- Essay Guides
- Other Essays
- Happiness Essay: Definition, Outline & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Happiness Essay: Definition, Outline & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A happiness essay is an academic paper that explores the concept of happiness, and how it can be achieved and maintained in our lives. The purpose of a happiness essay is to explore the psychological, social, and cultural factors that contribute to happiness. On this type of essay, students should provide insights into how individuals can cultivate a happy and fulfilling life.
In this article, we will explore the definition of happiness and its various components and outline the key elements of happiness essay structure. Whether you are seeking how to write a happiness essay or want to know more about this feeling, this is the right article. You will also find en example for your inspiration. Struggling with your writing? Say goodbye to stress and let our experts handle your ' write my essay for me ' challenge. Our team of skilled writers is ready to tackle any topic and deliver top-notch papers tailored to your instructions.
What Is a Happiness Essay?
The definition of a happiness essay can differ, but in general, a happiness essay is a paper that examines emotions, experiences, and perspectives related to the pursuit of contentment. Likewise, it may explore the philosophical and psychological aspects of delight and how it is affected by factors like wealth, relationships, and personal circumstances. A happiness essay provides a deeper understanding of enjoyment, how it can be achieved, and its influence on society. It is an opportunity to take readers on a reflective and stimulating journey, exploring the essence of joy. Writing a thematic essay on happiness is also a chance for writers to share their thoughts and observations with other people. Let's dive in and explore what delight really means to you!
Purpose of an Essay on Happiness
The reason for writing an essay about happiness is to explore the concept of delight to understand what it means to different people. For example, many believe it primarily depends on external factors such as wealth, success, or material possessions. However, it can be illustrated that true joy largely comes from internal factors, like one's outlook, personal growth, and relationships, especially with family and friends. A happiness essay helps to dispel common misconceptions about what satisfaction truly is. Writing a paper on this subject can describe a deeper, healthy understanding of this universal pursuit.
Ideas to Write a Happiness Essay on
When you want to write a happiness essay , first, it is important to ask: What is happiness to you? How can it be understood? One approach is to define happiness and examine its various dimensions, such as psychological, emotional, and physiological. For example, career satisfaction is a crucial factor in achieving contentment. When people enjoy their jobs and feel fulfilled, they tend to report higher levels of delight. It's worth exploring the link between happiness and career satisfaction and how people can find meaning in their work. Another idea of how to be happy would look at factors like relationships, personal growth, and achievement. Besides, the connection between money and happiness can also be a significant factor in the quality of life. Can you buy satisfaction? The pursuit of happiness is a fundamental aspect of life, and analyzing its various dimensions can help us gain valuable insights into what leads to a happy life.
Happiness Essay Outline
An outline for a happiness essay serves as a roadmap for writers to keep their paper organized. It helps to break down researched content into manageable sections while ensuring that all necessary information is included. The essay outline on happiness example might look something like this:
- Topic definition
- Topic importance
- Thesis statement
- Topic sentence
- Supporting evidence
- Concluding sentence, connected to your thesis
- Summarizing main points
- Final thoughts and future recommendations
- Encouraging readers to reflect on their delight
This outline provides a comprehensive format for an essay about happiness, ensuring that articles are well-structured, easy to understand, and cover all the necessary information.
Structure of a Happiness Essay
Happiness essay structure is critical to a successful article because it helps to organize the ideas clearly and coherently. It is easier for readers to follow and understand writers' perspectives on this complex and multifaceted topic if the essay has the following sections: Introduction: provides context for the topic with a clear thesis statement. Body: delves into the details while providing evidence to support the thesis. Conclusion: summarizes the main points while restating the thesis statement in a new way. By following this structure, writers can produce compelling essays on happiness in life that engage and inform readers.
Happiness Essay Introduction
The introduction of a happiness essay is critical to setting the stage for the article’s body. Good introductions should have three key elements: a hook, background information, and a thesis statement. The hook draws readers in and keeps them engaged, but a boring or generic one may make them lose interest. The background information provides context for the topic and gives the audience a better understanding of why the essay is being written. Lastly, the thesis statement states the writer's stance on contentment, providing a roadmap for the rest of the essay. An essay about happiness introduction is an important part that sets the tone and lays the foundation for the paper. By following this structure, authors can ensure that the introduction of their paper is well-organized, concise, and effective in drawing the readers into their piece.
Happiness Essay Introduction Example
An introduction to your paper should be engaging, interesting, brief, and to the point. It clearly states the objectives of the research and introduces readers to the key arguments that will be discussed. Here is an example of a happiness essay introduction:
Happiness Essay Thesis Statement
A happiness essay thesis statement is the backbone of an article and a crucial element in your paper. A good thesis statement about happiness should be arguable, specific, and relevant to the topic. It is important for defining the scope of an article and highlighting its focus while also identifying what it will not cover. Finally, the thesis statement tells readers the writer's point of view and sets a standard for judging whether the essay achieves its goal. By creating an effective statement, writers can significantly impact their paper's quality by providing direction and focus to the author’s argument.
Happiness Thesis Statement Example
This thesis statement defines the pursuit of delight and outlines its contributing factors. Here is an example of a happiness essay thesis statement sample:
Happiness Essay Body
A happiness body paragraph is a component of the body section of an article that provides evidence, examples, and supporting arguments to develop an essay's central idea. Good paragraphs cover a topic in-depth and engage readers, prompting them to reflect on what brings joy and how to pursue it. A paragraph about happiness should be well-structured and focused, analyzing factors contributing to contentment in a logical and coherent manner. A well-crafted essay body on happiness includes several paragraphs, each focused on specific aspects of enjoyment while supporting an article's overall argument. Following these guidelines, writers can create persuasive essay paragraphs.
Happiness Body Paragraph Example
Body paragraphs should provide a deeper understanding of the topic while engaging readers with relevant, thought-provoking information. Happiness body paragraph example:
Happiness Essay Conclusion
A conclusion is the last section of an essay that summarizes the main points while offering a final perspective on the topic. To write a strong conclusion on a happiness essay, consider these key elements:
- summarize the main arguments
- provide closure
- include a final thought or reflection
- leave a lasting impression
- avoid introducing new information.
A good conclusion can make the difference between a forgettable essay and one that stays with the reader long after they've finished. Following these guidelines ensures that your essay conclusion about happiness effectively wraps up the argument and provides readers with memorable final impressions.
Happiness Essay Conclusion Sample
Conclusion helps readers better understand the topic by providing a sense of resolution or insight. Here is an example of a happiness essay conclusion:
How to Write an Essay on Happiness?
If you want to write an essay on happiness, remember that it can be a hard yet rewarding experience. Whether you are doing it for a class assignment, a job, a scholarship application, or personal growth, exploring what contentment means to you can be the journey of self-discovery. You should clearly understand the topic and have a well-structured plan. The steps to effective happiness essay writing include defining satisfaction, conducting research, and organizing thoughts. When writing, it's crucial to consider factors that contribute to delight and obstacles that can hinder the process. Following the steps below, you can craft an article that effectively communicates your perspective on this topic.
1. Pick a Topic About Happiness
Choosing a topic about happiness essay can be daunting, but with some guidance and creativity, you may find a subject that is both interesting and relevant. When brainstorming for happiness essay topics, follow these steps:
- Start with a broad idea related to your issue. Narrow the focus to a specific aspect, gather information, list potential cases, evaluate options, refine the matter, and check for relevance to your audience.
- Gather information, consider the different perspectives, and take note of the arguments you come across.
- Come up with five to ten potential concerns and evaluate each, asking questions such as if it is interesting, has enough information available, and if you can find a unique approach.
- Refine your chosen discussion to make it specific, focused, relevant, and interesting to your audience.
2. Do In-Depth Research
Gathering information from credible sources is crucial when writing an essay about happiness. Here are some tips to ensure that you collect accurate and relevant facts:
- Research from trustworthy sources like academic journals, books by experts, and government websites.
- Evaluate information's credibility and reliability. When you are reading, take notes on the information that you find. Write down the author, title, and publication date of each source to keep track of your research.
- Use multiple sources to broaden your understanding of your topic.
- Organize your research with a citation manager or bibliography.
Following these tips, you can delve into a wealth of credible sources for your happiness essays to elevate your article to new heights of insight.
3. Create an Outline for a Happiness Essay
Crafting an outline is essential in writing an essay on happiness and can give your work the structure and direction it needs to succeed. Here's how to create an effective happiness essay outline:
- Framework Start by outlining the main sections of your essay - introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Pinpoint your ideas Determine the key points you want to convey in each section.
- Supplement with specifics Add details that reinforce and support your ideas under each main point.
- Follow the guide Use the happiness essay outline example above as a starting point, but feel free to customize depending on the situation.
By following these steps and utilizing an essay outline , you'll have a clear map to guide you as you craft your paper, ensuring that your ideas are coherently organized, and your writing flows effortlessly.
4. Write an Essay About Happiness
In this essay about happiness, we will delve into the elusive and complex nature of this emotion. Here is an example to follow when you write your happiness essay.
5. Proofread Your Happiness Essay
When proofreading your happiness essay, make sure to take your time and approach it methodically. Follow these steps:
- Read through the entire essay to get a sense of its overall structure and flow.
- Pay close attention to the introduction, as this sets the tone for the entire piece.
- Look for typos, grammatical errors, and awkward phrasing .
- Ensure your paragraphs are well-organized, with clear transitions between ideas. Check that your happy essay accurately reflects your thoughts and clearly conveys the message you want.
- Finally, read the paper out loud to yourself, or have someone else read it to you.
This can help you pick up on any errors that you might have missed during your initial proofreading. Finally, the article will leave a lasting impression on your reader and enhance your credibility as a writer.
Happiness Essay Examples
If you're looking to write truly captivating happiness essays, it's always helpful to seek inspiration from various sources. Consider checking out these excellent essay examples about happiness: Happiness essay example 1
Essay example about happiness 2
Happiness essay sample 3
Essay on happiness example 4
Example of a happiness essay 5
They offer a rich tapestry of perspectives on what enjoyment truly means. Whether you draw on your own experiences or delve into the experiences of others, a happiness essay example will serve as a valuable resource as you strive to make your mark on this timeless topic.
Happiness Essay Writing Tips
When writing a happiness essay, there are key tips to keep in mind to help you create a compelling piece of work. Here are a few suggestions to get you started in happiness essays writing:
- Explore the concept from a cultural or historical perspective, looking at how attitudes towards your topic have changed over time across different societies.
- Consider how relationships, community, and social connections shape our enjoyment. How can these factors interact?
- Weigh the benefits and drawbacks of different approaches, such as positive or negative thinking, mindfulness, and self-care, offering a well-rounded perspective on the topic.
- Reflect on the connection between happiness and success, considering whether one necessarily leads to the other or can be pursued independently of success.
- Incorporate humor and lightheartedness into your writing, making your essay entertaining.
By going about integrating these unique tips into your writing day by day, you'll be able to craft essays on happiness that are both original and memorable, capturing the reader's imagination from start to finish. Students can explore a vast range of topics through our platform, from an essay about true friendship and a family essay to an illustration essay that will show how to convey complex ideas in a clear and engaging way.
Bottom Line on Happiness Essay Writing
To write a happiness essay, you should consider providing long and in-depth ways to explore what truly brings us joy. Instead of repeating common knowledge, take a personal approach and reflect on the things that delight you. Consider the fact that relationships, gratitude, mindfulness, and activities all contribute to shaping our joy. Your happiness essays should also showcase your introspective side. Examine any challenges or obstacles you have faced in your journey toward contentment. This will make your paper not only unique but also relatable and insightful. The goal is to create a piece that offers a fresh perspective on the concept of happiness and a true reflection of your experiences.
Buy custom essay online from StudyCrumb and get a happiness paper delivered on time. Top-notch quality is guaranteed!

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

Satisfaction is never a straightforward and easily attainable idea. It has intrigued philosophers, religious figures, and people alike for centuries. Some say contentment is found inside a material wealth lifestyle, and others believe it is a state of mind or a result of spiritual fulfillment. But what is happiness, really? And how can we cultivate it in our own lives?
True happiness comes from family, friends, and learning to be content in life, while money can only purchase momentary happiness.
Contentment brings a smile to our faces, peace to our hearts, and a skip in our steps. It's what many of us strive for every day, and it turns out it's not just good for our spirits but our health too! Studies have linked contentment to lower stress, reduced risk of heart disease, and elevated life satisfaction. Delight can come from doing what you love, being with loved ones, or having a sense of purpose. Or, it may simply be found in everyday moments like a sunny day, a good meal, or a breathtaking sunset. Although joy can be fleeting and affected by life events, we can still work to cultivate it in our lives.
In conclusion, delight is a difficult and multi-faceted concept that can influence various factors, including personal relationships, life events, and individual perspectives. The pursuit of contentment is a common initiative for all humans, and it is evident that becoming content requires a perfect balance and order of internal and external factors. This article presents evidence that helps you see clearly that contentment is not a fixed state. It is a journey that needs effort, reflection, and self-awareness to enjoy. I hope this paper has helped you realize a deeper understanding of this topic and become better equipped to embark on your pursuit of joy.
Contentment is a subjective experience that varies significantly from person to person. It is often considered the ultimate goal of human life, and many people spend their entire lives searching for it. Despite its elusive nature, it is a crucial component of well-being and has been linked to numerous benefits for physical, mental, and emotional health. The reasons to smile or experience joy are varied and can be both internal and external. Some individuals find joy in the simple things in life, like being with family, pursuing their passions, or exploring new experiences. On the other hand, others may find it through accomplishing personal goals, acquiring material goods, or attaining financial security. Nonetheless, it's crucial to keep in mind that these external sources of happiness may not always be possible and may not alleviate suffering. Conversely, true joy comes from within and is characterized by a sense of being content, satisfied, and with purpose. It can be cultivated through mindfulness, gratitude, and self-reflection. By focusing on personal growth, forming meaningful relationships, and finding meaning and purpose in life, individuals, including children, can develop a deep sense of satisfaction that is not dependent on external circumstances and is not easily disturbed by life's problems. In conclusion, delight is a complex and multifaceted experience that both internal and external factors can influence. While external sources can bring temporary joy, true and lasting contentment can only be found within. Individuals can create a foundation for joy that will endure throughout their lives by focusing on personal growth and cultivating a positive mindset.

Thesis Statement About Happiness
Thesis statement about happiness.
Happiness is not reduced to the emotional well-being of an organism adapted to its environment. Man must reflect to build his life according to values. He can not neglect his freedom, or his responsibility before the voluntary commitment of his action. Being happy means that man is capable of achieving a balance that overcomes his contradictions and conflicts. If man wants to be happy, he must not forget that happiness is the result of a conquest first over himself and then over a world in which he must take into account not only natural forces, but also other men.
Statements about happiness: the notion of issue
The idea of salvation is a new fashion according to the happiness thesis. We live in a time of great desolation. Loneliness is perceived in the bosom of the considerable cacophony of sciences and techniques that do not fulfill some of our demands: those of happiness, on the one hand, that is, earthly salvation; those of the future, on the other hand, that is, the salvation of the soul.
Is there eternal happiness thesis? And if there is, would we be entitled to it? Here are two questions to which the idea of salvation responds. The idea of salvation was born at the beginning of the Middle Ages: it is about finding again the Garden of Eden, the world before the original sin of which the Bible speaks, the conversation alone with God, which seeks eternal happiness. St. Augustine has theorized a lot about the notion of salvation and his words are surprisingly topical. For a long time Agustín traveled away from God, mainly in the sect of the Manichaeans, for whom there was good on the one hand and evil on the other. The question that arises is the following one: where to find the strength to save oneself when one is a sinner and one lives in an inner world where one is lost and all is abandoned to evil? In line with happiness essay, St. Augustine believes that man’s freedom can not save him, since man is, by nature, separated from God since the original fall. His conception of salvation then leads him to say:
“Look as if you have to find, and when you have found, keep looking.”
Such is salvation, in the Middle Ages as it is in our age: always seek for yourself to be at the disposition of the extraordinary beyond to which you aspire. This conception of salvation is that of a mystic agnostic, a bit like Adso de Melk, the narrator of The Name of the Rose, by Umberto Eco, who ends up losing himself in the divinity, where the pious soul succumbs.
Happiness definition essay: general conditions of happiness
It is easy to list the general conditions of happiness:
- good health
- economic comfort, etc.
However, the agreement is no longer unanimous: although these conditions are more or less indispensable, they can all be presented without us being happy; that is, when trying to define what happiness is, these conditions are necessary but not sufficient. It is obvious that these general conditions are necessary. If a man lives in physical and moral misery, if his freedom and his dignity as a human being are only words, it is even indecent to speak of happiness. But, thesis about happiness is always beyond these general conditions, therefore, they are not enough; happiness is linked to a personal appreciation, a subjective appreciation that varies according to the social condition, the degree of culture, age, etc., and this is the reason why it can be discussed. To say that our idea of happiness has a subjective element does not imply that each of us invents his ideal of happiness: this ideal is constructed according to the forms and criteria that are provided by culture and society: the conception of happiness varies according to the time and the type of society.
It can be noted, following R. Benedict thesis statement on happiness (Échantillos de civilization), two fundamental trends in societies, an Apollonian and another Dionysian. The Apollonian societies see happiness as a lasting state, a balance that is the result of the harmonious meeting of several values that define what is good, beautiful and useful; a state of well-being of the spirit and the body, linked to the appeasement of internal conflicts, to the conquest of a personal balance. Dionysian societies, on the other hand, seek a state of wild happiness, pleasures as diverse as numerous. In the Dionysian societies the pleasures do not seek a definite satiety, their search is infinite. The memory of the intense pleasures that they know is assimilated to a lost paradise, but they do not know in what values to found their future happiness.
When it comes to vast and complex societies, these two tendencies are mixed, although one always predominates. Thus, our contemporary western civilization is committed to a race towards a Dionysian-type happiness – there are many needs that the individual tries vainly to satisfy – but it often tries to appease his discomfort by re-founding the Apollonian values: simple and quiet life, search of an interior balance. Along with this tension between the Dionysian and the Apollonian there are other factors that determine what a society understands as happiness. Historical circumstances are an example of this: during a period of calm, security and abundance, happiness is not considered under the same angle as during periods of war or hardship. In addition, in the same society, the conception of happiness changes according to social classes. Sociology teaches us that there is a threshold of misery below which the individual no longer has any idea of what can be called happiness. This relativity of conceptions about happiness explains, to a large extent, the halo of darkness that surrounds this notion.
Happiness thesis statement linked to time
Happiness is linked to time: it demands stability and continuity. To think that happiness can come to an end is to vitiate the happy moment that we live, with the anguish that it will cease. This temporary character makes it possible to distinguish between happiness and pleasure. Happiness is not pleasure, since the latter indicates the momentary satisfaction of a particular tendency; It remains limited, superficial and ephemeral. Happiness is, on the contrary, the overall tonality of a whole life, at least of a period of this and, paradoxically, it is rare for happiness to be lived as a present that is eternalized. If unhappiness involves retreating oneself and sharpens self-consciousness, the happy man usually lets himself live without being clearly aware of his state, without questioning himself about the nature of his happiness. Proof of the temporal character of thesis on happiness is that it is usually spoken in the past of happy time: we were happy during a period of our life. We contrast the past happiness with the present misfortunes, and our past, decanted by memory, is revalued. And in this past we get new strengths, even new reasons to wait. It is then in the future that we project our happiness. We live the present too passively and neutrally too often. Everyday banality, neither happy nor unhappy, full of monotonous tasks, unfolds under the mode of boredom, of distraction or of waiting. Dragged by the flight of time, rejected in the past, projected in the future, happiness seems, in fact, difficult to grasp.
Seek happiness in a world so upset by injustice and drama may seem selfish. Our own happiness is always linked to the search for the happiness of others. This search helps us to live. In the value of happiness, R. Polin sees one of the “reference poles” of existence. However, the human condition seems very unfavorable to thesis for happiness. Man is a being for death. He is imprisoned by the time that drags him inexorably towards decadence. Man is a limited being in his power, condemned to failure, doubt and dissatisfaction. Man needs the other, but it runs away. Most of these classic themes have been taken up by Christian moralists, to underline the misery of fallen man: although man can seek the oblivion of his misery in “fun”, he cannot find happiness but in salvation.
309 Happiness Essay Topics & Research Questions
What is happiness? This is one of the fundamental questions discussed in philosophy, psychology, religion, sociology, and other sciences. Many research papers and essays explore this phenomenon, and the topic of happiness is an infinite source of inspiration.

If you decide to write a paper on happiness, this is a great chance to learn what happiness is for you. To help you create outstanding writing, our expert team has collected the best happiness essay topics.
🔝 Top 10 Happiness Essay Topics
✍️ happiness essay prompts, ❓ happiness research questions.
- ⚖️ Happiness Argumentative Essay
- ➡️ Essay about Cause and Effect of Happiness
🤩 More Happiness Essay Titles
✏️ writing about happiness: step by step, 🔗 references.
- How to find happiness?
- What are the signs of a happy person?
- The most common myths around happiness.
- The effects of positive psychology on happiness.
- How does happiness change over the lifespan?
- The effects of happiness on physical well-being.
- The most popular theories of happiness.
- The world’s happiest countries.
- The definition of family happiness.
- Can money buy happiness?
Writing an essay on happiness can be tricky since this is a very complex phenomenon. However, if you focus on its specific aspect, you can easily do research and write a well-crafted paper. Consider our ideas on how you can narrow the topic of happiness.
Can Money Buy Happiness: Argumentative Essay Prompt
There’s an ongoing debate about the connections between happiness and money. If you want to investigate this controversial topic in your essay, it’s essential to consider both sides before jumping to conclusions.
Recent research by Kahneman, Killingsworth, and Mellers suggests that people are generally happier as they earn more. More than 30,000 adults aged between 18 and 65 living in the US with different incomes participated in a survey. Researchers measured their happiness at random intervals in the day via an app called Track Your Happiness.
The results revealed that happiness rises with income, even in the high salary range. However, there was a so-called “unhappy minority” — about 20 percent of participants, whose happiness didn’t progress after the person reached a certain income level. You might want to mention this research as an argument in your essay.

What Does Happiness Mean to You: Essay Prompt
There’s no one universal definition of happiness. It differs from person to person. If you’re writing a narrative essay , you can describe what happiness is for you. For more formal assignments, you might want to define happiness from a psychological, philosophical, or religious perspective.
Neuroscientists have demonstrated a great interest over the past years in what happens in our brains when we’re happy. According to neuroscience , happiness is the release of dopamine and serotonin (two types of neurotransmitters) in response to external factors.
While medical studies see happiness as a physiological process, in religion, happiness is sacral. To be precise, biblical scholar Jonathan Pennington defines happiness as something that cannot be found outside since this is a feeling of complete alignment with God and his coming kingdom.
Aristotle Happiness: Essay Prompt
When writing a happiness essay, it’s almost impossible not to mention the Ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle. In one of his works, The Nicomachean Ethics , he presented one of the first happiness theories, which is still relevant today.
According to Aristotle, happiness lies in achieving all the good, such as health, knowledge, wealth, and friends , which leads to the perfection of human nature. Often, happiness requires us to make choices, some of which may be very challenging. For example, the lesser good sometimes promises immediate pleasure, while the greater good requires sacrifice. Aristotle’s theory of happiness remains one of the most influential frameworks and is worth mentioning in your writing.
Prompt for Happiness Is a Choice Essay
Is happiness a choice? This is another complex question you can build your essay around.
To give you some food for thought, psychologist Sonja Lyubomirsky believes that roughly 50 percent of people’s natural happiness level is genetically determined . However, if we work on our happiness consistently, with effort and dedication, we can boost it.
It sounds shocking, but we make around 35,000 conscious decisions daily, each contributing to our happiness. As mentioned earlier, genetics make up roughly half of the happiness levels. The rest depends on our choices, and only 10% of happiness depends on circumstances.

