- Privacy Policy

Home » Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples
Table of Contents

Questionnaire
Definition:
A Questionnaire is a research tool or survey instrument that consists of a set of questions or prompts designed to gather information from individuals or groups of people.
It is a standardized way of collecting data from a large number of people by asking them a series of questions related to a specific topic or research objective. The questions may be open-ended or closed-ended, and the responses can be quantitative or qualitative. Questionnaires are widely used in research, marketing, social sciences, healthcare, and many other fields to collect data and insights from a target population.
History of Questionnaire
The history of questionnaires can be traced back to the ancient Greeks, who used questionnaires as a means of assessing public opinion. However, the modern history of questionnaires began in the late 19th century with the rise of social surveys.
The first social survey was conducted in the United States in 1874 by Francis A. Walker, who used a questionnaire to collect data on labor conditions. In the early 20th century, questionnaires became a popular tool for conducting social research, particularly in the fields of sociology and psychology.
One of the most influential figures in the development of the questionnaire was the psychologist Raymond Cattell, who in the 1940s and 1950s developed the personality questionnaire, a standardized instrument for measuring personality traits. Cattell’s work helped establish the questionnaire as a key tool in personality research.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the use of questionnaires expanded into other fields, including market research, public opinion polling, and health surveys. With the rise of computer technology, questionnaires became easier and more cost-effective to administer, leading to their widespread use in research and business settings.
Today, questionnaires are used in a wide range of settings, including academic research, business, healthcare, and government. They continue to evolve as a research tool, with advances in computer technology and data analysis techniques making it easier to collect and analyze data from large numbers of participants.
Types of Questionnaire
Types of Questionnaires are as follows:
Structured Questionnaire
This type of questionnaire has a fixed format with predetermined questions that the respondent must answer. The questions are usually closed-ended, which means that the respondent must select a response from a list of options.
Unstructured Questionnaire
An unstructured questionnaire does not have a fixed format or predetermined questions. Instead, the interviewer or researcher can ask open-ended questions to the respondent and let them provide their own answers.
Open-ended Questionnaire
An open-ended questionnaire allows the respondent to answer the question in their own words, without any pre-determined response options. The questions usually start with phrases like “how,” “why,” or “what,” and encourage the respondent to provide more detailed and personalized answers.
Close-ended Questionnaire
In a closed-ended questionnaire, the respondent is given a set of predetermined response options to choose from. This type of questionnaire is easier to analyze and summarize, but may not provide as much insight into the respondent’s opinions or attitudes.
Mixed Questionnaire
A mixed questionnaire is a combination of open-ended and closed-ended questions. This type of questionnaire allows for more flexibility in terms of the questions that can be asked, and can provide both quantitative and qualitative data.
Pictorial Questionnaire:
In a pictorial questionnaire, instead of using words to ask questions, the questions are presented in the form of pictures, diagrams or images. This can be particularly useful for respondents who have low literacy skills, or for situations where language barriers exist. Pictorial questionnaires can also be useful in cross-cultural research where respondents may come from different language backgrounds.
Types of Questions in Questionnaire
The types of Questions in Questionnaire are as follows:
Multiple Choice Questions
These questions have several options for participants to choose from. They are useful for getting quantitative data and can be used to collect demographic information.
- a. Red b . Blue c. Green d . Yellow
Rating Scale Questions
These questions ask participants to rate something on a scale (e.g. from 1 to 10). They are useful for measuring attitudes and opinions.
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend this product to a friend?
Open-Ended Questions
These questions allow participants to answer in their own words and provide more in-depth and detailed responses. They are useful for getting qualitative data.
- What do you think are the biggest challenges facing your community?
Likert Scale Questions
These questions ask participants to rate how much they agree or disagree with a statement. They are useful for measuring attitudes and opinions.
How strongly do you agree or disagree with the following statement:
“I enjoy exercising regularly.”
- a . Strongly Agree
- c . Neither Agree nor Disagree
- d . Disagree
- e . Strongly Disagree
Demographic Questions
These questions ask about the participant’s personal information such as age, gender, ethnicity, education level, etc. They are useful for segmenting the data and analyzing results by demographic groups.
- What is your age?
Yes/No Questions
These questions only have two options: Yes or No. They are useful for getting simple, straightforward answers to a specific question.
Have you ever traveled outside of your home country?
Ranking Questions
These questions ask participants to rank several items in order of preference or importance. They are useful for measuring priorities or preferences.
Please rank the following factors in order of importance when choosing a restaurant:
- a. Quality of Food
- c. Ambiance
- d. Location
Matrix Questions
These questions present a matrix or grid of options that participants can choose from. They are useful for getting data on multiple variables at once.
| The product is easy to use | ||||
| The product meets my needs | ||||
| The product is affordable |
Dichotomous Questions
These questions present two options that are opposite or contradictory. They are useful for measuring binary or polarized attitudes.
Do you support the death penalty?
How to Make a Questionnaire
Step-by-Step Guide for Making a Questionnaire:
- Define your research objectives: Before you start creating questions, you need to define the purpose of your questionnaire and what you hope to achieve from the data you collect.
- Choose the appropriate question types: Based on your research objectives, choose the appropriate question types to collect the data you need. Refer to the types of questions mentioned earlier for guidance.
- Develop questions: Develop clear and concise questions that are easy for participants to understand. Avoid leading or biased questions that might influence the responses.
- Organize questions: Organize questions in a logical and coherent order, starting with demographic questions followed by general questions, and ending with specific or sensitive questions.
- Pilot the questionnaire : Test your questionnaire on a small group of participants to identify any flaws or issues with the questions or the format.
- Refine the questionnaire : Based on feedback from the pilot, refine and revise the questionnaire as necessary to ensure that it is valid and reliable.
- Distribute the questionnaire: Distribute the questionnaire to your target audience using a method that is appropriate for your research objectives, such as online surveys, email, or paper surveys.
- Collect and analyze data: Collect the completed questionnaires and analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods. Draw conclusions from the data and use them to inform decision-making or further research.
- Report findings: Present your findings in a clear and concise report, including a summary of the research objectives, methodology, key findings, and recommendations.
Questionnaire Administration Modes
There are several modes of questionnaire administration. The choice of mode depends on the research objectives, sample size, and available resources. Some common modes of administration include:
- Self-administered paper questionnaires: Participants complete the questionnaire on paper, either in person or by mail. This mode is relatively low cost and easy to administer, but it may result in lower response rates and greater potential for errors in data entry.
- Online questionnaires: Participants complete the questionnaire on a website or through email. This mode is convenient for both researchers and participants, as it allows for fast and easy data collection. However, it may be subject to issues such as low response rates, lack of internet access, and potential for fraudulent responses.
- Telephone surveys: Trained interviewers administer the questionnaire over the phone. This mode allows for a large sample size and can result in higher response rates, but it is also more expensive and time-consuming than other modes.
- Face-to-face interviews : Trained interviewers administer the questionnaire in person. This mode allows for a high degree of control over the survey environment and can result in higher response rates, but it is also more expensive and time-consuming than other modes.
- Mixed-mode surveys: Researchers use a combination of two or more modes to administer the questionnaire, such as using online questionnaires for initial screening and following up with telephone interviews for more detailed information. This mode can help overcome some of the limitations of individual modes, but it requires careful planning and coordination.
Example of Questionnaire
Title of the Survey: Customer Satisfaction Survey
Introduction:
We appreciate your business and would like to ensure that we are meeting your needs. Please take a few minutes to complete this survey so that we can better understand your experience with our products and services. Your feedback is important to us and will help us improve our offerings.
Instructions:
Please read each question carefully and select the response that best reflects your experience. If you have any additional comments or suggestions, please feel free to include them in the space provided at the end of the survey.
1. How satisfied are you with our product quality?
- Very satisfied
- Somewhat satisfied
- Somewhat dissatisfied
- Very dissatisfied
2. How satisfied are you with our customer service?
3. How satisfied are you with the price of our products?
4. How likely are you to recommend our products to others?
- Very likely
- Somewhat likely
- Somewhat unlikely
- Very unlikely
5. How easy was it to find the information you were looking for on our website?
- Somewhat easy
- Somewhat difficult
- Very difficult
6. How satisfied are you with the overall experience of using our products and services?
7. Is there anything that you would like to see us improve upon or change in the future?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Conclusion:
Thank you for taking the time to complete this survey. Your feedback is valuable to us and will help us improve our products and services. If you have any further comments or concerns, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Applications of Questionnaire
Some common applications of questionnaires include:
- Research : Questionnaires are commonly used in research to gather information from participants about their attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and experiences. This information can then be analyzed and used to draw conclusions and make inferences.
- Healthcare : In healthcare, questionnaires can be used to gather information about patients’ medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle habits. This information can help healthcare professionals diagnose and treat medical conditions more effectively.
- Marketing : Questionnaires are commonly used in marketing to gather information about consumers’ preferences, buying habits, and opinions on products and services. This information can help businesses develop and market products more effectively.
- Human Resources: Questionnaires are used in human resources to gather information from job applicants, employees, and managers about job satisfaction, performance, and workplace culture. This information can help organizations improve their hiring practices, employee retention, and organizational culture.
- Education : Questionnaires are used in education to gather information from students, teachers, and parents about their perceptions of the educational experience. This information can help educators identify areas for improvement and develop more effective teaching strategies.
Purpose of Questionnaire
Some common purposes of questionnaires include:
- To collect information on attitudes, opinions, and beliefs: Questionnaires can be used to gather information on people’s attitudes, opinions, and beliefs on a particular topic. For example, a questionnaire can be used to gather information on people’s opinions about a particular political issue.
- To collect demographic information: Questionnaires can be used to collect demographic information such as age, gender, income, education level, and occupation. This information can be used to analyze trends and patterns in the data.
- To measure behaviors or experiences: Questionnaires can be used to gather information on behaviors or experiences such as health-related behaviors or experiences, job satisfaction, or customer satisfaction.
- To evaluate programs or interventions: Questionnaires can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions by gathering information on participants’ experiences, opinions, and behaviors.
- To gather information for research: Questionnaires can be used to gather data for research purposes on a variety of topics.
When to use Questionnaire
Here are some situations when questionnaires might be used:
- When you want to collect data from a large number of people: Questionnaires are useful when you want to collect data from a large number of people. They can be distributed to a wide audience and can be completed at the respondent’s convenience.
- When you want to collect data on specific topics: Questionnaires are useful when you want to collect data on specific topics or research questions. They can be designed to ask specific questions and can be used to gather quantitative data that can be analyzed statistically.
- When you want to compare responses across groups: Questionnaires are useful when you want to compare responses across different groups of people. For example, you might want to compare responses from men and women, or from people of different ages or educational backgrounds.
- When you want to collect data anonymously: Questionnaires can be useful when you want to collect data anonymously. Respondents can complete the questionnaire without fear of judgment or repercussions, which can lead to more honest and accurate responses.
- When you want to save time and resources: Questionnaires can be more efficient and cost-effective than other methods of data collection such as interviews or focus groups. They can be completed quickly and easily, and can be analyzed using software to save time and resources.
Characteristics of Questionnaire
Here are some of the characteristics of questionnaires:
- Standardization : Questionnaires are standardized tools that ask the same questions in the same order to all respondents. This ensures that all respondents are answering the same questions and that the responses can be compared and analyzed.
- Objectivity : Questionnaires are designed to be objective, meaning that they do not contain leading questions or bias that could influence the respondent’s answers.
- Predefined responses: Questionnaires typically provide predefined response options for the respondents to choose from, which helps to standardize the responses and make them easier to analyze.
- Quantitative data: Questionnaires are designed to collect quantitative data, meaning that they provide numerical or categorical data that can be analyzed using statistical methods.
- Convenience : Questionnaires are convenient for both the researcher and the respondents. They can be distributed and completed at the respondent’s convenience and can be easily administered to a large number of people.
- Anonymity : Questionnaires can be anonymous, which can encourage respondents to answer more honestly and provide more accurate data.
- Reliability : Questionnaires are designed to be reliable, meaning that they produce consistent results when administered multiple times to the same group of people.
- Validity : Questionnaires are designed to be valid, meaning that they measure what they are intended to measure and are not influenced by other factors.
Advantage of Questionnaire
Some Advantage of Questionnaire are as follows:
- Standardization: Questionnaires allow researchers to ask the same questions to all participants in a standardized manner. This helps ensure consistency in the data collected and eliminates potential bias that might arise if questions were asked differently to different participants.
- Efficiency: Questionnaires can be administered to a large number of people at once, making them an efficient way to collect data from a large sample.
- Anonymity: Participants can remain anonymous when completing a questionnaire, which may make them more likely to answer honestly and openly.
- Cost-effective: Questionnaires can be relatively inexpensive to administer compared to other research methods, such as interviews or focus groups.
- Objectivity: Because questionnaires are typically designed to collect quantitative data, they can be analyzed objectively without the influence of the researcher’s subjective interpretation.
- Flexibility: Questionnaires can be adapted to a wide range of research questions and can be used in various settings, including online surveys, mail surveys, or in-person interviews.
Limitations of Questionnaire
Limitations of Questionnaire are as follows:
- Limited depth: Questionnaires are typically designed to collect quantitative data, which may not provide a complete understanding of the topic being studied. Questionnaires may miss important details and nuances that could be captured through other research methods, such as interviews or observations.
- R esponse bias: Participants may not always answer questions truthfully or accurately, either because they do not remember or because they want to present themselves in a particular way. This can lead to response bias, which can affect the validity and reliability of the data collected.
- Limited flexibility: While questionnaires can be adapted to a wide range of research questions, they may not be suitable for all types of research. For example, they may not be appropriate for studying complex phenomena or for exploring participants’ experiences and perceptions in-depth.
- Limited context: Questionnaires typically do not provide a rich contextual understanding of the topic being studied. They may not capture the broader social, cultural, or historical factors that may influence participants’ responses.
- Limited control : Researchers may not have control over how participants complete the questionnaire, which can lead to variations in response quality or consistency.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Quasi-Experimental Research Design – Types...

