
151+ Public Health Research Topics [Updated 2024]

The important area of public health research is essential to forming laws, influencing medical procedures, and eventually enhancing community well-being. As we delve into the vast landscape of public health research topics, it’s essential to understand the profound impact they have on society.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide to selecting and understanding the diverse array of public health research topics.
Overview of Public Health Research Topics
Table of Contents
Public health research encompasses a wide range of subjects, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of the field. From epidemiology and health policy to environmental health and infectious diseases, researchers navigate through various dimensions to address complex health challenges.
Each category holds its own significance, contributing to the overall understanding of public health dynamics.
Key Considerations in Selecting Public Health Research Topics
- Current Relevance: Assess the timeliness of potential topics by considering recent health trends, emerging issues, and societal concerns.
- Impact on Public Health: Evaluate the potential impact of the research on improving health outcomes, addressing disparities, or influencing policy and interventions.
- Feasibility and Resources: Gauge the practicality of conducting research on a particular topic, considering available resources, data accessibility, and research infrastructure.
- Ethical Considerations: Scrutinize the ethical implications of the research, ensuring it aligns with ethical standards and guidelines, especially when dealing with vulnerable populations or sensitive topics.
Top 151+ Public Health Research Topics
Epidemiology.
- The Impact of Social Determinants on Disease Outcomes
- Patterns and Trends in Emerging Infectious Diseases
- Investigating Health Disparities among Different Ethnic Groups
- Childhood Obesity and its Long-Term Health Consequences
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Contact Tracing in Disease Control
Health Policy
- Universal Healthcare: Comparative Analysis of Global Models
- The Role of Telemedicine in Improving Healthcare Access
- Evaluating Mental Health Policies and Their Impact on Communities
- Assessing the Impact of Affordable Care Act on Public Health
- Vaccine Policies and Public Perception: A Comprehensive Study
Environmental Health
- Climate Change and Health: Adapting to the Challenges
- Air Quality and Respiratory Health in Urban Environments
- Waterborne Diseases and Strategies for Safe Water Supply
- Occupational Health Hazards: A Comprehensive Workplace Analysis
- The Impact of Green Spaces on Mental Health in Urban Areas
Infectious Diseases
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Strategies for Mitigation
- Vaccination Strategies and Herd Immunity
- Global Health Security: Preparedness for Pandemics
- The Impact of Vector-Borne Diseases on Public Health
- Emerging Trends in Antibiotic-Resistant Infections
Chronic Diseases
- Lifestyle Interventions for Preventing Cardiovascular Diseases
- Genetic Factors in the Development of Cancer: A Comprehensive Study
- Aging and Health: Addressing the Healthcare Needs of the Elderly
- Diabetes Prevention Programs: Efficacy and Implementation
- Mental Health in Chronic Disease Patients: Bridging the Gap
Maternal and Child Health
- Maternal Mortality: Understanding Causes and Prevention
- The Impact of Breastfeeding on Infant Health and Development
- Childhood Immunization: Barriers and Strategies for Improvement
- Teenage Pregnancy and Its Long-Term Health Consequences
- Mental Health Support for Postpartum Women: Current Gaps and Solutions
Health Behavior and Promotion
- Smoking Cessation Programs: Effectiveness and Challenges
- Physical Activity Promotion in Schools: Strategies for Success
- Nutrition Education and Its Impact on Healthy Eating Habits
- Mental Health Awareness Campaigns: Assessing Public Perceptions
- The Role of Social Media in Health Promotion
Global Health
- Assessing the Impact of International Aid on Global Health
- Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) Programs in Developing Countries
- The Role of Non-Governmental Organizations in Global Health
- Communicable Disease Control in Refugee Populations
- Global Access to Essential Medicines: Challenges and Solutions
Community Health
- Community-Based Participatory Research: Best Practices and Challenges
- The Impact of Community Health Workers on Health Outcomes
- Health Literacy and its Relationship to Health Disparities
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Mobile Health (mHealth) Interventions
- Community Resilience in the Face of Public Health Crises
Healthcare Quality and Patient Safety
- Hospital-Acquired Infections: Strategies for Prevention
- Patient Safety Culture in Healthcare Organizations
- Quality Improvement Initiatives in Primary Care Settings
- Healthcare Accreditation: Impact on Patient Outcomes
- Implementing Electronic Health Records: Challenges and Benefits
Mental Health
- Stigma Reduction Programs for Mental Health Disorders
- Integrating Mental Health into Primary Care Settings
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Mental Health: Long-Term Implications
- Mental Health in the Workplace: Strategies for Employee Well-being
- Suicide Prevention Programs: Effectiveness and Outreach
Health Disparities
- Racial Disparities in Healthcare: Addressing Systemic Inequities
- LGBTQ+ Health Disparities and Inclusive Healthcare Practices
- Socioeconomic Status and Access to Healthcare Services
- Geographical Disparities in Health: Rural vs. Urban
- The Impact of Gender on Health Outcomes and Access to Care
Public Health Education
- Evaluation of Public Health Education Programs
- Innovative Approaches to Teaching Public Health Concepts
- Online Health Education Platforms: Opportunities and Challenges
- Interdisciplinary Training in Public Health: Bridging Gaps
- Continuing Education for Public Health Professionals: Current Landscape
Digital Health
- The Role of Wearable Devices in Health Monitoring
- Telehealth Adoption: Barriers and Opportunities
- Health Apps for Chronic Disease Management: User Perspectives
- Blockchain Technology in Healthcare: Privacy and Security Implications
- Artificial Intelligence in Disease Diagnosis and Prediction
Health Economics
- Cost-Effectiveness of Preventive Health Interventions
- The Impact of Healthcare Financing Models on Access to Care
- Pharmaceutical Pricing and Access to Essential Medicines
- Economic Evaluation of Health Promotion Programs
- Health Insurance Coverage and Health Outcomes: A Global Perspective
Innovations in Public Health
- 3D Printing in Healthcare: Applications and Future Prospects
- Gene Editing Technologies and their Ethical Implications
- Smart Cities and Public Health: Integrating Technology for Well-being
- Nanotechnology in Medicine: Potential for Disease Treatment
- The Role of Drones in Public Health: Surveillance and Intervention
Food Safety and Nutrition
- Foodborne Illness Outbreaks: Investigating Causes and Prevention
- Sustainable Food Systems: Implications for Public Health
- Nutritional Interventions for Malnutrition in Developing Countries
- Food Labeling and Consumer Understanding: A Critical Review
- The Impact of Fast Food Consumption on Public Health
Substance Abuse
- Opioid Epidemic: Strategies for Prevention and Treatment
- Harm Reduction Approaches in Substance Abuse Programs
- Alcohol Consumption Patterns and Public Health Outcomes
- Smoking and Mental Health: Exploring the Connection
- Novel Psychoactive Substances: Emerging Threats and Strategies
Occupational Health
- Workplace Stress and Mental Health: Intervention Strategies
- Occupational Hazards in Healthcare Professions: A Comparative Analysis
- Ergonomics in the Workplace: Improving Worker Health and Productivity
- Night Shift Work and Health Consequences: Addressing Challenges
- Occupational Health and Safety Regulations: A Global Overview
Disaster Preparedness and Response
- Pandemic Preparedness and Lessons from COVID-19
- Natural Disasters and Mental Health: Post-Traumatic Stress
- Emergency Response Systems: Improving Timeliness and Efficiency
- Communicating Health Risks During Emergencies: Public Perception
- Collaborative Approaches to Disaster Response in Global Health
Cancer Research
- Precision Medicine in Cancer Treatment: Current Advancements
- Cancer Screening Programs: Efficacy and Challenges
- Environmental Factors and Cancer Risk: Exploring Connections
- Survivorship Care Plans: Enhancing Quality of Life after Cancer
- Integrative Therapies in Cancer Care: Complementary Approaches
Sexual and Reproductive Health
- Access to Contraception in Developing Countries: Challenges and Solutions
- Comprehensive Sex Education Programs: Impact on Teen Pregnancy
- Reproductive Health Rights: Global Perspectives and Challenges
- Infertility Treatment: Ethical Considerations and Societal Impact
- Maternal and Child Health in Conflict Zones: Addressing Challenges
Cardiovascular Health
- Hypertension Prevention Programs: Strategies and Effectiveness
- Cardiovascular Disease in Women: Gender-Specific Risk Factors
- Innovations in Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
- Artificial Heart Technology: Advancements and Ethical Implications
- Impact of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Health: A Global Concern
Social Determinants of Health
- Educational Attainment and Health Outcomes: Exploring Links
- Income Inequality and its Impact on Population Health
- Social Support Networks and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Study
- Neighborhood Environments and Health Disparities
- Employment and Health: The Interplay of Work and Well-being
Genomics and Public Health
- Population Genomics and its Implications for Public Health
- Genetic Counseling and Education: Empowering Individuals and Families
- Ethical Issues in Genetic Research: Privacy and Informed Consent
- Pharmacogenomics: Tailoring Drug Therapies to Individual Genotypes
- Gene-Environment Interactions in Disease Risk: Unraveling Complexities
Public Health Ethics
- Informed Consent in Public Health Research: Current Practices
- Ethical Challenges in Global Health Research: Balancing Priorities
- Confidentiality in Public Health Reporting: Striking the Right Balance
- Research with Vulnerable Populations: Ethical Considerations
- Ethical Implications of Emerging Technologies in Healthcare
Health Communication
- The Role of Media in Shaping Public Health Perceptions
- Health Literacy Interventions: Improving Understanding of Health Information
- Social Media Campaigns for Public Health Promotion: Best Practices
- Tailoring Health Messages for Diverse Audiences: Cultural Competency
- Risk Communication in Public Health Emergencies: Lessons Learned
Nutrigenomics
- Personalized Nutrition Plans based on Genetic Makeup
- Impact of Nutrigenomics on Chronic Disease Prevention
- Ethical Considerations in Nutrigenomics Research
- Public Perceptions of Nutrigenomic Testing: A Qualitative Study
- Integrating Nutrigenomics into Public Health Policies
Public Health and Artificial Intelligence
- Predictive Analytics in Disease Surveillance: Harnessing AI for Early Detection
- Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Health Decision Support Systems
- Machine Learning in Epidemiology: Predicting Disease Outbreaks
- Natural Language Processing in Public Health: Text Mining for Insights
- Bias in AI Algorithms: Implications for Health Equity
Health Disparities in Aging
- Geriatric Health Disparities: Bridging the Gap in Elderly Care
- Ageism in Healthcare: Addressing Stereotypes and Discrimination
- Social Isolation and Health Consequences in Aging Populations
- Access to Palliative Care for Older Adults: A Global Perspective
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Ethnic Disparities in Diagnosis and Treatment
- Loneliness and Mental Health in the Elderly: Interventions and Support
Research Methodologies in Public Health
Public health research employs various methodologies, including quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods approaches. Each method brings its own strengths to the research process, allowing researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the complex issues they investigate.
Community-based participatory research is another valuable approach, emphasizing collaboration with communities to address their specific health concerns.
Challenges and Opportunities in Public Health Research
While public health research is immensely rewarding, it comes with its own set of challenges. Funding constraints, ethical dilemmas, the need for interdisciplinary collaboration, and the integration of technology pose both obstacles and opportunities.
Researchers must navigate these challenges to ensure their work has a meaningful impact on public health.
In conclusion, public health research topics are diverse and dynamic, reflecting the complex nature of the field. As researchers embark on their journeys, they must carefully consider the relevance, impact, and ethical implications of their chosen topics.
The collaborative and interdisciplinary nature of public health research positions it as a powerful tool in addressing the health challenges of our time. By exploring the depths of these topics, researchers contribute to the collective effort to build healthier and more equitable communities.
As we move forward, a continued exploration of relevant public health research topics is essential for shaping the future of healthcare and improving the well-being of populations worldwide.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
ORSD’s Proposal Toolkit
The Office of Research Strategy and Development’s Proposal Toolkit is a new PIN-protected online tool for investigators to find important information meant to support proposal development and funding strategies. Examples of information to be found on the website include sample letters of support and other non-disciplinary grant templates, NIH paylines and research priorities, as well as HSPH-specific policies and processes. Faculty, research scientists, and post-docs can access curated lists of funding opportunities, links to funding search engines, and other resources to help in finding funding and developing proposals.
Resources available in the toolkit include:
- Institutional Info
- Funding Opportunities
- Proposal Development Resources
- NIH Resources
- Proposal Repository
- Research Computing
Need more help?
Learn about which offices to go to for questions relating to proposal support, funding, faculty development, and more in the graphic below.
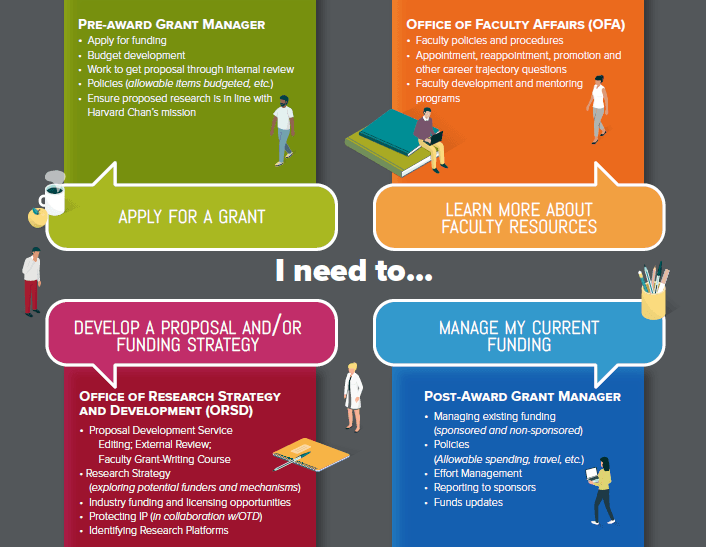
News from the School

Bethany Kotlar, PhD '24, studies how children fare when they're born to incarcerated mothers

Soccer, truffles, and exclamation points: Dean Baccarelli shares his story

Health care transformation in Africa highlighted at conference

COVID, four years in
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.23(2); 2008 Apr

How to prepare a Research Proposal
Health research, medical education and clinical practice form the three pillars of modern day medical practice. As one authority rightly put it: ‘Health research is not a luxury, but an essential need that no nation can afford to ignore’. Health research can and should be pursued by a broad range of people. Even if they do not conduct research themselves, they need to grasp the principles of the scientific method to understand the value and limitations of science and to be able to assess and evaluate results of research before applying them. This review paper aims to highlight the essential concepts to the students and beginning researchers and sensitize and motivate the readers to access the vast literature available on research methodologies.
Most students and beginning researchers do not fully understand what a research proposal means, nor do they understand its importance. 1 A research proposal is a detailed description of a proposed study designed to investigate a given problem. 2
A research proposal is intended to convince others that you have a worthwhile research project and that you have the competence and the work-plan to complete it. Broadly the research proposal must address the following questions regardless of your research area and the methodology you choose: What you plan to accomplish, why do you want to do it and how are you going to do it. 1 The aim of this article is to highlight the essential concepts and not to provide extensive details about this topic.
The elements of a research proposal are highlighted below:
1. Title: It should be concise and descriptive. It must be informative and catchy. An effective title not only prick’s the readers interest, but also predisposes him/her favorably towards the proposal. Often titles are stated in terms of a functional relationship, because such titles clearly indicate the independent and dependent variables. 1 The title may need to be revised after completion of writing of the protocol to reflect more closely the sense of the study. 3
2. Abstract: It is a brief summary of approximately 300 words. It should include the main research question, the rationale for the study, the hypothesis (if any) and the method. Descriptions of the method may include the design, procedures, the sample and any instruments that will be used. 1 It should stand on its own, and not refer the reader to points in the project description. 3
3. Introduction: The introduction provides the readers with the background information. Its purpose is to establish a framework for the research, so that readers can understand how it relates to other research. 4 It should answer the question of why the research needs to be done and what will be its relevance. It puts the proposal in context. 3
The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1
The importance of the statement of the research problem 5 : The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology, work plan and budget etc). It is an integral part of selecting a research topic. It will guide and put into sharper focus the research design being considered for solving the problem. It allows the investigator to describe the problem systematically, to reflect on its importance, its priority in the country and region and to point out why the proposed research on the problem should be undertaken. It also facilitates peer review of the research proposal by the funding agencies.
Then it is necessary to provide the context and set the stage for the research question in such a way as to show its necessity and importance. 1 This step is necessary for the investigators to familiarize themselves with existing knowledge about the research problem and to find out whether or not others have investigated the same or similar problems. This step is accomplished by a thorough and critical review of the literature and by personal communication with experts. 5 It helps further understanding of the problem proposed for research and may lead to refining the statement of the problem, to identify the study variables and conceptualize their relationships, and in formulation and selection of a research hypothesis. 5 It ensures that you are not "re-inventing the wheel" and demonstrates your understanding of the research problem. It gives due credit to those who have laid the groundwork for your proposed research. 1 In a proposal, the literature review is generally brief and to the point. The literature selected should be pertinent and relevant. 6
Against this background, you then present the rationale of the proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing.
4. Objectives: Research objectives are the goals to be achieved by conducting the research. 5 They may be stated as ‘general’ and ‘specific’.
The general objective of the research is what is to be accomplished by the research project, for example, to determine whether or not a new vaccine should be incorporated in a public health program.
The specific objectives relate to the specific research questions the investigator wants to answer through the proposed study and may be presented as primary and secondary objectives, for example, primary: To determine the degree of protection that is attributable to the new vaccine in a study population by comparing the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups. 5 Secondary: To study the cost-effectiveness of this programme.
Young investigators are advised to resist the temptation to put too many objectives or over-ambitious objectives that cannot be adequately achieved by the implementation of the protocol. 3
5. Variables: During the planning stage, it is necessary to identify the key variables of the study and their method of measurement and unit of measurement must be clearly indicated. Four types of variables are important in research 5 :
a. Independent variables: variables that are manipulated or treated in a study in order to see what effect differences in them will have on those variables proposed as being dependent on them. The different synonyms for the term ‘independent variable’ which are used in literature are: cause, input, predisposing factor, risk factor, determinant, antecedent, characteristic and attribute.
b. Dependent variables: variables in which changes are results of the level or amount of the independent variable or variables.
Synonyms: effect, outcome, consequence, result, condition, disease.
c. Confounding or intervening variables: variables that should be studied because they may influence or ‘mix’ the effect of the independent variables. For instance, in a study of the effect of measles (independent variable) on child mortality (dependent variable), the nutritional status of the child may play an intervening (confounding) role.
d. Background variables: variables that are so often of relevance in investigations of groups or populations that they should be considered for possible inclusion in the study. For example sex, age, ethnic origin, education, marital status, social status etc.
The objective of research is usually to determine the effect of changes in one or more independent variables on one or more dependent variables. For example, a study may ask "Will alcohol intake (independent variable) have an effect on development of gastric ulcer (dependent variable)?"
Certain variables may not be easy to identify. The characteristics that define these variables must be clearly identified for the purpose of the study.
6. Questions and/ or hypotheses: If you as a researcher know enough to make prediction concerning what you are studying, then the hypothesis may be formulated. A hypothesis can be defined as a tentative prediction or explanation of the relationship between two or more variables. In other words, the hypothesis translates the problem statement into a precise, unambiguous prediction of expected outcomes. Hypotheses are not meant to be haphazard guesses, but should reflect the depth of knowledge, imagination and experience of the investigator. 5 In the process of formulating the hypotheses, all variables relevant to the study must be identified. For example: "Health education involving active participation by mothers will produce more positive changes in child feeding than health education based on lectures". Here the independent variable is types of health education and the dependent variable is changes in child feeding.
A research question poses a relationship between two or more variables but phrases the relationship as a question; a hypothesis represents a declarative statement of the relations between two or more variables. 7
For exploratory or phenomenological research, you may not have any hypothesis (please do not confuse the hypothesis with the statistical null hypothesis). 1 Questions are relevant to normative or census type research (How many of them are there? Is there a relationship between them?). Deciding whether to use questions or hypotheses depends on factors such as the purpose of the study, the nature of the design and methodology, and the audience of the research (at times even the outlook and preference of the committee members, particularly the Chair). 6
7. Methodology: The method section is very important because it tells your research Committee how you plan to tackle your research problem. The guiding principle for writing the Methods section is that it should contain sufficient information for the reader to determine whether the methodology is sound. Some even argue that a good proposal should contain sufficient details for another qualified researcher to implement the study. 1 Indicate the methodological steps you will take to answer every question or to test every hypothesis illustrated in the Questions/hypotheses section. 6 It is vital that you consult a biostatistician during the planning stage of your study, 8 to resolve the methodological issues before submitting the proposal.
This section should include:
Research design: The selection of the research strategy is the core of research design and is probably the single most important decision the investigator has to make. The choice of the strategy, whether descriptive, analytical, experimental, operational or a combination of these depend on a number of considerations, 5 but this choice must be explained in relation to the study objectives. 3
Research subjects or participants: Depending on the type of your study, the following questions should be answered 3 , 5
- - What are the criteria for inclusion or selection?
- - What are the criteria for exclusion?
- - What is the sampling procedure you will use so as to ensure representativeness and reliability of the sample and to minimize sampling errors? The key reason for being concerned with sampling is the issue of validity-both internal and external of the study results. 9
- - Will there be use of controls in your study? Controls or comparison groups are used in scientific research in order to increase the validity of the conclusions. Control groups are necessary in all analytical epidemiological studies, in experimental studies of drug trials, in research on effects of intervention programmes and disease control measures and in many other investigations. Some descriptive studies (studies of existing data, surveys) may not require control groups.
- - What are the criteria for discontinuation?
Sample size: The proposal should provide information and justification (basis on which the sample size is calculated) about sample size in the methodology section. 3 A larger sample size than needed to test the research hypothesis increases the cost and duration of the study and will be unethical if it exposes human subjects to any potential unnecessary risk without additional benefit. A smaller sample size than needed can also be unethical as it exposes human subjects to risk with no benefit to scientific knowledge. Calculation of sample size has been made easy by computer software programmes, but the principles underlying the estimation should be well understood.
Interventions: If an intervention is introduced, a description must be given of the drugs or devices (proprietary names, manufacturer, chemical composition, dose, frequency of administration) if they are already commercially available. If they are in phases of experimentation or are already commercially available but used for other indications, information must be provided on available pre-clinical investigations in animals and/or results of studies already conducted in humans (in such cases, approval of the drug regulatory agency in the country is needed before the study). 3
Ethical issues 3 : Ethical considerations apply to all types of health research. Before the proposal is submitted to the Ethics Committee for approval, two important documents mentioned below (where appropriate) must be appended to the proposal. In additions, there is another vital issue of Conflict of Interest, wherein the researchers should furnish a statement regarding the same.
The Informed consent form (informed decision-making): A consent form, where appropriate, must be developed and attached to the proposal. It should be written in the prospective subjects’ mother tongue and in simple language which can be easily understood by the subject. The use of medical terminology should be avoided as far as possible. Special care is needed when subjects are illiterate. It should explain why the study is being done and why the subject has been asked to participate. It should describe, in sequence, what will happen in the course of the study, giving enough detail for the subject to gain a clear idea of what to expect. It should clarify whether or not the study procedures offer any benefits to the subject or to others, and explain the nature, likelihood and treatment of anticipated discomfort or adverse effects, including psychological and social risks, if any. Where relevant, a comparison with risks posed by standard drugs or treatment must be included. If the risks are unknown or a comparative risk cannot be given it should be so stated. It should indicate that the subject has the right to withdraw from the study at any time without, in any way, affecting his/her further medical care. It should assure the participant of confidentiality of the findings.
Ethics checklist: The proposal must describe the measures that will be undertaken to ensure that the proposed research is carried out in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki on Ethical Principles for Medical research involving Human Subjects. 10 It must answer the following questions:
- • Is the research design adequate to provide answers to the research question? It is unethical to expose subjects to research that will have no value.
- • Is the method of selection of research subjects justified? The use of vulnerable subjects as research participants needs special justification. Vulnerable subjects include those in prison, minors and persons with mental disability. In international research it is important to mention that the population in which the study is conducted will benefit from any potential outcome of the research and the research is not being conducted solely for the benefit of some other population. Justification is needed for any inducement, financial or otherwise, for the participants to be enrolled in the study.
- • Are the interventions justified, in terms of risk/benefit ratio? Risks are not limited to physical harm. Psychological and social risks must also be considered.
- • For observations made, have measures been taken to ensure confidentiality?
Research setting 5 : The research setting includes all the pertinent facets of the study, such as the population to be studied (sampling frame), the place and time of study.
Study instruments 3 , 5 : Instruments are the tools by which the data are collected. For validated questionnaires/interview schedules, reference to published work should be given and the instrument appended to the proposal. For new a questionnaire which is being designed specifically for your study the details about preparing, precoding and pretesting of questionnaire should be furnished and the document appended to the proposal. Descriptions of other methods of observations like medical examination, laboratory tests and screening procedures is necessary- for established procedures, reference of published work cited but for new or modified procedure, an adequate description is necessary with justification for the same.
Collection of data: A short description of the protocol of data collection. For example, in a study on blood pressure measurement: time of participant arrival, rest for 5p. 10 minutes, which apparatus (standard calibrated) to be used, in which room to take measurement, measurement in sitting or lying down position, how many measurements, measurement in which arm first (whether this is going to be randomized), details of cuff and its placement, who will take the measurement. This minimizes the possibility of confusion, delays and errors.
Data analysis: The description should include the design of the analysis form, plans for processing and coding the data and the choice of the statistical method to be applied to each data. What will be the procedures for accounting for missing, unused or spurious data?
Monitoring, supervision and quality control: Detailed statement about the all logistical issues to satisfy the requirements of Good Clinical Practices (GCP), protocol procedures, responsibilities of each member of the research team, training of study investigators, steps taken to assure quality control (laboratory procedures, equipment calibration etc)
Gantt chart: A Gantt chart is an overview of tasks/proposed activities and a time frame for the same. You put weeks, days or months at one side, and the tasks at the other. You draw fat lines to indicate the period the task will be performed to give a timeline for your research study (take help of tutorial on youtube). 11
Significance of the study: Indicate how your research will refine, revise or extend existing knowledge in the area under investigation. How will it benefit the concerned stakeholders? What could be the larger implications of your research study?
Dissemination of the study results: How do you propose to share the findings of your study with professional peers, practitioners, participants and the funding agency?
Budget: A proposal budget with item wise/activity wise breakdown and justification for the same. Indicate how will the study be financed.
References: The proposal should end with relevant references on the subject. For web based search include the date of access for the cited website, for example: add the sentence "accessed on June 10, 2008".
Appendixes: Include the appropriate appendixes in the proposal. For example: Interview protocols, sample of informed consent forms, cover letters sent to appropriate stakeholders, official letters for permission to conduct research. Regarding original scales or questionnaires, if the instrument is copyrighted then permission in writing to reproduce the instrument from the copyright holder or proof of purchase of the instrument must be submitted.
Research Topics & Ideas: Public Health
50 Topic Ideas To Kickstart Your Research Project

If you’re just starting out exploring public health and/or epidemiology-related topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research by providing a hearty list of research ideas , including examples from recent studies in public health and epidemiology.
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . These topic ideas provided here are intentionally broad and generic , so keep in mind that you will need to develop them further. Nevertheless, they should inspire some ideas for your project.
To develop a suitable research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan to fill that gap. If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .

Public Health-Related Research Topics
- Evaluating the impact of community-based obesity prevention programs in urban areas.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of public smoking bans on respiratory health outcomes.
- Investigating the role of health education in reducing the prevalence of HIV/AIDS in sub-Saharan Africa.
- The impact of air pollution on asthma rates in industrial cities.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of school nutrition programs on childhood obesity rates.
- The role of public health policies in addressing mental health stigma.
- Analyzing the impact of clean water access on infectious disease rates in rural communities.
- The effectiveness of needle exchange programs in reducing the spread of hepatitis C.
- Investigating the impact of social determinants on maternal and child health in low-income neighborhoods.
- The role of digital health interventions in managing chronic diseases.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of workplace wellness programs on employee health and productivity.
- The impact of urban green spaces on community mental health.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns in preventing outbreaks of infectious diseases.
- The role of public health initiatives in reducing alcohol-related harm.
- Analyzing the impact of aging populations on healthcare systems.
- Analyzing the impact of urbanization on mental health disorders in metropolitan areas.
- The effectiveness of telemedicine services in improving healthcare access in remote regions.
- Investigating the health impacts of electronic waste recycling practices.
- The role of health literacy in managing non-communicable diseases in aging populations.
- Evaluating the public health response to opioid addiction in rural communities.
- Analyzing the relationship between housing quality and respiratory illnesses.
- The effectiveness of community engagement in improving reproductive health services.
- Investigating the health effects of long-term exposure to low-level environmental radiation.
- The role of public health campaigns in reducing the prevalence of tobacco use among teenagers.
- Analyzing the impact of food deserts on nutritional outcomes in urban communities.

Epidemiology Research Ideas (Continued)
- Investigating the epidemiology of antibiotic-resistant infections in hospital settings.
- The impact of climate change on the spread of vector-borne diseases.
- Evaluating the factors contributing to the rise in type 2 diabetes prevalence.
- Analyzing the epidemiology of mental health disorders in conflict zones.
- The role of epidemiological surveillance in pandemic preparedness and response.
- Investigating the link between environmental exposures and the incidence of childhood cancers.
- The impact of dietary patterns on the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of intervention strategies in controlling obesity epidemics.
- Analyzing the spread and control of zoonotic diseases in rural communities.
- The role of genetic factors in the epidemiology of autoimmune diseases.
- Investigating the socio-economic disparities in cancer incidence and outcomes.
- The impact of urbanization on the epidemiology of infectious diseases.
- Evaluating the public health consequences of occupational exposures to hazardous substances.
- Analyzing the trends and determinants of mental health disorders among adolescents.
- The role of lifestyle factors in the epidemiology of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Investigating the patterns of mental health service utilization during economic recessions.
- The epidemiology of sports-related concussions in youth athletics.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of public health interventions in reducing the spread of tuberculosis in high-risk populations.
- Analyzing the geographic distribution of Lyme disease in relation to climate change.
- The role of international travel in the spread of emerging infectious diseases.
- Investigating the demographic predictors of chronic kidney disease in population-based studies.
- The epidemiological impact of air pollution on asthma and other respiratory conditions.
- Evaluating the long-term health effects of exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals.
- Analyzing the incidence and risk factors of post-traumatic stress disorder in first responders.
- The role of socioeconomic status in the prevalence and management of diabetes.
Recent Studies: Public Health & Epidemiology
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual studies in the public health and epidemiology space to see how this all comes together in practice.
Below, we’ve included a selection of recent studies to help refine your thinking. These are actual studies, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- Tutorials in population neuroimaging: Using epidemiology in neuroimaging research (Godina et al., 2022)
- Application of Big Data in Digital Epidemiology (Naaz & Siddiqui, 2022)
- Response to comment on: Incidence of ocular and systemic disease affecting visual function among state bus drivers (Kohli et al., 2022)
- Why epidemiology is incomplete without qualitative and mixed methods (Lane-Fall, 2023)
- Teaching epidemiology: An overview of strategies and considerations (Hossain, 2022)
- Social Epidemiology: Past, Present, and Future (Roux, 2022)
- Population health assessment project: An innovative strategy for teaching principles of epidemiology (Keen et al., 2022)
- The functions of veterinary epidemiology in public health (Shaffi, 2023)
- Readying the Applied Epidemiology Workforce for Emerging Areas of
- Public Health Practice (Daly et al., 2022)
- Some Social Epidemiologic Lessons from the COVID-19 Pandemic (Schnake-Mahl & Bilal, 2023)
- The Filth Disease: Typhoid Fever and the Practices of Epidemiology in Victorian England by Jacob Steere-Williams (review) (Steere-Williams et al., 2022)
- Epidemiology of Adult Obesity, Measurements, Global Prevalence and Risk Factors (Orukwowu, 2022).
- Which disciplines form digital public health, and how do they relate to each other? (Pan, 2022)
- Information Flow and Data Gaps in COVID-19 Recording and Reporting at National and Provincial Levels in Indonesia (Barsasella et al., 2022). Epidemiology Blog of Neal D. Goldstein, PhD, MBI (Goldstein, 2023)
- Sensitivity analysis of SEIR epidemic model of Covid 19 spread in Indonesia (Rangkuti et al., 2022)
As you can see, these research topics are a lot more focused than the generic topic ideas we presented earlier. So, for you to develop a high-quality research topic, you’ll need to get specific and laser-focused on a specific context with specific variables of interest. In the video below, we explore some other important things you’ll need to consider when crafting your research topic.
Get 1-On-1 Help
If you’re still unsure about how to find a quality research topic, check out our Research Topic Kickstarter service, which is the perfect starting point for developing a unique, well-justified research topic.

You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Unicaf: MSc Public Health for Sept 2022: Research Project 2: Proposal Design and Dissemination
- Health Promotion
- Principles of Public Health
- Epidemiology
- Research Methods: Evidence-based Practice in Public Health
- Health Protection
- Health Economics
- Public Health Leadership
- Research Project 1: Global Health
- Research Project 2: Proposal Design and Dissemination
- Books and eBooks
- Databases, Journals and Specialist Websites
- Using Images and Videos
- Referencing This link opens in a new window
- Assignment Toolkit
Welcome to your Research Project 2: Proposal Design and Dissemination Reading and Resource List. Here you will find your essential and recommended reading, as well as suggested Journals and Online Resources.
Please be advised that not all of your essential and recommended reading is available through the University of Suffolk.
Essential Reading
Recommended Reading
Online Resources
Health Evidence
National Collaborating Centre for Methods and Tools
National Institute for Health Research
WHO Recommended Format for a Research Protocol
- << Previous: Research Project 1: Global Health
- Next: Subject Guide >>
- Last Updated: Sep 14, 2023 12:04 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uos.ac.uk/msc-public-health
➔ About the Library
➔ Meet the Team
➔ Customer Service Charter
➔ Library Policies & Regulations
➔ Privacy & Data Protection
Essential Links
➔ A-Z of eResources
➔ Frequently Asked Questions
➔Discover the Library
➔Referencing Help
➔ Print & Copy Services
➔ Service Updates
Library & Learning Services, University of Suffolk, Library Building, Long Street, Ipswich, IP4 1QJ
✉ Email Us: [email protected]
✆ Call Us: +44 (0)1473 3 38700
How to prepare a research proposal in the health sciences?
Affiliations.
- 1 Servicio de Aparato Digestivo, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Princesa (IIS-IP), Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBEREHD), Madrid, España. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 2 Servicio de Aparato Digestivo, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Princesa (IIS-IP), Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBEREHD), Madrid, España.
- PMID: 33277051
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2020.07.028
Knowing how to properly prepare a research proposal is a real challenge - and being able to prepare an excellent research proposal is increasingly a requirement to compete for funding with assurances of success. With this in mind, we aim to share with the reader our experience (in many cases, unsuccessful) as applicants on the most important aspects of preparing a research proposal and securing its approval and funding. This article aims not only to list theoretical recommendations but also to share some personal and eminently practical suggestions on the following elements of a research proposal: the title, the abstract, the introduction, the objectives, the methodology, the work plan or schedule, the proposal's consistency and coherence, its viability, its applicability, the importance of the principal investigator and the research team, the proposal's limitations and alternatives, its budget, its references, and, finally, the research proposal's form or wording. In summary, a research proposal is a carefully written plan that includes all the scientific, ethical and logistical aspects of the study to be conducted. Writing a good research proposal requires considerable effort and a great deal of time, but it's worth it.
Keywords: Ciencias de la salud; Health sciences; Protocol; Protocolo; Proyecto de investigación; Research proposal.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
- Guidelines as Topic*
- Research Design / standards*
- Research Support as Topic
- Writing / standards*
We're still accepting applications for fall 2024!
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Accessibility Policy
- Report an Accessibility Issue

Research Proposal
DOCTORAL AND POSTDOCTORAL
Doctoral and postdoctoral applicants must propose a supplemental independent research project to complete simultaneously with the main assigned project. Trainees that have reached candidacy are required to prepare a concept paper for the supplemental project that outlines the project goals and hypothesis, summarizes the literature, and discusses the plan for methodology and data analysis. Trainees will be guided in completing the online application to secure the IRB approval for their project.
The brief 3-5 page research proposal should include the following:
- A brief statement of the problem or issue your project will address, including any citations from previous research on the topic;
- A hypothesis of what you expect to find;
- A brief description of the methods you will use for your research project;
- How you expect the outcome to be useful to the local community; and
- How you expect the project will support your personal and professional growth and development
NOTE: PhD students may use this supplemental project as a pilot for future research related to their PhD program, but not to directly support their dissertation.
While the primary assignment of Masters level trainees will be to the listed projects and topic areas on each training site's page, applicants may propose an additional health disparities project to complete during their training. These projects may fall outside the scope of the listed projects for each training site but must build upon the expertise of the existing site mentor(s). Approval will be at the discretion of each individual site.
Masters level applicants may upload an OPTIONAL research proposal at the time of their application indicating their interest in completing an additional project.
The brief 1-2 page proposal should include the following:
- A brief statement of the problem or issue your proposed project will address and how completion of this project will support your personal and professional growth
- How you expect the outcome to be useful to the local community
- Please include any citations as appropriate
Upon selection, trainees must work with their assigned international mentor to develop and approve the project prior to conducting any supplemental research.
Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Alumni and Donors
- Community Partners and Employers
- About Public Health
- How Do I Apply?
- Departments
- Findings magazine
Student Resources
- Career Development
- Certificates
- Internships
- The Heights Intranet
- Update Contact Info
- Report Website Feedback
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
226 Hot Public Health Thesis Topics For Top Grades