- How do sociological perspectives shed light on factors contributing to happiness?
- How does a cross-disciplinary approach enrich our understanding of happiness?
- What is the impact of relationships on well-being?
- How can happiness be measured subjectively and objectively?
- What does the economics of happiness say about human well-being ?
- How does health contribute to human happiness?
- Does income directly relate to happiness?
- What are the socio-economic and sociodemographic characteristics of happiness?
- How do classical and neo-classical economic theories conceptualize happiness?
- How do social security and welfare contribute to happiness?
- Can employment affect happiness?
- Who is happier: self-employed or those working for hire?
- What is the impact of retirement on happiness?
- What is the link between female happiness and marital status?
- Should sacrifices be made for the sake of children’s well-being?
- How do meaningful personal relationships contribute to happiness?
- How does feeling in control of one’s life affect happiness?
- What is the relationship between freedom and happiness ?
- What is the connection between a community’s religious diversity and happiness?
- What is the link between the amount of leisure time and happiness?
- How do outdoor activities affect happiness?
- How does culture affect the way people evaluate happiness?
- How do social networks influence a person’s happiness?
- What is the difference between top-down and bottom-up theories of life satisfaction ?
- What is the impact of regular involvement in sports on happiness?
- How often should one meet with friends to feel happy?
- Is loneliness inversely related to happiness?
- What is the impact of political stability on happiness?
- Is living in a democratic state a determinant of happiness?
- Can economic freedom contribute to one’s happiness levels?
- What are the economic consequences of social happiness?
- Is happiness a fundamental goal of a democratic society ?
- Can happiness be attained by well-organized governmental efforts?
- Happiness versus well-being: are these concepts the same?
- What is the math behind the Gross National Happiness (GNH) index?
Questions about Happiness: Psychology
- What is the impact of family bonds on subjective well-being?
- Psychology Answers Whether Money Buys Happiness .
- Can physical health be a reflection of internal happiness?
- Are life challenges a stimulant of happiness?
- How to Increase Happiness Across All Three Types of Subjective Well-Being .
- Are psychometric scales valid and reliable for measuring happiness?
- What is the role of gratitude in positive psychology?
- Does Your Personality Predict Your Happiness?
- What is the link between gratitude and happiness?
- Is gratitude an alternative to materialism and a tool for attaining happiness?
- Happiness and Academic Success Relationship .
- What is the concept of “good human life” in psychology?
- How does evolutionary psychology explain the origins of happiness?
- How has the concept of happiness evolved across different psychological theories?
- Self-Esteem and Happiness Analysis .
- How does subjective well-being vary across different age groups?
- What is the role of social support in happiness?
- To what extent does genetics determine the baseline happiness level?
- The Happiness Tips and Examples from Real Life.
- How do cultural norms influence the understanding of happiness?
- How does the experience of flow states contribute to happiness?
- How can mindfulness meditations increase happiness?
- Do Stay-at-Home Mothers Exhibit More Indicators of Happiness Than Full-Time Working Mothers ?
- Is there a genuine science of happiness?
- Positive psychology : a new science of happiness or old data in a new package?
- How does the quality of interpersonal relationships affect happiness?
- What cognitive and emotional processes are involved in positive self-appraisal ?
- Generosity Motivating Factors and Wellbeing .
- What are the dimensions of psychological well-being?
- How does the engagement in prosocial behaviors contribute to happiness?
- What is the impact of pursuing extrinsic and intrinsic goals on happiness?
- How does having a life purpose contribute to happiness?
- Spiritual Satisfaction of Basic Psychological Needs .
- Positive psychology coaching: how to learn to help others attain happiness?
- What are the neurobiological correlates of happiness?
- Relationship of Proactive Personality, Financial Planning Behavior, and Life Satisfaction.
- What is the impact of spiritual well-being on happiness?
- Happiness on prescription: do anti-depressants contribute to well-being?
- What personality traits are associated with sustained happiness levels?
- How Does Regular Alcohol Consumption Affect Happiness?
- How do positive psychology interventions at school affect young adults’ happiness?
- What is the link between physical attractiveness and subjective happiness?
- What is the connection between happiness and neuroticism?
- What are the positive psychology teachings of Buddhism ?
- Is yoga a path to mature happiness?
- What is the impact of social comparison on happiness?
Philosophical Questions about Happiness
- How to achieve ultimate happiness?
- The dark side of happiness: what are the wrong ways of pursuing happiness?
- Can there be wrong types of happiness?
- Bhutanese Views on Happiness and Subjective Wellbeing.
- Is happiness egoistic self-indulgence?
- What are the philosophical problems in the study of happiness?
- Is there a link between happiness and compassion?
- Philosophy on Knowledge, Reality, and Good Life.
- Can happiness be universally possible?
- What are the conditions and causes of happiness?
- Relativity of happiness: are lottery winners happier than accident survivors?
- People and the Meaning of Life.
- How do emotional styles contribute to happiness?
- What are the personality traits of a happy person?
- What is Carson’s approach to happiness and satisfaction?
- Philosophical Views and Cultural Influences.
- What is the philosophical stance on happiness and pleasure?
- Can happiness be equated to hedonism?
- How can the pursuit of happiness be analyzed from a utilitarian perspective ?
- What is Benditt’s view of happiness and contentment?
- What were Aristotle’s ideas on the human good?
- What is the difference between classical and contemporary philosophy readings on happiness?
- What is the link between happiness and the meaning of life?
- What is eudaimonic well-being ?
- What are the features of Diener’s happiness philosophy?
- What is the happiness philosophy of Plato?
- How has happiness research in philosophy progressed over time?
- Money Cannot Bring True Happiness.
- What is the concept of happiness in English sayings?
- Is ancient happiness wisdom applicable to modern times?
- What are the contributions of the world’s famous happiness philosophers?
- What does Islam say about happiness?
- What were John Stuart Mill’s views on the moral and political philosophy of happiness?
- Personal happiness or societal well-being: what should be prioritized?
- How do Foucault’s teachings describe children’s happiness?
- What were Ibn Rushd’s ideas on happiness?
- How have ancient philosophers influenced contemporary debates on the nature of happiness?
- Human Development and Wellbeing .
- How do Eastern and Western approaches to happiness differ?
- How did stoics achieve happiness?
- Is greater happiness for a greater number of people desirable?
⚖️ Happiness Argumentative Essay: Topic Ideas
- Nature vs. nurture : the role of personal choices in achieving happiness.
- Can happiness be increased by technological advancements?
- The Relationship between Money and Happiness .
- Happiness can’t be achieved with anti-depressants.
- Cultivating positive brains is vital for happiness.
- Happiness levels in rich and poor nations .
- Is unhappiness more important in moral terms than happiness?
- Gay Marriages: Isn’t It Time to Allow Them Feel Happy?
- Emotional control plays a vital role in a person’s ability to be happy.
- Happiness is inseparable from pleasure.
- Happiness inevitably leads to human flourishing.
- Are there moral limits to satisfaction?
- Improving Decisions about Health, Wealth, and Happiness .
- There should always be a place for virtue in happiness.
- Happiness is a stochastic phenomenon: examining Lykken and Tellegen’s views.
- Suffering is not mutually exclusive with happiness.
- Technological progress distances people from simple happiness.
- Goodness means different things to people.
- Health, Wealth, and Happiness: Government’s Responsibility .
- Happiness and meaning are two main aspects of a virtuous life.
- Is happiness research relevant for economists?
- Happiness research can offer implications for public policy .
- Happiness: a contribution to an economic revolution.
- How To Achieve Well-being and Enjoyment in Life?
- The paradox of choice: does an abundance of options lead to greater happiness?
- Implications of happiness research for environmental economics .
- Diversity is a vital determinant in modern happiness research.
- Happiness research should be country-specific.
- National Well-Being Before and During the Pandemic.
- A need for more programs for increasing personal happiness.
- Happiness is a relative concept.
- Happiness can prosper only in democracies.
- Collective and individual happiness are interrelated.
- Psychological Well-Being, Self-Efficacy, and Personal Growth .
- Happiness affects mental and physical health in many ways.
- The impact of happiness on achievement.
- Do acts of kindness increase happiness levels?
- The impact of relationships on individual happiness: quantity vs. quality.
- Hedonism vs. eudaimonism: which leads to a more fulfilling life?
- Happiness depends on income, but not exclusively.
- Should maximizing happiness be the government’s social policy ?
- Insights of happiness research for public policy and administration.
- Democracy: Equality of Income and Egalitarianism .
- Human happiness is impossible without favorable social conditions.
- Happiness scales don’t work.
- There’s a tangible degree of utility for human happiness.
- Instagram Use and Psychological Well-Being in Women .
- The significance of adaptation and change in sustaining lasting happiness.
- Happiness is culturally constructed.
- Happiness is not equal to well-being.
- Personal happiness is a principal element of productivity.
- Preventive healthcare can boost people’s well-being and happiness.
- Happiness at work determines general happiness to a large degree.
- Morality plays a huge role in the folk conceptions of happiness.
➡️ Essay about Cause and Effect of Happiness: Topics
- Causes of happiness and unhappiness.
- Culturally specific causes of happiness.
- Physical appearance peculiarities and happiness.
- Individual traits’ impact on perceived happiness.
- Chinese Population: Future Growth and Wellbeing.
- Effect of overestimating and underestimating the importance of happiness on well-being.
- Influence of happiness on one’s body and mind.
- Absence of happiness as a probable cause of mental health disorders .
- Can unhappiness cause cancer?
- The Citizen Science: Impact on Personal Wellbeing.
- Causes of marital unhappiness.
- Effects of chronic stress and unhappiness at work.
- Unhappiness as a cause or effect of loneliness.
- Happiness and success – what’s the cause in this relationship?
- Effect of wealth on happiness.
- Social Justice, Feminism and Well-Being.
- The impact of living in a democracy versus autocracy on people’s perceived happiness.
- Causes of male happiness.
- The influence of consumerism culture on happiness.
- Differences between the causes of male and female happiness.
- Instagram Use and Psychological Well-Being .
- How do the causes and effects of happiness change with age?
- Effects of happiness on the elderly.
- The impact of education level on happiness.
- Causes of happiness in Eastern and Western cultures.
- Can a cause of happiness in one culture be a cause of unhappiness in another one?
- Divorce of Parents and Impact on Child’s Well-Being.
- The influence of the number of children one has on the perceived happiness level.
- Can the pursuit of one’s dream be a cause of happiness?
- Freedom as a cause of happiness.
- The causes of material versus spiritual happiness.
- Video Gaming and Children’s Psychosocial Well-Being .
- Causes of happiness in the workplace.
- Effects of being happy and emotionally stable on academic performance.
- The impact of happiness on the quality of social relationships.
- Can happiness be a source of productivity?
- The Impact of Self-Care on Well-Being among Practicing Psychologists .
- Individually determined causes of happiness and misery.
- Environmental causes of human happiness.
- How do causes of happiness change over time?
- The COVID-19 Pandemic Impact on Social Well-Being .
- Can happiness cause health improvements?
- Moral causes of happiness.
- The effect of positive body image on a person’s happiness.
- How does high self-esteem affect one’s happiness?
- People’s recipes for long-term happiness across cultures.
- Polling Exercise: Self-Fulfillment Over Self-Indulgence .
- Effects of happiness on sociability.
- Happiness causes in single-parent families and double-parent families.
- Causes of happiness among very wealthy people.
- Positive Impact of the Environment on Families .
- Is happiness a stable concept? What causes happiness to change?
- Causes of happiness as seen by feminists.
- Strong friendship bonds as a cause of happiness.
- Psychological wealth as a precondition of happiness.
Pursuit of Happiness Essay Topics
- The unending pursuit of happiness is too commercialized.
- Pursuit of happiness in the movies.
- History: In Search of the American Dream.
- The scientific pursuit of happiness: approaches from different sciences’ perspectives.
- People often get lonely in the pursuit of happiness.
- Self-defeating pursuit of happiness.
- Historical cases of happiness pursuits.
- Materialism and pursuit of happiness.
- Positive Psychology to Lead a Normal Life.
- Experientialism and happiness.
- Time, money, and social connections in the happiness equation.
- Therapy vs. medications in the pursuit of happiness.
- What should a person know to pursue happiness successfully?
- Pursuit of happiness: rural vs. urban perspectives.
- Pursuit of happiness in the Age of Enlightenment .
- How do advances in biotechnology serve the pursuit of happiness?
- Psychobiotics and gut-brain relationships: happiness via nutrition.
- Downshifting for the sake of happiness.
- The impact of race on the choice of happiness pursuit methods.
- Perceived security and pursuit of happiness.
- Experiential consumption in the pursuit of happiness.
- The origins of the hunt for happiness.
Happiness at Work: Topic Ideas
- The benefits of happy employees for the organization.
- The reciprocal relationship between happiness and success.
- Job Satisfaction and Ethical Behavior in Prisons .
- Impact of happiness and optimism on performance .
- Waiting to become happy as the greatest success limitation.
- Police: Issue of Job Satisfaction, Hazards and Risks .
- Cultivation of positive brains for motivation, workplace creativity, and resilience.
- Escaping the cult of the average for the sake of happiness.
- Psychological flexibility is the key to workplace success.
- Human Resource Regulations: Working Hours and Minimum Salary .
- Independence as a cause of happiness at work.
- Work-life balance and happiness.
- Attaining happiness in the knowledge-intensive workplace.
- Approaches to measuring happiness at work.
- Diversity at the Workplace: Problem and Importance.
- Happiness at work: small firms, SMBs, and corporations.
- Cross-cultural correlates of happiness at work.
- The art of staying happy in the workplace.
- Work-Life Balance in the Last Decade .
- The quality of relationships with colleagues as a determinant of happiness.
- Workplace conflict and happiness.
- Happiness and financial/non-financial rewards.
- Positive psychology coaching for staff.
- Impacts of Parenting on Work, Life, and Family.
- Can a person working nine-to-five be really happy?
- Happiness and overtime work.
- Happiness in the educational workplace.
- Steps to Reduce Stress at Work .
- Happy doctors and nurses: can seeing suffering every day align with happiness?
- Anger control and happiness at work.
- Culture of respect and workplace happiness.
- Exploring the Concepts of Productivity and Stress Levels in the Workplace.
- Happiness at work and broader life satisfaction.
- Happiness among emergency workers.
- Happiness and workplace burnout.
- Work Efficiency Impact Factors.
- Can real happiness be attained through work?
- Organizational learning measures for supporting staff happiness.
- Happiness at work and organizational effectiveness.
- Human Factors: Workload and Stress Relationship .
- Are happy employees more committed to their employer?
- Happiness at work and motivation.
- Happy staff and growth mindsets.
- Work-Related Stress and Meditation & Mindfulness .
- How do workers of different ages conceptualize happiness at work?
- Self- and peer-related orientations and happiness at work.
We’ve prepared a small writing guide to help you make a well-structured and captivating happiness essay. Consider the best tips for the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion .
Happiness Essay Introduction
The introduction is an essential part of an academic essay that presents the topic, provides background information, and catches readers’ attention. Here are the three main elements to include in your introduction.
Body Paragraphs about Happiness
The body is the longest essay part, leading readers through your ideas, arguments, and evidence for your thesis . It’s always divided into two or more paragraphs, each centering around a topic sentence.
A topic sentence describes the paragraph’s central idea and should be expanded with evidence and examples. It also helps to transition smoothly from one section to another.
Remember, we’ve already developed a thesis statement about the connection between happiness and productivity. An example of a happiness topic sentence for this essay is shown below.

To find supporting evidence for your thesis, you can check out major theories, previously done research, statistics , case studies, and articles on the topic.
Happiness Essay Conclusion
The conclusion is a vital part of an essay that reminds readers of your thesis statement and summarizes the main points. Nothing new is presented in this section, but you might want to encourage readers to think deeper about the topic.
The critical requirement for the conclusion is paraphrasing your thesis statement from the introduction. You can keep the keywords but change the rest.
Happiness is a complex phenomenon many writers, poets, and scientists try to explore. If you also want to contribute to happiness discussion and share your ideas, writing an essay is a great opportunity. Consider our top happiness essay topics and writing tips to write a memorable paper.
- Happiness | Harvard Business School
- Happiness | TED
- Research Topic: Happiness | Association for Psychological Science
- Three New Ideas About Happiness and Well-Being | Greater Good Magazine
- Happiness Articles & More | Greater Good Magazine
- Happiness in Psychology and Philosophy | Cogut Institute for the Humanities
- Happiness | UCLA Anderson Review
- The Five Big Questions of Happiness Research | Longevity
- 10 Questions: How Can We Be Happy? | CBS News
- Can Money Buy Happiness? Scientists Say It Can. | The Washington Post
301 Abortion Essay Topics & Research Questions on Laws, Ethical Issues & More
333 football research topics & essay titles.
Thesis Statement about Happiness: Unraveling its Ephemeral and Personal Nature
This essay will discuss the complex and subjective nature of happiness. It will present a thesis statement that happiness is both ephemeral and deeply personal, shaped by individual experiences, values, and perceptions. The piece will explore philosophical and psychological perspectives on happiness, and how it is influenced by internal and external factors. More free essay examples are accessible at PapersOwl about Cognition.
How it works
It is tough to explain what lies below the word’ happiness.’ This is something unstable, ephemeral, and not eternal. All human beings strive to be happy; however, it is impossible to describe the full depth of this feeling in words. The knowledge of happiness for absolutely everyone is solely individual. Happiness is moments when all your dreams, aspirations, and expectations suddenly come true. Happiness can overtake us anytime and anywhere.
- 1 Thesis on Happiness: Its Complexity and Universality
- 2.1 References
Thesis on Happiness: Its Complexity and Universality
Happiness can manifest itself in material values, the comfort of home, and the reciprocity of a loved one.
To an individual — his manifestation of happiness depends on his life situation. For the hungry, a piece of bread will be happiness; for the frozen — the warmth of the hearth; for the tired – a soft bed. Aristotle (348 BC) suggested that the secret of joy lies in a person’s self-realization. Only the one who has known himself and his destiny and revealed his potential can be pleased.
Moreover, indeed, doing what we love makes us happy. Not only philosophers and psychologists but also writers tried to convey, show, tell, and open their eyes to ‘what is happiness?’. “Life with the possibility of being beneficial to humanity to whom it is easy to do good, and who are not accustomed to having it done to them; said Lev Tolstoy (1859). “A modest and happy life is better than success with restlessness” (Albert Einstein, 1922). Happiness is when native people think about you and take care of you when they are ready to sacrifice themselves for you. Understanding each other, the desire to be close – this is happiness.
The Many Faces of Happiness: Philosophical and Practical Perspectives
Happiness is the state of a person’s soul, the highest satisfaction with life. Each person puts their understanding into this. One person has a lot of money and says that he is pleased. However, he is not entirely honest. He cannot be happy just because he has much money. ‘The rich cry too’… I am sure this expression did not come out of nowhere. It has a foundation. Yes, a wealthy man can afford a lot. Of course, benefits improve and facilitate human life. However, to be happy for a person to be pleased, wealth must be accompanied by no less critical ‘details,’ such as health, love of loved ones, mutual understanding in the family, luck in business, and so on. “There is no relation between happiness and the amount of money” (Kesha, 2015). It is enough for someone to buy a jar of caviar and feel happy.
Moreover, someone will go fishing for the weekend and be happy. A little child will see his mother, snuggle up to her, and be happy! It is such small, momentary happiness. The happiness that helps a person cope with problems, forget about the pain and even grieve for a while.
Happiness often manifests itself in small things. For example, someone lives in a southern city and feels childishly happy when a large amount of snow falls and sparkles, plays in the sun and creaks when walking. For those who have not seen the sea, visiting there for the first time is happiness; for some, conquering a mountain peak is happiness. However, everyone can agree that happiness is when you and everyone dear and close to you are healthy.
Happiness can be characterized as harmony between a person’s inner worldview and the surrounding reality. Close people, stability, and a peaceful sky above your head are happiness. All people, regardless of age and place of residence, have many reasons to be happy because the opportunity to live, breathe, and feel is already happiness. To put it in a nutshell, happiness is a magical thing, and when human beings are happy, they live healthy, long, and beneficial lives and make others jubilant, too.
- Tolstoy, L. (1859). On the essence of life. Placeholder Press.
- Einstein, A. (1922). Reflections on success and life. Einstein Publications.
- Kesha. (2015). The truth about happiness. PopStar Publications.
Cite this page
Thesis Statement About Happiness: Unraveling Its Ephemeral and Personal Nature. (2023, Aug 30). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/thesis-statement-about-happiness-unraveling-its-ephemeral-and-personal-nature/
"Thesis Statement About Happiness: Unraveling Its Ephemeral and Personal Nature." PapersOwl.com , 30 Aug 2023, https://papersowl.com/examples/thesis-statement-about-happiness-unraveling-its-ephemeral-and-personal-nature/
PapersOwl.com. (2023). Thesis Statement About Happiness: Unraveling Its Ephemeral and Personal Nature . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/thesis-statement-about-happiness-unraveling-its-ephemeral-and-personal-nature/ [Accessed: 31 May. 2024]
"Thesis Statement About Happiness: Unraveling Its Ephemeral and Personal Nature." PapersOwl.com, Aug 30, 2023. Accessed May 31, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/thesis-statement-about-happiness-unraveling-its-ephemeral-and-personal-nature/
"Thesis Statement About Happiness: Unraveling Its Ephemeral and Personal Nature," PapersOwl.com , 30-Aug-2023. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/thesis-statement-about-happiness-unraveling-its-ephemeral-and-personal-nature/. [Accessed: 31-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2023). Thesis Statement About Happiness: Unraveling Its Ephemeral and Personal Nature . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/thesis-statement-about-happiness-unraveling-its-ephemeral-and-personal-nature/ [Accessed: 31-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

Happiness Essay
Our activity
Finished orders
Professional writers
Writers online now
Operators are online
Of 5 average writers' score
While learning, there are times you will encounter the most peculiar types of assignments and exams, and not because they are weird but mostly because they are personal. One of those moments will demand you to know how to write a happiness essay. The incredible thing about such topics is their flexibility in terms of creativity and vocabulary. Writing such an article will take you on a spiritual journey and will help you discover more on the social aspects of life than any school could teach you. The important thing when writing any essay is to put your effort into it no matter how demanding it can be.
A quick rundown on happiness essays is that we have all encountered moments of highs and lows in our lives. We are never pleased all the time, and yet we can learn to be. You will discover more about true happiness researching materials from philosophers, psychologists, and authors from all around the world. We know the task may be tedious and may be out of your abilities for now. However, in good time, you will learn all there is to know on writing happiness essays.
We have taken the liberty to highlight the crucial guidelines that will set you apart as an excellent student as you write a short essay about happiness in life. You will learn how to explore controversial statements such as money can’t buy happiness in great detail. Here is the blueprint for your perfect essay.
Choosing the Topic
Before beginning to write your paper, follow the instructions on the essay. This prompt from your teacher can be the very difference between a pass and a fail. The prompt will specify on word count, format and perhaps even allocate a topic for your essay. Be sure to ask for help understanding the instructions if in doubt. Sometimes, the teacher will demand creativity by letting you choose the topic for discussion under the happiness essay.
A great way to choose a topic is self-reflection and by meditating on it. The question will be something you are passionate to write about and explore further with your audience. People face a lot of fears and anxieties in life, and they’ll understand your topic better if it resonates with them. A good subject clicks with the audience or is personal to the writer. It may have been a heartbreak, the death of a loved one or even the importance of therapy. All these may be put under a happiness essay because they speak on what happens when one is happy or when one is not happy. You may write about something that makes many people happy, an example being how pets prolong the life of their owners. It should be a creative guess, something your teacher or audience may have never read before.
Happiness essays are a fascinating topic and maybe convenient to earn you good grades. People are curious to know more about it will pay great attention if you’re creative from the start to the finish line.
Writing the Thesis Statements
The thesis statement is the core generator of your spaceship. The heart of your paper that breathes life into it. This is because it should give the reader a general idea of what your paper purposes to do and explain. It is vital to the paper and should be executed well enough to start your essay with a bang.
The topic of your paper is based on a subjective sentiment that is happiness is different to many people. Thus, you should make your thesis statement something that is disputable and is your own opinion. It is not a research paper. Therefore you won’t have to argue for a particular point if it does not apply to anyone. Be objective and straight to the point when stating your main idea. Preferably, place it at the end of your introduction paragraph for a smooth transition to the main body paragraphs.
There are a few different ways of stating the main idea of your happiness essay, and here they are. First, you may choose to use phrases that show a cause and effect relationship on the topic. An example would be, “Whenever people lose a loved one, it is often difficult to express happiness even amidst friends.” Thus, either use happiness as the subject or the object, relating the thesis with happiness on the frontline. Support your thesis statement with some information. Reclassify your data into two groups. One should be arguing for the factor that affects happiness, and the other group should be the effects it has on happiness. Or the first group should have details supporting the causes of happiness and the other supporting the impact happiness has on an individual. Give citations from material researched from psychologists, philosopher, professor, and even online sites.
Check Our Samples
Argumentative Essay
New Technology: Beneficial or Dangerous?
Academic level: Bachelor
Subject: Communication
Paper format: MLA
Corporate Social Responsibility
Subject: Management
Paper format: Harvard
Master’s Prepared Nurse Interview
Academic level: Master
Paper format: APA
Research Paper
The Maya Tribe
Academic level: Undergraduate
Subject: History
Sample Thesis Statements on Happiness
Wealth is not the key to a happy life as we would not need therapy or rich people.
The paycheck should not determine happiness from our workplaces but rather from how we are respected and appreciated there.
Happy marriages are not based on love, wealth, or sex but rather on a good friendship, trust, and respect.
Our happiness should not be measured by our wealth but by our self-progress and the achievement of our goals.
Contentment is the doorway to true happiness because coveting what we don’t have is as bad a not appreciating what we do have at the moment.
The pursuit of happiness is a fundamental human right, as stated by Thomas Jefferson in the Declaration of independence. It should, therefore, be as important to us as breathing purified air.
How to Write and Summarize the Essay
There’s a way that makes your conclusion easy and remarkable at first glance.
Create an outline for your essay that makes it easier to write on the first draft.
Remember to proofread your document for any grammar and spelling errors.
Follow the prompt provided by your teacher. These are the instructions that will guide you when writing your paper.
Follow the structure of a good essay and adhere to the rules of Literature. Make your first paragraph the introduction that includes the thesis statement. The main body paragraphs should legitimize your thesis statement and should consist of illustrations and examples. A minimum of 3 and a maximum of 5 sections should do.
Write about things that are close to your heart. That way you won’t mess up.
Helpful Pointers for Crafting a Happiness Essay
Once you’ve determined the topic worth discussion, there are a few more helpful tips that you need to know before embarking on the quest before you. Writing a short essay about happiness has never been easier than this.
Pick a group of people with similar characteristics and discuss how the topic is related to the. For example, ‘How depression may have set into the relatives of the people who died in the 9/11 attack.’ Or you could pick an individual, including yourself and talk more about how you or they define happiness. An example would be,’ How Lexi my pet snake changed my life when I had leukemia.’
Juggle with bright ideas on how happiness is defined and what are its effects. Cover most of your ground from having necessities to appreciating the little things in life. Good research will also be of help in documenting how different groups, cultures, and people view happiness and experience it.
Create an outline with your main points explaining the main idea from your introduction paragraph . Use a bubble map to sketch out these ideas into cardinal points.
Be creative within your main body paragraphs. Maturely express yourself and your ideas, giving reasons for the thesis statement in each paragraph. The topic sentence of each paragraph should be an explanation of the thesis statement. Follow through with a logical explanation that supports your opinion. The more creative you get, the better your grades, and the more interested your essay would be.
When writing your conclusion, be sure to highlight the most critical points and restate your thesis statement for emphasis. Make a summary of the causes and effects of happiness and give an inspiring call to action for your readers. An example would be to say, ‘Happiness is a state of mind, so don’t forget to meditate every day.”
Use linking phrases and words that connect illustrations to the thesis statement or statements to each other in a synchronized way. The level of harmony in your paper should be creative and flow smoothly throughout the article. Let the readers connect to the story magically without having to use much of their thinking. They should be able to meditate on your words afterward rather than struggle to get through your paper.
Do not overextend yourself beyond the necessary word limit that is required of you simply because you may have made a mistake in understanding the instructions. This will make you have to do the task again. Save yourself the pain of a low grade by adhering to the given rules and composing a quality paper that answers the question on the teacher’s mind. High school papers are meant to see if you are learning well and sticking to instructions is one way they gauge your intellect. So don’t give them a chance to fail you as you write your essay about happiness in life.
Hot to Be Rid of Distractions as You Write You Essays about Happiness
It is fairly wise to write your happiness essay while you’re happy. And quite often we are stimulated by external forces that won’t give us a moment’s peace. Even as we conjure our brilliant happiness definition essay, the pursuit of happiness essay, or just talking about how money can’t buy happiness. And often we assume the piece until the deadline is close before we jump into a hurried frenzy to get it out of the way.
Well, this is not an excellent way to earn a perfect grade. If you procrastinate a lot, chances are you might continue this habit for a very long time. However, kudos to you if control comes natural to you and you do tasks on time. Use wise tactics such as switching off your phone or putting it on airplane mode and eating early before doing your assignment. Forget Netflix or that game that you so desperately need to watch. Come to terms with the fact that the task is essential and will earn you good grades.
Examples of Happiness Essays
Below are four examples of well-crafted essays about happiness. The first is can money buy happiness essay, and the second is the happiness definition essay, the third is the pursuit of happiness essay, and the fourth is the essay about happiness in life. All these essays are essays about happiness and are fantastic examples.
Can Money Buy Happiness Essay?
The abstract concept of happiness has been a contentious topic for the longest time. For many, the journey towards happiness is higher than the destination of happiness. Every single person has their sources of joy. Others draw it from their achievements, others from seeing their fellow man becoming successful while other choices see controversial. Happiness is a state of mind more often than not. It is usually not the expression of joy or laughter, as some might think. Studies on depression have shown that even sad people mask generally their emotions with these outward expressions of happiness. The source of happiness has different foundations based on biology, physiology, religion, and psychology of the human psyche. This essay works to explore more on the economic aspect of this profoundly puzzling topic.
The very thought of happiness may trigger superficial expectations of a stable life. It may be idealized as the American dream of an excellent suburban home. A picket fence and children playing freely around the house while the parents have a good talk in the living room. The reality is, money cannot buy all the necessary components that will make up a delighted individual. A Polish researcher once identified the four essential values for happiness. The first is a state of profound joy, possession of the best goods, pure luck, and a sense of self-actualization with life satisfaction.
It is common knowledge that humanity is economically classed into some different categories. We have the upper class, the middle class, and the lower class citizens. So does this make any class happier than the other? Obviously, as with any other philosophical question, the answer lies more in-depth than the surface. Hunger, disaster, and suffering may be a fate of the poor. But in some outcomes, the rich also have their version of this, and their money does not make them any happier. Happiness may not be fully explained by one’s pleasure and prosperity, seeing that all humans go through stages of highs and lows. Happiness is an immaterial possession, and even the lowest class of citizens may find pleasure in such commonplace things as life and contentment.
Then arises the question of why even the richest people still work. It’s not about maintaining their billionaire statuses but rather for the feeling of self-actualization. The work we put ourselves to do may be the source of our greatest happiness and satisfaction. What’s more, people who are most motivated to work because of money are usually very problematic at work and fatigued by the end of the day.
In all honesty, happiness can only be truly understood and felt by having moments of deep sadness and dissatisfaction. Our ability to overcome these dark moments is what distinguishes happiness from deep depressive states. The pleasure we feel after overcoming a difficult task, healing from a significant illness, or being promoted after years of hard toil are all ways we can experience true satisfaction. Money may buy away our moments of sadness, but it cannot buy happiness.
Happiness Definition Essay
Happiness is a versatile and multifaceted subject worth exploring and defining. Is it perhaps the things money can buy or is it the pleasure we get from the things we treasure. I mostly believe that happiness is a personal affair that can be defined in different ways. In most cases, humans can’t pick out the moments of happiness because we think it is based on material things and the opinions of others. Especially in the age of social media where happiness is mediated by the number of likes and comments on the things we post to our accounts. Whatever the case, happiness is evasive and can change definitions depending on our expectations and our long term goals.
However, most people agree that happiness is an overwhelming emotion that is generated from a fate of well-being or fulfillment. It is the culmination of your thoughts, feelings, achievements, wealth, spirituality, philosophies, and relationships in your life. Somehow, different people may have common definitions of happiness. A great example is that we all love going to amusement parks, riding rollercoasters, going to the movies, and playing with children or pets in the park. These are all commonplace activities that fill us with a sense of fulfillment by human interaction and giving access to simple pleasures. These feelings fill our body with feel-good hormones such as adrenaline, oxytocin, serotonin ad dopamine that wash over us with an overwhelming wave of happiness. Whenever we feel low, these activities return us to our better, happier state of mind.
By another definition, happiness is fleeting and involves momentary feelings of pleasure. Comics and stand-up comedians have learned the value of telling jokes as they help people relate to the dark moments in a happier way. People laugh for different reasons such as funny pranks, well-written jokes, and moments of stimulating social interaction and to alleviate anxiety in public places. Therefore, laughter can be one of the more straightforward definitions of happiness.
Achievements in our lives give us a general sense of joy and maybe equated to real happiness. Whether they are promoted, finally go out on a date or learn to ride a bike, people usually feel happy about these things. Achievements define an improvement of our social standing or personal progress, and it is a way to be satisfied.
Sometimes, happiness is about being content with whatever is happening in your life. It means being happy and jovial without any real achievement or wealth of any form. This may be the actual form of happiness as it is not an outward emotion but based on a feeling of satisfaction with who you are at that point in time. Inner peace is the most accurate definition of lasting happiness.
Lastly, happiness can be found in having material wealth. This does not go against any moral laws and should be encouraged as it promotes hard work, patience, and even contentment with what you have achieved so far. When all is said and done, happiness is satisfying your desires in the way that you feel is best.
Pursuit of Happiness Essay
America is founded on a system that allows their citizens to pursue achievement and happiness with freedom and honor. The founding father, Thomas Jefferson famously included the phrase ‘pursuit of happiness’ in the U.S. Declaration of independence as a human right. By that definition, happiness is, therefore, a fundamental truth and a human right that should be pursued until one’s dying breath.
Most philosophers and scientists have agreed that it is human nature to follow their heart’s desires and aim to achieve them. This free will and independence is what makes happiness unique to each person and redefines happiness from every person’s perspective. The truth is that most human inventions and discoveries have been founded on the idea that humanity could avoid particular misfortunes. An example would be vaccinations in the field of medicine, and even space exploration is meant to find new homes for humanity in case Earth becomes uninhabitable.
Happiness is based on evolution, and once we have a sense of achievement, most people seek a higher state of that feeling. An example would be buying a new pair of shoe, then matching it up with some good socks and hen a new tie plus a striking blazer and finally a new car for yourself. With every achievement, our standards of happiness keep evolving and improving. This is what defines the pursuit of happiness and causes either contentment or social pressure to achieve something big. Generally, people will know when they feel happy or when they are dissatisfied with the direction of their life and their achievements.
Seeing that happiness is a state of mind, a person must always convince themselves to be happy despite the troubles they might be facing. You must expect and affirm your happiness each day for it is as visible yet elusive as smoke. Most people do this by meditating, doing yoga, exercising, reciting positive affirmations, and assessing their state of mind constantly. These are all healthy ways of coping with the constant pressure of pursuing material wealth, relationships, and achievements despite the mishaps that always occur. They help one to appreciate and celebrate little to considerable achievements in their lives and encourage a spirit of contentment.
An accurate way of pursuing happiness is by doing t others as we wish done unto us. Showing kindness, forgiveness, and other complementary virtues all give us a sense of peace and joy. These actions help us to be grateful and appreciate the little things in life. We should lose our focus on the negativity that is accompanied by the pursuit of happiness. Some of these things include; pending bills, car loans, mortgages, relationship issues, and even health issues. The ore we focus on them, the more they feed away on our happiness. As a ritual, we should meditate on the things that give us happiness and even share them with our friends and family.
In conclusion, the pursuit of happiness is a right that we get to enjoy at our pleasure. The truth is, we can achieve happiness and enjoy it every single day. Happiness is not an end goal, but the culmination of our thoughts and attitudes towards life’s crazy cycles of joy and sadness. Make it a habit to be grateful every day and stay positive.
Essay about Happiness in Life
Legends and fairy tale stories of fiction usually have a particular n formula that leaves the reader satisfied at the end. It is when the frog finally becomes a prince, when the dragon is slain, went the prince rescues and marries a princess and when the kingdom is restored to its true glory. The line is usually too famous to even repeat, but here it goes, “And they lived happily ever after.” It defines one of humanity’s greatest pursuit and forms an excellent line for ending stories.
Happiness is a psychological state. It has been sought after by monks, philosophers, and scientists from all around the world. But is there a formula or secret to happiness that we do not know about? I think not, simply because we all can find joy wherever we are in the stations of our lives.
It is a big world that has been existent before since any of us was here. The confusion is imminent when we are faced with advertisements and easy-going options for finding happiness. Therefore, it is no one’s fault when happiness becomes an illusion too hard to capture in their hands. It almost seems impossible to be simply happy and content with the blessings that they already have. Anyone willing to find they can always discover the solution for this. One should always stay motivated despite any challenges they face because everyone is facing some form of mishap to another. No one is perfect in this big bad wolf world.
The only way to achieve happiness is to be content with the environment we find ourselves in. Be grateful for the people in your life, the friends keeping you company and the family that is more loyal to you than you might notice. Pick out a hobby or visit amusement parks and movie theatres for an enjoyable time. Find whatever gives you purpose and pursue it without restrictions and permission.
Be willing to build happy relationships and friendships based on similar characteristics and mutual love from each other. Whatever relationship you might find yourself in, know your worth and leave whenever it becomes too toxic to bear. This is because close relationships might cause us depression and anxiety in the long run. Simply put, your loneliness can be very detrimental to your health, and you should find the birds of your feather and happily flock together. Also, make time for your loved ones, even with busy schedules and jobs. Your employment should not drag the happiness out of your life but should be a fountain of happiness as you achieve the goals and dreams of your youth.
Stay positive throughout your day and find positive affirmations that keep you connected to your inner strengths. Every single thought we have either eats away on our happiness or gives us a positive spin on life. Reinforce your joy with a purpose and satisfaction that is not based on the wealth you have or the way you are but the way you want to feel.
Nothing is as good as tackling a giant to the floor and cutting its head off. And that’s what we have done today as we explored the fantastic world of happiness essays. The instructions and guidelines provided are simple enough to answer all your problems and provided more solutions than one. We hope that this article will be of great help in your essay writing endeavors and that you will have an easy time as you tackle your next essay on happiness.
All the best as you write more pieces about happiness and discover for yourself why money can’t buy happiness. For more information and essay writing services, contact us.

