

How to write recommendations for the study in a thesis report?
Typically noted as ‘Conclusion and Recommendations for the study’ in thesis reports, the section dedicated to recommendations for the study is brief and direct. In many thesis reports it is also presented as a standalone section. Recommendations for the study do not explain anything as other sections of the research would do. Instead, the focus here is on highlighting what more can be done in that field of study. It also gives direction to fellow researchers to dive into the discussion in the future.
The main themes of this section are:
- Improvement
- Development
The recommendations for the study section present possible areas of improvement for future studies.
Constituents of the recommendations for the study section
Since this section of the thesis report is most often set along with the conclusion of the study, it is better presented in a brief but direct approach. It is introduced by one direct sentence that separates it from the conclusion of the study. The preceding statements should immediately note the recommendations and why these suggestions are important. It should then explain how such suggestions can be achieved in a future research. While writing the recommendations for the study section, it is important that the suggestions are:
- Measurable,
- Attainable,
- Realistic, and
This section can also be presented in bullet points and focus to cover:
While there is no required specific number of recommendations but 4 recommendations for every 20000 words in a thesis report is a general thumb. Limit the number of words in this section up to 5% of the total word count of your thesis report. This is to set a balance as to what else can be done and the current investigation.
What not to do?
Remember that the recommendations for the study section should not be confused with the conclusion or the summary of the study. It should only focus on the suggestions for future possibilities. Do not present new findings or statistical or experimental data. Do not include theoretical concepts. Start with an introductory statement.
This section enlists the recommendations of the study. The purpose is to offer ideas on how the findings of this study can be implemented in academia to further this field of study. It also offers suggestions on how the challenges of the industry or individuals can be addressed for better outcomes.
Thereafter, split the section into three sub-sections as explained above. After writing the recommendations for each sub-section, close the thesis with ‘ Scope for further research ‘.
It is suggested that direct interviews with individuals who have been diagnosed with PNES be pursued in the future to allow the researchers to closely look into the situation more closely. After accomplishing the interview, a few context suggestions on how to improve the lives of the said individuals ought to be given particular attention.
The above recommendation focuses on improving the idea behind exploring the issue of how Psychological Non-Epileptic Seizures affect the functionality of a person suffering from the condition. This recommendation is for a 1000-word research paper on PNES or Psychological Non-Epileptic Seizures. There is only one specific recommendation which is explained in a few statements- which remains true to the idea behind keeping the recommendations section brief and focused.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
proofreading

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of exploration. In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and an ever-expanding knowledge base, refining the process of generating research recommendations becomes imperative.
But, what is a research recommendation?
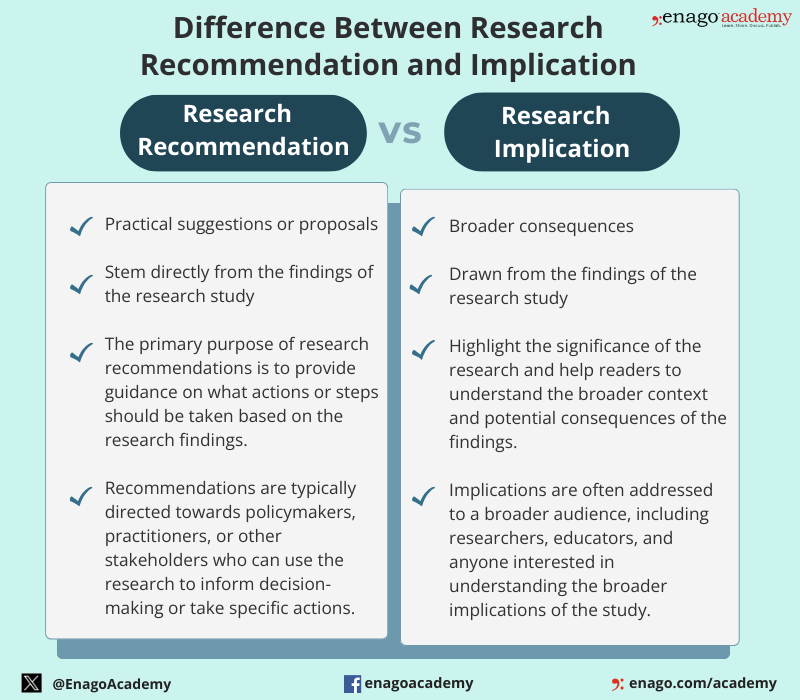
Research recommendations are suggestions or advice provided to researchers to guide their study on a specific topic . They are typically given by experts in the field. Research recommendations are more action-oriented and provide specific guidance for decision-makers, unlike implications that are broader and focus on the broader significance and consequences of the research findings. However, both are crucial components of a research study.
Difference Between Research Recommendations and Implication
Although research recommendations and implications are distinct components of a research study, they are closely related. The differences between them are as follows:
Types of Research Recommendations
Recommendations in research can take various forms, which are as follows:
These recommendations aim to assist researchers in navigating the vast landscape of academic knowledge.
Let us dive deeper to know about its key components and the steps to write an impactful research recommendation.
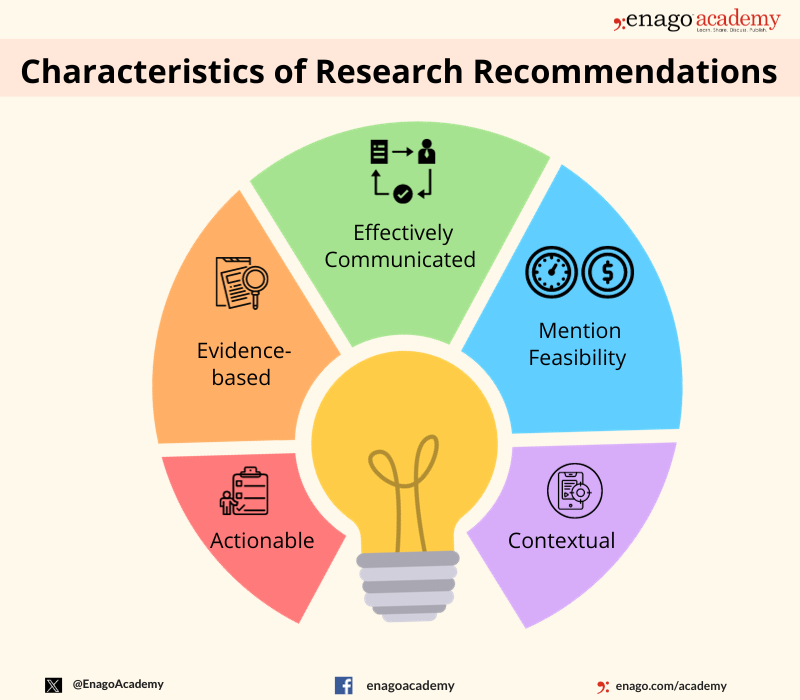
Key Components of Research Recommendations
The key components of research recommendations include defining the research question or objective, specifying research methods, outlining data collection and analysis processes, presenting results and conclusions, addressing limitations, and suggesting areas for future research. Here are some characteristics of research recommendations:
Research recommendations offer various advantages and play a crucial role in ensuring that research findings contribute to positive outcomes in various fields. However, they also have few limitations which highlights the significance of a well-crafted research recommendation in offering the promised advantages.
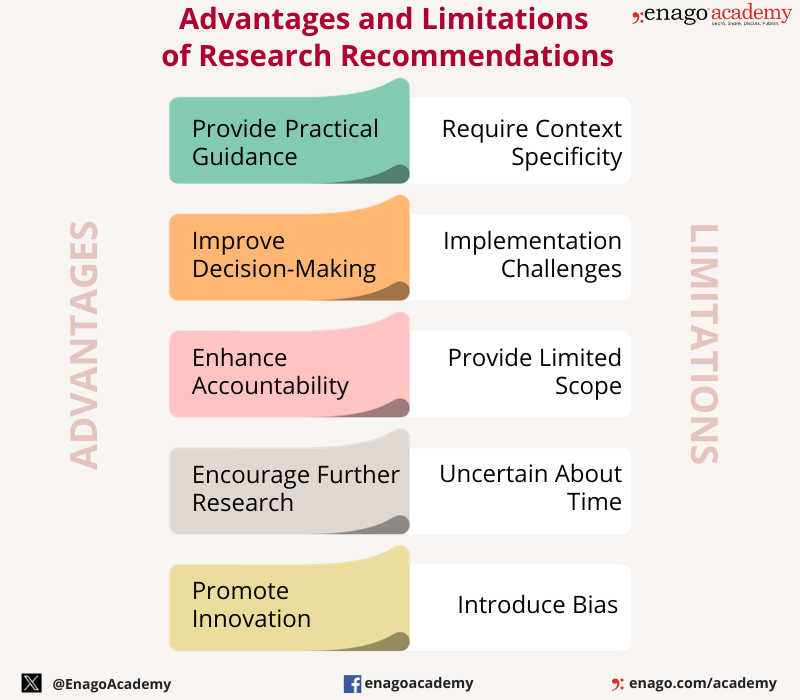
The importance of research recommendations ranges in various fields, influencing policy-making, program development, product development, marketing strategies, medical practice, and scientific research. Their purpose is to transfer knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, or stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and improving outcomes in different domains.
How to Write Research Recommendations?
Research recommendations can be generated through various means, including algorithmic approaches, expert opinions, or collaborative filtering techniques. Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations.
1. Understand the Research Question:
Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study.
2. Review Existing Literature:
Familiarize yourself with relevant existing literature to help you identify gaps , and offer informed recommendations that contribute to the existing body of research.
3. Consider Research Methods:
Evaluate the appropriateness of different research methods in addressing the research question. Also, consider the nature of the data, the study design, and the specific objectives.
4. Identify Data Collection Techniques:
Gather dataset from diverse authentic sources. Include information such as keywords, abstracts, authors, publication dates, and citation metrics to provide a rich foundation for analysis.
5. Propose Data Analysis Methods:
Suggest appropriate data analysis methods based on the type of data collected. Consider whether statistical analysis, qualitative analysis, or a mixed-methods approach is most suitable.
6. Consider Limitations and Ethical Considerations:
Acknowledge any limitations and potential ethical considerations of the study. Furthermore, address these limitations or mitigate ethical concerns to ensure responsible research.