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types...

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Designing a Questionnaire for a Research Paper: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Develop an Effective Questionnaire

A questionnaire is an important instrument in a research study to help the researcher collect relevant data regarding the research topic. It is significant to ensure that the design of the questionnaire is arranged to minimize errors. However, researchers commonly face challenges in designing an effective questionnaire including its content, appearance and usage that leads to inappropriate and biased findings in a study. This paper aims to review the main steps to design a questionnaire introducing the process that starts with defining the information required for a study, then continues with the identification of the type of survey and types of questions, writing questions and building the construct of the questionnaire. It also develops the demand to pre-test the questionnaire and finalizing the questionnaire to conduct the survey.
Related Papers
Innovations in Measuring and Evaluating Scientific Information
Rayees Farooq
Indian Journal of Anaesthesia
Narayana Yaddanapudi
Edrine Wanyama
Questionnaire construction has overtime evolved with consistency and rarely, it has been skipped in the world’s researches. Questionnaires form the basis for which most pieces of information can be obtained. In the very light, response rates to questions and accuracy of data findings are possible through the use of questionnaire usage. Where a questionnaire is poorly constructed, one faces the risk of missing out vital information which could be forming the basis for research. This paper discusses the relevance and importance of questionnaire construction in data collection and research. An attempt is made to show questionnaire usage in social research and other research processes. Ultimately, questionnaire construction is considered just as important as any other research process used while collecting data. Some key recommendations that could make questionnaire usage in research better are also briefly considered.
Trisha Greenhalgh
Abla BENBELLAL
International Dental & Medical Journal of Advanced Research - VOLUME 2015
Saumya Dubey
Ebenezer Consultan
International Journal of Market Research
Petra Lietz
Some consider responding to survey questions as a sophisticated cognitive process whereby respondents go through, often iterative, steps to process the information provided to them by questions and response options. Others focus more on the interplay between questions and answers as a complex communication process between researchers and respondents, their assumptions, expectations and perceptions. In this article, cognitive and communication research is reviewed that has tested the impact of different question and answer alternatives on the responses obtained. This leads to evidence-based recommendations for market researchers, who frequently have to make decisions regarding various aspects of questionnaire design such as question length and order, question wording, as well as the optimal number of response options and the desirability or otherwise of a ‘don't know’ option or a middle alternative.
Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care
Gill Wakley
Daniela Garcia
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
De Wet Schutte
Lyberg/Survey
Norbert Schwarz
International Statistical Review
massimo borelli
Health Information & Libraries Journal
Andrew Booth
Nursing Times Research
michael kirk-smith
Petra Boynton
Market Research Society. Journal.
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Mohamad Adam Bujang
Medical Teacher
Anthony Artino
Jiayi Zhang
Sallie Newell
Health technology assessment (Winchester, England)
Lois Thomas , Claire Bamford , E. McColl
Burcu Akhun
International Journal of Assessment Tools in Education
Betty Adams
Jason Harlacher
Clinical Nurse Specialist
Sandra Siedlecki
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery
Randal Paniello
Nipuni Rangika
André Pereira
Biometrics & Biostatistics International Journal
Prof. Dr. İlker Etikan
International Journal of Management, Technology, and Social Sciences (IJMTS)
Srinivas Publication , Sreeramana Aithal
Zurina Saaya
Amanda Hunn
Anco Hundepool
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- 10 Research Question Examples to Guide Your Research Project
10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project
Published on October 30, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on October 19, 2023.
The research question is one of the most important parts of your research paper , thesis or dissertation . It’s important to spend some time assessing and refining your question before you get started.
The exact form of your question will depend on a few things, such as the length of your project, the type of research you’re conducting, the topic , and the research problem . However, all research questions should be focused, specific, and relevant to a timely social or scholarly issue.
Once you’ve read our guide on how to write a research question , you can use these examples to craft your own.
| Research question | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The first question is not enough. The second question is more , using . | |
| Starting with “why” often means that your question is not enough: there are too many possible answers. By targeting just one aspect of the problem, the second question offers a clear path for research. | |
| The first question is too broad and subjective: there’s no clear criteria for what counts as “better.” The second question is much more . It uses clearly defined terms and narrows its focus to a specific population. | |
| It is generally not for academic research to answer broad normative questions. The second question is more specific, aiming to gain an understanding of possible solutions in order to make informed recommendations. | |
| The first question is too simple: it can be answered with a simple yes or no. The second question is , requiring in-depth investigation and the development of an original argument. | |
| The first question is too broad and not very . The second question identifies an underexplored aspect of the topic that requires investigation of various to answer. | |
| The first question is not enough: it tries to address two different (the quality of sexual health services and LGBT support services). Even though the two issues are related, it’s not clear how the research will bring them together. The second integrates the two problems into one focused, specific question. | |
| The first question is too simple, asking for a straightforward fact that can be easily found online. The second is a more question that requires and detailed discussion to answer. | |
| ? dealt with the theme of racism through casting, staging, and allusion to contemporary events? | The first question is not — it would be very difficult to contribute anything new. The second question takes a specific angle to make an original argument, and has more relevance to current social concerns and debates. |
| The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not . The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically . For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries. |
Note that the design of your research question can depend on what method you are pursuing. Here are a few options for qualitative, quantitative, and statistical research questions.
| Type of research | Example question |
|---|---|
| Qualitative research question | |
| Quantitative research question | |
| Statistical research question |
Other interesting articles
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, October 19). 10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project. Scribbr. Retrieved June 28, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-question-examples/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, evaluating sources | methods & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings
As a staple in data collection, questionnaires help uncover robust and reliable findings that can transform industries, shape policies, and revolutionize understanding. Whether you are exploring societal trends or delving into scientific phenomena, the effectiveness of your research questionnaire can make or break your findings.
In this article, we aim to understand the core purpose of questionnaires, exploring how they serve as essential tools for gathering systematic data, both qualitative and quantitative, from diverse respondents. Read on as we explore the key elements that make up a winning questionnaire, the art of framing questions which are both compelling and rigorous, and the careful balance between simplicity and depth.
Table of Contents
The Role of Questionnaires in Research
So, what is a questionnaire? A questionnaire is a structured set of questions designed to collect information, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. It is one of the most commonly used data collection methods in research. Moreover, questionnaires can be used in various research fields, including social sciences, market research, healthcare, education, and psychology. Their adaptability makes them suitable for investigating diverse research questions.
Questionnaire and survey are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in the context of research. A survey refers to the broader process of data collection that may involve various methods. A survey can encompass different data collection techniques, such as interviews , focus groups, observations, and yes, questionnaires.
Pros and Cons of Using Questionnaires in Research:
While questionnaires offer numerous advantages in research, they also come with some disadvantages that researchers must be aware of and address appropriately. Careful questionnaire design, validation, and consideration of potential biases can help mitigate these disadvantages and enhance the effectiveness of using questionnaires as a data collection method.