What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Psychology of Happiness: A Summary of the Theory & Research

Little did I know the overwhelming depth of this topic! I found myself asking questions – can science explain happiness?
Can happiness be measured? What is happiness, anyway?
Arguably, a lot has been written on the topic of happiness , including on this website. The following provides an exploration of happiness, and, importantly, it provides you with links to further resources on this important topic.
Keep reading to discover a range of topics including the main theories of happiness, and a fascinating look at the neuroscience of happiness, as well as an interesting discussion on topics such as subjective wellbeing (the more scientific term for happiness), what positive psychology has to say about happiness, success and happiness, and more. Hopefully, it will answer some questions about happiness. Please enjoy!
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Happiness & Subjective Wellbeing Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients identify sources of authentic happiness and strategies to boost wellbeing.
This Article Contains:
A scientific explanation of happiness, a look at the theory and science of happiness, the psychology of happiness, happiness and positive psychology, interesting research and studies, the happiness research institute, the happiness professor, other well-known researchers, articles on success and happiness, 16 most important happiness articles, other recommended journal and scholarly articles (pdf), a take-home message.
What exactly do we mean when we talk about a scientific explanation of happiness? What, in fact, is the science of happiness?
Put very simply, the science of happiness looks at “ what makes happy people happy ” (Pursuit of Happiness, 2018). If you think about it, the subjective nature of happiness makes it incredibly difficult to define and also challenging to measure (Kringelbach & Berridge, 2010).
Let’s look into this further …
In the past
Happiness has been the topic of discussion and debate since the ancient Greek times. Hedonism has a long history (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Science has looked closely at happiness as ‘hedonically’ defined – or, in other words, happiness is the outcome of the pursuit of pleasure over pain (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
Aristippus, a Greek philosopher from the 4th century BC claimed happiness was the sum of life’s ‘hedonic’ moments (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Hedonic enjoyment is a state whereby an individual feels relaxed, has a sense of distance from their problems and, can be said to feel ‘happy’ (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
Since the days of Aristotle, happiness has been conceptualized as being composed of at least 2 aspects – hedonia (or, pleasure) and eudaimonia (a sense that life is well-lived) (Kringelbach & Berridge, 2010).
In the present
What does science say about this? Well, research has shown that, whilst these two aspects are definitely distinct and that, in ‘happy’ people, both hedonic and eudaimonic components of happiness correspond (Kringelbach & Berridge, 2010).
A study by Kesebir and Diener (2008) report that in happiness surveys , more than 80% of interviewees rated their overall ‘eudaimonic’ life satisfaction as “pretty to very happy” and, at the same time, 80% of people interviewed also rate their current, hedonic ‘mood’ as positive (e.g. giving a rating of 6-7 on a 10-point valence scale, where 5 is ‘hedonically neutral’).
Neuroscientists have made substantial progress into investigating the functional neuroanatomy of pleasure (which, according to Kringelbach and Berridge 2010, makes an important contribution to our experience of happiness and plays a key role in our sense of wellbeing).
Pleasure has, for many years in the discipline of psychology, been closely associated with happiness (Kringelbach & Berridge, 2010).
According to Sigmund Freud (1930), people: ‘ strive after happiness; they want to become happy and to remain so. This endeavor has two sides, a positive and a negative aim. It aims, on the one hand, at an absence of pain and displeasure, and, on the other, at the experiencing of strong feelings of pleasure ’ (p. 76).
Kringelbach and Berridge (2010) argue that the neuroscience of both pleasure and happiness can be found by studying hedonic brain circuits. This is because, according to most modern perspectives, pleasure is an important component of happiness.
Does this provide the opportunity to ‘measure’ happiness, therefore providing a scientific explanation of happiness?
In fact, work of neuroscientists has found that pleasure is not merely a sensation, or thought, but rather an outcome of brain activity in dedicated ‘hedonic systems’ (Kringelbach & Berridge, 2010).
All pleasures, from the most fundamental (food, sexual pleasure) right through to higher-order pleasures (e.g. monetary, medical, and altruistic pleasures) seem to involve the same brain systems (Kringelbach & Berridge, 2010).
Some of the hedonic mechanisms are found deep within the brain (the nucleus accumbens, ventral pallidum, and brainstem) and others are located in the cortex (orbitofrontal, cingulate, medial prefrontal and insular cortices) (Kringelbach & Berridge, 2010).
In the future
It can be said, then, that pleasure activated brain networks are widespread. Despite this exciting finding – a brain network for happiness – Kringelbach and Berridge (2010) say that further research is needed to fully comprehend the functional neuroanatomy of happiness.
As well as the findings from neuroscience supporting an anatomical basis to happiness, another component of a scientific explanation of happiness is the issue of measurement.
Can happiness be measured?
Some individuals argue that maybe happiness should not be the subject of scientific explanation because it is impossible to objectively measure it (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
Perhaps, though, as argued by Ed Diener, happiness is subjective. According to Ed Diener, people are happy if they think they are, and each person is the best judge of whether they are, in fact, happy or not (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
He introduced a term to describe this ‘measure’ of happiness: Subjective wellbeing .
Having the measure of subjective wellbeing makes a scientific explanation of happiness possible… by asking questions such as:
- Are you happy?
- How would you rate your happiness on a scale of 1 – 10
Controlled experiments can be devised to determine what can be done to raise/lower these responses.
The Experience Sampling Method (ESM) has been valuable in the assessment of subjective wellbeing. It has been a positive development in the science of happiness.
ESM provides an overall indication of wellbeing over time, based on the total balance of measurement of positive and negative affect at different times (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
Diener provided evidence that subjective wellbeing has “construct validity” meaning that, yes, it is measuring something ‘real’! This is because Diener showed that subjective wellbeing is constant over time, is highly correlated with some personality traits and has the capacity to predict future outcomes.
Diener and colleagues suggest that it is possible to measure happiness using valid, reliable methods including using instruments, looking at observable indicators of happiness such as smiling behavior, and objective reports from one’s friends and family (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
Nevertheless, many critics have opposed the concept of subjective wellbeing, including psychologist Michael Argyle (2001). Argyle states
“the main weakness of subjective measure is that they are affected by cognitive biases such as the effects of expectation and adaptation so that we don’t know how far to believe the scores”
However, other researchers have developed several well-validated scales for measuring happiness, supporting its’ validity as a scientific construct.
The Steen Happiness Index (Seligman, Steen, Park & Peterson, 2005)
Consists of twenty items. Participants read a series of statements and select the one that best describes how they are at the present time. Items indicate three kinds of ‘happy life’ – the pleasant life, the engaged life, and the meaningful life.
These dimensions will be explored closely very soon!
Subjective Happiness Scale (Lyubomirsky & Lepper, 1999)
Consists of four items to assess global subjective happiness. The participants read four statements, including ‘In general, I consider myself…’ and the individual then selects an item from 1 to 7 from, for example, ‘not a very happy person’ to ‘a very happy person’.
Test-retest and self-peer correlations have suggested good to excellent reliability, and construct validation studies of convergent and discriminant validity have confirmed the use of this scale to measure the construct of subjective happiness.
Happiness Scale (Fordyce, 1977)
This scale is also referred to as the Emotion Questionnaire as it assesses emotional wellbeing as an indication of perceived happiness. It is comprised of two items. The first is a scale measuring happiness/unhappiness by participants ranking descriptive phrases on a 0 – 10 scale.
The other item making up the test requires participants to give an approximate percentage of time that he/she feels happy, unhappy and neutral. The test has shown to have adequate reliability and validity.
Therefore, evidence from neuroscience, paired with evidence from the measurement of subjective wellbeing, or, happiness, suggest that a scientific explanation of happiness is, in fact, possible.
It is overwhelming to consider what happiness is… where to begin?! Happiness has been the topic of discussion and debate since the ancient Greek times.
In 1973, ‘Psychology Abstracts International’ began listing happiness as an index term (Diener, 1984). However, because happiness is a term that is used widely and frequently, it has various meanings and connotations (Diener, 1984).
The construct of happiness is still evolving, and although challenging to define, it is a construct that can be empirically evaluated through qualitative and quantitative assessment (Delle Fave, Brdar, Freire, Vella-Brodrick & Wissing, 2011). Delle Fave and colleagues (2011) noted that happiness is also an ambiguous term which can have a number of meanings:
- A transient emotion (that is synonymous with joy)
- An experience of fulfillment and accomplishment (characterized by a cognitive evaluation)
- A long-term process of meaning-making and identity development through achieving one’s potential and the pursuit of subjectively relevant goals.
Historically, since the days of Aristotle, happiness has been conceptualized as being composed of at least 2 aspects – hedonia (or, pleasure) and eudaimonia (a sense that a life is well-lived) (Kringelbach & Berridge, 2010).
Research has shown that, whilst these two aspects are definitely distinct, that in ‘happy’ people, both hedonic and eudaimonic components of happiness correspond (Kringelbach & Berridge, 2010).
A study by Kesebir and Diener (2008) report that in happiness surveys, more than 80% of interviewees rated their overall ‘eudaimonic’ life satisfaction as “pretty to very happy” and, at the same time, 80% of the people interviewed also rate their current, hedonic ‘mood’ as positive (e.g. giving a rating of 6-7 on a 10-point valence scale, where 5 is ‘hedonically neutral’).
Moving forward into the modern era, there is some agreement about the aspects that make up theories of happiness. There are, according to Haybron (2003), when looking at theories of happiness, 3 basic views:
- Hedonism – in other words, to be happy is to experience, on the whole, a majority of pleasure. Hedonia.
- Life-satisfaction view – to be happy is to have a favorable attitude about one’s life as a whole, either over its entirety or just over a limited period of time. Eudaimonia.
- Affective state theory – that happiness depends on an individual’s overall emotional state.
Other theories of happiness are so-called ‘hybrid’ theories that combine the life satisfaction theory with other hedonistic or affective-state theories (Haybron, 2003). One of these hybrid theories is the one that is the most widely accepted theory of happiness: subjective wellbeing (Haybron, 2003). Subjective wellbeing is considered to be a more scientific term than happiness.
A closer look at hedonia
Hedonism has a long history (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Science has looked closely at happiness as ‘hedonically’ defined – or, in other words, the pursuit of pleasure over pain (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Aristippus, a Greek philosopher from the 4th century BC claimed happiness was the sum of life’s ‘hedonic’ moments (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
Hedonic enjoyment is a state whereby an individual feels relaxed, has a sense of distance from their problems and, can be said to feel ‘happy’ (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
Hedonia refers, in simple terms, to the pursuit of pleasure. It was argued by Hobbes that happiness is found in the successful pursuit of our human appetites, and DeSade went on to say that the pursuit of sensation and pleasure is the ultimate goal of life (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
The Utilitarian philosophers, including Bentham, put forth the argument that a good society is one which is developed out of individuals attempting to maximize pleasure and pursue self-interest (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
It should be clarified that hedonia, in respects to happiness, does not have the same meaning as physical hedonism: happiness can come not only from short-term pleasure, but can also arise from achieving goals or other valued outcomes (Ryan & Deci, 2001). So-called hedonic psychologists are of the belief that happiness can include the preferences and pleasures of the mind, as well as the body (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
Kahneman (1999) defined hedonic psychology as the study of “what makes experiences and life pleasant and unpleasant” (p. ix). Within the framework of hedonic psychology, the terms wellbeing and hedonism are used interchangeably (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Hedonic psychology explains wellbeing in terms of pleasure versus pain, and it, therefore, becomes the center of much research and also interventions that principally aim to enhance human happiness (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
Hedonic psychology has been a focus of the theory of happiness, in part, due to the links between hedonia and other dominant theories. For example, hedonia ties in with behavioral theories of reward and punishment, as well as theories that focus on the cognitive expectations of the outcomes of reward and punishment (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
Despite there being a variety of ways to consider the human experience of pleasure/pain, the majority of research in hedonic psychology looks into the assessment of subjective wellbeing. To introduce the term, briefly, subjective wellbeing (or ‘happiness’) consists of three components (Ryan & Deci, 2001):
- Life satisfaction
- The presence of a positive mood
- The absence of a negative mood
Elsewhere in this website, you can read more about eudaimonia and the Aristotelian view of happiness . For the purpose of exploring theories of happiness, I will briefly look at eudaimonia now:
What is eudaimonia? (The life satisfaction view of happiness)
Aristotle argued that, because of man’s unique capacity to reason, pleasure alone cannot achieve happiness – because animals are driven to seek pleasure, and man has greater capacity than animals (The Pursuit of Happiness, 2018).
In striving for happiness, the most important factor is for a person to have ‘complete virtue’ – in other words, to have good moral character (Pursuit of Happiness, 2018).
Eudaimonia was, according to Aristotle, “activity expressing virtue” that will therefore lead to a happy life. Aristotle proposed that happiness was neither virtue, or pleasure, but rather the exercise of virtue.
The argument taken by the Aristotelian view is that happiness, per se, is not the principal criterion of wellbeing (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Proponents of this view see wellbeing as achieved by people living in accordance with the ‘daimon’ (true self). (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Eudaimonic theories of happiness argue that rather than the pursuit of pleasure, happiness is the result of the development of individual strengths and virtues (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
The theory of eudaimonic happiness has its basis in the concept of the self-actualising individual (proposed by Maslow ) and the concept of the ‘fully functioning person’ (Rogers) (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008). Many modern scientific explanations of happiness are conducive with the theory of eudaimonic happiness.
For example, Waterman suggested that happiness is enhanced by people acting in accordance with their most deeply held values (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008). Waterman also introduced the term ‘personal expressiveness’ to describe the state of authenticity that occurs when people’s activities reflect their values.
The eudaimonic theory of happiness adopts the Self-Determination Theory to conceptualize happiness (Deci & Ryan, 2000). This theory argues that fulfillment in the areas of autonomy and competence will enhance happiness. In other words, this view suggests that subjective wellbeing (i.e. happiness) can be achieved through engaging in eudaimonic pursuits (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
Affective state theory
To recap, this theory of happiness proposes that happiness is the result of one’s overall emotional state. Bradburn (1969) put forward the argument that happiness is made up of two separate components that are quite independent and uncorrelated: positive affect and negative affect. According to Bradburn, happiness is a global judgment people make by comparing their negative affect and positive affect (Diener, 1984).
This led to the development of the Affect Balance Scale (Diener, 1984). The Bradburn Affect Balance Scale is a self-report measure of the quality of life. The scale is made up of descriptions of ten mood states (for example, item one is feeling “particularly excited or interested in something”), and the subject reflects upon whether they have been in that mood state during the last week.
A measure of the quality of life, as an indication of happiness, is derived by the sum of the ‘negative’ items are taken away from the sum of the ‘positive’ items (Diener, 1984).
Affect state theory also takes the view that the absence of negative affect is not the same thing as the presence of positive affect (Diener, 1984).
Theories developed by positive psychologists
The discipline of positive psychology has developed some unique theories of happiness. For example, Seligman (2002) introduced the Authentic Happiness theory. This theory is based around the notion that authentic happiness results from a person living according to their ‘signature strengths’ which develop as people become aware of their own personal strengths and take ownership of them (Seligman, 2002).
Another theory of happiness is Csikszentmihalyi’s ‘flow’ theory. Flow may be defined as “ the state of engagement, optimal happiness, and peak experience that occurs when an individual is absorbed in a demanding and intrinsically motivating challenge ” (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008, p. 395). This state of engagement has been proposed to be a pathway to happiness (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
Some psychologists suggest that perhaps, in fact, happiness is relative – or, in other words, it is an evaluation of subjective judgments about one’s situations, comparing others’ situations to one’s own or even one’s earlier situations, goals or aspirations (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008). This argument has, however, been refuted.
Veenhoven explains that comparison may affect the cognitive or life-satisfaction aspects of happiness, but that the affective component results from hedonic experience (meeting one’s fundamental needs) and is therefore quite separate of any comparisons (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
To summarise these related topics – the scientific explanation of happiness and the theory and science of happiness – there are a number of theories conceptualizing happiness and in keeping with these theories, the term can have slightly different meanings.

