- Color Palettes
- Superhero Fonts
- Gaming Fonts
- Brand Fonts
- Fonts from Movies
- Similar Fonts
- What’s That Font
- Photoshop Resources
- Slide Templates
- Fast Food Logos
- Superhero logos
- Tech company logos
- Shoe Brand Logos
- Motorcycle Logos
- Grocery Store Logos
- Pharmaceutical Logos
- Beer Brand Ads
- Car Brand Ads
- Fashion Brand Ads
- Fast Food Brand Ads
- Shoe Brand Ads
- Tech Company Ads
- Motion graphics
- Infographics
- Design Roles
- Tools and apps
- CSS & HTML
- Program interfaces
- Drawing tutorials


PX to PT Converter

The Amgen Logo History, Colors, Font,

PX to MM Converter

The Novartis Logo History, Colors, Font,
Design Your Way is a brand owned by SBC Design Net SRL Str. Caminului 30, Bl D3, Sc A Bucharest, Romania Registration number RO32743054 But you’ll also find us on Blvd. Ion Mihalache 15-17 at Mindspace Victoriei
Academic Appeal: The 11 Best Fonts for Academic Papers
- BY Bogdan Sandu
- 26 February 2024

Imagine settling into the rhythm of crafting your academic magnum opus—the words flow, ideas chime, yet it all hinges on how your prose meets the reader’s eye. You’re well aware that the best fonts for academic papers don’t just whisper to the intellect; they shout to the discerning critic in each evaluator. Here unfolds a narrative, not merely of typography but your academic saga’s silent ambassador.
In forging this guide, I’ve honed focus on one pivotal, often underestimated player in the academic arena: font selection .
Navigate through this roadmap and emerge with a treasure trove of legible typefaces and format tips that ensure your paper stands hallmark to clarity and professionalism.
Absorb insights—from the revered Times New Roman to the understated elegance of Arial —paired with indispensable formatting nuggets that transcend mere compliance with university guidelines .
Dive deep, and by article’s end, unlock a dossier of sage advice, setting your documents a class apart in the scrutinous world of academic scrutiny. Here’s to typography serving not just as a vessel but as your ally in the scholarly discourse.
The Best Fonts for Academic Papers
| Serif | High | Formal papers, journals | Standard and widely accepted | |
| Sans-serif | High | Presentations, less formal | Clean and modern appearance | |
| Sans-serif | High | General academic work | Default in Microsoft Word, well-balanced | |
| Sans-serif | High | Professional papers | Classic and neutral, can be less formal | |
| Serif | Moderate | Long texts, books | Old-style, gives a classic look | |
| Serif | High | Humanities papers | Elegant and easy-to-read | |
| Serif | Moderate | Formal and traditional works | Professional and authoritative | |
| Serif | High | Academic journals | Traditional and long-lasting readability | |
| Serif | High | Online and printed text | Specifically designed for screen readability | |
| Serif | High | Electronic and printed papers | Designed for on-screen readability and output |
Traditional Choices and Their Limitations
Times new roman : ubiquity and readability vs. overuse.

The Pittsburgh Penguins Logo History, Colors, Font, And Meaning
The dallas stars logo history, colors, font, and meaning.

You may also like

Ad Impact: The 19 Best Fonts for Advertising
- Bogdan Sandu
- 20 December 2023

T-Shirt Typography: 30 Best Fonts for T-Shirts
- 21 December 2023
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
What is the standard/recommended font to use in papers?
I looked around but did not find that anyone has asked this before, but what are the fonts that are standard/recommended while writing academic reports/papers?
- publications
- 19 No need to search for the perfect font. You just download the latex/word template that the journal / conference provides and you stick to it. – Alexandros Commented Aug 7, 2014 at 10:12
- 3 In my case there isn't a template, that is the problem. – Man Commented Aug 7, 2014 at 10:12
- 1 @O.R.Mapper yes very true, although I assume if the OP was looking for the standard font of every language in the world for academic publishing, we could close it as "too broad" – user-2147482637 Commented Aug 7, 2014 at 15:35
- 10 People stick with the Computer Modern default in LaTeX so much that I once had someone tell me a paper where I intentionally chose a different serif font "looked unprofessional." – Matt Reece Commented Aug 7, 2014 at 17:32
- 3 Please do not be "that person" who has the only paper in the journal or proceedings with a different font from the others. – Max Commented Aug 8, 2014 at 8:42
4 Answers 4
If there's no template, then the choice is yours. However, you should make sure to pick a font that's easy to read. The usual standards in academia tend to be the Times, Helvetica/Arial, and Computer Modern families. This doesn't restrict you from using fonts like Book Antiqua, Myriad Pro, Goudy Old Style, or Garamond, but they're definitely not standard.
- 9 As to Helvetica/Arial: I think conventional wisdom is that serif fonts are preferred for large bodies of text, while sans serif should be reserved for short chunks like labels, headings, etc. I've certainly never seen a published paper set entirely in Helvetica. Then again, in my field everyone uses LaTeX, so unless you make a special effort, everything comes out in Computer Modern. – Nate Eldredge Commented Aug 7, 2014 at 15:52
- @NateEldredge: You are correct that serif fonts are easier to handle in large doses, but Helvetica is the "default" font for most "official" documents and reports throughout most of Europe. And this extends to preprints when not done in LaTeX. – aeismail Commented Aug 7, 2014 at 15:56
- 14 Eurghhhhhhhhhhh. – Nate Eldredge Commented Aug 7, 2014 at 16:14
- @NateEldredge: This is not undisputed. @ aeismail: It’s rather Arial due that popular operating system (which does not make this any better; not because of serif vs. sans-serif, but because I do not want to see that font anymore to the extent that I tweaked my browser to auto-replace any resembling fonts). – Wrzlprmft ♦ Commented Aug 8, 2014 at 8:35
- @Wrzlprmft: True, it is normally Arial that is specified; fortunately the differences are small enough that I use Helvetica and no one complains. (And actually I'm starting to see more references to Helvetica nowadays.) – aeismail Commented Aug 8, 2014 at 12:00
For an academic paper each publisher journal have their standards. These do not affect or are affected by the manuscripts sent in to the journal. Some journals specify fonts, commonly standard Times Roman, for their manuscripts. If the journal specifies something, follow that specification. Otherwise use a font that is easy to read. There is no need to use anything but a standard font for whatever typesetting/word processor system.
There isn't any.
Focus on the content, write using your favorite writing software's default font, and let the journal's typesetting staff worry about the looks of the published version.
For the subset of journals that do not take care of typesetting, first make sure they are legitimate, then use the template they provide.
If no template is provided discuss with your supervisor and colleagues whether the journal is really worth your time, if it is then use your favorite software's default font.
As others have mentioned, the standard font varies, but is usually a serif font such as Times New Roman, although sans serif fonts such as Arial and Helvetica seem to be gaining traction as well. Their is major disagreement over which is easier to read--serif or sans serif fonts, with no clear consensus on the outcome. For example, see this paper .
Font size is typically twelve point. Follow the guidelines on this one, and make sure to keep your font consistent. Nothing is more likely to get you minus points than some obvious monkeying with the font size, whether to lengthen your manuscript (most commonly seen in undergrad papers) or to fit your text into the page limit (the rest of us!).
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged publications writing formatting ., hot network questions.
- Paris Taxi with children seats (from and to airport)
- What would cause desoldering braid to simply not work?
- How to tell if the item language is the fallback language or the regular language version
- What is 得な性格? How is it used in this sentence?
- How to repair a "pull" shut-off valve for the toilet?
- What is the meaning of "Attempt any air"?
- Securing HTTP File Transfer over local network
- Chain slipping when under pressure
- How to find gaps in mathematics/theoretical physics/mathematical physics ? How to proceed after you found them?
- What is the explicit list of the situations that require RAII?
- NaN is not equal to NaN
- Episode of a sci-fi series about a salesman who loses the ability to understand English
- Why a battery has a limit usage of current in amps?
- Wishart matrices: are eigenvalues and eigenvectors independent?
- Sink vs Basin distinction
- Adding shadows to spiric sections of a torus
- Would a PhD from Europe, Canada, Australia, or New Zealand be accepted in the US?
- Definition of the subcategory in book "Category Theory for Computing Science"
- How does a vehicle's brake affect the friction between the vehicle and ground?
- Numerical approximation of the integral by using data
- Old science fiction short story about a lawyer attempting to patent a new kind of incredibly strong cloth
- Implement Huffman code in C17
- if people are bred like dogs, what can be achieved?
- Creating a command to display blackboard font

5 fonts that add credibility and professionalism to scientific research
by ikumikayama | Apr 29, 2013 | Uncategorized | 14 comments

Choosing the right fonts can affect how your scientific research is received.
Note: This is part 2 of a 2-part blog series about choices in fonts. You can read part 1 here .
You are dressed in your best. You edited the manuscript with a fine-tooth comb…but are your figures and images wearing flip-flops?
Last time we talked about fonts that suck professionalism out of your scientific research . In this article, we’ll talk about fonts that actually add credibility and professionalism to your research. Dress your research in a custom-tailored suit by just using these fonts!
My friend and colleague, Cassio Lynm described how a good figure should be like a billboard found in many highways around the country. Anyone who sees the billboard will understand what they are advertising in a split second. If someone is confused or gets the wrong idea, the image is not very successful.
Similarly, the best professional fonts should be one that’s easy to read with very little “bells and whistles”. When writing prose of informational value such as scientific research, a reader should pay attention to what the text is describing, not how the text looks. A good professional font should be like air–we don’t really even pay attention to it most of the time.
Some of the fonts I’ll share with you today are considered “boring” and “overused” by some. These fonts are everywhere because they are champions of legibility and simplicity. Make your work professional and trustworthy by using a time-tested font.
[bra_divider height=’40’]
1. Arial- “All-Around Champion with IBM Roots”

According to fonts.com , Arial is one of the most used typefaces of the last 30 years. Its electronic origins go back to 1982 for IBM laser-xerographic printers by designers Robin Nicholas and Patricia Saunders. When it came out, it was supposed to compete with Helvetica, which was one of the core fonts in Apple Computers in the mid 1980’s.
Arial letters have more round shapes and the edges of letters do not end in a horizontal line. Instead, the edges are at an angle.
Arial is an easy-to-read font in small and large blocks of text. Nature requests that the figure text be in Arial or Helvetica. It’s especially nice for figure labels and legends. When using Arial as figure legends, keep the font size small ~8 points for best results.
2. Helvetica- “All-Around Champion with Apple Roots”

Helvetica is the most heavily-used font. Helvetica was originally designed by a Swiss designer named Max Miedinger in 1957. The font was designed to be an easy-to-read font. The name “Helvetica” comes from “Helvetia” – Latin name for Switzerland. Actually, the font received a facelift in 1983-the newer version is called, you guessed it, Neue Helvetica.
Helvetica even has its own movie . I haven’t seen it yet, but please comment in the section below if you have.
Besides its Hollywood (Indie) status, Helvetica is a font that looks great on both print and on screen. Nature , Science , and Cell request that their figure labels be in Helvetica. (If you need assistance setting up figures, I’m here to help). It looks great small as in figure labels, and it looks pretty good in large formats as posters. I lost count of how many figures I labeled using Helvetica, since that’s what one of the publishers used for their books.
3. Baskerville- “Tends to have positive influence on readers”

Baskerville’s history goes all the way back to 1757 when John Baskerville designed a typeface that works well in print and easy to read. Mr. Baskerville preferred his letters simple and refined. He was also a writing master, so he had some ornamental letters like the upper case Q.
There was an informal study (not official, but some experiments here and there) that showed using Baskerville font increased trustworthiness of the text compared to other fonts. In the same study, Comic Sans had the most negative influence on the readers.
Baskerville is a serif font, which means that there are “tails” at the edge of the letters. Generally, serif fonts are better suited for print. This font works best when used in long blocks of text. Try to keep this font between 8 and 14pts for best results. This font looks dignified, so use this for your important professional occasions-award ceremonies, recognitions, etc.
4. Caslon- “When in doubt, use Caslon”

Caslon is another font with a long history. William Cason I designed the typeface back in the early 1700’s. This font is considered as the first original typeface from England. This font was very popular in colonial America, and it was used for many historical documents including the US Declaration of Independence.
Caslon is a serif font (with tails), and is best used in blocks of text. Like Baskerville, try to keep this font between 8 and 14 points for best results. Using this in a report or an application would be a good places.
5. Garamond – “Second best font after Helvetica”

This font’s history also goes way back. The font was designed by Claude Garamond (or Jean Jannon), who was commissioned to make a typeface for King Francis I of France (1515-47) to be used in series of books. The modern, electric version was revived in 1989 by Robert Slimbach.
Because there are different sources available for Garamond, there are numbers of different variations of the font. Adobe Garamond is the most popular and widely-available version today.
Garamond is still used extensively by French publishers. They also insist that Garamond be printed in size 9. Some of the most famous publications in France are in Garamond such as Histoire de l’édition français. The publishers prefer this font “for its beauty, its richness and its legibility” combined with “an uncluttered graphic style that underscores the rigour of essays and analysis providing a radical critique of contemporary society”.
Garamond is a great font to be used in long proses such as textbooks, dissertations and theses. Keeping it at 9 point is optional. In fact, my master’s thesis was in Garamond.
So that’s the 5 fonts that add credibility and professionalism to your scientific research. Did you find your favorite fonts here? Do you have other favorites? Please share your thoughts in the comment section. Also, please feel free to send this article along to those who might benefit from this short article.
[bra_border_divider top=’10’ bottom=’10’]
Now that you know about great scientific fonts, learn more about: PowerPoint Tips for the Scientist

Sources and Further reading:
Arial vs Helvetica – fonts.com
Research on font trustworthiness: Baskerville vs. Comic Sans
Caslon typeface
History of Garamond
Cell Press Figure Guide
Nature -Guide to preparing final artwork
Science Magazine: Preparing your manuscript
14 Comments
I’d rather like to know which font was used to write that article – it’s simple and readable, better than all presented above.
And the font being used for that article is Helvetica, which is one of the fonts mentioned above 😀
Hi Ewa! Great point. The font used is called “Open Sans” by Steve Matteson. For my blog, I made the font color dark grey to make it easier on the eyes, and also made them slightly bigger than average for easier reading. Hope this helps!
Hollo there, i liked the article but none of this fonts looks like the one used in the papers i read, (Journals of the American Chemical Society), do you know which one they use?
Hi There! Thank you for the note! ACS suggests Arial and Helvetica for their journal figures, so that’s what I introduced in this article–for the text, they might very well have their own custom font they use for their publications. I’ll dig into this a little deeper–thank you again!
I’m sorry, but this article is full of misinformation. Part 1 is a reiteration of articles that have been around for years. Absolutely nothing new there, and honestly, is there anyone even considering the typefaces you name there for scientific articles? Is it conceivable that anyone would use Curlz for his essay?
But my real concern goes to the second part. Arial and Helvetica are absolutely not scientific typefaces. The notion that ACS suggests these typefaces doesn’t make them suitable for scientific works. I think you ought to do research as to WHY these typefaces came recommended. Helvetica has history, as it won out of contemporaries like Univers as Helvetica was very heavily marketed. As a side note, Helvetica is actually based on the Akzidenz Grotesk model. Arial was designed to have the same metrics as Helvetica so it could be used on the same printers without having to pay a license fee to use Helvetica. Arial is more legible while Helvetica is more neutral and clear, but neither is particularly great.
So I would say Helvetica and Arial haven’t been chosen because they’re perfect. They’ve been chosen because they’re popular, and Arial is on every Windows computer, so people don’t have to purchase any fonts. I would say neither Arial and Helvetica are known to be particularly good to read. I suspect typefaces like Proxima Nova and Avenir will fair better. To be clear, I don’t think Arial or Helvetica are bad choices for labels and such, but to suggest them as top 5 typefaces, that’s very clearly misinformation.
“When using Arial as figure legends, keep the font size small ~8 points for best results.” For best results? Not entirely. It’s probably a good estimate, but in actuality the pt size should depend on the layout. I would recommend always making a test print to see if the text looks good in print, if that’s what it is intended for. Sometimes 0.2pts more or less could make the difference.
“Helvetica is the most heavily-used font.” I don’t think so. First off, Helvetica is not a font. It’s a typeface. Helvetica Regular would be a font. Helvetica is the most heavily-used typeface in graphic design, and likely the most heavily-used sans typeface. It’s not the most heavily-used typeface. At least, I would be very surprised if it was. I suspect Times New Roman is the most heavily-used.
“The font was designed to be an easy-to-read font.” No, Helvetica was designed to steal the popularity of Akzidenz Grotesk away.
Also, follow this link to see some of the problems of Helvetica at small sizes, and what professionals in the field have to say about it: http://spiekermann.com/en/helvetica-sucks/
“Actually, the font received a facelift in 1983-the newer version is called, you guessed it, Neue Helvetica.” Who would guess that the prefix for the new Helvetica would be German though? Small detail… Anyway, if you like Helvetica but want a more professional typeface (because really, Max Miedinger was not a type designer and as far as I’m concerned that shows), I can recommend Neue Haas Grotesk (a typeface that is true to the original Helvetica, but improved) or Neue Haas Unica (a more fresh looking Helvetica that deviates from the original).
“Helvetica even has its own movie. I haven’t seen it yet, but please comment in the section below if you have.” I have seen it a few times now. It’s quite a pleasure to watch, but there’s a lot of propaganda involved as well. You have the likes of Massimo Vignelli drooling over how great Helvetica is. The man was a pretty great graphic designer (although insisting on always using Helvetica has little to do with graphic design, as one ought to select the perfect typeface for the job, not use one typeface for every job), but he had no insight in type design. On the other hand, you have Erik Spiekermann formulate perfectly what Helvetica stands for. I would say for a type designer the Helvetica documentary is quite pleasant to watch. For the layman I’m afraid the documentary amounts to propaganda. It gives the layman the feeling this is one of the best typefaces out there and it’s simply not, by far.
“Besides its Hollywood (Indie) status, Helvetica is a font that looks great on both print and on screen.” Absolutely not! On Windows computers, websites set in Helvetica tend to look horrendous. The problem is that Helvetica is not well hinted, and so rendering problems occur. Helvetica was obviously not designed for monitors. Neue Helvetica doesn’t have the rendering problem to the same extent I believe, but relatively few people have Neue Helvetica, so it wouldn’t be wise to use that on your website, unless you embed the fonts. For websites I highly recommend using Arial rather than Helvetica.
“Baskerville’s history goes all the way back to 1757 when John Baskerville designed a typeface that works well in print and easy to read.” Easy to read? Not particularly, though it’s not bad either. Baskerville is a transitional typeface, meaning the weight modulation is vertical and the contrast is high. This is the tradition of the Baroque, but it’s not the most pleasant to read. However, Baskerville does look quite academic. For typefaces that are more pleasant to read, I would look at the Garalde style. Garamond and Caslon belong to that classification. They have a diagonal weight modulation, which naturally leads the eyes to the next letters. Typefaces with vertical weight modulation and high contrast tend to feature a fence effect, which disturbs the reading experience. To see this effect well, look at Didone typefaces like Didot and Bodoni.
“This font works best when used in long blocks of text. Try to keep this font between 8 and 14pts for best results.” 14pt seems quite large. Try 9–12pt. This goes for any serif typeface to be used for body text that is intended for print (for the web try 10–14pt, also depending on which device it’s intended for). But again, it will depend on the layout, and always make test prints to make sure it’s pleasant to read.
“Garamond is a great font to be used in long proses such as textbooks, dissertations and theses. Keeping it at 9 point is optional. In fact, my master’s thesis was in Garamond.” I distinctly remember years ago I noticed my Harry Potter book was set in Garamond. Both Garamond and Caslon are still used extensively for books.
However, Garamond may be a bit much for scientific documents. It’s quite classical and it has a low x-height, which these days is not preferable. Caslon is a bit less expressive and has a taller x-height. I would say Caslon is probably better for scientific articles.
One group of typefaces that certainly seems to be missing here is Century. Typefaces like Century Roman and Century Schoolbook. They belong to the Clarendon classification and are reminiscent of typefaces like Baskerville. These typefaces have been popular since the late 19th century and are still used extensively in academic literature. But I suppose you should also make a consideration of whether your article should be about the most comfortable typefaces to read, or the best suitable for scientific work, because they most certainly don’t amount to the same thing, yet you seem to be equating the two in this article.
Hi Martin! Thank you so much for your in-depth note! I have to look over and digest all your excellent points. Would you be open to expanding your writing and be a guest author or send me a link to your website/blog so the readers can have more information about what types to use for their work?
THE quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog!!!!!
Leelawadee is a bit underrated. It is easy on the eyes, and simple. It could use a bit of a TimesNewRoman-punch to it, though.
Where can I download Helvetica from? I couldn’t find it anywhere
Seriously? I don’t know what this smug guy does with typography, in which he seems to be well versed, but if he were to take up writing he would need to work on his grammar.
I’m not an expert on fonts, but I’m currently using Helvetica for headlines and other Sans text in my thesis and DejaVu for the main text. Feels pretty scientific to me 🙂
I enjoyed the historical aspect of this article. Thanks! PS. I see you use a sans serif font.
How i download these font types?

