiration was conducted, but failed due to unextracted cystic fluid. In addition, significant resistance was encountered when injecting with physiological saline. As for the undefined nature of the mass and the associated serious symptoms, malignancy could not be excluded; the patient was suggested to undergo piriformis muscle mass resection and neurolysis of sciatic nerve. Operative finding showed the compression of right sciatic nerve by a fat-like mass at the lower margin of piriformis muscle measuring 5 cm mediolateral, 2 cm anteroposterior, and 2 cm craniocaudal. Final histology revealed that the lesion was fibrous adipose tissue, which was consistent with diagnosis of lipoma (Fig. 3 ). The patient exhibited significant relief of symptoms 3 days post-surgery. No recurrence of relevant symptoms was observed during 24-month follow-up period.
Under microscope inspection, removed specimen revealed fibrous adipose tissue within the lesion, consistent with lipoma
Lower back pain can present with radicular pain caused by lumbosacral nerve root pathology. As a major cause of lower back pain, sciatica, and radicular leg pain, LDH is usually the first considered diagnosis. Similarly, in our case LDH was initially considered according to the MRI of the lumbar/sacral spine. However, the primary pain in the right buttock of this patient was unexplained on the diagnosis of LDH.
PS, also known as sciatic nerve outlet syndrome, is a type of sciatic neuralgia caused by compression of the piriformis muscle on the sciatic nerve. Typical manifestations include buttock pain and radiating pain in the innervated area of the sciatic nerve. In general, etiologies are composed of traumatic bleeding, adhesions, scars, anatomical variations, and so forth [ 2 ]. Of note, intrapiriformis lesion enlarging the muscle may be the common cause of sciatic nerve compression-induced secondary PS, whereas PS triggered by space-occupying lesions of the piriformis muscle is very rare. To the best of our knowledge, only 11 cases have been reported in the literature thus far; these patients and our present case are summarized in Table 1 [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ], among which only 1 case of intramuscular lipomas occurring within the piriformis muscle leading to secondary PS have been previously reported in the literature [ 6 ].
Lipomas can be classified into superficial and deep lesions according to the location. Deep-seated lipomas are less common than superficial lipomas, which may be located under the muscle (submuscular), within the muscle (intramuscular), between the muscles (intermuscular), or on top of the muscle (supramuscular) [ 11 ]. Clinically, lipomas often present as asymptomatic slow-growing mass or swelling with no palpable mass. The application of ultrasound (US) in the examination of lipomas is very frequent. Usually, superficial lipomas might manifest as a hyperechoic solid mass without posterior acoustic enhancement or show as a isoechoic mass on gray-scale US. Compared with superficial lipomas, the deep-seated type can present as various US characteristics. In addition, few reports in the literature show the hypoechoic, isoechoic, or anechoic properties of deep ones [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. However, the intrapiriformis lipoma in our case was featured as an anechoic lesion, usually indicated as cystic lesions. The MRI of the pelvis and ipsilateral hip showed the same signal characteristics as those of water on all sequences. Therefore, the lesion within piriformis muscle region was then misdiagnosed as ganglion and distinguished from neuschwannoma, liposarcoma, hematoma, lymphoma, metastatic tumor, and so on. Therefore, ultrasonography-guided aspiration was performed while noncystic fluid was extracted.
The echogenicity of lipomas may range from hyperechoic to anechoic, depending on the component percentage of connective tissue and other reflective interfaces presented within a lipoma [ 15 ]. It has been postulated that US and MRI appearance of lipomas are largely dependent on the internal cellularity, specifically on the proportion of fat and water within the lesion [ 16 ]. When the proportion of water in the lipoma is high, it may present the same imaging characteristics as this case.
Generally, intrapiriformis lipoma does not require treatment in the absence of symptoms, while for our case, considering the serious symptoms of this patient and undefined nature, even including malignancy, after series of examinations, surgical treatment was recommended. Fortunately, the patient showed significant relief of symptoms 3 days after surgery. No recurrence of associated symptoms was observed during 24-month follow-up period.
Despite the potentially significant challenges for the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of radicular pain, it is highly necessary and essential. It is notable that medical practitioners should be aware of this condition and exclude space-occupying lesions of piriformis muscles when encountering patients presenting with radicular pain. Our case highlighted the atypical manifestations of lipomas in rare areas such as piriformis muscles, for which condition-adequate examinations should be performed and surgery might be finally suggested to reach the final diagnosis, thus avoiding misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment and increasing the life quality of these patients.