Are you stuck trying to get the best current public health research topics for thesis and writing it? If yes, know you are not alone. A lot of students find the tasks challenging, but we are here to help. Keep reading our informative guide that demonstrates how to prepare an engaging public health paper.
We will also highlight hot 226 health policy topics for paper and other public health ideas for dissertation that you can use for top grades. Why settle for less when we can help you select the best college or university papers?
What Is Public Health?
Before looking at the top public health statistics undergraduate thesis topics or other public health research ideas, let’s start with the definition. So, what is public health?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), public health is “the art and science of preventing diseases, helping to prolong life and promote health using organized efforts. Good examples of public health efforts include preventing outbreaks, educating the public on health choices, promoting fitness, preparing for emergencies, and avoiding the spread of infectious diseases. Public health
How To Write A Great Public Health Dissertation
If you are a graduate or masters student, one of the most comprehensive documents that you need to prepare is the dissertation. It is an expansive paper and comes at the end of your course. Remember that you need to ensure it is prepared well because a team of professors will ultimately evaluate it. So, here are the main steps that you need to follow to prepare a high quality dissertation:
Identify the topic of study Comprehensively research the topic and identify the main points to support it Develop the thesis statement for the dissertation (this thesis will ultimately be tested after gathering your data) Develop an outline for the dissertation. This guide should tell you what to write at what specific instance. Here is a sample outline: Topic of the study Introduction. Start with the thesis statement, followed by the objectives of the study. Then, the rest of the introduction should be used to set the background for the study. Literature review: Review relevant resources about the topic. Methodology: Explain the methodology that was used during the study. Is Results and analysis: Provide the results gathered during the study. Discussion and conclusion: Here, you should discuss the study results and demonstrate whether they approve or disapprove the thesis statement. If you found any gaps in the previous studies, highlight them too and call for further studies. Bibliography: This is a list of all the resources you used to prepare the paper. Write the first draft following the outline we have just listed above. Write the final copy by refining the first draft, proofreading, and editing it.
Awesome Public Health Thesis Topics
Here are the leading thesis topics in public health for top grades. You can use them as they are or tweak a little to suit your preference.
Public Health Thesis Topics In Mental Issues
- What is the role of public health in addressing mental issues in society?
- Seasonal affective disorder: A review of the disorder’s prevalence rates.
- Society should always listen to the needs of mentally ill persons.
- Eating disorders in adults: A review of the treatment strategies used for adults in the UK.
- What is the relation between climate change and emerging public health issues?
- Comparing depression prevalence rates in the UK to those of the US.
- What are the main causes of anxiety disorders in society?
- A review of the connection between HIV/AIDS and mental health issues in society.
- Running a public health facility: What is the most important equipment?
- Emerging public health issues in developing countries.
- Analyzing the psychological problems of breast cancer.
- What strategies should people use to prevent their mental health from social media dangers?
- A review of the public health benefits associated with active lifestyles.
- Stress: Why is it a major risk factor for mental health in many communities?
- What are the most common mental health issues in society today?
- Comparing the rates of depression and stress in China and the UK.
- Addressing anxiety-related disorders: Is cognitive-behavior therapy the best treatment method?
- A review of the economic burden of living with a person suffering from anxiety disorders.
- How does depression impact the quality of life?
- Comparing training of public health officers in the US to India.
Unique Research Topics In Public Health
- Surrogacy: A review of associated ethical issues.
- Prevalence of medical errors in hospitals: A review of the policies used to prevent the problem in the United States.
- Blood transfusion: What are the side effects?
- A review of doctors’ roles in promoting healthy lifestyles.
- Maintaining healthy body weight: Comparing the effectiveness of the recommended methods.
- A review of organ donation trends in Europe and Asia.
- Analyzing the ethical factors around cloning: When should it be allowed?
- The ethics of human experimentation.
- Comparing the rates of heart attacks in women to men in the United States.
- What are the main causes of heart attacks? Can it be prevented?
- Progress in diabetes studies and treatment: Is it possible to get a cure in the future?
- Biological weapons and their impacts on society: A review of the Leukemia rates in Japan.
- Pre-diabetes in children: What are the main symptoms, and how can it be addressed?
Public Health Paper Topics On COVID-19
- How will COVID-19 change life?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of self-isolation?
- Life lessons that you learned during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- What challenges has your community faced during COVID-19 pandemic?
- School life during COVID-19 pandemic.
- A review of mass media operations during pandemic.
- What projects did you undertake during the pandemic?
- A review of projects that your community undertook during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- A closer look at the backlash against Asians in Europe at the start COVID-19 pandemic period.
- Preparing for the next pandemic: What lessons did the world learn from the COVID-19 pandemic?
- The best strategies for staying healthy during a pandemic.
- Is there anything that we could have done to prevent the COVID-19 pandemic?
- Comparing the effectiveness of Europe and American healthcare preparedness for tackling disasters.
- A review of mental health status in a community of your choice during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- A review of COVID-19 emergence theories: Which one do you think is more credible?
- Comparing the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic to Ebola.
- Vaccines development for viral infections: What made the development of the COVID-19 vaccine possible so fast, whereas that of HIV/AIDS has taken so long?
- A review of the vaccine development process.
- Time for review: How effectively do you think your government responded to the COVID-19 pandemic?
- Rethinking public health on a global scale: Demonstrating why effective healthcare is only possible when looked at globally.
Interesting Public Health Research Topic Ideas
- What is the importance of learning public health in school?
- Identify and review a common public health issue in your community.
- The history of human health: Comparing what was considered healthy in ancient times to what is referred to as healthy today.
- Going vegan: How can it impact your health?
- Excessive weight: Is it the new threat to human civilization?
- Is bodybuilding healthy?
- Body positive: Is it a new health standard or ignorance of body issues?
- Things to consider when selecting healthy food to eat.
- Why psychological health should be part of every community in society.
- The health of newborns: What is the difference between their healthcare and that of adults?
- Emerging trends in the healthcare industry: How can the latest trends benefit society?
- Comparing depression and anxiety in two countries of your choice.
- Physical wellness must include healthy behavioral patterns and nutrition.
- A sense of belonging is paramount to personal and community health.
- What is the relationship between spirituality and public health?
- A review of stigmatization of mental health issues in a community of your choice.
- Is it possible to prevent depression?
- At what point should children start learning sex-related education?
- Comparing the two main public health issues in two cities: London and New York.
- What is the relationship between poverty and public health?
Hot Researchable Topics In Public Health
- The resurgence of measles in society: The best guidance for clinicians.
- Tackling the growing national drug problem.
- Bioterrorism preparedness for global disasters.
- A review of recent vitamin D recommendations for older adults.
- Strategies for maintaining maternal mortality at low levels across the globe.
- Efforts by Asian governments to reduce infections from using unsafe water.
- Over-the-counter drug abuse in Europe: Compare two countries of your choice.
- Health care providers’ roles in preventing bullying in society.
- Knowledge management in the UK healthcare organizations.
- The health benefits of good healthcare waste management.
- Characteristics of dental wastes in hospitals.
- Comparing the most prevalent public health issues in developed and developing nations.
- Latest trends in financing public health.
- The relevance of clinical epidemiology in public health.
- Evidence based public health.
- Epidemiological burden of HIV/AIDS in developing countries.
- Addressing cervical cancer in developing countries: Is it possible to eliminate it completely?
- Ethics in public health clinical research.
- Comparing the strategies used in teaching and motivating public health professionals in developing and developed countries.
Research Topics In Public Health For Masters
- Advertising and impacts on food choices in the community.
- The use of stem cell technologies for cancer treatment: What are the latest trends?
- Bio-printing: Is it the future of organ transplants?
- Nutrition education: How does it promote healthy diets?
- Exercising: What role does it play in promoting strength and balance in the elderly?
- Weight loss surgery: What are the key advantages and disadvantages?
- Heart disease is a major public health issue in society.
- Alternative strategies for treating depression in society: Are they effective?
- Healthcare leadership and its importance in public health.
- Legal aspects of public health care in the society.
- Mental disabilities in patients: A review of the emerging trends in the UK.
- How does the United States promote the development of public health?
- Inequalities in medicine: What impact does it have in public health?
- The most controversial issues in public health in the UK.
- What are the most preferred storage systems for medical supplies in the UK public health facilities?
- Reimagining the public health systems on the globe: Where do you see the UK health system in the next 20 years?
Top Thesis Topics In Dental Public Health
- Common oral health issues in Ireland.
- A review of common problems of endodontically treated teeth.
- The role of good leadership skills in dental education.
- Child management techniques between male and female practitioners.
- What role does ergonomics play in dentistry?
- Dental material and bio-engineering: What are the latest trends?
- A review of the relationship between diabetes and oral health in the society.
- The role of electronic health care record systems used in public health.
- Comparing dental health issues in the developing and developed countries.
- A review of public awareness of dental health issues in a community of choice.
- How can you ensure that all the food you buy is safe and healthy?
- What strategies are used by your local health community to promote dental awareness?
- Dental health management in California: What do you think should be done differently?
- Are you satisfied with the strategies used to address dental issues?
Hot Thesis Topics Public Health
- Mandatory overtime work for medical staff: How does it impact their commitment to their job?
- Nursing shortage and its impact in public health.
- Strategies for improving public health in the EU.
- Mental health issues among asylum seekers in the United States.
- Common mental issues among veterans returning from war: A case study of the United States.
- What functions does management play in healthcare settings when handling key public health issues?
- How poor relationships between nurses and doctors can impact public health services delivery.
- Third-party players in public health and their roles.
- Financial reporting standards in public health facilities.
- What is the correlation between revenue collection in society and the quality of patient services?
- Reviewing the coordination of public health officials during disasters.
- The importance of staff training on quality of health services.
- Comparing the differences between alternative medicine and conventional medicine in addressing public health issues in society.
- Obesity: What are the main causes in child-going age?
- A review of health consequences of caffeine.
- Medical marijuana: What are the main pros and cons?
- A review of the US Farm Bill Amendments that legalized use of cannabis in the US.
- Doing sports: Is it always healthy?
- Low-fat or low-carb diet: Which one is better in addressing overweight and diabetes issues?
- Preventing communicable diseases: Evaluating the prevention strategies used in Asia.
- What is the estimated cost of treating heart problems?
Controversial Public Health Dissertation Topics
- Smoking and impacts of current efforts to address cancer in the society.
- A review of the main causes of heart attacks in society today.
- Tobacco ads: Evaluating their impacts and the relationship to the current cancer trends in the society.
- Sleep disorders: Explain why they should be considered a public health issue.
- Staffing shortage and the impacts in fighting COVID-19 pandemic in Asia.
- Analyzing risk management of treating different diseases in the community.
- COVID-19 pandemic in numbers: Comparing the infection rates in the developed and developing countries.
- Reviewing strategies used in the US public health system to achieve equity: How effective are they?
- Analyzing the main challenges in the UK medical care system.
- Rising cases of suicides in the society: What are the main causes?
- A comprehensive review of strategies used to prevent suicides in the 21st century in the US.
- Use of vaccines to prevent diseases: Do adults still need the vaccines?
- Heat-related deaths: What strategies should be adopted?
- Chronic-diseases prevention: Comparing the strategies used in developing and developed countries.
- Are we becoming too dependent on antibiotics in fighting diseases?
- Opioid crisis: Are the doctors to blame for it?
- Use of blockchain in growing accuracy of clinical trials in medicine.
- What dangers are posed by nuclear wastes in society?
- Assessing US industrial facilities compliance rates to cut down emissions.
- Using clean energy as a strategy of improving public health: What are the expectations?
- What is the healthiest country?
- Evaluating the correlation between gaming and deviant behavior among children in society.
- COVID-19 could have been prevented if WHO was more vigilant?
Public Health Research Questions
- Is the high cost of medical healthcare in the United States justified?
- What is the correlation between poverty and poor health in society?
- Should health care for homeless people be free?
- Unconventional medicine: Should it be part of the UK healthcare system?
- Should doctors be responsible for medical errors?
- Should medical officers or health facilities be allowed to promote selective medical products?
- Should all healthcare facilities in the UK be required to have translators for non-English speaking clients?
- Mental health issues associated with domestic violence: A case study of France.
- Is it a good idea to legalize euthanasia?
- What are the benefits of using surgical masks in public?
- What are the most important lessons from the different waves of the COVID-19 pandemic reported on the globe?
- Who is more responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic?
- Ebola or COVID-19 pandemic: Which is worse?
- What are the main causes of epidemics on the globe?
- Public health planning: What are the most important things to think about?
- Should governments pay the cost of rehabilitating drug addicts in society?
- Teaching children healthy lifestyles: What are the best strategies?
- What problems do people with autism face in society?
- What are the leading causes of child mortality in your community?
- Gun violence in the United States: Should it be considered a public health issue?
- What illnesses are considered foodborne?
Easy Topics In Public Health
- All workplaces should support breastfeeding.
- What are the best strategies to reduce pollution in society?
- Public health benefits of recycling waste in society.
- Reviewing the causes of poor water quality in the developing world.
- Comparing water quality standards policies in the UK and US.
- Health impacts of the rapid depletion of o-zone depletion.
- Better planning of infrastructural development is important for healthier societies: Discuss.
- The US is better prepared to handle pandemics that might arise after the COVID-19 pandemic. Discuss.
- A review of common diseases spread by vectors.
- A review of key policies installed to protect employee health.
- Legal age for consuming energy drinks should be set by the government to address the problem of diabetes.
- Smoking: Should it be banned in public?
- What are the best strategies for raising awareness in public?
- Can reducing the workload of employees in manufacturing facilities improve their health?
- Sunbathing should be restricted to prevent the risk of cancer: Discuss.
- Should abortion be banned in society?
- School-related stress: How can it be prevented?
- Should birth control be made available and free for all teenagers?
- What should be categorized as a bad health habit?
- Compare and contrast two common treatment methods for treating behavioral disorders.
- Internet addiction: What are the main dangers of internet addiction?
Other Public Health Topics For Research
- How to stay healthy and safe during a pandemic.
- Using a bicycle instead of driving is healthier.
- Common mental disorders in India.
- What is the biggest health issue among young people?
- The impact of exercising in teenagers.
- Why do teenagers experiment with drugs?
- What impact does dispositional violence have on mental disorders?
- Is telemedicine helpful in promoting better healthcare?
- Unproven alternative medicine: What are the associated risks?
- What alternatives do we have for antibiotics?
- What is the difference between private and public healthcare?
- A review of the main health issues associated with puberty.
- What is the most dangerous disease of the 21st century?
- Why are some people still afraid of vaccines?
- Experimental treatment: Why do people agree to undergo it?
- How can we improve the health of people living with chronic illnesses?
- The best strategies to make people aware of the basics of healthcare.
- A review of the growing awareness about reproductive health in the society.
Seek Thesis Help from Experts
As we indicated earlier, writing a dissertation or other advanced papers is never easy. However, you should not give up or get content with poor quality work. If you do, defending the paper in front of a team of professors will be challenging. The best way out is to pay master thesis help .
We work with the best writers who are always ready to help you craft A-rated papers. They are educated in top schools and have a lot of experience in preparing both undergraduate papers and masters thesis. When you buy medical thesis , we also offer editing and proofreading services to guarantee students of highly refined work. Our services are also affordable and we also use secure communication to guarantee every student high confidentiality. When your teacher issues the assignment prompt, whether for a research paper or dissertation, let our professionals help you to get the best grades.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
Public health and research: an overview
Journal of Health Research
ISSN : 2586-940X
Article publication date: 15 October 2020
Issue publication date: 15 June 2021
This paper was to describe the overview of public health research.
Design/methodology/approach
It is a commentary piece of work from own long experience in working with the World Health Organization.
This study has innovative ideas in approaching priority areas in public health research.
Originality/value
This study opens up new thought in public health research.
- Public health
Public health research
Plianbangchang, S. (2021), "Public health and research: an overview", Journal of Health Research , Vol. 35 No. 4, pp. 374-378. https://doi.org/10.1108/JHR-03-2020-0074
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2020, Samlee Plianbangchang
Published in Journal of Health Research . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
An overview of public health
Public health is the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting human health through organized community efforts as well as the informed choice of society, public, private and voluntary organizations and communities at large. Analyzing the health of a population and the threats to that health forms the basis for public health.
Additionally, “health”, as defined in the WHO Constitution in 1948 [ 1 ], considers physical, mental and social well-being and is not merely the absence of disease or infirmity. Furthermore, public health is interdisciplinary, thus, a “public health team” may include several related disciplines in health and other social fields. Access to public health initiatives for comprehensive and integrated health care and services is always a difficult challenge in any population setting.
The objective of this commentary is to provide an overview of public health research and highlight innovative thinking in the field.
Public health systems
Public health systems are commonly defined as “all public, private, and voluntary entities that contribute to the delivery of essential public health services to people within a jurisdiction” [ 2 ]. This concept is to ensure, among other things, that all contributions to the improved health and well-being of the community or state are appropriately recognized and counted in the assessment of the provision of public health services to the community. The public health system includes public health agencies at state and local levels; all healthcare providers; public safety agencies; human services and charity organizations; education and youth development agencies; recreation and art-related organizations; economic and philanthropic agencies and environmental organizations.
The 10 essential public health services/functions
Monitoring community health situations to identify and solve health problems and prevent any health risks in the community;
Investigating and diagnosing specific health threats and health hazards in the community with the view to their early prevention;
Through modern technology in communication, informing, educating and empowering people in the community about health issues and challenges and their interventions;
Identifying/investigating and solving any problems of public health importance;
Through the full participation of people, developing policies and plans that support individual and combined health efforts in the community;
Ensuring effective enforcement of laws and regulations that protect environmental health and assure the safety of the population;
Linking people to needed personal health services and ensuring the provision of quality health care when otherwise unavailable;
Assuring the availability of effective public health workforce and competent healthcare personnel in both public and private facilities;
Objectively evaluating efficiency, effectiveness, accessibility and quality of personal as well as population-based health care facilities and services and
Undertaking study/research for new insights and innovative solutions to effectively counter prevailing and emerging health problems.
Public health rsearch aims to elucidate the influence of factors that determine the health of a population, i.e. genetic, environmental, social-cultural, economic, political, etc. The objective of public health research is to use the knowledge gained to propose policies and interventions, based on scientific evidence, and to help improve the health and well-being of the population and ultimately reduce/eradicate health inequalities.
Public health research is characterized by its multidisciplinary approach. It draws on several disciplines in its development and management, especially epidemiology/human ecology; biostatistics; physical and social sciences as applied to health; biology; genetics and toxicology. It usually entails the analysis of data on population samples on varying scales, depending on the scope and purpose of the research [ 4 ].
In practical terms, public health researchers study the statuses of population health and well-being, disability and loss of independence. They analyze the determining risk factors of these statuses or conditions, whether biological, behavioral, psycho-social or environmental. In addition, the researchers develop and assess the interventions aiming to effectively promote population health, prevent disease and compensate for disabilities and loss of independence. They also develop and assess innovation to improve efficiency and effectiveness of the organization of healthcare facilities and personnel, in public health, medical and other social service areas.
Research in health may be in the fields of health research, medical research, public health research, health services research, health systems research, environmental health research and others. These are interlinked and need to be pursued in a parallel manner in public health development.
Funding agencies
Mission and role of funding agencies
(2)Quality of research proposal
Relevance to current health-related issues and problems; responding to priority public health needs and the challenges of community and country are crucial. Applications should also be in the interest of the international/global health community.
Formulation with rational and logical thinking; Research proposals should be well-conceived and developed according to sound research methodology/protocol on epidemiological principles.
Expected result of the proposal; The result must be of high quality and should imply strong feasibility in its subsequent application/implementation in both technical, managerial and financial terms.
Public health system development research
DEIDS (development and evaluation of integrated health delivery system) (Thailand Lampang Health Development Project), 1973-1978 [ 6 ].
(2)District Health Services Development Project based on the principle of the primary health care approach, Mongar Health Development Project in Bhutan, 1984–1990 [ 7 ].
(3)Comprehensive and Integrated Health Research Development Project on hill- tribe population, 2014–present (still ongoing)
This is a long-term large research and development project with many sub-projects focusing on various specific issues of the target population. It is a multi-agency and interdisciplinary endeavor developed and implemented through the coordination of the Maefah Luang University Center of Excellence on health of the hill-tribe population. It includes the development of integrated and comprehensive social and health care services with an emphasis on equity, social justice and self-reliance in the community. There are multiple sources of funding, however mainly from the National Research Council of Thailand.
Some suggested areas for contemporary public health research
Universal health coverage for all
Financial sustainability in the long term
Equal accessibility by all people, regardless of their social and economic status
The right approach to development, proactive or passive strategy
Affordability in financial and managerial terms of the country concerned.
(2)Social impact of drug abuse /addiction
The social and economic impact of (chaotic situations created by) drug abuse and addiction
The general health of a population that is gradually undermined by drug abuse and drug addiction, leading, among other things to worsened national social and economic growth.
(3)Health and social care of elderly population
Intervention to reduce the degree of morbidity/disability and dependence
Efforts to increase social and economic productivity/independence
Program for self-help and self-reliance in an aged population
Preference between aging and aged programs, the difference between the two.
(4)Emerging infectious disease (EID)
The epidemiological, environmental and ecological approach in an integrated manner
The importance of social and behavioral change
Emerging mutation, assortment and genetic change in infectious agents
Impact of global climate change on EID, etc.
Even though it is mainly conceptual, the article may be able to help open new visions in public health research for better and sustainable health in the entire population in various localities.
1 World Health Organization [WHO] . WHO basic document . 47th ed. Geneva : WHO ; 2009 [cited 2019 Nov 28]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44192 .
2 World Health Organization [WHO] . What is health policy and systems research (HPSR)? [cited 2019 Nov 28]. Available from: https://www.who.int/alliance-hpsr/about/hpsr/en/ .
3 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC] , Office for state, tribal, local and territorial support . The 10 Essential Public Health Services: An Overview [cited 2019 Nov 28]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/publichealthgateway/publichealthservices/pdf/essential-phs.pdf .
4 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC] . Public health 101 series [cited 2019 Nov 28]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/publichealth101/ .
5 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC] . 24/7 Saving Lives, Protecting People [cited 2019 Nov 28]. Available from: https://www.cdcfoundation.org/cdc-247-saving-lives-protecting-people# .
6 Memoir on Occasion of the Death Anniversary of Dr. Somboon Vacharothai . Bangkok ; 2014 : 39 - 43 . (On Thailand DEIDS Project) .
7 World Health Organization [WHO] , Regional office for south-east asia [SEARO]. Sasakawa health prize: stories from south-east asia . New Delhi : WHO/SEARO ; 2012 : 125 - 146 [cited 2019 Nov 28]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/205878/B4905.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y .
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
MSc thesis proposal
Master’s thesis proposal checklist, master’s thesis proposal defence, sphs policy on absent committee members for master’s proposal defences, master’s thesis proposal decisions, master’s thesis final defence, sphs policy on absent committee members for msc thesis defence, decision categories for master’s thesis defences.
Once you and your supervisor agree that the written proposal is ready for presentation, there are several steps to follow:
- Contact all members of the thesis committee to determine possible dates and times for the presentation.
- Book a room for a two-hour period (or book a remote videoconference if this option is available) and inform all committee members of the date, time and room booking. The Faculty of Health receptionist can assist with room bookings. The receptionist can also advise you on which rooms are typically booked for proposal presentations. Ultimately, you are responsible for confirming that the room contains all necessary AV equipment for your presentation. If not, then you must book this equipment in advance or change rooms. Please note, IT support is not normally available for remote videoconferencing.
- Complete the MSc Thesis Proposal Notification Form (available on LEARN in the SPHS Research Grad Community Group) and submit it to the graduate coordinator a minimum of three weeks in advance of the proposal. Note: the information provided in the MSc Thesis Proposal Notification Form will be used to draft a LEARN announcement and the thesis proposal paperwork.
- Provide each member of the committee, as well as the graduate coordinator, with a copy of the proposal at least three weeks in advance of the presentation. A PDF is recommended to retain your formatting, although individual committee members may request their copy in Word format.
The graduate coordinator will provide the supervisor with the decision form and a set of guidelines for conducting the defense at least one day before the scheduled defense date. The thesis supervisor chairs the thesis proposal defence, which consists of a 20 minute presentation, followed by two rounds of questions wherein each committee member has a maximum of 15 minutes to ask questions in the first round and a maximum of 10 minutes to ask questions in the second round. Between the first and second round of questions, the student may elect to take a brief break (five minutes maximum). After the question rounds are completed, the student leaves the room or videoconference, and the thesis committee deliberates to reach a decision. Following deliberations, the supervisor will share the decision with the student and indicate the committee’s decision to the graduate research coordinator immediately. If the decision is anything other than Accepted (see below), the supervisor must submit a list of required changes, or reasons for rejections as stipulated for each category above. The supervisor must re-submit the thesis proposal form to the research graduate coordinator once all the changes have been made. The coordinator does not process the form until all changes to the thesis have been made.
Back to top
The master's thesis proposal usually outlines the rationale for the research, including a brief review of relevant background, research questions and/or objectives and plans, and a description of the proposed research design, methods, and analysis. Supervisors may have specific content they wish their students to include in the proposals. Please see the LEARN site for the document entitled MSc and PhD Thesis Proposal Guidelines for further information on how the thesis proposal should be formatted. Please note that the page limit for the proposal itself, excluding title page, abstract, work plan, and references, is a maximum of 10 to 12 full pages (single spaced, size 12 font, normal margins). Double-spacing is permitted, in which case the page limit doubles to 20 to 24 full pages. You may add appendices with additional tables, figures, or details.
Both the thesis proposal and final thesis will be defended in oral examinations. The MSc thesis committee (sometimes called the advisory committee) consists of a minimum of three faculty members and includes the student's thesis supervisor and at least one other faculty member from the School of Public Health Sciences (SPHS), which includes faculty who are joint- or cross appointed to the school). One of the three committee members may be from outside the school. A fourth committee member may also be from outside the school if the thesis topic is highly specialized and no current faculty members in SPHS have the requisite expertise.
If a committee member does not have a regular appointment with the University of Waterloo, then they will need to have an adjunct appointment with SPHS to serve on a thesis committee. To obtain adjunct status, the supervisor must provide a written request to the school director, indicating the reason for requesting status, the contributions the adjunct candidate will make to the thesis committee composition/school, and append the adjunct candidate’s CV. These documents will be reviewed by the SPHS executive committee for approval. SPHS adjunct faculty are considered as school members for the purpose of determining the composition of MSc thesis committees.
Students with two supervisors (‘co-supervisors’) will have at least four faculty members on their thesis committees because co-supervisors count as one vote in thesis deliberations.
Master’s theses previously published by SPHS graduates are available online at UW Space .
The thesis supervisor will chair the proposal presentation, questioning period and deliberations.
All committee members are expected to make every attempt to be present at the proposal presentation. ‘Being present’ for in-person defences is defined as being physically present or connecting via videoconference. The defence cannot take place unless at least two committee members, one of whom must be the supervisor or co-supervisor, are present. If one committee member (other than the supervisor) cannot attend and notice thereof is of a ‘last-minute’ nature, the defense may proceed. If this situation is known in advance, the supervisor must contact the absent member and obtain their written questions, expected responses, assessment of proposal acceptability, and suggestions for modifications. The supervisor is responsible for relaying this information during the defence. If a committee member is unable to submit questions in advance or fails to attend as planned due to unforeseen circumstances, the supervisor must obtain written feedback from the absent member prior to reaching a final decision concerning the acceptability of the proposal and permission for the student to proceed with the proposed research.
The supervisor must ensure that all committee members’ concerns (whether present at the proposal or not) are adequately addressed by the student prior to approval of the proposal and permission to proceed. As a means of documenting changes to the original proposal, particularly the methods, the candidate may be asked to develop a brief addendum that is circulated to all members of the committee (and to the graduate coordinator for the student’s file).
Note: If a committee member is unable to continue serving on a thesis committee, then the student and supervisor are responsible for finding a replacement.
- Accepted: The thesis proposal may require typographical or minor editorial corrections to be made to the satisfaction of the supervisor.
- Accepted conditionally: The thesis proposal requires more substantive changes but will be acceptable when these changes are made to the satisfaction of those members of the committee designated by the committee. The supervisor’s report will include a brief outline of the nature of the changes required, the maximum timeline of two months * , and the consequences (examination failure † ) if the changes are not made satisfactorily. The supervisor must inform the graduate coordinator when the changes are complete. The thesis proposal acceptance form will not be processed until the graduate coordinator is so notified.
- Decision deferred: The thesis proposal requires modifications of a substantial nature that make the acceptability of the thesis questionable. The supervisor’s report will contain a brief outline of the modifications expected and the date by which the changes are to be completed. The revised thesis must be resubmitted for re-examination following the process described in Master’s thesis proposal checklist above. The re-examination will follow the same procedures as for the initial submission except that the display period may be reduced or eliminated at the discretion of the associate director, graduate studies. Typically, the same committee will serve. A decision to defer is open only once for each candidate.
*The associate director may approve an extension to the two-month deadline under extenuating circumstances, at the request of the student and supervisor. Back to text
† In the case of examination failure because of not making required revisions, the student will be Required to Withdraw from the program. Back to text
If the decision is for a conditional acceptance (category 2), the designated committee members must be satisfied that the changes requested of the student have been made to their satisfaction.
If the decision is deferred (category 3), the student will go to re-examination. When a candidate is re-examined, the outcomes are limited to:
- Rejected: the candidate will be deemed to have failed to satisfy the program’s proposal exam requirement. In this case, the student shall receive written communication identifying the deficiencies in the proposal that led to this outcome.
A student who is deemed to have failed to satisfy the proposal requirement (Rejected) may not continue in the current MSc program. The student’s will be Required to Withdraw.
The outcome of the exam is determined by the majority vote of the thesis committee. Those members of the thesis committee who are voting members shall be clearly communicated to the candidate.
Once your committee decides you are ready to proceed to defence, please follow these steps.
- Contact all members of the committee re: available dates and times.
- Book a room for at least a two-hour period for the date and time agreed to by all committee members (or book a videoconference). Notify all committee members of room and time.
- Complete the Thesis Defence Notification Form (available on LEARN in SPHS Research Grad Community Group) and return this form to the graduate coordinator or research assistant a minimum of three weeks prior to the scheduled defence.
- Provide each member of the committee as well as the graduate coordinator with a copy of the thesis at least three weeks in advance of the defence date. The graduate coordinator will announce the upcoming thesis defence and place a copy of the thesis on public display via LEARN for at least two weeks prior to the scheduled defence.
Note: notwithstanding agreement between the student and thesis committee, Graduate Studies and Postdoctoral Affairs (GSPA) strongly discourages holding thesis defences during holiday periods or close to the end of term.
The supervisor can retrieve a set of guidelines for conducting the defense from LEARN. Supervisors are to familiarize themselves with the relevant standard operating procedures prior to the defense. The thesis supervisor chairs the thesis proposal defence, which consists of a 20 minute presentation, followed by two rounds of questions. In the first round, each committee member has a maximum of 15 minutes to ask questions. In the second round, each committee member has a maximum of 10 minutes. Between the first and second round of questions, the student may elect to take a brief break (five minutes maximum). After the question rounds are completed, the student leaves the room or videoconference, and the thesis committee deliberates to reach a decision. Following deliberations, the supervisor will share the decision with the student and indicate the committee’s decision to the graduate research coordinator immediately. The c oordinator will collect the necessary signatures from the committee. If the decision is anything other than Accepted (see below), the supervisor must submit a list of required changes, or reasons for rejections as stipulated for each category above. The supervisor must re-submit a proposal decision once the necessary conditions have been met. The coordinator does not process any administrative documents until all changes to the thesis have been made.
The policy of SPHS is that no more than one committee member, and not the thesis supervisor, may be absent for the MSc thesis defence to take place. The absent member must be contacted in advance by the thesis supervisor and submit the following to the thesis supervisor and associate director, graduate studies at least 24 hours prior to the scheduled defence: a list of questions, expected responses, a final recommendation (refer to decision categories below), and a list of required revisions (if necessary). Questions from an absent committee member will be read by the supervisor (and shall be submitted via email). Note: the supervisor should email a description of the decision categories to the absent member. In contrast to the proposal defence, feedback from an absent committee member cannot be submitted after the defence has taken place. If the above stipulations cannot be met, the defence will have to be cancelled and rescheduled. If the defense is being held in person, then a committee member may attend remotely via videoconference and be considered ‘present’ for the purpose of this requirement.
If a committee member fails to attend as scheduled, allow at least 30 minutes to pass and have someone attempt to contact the individual. If 30 minutes have elapsed and no contact has been made, then the chair/supervisor should consult the associate director, graduate studies or the associate dean, graduate studies. In most cases, the defence will have to be rescheduled.
- Accepted: The thesis may require typographical or minor editorial corrections to be made to the satisfaction of the supervisor.
- Accepted conditionally: The thesis requires more substantive changes but will be acceptable when these changes are made to the satisfaction of those members of the committee designated by the committee. The supervisor’s report will include a brief outline of the nature of the changes required, the maximum timeline of two months ** , and the consequences (examination failure †† ) if the changes are not made satisfactorily. The supervisor must inform the graduate coordinator when the changes are complete. The thesis acceptance form will not be processed until the graduate coordinator is so notified.
- Decision deferred: The thesis requires modifications of a substantial nature which makes the acceptability of the thesis questionable. The supervisor’s report will contain a brief outline of the modifications expected, the date by which the changes are to be completed, and the consequences if the changes are not made satisfactorily. The re-examination will follow the same procedures as for the initial submission except that the display period may be reduced or eliminated at the discretion of the associate director, graduate studies. Typically, the same committee will serve. A decision to defer is open only once for each candidate.
- Rejected: The thesis is rejected.
**The associate director, graduate studies may approve an extension to the two-month deadline under extenuating circumstances, at the request of the student and supervisor. Back to text
†† In the case of examination failure because of not making required revisions, the student will be Required to Withdraw from the program. Back to text
The chair may retrieve a copy of the thesis defense prior to the defence. Following deliberations of the examining committee, and upon reaching a decision on the thesis (as described above), the chair will communicate the committee’s decision to the graduate coordinator. All committee members present the day of the defence will sign the examination report form electronically. If the decision is other than Accepted, the chair must also submit a list of required changes, or reasons for rejections as stipulated for each category above.
If the decision is for a conditional acceptance (category 2), the designated committee members must be satisfied that the changes requested of the student have been made to their satisfaction. The supervisor will then sign on behalf of the committee to indicate that the thesis is now considered accepted. Then the associate director, graduate studies and associate dean, graduate studies will give their approval. The student can then apply to graduate in Quest.
If the decision is deferred, the student will go to re-examination. When a candidate is re-examined, the outcomes are limited to:
- Rejected: the candidate will be deemed to have failed to satisfy the MSc thesis milestone and they will receive written communication from the supervisor identifying the deficiencies in the proposal that led to this outcome. The student’s status will change to Required to Withdraw.
The supervisor and chair must clearly communicate to the graduate research coordinator if an embargo is to be placed on a student thesis.
Grant Writing Guidance & Tips

Find and apply for federal grants at Grants.gov
CDC uses grants and cooperative agreements to fund public health programs that advance the agency’s public health mission to keep Americans safe and healthy where they work, live, and play. The resources below can help health departments navigate the federal grant writing process.
CDC Grants Policy guidelines, references, FAQs, and more
CDC Contracts Information about how to do business with CDC, regulations and policy, and common contracting terms
Tips for Applying for a CDC Notice of Funding Opportunity (NOFO) Information about applying for grants and how to increase your competitiveness in the award process.
Grants.gov The portal where organizations and individuals can search for and apply for grants throughout the federal government
To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address:

Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

Impact of public health guidance is focus of new NSF partnership with Social Science Research Council
The U.S. National Science Foundation is partnering with the Social Science Research Council (SSRC) to support research that advances scientific knowledge about public health guidance and its impact on the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
SSRC will donate up to $7.5 million to NSF over the next two years to support fundamental research exploring the effects of public health guidance on society. NSF will invest an additional $12.5 million for a combined total of up to $20 million in research funding.
SSRC is an independent nonprofit organization that has supported social science research since 1923. The partnership will leverage the unique capabilities of NSF and SSRC through their diverse connections to the research community and public health organizations.
"Fundamental social and behavioral science has the power to help every American live a healthier and more prosperous life," says NSF Social and Economic Sciences Division Director Rayvon Fouché. "The societal benefits from robust exploratory research are amplified by dynamic partnerships like this one. We are grateful to SSRC for partnering with NSF in our shared mission to enhance the resilience and strength of communities across the entire country."
"Information networks are a critical component of our public health infrastructure. However, in today's complex information ecosystem, accurate information is not equally accessible for everyone," says SSRC President Anna Harvey. "This partnership will fund social and behavioral scientists to understand the causal impacts of methods that increase the sharing and uptake of critical health-related information, contributing to an information environment that benefits everyone."
The challenge of understanding the diverse effects that public health guidance can have on U.S. society and the economy has been underscored by the COVID-19 pandemic. The health and well-being of individuals, communities and entire regions of the U.S. can be fortified through fundamental scientific insights into how public health guidance is created and distributed and how people perceive it.
NSF and SSRC invite research proposals that can reveal the complex factors that contribute to effective public health guidance and provide rigorous evidence that will be useful for decision-makers seeking to improve and protect the health of their communities.
For details on how to prepare and submit a research proposal, see Dear Colleague Letter: NSF and SSRC Partnership to Advance Scientific Knowledge About the Impact of Public Health Guidance .
Research areas
- About Grants
- How to Apply - Application Guide
Samples: Applications, Attachments, and Other Documents
As you learn about grantsmanship and write your own applications and progress reports, examples of how others presented their ideas can help. NIH also provides attachment format examples, sample language, and more resources below.
On This Page:
Sample Grant Applications
Nih formats, sample language, and other examples.
With the gracious permission of successful investigators, some NIH institutes have provided samples of funded applications, summary statements, and more. When referencing these examples, it is important to remember:
- The applications below used the form version and instructions that were in effect at the time of their submission. Forms and instructions change regularly. Read and carefully follow the instructions in your chosen funding opportunity and the Application Guide .
- The best way to present your science may differ substantially from the approaches used in these examples. Seek feedback on your draft application from mentors and others.
- Talk to an NIH program officer in your area of science for advice about which grant program would be a good fit for you and the Institute or Center that might be interested in your idea.
- Samples are not available for all grant programs. Because many programs have common elements, the available samples can still provide helpful information and demonstrate effective ways to present information.
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- Sample Applications and Summary Statements (R01, R03, R15, R21, R33, U01, SBIR, STTR, G11, K, and F)
- NIAID Sample Forms, Plans, Letters, Emails, and More
National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Behavioral Research Grant Applications (R01, R21, R03)
- Cancer Epidemiology Grant Applications (R01, R21, R03, R37)
- Cancer Control and Population Sciences Grant Applications (R01, R21, R37)
- Healthcare Delivery Research Grant Applications (R01, R03, R21, R50)
National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- ELSI Applications and Summary Statements and biosketches (K99/R00, K01, R01, R03, and R21)
- NHGRI Sample Consent Forms
National Institute on Aging (NIA)
- K99/R00: Pathway to Independence Awards Sample Applications
- NIA Small Business Sample Applications (SBIR and STTR Phase 1, Phase 2, and Fast-Track)
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
- Research Project Grants (R01) Sample Applications and Summary Statements
- Early Career Research (ECR) R21 Sample Applications and Summary Statements
- Exploratory/Developmental Research Grant (R21) Sample Applications and Summary Statements
NIH provides additional examples of completed forms, templates, plans, and other sample language for reference. Your chosen approach must follow the instructions in your funding opportunity and the Application Guide .
- Application Format Pages
- Annotated Form Sets
- Animal Document Samples from Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare (OLAW) for animal welfare assurances, study proposals, Memorandum of Understanding , and more
- Allowable Appendix Materials Examples
- Authentication of Key Biological and/or Chemical Resources Plan Examples
- Biosketch Format Pages, Instructions, and Samples
- Data Management and Sharing (DMS) Plan Samples
- Informed Consent Example for Certificates of Confidentiality
- Informed Consent Sample Language for secondary research with data and biospecimens and for genomic research
- Model Organism Sharing Plans
- Multiple PI Leadership Plan Examples
- Other Support format page, samples, and instructions
- Scientific Rigor Examples
- Person Months FAQ with example calculations
- Plain Language Examples for application title, abstract, and public health relevance statements
- Project Outcome Description Examples for interim or final Research Performance Progress Report (RPPR)
This page last updated on: February 7, 2024
- Bookmark & Share
- E-mail Updates
- Help Downloading Files
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility
- National Institutes of Health (NIH), 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
- NIH... Turning Discovery Into Health
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Browse content in Art
- History of Art
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- History by Period
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Regional and National History
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Language Evolution
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Browse content in Religion
- Christianity
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Company and Commercial Law
- Comparative Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Financial Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Legal System and Practice
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Anaesthetics
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Forensic Medicine
- History of Medicine
- Medical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
Occupational Medicine
- Paediatrics
- Browse content in Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Physical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Browse content in Computing
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Environmental Sustainability
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Analysis
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Classical Mechanics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Browse content in Psychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Health Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Human Evolution
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Schools Studies
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Environment
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Economic Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Security Studies
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Research and Information
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Browse content in Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Migration Studies
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Journals A to Z
- Books on Oxford Academic
What are the trending topics in Public Health and related disciplines?
You can identify some of the most discussed and influential topics with the help of Altmetric attention scores, which take into account several outlets including social media, news articles, and policy documents.
Drawing from a selection of Public Health and Medicine journals, we have compiled a list of the articles that have been mentioned the most over the past few months.
Discover the articles that are trending right now, and catch up on current topics in Public Health and related disciplines. We will update our collection every few weeks; come back to this page to be on top of the latest conversations in Public Health and Medicine. Previously featured articles are listed here .
You can also sign up for e-alerts to make sure you never miss the latest research from our journals.
*Last updated October 2021*
Age and Ageing
Alcohol and alcoholism, american journal of epidemiology, annals of work exposures and health, epidemiologic reviews, european journal of public health, family practice, health education research, health policy and planning, health promotion international, international health, international journal of epidemiology, international journal for quality in health care, journal of public health, journal of travel medicine, journal of tropical pediatrics, nicotine & tobacco research, transactions of the royal society of tropical medicine & hygiene, behaviour change interventions to increase physical activity in hospitalised patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression.
There is moderate-certainty evidence that behaviour change interventions are associated with increased physical activity levels among older hospitalised patients.
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Alcohol and Other Substance Use Disorders in Young Adulthood: Findings from a Canadian Nationally Representative Survey
This study from Canada found that one in three young adults with ADHD had a lifetime alcohol use disorder, and that young adults with ADHD were also three times more likely to develop a substance use disorder. Targeted outreach and interventions for this extremely vulnerable population are warranted.
Expiring Eviction Moratoriums and COVID-19 Incidence and Mortality
According to this study, resuming evictions in summer 2020 was associated with increased COVID-19 incidence and mortality in US states, with an estimated 433,700 excess cases and 10,700 excess deaths. Explore more research on COVID-19 in a curated collection from the AJE: https://academic.oup.com/aje/pages/covid-19