7. Justify Recommendations:
Explain how your recommendation contributes to addressing the research question or objective. Provide a strong rationale to help researchers understand the importance of following your suggestions.
8. Summarize Recommendations:
Provide a concise summary at the end of the report to emphasize how following these recommendations will contribute to the overall success of the research project.
By following these steps, you can create research recommendations that are actionable and contribute meaningfully to the success of the research project.
Download now to unlock some tips to improve your journey of writing research recommendations.
Example of a Research Recommendation
Here is an example of a research recommendation based on a hypothetical research to improve your understanding.
Research Recommendation: Enhancing Student Learning through Integrated Learning Platforms
Background:
The research study investigated the impact of an integrated learning platform on student learning outcomes in high school mathematics classes. The findings revealed a statistically significant improvement in student performance and engagement when compared to traditional teaching methods.
Recommendation:
In light of the research findings, it is recommended that educational institutions consider adopting and integrating the identified learning platform into their mathematics curriculum. The following specific recommendations are provided:
- Implementation of the Integrated Learning Platform:
Schools are encouraged to adopt the integrated learning platform in mathematics classrooms, ensuring proper training for teachers on its effective utilization.
- Professional Development for Educators:
Develop and implement professional programs to train educators in the effective use of the integrated learning platform to address any challenges teachers may face during the transition.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
Establish a monitoring and evaluation system to track the impact of the integrated learning platform on student performance over time.
- Resource Allocation:
Allocate sufficient resources, both financial and technical, to support the widespread implementation of the integrated learning platform.
By implementing these recommendations, educational institutions can harness the potential of the integrated learning platform and enhance student learning experiences and academic achievements in mathematics.
This example covers the components of a research recommendation, providing specific actions based on the research findings, identifying the target audience, and outlining practical steps for implementation.
Using AI in Research Recommendation Writing
Enhancing research recommendations is an ongoing endeavor that requires the integration of cutting-edge technologies, collaborative efforts, and ethical considerations. By embracing data-driven approaches and leveraging advanced technologies, the research community can create more effective and personalized recommendation systems. However, it is accompanied by several limitations. Therefore, it is essential to approach the use of AI in research with a critical mindset, and complement its capabilities with human expertise and judgment.
Here are some limitations of integrating AI in writing research recommendation and some ways on how to counter them.
1. Data Bias
AI systems rely heavily on data for training. If the training data is biased or incomplete, the AI model may produce biased results or recommendations.
How to tackle: Audit regularly the model’s performance to identify any discrepancies and adjust the training data and algorithms accordingly.
2. Lack of Understanding of Context:
AI models may struggle to understand the nuanced context of a particular research problem. They may misinterpret information, leading to inaccurate recommendations.
How to tackle: Use AI to characterize research articles and topics. Employ them to extract features like keywords, authorship patterns and content-based details.
3. Ethical Considerations:
AI models might stereotype certain concepts or generate recommendations that could have negative consequences for certain individuals or groups.
How to tackle: Incorporate user feedback mechanisms to reduce redundancies. Establish an ethics review process for AI models in research recommendation writing.
4. Lack of Creativity and Intuition:
AI may struggle with tasks that require a deep understanding of the underlying principles or the ability to think outside the box.
How to tackle: Hybrid approaches can be employed by integrating AI in data analysis and identifying patterns for accelerating the data interpretation process.
5. Interpretability:
Many AI models, especially complex deep learning models, lack transparency on how the model arrived at a particular recommendation.
How to tackle: Implement models like decision trees or linear models. Provide clear explanation of the model architecture, training process, and decision-making criteria.
6. Dynamic Nature of Research:
Research fields are dynamic, and new information is constantly emerging. AI models may struggle to keep up with the rapidly changing landscape and may not be able to adapt to new developments.
How to tackle: Establish a feedback loop for continuous improvement. Regularly update the recommendation system based on user feedback and emerging research trends.
The integration of AI in research recommendation writing holds great promise for advancing knowledge and streamlining the research process. However, navigating these concerns is pivotal in ensuring the responsible deployment of these technologies. Researchers need to understand the use of responsible use of AI in research and must be aware of the ethical considerations.
Exploring research recommendations plays a critical role in shaping the trajectory of scientific inquiry. It serves as a compass, guiding researchers toward more robust methodologies, collaborative endeavors, and innovative approaches. Embracing these suggestions not only enhances the quality of individual studies but also contributes to the collective advancement of human understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
The purpose of recommendations in research is to provide practical and actionable suggestions based on the study's findings, guiding future actions, policies, or interventions in a specific field or context. Recommendations bridges the gap between research outcomes and their real-world application.
To make a research recommendation, analyze your findings, identify key insights, and propose specific, evidence-based actions. Include the relevance of the recommendations to the study's objectives and provide practical steps for implementation.
Begin a recommendation by succinctly summarizing the key findings of the research. Clearly state the purpose of the recommendation and its intended impact. Use a direct and actionable language to convey the suggested course of action.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Using AI for Journal Selection — Simplifying your academic publishing journey in the smart way
Strategic journal selection plays a pivotal role in maximizing the impact of one’s scholarly work.…