Availability of data and materials
The authors of this manuscript are willing to provide additional information regarding the case report.
Abbreviations
Musculoskeletal ultrasound
Magnetic resonance imaging
Piriformis syndrome
Lumbar disc herniation
Hopayian K, Song F, Riera R, Sambandan S. The clinical features of the piriformis syndrome: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2010;19:2095–109.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kirschner JS, Foye PM, Cole JL. Piriformis syndrome, diagnosis and treatment. Muscle Nerve. 2009;40(1):10–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Byrd JWT. Piriformis syndrome. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2005;13(1):71–9.
Article Google Scholar
Salar O, Flockton H, Singh R, Reynolds J. Piriformis muscle metastasis from a rectal polyp. Case Rep. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2012-007208 .
Domínguez-Páez M, De Miguel-Pueyo LS, Medina-Imbroda JM, González-García L, Moreno-Ramírez V, Martín-Gallego A, et al . Sciatica secondary to extrapelvic endometriosis affecting the piriformis muscle. Case report. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2012;23(4):170–4.
Drampalos E, Sadiq M, Thompson T, Lomax A, Paul A. Intrapiriformis lipoma: an unusual cause of piriformis syndrome. Eur Spine J. 2015;24:551–4.
Park JH, Jeong HJ, Shin HK, Park SJ, Lee JH, Kim E. Piriformis ganglion: an uncommon cause of sciatica. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016;102(2):257–60.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Lodin J, Brušáková Š, Kachlík D, Sameš M, Humhej I. Acute piriformis syndrome mimicking cauda equina syndrome: illustrative case. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2021;2(17): CASE21252.
Sanuki N, Kodama S, Seta H, Sakai M, Watanabe H. Radiation therapy for malignant lumbosacral plexopathy: a case series. Cureus. 2022;14(1): e20939.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ward TRW, Garala K, Dos Remedios I, Lim J. Piriformis syndrome as a result of intramuscular haematoma mimicking cauda equina effectively treated with piriformis tendon release. BMJ Case Reports CP. 2022;15(3): e247988.
Paunipagar BK, Griffith J, Rasalkar DD, Chow LTC, Kumta SM, Ahuja A. Ultrasound features of deep-seated lipomas. Insights Imaging. 2010;1(3):149–53.
Goldberg BB. Ultrasonic evaluation of superficial masses. J Clin Ultrasound. 1975;3(2):91–4.
Rahmani G, McCarthy P, Bergin D. The diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography for soft tissue lipomas: a systematic review. Acta radiologica open. 2017;6(6):2058460117716704.
Fujioka K. A comparison between superficial and deep-seated lipomas on high-resolution ultrasonography: with RTE and MRI appearances. Biomed J Sci Tech Res. 2019;19:14220–4.
Google Scholar
Behan M, Kazam E. The echographic characteristics of fatty tissues and tumors. Radiology. 1978;129(1):143–51.
Inampudi P, Jacobson JA, Fessell DP, Carlos RC, Patel SV, Delaney-Sathy LO, et al . Soft-tissue lipomas: accuracy of sonography in diagnosis with pathologic correlation. Radiology. 2004;233(3):763–7.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The author(s) gratefully acknowledge the useful suggestions given by Dr Ji-Bin Liu of Thomas Jefferson University, and the author(s) thank Xiaobo Luo for providing language assistance during article writing.
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Ultrasound, Suining Central Hospital, 127 Desheng West Road, Suining, Sichuan, China
Xiao Qiu, Xiaoyong Luo & Renmei Wu
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Renmei Wu contributed to the collection of the medical history data. Xiao Qiu contributed to the manuscript preparation of this case report. Xiaoyong Luo supervised the case report.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Renmei Wu .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study protocol was approved by the ethics review board of Suining Central Hospital (no. LLSLH20220011).
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Qiu, X., Luo, X. & Wu, R. Atypical lipoma of the right piriformis muscle: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Reports 18 , 189 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04507-1
Download citation
Received : 04 April 2022
Accepted : 13 March 2024
Published : 31 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04507-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Piriformis muscle
Journal of Medical Case Reports
ISSN: 1752-1947
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.112(1); Jan-Feb 2015

Systematically Reviewing the Literature: Building the Evidence for Health Care Quality
There are important research and non-research reasons to systematically review the literature. This article describes a step-by-step process to systematically review the literature along with links to key resources. An example of a graduate program using systematic literature reviews to link research and quality improvement practices is also provided.