Download 3 Free Happiness Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to discover authentic happiness and cultivate subjective well-being.
Download 3 Free Happiness Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Way back in 1929, Walter A. Pitkin wrote ‘ The Psychology of Happiness ’ and in this book, he differentiated between happiness and related emotions including pleasure and enjoyment (Samuel, 2019). He argued that achieving happiness was not merely the result of luck or chance. Since this time, psychologists have continued to try and define happiness.
According to psychology, happiness is about more than simply the experience of a positive mood. In order to describe happiness, psychologists commonly refer to subjective wellbeing (Kesebir & Diener, 2008). In other words, happiness is “ people’s evaluations of their lives and encompasses both cognitive judgments of satisfaction and affective appraisals of moods and emotions ” (Kesebir & Diener, 2008, p. 118).
The psychological inquiry into happiness is important because happiness is not only associated with improved physical health and even longevity, but it is also a priority for people – across the world, happiness has been rated as being more important than other desirable outcomes including living a meaningful life or making a lot of money (Psychology Today, 2019).
There are three ways that psychologists study happiness:
1. Need and goal satisfaction theories
These theories suggest that happiness results from striving to achieve appropriate goals and meeting one’s fundamental human needs (Nelson, Kurtz & Lyubomirsky, in press). Deci and Ryan (2000) for example, proposed Self-determination Theory, which stipulates that wellbeing is achieved when one meets their basic human needs including autonomy, competence, and relatedness.
2. Genetic and personality predisposition theories
These propose that wellbeing is influenced by genes, and is associated with the personality traits of extraversion and neuroticism (Nelson et al., in press). This, in turn, implies that wellbeing does not change much over time.
3. Process/activity theories
Process/activity theories argue that wellbeing may be improved by participating in activities that are engaging and require effort (Nelson et al., in press).
Psychologists ask the question, ‘is it possible to increase one’s happiness?’. Some psychologists claim that making an attempt to enhance happiness is pointless because happiness levels are predetermined and stable over time (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
Consistent with this argument is the happiness set point. The happiness set point argues that a person’s state of happiness will be constant over time, regardless of changes in circumstances (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
Adapting to environmental changes is termed ‘the hedonic treadmill ’ or ‘homeostatic control’ (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008). This notion of adaptation (leading to relatively stable levels of happiness) is supported by findings in research that individuals who may be high in either positive or negative affect (e.g. lottery winners, paralysis victims) demonstrate that their happiness levels revert to their ‘usual’ range after a period of time (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
Some psychologists argue that the happiness set point provides evidence that happiness cannot be enhanced (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008). There is a perspective taken by some psychologists that happiness is a ‘trait’ or a personal disposition to experience a certain affect.
This perspective suggests that happiness is relatively stable over time, and therefore efforts to increase happiness are futile (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008). However, research has shown that although subjective wellbeing may be associated with personality traits (e.g. extraversion), that differences in reports of happiness levels over time suggest that, in fact, happiness is not a trait (Norrish & Vella-Brodrick, 2008).
Thus, happiness has been an important area of focus for psychologists. What, then, about the more recent science of happiness…positive psychology?
Positive psychology can be described as a psychology of potential, and what ‘could be’ as compared to what ‘is’ (Seligman & Csikszentmihalyi, 2000). It aims to shift what has historically been the predominant focus of psychology – pathology – to examining the development of positive qualities in individuals and communities (Seligman & Csikszentmihalyi, 2000).
In other words, Positive Psychology aims to understand and cultivate the factors that put individuals, communities, and societies in a position where they are able to ‘flourish’ (Fredrickson, 2001).
What does it mean to ‘flourish’? Put simply, it is a state of optimal wellbeing (Fredrickson, 2001). Fredrickson (2001) asked the question “ What role do positive emotions play in positive psychology? ”
Well, as it turns out, happiness can be thought of as experiencing predominantly positive emotions , or affective states, rather than negative ones (Tkach & Lyubomirsky, 2006). Thus, positive emotions are a sign of flourishing, or, in other words, happiness (Fredrickson, 2001). Happiness is central to the assumptions of positive psychology.
Seligman (2011) described the PERMA model of flourishing. This model defines psychological wellbeing in terms of 5 domains:
- P ositive emotions
- E ngagement
- R elationships
- A ccomplishment
For more detail on flourishing and how to achieve it, check out our article on Seligman’s PERMA+ model .
Let’s look at some interesting happiness research! In a large random-assignment experiment, Seligman and colleagues (2005) operationalized then evaluated 5 different happiness interventions.
They found that two of the interventions – writing about three good things the person had experienced each day and why they occurred, and using ‘signature strengths’ in a novel way – made people happier, and less depressed up to six months later! Compared to participants who engaged in the intervention, those in the placebo control group returned to the baseline levels of happiness and depression symptoms after just one week!
Lyubomirsky and colleagues (2006) conducted three studies examining the effects of writing, talking and thinking about significant life events – ‘triumphs and defeats’. While the majority of psychological research has focused on the way in which negative life circumstances are processed and managed, this unique study looked at the processing a positive life experience (Lyubomirsky, Sousa & Dickerhoof, 2006). This aspect of the study involved participants reflecting on their happiest day.
The researchers found that when participants thought while ‘replaying’ their happiest moment, it resulted in enhanced personal growth, improvements in general health and physical functioning, as well as lower pain levels, compared to the outcomes if the person was writing while analyzing their happiest moments.
The findings of the study suggest that people should be advised against over-analyzing or trying to make sense of a happy experience. Rather, Lyubomirsky and associates suggest that individuals should feel content in reliving and savoring happy experiences rather than trying to understand their meanings or causes.
Even though the experience of happiness is related to greater wellbeing and psychological health, in fact, some studies have shown that the desire to feel happy in an extreme form, or even simply placing a high value on happiness, can be detrimental in terms of wellbeing. In fact, in a research study by Ford and colleagues (2014), it was found that the emphasis placed upon attaining happiness can present a risk factor for symptoms and even a diagnosis of depression.
In a study of 181 participants, Sheldon et al. (2010) conducted a 6-month longitudinal experiment that sought to increase the happiness levels of those in the ‘treatment’ condition. The treatment group set goals to increase their feelings of autonomy, competence or relatedness in life while the comparison group set out to improve their life experiences.
In fact, it was found that those individuals in the treatment group had sustained increases in happiness (Sheldon et al., 2010). However, this gain lasted only while the individuals were actively engaged with the goals.
Interestingly, those who initially had a positive attitude towards change in happiness experienced greater benefits from the treatment! (Sheldon et al., 2010).

What, do you ask, is the Happiness Research Institute ? Well, it is an independent ‘think tank’ developed to investigate the reasons that some societies are happier than others.
The Happiness Research Institute aims to provide relevant parties with up-to-date information about the origins and effects of happiness, as well as to draw attention to subjective wellbeing as an important area for public policy debate. Furthermore, the Institute aims to improve the quality of life of all people.
The Happiness Research Institute provides knowledge, consultancy, and presentations. An example of the knowledge-building activities carried out by the Institute was that, in 2018, the Happiness Research Institute, in conjunction with the Nordic Council of Ministers compiled a study that was called ‘In the shadow of happiness’.
The study examined the reasons why some people living in Nordic countries are happy whilst others are suffering or struggling. The research also involved an analysis of why some groups within this cluster are struggling more often, and the impact this has on society.
In terms of consultancy, the Happiness Research Institute has also worked with groups including the Danish government, the Minister of State for Happiness in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the city of Goyang in South Korea. The aim of these partnerships is to improve quality of life and wellbeing of citizens.
Presentations by the Happiness Research Institute have taken place globally and featured at more than 1000 international events to share knowledge about what drives happiness, wellbeing, and quality of life.
The Happiness Research Institute analyses the somewhat separate components of the different cognitive, affective and eudaimonic dimensions of happiness, wellbeing and quality of life in order to explore these complex concepts. As previously explained, the cognitive dimension refers to the appraisal of overall life satisfaction, while the affective dimension focuses on the emotions that people experience on a daily basis.
Finally, the eudaimonic dimension looks at Aristotle’s perception of the ‘good life’ and is centered on purpose and meaning.
The reason that the Happiness Research Institute measures happiness is in order to shift policy priorities and therefore try and improve quality of life in societies, that will facilitate, in turn, the achievement of goals such as longevity and productivity. The Institute focuses not on the factors that cannot be changed (i.e. genetics, biology) but rather policies (that can be changed over time) and behavior (that can be changed immediately).
By examining the policies related to overall life satisfaction (i.e. the cognitive dimension of happiness) the Happiness Research Institute can explain 75% of the variance between more than 150 countries which were included in the 2018 World Happiness Report. The Institute also hopes to highlight the overlooked dimension of inequality in wellbeing, and increase the awareness and understanding of this inequality. The Happiness Research Institute is accessible via Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn, and Meik Wiking is the CEO.
Professor Paul Dolan was coined ‘the happiness professor’ in The Telegraph in July, 2018. Professor Dolan is the Professor of Behavioural Science at the London School of Economics and Political Science. He is a leading expert in the fields of human behaviour and happiness.
Prof Dolan wrote the best-selling book , Happiness by Design and, more recently, Happy Ever After . His work is centred around two themes:
- The development of measures of happiness and subjective wellbeing that can then be used in policy, and by individuals who are looking to be happier.
- Utilising work from behavioural science that can be used to understand and change individual behaviour, and contribute more to this evidence base.
What would positive psychology be without its founding fathers , and other famous contributors?
Martin Seligman:
Dr. Seligman was born in 1942, and is credited as being the ‘father of Positive Psychology’ (The Pursuit of Happiness, 2018). Seligman suggests that there are three kinds of happiness:
- Pleasure and gratification
- Embodiment of strengths and virtues
- Meaning and purpose
One can remember that, as discussed earlier, happiness – or, subjective wellbeing – had three similar, distinct components like Seligman suggested. In his book , Authentic Happiness: Using the new positive psychology to realize your potential for lasting fulfillment , Seligman (2002) says:
‘[Positive Psychology] takes you through the countryside of pleasure and gratification, up into the high country of strength and virtue, and finally to the peaks of lasting fulfillment: meaning and purpose’
Seligman also wrote a book titled Learned Optimism: How to Change Your Mind and Your Life . He is an acclaimed author, and psychologist, also known for his work on ‘learned helplessness’ which has been popular within the discipline of psychology.
Michael W. Fordyce
Fordyce (December 14, 1944 – January 24, 2011) was a pioneer in the subject of happiness research (Friedman, 2013). In 1977, in the journal Social Indicators Research, the Fordyce Happiness Scale was published. In his multitude of research, Fordyce demonstrated that happiness can be measured statistically, and that also, by engaging in ‘volitional behavior’, happiness can also be deliberately increased (Friedman, 2013).
Diener was born in 1946, and is also known as ‘Dr. Happiness’ (Pursuit of Happiness, 2018). He is a leading researcher in the field of positive psychology. Diener is perhaps best known for coming up with the term “subjective wellbeing”, which is the component of happiness that can be empirically measured (Pursuit of Happiness, 2018). Diener believes that happiness has a strong genetic component, and thus is relatively stable. He also developed the Satisfaction with Life Scale.

Sonja Lyubomirsky
Lyubomirsky is a research psychologist who writes the Psychology Today blog titled ‘ The How of Happiness ’ (Sonja Lyubomirsky, 2019). She is a professor and vice chair at the University of California, Riverside. Lyubomirsky is the author of two books : The How of Happiness , and The Myths of Happiness .
Daniel Gilbert
Gilbert, a social psychologist, is also referred to as Professor Happiness at Harvard University (Dreifus, 2008). He is in charge of a laboratory that has been set up to investigate the nature of happiness. Gilbert’s main work centres around the fact that relationships with family and friends, and that the time spent investing in these social relationships contribute more to happiness than material possessions (Dreifus, 2008).
He suggests that more pleasure can be found in experiences, rather than goods or objects – perhaps, he argues, because experiences can be shared with others whereas possessions are generally not shared (Dreifus, 2008).
The psychology of happiness – WOBI
Research has suggested that there might be a causal relationship between positive affect and success … that not only does success bring happiness but, interestingly, that a happy person is more likely to achieve success (Psychology of Happiness, 2019). These three articles provide an account of success and happiness:
- Boehm, J. K., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2008). Does happiness promote career success? Journal of Career Assessment, 16 , 101–116.
- Lyubomirsky, S., King, L., & Diener, E. (2005). The benefits of frequent positive affect: Does happiness lead to success? Psychological Bulletin, 131 , 803–855.
- Uusiautti, S. (2013). On the positive connection between success and happiness. International Journal of Research Studies in Psychology , 1–12.
[Reviewer’s update:
Since this post was originally published, additional research has come out suggesting that the original theory at the heart of Uusiautti’s (2013) research doesn’t seem to hold true. As a replacement, you may want to check out the article by Okabe-Miyamoto et al. (2021), who recently found that increasing the variety of experiences to escape the hedonic treadmill may actually result in smaller boosts in wellbeing – not larger ones.]
In recent times, a wealth of research has been published into the topic of happiness, such as:
- Diener, E., Heintzelman, S. J., Kushlev, K., Tay, L., Wirtz, D., Lutes, L. D., & Shigehiro, O. (2017). Findings all psychologists should know from the new science on subjective well-being. Canadian Psychologist, 58 , 87 – 104
- Oerlemans, W. G. M., & Bakker, A. B. (2018). Motivating job characteristics and happiness at work: A multilevel perspective. Journal of Applied Psychology, 103 , 1230 – 1241.
- Kaufman, M., Goetz, T., Lipnevich, A. A., & Pekrun, R. (2018). Do positive illusions of control foster happiness? Emotion, September 20, no pagination specified .
- Hoffman, J., Gander, F., & Ruch, W. (2018). Exploring differences in well-being across occupation type and skill. Translational Issues in Psychological Science, 4 , 290 – 303.
- Piff, P. K., & Moskowitz, J. P. (2018). Wealth, poverty, and happiness: Social class is differentially associated with positive emotions. Emotion, 18 , 902 – 905.
- McGuirk, L., Kuppens, P., Kingston, R., & Bastian, B. (2018). Does a culture of happiness increase rumination over failure? Emotion, 18 , 755 – 764.
- Warr, P. (2018). Self-employment, personal values, and varieties of happiness-unhappiness. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 23 , 388 – 401.
- Liao, K Y-H, & Weng, C-Y. (2018). Gratefulness and subjective well-being: Social connectedness and presence of meaning as mediators. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 65 , 383 – 393.
- Blanke, E. S., Riediger, M., & Brose, A. (2018). Pathways to happiness are multidirectional: Association between state mindfulness and everyday affective experience. Emotion, 18 , 202 – 211.
- Fuochi, G., Veneziani, C. A., & Voci, A. (2018). Differences in the way to conceive happiness relate to different reactions to negative events. Journal of Individual Differences, 39 , 27 – 38.
- Weber, S., & Hagmayer, Y. (2018). Thinking about the Joneses? Decreasing rumination about social comparison increases well-being. European Journal of Health Psychology, 25 , 83 – 95.
- Felsman, P., Verduyn, P., Ayduk, O., & Kross, E. (2017). Being present: Focusing on the present predicts improvements in life satisfaction but not happiness. Emotion, 17 , 1047 – 1051.
- Tamir, M., Schwartz, S. H., Oishi, S., & Kim, M. Y. (2017). The secret to happiness: Feeling good or feeling right? Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 146 , 1448 – 1459.
- Phillips, J., De Freitas, J., Mott, C., Gruber, J., & Knobe, J. (2017). True happiness: The role of morality in the folk concept of happiness. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 165 – 181.
- Chopik, W. J., & O’Brien, E. (2017). Happy you, healthy me? Having a happy partner is independently associated with better health in oneself. Health Psychology, 36 , 21 – 30.
- Gross-Manos, D., & Ben-Arieh, A. (2017). How subjective well-being is associated with material deprivation and social exclusion on Israeli 12-year-olds. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 87 , 274 – 290.

17 Exercises To Increase Happiness and Wellbeing
Add these 17 Happiness & Subjective Well-Being Exercises [PDF] to your toolkit and help others experience greater purpose, meaning, and positive emotions.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
Follow the links below to some intriguing research in PDF form!
- How Do Simple Positive Activities Increase Well-Being? – Sonja Lyubomirsky, Kristin Layous (Access here )
- The How, Why, What, When and Who of Happiness: Mechanisms Underlying the Success of Positive Activity Interventions – Kristin Layous & Sonja Lyubomirsky (Access here )
- Variety is the Spice of Happiness: The Hedonic Adaptation Prevention (HAP) Model – Kennon M. Sheldon, Julia Boehm, Sonja Lyubomirsky (Access here )
- Pursuing happiness: The architecture of sustainable change – Lyubomirsky, S, Sheldon, K M, Schkade, D (Access here )
- A measure of subjective happiness: Preliminary reliability and construct validation – Lyubomirsky, S, Lepper, HS (Access here )
- Will raising the incomes of all increase the happiness of all? – Richard A. Easterlin (Access here )
- Lottery Winners and Accident Victims: Is Happiness Relative? – Philip Brickman, Dan Coates, Ronnie Janoff-Bulman (Access here )
This article provides a snapshot of a huge topic which is, in fact, the overarching focus of positive psychology: happiness. It has been shown that subjective wellbeing is the closest thing to a scientific equivalent to happiness, which can be measured. The main feature of this article is that it has provided a range of resources which you can refer to in the future, including 16 key papers published in the last two years.
So, happiness… an elusive phenomenon, which we all seem to strive for. Hopefully this article has provided an overview of what is, undoubtedly, a very important issue. We all strive to be happier.
What is your understanding of happiness? What do you think makes happy people happy? Do you think that happiness can be measured, or, like some argue, do you think it is purely subjective?
What do you think about the recent articles shared? Please feel free to discuss this interesting topic further! I hope you have claimed some important take-home messages on happiness. Thanks for reading!
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Happiness Exercises for free .
- Argyle, M. (2001). The Psychology of Happiness . Routledge.
- Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2000). The “what” and “why” of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behaviour. Psychological Inquiry, 11 , 227 – 268.
- Delle Fave, A., Brdar, I., Freire, T., Vella-Brodrick, D., & Wissing, M. P. (2011). The eudaimonic and hedonic components of happiness: Qualitative & quantitative findings. Social Indicators Research, 100 , 185 – 207.
- Diener, E. (1984). Subjective well-being. Psychological Bulletin, 95 , 542 – 575.
- Dreifus, C. (2008). The smiling professor. New York Times. Retrieved from https://www.nytimes.com/2008/04/22/science/22conv.html
- Ford, B. Q., Shallcross, A. J., Mauss, I. B., Floerke, V. A., & Gruber, J. (2014). Desperately seeking happiness: Valuing happiness is associated with symptoms and diagnosis of depression. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 33 , 890 – 905.
- Fordyce, M. W. (1977). Development of a program to increase personal happiness. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 24 , 511 – 521.
- Fredrickson, B. L. (2001). The role of positive emotions in positive psychology. American Psychologist, 56 , 218 – 226
- Freud, S., & Riviere, J. (1930). Civilization and Its Discontents . New York: J Cape & H Smith.
- Friedman, H. L. (2013). The legacy of a pioneering happiness researcher: Michael W. Fordyce (Dec 14, 1944 – Jan 24, 2011). Journal of Happiness Studies, 14 , 363 – 366
- Happiness (2019). In Psychology Today. Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/au/basics/happiness
- Haybron, D. M. (2003). What do we want from a theory of happiness? Metaphilosophy, 34 , 305 – 329
- Kahneman, D. (1999). Objective happiness. In Well-being: The foundations of hedonic psychology. D. Kahneman, E. Diener, & N. Schwartz (Eds). USA: Russell Sage Foundation.
- Kesebir, P., & Diener, E. (2008). In pursuit of happiness: Empirical answers to philosophical questions. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 3 , 117 – 125.
- Kringelbach, M. L., & Berridge, K. C. (2010). The Neuroscience of Happiness and Pleasure. Social Research (New York) , 77, 659 – 678.
- Lyubomirsky, S. (2019). Sonja Lyubomirsky. Retrieved from http://www.sonjalyubomirsky.com/
- Lyubomirsky, S., & Lepper, H. S. (1999). A measure of subjective well-being: Preliminary reliability and construct validation. Social Indicators Research, 46 , 137 – 155.
- Lyubomirsky, S., Sousa, L., & Dickerhoof, R. (2006). The costs and benefits of writing, talking, and thinking about life’s triumphs and defeats. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 90, 692 – 708.
- Nelson, S. K., Kurtzy, J. L., & Lyubomirsky, S. (in press). What psychological science knows about happiness . In S. J. Lynn, W. O’Donohue & S. Lilienfeld (Eds.) Better, stronger, wiser: Psychological science and well-being. New York: Sage
- Norrish, J. M., & Vella-Brodrick, D. A. (2008). Is the study of happiness a worthy scientific pursuit? Social Indicators Research, 87 , 393 – 407.
- Okabe-Miyamoto, K., Margolis, S., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2021). Is variety the spice of happiness? More variety is associated with lower efficacy of positive activity interventions in a sample of over 200,000 happiness seekers. The Journal of Positive Psychology.
- Psychology of Happiness (2019). Psychologist World. Retrieved from https://www.psychologistworld.com/emotion/psychology-of-happiness-positive-affect
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2001). On happiness and human potentials: A review of research on hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. Annual Review of Psychology, 52 , 141 – 166.
- Samuel, L. R. (2019). The Psychology of Happiness (Circa 1929). Psychology Today. Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/au/blog/psychology-yesterday/201901/the-psychology-happiness-circa-1929
- Seligman, M. E. P. (2002). Authentic Happiness: Using the new Positive Psychology to realize your potential for lasting fulfillment . New York, NY: Free Press.
- Seligman, M. E. P. (2011). Flourish . New York, NY: Simon & Schuster.
- Seligman, M. E. P., & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2000). Positive Psychology: An introduction. American Psychologist, 55 , 5 – 14.
- Seligman, M. E. P., Steen, T. A., Park, N., & Peterson, C. (2005). Positive psychology progress: empirical validation of interventions. American Psychologist, 60 , 410 – 421
- Sheldon, K. M., Abad, N., Ferguson, Y., Gunz, A., Houser-Marko, L., Nichols, C. P., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2010). Persistent pursuit of need-satisfying goals leads to increased happiness: A 6-month experimental longitudinal study. Motivation and Emotion, 34 , 39 – 48.
- The Pursuit of Happiness (2019). Retrieved from https://www.pursuit-of-happiness.org
- Tkach, C., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2006). How do people pursue happiness? Relating personality, happiness-increasing strategies and well-being. Journal of Happiness Studies, 7 , 183 – 225.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
I am impressed by the organization of ideas and materials on happiness. I would be interested to get more materials on happiness if you can supply me, with or refer me to some articles or books.
Hi Mohammad,
Thank you for your kind words and interest in learning more about happiness. I’m glad to hear that you found our resources helpful.
In addition to the article you mentioned, we have a wealth of resources on the psychology of happiness. Here are some additional articles that you may find useful:
– “ The Science of Gratitude: How It Improves Your Health and Happiness “: This article explores the benefits of practicing gratitude, including improved relationships, better physical health, and increased happiness. It also includes practical tips for cultivating gratitude in your daily life. – “ The Power of Positive Self-Talk: How It Can Improve Your Mental Health “: This article explores the benefits of positive self-talk, including increased self-esteem and reduced anxiety. It also provides practical tips for cultivating positive self-talk.
And here are some additional book recommendations on happiness: – “ The How of Happiness: A Scientific Approach to Getting the Life You Want ” by Sonja Lyubomirsky: This book is based on years of scientific research on the psychology of happiness and provides evidence-based strategies for increasing happiness and life satisfaction. – “ Stumbling on Happiness ” by Daniel Gilbert: This book explores the science of happiness and why humans often struggle to predict what will make them happy. Gilbert provides insight into the psychological processes that influence our happiness and offers practical tips for living a more fulfilling life.
Hope this helps! Kind regards, Julia | Community Manager
Were you happy while typing this article? How did you feel throughout the entire writing process?
in precise… PHENOMENAL SNAPSHOT.
Thank you for the snapshot on the concepts and theories of happiness . It is really helpful for my thesis writing.
Nice article, but incomplete . You should have discusses ed neurobiochemistry. How dopamine , endorphins serotonin & oxytocin are invested by nature in happiness circuitry. How have we evolved to incorporate release of these chemicals through daily activities
Thank you for this article. I’m sure that it’ll help me to defining happiness in my research.
This article is a really informative overview of Happiness, the subject that I believe is the most important driver of life advancement. Focusing on happiness and its pursuit as a positive discipline instead of focusing on ailments and pathologies that need to be “treated” or “cured” to find some happiness is the best approach. I recently published my book, “America, The Happy” addressing the pursuit happiness and its role in American life. I would have liked to have found this piece earlier, but I’ll reference it in my next one. Very good work.
Thank you so much for this overview it’s contributing greatly to my research into happiness.
A Happiness ‘Recipe’ In its rudiments a neuro-anatomy of happiness maps positive affective states of attentive arousal and pleasure to neurological processes, respectively the activity of dopamine and opioid systems. These systems can be hijacked by addictive drugs, but I submit that they can also be conjointly activated by simple cognitive protocols detailed below. This is achieved through opioid/dopamine interactions induced from concurrent contingencies that induce relaxation and attentive arousal. This simple, innocuous, and easily falsifiable procedure is in short a ‘recipe’ for happiness that conforms with commonplace notions that happiness is coextensive with a committed and meaningful life. My work is largely based on the latest iteration of incentive or discrepancy-based models of motivation representative of the work of Dr. Kent Berridge of the University of Michigan. Berridge is a renowned bio-behaviorist and neuroscientist who has contributed significantly to the neuroscience of happiness (see link below) and was kind to vet and endorse the little book I have linked below. My explanation and argument are tiered into three parts, for a lay audience (pp.7-52), an expanded academic version (pp.53-86), and a formal journal article published on the topic in the International Journal of Stress Management. The procedure is a variant of mindfulness practice but entails a new definition of mindfulness based on affective neuroscience. Still, all is moot if the procedure is ineffective. A brief summary of my argument In discrepancy models of motivation (or bio-behaviorism), affect is schedule dependent. VR (variable-ratio) schedules of reinforcement or reward (gaming, gambling, creative behavior) are characterized by moment to moment positive act-outcome discrepancy or uncertainty between what is expected and what actually happens, which parallels the release of the neuro-modulator dopamine that is felt a state of attentive arousal, but not pleasure. However, heightened pleasurable affect as well as heightened attentive arousal is also reported while performing under VR schedules, but only when the musculature is in a state of inactivity or relaxation. Relaxation induces the activity of mid-brain opioid systems and is felt as pleasure. Because dopamine and opioid systems can co-activate each other, concurrent contingencies which induce relaxation (mindfulness protocols) and attentive arousal (purposive or meaningful behavior) will result in a significant spike in affective tone as both dopaminergic and opioid activity will be much higher due to their synergistic effects. The procedure to do this, outlined on pp. 47-52, has several important characteristics. Behavior Analytic- no appeal to events outside of objective behavior. Simple – explained in five minutes, and refutable as quickly. Cognitive Behavioral – coheres to CBT principles, and is structured, brief, and rational. Also, as a layman (though academically trained in behavioral psychology, I am an executive for a tech company in New Orleans), I am most curious to see if this procedure is effective. Formal test is not at first necessary, but informal exposure is since the procedure is simple in aspect but possibly very useful in practice. (But again, I may be wrong!) https://www.scribd.com/doc/284056765/The-Book-of-Rest-The-Odd-Psychology-of-Doing-Nothing https://www.scribd.com/doc/121345732/Relaxation-and-Muscular-Tension-A-bio-behavioristic-explanation Berridge, Kringelbach article on the neuro-anatomy of happiness https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3008353/ And Holmes’ Article on Meditation and Rest from ‘The American Psychologist’ https://www.scribd.com/document/291558160/Holmes-Meditation-and-Rest-The-American-Psychologist
I am amazed at no mention of BROADEN AND BUILT THEORY by Barb Frederickson, nor of DR PAUL WONG’S POSITIVE PSYCHOLOGY 2. Thank you for your amazing work.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Embracing JOMO: Finding Joy in Missing Out
We’ve probably all heard of FOMO, or ‘the fear of missing out’. FOMO is the currency of social media platforms, eager to encourage us to [...]

The True Meaning of Hedonism: A Philosophical Perspective
“If it feels good, do it, you only live once”. Hedonists are always up for a good time and believe the pursuit of pleasure and [...]