The Development of a Covid-19 Control Measures Risk Matrix for Occupational Hygiene Protective Measures
The British Occupational Hygiene Society (BOHS) developed a control banding matrix for employers and others to help assess the risks of COVID-19 infection, and calls for further work to validate the reliability of the tool. Browse the Annals' collection on occupational hygiene for virus protection: https://academic.oup.com/annweh/pages/covid-19
Immunization to Protect the US Armed Forces: Heritage, Current Practice, and Prospects
In 1777, George Washington ordered a mandatory inoculation program for his troops, in what would become the first mass immunization mandate in the US. This archival article discussess and contextualizes immunization practices for US Armed Forces.
Does face mask use elicit risk-compensation? Quasi-experimental evidence from Denmark during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
Responding to concerns that that face mask use could elicit a false sense of security and lead to riskier behaviours, this study from Denmark found that mask use overall correlated positively with protective behaviours.
Evidence reversals in primary care research: a study of randomized controlled trials
While medical practice is often undermined by subsequent investigation, randomized trials relevant to primary care generally hold up over time.
Social media influencers can be used to deliver positive information about the flu vaccine: findings from a multi-year study
This study shows the potential for using social media influencers to inspire positive engagements on pro-vaccine health messaging. For more content on accurate information's importance for public health, browse the latest article collection from HER: https://academic.oup.com/her/pages/covid-19
COVID-19 Preparedness and Response Plans from 106 countries: a review from a health systems resilience perspective
Current emergency response planning does not have adequate coverage to maintain health systems functionality for essential health service delivery alongside emergency-specific interventions and healthcare. The findings from this study can help align health emergency planning with broader population health needs.
Rise and demise: a case study of public health nutrition in Queensland, Australia, over three decades
This case study shows that that ongoing efforts are needed to improve sustainability of nutrition policy and programmes to address all diet-related diseases.
Institutional and behaviour-change interventions to support COVID-19 public health measures: a review by the Lancet Commission Task Force on public health measures to suppress the pandemic
This review article outlines evidence for a range of institutional measures and behaviour-change measures, and highlights research and knowledge gaps.
Quantifying impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic through life-expectancy losses: a population-level study of 29 countries
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered significant mortality increases in 2020 of a magnitude not witnessed since World War II in Western Europe or the breakup of the Soviet Union in Eastern Europe.
Gender in the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) Checklist
The authors propose an update to the Equator’s Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ) checklist, with the aim of enhancing inclusivity.
Rate of reinfections after SARS-CoV-2 primary infection in the population of an Italian province: a cohort study
This study confirms previous findings on a low risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection. If confirmed, these findings suggest that more targeted restriction policies can be applied to the subjects that recovered after a first infection. Read highly cited papers on COVID-19 from the Journal of Public Health: https://academic.oup.com/jpubhealth/pages/covid-19
The reproductive number of the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 is far higher compared to the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 virus
Given the Delta variant's high reproductive number associated with higher transmissibility, in a context of globally still low vaccine coverage rates and lower vaccine effectiveness, public health and social measures will need to be substantially strengthened. A high reproductive number also means that much higher vaccine coverage rates need to be achieved compared to the originally assumed.
Neurological Complications of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Neurological complications are rare in children suffering from COVID-19. Still, these children are at risk of developing seizures and encephalopathy, more in those suffering from severe illness.
Reactions to Sales Restrictions on Flavored Vape Products or All Vape Products Among Young Adults in the United States
The researchers examined support for and perceived impact of e-cigarette sales restrictions. Findings suggest that bans on flavored vape products could have a positive impact on lower-risk users, but that other young adult user subgroups may not experience benefit.
Covid-19 and Health at Work
An editorial from the earlier stages of the pandemic highlights the importance of properly fitted respirators for worker safety and outlines occupational hygiene measures.
Lessons from the field: delivering trachoma mass drug administration safely in a COVID-19 context
Guidelines for safe mass drug administration for neglected tropical diseases were developed in a COVID-19 context; training and implementation were assessed through an observation checklist.
For more research on the impact of COVID-19 on NTDs, explore the March 2021 special issue: https://academic.oup.com/trstmh/issue/115/3
Previously featured
Age and frailty are independently associated with increased COVID-19 mortality and increased care needs in survivors: results of an international multi-centre study
Trajectories of Alcohol Use and Related Harms for Managed Alcohol Program Participants over 12 Months Compared with Local Controls: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Estimating the Effect of Social Distancing Interventions on COVID-19 in the United States
Selecting Controls for Minimizing SARS-CoV-2 Aerosol Transmission in Workplaces and Conserving Respiratory Protective Equipment Supplies
What Do We Know About the Association Between Firearm Legislation and Firearm-Related Injuries?
Denialism: what is it and how should scientists respond?
Acute cooling of the feet and the onset of common cold symptoms
The effect of falsely balanced reporting of the autism–vaccine controversy on vaccine safety perceptions and behavioral intentions
Climate change: an urgent priority for health policy and systems research
Power, control, communities and health inequalities I: theories, concepts and analytical frameworks
Research ethics in context: understanding the vulnerabilities, agency and resourcefulness of research participants living along the Thai–Myanmar border
Tobacco smoking and mortality among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander adults in Australia
Quality and safety in the time of Coronavirus: design better, learn faster
Years of life lost associated with COVID-19 deaths in the United States
In-flight transmission of SARS-CoV-2: a review of the attack rates and available data on the efficacy of face masks
Stability of the Initial Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder by DSM-5 in Children: A Short-Term Follow-Up Study
Impact of Tobacco Smoking on the Risk of COVID-19: A Large Scale Retrospective Cohort Study
Mental health of staff working in intensive care during COVID-19
The benefits and costs of social distancing in high- and low-income countries
A classification tree to assist with routine scoring of the Clinical Frailty Scale
Recent Advances in the Potential of Positive Allosteric Modulators of the GABAB Receptor to Treat Alcohol Use Disorder
The recent oubreak of smallpox in Meschede, West Germany
Your Hair or Your Service: An Issue of Faith for Sikh Healthcare Professionals During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Emerging Infections: Pandemic Influenza
Identifying the views of adolescents in five European countries on the drivers of obesity using group model building
Novel multi-virus rapid respiratory microbiological point-of-care testing in primary care: a mixed-methods feasibility evaluation
Public health crisis in the refugee community: little change in social determinants of health preserve health disparities
In search of ‘community’: a critical review of community mental health services for women in African settings
COVID-19, a tale of two pandemics: novel coronavirus and fake news messaging
Disrupting vaccine logistics
Use of directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) to identify confounders in applied health research: review and recommendations
Measurement and monitoring patient safety in prehospital care: a systematic review
Black Lives Matter protests and COVID-19 cases: relationship in two databases
The positive impact of lockdown in Wuhan on containing the COVID-19 outbreak in China
Severe Malnutrition and Anemia Are Associated with Severe COVID in Infants
A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Pilot, and Feasibility Study of a High Nicotine Strength E-Cigarette Intervention for Smoking Cessation or Reduction for People With Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Who Smoke Cigarettes
Healthcare workers and protection against inhalable SARS-CoV-2 aerosols
Affiliations
- Copyright © 2024
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Internet Explorer is no longer supported by Microsoft. To browse the NIHR site please use a modern, secure browser like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Edge.

Public Health Research Programme

The Public Health Research (PHR) Programme funds research that generates evidence to improve the health of the public and reduce health inequalities.
We want to help researchers address critical population health issues, like climate change.
Latest funding opportunities for Public Health Research
NIHR Population Health Career Scientist Awards Public Health Intervention Responsive Studies Teams (PHIRST) 2024 24/27 Interventions to deliver inclusive economies 24/28 Parenting Interventions 24/29 The health of children and young people in contact with the criminal justice system
All Public Health Research funding opportunities
Scope of funding
We focus on funding health-related research into services that:
- are not provided or funded by the NHS
- can be rolled out on a large scale
- have potential to create sustainable, population-level changes
We are particularly interested in studies that focus on the wider determinants of health and will generally ask for health-related outcome measures.
What do we fund?
We fund studies that evaluate the impact on health and health inequalities of real-world interventions in the UK. This includes:
- Natural experiments
- Secondary research
- Studies using a wide range of quantitative and qualitative methodologies, including modelling studies
- Interventions that may not conventionally be seen as public health interventions but have an impact on health and health inequalities
- Studies that employ longitudinal datasets and attempt to link data across sectors when relevant to studying the broader determinants of health
A limited amount of intervention development before evaluation, including feasibility studies
This list is not exhaustive. If you have a research idea that addresses crucial population health issues and has the potential for significant impact at scale, please contact us to discuss your ideas.
Please email [email protected]
Multidisciplinary research proposals
We encourage multi-disciplinary research proposals led-by, or involving, researchers from outside the disciplines usually associated with public health.
This is particularly important given our intention to focus on population health priorities such as climate change.
What we don't fund
We do not fund:
- studies of specific disease or condition
- treatments research where primary outcomes are social care outcomes. See our Research programme for Social Care
- the development of new websites, apps, or software. See the MRC Public Health Intervention Development (PHIND) Programme
If you are unsure if your proposal is within our remit, please contact [email protected] for advice.
Projects we have funded
Examples of PHR-funded research include:
- evaluations of air pollution interventions
- evaluations of transport and traffic initiatives
- evaluations of interventions to tackle obesity such as helping football fans to lose weight , the placement of food in supermarkets , planning regulations for takeaway food outlets , and early years nutrition and physical activity
- evaluations of the health impacts of Universal Credit
- community-based initiatives such as age-friendly environments and community health assets
- changes to alcohol outlet density and opening hours on alcohol harm
- tobacco policies and initiatives such as the impacts of e-cigarette legislation on young people’s use of e-cigarettes, and the health benefits of smokefree prisons .
View details of the public health research we have funded on our Funding and Awards website
How to apply for funding
We fund research through two routes: commissioned and researcher-led work streams.
Criteria for funding
We will consider applications for funding that:
- demonstrate value to public health
- maintain high scientific quality
- make an impact to people’s lives
- provide value for money
There is no upper limit to the amount of funding that researchers can apply for.
Commissioned funding
View all PHR Programme funding opportunities
Researcher-led work streams
If you have an idea for a research study and it meets the criteria outlined above, you can apply for funding from us.
You can submit an application at any point. Our funding calls have cut-off dates throughout the year.
See Researcher-led PHR Programme funding calls
Help with your application
Tips for success
Research Support Service Specialist Centre for Public Health
Application process
You will need to create an account and log into the Research Awards Lifecycle Management System (REALMS) to submit and manage your funding application or proposal.
Our committees consider applications, usually as part of a two-stage assessment process. See the Committees section below for more information.
Fast-track scheme
While most research supported by the PHR Programme follows a two-stage assessment process, we recognise that there may be instances where research needs to be accelerated.
The fast-track scheme provides an opportunity to submit a stage 2 proposal directly, shortening the length of time it takes for a funding decision to be made.
The fast-track scheme is particularly suitable for situations where research needs to start within a limited timeframe, such as natural experiments.
If you believe your proposal should be considered for the fast-track scheme, please email [email protected] and we will consider it.
You will need to:
- convince the secretariat that there is significant benefit to fast-tracking your application, and
- submit a written summary of your proposal (usually about one side of A4) in a PICO format.
Who identifies and prioritises research topics? Prioritisation Committee
The PHR Prioritisation Committee helps identify and prioritise:
- research topics
- stage 1 proposals
based on public health importance.
Professor Brian Ferguson is Prioritisation Committee Chair and PHR Programme Director.
See PHR Programme Prioritisation Committee members
Who assesses funding applications? Funding Committee
The PHR Funding Committee assesses applications that have passed stage 1. They are assessed on:
- scientific quality
- feasibility
- value for money
Professor Peymane Adab is Funding Committee Chair.
See PHR Programme Funding Committee members
Committee minutes and outcomes
See all Public Health Committee meeting minutes and outcomes
Conflicts of interest
Committee members need to declare any conflicts of interest annually.
Conflicts of interest register
Findings from our research
The findings from the research we fund help: decision-makers in local and national government voluntary sector organisations national agencies concerned with improving public health and reducing health inequalities researchers public health practitioners
Find NIHR published evidence and ongoing research to help with data analysis and improving health in your area:
Evidence and research for public health
More information
Who funds the phr programme.
The PHR Programme is funded by the NIHR, with contributions from the:
- the Chief Scientist Office (CSO) in Scotland
- Health and Care Research Wales
- the HSC R&D Division, Public Health Agency in Northern Ireland
Contact and more information
Please email [email protected]
Find out more about how we support Public health research at NIHR:
Public health research
See how researchers are working with local authorities to boost research in communities and tackle health inequalities, through our Health Determinants Research Collaborations (HDRCs)
See how Public Health Intervention Responsive Studies Teams (PHIRST) are evaluating health initiatives
Latest news from Public Health Research

New report reveals key features of no- and low-alcohol drinks market

NIHR Chief Executive Professor Lucy Chappell attends COP28 Health Day

NIHR invests a further £55m to tackle health inequalities through local government research
Latest blogs from public health research.

Alcohol, obesity and chronic liver disease research: A call to action

Catching golden opportunities to create public health evidence as they fly by...

What is the value in local outdoor space for our mental health and wellbeing?
- How it works