- Career Corner
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 6 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Beyond the Podium: Understanding the differences in conference and academic…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Dissertation Recommendations — How To Write Them
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Recommendations are crucial to your paper because they suggest solutions to your research problems. You can include recommendations in the discussion sections of your writing and briefly in the conclusions of your dissertation , thesis, or research paper . This article discusses dissertation recommendations, their purpose, and how to write one.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Dissertation Recommendations — In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Dissertation recommendations
- 3 How to write dissertation recommendations
- 4 Dissertation recommendations based on your findings
- 5 Purpose of dissertation recommendations
Dissertation Recommendations — In a Nutshell
- Dissertation recommendations are an important aspect of your research paper.
- They should be specific, measurable, and have the potential of future possibilities.
- Additionally, these recommendations should offer practical insights and suggestions for solving real-life problems.
When making your recommendations, please ensure the following:
- Your recommendations are an extension of your work instead of a basis for self-criticism
- Your research stands independently instead of suggesting recommendations that will complete it
- Your dissertation recommendations offer insights into how future research can build upon it instead of undermining your research
Definition: Dissertation recommendations
Dissertation recommendations are the actionable insights and suggestions presented after you get your research findings. These suggestions are usually based on what you find and help to guide future studies or practical applications. It’s best to place your dissertation recommendations at the conclusion.
How to write dissertation recommendations
When writing your academic paper, you can frame dissertation recommendations using one of the following methods:
Use the problem: In this approach, you should address the issues highlighted in your research.
Offer solutions: You can offer some practical solutions to the problems revealed in your research.
Use a theory: Here, you can base your recommendations on your study’s theoretical approach.
Here are some helpful tips for writing dissertation recommendations that you should incorporate when drafting a research paper:
- Avoid general or vague recommendations
- Be specific and concrete
- Offer measurable insights Ensure your suggestions are practical and implementable
- Avoid focusing on theoretical concepts or new findings but on future possibilities
“Based on the study’s outcomes, it’s recommended that businesses and organizations develop mental health well-being frameworks to reduce workplace stress. This training should be mandatory for all employees and conducted on a monthly basis.”
Dissertation recommendations based on your findings
After analysing your findings, you can divide your dissertation recommendations into two subheadings as discussed below:
What can be done?
This section highlights the steps you can use when conducting the research. You may also include any steps needed to address the issues highlighted in your research question. For instance, if the study reveals a lack of emotional connection between employees, implementing dynamic awareness training or sit-downs could be recommended.
Is further research needed?
This section highlights the benefits of further studies that will help build on your research findings. For instance, if your research found less data on employee mental well-being, your dissertation recommendations could suggest future studies.
Purpose of dissertation recommendations
Note: Dissertation recommendations have the following purposes:
- Provide guidance and improve the quality of further studies based on your research findings
- Offer insights, call to action, or suggest other studies
- Highlight specific, clear, and realistic suggestions for future studies
When writing your dissertation recommendations, always remember to keep them specific, measurable, and clear. You should also ensure that a comprehensible rationale supports these recommendations. Additionally, your requests should always be directly linked to your research and offer suggestions from that angle.
Note that your suggestions should always focus on future possibilities and not on present new findings or theoretical concepts. This is because future researchers may use your results to draw further conclusions and gather new insights from your work.
Can I include new arguments in the conclusion of a dissertation
Dissertations follow a more formal structure; hence, you can only present new arguments in the conclusion. Use your dissertation’s concluding part as a summary of your points or to provide recommendations.
How is the conclusion different from the discussion sections?
The discussion section describes a detailed account of your findings, while the conclusion answers the research question and highlights some recommendations.
What shouldn't I include in the dissertation recommendations?
Avoid concluding with weak statements like “there are good insights from both ends…”, generic phrases like “in conclusion…” or evidence that you failed to mention in the discussion or results section.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

How to write recommendations in a research paper
Many students put in a lot of effort and write a good report however they are not able to give proper recommendations. Recommendations in the research paper should be included in your research. As a researcher, you display a deep understanding of the topic of research. Therefore you should be able to give recommendations. Here are a few tips that will help you to give appropriate recommendations.
Recommendations in the research paper should be the objective of the research. Therefore at least one of your objectives of the paper is to provide recommendations to the parties associated or the parties that will benefit from your research. For example, to encourage higher employee engagement HR department should make strategies that invest in the well-being of employees. Additionally, the HR department should also collect regular feedback through online surveys.
Recommendations in the research paper should come from your review and analysis For example It was observed that coaches interviewed were associated with the club were working with the club from the past 2-3 years only. This shows that the attrition rate of coaches is high and therefore clubs should work on reducing the turnover of coaches.
Recommendations in the research paper should also come from the data you have analysed. For example, the research found that people over 65 years of age are at greater risk of social isolation. Therefore, it is recommended that policies that are made for combating social isolation should target this specific group.
Recommendations in the research paper should also come from observation. For example, it is observed that Lenovo’s income is stable and gross revenue has displayed a negative turn. Therefore the company should analyse its marketing and branding strategy.
Recommendations in the research paper should be written in the order of priority. The most important recommendations for decision-makers should come first. However, if the recommendations are of equal importance then it should come in the sequence in which the topic is approached in the research.
Recommendations in a research paper if associated with different categories then you should categorize them. For example, you have separate recommendations for policymakers, educators, and administrators then you can categorize the recommendations.
Recommendations in the research paper should come purely from your research. For example, you have written research on the impact on HR strategies on motivation. However, nowhere you have discussed Reward and recognition. Then you should not give recommendations for using rewards and recognition measures to boost employee motivation.
The use of bullet points offers better clarity rather than using long paragraphs. For example this paragraph “ It is recommended that Britannia Biscuit should launch and promote sugar-free options apart from the existing product range. Promotion efforts should be directed at creating a fresh and healthy image. A campaign that conveys a sense of health and vitality to the consumer while enjoying biscuit is recommended” can be written as:
- The company should launch and promote sugar-free options
- The company should work towards creating s fresh and healthy image
- The company should run a campaign to convey its healthy image
The inclusion of an action plan along with recommendation adds more weightage to your recommendation. Recommendations should be clear and conscience and written using actionable words. Recommendations should display a solution-oriented approach and in some cases should highlight the scope for further research.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on September 14, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master’s program or a capstone to a bachelor’s degree.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation , it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic , crafting a proposal , designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement for Master’s programs, and is also sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts colleges.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
- In other countries (particularly the UK), a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807” by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: “’A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man’: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947″ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces

Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the “Insert Caption” feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialized or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetize the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyzes the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasize what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense , your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation , you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimizing confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A thesis is typically written by students finishing up a bachelor’s or Master’s degree. Some educational institutions, particularly in the liberal arts, have mandatory theses, but they are often not mandatory to graduate from bachelor’s degrees. It is more common for a thesis to be a graduation requirement from a Master’s degree.
Even if not mandatory, you may want to consider writing a thesis if you:
- Plan to attend graduate school soon
- Have a particular topic you’d like to study more in-depth
- Are considering a career in research
- Would like a capstone experience to tie up your academic experience
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, what is your plagiarism score.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Evans D, Coad J, Cottrell K, et al. Public involvement in research: assessing impact through a realist evaluation. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2014 Oct. (Health Services and Delivery Research, No. 2.36.)