Happiness Economics: Can Money Buy Happiness?
Do you ever daydream about winning the lottery? After all, it only costs a small amount, a slight risk, with the possibility of a substantial [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (49)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (25)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (21)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (19)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (17)
- Relationships (44)
- Resilience & Coping (38)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

3 Happiness Exercises Pack [PDF]

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Toggle navigation
The Composition of Happiness
Eng 1101 / hus 1101 learning community (fall 2014).
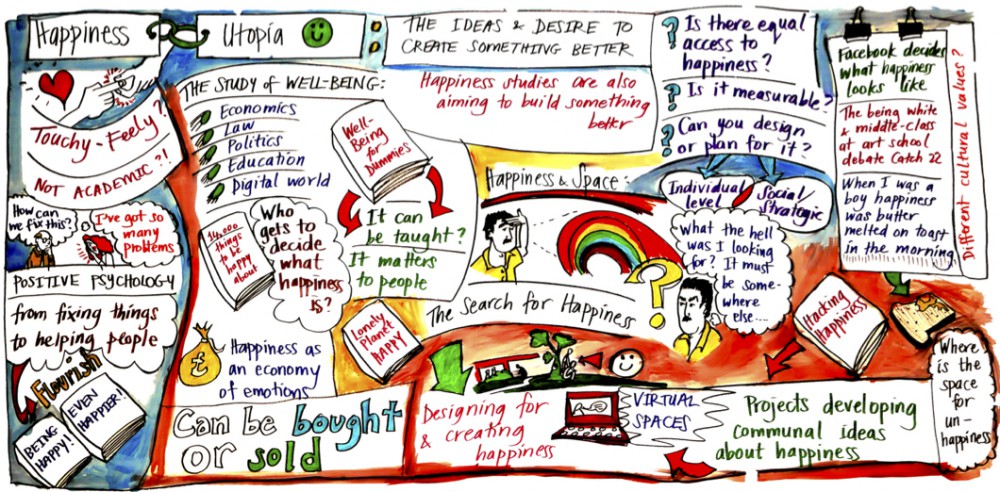
Category Archives: Essay 1 Pre-Draft: Thesis Paragraphs
What happiness is..
Happiness is a gift sent from heaven, a smile on the face of someone you love. Happiness is doing a good deed to someone, giving a kiss to your parents on a regular basis, telling someone you love them because life is short and being happy is the first thing people want to be. Happiness is closing your eyes, taking a deep breath and getting tears in your eyes because you just love life, happiness is learning and letting go of gods beauty.
Happiness is being broken down to your roots, being knocked and still having the ability and will to get back up and show the world what there about. happiness isn’t about the money its about having the love to back it up. loyalty is more powerful than a dollar bill.
Happiness is being humble and staying simple, and being the best person you can ever be. Happiness is writing a story about heartbreaks, disappointments that turn into well being. Happiness is dancing to a beat that carries you on a thin air of happily ever afters and people who care.
Happiness is dreaming of being free, waking up and being chainless. Happiness is finding something you never expected to find—and love it. Happiness is a round-way ticket to heaven of smiling faces and friendly crowds. Being loved is happiness. Happiness is a word you can’t explain, but your heart does that certain jump that makes you smile endlessly. Being happy is love.
when the world feels like its eating you alive, just look at the people who surround you , not what you have in your wallet and they will lift you up and get you back on track way quicker than a dollar bill.
Research paper proposal
For my research project I would like to focus on the effects of mass media on individual’s well-being. Mass media includes everything on T.V, news papers and on the radio. We tend to be influenced by our surroundings so I’m interested to see how our everyday entertainment or things we find normal influence our decision making and even our ethical behaviors. We pick up on trends that are constantly promoted such as the recent Ebola scare. It is flu season but since for a long period of time everyone was discussing this virus every time someone would sneeze or look sick others would automatically be scared or assume that they had the virus. Although some of the things we hear or see on mass media have negative effects on our behavior some are used to improve policies or to make people aware of risky situations. For example recently I have noticed that elementary schools are creating safety drills that were never in place when I went to grade school. considering a recent spike in school shootings I believe that the awareness the media has created makes a safer school environment.
Coleman, Loren. ” The Copycat Effect: How the media and Popular Culture Trigger the Mayhem in Tomorrow’s Headlines New York : Paraview Pocket Books, 2004.
I found this book interesting and relevant to my topic considering that it uses the effects of mass media relating to crimes. This book discusses copycat crimes and how because of the media people get the idea to commit their own crimes, these people feel encouraged and even inspired by people who have already committed such crimes and believe that they can get away with it. Because of the media they are able to follow closely on such cases and plan their own.
The road to your happiness (Thesis paragraph)
Measuring your happiness should not be about the amount of money you make but how you spend it according to Sonja Lyubomirsky in her article “How to buy happiness.” We worry too much about getting to the top of the status hierarchy that we forget about ourselves and even our loved ones according to David Brooks in his article “What suffering does.” Another way to measure happiness is by seeing how much you have overcome a suffering. When the weights are lifted off your shoulders the feeling is relieving because you are no longer suffering. Both articles display different perceptions of happiness.
Pre-Draft Essay thesis
what does Happiness fulfill for us?Happiness can mean different things and different people experience happiness in many ways.Happiness have always been a big part of people lives along with hope .It became a huge factor in society .Happiness cannot be brought by money ,possessions like a car,jewelry or name brand clothes .In the article “how to buy happiness” by Elizabeth Dunn and Michael Norton , doing the little things with people it make a difference of happiness .Even spending money on others it provide an boost In moral . Like the article says How we use our money may matter as much or more then how much of it we got.So get up and make yourself happy instead of waiting around for it to get to you .So what make you happy ?
Thesis statement draft #1
When the topic of happiness comes up a million things can pop into your head. Happiness has millions of different meanings to the billions of people in the world and beyond. But what does it really mean to be happy ? Is it that new iPhone or those new shoes you just couldn’t live without ? Or is it that Sunday afternoon you get to share with your family after a long week? Or could it be that satisfaction that you are no longer facing a problem? Whether your ideal happiness is material or more sentimental, achieving such a thing has been proven to be difficult. Our society is awash with the ideal happiness. In an Op-Ed article from the L.A Times, How to buy happiness , Elizabeth Dunn and Michael Norton discuss that you can actually be happier by spending money on others than on yourself. It’s the memories you make that matter rather than the money you have on your own. While on the other hand people like David Brooks, from The New York Times in What suffering does , think that it’s suffering that shapes you to become a happier person. The lessons you learn from suffering make you make better choices or even help you help others that have been in your situation or dilemma.
Happiness is something everyone seems to crave but doesn’t know how exactly to achieve it. In the society we live in it’s easy to believe getting the newest shoes or the iPhone 6 will increase ones happiness. While this stuff does increase happiness for some time, it’s mostly all for show, we want it because it’s what everyone else has which leads us to believe it will make us happier. The way to get these things is with money, mula, dinero etc. Money is something that is supposed to increase ones happiness because it can get us the things we want. But the things we want are not always the things we need. Yes, I think we all can agree material things are great, but something like the love of a friend or a family doesn’t compare to it. There are different theories out there but happiness can only come from within, only you can make yourself happy regardless of how you do it.
rough draft
Happiness is what you want. It’s what everybody wants right. How do we come to achieve it though? It is not about buying the new iPhone or the latest Jordan’s. After all these are just materialistic things. What really brings person happiness is an experience a memory. Who did you go shopping with; remember what happened, that funny incident, that unbelievable thing. Money cannot buy happiness? Well that depends what you put your money towards. How you spend that dollar makes all the difference. Happiness is achieved through experiences, through thoughts, and actions.
Pre draft Essay Thesis
What is your definition of happiness and can you explain it in an easy way to someone? Or is happiness just a “thing” that isn’t explainable and just an emotion or feeling? Can anybody buy happiness? Happiness has been put out to everyone that it can be bought and material things can make you happy. Having everything in the world does not necessarily make you happy, it has been proven that being rich and having all of the things in the world doesn’t make you happy but miserable. “How to buy happiness” by Sonja Lyubomirsky and the Op-Ed of “How to buy happiness” by Elizabeth Dunn and Michael Norton both speak about the ways people think being happy is and what people do. But the reality of all of this is that happiness can’t be bought but it can be gained by experiences with others.
Intro Rough Draft #1
Happiness is not a simple topic to discuss because of the the different opinions on it. To me happiness is feeling good about what you do and who you are, it is being at your own peace of mind. Although suffering is the opposite of happiness, i believe suffering can help achieve peoples true happiness. In todays society people use money to define happiness, but money can only bring happiness or joy to a certain extent. From articles i have recently read and analyzed, i have come to the conclusion that experience and memories make up much of our true happiness. Pain, money and experience have an effect on peoples wellbeing, and all these factors contribute to helping boost ones happiness.
Essay 1 Pre-Draft: Thesis Paragraph
Happiness is one word, however with many meanings and definitions. For some people happiness can mean wealth or for others happiness can be the moment they bring a child into this world. What exactly is happiness? What really makes us happy? The money or the moments? Or maybe buying happiness? In the article “How to buy happiness” by Sonia Lyubomirsky, it states “An additional strategy for buying happiness is to spend money on others instead of ourselves” and i believe that the best way to achieve great happiness is to make others happy.
The OpenLab at City Tech: A place to learn, work, and share
The OpenLab is an open-source, digital platform designed to support teaching and learning at City Tech (New York City College of Technology), and to promote student and faculty engagement in the intellectual and social life of the college community.

New York City College of Technology | City University of New York
Accessibility
Our goal is to make the OpenLab accessible for all users.
Learn more about accessibility on the OpenLab
Creative Commons
- - Attribution
- - NonCommercial
- - ShareAlike

© New York City College of Technology | City University of New York
Is Happiness the Beginning or the End? Essay (Critical Writing)
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
The concept of happiness is undoubtedly an attractive one and the ultimate goal for many people regardless of age, nationality, gender, and other characteristics. Yet, despite being universally desirable, happiness is hard to describe or characterize. Jamie Anderson’s “Is Happiness the Beginning or the End?” discusses the view on happiness in the American cultural consciousness and the perceived ideological conflict regarding the specificities of its nature. An idea of happiness existing “at the end of the chase” is a prevalent one in culture and philosophy, yet other accounts claim it to be an innate right that should be a given. This paper aims to analyze the author’s thesis on the subject and evaluate whether he was convincing in delivering his perspective.
American Declaration of Independence conceptualizes happiness as one of the universal rights granted to every individual by virtue of existing. However, as stated in the article, contemporary research indicates broad casual dissatisfaction with life respondents’ lives. Anderson refers to the 2013 Gallup poll stating that only 30% of Americans are happy at work, which constitutes the core of daily activities for most of the population. This data illustrates the general level of unhappiness, mainly due to the high percentage of time working Americans dedicate to their occupation. Whether due to stress or a generally negative attitude towards their field, people are much less happy with their routine than the philosophical ideals demand them to be.
Anderson later applies the findings from the lecture of Shawn Achor, who has analyzed the ways the human brain responds to casual failures and successes. Momentary satisfaction is easy to achieve, but it does not equal happiness for the majority of people. The idea of happiness has more in common with the lasting sense of satisfaction and prosperity, which, according to Achor, is not a natural condition for the human brain.
As both the paper and Achor’s lecture suggest, lasting happiness from successes and achievements is an exception, rather than the rule. After achieving a goal, people experience a brief sense of triumph and move on to the next goalpost. Therefore, the connection between these achievements and happiness is very relative, and daily successes usually have little to do with the overall feeling of satisfaction.
However, as Anderson suggests in the closing section of his paper, perception shapes the facts instead of the opposite. He effectively comments on this idea in the discussion of the role of optimism. The optimistic approach to life and conscious positivity might improve one’s level of simple happiness, as the person becomes aware of the degree to which their attitude is involved. Such ideology requires self-improvement and dedication to the new mindset, which might be emotionally taxing under daily stress. Yet overall, it is a comforting notion to know that everyone has greater power over their happiness than suggested.
In conclusion, Armstrong’s article is effective in its attempts to comment on the relationship between an individual’s attitude and level of happiness. It touches briefly on the specifics of the brain without getting into excessive neurological detail and remains comprehensible at all times. Anderson is generally successful in simplifying the abstract idea of happiness and presenting it as an accessible goal that one can achieve despite the existing difficulties.
- Character Analysis of Jamie and Reason why She is Likeable
- Contributions of Max Weber's Bureaucracy to Public Administration
- "One Family's Fight Against PTSD" by Shawn Gourley
- Confidence and Emotional Experience
- Emotions and Their Value for Us
- The Reality of Love Explained
- The Emotions and Communication
- Social Aspects of Emotions
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, October 23). Is Happiness the Beginning or the End? https://ivypanda.com/essays/is-happiness-the-beginning-or-the-end/
"Is Happiness the Beginning or the End?" IvyPanda , 23 Oct. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/is-happiness-the-beginning-or-the-end/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Is Happiness the Beginning or the End'. 23 October.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Is Happiness the Beginning or the End?" October 23, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/is-happiness-the-beginning-or-the-end/.
1. IvyPanda . "Is Happiness the Beginning or the End?" October 23, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/is-happiness-the-beginning-or-the-end/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Is Happiness the Beginning or the End?" October 23, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/is-happiness-the-beginning-or-the-end/.
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Happiness
List of essays on happiness, essay on happiness – short essay (essay 1 – 150 words), essay on happiness – for kids and children (essay 2 – 200 words), essay on happiness – 10 lines on happiness written in english (essay 3 – 250 words), essay on happiness (essay 4 – 300 words), essay on happiness – ways to be happy (essay 5 – 400 words), essay on happiness – for school students (class 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 standard) (essay 6 – 500 words), essay on happiness – ways of developing happiness (essay 7 – 600 words), essay on happiness – sources of suffering, happiness and conclusion (essay 8 – 750 words), essay on happiness – long essay on happiness (essay 9 – 1000 words).
Happiness is defined by different people in different ways. When we feel positive emotions we tend to feel happy. That is what happiness is all about. Happiness is also regarded as the mental state of a person in an optimistic manner.
Every person defines happiness in his/her own manner. In whatever manner you may define happiness; the truth is that it is vital for a healthy and prosperous life.
In order to make students understand what true happiness is all about, we have prepared short essays for students which shall enlighten them further on this topic.
Audience: The below given essays are exclusively written for school students (Class 3, 4 ,5, 6 and 7 Standard).
Introduction:
Happiness is a state of mind and the feeling expressed when things are going great. It is what we feel when we get our first car, buy a new house or graduate with the best grades. Happiness should be distinguished from joy. When joy is a constant state of mind, happiness depends on events in our lives.
Importance of Happiness:
The opposite of happiness is sadness which is a state of negativity in the mindset. When we remain sad for an extended period of time it can lead to depression. To avoid this state of mind we must always remind ourselves of happenings in our lives that made us happy.
Conclusion:
Though life throws countless challenges at us on a daily basis, if we drown in those challenges we would definitely become depressed. It is important that we find positive things in our daily lives to get excited about and feel the happiness.
Happiness is a state of mind which makes you feel accomplished in life and having everything in this world without a single reason to repent. Well, although there can be no perfect definition of happiness; happiness is when you feel you’re at the top of the world where a sense of complete satisfaction prevails.
The meaning of happiness is relative and varies from people to people. For some, happiness is when you experience professional success, reunions with family and friends, eating out, reading books or watching good movies. While for others, happiness can be accomplished by some weekend activities which might help you de-stress and get the satisfaction of mind.
If you involve yourself in social activities where you help the needy and provide support to the weaker section of the society, you can experience happiness if not anything else. When a young boy flies a kite, plays with mud, and watches the nature, for him, that is the greatest happiness in the world.
The happiness of mind is often considered quite contrary to jealousy and anger which you experience once you have failed or unaccomplished any desired goal. You should always try to rehearse the ways of keeping yourself satisfied and keeping away from negativity to experience peace and happiness in life. True happiness begins where desire ends!
What is happiness? It is a state of being happy. But it does not mean to be happy all the time. Happiness is a feeling of something good that is happening in our life. We feel happy when we achieve something. But happiness is spread when our dear one is happy as well. Some people find true happiness in playing with their pets, while some may find happiness in staying engaged in creative work.
Happiness is often derived from channelizing thoughts to positive thinking. However, it is not as simple as it may sound.
To achieve the state of complete happiness one has to practice on improving the state of life by:
1. Staying contended in life with what you have. Cribbing and grumbling never lead to happiness.
2. Staying focused on the current life instead of daydreaming of the good days or old days.
3. Stop blaming for something that went terribly wrong in life. The life is all about moving on. Stop worrying and set new goals in life.
4. Being thankful to God for all the good things that you have in your life.
5. Having good people around you who can boost up positivity in your life.
Everyone desires to be happy in life. Happiness cannot be achieved without establishing complete control of one’s thoughts as it is very easy to be carried away by the waves of thoughts and emotions surrounding us. Remind yourself of the good things of your life and be thankful about it.
What is happiness? Some would state that happiness implies being well off. Others would state that for them, happiness intends to be sound. You will discover individuals saying that for them happiness implies having love in their life, having numerous companions, a great job, or accomplishing a specific objective. There are individuals, who trust that the want of a specific wish would make happiness in their life; however, it may not be so. Having true happiness is something which is desired by all.
The Path to Happiness:
There are small things which when incorporated into our daily lives, can lead us to the path of happiness. For instance, instead of thinking about problems, we should actually be thinking about the solutions. Not only will we be happier but we shall also be able to solve our problems faster. Similarly, once in a while, you start the day with the longing to achieve a few targets. Toward the day’s end, you may feel disappointed and miserable, in light of the fact that you haven’t possessed the capacity to do those things. Take a look at what you have done, not at what you have not possessed the capacity to do. Regularly, regardless of whether you have achieved a ton amid the day, you let yourself feel disappointed, due to some minor assignments you didn’t achieve. This takes away happiness from you.
Again, now and then, you go throughout the day effectively completing numerous plans, yet as opposed to feeling cheerful and fulfilled, you see what was not cultivated and feel troubled. It is out of line towards you.
Each day accomplishes something good which you enjoy doing. It may tend to be something little, such as purchasing a book, eating something you cherish, viewing your most loved program on TV, heading out to a motion picture, or simply having a walk around the shoreline. Even small things can bring great levels of happiness in our lives and motivate us for new goals.
Happiness is not what you feel from outside, rather it is something which comes from your inner soul. We should find happiness in us rather than searching for it in worldly desires.
Happiness is defined by different people in different ways. Some find happiness in having a luxurious life while some find it in having loving people around them rather than money. True happiness lies within us and our expectation of happiness. It is something that should be felt and cannot be explained in words.
Even though this simple word has a lot of meaning hidden in it, many fail to understand the real one or feel the real happiness. Finding happiness in the outer world is the main reason for this failure. Nothing can buy you happiness, whether be the favorite thing you desire for or the person you love the most or the career you build, unless and until you feel it within yourself.
Ways to be Happy:
Bring happiness and soulful life to yourself rather than expecting it from the outside world like things, money, etc. Being happy is not as easy as advised to be one happier person. To be content and happy with whatever you have and yourself it takes time and patience. You should practice to be a happier person in all moments and eventually you will notice that no sorrow can sink you down.
Whatever good or bad happened in your past shouldn’t bother your present. Learn to live today with more happiness than yesterday and forget about your past sadness for a harmonious life. Thankfulness to the life you got is another important character you should acquire to be happy. If you compare yourself with someone with better luxurious life, then you will never be happy or content and do it the other way.
Don’t depress your mind with bad and negative thoughts about yourself and around. Try to find every goodness in a situation you face and accept the things that already happened, whether good or bad. Never forget to choose merrier and positive people to be closer to you so that their vibes will also help you in being one merrier person.
Whenever you feel low and depressed never hesitate to go to those around you to find happiness. But be aware of those negative ones that may pull you even deeper into the bad thoughts. Always surround yourself with positive thinking and motivating people so that you can rise higher even from the deepest fall.
Happiness is nothing but a feeling that will be seeded into your soul only if you wish to and nothing other than yourself can indulge this feeling in you. Don’t spoil your life finding happiness somewhere else.
Happiness is a very complicated thing. Happiness can be used both in emotional or mental state context and can vary largely from a feeling from contentment to very intense feeling of joy. It can also mean a life of satisfaction, good well-being and so many more. Happiness is a very difficult phenomenon to use words to describe as it is something that can be felt only. Happiness is very important if we want to lead a very good life. Sadly, happiness is absent from the lives of a lot of people nowadays. We all have our own very different concept of happiness. Some of us are of the opinion that we can get happiness through money, others believe they can only get true happiness in relationships, some even feel that happiness can only be gotten when they are excelling in their profession.
As we might probably know, happiness is nothing more than the state of one being content and happy. A lot of people in the past, present and some (even in the future will) have tried to define and explain what they think happiness really is. So far, the most reasonable one is the one that sees happiness as something that can only come from within a person and should not be sought for outside in the world.
Some very important points about happiness are discussed below:
1. Happiness can’t be bought with Money:
A lot of us try to find happiness where it is not. We associate and equate money with happiness. If at all there is happiness in money then all of the rich people we have around us would never feel sad. What we have come to see is that even the rich amongst us are the ones that suffer depression, relationship problems, stress, fear and even anxiousness. A lot of celebrities and successful people have committed suicide, this goes a long way to show that money or fame does not guarantee happiness. This does not mean that it is a bad thing to be rich and go after money. When you have money, you can afford many things that can make you and those around you very happy.
2. Happiness can only come from within:
There is a saying that explains that one can only get true happiness when one comes to the realisation that only one can make himself/herself happy. We can only find true happiness within ourselves and we can’t find it in other people. This saying and its meaning is always hammered on in different places but we still refuse to fully understand it and put it into good use. It is very important that we understand that happiness is nothing more than the state of a person’s mind. Happiness cannot come from all the physical things we see around us. Only we through our positive emotions that we can get through good thoughts have the ability to create true happiness.
Our emotions are created by our thoughts. Therefore, it is very important that we work on having only positive thoughts and this can be achieved when we see life in a positive light.
Happiness is desired by every person. However, there are very few persons that attain happiness easily in life.
It is quite tough to get happiness in life as people usually link it with the things and the people around them. The simple fact is that happiness usually starts as well as finishes with your own life. All those people who understand this fact easily get the true happiness in their life.
Happiness in Relationships:
There are lots of people who link happiness with the money and there are few others also who link it with the personal relations. It is very important to know that if you are not happy with yourself then, it is not possible to remain happy in your relationship as well.
The problems in the relationship have been increasing speedily and the main cause behind it is the huge amount of expectation that we have from the other individual. We always want them to make us feel happy. For example, some people feel happy if their partner plans a surprise for them or if he/she buy them a new dress. But all these things are not a true source of happiness in life.
Ways of Developing Happiness:
The lack of happiness in the relationship not only exists in couples but also in the relationship of friends, sister – brother or parent-child.
The following are the few ways that help in creating happiness in the relationships:
1. Pay Attention to Yourself:
You should always pay attention to yourself to get happiness. You should not give importance to any other person in your life in comparison to yourself and also expect the same from that person. Giving too much importance to the other and not receiving anything back from them makes a person disappointed and happiness gets lost.
2. Have some Initiative:
You can make the plan of traveling outside yourself. Don’t wait for your parent, partner or kid to take you outside. You can ask them to come along with you if they want. But, if they decline your offer then, don’t get discouraged and carry on your trip plan along with full happiness.
3. Provide some Space:
It is necessary to provide some amount of space to every individual and spend some time with oneself. It helps in creating happiness.
Happiness is Necessary for Good Life:
It does not matter that whether you are a working expert, a schoolchild, a retired person or a housewife, happiness is necessary for everybody to live a good and happy life. Happiness is essential for an individual’s emotional comfort. A person who is not fit emotionally will feel an impact on his complete health that will drain very soon.
Unluckily, despite the fact that happiness is tremendously necessary, people do not give so much importance to all those habits which can keep them happy. They are so excessively captivated inside their professional lives as well as other nuts and bolts of life that they overlook to relish the happy memories of their life. It is also the main reason that problems like anxiety, stress, and depression are increasing gradually in people’s lives today.
Happiness is an internal feeling. It is a healthy emotion. Happiness helps us to stay fit both mentally and physically. Happiness helps in lowering stress and keeping away from any health issues. The reason of happiness may be different for different person. You just need to find out what actually makes you happy. So, if you want real happiness in life then, you need to understand that only you can make yourself happy.
“There is no way to happiness, happiness is the way” this sentence has been attributed to Buddha. Well, at least that’s what it says on one sticker in my dorm room. The fact is that man has occupied himself with the path to happiness for millennia. Something happened during our evolution that made us deeply question the purpose of our existence. People like Buddha are part of the answer, or at least they try to give us the answer.
Since these questions have troubled us there have been many who sought to answer them and by doing so, they formed philosophies and religions. The search for earthly happiness will make many do incredible deeds but if this energy is used in the wrong way it can cause great suffering. How can we know which recipe for happiness is the best one and what we should devote our time and attention to? The trick is, there is no right answer and as the first sentence of this essay states, there is no way to be happy because being happy is the way. That’s how I got my head around this problem, let me explain some more.
Source of Suffering:
At the expense of sounding Buddhist, when you think about most of the things that make us unhappy are material in nature. They are the things that we really do not need but they make us feel happy. This notion is not just something the wise man from the 6 th century BC India expressed but many more have said this before and after him. Socrates and Jesus to name just a few.
What I find interesting in the struggle for happiness is the paradox present in the instructions to reach it. One has a thought all through life to be good and hard working so he can get the things he wants and needs later on in life but then as you start to struggle for the money you realize that your life is turning into a money grabbing game. So, the source of happiness and stability becomes the source of all your anxiety and aggression. Naturally, we can see how some people thought that all material things stand on the path to our happiness.
But what about the immaterial, what if you are in love with someone you are not supposed to love? The above instruction would tell you to surrender your heart’s desire and you will be free from constraints. Is this happiness? Or is it the struggle to do and achieve the impossible the real source of happiness?
Source of Happiness:
People often forget that they are animals and like all of them they have a logic to their nature and their own specific needs. Like all the other animal’s people are caught in the struggle for existence and sometimes surviving the day can be a real ordeal if you get caught in the wrong circumstances. Men has made himself safe from most of the things that could have harmed him in nature but in doing so he forgot what he has made.
Think about the present from a historical perspective. Even a hundred years ago most people lost up to 80% of all their children to diseases, clean water was a rarity for most of our existence, and people actually had to labor to make food and to have enough to feed their family all through the year. The fact is we have a lot to be grateful for in the present age and the fact that some of us are unhappy because we do not have all our heart’s desires is just a symptom of collective infancy. Having all of your loved ones around you, with a roof to shelter under and with lots of delicious food is the only source of happiness man needs everything else should just be a bonus.
Happiness cannot be found by rejecting everything that is material or by earning more money then you can spend. The trick is to find balance by looking at yourself and the lives of people around you and by understanding that there is a lot to be grateful for, the trick is to stop searching for a path and to understand that we are already walking on one. As long as we are making any type of list of the prerequisite for our life of happiness, we will end up unsatisfied because life does not grant wishes we are the ones that make them come true. Often the biggest change in our lives comes from a simple change of perspective rather than from anything we can own.
Happiness is the state of emotional wellbeing and being contented. Happiness is expressed through joyful moments and smiles. It is a desirable feeling that everybody want to have at all times. Being happy is influenced by situations, achievements and other circumstances. Happiness is an inner quality that reflects on the state of mind. A peaceful state of mind is considered to be happiness. The emotional state of happiness is mixture of feelings of joy, satisfaction, gratitude, euphoria and victory.
How happiness is achieved:
Happiness is achieved psychologically through having a peaceful state of mind. By a free state of mind, I mean that there should be no stressful factors to think about. Happiness is also achieved through accomplishment of goals that are set by individuals. There is always happiness that accompanies success and they present feelings of triumph and contentment.
To enable personal happiness in life, it is important that a person puts himself first and have good self-perception. Putting what makes you happy first, instead of putting other people or other things first is a true quest towards happiness. In life, people tend to disappoint and putting them as a priority always reduces happiness for individuals. There is also the concept of practicing self-love and self-acceptance. Loving oneself is the key to happiness because it will mean that it will not be hard to put yourself first when making decisions.
It is important for an individual to control the thoughts that goes on in their heads. A peaceful state of mind is achieved when thoughts are at peace. It is recommended that things that cause a stressful state of mind should be avoided.
Happiness is a personal decision that is influenced by choices made. There is a common phrase on happiness; “happiness is a choice” which is very true because people choose if they want to be happy or not. Happiness is caused by circumstances and people have the liberty to choose those circumstance and get away from those that make them unhappy.
Happiness is also achieved through the kind of support system that an individual has. Having a family or friends that are supportive will enable the achievement of happiness. Communicating and interacting with the outside world is important.
Factors Affecting Happiness:
Sleep patterns influence the state of mind thus influence happiness. Having enough sleep always leads to happy mornings and a good state of mind for rest of the day. Sleep that is adequate also affects the appearance of a person. There is satisfaction that comes with having enough sleep. Enough rest increases performance and productivity of an individual and thus more successes and achievements are realized and happiness is experienced.
Another factor affecting happiness is the support network of an individual. A strong support network of family and friends results in more happiness. Establishing good relationships with neighbors, friends and family through regular interactions brings more happiness to an individual. With support network, the incidences of stressful moments will be reduced because your family and friends will always be of help.
Sexual satisfaction has been established to affect happiness. It is not just about getting the right partner anymore. It is about having a partner that will satisfy you sexually. There is a relationship between sex and happiness because of the hormones secreted during sexual intercourse. The hormone is called oxytocin and responsible for the happiness due to sexual satisfaction. Satisfaction also strengthens the relationships between the partners and that creates happiness.
Wealth also plays a significant role in happiness. There is a common phrase that is against money and happiness: “money cannot buy happiness” is this true? Personally, I believe that being financially stable contributes to happiness because you will always have peace of mind and many achievements. Peace of mind is possible for wealthy people because they do not have stressors here and then compared to poor people. Also, when a person is wealthy, they can afford to engage in luxurious activities that relaxes the mind and create happiness. For a person to be wealthy, they will have had many achievements in life. These achievement make them happy.
A good state of health is an important factor that influences the happiness of individuals. A healthy person will be happy because there are no worries of diseases or pain that they are experiencing. When a person is healthy, their state of mind is at peace because they are not afraid of death or any other health concerns. Not only the health of individuals is important, but also the health of the support system of the person. Friends and family’s state of health will always have an impact on what we feel as individuals because we care about them and we get worried whenever they are having bad health.
Communication and interactions are important in relation to an individual’s happiness. Having a support system is not enough because people need to communicate and interact freely. Whenever there are interactions like a social gathering where people talk and eat together, more happiness is experienced. This concept is witnessed in parties because people are always laughing and smiling in parties whenever they are with friends.
Communication is key to happiness because it helps in problem solving and relieving stressors in life. Sharing experiences with a support system creates a state of wellbeing after the solution is sought. Sometime when I am sad, I take my phone and call a friend or a family member and by the time the phone call is over, I always feel better and relieved of my worries.
Happiness is an important emotion that influences how we live and feel on a daily basis. Happiness is achieved in simple ways. People have the liberty to choose happiness because we are not bound by any circumstances for life. Factors that influence happiness are those that contribute to emotional wellbeing. Physical wellbeing also affects happiness. Every individual finds happiness in their own because they know what makes them happy and what doesn’t.
Emotions , Happiness , Psychology
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Which is More Important in Life: Love or Money | Essay
- Essay on My School
- Essay on Solar Energy
- Essay on Biodiversity
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college
From economic wealth to well-being: exploring the importance of happiness economy for sustainable development through systematic literature review
- Open access
- Published: 23 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Shruti Agrawal ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1620-9429 1 , 5 ,
- Nidhi Sharma 1 , 5 ,
- Karambir Singh Dhayal ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0000-4330 2 &
- Luca Esposito ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5983-6898 3 , 4
464 Accesses
Explore all metrics
The pursuit of happiness has been an essential goal of individuals and countries throughout history. In the past few years, researchers and academicians have developed a huge interest in the notion of a ‘happiness economy’ that aims to prioritize subjective well-being and life satisfaction over traditional economic indicators such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Over the past few years, many countries have adopted a happiness and well-being-oriented framework to re-design the welfare policies and assess environmental, social, economic, and sustainable progress. Such a policy framework focuses on human and planetary well-being instead of material growth and income. The present study offers a comprehensive summary of the existing studies on the subject, exploring how a happiness economy framework can help achieve sustainable development. For this purpose, a systematic literature review (SLR) summarised 257 research publications from 1995 to 2023. The review yielded five major thematic clusters, namely- (i) Going beyond GDP: Transition towards happiness economy, (ii) Rethinking growth for sustainability and ecological regeneration, (iii) Beyond money and happiness policy, (iv) Health, human capital and wellbeing and (v) Policy push for happiness economy. Furthermore, the study proposes future research directions to help researchers and policymakers build a happiness economy framework.
Similar content being viewed by others