Structured vs Unstructured Questionnaires
Structured questionnaire:.
A structured questionnaire consists of questions with predefined response options. Respondents are presented with a fixed set of choices and are required to select from those options. The questions in a structured questionnaire are designed to elicit specific and quantifiable responses. Structured questionnaires are particularly useful for collecting quantitative data and are often employed in surveys and studies where standardized and comparable data are necessary.
Advantages of Structured Questionnaires:
- Easy to analyze and interpret: The fixed response options facilitate straightforward data analysis and comparison across respondents.
- Efficient for large-scale data collection: Structured questionnaires are time-efficient, allowing researchers to collect data from a large number of respondents.
- Reduces response bias: The predefined response options minimize potential response bias and maintain consistency in data collection.
Limitations of Structured Questionnaires:
- Lack of depth: Structured questionnaires may not capture in-depth insights or nuances as respondents are limited to pre-defined response choices. Hence, they may not reveal the reasons behind respondents’ choices, limiting the understanding of their perspectives.
- Limited flexibility: The fixed response options may not cover all potential responses, therefore, potentially restricting respondents’ answers.
Unstructured Questionnaire:
An unstructured questionnaire consists of questions that allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses. Unlike structured questionnaires, there are no predefined response options, giving respondents the freedom to express their thoughts in their own words. Furthermore, unstructured questionnaires are valuable for collecting qualitative data and obtaining in-depth insights into respondents’ experiences, opinions, or feelings.
Advantages of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Rich qualitative data: Unstructured questionnaires yield detailed and comprehensive qualitative data, providing valuable and novel insights into respondents’ perspectives.
- Flexibility in responses: Respondents have the freedom to express themselves in their own words. Hence, allowing for a wide range of responses.
Limitations of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Time-consuming analysis: Analyzing open-ended responses can be time-consuming, since, each response requires careful reading and interpretation.
- Subjectivity in interpretation: The analysis of open-ended responses may be subjective, as researchers interpret and categorize responses based on their judgment.
- May require smaller sample size: Due to the depth of responses, researchers may need a smaller sample size for comprehensive analysis, making generalizations more challenging.
Types of Questions in a Questionnaire
In a questionnaire, researchers typically use the following most common types of questions to gather a variety of information from respondents:
1. Open-Ended Questions:
These questions allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses in their own words. Open-ended questions are valuable for gathering qualitative data and in-depth insights.
Example: What suggestions do you have for improving our product?
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Respondents choose one answer from a list of provided options. This type of question is suitable for gathering categorical data or preferences.
Example: Which of the following social media/academic networking platforms do you use to promote your research?
- ResearchGate
- Academia.edu
3. Dichotomous Questions
Respondents choose between two options, typically “yes” or “no”, “true” or “false”, or “agree” or “disagree”.
Example: Have you ever published in open access journals before?
4. Scaling Questions
These questions, also known as rating scale questions, use a predefined scale that allows respondents to rate or rank their level of agreement, satisfaction, importance, or other subjective assessments. These scales help researchers quantify subjective data and make comparisons across respondents.
There are several types of scaling techniques used in scaling questions:
i. Likert Scale:
The Likert scale is one of the most common scaling techniques. It presents respondents with a series of statements and asks them to rate their level of agreement or disagreement using a range of options, typically from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree”.For example: Please indicate your level of agreement with the statement: “The content presented in the webinar was relevant and aligned with the advertised topic.”
- Strongly Agree
- Strongly Disagree
ii. Semantic Differential Scale:
The semantic differential scale measures respondents’ perceptions or attitudes towards an item using opposite adjectives or bipolar words. Respondents rate the item on a scale between the two opposites. For example:
- Easy —— Difficult
- Satisfied —— Unsatisfied
- Very likely —— Very unlikely
iii. Numerical Rating Scale:
This scale requires respondents to provide a numerical rating on a predefined scale. It can be a simple 1 to 5 or 1 to 10 scale, where higher numbers indicate higher agreement, satisfaction, or importance.
iv. Ranking Questions:
Respondents rank items in order of preference or importance. Ranking questions help identify preferences or priorities.
Example: Please rank the following features of our app in order of importance (1 = Most Important, 5 = Least Important):
- User Interface
- Functionality
- Customer Support
By using a mix of question types, researchers can gather both quantitative and qualitative data, providing a comprehensive understanding of the research topic and enabling meaningful analysis and interpretation of the results. The choice of question types depends on the research objectives , the desired depth of information, and the data analysis requirements.
Methods of Administering Questionnaires
There are several methods for administering questionnaires, and the choice of method depends on factors such as the target population, research objectives , convenience, and resources available. Here are some common methods of administering questionnaires:

Each method has its advantages and limitations. Online surveys offer convenience and a large reach, but they may be limited to individuals with internet access. Face-to-face interviews allow for in-depth responses but can be time-consuming and costly. Telephone surveys have broad reach but may be limited by declining response rates. Researchers should choose the method that best suits their research objectives, target population, and available resources to ensure successful data collection.
How to Design a Questionnaire
Designing a good questionnaire is crucial for gathering accurate and meaningful data that aligns with your research objectives. Here are essential steps and tips to create a well-designed questionnaire:
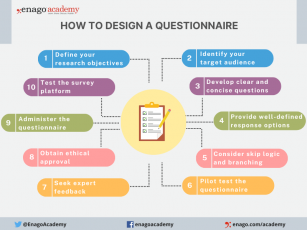
1. Define Your Research Objectives : Clearly outline the purpose and specific information you aim to gather through the questionnaire.
2. Identify Your Target Audience : Understand respondents’ characteristics and tailor the questionnaire accordingly.
3. Develop the Questions :
- Write Clear and Concise Questions
- Avoid Leading or Biasing Questions
- Sequence Questions Logically
- Group Related Questions
- Include Demographic Questions
4. Provide Well-defined Response Options : Offer exhaustive response choices for closed-ended questions.
5. Consider Skip Logic and Branching : Customize the questionnaire based on previous answers.
6. Pilot Test the Questionnaire : Identify and address issues through a pilot study .
7. Seek Expert Feedback : Validate the questionnaire with subject matter experts.
8. Obtain Ethical Approval : Comply with ethical guidelines , obtain consent, and ensure confidentiality before administering the questionnaire.
9. Administer the Questionnaire : Choose the right mode and provide clear instructions.
10. Test the Survey Platform : Ensure compatibility and usability for online surveys.
By following these steps and paying attention to questionnaire design principles, you can create a well-structured and effective questionnaire that gathers reliable data and helps you achieve your research objectives.
Characteristics of a Good Questionnaire
A good questionnaire possesses several essential elements that contribute to its effectiveness. Furthermore, these characteristics ensure that the questionnaire is well-designed, easy to understand, and capable of providing valuable insights. Here are some key characteristics of a good questionnaire:
1. Clarity and Simplicity : Questions should be clear, concise, and unambiguous. Avoid using complex language or technical terms that may confuse respondents. Simple and straightforward questions ensure that respondents interpret them consistently.
2. Relevance and Focus : Each question should directly relate to the research objectives and contribute to answering the research questions. Consequently, avoid including extraneous or irrelevant questions that could lead to data clutter.
3. Mix of Question Types : Utilize a mix of question types, including open-ended, Likert scale, and multiple-choice questions. This variety allows for both qualitative and quantitative data collections .
4. Validity and Reliability : Ensure the questionnaire measures what it intends to measure (validity) and produces consistent results upon repeated administration (reliability). Validation should be conducted through expert review and previous research.
5. Appropriate Length : Keep the questionnaire’s length appropriate and manageable to avoid respondent fatigue or dropouts. Long questionnaires may result in incomplete or rushed responses.
6. Clear Instructions : Include clear instructions at the beginning of the questionnaire to guide respondents on how to complete it. Explain any technical terms, formats, or concepts if necessary.
7. User-Friendly Format : Design the questionnaire to be visually appealing and user-friendly. Use consistent formatting, adequate spacing, and a logical page layout.
8. Data Validation and Cleaning : Incorporate validation checks to ensure data accuracy and reliability. Consider mechanisms to detect and correct inconsistent or missing responses during data cleaning.
By incorporating these characteristics, researchers can create a questionnaire that maximizes data quality, minimizes response bias, and provides valuable insights for their research.
In the pursuit of advancing research and gaining meaningful insights, investing time and effort into designing effective questionnaires is a crucial step. A well-designed questionnaire is more than a mere set of questions; it is a masterpiece of precision and ingenuity. Each question plays a vital role in shaping the narrative of our research, guiding us through the labyrinth of data to meaningful conclusions. Indeed, a well-designed questionnaire serves as a powerful tool for unlocking valuable insights and generating robust findings that impact society positively.
Have you ever designed a research questionnaire? Reflect on your experience and share your insights with researchers globally through Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform . Join our diverse community of 1000K+ researchers and authors to exchange ideas, strategies, and best practices, and together, let’s shape the future of data collection and maximize the impact of questionnaires in the ever-evolving landscape of research.
Frequently Asked Questions
A research questionnaire is a structured tool used to gather data from participants in a systematic manner. It consists of a series of carefully crafted questions designed to collect specific information related to a research study.
Questionnaires play a pivotal role in both quantitative and qualitative research, enabling researchers to collect insights, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. This aids in hypothesis testing, understanding, and informed decision-making, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and facilitating comparisons.
Questionnaires are a versatile tool employed in various research designs to gather data efficiently and comprehensively. They find extensive use in both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies, making them a fundamental component of research across disciplines. Some research designs that commonly utilize questionnaires include: a) Cross-Sectional Studies b) Longitudinal Studies c) Descriptive Research d) Correlational Studies e) Causal-Comparative Studies f) Experimental Research g) Survey Research h) Case Studies i) Exploratory Research
A survey is a comprehensive data collection method that can include various techniques like interviews and observations. A questionnaire is a specific set of structured questions within a survey designed to gather standardized responses. While a survey is a broader approach, a questionnaire is a focused tool for collecting specific data.
The choice of questionnaire type depends on the research objectives, the type of data required, and the preferences of respondents. Some common types include: • Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires consist of predefined, closed-ended questions with fixed response options. They are easy to analyze and suitable for quantitative research. • Semi-Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires combine closed-ended questions with open-ended ones. They offer more flexibility for respondents to provide detailed explanations. • Unstructured Questionnaires: These questionnaires contain open-ended questions only, allowing respondents to express their thoughts and opinions freely. They are commonly used in qualitative research.
Following these steps ensures effective questionnaire administration for reliable data collection: • Choose a Method: Decide on online, face-to-face, mail, or phone administration. • Online Surveys: Use platforms like SurveyMonkey • Pilot Test: Test on a small group before full deployment • Clear Instructions: Provide concise guidelines • Follow-Up: Send reminders if needed
Thank you, Riya. This is quite helpful. As discussed, response bias is one of the disadvantages in the use of questionnaires. One way to help limit this can be to use scenario based questions. These type of questions may help the respondents to be more reflective and active in the process.
Thank you, Dear Riya. This is quite helpful.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![research paper with questionnaires What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What would be most effective in reducing research misconduct?
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.328(7452); 2004 Jun 5
Hands-on guide to questionnaire research
Administering, analysing, and reporting your questionnaire, petra m boynton.
1 Department of Primary Care and Population Sciences, University College London, London N19 5LW [email protected]
Associated Data
Short abstract.
Understanding your study group is key to getting a good response to a questionnaire; dealing with the resulting mass of data is another challenge
The first step in producing good questionnaire research is getting the right questionnaire. 1 However, even the best questionnaire will not get adequate results if it is not used properly. This article outlines how to pilot your questionnaire, distribute and administer it; and get it returned, analysed, and written up for publication. It is intended to supplement published guidance on questionnaire research, three quarters of which focuses on content and design. 2
Questionnaires tend to fail because participants don't understand them, can't complete them, get bored or offended by them, or dislike how they look. Although friends and colleagues can help check spelling, grammar, and layout, they cannot reliably predict the emotional reactions or comprehension difficulties of other groups. Whether you have constructed your own questionnaire or are using an existing instrument, always pilot it on participants who are representative of your definitive sample. You need to build in protected time for this phase and get approval from an ethics committee. 3
During piloting, take detailed notes on how participants react to both the general format of your instrument and the specific questions. How long do people take to complete it? Do any questions need to be repeated or explained? How do participants indicate that they have arrived at an answer? Do they show confusion or surprise at a particular response—if so, why? Short, abrupt questions may unintentionally provoke short, abrupt answers. Piloting will provide a guide for rephrasing questions to invite a richer response (box 1). 1).

Box 1: Patient preference is preferable
I worked on a sexual health study where we initially planned to present the questionnaire on a computer, since we had read people were supposedly more comfortable “talking” to a computer. Although this seemed to be the case in practices with middle class patients, we struggled to recruit in practices where participants were less familiar with computers. Their reasons for refusal were not linked to the topic of the research, but because they saw our laptops as something they might break, could make them look foolish, or would feed directly to the internet (which was inextricably linked to computers in some people's minds). We found offering a choice between completing the questionnaire on paper or the laptop computer greatly increased response rates.
Planning data collection
You should be aware of the relevant data protection legislation (for United Kingdom see www.informationcommissioner.gov.uk ) and ensure that you follow internal codes of practice for your institution—for example, obtaining and completing a form from your data protection officer. Do not include names, addresses, or other identifying markers within your electronic database, except for a participant number linked to a securely kept manual file.
The piloting phase should include planning and testing a strategy for getting your questionnaire out and back—for example, who you have invited to complete it (the sampling frame), who has agreed to do so (the response rate), who you've had usable returns from (the completion rate), and whether and when you needed to send a reminder letter. If you are employing researchers to deliver and collect the questionnaire it's important they know exactly how to do this. 4
Administrative errors can hamper the progress of your research. Real examples include researchers giving the questionnaire to wrong participants (for example, a questionnaire aimed at men given to women); incomplete instructions on how to fill in the questionnaire (for example, participants did not know whether to tick one or several items); postal surveys in which the questionnaire was missing from the envelope; and a study of over 3000 participants in which the questionnaire was sent out with no return address.
Administering your questionnaire
The choice of how to administer a questionnaire is too often made on convenience or cost grounds (see table A on bmj.com ). Scientific and ethical considerations should include:
- The needs and preferences of participants, who should understand what is required of them; remain interested and cooperative throughout completion; be asked the right questions and have their responses recorded accurately; and receive appropriate support during and after completing the questionnaire
- The skills and resources available to your research team
- The nature of your study—for example, short term feasibility projects, clinical trials, or large scale surveys.
Maximising your response rate
Sending out hundreds of questionnaires is a thankless task, and it is sometimes hard to pay attention to the many minor details that combine to raise response and completion rates. Extensive evidence exists on best practice (box 2), and principal investigators should ensure that they provide their staff with the necessary time and resources to follow it. Note, however, that it is better to collect fewer questionnaires with good quality responses than high numbers of questionnaires that are inaccurate or incomplete. The third article in this series discusses how to maximise response rates from groups that are hard to research. 15
Accounting for those who refuse to participate
Survey research tends to focus on people who have completed the study. Yet those who don't participate are equally important scientifically, and their details should also be recorded (remember to seek ethical approval for this). 4 , 16 , 17
Box 2: Factors shown to increase response rates
- The questionnaire is clearly designed and has a simple layout 5
- It offers participants incentives or prizes in return for completion 6
- It has been thoroughly piloted and tested 5
- Participants are notified about the study in advance with a personalised invitation 7
- The aim of study and means of completing the questionnaire are clearly explained 8 , 9
- A researcher is available to answer questions and collect the completed questionnaire 10
- If using a postal questionnaire, a stamped addressed envelope is included 7
- The participant feels they are a stakeholder in the study 11
- Questions are phrased in a way that holds the participant's attention 11
- Questionnaire has clear focus and purpose and is kept concise 7 , 8 , 11
- The questionnaire is appealing to look at, 12 as is the researcher 13
- If appropriate, the questionnaire is delivered electronically 14
One way of reducing refusal and non-completion rates is to set strict exclusion criteria at the start of your research. For example, for practical reasons many studies exclude participants who are unable to read or write in the language of the questionnaire and those with certain physical and mental disabilities that might interfere with their ability to give informed consent, cooperate with the researcher, or understand the questions asked. However, research that systematically excludes hard to reach groups is increasingly seen as unethical, and you may need to build additional strategies and resources into your study protocol at the outset. 15 Keep a record of all participants that fit the different exclusion categories (see bmj.com ).
Collecting data on non-participants will also allow you to monitor the research process. For example, you may find that certain researchers seem to have a higher proportion of participants refusing, and if so you should work with those individuals to improve the way they introduce the research or seek consent. In addition, if early refusals are found to be unusually high, you might need to rethink your overall approach. 10