Sample Masters Public Health Dissertation Proposal
Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness.
View a different grade
Critical Analysis of Factors Affecting Public Health Promotion: A Case Study of Saudi Arabia
This research will be conducted to fulfil the study’s aim to analyse the influence of public health on health promotion intervention within the case of Saudi Arabia as a developing country. To fulfil the research’s aim and objectives, the researcher will use a qualitative approach and secondary data sources regarding public health promotion intervention in Saudi Arabia.
The researcher will examine relevant secondary sources and then present a systematic overview of the literature to understand the impact of public health on the public health promotion intervention in the region of Saudi Arabia.
Introduction
From the overview of past literature, it can be found that there is an increased interest of researchers and practitioners concerning public health and its promotion (Baum, 2016). The information and know-how regarding public health are important because public health programs and public health interventions are based on this knowledge and research (Boulware et al., 2016).
Now, several different elements tend to impact public health and programs related to public health. The governmental and health organisations have shifted their focus from removing and preventing the disease towards the socio-economic, behavioural, and environmental factors that significantly impact public health (Wiene et al., 2017).
From the research point of view, there have been very few researches in the past that have been carried out in this regard. Different countries aim to improve public health by introducing effective programs and interventions (Watts et al., 2015). The health sector continually works towards ensuring that their public health-related goals are met efficiently to make a significant mark.
The promotion of public health is undeniably an essential aspect of public health. Several types of research have been carried out in this regard (Rosenbaum, 2011). Health promotion is carried out to raise awareness among the public regarding the negative consequences of a disease or notify the public regarding living a healthy lifestyle.
Health promotion is an expression in practical terms as a source that lets the public lead a productive life regarding social, economic, and individual perspectives. Health is a source for a routine life, not an object that can be ignored easily (Anderson et al., 2005). According to WHO, public health is a fundamental human right, and all individuals should have the right to get rudimentary resources (WHO, 2018).
The interventions for the promotion of public health are carried out to ensure that public health is not at stake and that the public is aware of the importance of their health (Nutley, Smith, & Davies, 2000). Through public health intervention, the government can control several health problems.
Regarding Saudi Arabia’s public health, WHO has notified that more than 60% of the population is inactive, which is quite alarming concerning the individuals’ health (WHO, 2011). Physical activity is of great importance because it mainly decreases the many common diseases like diabetes, hypertension, cancer, and heart disease.
It also prevents one of the major problems regarding health, i.e., obesity (Frohlich & Potvin, 2008). It has been established that with time, the health sector of Saudi Arabia has been experiencing growth. However, there are still specific problems faced (Almalki, FitzGerald, & Clark, 2011).
One of the major problems of the health sector of Saudi Arabia is that there is a language barrier among physicians, doctors, and patients. Although some research has been carried out in the context of public health and its impact on health promotion intervention, there is still a need for more research to evaluate public health in terms of promotion.
Yet, according to Sharaf (2010), social media platforms, particularly Twitter, have inculcated new prospects for definitely influencing audiences’ health at large. As Saudi Arabia is coined to be the country with the highest number of Twitter users, practitioners believe that Twitter can contribute to the propagation of health promotion ideas.
According to Mckenzie (2016), with the help of developing different health intervention promotion programs, public health is improving daily. The researcher needs to carry out more research to ensure that public health is impacted efficiently. The country’s major goal is to ensure that the public is provided with high-quality healthcare services.
The well-being of society is promoted. According to Peltzer (2011), the health care promotional campaigns and interventions are focused more on developed nations than developing nations. Several different factors tend to have a significant impact on the health promotion intervention. Socio-economic factors play a critical role in people’s lives, affecting each individual’s health in many ways.
Every country has its characteristics that dominate other factors compared to other places according to specific policies and particular laws. But few general ones can be easily recognised in all parts of the world.
Aim and Objectives
The present research’s main aim is to analyse the influence of public health on the health promotion intervention within the case of Saudi Arabia as a developing country. The objectives of the study are as follows,
- To study the concept and significance of public health interventions.
- To identify factors affecting health promotion interventions concerning public health in the case of Saudi Arabia.
- To analyse the influence of public health on the health promotion intervention in the case of Saudi Arabia.
- To suggest effective recommendations for improving the health promotion intervention from the influence of public health in Saudi Arabia.
Research Question
Based on the preliminary overview of the literature review on this topic, the research question that is going to be answered by this research is:
How can public health be determined through various factors affecting public health promotion in the context of Saudi Arabia?
Problem Statement
This research will be carried out to analyse the impact of public health on public health promotion intervention, specifically in Saudi Arabia. In terms of the public health of Saudi Arabia, the company is experiencing significant improvement; however, they are still lacking in providing high-quality health care advice through public health promotion intervention. One of the important problems prevalent in the region is a language barrier among physicians, doctors, and patients.
The Rationale of the Research
The study has established that certain researches have been carried out concerning public health and its impact on evaluating the health promotion intervention. This particular research is significant because it focuses on analysing how public health in the region of Saudi Arabia impacts their health promotion intervention.
There are not many academic types of research carried out on Saudi Arabia’s public health. This research will contribute positively towards the existing body of literature mainly inclined towards Western countries’ general health (Glanz & Bishop, 2010). One of the significant hindrances with the effective provision of public health to a country’s citizens is that there is no consistent framework of public health that promotes the evaluation of public health promotion intervention (Frieden, 2010).
This research is particularly significant because it will look into different factors that combine to form the public health of Saudi Arabia. Moreover, it will also address the issues faced by the country regarding the implementation and evaluation of their health campaigns. The major rationale behind this research is that there are very few research studies carried out.
Structure of the Research
The following study comprises five significant sections: introduction, literature review, methodology, findings and conclusion, and recommendations. The first chapter of the study highlights the research study’s topic, the research problem, aims and objectives of the study, rationale, and significance. It provides a brief introduction to the analysis.
The second chapter of this study was a literature review. In this chapter, the researcher identifies the study variables and includes different theories and backgrounds concerning the view and opinions of various researchers. It consists of a theoretical framework and the development of a hypothesis.
The third chapter of the study was methodology. This section identified the methods and techniques used in a research study to examine the results. Data collection methods and techniques are described in this chapter, along with ethical considerations and limitations.
The fourth chapter of the study was findings and analysis. This chapter analyses and evaluates the data obtained from different sources based on other techniques and methods. A significant portion of this section includes an analysis of results and discussion.
The last chapter of the study is the conclusion and recommendations. It concludes the entire research along with summarised findings of the study.
Literature Review
Public health intervention and promotion.
Public Health is known for inhibiting the disease, health promotions, healthily improving lifestyle, and systematised society effort. The central focus is on the health betterment of the population and doing interventions to prevent disease. The protection, promotion, prolonging of public life, and betterment of society’s health are the main goals of public health (Brownson, 2017).
The progress in the social machinery by health promotions satisfies the people regarding maintenance and betterment of health. Better cure of advanced and severe diseases is required, specifically in developing countries. The interventions of Public health regarding the reduction in risk factors related to health are significant. The preventions are done of medicines to preserve or promote health and decrease the suffering when health is impaired (Gostin, 2016).
There are significant disciplines in which health sectors mostly perform to promote health. A healthy nutrient balances health and any disease, and reproductive health is taken care of the most because it includes mental, physical, and social health that should be healthy. In environmental health, the approach is to classify the particular biological or physical aspects that present all health risks.
It can be replaced and modified to protect people from it, like sanitisation of water, disposal of waste management, etc. (Frieden, 2010). The combination of health education and economics is beneficial for health promotions and their interventions. It helps in the substitution use of resources and their effective utilisation in the health service sector.
Many types of research have been done that focus on the distribution, frequency, biostatistics, and causes of disease. Such researches are an action to attain more information about the technical or scientific overview of public health. The health service sector management tries to work together and utilise the available resources to achieve the goal (Fleming, 2014).
Health promotion is the central part of public health, defined as the betterment of health in the population. It presents wide-ranging environmental and social conditions directed towards changing the negative aspects of such states to ease their effect on individual and public health. It enables individuals to elevate control over the factors of health and thus improve their health.
Contribution in health promotion is vital to endure promotions’ actions and efforts (Naidoo, 2016). Health promotion is an expression in practical terms as a source which let public to lead a productive life regarding social, economic and individual prospective because health is a source for a routine life, not an object that can be ignored easily.
It emphasises the physical capabilities of a person. WHO has recognised public health as a fundamental human right, and all individuals should have the right to get rudimentary resources (Lupton, 2014). The prospective health concept applies that the organisations that rule social, physical, and economic conditions should take responsibility for their activities in terms of their effect on the public and health (Leischik, 2016).
After the research many years, health promotion is now getting in trend. It became clear that health promotion interventions should be seen in the framework of difficult interrelationships encircling the public, societies, and health care sectors (Duplaga, 2015) and (Sitko, 2016). The approaches have found out that the effective interventions and consequent promotions that are in practice.
The interventions of health promotions should be for the betterment of local practice. The advanced interventions in public health lead to many issues and challenges regarding promotions. Interventions are commonly recognised by combining factors of a supplied intervention like theory and all with factors present in the local context such as funding etc. Interventions help a lot in controlling and preventing health problems (Kok, 2012).
Overview of Saudi Arabia’s Public Health Intervention and Promotion
The WHO reports show that 60% of the overall population of Saudi Arabia is physically inactive, which is not suitable for health at all. According to recent studies, physical activity is one of the significant health-promoting practices (Kraus, 2015). Physical activity mainly decreases the many common diseases like diabetes, hypertension, cancer, and heart disease.
It also prevents one of the major problems regarding health, i.e., obesity. It improves an individual’s mental health by decreasing depression and anxiety, showing the inverse relation of health outcomes with the amount of physical activity performed (Alahmed, 2017).
The health sector of Saudi Arabia has ranked the growth of health care services at the overall rate of care, due to which betterment has been seen in the health range of Saudi Arabia (Almalki, 2011). Besides such improvements, the major issue in Saudi Arabia’s health sector is the language hurdle among the physician and their patients. Many interventions have been taken to solve this issue by health promotions using posters, leaflets, or other ways (Vyas, 2012).
After facing constant failure, alternative techniques have been applied, i.e., spreading awareness by using promotional items in health promotions, which was beneficial to give important messages to the public (Al Aboud, 2013). It succeeds whenever implemented correctly, which was also seen in TB patients (Alahmed, 2017).
Factors Affecting Public Health Promotion Intervention
Public Health revolves around the study of highlighting the issues that affect human health. It focuses on the preventive measures of diseases and prolonging humans’ lives by bringing awareness through different campaigns and promotions that could improve the public’s health. The research has been done to work on the public health sector as it is one of the significant elements that influence any country’s environment.
It is also essential to look out for the reasons that can affect the promotions and interventions to maintain public health stability. Social determinants include the status and affiliations that determine health (Shaw, 2008). In socio-economic factors, social attributes play a critical role in people’s lives, affecting each individual’s health in many ways.
The socio-economic factors are one of the major influences for public health in any country, whereas; cultural factors are based on the thoughts and behaviours shared by a group of people in any country. Culture always has a significant impact on all aspects of life. It contributes to every individual in an integrated pattern of values and morals.
In political factors, government policies and programs also profoundly affect health interventions in many ways (Mackenbach, 2014). At the same time, national health factors are about taking account of public health to local needs and includes the development level for the entire health sector.
Income is one of the main features that can affect public health promotion. It is directly proportional to individuals’ health related to the amount of money that a person is earning. When the making is high, the health is automatically influenced better, but if it is low, it can affect the quality of the food you take or the health services that are not affordable (Abel-Smith, 2016).
It can also be described as an example that not everyone can afford to see experienced doctors of sickness or other major health issues due to their high fees. It also goes in a way that they cannot purchase better foods to remain healthy. Income also influences the location one chose to live in as the surrounding influences health at a higher level. It can be perceived as lower earnings can lead to poorer health choices and increased health risks (Stoddart, 2017).
It is a crucial element that determines people’s social and economic position related to health outcomes. Education helps learn about the positive and negative aspects of health classified as better or poor health status. It elaborates the benefits of a healthy diet, increases the knowledge, and guides in making good choices compared to those who are not well educated or more aware of effective food products (Rosen, 2015).
The factor of employment contributes to health promotion intervention to enhance social status and self-esteem, leading to community life participation by bringing more opportunities that improve health and well-being. Career also surrounds being physically active or getting exhausted and tired due to long work hours that affect an individual’s health. The nature of the job is considered in this sector that can be classified as working at a farm, factory, chemicals or radiology, sports, and a proper organisation (Garthwaite, 2014).
Social Inequalities
There can be many cultures within a society, and it differs in views and norms that affect health in various ways. One major factor that developing countries face is social inequality which means all the people do not meet human needs. The lack of food, water, shelter, and clothing influences the health of the individuals. It affects the lifestyle and causes serious health problems as well. The easy access to these factors does create a difference in human beings’ lives as these are the most critical elements to survive (Berkman, 2014).
Early Marriages
Developing countries like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and others have some of the most disturbing factors that destroy a person’s health: early marriages. Children are forced to marry at the early stages in many rural areas in these developing countries, which is not suitable for their future health (García-Moreno, 2015). Since the people in rural areas are not so educated or aware of these things, it results in early pregnancies, labour complications, and severe infections that could lead to life-ending diseases.
Another factor that comes under the cultural environment is family. It means the number of people in a family that does make a difference at a greater rate. People in rural areas in developing countries usually have many children with very few gaps. They do not know the preventive measures or the effect of such fast pregnancies on health. Moreover, they also face financial issues due to less income, which cannot provide quality food and daily life necessities.
Poverty has been a critical factor in health determinants as it is directly linked with poor health. The less fortunate people are affected at so many levels that destroy their health. They are deprived of basic knowledge, money, and access to the services of health. Poor people cannot get treatment for diseases or see doctors due to a lack of money (Poverty and Health, 2014). Usually, only one member earns for the family that brings too much of a burden. Therefore, when everyday life’s basic needs are not easy for them to get, health is mostly the last thing to be given attention to for poor people.
Environment
The physical environment plays a great role in affecting people’s health positively or negatively. Clean air and water are two substantial means towards a healthy lifestyle. Lack of access to clean water and sanitation as well as polluted air develops major health issues. It also includes noise pollution, access to green and open space, transportation, housing, and food. Moreover, climate seasons influence the health of infants. They all are of equal importance in environmental conditions that directly affect health. Developing countries face air and noise pollution and the limited amount of clean water, which creates trouble for them, if not right away then in the future (Lü, 2015).
The living area of a person or improper untidy housing develops certain health conditions. Poor housing is associated with significant diseases like respiratory and skin infection, morbidity and mortality, and psychological effects. The overcrowded places usually do not consider a healthy lifestyle, whereas; homelessness develops sleep deprivation, mental health disorders, chronic stress, nutritional and psychic disorders.
Age and Gender
This has a significant part, like other factors, in determining health. People develop various health problems at different stages of life. For example, the diseases found in infants like pneumonia, diarrhoea, and skin rashes would not be quickly adopted by elders. In this manner, gender differences like men and women rarely have the same types of diseases. There are few common diseases found in women, like thyroid or kidney issues, whereas; men are mostly heart problems. This variance is the reason for distinctive lifestyles acquired by both of them.
Hire an Expert Dissertation Proposal Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in the academic style
- 100% Plagiarism-free & 100% Confidential
- Never resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Influence of Public Health on the Health Promotion Intervention
Health Promotions has progressed a lot in the past years, but some of its procedures are limited due to the assessment methods (Peltzer, 2011). Research is much needed in the evaluation of health importance and interventions. Health promotions focus on developing more significant results that create demanding and expensive interventions for both the physician and the patient.
Such interventions are being studied deeply using a high level of standardised protocols (McKenzie, 2016). The effectiveness of health promotions does not show the positive or negative outcomes of busy, understaffed public health clinics and huge health sectors (Baum, 2016).
The medical trend focuses on the surgical interference that gives instant outcomes. As compared to the health promotions, less research is done on their interventions. There is little research on interventions that report the population. The interventions that show adequate randomised trials results are not effective when applied to the common public (Schmidt 2015).
According to the RE-AIM model, the intellectualising is done on the general population’s health that affects the applied interventions in health promotions as five elements that include efficacy, implementation, learning, reach, and management (Ward, 2018).
When health sector interventions have been taken in health promotions, their main focus is constantly developing countries. Like in Malawi, it has been applied, and their outcome was good. Health promotions are also designed specifically for children and young people. It depends on the requirement of public health. It helps in dealing with the mortality or morbidity issue and others also (Eldredge, 2016).
Overall, developing countries show the interventions in health promotions, and their applications differ a lot according to sustainability and effectiveness. If the government supports health promotions rightfully, it puts a high level of impact on public health.
In Ethiopia, hygiene practices are very poor, and the sanitary situation is insufficient, resulting in the elevation of transmissible diseases in the population and worsen public health. Health promotion interventions are done to spread knowledge and apply hygiene practices in rural schools of Ethiopia and improve their hygiene characteristics (Vivas, 2010).
Children were targeted for promotions because they are more approachable for adopting healthy attitudes by them it will spread among the families and community (Lopez-Quintero, 2009).
Brazil is also considered a developing country, in which health promotions have been implemented many times in the past and present. Currently, the major concern is heart diseases, hygiene, and unhealthy lifestyle issue. The health promotions did interventions for the betterment of living and unhealthy situation of people.
The infectious disease in Brazil was a high level of public health issue in the country before. Still, after many interventions regarding health promotions, including campaigns, such disease decreased from the government. Now circulatory diseases are the main reason for mortality. All of the issues needed basin sanitation awareness and health education.
The particular activities of health promotions include improving physical activity practices, reducing smoking, decreasing death and morbidity rate due to any disease or accident, reducing alcohol intake, adopting healthy habits, and inhibiting violence (Horta, 2017). Health promotion was also done in schools, leading to positive outcomes and a lot of betterment. The growth of the Brazilian Unified Health System has been influenced by Brazil’s public health sector (Ramos, 2014).
Research Methodology
Research philosophy.
Research philosophy describes the set of beliefs that the researcher has while carrying out the research. It provides the significance of how the data will be analysed and used in the research. The research philosophies are categorised into different types that can be used according to the researcher’s analysis and feasibility. The research philosophies that are commonly used in the study are positivism, interpretivism, and realism (Merriam and Tisdell, 2015)
The study in hand has used the interpretivism philosophy for conducting the research. This philosophy is based on the social sciences and focuses on the disciplines and the school of thought that the respondents carry out in the research. On the other hand, the positivism philosophy is based on realistic data and carries out the information found in reality.
The realism philosophy is commonly observed in scientific research and collects data based on experiments and scientific tests. The researcher may face problems with interpretivism philosophy because the respondents are not observed to provide justified opinions for theirs. The problems may also be faced in interpreting views carried out by the researcher (Teherani et al., 2015). Concerning the attitudes and behaviours, interpretivism philosophy is highly suitable for the research that is being observed.
The following study will use interpretivism to identify the impact of public health on health promotion interventions within Saudi Arabia because the research is purely based on qualitative analysis; therefore, interpretivism philosophy helps to understand the in-depth information about variables.
Research Approach
According to the study of Sekaran and Bougie (2016) research approach is stated as the pattern that has been selected for conducting the research. The research approaches are mainly divided into inductive and deductive approaches that provide research patterns to get significant results.
Both the approaches have their existence and vary based on the hypothesis and models used in the research. The inductive approach provides the research pattern that starts with observation and tests conducted by the researcher. It moves on to the identification of patterns used in the research and finalises the theory.
On the other hand, the deductive approach is based on the theory that has been selected. The researcher carries out the hypothesis and develops observations and tests for accepting or rejecting the idea based on the theory. The statement and tests confirm and reject the hypothesis that carries out the result of the research carried out.
For the research in hand, the approach that has been used is the deductive approach as it has used the theory that has been used before and has developed. The researcher has also conducted tests and observations to identify whether the hypothesis can be accepted or rejected. The deductive approach justifies the research carried out and is correct (Silverman, 2016). Moreover, the researcher may not lead to falsification and gets the justified results of the approaches used.
The following study will use the inductive research approach because the underlying factors of public health promotions and their impact on health promotion interventions were analysed through systematic analysis of information. The deductive approach provides a structured way of examining Saudi Arabia’s case to assess the impact.
Type of Investigation
Marshall and Rossman (2014) have identified three types of research investigation under which the research is carried out. The types of investigation methods used in the researches are exploratory, explanatory, and descriptive research. The experimental research refers to the explore the new techniques and phenomenon that has not been used before.
As the name identifies, it provides the significance of starting the research from the groundwork. Exploratory research is aimed to find something new and carry out the research in a new direction. Descriptive research tends to explore and explain the phenomenon in detail. It provides additional information regarding the topic and fills the missing part of the research. It carries out the gap analysis and gets the work done until the gap is filled (Lewis, 2015).
Another type of investigation method followed by the researchers is explanatory research. It is also known as causal research and determines the identification of cause and effect relationships. The explanatory research is determined to explain the phenomenon that has been used before in previous researches.
It explains the description of topics and determines the causes and effects of the particular topic on another (McCusker and Gunaydin, 2015). The following research is based on the cause and effect relationship, and hence the type of investigation used in the next study is explanatory research. The cause and effect relationship used in the explanatory research has provided the best fit for the relationship between the variables.
For the following study, the researcher will use the descriptive method of investigation to examine the relationship between public health and health promotion interventions. The explanatory study will provide information about how public health impacts the various health promotion activities.
Research Design
The studies of Choy, (2014) have determined the types of research design used in the following research. The design is categorised into three main types that are qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods. All three types are used according to the needs and requirements of the selected topic. Qualitative research is dependent upon the collection of behavioural data.
The data is collected and analysed in the form of statements and descriptions used to carry out the results. Another commonly used research design is the quantitative method. The data is collected in numeric and numbers that are analysed using statistical tools and techniques. Another commonly used method is mixed (Merriam and Tisdell, 2015).
The following research will use qualitative research design methods to examine how public health affects health promotion intervention. Using the qualitative method, the researcher will shed light on the existing articles and journals collected by different researchers and scholars.
Data Collection Method
The identified data collection methods used in the researches are categorised into primary and secondary research. The researcher collects data from the respondents based on the primary and secondary methods of collecting data. Both the methods have their ways of collecting data. The data collection for the primary research is interviews, questionnaires, experiments, and observation.
On the other hand, is the data collected from previous studies. The research, based on secondary data, uses the information available on the internet and carries out the data analysis (Mertens, 2014).
The study in hand has used the primary method of data collection. The data has been collected based on the qualitative methods and has gathered the information from the primary sources, including questionnaire surveys, interviews, and first-hand observation of the researcher. The researcher has faced some constraints while carrying out the primary data that is limited time and cost used for the research. Respondents are not ready to provide detailed information regarding their feelings and practices (Silverman, 2016).
The data collection method selected for this study is the secondary method of data collection. The researcher will use the second method to conduct a systematic review and answer the study’s research questions. The study will also select articles from 2010 to 2018, and a health-related database will be used for examining the information.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion criteria refer to the characteristics of the study’s characteristics that are included in particular research. On the other hand, exclusion criteria refer to specific characteristics or elements that disqualify the subjects from being included in the research. The inclusion criteria of this research are different studies related to public health and public health promotion.
Majorly the studies taken into account are those carried out in the region of Saudi Arabia and other parts of the Middle East. The exclusion criteria for the research are the studies that do not belong to credible journals and publishers.
Sampling Method, Technique, and Sample Size
Sampling is an integral part of the research and determines the population selected for carrying out the research. The selected population for collecting the data is known as the sample. The sampling method is further divided into non-probability and probability sampling. Probability sampling provides an equal chance to all the sample population for getting the responses. On the other hand is the non-probability sampling does not provide an equal chance to all the respondents (Silverman, 2016).
The following study is based on non-probability sampling. The technique that has been used in the study is convenience sampling. The researcher has carried out the respondents’ information based on convenience for gathering data through a systematic review of articles and journals. From 2010 to 2018, the articles will be selected for obtaining information about health promotions and interventions therefore, an article out from this domain will not be used.
Data Analysis Method
According to Smith, (2015), data analysis is a critical stage of the research process. The tool that has been used in the following research is thematic analysis because the study is based on qualitative techniques. The interviews gathered by the researcher and the observations have been analysed using the method of thematic analysis.
The thematic analysis is based on the pinpointing and examination of the patterns within the data that has been collected. On the other hand, the tool for quantitative analysis is SPSS. As the study is qualitative, so the data has been analysed using themes and defining them according to the research. The researcher will use content analysis to analyse the information obtained from different sources and critically examine the data about health promotion interventions, particularly in Saudi Arabia.
The researcher will conduct a systematic review through existing studies and with the help of a descriptive approach. A systematic literature review is going to be carried out in five steps (Khan et al. 2003). The research question has been framed in the first step, after which relevant publications regarding the research questions are identified. The next step covers the assessment of the quality of the study. The next step is related to summarising the evidence that has been collected. Lastly, the findings collected from different relevant articles are interpreted.
Ethical Considerations
It is an integral part of the research and identifies the researcher’s ethical considerations while carrying out the research. For the following research, the researcher has ensured the respondents that the data collected is valid and authentic. The confidentiality of the respondent’s information has been considered. The researcher has avoided any sort of unethical activity while carrying out the research.
If you need assistance with writing your dissertation proposal, our professional dissertation proposal writers are here to help!
Abel-Smith, B. (2016). An introduction to health: policy, planning and financing . Routledge.
Al Aboud, K., Jameel, W., Al Asmari, Z., Al Osaimy, H., Al Sobiani, A., Salam, S. A., & Al Zahrani, Y. (2013). Use of Public Health Promotion Items to Improve Health in Saudi Arabia. Central Asian Journal of Global Health , 2 (2).
Alahmed, Z., & Lobelo, F. (2017). Physical activity promotion in Saudi Arabia: A critical role for clinicians and the health care system. Journal of Epidemiology and Global Health .
Almalki, M., FitzGerald, G., & Clark, M. (2011). Health care system in Saudi Arabia: an overview/Aperçu du système de santé en Arabie saoudite. Eastern Mediterranean health journal , 17 (10), 784.
Anderson, L. M., Brownson, R. C., Fullilove, M. T., Teutsch, S. M., Novick, L. F., Fielding, J., & Land, G. H. (2005). Evidence-based public health policy and practice: promises and limits. American Journal of Preventive Medicine , 28 (5), 226-230.
Baum, F. (2016). The new public health (No. Ed. 4). Oxford University Press.
Berkman, L. F., Kawachi, I., & Glymour, M. M. (Eds.). (2014). Social epidemiology . Oxford University Press.
Boulware, L. E., Cooper, L. A., Ratner, L. E., LaVeist, T. A., & Powe, N. R. (2016). Race and trust in the health care system. Public health reports .
Brinkmann, S., 2014. Interview. In Encyclopedia of critical psychology (pp. 1008-1010). Springer, New York.
Brownson, R. C., Deshpande, A. D., & Gillespie, K. N. (2017). Evidence-based public health . Oxford university press.
Choy, L.T., 2014. The strengths and weaknesses of research methodology: comparison and complimentary between qualitative and quantitative approaches. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 19(4), pp.99-104.
Duplaga, M. (2015). The evolving concept of health promotion: definitions, outcomes and classification of interventions. Zdr Publiczne Zarządzanie , 2015 , 141149.
Eldredge, L. K. B., Markham, C. M., Ruiter, R. A., Kok, G., & Parcel, G. S. (2016). Planning health promotion programs: an intervention mapping approach . John Wiley & Sons.
Fleming, M. L., & Parker, E. (2014). Introduction to public health . Elsevier Australia.
Frieden, T. R. (2010). A framework for public health action: the health impact pyramid. American journal of public health , 100 (4), 590-595.
Frohlich, K. L., & Potvin, L. (2008). Transcending the known in public health practise: the inequality paradox: the population approach and vulnerable populations. American journal of public health , 98 (2), 216-221.
García-Moreno, C., Zimmerman, C., Morris-Gehring, A., Heise, L., Amin, A., Abrahams, N., … & Watts, C. (2015). Addressing violence against women: a call to action. The Lancet , 385 (9978), 1685-1695.
Garthwaite, C., Gross, T., & Notowidigdo, M. J. (2014). Public health insurance, labour supply, and employment lock. The Quarterly Journal of Economics , 129 (2), 653-696.
Glanz, K., & Bishop, D. B. (2010). The role of behavioural science theory in the development and implementation of public health interventions. Annual review of public health, 31, 399-418.
Gostin, L. O., & Wiley, L. F. (2016). Public health law: power, duty, restraint . Univ of California Press.
Horta, R. L., Andersen, C. S., Pinto, R. O., Horta, B. L., Oliveira-Campos, M., Andreazzi, M. A. R. D., & Malta, D. C. (2017). Health promotion in the school environment in Brazil. Revista de saude publica , 51 , 27.
Khan, K. S., Kunz, R., Kleijnen, J., & Antes, G. (2003). Five steps to conducting a systematic review. Journal of the royal society of medicine, 96(3), 118-121.
Kok, M. O., Vaandrager, L., Bal, R., & Schuit, J. (2012). Practitioner opinions on health promotion interventions that work: Opening the ‘black box of a linear evidence-based approach. Social science & medicine , 74 (5), 715-723.
Kraus, W. E., Bittner, V., Appel, L., Blair, S. N., Church, T., Després, J. P., … & Vafiadis, D. K. (2015). American Heart Association Physical Activity Committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Metabolic Health, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Hypertension, and Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing. The National Physical Activity Plan: a call to action from the American Heart Association: a science advisory. Circulation , 131 (21), 1932-40.
Leischik, R., Dworrak, B., Strauss, M., Przybylek, B., Schöne, D., Horlitz, M., Mügge, A. and Dworrak, T., 2016. Plasticity of health. German Journal of Medicine , 1 , pp.1-17.
Lewis, S., 2015. Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. Health promotion practice, 16(4), pp.473-475.
Lopez-Quintero, C., Freeman, P., & Neumark, Y. (2009). Hand washing among school children in Bogota, Colombia. American Journal of Public Health , 99 (1), 94-101.
Lü, J., Liang, L., Feng, Y., Li, R., & Liu, Y. (2015). Air pollution exposure and physical activity in China: current knowledge, public health implications, and future research needs. International journal of environmental research and public health , 12 (11), 14887-14897.
Lupton, D. (2014). Health promotion in the digital era: a critical commentary. Health promotion international , 30 (1), 174-183.
Macfarlane, A. (2005). What are the main factors that influence disease prevention and health promotion programmes in children and adolescents? Copenhagen, WHO Regional Office for Europe (Health Evidence Network report .
Mackenbach, J. P. (2014). Political determinants of health.
Mackey, A. and Gass, S.M., 2015. Second language research: Methodology and design. Routledge.
Marshall, C. and Rossman, G.B., 2014. Designing qualitative research. Sage publications.
McCusker, K. and Gunaydin, S., 2015. Research using qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods and choice based on the research. Perfusion, 30(7), pp.537-542.
McKenzie, J. F., Neiger, B. L., & Thackeray, R. (2016). Planning, implementing & evaluating health promotion programs: A primer. Pearson.
McKenzie, J. F., Neiger, B. L., & Thackeray, R. (2016). Planning, implementing & evaluating health promotion programs: A primer . Pearson.
Merriam, S.B. and Tisdell, E.J., 2015. Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. John Wiley & Sons.
Mertens, D.M., 2014. Research and evaluation in education and psychology: Integrating diversity with quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods. Sage publications.
Ministry of Health. Survey of Health Information in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia 2013.
Naidoo, J., & Wills, J. (2016). Foundations for Health Promotion-E-Book . Elsevier Health Sciences.
Peltzer, K., & Pengpid, S. (2011). Health Behaviuor Interventions In Developing Countries. Malawi Medical Journal , 26 (2), 50-50.
Poverty and Health, (2014). Retrieved from <http://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/health/brief/poverty-health> (Accessed on 19/04/2018)
Ramos, L. R., Malta, D. C., Gomes, G. A. D. O., Bracco, M. M., Florindo, A. A., Mielke, G. I., … & Hallal, P. C. (2014). Prevalence of health promotion programs in primary health care units in Brazil. Revista de saude publica , 48 (5), 837-844.
Rosen, G. (2015). A history of public health . JHU Press.
Rosenbaum, S. (2011). The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act: implications for public health policy and practice. Public health reports , 126 (1), 130-135.
Schmidt, H., Gostin, L. O., & Emanuel, E. J. (2015). Public health, universal health coverage, and Sustainable Development Goals: can they coexist?.
Sekaran, U. and Bougie, R., 2016. Research methods for business: A skill-building approach. John Wiley & Sons.
Sharaf, F. (2010). Impact of health education on compliance among patients of chronic diseases in Al Qassim, Saudi Arabia. International journal of health sciences, 4(2), 139.
Shaw, D. (2008). Social determinants of health. Clinical Medicine , 8 (2), 225-226.
Silverman, D. ed., 2016. Qualitative research. Sage.
Sitko, S. J., Kowalska-Bobko, I., Mokrzycka, A., Zabdyr-Jamróz, M., Domagała, A., Magnavita, N., … & Golinowska, S. (2016). Institutional analysis of health promotion for older people in Europe-concept and research tool. BMC health services research , 16 (5), 327.
Smith, J.A. ed., 2015. Qualitative psychology: A practical guide to research methods. Sage.
Stoddart, G. L., & Evans, R. G. (2017). Producing health, consuming health care. In Why are some people healthy and others not? (pp. 27-64). Routledge.
Taylor, S.J., Bogdan, R. and DeVault, M., 2015. Introduction to qualitative research methods: A guidebook and resource. John Wiley & Sons.
Teherani, A., Martimianakis, T., Stenfors-Hayes, T., Wadhwa, A. and Varpio, L., 2015. Choosing a qualitative research approach. Journal of graduate medical education, 7(4), pp.669-670.
Vivas, A., Gelaye, B., Aboset, N., Kumie, A., Berhane, Y., & Williams, M. A. (2010). Knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) of hygiene among school children in Angolela, Ethiopia. Journal of preventive medicine and hygiene , 51 (2), 73.
Vyas, A. N., Landry, M., Schnider, M., Rojas, A. M., & Wood, S. F. (2012). Public health interventions: reaching Latino adolescents via short message service and social media. Journal of medical Internet research , 14 (4).
Ward, S., Chow, A. F., Humbert, M. L., Bélanger, M., Muhajarine, N., Vatanparast, H., & Leis, A. (2018). Promoting physical activity, healthy eating and gross motor skills development among preschoolers attending childcare centres: Process evaluation of the Healthy Start-Départ Santé intervention using the RE-AIM framework. Evaluation and program planning , 68 , 90-98.
Watts, N., Adger, W. N., Agnolucci, P., Blackstock, J., Byass, P., Cai, W., … & Cox, P. M. (2015). Health and climate change: policy responses to protect public health. The Lancet , 386 (10006), 1861-1914.
Weine, S., Eisenman, D. P., Kinsler, J., Glik, D. C., & Polutnik, C. (2017). Addressing violent extremism as public health policy and practice. Behavioral sciences of terrorism and political aggression , 9 (3), 208-221.
WHO, (2011). Health care system in Saudi Arabia: an overview. Retrieved from http://www.emro.who.int/emhj-volume-17/volume-17-issue-10/article-11.html (Accessed on 4/20/18)
WHO, (2018). Public health services. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/europe/health-topics (Accessed on 4/20/18)
World Health Organization. (2009). Milestones in health promotion: Statements from global conferences.
World Health Organization. (2012). Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study: international report from the 2009/2010 survey. Copenhagen: WHO .
Yoshikawa, H., Aber, J. L., & Beardslee, W. R. (2012). The effects of poverty on the mental, emotional, and behavioural health of children and youth: implications for prevention. American Psychologist , 67 (4), 272.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a masters dissertation proposal.
To write a Masters dissertation proposal:
- Choose a relevant topic.
- Provide context and background.
- State research questions and objectives.
- Outline the methodology.
- Include a literature review.
- Specify the significance of the study.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Recommendations
Public comments and nominations, about the uspstf.
- Recommendation In Progress
- Draft Recommendation: Breast Cancer: Screening
Draft Recommendation Statement
Breast cancer: screening, may 09, 2023.
Recommendations made by the USPSTF are independent of the U.S. government. They should not be construed as an official position of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality or the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Update in Progress for Breast Cancer: Screening
Breast Cancer Screening Saves Lives: New Draft Available
The Task Force is now recommending that all women get screened every other year starting at age 40. The draft recommendation also urgently calls for research in key areas.
Explore this page to learn more about the latest Task Force draft recommendation on screening for breast cancer.
Dr. Carol Mangione shares key information about the draft.
Frequently asked questions.
In this draft recommendation statement, the Task Force recommends that all women get screened for breast cancer every other year starting at age 40 to reduce their risk of dying from this disease. This is a B grade .
We are also urgently calling for more research that will allow us to build on our existing recommendations and help all women live longer and healthier lives. Specifically, we need to know how best to address the health disparities across screening and treatment experienced by Black, Hispanic, Latina, Asian, Pacific Islander, Native American, and Alaska Native women.
We also need studies showing how additional screening with breast ultrasound or MRI might help women with dense breasts and evidence on the benefits and harms of screening in older women. These are I statements .
New and more inclusive science about breast cancer in people younger than 50 has enabled us to expand our prior recommendation and encourage all women to get screened in their 40s. We have long known that screening for breast cancer saves lives, and the science now supports all women getting screened, every other year, starting at age 40.
Nearly half of all women have dense breasts, which increases their risk for breast cancer and means that mammograms do not work as well for them. Women are generally told by their clinician that they have dense breasts after they've had a mammogram. These women deserve to know whether and how additional screening might help them stay healthy. Unfortunately, there is not yet enough evidence for the Task Force to recommend for or against additional screening with breast ultrasound or MRI. We are urgently calling for more research on whether and how additional screening might help women with dense breasts find cancers earlier.
Black women are 40 percent more likely to die from breast cancer than White women and too often get aggressive cancers at young ages. Ensuring Black women start screening at 40 is an important first step, yet it is not enough to improve these inequities. It's important that healthcare professionals involve patients in a conversation on how best to support them to ensure equitable follow-up after screening and timely and effective treatment of breast cancer.
We are urgently calling for more evidence to better understand whether Black women could potentially be helped by different screening strategies.
Get the Facts
- May 25, 2023 | MedPage Today (USPSTF Opinion Piece) USPSTF: What Our Patients With Dense Breasts Deserve to Know May 9, 2023 | USPSTF Task Force Issues Draft Recommendation Statement on Screening for Breast Cancer May 9, 2023 | PBS News Hour New guidelines recommend earlier mammograms amid rise in breast cancer among younger women May 9, 2023 | The Washington Post Health panel recommends women get screening mammograms at age 40
Media Contact
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: (301) 951-9203
- Visit the Newsroom
Recommendation Summary
Pathway to benefit.
To achieve the benefit of screening and mitigate disparities in breast cancer mortality by race and ethnicity, it is important that all persons with abnormal screening mammography receive equitable and appropriate followup evaluation and additional testing, inclusive of indicated biopsies, and that all persons diagnosed with breast cancer receive effective treatment.
Additional Information
- Supporting Evidence and Research Taxonomy
- Related Resources & Tools
- Draft Modeling Report (May 09, 2023)
- Draft Evidence Review (May 09, 2023)
- Final Research Plan (May 06, 2021)
- Draft Research Plan (January 21, 2021)
- Screening for Breast Cancer (Consumer Guide): Draft Recommendation | Link to File
Recommendation Information
Full recommendation:.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) makes recommendations about the effectiveness of specific preventive care services for patients without obvious related signs or symptoms to improve the health of people nationwide.