A variety of fonts are permitted in APA Style papers. Font options include the following:
- sans serif fonts such as 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, or 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode
- serif fonts such as 12-point Times New Roman, 11-point Georgia, or normal (10-point) Computer Modern (the default font for LaTeX)
We recommend these fonts because they are legible and widely available and because they include special characters such as math symbols and Greek letters. Historically, sans serif fonts have been preferred for online works and serif fonts for print works; however, modern screen resolutions can typically accommodate either type of font, and people who use assistive technologies can adjust font settings to their preferences. For more on how font relates to accessibility, visit the page on the accessibility of APA Style .
Use the same font throughout your paper, with the following exceptions:
- figures: Within figure images, use a sans serif font with a type size between 8 and 14 points.
- computer code: To present computer code, use a monospace font such as 10-point Lucida Console or 10-point Courier New.
- footnotes: When inserting footnotes with the footnotes function of your word-processing program, use the default font settings. The footnote font might be smaller than the text font (and have different line spacing), and it is not necessary to change it.
Instructors and publishers vary in how they specify length requirements. Different fonts take up different amounts of space on the page; thus, we recommend using word count rather than page count to gauge paper length if possible.
Font is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 2.19 and the Concise Guide Section 1.18
Related handout
- Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3MB)
From the APA Style blog

APA Style student papers webinar
A new APA Style webinar, “A Step-by-Step Guide for APA Style Student Papers,” taking place on September 10, 2020, will provide detailed guidance on creating, formatting, and organizing APA Style student papers.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
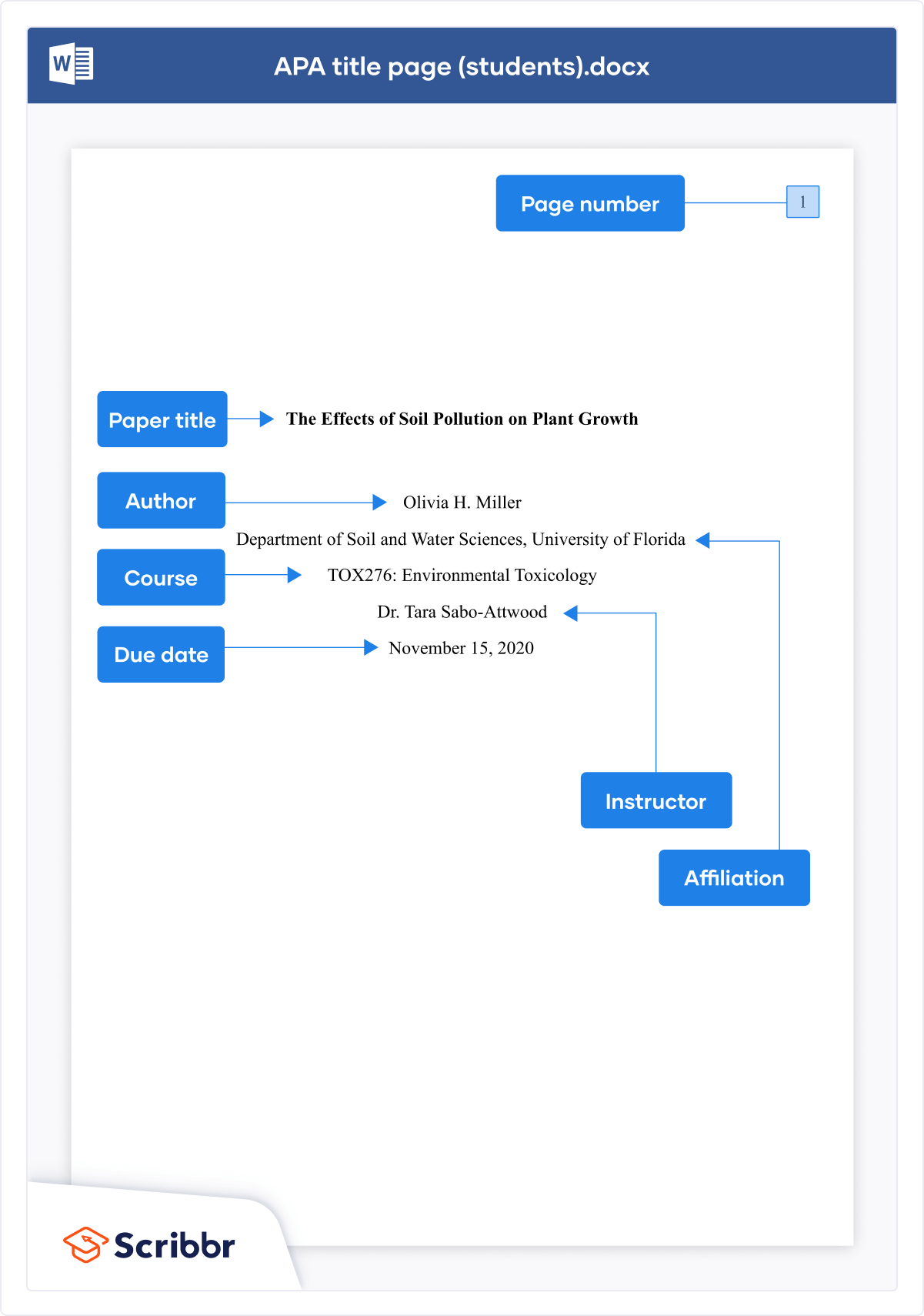
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
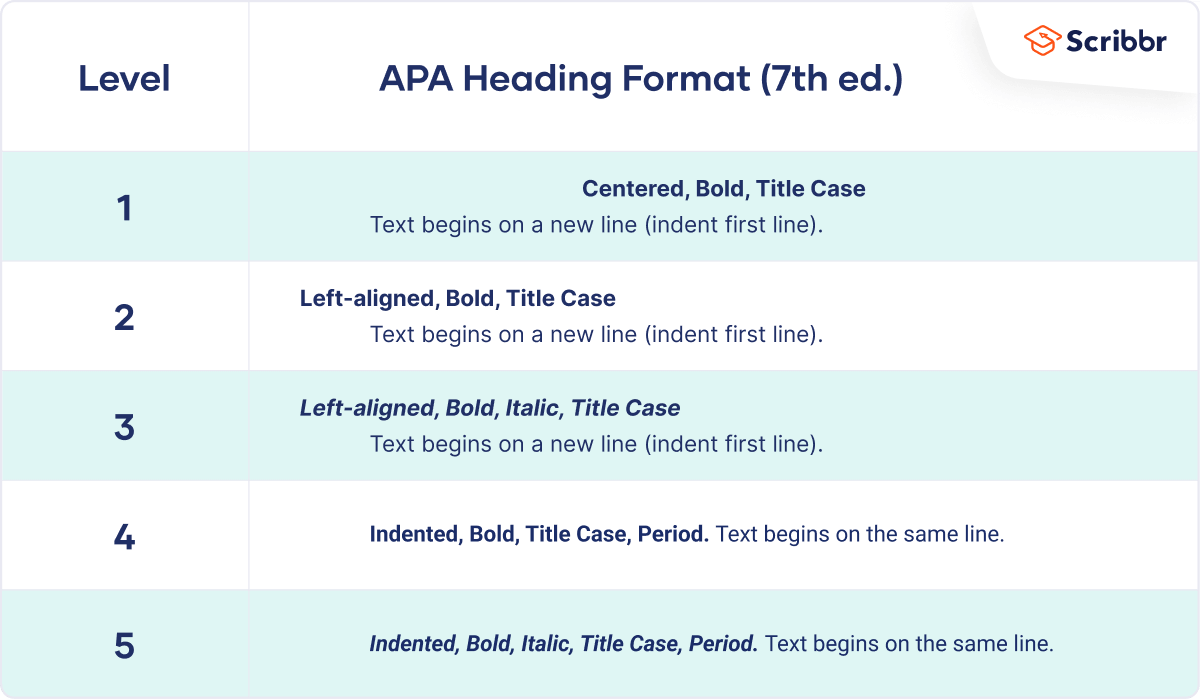
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
| Level of Information | Text Example |
|---|---|
| Level 1 | |
| Level 2 | |
| Level 3 | |
| Level 4 | |
| Level 5 |
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
| Level of Information | Text Example |
|---|---|
| Level 1 | |
| Level 1 | |
| Level 1 | |
| Level 1 |
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

Best Research Paper Font and Size: Best Styles for an Essay

The Best Word Font in Research Paper
As you edit and polish your research paper, you should know the suitable font when formatting. Many students struggle to locate suitable fonts that are appropriate for academia. Thankfully, most of the writing styles such as APA or MLA end this frustration by indicating the right fonts to use in your work.
Many instructors indicate the type of fonts students should use in their assignments. That is because some fonts are large hence prompting one to use more pages than indicated in the instructions section.

People Also Read: Can Dissertation be a Case Study: Research Example and Format
Best Font for Research Paper
The choice of fonts can affect your academic writing work. The right font should make your work remain credible and professional. Dressing your work with the right fonts is procuring a suitable image.
Ideally, the best font for a research paper is the Times New Roman as it is clear and most requested by university and college faculties. Other common ones are the Arial and Calibri fonts, which are preferred because of their large size compared with New Times Roman.

Some fonts can be attractive but hard to read because they have several curls and curves.
When handling research work, use the correct font which has enough allowance between letters to avoid overcrowding.
The professional fonts should be easy to read. The good news for you is that Times New Roman is a popular choice for academic documents.
It is the safest option because most examiners are comfortable with it. Notably, New Times Roman has sound APA support.
People Also Read: Can a Research Paper be Opinionated: Persuasive or Personal
Best Font Size for Research Paper
The best font size for a research paper is point 12. This size is the most common ones, especially for New Times Roman, Arial or Calibri fonts. Basically, the size of the fonts should make your work to be readable without straining the audience. We measure size using ‘points’.
Most academic research papers use MLA, APA, and Harvard references and formats.
The point is a percentage of the screen that the font is occupying. For academic papers, the recommended size is 12 points. It is the most comfortable size for the audience without looking oversized or bulky.

The font size plays a critical role in making your research work impressive and appealing.
The writer should use the official font size when submitting the project.
This size is key when you want to determine the number of pages that your project should carry.
We use font 12 to calculate and know the number of pages the entire work will have to avoid going beyond or under the given guideline.
If you use a different font size, you may exceed or hit below the word count leading to disqualification or any other penalty as the lecturer may decide.
Commonly Used Fonts for Academic Work
Different writing styles recommend certain fonts for students to use while tackling academic work. Some of them are as follows:
Times New Roman
Times New Roman has an authoritative look and feel. It became into practice in 1932 to enhance the legibility and economy of space. This Times New Roman has a narrow printing point that is easily readable.
Arial has been the most used font for the past thirty years. One of the characteristics of Arial fonts is that they have rounded faces. Furthermore, the edges of the letters do not manifest in the horizontal line. Instead, these edges are at an angle.
Besides, this font is easy to read whether used in both large and small blocks. It is a perfect format that one can use in academic work.
Calibri is a humanist font with variable strokes and designs. It is a pretty-looking font suitable for large displays such as presentations.
People Also Read : Research Paper Due Tomorrow: Not started, we Write in hours
Factors Determining the Font and Size for Academic Writing
1. teachers instructions.

When you receive your essay assignment, peruse through and find the preferred font type and size. Some professors are comfortable with particular fonts.
The professor will indicate the preferred font for your work. You can begin by writing and polishing your work with your font and size and later format it according to instructions.
Most academic papers target certain pages of the assignments.
For example, when the instructions demand that you use Times New Roman, you should stick to that for you to produce the right number of pages as guided by the instructions.
Teachers know that when you use a particular font and size for your research, you will produce the correct quantity after researching.
2. Your Eye Ability
One will feel comfortable when using certain fonts than others. Reading and writing while you are straining your eyes to see your work can be disastrous. The cool thing is you can settle for the fonts that can make your eye enjoy beholding your work.
Several fonts exist to use for your work without straining your eyes. However, you should ensure that you settle for the right font when formatting your final documents.
For example, some fonts have curls or curves that make affect the readability of your work. Such can make your professor respond unkindly.
If the professor did not offer guidance to you, then you can use the correct font according to the writing styles recommendations.
3. Teacher’s Font Preference and Eye Abilities
A teacher may instruct that you use certain fonts when submitting your project work. More importantly, even if it is not your favorite font to use, you should stick to the instructions and complete your work as guided.
We have varying eye abilities. Some are comfortable and safe to use a particular font like Arial because they do not strain the eyes while using it. Some fonts are not friendly to some people when working, making your entire writing experience to be hostile.
If you can work well with 12 point font size, well and good. In case the lecturer wants point size 10, use a comfortable font during your writing and editing process then change it to the recommended size before submitting.
4. Type of the Academic work, Essays vs Graphics
The type of academic work dictates the type of font to use for effective delivery. If you are writing an essay, you should use the recommended fonts and sizes as per the writing styles. These styles are MLA, APA, and so on.
You should not use any font which is not official to any writing style. If unsure, it is sensible to consult your instructor and remain on the correct track.
On the other hand, you should also use the correct font when you are working with graphics in your academic projects.
Just like essays, the graphics also have official fonts that students should use when designing and captioning them. Sticking to the rules makes your work hold a professional appeal.
Graphics are the perfect ways of presenting information to make readers create the right perceptions at a glance. Luckily, you should caption them with the recommended fonts and sizes for better delivery.
5. Personal Preference
What appeals to one writer differs from what makes a different writer excited and comfortable. What does that mean? Different writers have varying impressions about what fonts and sizes work for them.
If the instructions for your projects are open to allow you to use multiple fonts from the given list, you should settle for your favorite from the list.
That implies that the instructor may be marking papers that will come with varying font types according to the writer’s preference from the given list of options.
6. Readability

There is no secret in this. Some fonts are more readable than others.
For example, when you are using Times New Roman as your favorite font, it will consume less space but score high on legibility.
Remember, a readable document is an attractive document. Do not compromise on this. Use the right font that is legible and easy to read.
Based on the recommended fonts for particular styles, choose the one that looks more attractive.
Check out our tips on how to name a research paper for more guidance on how to prepare your paper before submitting it. This may improve the clarity of your file and promote grading.