Public involvement in research: assessing impact through a realist evaluation.
Chapter 9 conclusions and recommendations for future research.
- How well have we achieved our original aim and objectives?
The initially stated overarching aim of this research was to identify the contextual factors and mechanisms that are regularly associated with effective and cost-effective public involvement in research. While recognising the limitations of our analysis, we believe we have largely achieved this in our revised theory of public involvement in research set out in Chapter 8 . We have developed and tested this theory of public involvement in research in eight diverse case studies; this has highlighted important contextual factors, in particular PI leadership, which had not previously been prominent in the literature. We have identified how this critical contextual factor shapes key mechanisms of public involvement, including the identification of a senior lead for involvement, resource allocation for involvement and facilitation of research partners. These mechanisms then lead to specific outcomes in improving the quality of research, notably recruitment strategies and materials and data collection tools and methods. We have identified a ‘virtuous circle’ of feedback to research partners on their contribution leading to their improved confidence and motivation, which facilitates their continued contribution. Following feedback from the HS&DR Board on our original application we did not seek to assess the cost-effectiveness of different mechanisms of public involvement but we did cost the different types of public involvement as discussed in Chapter 7 . A key finding is that many research projects undercost public involvement.
In our original proposal we emphasised our desire to include case studies involving young people and families with children in the research process. We recruited two studies involving parents of young children aged under 5 years, and two projects involving ‘older’ young people in the 18- to 25-years age group. We recognise that in doing this we missed studies involving children and young people aged under 18 years; in principle we would have liked to have included studies involving such children and young people, but, given the resources at our disposal and the additional resource, ethical and governance issues this would have entailed, we regretfully concluded that this would not be feasible for our study. In terms of the four studies with parental and young persons’ involvement that we did include, we have not done a separate analysis of their data, but the themes emerging from those case studies were consistent with our other case studies and contributed to our overall analysis.
In terms of the initial objectives, we successfully recruited the sample of eight diverse case studies and collected and analysed data from them (objective 1). As intended, we identified the outcomes of involvement from multiple stakeholders‘ perspectives, although we did not get as many research partners‘ perspectives as we would have liked – see limitations below (objective 2). It was more difficult than expected to track the impact of public involvement from project inception through to completion (objective 3), as all of our projects turned out to have longer time scales than our own. Even to track involvement over a stage of a case study research project proved difficult, as the research usually did not fall into neatly staged time periods and one study had no involvement activity over the study period.
Nevertheless, we were able to track seven of the eight case studies prospectively and in real time over time periods of up to 9 months, giving us an unusual window on involvement processes that have previously mainly been observed retrospectively. We were successful in comparing the contextual factors, mechanisms and outcomes associated with public involvement from different stakeholders‘ perspectives and costing the different mechanisms for public involvement (objective 4). We only partly achieved our final objective of undertaking a consensus exercise among stakeholders to assess the merits of the realist evaluation approach and our approach to the measurement and valuation of economic costs of public involvement in research (objective 5). A final consensus event was held, where very useful discussion and amendment of our theory of public involvement took place, and the economic approach was discussed and helpfully critiqued by participants. However, as our earlier discussions developed more fully than expected, we decided to let them continue rather than interrupt them in order to run the final exercise to assess the merits of the realist evaluation approach. We did, however, test our analysis with all our case study participants by sending a draft of this final report for comment. We received a number of helpful comments and corrections but no disagreement with our overall analysis.
- What were the limitations of our study?
Realist evaluation is a relatively new approach and we recognise that there were a number of limitations to our study. We sought to follow the approach recommended by Pawson, but we acknowledge that we were not always able to do so. In particular, our theory of public involvement in research evolved over time and initially was not as tightly framed in terms of a testable hypothesis as Pawson recommends. In his latest book Pawson strongly recommends that outcomes should be measured with quantitative data, 17 but we did not do so; we were not aware of the existence of quantitative data or tools that would enable us to collect such data to answer our research questions. Even in terms of qualitative data, we did not capture as much information on outcomes as we initially envisaged. There were several reasons for this. The most important was that capturing outcomes in public involvement is easier the more operational the focus of involvement, and more difficult the more strategic the involvement. Thus, it was relatively easy to see the impact of a patient panel on the redesign of a recruitment leaflet but harder to capture the impact of research partners in a multidisciplinary team discussion of research design.
We also found it was sometimes more difficult to engage research partners as participants in our research than researchers or research managers. On reflection this is not surprising. Research partners are generally motivated to take part in research relevant to their lived experience of a health condition or situation, whereas our research was quite detached from their lived experience; in addition people had many constraints on their time, so getting involved in our research as well as their own was likely to be a burden too far for some. Researchers clearly also face significant time pressures but they had a more direct interest in our research, as they are obliged to engage with public involvement to satisfy research funders such as the NIHR. Moreover, researchers were being paid by their employers for their time during interviews with us, while research partners were not paid by us and usually not paid by their research teams. Whatever the reasons, we had less response from research partners than researchers or research managers, particularly for the third round of data collection; thus we have fewer data on outcomes from research partners‘ perspectives and we need to be aware of a possible selection bias towards more engaged research partners. Such a bias could have implications for our findings; for example payment might have been a more important motivating factor for less engaged advisory group members.
There were a number of practical difficulties we encountered. One challenge was when to recruit the case studies. We recruited four of our eight case studies prior to the full application, but this was more than 1 year before our project started and 15 months or more before data collection began. In this intervening period, we found that the time scales of some of the case studies were no longer ideal for our project and we faced the choice of whether to continue with them, although this timing was not ideal, or seek at a late moment to recruit alternative ones. One of our case studies ultimately undertook no involvement activity over the study period, so we obtained fewer data from it, and it contributed relatively little to our analysis. Similarly, one of the four case studies we recruited later experienced some delays itself in beginning and so we had a more limited period for data collection than initially envisaged. Research governance approvals took much longer than expected, particularly as we had to take three of our research partners, who were going to collect data within NHS projects, through the research passport process, which essentially truncated our data collection period from 1 year to 9 months. Even if we had had the full year initially envisaged for data collection, our conclusion with hindsight was that this was insufficiently long. To compare initial plans and intentions for involvement with the reality of what actually happened required a longer time period than a year for most of our case studies.
In the light of the importance we have placed on the commitment of PIs, there is an issue of potential selection bias in the recruitment of our sample. As our sampling strategy explicitly involved a networking approach to PIs of projects where we thought some significant public involvement was taking place, we were likely (as we did) to recruit enthusiasts and, at worst, those non-committed who were at least open to the potential value of public involvement. There were, unsurprisingly, no highly sceptical PIs in our sample. We have no data therefore on how public involvement may work in research where the PI is sceptical but may feel compelled to undertake involvement because of funder requirements or other factors.
- What would we do differently next time?
If we were to design this study again, there are a number of changes we would make. Most importantly we would go for a longer time period to be able to capture involvement through the whole research process from initial design through to dissemination. We would seek to recruit far more potential case studies in principle, so that we had greater choice of which to proceed with once our study began in earnest. We would include case studies from the application stage to capture the important early involvement of research partners in the initial design period. It might be preferable to research a smaller number of case studies, allowing a more in-depth ethnographic approach. Although challenging, it would be very informative to seek to sample sceptical PIs. This might require a brief screening exercise of a larger group of PIs on their attitudes to and experience of public involvement.
The economic evaluation was challenging in a number of ways, particularly in seeking to obtain completed resource logs from case study research partners. Having a 2-week data collection period was also problematic in a field such as public involvement, where activity may be very episodic and infrequent. Thus, collecting economic data alongside other case study data in a more integrated way, and particularly with interviews and more ethnographic observation of case study activities, might be advantageous. The new budgeting tool developed by INVOLVE and the MHRN may provide a useful resource for future economic evaluations. 23
We have learned much from the involvement of research partners in our research team and, although many aspects of our approach worked well, there are some things we would do differently in future. Even though we included substantial resources for research partner involvement in all aspects of our study, we underestimated how time-consuming such full involvement would be. We were perhaps overambitious in trying to ensure such full involvement with the number of research partners and the number and complexity of the case studies. We were also perhaps naive in expecting all the research partners to play the same role in the team; different research partners came with different experiences and skills, and, like most of our case studies, we might have been better to be less prescriptive and allow the roles to develop more organically within the project.
- Implications for research practice and funding
If one of the objectives of R&D policy is to increase the extent and effectiveness of public involvement in research, then a key implication of this research is the importance of influencing PIs to value public involvement in research or to delegate to other senior colleagues in leading on involvement in their research. Training is unlikely to be the key mechanism here; senior researchers are much more likely to be influenced by peers or by their personal experience of the benefits of public involvement. Early career researchers may be shaped by training but again peer learning and culture may be more influential. For those researchers sceptical or agnostic about public involvement, the requirement of funders is a key factor that is likely to make them engage with the involvement agenda. Therefore, funders need to scrutinise the track record of research teams on public involvement to ascertain whether there is any evidence of commitment or leadership on involvement.
One of the findings of the economic analysis was that PIs have consistently underestimated the costs of public involvement in their grant applications. Clearly the field will benefit from the guidance and budgeting tool recently disseminated by MHRN and INVOLVE. It was also notable that there was a degree of variation in the real costs of public involvement and that effective involvement is not necessarily costly. Different models of involvement incur different costs and researchers need to be made aware of the costs and benefits of these different options.
One methodological lesson we learned was the impact that conducting this research had on some participants’ reflection on the impact of public involvement. Particularly for research staff, the questions we asked sometimes made them reflect upon what they were doing and change aspects of their approach to involvement. Thus, the more the NIHR and other funders can build reporting, audit and other forms of evaluation on the impact of public involvement directly into their processes with PIs, the more likely such questioning might stimulate similar reflection.
- Recommendations for further research
There are a number of gaps in our knowledge around public involvement in research that follow from our findings, and would benefit from further research, including realist evaluation to extend and further test the theory we have developed here:
- In-depth exploration of how PIs become committed to public involvement and how to influence agnostic or sceptical PIs would be very helpful. Further research might compare, for example, training with peer-influencing strategies in engendering PI commitment. Research could explore the leadership role of other research team members, including research partners, and how collective leadership might support effective public involvement.
- More methodological work is needed on how to robustly capture the impact and outcomes of public involvement in research (building as well on the PiiAF work of Popay et al. 51 ), including further economic analysis and exploration of impact when research partners are integral to research teams.
- Research to develop approaches and carry out a full cost–benefit analysis of public involvement in research would be beneficial. Although methodologically challenging, it would be very useful to conduct some longer-term studies which sought to quantify the impact of public involvement on such key indicators as participant recruitment and retention in clinical trials.
- It would also be helpful to capture qualitatively the experiences and perspectives of research partners who have had mixed or negative experiences, since they may be less likely than enthusiasts to volunteer to participate in studies of involvement in research such as ours. Similarly, further research might explore the (relatively rare) experiences of marginalised and seldom-heard groups involved in research.
- Payment for public involvement in research remains a contested issue with strongly held positions for and against; it would be helpful to further explore the value research partners and researchers place on payment and its effectiveness for enhancing involvement in and impact on research.
- A final relatively narrow but important question that we identified after data collection had finished is: what is the impact of the long periods of relative non-involvement following initial periods of more intense involvement for research partners in some types of research, particularly clinical trials?
Included under terms of UK Non-commercial Government License .
- Cite this Page Evans D, Coad J, Cottrell K, et al. Public involvement in research: assessing impact through a realist evaluation. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2014 Oct. (Health Services and Delivery Research, No. 2.36.) Chapter 9, Conclusions and recommendations for future research.
- PDF version of this title (4.3M)
In this Page
Other titles in this collection.
- Health Services and Delivery Research
Recent Activity
- Conclusions and recommendations for future research - Public involvement in rese... Conclusions and recommendations for future research - Public involvement in research: assessing impact through a realist evaluation
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
Published on 15 September 2022 by Tegan George .
Recommendations in research are a crucial component of your discussion section and the conclusion of your thesis , dissertation , or research paper .
As you conduct your research and analyse the data you collected , perhaps there are ideas or results that don’t quite fit the scope of your research topic . Or, maybe your results suggest that there are further implications of your results or the causal relationships between previously-studied variables than covered in extant research.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What should recommendations look like, building your research recommendation, how should your recommendations be written, recommendation in research example, frequently asked questions about recommendations.
Recommendations for future research should be:
- Concrete and specific
- Supported with a clear rationale
- Directly connected to your research
Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
Relatedly, when making these recommendations, avoid:
- Undermining your own work, but rather offer suggestions on how future studies can build upon it
- Suggesting recommendations actually needed to complete your argument, but rather ensure that your research stands alone on its own merits
- Using recommendations as a place for self-criticism, but rather as a natural extension point for your work
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
There are many different ways to frame recommendations, but the easiest is perhaps to follow the formula of research question conclusion recommendation. Here’s an example.
Conclusion An important condition for controlling many social skills is mastering language. If children have a better command of language, they can express themselves better and are better able to understand their peers. Opportunities to practice social skills are thus dependent on the development of language skills.
As a rule of thumb, try to limit yourself to only the most relevant future recommendations: ones that stem directly from your work. While you can have multiple recommendations for each research conclusion, it is also acceptable to have one recommendation that is connected to more than one conclusion.
These recommendations should be targeted at your audience, specifically toward peers or colleagues in your field that work on similar topics to yours. They can flow directly from any limitations you found while conducting your work, offering concrete and actionable possibilities for how future research can build on anything that your own work was unable to address at the time of your writing.
See below for a full research recommendation example that you can use as a template to write your own.
The current study can be interpreted as a first step in the research on COPD speech characteristics. However, the results of this study should be treated with caution due to the small sample size and the lack of details regarding the participants’ characteristics.
Future research could further examine the differences in speech characteristics between exacerbated COPD patients, stable COPD patients, and healthy controls. It could also contribute to a deeper understanding of the acoustic measurements suitable for e-health measurements.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, September 15). How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/research-recommendations/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, how to write a results section | tips & examples.