Entering, checking, and cleaning data
Novice researchers often assume that once they have selected, designed, and distributed their questionnaire, their work is largely complete. In reality, entering, checking, and cleaning the data account for much of the workload. Some principles for keeping quantitative data clean are listed on bmj.com .
Even if a specialist team sets up the database(s), all researchers should be taught how to enter, clean, code, and back up the data, and the system for doing this should be universally agreed and understood. Agree on the statistical package you wish to use (such as SPSS, Stata, EpiInfo, Excel, or Access) and decide on a coding system before anyone starts work on the dataset.
It is good practice to enter data into an electronic database as the study progresses rather than face a mountain of processing at the end. The project manager should normally take responsibility for coordinating and overseeing this process and for ensuring that all researchers know what their role is with data management. These and other management tasks are time consuming and must be built into the study protocol and budget. Include data entry and coding in any pilot study to get an estimate of the time required and potential problems to troubleshoot.
Analysing your data
You should be able to predict the type of analysis required for your different questionnaire items at the planning stage of your study by considering the structure of each item and the likely distribution of responses (box 3). 1 Table B on bmj.com shows some examples of data analysis methods for different types of responses. 18 , 19 w1
Writing up and reporting
Once you have completed your data analysis, you will need to think creatively about the clearest and most parsimonious way to report and present your findings. You will almost certainly find that you have too much data to fit into a standard journal article, dissertation, or research report, so deciding what to include and omit is crucial. Take statistical advice from the outset of your research. This can keep you focused on the hypothesis or question you are testing and the important results from your study (and therefore what tables and graphs to present).
Box 3: Nasty surprise from a simple questionnaire
Moshe selected a standardised measure on emotional wellbeing to use in his research, which looked easy to complete and participants answered readily. When he came to analysing his data, he discovered that rather than scoring each response directly as indicated on the questionnaire, a complicated computer algorithm had to be created, and he was stumped. He found a statistician to help with the recoding, and realised that for future studies it might be an idea to check both the measure and its scoring system before selecting it.
Box 4: An unexpected result
Priti, a specialist registrar in hepatology, completed an attitude questionnaire in patients having liver transplantation and those who were still waiting for a donor. She expected to find that those who had received a new liver would be happier than those awaiting a donor. However, the morale scale used in her questionnaire showed that the transplantation group did not have significantly better morale scores. Priti felt that this negative finding was worth further investigation.
Methods section
The methods section should give details of your exclusion criteria and discuss their implications for the transferability of your findings. Data on refusals and unsuitable participants should also be presented and discussed, preferably using a recruitment diagram. w2 Finally, state and justify the statistical or qualitative analyses used. 18 , 19 w2
Results section
When compiling the results section you should return to your original research question and set out the findings that addressed this. In other words, make sure your results are hypothesis driven. Do not be afraid to report non-significant results, which in reality are often as important as significant results—for example, if participants did not experience anxiety in a particular situation (box 4). Don't analyse and report on every question within your questionnaire
Choose the most statistically appropriate and visually appealing format for graphs ( table ). w3 Label graphs and their axes adequately and include meaningful titles for tables and diagrams. Refer your reader to any tables or graphs within your text, and highlight the main findings.
Examples of ways of presenting data and when to use them
| Data table | If you need to produce something that is simple and quick and that has a low publication cost for journals. If you want to make data accessible to the interested reader for further manipulations | Do not use if you want to make your work look visually appealing. Too many tables can weigh down the results section and obscure the really key results. The reader is forced to work too hard and may give up reading your report |
| Bar chart | If you need to convey changes and differences, particularly between groups (eg how men and women differed in their views on an exercise programme for recovering heart attack patients) | If your data are linear and each item is related to the previous then you should use a (line) graph. Bar charts treat data as though they are separate groups not continuous variables |
| Scatter graph | Mostly used for displaying correlations or regressions (eg association between number of cigarettes smoked and reduced lung capacity) | If your data are based on groups or aggregated outcomes rather than individual scores |
| Pie chart | Used for simple summaries of data, particularly if a small number of choices were provided | As with bar charts, avoid if you want to present linear or relational data |
| Line graph | Where the points on the graph are logically linked, usually in time (eg scores on quality of life and emotional wellbeing measures taken monthly over six months) | If your data were not linked over time, repetition, etc it is inappropriate to suggest a linear relation by presenting findings in this format |
If you have used open ended questions within your questionnaire, do not cherry pick quotes for your results section. You need to outline what main themes emerged, and use quotes as necessary to illustrate the themes and supplement your quantitative findings.
Discussion section
The discussion should refer back to the results section and suggest what the main findings mean. You should acknowledge the limitations of your study and couch the discussion in the light of these. For example, if your response rate was low, you may need to recommend further studies to confirm your preliminary results. Your conclusions must not go beyond the scope of your study—for example, if you have done a small, parochial study do not suggest changes in national policy. You should also discuss any questions your participants persistently refused to answer or answered in a way you didn't expect.
Taking account of psychological and social influences
Questionnaire research (and indeed science in general) can never be completely objective. Researchers and participants are all human beings with psychological, emotional, and social needs. Too often, we fail to take these factors into account when planning, undertaking, and analysing our work. A questionnaire means something different to participants and researchers. w4 Researchers want data (with a view to publications, promotion, academic recognition, and further grant income). Junior research staff and administrators, especially if poorly trained and supervised, may be put under pressure, leading to critical errors in piloting (for example, piloting on friends rather than the target group), sampling (for example, drifting towards convenience rather than random samples) and in the distribution, collection, and coding of questionnaires. 15 Staff employed to assist with a questionnaire study may not be familiar with all the tasks required to make it a success and may be unaware that covering up their ignorance or skill deficits will make the entire study unsound.
Summary points
Piloting is essential to check the questionnaire works in the study group and identify administrative and analytical problems
The method of administration should be determined by scientific considerations not just costs
Entering, checking, and cleaning data should be done as the study progresses
Don't try to include all the results when reporting studies
Do include exclusion criteria and data on non-respondents
Research participants, on the other hand, may be motivated to complete a questionnaire through interest, boredom, a desire to help others (particularly true in health studies), because they feel pressurised to do so, through loneliness, or for an unconscious ulterior motive (“pleasing the doctor”). All of these introduce potential biases into the recruitment and data collection process.
Supplementary Material
This is the second in a series of three articles edited by Trisha Greenhalgh
I thank Alicia O'Cathain, Trish Greenhalgh, Jill Russell, Geoff Wong, Marcia Rigby, Sara Shaw, Fraser Macfarlane, and Will Callaghan for their helpful feedback on earlier versions of this paper and Gary Wood for advice on statistics and analysis.
PMB has taught research methods in a primary care setting for the past 13 years, specialising in practical approaches and using the experiences and concerns of researchers and participants as the basis of learning. This series of papers arose directly from questions asked about real questionnaire studies. To address these questions she and Trisha Greenhalgh explored a wide range of sources from the psychological and health services research literature.
Competing interests: None declared.

- Hirsh Health Sciences
- Lilly Music
- Webster Veterinary
- Hirsh Health Sciences Library
Finding and Creating Surveys/Questionnaires
- Published Questionnaires
- Finding Info about Tests
Look for a Test
- PsycTESTS Provides access to abstracts and some full-text of psychological tests, measures, scales, surveys, and other assessments as well as descriptive information about the test and its development and administration. Most records include the actual instrument.
Searching for Surveys/Questionnaires
Some questionnaires or surveys are published within an article. To find them, conduct an article search in a bibliographic database on the topic of interest and add in the Keywords: survey* or questionnaire*
In some cases the actual questionnaire or survey is not published with the article, but referred to within the text. In this case look at the bibliography and find the reference to the questionnaire/survey itself, or to the original article where the instrument was published. From that information track down the instrument.
Some instruments are not free. They can be purchased from the developer.
Tips for searching for an already established survey or questionnaire. Be sure to read the definition if there is one and also look to see if there is a broader or narrower concept that might be more specific to your needs.
- In Ovid MEDLINE or PubMed using MeSH terminology
- Use the subheading for Statistics and Numerical Data (sn) with your topic
- In conjunction with your topic use the term AND to combine the topic with any of the terms below.
- There is a broader term Data Collection or a narrower term Self Report , if those are more appropriate.
- There are more discipline specific subject headings or MeSH, such as the ones below. Be sure to read the definitions of these terms to make sure they are correct for what you want to find.
- Health Surveys
- Dental Health Surveys
- Health Status Indicators
- Nutrition Surveys
- Diet Surveys
- Health Care Surveys
- Nutrition Assessment
- Questionnaires
- In PsycInfo, these terms might be helpful:
- Attitude Measures
- Opinion Survey
- General Health Questionnaires
- Mail Surveys
- Consumer Surveys
- Telephone Surveys
- Test Construction
- In Sociological Abstracts
- Attitudes
- In ERIC (education research)
- Evaluation Methods
- << Previous: Surveys
- Next: Finding Info about Tests >>