Beyond GDP: A Movement Toward Happiness Economy to Achieve Sustainability

National progress, sustainability and higher goals: the case of Bhutan’s Gross National Happiness
Economic Performance, Happiness, and Sustainable Development in OECD Countries
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Happiness is considered the ultimate goal of human beings (Ikeda, 2010 ; Lama, 2012 ). All economic, social, environmental and political human activities are aligned towards achieving this goal. This fundamental pursuit of human life introduces a new scope of research, namely the ‘happiness economy’ (Agrawal and Sharma 2023 ). The happiness economy is an emerging economic domain wherein many countries are working to envision and implement a happiness-oriented framework by expanding how they measure economic success, which includes wellbeing and sustainability (Cook and Davíðsdóttir 2021 ; Forgeard et al., 2011 ). The investigation of happiness, life-satisfaction and subjective well-being has witnessed increasing research interest across the disciplines- from psychology, philosophy, psychiatry, and cognitive neuroscience to sociology, economics and management (Diener 1984 ; Hallberg and Kullenberg, 2019 ).
In the post-Covid era, the world seeks an enormous transformation shift in the public system (Costanza 2020 ). However, public authorities need more time to realize such needs. To experience the ‘policy transformation’ within the coming few years, we require a paradigm shift that helps warm peoples’ hearts and minds. The new economic paradigm can penetrate the policy processes in advanced economies and every part of the world affected by the epidemic with the support of intellectuals, researchers, entrepreneurs and professionals.
OECD ( 2016 ) proposed a well-being economy framework to measure living conditions and people’s well-being. In 2020, developed countries like Finland, New Zealand, Iceland, Scotland and Wales have become members of the Wellbeing Economy Government (WEGo) (Abrar 2021 ). Since then, the network of government and international authorities across the globe has gained a quick momentum concerning an increasing tendency about a growing tendency to concentrate governmental decisions around human well-being rather than wealth and economic growth (Coscieme et al. 2019 ; Costanza et al. 2020 ).
In light of these circumstances, the purpose of this article is to describe the concept of a “happiness economy” or one that seeks to give everyone fair possibilities for growth, a sense of social inclusion, and stability that can support human resilience (Coyne and Boettke 2006 ). It provides a promising route towards improved social well-being and environmental health and is oriented towards serving individuals and communities (Skul’skaya & Shirokova, 2010 ). Moreover, the happiness economy paradigm is a transition from material production and consumption of commodities and services as the only means to economic development towards embracing a considerable variety of economic, social, environmental and subjective well-being dynamics that are considered fundamental contributors to human happiness (Atkinson et al., 2012 ; King et al., 2014 ; Agrawal and Sharma 2023 ). In following so, it reflects the ‘beyond growth’ approach that empathizes with the revised concept of growth, which is not centred around an increase in income or material production; instead it is grounded in the philosophy of achieving greater happiness for more people (Fioramonti et al. 2019a ).
Whereas the other critiques of economic growth emphasize contraction, frugality and deprivation, the happiness economy relies on a cumulative approach of humanity, hope and well-being, with a perceptive to build a ‘forward-looking’ narrative of ways for humans to live a happy and motivated life by inspiring the cumulative actions and encouraging policy-reforms in the measuring growth of an economy (Stucke 2013 ). Agrawal et al. ( 2023a , b ) explore the domain of happiness economics through a review of the various trends coupled with the future directions and highlight why it needs to be supported for a well-managed economic system and a happy society.
In this paper, we define a “happiness economy as an economy that aims to achieve the well-being of individuals in a nation, promoting human happiness, environmental up-gradation, and sustainability. Alternatively, as an economy where the wellbeing of people counts more than the goals of production and income”. Moreover, we have examined the existing body of research on the happiness economy and analyzed the emerging research themes related to rethinking the conventional approach to economic growth. We conclude by discussing how the happiness economy concept has been accepted so far and realizing its importance by triggering policy reforms at the societal level, by outlining potential future directions that might be included into the current national post-growth policies.
Various researchers and experts in the field of happiness economy support the idea that there is a lack of thorough studies related to the concept, definitions, and themes of the happiness economy model in the nations. This gap has motivated us to conduct a SLR in order to identify the evolution in the domain of happiness economy and to identify the emerging themes in this context. Therefore, this present study seeks to offer a holistic outline of the emerging research area of the happiness economy and helps to understand how the happiness economy can accelerate sustainable development. With the following research questions, this study seeks to give an all-encompassing review of this subject.
What is the annual publication trend in this domain and the most contributing authors, journals, countries etc?
Which themes and upcoming research areas are present in this field?
What directions will the happiness economics study field go in the future?
The SCOPUS database was used to achieve the above research objectives. We have selected 257 articles for examination by hand-selecting the pertinent keywords and going over each one. In the methods section, a thorough explanation of the procedures for gathering, reviewing, and selecting documents is provided.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows; A thorough survey of the literature on the happiness economy is provided in Sect. 2 . The research approach employed in the study is presented in Sect. 3 . A thorough data analysis of the research findings is given in Sect. 4 . After discussing the results in Sect. 5 , Sect. 6 suggests areas for further research in this field. The study is summarised with a conclusion in Sect. 7 . Section 8 outlines the study’s limitation.
2 Literature review
The supporters of conventional economic growth proclaim that the material production of goods and services and consumption is vital to enhancing one’s living standards. The statement is true to some degree, mainly in countries of enormous deprivation. Some studies have found significantly less correlation between growth and happiness after fulfilling minimum threshold needs (Easterlin 1995 ; Kahneman and Krueger, 2006 ; Inglehart et al., 2008 ). These studies recommend that rather than concentrating solely on economic growth, governmental policy should give priority to non-economic aspects of human existence above a particular income level. According to some researchers, it is challenging to distinguish between the use and emissions of natural resources and economic growth (absolute decoupling) because of the interdependence between socioeconomic conditions and their biophysical basis (Wiedenhofer et al. 2020 ; Wang and Su, 2019 ; Wu et al., 2018 ). However, a shred of increasing evidence shows that it could be possible for humans to maintain a quality of life and a decent standard of living inside the ecological frontier of the environment, given that a contemporary perspective on the production and use of materials are adopted in conjunction with more fair wealth distribution (Millward-Hopkins et al. 2020 ; Bengtsson et al., 2018 ; Ni et al., 2022 ).
The scholarly discourse and institutional framework on the relationship between happiness and economic progress are synthesised in the happiness economy (Frey and Gallus 2012 ; Sohn, 2010 ; Clark et al., 2016 ; Easterlin, 2015 ; Su et al., 2022 ). From a happiness economy perspective, extreme materialism is unsustainable as it significantly impacts natural resources and hinders social coherence and individuals psychological and physical well-being (Fioramonti et al. 2022a ). Additionally, inequalities within countries have grown, while psychological suffering has increased, especially during accelerated growth (Vicente 2020 ; Galbraith, 2009 ). The modern world is witnessing anxiety, depression, wars, reduction of empathy, climate change, pandemics, loss of social bonds and other psychological disorders (Brahmi et al., 2022 ; Santini et al., 2015 ).
It has been scientifically proven that cordial human relations, care-based activity, voluntary activities and the living environment immensely impact a person’s health and societal well-being (Bowler et al. 2010 ; Keniger et al., 2013 ). Ecological economists demonstrated that free ecosystem services have enhanced human well-being (Fang et al. 2022 ). Social epidemiologists have long argued that an increase in inequalities has a negative influence on society while providing equality tends to improve significant objective ways of well-being, from healthier communities to happier communities, declining hate and crime and enhancing social cohesion, productivity, unity and mutual trust (Aiyar and Ebeke 2020 ; Ferriss, 2010 ).
From moving beyond materialistic growth, the happiness economy promotes, appreciates, and protects the environmental, societal, and human capital contributions that lead to cummalative well-being. In a happiness economy framework, a multidimensional approach is needed to evaluate the level of development based on the environmental parameters, health outcomes, as well as public trust, hope, value-creating education and social bonds (Agrawal and Sharma 2023 ; Bayani et al. 2023 ; Lavrov, 2010 ). Such factors have consistently been excluded from any traditional concept or assessment of economic growth. As a result, countries have promoted more industrial activities that deteriorate the authentic ways of human well-being and, hence, the foundations of economic progress.
An excess of production can create a detrimental effect on climate and people’s health, thereby creating a negative externality for society (Fioramonti et al. 2022b ). Moderation of output may be more efficient and desirable than hyper/over-production, as the former can reduce negative environmental externalities (e.g. waste, climate change) and create positive externalities (e.g. employment of the local resources and community) (Kim et al. 2019 ; Kinman and Jones, 2008 ). Moreover, people can also be productive in other contexts outside of the workplace, such as as volunteers, business owners, artists, friends, or members of the community (Fioramonti et al. 2022a ).
Various scholars and scientific research have established that the essential contributions to happiness in one’s life are made by natural surroundings, green and blue spaces, eco-friendly environment, healthy social relations, spirituality, good health, responsible consumption and value-creating education (Helliwell et al. 2021 ; Francart et al., 2018 ; Armstrong et al., 2016 ; Gilead, 2016 ; Giannetti et al., 2015 ). Unfortunately, existing conventional growth theories have ignored all these significant contributions. For example, GDP considers natural ecosystems as economically helpful only up until they are mined and their products are traded (Carrero et al. 2020 ). The non-market benefits they generate, such as natural fertilization, soil regeneration, climate regulation, clean air and maintenance of biodiversity, are entirely ignored (Boyd 2007 ; Hirschauer et al., 2014). The quality time people spend with their families and communities for leisure, educating future generations and making a healthy communal harmony is regarded meaningless, even in the event that they are important to enhance people’s well-being and, hence, to assist any dimension of economic engagement (Griep et al. 2015 ; Agrawal et al., 2020 ). Similarly, if an economy is focusing on people’s healthy lifestyle (for example, by providing comfortable working hours, improving work-life balance, emphasizing mental health, focusing on healthy food, reducing pollution, and promoting sustainable consumption), it is not considered in sync with the growth paradigm (Roy 2021 ; Scrieciu et al., 2013; Shrivastava and Zsolnai 2022 ; Lauzon et al., 2023 ).
Among the latest reviews, Bayani et al. ( 2023 ) highlight that the economics of happiness helps reduce the country’s financial crime by providing a livelihood that reduces financial delinquency. Chen ( 2023 ) highlights that smart city performance enhances urban happiness by adopting green spaces, reusing and recycling products, and controlling pollution. The study by (Agrawal and Sharma 2023 ) proposed a conceptual framework for a happiness economy to achieve sustainability by going beyond GDP. Similarly, Fioramonti et al. ( 2019b ) explored going beyond GDP for a transition towards a happy and well-being economy. The article by Laurent et al. ( 2022 ) has intensively reviewed the well-being indicators in Rome and proposed a conceptual framework for it.
Table 1 provides a thorough summary of the prior review studies about the happiness economy and its contribution to public policy and sustainable development.
3 Research methodology
In the current study, we have adopted an integrative review approach of SLR and bibliometric analysis of the academic literature to get a detailed knowledge of the study, which could also help propose future research avenues. The existing scientific production’s qualitative and quantitative context must be incorporated for a conclusive decision. The study by Meredith ( 1993 ) defines that SLR enables an “integrating several different works on the same topic, summarising the common elements, contrasting the differences, and extending the work in some fashion”. In the present study, the “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses” (PRISMA) is applied to perform the SLR to follow systematic and transparent steps for the research methodology, as shown in Fig. 1 . The PRISMA technique includes the identification, screening, eligibility, and exclusion criteria parts of the review process.
Additionally, examples of the data abstraction and analysis processes are provided (Mengist et al. 2020 ; Moher et al., 2015 ). The four main phases of the PRISMA process are eligibility, identification, screening, and data abstraction and analysis. Because the PRISMA technique employs sequential steps to accomplish the study’s purpose, it benefits SLR research. Moreover, the bibliometric analysis helps summarise the existing literature’s bibliographic data and determine the emerging condition of the intellectual structure and developing tendencies in the specified research domain (Dervis 2019 ).
3.1 Identification
The step to conduct the PRISMA is the identification of the relevant keywords to initiate the search for material. Next, search strings for the digital library’s search services are created using the selected keywords. The basic search query is for digital library article titles, keywords, and abstracts. Next, a Boolean AND or OR operator is used to generate the search string (Boolean combinations of the operators may also be used).
There are different search databases to conduct the review studies, such as Scopus, Sage, Web of Science, IEEE, and Google Scholar. Among all the available search databases, we have used the Scopus database to identify the articles; since 84% of the material on Web of Science (WoS) overlaps with Scopus, very few authors have addressed the benefits of adopting Scopus over WoS (Mongeon and Paul-Hus 2016 ). Scopus is widely used by academicians and researchers for quantitative analysis (Donthu et al. 2021 ). It is the biggest database of scientific research and contains citations and abstracts from peer-reviewed publications consisting of journal research articles, books and conference articles (Farooque et al., 2019 ; Dhayal et al., 2022 ; Brahmi et al., 2022 ). The following search term was used: (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“happiness economy” OR “economics of happiness” OR “happiness in economy” OR “economy of happiness” OR “economy of wellbeing” OR “wellbeing economy” OR “wellbeing in economy” OR “beyond growth”). This process yields 380 artciles in the initial phase.
3.2 Screening
The second phase is completed by all identified articles from the Scopus database obtained from the search string in the identification phase. The publications are either included or excluded throughout the screening process based on the standards established by the authors and with the aid of particular databases. Exclusion and inclusion criteria are shown during the screening phase to identify pertinent articles for the systematic review procedure. The timeline of this study’s selected articles is from 1995 to 2023. The first article related to the research domain was published in 1995. The second criterion for the inclusion includes the types of documents. In the present research, the authors have regarded only peer-reviewed journals and review articles. Other types of articles, such as books, book chapters, conference articles, notes, and editorials, are excluded to maintain the quality of the review. The third inclusion and exclusion criterion is based on language. All the non-English language documents are excluded to avoid translation confusion; hence, only the English language articles are considered for the final review. After the screening process, 297 articles are obtained.
3.3 Eligibility
Articles are manually selected or excluded depending on specific criteria specified by the authors during the eligibility process. During the elimination process, the authors excluded the articles that did not fit into the scope of review after manual screening of the articles. Two hundred fifty-seven articles were selected after the eligibility procedure. These selected articles are carefully reviewed for the study by reviewing the titles, abstracts, and standards from earlier screening processes.
3.4 Data abstraction and analysis
Analysis and abstraction of data are part of the fourth step. Finally, 257 papers were taken into account for final review. After that, the studies are culled to identify pertinent themes and subthemes for the current investigation by thoroughly reviewing each article’s text. An integrative review is a form of study that combines mixed, qualitative, and quantitative research procedures. It is carried out as shown in Fig. 1 . R-studio Bibliometrix and VOSviewer version 1.6.18 were used to evaluate the final study dataset corpus of 257 articles. Since the Bibliometrix software package is a free-source tool programmed in the R language. It is proficient of conducting comprehensive scientific mapping. It also contains several graphical and statistical features with flexible and frequent updates (Agrawal et al. 2023a , b ).
Extraction of articles and selection process
This section provides an answer to the first research question, RQ1, by indicating the main information of corpus data, research publication trends, influential prolific authors, journals, countries and most used keywords, etc. (Refer to Tables 2 , 3 and 4 ) and (Refer to Figs. 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 and 6 ).
4.1 Bibliometric analysis
Table 2 shows the relevant information gathered from the publication-related details. It presents the cognitive knowledge of the research area, for instance, details about authors, annual average publication, average citations and collaboration index. By observing the rate of document publishing, the study illustrates how much has already been done and how much remains to be investigated.
The annual publication trend is shown in Fig. 2 . It is reflected that the first article related to happiness in an economy was released in the year 1995 when (Bowling 1995 ) published the article “What things are important in people’s lives? A survey of the public’s judgements to inform scales of health related quality of life” where the article discussed “quality of life” and “happiness” as an essential component of a healthy life. Oswald ( 1997 ) brought the concept of happiness and economics together and raised questions such as “Does money buy happiness?” or “Do you think your children’s lives will be better than your own?”. Eventually, the gross national product of the past year and the coming year’s exchange rate was no longer the concern; instead, happiness as the sublime moment became more accurate (Schyns 1998 ; Easterlin, 2001; Frey and Stutzer, 2005 ). Post-2013, we can see exponential growth in the publication trend, and the reason behind the growth is the report published by the “ Stiglitz-Sen-Fitoussi” Commission, which has identified limitations of GDP and questioned the metric of wealth, economic and societal progress. The affirmed questions have gained the attention of researchers and organizations, and thus, they have explored the alternatives to GDP. As a result, the “Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development” (OECD) have proposed a wellbeing framework. Some research work has significantly impacted that time, contributing to the immense growth in this research area (Sangha et al. 2015 ; Spruk and Kešeljević, 2015 ; Nunes et al., 2016 ).
Publication trend
Table 3 shows the top prolific journals concerning the topmost publications in the domain of happiness economy for the corpus of 257 articles, namely “International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health”, “Ecological Economics”, “Ecological Indicators”, “Sustainability” and “Journal of Cleaner Production” with 5, 4, 4,4 and 4 articles respectively (Refer to Table 4 ). Moreover, the most influential journals with maximum citations are “Nature Human Behavior”, “Quality of Life Research”, “Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis”, “Journal of Cleaner Production” and “Ecological Economics”, with 219, 205, 186, 154 and 142 citations, respectively. “Journal of Cleaner Production” and “Ecological Economics” are highly prolific and the most influential journals in the happiness economy research domain.
Table 4 shows the most influential authors. Baños, R.M. and Botella, C. are the two most contributing authors with maximum publications. For the maximum number of citations, Zheng G. and Coscieme L. are the topmost authors for their research work. The nations were sorted according to the quantity of publications, and Fig. 3 showed where the top ten countries with the highest number of publications are listed originated. It can be seen from the figure that the United Stated has contributed the maximum publications, 66, followed by the United Kingdom with 41 articles, followed by Germany with 32 articles. It is worth noting that emerging nation such as India and China have also made significant contributions.
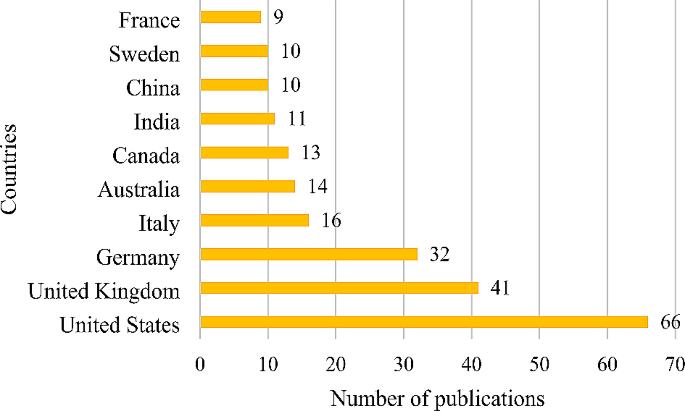
Top ten contributing countries
Figure 4 shows semantic network analysis in which the relationships between words in individual texts are performed. In the present study, we have identified word frequency distributions and the co-occurrences of the authors’ keywords in this study. We employed co-word analysis to find repeated keywords or terms in the title, abstract, or body of a text. In Fig. 5 , the circle’s colour represents a particular cluster, and the circle’s radius indicates how frequently the words occur. The size of a keyword’s node indicates how frequently that keyword appears. The arcs connecting the nodes represent their co-occurrence in the same publication. The greater the distance between two nodes, the more often the two terms co-occur. It can be seen that “happiness” is linked with “growth” and “life satisfaction”. The nodes of “green economy”, “ecological economics”, and “climate change” are in a separate cluster that shows they are emerging areas, and future studies can explore the relationship between happiness economy with these keywords.
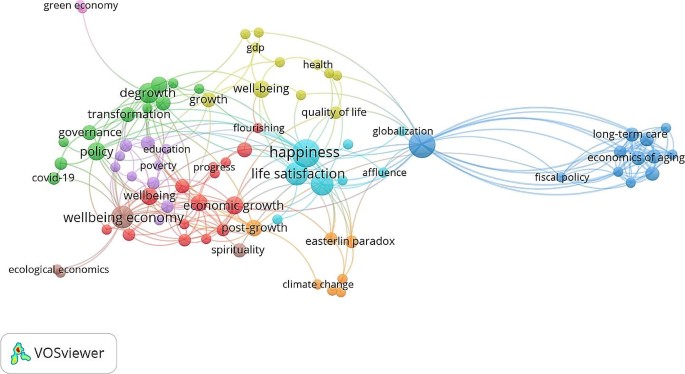
Co-ocurrance of author’s keyword (Author’s compilation)
4.2 Thematic map analysis through R studio
The thematic analysis map, as shown in Fig. 5 , displays, beneath the author’s keywords, the visualisation of four distinct topic typologies produced via a biblioshiny interface. The thematic map shows nine themes/clusters under four quadrants segregated in “Callon’s centrality” and “density value”. The degree of interconnectedness between networks is determined by Callon’s centrality, while Callon’s density determines the internal strength of networks. (Chen et al. 2019 ). The rectangular boxes in Fig. 5 represent the subthemes under each topic or cluster that are either directly or indirectly connected to the major themes, based on the available research. In the upper-right quadrant, four themes have appeared, namely “circular economy”, “well-being economy”, “depression”, and “sustainable development”, they fall under the category of motor themes since they are extremely pertinent to the research field, highly repetitious, and well-developed. When compared to other issues with internal linkages but few exterior relations, “urban population” in the upper-left quadrant is seen as a niche concern since it is not as significant. This cluster may have affected the urban population’s happiness (Knickel et al. 2021 ). “Social innovation” is categorised as an emerging or declining subject with low centrality and density, meaning it is peripheral and undeveloped. It is positioned in the lower-left quadrant. Last but not least, the transversal and fundamental themes “happiness economy”, “subjective well-being”, and “climate change” in the lower-right quadrant are seen to be crucial to the happiness economy study field but are still in the early stages of development. As a result, future research must place greater emphasis on the quantitative and qualitative growth of the study area in light of the key themes that have been identified.
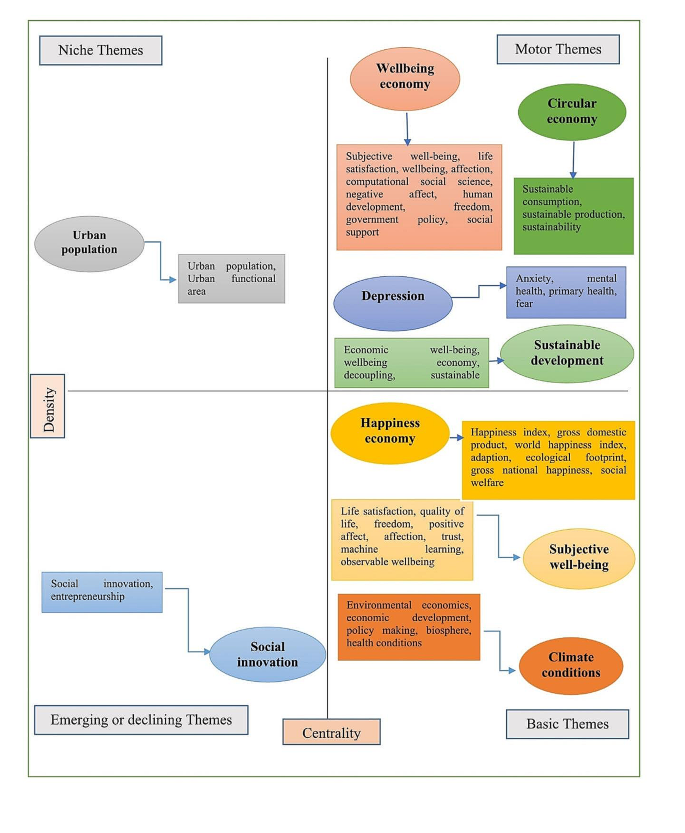
Thematic map analysis
4.3 Science mapping through cluster analysis
In the study, science mapping was conducted to examine the interrelationship between the research domains that could be intellectual (Aria and Cuccurullo 2017 ; Donthu et al. 2021 ). It includes various techniques, such as co-authorship analysis, co-occurrence analysis, bibliographic coupling, etc. We have used R-Studio for the study’s temporal analysis by cluster analysis. To answer RQ2, the authors have performed a qualitative examination of the emerging cluster themes through the science mapping of the existing research corpus of 257 articles by performing bibliographic coupling of documents. Bibliographic coupling analysis helps identify clusters reflecting the most recent research themes in the happiness economy field to illuminate the field’s current areas of interest.
The visual presentation of science mapping relied on VoSviewer version 1.6.18 (refer to Fig. 6 ). Five significant clusters emerged in this research domain (refer to Table 5 ). Going beyond GDP: Transition towards happiness economy, rethinking growth for sustainability and ecological regeneration, beyond money and happiness policy, health, human capital and wellbeing and Policy-Push for happiness economy. A thorough examination identified cluster analyzes has also assists us in identifying potential future research proposals. (Franceschet 2009 )
4.4 Cluster 1: Going beyond GDP: transition towards happiness economy
It depicts from the green colour circles and nodes, where seven research articles were identified with a common theme of beyond GDP that can be seen in Fig. 6 . Cook and Davíðsdóttir ( 2021 ) investigated the linkages between the alternative measure of the beyond growth approach such as a well-being economy prespective and the SDGs. They proposed a conceptual model of a well-being economy consisting of four capital assets interrelated with SDGs that promote well-being goals and domains. To extend the concept of going beyond GDP, various economic well-being indicators are being aligned with the different economic, environmental, and social dimensions to target the set goals of SDG. It is found that the “Genuine Progress Indicator” (GPI) is consider as the most extensive method that covers the fourteen targets among the seventeen’s SDG’s. Cook et al. ( 2022 ) consider SDGs to represent the classical, neoclassical and growth-based economy model and as an emerging paradigm for a well-being economy. The significance of GDP is more recognized within the goals of sustainable development.
GPI is considered an alternative indicator of economic well-being. On this basis, excess consumption of high-quality energy will expand macro-economic activity, which GDP measures. For such, a conceptual exploration of the study is conducted on how pursuing “Sustainable Energy Development” (SED) that can increase the GPI results. As the study’s outcome, according to the GPI, SED will have a significant advantage in implementing energy and environment policy and will also contribute to the advancement of social and economic well-being. Coscieme et al. ( 2020a ) explored the connection between the unconditional growth of GDP and SDG. The author considered that policy coherence for sustainable development should lessen the damaging effects of cyclic manufacturing on the ecosystem. Thus, the services considered free of charge in the GDP model should be valued as a component of society. Generally, such services include ecosystem services and a myriad of “economic” functions like rainfall and carbon sequestration. To work for SDG 8, defined by the “United Nations Sustainable Development Goals” (UNSDGs), a higher GDP growth rate would eventually make it more difficult to achieve environmental targets and lessen inequality. Various guidelines were proposed to select alternative variables for SDG-8 to enhance coherence among all the SDG and other policies for sustainability.
Fioramonti et al. ( 2019a ) state their focus is to go beyond GDP toward a well-being economy rather than material output with the help of convergence reforms in policies and economic shifts. To achieve the SDG through protecting the environment, promoting equality, equitable development and sharing economy. The authors have developed the Sustainable Well-Being Index (SWBI) to consolidate the “Beyond GDP” streams as a metric of well-being matched with the objectives to achieve SDG. The indicators of well-being for an economy have enough possibility to connect current transformations in the economic policies and the economy that, generally, GDP is unable to capture.
Fioramonti et al. ( 2022a ) investigate the critical features of the Wellbeing Economy (WE), including its various parameters like work, technology, and productivity. Posting a WE framework that works for mainstream post-growth policy at the national and international levels was the study’s primary goal. The authors have focused on building a society that promotes well-being that should be empowering, adaptable, and integrative. A well-being economic model should develop new tools and indicators to monitor all ecological and human well-being contributors. A multidimensional approach including critical components for a well-being economy was proposed that creates value to re-focus on economic, societal, personal, and natural aspects. Rubio-Mozos et al. ( 2019 ) conducted in-depth interviews with Fourth Sector business leaders, entrepreneurs, and academicians to investigate the function of small and medium-sized businesses and the pressing need to update the economic model using a new measure in line with UN2030. They have proposed a network from “limits to growth” to a “sustainable well-being economy”.
4.5 Cluster 2: Rethinking growth for sustainability and ecological regeneration
Figure 6 depicts it from blue circles and nodes, wherein four papers were identified. Knickel et al. ( 2021 ) proposed an analytical approach by collecting the data from 11 European areas to examine the existing conditions, difficulties, and anticipated routes forward. The goal of the study is to define the many ideas of a sustainable well-being economy and territorial development plans that adhere to the fundamental characteristics of a well-being economy. A transition from a conventional economic viewpoint to a broader view of sustainable well-being is centred on regional development plans and shifting rural-urban interactions.
Pillay ( 2020 ) investigates the new theories of de-growth, ecosocialism, well-being and happiness economy to break the barriers of traditional economic debates by investigating ways to commercialise and subjugate the state to a society in line with non-human nature. The significant indicator of Gross National Happiness (GNH) is an alternative working indicator of development; thus, the Chinese wall between Buddha and Marx has been built. They questioned the perspective of Buddha and Marx, whether they were harmonized or became a counter-hegemonic movement. In order to determine if the happiness principle is grounded in spiritual values and aligns with the counter-hegemonic ecosocialist movement, the author examined the ecosocialist perspective. Shrivastava and Zsolnai ( 2022 ) have investigated the theoretical and practical ramifications of creative organisations for well-being rooted in the drive for a well-being economy. Wellbeing and happiness-focused economic frameworks are emerging primarily in developed countries. This new policy framework also abolishes GDP-based economic growth and prioritizes individual well-being and ecological regeneration. To understand its application and interpretation, Van Niekerk ( 2019 ) develops a conceptual framework and theoretical analysis of inclusive economics. It contributes to developing a new paradigm for economic growth, both theoretically and practically.
4.6 Cluster 3: ‘Beyond money’ and happiness policy
It depicts pink circles and nodes, wherein five articles were identified, as shown in Fig. 6 . According to Diener and Seligman ( 2004a ) economic indicators are critical in the early phases of economic growth when meeting basic requirements is the primary focus. However, as society becomes wealthier, an individual’s well-being becomes less dependent on money and more on social interactions and job satisfaction. Individuals reporting high well-being outperform those reporting low well-being in terms of income and performance. A national well-being index is required to evaluate well-being variables and shape policies systematically. Diener and Seligman ( 2018 ) propounded the ‘Beyond Money’ concept in 2004. In response to the shortcomings of GDP and economic measures, other quality-of-life indicators, such as health and education, have been created. The national account of well-being has been proposed as a common path to provide societies with an overall quality of life metric. While measuring the subjective well-being of people, the authors reasoned a societal indicator of the quality of life. In this article, the authors have proposed an economy of well-being model by combining subjective and objective measures to convince policymakers and academicians to enact policies that enhance human welfare. The well-being economy includes quality of life indicators and life satisfaction, subjective well-being and happiness.
Frey and Stutzer ( 2000 ) perceived the microeconomic well-being variables in countries. In the study, survey data was used from 6000 individuals in Switzerland and showed that the individuals are happier in developed democracies and institutions (government federalization). They analyzed the reported subjective well-being data to determine the function of federal and democratic institutions on an individual’s satisfaction with life. The study found a negative relationship between income and unemployment. Three criteria have been employed in the study to determine happiness: demographic and psychological traits, macro- and microeconomic factors, and constitutional circumstances. Thus, a new pair of determinants reflects happiness’s effect on individuals’ income, unemployment, inflation and income growth.
Happiness policy, according to Frey and Gallus ( 2013b ), is an intrinsic aspect of the democratic process in which various opinions are collected and examined. “Happiness policy” is far more critical than continuing a goal such as increasing national income and instead considered an official policy goal. The article focuses on how politicians behave differently when they believe that achieving happiness is the primary objective of policy. Frey et al. ( 2014 ) explored the three critical areas of happiness, which are positive and negative shocks on happiness, choice of comparison and its extent to derive the theoretical propositions that can be investigated in future research. It discussed the areas where a more novel and comprehensive theoretical framework is needed: comparison, adaptation, and happiness policy. Wolfgramm et al. ( 2020 ) derived a value-driven transformation framework in Māori economics of wellbeing. It contributes to a multilevel and comprehensive review of Māori economics and well-being. The framework is adopted to advance the policies and implement economies of well-being.
4.7 Cluster 4: Health, human capital and wellbeing
It is depicted as a red colour circle and nodes in Fig. 6 , and only three papers on empirical investigations were found. Laurent et al. ( 2022 ) investigated the Health-Environment Nexus report published by the “Wellbeing Economy Alliance”. In place of increased production and consumption, they suggested a comprehensive framework for human health and the environment that includes six essential paths. The six key pathways are well-being energy, sustainable food, health care, education, social cooperation and health-environment nexus. The proposed variables yield the co-benefits for the climate, health and sustainable economy. Steer clear of the false perception of trade-offs, such as balancing the economy against the environment or the need to save lives. McKinnon and Kennedy ( 2021 ) focuses on community economics of well-being that benefits entrepreneurs and employees. They investigated the interactions of four social enterprises that work for their employees inside and within the broader community. Cylus et al. ( 2020 ) proposed the opportunities and challenges in adopting the model of happiness or well-being in an economy as an alternative measure of GDP. Orekhov et al. ( 2020 ) proposed the derivation of happiness from the World Happiness Index (WHI) data to estimate the regression model for developed countries.
4.8 Cluster 5: Policy-push for happiness economy
It is depicted as an orange circle and nodes in Fig. 6 , and only five papers on empirical and review investigations were found. Oehler-Șincai et al. ( 2023 ) proposed the conceptual and practical perspective of household-income-labour dynamics for policy formulation. It discusses the measurement of well-being as a representation of various policies focusing on health, productivity, and longevity. It focuses on the role of policy in building the subjective and objective dimensions of well-being, defines the correlation between well-being, employment policies, and governance, is inclined to the well-being performance of various countries, and underscores present risks that jeopardize well-being. Musa et al. ( 2018 ) have developed a “community happiness index” by incorporating the four aspects of sustainability—economic, social, environmental, and urban governance—as well as the other sustainability domains, such as human well-being and eco-environmental well-being. From then onwards, community happiness and sustainable urban development emerged. Chernyahivska et al. ( 2020 ) developed strategies to raise the standard of living for people in countries undergoing economic transition by using the quality of life index. The methods uncovered are enhancing employment opportunities and uplifting the international labour market in urban and rural areas, prioritizing human capital, eliminating gender inequality, focusing on improving the individual’s health, and enhancing social protection. Zheng et al. ( 2019 ) investigated the livelihood and well-being index of the population that makes liveable conditions and city construction in society based on people’s happiness index. The structure of a liveable city should be emphasised on sustainable development. The growth strategy in urban areas is an essential aspect of building a liveable city. Frey and Gallus ( 2013a ) criticised the National Happiness Index as a policy goal in a country because it cannot be measured and thus fails to measure the true happiness of people. To measure real happiness, the government should establish living conditions that enable individuals to become happy. The rule of law and human rights must support the process.
The structure of a liveable city should be emphasized in sustainable development. The growth strategy in urban areas is an essential aspect of building a liveable city. Frey and Gallus ( 2013a ) criticized the National Happiness Index as a policy goal in a country because it cannot be measured and thus fails to identify the true individuals happiness. To measure real happiness, the government should establish living conditions that enable individuals to be happy. The process needs to be supported by human rights and the rule of law.
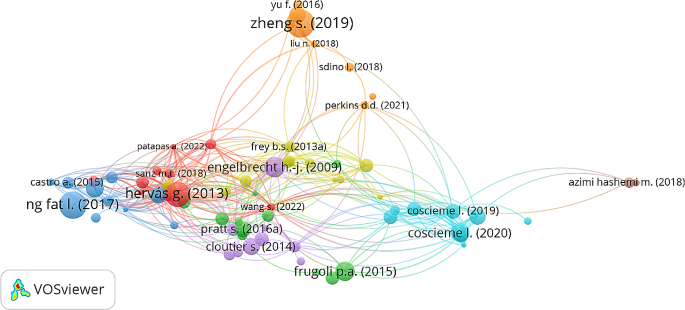
Visualization of cluster analysis
5 Discussion of findings
Concerns like the improved quality-of-life and a decent standard of living within the ecological frontier of the environment have various effects on individuals overall well-being and life satisfaction. The ‘beyond growth’ approach empathized with the revised concept of growth, which is based on the idea of maximising happiness for a larger number of people rather than being driven by a desire for financial wealth or production. In that aspect, the notion of happiness economy is designed that prioritizes serving both people and the environment over the other. This present article has focused on the beyond growth approach and towards a new economic paradigm by doing bibliometric and visual analysis on the dataset that was obtained from Scopus, helping to determine which nations, publications, and authors were most significant in this field of study.