Improved Surface Drainage of Pavements: Final Report (1998)
Chapter: chapter 5 summary, findings, and recommendations.
Below is the uncorrected machine-read text of this chapter, intended to provide our own search engines and external engines with highly rich, chapter-representative searchable text of each book. Because it is UNCORRECTED material, please consider the following text as a useful but insufficient proxy for the authoritative book pages.
CHAPIER 5 SI~MARY, FINDINGS, AND RECOMMENDATIONS SUGARY The primary objective of this research was to identify unproved methods for draining rainwater from the surface of multi-lane pavements and to develop guidelines for their use. The guidelines, along with details on the rationale for their development, are presented in a separate document' "Proposed Design Guidelines for Improving Pavement Surface Drainage" (2J. The guidelines support an interactive computer program, PAVDRN, that can be used by practicing engineers In the process of designing new pavements or rehabilitating old pavements' is outlined In figure 39. The intended audience for the guidelines is practicing highway design engineers that work for transportation agencies or consulting firms. Improved pavement surface drainage is needed for two reasons: (~) to minimize splash and spray and (2) to control the tendency for hydroplaning. Both issues are primary safety concerns. At the request of the advisory panel for the project, the main focus of this study was on ~mprov~g surface drainage to mammae the tendency for hydroplaning. In terms of reducing the tendency for hydroplaTuT g, the needed level of drainage is defined in terms of the thickness of the film of water on the pavement. Therefore, the guidelines were developed within the context of reducing the thickness of the water film on pavement surfaces to the extent that hydroplaning is unlikely at highway design speeds. Since hydroplaning is ~7
DESIGN CRITERIA Pavement Geometry Number of lanes Section type - Tangent - Horizontal curve - Transition - Vertical crest curve - Vertical sag curve Enviromnental oramaters Rainfall intensity ~ Temperature Pavement Tvpe Dense-graded asphalt Porous asphalt Portland cement concrete ~ Grooved Portland cement concrete Desion Soeed Allowable speed for onset of hydroplaning Recommend Desion Changes Alter geometry Alter pavement surface Add appurtenances Groove (Portland cement concrete) CALCULATIONS Lenoth of flow path Calculate on basis of pavement geometry IT Hydraulic Analvses . No? Water film thickness Equation No. 10 Equation No.'s. 16-19 1 Hvdroolanino Analvsis Hydroplaning speed Equation No.'s 21-24 Rainfall Intensity Equation No. 25 -A I / Meet Design ~ \ Cntena? / \<es? Accent Desinn | Figure 39. Flow diagram representing PAVI)RN design process In "Proposed Guidelines for Improving Pavement Surface DrmT~age" (2). 118
controlled primarily by the thickness of the water film on the pavement surface, the design guidelines focus on the prediction and control of ache depth of water flowing across the pavement surface as a result of rainfall, often referred to as sheet flow. Water film thickness on highway pavements can be controlled In three fundamental ways, by: I. Minimizing the length of the longest flow path of the water over We pavement and thereby the distance over which the flow can develop; 2. Increasing the texture of the pavement surface; and 3. Removing water from the pavement's surface. In the process of using PAVDRN to implement the design guidelines, the designer is guided to (~) minimize the longest drainage path length of the section under design by altering the pavement geometry and (2) reduce the resultant water film thickness that will develop along that drainage path length by increasing the mean texture depth, choosing a surface that maximizes texture, or using permeable pavements, grooving, and appurtenances to remove water from the surface. Through the course of a typical design project, four key areas need to be considered in order to analyze and eventually reduce the potential for hydroplaning. These areas are: ~9
I. Environmental conditions: 2. Geometry of the roadway surface; 3. Pavement surface (texture) properties; and 4. Appurtenances. Each of these areas and their influence on the resulting hydroplaning speed of the designed section are discussed In detail In the guidelines (21. The environmental conditions considered are rainfall ~ntensibr and water temperature, which determines the kinematic viscosity of the water. The designer has no real control over these environmental factors but needs to select appropriate values when analyzing the effect of flow over the pavement surface and hydroplaning potential. Five section types, one for each of the basic geometric configurations used In highway design, are examined. These section are: 1. TaIlgent; 2. Superelevated curve; 3. Transition; 4. Vertical crest curve; and 5. Vertical sag curve. 120
Pavement properties that affect the water fihn thickness mclude surface characteristics, such as mean texture depth and grooving of Portland cement concrete surfaces, are considered In the process of applying PAVDRN. Porous asphalt pavement surfaces can also reduce He water film thickness and thereby contribute to the reduction of hydroplaning tendency and their presence can also be accounted for when using PAVDRN. Finally, PAVDRN also allows the design engineer to consider the effect of drainage appurtenances, such as slotted drain inlets. A complete description of the various elements that are considered In the PAVDRN program is illustrated In figure 40. A more complete description of the design process, the parameters used in the design process, and typical values for the parameters is presented In the "Proposed Design Guidelines for Improving Pavement Surface Drainage" (2) alla in Appendix A. fIN1)INGS The following findings are based on the research accomplished during the project, a survey of the literature, and a state-of-the-art survey of current practice. I. Model. The one~unensional mode} is adequate as a design tool. The simplicity and stability of the one~imensional mode} offsets any increased accuracy afforded by a two-d~mensional model. The one~mensional model as a predictor of water fiDn thickness and How path length was verified by using data from a previous study (11). 121
No. of Planes Length of Plane Grade Step Increment Wdth of Plane Cross Slope Section T,rne 1) Tangent 2) Honzontal Curare 3) Transition 4) Vertical Crest 5) Vertical Sag U=tS 1)U.S. 2) S. I. Rainfall Intenstity ~ , \ |Kinematic Viscosity |Design Speed Note: PC = Point of Curvature PI. = Point of Tangency PCC = Portland cement concrete WAC = Dense graded asphalt concrete 0GAC = 0pcn~raded asphalt concrete where OGAC includes all types of intentally draining asphalt surfaces GPCC = Grooved Ponland cement concrete Taneent Pavement Type Mean Texture Depth 1) PCC 2) DGAC 3) OGAC 4) GPCC Horizontal Cun~c Grade Cross Slope Radius of Cunran~re Wdth Pavement Type _ 2) DGAC 3) OGAC 4) GPCC Mean Texture Depth Step Increment _ Transition Length of Plane Super Elevation Tangent Cross Slope Tangent Grade width of Curve Transition Width Pavement Type_ 1) PCC 3) OGAC 4) GPCC Mean Texture Depth Step Increment Horizontal Length Cross slope width PC Grade PI' Grade Elevation: Pr-PC Vertical Crest Flow Direction Step Increment Pavement Type 1) PC Side I 2) PI. Side | 1)PCC 2) DGAC 3) OGAC 4) GPCC Mean Tex~rc Depth _ _ ~ Figure 40. Factors considered in PAVDRN program. 122 ~1 r - . , Vertical Sad | Horizontal Length | Cross slope Wldth PC Grade PI Grade Elevation: PIE Flow Direction Step Increment / Stored :_ ~ cats ~ 1) PC Side | 2) PI Side | . Pavement Typed 1) PCC 3) OGAC 14) GPCC Mean Texture Depth I I
~ Stored data V ~ 3 L IN1T For use with a second nut using data from the first run.) , 1 EPRINT (Echos input to output ) 1 CONVERT (Converts units to and from SI and English.) ~ , ADVP (Advances Page of output.) KINW (Calculates Minning's n, Water Film Thickness (WEIR), and Hydroplaning Speed UPS).) , EDGE (Determines if flow has reached the edge of the pavement.) out roar Figure 40. Factors considered in PAVDRN program (continued). 123
2. Occurrence of Hydropl~r g. In general, based on the PAVDRN mode! and the assumptions inherent in its development, hydroplaning can be expected at speeds below roadway design speeds if the length of the flow path exceeds two lane widths. 3. Water Film Thickness. Hydroplaning is initiated primarily by the depth of the water film thickness. Therefore, the primary design objective when controlling hydroplaning must be to limit the depth of the water film. 4. Reducing Water Film Thickness. There are no simple means for controlling water John thickness, but a number of methods can effectively reduce water film thickness and consequently hydroplaning potential. These include: Optimizing pavement geometry, especially cross-slope. Providing some means of additional drainage, such as use of grooved surfaces (PCC) or porous mixtures (HMA). Including slotted drains within the roadway. 5. Tests Needed for Design. The design guidelines require an estimate of the surface texture (MTD) and the coefficient of permeability Porous asphalt only). The sand patch is an acceptable test method for measuring surface texture, except for the more open (20-percent air voids) porous asphalt mixes. In these cases, an estimate of the surface texture, based on tabulated data, is sufficient. As an alternative, 124
sand patch measurements can be made on cast replicas of the surface. For the open mixes, the glass beads flow into the voids within the mixture, giving an inaccurate measure of surface texture. Based on the measurements obtained In the laboratory, the coefficient of permeability for the open-graded asphalt concrete does not exhibit a wide range of values, and values of k may be selected for design purposes from tabulated design data (k versus air voids). Given the uncertainty of this property resulting from compaction under traffic and clogging from contaminants and anti-skid material, a direct measurement (e.g., drainage lag permeameter) of k is not warranted. Based on the previous discussion, no new test procedures are needed to adopt the design guidelines developed during this project. 6. Grooving. Grooving of PCC pavements provides a reservoir for surface water and can facilitate the removal of water if the grooves are placed parallel to the flow oath. Parallel orientation is generally not practical because the flow on highway pavements is typically not transverse to the pavement. Thus, the primary contribution offered by grooving is to provide a surface reservoir unless the grooves comlect with drainage at the edge of the pavement. Once the grooves are filled with water, the tops of the grooves are the datum for the Why and do not contribute to the reduction in the hydroplaning potential. 125
7. Porous Pavements. These mixtures can enhance the water removal and Hereby reduce water film tHch~ess. They merit more consideration by highway agencies In the United States, but they are not a panacea for eliminating hydroplaning. As with grooved PCC pavements, the internal voids do not contribute to the reduction of hydroplaning; based on the field tests done In this study. hv~ronImiina can be if, , , ~ expected on these mixtures given sufficient water fiLn thickness. Other than their ability to conduct water through internal flow, the large MTD offered by porous asphalt is the main contribution offered by the mixtures to the reduction of hydroplaning potential. The high-void ~ > 20 percent), modified binder mixes used In Europe merit further evaluation in the United States. They should be used In areas where damage from freezing water and the problems of black ice are not likely. 8. Slotted Drains. These fixtures, when installed between travel lanes, offer perhaps the most effective means of controlling water film thickness from a hydraulics standpoint. They have not been used extensively In the traveled lanes and questions remain unanswered with respect to their installation (especially in rehabilitation situations) and maintenance. The ability to support traffic loads and still maintain surface smoothness has not been demonstrated and they may be susceptible to clogging from roadway debris, ice, or snow. 126
RECOMMENDATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS The following recommendations are offered based on the work accomplished during this project and on the conclusions given previously: I. Implementation. The PAVDRN program and associated guidelines need to be field tested and revised as needed. The program and the guidelines are sufficiently complete so that they can be used in a design office. Some of the parameters and algorithms will I~ely need to be modified as experience is gained with the program. 2. Database of Material Properties. A database of material properties should be gathered to supplement the information contained in PAVDRN. This information should Include typical values for the permeability of porous asphalt and topical values for the surface texture (MTD) for different pavement surfaces to include toned Portland cement concrete surfaces. A series of photographs of typical pavement sections and their associated texture depths should be considered as an addition to the design guide (21. 3. Pavement Geometry. The AASHTO design guidelines (~) should be re-evaluated In terms of current design criteria to determine if they can be modified to enhance drainage without adversely affecting vehicle handling or safety. ~27
4. Use of appurtenances. Slotted drams should be evaluated In the field to determine if they are practical when Installed In the traveled way. Manufacturers should reconsider the design of slotted drains and their Installation recommendations currently In force to maximize them for use In multi-lane pavements and to determine if slotted drains are suitable for installations In the traveled right of way. 5. Porous Asphalt Mixtures. More use should be made of these mixtures, especially the modified high a~r-void mixtures as used In France. Field trials should be conducted to monitor HPS and the long-term effectiveness of these mixtures and to validate the MPS and WDT predicted by PAVDRN. 6. Two-D~mensional Model. Further work should be done with two~mensional models to determine if they improve accuracy of PAVDRN and to determine if they are practical from a computational standpoint. ADDITIONAL STUDIES On the basis of the work done during this study, a number of additional items warrant furler study. These Include: 1. Full-scale skid resistance studies to validate PAVDRN in general and the relationship between water film thickness and hydroplaning potential in particular are needed in light of the unexpectedly low hvdronlanin~ speeds predicted during 128 , . ~. , ~
this study. The effect of water infiltration into pavement cracks and loss of water by splash and spray need to be accounted for In the prediction of water fihn Sickness. Surface Irregularities, especially rutting, need to be considered in the prediction models. 2. Field trials are needed to confirm the effectiveness of alternative asphalt and Portland cement concrete surfaces. These include porous Portland cement concrete surfaces, porous asphalt concrete, and various asphalt m~cro-surfaces. 3. The permeability of porous surface mixtures needs to be confirmed with samples removed from the field, and the practicality of a simplified method for measuring in-situ permeability must be investigated and compared to alternative measurements, such as the outflow meter. 4. For measuring pavement texture, alternatives to the sand patch method should be investigated, especially for use with porous asphalt mixtures. 129
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Thesis Format – Templates and Samples
Thesis Format – Templates and Samples
Table of contents.