It bases its recommendations on the evidence of both the benefits and harms of the service and an assessment of the balance. The USPSTF does not consider the costs of providing a service in this assessment.
The USPSTF recognizes that clinical decisions involve more considerations than evidence alone. Clinicians should understand the evidence but individualize decision-making to the specific patient or situation. Similarly, the USPSTF notes that policy and coverage decisions involve considerations in addition to the evidence of clinical benefits and harms.
The USPSTF is committed to mitigating the health inequities that prevent many people from fully benefiting from preventive services. Systemic or structural racism results in policies and practices, including health care delivery, that can lead to inequities in health. The USPSTF recognizes that race, ethnicity, and gender are all social rather than biological constructs. However, they are also often important predictors of health risk. The USPSTF is committed to helping reverse the negative impacts of systemic and structural racism, gender-based discrimination, bias, and other sources of health inequities, and their effects on health, throughout its work.
Among all U.S. women, breast cancer is the second most common cancer and the second most common cause of cancer death. In 2022, an estimated 43,250 women died of breast cancer. 1 Non-Hispanic White women have the highest incidence of breast cancer (5-year age-adjusted incidence rate, 137.6 cases per 100,000 women) and non-Hispanic Black women have the second highest incidence rate (5-year age-adjusted incidence rate, 129.6 cases per 100,000 women). 2 Incidence has gradually increased among women ages 40 to 49 years from 2000 to 2015 but increased more noticeably from 2015 to 2019, with a 2.0% average annual increase. 3 Despite having a similar or higher rate of mammography screening, 4 Black women are more likely to be diagnosed with breast cancer beyond stage 1 than other racial and ethnic groups, are more likely to be diagnosed with triple-negative cancers (i.e., ER-, PR-, and HER2-), which are more aggressive tumors, compared with White women, 5 and are approximately 40% more likely to die from breast cancer compared with White women. 6
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concludes with moderate certainty that biennial screening mammography in women ages 40 to 74 years has a moderate net benefit .
The USPSTF concludes that the evidence is insufficient to determine the balance of benefits and harms of screening mammography in women age 75 years or older.
The USPSTF concludes that the evidence is insufficient to determine the balance of benefits and harms of supplemental screening for breast cancer with breast ultrasound or MRI, regardless of breast density.
Go to Table 1 for more information on the USPSTF recommendation rationale and assessment. For more details on the methods the USPSTF uses to determine the net benefit, see the USPSTF Procedure Manual. 7
Patient Population Under Consideration
These recommendations apply to cisgender women and all other persons assigned female at birth (including transgender men and nonbinary persons) age 40 years or older at average risk of breast cancer. This is because the net benefit estimates are driven by sex (i.e., female) rather than gender identity, although the studies reviewed for this recommendation generally used the term “women.” These recommendations apply to persons with a family history of breast cancer (i.e., those with a first-degree relative with breast cancer) and to persons who have other risk factors such as having dense breasts. They do not apply to persons who have a genetic marker or syndrome associated with a high risk of breast cancer (e.g., BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic mutations), a history of high-dose radiation therapy to the chest at a young age, or previous breast cancer or a high-risk breast lesion on previous biopsies.
Screening Tests
Both digital mammography (DM) and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT or “3D mammography”) are effective mammographic screening modalities. DBT must be accompanied by traditional DM or synthetic DM, which is a two-dimensional image constructed from DBT data; 8 , 9 hereafter, references to DBT will imply concurrent use with DM or synthetic DM. In general, studies have reported small increases in positive predictive value with DBT compared with DM. Trials reporting on at least two consecutive rounds of screening have generally found no statistically significant difference in breast cancer detection or in tumor characteristics (tumor size, histologic grade, or node status) when comparing screening with DBT vs. DM. 4
The Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) is a network of six active breast imaging registries and two historic registries, providing a large observational database related to breast cancer screening. 10 Collaborative modeling, using inputs from BCSC data, suggests similar benefits and fewer false-positive results with DBT compared with DM. 11
Screening Interval
Available evidence suggests a more favorable trade-off of benefits vs. harms with biennial vs. annual screening. BCSC data showed no difference in detection of stage IIB+ cancers and cancers with less favorable prognostic characteristics with annual vs. biennial screening interval for any age group, 12 and modeling data estimate that biennial screening has a more favorable balance of benefits to harms compared with annual screening. 11
Treatment or Intervention
Breast cancer treatment regimens are highly individualized according to each patient’s clinical status, cancer stage, tumor biomarkers, clinical subtype, and personal preferences. 13 Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a noninvasive condition with abnormal cells in the breast duct lining and there is uncertainty regarding the prognostic importance of DCIS. Consequently, there is clinical variability in the treatment approach when DCIS is identified at screening. It is unknown what proportion of screen-detected DCIS represents overdiagnosis (i.e., a lesion that would not have led to health problems in the absence of detection by screening). In general, DCIS treatment, which may include surgery, radiation, and endocrine treatment, is intended to reduce the risk for future invasive breast cancer.
Disparities in Breast Cancer Outcomes and Implementation Considerations
Mortality from breast cancer is highest for Black women even when accounting for differences in age and stage at diagnosis; mortality is approximately 40% higher for Black women compared with White women. 6 While the underlying causes of this disparity are complex, the National Institute of Minority Health and Disparities has developed a framework that recognizes multiple determinants, including the healthcare system, the sociocultural and built environments, behavioral factors, and genetic factors, that can contribute to health inequities. 14 Inequities in breast cancer mortality can be examined at each step along the cancer screening, diagnosis, treatment, and survival pathway with these factors in mind. The higher mortality rate for Black women diagnosed with breast cancer in the United States aligns with other health inequities that are attributed to the effects of structural racism, which include inequalities in resources, harmful exposures, and access to and delivery of high-quality healthcare. 15-17 Racial and economic residential segregation driven by discriminatory housing policies has been associated with poorer breast cancer survival. Residential segregation also increases exposure to toxic environments such as air pollution, industrial waste, and built environments that do not support health, and stressful life conditions, which can increase cancer risk. 18-20
Black women have a higher incidence of breast cancer with at least one negative molecular marker, and the incidence of triple-negative cancers (i.e., ER-, PR-, and HER2-) is twice as high compared with White women (24.1 vs. 12.4 cases per 100,000 women). 5 The higher incidence of negative hormonal receptor (HR) status leads to worse outcomes because these subtypes are less readily detected through screening and less responsive to current therapy, 21 and triple-negative cancers are more likely to be aggressive and diagnosed at later stages than other subtypes. It is important to note that observed regional differences in the incidence of HR-negative cancer within and between racial groups suggest that environmental factors and social determinants of health, including racism, are largely responsible for the differential risk of developing HR-negative cancer. 22 , 23 Although differences in the incidence of cancer subtypes explain some of the differences in breast cancer mortality, racial differences in mortality within subtypes point to barriers to obtaining high-quality healthcare and disparities in screening followup and treatment initiation as contributors. 22
Of note, Black women have a similar or higher rate of self-reported mammography screening as all women (84.5% vs 78%, respectively, in the past 2 years). 4 However, benefits from mammography screening require initiation and completion of appropriate and effective followup evaluation and treatment. Both screening and guideline-concordant treatment are essential for reducing breast cancer mortality, 24 highlighting the importance of timely and effective treatment at the earliest stage of diagnosis. Delays and inadequacies in the diagnostic and treatment pathway downstream from screening likely contribute to increased mortality compared with women receiving prompt, effective care.
Disparities in followup after screening and treatment have been observed for Black, Hispanic, and Asian women. 25-34 Adjuvant endocrine therapy reduces the risk of cancer recurrence among individuals with HR-positive cancers, but long-term adherence can be difficult. Black women are more likely to discontinue adjuvant endocrine therapy compared with White women, in part due to greater physical (vasomotor, musculoskeletal, or cardiorespiratory) and psychological (distress or despair) symptom burdens. 33 , 34 Improvements in access to effective healthcare, removal of financial barriers, and use of support services to ensure equitable followup after screening and timely and effective treatment of breast cancer have the potential to reduce mortality for individuals experiencing disparities related to racism, rural location, 35 low income, or other factors associated with lower breast cancer survival.
Suggestions for Practice Regarding the I Statement
Potential preventable burden.
Breast cancer incidence increases with age and peaks among persons ages 70 to 74 years, though rates in persons age 75 years or older remain high (460.2 and 416.5 cases per 100,000 women ages 75–79 and 80–84 years, respectively, compared with 477.7 cases per 100,000 women ages 70–74 years), and mortality from breast cancer increases with increasing age. 36 , 37 However, no randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of breast cancer screening included women age 75 years or older. 4 Collaborative modeling suggests that screening in women age 75 years or older is of benefit, 11 but a trial emulation found no benefit with breast cancer screening in women ages 75 to 84 years. 38 Thus, there is insufficient evidence to recommend for or against screening mammography in women age 75 years or older.
There is insufficient evidence about the effect of supplemental screening using breast ultrasonography or MRI on health outcomes such as breast cancer morbidity and mortality in women with dense breasts who have an otherwise normal screening mammogram. Dense breasts are associated with both reduced sensitivity and specificity of mammography and with an increased risk of breast cancer. 39 , 40 However, increased breast density itself is not associated with higher breast cancer mortality among women diagnosed with breast cancer, after adjustment for stage, treatment, method of detection, and other risk factors, according to data from the BCSC. 41
Potential Harms
Potential harms of screening mammography include false-positive results, which may lead to psychological harms, additional testing, and invasive followup procedures; overdiagnosis and overtreatment of lesions that would not have led to health problems in the absence of detection by screening; and radiation exposure.
Current Practice
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show that as of 2015, over 50% of women age 75 years or older reported having a mammogram within the past 2 years. 42 At the present time, 38 states and the District of Columbia require patient notification of breast density when mammography is performed; in some states, legislation also includes notification language informing women that they should consider adjunctive screening. 43 Starting in September 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration will require mammography centers to notify patients of their breast density, inform them that dense breast tissue raises the risk of breast cancer and makes it harder to detect on a mammogram, and that other imaging tests may help to find cancer. 44
Additional Tools and Resources
The National Cancer Institute has information on breast cancer screening for healthcare professionals ( https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/hp/breast-screening-pdq ) and for patients ( https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/breast-screening-pdq ).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has information on breast cancer screening ( https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/basic_info/screening.htm ).
Other Related USPSTF Recommendations
The USPSTF has made recommendations about the use of medications to reduce women’s risk for breast cancer, 45 as well as risk assessment, genetic counseling, and genetic testing for BRCA1 - or BRCA2 -related cancer. 46
When final, this recommendation will update the 2016 recommendation on breast cancer screening. In 2016, the USPSTF recommended biennial screening mammography for women ages 50 to 74 years and individualizing the decision to undergo screening for women ages 40 to 49 years, based on factors such as individual risk and personal preferences and values. The USPSTF concluded that the evidence was insufficient to assess the benefits and harms of DBT as a primary screening method; the balance of benefits and harms of adjunctive screening for breast cancer using breast ultrasonography, MRI, or DBT in women identified to have dense breasts on an otherwise negative screening mammogram; and the balance of benefits and harms of screening mammography in women age 75 years or older. 47 For the current draft recommendation, the USPSTF recommends biennial screening mammography for women ages 40 to 74 years. The USPSTF again finds that the evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of supplemental screening for breast cancer using breast ultrasonography or MRI in women identified to have dense breasts on an otherwise negative screening mammogram and the balance of benefits and harms of screening mammography in women age 75 years or older. Current evidence suggests that both DM and DBT are effective primary screening modalities.
Scope of Review
To update its 2016 recommendation, the USPSTF commissioned a systematic review on the comparative effectiveness of different mammography-based breast cancer screening strategies by age to start and stop screening, screening interval, modality, use of supplemental imaging, or personalization of screening for breast cancer on the incidence and progression to advanced breast cancer, breast cancer morbidity, and breast cancer–specific or all-cause mortality. The review also assessed the harms of different breast cancer screening strategies. 4 Evidence from the trials that established breast cancer screening effectiveness has not been updated, as there are no new studies that include a group that is not screened. Analyses from prior reviews of that evidence were considered foundational evidence for the current recommendation.
In addition to the systematic evidence review, the USPSTF commissioned collaborative modeling studies from CISNET (Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network) to provide information about the benefits and harms of breast cancer screening strategies that vary by the ages to begin and end screening, screening modality, screening interval, and by race. 11 The modeling studies complement the evidence that the systematic review provides.
In alignment with the USPSTF’s commitment to improve health equity, the evidence review included contextual questions on the drivers behind and approaches to address disparities in health outcomes related to breast cancer, particularly the higher mortality in Black women, and the CISNET collaborative modeling investigated outcomes of screening for Black women.
Benefits and Comparative Benefits of Early Detection and Treatment
Randomized trials that began enrolling participants more than 30 to 40 years ago have established the effectiveness of screening mammography to reduce breast cancer mortality. A meta-analysis conducted in support of the 2016 USPSTF breast cancer screening recommendation found that screening mammography was associated with relative risk (RR) reductions in breast cancer mortality of 0.88 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.73 to 1.00; 9 trials) for women ages 39 to 49 years, 0.86 (95% CI, 0.68 to 0.97; 7 trials) for women ages 50 to 59 years, 0.67 (95% CI, 0.54 to 0.83; 5 trials) for women ages 60 to 69 years, and 0.80 (95% CI, 0.51 to 1.28; 3 trials) for women ages 70 to 74 years, 48 and an updated analysis of three Swedish screening trials reported a 15% relative reduction in breast cancer mortality for women ages 40 to 74 years (RR, 0.85 [95% CI, 0.73 to 0.98]). 49 Only one of these trials enrolled a significant proportion of Black women. 50 None of the trials nor the combined meta-analysis demonstrated a difference in all-cause mortality with screening mammography. The current USPSTF review focused on the comparative benefits of different screening strategies.
Age to Start or Stop Screening
The USPSTF did not identify any RCTs designed to test the comparative effectiveness of different ages to start or stop screening that reported morbidity, mortality, or quality of life outcomes. One trial emulation study (N=264,274), using a random sample from Medicare claims data, estimated the effect of women stopping screening at age 70 years compared with those who continued annual screening after age 70 years. Based on survival analysis, this study reported that continued screening between the ages of 70 and 74 years was associated with a 22% decrease in the risk of breast cancer mortality, compared with a cessation of screening at age 70 years, and there was no difference in the hazard ratio or absolute rates of breast cancer mortality with continued screening vs. discontinued screening from ages 75 to 84 years. 38
Collaborative modeling data estimated that compared with biennial screening from ages 50 to 74 years, biennial screening starting at age 40 years until 74 years would lead to 1.3 additional breast cancer deaths averted per 1,000 women screened over a lifetime of screening for all women. Modeling also estimated that screening benefits for Black women are similar for breast cancer mortality reduction and greater for life-years gained and breast cancer deaths averted compared with all women. Thus, biennial screening starting at age 40 years would result in 1.8 additional breast cancer deaths averted per 1,000 women screened for Black women. 11 Epidemiologic data has shown that the incidence rate of invasive breast cancer for 40- to 49-year-old women has increased an average of 2.0% annually between 2015 and 2019, a higher rate than in previous years. 3 These factors led the USPSTF to conclude that screening mammography in women ages 40 to 49 years has a moderate benefit in reducing the risk of breast cancer mortality.
The USPSTF did not identify any randomized trials directly comparing annual vs. biennial screening that reported morbidity, mortality, or quality of life outcomes. One controlled trial (N=14,765) conducted in Finland during the years 1985 to 1995 assigned participants ages 40 to 49 years to annual or triennial screening invitations based on birth year (even birth year: annual; odd birth year: triennial) and reported similar mortality from incident breast cancer and for all-cause mortality between the two groups, with followup to age 52 years. 51
A nonrandomized study using BCSC data (N=15,440) compared the tumor characteristics of cancers detected following annual vs. biennial screening intervals. 12 The relative risk of being diagnosed with a stage IIB or higher cancer and cancer with less favorable characteristics was not statistically different for biennially vs. annually screened women in any of the age categories. The risk of a stage IIB or higher cancer diagnosis and of having a tumor with less favorable prognostic characteristics were higher for premenopausal women screened biennially vs. annually (RR, 1.28 [95% CI, 1.01 to 1.63] and RR, 1.11 [95% CI, 1.00 to 1.22], respectively). However, this study did not conduct formal tests for interaction in the subgroup comparisons and did not adjust for multiple comparisons.
One RCT (n=76,022) conducted between 1989 and 1996 randomized individuals to annual or triennial screening and reported on breast cancer incidence. The number of screen-detected cancers was higher in the annual screening study group (RR, 1.64 [95% CI, 1.28 to 2.09]). However, the total number of cancers diagnosed either clinically or with screening was similar after 3 years of screening. Cancers occurring in the annual screening group (including clinically diagnosed cancers) did not differ by prognostic features such as tumor size, node positivity status, or histologic grade compared with those in the triennial screening group. 52
Collaborative modeling estimated that biennial screening results in greater incremental life-years gained and mortality reduction per mammogram and has a more favorable balance of benefits to harms for all women and for Black women, compared with annual screening. While modeling suggests that screening Black women annually and screening other women biennially would reduce the disparity in breast cancer mortality, 11 trial or observational evidence is lacking that screening any group of women annually compared with biennial screening improves mortality from breast cancer. 4
The USPSTF did not identify any RCTs or observational studies that compared screening with DBT vs. DM and reported morbidity, mortality, or quality of life outcomes.
Three RCTs 53-55 and one nonrandomized study 56 compared detection of invasive cancer over two rounds of screening with DBT vs. DM. These trials screened all participants with the same screening modality at the second screening round—DM in two trials and the nonrandomized study, and DBT in one trial. Stage shift or differences in tumor characteristics across screening rounds could offer indirect evidence of potential screening benefit. The trials found no statistically significant difference in detection at the second screening round (pooled RR, 0.87 [95% CI, 0.73 to 1.05]; 3 trials; n=105,064). 4 The nonrandomized study (n=92,404) found higher detection at round one for the group screened with DBT and higher detection at round two for the group screened with DM at both rounds. There were no statistically significant differences in tumor diameter, histologic grade, and node status at the first or second round of screening in any of these studies.
Collaborative modeling data estimated that the benefits of DBT are similar to the estimated benefits of DM (e.g., approximately 5 to 6 more life-years gained per 1,000 women screened). 11
Supplemental Screening With MRI or Ultrasonography, or Personalized Screening
The USPSTF found no studies of supplemental screening with MRI or ultrasonography, or studies of personalized (e.g., risk-based) screening strategies, that reported on morbidity or mortality or on cancer detection and characteristics over multiple rounds of screening. 4 Collaborative modeling studies did not investigate the effects of screening with MRI or ultrasonography. Modeling generally estimated that the benefits of screening mammography would be greater for persons at modestly increased risk (e.g., the risk of breast cancer associated with a first-degree family history of breast cancer). 11
Harms of Screening
For this recommendation, the USPSTF also reviewed the harms of screening for breast cancer and whether the harms varied by screening strategy. Potential harms of screening for breast cancer include false-positive and false-negative results, need for additional imaging and biopsy, overdiagnosis, and radiation exposure.
The most common harm is a false-positive result, which can lead to psychological harms, as well as additional testing and invasive followup procedures without the potential for benefit. Collaborative modeling data estimated that a strategy of screening biennially from ages 40 to 74 years would result in 1,376 false-positive results per 1,000 women screened over a lifetime of screening. 11
Overdiagnosis occurs when breast cancer that would never have become a threat to a person’s health, or even apparent, during their lifetime is found due to screening. It is not possible to directly observe for any individual person whether they have or do not have an overdiagnosed tumor; it is only possible to indirectly estimate the frequency of overdiagnosis that may occur across a screened population. Estimates of overdiagnosis from RCTs that had comparable groups at baseline, had adequate followup, and did not provide screening to the control group at the end of the trial range from approximately 11% to 19%. 4 Collaborative modeling data estimate that a strategy of screening biennially from ages 40 to 74 years would lead to 14 overdiagnosed cases of breast cancer per 1,000 persons screened over the lifetime of screening, though with a very wide range of estimates (4 to 37 cases) across models. 11
One trial emulation (n=264,274) compared discontinuation of mammography screening at age 70 years or older with continued annual screening beyond this age. 38 Overall, the 8-year cumulative risk of a breast cancer diagnosis was higher for the continued annual screening strategy after age 70 years (5.5% overall; 5.3% in women ages 70–74 years; 5.8% in women ages 75–84 years) compared with the stop screening strategy (3.9% overall; same proportion for both age groups). Fewer cancers were diagnosed under the stop screening strategy (ages 70 to 84 years); consequently, there was a lower risk of undergoing followup and treatment. For women aged 75 to 84 years, additional diagnoses did not contribute to a difference in the risk of breast cancer mortality, raising the possibility that the additionally diagnosed cancers represent overdiagnosis.
Collaborative modeling data estimated that lowering the age to start screening to 40 years from 50 years would result in about a 60% increase in false-positive results, and 2 additional overdiagnosed cases of breast cancer (range, 0–4) per 1,000 women over a lifetime of screening. 11
Rates of interval cancers (cancer diagnosis occurring between screening) reported in screening studies reflect a combination of cancers that were missed during previous screening examinations (false-negative results) and incident cancers emerging between screening rounds. Evidence from studies comparing various intervals and reporting on the effect of screening interval on the rate of interval cancers is mixed. One RCT comparing annual vs. triennial screening reported that the rate of interval cancers was significantly lower in the annual invitation group (1.84 cases per 1,000 women initially screened) than in the triennial invitation group (2.70 cases per 1,000 women initially screened) (RR, 0.68 [95% CI, 0.50 to 0.92]), 52 while a second quasirandomized study, also comparing annual vs. triennial screening, found no difference in the number of interval cancers between the two groups. 51
Based on two studies, false-positive recall was more likely to occur with annual screening compared with longer intervals between screening. 57 , 58 One of these studies, using data from the BCSC, reported that biennial screening led to a 5% absolute decrease in the 10-year cumulative false-positive biopsy rate compared with annual screening, whether screening was conducted with DBT or DM. 57 Collaborative modeling estimated that annual screening results in more false-positive results and breast cancer overdiagnosis. For example, a strategy of screening annually from ages 40 to 74 years would result in about 50% more false-positive results and 50% more overdiagnosed cases of breast cancer compared with biennial screening for all women and a similar increase in false-positive results and a somewhat smaller increase in overdiagnosed cases for Black women. 11
Three RCTs did not show statistically significant differences in the risk of interval cancer following screening with DBT or DM (pooled RR, 0.87 [95% CI, 0.64 to 1.17]; 3 trials; n=130,196). 4 Five nonrandomized studies generally support the RCT findings. Three of the nonrandomized studies found no significant difference in the rate of interval cancers diagnosed following screening with DBT or DM, 56 , 59 , 60 while one study found a slight increased risk with DBT screening, 61 and one study found an unadjusted decreased risk with DBT screening. 62
A pooled analysis of three RCTs (n=105,244) comparing screening with DBT vs. DM did not find a difference in false-positive recalls at the second round of screening. 4 A nonrandomized study using BCSC data reported that the estimated cumulative probability of having at least one false-positive recall over 10 years of screening was generally lower with DBT screening compared with DM screening (annual screening: 10-year cumulative probability of a false-positive recall was 49.6% with DBT and 56.3% with DM; biennial screening: 10-year cumulative probability of a false-positive recall was 35.7% for DBT and 38.1% for DM). The risk of having a biopsy over 10 years of screening was slightly lower when comparing annual screening with DBT vs. DM but did not differ between DBT and DM for biennial screening (annual screening: 10-year cumulative probability of a false-positive biopsy was 11.2% with DBT and 11.7% with DM; biennial screening: 10-year cumulative probability of a false-positive biopsy was 6.6% for DBT and 6.7% for DM). When results were stratified by breast density, the difference in false-positive recall probability with DBT vs. DM was largest for women with nondense breasts and was not significantly different among women with extremely dense breasts. 57 Collaborative modeling, using inputs from BCSC data, estimated that screening women ages 40 to 74 years with DBT would result in 167 fewer false-positive results (range, 166 to 169) per 1,000 persons screened, compared with DM. 11
In the three RCTs cited above, rates of DCIS detected did not differ between persons screened with DBT and DM. 53-55
Screening with DBT includes evaluation of a two-dimensional image, generated either with DM or using the DBT scan to produce a synthetic DM image. 8 , 9 Studies using DBT with DM screening reported radiation exposure approximately two times higher compared with the DM-only control group. 53 , 55 , 63 Differences in radiation exposure were smaller in studies using DBT/synthetic DM compared with DM. 64 , 65
Supplemental Screening With Ultrasonography or MRI
The DENSE RCT, which compared invitation to screening with DM plus MRI compared with DM alone in participants ages 50 to 75 years with extremely dense breasts and a negative mammogram, reported a significantly lower rate of invasive interval cancers—2.2 cases per 1,000 women invited to screening with DM plus MRI, compared with 4.7 cases per 1,000 women invited to screening with DM only (RR, 0.47 [95% CI, 0.29 to 0.77]). 66
In this trial, the rate of recall among participants who underwent additional imaging with MRI was 94.9 per 1,000 screens, the false-positive rate was 79.8 per 1,000 women screened, and the rate of biopsy was 62.7 per 1,000 women screened. 67 In a nonrandomized study using U.S. insurance claims data, individuals who had an MRI compared with those receiving only a mammogram were more likely in the subsequent 6 months to have additional cascade events related to extramammary findings (adjusted difference between groups, 19.6 per 100 women screened [95% CI, 8.6 to 30.7]), mostly additional healthcare visits. 68
In an RCT comparing screening with DM plus ultrasonography vs. DM alone conducted in persons ages 40 to 49 years and not specifically among persons with dense breasts, the interval cancer rates reported were not statistically significantly different between the two groups (RR, 0.58 [95% CI, 0.31 to 1.08]); 69 similarly, in a nonrandomized study comparing DM plus ultrasonography vs. DM alone using BCSC data, there was no difference in interval cancers (adjusted RR, 0.67 [95% CI, 0.33 to 1.37]) (72), though in both studies the confidence intervals were wide for this uncommon outcome. In the BCSC analysis, the rates of referral to biopsy and false-positive biopsy recommendations were twice as high and short interval followup was three times higher for the group screened with ultrasonography. 70
See Table 2 for research needs and gaps related to screening for breast cancer.
The American Cancer Society recommends that women with an average risk of breast cancer should undergo regular screening mammography starting at age 45 years. It suggests that women ages 45 to 54 years should be screened annually, that women age 55 years or older should transition to biennial screening or have the opportunity to continue screening annually, that women should have the opportunity to begin annual screening between the ages of 40 and 44 years, and that women should continue screening mammography as long as their overall health is good and they have a life expectancy of 10 years or longer. 71
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that women at average risk of breast cancer should be offered screening mammography starting at age 40 years, using shared decision making, and if they have not initiated screening in their 40s, they should begin screening mammography by no later than age 50 years. It recommends that women at average risk of breast cancer should have screening mammography every 1 or 2 years and should continue screening mammography until at least age 75 years. Beyond age 75 years, the decision to discontinue screening mammography should be based on shared decision making informed by the woman’s health status and longevity. 72
The American Academy of Family Physicians supports the current USPSTF recommendation on screening for breast cancer. 73
1. National Cancer Institute; Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html 2. National Cancer Institute; Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program. Breast: SEER 5-Year Age-Adjusted Incidence Rates, 2016-2020, by Race/Ethnicity, Female, All Ages, All Stages. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/application.html?site=55&data_type=1&graph_type=10&compareBy=race&chk_race_6=6&chk_race_5=5&chk_race_4=4&chk_ race_9=9&chk_race_8=8&series=9&sex=3&age_range=1&stage=101&advopt_precision=1&advopt_show_ci=on&hdn_view=0#resultsRegion0 3. National Cancer Institute; Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program. SEER*Stat Database: Incidence - SEER Research Limited-Field Data with Delay-Adjustment, 22 Registries, Malignant Only, Nov 2021 Sub (2000-2019) - Linked To County Attributes - Time Dependent (1990-2019) Income/Rurality, 1969-2020 Counties. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2022. 4. Henderson JT, Webber, EM, Weyrich M, Miller M, Melnikow J. Screening for Breast Cancer: A Comparative Effectiveness Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Evidence Synthesis No. 231. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2023. AHRQ Publication No. 23-05303-EF-1. 5. National Cancer Institute; Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program. Breast: SEER 5-Year Age-Adjusted Incidence Rates, 2016-2020, by Subtype, Female, All Races/Ethnicities, All Ages, All Stages. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/application.html?site=55&data_type=1&graph_type=10&compareBy=subtype&chk_subtype_55=55&chk_subtype_622=622&chk_subtype_ 623=623&chk_subtype_620=620&chk_subtype_621=621&series=9&sex=3&race=1&age_range=1&stage=101&advopt_precision=1&advopt_show_ci=on&hdn_view=0 6. Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Miller KD, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin . 2022;72(6):524-541. 7. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Procedure Manual. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/about-uspstf/methods-and-processes/procedure-manual 8. Ciatto S, Houssami N, Bernardi D, et al. Integration of 3D digital mammography with tomosynthesis for population breast-cancer screening (STORM): a prospective comparison study. Lancet Oncol . 2013;14(7):583-589. 9. Skaane P, Bandos AI, Eben EB, et al. Two-view digital breast tomosynthesis screening with synthetically reconstructed projection images: comparison with digital breast tomosynthesis with full-field digital mammographic images. Radiology . 2014;271(3):655-663. 10. Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium. About the BCSC. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://www.bcsc-research.org/about 11. Trentham-Dietz A, Chapman CH, Jinani J, et al. Breast Cancer Screening With Mammography: An Updated Decision Analysis for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2023. AHRQ Publication No. 23-05303-EF-2. 12. Miglioretti DL, Zhu W, Kerlikowske K, et al. Breast tumor prognostic characteristics and biennial vs annual mammography, age, and menopausal status . JAMA Oncol . 2015;1(8):1069-1077. 13. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis. 2019. 14. Alvidrez J, Castille D, Laude-Sharp M, Rosario A, Tabor D. The National Institute on Minority Health and health disparities research framework. Am J Public Health . 2019;109(S1):S16-S20. 15. Williams DR, Priest N, Anderson NB. Understanding associations among race, socioeconomic status, and health: patterns and prospects. Health Psychol . 2016;35(4):407-411. 16. Bailey ZD, Krieger N, Agénor M, Graves J, Linos N, Bassett MT. Structural racism and health inequities in the USA: evidence and interventions. Lancet . 2017;389(10077):1453-1463. 17. Zavala VA, Bracci PM, Carethers JM, et al. Cancer health disparities in racial/ethnic minorities in the United States. Br J Cancer . 2021;124(2):315-332. 18. Bemanian A, Beyer KM. Measures matter: the local exposure/isolation (LEx/Is) metrics and relationships between local-level segregation and breast cancer survival. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev . 2017;26(4):516-524. 19. Goel N, Westrick AC, Bailey ZD, et al. Structural racism and breast cancer-specific survival: impact of economic and racial residential segregation. Ann Surg . 2022;275(4):776-783. 20. Siegel SD, Brooks MM, Lynch SM, Sims-Mourtada J, Schug ZT, Curriero FC. Racial disparities in triple negative breast cancer: toward a causal architecture approach. Breast Cancer Res . 2022;24(1):37. 21. Niraula S, Biswanger N, Hu P, Lambert P, Decker K. Incidence, characteristics, and outcomes of interval breast cancers compared with screening-detected breast cancers. JAMA Netw Open . 2020;3(9):e2018179. 22. Jatoi I, Sung H, Jemal A. The emergence of the racial disparity in U.S. breast-cancer mortality. New Engl J Med . 2022;386(25):2349-2352. 23. Davis Lynn BC, Chernyavskiy P, Gierach GL, Rosenberg PS. Decreasing incidence of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer in the United States: trends by race and region. J Natl Cancer Inst . 2022;114(2):263-270. 24. Plevritis SK, Munoz D, Kurian AW, et al. Association of screening and treatment with breast cancer mortality by molecular subtype in US women, 2000-2012. JAMA . 2018;319(2):154-164. 25. Fayanju OM, Ren Y, Stashko I, et al. Patient-reported causes of distress predict disparities in time to evaluation and time to treatment after breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer . 2021;127(5):757-768. 26. Selove R, Kilbourne B, Fadden MK, et al. Time from screening mammography to biopsy and from biopsy to breast cancer treatment among black and white, women Medicare beneficiaries not participating in a health maintenance organization. Womens Health Issues . 2016;26(6):642-647. 27. Nguyen KH, Pasick RJ, Stewart SL, Kerlikowske K, Karliner LS. Disparities in abnormal mammogram follow-up time for Asian women compared with non-Hispanic white women and between Asian ethnic groups. Cancer . 2017;123(18):3468-3475. 28. Warner ET, Tamimi RM, Hughes ME, et al. Time to diagnosis and breast cancer stage by race/ethnicity. Breast Cancer Res Treat . 2012;136(3):813-821. 29. Kovar A, Bronsert M, Jaiswal K, et al. The waiting game: how long are breast cancer patients waiting for definitive diagnosis? Ann Surg Oncol . 2020;27(10):3641-3649. 30. Elmore JG, Nakano CY, Linden HM, Reisch LM, Ayanian JZ, Larson EB. Racial inequities in the timing of breast cancer detection, diagnosis, and initiation of treatment. Med Care . 2005;43(2):141-148. 31. Emerson MA, Golightly YM, Aiello AE, et al. Breast cancer treatment delays by socioeconomic and health care access latent classes in Black and White women. Cancer . 2020;126(22):4957-4966. 32. Lawson MB, Bissell MC, Miglioretti DL, et al. Multilevel factors associated with time to biopsy after abnormal screening mammography results by race and ethnicity. JAMA Oncol . 2022;8(8):1115-1126. 33. Hu X, Walker MS, Stepanski E, et al. Racial differences in patient-reported symptoms and adherence to adjuvant endocrine therapy among women with early-stage, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. JAMA Netw Open . 2022;5(8):e2225485. 34. Hu X, Chehal PK, Kaplan C, et al. Characterization of clinical symptoms by race among women with early-stage, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer before starting chemotherapy. JAMA Netw Open . 2021;4(6):e2112076. 35. Clemons K, Blackford AL, Gupta A, et al. Geographic disparities in breast cancer mortality and place of death in the United States from 2003 to 2019. J Clin Oncol . 2022;40(16 Suppl):12034. 36. National Cancer Institute; Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program. Breast: SEER Incidence Rates by Age at Diagnosis, 2016-2020, by Sex, Delay-Adjusted SEER Incidence Rate, All Races/Ethnicities. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/application.html?site=55&data_type=1&graph_type=3&compareBy=sex&chk_sex_3=3&rate_type=2&race=1&advopt_precision=1&advopt_ show_ci=on&hdn_view=0#resultsRegion0 37. National Cancer Institute; Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program. Breast: U.S. Mortality Rates by Age at Death, 2016-2020, by Sex, All Races/Ethnicities. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/application.html?site=55&data_type=2&graph_type=3&compareBy=sex&chk_sex_3=3&race=1&advopt_precision=1&advopt_show_ci=on&hdn_ view=0#resultsRegion0 38. García-Albéniz X, Hernán MA, Logan RW, Price M, Armstrong K, Hsu J. Continuation of annual screening mammography and breast cancer mortality in women older than 70 years. Ann Intern Med . 2020;172(6):381-389. 39. Kerlikowske K, Zhu W, Tosteson AN, et al. Identifying women with dense breasts at high risk for interval cancer: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med . 2015;162(10):673-681. 40. Price ER, Hargreaves J, Lipson JA, et al. The California breast density information group: a collaborative response to the issues of breast density, breast cancer risk, and breast density notification legislation. Radiology . 2013;269(3):887-892. 41. Gierach GL, Ichikawa L, Kerlikowske K, et al. Relationship between mammographic density and breast cancer death in the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst . 2012;104(16):1218-1227. 42. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Health, United States, 2018. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus18.pdf 43. Dense Breast-info. State Legislation Map. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://densebreast-info.org/legislative-information/state-legislation-map/ 44. Mammography Quality Standards Act, 21 C.F.R. § 900 (2023). 45. US Preventive Services Task Force. Medication use to reduce risk of breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA . 2019;322(9):857-867. 46. US Preventive Services Task Force. Risk assessment, genetic counseling, and genetic testing for BRCA-related Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement . JAMA . 2019;322(7):652-665. 47. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med . 2016;164(4):279-296. 48. Nelson HD, Cantor A, Humphrey L, et al. Screening for Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review to Update the 2009 U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation. Evidence Synthesis No. 124. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2016. AHRQ Publication No. 14-05201-EF-1. 49. Nyström L, Bjurstam N, Jonsson H, Zackrisson S, Frisell J. Reduced breast cancer mortality after 20+ years of follow-up in the Swedish randomized controlled mammography trials in Malmö, Stockholm, and Göteborg. J Med Screen . 2017;24(1):34-42. 50. Jones BA, Patterson EA, Calvocoressi L. Mammography screening in African American women: evaluating the research. Cancer . 2003;97(1 Suppl):258-272. 51. Parvinen I, Chiu S, Pylkkänen L, Klemi P, Immonen-Räihä P, Kauhava L, et al. Effects of annual vs triennial mammography interval on breast cancer incidence and mortality in ages 40-49 in Finland. Br J Cancer . 2011;105:1388-91. 52. The frequency of breast cancer screening: results from the UKCCCR randomised trial. United Kingdom Co-ordinating Committee on Cancer Research. Eur J Cancer . 2002;38(11):1458-1464. 53. Armaroli P, Frigerio A, Correale L, et al. A randomised controlled trial of digital breast tomosynthesis versus digital mammography as primary screening tests: screening results over subsequent episodes of the Proteus Donna study. Int J Cancer . 2022;151(10):1778-1790. 54. Hofvind S, Moshina N, Holen ÅS, et al. Interval and subsequent round breast cancer in a randomized controlled trial comparing digital breast tomosynthesis and digital mammography screening. Radiology . 2021;300(1):66-76. 55. Pattacini P, Nitrosi A, Giorgi Rossi P, et al. A randomized trial comparing breast cancer incidence and interval cancers after tomosynthesis plus mammography versus mammography alone. Radiology . 2022;303(2):256-266. 56. Hovda T, Holen ÅS, Lång K, et al. Interval and consecutive round breast cancer after digital breast tomosynthesis and synthetic 2d mammography versus standard 2d digital mammography in BreastScreen Norway. Radiology . 2020;294(2):256-264. 57. Ho TH, Bissell MC, Kerlikowske K, et al. Cumulative probability of false-positive results after 10 years of screening with digital breast tomosynthesis vs digital mammography. JAMA Netw Open . 2022;5(3):e222440 58. McGuinness JE, Ueng W, Trivedi MS, et al. Factors associated with false positive results on screening mammography in a population of predominantly Hispanic women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev . 2018;27(4):446-453. 59. Conant EF, Beaber EF, Sprague BL, et al. Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography compared to digital mammography alone: a cohort study within the PROSPR consortium. Breast Cancer Res Treat . 2016;156(1):109-116. 60. Kerlikowske K, Su YR, Sprague BL, et al. Association of screening with digital breast tomosynthesis vs digital mammography with risk of interval invasive and advanced breast cancer. JAMA . 2022;327(22):2220-2230. 61. Richman IB, Long JB, Hoag JR, et al. Comparative effectiveness of digital breast tomosynthesis for breast cancer screening among women 40-64 years old. J Natl Cancer Inst . 2021;113(11):1515-1522. 62. Johnson K, Lang K, Ikeda DM, et al. Interval breast cancer rates and tumor characteristics in the prospective population-based Malmö breast tomosynthesis screening trial. Radiology . 2021;299(3):559-567. 63. Zackrisson S, Lång K, Rosso A, et al. One-view breast tomosynthesis versus two-view mammography in the Malmö Breast Tomosynthesis Screening Trial (MBTST): a prospective, population-based, diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Oncol . 2018;19(11):1493-1503. 64. Heindel W, Weigel S, Gerß J, et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis plus synthesized mammography versus digital screening mammography for the detection of invasive breast cancer (TOSYMA): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, superiority trial. Lancet Oncol . 2022;23(5):601-611. 65. Aase HS, Holen ÅS, Pedersen K, et al. A randomized controlled trial of digital breast tomosynthesis versus digital mammography in population-based screening in Bergen: interim analysis of performance indicators from the To-Be trial. Eur Radiol. 2019;29(3):1175-1186. 66. Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, et al. Supplemental MRI screening for women with extremely dense breast tissue. N Engl J Med . 2019;381(22):2091-2102. 67. Veenhuizen SG, de Lange SV, Bakker MF, et al. Supplemental breast MRI for women with extremely dense breasts: results of the second screening round of the DENSE trial. Radiology . 2021;299(2):278-286. 68. Ganguli I, Keating NL, Thakore N, Lii J, Raza S, Pace LE. downstream mammary and extramammary cascade services and spending following screening breast magnetic resonance imaging vs mammography among commercially insured women. JAMA Netw Open . 2022;5(4):e227234. 69. Ohuchi N, Suzuki A, Sobue T, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of mammography and adjunctive ultrasonography to screen for breast cancer in the Japan Strategic Anti-cancer Randomized Trial (J-START): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet . 2016;387(10016):341-348. 70. Lee JM, Arao RF, Sprague BL, et al. Performance of screening ultrasonography as an adjunct to screening mammography in women across the spectrum of breast cancer risk. JAMA Intern Med . 2019;179(5):658-667. 71. Oeffinger KC, Fontham ET, Etzioni R, et al; American Cancer Society. Breast cancer screening for women at average risk: 2015 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. JAMA . 2015;314(15):1599-1614. 72. Committee on Practice Bulletins—Gynecology. Practice Bulletin Number 179: breast cancer risk assessment and screening in average-risk women. Obstet Gynecol . 2017;130(1):e1-e16. 73. American Academy of Family Physicians. Clinical Preventive Service Recommendation: Breast Cancer. Accessed April 20, 2023. https://www.aafp.org/family-physician/patient-care/clinical-recommendations/all-clinical-recommendations/breast-cancer.html
Abbreviations: MRI=magnetic resonance imaging; USPSTF=U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
To fulfill its mission to improve health by making evidence-based recommendations for preventive services, the USPSTF routinely highlights the most critical evidence gaps for creating actionable preventive services recommendations. The USPSTF often needs additional evidence to create the strongest recommendations for everyone, especially those with the greatest burden of disease. In some cases, clinical preventive services have been well studied, but there are important evidence gaps that prevent the USPSTF from making recommendations for specific populations. In Table 2, the USPSTF summarizes the gaps in the evidence for screening for breast cancerand emphasizes health equity gaps that need to be addressed to advance the health of the nation. Although the health equity gaps focus on Black women because they have the poorest health outcomes from breast cancer, it is important to note that all studies should actively recruit enough women of all racial and ethnic groups, including Black, Hispanic, Asian, Native American/Alaska Native, and Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander participants, to investigate whether the effectiveness of screening, diagnosis, and treatment vary by group.
Abbreviations: DBT=digital breast tomosynthesis; DCIS=ductal carcinoma in situ; DM=digital mammography; MRI=magnetic resonance imaging.
IT Maintenance is being performed on Tuesday 23 April between 6.00am and 8.30am . This may affect your ability to access your Member Portal, the Fees List and the Medical Journal of Australia during this time. All endeavours are being made to limit the impact. If you experience login issues during this time, please try again in 15mins.
- Register to attend AMA24
Advocacy & Policy
Doctor & Student Resources
News & Media
Membership & Benefits
New AMA report card reveals uncomfortable truths about Australia’s health system
Planned surgery wait times in Australia’s public hospitals are now the longest on record, a new AMA report card has found.