In this field of study, developed nations have made significant contributions as compared to the developing nations. In total, 59 countries have made the substantial contribution to the beyond growth approach literature an some of them have proposed their respective national well-being economy framwework. Among 59 countries the United States and the United Kingdom have been crucial to the publishing. With the exception of five of the top 10 nations, Europe contributes the most to scientific research. The existing research shows the inclination of developed and developing countries to build a new economic paradigm that goes beyond growth by prioritizing the happiness level at individual as well as at collective level.
The most prolific journals in this research domain are the “International Journal of Environmental Research” and “Public Health” with the total publication of 5 and 4. The top two cited journals were the “ Nature Human Behavior” with 219 citations and the “Quality of Life Research” with 205 citations. Due to various economic and non-economic factors, these journals struggled to strike a balance between scientific accuracy and timeliness, and it became vital to spread accurate and logical knowledge. For, example, discussing the relationship between inequality and well-being, exploring the challenges and opportunites of happiness economy in different countries, assessing the role of health in all policies to support the transition to the well-being economy. Visualization of semantic network analysis of co-ocurrance of authors keywords from the VOSviewer showed the future research scope to explore the association between happiness economy along with green economy, climate change, spirituality and sustainability. However, in the thematic mapping, the motor themes denotes the themes that are well-developed and repetative in research, such as, well-being economy, depression, sustainable development and circular economy. The basic themes depicts the developing and transveral themes such as happiness economy, subjective well-being and climate condition. As a result, future research must place greater emphasis on the theoretical and practical expansion of the research field in view of the determined major subjects.
The present study have performed the cluster analysis to identify the emerging research themes in this domain through VOSviewer that helps to analyze the network of published documents. Based on published papers, the author can analyse the interconnected network structure with the use of cluster analysis. We have identified the top five clusters from the study. Each cluster denote the specific and defined theme of the research in this domain. In cluster 1, the majorly of the authors are working in the area of going beyond GDP and transition towards happiness economy, which consists of empirical and review studies. Cluster 2 represents that authors are exploring the relationship between rethinking growth for sustainability and ecological regeneration to evaluate the transition from a conventional economic thought to a broader view of sustainable well-being which is centred on regional development plans and shifting rural-urban interactions. In cluster 3, the authors are exploring the beyond money and happiness policy themes and identified the shortcomings of GDP and economic measures, other quality-of-life indicators, such as health and education. They have proposed the well-being index to evaluate the well-being variables and shape socio-economic policies systematically. The authors have proposed an economy of well-being model by combining subjective and objective measures to convince policymakers and academicians to enact policies that enhance human welfare. The well-being economy includes quality of life indicators and life satisfaction, subjective well-being and happiness. In cluster 4, the authors are working of related theme of Health, human capital and wellbeing, whereby they have put up a comprehensive framework for health and the environment that includes several important avenues for prioritising human and ecological well-being over increased production and consumption. In cluster 5, the authors have suggested the policy-push for happiness economy in which they have identified the conceptual and practical perspective of household-income-labour dynamics for policy formulation. Majorly of the authors in this clutster have focused on the role of policy in building the subjective and objective dimensions of well-being, defines the correlation between well-being, employment policies, and governance, is inclined to the well-being performance of various countries, and underscores present risks that jeopardize well-being. Hence, the present study will give academics, researchers, and policymakers a thorough understanding of the productivity, features, key factors, and research outcomes in this field of study.
6 Scope for future research avenues
The emergence of a happiness economy will transform society’s traditional welfare measure. Such changes will generate more reliable and practical means to measure the well-being or welfare of an economy. After a rigorous analysis of the existing literature, we have proposed the scope for future research in Table 6 .
7 Conclusion
In 2015, the United Nations proposed the pathbreaking and ambitious seventeen “Sustainable Development Goals” (SDGs) for countries to steer their policies toward achieving them by 2030. In reality, economic growth remains central to the agenda for SDGs, demonstrating the absence of a ground-breaking and inspirational vision that might genuinely place people and their happiness at the core of a new paradigm for development. As this research has reflect, there are various evidence that the happiness economy strategy is well-suited to permeate policies geared towards sustainable development. In this context, ‘happiness’ may be a strong concept that ensures the post-2030 growth will resonate with the socioeconomic and environmental traits of everyone around the world while motivating public policies for happiness.
The current research has emphasized the many dynamics of the happiness economy by using a bibliometric analytic study of 257 articles. We have concluded that the happiness economy is an emerging area that includes different dimensions of happiness, such as ecological regeneration, circular economy, sustainability, sustainable well-being, economic well-being, subjective well-being, and well-being economy. In addition to taking into consideration the advantages and disadvantages of human participation in the market, a happiness-based economic system would offer new metrics to assess all contributions to human and planetary well-being. In terms of theoretical ramifications, we suggest that future scholars concentrate on fusing the welfare and happiness theory with economic policy. As countries are predisposed to generate disharmony and imbalance, maximizing societal well-being now entails expanding sustainable development. Since the happiness economy is still a relatively novel field, it offers numerous potential research opportunities.
8 Limitations
Similar to every other research, this one has significant restrictions as well. We are primarily concerned that all our data were extracted from the Scopus database. Furthermore, future research can utilize other software like BibExcel and Gephi to expound novel variables and linkages. Given the research limitations, this article still provides insightful and relevant direction to policymakers, scholars, and those intrigued by the idea of happiness and well-being in mainstream economics.
The study offers scope for future research in connecting the happiness economy framework with different SDGs. Future studies can also carry empirical research towards creating a universally acceptable ‘happiness economy index’ with human and planetary well-being at its core.
Data availability
Data not used in this article.
Abrar, R.: Building the transition together: WEAll’s perspective on creating a Wellbeing Economy. Well-Being Transition. 157–180 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67860-9_9/COVER
Agrawal, R., Agrawal, S., Samadhiya, A., Kumar, A., Luthra, S., Jain, V.: Adoption of green finance and green innovation for achieving circularity: An exploratory review and future directions. Geosci. Front. 101669 (2023a). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GSF.2023.101669
Agrawal, S., Sharma, N., Singh, M.: Employing CBPR to understand the well-being of higher education students during covid-19 lockdown in India. SSRN Electron. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3628458
Agrawal, S., Sharma, N.: Beyond GDP: A movement toward happiness economy to achieve sustainability. Sustain. Green. Future. 95–114 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24942-6_5
Agrawal, S., Sharma, N., Bruni, M.E., Iazzolino, G.: Happiness economics: Discovering future research trends through a systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 416 , 137860 (2023b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137860
Article Google Scholar
Aiyar, S., Ebeke, C.: Inequality of opportunity, inequality of income and economic growth. World Dev. 136 , 105115 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WORLDDEV.2020.105115
Armstrong, C.M.J., Connell, K.Y.H., Lang, C., Ruppert-Stroescu, M., LeHew, M.L.A.: Educating for sustainable fashion: using clothing acquisition abstinence to explore sustainable consumption and life beyond growth. J Consum Policy. 39 (4), 417–439 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10603-016-9330-z
Approaches to Improving the Quality of Life: How to Enhance the Quality of Life - Abbott L. Ferriss - Google Books . (n.d.). Retrieved April 25, from (2023). https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=9AKdtNzGsGcC&oi=fnd&pg=PR8&dq=equality+tends+to+improve+major+objective+ways+of+wellbeing,+from+healthier+communities+to+happier+communities,+from+declining+hate+and+crime+and+to+improved+social+cohesion,+productivity,+unity+and+interpersonal+trust&ots=pZ5kbKdqrC&sig=vfwoVTo2Aur-nV9J9HNF4rbF74o&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false
Aria, M., Cuccurullo, C.: Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetrics. 11 (4), 959–975 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JOI.2017.08.007
Atkinson, S., Fuller, S., Painter, J.: Wellbeing and place, pp. 1–14. Ashgate Publishing (2012). https://researchers.mq.edu.au/en/publications/wellbeing-and-place
Bengtsson, M., Alfredsson, E., Cohen, M., Lorek, S., Schroeder, P.: Transforming systems of consumption and production for achieving the sustainable development goals: moving beyond efficiency. Sustain. Sci. 13 (6), 1533–1547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-018-0582-1
Bayani, E., Ahadi, F., Beigi, J.: The preventive impact of Happiness Economy on Financial Delinquency. Political Sociol. Iran. 5 (11), 4651–4670 (2023). https://doi.org/10.30510/PSI.2022.349645.3666
Better Life Initiative: Measuring Well-Being and Progress - OECD . (n.d.). Retrieved December 8, from (2022). https://www.oecd.org/wise/better-life-initiative.htm
Bowler, D.E., Buyung-Ali, L.M., Knight, T.M., Pullin, A.S.: A systematic review of evidence for the added benefits to health of exposure to natural environments. BMC Public. Health. 10 (1), 1–10 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-10-456/TABLES/1
Bowling, A.: What things are important in people’s lives? A survey of the public’s judgements to inform scales of health related quality of life. Soc. Sci. Med. 41 (10), 1447–1462 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0277-9536(95)00113-L
Boyd, J.: Nonmarket benefits of nature: What should be counted in green GDP? Ecol. Econ. 61 (4), 716–723 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLECON.2006.06.016
Brahmi, M., Aldieri, L., Dhayal, K.S., Agrawal, S.: Education 4.0: can it be a component of the sustainable well-being of students? pp. 215–230 (2022). https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-6684-4981-3.ch014
Carrero, G.C., Fearnside, P.M., Valle, D. R., de Alves, S., C: Deforestation trajectories on a Development Frontier in the Brazilian Amazon: 35 years of settlement colonization, policy and economic shifts, and Land Accumulation. Environ. Manage. 2020. 66:6 (6), 966–984 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/S00267-020-01354-W 66
Chen, C.W.: Can smart cities bring happiness to promote sustainable development? Contexts and clues of subjective well-being and urban livability. Developments Built Environ. 13 , 100108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DIBE.2022.100108
Chen, X., Lun, Y., Yan, J., Hao, T., Weng, H.: Discovering thematic change and evolution of utilizing social media for healthcare research. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak. 19 (2), 39–53 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/S12911-019-0757-4/FIGURES/10
Chernyahivska, V.V., Bilyk, O.I., Charkina, A.O., Zhayvoronok, I., Farynovych, I.V.: Strategy for improving the quality of life in countries with economies in transition. Int. J. Manag. 11 (4), 523–531 (2020).
Clark, A.E., Flèche, S., Senik, C.: Economic growth evens out happiness: evidence from six surveys. Rev Income Wealth. 62 (3), 405–419 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/roiw.12190
Construction strategies and evaluation models of livable city based on the happiness index | IEEE Conference Publication | IEEE Xplore . (n.d.). Retrieved April 1, from (2023). https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6640911
Cook, D., Davíðsdóttir, B.: An appraisal of interlinkages between macro-economic indicators of economic well-being and the sustainable development goals. Ecol. Econ. 184 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2021.106996
Cook, D., Davíðsdóttir, B., Gunnarsdóttir, I.: A conceptual exploration of how the pursuit of sustainable Energy Development is implicit in the genuine Progress Indicator. Energies. 15 (6) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/en15062129
Coscieme, L., Sutton, P., Mortensen, L.F., Kubiszewski, I., Costanza, R., Trebeck, K., Pulselli, F.M., Giannetti, B.F., Fioramonti, L.: Overcoming the myths of mainstream economics to enable a newwellbeing economy. Sustain. (Switzerland). 11 (16) (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164374
Coscieme, L., Mortensen, L.F., Anderson, S., Ward, J., Donohue, I., Sutton, P.C.: Going beyond gross domestic product as an indicator to bring coherence to the Sustainable Development Goals. J. Clean. Prod. 248 , 119232 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2019.119232
Coscieme, L., Mortensen, L.F., Anderson, S., Ward, J., Donohue, I., Sutton, P.C.: Going beyond gross domestic product as an indicator to bring coherence to the Sustainable Development Goals. J. Clean. Prod. 248 (2020a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119232
Costanza, R.: Ecological economics in 2049: Getting beyond the argument culture to the world we all want. Ecol. Econ. 168 , 106484 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLECON.2019.106484
Costanza, R., Caniglia, E., Fioramonti, L., Kubiszewski, I., Lewis, H., Lovins, H., McGlade, J., Mortensen, L.F., Philipsen, D., Pickett, K.E., Ragnarsdottir, K.V., Roberts, D.: Toward a Sustainable Wellbeing Economy. Solutions: For a Sustainable and Desirable Future . (2020). https://openresearch-repository.anu.edu.au/handle/1885/205271
Coyne, C.J., Boettke, P.J.: Economics and Happiness Research: Insights from Austrian and Public Choice Economics. Happiness Public. Policy. 89–105 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230288027_5
Cylus, J., Smith, P.C., Smith, P.C.: The economy of wellbeing: What is it and what are the implications for health? BMJ. 369 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m1874
Dervis, H.: Bibliometric analysis using bibliometrix an R package. J. Scientometr. Res. 8 (3), 156–160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.5530/JSCIRES.8.3.32
Dhayal, K.S., Brahmi, M., Agrawal, S., Aldieri, L., Vinci, C.P.: A paradigm shift in education systems due to COVID-19, pp. 157–166 (2022)
Diener, E.: Subjective well-being. Psychol. Bull. 95 (3), 542–575. (1984). https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.95.3.542. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1984-23116-001
Diener, E., Seligman, M.E.P.: Beyond money: Toward an economy of well-being. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, Supplement , 5 (1). (2004a). https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-3142774261&partnerID=40&md5=e86b2c930837502a9ce9cbd057c0df82
Diener, E., Seligman, M.E.P.: Beyond money: Toward an economy of well-being. Psychol. Sci. Public. Interest. 5 (1), 1–31 (2004b). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0963-7214.2004.00501001.x
Diener, E., Seligman, M.E.P.: Beyond money: Progress on an economy of well-being. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 13 (2), 171–175 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691616689467
Dolan, P., Peasgood, T., White, M.: Do we really know what makes us happy? A review of the economic literature on the factors associated with subjective well-being. J. Econ. Psychol. 29 (1), 94–122 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JOEP.2007.09.001
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., Lim, W.M.: How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 133 , 285–296 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Easterlin, R.A.: Will raising the incomes of all increase the happiness of all? J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 27 (1), 35–47 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2681(95)00003-B
Easterlin, R.A.: Happiness and economic growth - the evidence. In: Global Handbook of Quality of Life, pp. 283–299. Springer, Netherlands (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9178-6_12
Fang, Z., Wang, H., Xue, S., Zhang, F., Wang, Y., Yang, S., Zhou, Q., Cheng, C., Zhong, Y., Yang, Y., Liu, G., Chen, J., Qiu, L., Zhi, Y.: A comprehensive framework for detecting economic growth expenses under ecological economics principles in China. Sustainable Horizons. 4 , 100035 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HORIZ.2022.100035
Farooque, M., Zhang, A., Thürer, M., Qu, T., Huisingh, D.: Circular supply chain management: a definition and structured literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 228 , 882–900 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2019.04.303
Ferriss, A.L.: Approaches to improving the quality of life?: how to enhance the quality of life. 150 (2010)
Fioramonti, L., Coscieme, L., Mortensen, L.F.: From gross domestic product to wellbeing: How alternative indicators can help connect the new economy with the Sustainable Development Goals: Https://Doi.Org/10.1177/2053019619869947 , 6 (3), 207–222. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/2053019619869947
Fioramonti, L., Coscieme, L., Mortensen, L.F.: From gross domestic product to wellbeing: How alternative indicators can help connect the new economy with the Sustainable Development Goals. Anthropocene Rev. 6 (3), 207–222 (2019a). https://doi.org/10.1177/2053019619869947
Fioramonti, L., Coscieme, L., Costanza, R., Kubiszewski, I., Trebeck, K., Wallis, S., Roberts, D., Mortensen, L.F., Pickett, K.E., Wilkinson, R., Ragnarsdottír, K.V., McGlade, J., Lovins, H., De Vogli, R.: Wellbeing economy: An effective paradigm to mainstream post-growth policies? Ecol. Econ. 192 , 107261 (2022b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2021.107261
Fioramonti, L., Coscieme, L., Costanza, R., Kubiszewski, I., Trebeck, K., Wallis, S., Roberts, D., Mortensen, L.F., Pickett, K.E., Wilkinson, R., Ragnarsdottír, K.V., McGlade, J., Lovins, H., De Vogli, R.: Wellbeing economy: An effective paradigm to mainstream post-growth policies? Ecol. Econ. 192 (2022a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2021.107261
Forgeard, M.J.C., Jayawickreme, E., Kern, M.L., Seligman, M.E.P.: Doing the right thing: measuring wellbeing for public policy. Int J Wellbeing. 1 (1), 79–106 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5502/ijw.v1i1.15
Francart, N., Malmqvist, T., Hagbert, P.: Climate target fulfilment in scenarios for a sustainable Swedish built environment beyond growth. Futures. 98 , 1–18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUTURES.2017.12.001
Franceschet, M.: A cluster analysis of scholar and journal bibliometric indicators. J. Am. Soc. Inform. Sci. Technol. 60 (10), 1950–1964 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/ASI.21152
Frey, B.S., Gallus, J.: Happiness policy and economic development. Int. J. Happiness Dev. 1 (1), 102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHD.2012.050835
Frey, B.S., Gallus, J.: Political economy of happiness. Appl. Econ. 45 (30), 4205–4211 (2013a). https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2013.778950
Frey, B.S., Gallus, J.: Subjective well-being and policy. Topoi. 32 (2), 207–212 (2013b). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11245-013-9155-1/METRICS
Frey, B.S., Stutzer, A.: Happiness, economy and institutions. Econ. J. 110 (466), 918–938 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0297.00570
Frey, B.S., Stutzer, A.: What can economists learn from Happiness Research? Source: J. Economic Literature. 40 (2), 402–435 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1257/002205102320161320
Frey, B.S., Stutzer, A.: Happiness research: State and prospects. Rev. Soc. Econ. 63 (2), 207–228 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1080/00346760500130366
Frey, B.S., Gallus, J., Steiner, L.: Open issues in happiness research. Int. Rev. Econ. 61 (2), 115–125 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12232-014-0203-y
Frijters, P., Clark, A.E., Krekel, C., Layard, R.: A happy choice: Wellbeing as the goal of government. Behav. Public. Policy. 4 (2), 126–165 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1017/BPP.2019.39
Galbraith, J.K.: Inequality, unemployment and growth: new measures for old controversies. J. Econ. Inequal. 7 (2), 189–206 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10888-008-9083-2
Giannetti, B.F., Agostinho, F., Almeida, C.M.V.B., Huisingh, D.: A review of limitations of GDP and alternative indices to monitor human wellbeing and to manage eco-system functionality. J. Clean. Prod. 87 (1), 11–25. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.10.051
Gilead, T.: Education’s role in the economy: towards a new perspective. 47 (4), 457–473. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/0305764X.2016.1195790
Griep, Y., Hyde, M., Vantilborgh, T., Bidee, J., De Witte, H., Pepermans, R.: Voluntary work and the relationship with unemployment, health, and well-being: A two-year follow-up study contrasting a materialistic and psychosocial pathway perspective. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 20 (2), 190–204 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1037/A0038342
Hallberg, M., Kullenberg, C.: Happiness studies. Nord. J. Work. Life Stud. 7 (1), 42–50 (2019). https://doi.org/10.5324/NJSTS.V7I1.2530
Helliwell, J., Layard, R., Sachs, J., Neve, J.-E.: World Happiness Report 2021. Happiness and Subjective Well-Being . (2021). https://www.wellbeingintlstudiesrepository.org/hw_happiness/5
Ikeda, D. (2010). A New Humanism: The University Addresses of Daisaku Ikeda - Daisaku Ikeda - Google Books . books.google.co.in/books?hl = en&lr=&id = 17aKDwAAQBAJ&oi = fnd&pg = PP1&ots = gQvBHjJA7P&sig = wVOxQ_XlCIrj39Q08W-kxc_sPjA&redir_esc = y#v = onepage&q&f = false
Inglehart, R., Foa, R., Peterson, C., Welzel, C.: Development, freedom, and rising happiness: a global perspective (1981–2007). 3 (4), 264–285 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6924.2008.00078.x
Kahneman, D., Krueger, A.B.: Developments in the measurement of subjective well-being. J. Econ. Perspect. 20 (1), 3–24 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1257/089533006776526030
Keniger, L.E., Gaston, K.J., Irvine, K.N., Fuller, R.A.: What are the benefits of interacting with nature? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 10 (3), 913–935 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH10030913
Kinman, G., Jones, F.: A life beyond work? job demands, work-life balance, and wellbeing in UK academics. 17 (1–2), 41–60 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/10911350802165478
Kim, K.H., Kang, E., Yun, Y.H.: Public support for health taxes and media regulation of harmful products in South Korea. BMC Public. Health. 19 (1), 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/S12889-019-7044-2/TABLES/5
King, M.F., Renó V.F., Novo, E.M.L.M.: The concept, dimensions and methods of assessment of human well-being within a socioecological context: a literature review. Soc Indic Res. 116 (3), 681–698 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0320-0
Knickel, K., Almeida, A., Galli, F., Hausegger-Nestelberger, K., Goodwin-Hawkins, B., Hrabar, M., Keech, D., Knickel, M., Lehtonen, O., Maye, D., Ruiz-Martinez, I., Šūmane, S., Vulto, H., Wiskerke, J.S.C.: Transitioning towards a sustainable wellbeing economy—implications for rural–urban relations. Land. 10 (5) (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/land10050512
Kullenberg, C., Nelhans, G.: The happiness turn? Mapping the emergence of happiness studies using cited references. Scientometrics. 103 (2), 615–630 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11192-015-1536-3/FIGURES/5
Lama, D.: A human approach to world peace: his holiness the Dalai Lama. J. Hum. Values. 18 (2), 91–100 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/0971685812454479
Laurent, É., Galli, A., Battaglia, F., Libera Marchiori, D., G., Fioramonti, L.: Toward health-environment policy: Beyond the Rome Declaration. Global Environmental Change , 72 . (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2021.102418
Lauzon, C., Stevenson, A., Peel, K., Brinsdon, S.: A “bottom up” health in all policies program: supporting local government wellbeing approaches. Health Promot J Austr. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/hpja.712
Lavrov, I.: Prospect as a model of the future in the happiness economy - new normative theory of wellbeing. Published Papers (2010). https://ideas.repec.org/p/rnp/ppaper/che5.html
McKinnon, K., Kennedy, M.: Community economies of wellbeing: How social enterprises contribute to surviving well together. In: Social Enterprise, Health, and Wellbeing: Theory, Methods, and Practice. Taylor and Francis Inc (2021). https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003125976-5
Mengist, W., Soromessa, T., Legese, G.: Method for conducting systematic literature review and meta-analysis for environmental science research. MethodsX. 7 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.100777
Meredith, J.: Theory building through conceptual methods. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manage. 13 (5), 3–11 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1108/01443579310028120
Millward-Hopkins, J., Steinberger, J.K., Rao, N.D., Oswald, Y.: Providing decent living with minimum energy: A global scenario. Glob. Environ. Change. 65 , 102168 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GLOENVCHA.2020.102168
Moher, D., Shamseer, L., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., Shekelle, P., Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 4 (1), 1 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Mongeon, P., Paul-Hus, A.: The journal coverage of web of Science and Scopus: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics. 106 (1), 213–228 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11192-015-1765-5/FIGURES/6
Musa, H.D., Yacob, M.R., Abdullah, A.M., Ishak, M.Y.: Enhancing subjective well-being through strategic urban planning: Development and application of community happiness index. Sustainable Cities Soc. 38 , 184–194 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCS.2017.12.030
Ni, Z., Yang, J., Razzaq, A.: How do natural resources, digitalization, and institutional governance contribute to ecological sustainability through load capacity factors in highly resource-consuming economies? Resour. Policy. 79 , 103068 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RESOURPOL.2022.103068
Nunes, A.R., Lee, K., O’Riordan, T.: The importance of an integrating framework for achieving the sustainable development goals: the example of health and well-being. BMJ Glob Health. 1 (3), e000068 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1136/BMJGH-2016-000068
Ócsai, A.: The future of ecologically conscious business. Palgrave Stud. Sustainable Bus. Association Future Earth. 259–274 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60918-4_7
OECD.: Measuring and assessing well-being in Israel (2016). https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264246034-EN
Oehler-Șincai, I.M.: Well-Being, Quality of Governance, and Employment Policies: International Perspectives. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/07360932.2023.2189078
Orekhov, V.D., Prichina, O.S., Loktionova, Y.N., Yanina, O.N., Gusareva, N.B.: Scientific analysis of the happiness index in regard to the human capital development. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 12 (4 Special Issue), 467–478 (2020). https://doi.org/10.5373/JARDCS/V12SP4/20201512
Oswald, A.J.: Happiness and economic performance. Econ. J. 107 (445), 1815–1831 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1468-0297.1997.TB00085.X
Pillay, D.: Happiness, wellbeing and ecosocialism–a radical humanist perspective. Globalizations. 17 (2), 380–396 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/14747731.2019.1652470
Roy, M.J.: Towards a ‘Wellbeing Economy’: What Can We Learn from Social Enterprise? 269–284. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68295-8_13
Rubio-Mozos, E., García-Muiña, F.E., Fuentes-Moraleda, L.: Rethinking 21st-century businesses: An approach to fourth sector SMEs in their transition to a sustainable model committed to SDGs. Sustain. (Switzerland). 11 (20) (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205569
Santini, Z.I., Koyanagi, A., Tyrovolas, S., Mason, C., Haro, J.M.: The association between social relationships and depression: a systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 175 , 53–65 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAD.2014.12.049
Sangha, K.K., Le Brocque, A., Costanza, R., Cadet-James, Y.: Ecosystems and indigenous well-being: An integrated framework. Global Ecol. Conserv. 4 , 197–206 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GECCO.2015.06.008
Schyns, P.: Crossnational differences in happiness: Economic and cultural factors explored. Soc. Indic. Res. 43 (1–2), 3–26 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006814424293/METRICS
Shrivastava, P., Zsolnai, L.: Wellbeing-oriented organizations: Connecting human flourishing with ecological regeneration. Bus. Ethics Environ. Responsib. 31 (2), 386–397 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1111/beer.12421
Skul’skaya, L.V., Shirokova, T.K.: Is it possible to build an economy of happiness? (On the book by E.E. Rumyantseva Economy of Happiness (INFRA-M, Moscow, 2010) [in Russian]). Studies on Russian Economic Development 2010 21:4 , 21 (4), 455–456. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1075700710040131
Sohn, K.: Considering happiness for economic development: determinants of happiness in Indonesia. SSRN Electronic J. (2010). https://doi.org/10.2139/SSRN.2489785
Spruk, R., Kešeljević, A.: Institutional origins of subjective well-being: estimating the effects of economic freedom on national happiness. J. Happiness Stud. 17 (2), 659–712 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10902-015-9616-X
Su, Y.S., Lien, D., Yao, Y.: Economic growth and happiness in China: a Bayesian multilevel age-period-cohort analysis based on the CGSS data 2005–2015. Int. Rev. Econ. Finance. 77 , 191–205 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IREF.2021.09.018
Stucke, M.E.: Should competition policy promote happiness? Fordham Law Review , 81 (5), 2575–2645. (2013). https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84878026480&partnerID=40&md5=66be6f8cd1fe9df6ca216e7724c928b3
van Niekerk, A.: A conceptual framework for inclusive economics. South. Afr. J. Economic Manage. Sci. 22 (1) (2019). https://doi.org/10.4102/sajems.v22i1.2915
Vicente, M.J.V.: How more equal societies reduce stress, restore sanity and improve everyone’s well-being por Richard Wilkinson y Kate Pickett. Sistema: Revista de Ciencias Sociales, ISSN 0210–0223, No 257, 2020, Págs. 135–140 , 257 , 135–140. (2020). https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=7999261
Wang, Q., Su, M.: The effects of urbanization and industrialization on decoupling economic growth from carbon emission – a case study of China. Sustain Cities Soc. 51 , 101758 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCS.2019.101758
Wiedenhofer, D., Virág, D., Kalt, G., Plank, B., Streeck, J., Pichler, M., Mayer, A., Krausmann, F., Brockway, P., Schaffartzik, A., Fishman, T., Hausknost, D., Leon-Gruchalski, B., Sousa, T., Creutzig, F., Haberl, H.: A systematic review of the evidence on decoupling of GDP, resource use and GHG emissions, part I: Bibliometric and conceptual mapping. Environ. Res. Lett. 15 (6), 063002 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/AB8429
Wolfgramm, R., Spiller, C., Henry, E., Pouwhare, R.: A culturally derived framework of values-driven transformation in Māori economies of well-being (Ngā Hono ōhanga oranga). AlterNative. 16 (1), 18–28 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/1177180119885663
Wu, Y., Zhu, Q., Zhu, B.: Decoupling analysis of world economic growth and CO2 emissions: a study comparing developed and developing countries. J. Clean. Prod. 190 , 94–103 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.139
Zheng, S., Wang, J., Sun, C., Zhang, X., Kahn, M.E.: Air pollution lowers Chinese urbanites’ expressed happiness on social media. Nat. Hum. Behav. 3 (3), 237–243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-018-0521-2
Download references
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Open access funding provided by Università degli Studi di Salerno within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Humanities and Social Sciences, Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur, Malaviya Nagar, J.L.N. Marg, Jaipur, Rajasthan, 302017, India
Shruti Agrawal & Nidhi Sharma
Department of Economics and Finance, Birla Institute of Technology and Science (BITS), Pilani, Rajasthan, India
Karambir Singh Dhayal
Department of Economics and Statistics, University of Salerno, Fisciano, Italy
Luca Esposito
Karelian Institute, University of Eastern Finland, Joensuu, Finland
Erasmus Happiness Economics Research Organisation, Erasmus University, Rotterdam, Netherlands
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Shruti Agrawal: Conceptualization, Material preparation, Data Collection, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing - Original Draft, Review and Editing. Nidhi Sharma: Validation, Project Administration, Supervision, and Writing - Review & Editing. Karambir Singh Dhayal: Validation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing - Review and Editing. Luca Esposito: Validation, Writing - Review and Editing. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Shruti Agrawal and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Luca Esposito .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
This material is the authors’ own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere. The paper is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. The paper reflects the authors’ own research and analysis in a truthful and complete manner.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Agrawal, S., Sharma, N., Dhayal, K.S. et al. From economic wealth to well-being: exploring the importance of happiness economy for sustainable development through systematic literature review. Qual Quant (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-024-01892-z
Download citation
Accepted : 21 April 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-024-01892-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Happiness economy
- Sustainability
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Grayson Murray's parents say the two-time PGA Tour winner died of suicide
Grayson Murray's parents said Sunday their 30-year-old son took his own life, just one day after he withdrew from a PGA Tour event. The family asked for privacy and that people honor Murray by being kind to one another.
“If that becomes his legacy, we could ask for nothing else,” Eric and Terry Murray said in a statement released by the PGA Tour.
Murray, a two-time PGA Tour winner, spoke in January after winning the Sony Open in Honolulu about turning the corner in his life, his golf and battles with alcoholism and mental health. He died Saturday morning.
EDITOR’S NOTE — This story includes a discussion of suicide. If you or someone you know needs help, the national suicide and crisis lifeline in the U.S. is available by calling or texting 988. There is also an online chat at 988lifeline.org .
Murray had to go through the Korn Ferry Tour to get his PGA Tour card back. And then he birdied the last hole at the Sony Open to get into a playoff, and made a 40-foot birdie putt on the first extra hole for an emotional win.
“It's not easy,” Murray said immediately after winning. "I wanted to give up a lot of times. Give up on myself. Give up on the game of golf. Give up on life, at times.”
Murray tied for 43rd last week in the PGA Championship, which enabled him to hold his position among the top 60 to earn a spot in the U.S. Open next month at Pinehurst No. 2 in his native North Carolina.
He shot 68 in the opening round at Colonial. The next round, he was 5 over and coming off three straight bogeys when he withdrew citing an illness.
PGA Tour Commissioner Jay Monahan said he spoke with Murray's parents about halting play at Colonial and they insisted the golf tournament continue.
Monahan flew to Fort Worth, Texas, to be with players. Many of them wore black-and-red pins on their caps Sunday in honor of Murray. Those are the colors of the Carolina Hurricanes, his favorite NHL team.
“We have spent the last 24 hours trying to come to terms with the fact that our son is gone. It’s surreal that we not only have to admit it to ourselves, but that we also have to acknowledge it to the world. It’s a nightmare,” his parents shared in their statement.
"We have so many questions that have no answers. But one. Was Grayson loved? The answer is yes. By us, his brother Cameron, his sister Erica, all of his extended family, by his friends, by his fellow players and — it seems — by many of you who are reading this. He was loved and he will be missed.
“Life wasn't always easy for Grayson, and although he took his own life, we know he rests peacefully now.”
Grayson was a raw talent after taking up golf at age 8. He won his age division three straight years at the prestigious Junior World Championship in San Diego. But he struggled to fit in at college, going to Wake Forest, East Carolina and then Arizona State.
His first coach was Ted Kiegel in North Carolina, who like so many others was devastated.
“Words cannot express the tragedy of this moment,” Kiegel said in a statement sent to The Associated Press. “Grayson came from something that was ordinary and made it EXTRAORDINARY. ... He burned bright for the 30 years he gave us.”
Murray won as a 22-year-old rookie at the Barbasol Championship in Kentucky, and frustration began to set in as he didn't improve as quickly as others whom he routinely beat as amateurs.
He was always open about depression and anxiety, and his bouts with alcohol. One of his darker moments was at the Sony Open in 2021 when he was suspended for an incident in a Hawaii bar. Murray took to social media to say, "Why was I drunk? Because I’m a (expletive) alcoholic that hates everything to do with the PGA Tour life and that’s my scapegoat.”
He also accused the tour of not giving him proper help, which the tour denied.
Monahan said Saturday at Colonial that he called Murray right after that posting and subsequently spent a lot of time with him.
“I think one of the elements of his legacy is his resiliency,” Monahan said. "So you think of going back to 2017, winning the Barbasol Championship, going back and forth between the Korn Ferry Tour and the PGA Tour. ... self-assessing, coming back, becoming in his own eyes a stronger human being, and then winning three times in the past year.
“To me, that’s a level of resiliency that is extraordinary.”
When he won on the Korn Ferry Tour last year, Murray talked about his parents having “been through hell and back basically for the last six years for me fighting some mental stuff.”
“Everyone has their battles,” Murray said a year ago. “Sometimes people are able to hide them and function, and sometimes you're not. I think our society now is getting better about accepting that it's OK to not be OK. I've embraced that mentality. I'm not ashamed that I go through depression and anxiety.”
He also used social media to reach out to others dealing with similar issues in a sport where losing takes place far more than winning.
Murray said in January after he won the Sony Open that he often felt like a failure who had wasted his talent.
“It was a bad place, but like I said, you have to have courage," he said. "You have to have the willingness to keep going. Lo and behold, that’s what I did, and I’m here, and I’m so blessed and I’m thankful.”
He saw that Sony Open victory — which got him into the Masters for the first time — as the start of a new chapter. He said he had become a Christian and was engaged to Christiana Ritchie. He said in January the wedding had been planned for late April.
“My story is not finished. I think it’s just beginning,” Murray said in Hawaii. “I hope I can inspire a lot of people going forward that have their own issues.”
AP golf: https://apnews.com/hub/golf