Thesis Format
Thesis format refers to the structure and layout of a research thesis or dissertation. It typically includes several chapters, each of which focuses on a particular aspect of the research topic .
The exact format of a thesis can vary depending on the academic discipline and the institution, but some common elements include:
Introduction
Literature review, methodology.
The title page is the first page of a thesis that provides essential information about the document, such as the title, author’s name, degree program, university, and the date of submission. It is considered as an important component of a thesis as it gives the reader an initial impression of the document’s content and quality.
The typical contents of a title page in a thesis include:
- The title of the thesis: It should be concise, informative, and accurately represent the main topic of the research.
- Author’s name: This should be written in full and should be the same as it appears on official university records.
- Degree program and department: This should specify the type of degree (e.g., Bachelor’s, Master’s, or Doctoral) and the field of study (e.g., Computer Science, Psychology, etc.).
- University: The name of the university where the thesis is being submitted.
- Date of submission : The month and year of submission of the thesis.
- Other details that can be included on the title page include the name of the advisor, the name of the committee members, and any acknowledgments.
In terms of formatting, the title page should be centered horizontally and vertically on the page, with a consistent font size and style. The page margin for the title page should be at least 1 inch (2.54 cm) on all sides. Additionally, it is common practice to include the university logo or crest on the title page, and this should be placed appropriately.
Title of the Thesis in Title Case by Author’s Full Name in Title Case
A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Department Name at the University Name
Month Year of Submission
An abstract is a brief summary of a thesis or research paper that provides an overview of the main points, methodology, and findings of the study. It is typically placed at the beginning of the document, after the title page and before the introduction.
The purpose of an abstract is to provide readers with a quick and concise overview of the research paper or thesis. It should be written in a clear and concise language, and should not contain any jargon or technical terms that are not easily understood by the general public.
Here’s an example of an abstract for a thesis:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Adolescents
This study examines the impact of social media on mental health among adolescents. The research utilized a survey methodology and collected data from a sample of 500 adolescents aged between 13 and 18 years. The findings reveal that social media has a significant impact on mental health among adolescents, with frequent use of social media associated with higher levels of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. The study concludes that there is a need for increased awareness and education on the risks associated with excessive use of social media, and recommends strategies for promoting healthy social media habits among adolescents.
In this example, the abstract provides a concise summary of the thesis by highlighting the main points, methodology, and findings of the study. It also provides a clear indication of the significance of the study and its implications for future research and practice.
A table of contents is an essential part of a thesis as it provides the reader with an overview of the entire document’s structure and organization.
Here’s an example of how a table of contents might look in a thesis:
TABLE OF CONTENTS
I. INTRODUCTION ……………………………………………………..1
A. Background of the Study………………………………………..1
B. Statement of the Problem……………………………………….2
C. Objectives of the Study………………………………………..3
D. Research Questions…………………………………………….4
E. Significance of the Study………………………………………5
F. Scope and Limitations………………………………………….6
G. Definition of Terms……………………………………………7
II. LITERATURE REVIEW. ………………………………………………8
A. Overview of the Literature……………………………………..8
B. Key Themes and Concepts………………………………………..9
C. Gaps in the Literature………………………………………..10
D. Theoretical Framework………………………………………….11
III. METHODOLOGY ……………………………………………………12
A. Research Design………………………………………………12
B. Participants and Sampling……………………………………..13
C. Data Collection Procedures…………………………………….14
D. Data Analysis Procedures………………………………………15
IV. RESULTS …………………………………………………………16
A. Descriptive Statistics…………………………………………16
B. Inferential Statistics…………………………………………17
V. DISCUSSION ………………………………………………………18
A. Interpretation of Results………………………………………18
B. Discussion of Finding s …………………………………………19
C. Implications of the Study………………………………………20
VI. CONCLUSION ………………………………………………………21
A. Summary of the Study…………………………………………..21
B. Limitations of the Study……………………………………….22
C. Recommendations for Future Research……………………………..23
REFERENCES …………………………………………………………….24
APPENDICES …………………………………………………………….26
As you can see, the table of contents is organized by chapters and sections. Each chapter and section is listed with its corresponding page number, making it easy for the reader to navigate the thesis.
The introduction is a critical part of a thesis as it provides an overview of the research problem, sets the context for the study, and outlines the research objectives and questions. The introduction is typically the first chapter of a thesis and serves as a roadmap for the reader.
Here’s an example of how an introduction in a thesis might look:
Introduction:
The prevalence of obesity has increased rapidly in recent decades, with more than one-third of adults in the United States being classified as obese. Obesity is associated with numerous adverse health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Despite significant efforts to address this issue, the rates of obesity continue to rise. The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between lifestyle behaviors and obesity in young adults.
The study will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach, with both qualitative and quantitative data collection methods. The research objectives are to:
- Examine the relationship between lifestyle behaviors and obesity in young adults.
- Identify the key lifestyle factors that contribute to obesity in young adults.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of current interventions aimed at preventing and reducing obesity in young adults.
The research questions that will guide this study are:
- What is the relationship between lifestyle behaviors and obesity in young adults?
- Which lifestyle factors are most strongly associated with obesity in young adults?
- How effective are current interventions aimed at preventing and reducing obesity in young adults?
By addressing these research questions, this study aims to contribute to the understanding of the factors that contribute to obesity in young adults and to inform the development of effective interventions to prevent and reduce obesity in this population.
A literature review is a critical analysis and evaluation of existing literature on a specific topic or research question. It is an essential part of any thesis, as it provides a comprehensive overview of the existing research on the topic and helps to establish the theoretical framework for the study. The literature review allows the researcher to identify gaps in the current research, highlight areas that need further exploration, and demonstrate the importance of their research question.
April 9, 2023:
A search on Google Scholar for “Effectiveness of Online Learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic” yielded 1,540 results. Upon reviewing the first few pages of results, it is evident that there is a significant amount of literature on the topic. A majority of the studies focus on the experiences and perspectives of students and educators during the transition to online learning due to the pandemic.
One recent study published in the Journal of Educational Technology & Society (Liu et al., 2023) found that students who were already familiar with online learning tools and platforms had an easier time adapting to online learning than those who were not. However, the study also found that students who were not familiar with online learning tools were able to adapt with proper support from their teachers and institutions.
Another study published in Computers & Education (Tang et al., 2023) compared the academic performance of students in online and traditional classroom settings during the pandemic. The study found that while there were no significant differences in the grades of students in the two settings, students in online classes reported higher levels of stress and lower levels of satisfaction with their learning experience.
Methodology in a thesis refers to the overall approach and systematic process that a researcher follows to collect and analyze data in order to answer their research question(s) or achieve their research objectives. It includes the research design, data collection methods, sampling techniques, data analysis procedures, and any other relevant procedures that the researcher uses to conduct their research.
For example, let’s consider a thesis on the impact of social media on mental health among teenagers. The methodology for this thesis might involve the following steps:
Research Design:
The researcher may choose to conduct a quantitative study using a survey questionnaire to collect data on social media usage and mental health among teenagers. Alternatively, they may conduct a qualitative study using focus group discussions or interviews to gain a deeper understanding of the experiences and perspectives of teenagers regarding social media and mental health.
Sampling Techniques:
The researcher may use random sampling to select a representative sample of teenagers from a specific geographic location or demographic group, or they may use purposive sampling to select participants who meet specific criteria such as age, gender, or mental health status.
Data Collection Methods:
The researcher may use an online survey tool to collect data on social media usage and mental health, or they may conduct face-to-face interviews or focus group discussions to gather qualitative data. They may also use existing data sources such as medical records or social media posts.
Data Analysis Procedures:
The researcher may use statistical analysis techniques such as regression analysis to examine the relationship between social media usage and mental health, or they may use thematic analysis to identify key themes and patterns in the qualitative data.
Ethical Considerations: The researcher must ensure that their research is conducted in an ethical manner, which may involve obtaining informed consent from participants, protecting their confidentiality, and ensuring that their rights and welfare are respected.
In a thesis, the “Results” section typically presents the findings of the research conducted by the author. This section typically includes both quantitative and qualitative data, such as statistical analyses, tables, figures, and other relevant data.
Here are some examples of how the “Results” section of a thesis might look:
Example 1: A quantitative study on the effects of exercise on cardiovascular health
In this study, the author conducts a randomized controlled trial to investigate the effects of exercise on cardiovascular health in a group of sedentary adults. The “Results” section might include tables showing the changes in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other relevant indicators in the exercise and control groups over the course of the study. The section might also include statistical analyses, such as t-tests or ANOVA, to demonstrate the significance of the results.
Example 2: A qualitative study on the experiences of immigrant families in a new country
In this study, the author conducts in-depth interviews with immigrant families to explore their experiences of adapting to a new country. The “Results” section might include quotes from the interviews that illustrate the participants’ experiences, as well as a thematic analysis that identifies common themes and patterns in the data. The section might also include a discussion of the implications of the findings for policy and practice.
A thesis discussion section is an opportunity for the author to present their interpretation and analysis of the research results. In this section, the author can provide their opinion on the findings, compare them with other literature, and suggest future research directions.
For example, let’s say the thesis topic is about the impact of social media on mental health. The author has conducted a survey among 500 individuals and has found that there is a significant correlation between excessive social media use and poor mental health.
In the discussion section, the author can start by summarizing the main findings and stating their interpretation of the results. For instance, the author may argue that excessive social media use is likely to cause mental health problems due to the pressure of constantly comparing oneself to others, fear of missing out, and cyberbullying.
Next, the author can compare their results with other studies and point out similarities and differences. They can also identify any limitations in their research design and suggest future directions for research.
For example, the author may point out that their study only measured social media use and mental health at one point in time, and it is unclear whether one caused the other or whether there are other confounding factors. Therefore, they may suggest longitudinal studies that follow individuals over time to better understand the causal relationship.
Writing a conclusion for a thesis is an essential part of the overall writing process. The conclusion should summarize the main points of the thesis and provide a sense of closure to the reader. It is also an opportunity to reflect on the research process and offer suggestions for further study.
Here is an example of a conclusion for a thesis:
After an extensive analysis of the data collected, it is evident that the implementation of a new curriculum has had a significant impact on student achievement. The findings suggest that the new curriculum has improved student performance in all subject areas, and this improvement is particularly notable in math and science. The results of this study provide empirical evidence to support the notion that curriculum reform can positively impact student learning outcomes.
In addition to the positive results, this study has also identified areas for future research. One limitation of the current study is that it only examines the short-term effects of the new curriculum. Future studies should explore the long-term effects of the new curriculum on student performance, as well as investigate the impact of the curriculum on students with different learning styles and abilities.
Overall, the findings of this study have important implications for educators and policymakers who are interested in improving student outcomes. The results of this study suggest that the implementation of a new curriculum can have a positive impact on student achievement, and it is recommended that schools and districts consider curriculum reform as a means of improving student learning outcomes.
References in a thesis typically follow a specific format depending on the citation style required by your academic institution or publisher.
Below are some examples of different citation styles and how to reference different types of sources in your thesis:
In-text citation format: (Author, Year)
Reference list format for a book: Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of work: Capital letter also for subtitle. Publisher.
Example: In-text citation: (Smith, 2010) Reference list entry: Smith, J. D. (2010). The art of writing a thesis. Cambridge University Press.
Reference list format for a journal article: Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range.
Example: In-text citation: (Brown, 2015) Reference list entry: Brown, E., Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2015). The impact of social media on academic performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 108(3), 393-407.
In-text citation format: (Author page number)
Works Cited list format for a book: Author. Title of Book. Publisher, Year of publication.
Example: In-text citation: (Smith 75) Works Cited entry: Smith, John D. The Art of Writing a Thesis. Cambridge University Press, 2010.
Works Cited list format for a journal article: Author(s). “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, date, pages.
Example: In-text citation: (Brown 394) Works Cited entry: Brown, Elizabeth, et al. “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance.” Journal of Educational Psychology, vol. 108, no. 3, 2015, pp. 393-407.
Chicago Style
In-text citation format: (Author year, page number)
Bibliography list format for a book: Author. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example: In-text citation: (Smith 2010, 75) Bibliography entry: Smith, John D. The Art of Writing a Thesis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010.
Bibliography list format for a journal article: Author. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (date): page numbers.
Example: In-text citation: (Brown 2015, 394) Bibliography entry: Brown, Elizabeth, John Smith, and Laura Johnson. “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance.” Journal of Educational Psychology 108, no. 3 (2015): 393-407.
Reference list format for a book: [1] A. A. Author, Title of Book. City of Publisher, Abbrev. of State: Publisher, year.
Example: In-text citation: [1] Reference list entry: A. J. Smith, The Art of Writing a Thesis. New York, NY: Academic Press, 2010.
Reference list format for a journal article: [1] A. A. Author, “Title of Article,” Title of Journal, vol. x, no. x, pp. xxx-xxx, Month year.
Example: In-text citation: [1] Reference list entry: E. Brown, J. D. Smith, and L. Johnson, “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance,” Journal of Educational Psychology, vol. 108, no. 3, pp. 393-407, Mar. 2015.
An appendix in a thesis is a section that contains additional information that is not included in the main body of the document but is still relevant to the topic being discussed. It can include figures, tables, graphs, data sets, sample questionnaires, or any other supplementary material that supports your thesis.
Here is an example of how you can format appendices in your thesis:
- Title page: The appendix should have a separate title page that lists the title, author’s name, the date, and the document type (i.e., thesis or dissertation). The title page should be numbered as the first page of the appendix section.
- Table of contents: If you have more than one appendix, you should include a separate table of contents that lists each appendix and its page number. The table of contents should come after the title page.
- Appendix sections: Each appendix should have its own section with a clear and concise title that describes the contents of the appendix. Each section should be numbered with Arabic numerals (e.g., Appendix 1, Appendix 2, etc.). The sections should be listed in the table of contents.
- Formatting: The formatting of the appendices should be consistent with the rest of the thesis. This includes font size, font style, line spacing, and margins.
- Example: Here is an example of what an appendix might look like in a thesis on the topic of climate change:
Appendix 1: Data Sources
This appendix includes a list of the primary data sources used in this thesis, including their URLs and a brief description of the data they provide.
Appendix 2: Survey Questionnaire
This appendix includes the survey questionnaire used to collect data from participants in the study.
Appendix 3: Additional Figures
This appendix includes additional figures that were not included in the main body of the thesis due to space limitations. These figures provide additional support for the findings presented in the thesis.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences
Thesis and Dissertation Guide
- « Thesis & Dissertation Resources
- The Graduate School Home
- Introduction
- Copyright Page
- Dedication, Acknowledgements, Preface (optional)
- Table of Contents
- List of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
- List of Abbreviations
- List of Symbols
Non-Traditional Formats
Font type and size, spacing and indentation, tables, figures, and illustrations, formatting previously published work.
- Internet Distribution
- Open Access
- Registering Copyright
- Using Copyrighted Materials
- Use of Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Submission Steps
- Submission Checklist
- Sample Pages