Desk Hours: M-F 7:45am-5pm
- Last Updated: Nov 22, 2023 10:58 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.tufts.edu/surveys
What Is a Questionnaire and How Is It Used in Research?
2022-06-29 Market Research
The importance of questionnaires in research is immense, helping researchers gain relevant information quickly and effectively. Before creating a questionnaire for your study, you should first understand the meaning of questionnaires and the advantages and disadvantages of using them.
What Is a Questionnaire?
A questionnaire is a research tool featuring a series of questions used to collect useful information from respondents. These instruments include either written or oral questions and comprise an interview-style format. Questionnaires may be qualitative or quantitative and can be conducted online, by phone, on paper or face-to-face, and questions don’t necessarily have to be administered with a researcher present.
Questionnaires feature either open or closed questions and sometimes employ a mixture of both. Open-ended questions enable respondents to answer in their own words in as much or as little detail as they desire. Closed questions provide respondents with a series of predetermined responses they can choose from.
Is “Questionnaire” Just Another Word for “Survey”?
While the two terms seem synonymous, there are not quite the same. A questionnaire is a set of questions created for the purpose of gathering information; that information may not be used for a survey. However, all surveys do require questionnaires. If you are using a questionnaire for survey sampling, it’s important to ensure that it is designed to gather the most accurate answers from respondents.
Why Are Questionnaires Effective in Research?
Questionnaires are popular research methods because they offer a fast, efficient and inexpensive means of gathering large amounts of information from sizeable sample volumes. These tools are particularly effective for measuring subject behavior, preferences, intentions, attitudes and opinions. Their use of open and closed research questions enables researchers to obtain both qualitative and quantitative data, resulting in more comprehensive results.
Pros and Cons of Using Questionnaires in Research
Though the importance of questionnaires in research is clear, there are both pros and cons to using these instruments to gather information. Learn more about questionnaire advantages and disadvantages to determine if they’re suitable for your study.
Advantages of Questionnaires
Some of the many benefits of using questionnaires as a research tool include:
- Practicality: Questionnaires enable researchers to strategically manage their target audience, questions and format while gathering large data quantities on any subject.
- Cost-efficiency: You don’t need to hire surveyors to deliver your survey questions — instead, you can place them on your website or email them to respondents at little to no cost.
- Speed: You can gather survey results quickly and effortlessly using mobile tools, obtaining responses and insights in 24 hours or less.
- Comparability: Researchers can use the same questionnaire yearly and compare and contrast research results to gain valuable insights and minimize translation errors.
- Scalability: Questionnaires are highly scalable, allowing researchers to distribute them to demographics anywhere across the globe.
- Standardization: You can standardize your questionnaire with as many questions as you want about any topic.
- Respondent comfort: When taking a questionnaire, respondents are completely anonymous and not subject to stressful time constraints, helping them feel relaxed and encouraging them to provide truthful responses.
- Easy analysis: Questionnaires often have built-in tools that automate analyses, making it fast and easy to interpret your results.
Disadvantages of Questionnaires
Questionnaires also have their disadvantages, such as:
- Answer dishonesty: Respondents may not always be completely truthful with their answers — some may have hidden agendas, while others may answer how they think society would deem most acceptable.
- Question skipping: Make sure to require answers for all your survey questions. Otherwise, you may run the risk of respondents leaving questions unanswered.
- Interpretation difficulties: If a question isn’t straightforward enough, respondents may struggle to interpret it accurately. That’s why it’s important to state questions clearly and concisely, with explanations when necessary.
- Survey fatigue: Respondents may experience survey fatigue if they receive too many surveys or a questionnaire is too long.
- Analysis challenges: Though closed questions are easy to analyze, open questions require a human to review and interpret them. Try limiting open-ended questions in your survey to gain more quantifiable data you can evaluate and utilize more quickly.
- Unconscientious responses: If respondents don’t read your questions thoroughly or completely, they may offer inaccurate answers that can impact data validity. You can minimize this risk by making questions as short and simple as possible.
Types of Questionnaires in Research
There are various types of questionnaires in survey research, including:
- Postal: Postal questionnaires are paper surveys that participants receive through the mail. Once respondents complete the survey, they mail them back to the organization that sent them.
- In-house: In this type of questionnaire, researchers visit respondents in their homes or workplaces and administer the survey in person.
- Telephone: With telephone surveys, researchers call respondents and conduct the questionnaire over the phone.
- Electronic: Perhaps the most common type of questionnaire, electronic surveys are presented via email or through a different online medium.
Learn More About Our Tools
Contact us today to get started.
More from our blog

Case Study: Paramount Australia and New Zealand
Paramount Australia and New Zealand partners with Lucid Measurement by Cint to provide essential brand metrics for multi-device CTV streaming

The Market Research Industry Isn’t Focusing Enough on Data Ethics; How to Solve It
Lindsay Fordham, SVP Product at Cint shares her thoughts on ethics in our industry

CintSnap reveals top reasons people in the UK flock to music festivals
With Glastonbury around the corner and a summer of festivals in full swing, we delve into everything from sustainability to the allure of secret sets.

Research Questionnaire
Questionnaire generator.

When a researcher creates a research paper using the scientific method they will need to use a gathering method that is adjacent to the research topic. This means that the researcher will use a quantitative research method for a quantitive topic and a qualitative method for a qualitative one. The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper.
1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example
- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 38 KB
2. Market Research Questionnaire Example

Size: 94 KB
3. Research Questionnaire Example

4. Sample Market Research Questionnaire
Size: 35 KB
5. Research Survey Questionnaire

Size: 42 KB
6. Research Survey Questionnaire Construction

Size: 80 KB
7. Research Questionnaire Survey of Consumers

Size: 39 KB
8. Guide to the Design of Research Questionnaires

Size: 77 KB
9. Planning Survey Research Questionnaires

Size: 85 KB
10. Climate Change Survey Questionnaires
Size: 41 KB
11. Survey Questionnaire Design

Size: 96 KB
12. Developing Questionnaires for Educational Research

Size: 81 KB
13. Graudate Research Student Questionnaires

14. Sample Research Survey Questionnaires

Size: 46 KB
15. Market Research Questionnaire Example

16. Research Survey Questionnaire Example
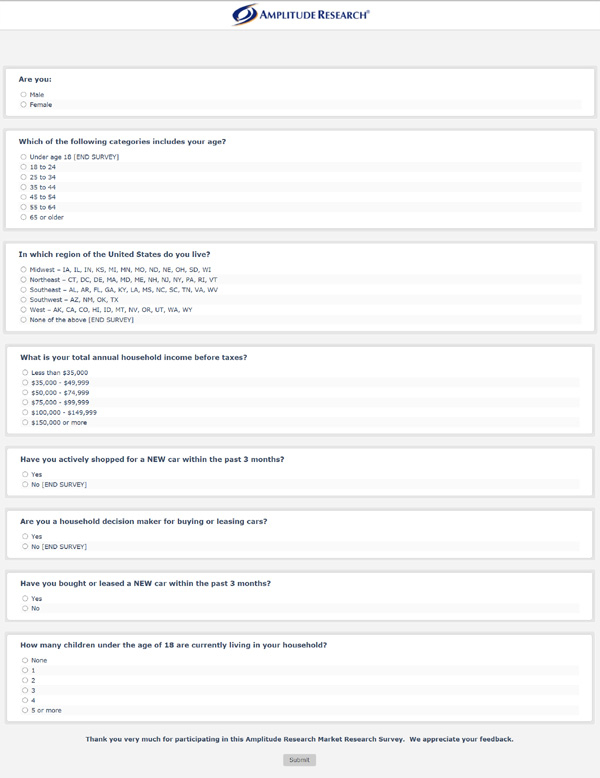
17. Product X Research Study Questionnaire Example