When not handling complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Is a Person a Primary Source
Is a Person a Primary or Secondary Source of Research?

essay research paper differences
Is an Essay a Research Paper: The Differences from Each

Write Annotated Bibliography
Write Annotated Bibliography for Me: Best Writers to Hire
Foreign Imitation
Handwriting, scientific fonts, permalink to these settings, good times by raymond larabie, pricedown by raymond larabie, ethnocentric +1 by raymond larabie, sofachrome +1 by raymond larabie, neuropolitical by raymond larabie, steelfish +6 by raymond larabie, nasalization by raymond larabie, libel suit by raymond larabie, kenyan coffee +3 by raymond larabie, pirulen by raymond larabie.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Published on November 19, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 20, 2023.
The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you’re following. In addition to citations , APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the reference page.
Scribbr offers free Microsoft Word templates for the most common formats. Simply download and get started on your paper.
APA | MLA | Chicago author-date | Chicago notes & bibliography
- Generate an automatic table of contents
- Generate a list of tables and figures
- Ensure consistent paragraph formatting
- Insert page numbering
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting an apa paper, formatting an mla paper, formatting a chicago paper, frequently asked questions about research paper formatting.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial.
- Set 1 inch page margins.
- Apply double line spacing.
- If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page.
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Watch the video below for a quick guide to setting up the format in Google Docs.
The image below shows how to format an APA Style title page for a student paper.
Running head
If you are submitting a paper for publication, APA requires you to include a running head on each page. The image below shows you how this should be formatted.
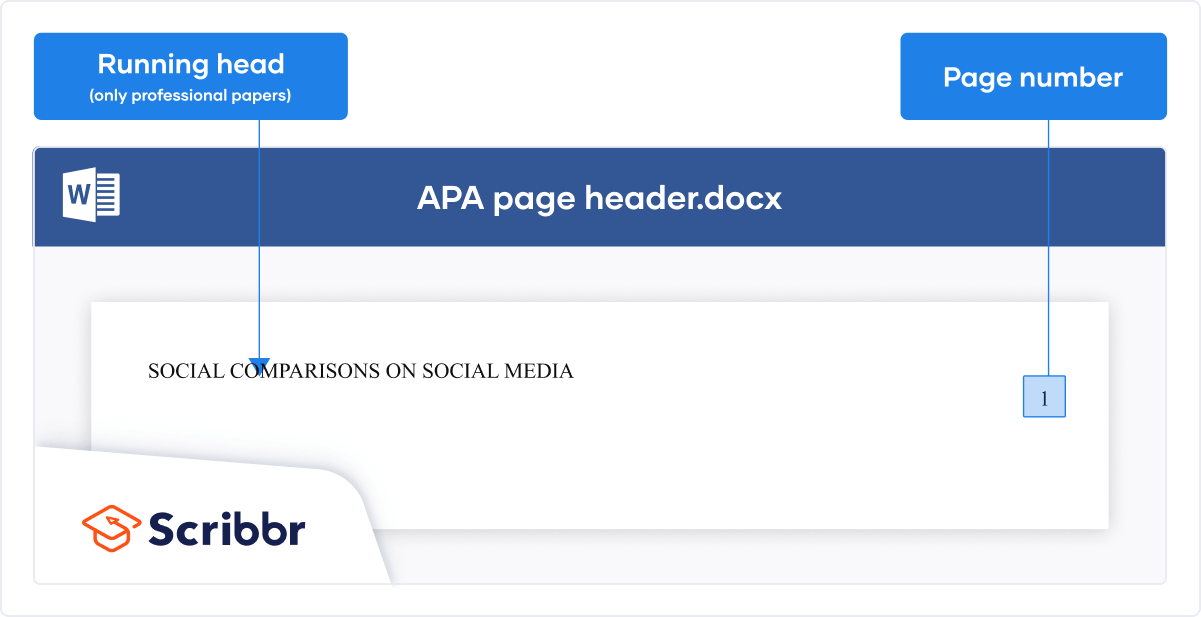
For student papers, no running head is required unless you have been instructed to include one.
APA provides guidelines for formatting up to five levels of heading within your paper. Level 1 headings are the most general, level 5 the most specific.
Reference page
APA Style citation requires (author-date) APA in-text citations throughout the text and an APA Style reference page at the end. The image below shows how the reference page should be formatted.
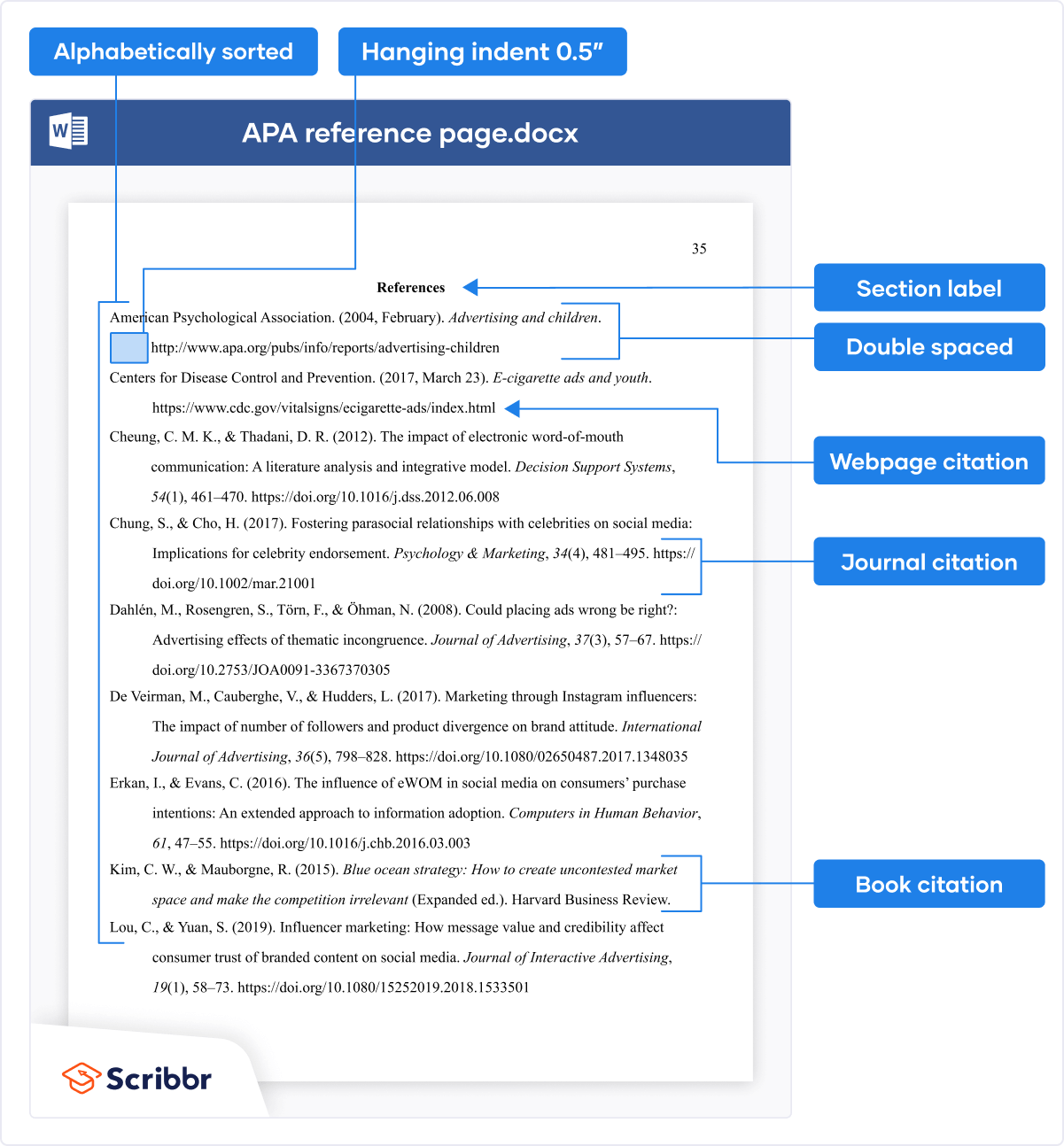
Note that the format of reference entries is different depending on the source type. You can easily create your citations and reference list using the free APA Citation Generator.
Generate APA citations for free
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The main guidelines for writing an MLA style paper are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use title case capitalization for headings .
Check out the video below to see how to set up the format in Google Docs.
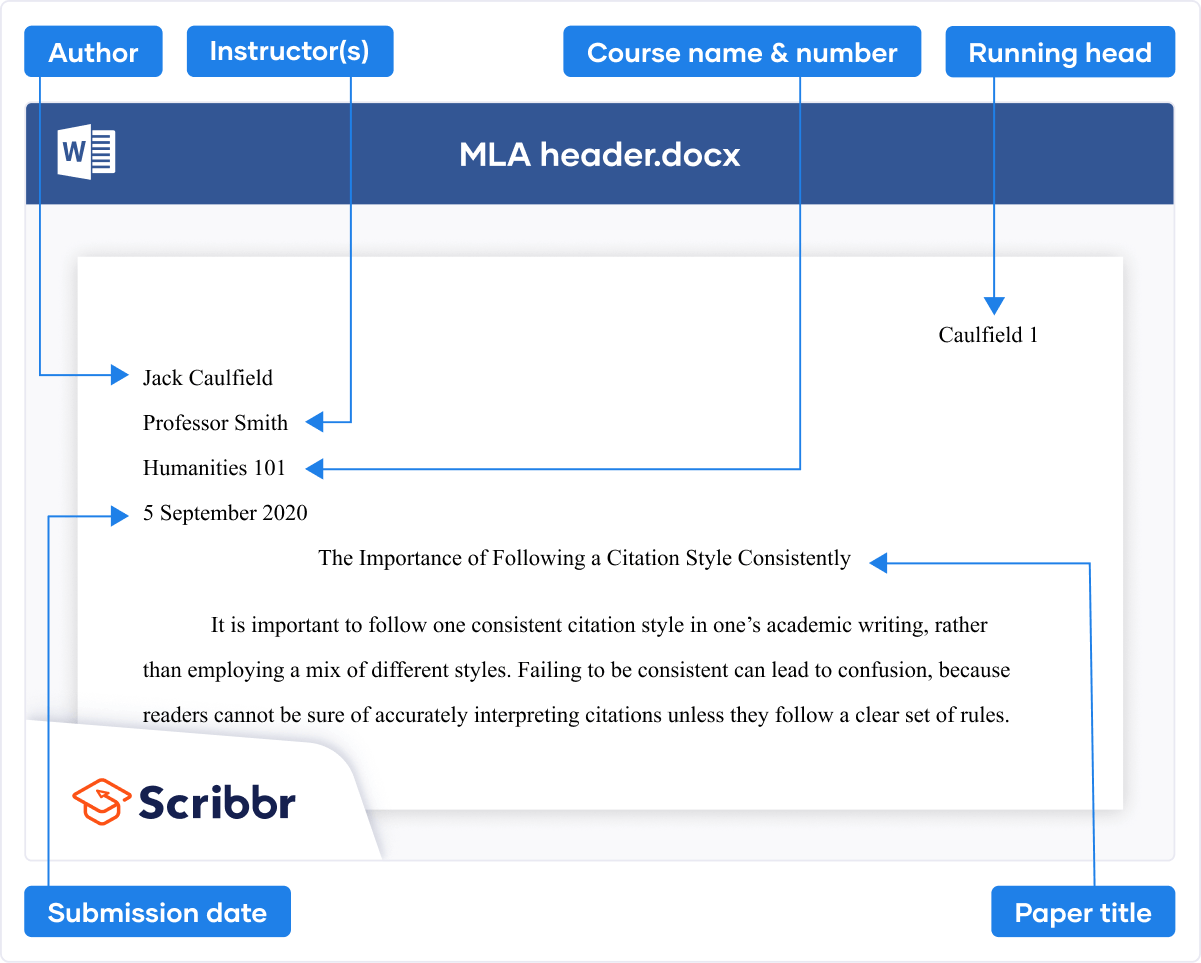
On the first page of an MLA paper, a heading appears above your title, featuring some key information:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s or supervisor’s name
- The course name or number
- The due date of the assignment
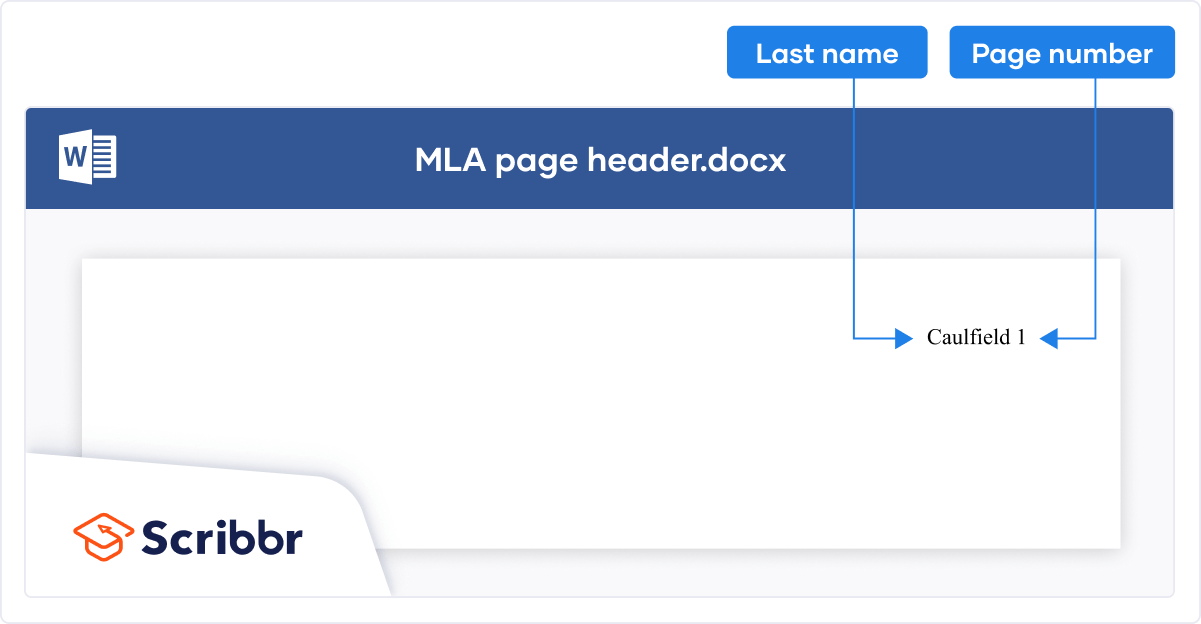
Page header
A header appears at the top of each page in your paper, including your surname and the page number.
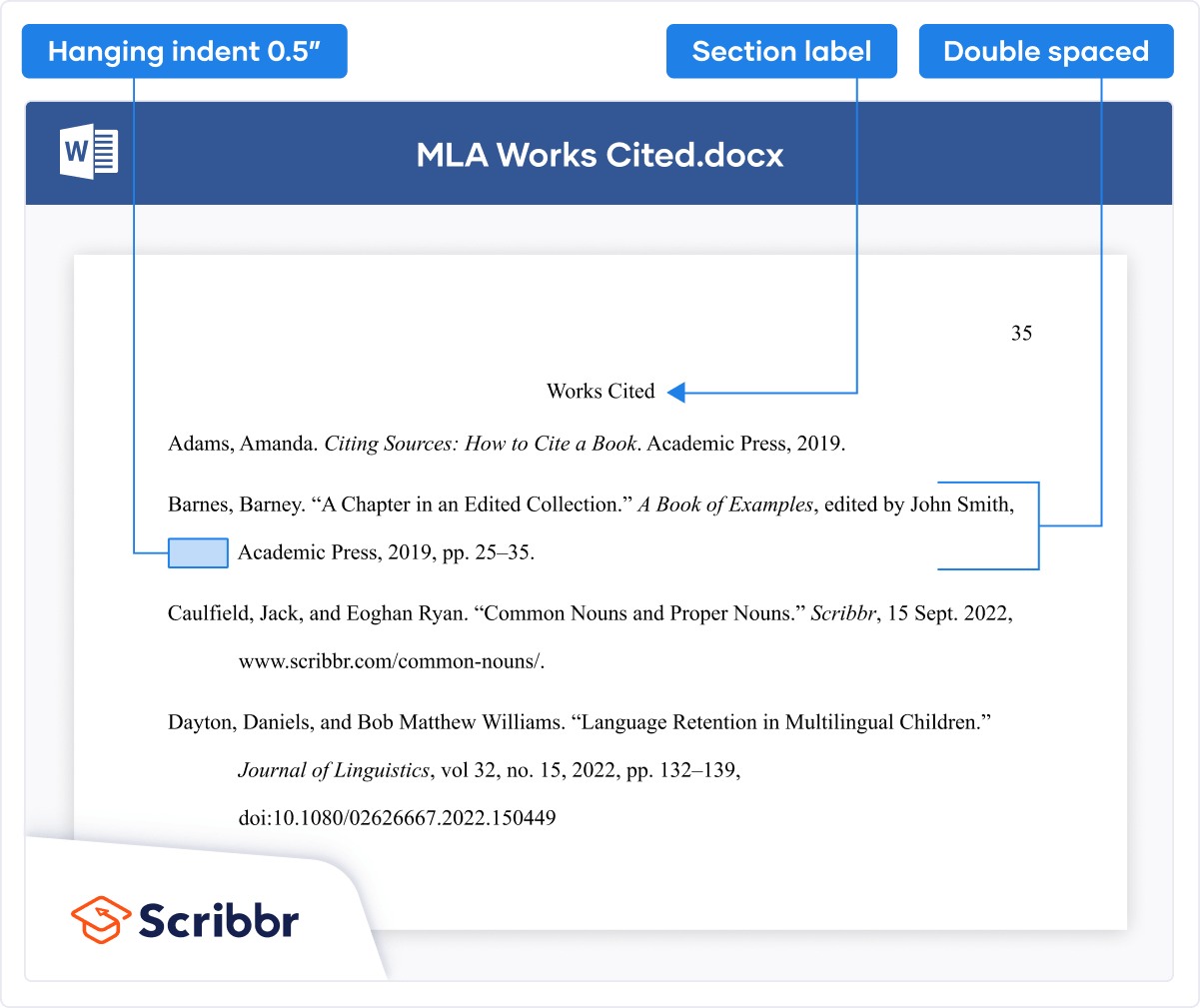
Works Cited page
MLA in-text citations appear wherever you refer to a source in your text. The MLA Works Cited page appears at the end of your text, listing all the sources used. It is formatted as shown below.
You can easily create your MLA citations and save your Works Cited list with the free MLA Citation Generator.
Generate MLA citations for free
The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use 1 inch margins or larger.
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
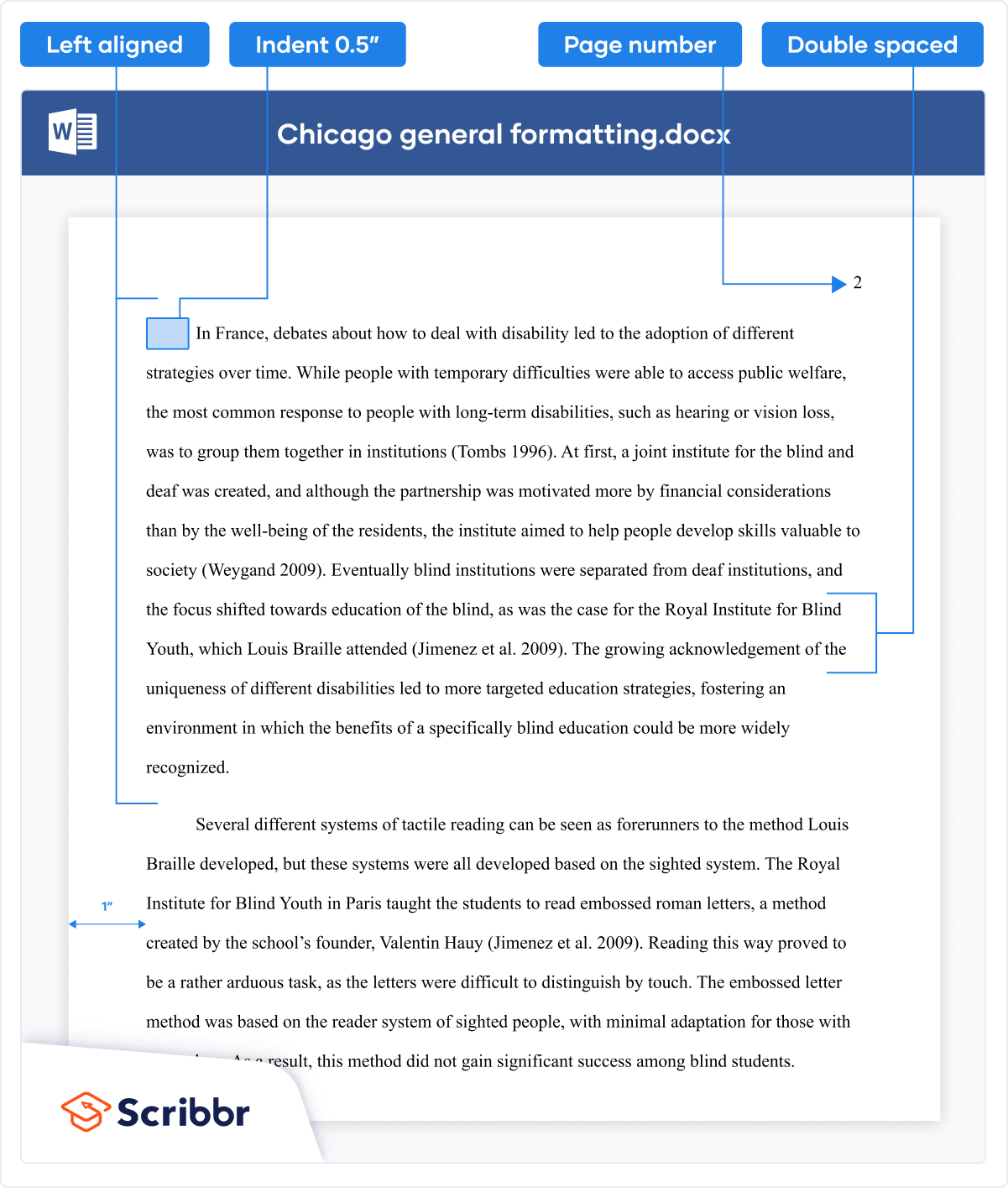
Chicago doesn’t require a title page , but if you want to include one, Turabian (based on Chicago) presents some guidelines. Lay out the title page as shown below.
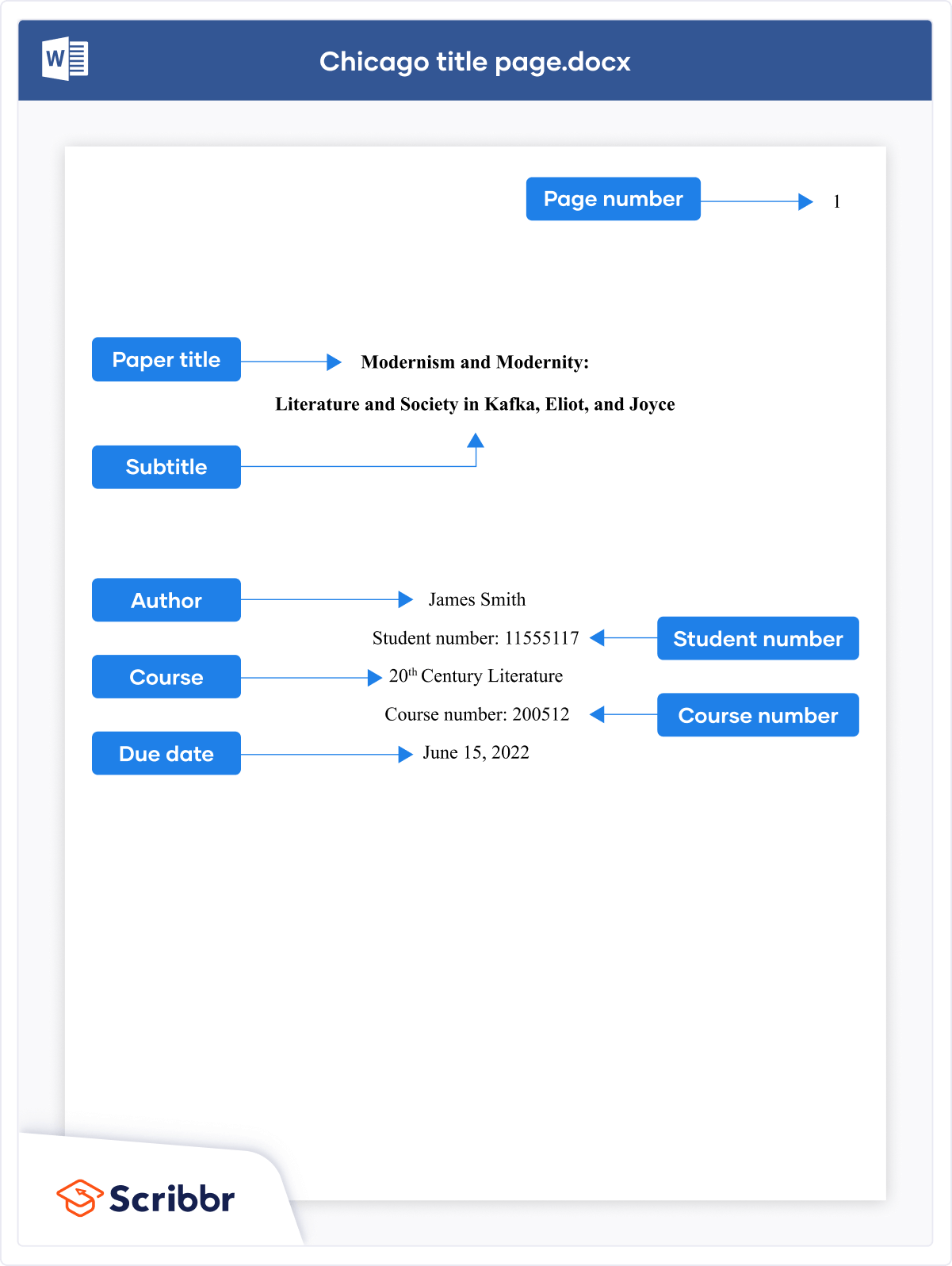
Bibliography or reference list
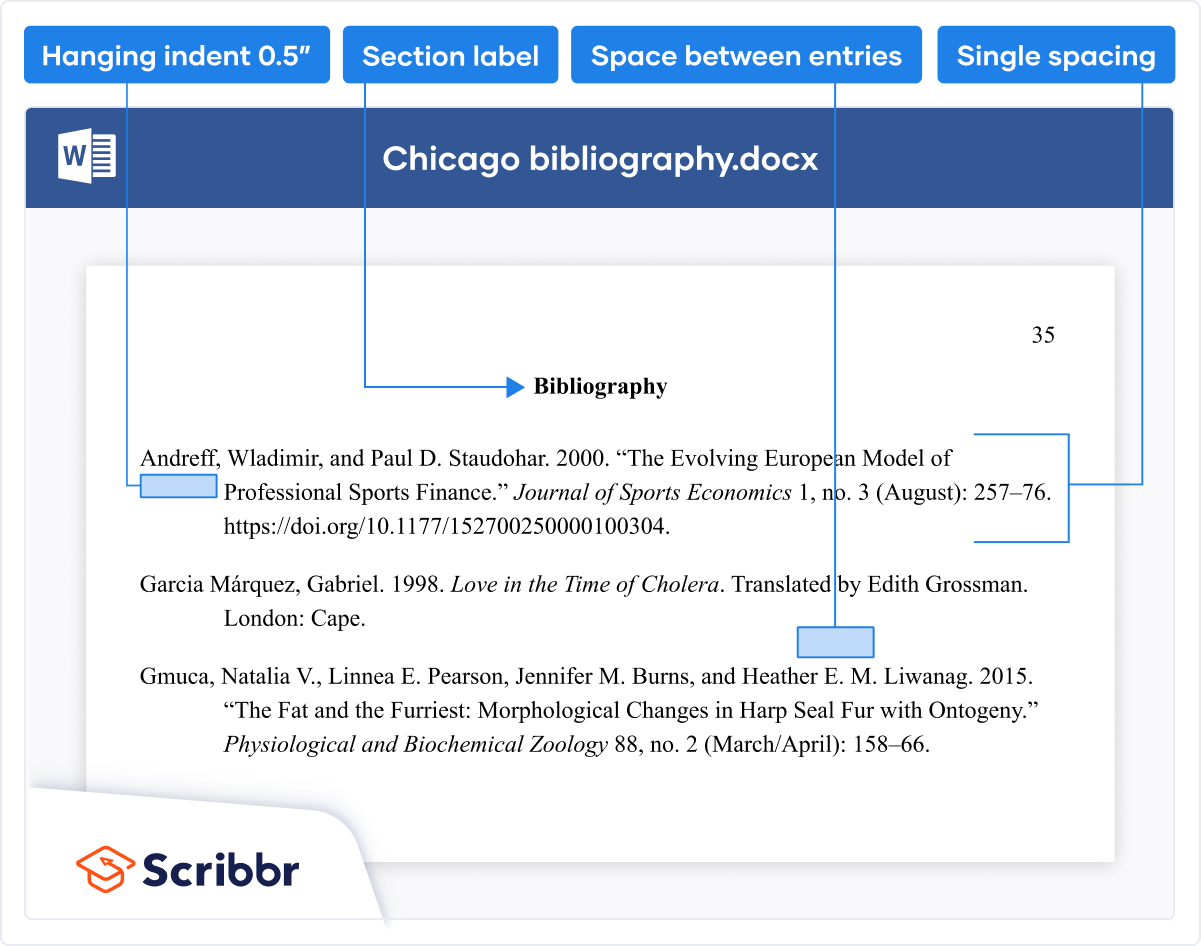
Chicago offers two citation styles : author-date citations plus a reference list, or footnote citations plus a bibliography. Choose one style or the other and use it consistently.
The reference list or bibliography appears at the end of the paper. Both styles present this page similarly in terms of formatting, as shown below.
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Apply double line spacing
- Include a title page
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, January 20). Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-format/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, apa format for academic papers and essays, mla format for academic papers and essays, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