II. Formatting Guidelines
All copies of a thesis or dissertation must have the following uniform margins throughout the entire document:
- Left: 1″ (or 1 1/4" to ensure sufficient room for binding the work if desired)
- Right: 1″
- Bottom: 1″ (with allowances for page numbers; see section on Pagination )
- Top: 1″
Exceptions : The first page of each chapter (including the introduction, if any) begins 2″ from the top of the page. Also, the headings on the title page, abstract, first page of the dedication/ acknowledgements/preface (if any), and first page of the table of contents begin 2″ from the top of the page.
Non-traditional theses or dissertations such as whole works comprised of digital, artistic, video, or performance materials (i.e., no written text, chapters, or articles) are acceptable if approved by your committee and graduate program. A PDF document with a title page, copyright page, and abstract at minimum are required to be submitted along with any relevant supplemental files.
Fonts must be 10, 11, or 12 points in size. Superscripts and subscripts (e.g., formulas, or footnote or endnote numbers) should be no more than 2 points smaller than the font size used for the body of the text.
Space and indent your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:

- The text must appear in a single column on each page and be double-spaced throughout the document. Do not arrange chapter text in multiple columns.
- New paragraphs must be indicated by a consistent tab indentation throughout the entire document.
- The document text must be left-justified, not centered or right-justified.
- For blocked quotations, indent the entire text of the quotation consistently from the left margin.
- Ensure headings are not left hanging alone on the bottom of a prior page. The text following should be moved up or the heading should be moved down. This is something to check near the end of formatting, as other adjustments to text and spacing may change where headings appear on the page.
Exceptions : Blocked quotations, notes, captions, legends, and long headings must be single-spaced throughout the document and double-spaced between items.
Paginate your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:
- Use lower case Roman numerals (ii, iii, iv, etc.) on all pages preceding the first page of chapter one. The title page counts as page i, but the number does not appear. Therefore, the first page showing a number will be the copyright page with ii at the bottom.
- Arabic numerals (beginning with 1, 2, 3, 4, etc.) start at chapter one or the introduction, if applicable. Arabic numbers must be included on all pages of the text, illustrations, notes, and any other materials that follow. Thus, the first page of chapter one will show an Arabic numeral 1, and numbering of all subsequent pages will follow in order.
- Do not use page numbers accompanied by letters, hyphens, periods, or parentheses (e.g., 1., 1-2, -1-, (1), or 1a).
- Center all page numbers at the bottom of the page, 1/2″ from the bottom edge.
- Pages must not contain running headers or footers, aside from page numbers.
- If your document contains landscape pages (pages in which the top of the page is the long side of a sheet of paper), make sure that your page numbers still appear in the same position and direction as they do on pages with standard portrait orientation for consistency. This likely means the page number will be centered on the short side of the paper and the number will be sideways relative to the landscape page text. See these additional instructions for assistance with pagination on landscape pages in Microsoft Word .

Format footnotes for your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:

- Footnotes must be placed at the bottom of the page separated from the text by a solid line one to two inches long.
- Begin at the left page margin, directly below the solid line.
- Single-space footnotes that are more than one line long.
- Include one double-spaced line between each note.
- Most software packages automatically space footnotes at the bottom of the page depending on their length. It is acceptable if the note breaks within a sentence and carries the remainder into the footnote area of the next page. Do not indicate the continuation of a footnote.
- Number all footnotes with Arabic numerals. You may number notes consecutively within each chapter starting over with number 1 for the first note in each chapter, or you may number notes consecutively throughout the entire document.
- Footnote numbers must precede the note and be placed slightly above the line (superscripted). Leave no space between the number and the note.
- While footnotes should be located at the bottom of the page, do not place footnotes in a running page footer, as they must remain within the page margins.
Endnotes are an acceptable alternative to footnotes. Format endnotes for your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:

- Always begin endnotes on a separate page either immediately following the end of each chapter, or at the end of your entire document. If you place all endnotes at the end of the entire document, they must appear after the appendices and before the references.
- Include the heading “ENDNOTES” in all capital letters, and center it 1″ below the top of the first page of your endnotes section(s).
- Single-space endnotes that are more than one line long.
- Number all endnotes with Arabic numerals. You may number notes consecutively within each chapter starting over with number 1 for the first note in each chapter, or you may number notes consecutively throughout the entire document.
- Endnote numbers must precede the note and be placed slightly above the line (superscripted). Leave no space between the number and the note.
Tables, figures, and illustrations vary widely by discipline. Therefore, formatting of these components is largely at the discretion of the author.
For example, headings and captions may appear above or below each of these components.
These components may each be placed within the main text of the document or grouped together in a separate section.
Space permitting, headings and captions for the associated table, figure, or illustration must be on the same page.
The use of color is permitted as long as it is consistently applied as part of the finished component (e.g., a color-coded pie chart) and not extraneous or unprofessional (e.g., highlighting intended solely to draw a reader's attention to a key phrase). The use of color should be reserved primarily for tables, figures, illustrations, and active website or document links throughout your thesis or dissertation.
The format you choose for these components must be consistent throughout the thesis or dissertation.
Ensure each component complies with margin and pagination requirements.
Refer to the List of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations section for additional information.
If your thesis or dissertation has appendices, they must be prepared following these guidelines:

- Appendices must appear at the end of the document (before references) and not the chapter to which they pertain.
- When there is more than one appendix, assign each appendix a number or a letter heading (e.g., “APPENDIX 1” or “APPENDIX A”) and a descriptive title. You may number consecutively throughout the entire work (e.g., 1, 2 or A, B), or you may assign a two-part Arabic numeral with the first number designating the chapter in which it appears, separated by a period, followed by a second number or letter to indicate its consecutive placement (e.g., “APPENDIX 3.2” is the second appendix referred to in Chapter Three).
- Include the chosen headings in all capital letters, and center them 1″ below the top of the page.
- All appendix headings and titles must be included in the table of contents.
- Page numbering must continue throughout your appendix or appendices. Ensure each appendix complies with margin and pagination requirements.
You are required to list all the references you consulted. For specific details on formatting your references, consult and follow a style manual or professional journal that is used for formatting publications and citations in your discipline.

Your reference pages must be prepared following these guidelines:
- If you place references after each chapter, the references for the last chapter must be placed immediately following the chapter and before the appendices.
- If you place all references at the end of the thesis or dissertation, they must appear after the appendices as the final component in the document.
- Select an appropriate heading for this section based on the style manual you are using (e.g., “REFERENCES”, “BIBLIOGRAPHY”, or “WORKS CITED”).
- Include the chosen heading in all capital letters, and center it 1″ below the top of the page.
- References must be single-spaced within each entry.
- Include one double-spaced line between each reference.
- Page numbering must continue throughout your references section. Ensure references comply with margin and pagination requirements.
In some cases, students gain approval from their academic program to include in their thesis or dissertation previously published (or submitted, in press, or under review) journal articles or similar materials that they have authored. For more information about including previously published works in your thesis or dissertation, see the section on Use of Your Own Previously Published Materials and the section on Copyrighting.
If your academic program has approved inclusion of such materials, please note that these materials must match the formatting guidelines set forth in this Guide regardless of how the material was formatted for publication.
Some specific formatting guidelines to consider include:

- Fonts, margins, chapter headings, citations, and references must all match the formatting and placement used within the rest of the thesis or dissertation.
- If appropriate, published articles can be included as separate individual chapters within the thesis or dissertation.
- A separate abstract to each chapter should not be included.
- The citation for previously published work must be included as the first footnote (or endnote) on the first page of the chapter.
- Do not include typesetting notations often used when submitting manuscripts to a publisher (i.e., insert table x here).
- The date on the title page should be the year in which your committee approves the thesis or dissertation, regardless of the date of completion or publication of individual chapters.
- If you would like to include additional details about the previously published work, this information can be included in the preface for the thesis or dissertation.
Previous: Order and Components
Next: Distribution

- Dissertation Blogs
How to Write a Thesis Conclusion and Recommendation Chapter?