What Is a Research Questionnaire?
A research questionnaire is a physical or digital questionnaire that researchers use to obtain quantitative data. The research questionnaire is a more in-depth version of a survey as its questions often delve deeper than survey questions .
How to Write a Research Questionnaire
A well-made research questionnaire can effectively and efficiently gather data from the population. Creating a good research questionnaire does not require that many writing skills , soft skills , or hard skills , it just requires the person to properly understand the data set they are looking for.
Step 1: Select a Topic or Theme for the Research Questionnaire
Begin by choosing a topic or theme for the research questionnaire as this will provide much-needed context for the research questionnaire. Not only that but the topic will also dictate the tone of the questions in the questionnaire.
Step 2: Obtain or Use a Research Questionnaire Outline
You may opt to use a research questionnaire outline or outline format for your research questionnaire. This outline will provide you with a structure you can use to easily make your research questionnaire.
Step 3: Create your Research Questionnaire
Start by creating questions that will help provide you with the necessary data to prove or disprove your research question. You may conduct brainstorming sessions to formulate the questions for your research questionnaire.
Step 4: Edit and Have Someone Proofread the Questionnaire
After you have created and completed the research questionnaire, you must edit the contents of the questionnaire. Not only that but it is wise to have someone proofread the contents of your questionnaire before deploying the questionnaire.
How does a research questionnaire help businesses?
A successful business or company utilizes research questionnaires to not only obtain data from their customers but also to gather data about the performance and quality of the employees in the business. The research questionnaire provides the business or company with actionable data, which they can use to improve the product, service, or commodity to obtain more customers.
Do I need to provide a consent form when I ask someone to answer the research questionnaire?
Yes, consent is very important as without this the data you have gathered from your questionnaires or surveys are useless. Therefore it is important to provide a consent form with your research questionnaire when you are asking a participant to answer the document.
What type of answers are allowed in the research questionnaire?
Research questionnaires can host a multitude of types of questions each with its specific way of answering. A questionnaire can use multiple-choice questions, open-ended questions, and closed questions. Just be sure to properly pace the questions as having too many different types of answering styles can demotivate or distract the target audience, which might lead to errors.
A research questionnaire is a data-gathering document people can use to obtain information and data from a specific group of people. Well-made and crafted research questionnaires will provide much-needed information one can use to answer a specific research question.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a fun quiz to find out which historical figure you're most like in your study habits
Design a survey to discover students' favorite school subjects and why they love them.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 10 October 2022.
A questionnaire is a list of questions or items used to gather data from respondents about their attitudes, experiences, or opinions. Questionnaires can be used to collect quantitative and/or qualitative information.
Questionnaires are commonly used in market research as well as in the social and health sciences. For example, a company may ask for feedback about a recent customer service experience, or psychology researchers may investigate health risk perceptions using questionnaires.
Table of contents
Questionnaires vs surveys, questionnaire methods, open-ended vs closed-ended questions, question wording, question order, step-by-step guide to design, frequently asked questions about questionnaire design.
A survey is a research method where you collect and analyse data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.
Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
But designing a questionnaire is only one component of survey research. Survey research also involves defining the population you’re interested in, choosing an appropriate sampling method , administering questionnaires, data cleaning and analysis, and interpretation.
Sampling is important in survey research because you’ll often aim to generalise your results to the population. Gather data from a sample that represents the range of views in the population for externally valid results. There will always be some differences between the population and the sample, but minimising these will help you avoid sampling bias .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Questionnaires can be self-administered or researcher-administered . Self-administered questionnaires are more common because they are easy to implement and inexpensive, but researcher-administered questionnaires allow deeper insights.
Self-administered questionnaires
Self-administered questionnaires can be delivered online or in paper-and-pen formats, in person or by post. All questions are standardised so that all respondents receive the same questions with identical wording.
Self-administered questionnaires can be:
- Cost-effective
- Easy to administer for small and large groups
- Anonymous and suitable for sensitive topics
But they may also be:
- Unsuitable for people with limited literacy or verbal skills
- Susceptible to a nonreponse bias (most people invited may not complete the questionnaire)
- Biased towards people who volunteer because impersonal survey requests often go ignored
Researcher-administered questionnaires
Researcher-administered questionnaires are interviews that take place by phone, in person, or online between researchers and respondents.
Researcher-administered questionnaires can:
- Help you ensure the respondents are representative of your target audience
- Allow clarifications of ambiguous or unclear questions and answers
- Have high response rates because it’s harder to refuse an interview when personal attention is given to respondents
But researcher-administered questionnaires can be limiting in terms of resources. They are:
- Costly and time-consuming to perform
- More difficult to analyse if you have qualitative responses
- Likely to contain experimenter bias or demand characteristics
- Likely to encourage social desirability bias in responses because of a lack of anonymity
Your questionnaire can include open-ended or closed-ended questions, or a combination of both.
Using closed-ended questions limits your responses, while open-ended questions enable a broad range of answers. You’ll need to balance these considerations with your available time and resources.
Closed-ended questions
Closed-ended, or restricted-choice, questions offer respondents a fixed set of choices to select from. Closed-ended questions are best for collecting data on categorical or quantitative variables.
Categorical variables can be nominal or ordinal. Quantitative variables can be interval or ratio. Understanding the type of variable and level of measurement means you can perform appropriate statistical analyses for generalisable results.
Examples of closed-ended questions for different variables
Nominal variables include categories that can’t be ranked, such as race or ethnicity. This includes binary or dichotomous categories.
It’s best to include categories that cover all possible answers and are mutually exclusive. There should be no overlap between response items.
In binary or dichotomous questions, you’ll give respondents only two options to choose from.
White Black or African American American Indian or Alaska Native Asian Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander
Ordinal variables include categories that can be ranked. Consider how wide or narrow a range you’ll include in your response items, and their relevance to your respondents.
Likert-type questions collect ordinal data using rating scales with five or seven points.
When you have four or more Likert-type questions, you can treat the composite data as quantitative data on an interval scale . Intelligence tests, psychological scales, and personality inventories use multiple Likert-type questions to collect interval data.
With interval or ratio data, you can apply strong statistical hypothesis tests to address your research aims.
Pros and cons of closed-ended questions
Well-designed closed-ended questions are easy to understand and can be answered quickly. However, you might still miss important answers that are relevant to respondents. An incomplete set of response items may force some respondents to pick the closest alternative to their true answer. These types of questions may also miss out on valuable detail.
To solve these problems, you can make questions partially closed-ended, and include an open-ended option where respondents can fill in their own answer.
Open-ended questions
Open-ended, or long-form, questions allow respondents to give answers in their own words. Because there are no restrictions on their choices, respondents can answer in ways that researchers may not have otherwise considered. For example, respondents may want to answer ‘multiracial’ for the question on race rather than selecting from a restricted list.
- How do you feel about open science?
- How would you describe your personality?
- In your opinion, what is the biggest obstacle to productivity in remote work?
Open-ended questions have a few downsides.
They require more time and effort from respondents, which may deter them from completing the questionnaire.
For researchers, understanding and summarising responses to these questions can take a lot of time and resources. You’ll need to develop a systematic coding scheme to categorise answers, and you may also need to involve other researchers in data analysis for high reliability .
Question wording can influence your respondents’ answers, especially if the language is unclear, ambiguous, or biased. Good questions need to be understood by all respondents in the same way ( reliable ) and measure exactly what you’re interested in ( valid ).
Use clear language
You should design questions with your target audience in mind. Consider their familiarity with your questionnaire topics and language and tailor your questions to them.
For readability and clarity, avoid jargon or overly complex language. Don’t use double negatives because they can be harder to understand.
Use balanced framing
Respondents often answer in different ways depending on the question framing. Positive frames are interpreted as more neutral than negative frames and may encourage more socially desirable answers.
| Positive frame | Negative frame |
|---|---|
| Should protests of pandemic-related restrictions be allowed? | Should protests of pandemic-related restrictions be forbidden? |
Use a mix of both positive and negative frames to avoid bias , and ensure that your question wording is balanced wherever possible.
Unbalanced questions focus on only one side of an argument. Respondents may be less likely to oppose the question if it is framed in a particular direction. It’s best practice to provide a counterargument within the question as well.
| Unbalanced | Balanced |
|---|---|
| Do you favour …? | Do you favour or oppose …? |
| Do you agree that …? | Do you agree or disagree that …? |
Avoid leading questions
Leading questions guide respondents towards answering in specific ways, even if that’s not how they truly feel, by explicitly or implicitly providing them with extra information.
It’s best to keep your questions short and specific to your topic of interest.
- The average daily work commute in the US takes 54.2 minutes and costs $29 per day. Since 2020, working from home has saved many employees time and money. Do you favour flexible work-from-home policies even after it’s safe to return to offices?
- Experts agree that a well-balanced diet provides sufficient vitamins and minerals, and multivitamins and supplements are not necessary or effective. Do you agree or disagree that multivitamins are helpful for balanced nutrition?
Keep your questions focused
Ask about only one idea at a time and avoid double-barrelled questions. Double-barrelled questions ask about more than one item at a time, which can confuse respondents.
This question could be difficult to answer for respondents who feel strongly about the right to clean drinking water but not high-speed internet. They might only answer about the topic they feel passionate about or provide a neutral answer instead – but neither of these options capture their true answers.
Instead, you should ask two separate questions to gauge respondents’ opinions.
Strongly Agree Agree Undecided Disagree Strongly Disagree
Do you agree or disagree that the government should be responsible for providing high-speed internet to everyone?
You can organise the questions logically, with a clear progression from simple to complex. Alternatively, you can randomise the question order between respondents.
Logical flow
Using a logical flow to your question order means starting with simple questions, such as behavioural or opinion questions, and ending with more complex, sensitive, or controversial questions.
The question order that you use can significantly affect the responses by priming them in specific directions. Question order effects, or context effects, occur when earlier questions influence the responses to later questions, reducing the validity of your questionnaire.
While demographic questions are usually unaffected by order effects, questions about opinions and attitudes are more susceptible to them.
- How knowledgeable are you about Joe Biden’s executive orders in his first 100 days?
- Are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way Joe Biden is managing the economy?
- Do you approve or disapprove of the way Joe Biden is handling his job as president?
It’s important to minimise order effects because they can be a source of systematic error or bias in your study.
Randomisation
Randomisation involves presenting individual respondents with the same questionnaire but with different question orders.
When you use randomisation, order effects will be minimised in your dataset. But a randomised order may also make it harder for respondents to process your questionnaire. Some questions may need more cognitive effort, while others are easier to answer, so a random order could require more time or mental capacity for respondents to switch between questions.
Follow this step-by-step guide to design your questionnaire.
Step 1: Define your goals and objectives
The first step of designing a questionnaire is determining your aims.
- What topics or experiences are you studying?
- What specifically do you want to find out?
- Is a self-report questionnaire an appropriate tool for investigating this topic?
Once you’ve specified your research aims, you can operationalise your variables of interest into questionnaire items. Operationalising concepts means turning them from abstract ideas into concrete measurements. Every question needs to address a defined need and have a clear purpose.
Step 2: Use questions that are suitable for your sample
Create appropriate questions by taking the perspective of your respondents. Consider their language proficiency and available time and energy when designing your questionnaire.
- Are the respondents familiar with the language and terms used in your questions?
- Would any of the questions insult, confuse, or embarrass them?
- Do the response items for any closed-ended questions capture all possible answers?
- Are the response items mutually exclusive?
- Do the respondents have time to respond to open-ended questions?
Consider all possible options for responses to closed-ended questions. From a respondent’s perspective, a lack of response options reflecting their point of view or true answer may make them feel alienated or excluded. In turn, they’ll become disengaged or inattentive to the rest of the questionnaire.
Step 3: Decide on your questionnaire length and question order
Once you have your questions, make sure that the length and order of your questions are appropriate for your sample.
If respondents are not being incentivised or compensated, keep your questionnaire short and easy to answer. Otherwise, your sample may be biased with only highly motivated respondents completing the questionnaire.
Decide on your question order based on your aims and resources. Use a logical flow if your respondents have limited time or if you cannot randomise questions. Randomising questions helps you avoid bias, but it can take more complex statistical analysis to interpret your data.
Step 4: Pretest your questionnaire
When you have a complete list of questions, you’ll need to pretest it to make sure what you’re asking is always clear and unambiguous. Pretesting helps you catch any errors or points of confusion before performing your study.
Ask friends, classmates, or members of your target audience to complete your questionnaire using the same method you’ll use for your research. Find out if any questions were particularly difficult to answer or if the directions were unclear or inconsistent, and make changes as necessary.
If you have the resources, running a pilot study will help you test the validity and reliability of your questionnaire. A pilot study is a practice run of the full study, and it includes sampling, data collection , and analysis.
You can find out whether your procedures are unfeasible or susceptible to bias and make changes in time, but you can’t test a hypothesis with this type of study because it’s usually statistically underpowered .
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analysing data from people using questionnaires.
Closed-ended, or restricted-choice, questions offer respondents a fixed set of choices to select from. These questions are easier to answer quickly.
Open-ended or long-form questions allow respondents to answer in their own words. Because there are no restrictions on their choices, respondents can answer in ways that researchers may not have otherwise considered.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviours. It is made up of four or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with five or seven possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
You can organise the questions logically, with a clear progression from simple to complex, or randomly between respondents. A logical flow helps respondents process the questionnaire easier and quicker, but it may lead to bias. Randomisation can minimise the bias from order effects.
Questionnaires can be self-administered or researcher-administered.
Researcher-administered questionnaires are interviews that take place by phone, in person, or online between researchers and respondents. You can gain deeper insights by clarifying questions for respondents or asking follow-up questions.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, October 10). Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 24 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/questionnaire-design/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, doing survey research | a step-by-step guide & examples, what is a likert scale | guide & examples, reliability vs validity in research | differences, types & examples.
对不起,该问卷仅支持IE9及以上版本的浏览器才能打开,
请升级浏览器或者使用chrome等其它浏览器打开