- Remember me Not recommended on shared computers
Forgot your password?
- Sign up to post
Fonts by topic/style

Font Lists: Fonts by topic/style
Free font lists.
- Good free display families
- Notable free super-families
- The Best Free Blackletter Fonts
- The best free sans serif font families
- The Best Free Serif Font Families
- The Best Free Slab Serif Font Families
Font alternatives
- Franklin Gothic’s Alternatives
- Gill Sans’ Alternatives
- The best Helvetica alternatives
- Today’s Best Futura Alternatives
- Bauhaus Fonts
- Best fonts for academic papers/writing
- Emoji Fonts
- Fairy Tale Fonts
- Modern reverse-contrast Fonts
- Rough Brush Lettering Fonts
- Serif, but no curves allowed
- The Best Coding Fonts
- The Best Contemporary Blackletter Fonts
- The Best Layer/Chromatic Fonts
- The Best Monolinear Script Fonts
- The Best Sports and College Fonts
Fonts by region
- Typefaces of Ukrainian Cities
- Typical British Fonts
- Typical French Fonts
- Typical German fonts

Signage Fonts
- Recommendable Signage Fonts
- Road Signage Typefaces
- Subway Typefaces
Fonts by User
- The Fonts of Car Brands
Best fonts for academic papers/writing (2024)

By Ralf Herrmann (edited) | Views: 12493
- March 26, 2019
A selection of free and commercial fonts for academic use.
A robust text typeface by David Březina. Skolar’s vast character set caters for 90+ Latin-script languages, polytonic Greek, 44+ Cyrillic languages, various Latin transliterations (Pinyin, Sanskrit), Devanagari (Sanskrit, Hindi, Marathi, Nepali, …), and Gujarati.

Cambria Math
This is a variant of Cambria designed for mathematical and scientific texts. Cambria Math was the first font to implement the OpenType math extension, itself inspired by TeX.
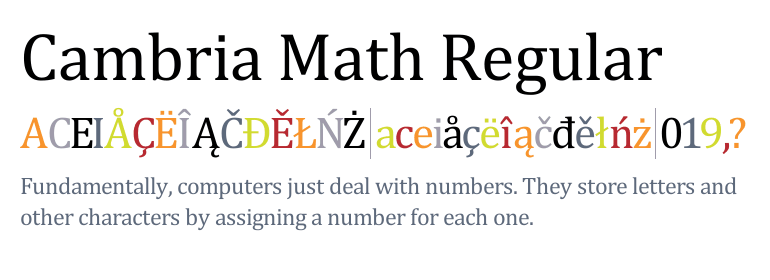
The STIX Fonts project (Scientific and Technical Information Exchange) is a project sponsored by several leading scientific and technical publishers to provide, under royalty-free license, a comprehensive font set of mathematical symbols and alphabets, intended to serve the scientific and engineering community for electronic and print publication. The STIX fonts are available as hinted OpenType/CFF fonts.

Commissioned by Dutch publisher Brill and designed by Tiro Typework’s John Hudson, it presents complete coverage of the Latin script with the full range of diacritics and linguistics (IPA) characters used to display any language from any period correctly, and Greek and Cyrillic are also covered, for a total of 5,100 characters, each available in roman, italic, bold, and bold italic. These fonts will be especially suited for humanities scholars quoting from texts in any language, ancient or modern. Freely available for non-commercial use.

Designed by TypeTogether for the Google Play Books app, it supports Greek, Cyrillic, PinYin, and Vietnamese.
Now with optical sizes and also available in variable font format.

Andron Mega
Andron Mega Corpus is a particular comprehensive font family designed to meet the peculiar requirements of multiscriptual scientific editing. The Andron Mega 1.4 package contains now altogether about 14,700 glyphs in six separate fonts: Regular, Italic, Semibold, Semibold italic, Regular small capitals and Italic small capitals. The Regular font is by far the most comprehensive one: it contains about 5,800 glyphs.

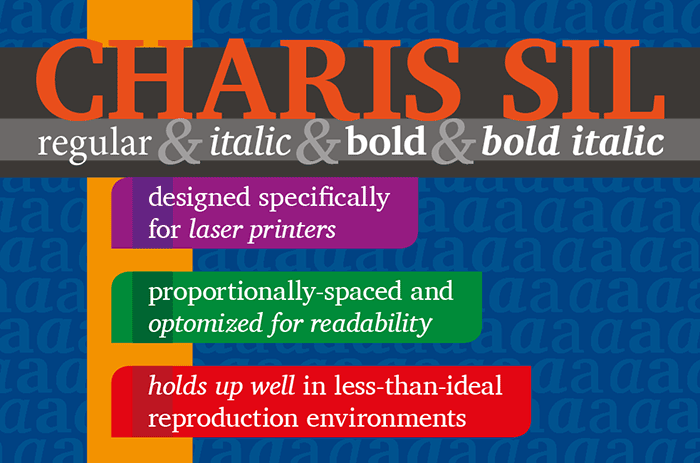
Charis SIL is a Unicode-based font family that supports the wide range of languages that use the Latin and Cyrillic scripts. It is specially designed to make long texts pleasant and easy to read, even in less than ideal reproduction and display environments.
Designed by Matthew Butterick specifically with legal writing in mind.

Gentium is a typeface family designed to enable the diverse ethnic groups around the world who use the Latin, Cyrillic and Greek scripts to produce readable, high-quality publications. It supports a wide range of Latin- and Cyrillic-based alphabets.
Junicode (short for Junius-Unicode) is a TrueType/OpenType font for medievalists with extensive coverage of the Latin Unicode ranges, plus Runic and Gothic. The font comes in four faces. Of these, regular and italic are fullest, featuring complete implementation of the Medieval Unicode Font Initiative recommendation, version 4.0.
User Feedback
Recommended comments.
Posted January 17, 2020
- Share this comment
I suppose this list could be extended ad infinitum (or perhaps even ad nauseam ), but these options (applicable especially in Linguistics work, or anything that stress-tests Latin Extended, Additional, etc. ranges) should be welcome additions here (and all “free” of one kind or another):
- Alegreya ht :: Huerta Tipográfica
- EB Garamond
- Linguistics Pro | which is based on Slimbach’s Utopia
- Vollkorn Typeface
Link to comment
Share on other sites, create an account or sign in to comment.
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Already have an account? Sign in here.

- Existing user? Sign In
- Typography feed (default)
- Typography Feed (complete)
- Forum Index
- Recent Typography Discussions
News & Events
- Typography Weekly
- Typography Events
- Font of the Month (Archive)
- Exclusive content
- Why support us?
- Return/Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Create New...
Important Information
We are placing functional cookies on your device to help make this website better.
Scientific Fonts: How to Select the Right One
Choosing the right font for the right kind of content is imperative, this article will aid your decision when it comes to scientific fonts.
It can be very difficult to choose the ideal font for a project, as any graphics designer could confirm. Deciding the font becomes more important when you anticipate its extensive and frequent usage.
It’s an essential part of typography , which is the art of making your design appear visually cohesive. A font group’s general design usually kicks off the search, but with a little digging, you can find yourself in the creator’s most detailed selection.
There are a number of research studies that have focused on typography to discover some good grounds for selecting a particular font for a particular project category.
It is also best to pick a professional font that is easy to read without many extraneous features.
Scientific research, for example, should be written in such a manner that the reader focuses on the information, not just the format.
Some people find today’s scientific fonts boring and overdone. Because of their legibility and simplicity, these fonts are everywhere. Use a trusted font to make your work appear professional.
In terms of font selection, there are more considerations than seem to be apparent at first glance. For instance, some fonts have a reputation for being legitimate, while others don’t.
We have a handful of scientific findings to share throughout this article in the hopes that they will aid your decision-making when it comes to scientific fonts.
If you have ever found the choice of fonts intimidating, the purpose of this article is to offer guidance and information to help you make a decision.
What is the importance of Fonts?
When a typeface is carefully chosen, it is able to deliver the desired effect to the reader, and give the words the sense of life they deserve, all the while reflecting the field it represents.
The font represents the words on a page visually instead of an image, allowing the words to convey their intended meanings as they are read. A font that is too large or small may not convey the seriousness of some issues or messages.
What is the most recent time that you wrote a text or sent an email and the words were read incorrectly? We can communicate more effectively using our vocal tonality, simple hand gestures and expressions, we can convey our message more effectively than simple words on a paper.
On fancy documents such as invitations, using a script font can be spectacular, but on children’s books it can look off, and in the event of too much text it may not be readable.
As you can see, choosing the right font for the right kind of content is very important. However, using the right font is only part of the equation. Misleading fonts result in incorrect information.
7 fonts that strengthen scientific research’s credibility and professional appearance

In recent years, fonts.com has reported that Arial is among the most used typefaces. With its distinctly contemporary design, Arial is more in sync with the last decade of the twentieth century than many of its predecessors.
There is no horizontal line at the bottom of the edges of Arial letters. They are angled instead. It helps give the face a more organic appearance by cutting the terminals on a diagonal.
The Arial family of typefaces is incredibly robust. Suitable for setting text for reports, articles, publications, and for use in display media, newspapers, and promotional materials.
Whether you’re writing small or large chunks of text, Arial makes reading easy. Figures should be formatted in Arial or Helvetica as per Nature’s instructions.
Labels and legends in particular benefit from this typeface. As a rule of thumb, keep font sizes small *8 points when using Arial for figure legends.
2. Baskerville

Designed by John Baskerville in 1757, Baskerville is a typeface that can be read easily and looks good in print. The letters were straightforward and elegant according to Baskerville.
Here and there, Baskerville font was found to increase reliability of text in comparison to other fonts. The readers’ behavior on the same study was most negatively influenced by Comic Sans.
The Baskerville family of fonts are known as the first transitional roman. These fonts distinguish between thin and thick strokes. The large size of Baskerville looks good because of this feature.
Based on its serif style, Baskerville has “tails” on the edges of its letters. This font is best suited for printing. For long text blocks, it is most suitable.
For best results, try to keep the font size between 8 and 14 points. Then your text will look more professional.
3. Helvetica

The most commonly used font is Helvetica. Max Miedinger, a Swiss designer, initially created Helvetica in 1957.
Designed to be simple to read, the font immediately gained popularity. It is named after the Latin term for Switzerland, Helvetia. Neue Helvetica is the name of the newer version of the font, which was introduced in 1983.
Even a movie has been made about Helvetica. Helvetica is not only a Hollywood (Indie) font, it looks fantastic on screen and print.
Science, Nature, and Cell ask for the figure captions to be in Helvetica. Even though it looks good when printed in small formats, it looks even better when printed in large formats.
It’s hard for authors to keep track of how many figures they’ve labelled with Helvetica now, since that’s what publishers use.