Introduction
Systematic reviews that summarize the available information on a topic are an important part of evidence-based health care. There are both research and non-research reasons for undertaking a literature review. It is important to systematically review the literature when one would like to justify the need for a study, to update personal knowledge and practice, to evaluate current practices, to develop and update guidelines for practice, and to develop work related policies. 1 A systematic review draws upon the best health services research principles and methods to address: What is the state of the evidence on the selected topic? The systematic process enables others to reproduce the methods and to make a rational determination of whether to accept the results of the review. An abundance of articles on systematic reviews exist focusing on different aspects of systematic reviews. 2 – 9 The purpose of this article is to describe a step by step process of systematically reviewing the health care literature and provide links to key resources.
Systematic Review Process: Six Key Steps
Six key steps to systematically review the literature are outlined in Table 1 and discussed here.
Systematic Review Steps
1. Formulate the Question and Refine the Topic
When preparing a topic to conduct a systematic review, it is important to ask at the outset, “What exactly am I looking for?” Hopefully it seems like an obvious step, but explicitly writing a one or two sentence statement of the topic before you begin to search is often overlooked. It is important for several reasons; in particular because, although we usually think we know what we are searching for, in truth our mental image of a topic is often quite fuzzy. The act of writing something concise and intelligible to a reader, even if you are the only one who will read it, clarifies your thoughts and can inspire you to ask key questions. In addition, in subsequent steps of the review process, when you begin to develop a strategy for searching the literature, your topic statement is the ready raw material from which you can extract the key concepts and terminology for your strategies. The medical and related health literature is massive, so the more precise and specific your understanding of your information need, the better your results will be when you search.
2. Search, Retrieve, and Select Relevant Articles
The retrieval tools chosen to search the literature should be determined by the purpose of the search. Questions to ask include: For what and by whom will the information be used? A topical expert or a novice? Am I looking for a simple fact? A comprehensive overview on the topic? Exploration of a new topic? A systematic review? For the purpose of a systematic review of journal research in the area of health care, PubMed or Medline is the most appropriate retrieval tool to start with, however other databases may be useful ( Table 2 ). In particular, Google Scholar allows one to search the same set of articles as PubMed/MEDLINE, in addition to some from other disciplines, but it lacks a number of key advanced search features that a skilled searcher can exploit in PubMed/MEDLINE.
Examples of Electronic Bibliographic Databases Specific to Health Care
Note: These databases may be available through university or hospital library systems.
An effective way to search the literature is to break the topic into different “building blocks.” The building blocks approach is the most systematic and works the best in periodical databases such as PubMed/MEDLINE. The “blocks” in a “building blocks” strategy consist of the key concepts in the search topic. For example, let’s say we are interested in researching about mobile phone-based interventions for monitoring of patient status or disease management. We could break the topic into the following concepts or blocks: 1. Mobile phones, 2. patient monitoring, and 3. Disease management. Gather synonyms and related terms to represent each concept and match to available subject headings in databases that offer them. Organize the resulting concepts into individual queries. Run the queries and examine your results to find relevant items and suggest query modifications to improve your results. Revise and re-run your strategy based on your observations. Repeat this process until you are satisfied or further modifications produce no improvements. For example in Medline, these terms would be used in this search and combined as follows: cellular phone AND (ambulatory monitoring OR disease management), where each of the key word phrases is an official subject heading in the MEDLINE vocabulary. Keep detailed notes on the literature search, as it will need to be reported in the methods section of the systematic review paper. Careful noting of search strategies also allows you to revisit a topic in the future and confidently replicate the same results, with the addition of those subsequently published on your topic.
3. Assess Quality
There is no consensus on the best way to assess study quality. Many quality assessment tools include issues such as: appropriateness of study design to the research objective, risk of bias, generalizability, statistical issues, quality of the intervention, and quality of reporting. Reporting guidelines for most literature types are available at the EQUATOR Network website ( http://www.equator-network.org/ ). These guidelines are a useful starting point; however they should not be used for assessing study quality.