https://discord.com/invite/marvelrivals

- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-19037-0
- Corpus ID: 270615157
Thriving from work questionnaire: German translation and validation
- S. Neidlinger , Susan E. Peters , +1 author Jörg Felfe
- Published in BMC Public Health 19 June 2024
32 References
Thriving from work questionnaire: spanish translation and validation.
- Highly Influential
Thriving from Work Questionnaire: Dimensionality, reliability, and validity of the long and short form questionnaires.
Thriving from work: conceptualization and measurement, measuring psychological stress and strain at work - evaluation of the copsoq questionnaire in germany, thriving at work: toward its measurement, construct validation, and theoretical refinement, burnout assessment tool (bat)—development, validity, and reliability, guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures., the satisfaction with life scale and the emerging construct of life satisfaction, a measure of subjective happiness: preliminary reliability and construct validation, expanding the paradigm of occupational safety and health: a new framework for worker well-being, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Political Typology Quiz
Where do you fit in the political typology, are you a faith and flag conservative progressive left or somewhere in between.

Take our quiz to find out which one of our nine political typology groups is your best match, compared with a nationally representative survey of more than 10,000 U.S. adults by Pew Research Center. You may find some of these questions are difficult to answer. That’s OK. In those cases, pick the answer that comes closest to your view, even if it isn’t exactly right.
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Using questionnaires
- January 2019
- In book: Practical Research Methods in Education: An Early Researcher’s Critical Guide
- Publisher: Routledge

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- INT J CIRCUMPOL HEAL

- TEACH TEACH EDUC
- Jason Y.L. Wong
- Trav Med Infect Dis

- Hamada Hassan

- Karol Sadowski

- Clinton Aigabvboa

- Andrzej Witusik

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The questionnaire is a tool widely used for data collection compared to interview and observation in empirical research; this study used Closed (multiple choice) and Open (descriptive) questions ...
Questionnaires vs. surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyze data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
However, the quality and accuracy of data collected using a questionnaire depend on how it is designed, used, and validated. In this two-part series, we discuss how to design (part 1) and how to use and validate (part 2) a research questionnaire. It is important to emphasize that questionnaires seek to gather information from other people and ...
To minimize response errors, questionnaires should be crafted in accordance with best practices. Recommendations about best practices stem from experience and common lore, on the one hand, and methodological research, on the other. In this chapter, we first offer recommendations about optimal questionnaire design based on conventional
2. Questionnaire researchers, journal editors and reviewers should be more careful and suspicious about using published measures in management research. Designing new questionnaires is tricky and time consuming, so it is tempting to use and re-use existing ones for practical and legitimation reasons (Scherbaum & Meade, 2009). Moreover, the use ...
Like questionnaires, interviews can be used to collect quantitative data: the researcher records each response as a category or rating and statistically analyzes the results. ... or research paper. In the methodology section, you describe exactly how you conducted the survey. You should explain the types of questions you used, the sampling ...
This is the first in a series of three articles on questionnaire research. References w1-w17, further illustrative examples, and checklists are on bmj.com. ... This series of papers arose directly from questions asked about real questionnaire studies. To address these questions we explored a wide range of sources from the psychological and ...
Refine the questionnaire: Based on feedback from the pilot, refine and revise the questionnaire as necessary to ensure that it is valid and reliable. Distribute the questionnaire: Distribute the questionnaire to your target audience using a method that is appropriate for your research objectives, such as online surveys, email, or paper surveys.
an effective questionnaire including its content, appearance and usage that leads to inappropriate and biased findings in a study. This paper aims to review the main steps to design a questionnaire introducing the process that starts with defining the information required for a study, then continues with the
Thus, questionnaire building and data collection through the questionnaires have become an active area of research. However, questionnaire development can be challenging and suboptimal in the absence of careful planning and user-friendly literature guide. Keeping in mind the intricacies of constructing a questionnaire, researchers need to ...
AJMS Vol.11 No.1 January-June 2022 10 Designing a Questionnaire for a Research Paper: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Develop an Effective Questionnaire The main scaling types are as the following. commonly chosen between 5 to 7-point as this range is easily rescaled which can help to facilitate the comparisons. It can also be noted as a ...
ChapterPDF Available. Questionnaires and Surveys. December 2015. December 2015. DOI: 10.1002/9781119166283.ch11. In book: Research Methods in Intercultural Communication: A Practical Guide (pp.163 ...
The design and use of questionnaires are important aspects of. educational research (Newby, 2013, Cohen et al., 2017). By. following key considerations about the design and. operationalization of ...
10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project. Published on October 30, 2022 by Shona McCombes. Revised on October 19, 2023. The research question is one of the most important parts of your research paper, thesis or dissertation. It's important to spend some time assessing and refining your question before you get started.
Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in ...
10. Test the Survey Platform: Ensure compatibility and usability for online surveys. By following these steps and paying attention to questionnaire design principles, you can create a well-structured and effective questionnaire that gathers reliable data and helps you achieve your research objectives.
PMB has taught research methods in a primary care setting for the past 13 years, specialising in practical approaches and using the experiences and concerns of researchers and participants as the basis of learning. This series of papers arose directly from questions asked about real questionnaire studies.
Some questionnaires or surveys are published within an article. To find them, conduct an article search in a bibliographic database on the topic of interest and add in the Keywords: survey* or questionnaire* In some cases the actual questionnaire or survey is not published with the article, but referred to within the text.
There are various types of questionnaires in survey research, including: Postal: Postal questionnaires are paper surveys that participants receive through the mail. Once respondents complete the survey, they mail them back to the organization that sent them. In-house: In this type of questionnaire, researchers visit respondents in their homes ...
The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper. 1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example. Details. File Format. Size: 38 KB. Download. 2. Market Research Questionnaire Example.
Questionnaires vs surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyse data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
Questionnaires are frequently used in quantitative marketing research and social research. A questionnaire is a series of questions asked to individuals to obtain statistically useful information ...
By agreeing to participate, you acknowledge that any personal information provided in this questionnaire will be collected and processed. If you are under 14 years old, please obtain consent from your guardian before participating. Your participation is entirely voluntary, and you are not obligated to consent.
Background The Thriving from Work questionnaire is a comprehensive indicator of positive well-being for employees, applicable in both research and practical contexts. Current discussions underline the crucial impact that employment should have in enriching workers' lives positively and meaningfully, along with the necessity for accurate and dependable tools to assess employee well-being.
Take our quiz to find out which one of our nine political typology groups is your best match, compared with a nationally representative survey of more than 10,000 U.S. adults by Pew Research Center. You may find some of these questions are difficult to answer. That's OK.
This chapter explores the use of questionnaires as a. data-collection method in educational research and. offers critical discussion of their benefits and. limitations. It considers different ...
Access the portal of NASS, the official source of agricultural data and statistics in the US, and explore various reports and products.