In spite of Georgia’s role in providing clarity at low resolutions on the screen, it is imbued with a typographic aesthetic that strikes a chord with readers.
This friendly face is evident even at small sizes. A stunning, smooth italic accompanies Georgia’s design; the artwork minimizes the complexity of making a screen-friendly italic.
As opposed to many contemporary typefaces, it has authentic italics, including the slender lowercase letters a and g.
The bold weight is also carefully tailored, with a heavier weight than the regular; this is particularly useful at small screen sizes where the two weights must be distinguished(phone screens).
5. Garamond

The history of this font also dates back a long way. French King Francis I of France (1515-1547) commissioned Claude Garamond to design a typeface for use in a series of books.
It was revived by Robert Slimbach in 1989 as an electric typeface. Garamond comes in many different variations because there are different sources available. The most commonly used version is Adobe Garamond.
French publishers continue to use Garamond extensively. Size 9 is also a must for Garamond in France. The history of France’s publishing industry is published in Garamond, as is Histoire de l’édition française .
This font was chosen due to its elegance, opulence, and legibility as well as a simple layout highlighting the detailed writing and offer an enlightened insight on the contemporary aspect of the content.
In long documents such as thesis papers, dissertations, and academic books, Garamond is a reliable font to use. Garamond is the font that many master’s thesis writers use.

Among the long-established fonts is Caslon. The typeface was designed in the early 1700s by William Caslon. English typefaces began with this one. It was a common font used in colonial America, and even the US Declaration of Independence was written with this font.
Because there is no enforceable trademark on the name “Caslon”, there are many typefaces called “Caslon”, some of which are exact copies of the originals, while others are not.
It is best used in blocks of text since it is a serif font (with tails). If you want best results, keep the font size between 8 and 14 points, as you would with Baskerville. The best place to make use of this would be in an application or a report.
7. Times New Roman
First published by The Times of London newspaper in 1932, this typeface was designed for the publication.
In the years since, it has evolved into one of the most popular typefaces in the world. Victor Lardent at The Times created the original designs under the direction of Stanley Morison.
Monotype’s Type Drawing Office then further refined it in an extensive step-by-step process. Many of its characteristics were taken from Morison’s experiments with Perpetua and Plantin, but it was adapted so that it was highly readable and also very efficient.
There are vast uses for it in books and journals, in reports, in presentations, and in advertising.
Is there anything else you need to think about when selecting the right font?
When choosing a font, there are a number of things to keep in mind besides these categories. For example, does it have all the features you are looking for?
You may be able to get away with just using the letters of the alphabet for the first piece, but what if you have to write a quick article for the public?
Are there symbols such as a currency symbol or exclamation point in the text? Especially when you are submitting a funding proposal. (Read our guide to everything you need to know about Research Proposals .)
Every once in a while, we find ourselves trying to add a price but the symbol we need isn’t there.
As well as the font size, there are other considerations, such as does it come in many sizes and styles or are only light, regular and bold available?
If you don’t have a lot of specifics, that’s alright, but you should take into account a broader perspective and what you intend to accomplish.
When it comes to communicating your message, different font sizes can be really helpful. Despite the fact that it’s good to have different typefaces, there is a rule that suggests only using a maximum of three typefaces in one contribution.
If you use any more than that, you risk-taking away the emphasis of what is being said. Complementary fonts are important, but they shouldn’t be too similar as this could result in a cluttered look that could be confusing.
Lastly, when picking a font, we should consider the print aspects to ensure it will be easy to read. These factors include colour, size, and style. The most decorative script fonts may look good, but they aren’t always a good option.
Hence, make sure to put into consideration every possible aspect of the information that may be published around the world through various mediums.
How to use Scientific fonts?
A reader’s primary objective should be to understand the facts about your project clearly. An easy-to-read document will help you achieve that goal.
The editors of newspapers, as well as publishers of journals, have developed many guidelines to make text more readable. These guidelines are now available for scientific purposes.
- Keep the main body text font size at least 16 points . Any smaller would make the text difficult to read.
- A project title should have a minimum height of 2 inches.
- It is recommended that headlines have at least one inch tall letters .
- If you want to stay with the norm, use Arial , Times New Roman , or another typeface similar to these.
- If you intend to draw attention to anything, use italics or boldface .
- Place your text below your picture ; that makes it easier to read.
- Please refrain from using ALL CAPS ; they can be difficult to perceive.
- You should not use reverse typeface (light text on dark background).
- If you type in a script font, avoid using artistic fonts , since they are harder to follow.
- You can choose between Serif or Sans Serif depending on the medium or the audience you will be addressing to.
- Your poster or paper should not contain more than two or three contrasting fonts .
- For body copy and headings, Time New Roman and Arial combine nicely.
Please note that every journal or publication house has different guidelines based on how they handle submissions, so make sure you check them.
It is also important to consider the medium on which the text will appear when choosing a font. Posters will need to have better fonts that appear decent when printed.
Selecting the wrong font can negatively affect future decision-making. It is important to remember that the typeface that you select to present your research or information will have a major impact on its effectiveness.
Make sure you make the right choice because it will leave a meaningful impression on the reader. (You can learn how to create an outstanding presentation that will leave the audience impressed, here )
Fonts for scientific illustrations and infographics
Infographics, or informational graphics, are a growing trend in data presentation. This style of presentation allows you to convey your message quickly and easily.
In order to make complex topics understandable, illustrations are extremely useful. A good font is essential no matter what.(See our guide to scientific illustrations )
Your choice of font is as important as the research itself when it comes to presenting it. (In most cases.) Generally, book, journal, and newspaper fonts are serif fonts, which are characterized by small lines at the end of each stroke.
The vast majority of online content uses sans serif fonts. Serif fonts make it easier for readers to follow lines of text, which is certainly useful when designing illustrations or use the infographic maker.
The best typeface for graphic design is sans serif. Arial, Calibri, Helvetica, Verdana, and open sans, which are readily available, improve content legibility significantly.
If you understand how certain font choices affect the composition of your content, deciding on a family of fonts and a typography scheme becomes much more straightforward.
As you become more familiar with the values, tone, and vision of the work, you will begin to can identify what works. It is possible to convey your ideas in a non-verbal and yet powerful way, using fonts.
Now that we have reached our final section, you should also know where to find all the fonts in one place.
You can find all the best science fonts for graphic design at one place
We at mind the graph understand the importance of typography and how it plays an integral part in representation of scientific ideas. Mind the graph, the most user-friendly tool.
Scientists and academicians from over 100 top academic, educational, and industrial institutions trust Mind the Graph. This is why everything is up-to-date and scientifically sound.
You will find all the A to Z fonts you need for all things scientific here. Besides that, we also suggest fonts that are appropriate for your content type. You can choose from the list we have.
Furthermore, we have many templates to assist in the creation of posters and graphics. Additionally, they can be customized according to your needs. However, guess what is even better than that? We offer a FREE trial, so you can decide what plan fits you best.
When you join, you join us in our mission to increase easy access to the best science tool for as many people as possible. Our blog section has a variety of information about everything from making Science posters to a list of the best science podcasts of 2022, definitely worth checking out.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
About Fabricio Pamplona
Fabricio Pamplona is the founder of Mind the Graph - a tool used by over 400K users in 60 countries. He has a Ph.D. and solid scientific background in Psychopharmacology and experience as a Guest Researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry (Germany) and Researcher in D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR, Brazil). Fabricio holds over 2500 citations in Google Scholar. He has 10 years of experience in small innovative businesses, with relevant experience in product design and innovation management. Connect with him on LinkedIn - Fabricio Pamplona .
Content tags
What font should I choose for my thesis?
This post is by DrJanene Carey, a freelance writer and editor based in Armidale NSW. She occasionally teaches academic writing at the University of New England and often edits academic theses, articles and reports. Her website is http://www.janenecarey.com
Arguably, this question is a classic time waster and the student who poses it should be told to just get on with writing up their research. But as someone who edits theses for a living, I think a bit of time spent on fonts is part of the process of buffing and polishing what is, after all, one of the most important documents you will ever produce. Just bear in mind that there is no need to immerse yourself so deeply in the topic that you start quibbling about whether it’s a font or a typeface that you are choosing .
Times New Roman is the standard choice for academic documents, and the thesis preparation guidelines of some universities stipulate its use. For many years, it was the default body text for Microsoft Word. With the release of Office 2007, the default became a sans serif typeface called Calibri. Lacking the little projecting bits (serifs) at the end of characters makes Calibri and its many friends, such as Arial, Helvetica and Verdana, look smoother and clearer on a screen, but generally makes them less readable than a serif typeface when used for printed text . The other problem with choosing a sans serif for your body text is that if you want passages in italics (for example, lengthy participant quotes) often this will be displayed as slanted letters, rather than as a true italic font.
You would like your examiners to feel as comfortable as possible while their eyes are traversing the many, many pages of your thesis, so maximising legibility and readability is a good idea. Times New Roman is ubiquitous and familiar, which means it is probably the safest option, but it does have a couple of drawbacks. Originally designed for The Times in London, its characters are slightly narrowed, so that more of them can be squished into a newspaper column. Secondly, some people intensely dislike TNR because they think it has been overused, and regard it as the font you choose when you are not choosing a font .
If you do have the luxury of choice (your university doesn’t insist you use Times New Roman, and you have defined document styles that are easy to modify, and there’s enough time left before the submission deadline) then I think it is worth considering what other typefaces might work well with your thesis. I’m not a typographical expert, but I have the following suggestions.
- Don’t use Calibri, or any other sans serif font, for your body text, though it is fine for headings. Most people agree that dense chunks of printed text are easier to read if the font is serif, and examiners are likely to expect a typeface that doesn’t stray too far from the standard. To my eye, Calibri looks a little too casual for the body of a thesis.
- Typefaces like Garamond, Palatino, Century Schoolbook, Georgia, Minion Pro, Cambria and Constantia are all perfectly acceptable, and they come with Microsoft Word. However, some of them (Georgia and Constantia, for example) feature non-lining numerals, which means that instead of all sitting neatly on the base line, some will stand higher or lower than others, just like letters do. This looks nice when they are integrated with the text, but it is probably not what you want for a tabular display.
- Consider using a different typeface for your headings. It will make them more prominent, which enhances overall readability because the eye scanning the pages can quickly take in the hierarchy of ideas. The easiest way to get a good contrast with your serif body text is to have sans serif headings. Popular combinations are Garamond/Helvetica; Minion Pro/Myriad Pro; Times New Roman/Arial Narrow. But don’t create a dog’s breakfast by having more than two typefaces in your thesis – use point sizes, bold and italics for variety.
Of late, I’ve become quite fond of Constantia. It’s an attractive serif typeface that came out with Office 2007 at the same time as Calibri, and was specifically designed to look good in print and on screen. Increasingly, theses will be read in PDF rather than book format, so screen readability is an important consideration. Asked to review Microsoft’s six new ClearType fonts prior to their release, typographer Raph Levien said Constantia was likely to be everyone’s favourite, because ‘Even though it’s a highly readable Roman font departing only slightly from the classical model, it still manages to be fresh and new.’
By default, Constantia has non-lining numerals, but from Word 2010 onwards you can set them to be lining via the advanced font/number forms option, either throughout your document or in specific sections, such as within tables.
Here is an excerpt from a thesis, shown twice with different typefaces. The first excerpt features Calibri headings with Constantia body text, and the second has that old favourite, Times New Roman. As these examples have been rendered as screenshots, you will get a better idea of how the fonts actually look if you try them on your own computer and printer.
Related posts
Should I get an editor for my thesis?
Love the Thesis whisperer and want it to continue? Consider becoming a $1 a month Patreon and get special, Patreon only, extra Thesiswhisperer content every two weeks!
Share this:
The Thesis Whisperer is written by Professor Inger Mewburn, director of researcher development at The Australian National University . New posts on the first Wednesday of the month. Subscribe by email below. Visit the About page to find out more about me, my podcasts and books. I'm on most social media platforms as @thesiswhisperer. The best places to talk to me are LinkedIn , Mastodon and Threads.
- Post (606)
- Page (16)
- Product (6)
- Getting things done (258)
- On Writing (138)
- Miscellany (137)
- Your Career (113)
- You and your supervisor (66)
- Writing (48)
- productivity (23)
- consulting (13)
- TWC (13)
- supervision (12)
- 2024 (5)
- 2023 (12)
- 2022 (11)
- 2021 (15)
- 2020 (22)
Whisper to me....
Enter your email address to get posts by email.
Email Address
Sign me up!
- On the reg: a podcast with @jasondowns
- Thesis Whisperer on Facebook
- Thesis Whisperer on Instagram
- Thesis Whisperer on Soundcloud
- Thesis Whisperer on Youtube
- Thesiswhisperer on Mastodon
- Thesiswhisperer page on LinkedIn
- Thesiswhisperer Podcast
- 12,147,391 hits
Discover more from The Thesis Whisperer
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- How it works