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Meaning of Happiness. The word "happiness" means various things to various people, and it would be a good idea to explore this topic in your paper. To get some perspectives, you could ask your friends or family members what happiness is to them. Alternatively, browse sample essays on happiness online.
Happiness Essay Thesis Statement. A happiness essay thesis statement is the backbone of an article and a crucial element in your paper. A good thesis statement about happiness should be arguable, specific, and relevant to the topic. It is important for defining the scope of an article and highlighting its focus while also identifying what it ...
Happiness thesis statement linked to time. Happiness is linked to time: it demands stability and continuity. To think that happiness can come to an end is to vitiate the happy moment that we live, with the anguish that it will cease. This temporary character makes it possible to distinguish between happiness and pleasure.
Thesis statement: Finally, you need a thesis statement to narrow down your topic. It is a sentence or two that sums up your opinion on the issue. An example of a good thesis statement about happiness is: "Happy people are more motivated and demonstrate a higher level of productivity. ...
In the thesis statement, you have to express your main idea about the topic of your essay. Of course, the thesis statement will not always remain the same by the end of your essay, so you may need to adjust it when you have finished. ... Nudge: Improving Decisions about Health, Wealth, and Happiness. Penguin Books, 2009. Help with your essay ...
Step 1: Start with a question. You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis, early in the writing process. As soon as you've decided on your essay topic, you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
It will present a thesis statement that happiness is both ephemeral and deeply personal, shaped by individual experiences, values, and perceptions. The piece will explore philosophical and psychological perspectives on happiness, and how it is influenced by internal and external factors. More free essay examples are accessible at PapersOwl ...
Consider the word limit and the guidelines provided by a teacher. Check your essay for grammar and spelling mistakes and edit if necessary. When you choose a topic, write about the things that are close to you. Ask for the opinion of other people about your essay. Ensure all your arguments support the thesis statement.
The thesis statement is the heart of every paper. It is a focused statement that summarizes the main argument and broadcasts the order in which the ideas will be discussed. Thesis statements have three parts: the topic, the claim, and the major points. The claim is your argument, opinion, or stance that will be supported by your evidence and ...
Writing the Thesis Statements. The thesis statement is the core generator of your spaceship. The heart of your paper that breathes life into it. ... Thus, either use happiness as the subject or the object, relating the thesis with happiness on the frontline. Support your thesis statement with some information. Reclassify your data into two groups.
of happiness as one of the inherent rights of its citizens. In many cultures, happiness is glorified as an innate virtue, an intrinsic value of what it means to be a human-being. Indeed, Diener (2000) found that people of every country in the world indicated that happiness was the most important quality of life to attain.
The undersigned recommended acceptance of the thesis "Relationship between Happiness, Life Satisfaction, and Well-Being, and the Impact of Inspirational Quotes" Submitted by Shannara L. Klassen in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree Bachelor of Science, Honours _____ Dr. Sonya Corbin Dwyer ...
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
Affective state theory. To recap, this theory of happiness proposes that happiness is the result of one's overall emotional state. Bradburn (1969) put forward the argument that happiness is made up of two separate components that are quite independent and uncorrelated: positive affect and negative affect.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Happiness is dreaming of being free, waking up and being chainless. Happiness is finding something you never expected to find—and love it. Happiness is a round-way ticket to heaven of smiling faces and friendly crowds. Being loved is happiness. Happiness is a word you can't explain, but your heart does that certain jump that makes you smile ...
An idea of happiness existing "at the end of the chase" is a prevalent one in culture and philosophy, yet other accounts claim it to be an innate right that should be a given. This paper aims to analyze the author's thesis on the subject and evaluate whether he was convincing in delivering his perspective.
To achieve the state of complete happiness one has to practice on improving the state of life by: 1. Staying contended in life with what you have. Cribbing and grumbling never lead to happiness. 2. Staying focused on the current life instead of daydreaming of the good days or old days. 3.
114 • Virtue, Happiness , and Well-Being 2. VIRTUE AND EMOTIONS In this section, we shall consider thesis (l), according to which virtue is constituted by a disposition to experience fitting emotions.3 We shall proceed as follows. First, we shall clarify what we mean by fitting emotions. Second, we shall argue that the
They want to try to make people happy. They want to use others as a way of making themselves happy. Some are okay being single but continue to date. Some stay monogamous and put effort into their relationship, growing. Free Essay: Scientifically, happiness is satisfaction, positive feelings, and a lack negative feelings (Porter 459).
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement. 1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing: An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies ...
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
The pursuit of happiness has been an essential goal of individuals and countries throughout history. In the past few years, researchers and academicians have developed a huge interest in the notion of a 'happiness economy' that aims to prioritize subjective well-being and life satisfaction over traditional economic indicators such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Over the past few years ...
A suburban high school released a statement as it investigates an entry published in its yearbook, which expressed happiness over the Oct. 7 attacks against Israel that sparked an ongoing conflict ...
Grayson Murray's parents said Sunday their 30-year-old son took his own life, just one day after he withdrew from a PGA Tour event. The family asked for privacy and that people honor Murray by ...
Link Copied! Professional golfer Grayson Murray died by suicide, his parents confirmed in a statement released through the PGA Tour . "We have spent the last 24 hours trying to come to terms ...