Australia’s health ministers have been presented with grim evidence of the country’s public hospital logjam ahead of their crucial meeting today.
The AMA has released its annual Public Hospital Report Card, showing planned surgery wait times in Australia’s public hospitals are now the longest on record, and emergency departments remain strangled by access block.
The AMA wrote to all health ministers ahead of their meeting, saying the findings highlight the need for all governments to take further action against the logjam.
AMA President Professor Steve Robson said the annual report card, first published in 2007, clearly demonstrated the need for urgent action on top of existing planned changes to the National Health Reform Agreement (NHRA).
“Last year we welcomed the federal government’s announcement of a significant public funding boost to the hospital funding agreement and the decision to replace the 6.5 per cent funding growth cap with a more generous approach,” Professor Robson said.
“This announcement followed tireless AMA advocacy for funding reform, but it doesn’t come into effect until 2025. Urgent action is needed now.”
The report card found Australians are now waiting almost twice as long on average for planned surgery than they were 20 years ago, while the national proportion of individuals receiving category two planned surgeries on time has again fallen to the lowest point of record.
Emergency departments, too, remain under stress as they are strangled by access block.
Read the Public Hospital Report Card
Read the AMA’s public hospital federal budget submission
Related Download
Related topics, more across the ama.

Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key facts about Americans and guns