What Is The Best Font For A Dissertation?
Published by Alvin Nicolas at April 9th, 2024 , Revised On April 9, 2024
For many students, embarking on a dissertation is a daunting task. Beyond the research, writing, and analysis , a seemingly insignificant detail can cause unexpected stress: font selection. While it might seem like a minor concern, the right font can significantly impact the readability, professionalism, and overall look of your dissertation and can highly influence the decision of the readers.
This blog will help you in choosing the right font for your dissertation. Let’s explore!
Why Does Font Choice Matter?
While the content of your dissertation is paramount, the presentation also plays a crucial role. The chosen font can influence how easily your reader absorbs the information. A poorly chosen font can lead to eye strain, reduced comprehension, and even a negative first impression.
Here are some specific reasons why font choice matters:
- Readability: The primary function of your dissertation is to communicate your research effectively. A clear and readable font is essential for ensuring your reader can easily grasp the information presented.
- Professionalism: Certain fonts convey a sense of seriousness and formality, aligning with the academic tone of your dissertation.
- Consistency: Maintaining a consistent font throughout your dissertation creates a sense of unity and professionalism.
Key Factors To Consider When Choosing A Font
Before discussing the specific font recommendations, let’s explore some key factors to consider when making your decision:
University Guidelines
Many universities have specific guidelines regarding font choices for dissertations. Always refer to your university’s style guide or handbook to ensure you adhere to any established requirements.
Readability
Opt for fonts with clear letterforms, adequate spacing, and sufficient contrast between the font and background colour. Avoid decorative or script fonts that can be challenging to read.
Serif Vs Sans-Serif
Serif fonts, characterised by small lines extending from the ends of characters (e.g., Times New Roman), are generally considered more readable for extended reading, making them ideal for the body text of your dissertation. Sans-serif fonts lacking these serifs (e.g., Arial) can be suitable for headings or short text snippets.
Font Size & Line Spacing
Maintain a comfortable reading experience with an appropriate font size (typically 10-12 points) and line spacing (usually 1.15 or 1.5 lines).
Hire an Expert Writer
Proposal and dissertation orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Popular Font Choices For Dissertations
Now, let’s explore some popular font options that meet the criteria for dissertation writing:
Times New Roman
The classic academic font, Times New Roman, remains a widely accepted and safe choice for dissertations due to its readability and formal appearance.
Similar to Times New Roman, Georgia offers good readability with a slightly wider design, making it suitable for screen-based reading.
This elegant serif font adds a touch of sophistication while maintaining excellent readability.
A modern serif font, Cambria provides a clean and professional look often favoured for on-screen reading.
While not ideal for the body text due to its lack of serifs, Arial can be a good choice for headings and subheadings due to its clarity and clean lines.
Additional Tips for Font Selection
Here are some additional tips to ensure your font choice shines:
- Consistency is key: Maintain the same font throughout your dissertation, including body text, headings, subheadings, and captions.
- Avoid excessive font variations: Stick to one or two fonts, with variations reserved for specific purposes (e.g., different fonts for headings).
- Consider the overall design: Ensure your chosen font complements the overall visual style of your dissertation, including layout and graphics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What font should i use for my dissertation uk.
Use a clear and readable font like Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri for a UK dissertation. Most universities recommend a serif font like Times New Roman, size 12, for the main text, with clear distinctions for headings and subheadings. Always follow your institution’s guidelines for formatting and font selection.
What font should a dissertation be in?
Use a legible serif font such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri for a dissertation. Typically, the font size should be 12 points for the main text, with variations for headings and subheadings as specified by your institution’s guidelines. Consistency and readability are key for academic documents.
What size font should my dissertation be?
Your dissertation’s main text should generally be in a 12-point font size for readability and consistency. Headings and subheadings may vary, typically larger than the main text, to emphasise hierarchy and organisation. Always adhere to your institution’s specific formatting requirements for font sizes and styles to ensure compliance.
What font shall I use for my undergraduate dissertation?
For an undergraduate dissertation, using a clear and legible font like Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri is advisable. Aim for a font size of 12 points for the main text to ensure readability. Follow any specific formatting guidelines your university or department provides for consistency and professional presentation.
You May Also Like
If you’ve got kids, writing a dissertation is even harder, because kids do tend to take up a fair amount of time. That said, it’s not impossible.
Students around the globe always make sure to run assignments or other academic work through an online plagiarism checker. Still, the question arises over here,
Struggling to write a high quality research paper? Here is all you need to know if you need help with writing research paper for your degree programme.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
12 Best Fonts for Academic Papers in Microsoft Word
Good academic papers deserve good academic fonts. You might not have thought too much about which font you use before, but they play a big part in whether people will take your paper seriously or not. This article will explore the best fonts for academic papers.
Best Fonts for Academic Papers in Microsoft Word
Times new roman, baskerville old face.
Baskerville is a fairly popular choice for published novels, so you might already be familiar with the font style. If you like the way it looks in some of the novels or publications you’ve read, you’ll find that it converts very well to your academic papers.
Georgia ranks very highly when looking for a formal font that will work well in an academic paper. It’s slightly larger than Times New Roman, but a lot of people say that this helps it to become a more “readable” font.
When writing academic papers, it’s wise not to overwhelm your reader with information. The more condensed the font is, the harder it can be to make sense of what you’re writing. With Georgia, this isn’t an issue.
Garamond is another decent option that can work well for academics. Garamond is the smallest font we have included on the list, which can allow you to get a lot of information into a very small space without overwhelming a reader too much.
It’s also quite a popular choice for many writers. You’ll find that it ranks quite highly simply because of how popular it’s become among a lot of writers on Word.
The serif style of this font makes it easy to read. It’s nearly indistinguishable from some of the other more popular serif fonts like Times New Roman and Georgia, which is why it is such a popular choice.
Book Antiqua
Book Antiqua is another suitable serif font. It’s not as popular as some of the others, but it looks really good as far as formal fonts go. People like it because it offers a slightly more authentic feel and looks like it could be used in a published novel or academic study.
It’s a standard-sized font, and it’s quite easy to read. A lot of people enjoy using it because it can offer a lot of character to their writing. You might not think that a font has that much power, but you’d be surprised once you try and use Book Antiqua a bit more.
Bookman Old Style
We encourage you to try this one in multiple different situations. It can work both formally and informally, depending on what you’re looking to get out of it.
Palatino Linotype
Lucida bright.
Lucida Bright is a great font that is very large compared to most. It works well in academic papers, but you’ve got to make sure you know when to use it. If your paper is particularly word-heavy, it might not be wise to use a font that makes each word much larger.
Calibri is like the Times New Roman of the sans serif fonts. It is very popular, and most Microsoft Word versions come with it preloaded as the default font for most written pieces.
Arial is much larger than Calibri when the same font size is used. This makes it a lot more visually appealing, though you have to make sure you don’t overdo it with the number of pages it uses.
Century Gothic
Century Gothic is the final font we want to cover. It’s a sans serif font that can work really well if you’re looking for a slightly larger font. It’s larger than Arial, making it an easy-to-read font that a lot of people like to utilize.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Formatting guide
This guide describes how to prepare contributions for submission. We recommend you read this in full if you have not previously submitted a contribution to Nature . We also recommend that, before submission, you familiarize yourself with Nature ’s style and content by reading the journal, either in print or online, particularly if you have not submitted to the journal recently.
Formats for Nature contributions
Articles are the main format for original research contributions to Nature . In addition, Nature publishes other submitted material as detailed below.
Articles are original reports whose conclusions represent a substantial advance in understanding of an important problem and have immediate, far-reaching implications. In print, physical sciences papers do not normally exceed 6 pages on average, and biological, clinical and social-sciences papers do not normally exceed 8 pages on average. However, the final print length is at the editor’s discretion.
Articles start with a fully referenced summary paragraph, ideally of no more than 200 words, which is separate from the main text and avoids numbers, abbreviations, acronyms or measurements unless essential. It is aimed at readers outside the discipline. This summary paragraph should be structured as follows: 2-3 sentences of basic-level introduction to the field; a brief account of the background and rationale of the work; a statement of the main conclusions (introduced by the phrase 'Here we show' or its equivalent); and finally, 2-3 sentences putting the main findings into general context so it is clear how the results described in the paper have moved the field forwards. Please refer to our annotated example to see how the summary paragraph should be constructed.
The typical length of a 6-page article with 4 modest display items (figures and tables) is 2500 words (summary paragraph plus body text). The typical length of an 8-page article with 5-6 modest display items is 4300 words. A ‘modest’ display item is one that, with its legend, occupies about a quarter of a page (equivalent to ~270 words). If a composite figure (with several panels) needs to occupy at least half a page in order for all the elements to be visible, the text length may need to be reduced accordingly to accommodate such figures. Keep in mind that essential but technical details can be moved into the Methods or Supplementary Information.
As a guideline, articles typically have no more than 50 references. (There is no such constraint on any additional references associated with Methods or Supplementary Information.)
Sections are separated with subheadings to aid navigation. Subheadings may be up to 40 characters (including spaces).
Word counts refer to the text of the paper. Title, author list, acknowledgements and references are not included in total word counts.
Matters Arising and Corrections
Matters Arising are exceptionally interesting or important comments and clarifications on original research papers or other peer-reviewed material published within the past 18 months in Nature . They are published online but not in print.
For further details of and instructions for how to submit such comments on peer-reviewed material published in Nature — or to notify editors of the potential need for a correction — please consult our Matters Arising page.
Other contributions to Nature
Please access the other submitted material pages for further details on any of the contribution types below:
News and Comment
Correspondence
Books & Arts
News & Views
Insights, Reviews and Perspectives
Technology Features
The editorial process
See this section for an explanation of Nature 's editorial criteria for publication, refereeing policy and how editors handle papers after submission. Submission to a Nature journal is taken by the journal to mean that all the listed authors have agreed to all of the contents. See authorship policy for more details.
Presubmission enquiries
If you wish to enquire whether your Article might be suitable for consideration by Nature , please use our online presubmission enquiry service . All presubmission enquiries must include a cover paragraph to the editor stating the interest to a broad scientific readership, a fully referenced summary paragraph, and a reference list.
Readability
Nature is an international journal covering all the sciences. Contributions should therefore be written clearly and simply so that they are accessible to readers in other disciplines and to readers for whom English is not their first language. Thus, technical jargon should be avoided as far as possible and clearly explained where its use is unavoidable. Abbreviations, particularly those that are not standard, should also be kept to a minimum. The background, rationale and main conclusions of the study should be clearly explained. Titles and abstracts in particular should be written in language that will be readily intelligible to any scientist. Essential but specialized terms should be explained concisely but not didactically.
For gene, protein and other specialized names authors can use their preferred terminology so long as it is in current use by the community, but they must give all known names for the entity at first use in the paper. Nature prefers authors to use internationally agreed nomenclature. Papers containing new or revised formal taxonomic nomenclature for animals, whether living or extinct, are accepted conditional on the provision of LSIDs (Life Science Identifiers) by means of registration of such nomenclature with ZooBank, the proposed online registration system for the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN).
Even though no paper will be rejected because of poor language, non–native English speakers occasionally receive feedback from editors and reviewers regarding language and grammar usage in their manuscripts. You may wish to consider asking colleagues to read your manuscript and/or to use a professional editing service such as those provided by our affiliates Nature Research Editing Service or American Journal Experts . You can also get a fast, free grammar check of your manuscript that takes into account all aspects of readability in English. Please note that the use of a language editing service is not a requirement for publication in Nature .
Nature 's editors provide detailed advice about the expected print length when asking for the final version of the manuscript. Nature 's editors often suggest revised titles and rewrite the summary paragraphs of Articles so the conclusions are clear to a broad readership.
After acceptance, Nature 's subeditors (copyeditors) ensure that the text and figures are readable and clear to those outside the field, and edit papers into Nature 's house style. They pay particular attention to summary paragraphs, overall clarity, figures, figure legends and titles.
Proofs are sent before publication; authors are welcome to discuss proposed changes with Nature 's subeditors, but Nature reserves the right to make the final decision about matters of style and the size of figures.
A useful set of articles providing general advice about writing and submitting scientific papers can be found on the SciDev.Net website.
Format of Articles
Contributions should be double-spaced and written in English (spellings as in the Oxford English Dictionary ).
Contributions should be organized in the sequence: title, authors, affiliations (plus present addresses), bold first paragraph, main text, main references, tables, figure legends, methods (including separate data and code availability statements), methods references, acknowledgements, author contributions, competing interest declaration, additional information (containing supplementary information line (if any) and corresponding author line), extended data figure/table legends. In order to facilitate the review process, for initial submissions we encourage authors to present the manuscript text and figures together in a single file (Microsoft Word or PDF, up to 30 MB in size). The figures may be inserted within the text at the appropriate positions or grouped at the end, and each figure legend should be presented together with its figure. Also, please include line numbers within the text.
Titles do not exceed two lines in print. This equates to 75 characters (including spaces). Titles do not normally include numbers, acronyms, abbreviations or punctuation. They should include sufficient detail for indexing purposes but be general enough for readers outside the field to appreciate what the paper is about.
An uninterrupted page of text contains about 1250 words.
A typical 6-page Article contains about 2,500 words of text and, additionally, 4 modest display items (figures and/or tables) with brief legends, reference list and online-only methods section if applicable. A composite figure (with several panels) usually needs to take about half a page, equivalent to about 600 words, in order for all the elements to be visible (see section 5.9 for instructions on sizing figures).
A typical 8-page Article contains about 4300 words of text and, additionally, 5-6 modest display items (figures and/or tables) with brief legends, reference list and online-only methods section if applicable. A composite figure (with several panels) usually needs to take about half a page, equivalent to about 600 words, in order for all the elements to be visible (see section 5.9 for instructions on sizing figures).
Authors of contributions that significantly exceed the limits stated here (or as specified by the editor) will have to shorten their papers before acceptance, inevitably delaying publication.
Nature requires authors to specify the contribution made by their co-authors in the end notes of the paper (see section 5.5). If authors regard it as essential to indicate that two or more co-authors are equal in status, they may be identified by an asterisk symbol with the caption ‘These authors contributed equally to this work’ immediately under the address list. If more than three co-authors are equal in status, this should be indicated in the author contributions statement. Present addresses appear immediately below the author list (below the footnote rule at the bottom of the first page) and may be identified by a dagger symbol; all other essential author-related explanation is placed in the acknowledgements.
Our preferred format for text is Microsoft Word, with the style tags removed.
TeX/LaTeX: If you have prepared your paper using TeX/LaTeX, we will need to convert this to Word after acceptance, before your paper can be typeset. All textual material of the paper (including references, tables, figure captions, online methods, etc.) should be included as a single .tex file.
We prefer the use of a ‘standard’ font, preferably 12-point Times New Roman. For mathematical symbols, Greek letters and other special characters, use normal text or Symbol font. Word Equation Editor/MathType should be used only for formulae that cannot be produced using normal text or Symbol font.
The ‘Methods’ section is in the main text file, following the figure legends. This Methods section will appear in the PDF and in the full-text (HTML) version of the paper online, but will not appear in the printed issue. The Methods section should be written as concisely as possible but should contain all elements necessary to allow interpretation and replication of the results. As a guideline, the Methods section does not typically exceed 3,000 words. To increase reproducibility, authors are encouraged to deposit a detailed description of protocols used in their study in a protocol sharing platform of their choice. Springer Nature’s protocols.io is a free and open service designed to help researchers share experimental know-how. Protocols deposited by the authors in www.protocols.io will be linked to the online Methods section upon publication
Detailed descriptions of methods already published should be avoided; a reference number can be provided to save space, with any new addition or variation stated.
The Methods section should be subdivided by short bold headings referring to methods used and we encourage the inclusion of specific subsections for statistics, reagents and animal models. If further references are included in this section their numbering should continue from the end of the last reference number in the rest of the paper and they are listed after the Methods section.
Please provide separate Data Availability and Code Availability statements after the main text statements and before the Extended Data legends; detailed guidance can be found in our data availability and data citations policy . Certain data types must be deposited in an appropriate public structured data depository (details are available here ), and the accession number(s) provided in the manuscript. Full access is required at the time of publication. Should full access to data be required for peer review, authors must provide it.
The Methods section cannot contain figures or tables (essential display items should be included in the Extended Data or exceptionally in the Supplementary Information).
References are each numbered, ordered sequentially as they appear in the text, tables, boxes, figure legends, Methods, Extended Data tables and Extended Data figure legends.
When cited in the text, reference numbers are superscript, not in brackets unless they are likely to be confused with a superscript number.
Do not use linked fields (produced by EndNote and similar programs). Please use the one-click button provided by EndNote to remove EndNote codes before saving your file.
As a guideline, Articles allow up to 50 references in the main text if needed and within the average page budget. Only one publication can be listed for each number. Additional references for Methods or Supplementary Information are not included in this count.
Only articles that have been published or accepted by a named publication, or that have been uploaded to a recognized preprint server (for example, arXiv, bioRxiv), should be in the reference list; papers in preparation should be mentioned in the text with a list of authors (or initials if any of the authors are co-authors of the present contribution).
Published conference abstracts, numbered patents, preprints on recognized servers, papers in press, and research datasets that have been assigned a digital object identifier may be included in reference lists, but text, grant details and acknowledgements may not. (An exception is the highlighted references which we ask authors of Reviews, Perspectives and Insights articles to provide.)
All authors should be included in reference lists unless there are more than five, in which case only the first author should be given, followed by ‘et al.’.
Please follow the style below in the published edition of Nature in preparing reference lists.
Authors should be listed surname first, followed by a comma and initials of given names.
Titles of all cited articles are required. Titles of articles cited in reference lists should be in upright, not italic text; the first word of the title is capitalized, the title written exactly as it appears in the work cited, ending with a full stop. Book titles are italic with all main words capitalized. Journal titles are italic and abbreviated according to common usage. Volume numbers are bold. The publisher and city of publication are required for books cited. (Refer to published papers in Nature for details.)
Research datasets may be cited in the reference list if they have been assigned digital object identifiers (DOIs) and include authors, title, publisher (repository name), identifier (DOI expressed as a URL). Example: Hao, Z., AghaKouchak, A., Nakhjiri, N. & Farahmand, A. Global Integrated Drought Monitoring and Prediction System (GIDMaPS) data sets. figshare http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.853801 (2014).
Recognized preprints may be cited in the reference list. Example: Babichev, S. A., Ries, J. & Lvovsky, A. I. Quantum scissors: teleportation of single-mode optical states by means of a nonlocal single photon. Preprint at http://arXiv.org/quant-ph/0208066 (2002).
References to web-only journals should give authors, article title and journal name as above, followed by URL in full - or DOI if known - and the year of publication in parentheses.
References to websites should give authors if known, title of cited page, URL in full, and year of posting in parentheses.
End notes are brief and follow the Methods (or Methods References, if any).
Acknowledgements should be brief, and should not include thanks to anonymous referees and editors, inessential words, or effusive comments. A person can be thanked for assistance, not “excellent” assistance, or for comments, not “insightful” comments, for example. Acknowledgements can contain grant and contribution numbers.
Author Contributions: Authors are required to include a statement to specify the contributions of each co-author. The statement can be up to several sentences long, describing the tasks of individual authors referred to by their initials. See the authorship policy page for further explanation and examples.
Competing interests statement.
Additional Information: Authors should include a set of statements at the end of the paper, in the following order:
Papers containing Supplementary Information contain the statement: “Supplementary Information is available for this paper.”
A sentence reading "Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to XX.” Nature expects this identified author to respond to readers’ enquiries and requests for materials, and to coordinate the handling of any other matters arising from the published contribution, including corrections complaints. The author named as corresponding author is not necessarily the senior author, and publication of this author’s name does not imply seniority. Authors may include more than one e-mail address if essential, in which event Nature will communicate with the first-listed address for any post-publication matters, and expect that author to coordinate with the other co-authors.
Peer review information includes the names of reviewers who agree to be cited and is completed by Nature staff during proofing.
A sentence reading “Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints.”
Life sciences and behavioural & social sciences reporting guidelines
To improve the transparency of reporting and the reproducibility of published results, authors of life sciences and behavioural & social sciences Articles must provide a completed Reporting Summary that will be made available to editors and reviewers during manuscript assessment. The Reporting Summary will be published with all accepted manuscripts.
Please note: because of the advanced features used in these forms, you must use Adobe Reader to open the documents and fill them out.
Guidance and resources related to the use and reporting of statistics are available here .
Tables should each be presented on a separate page, portrait (not landscape) orientation, and upright on the page, not sideways.
Tables have a short, one-line title in bold text. Tables should be as small as possible. Bear in mind the size of a Nature page as a limiting factor when compiling a table.
Symbols and abbreviations are defined immediately below the table, followed by essential descriptive material as briefly as possible, all in double-spaced text.
Standard table formats are available for submissions of cryo-EM , NMR and X-ray crystallography data . Authors providing these data must use these standard tables and include them as Extended Data.
Figure legends
For initial submissions, we encourage authors to present the manuscript text and figures together in a single Word doc or PDF file, and for each figure legend to be presented together with its figure. However, when preparing the final paper to be accepted, we require figure legends to be listed one after the other, as part of the text document, separate from the figure files, and after the main reference list.
Each figure legend should begin with a brief title for the whole figure and continue with a short description of each panel and the symbols used. If the paper contains a Methods section, legends should not contain any details of methods. Legends should be fewer than 300 words each.
All error bars and statistics must be defined in the figure legend, as discussed above.
Nature requires figures in electronic format. Please ensure that all digital images comply with the Nature journals’ policy on image integrity .
Figures should be as small and simple as is compatible with clarity. The goal is for figures to be comprehensible to readers in other or related disciplines, and to assist their understanding of the paper. Unnecessary figures and parts (panels) of figures should be avoided: data presented in small tables or histograms, for instance, can generally be stated briefly in the text instead. Avoid unnecessary complexity, colouring and excessive detail.
Figures should not contain more than one panel unless the parts are logically connected; each panel of a multipart figure should be sized so that the whole figure can be reduced by the same amount and reproduced on the printed page at the smallest size at which essential details are visible. For guidance, Nature ’s standard figure sizes are 90 mm (single column) and 180 mm (double column) and the full depth of the page is 170 mm.
Amino-acid sequences should be printed in Courier (or other monospaced) font using the one-letter code in lines of 50 or 100 characters.
Authors describing chemical structures should use the Nature Research Chemical Structures style guide .
Some brief guidance for figure preparation:
Lettering in figures (labelling of axes and so on) should be in lower-case type, with the first letter capitalized and no full stop.
Units should have a single space between the number and the unit, and follow SI nomenclature or the nomenclature common to a particular field. Thousands should be separated by commas (1,000). Unusual units or abbreviations are defined in the legend.
Scale bars should be used rather than magnification factors.
Layering type directly over shaded or textured areas and using reversed type (white lettering on a coloured background) should be avoided where possible.
Where possible, text, including keys to symbols, should be provided in the legend rather than on the figure itself.
Figure quality
At initial submission, figures should be at good enough quality to be assessed by referees, preferably incorporated into the manuscript text in a single Word doc or PDF, although figures can be supplied separately as JPEGs if authors are unable to include them with the text. Authors are advised to follow the initial and revised submissions guidelines with respect to sizing, resolution and labelling.
Please note that print-publication quality figures are large and it is not helpful to upload them at the submission stage. Authors will be asked for high-quality figures when they are asked to submit the final version of their article for publication.At that stage, please prepare figures according to these guidelines .
Third party rights
Nature discourages the use or adaptation of previously published display items (for example, figures, tables, images, videos or text boxes). However, we recognize that to illustrate some concepts the use of published data is required and the reuse of previously published display items may be necessary. Please note that in these instances we might not be able to obtain the necessary rights for some images to be reused (as is, or adapted versions) in our articles. In such cases, we will contact you to discuss the sourcing of alternative material.
Figure costs
In order to help cover some of the additional cost of four-colour reproduction, Nature Portfolio charges our authors a fee for the printing of their colour figures. Please contact our offices for exact pricing and details. Inability to pay this charge will not prevent publication of colour figures judged essential by the editors, but this must be agreed with the editor prior to acceptance.
Production-quality figures
When a manuscript is accepted in principle for publication, the editor will ask for high-resolution figures. Do not submit publication-quality figures until asked to do so by an editor. At that stage, please prepare figures according to these guidelines .
Extended Data
Extended Data figures and tables are online-only (appearing in the online PDF and full-text HTML version of the paper), peer-reviewed display items that provide essential background to the Article but are not included in the printed version of the paper due to space constraints or being of interest only to a few specialists. A maximum of ten Extended Data display items (figures and tables) is typically permitted. See Composition of a Nature research paper .
Extended Data tables should be formatted along similar lines to tables appearing in print (see section 5.7) but the main body (excluding title and legend, which should be included at the end of the Word file) should be submitted separately as an image rather than as an editable format in Word, as Extended Data tables are not edited by Nature’s subediting department. Small tables may also be included as sub-panels within Extended Data figures. See Extended Data Formatting Guide .
Extended Data figures should be prepared along slightly different guidelines compared to figures appearing in print, and may be multi-panelled as long as they fit to size rules (see Extended Data Formatting Guide ). Extended Data figures are not edited or styled by Nature’s art department; for this reason, authors are requested to follow Nature style as closely as possible when preparing these figures. The legends for Extended Data figures should be prepared as for print figures and should be listed one after the other at the end of the Word file.
If space allows, Nature encourages authors to include a simple schematic, as a panel in an Extended Data figure, that summarizes the main finding of the paper, where appropriate (for example, to assist understanding of complex detail in cell, structural and molecular biology disciplines).
If a manuscript has Extended Data figures or tables, authors are asked to refer to discrete items at an appropriate place in the main text (for example, Extended Data Fig. 1 and Extended Data Table 1).
If further references are included in the Extended Data tables and Extended Data figure legends, the numbering should continue from the end of the last reference number in the main paper (or from the last reference number in the additional Methods section if present) and the list should be added to the end of the list accompanying the additional Methods section, if present, or added below the Extended Data legends if no additional Methods section is present.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (SI) is online-only, peer-reviewed material that is essential background to the Article (for example, large data sets, methods, calculations), but which is too large or impractical, or of interest only to a few specialists, to justify inclusion in the printed version of the paper. See the Supplementary Information page for further details.
Supplementary Information should not contain figures (any figures additional to those appearing in print should be formatted as Extended Data figures). Tables may be included in Supplementary Information, but only if they are unsuitable for formatting as Extended Data tables (for example, tables containing large data sets or raw data that are best suited to Excel files).
If a manuscript has accompanying SI, either at submission or in response to an editor’s letter that requests it, authors are asked to refer to discrete items of the SI (for example, videos, tables) at an appropriate point in the main manuscript.
Chemical structures and characterization of chemical materials
For guidelines describing Nature ’s standards for experimental methods and the characterization of new compounds, please see the information sheet on the characterization of chemical materials .
We aim to produce chemical structures in a consistent format throughout our articles. Please use the Nature Portfolio Chemical Structures Guide and ChemDraw template to ensure that you prepare your figures in a format that will require minimal changes by our art and production teams. Submit final files at 100% as .cdx files.
Registered Reports
Registered Reports are empirical articles testing confirmatory hypotheses in which the methods and proposed analyses are pre-registered and peer reviewed prior to research being conducted. For further details about Registered Reports and instructions for how to submit such articles to Nature please consult our Registered Reports page.
All contributions should be submitted online , unless otherwise instructed by the editors. Please be sure to read the information on what to include in your cover letter as well as several important content-related issues when putting a submission together.
Before submitting, all contributors must agree to all of Nature's publication policies .
Nature authors must make data and materials publicly available upon publication. This includes deposition of data into the relevant databases and arranging for them to be publicly released by the online publication date (not after). A description of our initiative to improve the transparency and the reproducibility of published results is available here . A full description of Nature’s publication policies is at the Nature Portfolio Authors and Referees website .
Other Nature Research journals
An account of the relationship between all the Nature journals is provided at the Nature family page .
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Table of Contents

Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings . The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research. It includes guidelines for the structure, citation style, referencing , and other elements of the paper that contribute to its overall presentation and coherence. Adhering to the appropriate research paper format is vital for ensuring that the research is accurately and effectively communicated to the intended audience. In this era of information, it is essential to understand the different research paper formats and their guidelines to communicate research effectively, accurately, and with the required level of detail. This post aims to provide an overview of some of the common research paper formats used in academic writing.
Research Paper Formats
Research Paper Formats are as follows:
- APA (American Psychological Association) format
- MLA (Modern Language Association) format
- Chicago/Turabian style
- IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) format
- AMA (American Medical Association) style
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- ACS (American Chemical Society) style
- ASA (American Sociological Association) style
- APSA (American Political Science Association) style
APA (American Psychological Association) Format
Here is a general APA format for a research paper:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of your paper, your name, and your institutional affiliation. It should also include a running head, which is a shortened version of the title, and a page number in the upper right-hand corner.
- Abstract : The abstract is a brief summary of your paper, typically 150-250 words. It should include the purpose of your research, the main findings, and any implications or conclusions that can be drawn.
- Introduction: The introduction should provide background information on your topic, state the purpose of your research, and present your research question or hypothesis. It should also include a brief literature review that discusses previous research on your topic.
- Methods: The methods section should describe the procedures you used to collect and analyze your data. It should include information on the participants, the materials and instruments used, and the statistical analyses performed.
- Results: The results section should present the findings of your research in a clear and concise manner. Use tables and figures to help illustrate your results.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret your results and relate them back to your research question or hypothesis. It should also discuss the implications of your findings and any limitations of your study.
- References : The references section should include a list of all sources cited in your paper. Follow APA formatting guidelines for your citations and references.
Some additional tips for formatting your APA research paper:
- Use 12-point Times New Roman font throughout the paper.
- Double-space all text, including the references.
- Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
- Use a hanging indent for the references (the first line should be flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines should be indented).
- Number all pages, including the title page and references page, in the upper right-hand corner.
APA Research Paper Format Template
APA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
Title Page:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Institutional affiliation
- A brief summary of the main points of the paper, including the research question, methods, findings, and conclusions. The abstract should be no more than 250 words.
Introduction:
- Background information on the topic of the research paper
- Research question or hypothesis
- Significance of the study
- Overview of the research methods and design
- Brief summary of the main findings
- Participants: description of the sample population, including the number of participants and their characteristics (age, gender, ethnicity, etc.)
- Materials: description of any materials used in the study (e.g., survey questions, experimental apparatus)
- Procedure: detailed description of the steps taken to conduct the study
- Presentation of the findings of the study, including statistical analyses if applicable
- Tables and figures may be included to illustrate the results
Discussion:
- Interpretation of the results in light of the research question and hypothesis
- Implications of the study for the field
- Limitations of the study
- Suggestions for future research
References:
- A list of all sources cited in the paper, in APA format
Formatting guidelines:
- Double-spaced
- 12-point font (Times New Roman or Arial)
- 1-inch margins on all sides
- Page numbers in the top right corner
- Headings and subheadings should be used to organize the paper
- The first line of each paragraph should be indented
- Quotations of 40 or more words should be set off in a block quote with no quotation marks
- In-text citations should include the author’s last name and year of publication (e.g., Smith, 2019)
APA Research Paper Format Example
APA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health
University of XYZ
This study examines the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Data was collected through a survey of 500 students at the University of XYZ. Results suggest that social media use is significantly related to symptoms of depression and anxiety, and that the negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users.
Social media has become an increasingly important aspect of modern life, especially among young adults. While social media can have many positive effects, such as connecting people across distances and sharing information, there is growing concern about its impact on mental health. This study aims to examine the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students.
Participants: Participants were 500 college students at the University of XYZ, recruited through online advertisements and flyers posted on campus. Participants ranged in age from 18 to 25, with a mean age of 20.5 years. The sample was 60% female, 40% male, and 5% identified as non-binary or gender non-conforming.
Data was collected through an online survey administered through Qualtrics. The survey consisted of several measures, including the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for depression symptoms, the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) for anxiety symptoms, and questions about social media use.
Procedure :
Participants were asked to complete the online survey at their convenience. The survey took approximately 20-30 minutes to complete. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression analysis.
Results indicated that social media use was significantly related to symptoms of depression (r = .32, p < .001) and anxiety (r = .29, p < .001). Regression analysis indicated that frequency of social media use was a significant predictor of both depression symptoms (β = .24, p < .001) and anxiety symptoms (β = .20, p < .001), even when controlling for age, gender, and other relevant factors.
The results of this study suggest that social media use is associated with symptoms of depression and anxiety among college students. The negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users. These findings have important implications for mental health professionals and educators, who should consider addressing the potential negative effects of social media use in their work with young adults.
References :
References should be listed in alphabetical order according to the author’s last name. For example:
- Chou, H. T. G., & Edge, N. (2012). “They are happier and having better lives than I am”: The impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15(2), 117-121.
- Twenge, J. M., Joiner, T. E., Rogers, M. L., & Martin, G. N. (2018). Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among U.S. adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time. Clinical Psychological Science, 6(1), 3-17.
Note: This is just a sample Example do not use this in your assignment.
MLA (Modern Language Association) Format
MLA (Modern Language Association) Format is as follows:
- Page Layout : Use 8.5 x 11-inch white paper, with 1-inch margins on all sides. The font should be 12-point Times New Roman or a similar serif font.
- Heading and Title : The first page of your research paper should include a heading and a title. The heading should include your name, your instructor’s name, the course title, and the date. The title should be centered and in title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- In-Text Citations : Use parenthetical citations to indicate the source of your information. The citation should include the author’s last name and the page number(s) of the source. For example: (Smith 23).
- Works Cited Page : At the end of your paper, include a Works Cited page that lists all the sources you used in your research. Each entry should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the medium of publication.
- Formatting Quotations : Use double quotation marks for short quotations and block quotations for longer quotations. Indent the entire quotation five spaces from the left margin.
- Formatting the Body : Use a clear and readable font and double-space your text throughout. The first line of each paragraph should be indented one-half inch from the left margin.
MLA Research Paper Template
MLA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
- Use 8.5 x 11 inch white paper.
- Use a 12-point font, such as Times New Roman.
- Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper, including the title page and works cited page.
- Set the margins to 1 inch on all sides.
- Use page numbers in the upper right corner, beginning with the first page of text.
- Include a centered title for the research paper, using title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- Include your name, instructor’s name, course name, and date in the upper left corner, double-spaced.
In-Text Citations
- When quoting or paraphrasing information from sources, include an in-text citation within the text of your paper.
- Use the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses at the end of the sentence, before the punctuation mark.
- If the author’s name is mentioned in the sentence, only include the page number in parentheses.
Works Cited Page
- List all sources cited in alphabetical order by the author’s last name.
- Each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and medium of publication.
- Use italics for book and journal titles, and quotation marks for article and chapter titles.
- For online sources, include the date of access and the URL.
Here is an example of how the first page of a research paper in MLA format should look:
Headings and Subheadings
- Use headings and subheadings to organize your paper and make it easier to read.
- Use numerals to number your headings and subheadings (e.g. 1, 2, 3), and capitalize the first letter of each word.
- The main heading should be centered and in boldface type, while subheadings should be left-aligned and in italics.
- Use only one space after each period or punctuation mark.
- Use quotation marks to indicate direct quotes from a source.
- If the quote is more than four lines, format it as a block quote, indented one inch from the left margin and without quotation marks.
- Use ellipses (…) to indicate omitted words from a quote, and brackets ([…]) to indicate added words.
Works Cited Examples
- Book: Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Year.
- Journal Article: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, publication date, page numbers.
- Website: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Webpage.” Title of Website, publication date, URL. Accessed date.
Here is an example of how a works cited entry for a book should look:
Smith, John. The Art of Writing Research Papers. Penguin, 2021.
MLA Research Paper Example
MLA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
Your Professor’s Name
Course Name and Number
Date (in Day Month Year format)
Word Count (not including title page or Works Cited)
Title: The Impact of Video Games on Aggression Levels
Video games have become a popular form of entertainment among people of all ages. However, the impact of video games on aggression levels has been a subject of debate among scholars and researchers. While some argue that video games promote aggression and violent behavior, others argue that there is no clear link between video games and aggression levels. This research paper aims to explore the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults.
Background:
The debate on the impact of video games on aggression levels has been ongoing for several years. According to the American Psychological Association, exposure to violent media, including video games, can increase aggression levels in children and adolescents. However, some researchers argue that there is no clear evidence to support this claim. Several studies have been conducted to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels, but the results have been mixed.
Methodology:
This research paper used a quantitative research approach to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults. A sample of 100 young adults between the ages of 18 and 25 was selected for the study. The participants were asked to complete a questionnaire that measured their aggression levels and their video game habits.
The results of the study showed that there was a significant correlation between video game habits and aggression levels among young adults. The participants who reported playing violent video games for more than 5 hours per week had higher aggression levels than those who played less than 5 hours per week. The study also found that male participants were more likely to play violent video games and had higher aggression levels than female participants.
The findings of this study support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to note that the study only examined the impact of video games on aggression levels and did not take into account other factors that may contribute to aggressive behavior. It is also important to note that not all video games promote violence and aggression, and some games may have a positive impact on cognitive and social skills.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, this research paper provides evidence to support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to conduct further research to examine the impact of video games on other aspects of behavior and to explore the potential benefits of video games. Parents and educators should be aware of the potential impact of video games on aggression levels and should encourage young adults to engage in a variety of activities that promote cognitive and social skills.
Works Cited:
- American Psychological Association. (2017). Violent Video Games: Myths, Facts, and Unanswered Questions. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2017/08/violent-video-games
- Ferguson, C. J. (2015). Do Angry Birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 10(5), 646-666.
- Gentile, D. A., Swing, E. L., Lim, C. G., & Khoo, A. (2012). Video game playing, attention problems, and impulsiveness: Evidence of bidirectional causality. Psychology of Popular Media Culture, 1(1), 62-70.
- Greitemeyer, T. (2014). Effects of prosocial video games on prosocial behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 106(4), 530-548.
Chicago/Turabian Style
Chicago/Turabian Formate is as follows:
- Margins : Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
- Font : Use a readable font such as Times New Roman or Arial, and use a 12-point font size.
- Page numbering : Number all pages in the upper right-hand corner, beginning with the first page of text. Use Arabic numerals.
- Title page: Include a title page with the title of the paper, your name, course title and number, instructor’s name, and the date. The title should be centered on the page and in title case (capitalize the first letter of each word).
- Headings: Use headings to organize your paper. The first level of headings should be centered and in boldface or italics. The second level of headings should be left-aligned and in boldface or italics. Use as many levels of headings as necessary to organize your paper.
- In-text citations : Use footnotes or endnotes to cite sources within the text of your paper. The first citation for each source should be a full citation, and subsequent citations can be shortened. Use superscript numbers to indicate footnotes or endnotes.
- Bibliography : Include a bibliography at the end of your paper, listing all sources cited in your paper. The bibliography should be in alphabetical order by the author’s last name, and each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and date of publication.
- Formatting of quotations: Use block quotations for quotations that are longer than four lines. Indent the entire quotation one inch from the left margin, and do not use quotation marks. Single-space the quotation, and double-space between paragraphs.
- Tables and figures: Use tables and figures to present data and illustrations. Number each table and figure sequentially, and provide a brief title for each. Place tables and figures as close as possible to the text that refers to them.
- Spelling and grammar : Use correct spelling and grammar throughout your paper. Proofread carefully for errors.
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template is as folows:
Title of Paper
Name of Student
Professor’s Name
I. Introduction
A. Background Information
B. Research Question
C. Thesis Statement
II. Literature Review
A. Overview of Existing Literature
B. Analysis of Key Literature
C. Identification of Gaps in Literature
III. Methodology
A. Research Design
B. Data Collection
C. Data Analysis
IV. Results
A. Presentation of Findings
B. Analysis of Findings
C. Discussion of Implications
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of Findings
B. Implications for Future Research
C. Conclusion
VI. References
A. Bibliography
B. In-Text Citations
VII. Appendices (if necessary)
A. Data Tables
C. Additional Supporting Materials
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Example
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Political Engagement
Name: John Smith
Class: POLS 101
Professor: Dr. Jane Doe
Date: April 8, 2023
I. Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of our daily lives. People use social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to connect with friends and family, share their opinions, and stay informed about current events. With the rise of social media, there has been a growing interest in understanding its impact on various aspects of society, including political engagement. In this paper, I will examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, specifically focusing on how social media influences political participation and political attitudes.
II. Literature Review:
There is a growing body of literature on the impact of social media on political engagement. Some scholars argue that social media has a positive effect on political participation by providing new channels for political communication and mobilization (Delli Carpini & Keeter, 1996; Putnam, 2000). Others, however, suggest that social media can have a negative impact on political engagement by creating filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue (Pariser, 2011; Sunstein, 2001).
III. Methodology:
To examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, I conducted a survey of 500 college students. The survey included questions about social media use, political participation, and political attitudes. The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Iv. Results:
The results of the survey indicate that social media use is positively associated with political participation. Specifically, respondents who reported using social media to discuss politics were more likely to have participated in a political campaign, attended a political rally, or contacted a political representative. Additionally, social media use was found to be associated with more positive attitudes towards political engagement, such as increased trust in government and belief in the effectiveness of political action.
V. Conclusion:
The findings of this study suggest that social media has a positive impact on political engagement, by providing new opportunities for political communication and mobilization. However, there is also a need for caution, as social media can also create filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue. Future research should continue to explore the complex relationship between social media and political engagement, and develop strategies to harness the potential benefits of social media while mitigating its potential negative effects.
Vii. References:
- Delli Carpini, M. X., & Keeter, S. (1996). What Americans know about politics and why it matters. Yale University Press.
- Pariser, E. (2011). The filter bubble: What the Internet is hiding from you. Penguin.
- Putnam, R. D. (2000). Bowling alone: The collapse and revival of American community. Simon & Schuster.
- Sunstein, C. R. (2001). Republic.com. Princeton University Press.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Format
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Research Paper Format is as follows:
- Title : A concise and informative title that accurately reflects the content of the paper.
- Abstract : A brief summary of the paper, typically no more than 250 words, that includes the purpose of the study, the methods used, the key findings, and the main conclusions.
- Introduction : An overview of the background, context, and motivation for the research, including a clear statement of the problem being addressed and the objectives of the study.
- Literature review: A critical analysis of the relevant research and scholarship on the topic, including a discussion of any gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Methodology : A detailed description of the methods used to collect and analyze data, including any experiments or simulations, data collection instruments or procedures, and statistical analyses.
- Results : A clear and concise presentation of the findings, including any relevant tables, graphs, or figures.
- Discussion : A detailed interpretation of the results, including a comparison of the findings with previous research, a discussion of the implications of the results, and any recommendations for future research.
- Conclusion : A summary of the key findings and main conclusions of the study.
- References : A list of all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to IEEE guidelines.
In addition to these elements, an IEEE research paper should also follow certain formatting guidelines, including using 12-point font, double-spaced text, and numbered headings and subheadings. Additionally, any tables, figures, or equations should be clearly labeled and referenced in the text.
AMA (American Medical Association) Style
AMA (American Medical Association) Style Research Paper Format:
- Title Page: This page includes the title of the paper, the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and any acknowledgments or disclaimers.
- Abstract: The abstract is a brief summary of the paper that outlines the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of the study. It is typically limited to 250 words or less.
- Introduction: The introduction provides a background of the research problem, defines the research question, and outlines the objectives and hypotheses of the study.
- Methods: The methods section describes the research design, participants, procedures, and instruments used to collect and analyze data.
- Results: The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and charts where appropriate.
- Discussion: The discussion section interprets the results, explains their significance, and relates them to previous research in the field.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the main points of the paper, discusses the implications of the findings, and suggests future research directions.
- References: The reference list includes all sources cited in the paper, listed in alphabetical order by author’s last name.
In addition to these sections, the AMA format requires that authors follow specific guidelines for citing sources in the text and formatting their references. The AMA style uses a superscript number system for in-text citations and provides specific formats for different types of sources, such as books, journal articles, and websites.
Harvard Style
Harvard Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title page: This should include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date of submission.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your paper, usually no more than 250 words. It should outline the main points of your research and highlight your findings.
- Introduction : This section should introduce your research topic, provide background information, and outline your research question or thesis statement.
- Literature review: This section should review the relevant literature on your topic, including previous research studies, academic articles, and other sources.
- Methodology : This section should describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including any data collection methods, research instruments, and sampling techniques.
- Results : This section should present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables, graphs, and other visual aids if necessary.
- Discussion : This section should interpret your findings and relate them to the broader research question or thesis statement. You should also discuss the implications of your research and suggest areas for future study.
- Conclusion : This section should summarize your main findings and provide a final statement on the significance of your research.
- References : This is a list of all the sources you cited in your paper, presented in alphabetical order by author name. Each citation should include the author’s name, the title of the source, the publication date, and other relevant information.
In addition to these sections, a Harvard Style research paper may also include a table of contents, appendices, and other supplementary materials as needed. It is important to follow the specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or academic institution when preparing your research paper in Harvard Style.
Vancouver Style
Vancouver Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The Vancouver citation style is commonly used in the biomedical sciences and is known for its use of numbered references. Here is a basic format for a research paper using the Vancouver citation style:
- Title page: Include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your research paper, usually no more than 250 words.
- Introduction : Provide some background information on your topic and state the purpose of your research.
- Methods : Describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including the study design, data collection, and statistical analysis.
- Results : Present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables and figures as needed.
- Discussion : Interpret your results and explain their significance. Also, discuss any limitations of your study and suggest directions for future research.
- References : List all of the sources you cited in your paper in numerical order. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the article or book, the name of the journal or publisher, the year of publication, and the page numbers.
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The American Chemical Society (ACS) Style is a citation style commonly used in chemistry and related fields. When formatting a research paper in ACS Style, here are some guidelines to follow:
- Paper Size and Margins : Use standard 8.5″ x 11″ paper with 1-inch margins on all sides.
- Font: Use a 12-point serif font (such as Times New Roman) for the main text. The title should be in bold and a larger font size.
- Title Page : The title page should include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the date of submission. The title should be centered on the page and written in bold font. The authors’ names should be centered below the title, followed by their affiliations and the date.
- Abstract : The abstract should be a brief summary of the paper, no more than 250 words. It should be on a separate page and include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the text of the abstract.
- Main Text : The main text should be organized into sections with headings that clearly indicate the content of each section. The introduction should provide background information and state the research question or hypothesis. The methods section should describe the procedures used in the study. The results section should present the findings of the study, and the discussion section should interpret the results and provide conclusions.
- References: Use the ACS Style guide to format the references cited in the paper. In-text citations should be numbered sequentially throughout the text and listed in numerical order at the end of the paper.
- Figures and Tables: Figures and tables should be numbered sequentially and referenced in the text. Each should have a descriptive caption that explains its content. Figures should be submitted in a high-quality electronic format.
- Supporting Information: Additional information such as data, graphs, and videos may be included as supporting information. This should be included in a separate file and referenced in the main text.
- Acknowledgments : Acknowledge any funding sources or individuals who contributed to the research.
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page of an ASA style research paper should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, and the institutional affiliation. The title should be centered and should be in title case (the first letter of each major word should be capitalized).
- Abstract: An abstract is a brief summary of the paper that should appear on a separate page immediately following the title page. The abstract should be no more than 200 words in length and should summarize the main points of the paper.
- Main Body: The main body of the paper should begin on a new page following the abstract page. The paper should be double-spaced, with 1-inch margins on all sides, and should be written in 12-point Times New Roman font. The main body of the paper should include an introduction, a literature review, a methodology section, results, and a discussion.
- References : The reference section should appear on a separate page at the end of the paper. All sources cited in the paper should be listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the date of publication.
- Appendices : Appendices are optional and should only be included if they contain information that is relevant to the study but too lengthy to be included in the main body of the paper. If you include appendices, each one should be labeled with a letter (e.g., Appendix A, Appendix B, etc.) and should be referenced in the main body of the paper.
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, the name of the course or instructor, and the date.
- Abstract : An abstract is typically not required in APSA style papers, but if one is included, it should be brief and summarize the main points of the paper.
- Introduction : The introduction should provide an overview of the research topic, the research question, and the main argument or thesis of the paper.
- Literature Review : The literature review should summarize the existing research on the topic and provide a context for the research question.
- Methods : The methods section should describe the research methods used in the paper, including data collection and analysis.
- Results : The results section should present the findings of the research.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret the results and connect them back to the research question and argument.
- Conclusion : The conclusion should summarize the main findings and implications of the research.
- References : The reference list should include all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to APSA style guidelines.
In-text citations in APSA style use parenthetical citation, which includes the author’s last name, publication year, and page number(s) if applicable. For example, (Smith 2010, 25).
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide...