4. Extract Data and Information
Extract information from each eligible article into a standardized format to permit the findings to be summarized. This will involve building one or more tables. When making tables each row should represent an article and each column a variable. Not all of the information that is extracted into the tables will end up in the paper. All of the information that is extracted from the eligible articles will help you obtain an overview of the topic, however you will want to reserve the use of tables in the literature review paper for the more complex information. All tables should be introduced and discussed in the narrative of the literature review. An example of an evidence summary table is presented in Table 3 .
Example of an evidence summary table
Notes: BP = blood pressure, HbA1c = Hemoglobin A1c, Hypo = hypoglycemic, I = Internet, NS = not significant, PDA = personal digital assistant, QOL = quality of life, SMBG = self-monitored blood glucose, SMS = short message service, V = voice
5. Analyze and Synthesize Data and information
The findings from individual studies are analyzed and synthesized so that the overall effectiveness of the intervention can be determined. It should also be observed at this time if the effect of an intervention is comparable in different studies, participants, and settings.
6. Write the Systematic Review
The PRISMA 12 and ENTREQ 13 checklists can be useful resources when writing a systematic review. These uniform reporting tools focus on how to write coherent and comprehensive reviews that facilitate readers and reviewers in evaluating the relative strengths and weaknesses. A systematic literature review has the same structure as an original research article:
TITLE : The systematic review title should indicate the content. The title should reflect the research question, however it should be a statement and not a question. The research question and the title should have similar key words.
STRUCTURED ABSTRACT: The structured abstract recaps the background, methods, results and conclusion in usually 250 words or less.
INTRODUCTION: The introduction summarizes the topic or problem and specifies the practical significance for the systematic review. The first paragraph or two of the paper should capture the attention of the reader. It might be dramatic, statistical, or descriptive, but above all, it should be interesting and very relevant to the research question. The topic or problem is linked with earlier research through previous attempts to solve the problem. Gaps in the literature regarding research and practice should also be noted. The final sentence of the introduction should clearly state the purpose of the systematic review.
METHODS: The methods provide a specification of the study protocol with enough information so that others can reproduce the results. It is important to include information on the:
- Eligibility criteria for studies: Who are the patients or subjects? What are the study characteristics, interventions, and outcomes? Were there language restrictions?
- Literature search: What databases were searched? Which key search terms were used? Which years were searched?
- Study selection: What was the study selection method? Was the title screened first, followed by the abstract, and finally the full text of the article?
- Data extraction: What data and information will be extracted from the articles?
- Data analysis: What are the statistical methods for handling any quantitative data?
RESULTS: The results should also be well-organized. One way to approach the results is to include information on the:
- Search results: What are the numbers of articles identified, excluded, and ultimately eligible?
- Study characteristics: What are the type and number of subjects? What are the methodological features of the studies?
- Study quality score: What is the overall quality of included studies? Does the quality of the included studies affect the outcome of the results?
- Results of the study: What are the overall results and outcomes? Could the literature be divided into themes or categories?
DISCUSSION: The discussion begins with a nonnumeric summary of the results. Next, gaps in the literature as well as limitations of the included articles are discussed with respect to the impact that they have on the reliability of the results. The final paragraph provides conclusions as well as implications for future research and current practice. For example, questions for future research on this topic are revealed, as well as whether or not practice should change as a result of the review.
REFERENCES: A complete bibliographical list of all journal articles, reports, books, and other media referred to in the systematic review should be included at the end of the paper. Referencing software can facilitate the compilation of citations and is useful in terms of ensuring the reference list is accurate and complete.
The following resources may be helpful when writing a systematic review:
CEBM: Centre for Evidence-based Medicine. Dedicated to the practice, teaching and dissemination of high quality evidence based medicine to improve health care Available at: http://www.cebm.net/ .
CITING MEDICINE: The National Library of Medicine Style Guide for Authors, Editors, and Publishers. This resource provides guidance in compiling, revising, formatting, and setting reference standards. Available at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7265/ .
EQUATOR NETWORK: Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research. The EQUATOR Network promotes the transparent and accurate reporting of research studies. Available at: http://www.equator-network.org/ .
ICMJE RECOMMENDATIONS: International Committee of Medical Journal Editors Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals. The ICJME recommendations are followed by a large number of journals. Available at: http://www.icmje.org/about-icmje/faqs/icmje-recommendations/ .