Guns are deeply ingrained in American society and the nation’s political debates.
The Second Amendment to the United States Constitution guarantees the right to bear arms, and about a third of U.S. adults say they personally own a gun. At the same time, in response to concerns such as rising gun death rates and mass shootings , President Joe Biden has proposed gun policy legislation that would expand on the bipartisan gun safety bill Congress passed last year.
Here are some key findings about Americans’ views of gun ownership, gun policy and other subjects, drawn primarily from a Pew Research Center survey conducted in June 2023 .
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to summarize key facts about Americans and guns. We used data from recent Center surveys to provide insights into Americans’ views on gun policy and how those views have changed over time, as well as to examine the proportion of adults who own guns and their reasons for doing so.
The analysis draws primarily from a survey of 5,115 U.S. adults conducted from June 5 to June 11, 2023. Everyone who took part in the surveys cited is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the analysis on gun ownership , the questions used for the analysis on gun policy , and the survey’s methodology .
Additional information about the fall 2022 survey of parents and its methodology can be found at the link in the text of this post.
Measuring gun ownership in the United States comes with unique challenges. Unlike many demographic measures, there is not a definitive data source from the government or elsewhere on how many American adults own guns.
The Pew Research Center survey conducted June 5-11, 2023, on the Center’s American Trends Panel, asks about gun ownership using two separate questions to measure personal and household ownership. About a third of adults (32%) say they own a gun, while another 10% say they do not personally own a gun but someone else in their household does. These shares have changed little from surveys conducted in 2021 and 2017 . In each of those surveys, 30% reported they owned a gun.
These numbers are largely consistent with rates of gun ownership reported by Gallup , but somewhat higher than those reported by NORC’s General Social Survey . Those surveys also find only modest changes in recent years.
The FBI maintains data on background checks on individuals attempting to purchase firearms in the United States. The FBI reported a surge in background checks in 2020 and 2021, during the coronavirus pandemic. The number of federal background checks declined in 2022 and through the first half of this year, according to FBI statistics .
About four-in-ten U.S. adults say they live in a household with a gun, including 32% who say they personally own one, according to an August report based on our June survey. These numbers are virtually unchanged since the last time we asked this question in 2021.
There are differences in gun ownership rates by political affiliation, gender, community type and other factors.
- Republicans and Republican-leaning independents are more than twice as likely as Democrats and Democratic leaners to say they personally own a gun (45% vs. 20%).
- 40% of men say they own a gun, compared with 25% of women.
- 47% of adults living in rural areas report personally owning a firearm, as do smaller shares of those who live in suburbs (30%) or urban areas (20%).
- 38% of White Americans own a gun, compared with smaller shares of Black (24%), Hispanic (20%) and Asian (10%) Americans.
Personal protection tops the list of reasons gun owners give for owning a firearm. About three-quarters (72%) of gun owners say that protection is a major reason they own a gun. Considerably smaller shares say that a major reason they own a gun is for hunting (32%), for sport shooting (30%), as part of a gun collection (15%) or for their job (7%).
The reasons behind gun ownership have changed only modestly since our 2017 survey of attitudes toward gun ownership and gun policies. At that time, 67% of gun owners cited protection as a major reason they owned a firearm.
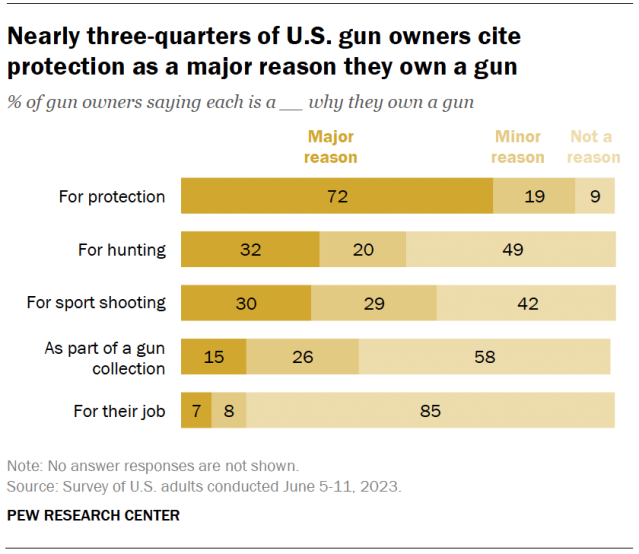
Gun owners tend to have much more positive feelings about having a gun in the house than non-owners who live with them. For instance, 71% of gun owners say they enjoy owning a gun – but far fewer non-gun owners in gun-owning households (31%) say they enjoy having one in the home. And while 81% of gun owners say owning a gun makes them feel safer, a narrower majority (57%) of non-owners in gun households say the same about having a firearm at home. Non-owners are also more likely than owners to worry about having a gun in the home (27% vs. 12%, respectively).
Feelings about gun ownership also differ by political affiliation, even among those who personally own firearms. Republican gun owners are more likely than Democratic owners to say owning a gun gives them feelings of safety and enjoyment, while Democratic owners are more likely to say they worry about having a gun in the home.
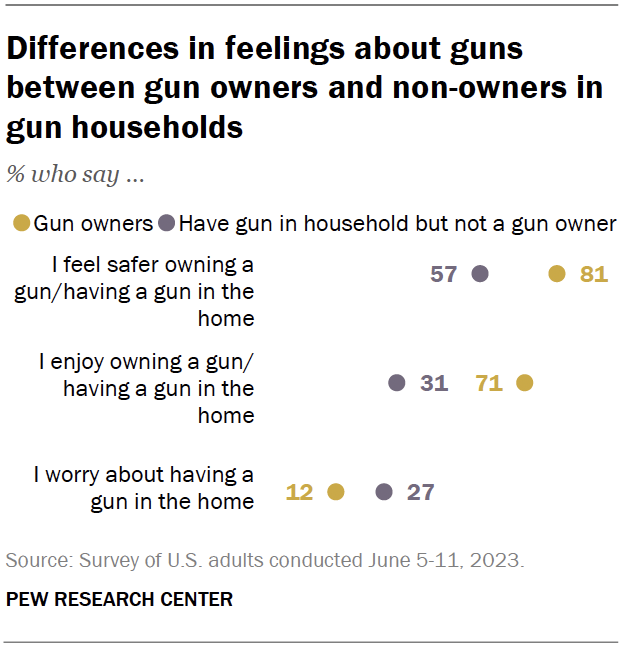
Non-gun owners are split on whether they see themselves owning a firearm in the future. About half (52%) of Americans who don’t own a gun say they could never see themselves owning one, while nearly as many (47%) could imagine themselves as gun owners in the future.
Among those who currently do not own a gun:
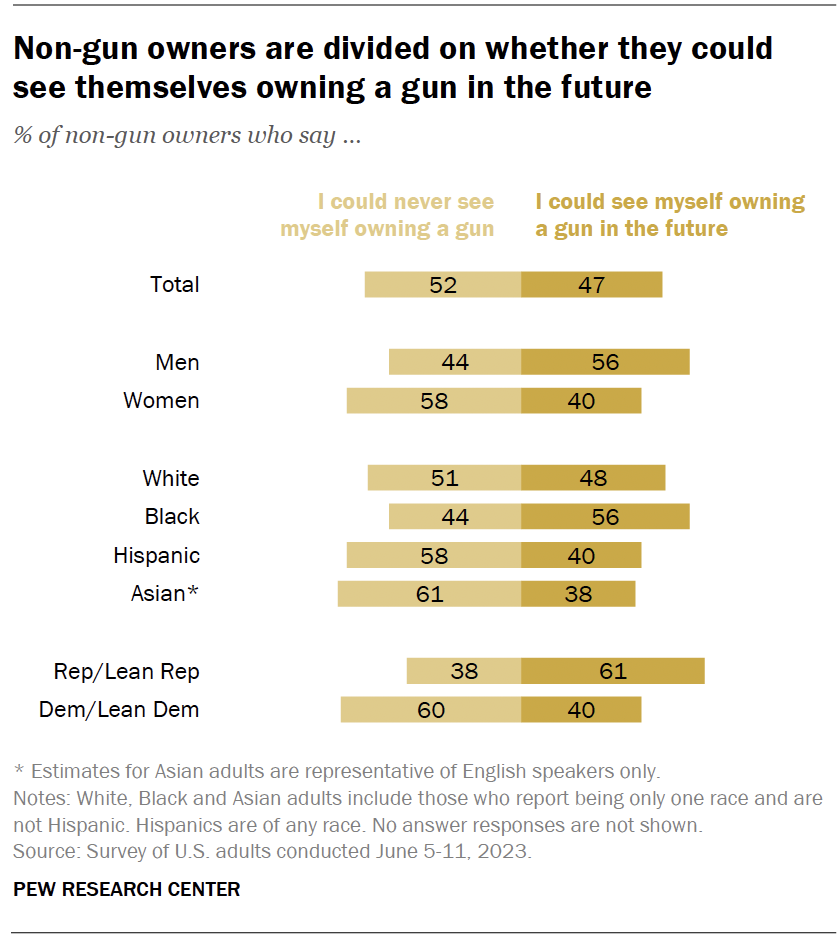
- 61% of Republicans and 40% of Democrats who don’t own a gun say they would consider owning one in the future.
- 56% of Black non-owners say they could see themselves owning a gun one day, compared with smaller shares of White (48%), Hispanic (40%) and Asian (38%) non-owners.
Americans are evenly split over whether gun ownership does more to increase or decrease safety. About half (49%) say it does more to increase safety by allowing law-abiding citizens to protect themselves, but an equal share say gun ownership does more to reduce safety by giving too many people access to firearms and increasing misuse.
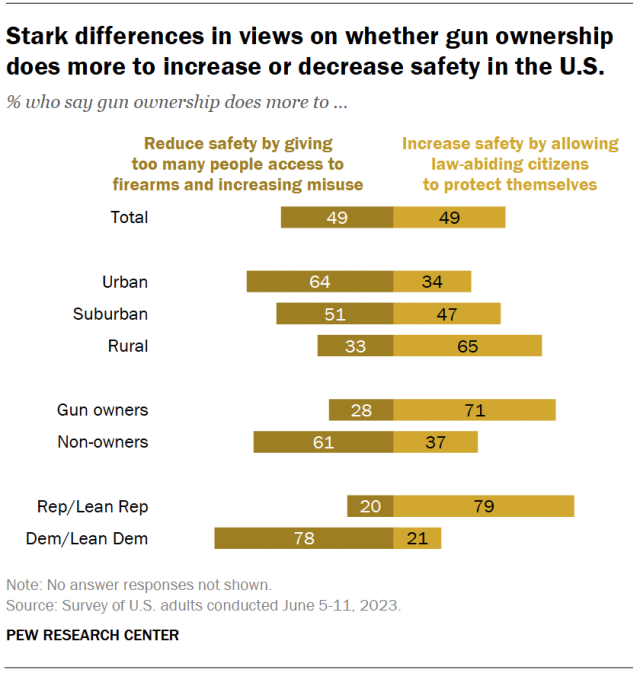
Republicans and Democrats differ on this question: 79% of Republicans say that gun ownership does more to increase safety, while a nearly identical share of Democrats (78%) say that it does more to reduce safety.
Urban and rural Americans also have starkly different views. Among adults who live in urban areas, 64% say gun ownership reduces safety, while 34% say it does more to increase safety. Among those who live in rural areas, 65% say gun ownership increases safety, compared with 33% who say it does more to reduce safety. Those living in the suburbs are about evenly split.
Americans increasingly say that gun violence is a major problem. Six-in-ten U.S. adults say gun violence is a very big problem in the country today, up 9 percentage points from spring 2022. In the survey conducted this June, 23% say gun violence is a moderately big problem, and about two-in-ten say it is either a small problem (13%) or not a problem at all (4%).
Looking ahead, 62% of Americans say they expect the level of gun violence to increase over the next five years. This is double the share who expect it to stay the same (31%). Just 7% expect the level of gun violence to decrease.
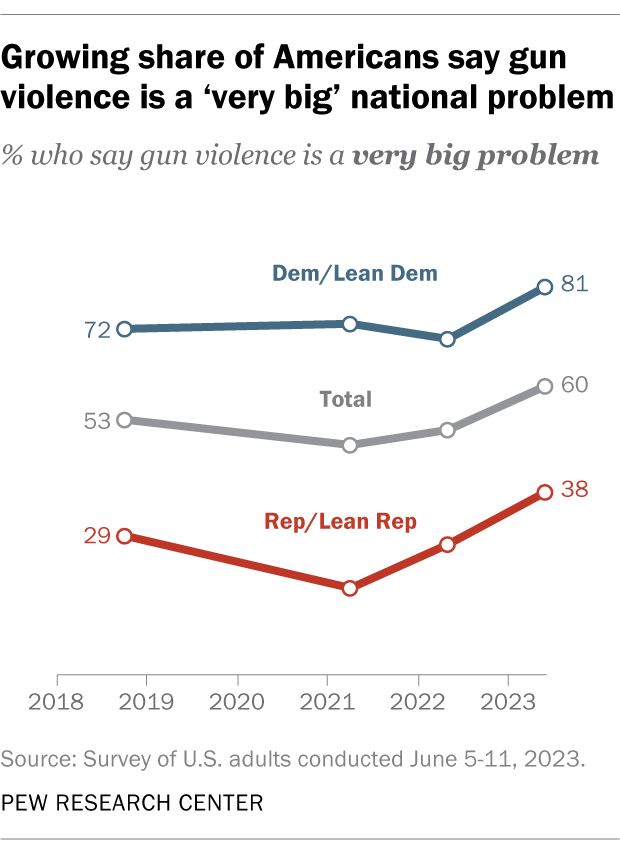
A majority of Americans (61%) say it is too easy to legally obtain a gun in this country. Another 30% say the ease of legally obtaining a gun is about right, and 9% say it is too hard to get a gun. Non-gun owners are nearly twice as likely as gun owners to say it is too easy to legally obtain a gun (73% vs. 38%). Meanwhile, gun owners are more than twice as likely as non-owners to say the ease of obtaining a gun is about right (48% vs. 20%).
Partisan and demographic differences also exist on this question. While 86% of Democrats say it is too easy to obtain a gun legally, 34% of Republicans say the same. Most urban (72%) and suburban (63%) dwellers say it’s too easy to legally obtain a gun. Rural residents are more divided: 47% say it is too easy, 41% say it is about right and 11% say it is too hard.
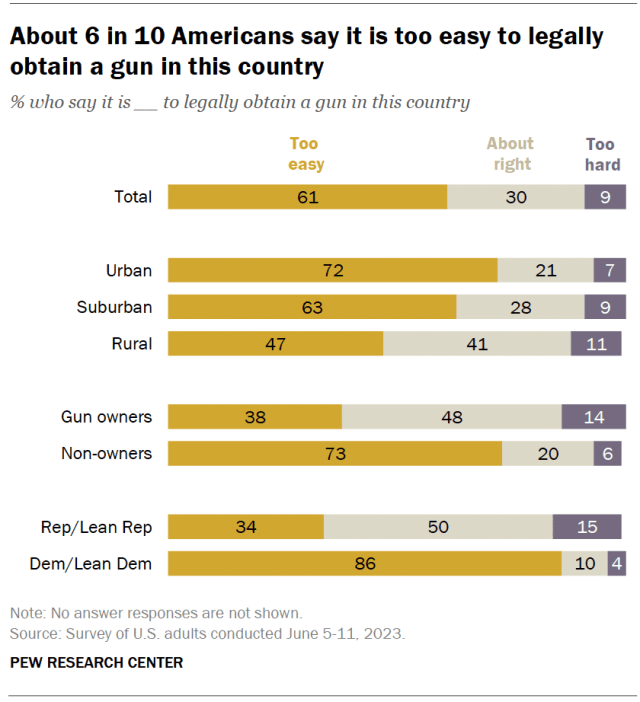
About six-in-ten U.S. adults (58%) favor stricter gun laws. Another 26% say that U.S. gun laws are about right, and 15% favor less strict gun laws. The percentage who say these laws should be stricter has fluctuated a bit in recent years. In 2021, 53% favored stricter gun laws, and in 2019, 60% said laws should be stricter.
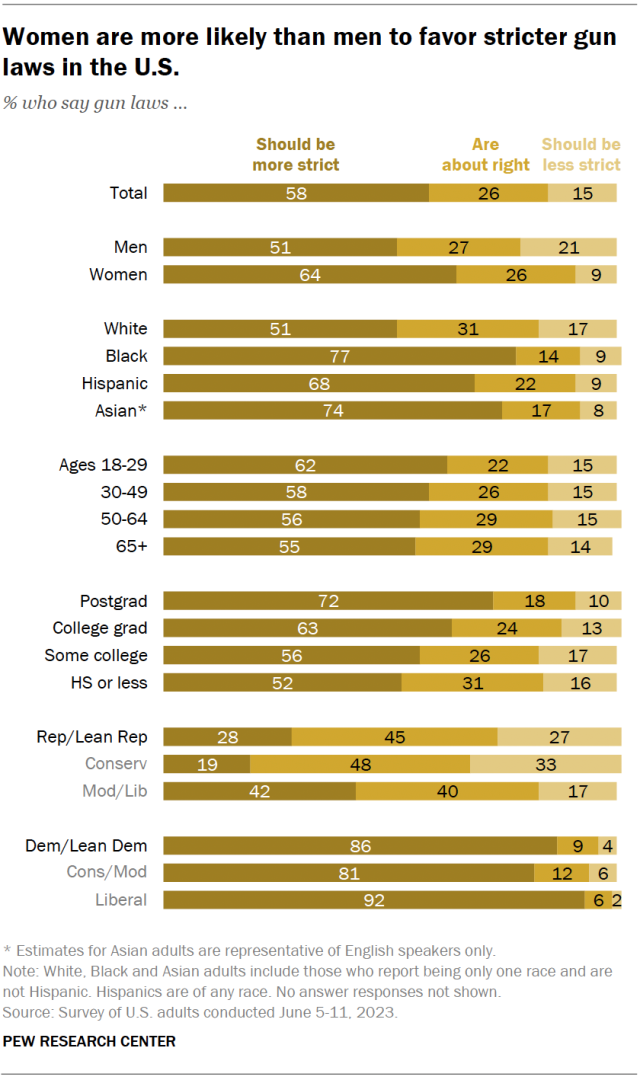
About a third (32%) of parents with K-12 students say they are very or extremely worried about a shooting ever happening at their children’s school, according to a fall 2022 Center survey of parents with at least one child younger than 18. A similar share of K-12 parents (31%) say they are not too or not at all worried about a shooting ever happening at their children’s school, while 37% of parents say they are somewhat worried.
Among all parents with children under 18, including those who are not in school, 63% see improving mental health screening and treatment as a very or extremely effective way to prevent school shootings. This is larger than the shares who say the same about having police officers or armed security in schools (49%), banning assault-style weapons (45%), or having metal detectors in schools (41%). Just 24% of parents say allowing teachers and school administrators to carry guns in school would be a very or extremely effective approach, while half say this would be not too or not at all effective.
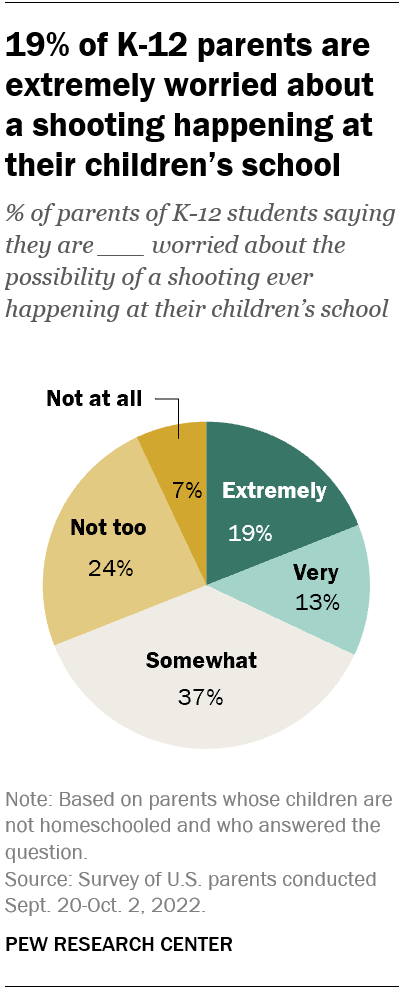
There is broad partisan agreement on some gun policy proposals, but most are politically divisive, the June 2023 survey found . Majorities of U.S. adults in both partisan coalitions somewhat or strongly favor two policies that would restrict gun access: preventing those with mental illnesses from purchasing guns (88% of Republicans and 89% of Democrats support this) and increasing the minimum age for buying guns to 21 years old (69% of Republicans, 90% of Democrats). Majorities in both parties also oppose allowing people to carry concealed firearms without a permit (60% of Republicans and 91% of Democrats oppose this).
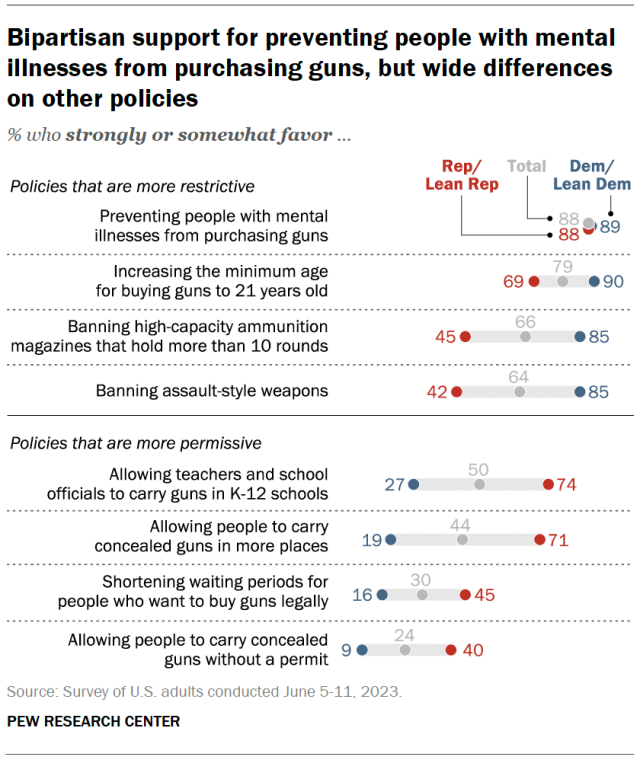
Republicans and Democrats differ on several other proposals. While 85% of Democrats favor banning both assault-style weapons and high-capacity ammunition magazines that hold more than 10 rounds, majorities of Republicans oppose these proposals (57% and 54%, respectively).
Most Republicans, on the other hand, support allowing teachers and school officials to carry guns in K-12 schools (74%) and allowing people to carry concealed guns in more places (71%). These proposals are supported by just 27% and 19% of Democrats, respectively.
Gun ownership is linked with views on gun policies. Americans who own guns are less likely than non-owners to favor restrictions on gun ownership, with a notable exception. Nearly identical majorities of gun owners (87%) and non-owners (89%) favor preventing mentally ill people from buying guns.
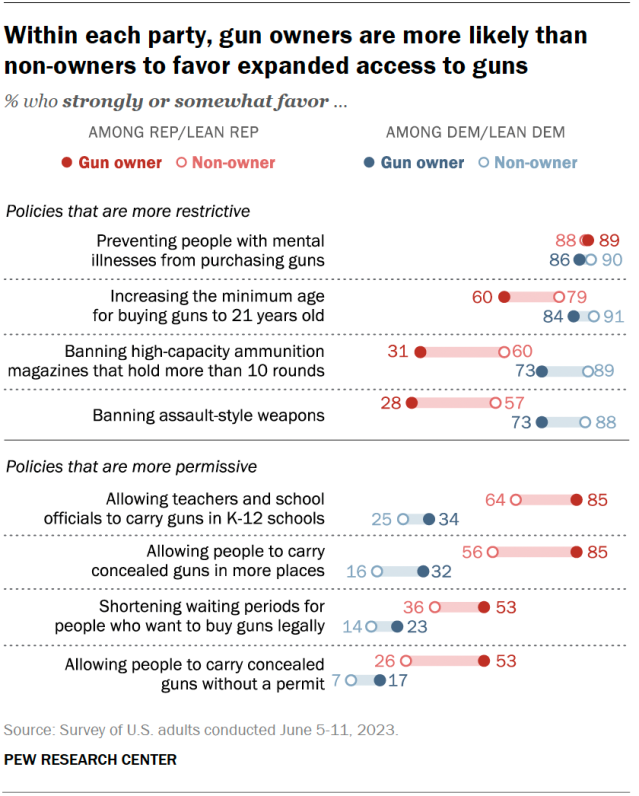
Within both parties, differences between gun owners and non-owners are evident – but they are especially stark among Republicans. For example, majorities of Republicans who do not own guns support banning high-capacity ammunition magazines and assault-style weapons, compared with about three-in-ten Republican gun owners.
Among Democrats, majorities of both gun owners and non-owners favor these two proposals, though support is greater among non-owners.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on Jan. 5, 2016 .
- Partisanship & Issues
- Political Issues

About 1 in 4 U.S. teachers say their school went into a gun-related lockdown in the last school year
Striking findings from 2023, for most u.s. gun owners, protection is the main reason they own a gun, gun violence widely viewed as a major – and growing – national problem, what the data says about gun deaths in the u.s., most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
KPMG Personalization

2024 Federal budget highlights
Canada's Deputy Prime Minister and Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland delivered Canada's 2024 federal budget on April 16, 2024
- Share Share close
- Download 2024 Federal budget highlights pdf Opens in a new window
- 1000 Save this article to my library
- View Print friendly version of this article Opens in a new window
- Go to bottom of page
- Home ›
- Insights ›
The budget expects a deficit of $40.0 billion for 2023-24 and forecasts deficits of $39.8 billion for 2024-25, and $38.9 billion for 2025-26. Although the budget does not change the federal personal or corporate tax rates, Finance announced that it will increase the inclusion rate for capital gains realized on or after June 25, 2024, in certain circumstances. Specifically, the inclusion rate will increase to 2/3 for corporations and trusts and to 2/3 for individuals on the portion of capital gains realized in the year that exceed $250,000. Finance also provided details on related changes to increase the Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption to $1.25 million, and clarified a temporary tax exemption on up to $10 million in capital gains that may be realized when a business is sold to an Employee Ownership Trust (EOT).
One of the major themes of this year’s budget is to increase the affordability of housing. In particular, the budget provides several incentives for purpose-built rental housing in Canada, including an elective exemption from the interest deductibility limitation and enhanced Capital Cost Allowance (CCA) for certain new additions of property. There are also new measures intended to benefit first-time homebuyers. Finance’s budget also focuses on clean economy changes, including to provide expected detail on the Clean Electricity investment tax credit, among others.
Download this edition of the TaxNewsFlash to learn more.

How new measures announced in this year’s budget may impact Canadians and businesses

KPMG in Canada provides the latest Canadian tax news and international tax news for you and your business
KPMG in Canada provides the latest Canadian and international tax news for your business

Quick tax information for corporations and individuals

COMMENTS
PDF | On May 1, 2015, Sriram Chandramohan published How to write a research proposal in public health", International Journal of Current Research, 7, (5), 16525-16529. | Find, read and cite all ...
151+ Public Health Research Topics [Updated 2024] The important area of public health research is essential to forming laws, influencing medical procedures, and eventually enhancing community well-being. As we delve into the vast landscape of public health research topics, it's essential to understand the profound impact they have on society.
Learn about which offices to go to for questions relating to proposal support, funding, faculty development, and more in the graphic below. ORSD Office Hours: April 25 ORSD hosts Open Office Hours, where ORSD team members are co-located within departments and available throughout the day to answer questions, discuss relevant issues, or just say hi!
4. Objectives: Research objectives are the goals to be achieved by conducting the research. 5 They may be stated as 'general' and 'specific'. The general objective of the research is what is to be accomplished by the research project, for example, to determine whether or not a new vaccine should be incorporated in a public health program.
Ima Business Manager University Department 1234 Research Way, Room 789 City, State, 12345. [email protected]. 555-555-7890. List the name, institution, contact information, and role for anyone who will contribute to publications resulting from this project. Everyone listed must submit a C.V or resume.
steps. It begins with selecting a study topic, reviewing. the literature, setting goals, choosing a study design and. appropriate statistical tools, and formulating a research proposal. to obtain ...
disease prevention. Collaborative agreements, guidelines for proposal writing, team building, budgeting, peer-review process, and transitioning from proposal to research project implementation. Additionally: During the quarter we will be developing your Soft Money Skillset & Toolbox™, which is essential for success in Public Health.
"The MPH thesis is an original research study that uses rigorous methods that are appropriate to the research question, generates new knowledge, applies concepts and methods from disciplines relevant to public health, and is presented in a scholarly format. The thesis demonstrates the student's comprehensive knowledge
If you're just starting out exploring public health and/or epidemiology-related topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you've come to the right place. In this post, we'll help kickstart your research by providing a hearty list of research ideas, including examples from recent studies in public health and epidemiology.. PS - This is just the start…
Oxford Textbook of Global Public Health 7th edn by Detels, R. et al. (eds) Invaluable for all practitioners, trainees, ... This is your step-by-step guide on how to write successful research proposals in the health sciences, whether it is for a thesis or dissertation review committee, an ethical review committee or a grant funding committee ...
Science*. Writing / standards*. Knowing how to properly prepare a research proposal is a real challenge - and being able to prepare an excellent research proposal is increasingly a requirement to compete for funding with assurances of success. With this in mind, we aim to share with the reader our experience (in many cases, unsucc ….
The guidelines for MSc/PhD thesis proposal defenses, MSc thesis defenses, and PhD comprehensive examinations have been temporarily modified to permit online or hybrid defenses/examinations, in addition to in-person defenses, due to COVID-19. In the case of hybrid defenses, the School of Public Health Sciences (SPHS) is permitting any ...
Masters level applicants may upload an OPTIONAL research proposal at the time of their application indicating their interest in completing an additional project. The brief 1-2 page proposal should include the following: ... School of Public Health | 734-764-5425 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-2029 US.
Ethics in public health clinical research. Comparing the strategies used in teaching and motivating public health professionals in developing and developed countries. Research Topics In Public Health For Masters. Advertising and impacts on food choices in the community. The use of stem cell technologies for cancer treatment: What are the latest ...
An overview of public health. Public health is the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting human health through organized community efforts as well as the informed choice of society, public, private and voluntary organizations and communities at large. Analyzing the health of a population and the threats to that ...
The thesis supervisor chairs the thesis proposal defence, which consists of a 20 minute presentation, followed by two rounds of questions. In the first round, each committee member has a maximum of 15 minutes to ask questions. In the second round, each committee member has a maximum of 10 minutes.
Title of the proposed research; Summary of research propposal and overall aim; Recommended sections include but not limited to background/rationale, aims, approach (including research team/mentors), future directions, and public health significance . If you are requested by the Scientific Review Committee to submit a detailed proposal, the ...
Grant Writing Guidance & Tips. Find and apply for federal grants at Grants.gov. CDC uses grants and cooperative agreements to fund public health programs that advance the agency's public health mission to keep Americans safe and healthy where they work, live, and play. The resources below can help health departments navigate the federal grant ...
The partnership will leverage the unique capabilities of NSF and SSRC through their diverse connections to the research community and public health organizations. ... NSF and SSRC invite research proposals that can reveal the complex factors that contribute to effective public health guidance and provide rigorous evidence that will be useful ...
NIAID Sample Forms, Plans, Letters, Emails, and More. National Cancer Institute (NCI) Behavioral Research Grant Applications (R01, R21, R03) Cancer Epidemiology Grant Applications (R01, R21, R03, R37) Cancer Control and Population Sciences Grant Applications (R01, R21, R37) Healthcare Delivery Research Grant Applications (R01, R03, R21, R50)
What are the trending topics in Public Health and related disciplines? Share. You can identify some of the most discussed and influential topics with the help of Altmetric attention scores, which take into account several outlets including social media, news articles, and policy documents. ... Health Education Research, Volume 36, Issue 3, June ...
1. Abstract. In 2011, the National Prevention, Health Promotion, and Public Health Council named mental and emotional well-being as 1 of. 7 priority areas for the National Prevention Strategy. In ...
Multidisciplinary research proposals. We encourage multi-disciplinary research proposals led-by, or involving, researchers from outside the disciplines usually associated with public health. This is particularly important given our intention to focus on population health priorities such as climate change. What we don't fund. We do not fund:
A framework for public health action: the health impact pyramid. American journal of public health, 100(4), 590-595. Frohlich, K. L., & Potvin, L. (2008). Transcending the known in public health practise: the inequality paradox: the population approach and vulnerable populations. American journal of public health, 98(2), 216-221.
The National Institute on Minority Health and health disparities research framework. Am J Public Health. 2019;109(S1):S16-S20. 15. Williams DR, Priest N, Anderson NB. Understanding associations among race, socioeconomic status, and health: patterns and prospects. Health Psychol. 2016;35(4):407-411. 16.
Australia's health ministers have been presented with grim evidence of the country's public hospital logjam ahead of their crucial meeting today. The AMA has released its annual Public Hospital Report Card, showing planned surgery wait times in Australia's public hospitals are now the longest on record, and emergency departments remain ...
The Pew Research Center survey conducted June 5-11, 2023, on the Center's American Trends Panel, asks about gun ownership using two separate questions to measure personal and household ownership. ... 63% see improving mental health screening and treatment as a very or extremely effective way to prevent school shootings. This is larger than ...
The budget expects a deficit of $40.0 billion for 2023-24 and forecasts deficits of $39.8 billion for 2024-25, and $38.9 billion for 2025-26. Although the budget does not change the federal personal or corporate tax rates, Finance announced that it will increase the inclusion rate for capital gains realized on or after June 25, 2024, in certain circumstances.