Description:
A student is asked to write many papers during their time in college. However, a thesis is the ultimate and most important paper they are supposed to write. A lot depends on their thesis. It is accounted for as their final paper before getting their degrees. There are many professionals who stress the importance of writing a good thesis. They tend to focus a lot on the literature and the overall format. The thesis conclusion and recommendation chapter are the most underrated chapters. There’s hardly any discussion about them. However, they are equally important. The thesis conclusion and recommendation are of great importance. They are very important and leave a lasting impact on the minds of the readers. Which is why it is extremely important that the thesis conclusion and recommendation chapter are very well written.
Let us get a better understanding of how to write the thesis conclusion and recommendation chapter. But before we get to that, we should have better knowledge of thesis conclusion chapter.
What Is a Thesis Conclusion and Recommendation Chapter?
A thesis conclusion chapter is not like the conclusions of the rest of the academic papers you write. Unlike most conclusions, a thesis conclusion chapter consists of the overall summary of your literature . Whatever you write in your literature, it is written in a concise format in the conclusion. A good thesis conclusion is a blend of all the facts you have written in your main body. It gives you a brief summary of whatever you have written in your main body. A good conclusion is able to explain the entire gist of your thesis without omitting any major facts or figures.
On the other hand, the recommendations consist of all the recommendations you make. These recommendations can mainly be for future researches, government offices, or even corporate offices.
How to Write a Good Thesis Conclusion?
Here are a few points you should keep in mind while writing a thesis conclusion and recommendation chapters.
Stick to the Question
Keep in mind to provide answers to your research problems in your conclusion chapter. Explain all the problems you have highlighted in the course of your research. Make sure you provide the readers with answers to these questions with reference to your research. This will satisfy the readers and will leave them with a sense of completeness.
You must keep in mind to address your hypothesis in your thesis conclusion chapter. There is always a hypothesis a student begins with while writing the dissertation . Make sure you either confirm that hypothesis or reject it in your conclusion chapter. You must give out a verdict in your conclusion. That is the whole point behind writing it. If you don’t give out a verdict, then your entire research is pointless.
Information
You must keep in mind that your conclusion is the summary of your literature. You must not introduce any new information in your thesis conclusion. This will completely confuse all your readers since they will be expecting a verdict on your hypothesis, not a new theory. Not only that, it will also leave a bad impression on their mind.
Say No to Examples
Like we’ve mentioned in the last step, you should not introduce any new facts and information in your conclusion. Introducing new facts in your conclusion will only confuse your readers.
No First Person’s
Because your conclusions are all about summarizing all the previously mentioned facts; you must make sure not to use the first person while writing. You are simply drawing a conclusion and giving a verdict considering all the facts you have mentioned in your main body. There is no room whatsoever for personal opinions. Which is why you shouldn’t use the first person.
Know the Difference Between Conclusion and Result
It is important that you understand the difference between a conclusion and a result. There’s a lot of difference between the two. Do not copy your result into the conclusion. In the result section, you write about what you have found while conducting your research. On the other hand, in the conclusion, you discuss your result and deliver a verdict.
Validate Your Sources
While recommending, you must make sure that your sources are credible and valid. Only recommend genuine sources and literature. Otherwise, it might leave a bad impression on the readers.
Now that you have understood all the points, you are capable of writing a good conclusion and recommendation chapter. In case you still need professional help or guidance, you can always opt for Uniresearchers . We have a highly trained and equipped team which is ready to help you with all your academic writings.
1 thought on “ How to Write a Thesis Conclusion and Recommendation Chapter? ”
Hey! Thanks so much for sharing this information. This is really helpful.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Sample Recommendations
By: Engr. Mary Rose Florence S. Cobar, Doctor of Philosophy in Education Thesis title: “Development of a Source Material in Food Dehydration Craft Technology for the Secondary Schools”
Recommendations After a thorough analysis of data, the following recommendations are hereby made:
- This research study suggests that education managers study diffusion theory for three reasons. First, education managers and instruction technologists’ do not know why most instructional innovations are or not adopted. Some blame teachers and a resistance to change while the others blamed bureaucracies and lack of funding. In the Philippine context, it’s more a case of lack in funding and political interference, but by and large, schools are commonly viewed as resistant to change. By studying diffusion theory, education managers may be able to explain, predict and account for factors that influence or impede adoption and diffusion of innovations in teaching methods. Therefore, understanding the best way to present innovations for possible adoption of a method is through communication channels. Third, education managers may be able to develop a systematic model for innovative methods in teaching not only the basic courses but in the Makabayan learning area which is one of the study area of this body of research, in simple terms: INNOVATIVENESS = RESOURFULNESS + ADAPTABILITY
- Given that food dehydration in some aspects is a technological innovation, it is useful to apply the tenets of diffusion theory to understand food dehydration’s diffusion in the social system. Diffusion theory provides a framework that helps food dehydration adopted, to be explained, predicted and accounted to by factors that increase or impede the diffusion of innovation. Diffusion theory helps the teachers in the education community identify qualities,ie. relative advantage, compatibility, triability and observability to potential adopters. The diffusion framework also provides a closer look at the communication channels used to spread the word about food dehydration, time span and the characteristics of the adopters.
- To provide a compelling argument as to the reasons behind the actions of individuals as adopters of an innovation, this study recommends for further research in the actuations of the adopters through the use of the actor-network theory (ANT) perspective. Diffusion theory approach is more of the cause and effect of innovation while actor-network theory traces the maneuvers, compromises, twists and turns of a negotiation as it is translated during the process of adoption. The scope of an actor-network theory (ANT) analysis is to yield a broader understanding relative to the professional development of the teachers concerned or attributed to in this study. In context, diffusion theory posits an innovation (food dehydration) ought to be adopted to be able to be diffused through a system (secondary education), while an actor-network theory approach will be primarily concerned with tracing the complex and contingent factors involved in the overall innovation process and the contributory influence to the education sector.
- For the source material, an inclusion of setting up a small home-based enterprise of the family size unit and its system operation and management information. This entrepreneurial segment runs parallel to what the Department of Education and the government would or have implemented starting school year 2006-2007 in key pilot areas, that is, business management for students in the secondary school level to prepare them after graduation and beyond. In the food dehydration craft technology segment, the teachers apply the study of science and technology to that of business management and economics that can be diffused to the students by their teachers as a learning paradigm to prepare them options after secondary school.
In the food dehydration craft technology area of this research study, the recommendations to the new design conceived are the following:
a) a built-in thermometer, hygrometer and psychrometer should be installed to monitor the conditions inside the dehydrator;
b) an additional circuit system designed to control the voltage input to the heating element for a stable hot air supply;
c) the material of construction to be used should be made of stainless steel so as not to oxidize the food being dried because the prototype unit made use of Aluminum which is not recommended for use in food like fruits having a high acid content;
d) the blower fans to be used should be regulated as low, medium and high for better regulation of the relative humidity inside the drying chamber;
e) if the prototype dehydrator has been built, experimentations should be done on a variety of foods to test its efficacy to deliver the desired output.
From the design simulation, the following materials of construction are needed:
Table 16. Table of Specifications
System Design
A system involving a small scale food dehydration enterprise requires minimal capital investment and technical and management skills. But changes due to market trends and to keep the business viable, managerial and technical skills are extremely important in any field where income generation is of primary importance, management knowledge is a must and that includes the teachers for whom this research study is attributed. In systems management, emphasis must be in integrating entrepreneurial technology, finance and marketing strategies instead of transfer of technique only and the most ignored factor, gut feel of the economic factors to be considered.
One thought to “Sample Recommendations”
Hi, very nice post. I have been wonder’n bout this issue,so thanks for posting
Comments are closed.
is a “rare breed” among custom essay writing services today
All the papers delivers are completely original as we check every single work for plagiarism via advanced plagiarism detection software. As a double check of the paper originality, you are free to order a full plagiarism PDF report while placing the order or afterwards by contacting our Customer Support Team.
Being tempted by low prices and promises of quick paper delivery, you may choose another paper writing service. The truth is that more often than not their words are hollow. While the main purpose of such doubtful companies is to cash in on credulity of their clients, the prime objective of is clients’ satisfaction. We do fulfill our guarantees, and if a customer believes that initial requirements were not met or there is plagiarism found and proved in paper, they can request revision or refund. However, a refund request is acceptable only within 14 days of the initial deadline.
Our paper writing service is the best choice for those who cannot handle writing assignments themselves for some reason. At , you can order custom written essays, book reviews, film reports, research papers, term papers, business plans, PHD dissertations and so forth. No matter what academic level or timeframe requested is – we will produce an excellent work for you!
Customers usually want to be informed about how the writer is progressing with their paper and we fully understand that – he who pays the piper calls the tune. Therefore, with you have a possibility to get in touch with your writer any time you have some concerns or want to give additional instructions. Our customer support staff is there for you 24/7 to answer all your questions and deal with any problems if necessary.
Of course, the best proof of the premium quality of our services is clients’ testimonials. Just take a few minutes to look through the customer feedback and you will see that what we offer is not taking a gamble.
is a company you can trust. Share the burden of academic writing with us. Your future will be in safe hands! Buy essays, buy term papers or buy research papers and economize your time, your energy and, of course, your money!
Finished Papers
Customer Reviews
EssayService strives to deliver high-quality work that satisfies each and every customer, yet at times miscommunications happen and the work needs revisions. Therefore to assure full customer satisfaction we have a 30-day free revisions policy.
My Custom Write-ups
Customer Reviews


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Recommendations for future research should be: Concrete and specific. Supported with a clear rationale. Directly connected to your research. Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
The conclusions are as stated below: i. Students' use of language in the oral sessions depicted their beliefs and values. based on their intentions. The oral sessions prompted the students to be ...
This can include recommendations related to sample size, data collection techniques, research instruments, data analysis methods, or other relevant factors. Justify recommendations: Justify why each recommendation is being made and how it will help to address the research question or objective. It is important to provide a clear rationale for ...
TIP. While there is no required specific number of recommendations but 4 recommendations for every 20000 words in a thesis report is a general thumb. Limit the number of words in this section up to 5% of the total word count of your thesis report. This is to set a balance as to what else can be done and the current investigation.
Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations. 1. Understand the Research Question: Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study. 2.
Recommendations are crucial to your paper because they suggest solutions to your research problems. You can include recommendations in the discussion sections of your writing and briefly in the conclusions of your dissertation, thesis, or research paper.This article discusses dissertation recommendations, their purpose, and how to write one.
Recommendations in the research paper should come from your review and analysis For example It was observed that coaches interviewed were associated with the club were working with the club from the past 2-3 years only. This shows that the attrition rate of coaches is high and therefore clubs should work on reducing the turnover of coaches.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
outlines recommendations for future research related to my study. 5.2. OVERVIEW OF THE THESIS The first chapter of this thesis provides a general background to the evolution of distance and transnational education, in addition to the aims and significance of this study. The overview of distance and transnational education (Section 1.1)
The initially stated overarching aim of this research was to identify the contextual factors and mechanisms that are regularly associated with effective and cost-effective public involvement in research. While recognising the limitations of our analysis, we believe we have largely achieved this in our revised theory of public involvement in research set out in Chapter 8. We have developed and ...
Recommendations for future research should be: Concrete and specific. Supported with a clear rationale. Directly connected to your research. Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
10 Conclusions, Recommendations, and Research Questions. This report looks at the available information on science investigation and engineering design in middle and high schools and the approaches and strategies that can be used by teachers, professional development providers, administrative leaders, education researchers, and policy makers to help provide all students with high-quality ...
5.1 INTRODUCTION. In this chapter the conclusions derived from the findings of this study on the experiences of registered nurses involved in the termination of pregnancy at Soshanguve Community Health Centre are described. The conclusions were based on the purpose, research questions and results of the study. The implications of these findings ...
RECOMMENDATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS The following recommendations are offered based on the work accomplished during this project and on the conclusions given previously: I. Implementation. The PAVDRN program and associated guidelines need to be field tested and revised as needed. The program and the guidelines are sufficiently complete so that they ...
Chapter 5 Summary, Conclusions, and Recommendations Summary. The overriding purpose of this study was to determine the relative importance of construction as a curriculum organizer when viewed from a general education perspective. To accomplish that goal it became necessary to reach some prerequis ite goals. Determining what general education ...
6.2.6 Chapter 6: Summary, conclusions and recommendations. Chapter six, this Chapt er, presents the conclusions, guided by the research questions. as outlined in section 1.4 and section 5.4 ...
Thesis Format. Thesis format refers to the structure and layout of a research thesis or dissertation. It typically includes several chapters, each of which focuses on a particular aspect of the research topic. The exact format of a thesis can vary depending on the academic discipline and the institution, but some common elements include:
Footnotes. Format footnotes for your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines: Footnotes must be placed at the bottom of the page separated from the text by a solid line one to two inches long. Begin at the left page margin, directly below the solid line. Single-space footnotes that are more than one line long.
Keep in mind to provide answers to your research problems in your conclusion chapter. Explain all the problems you have highlighted in the course of your research. Make sure you provide the readers with answers to these questions with reference to your research. This will satisfy the readers and will leave them with a sense of completeness.
Sample Recommendations. This research study suggests that education managers study diffusion theory for three reasons. First, education managers and instruction technologists' do not know why most instructional innovations are or not adopted. Some blame teachers and a resistance to change while the others blamed bureaucracies and lack of funding.
Thesis Recommendation Format, Assignments For University, Essay On My Favourite Game Badminton In Hindi For Class 8, Implicit Thesis Essay, Hamlet By Shakespeare Self Study Paper, Make My Thesis Better, Millennials Lack Critical Thinking Skills
Thesis Recommendation Format. Hire experienced tutors to satisfy your "write essay for me" requests. Enjoy free originality reports, 24/7 support, and unlimited edits for 30 days after completion. We are inclined to write as per the instructions given to you along with our understanding and background research related to the given topic.