PRISMA STATEMENT: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Authors can utilize the PRISMA Statement checklist to improve the reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Available at: http://prisma-statement.org .
THE COCHRANE COLLABORATION: A reliable source for making evidence generated through research useful for informing decisions about health. Available at: http://www.cochrane.org/ .
Examples of Systematic Reviews To Link Research and Quality Improvement
Over the past 17 years more than 300 learners, including physicians, nurses, and health administrators have completed a course as part of a Master of Health Administration or a Master of Science in Health Informatics degree at the University of Missouri. An objective of the course is to educate health informatics and health administration professionals about how to utilize a systematic, scientific, and evidence-based approach to literature searching, appraisal, and synthesis. Learners in the course conduct a systematic review of the literature on a health care topic of their choosing that could suggest quality improvement in their organization. Students select topics that make sense in terms of their core educational competencies and are related to their work. The categories of topics include public health, leadership, information management, health information technology, electronic medical records, telehealth, patient/clinician safety, treatment/screening evaluation cost/finance, human resources, planning and marketing, supply chain, education/training, policies and regulations, access, and satisfaction. Some learners have published their systematic literature reviews 14 – 15 . Qualitative comments from the students indicate that the course is well received and the skills learned in the course are applicable to a variety of health care settings.
Undertaking a literature review includes identification of a topic of interest, searching and retrieving the appropriate literature, assessing quality, extracting data and information, analyzing and synthesizing the findings, and writing a report. A structured step-by-step approach facilitates the development of a complete and informed literature review.
Suzanne Austin Boren, PhD, MHA, (above) is Associate Professor and Director of Academic Programs, and David Moxley, MLIS, is Clinical Instructor and Associate Director of Executive Programs. Both are in the Department of Health Management and Informatics at the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
Contact: ude.iruossim.htlaeh@snerob

None reported.

Detection Of Cannabis In Bodily Fluids Not Correlated With Driving Impairment, New Review Shows
This article was originally published by the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws (NORML) and appears here with permission.
Neither the detection of THC nor its metabolites in blood, breath, urine, or saliva is predictive of behavioral impairment, according to a literature review published in the Journal of AOAC (the Association of Official Analytical Chemists) International.
Researchers affiliated with the University of California at Davis affirmed that there is “no direct relationship between impairment and THC concentrations” in subjects’ bodily fluids – a finding that is consistent with the opinions of numerous traffic safety groups, including the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration and the American Automobile Association.
Trending: Donald Trump Reportedly Hid Billionaire's Bond Offer From Court To Save Millions
Must Read: Donald Trump Says It Would Be A 'Great Honor' If He Were Jailed For Breaching Gag Order: 'I Will Gladly Become A Modern Day Nelson Mandela'
The investigators further acknowledged, “Current methods that focus on THC and/or metabolite concentrations in blood, saliva, urine, or exhaled breath can lead to false-positive results for recent use due to the persistence of THC well outside of the typical 3-4-hour window of potential impairment following cannabis inhalation.”
Consequently, the study’s authors determined that per se traffic safety laws adopted in several states that criminalize drivers who test positive for trace levels of THC in their blood are “not supported by science,” and that they risk “wrongly accusing” motorists who are neither impaired nor have recently consumed cannabis.
Five states – Illinois, Montana, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Washington –impose various per se limits for the detection of trace amounts of THC in blood while ten states (Arizona, Delaware, Georgia, Indiana, Iowa, Michigan, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, Utah, and Wisconsin) impose zero tolerant per se standards. In these states, it is a traffic safety violation to operate a vehicle with detectable levels of THC in blood – even absent any demonstrable evidence of psychomotor impairment.
NORML has long opposed the imposition of per se THC limits for motorists and has alternatively called for the expanded use of mobile performance technology like DRUID.
In a peer-review paper published by the Humboldt Journal of Social Relations, NORML’s deputy director Paul Armentano wrote: “The sole presence of THC and/or its metabolites in blood, particularly at low levels, is an inconsistent and largely inappropriate indicator of psychomotor impairment in cannabis consuming subjects. … Lawmakers would be advised to consider alternative legislative approaches to address concerns over DUI cannabis behavior that do not rely solely on the presence of THC or its metabolites in blood or urine as determinants of guilt in a court of law. Otherwise, the imposition of traffic safety laws may inadvertently become a criminal mechanism for law enforcement and prosecutors to punish those who have engaged in legally protected behavior and who have not posed any actionable traffic safety threat.”