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...
Font To Choose for Your Research Paper: Best Font for Essays

We’ve all, at some time in our lives, pondered the question of how to create an essay that gets good grades. You may find millions of instructions that will walk you through the process of writing an excellent essay by doing a simple search on Google or pay for research paper . However, a lot of individuals neglect to think about typefaces. In addition to learning how to acquire material and present it in an organized manner, students should also be taught how to style their written assignments, such as essays. When it concerns font for essay , typefaces are also a very important factor.
You will require to choose a typeface that is easy on the eyes. The issue is that there are literally thousands upon thousands of typefaces from which to choose. And after you’ve decided which one is the greatest, you’ll need to choose the appropriate size. Is it preferable to have a font size of 12 for the body paragraph and 14 for the titles? Let’s see what the best fonts for essays are out there check DoMyEssay .
What About the Font Size?
When it comes to standard font size for essays, it’s usually 12 or 14. But 12 is usually recommended font size for college papers. New Times Roman, Arial, and Calibri are most often seen in this size. The typefaces you choose should be large enough so that your work can be read without putting undue strain on the eyes of the reader. Points are the standard unit of measurement for distances. MLA, American Psychological Association, and Harvard are the most used citation styles and conventions for scientific research publications. The value indicates the proportion of the display that the typeface uses.
Generally, 12 points are considered the minimum acceptable size for academic writing. Size-wise, it’s ideal for the target demographic without seeming too big or cumbersome. The text size you choose for your research paper is crucial in letting it seem professional and attractive. When completing the assignment, the author should utilize the prescribed font size. In figuring out how many webs pages your work needs, this aspect ratio is crucial. To ensure that we don’t go over or under the page count for the whole project, we’ve been using a font size of 12 to do the calculations.
Wensley Modern Serif Font Family
This one is a standard essay font that people use nowadays. Wensley is a contemporary serif font design that is widely used by undergraduates in a variety of educational institutions. This is the ideal look to go for if you wish to give off an air of sophistication and competence to your teachers, which is exactly what you should strive for. This typeface supports a variety of non-English letters, making it suitable for use in any language.
Serif Or Sans Serif, That’s Always A Dilemma
Serif and Sans Serif are always in sort of a rivalry within academic fonts. When deciding whether to choose one of them for your study, the level of formality of the document and the environment in which it will be presented are the two most important factors to consider. The informality of sans serif typefaces makes them a good choice for casual presentations, while the beauty of serif fonts makes them a good choice for more official scholarly articles. It is often advised to choose a sans serif since it is more readable and less tiresome to write on a pc screen. If we are thinking about the place it will be released, we should take this into consideration.
The majority of analyses and publications, regardless of the publication venue in which they appear, benefit from having either serif or sans serif font for college essay included in the same document. The headlines or restricted quotations in a piece of writing will often benefit link from using one style, whereas the main section of the text may benefit from using the other.
Our further font research leads us to Calibri. The popularity of this typeface is comparable to that of the font Times New Roman. In addition to that, Calibri is a Sans typeface. There are a number of advantages to using this font, including the fact that it is not unusual, that it is simple to read, that it is user-friendly for cell devices, and many more. It is one of the safest options for some of the best research paper writing services too. However, this does not always imply that every aspect of this typeface has solely positive qualities. The fact that it is easy to forget about and not particularly thrilling is another one of its many drawbacks. On the other hand, it is commonly used by electronic firms who are responsible for the creation of websites.
Times New Roman
If you ask any best essay writer service which font is the most appropriate to choose, he or she will pick Times New Roman. The Times of London, a magazine published in the United Kingdom, is where this typeface got its name. A new font was commissioned to be designed by the Times in 1929 by typographer Stanley Morison. He was in charge of leading the project, while Victor Lardent, an advertisement designer for the Times, was the one who designed the letterings under his supervision.
Even when it was brand new, Times New Roman was met with opposition. The fact that the new typeface was featured in a daily paper contributed to its meteoric rise to fame among manufacturers of the era. Times New Roman has consistently been one of the very first typefaces offered for each new writing device, despite the fact that composing technologies have changed significantly in the intervening decades. As a consequence of this, its scope has grown even more.
Creating an essay for high school or university requires the student to pay attention to numerous details. Among the most crucial aspects of an excellent college essay are its subject, structure, substance, trustworthiness of resources, the writer’s voice, simplicity of ideas, and continuity of views. There is, nevertheless, a factor that many university learners grossly undervalue. Making sure you choose a legible typeface is just as important as providing a well-thought-out argument throughout your academic paper.
Get the Reddit app
This sub is for discussions amongst college & university faculty. Whether you are an adjunct, a lecturer, a grad TA or tenured stream if you teach students at the college level, this space is for you! While we welcome students and non-academics lurking and learning, posts and comments are not allowed. If you're new here, please familiarize yourself with the sub rules and follow them. If you're ever unsure, feel free to reach out to the moderators for clarification.
What font are you using in your papers (research, white papers, etc.)?
I swear to god every co-author I work with has a different opinion of which font to use. Thankfully I'm always the first author so I stick with Times Roman. I have no emotional attachment, it's just what I've used forever.
I know publishing, we use whatever the editor wants, and that always seems to change.
What's your go to font. I know the standing joke is Comic Sans, but seriously, what is your default font?
Edit it appears we should all be doing this:
For official university documents, we should use comic sans so they know we put little effort into it.
For professional work Garamond seems to be the clear favor with TNR a strong second.
To menu | To main contents
Script can not be used because of invalid.
*Because style sheet is disabled , can not use.
This is the menu from here
- About NITech
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- International Relations
Home > Topics > The newest research paper of Associate Professor Takashi SHIRAI's group has been highlighted as the FRONT COVER of the latest issue of Nanoscale Advances
The newest research paper of Associate Professor Takashi SHIRAI's group has been highlighted as the FRONT COVER of the latest issue of Nanoscale Advances
Category:News|Publishing : June 20, 2024
The newest research paper of Associate Professor Takashi SHIRAI's group has been honored and highlighted as the FRONT COVER of the latest issue of Nanoscale Advances , a peer-reviewed scientific journal that published by Royal Society of Chemistry. The paper entitled with「 Role of polyvinylpyrrolidone in the polyol synthesis of platinum nanoparticles 」 reported the influence of surface passivation agent on metal particles formation mechanism in polyol process. The paper was authored by Assistant Professor Yunzi XIN ( Department of Engineering (Life Science and Applied Chemistry) ), Mr. TakuNAGATA ( Previous master student: Department of Life Science and Applied Chemistry ), Assistant Professor Kunihiko KATO ( Department of Engineering (Life Science and Applied Chemistry) ), Assistant Professor Yuping XU ( Department of Engineering (Life Science and Applied Chemistry) ), Associate Professor Takashi SHIRAI ( Department of Engineering (Life Science and Applied Chemistry) ) .

Metal nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted global interest in various applications, such as energy conversion, air and water purification, sensing, and medicine, owing to their extraordinary chemical and physical properties. Metal nanoparticles with altered size and morphology have been numerously prepared via different synthetic approaches. In particular, the synthesis of metal nanoparticles via liquid-phase polyol reaction has attracted worldwide attention as one of the most facile approaches. Since the multivalent alcohols utilized in polyol reaction possess high polarity and boiling point, various the metal salts precursors can be dissolved and then reduced into metal nanoparticles at a relatively lower temperature even under the boiling point. During polyol synthesis of metal nanoparticles, the surface passivation agent (also known as capping agent, surfactant) plays an important role in preventing the aggregation and agglomeration of formed particles、 as well as size and morphology controlling. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), is one of the most popular surface passivation agents that utilized in polyol system, due to its non-toxicity and non-ionic nature. In present work, platinum (Pt)nanoparticles were synthesized under altered PVP/Pt-ion molar ratio. The hydrodynamic size of synthesized Pt nanoparticles in different solvents, the crystal structure, solid-phase size and morphology, as well as the surface chemical state and thermal stability of passivated PVP, the reduction behavior and dynamic of Pt-ion in synthesis stage were elucidated systemically, during where the role of PVP in Pt nanoparticle formation and mechanism in size/surface structure controlling were also clarified in detail.
SHIRAI Laboratory Website
Nanoscale Advances
Title: Role of polyvinylpyrrolidone in the polyol synthesis of platinum nanoparticles Authors:Yunzi Xin, Taku Nagata, Kunihiko Kato, Yuping Xu, and Takashi Shirai * *Corresponding author Article information: DOI: doi.org/10.1039/D4NA00118D
Back to Topics
To page top

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Let's dive into a crucial piece of the puzzle when talking about the best fonts for academic papers: Font Size and Readability. Because, let's face it, nobody wants to squint or get lost in a sea of text. ... When you're knee-deep in thesis writing or scientific research, your font choice is like picking the right tool for a delicate job ...
20. If there's no template, then the choice is yours. However, you should make sure to pick a font that's easy to read. The usual standards in academia tend to be the Times, Helvetica/Arial, and Computer Modern families. This doesn't restrict you from using fonts like Book Antiqua, Myriad Pro, Goudy Old Style, or Garamond, but they're ...
These fonts are everywhere because they are champions of legibility and simplicity. Make your work professional and trustworthy by using a time-tested font. [bra_divider height='40'] 1. Arial- "All-Around Champion with IBM Roots". According to fonts.com, Arial is one of the most used typefaces of the last 30 years.
A variety of fonts are permitted in APA Style papers. Font options include the following: sans serif fonts such as 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, or 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode; serif fonts such as 12-point Times New Roman, 11-point Georgia, or normal (10-point) Computer Modern (the default font for LaTeX); We recommend these fonts because they are legible and widely available and because ...
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
The best font size for a research paper is point 12. This size is the most common ones, especially for New Times Roman, Arial or Calibri fonts. Basically, the size of the fonts should make your work to be readable without straining the audience. We measure size using 'points'.
Kristina Gill, an archaeobotanist and archaeologist at the University of Oregon, believes that typeface should vary between formats. For manuscript submission, she favours Times New Roman or ...
Experience the beauty of science with free scientific fonts - perfect for scientific papers, posters, and presentations. Clean and precise, they capture the essence of research. Font Categories
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial. Set 1 inch page margins. Apply double line spacing. If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Junicode (short for Junius-Unicode) is a TrueType/OpenType font for medievalists with extensive coverage of the Latin Unicode ranges, plus Runic and Gothic. The font comes in four faces. Of these, regular and italic are fullest, featuring complete implementation of the Medieval Unicode Font Initiative recommendation, version 4.0. Go to font lists.
If you type in a script font, avoid using artistic fonts, since they are harder to follow. You can choose between Serif or Sans Serif depending on the medium or the audience you will be addressing to. Your poster or paper should not contain more than two or three contrasting fonts. For body copy and headings, Time New Roman and Arial combine ...
Times New Roman is the standard choice for academic documents, and the thesis preparation guidelines of some universities stipulate its use. For many years, it was the default body text for Microsoft Word. With the release of Office 2007, the default became a sans serif typeface called Calibri. Lacking the little projecting bits (serifs) at the ...
This table describes how to format your research paper using either the MLA or APA guidelines. Be sure to follow any additional instructions that your teacher provides. 12-pt. Times Roman or Courier. For figures, however, use a sans serif font such as Arial. Leave one space after a period unless your teacher prefers two. Leave one space after a ...
For many students, embarking on a dissertation is a daunting task. Beyond the research, writing, and analysis, a seemingly insignificant detail can cause unexpected stress: font selection.While it might seem like a minor concern, the right font can significantly impact the readability, professionalism, and overall look of your dissertation and can highly influence the decision of the readers.
Best Fonts for Academic Papers in Microsoft Word. The best fonts for academic papers are Times New Roman, Baskerville Old Face, and Georgia. There are plenty of good options, but you'll mainly want to stick to serif fonts. They look much neater and more professional while showing that the reader can trust what you say.
We prefer the use of a 'standard' font, preferably 12-point Times New Roman. ... papers in press, and research datasets that have been assigned a digital object identifier may be included in ...
Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings. ... Margins: Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the paper. Font: Use a readable font such as Times New Roman or Arial, and use a 12-point font size. Page numbering: Number all pages in the upper right-hand corner ...
When it comes to standard font size for essays, it's usually 12 or 14. But 12 is usually recommended font size for college papers. New Times Roman, Arial, and Calibri are most often seen in this size. The typefaces you choose should be large enough so that your work can be read without putting undue strain on the eyes of the reader.
You could also go with MLA but APA is for science reports. If you use anything other than a regular typeface they will probably just throw your report out. I like Linux Libertine (serif) and Linux Biolinum (sans-serif) when paired together. Knuth's Computer Modern, default LaTeX font. "Scientific" report is a bit vague.
a five-page paper written in Times New Roman (TNR). Therefore, if a professor compares two papers--one written in TNR and one written in another, larger font, he will quickly know who has provided more research. Besides size, some fonts are very attractive but difficult to read, so APA recommends simpler fonts.
9. Autor. Autor is a set of sans serifs with a clean and sharp look. Created for editorials and body text, this typeface is a great font choice for papers and reports that utilize varying headers and titles. 10. Maine. Maine is a modernized version of the classic Book Antiqua serif, with 12 font styles.
Font Acceptable fonts are Times New Roman, 12 pt. or Courier New, 12 pt. • Title Page: APA style requires a title page. The title, author, and institution are centered in the upper half of the page. • Margins: All margins — top, bottom, left, and right — are set to 1" throughout the paper. Spacing The paper is double spaced throughout,
DaFatAlien. •. My personal feeling is that serif fonts are better for materials to be perused (e.g. full academic papers), and sans serif fonts are better for materials primarily consumed on screen or by a quick glance (e.g. presentation slides and references cards). Reply reply. thanksforthegift.
The newest research paper of Associate Professor Takashi SHIRAI's group has been honored and highlighted as the FRONT COVER of the latest issue of Nanoscale Advances, a peer-reviewed scientific journal that published by Royal Society of Chemistry.The paper entitled with「 Role of polyvinylpyrrolidone in the polyol synthesis of platinum nanoparticles 」 reported the influence of surface ...