The full text of the study , “Complexity of translating analytics to recent cannabis use and impairment,” appeared in the Journal of AOAC International.
Photo: Courtesy of Smarteless via Shutterstock
© 2024 Benzinga.com. Benzinga does not provide investment advice. All rights reserved.
Retirement can be a difficult part of life to navigate, and a financial advisor can help. Finding a qualified financial advisor doesn't have to be hard. SmartAsset's free tool matches you with up to three financial advisors who serve your area, and you can interview your advisor matches at no cost to decide which one is right for you. If you're ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
This article Detection Of Cannabis In Bodily Fluids Not Correlated With Driving Impairment, New Review Shows originally appeared on Benzinga.com .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say "literature review" or refer to "the literature," we are talking about the research (scholarship) in a given field. You will often see the terms "the research," "the ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply: be thorough, use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and. look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
A literature review is a surveys scholarly articles, books and other sources relevant to a particular. issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, providing a description, summary, and ...
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. ... SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
The Literature Review Defined. In medical education, no organization has articulated a formal definition of a literature review for a research paper; thus, a literature review can take a number of forms. Depending on the type of article, target journal, and specific topic, these forms will vary in methodology, rigor, and depth.
A literature review is an overview of the available research for a specific scientific topic. Literature reviews summarize existing research to answer a review question, provide context for new research, or identify important gaps in the existing body of literature.. An incredible amount of academic literature is published each year, by estimates over two million articles.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
A literature review - or a review article - is "a study that analyzes and synthesizes an existing body of literature by identifying, challenging, and advancing the building blocks of a theory through an examination of a body (or several bodies) of prior work (Post et al. 2020, p. 352).Literature reviews as standalone pieces of work may allow researchers to enhance their understanding of ...
Therefore, this paper discusses the purposes of LRs in dissertations and theses. Second, the paper considers five steps for developing a review: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, writing the review and reflecting on the writing. Ultimately, this study proposes a twelve-item LR checklist.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results. Writing a review of literature is to provide a ...
All good quality journal articles will include a small Literature Review after the Introduction paragraph. It may not be called a Literature Review but gives you an idea of how one is created in miniature. ... Fenelon, M. and Lyons, R. (2010). Non-verbal communication between nurses and people with an intellectual disability: A review of the ...
Cropanzano, R. (2009). Writing nonempirical articles for Journal of Management: General thoughts and suggestions. Journal of Management, 35(6), 1304-1311. ... Tips on finding a framework to structure a literature review article. More blog posts >> Random blog post >> < Older Cultures & Institutions: country-of-origin effects in MNC ...
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations. EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic.
Systematic literature review. A comprehensive search strategy was designed to identify English-language studies published in peer-reviewed journals providing data on risk factors or predictors of moderate or severe exacerbations in adults aged ≥ 40 years with a diagnosis of COPD (sample size ≥ 100).
Epidermoid cysts with rupture, infection, and formation of double cysts are even rarer. The diagnosis and therapy of a patient with giant epidermoid double cysts located on the left buttock, next to the anus were admitted to our hospital in November 2020. As well as the related literature review are detailed below. 1.1. Patient concerns
Background Piriformis muscle mass is rare, which is particular for intrapiriformis lipoma. Thus far, only 11 cases of piriformis muscle mass have been reported in the English literature. Herein, we encountered one patient with intrapiriformis lipoma who was initially misdiagnosed. Case presentation The patient is a 50-year-old Chinese man. He complained of osphyalgia, right buttock pain, and ...
Systematic reviews that summarize the available information on a topic are an important part of evidence-based health care. There are both research and non-research reasons for undertaking a literature review. It is important to systematically review the literature when one would like to justify the need for a study, to update personal ...
Neither the detection of THC nor its metabolites in blood, breath, urine, or saliva is predictive of behavioral impairment, according to a literature review published in the Journal of AOAC (the ...
Integrative literature reviews summarize past empirical and theoretical literature to help develop a broader understanding of a particular topic. 1 The purpose of an integrative literature review is to assess, critique, and synthesize literature on a variety of topics in a way that enables new theoretical frameworks and perspectives to emerge. . Integrative literature reviews include ...